|
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
|
FORM 10-Q
|
(Mark One) |
[X] | QUARTERLY REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
| For the quarterly period ended | September 30, 2010 |
| |
| or |
| |
[ ] | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
| For the transition period from | | | to | |
| | |
|
Commission File No. | Exact Name of Registrants as Specified in their Charters, Address and Telephone Number | States of Incorporation | I.R.S. Employer
Identification Nos. | Former name, former address and former fiscal year, if changed since last report |
1-14201 | SEMPRA ENERGY | California | 33-0732627 | No change |
| 101 Ash Street | | | |
| San Diego, California 92101 | | | |
| (619)696-2034 | | | |
| | | | |
1-3779 | SAN DIEGO GAS & ELECTRIC COMPANY | California | 95-1184800 | No change |
| 8326 Century Park Court | | | |
| San Diego, California 92123 | | | |
| (619)696-2000 | | | |
| | | | |
1-40 | PACIFIC ENTERPRISES | California | 94-0743670 | No change |
| 101 Ash Street | | | |
| S an Diego, California 92101 | | | |
| (619)696-2020 | | | |
| | | | |
1-1402 | SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA GAS COMPANY | California | 95-1240705 | No chang e |
| 555 West Fifth Street | | | |
| Los Angeles, California 90013 | | | |
| (213)244-1200 | | | |
| | | | |
|
Indicate by check mark whether the registrants (1) have filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrants were required to file such reports), and (2) have been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days.
|
| | | | | |
| Yes | X | | No | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrants have submitted electronically and posted on their corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrants were required to submit and post such files).
|
| | | | | |
Sempra Energy | Yes | X | | No | |
San Diego Gas & Electric Company | Yes | | | No | |
Pacific Enterprises | Yes | | | No | |
Southern California Gas Company | Yes | | | No | |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of "large accelerated filer," "accelerated filer" and "smaller reporting company" in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
|
|
| Large
accelerated filer | Accelerated filer | Non-accelerated filer | Smaller reporting company |
Sempra Energy | [ X ] | [ ] | [ ] | [ ] |
San Diego Gas & Electric Company | [ ] | [ ] | [ X ] | [ ] |
Pacific Enterprises | [ ] | [ ] | [ X ] | [ ] |
Southern California Gas Company | [ ] | [ ] | [ X ] | [ ] |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act).
|
| | | | | |
Sempra Energy | Yes | | | No | X |
San Diego Gas & Electric Company | Yes | | | No | X |
Pacific Enterprises | Yes | | | No | X |
Southern California Gas Company | Yes | | | No | X |
| | | | | |
Indicate the number of shares outstanding of each of the issuers' classes of common stock, as of the latest practicable date. |
| | | | | |
Common stock outstanding on November 5, 2010: | | | | | |
| | | | | |
Sempra Energy | 240,054,962 shares |
San Diego Gas & Electric Company | Wholly owned by Enova Corporation, which is wholly owned by Sempra Energy |
Pacific Enterprises | Wholly owned by Sempra Energy |
Southern California Gas Company | Wholly owned by Pacific Enterprises, which is wholly owned by Sempra Energy |
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
SEMPRA ENERGY FORM 10-Q
TABLE OF CONTENTS | |
| Page |
Information Regarding Forward-Looking Statements | 4 |
| |
PART I – FINANCIAL INFORMATION | |
Item 1. | Financial Statements | 5 |
Item 2. | Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations | 73 |
Item 3. | Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk | 99 |
Item 4. | Controls and Procedures | 100 |
| | |
PART II – OTHER INFORMATION | |
Item 1. | Legal Proceedings | 101 |
Item 1A. | Risk Factors | 101 |
Item 2. | Unregistered Sales of Equity Securities and Use of Proceeds | 102 |
Item 6. | Exhibits | 103 |
| &nb sp; | |
Signatures | 105 |
| | |
This combined Form 10-Q is separately filed by Sempra Energy, San Diego Gas & Electric Company, Pacific Enterprises and Southern California Gas Company. Information contained herein relating to any individual company is filed by such company on its own behalf. Each company provides information only as to itself and its consolidated entities and not as to any other company.
You should read this report in its entirety as it pertains to each respective reporting company. No one section of the report deals with all aspects of the subject matter. Separ ate Part I - Item 1 sections are provided for each reporting company, except for the Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements. The Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements for all of the reporting companies are combined. All Items other than Part I – Item 1 are combined for the reporting companies.
INFORMATION REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
We make statements in this report that are not historical fact and constitute forward-looking statements within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. Forward-looking statements are necessarily based upon assumptions with respect to the future, involve risks and uncertainties, and are not guarantees of performance. These forward-looking statements represent our estimates and assumptions only as of the date of this report.
In this report, when we use words such as "believes," "expects," "anticipates," "plans," "estimates," "projects," "contemplates," "intends," "depends," "should," "could," "would," "may," "potential," "target," "goals," or similar expressions, or when we discuss our strategy, plans or intentions, we are making forward-looking statements.
Factors, among others, that could cause our actual results and future actions to differ materially from those described in forward-looking statements include
§local, regional, national and international economic, competitive, political, legislative and regulatory conditions and developments;
§actions by the California Public Utilities Commission, the California State Legislature, the California Department of Water Resources, the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission, the Federal Reserve Board, and other regulatory and governmental bodies in the United States and other countries in which we operate;
§capital markets conditions and inflation, interest and exchange rates;
§energy and trading markets, including the timing and extent of changes and volatility in commodity prices;
§the availability of electric power, natural gas and liquefied natural gas;
§weather conditions and conservation efforts;
§war and terrorist attacks;
§business, regulatory, environmental and legal decisions and requirements;
§the status of deregulation of retail natural gas and electricity delivery;
§the t iming and success of business development efforts;
§the resolution of litigation; and
§other uncertainties, all of which are difficult to predict and many of which are beyond our control.
We caution you not to rely unduly on any forward-looking statements. You should review and consider carefully the risks, uncertainties and other factors that affect our business as described in this report and other reports that we file with the Securities and Exchange Commission.
PART I – FINANCIAL INFORMATI ON
ITEM 1. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
SEMPRA ENERGY |
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS |
(Dollars in millions, except per share amounts) |
| Three months ended | Nine months ended |
| September 30, | September 30, |
| 2010 | 2009 | 2010 | 2009 |
| (unaudited) |
REVENUES | | | | | | | | |
Sempra Utilities | $ | 1,575 | $ | 1,424 | $ | 4,999 | $ | 4,382 |
Sempra Global and parent | | 541 | | 429 | | 1,659 | | 1,268 |
Total revenues | | 2,116 | | 1,853 | | 6,658 | | 5,650 |
EXPENSES AND OTHER INCOME | | | | | | | | |
Sempra Utilities: | | | | | | | | |
Cost of natural gas | | (285) | | (208) | | (1,402) | | (997) |
Cost of electric fuel and purchased power | | (203) | | (208) | | (480) | | (508) |
Sempra Global and parent: | | | | | | | | |
Cost of natural gas, electric fuel and purchased power | | (292) | | (220) | | (887) | | (675) |
Other cost of sales | | (23) | | (19) | | (68) | | (52) |
Litigation expense | | (17) | | (3) | | (184) | | - |
Other operation and maintenance | | (590) | | (568) | | (1,782) | | (1,673) |
Depreciation and amortization | | (218) | | (196) | | (643) | | (568) |
Franchise fe es and other taxes | | (76) | | (77) | | (243) | | (228) |
Write-off of long-lived assets | | - | | - | | - | | (132) |
Equity earnings (losses): | | | | | | | | |
RBS Sempra Commodities LLP | | (281) | | 105 | | (290) | | 384 |
Other | | 8 | | 18 | | 24 | | 27 |
Other income, net | | 66 | | 24 | ; | 82 | | 97 |
Interest income | | 5 | | 5 | | 13 | | 16 |
Interest expense | | (111) | | (96) | | (323) | | (257) |
Income before income taxes and equity earnings | | | | | | | | |
of certain unconsolidated subsidiaries | | 99 | | 410 | | 475 | | 1,084 |
Income tax benefit (expense) | | 32 | | (128) | | (85) | | (327) |
Equity earnings (losses), net of income tax | | (4) | | 20 | | 42 | | 59 |
Net income | | 127 | | 302 | | 432 | | 816 |
Losses attributable to noncontrolling interests | | 6 | | 17 | | 34 | | 22 |
Preferred dividends of subsidiaries | | (2) | | (2) | | (7) | | (7) |
Earnings | $ | 131 | $ | 317 | $ | 459 | $ | 83 1 |
| | | | | | | | |
Basic earnings per common share | $ | 0.53 | $ | 1.30 | $ | 1.86 | $ | 3.42 |
Weighted-average number of shares outstanding, basic (thousands) | | 246,668 | | 243,925 | | 246,513 | | 242,806 |
| | | | | | | | |
Diluted earnings per common share | $ | 0.53 | $ | 1.27 | $ | 1.84 | $ | 3.37 |
Weighted-average number of shares outstanding, diluted (thousands) | | 249,811 | | 248,461 | | 249,773 | | 246,875 |
Dividends declared per share of common stock | $ | 0.3 9 | $ | 0.39 | $ | 1.17 | $ | 1.17 |
See Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements. |
SEMPRA ENERGY |
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS |
(Dollars in millions) |
| September 30, | December 31, |
| 2010 | 2009 |
| (unaudited) | | |
ASSETS | | | | |
Current assets: | | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 547 | $ | 110 |
Restricted cash | | 4 | | 35 |
Trade accounts receivable | | 632 | | 971 |
Other accounts and notes receivable | | 144 | | 159 |
Due from unconsolidated affiliate | | 30 | | 41 |
Income taxes receivable | | 312 | | 221 |
Def erred income taxes | | - | | 10 |
Inventories | | 296 | | 197 |
Regulatory assets | | 97 | | 54 |
Fixed-price contracts and other derivatives | | 84 | | 77 |
Insurance receivable related to wildfire litigation (Note 10) | | 150 | | 273 |
Other | | 199 | | 147 |
Total current assets | | 2,495 | | 2,295 |
| | | | |
Investments and other assets: | | | | |
Restricted cash | | 27 | | - |
Regulatory assets arising from fixed-price contracts and other derivatives | | 241 | | 241 |
Regulatory assets arising from pension and other postretirement | | | | |
benefit obligations | | 950 | | 959 |
Other regulatory assets | | 973 | | 603 |
Nuclear decommissioning trusts | | 737 | | 678 |
Investment in RBS Sempra Commodities LLP | | 825 | | 2,172 |
Other investments | | 2,317 | | 2,151 |
Goodwill and other intangible assets | | 542 | | 524 |
Sundry | | 621 | | 608 |
Total investments and other assets | | 7,233 | | 7,936 |
| | | | |
Property, plant and equipment: | | | | |
Property, plant and equi pment | | 26,286 | | 25,034 |
Less accumulated depreciation and amortization | | (7,065) | | (6,753) |
Property, plant and equipment, net ($523 at September 30, 2010 related to VIE) | | 19,221 | | 18,281 |
Total assets | $ | 28,949 | $ | 28,512 |
See Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements. |
SEMPRA ENERGY |
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS |
(Dollars in millions) |
| September 30, | December 31, |
| 2010 | 2009 |
&n bsp; | (unaudited) | | |
LIABILITIES AND EQUITY | | | | |
Current liabilities: | | | | |
Short-term debt | $ | 574 | $ | 618 |
Accounts payable - trade | | 572 | | 522 |
Accounts payable - other | | 130 | | &n bsp;171 |
Due to unconsolidated affiliates | | 12 | | 29 |
Deferred income taxes | | 16 | | - |
Dividends and interest payable | | 232 | | 190 |
Accrued compensation and benefits | | 247 | | 264 |
Regulatory balancing accounts, net | | 242 | | 382 |
Current portion of long-term debt | | 313 | | 573 |
Fixed-price contracts and other derivatives | | 107 | | 95 |
Customer deposits | | 133 | | 145 |
Reserve for wildfire litigation (Note 10) | | 344 | | 270 |
Other | | 855 | | 629 |
Total current liabilities | | 3,77 7 | | 3,888 |
Long-term debt ($357 at September 30, 2010 related to VIE) | | 8,032 | | 7,460 |
| | | | |
Deferred credits and other liabilities: | | | | |
Due to unconsolidated affiliate | | - | | 2 |
Customer advances for construction | | 147 | | 146 |
Pension and other postretirement benefit obligations, net of plan assets | | 1,225 | | 1,252 |
Deferred income taxes | | 1,516 | | 1,318 |
Deferred investment tax credits | | 52 | | 54 |
Regulatory liabilities arising from removal obligations | | 2,635 | | 2,557 |
Asset retirement obligations | | 1,327 | | 1,277 |
Other regulatory liabilities | | 144 | | 181 |
Fixed-price contracts and other derivatives | | 336 | | 312 |
Deferred credits and other | | 672 | | 735 |
Total deferred credits and other liabilities | | 8,054 | | 7,834 |
Contingently redeemable preferred stock of subsidiary | | 79 | | 79 |
| | | | |
Commitments and contingencies (Note 10) | | | | |
| | | | |
Equity: | | | | |
Preferred stock (50 million shares authorized; none issued) | | - | | - |
Common stock (750 million shares authorized; 242 million and 247 million shares | | | | |
outstanding at September 30, 2010 and December 31, 2009, respectively; no par | | | | |
value) | | 2,012 | | 2,418 |
Retained earnings | | 7,143 | | 6,971 |
Deferred compensation | | (9) | | (13) |
Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) | | (344) | | (369) |
Total Sempra Energy shareholders' equity | | 8,802 | | 9,007 |
Preferred stock of subsidiaries | | 100 | | 100 |
Other noncontrolling interests | | 105 | &nb sp; | 144 |
Total equity | | 9,007 | | 9,251 |
Total liabilities and equity | $ | 28,949 | $ | 28,512 |
See Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements. |
SEMPRA ENERGY |
CONDENSED STATEMENTS OF CONSOLIDATED CASH FLOWS |
(Dollars in millions) |
| Nine months ended Se ptember 30, |
| 2010 | 2009 |
| (unaudited) |
CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES | | | | |
Net income | $ | 432 | $ | 816 |
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided | | | | |
; by operating activities: | | | | |
Depreciation and amortization | | 643 | | 568 |
Deferred income taxes and investment tax credits | | 133 | | 181 |
Equity losses (earnings) | | 224 | | (470) |
Write-off of long-lived assets | | - | | 132 |
Fixed-price contracts and other derivatives | | 19 | | (27) |
Other | | (24) | | 42 |
Net change in other working capital components | | (77) | | 220 |
Distributions from RBS Sempra Commodities LLP | | 198 | | 407 |
Changes in other assets | | 76 | | 81 |
Changes in other liabilities | | (22) | | (66) |
Net cash provided by operating activities | | 1,602 | | 1,884 |
| | | | |
CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES | | | | |
Expenditures for property, plant and equipment | | (1,354) | | (1,371) |
Proceeds from sale of assets | | - | | 179 |
Expenditures for investments and acquisition of businesses, net of cash acquired | | (385) | | (762) |
Distributions from RBS Sempra Commodities LLP | | 849 | | - |
Distributions from other investments | | 2 59 | | 16 |
Purchases of nuclear decommissioning and other trust assets | | (261) | | (167) |
Proceeds from sales by nuclear decommissioning and other trusts | | 261 | | 155 |
Other | | (2) | | (20) |
Net cash used in investing activities | | (633) | | (1,970) |
| | | | |
CASH FLOWS FROM FIN ANCING ACTIVITIES | | | | |
Common dividends paid | | (269) | | (255) |
Preferred dividends paid by subsidiaries | | (7) | | (7) |
Issuances of common stock | | 29 | | 52 |
& nbsp; Repurchases of common stock | | (502) | | - |
Increase (decrease) in short-term debt, net | | 184 | | (52) |
Issuances of debt (maturities greater than 90 days) | | 771 | | 1,181 |
Payments on debt (maturities greater than 90 days) | | (727) | | (325) |
Purchase of noncontrolling interest | | - | | (94) |
Other | | (11) | | 11 |
Net cash (used in) provided by financing activities | | (532) | | 511 |
| | | | |
Increase in cash and cash equivalents | | 437 | | 425 |
Cash and cash equivalents, January 1 | | 110 | | 331 |
Cash and cash equivalents, September 30 | $ | 547 | $ | 756 |
See Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements. |
SEMPRA ENERGY |
CONDENSED STATEMENTS OF CONSOLIDATED CASH FLOWS |
(Dollars in millions) |
| Nine months ended September 30, |
| 2010 | 2009 |
| (unaudited) |
SUPPLEMENTAL DISCLOSURE OF CASH FLOW INFORMATION | | | | |
Interest payments, net of amounts capitalized | $ | 264 | $ | 201 |
Income tax payments, net of refunds | | 32 | | 98 |
| | | | |
SUPPLEMENTAL DISCLOSURE OF NONCASH ACTIVITIES | | | | |
Acquisition of business: | | | | |
Assets acquired | $ | 303 | $ | - |
Cash paid, net of cash acquired | | &n bsp;(292) | | - |
Liabilities assumed | $ | 11 | $ | - |
| | | | |
Increase in capital lease obligations for investments in property, plant and | | | | |
equipment | $ | 183 | $ | 2 |
Dividends declared but not paid | | 97 | | 99 |
See Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements. |
SAN DIEGO GAS & ELECTRIC COMPANY |
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS |
(Dollars in millions) |
| Three months ended | Nine months ended |
| September 30, | September 30, |
| 2010 | 2009 | 2010 | 2009 |
| (unaudited) |
Operating revenues | | | | | | | | |
Electric | $ | 718 | $ | 695 | $ | &nb sp;1,870 | $ | 1,783 |
Natural gas | | 93 | | 78 | | 375 | | 353 |
Total operating revenues | | 811 | | 773 | | 2,245 | | 2,136 |
Operating expenses | | | | | | | | |
Cost of electric fuel and purchased power | | 203 | | 208 | | 480 | | 508 |
Cost of natural gas | | 37 | | 30 | | 170 | | 154 |
Operation and maintenance | | 235 | | 236 | | 704 | | 649 |
Depreciation and amortization | | 96 | | 81 | | 283 | | 239 |
Franchise fees and other taxes | | 42 | | 46 | | 126 | | 126 |
Total operating expenses | | 613 | | 601 | | 1,763 | | 1,676 |
Operating income | | 198 | | 172 | | 482 | | 460 |
Other income (expense), net | | (2) | | 1 | | (18) | | 45 |
Interest income | | - | | 1 | | - | | 1 |
Interest expense | | (37) | | (29) | | (99) | | (75) |
Income before income taxes | | 159 | | 145 | | 365 | | 431 |
Income tax expense | | (56) | | (53) | | (131) | | (141) |
Net income | | 103 | | 92 | | 234 | | 290 |
Losses (earnings) attributable to noncontrolling interests | | 5 | | 18 | | 34 | | (9) |
Earnings | | 108 | | 110 | | 268 | | 281 |
Preferred dividend requirements | | (2) | | (2) | | (4) | ; | (4) |
Earnings attributable to common shares | $ | 106 | $ | 108 | $ | 264 | $ | 277 |
See Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements. |
SAN DIEGO GAS & ELECTRIC COMPANY |
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS |
(Dollars in millions) |
| September 30, | December 31, |
| 2010 | 2009 |
| (unaudited) | | |
ASSETS | | | | |
Current assets: | | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 332 | $ | 13 |
Restricted cash | | 4 | | 8 |
Accounts receivable - trade | | 216 | | 229 |
Accounts receivable - other | | 33 | | 85 |
Due from unconsolidated affiliates | | 4 | | 8 |
Income taxes receivable | | 114 | | 59 |
Deferred income taxes | | 36 | | 41 |
Inventories | | 67 | | 61 |
Regulatory assets arising from fixed-price contracts and other derivat ives | | 73 | | 30 |
Other regulatory assets | | 4 | | 4 |
Fixed-price contracts and other derivatives | | 29 | | 40 |
Insurance receivable related to wildfire litigation (Note 10) | | 150 | | 273 |
Other | | 61 | | 35 |
Total current assets | | 1,123 | | 886 |
| | | | |
Other assets: | | | | |
Due from unconsolidated affiliate | | - | | 2 |
Deferred taxes recoverable in rates | | 474 | | 415 |
Regulatory assets arising from fixed-price contracts and other derivatives | | 241 | | 241 |
Regulatory assets arising from pension and other postretirement | | | | |
benefit obligations | | 331 | | 342 |
Regulatory assets arising from wildfire litigation costs | | 311 | | - |
Other regulatory assets | | 72 | | 53 |
Nuclear decommissioning trusts | | 737 | | 678 |
Sundry | | 50 | | 43 |
Total other assets | | 2,216 | | 1,774 |
| | | | |
Property, plant and equipment: | | | | |
Property, plant and equipment | | 10,816 | | 10,156 |
Less accumulated depreciation and amortization | | (2,659) | | (2,587) |
Property, plant and equipment, net ($523 at September 30, 2010 related to VIE) | | 8,157 | | 7,569 |
Total assets | $ | 11,496 | $ | 10,229 |
See Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements. |
SAN DIEGO GAS & ELECTRIC COMPANY |
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS |
(Dollars in millions) |
| September 30, | December 31, |
| 2010 | 2009 |
| (unaudited) | | |
LIABILITIES AND EQUITY | | | | |
Current liabilities: | | | | |
Short-term debt | $ | - | $ | 33 |
Accounts payable | | 229 | | 249 |
Due to unconsolidated affiliate | | 21 | | - |
Accrued compensation and benefits | &nbs p; | 93 | | 104 |
Regulatory balancing accounts, net | | 79 | | 159 |
Current portion of long-term debt | | 22 | | 45 |
Fix ed-price contracts and other derivatives | | 50 | | 51 |
Customer deposits | | 53 | | 56 |
Reserve for wildfire litigation (Note 10) | | 344 | | 270 |
Other | | 172 | | 157 |
Total current liabilities | | 1,063 | | 1,124 |
Lo ng-term debt ($357 at September 30, 2010 related to VIE) | | 3,473 | | 2,623 |
| | | | |
Deferred credits and other liabilities: | | | | |
Customer advances for construction | | 21 | | 23 |
Pension and other postretirement benefit obligations, net of plan assets | | 354 | | 370 |
; Deferred income taxes | | 953 | | 774 |
Deferred investment tax credits | | 26 | | 26 |
Regulatory liabilities arising from removal obligations | | 1,376 | | 1,3 30 |
Asset retirement obligations | | 601 | | 585 |
Fixed-price contracts and other derivatives | | 278 | | 265 |
Deferred credits and other | | 161 | | 145 |
Total deferred credits and other liabilities | | 3,770 | | 3,518 |
Contingently redeemable preferred stock | | 79 | | 79 |
| | | | |
Commitments and contingencies (Note 10) | | | | |
| | | | |
Equity: | | | | |
Common stock (255 million shares authorized; 117 million shares outstanding; | | | | |
no par value) | | 1,138 | | 1,138 |
Retained earnings | | 1,875 | | 1,611 |
Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) | | (9) | | (10) |
Total SDG&E shareholders' equity | | 3,004 | | 2,739 |
Noncontrolling interest | | 107 | | 146 |
Total equity | | 3,111 | | 2,885 |
Total liabilities and equity | $ | 11,496 | $ | 10,229 |
See Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements. |
SAN DIEGO GAS & ELECTRIC COMPANY |
CONDENSED STATEMENTS OF CONSOLIDATED CASH FLOWS |
(Dollars in millions) |
| Nine months ended |
| September 30, |
| 2010 | 2009 |
| (unaudited) |
CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES | | | | |
Net income | $ | 234 | $ | 290&nb sp; |
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by | | | | |
operating activities: | | | | |
Depreciation and amortization | | 283 | | 239 |
Deferred income taxes and investment tax credits | | 125 | | 35 |
Fixed-price contracts and other derivatives | | 42 | | (28) |
Other | | (24) | | (14) |
Net change in other working capital components | | (247) | | 115 |
Changes in other assets | | 15 | | 20 |
Changes in other liabilities | | (12) | | (38) |
Net cash provided by operating activities | | 416 | | 619 |
| | | | |
CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES | | | | |
Expenditures for property, plant and equipment | | (822) | | (633) |
Expenditures for short-term investments | | - | | (152) |
Proceeds from sale of short-term investments | | - | | 176 |
Purchases of nuclear decommissioning trust assets | | (256) | | (161) |
Proceeds from sales by nuclear decommissioning trusts | | 248 | | 155 |
Decrease in loans to affiliates, net | | 13 | | 33 |
Net decrease in restricted cash | | 4 | | - |
Other | | -&nbs p; | | 2 |
Net cash used in investing activities | | (813) | | (580) |
| | | | |
CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES | | | | |
Common dividends paid | | - | | (150) |
Capital contribution received by Otay Mesa VIE | | - | | 4 |
Capital distribution made by Otay Mesa VIE | | (10) | | - |
Preferred dividends paid | | (4) | | (4) |
Issuances of long-term debt | | 744 | | 386 |
Payments on long-term debt | | (7) | | - |
Other | | (7) | | (3) |
Net cash provided by financing activities | | 716 | | 233 |
| | | | |
Increase in cash and cash equivalents | | 319 | | 272 |
Cash and cash equivalents, January 1 | | 13 | | 19 |
Cash and cash equivalents, September 30 | $ | 332 | $ | 291 |
| | | | |
SUPPLEMENTAL DISCLOSURE OF CASH FLOW INFORMATION | | | | |
Interest payments, net of amounts capitalized | $ | 67 | $ | 51 |
Income tax payments, net of refunds | | 61 | | 144 |
| | | | |
SUPPLEMENTAL DISCLOSURE OF NONCASH ACTIVITIES | | | | |
Increase in capital lease obligations for investments in property, plant and | | | | |
; equipment | $ | 183 | $ | - |
Dividends declared but not paid | | 1 | | 1 |
See Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements. |
PACIFIC ENTERPRISES AND SUBSIDIARIES |
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS |
(Dollars in millions) |
| Three months ended | Nine months ended |
| September 30, | September 30, |
| 2010 | 2009 | 2010 | 2009 |
| (unaudited) |
| | | | | | | | |
Operating revenues | $ | 776 | $ | 662 | $ | 2,792 | $ | 2,276 |
Operating expenses | | | | | | | | |
Cost of natural gas | | 252 | | 180 | | 1,244 | | 849 |
Operation and maintenance | | 283 | | 249 | | 838 | | 766 |
Depreciation | | 78 | | 73 | | 230 | | 220 |
Franchise fees and other taxes | | 27 | | 25 | | 92 | | 81 |
Total operating expenses | | 640 | | 527 | | 2,404 | | 1,916 |
Operating income | | 136 | | 135 | | 388 | | 360 |
Other income (expense), net | | 2 | | (4) | | 8 | | 1 |
Interest income | | - | | - | &n bsp; | 1 | | 3 |
Interest expense | | (17) | | (17) | | (50) | | (52) |
Income before income taxes | | 121 | | 114 | | 347 | | 312 |
Income tax expense | | (42) | | (41) | | (132) | | (117) |
Net income | | 79 | | 73 | | 215 | | 195 |
Preferred dividends of subsidiary | | - | | - | | (1) | | (1) |
Earnings | | 79 | | 73 | | 214 | | 194 |
Preferred dividend requirements | | (1) | | (1) | | (3) | | (3) |
Earnings attributable to common shares | $ | 78 | $ | 72 | $ | 211 | $ | 191 |
See Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements. |
PACIFIC ENTERPRISES AND SUBSIDIARIES |
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS |
(Dollars in millions) |
| September 30, | December 31, |
| 2010 | 2009 |
| (unaudited) | | |
ASSETS | | | | |
Current assets: | | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 72 | $ | 49&nbs p; |
Accounts receivable - trade | | 302 | | 567 |
Accounts receivable - other | | 57 | | 44 |
Due from unconsolidated affiliates | | 118 | | 12 |
Income taxes receivable | | 23 | | 36 |
Inventories | | 181 | | 93 |
Other regulatory assets | | 10 | | 9 |
Other | | 35 | | 39 |
Total current assets | | 798 | | 849 |
| | | | |
Other assets: | | | | |
; Due from unconsolidated affiliate | | 504 | | 513 |
Regulatory assets arising from pension and other postretirement | | | | |
benefit obligations | | 614 | | 617 |
Other regulatory assets | | 114 | | 131 |
Sundry | | 38 | | 40 |
Total other assets | | 1,270 | | 1,301 |
| | | | |
Property, plant and equipment: | | | | |
Property, plant and equipment | | 9,558 | | 9,299 |
Less accumulated depreciation and amortization | | (3,735) | | (3,615) |
Property, plant and equipment, net | | 5,823 | | 5,684 |
Total assets | $ | 7,891 | $ | 7,834 |
See Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements. |
PACIFIC ENTERPRISES AND SUBSIDIARIES |
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS |
(Dollars in millions) |
| September 30, | December 31, |
| 2010 | 2009 |
| (unaudited) | &n bsp; | |
LIABILITIES AND EQUITY | | | | |
Current liabilities: | | | | |
Accounts payable - trade | $ | 167 | $ | 207 |
Accounts payable - other | | 77 | | 120 |
Due to unconsolidated affiliates | | 87 | | 87 |
Deferred income taxes | | 3 | | 5 |
Accrued compensation and benefits | | 89 | | 86 |
Regulatory balancing accounts, net | | 163 | | 223 |
Current portion of long-term debt | | 260 | | 11 |
Customer deposits | | 77 | | 87 |
Other | | 193 | | 162 |
Total current liabilities | | 1,116 | | 988 |
Long-term debt | | 1,021 | | 1,283 |
Deferred credits and other liabilities: | | | | |
Customer advances for construction | | 125 | | 123 |
Pension and other postretirement benefit obligations, net of plan assets | | 643 | | 644 |
Deferred income taxes | | 373 | | 273 |
&nb sp; Deferred investment tax credits | | 26 | | 28 |
Regulatory liabilities arising from removal obligations | | 1,247 | | 1,227 |
Asset retirement obligations | | 690 | | 662 |
Deferred taxes refundable in rates | | 144 | | 175 |
Deferred credits and other | | 165 | | 203 |
&nbs p; Total deferred credits and other liabilities | | 3,413 | | 3,335 |
| | | | |
Commitments and contingencies (Note 10) | | | | |
| | | | |
Equity: | | | | |
Preferred stock | | 80 | | 80 |
Common stock (600 million shares authorized; 84 million shares outstanding; | | | | |
no par value) | | 1,462 | | 1,462 |
Retained earnings | | 802 | | 691 |
Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) | | (23) | | (25) |
Total Pacific Enterprises shareholders' equity | | 2,321 | | 2,208 |
Preferred stock of subsidiary | | 20 | | 20 |
Total equity | | 2,341 | | 2,228 |
Total liabilities and equity | $ | 7,891 | $ | 7,834 |
See Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements. |
PACIFIC ENTERPRISES AND SUBSIDIARIES |
CONDENSED STATEMENTS OF CONSOLIDATED CASH FLOWS |
(Dollars in millions) |
| Nine months ended September 30, |
| 2010 | 2009 |
| (unaudited) |
CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES | | | | |
Net income | $ | 215 | $ | 195 |
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by | | | | |
operating activities: | | | | |
Depreciation | | 230 | | 220 |
Deferred income taxes and invest ment tax credits | | 63 | | 24 |
Other | | 2 | | 2 |
Net change in other working capital components | | 56 | | 129 |
Changes in other assets | | 6 | | 8 |
Changes in other liabilities | | (10) | | (33) |
Net cash provided by operating activities | | 562 | | 545 |
| | | | |
CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES | | | | |
Expenditures for property, plant and equipment | | (337) | | (336) |
(Increase) d ecrease in loans to affiliates, net | | (97) | | 8 |
Other | | (1) | | (1) |
Net cash used in investing activities | | (435) | | (329) |
| | | | |
CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES | | | | |
Common dividends paid | | (100) | | - |
Preferred dividends paid | | (3) | | (3) |
Preferred dividends paid by subsidiary | | (1) | | (1) |
Net cash used in financing activities | | (104) | | (4) |
| | | | |
Increase in cash and cash equivalents | | 23 | | 212 |
Cash and cash equivalents, January 1 | | 49 | | 206 |
Cash and cash equivalents, September 30 | $ | 72 | $ | 418 |
| | | | |
SUPPLEMENTAL DISCLOSURE OF CASH FLOW INFORMATION | | | | |
Interest payments, net of amounts capitalized | $ | 38 | $ | 40 |
Income tax payments, net of refunds | | 63 | | 54 |
| | | | |
SUPPLEMENTAL DISCLOSURE OF NONCASH ACTIVITIES | | | | |
Increase in capital lease obligations for investments in property, plant and | | | | |
equipment | $ | - | $ | 2 |
Dividends declared but not paid | | 1 | | 1 |
See No tes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements. |
SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA GAS COMPANY AND SUBSIDIARIES |
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS |
(Dollars in millions) |
| Three months ended | Nine months ended |
| September 30, | September 30, |
| 2010 | 2009 | 2010 | 2009 |
| (unaudited) |
| | | | | | | | |
Operating revenues | $ | 776 | $ | 662 | $ | 2,792 | $ | 2,276 |
Operating expenses | | | | | | | | |
Cost of natural gas | | 252 | | 180 | | 1,244 | | 849 |
Operation and maintenance | | 285 | | 252 | | 840 | | 768 |
Depreciation | | 78 | | 73 | | 230 | | 220 |
Franchise fees and other taxes | | 27 | | 25 | | 92 | | 81 |
Total operating expenses | | 642 | | 530 | | 2,406 | | 1,918 |
Operating income | | 134 | | 132 | | 386 | | &n bsp;358 |
Other income (expense), net | | 2 | | (1) | | 8 | | 4 |
Interest income | | 1 | | 1 | | 1 | | 3 |
Interest expense | | (17) | | (16) | | (50) | | (51) |
Income before income taxes | | 120 | | 116 | | 345 | | 314 |
Income tax expense | | (42) | | (42) | | (132) | | (115) |
Net income | | 78 | | 74 | | 213 | | 199 |
Preferred dividend requirements | | - | | - | | (1) | | (1) |
Earnings attributable to common shares | $ | 78 | $ | 74 | $ | 212 | $ | 198 |
See Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements. |
SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA GAS COMPANY AND SUBSIDIARIES |
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS |
(Dollars in millions) |
| September 30, | December 31, |
| 2010 | 2009 |
| (unaudited) | | |
ASSETS | | | | |
Current assets: | | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 72 | $ | 49 |
Accounts receivable - trade | | 302 | | 567 |
Accounts receivable - other | | 55 | | 44 |
Due from unconsolidated affiliate | | 118 | | 6 |
Income taxes receivable | | 19 | | 35 |
Inventories | | 181 | | 93 |
Other regulatory assets | | 10 | | 9 |
Other | | 34 | | 40 |
Total current assets | | 791 | | 843 |
| | | | |
Other assets: | | | | |
Regulatory assets arising from pension and other postretirement | | | | |
benefit obligations | | 614 | | 617 |
Other regulatory assets | | 114 | | 131 |
Sundry | | 10 | | 14 |
Total other assets | | 738 | | 762 |
| | | | |
Property, plant and equipment: | & nbsp; | | | |
Property, plant and equipment | | 9,556 | | 9,297 |
Less accumulated depreciation and amortization | | (3,735) | | (3,615) |
& nbsp; Property, plant and equipment, net | | 5,821 | | 5,682 |
Total assets | $ | 7,350 | $ | 7,287 |
See Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements. |
SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA GAS COMPANY AND SUBSIDIARIES |
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS |
(Dollars in millions) |
| September 30, | December 31, |
| 2010 | 2009 |
| (unaudited) | | |
LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS' EQUITY | | | | |
Current liabilities: | | | | |
Accounts payable - trade | $ | 167 | $ | 207 |
Accounts payable - other | | 77 | | 120 |
Due to unconsolidated affiliate | | 3 | | 3 |
Deferred income taxes | | 5 | | 6 |
Accrued compensation and benefits | | 89 | | 86 |
Regulatory balancing accounts, net | | 163 | | 223 |
Current portion of long-term debt | | 260 | | 11 |
Customer deposits | | 77 | | 87 |
Other | | 191 | | 158 |
Total current liabilities | | 1,032 | | 901 |
Long-term debt | | 1,021 | | 1,283 |
Deferred credits and other liabilities: | | | | |
Customer advances for construction | | 125 | | 123 |
Pension and other postretirement benefit obligations, net of plan assets | | 643 | | 644 |
Deferred income taxes | | 379 | | 280 |
Deferred investment tax credits | | 26 | | 28 |
Regulatory liabilities arising from removal obligations | | 1,247 | | 1,227 |
Asset retirement obligations | | 690 | | 662 |
Deferred taxes refundable in rates | | 144 | | 175 |
Deferred credits and other | | 163 | | 198 |
Total deferred credits and other liabilities | | 3,417 | | 3,337 |
| | | | |
Commitments and contingencies (Note 10) | | | | |
| | | | |
Shareholders' equity: | | | | |
Preferred stock | | 22 | | 22 |
Common stock (100 million shares authorized; 91 million shares outstanding; | | | | |
no par value) | | 866 | | 866 |
Retained earnings | | 1,015 | | 903 |
Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) | | (23) | | (25) |
Total shareholders' equity | | 1,880 | | 1,766 |
Total liabilities and shareholders' equity | $ | 7,350 | $ | 7,287 |
See Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements. |
SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA GAS COMPANY AND SUBSIDIARIES |
CONDENSED STATEMENTS OF CONSOLIDATED CASH FLOWS |
(Dollars in millions) |
| Nine months ended September 30, |
| 2010 | 2009 |
| (unaudited) |
CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES | | | | |
Net income | $ | 213 | $ | 199 |
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by | | | | |
operating activities: | | | | |
Depreciation | | 230 | | 220 |
Deferred income taxes and investment tax credits | | 62 | | 22 |
Other | | 2 | | 6 |
Net change in other working capital components | | 62 | | 125 |
Changes in other assets | | 6 | | 4 |
Changes in other liabilities | | (6) | | (27) |
Net cash provided by operating activities | | 569 | | 549 |
| | | | |
CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES | | | | |
Expenditures for property, plant and equipment | | (337) | | (336) |
Increase in loans to affiliates, net | | (108) | | - |
Net cash used in investing activities | | (445) | | (336) |
| | | | |
CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES | | | | |
Common dividends paid | | (100) | | - |
Preferred dividends paid | | (1) | | (1) |
Net cash used in financing activities | | (101) | | (1) |
| | | | |
Increase in cash and cash equivalents | | 23 | | 212 |
Cash and cash equivalents, January 1 | | 49 | | 206 |
Cash and cash equivalents, September 30 | $ | 72 | $ | 418 |
| | | | |
SUPPLEMENTAL DISCLOSURE OF CASH FLOW INFORMATION | | | | |
Interest payments, net of amounts capitalized | $ | 37 | $ | 40 |
Income tax payments, net of refunds | | 63 | | 54 |
| | | | |
SUPPLEMENTAL DISCLOSURE OF NONCASH ACTIVITIES | | | | |
Increase in capital lease obligations for investments in property, plant and | | | | |
equipment | $ | - | $ | 2 |
See Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements. |
SEMPRA ENERGY AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
PRINCIPLES OF CONSOLIDATION
Sempra Energy
Sempra Energy's Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements include the accounts of Sempra Energy, a California-based Fortune 500 holding company, and its consolidated subsidiaries and a variable interest entity (VIE). Sempra Energy’s principal subsidiaries are
§San Diego Gas & Electric Company (SDG&E) and Southern Californi a Gas Company (SoCalGas), which we collectively refer to as the Sempra Utilities; and
§Sempra Global, which is the holding company for Sempra Commodities, Sempra Generation, Sempra Pipelines & Storage, and Sempra LNG.
Sempra Energy uses the equity method to account for investments in affiliated companies over which we have the ability to exercise significant influence, but not control. We discuss our investments in unconsolidated subsidiaries in Note 4 below and Note 4 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in the Annual Report.
SDG&E
SDG&E's Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements include its accounts and the accounts of a variable interest entity of which SDG&E is th e primary beneficiary, as we discuss in Note 5 under "Variable Interest Entities." SDG&E’s common stock is wholly owned by Enova Corporation, which is a wholly owned subsidiary of Sempra Energy.
Pacific Enterprises and SoCalGas
The Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements of Pacific Enterprises include the accounts of Pacific Enterprises (PE) and its subsidiary, SoCalGas. Sempra Energy owns all of PE’s common stock and PE owns all of SoCalGas’ common stock. SoCalGas’ Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements include its subsidiaries, which comprise less than one percent of its consolidated financial position and results of operations.
PE's operations consist solely of those of SoCalGas and additional items (e.g., cash, intercompany accounts and equity) attributable to serving a s a holding company for SoCalGas.
BASIS OF PRESENTATION
This is a combined report of Sempra Energy, SDG&E, PE and SoCalGas. We provide separate information for SDG&E, PE and SoCalGas as required. In the Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements (except in Note 11), when only information for SoCalGas is provided, it is the same for PE. References in this report to "we," "our" and "Sempra Energy Consolidated" are to Sempra Energy and its consolidated entities, unless otherwise indicated by the context. We have eliminated intercompany accounts and transactions within the consolidated financial statements of each reporting entity.
We have prepared the Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (GAAP) and in accordan ce with the interim-period-reporting requirements of Form 10-Q. Results of operations for interim periods are not necessarily indicative of results for the entire year. We evaluated events and transactions that occurred after September 30, 2010 through the date the financial statements were issued, and in the opinion of management, the accompanying statements reflect all adjustments necessary for a fair presentation. These adjustments are only of a normal, recurring nature.
You should read the information in this Quarterly Report in conjunction with our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2009 (the Annual Report), and our Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q for the quarters ended March 31, 2010 and June 30, 2010, which are combined reports for Sempra Energy, SDG&E, PE and SoCalGas.
Our significant accounting policies are described in Note 1 of the Notes to Consolidated Financia l Statements in the Annual Report. We follow the same accounting policies for interim reporting purposes, except for the adoption of new accounting standards as we discuss in Note 2.
The Sempra Utilities and Sempra Pipelines & Storage's Mobile Gas Service Corporation and Ecogas Mexico, S de RL de CV prepare their financial statements in accordance with GAAP provisions governing regulated operations, as we discuss in Note 1 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in the Annual Report.
Orange Grove Energy L.P.
SDG&E has a 25-year tolling agreement to purchase power generated by Orange Grove Energy L.P. (Orange Grove) at its 99-megawatt (MW) generating facility located in San Diego County, California. Under a tolling agreement, SDG&E purchases power generated by facilities for which it supplies all of the natural g as to fuel the power plant. In the third quarter of 2009, Sempra Energy and SDG&E determined that Orange Grove was a VIE and that SDG&E was the primary beneficiary of the VIE based on the criteria in GAAP as written at that time and applicable through December 31, 2009. Sempra Energy and SDG&E therefore consolidated Orange Grove beginning in the third quarter of 2009 through December 31, 2009.
In the first quarter of 2010, Accounting Standards Update (ASU) 2009-17, “Improvements to Financial Reporting by Enterprises Involved with Variable Interest Entities” (ASU 2009-17), which we discuss in Note 2 below, became effective. Applying the guidance in ASU 2009-17, because of SDG&E’s obligation to absorb the natural gas costs for the fuel to operate the facility, along with the power to direct the dispatch, Sempra Energy and SDG&E continued to consolidate Orange Grove in the first quarter of 2010.
In the second quarter, Sempra Energy and SDG&E reevaluated the provisions of ASU 2009-17 as they apply to Orange Grove. Sempra Energy and SDG&E determined that because the Orange Grove facility is a peaker plant, it operates infrequently to meet peak power needs. We believe that the owners of Orange Grove retain the most significant economic power through their control over operations and maintenance of the plant, which impacts the capacity payments under the agreement that are expected to have the greatest effect on the overall economic performance of the entity. Accordingly, SDG&E does not have the right to direct activities that most significantly impact the economic performance of Orange Grove, and Sempra Energy and SDG&E should not consolidate Orange Grove, but instead should record the agreement as a capital lease. The effect of this change has no effect on Sempra Energy’s or SDG&E’s earnings and is not material to their previously issued financi al statements.
Presentation of Restricted Cash
In Sempra Energy’s previously issued financial statements, we presented all restricted cash as a current asset on the balance sheet. At both September 30, 2010 and December 31, 2009, $27 million of restricted cash represents funds held in trust for construction financing of certain natural gas storage facilities of Sempra Pipelines & Storage. Because this restricted cash will be expended for construction of long-lived assets, we have concluded that these amounts should be presented as a noncurrent asset. At September 30, 2010, this restricted cash is presented as Restricted Cash under Investments and Other Assets on the Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheet. We believe that the effect of presentation of restricted cash is not material to the previously issued balance sheets and have not corrected the classification of the restricte d cash amount at December 31, 2009. The presentation of restricted cash on the balance sheet has no impact on earnings or cash flows for any period presented.
NOTE 2. NEW ACCOUNTING STANDARDS
We describe below recent pronouncements that have had or may have a significant effect on our financial statements. We do not discuss recent pronouncements that are not anticipated to have an impact on or are unrelated to our financial condition, results of operations, or disclosures.
SEMPRA ENERGY, SDG&E, PE AND SOCALGAS
ASU 2009-17, "Improvements to Financial Reporting by Enterprises Involved with Variable Interest Entities" (ASU 2009-17): ASU 2009-17 amends Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) Interpretation No. 46(R), Consolidation of Variable Interest Entities – an interpretation of ARB No. 51 (FIN 46(R)), which provides consolidation guidance related to variable interest entities.
ASU 2009-17 amends FASB Accounting Standards Codification (ASC) Topic 810, Consolidation, and requires
§a qualitative approach for identifying the primary beneficiary of a variable interest entity based on 1) the power to direct activities that most significantly impact the economic performance of the entity, and 2) the obligation to absorb losses or right to receive benefits that could be significant to the entity;
§ongoing reassessments of whether an enterprise is the primary beneficiary of a variable interest entity; and
§separate disclosure by the primary beneficiary on the face of the balance sheet to identify 1) assets that can only be used to settle obligations of the variable interest entity, and 2) liabilities for which creditors do not have recourse to the primary beneficiary.
We adopted ASU 2009-17 on January 1, 2010 and it did not have a material effect on earnings, nor on presentation on the interim Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheets for Sempra Energy and SDG&E. We provide the required additional disclosure in Note 5. ASU 2009-17 did not impact PE’s nor SoCalGas’ condensed consolidated financial statements.
ASU 2010-06, "Improving Disclosures About Fair Value Measurements" (ASU 2010-06): ASU 2010-06 amends ASC Topic 820, Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures, and requires the following additional fair value measurement disclosures:
§transfers into and out of Levels 1 and 2
§segrega tion of classes of assets and liabilities measured at fair value
§valuation techniques and inputs used for Level 2 and Level 3 instruments
§detailed activity for Level 3 instruments, including separate presentation of purchases, sales, issuances and settlements
We adopted ASU 2010-06on January 1, 2010, and we provide the additional disclosure in Note 8.
NOTE 3. RECENT INVESTMENT ACTIVITY
SEMPRA PIPELINES & STORAGE
Acquisition of Mexican Pipeline and Natural Gas Infrastructure
On April 30, 2010, Sempra Pipelines & Storage completed an acquisition resulting in the purchase of the Mexican pipeline and natural gas infrastructure assets of El Paso Corporation for $307 million ($292 million, net of cash acquired).
The acquisition consists of El Paso Corporation’s wholly owned natural gas pipeline and compression assets in the Mexican border state of Sonora and its 50-percent interest in a joint venture with PEMEX, the Mexican state-owned oil company. The joint venture operates two natural gas pipelines and a propane system in northern Me xico. The acquisition expands our scale and geographic footprint in a strong growth region in Mexico. The pipeline assets are backed substantially by long-term contracts with a history of consistent revenue streams, allowing us to expand our natural gas infrastructure business in northern Mexico.
The following table summarizes the consideration paid in the acquisition and the recognized amounts of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed at April 30, 2010:
(Dollars in millions) | | |
Cash consideration (fair value of total consideration) | $ | 307 |
Recognized amounts of identifiable assets acquired and liabilities assumed: | | |
| Cash | | 15 |
| Accounts receivable | | 4 |
| Investment in equity method investee | | 256 |
| Property, plant & equipment | | 25 |
| Other liabilities | | (11) |
Total identifiable net assets | | 289 |
Goodwill(1) | $ | 18 |
| | | |
Acquisition-related costs (included in Other Operation and Maintenance expense in | | |
| the Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations for the nine months | | |
| ended September 30, 2010) | $ | 1 |
(1) | The goodwill, which represents the residual of the consideration paid over the identifiable net assets, is assigned to the Sempra Pipelines & Storage segment and is attributed to the strategic value of the transaction. None of the goodwill recorded is deductible in Mexico for income tax purposes. |
Included in our Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations are revenues and earnings of $4 million and $12 million, respectively, for the period May 1, 2010 to September 30, 2010 related to the assets acquired from El Paso Corporation, including revenues and earnings of $3 million and $7 million, respectively, for the three months ended September 30, 2010. Proforma impacts on revenues and earnings for Sempra Energy had the acquisition occurred on January 1, 2009 were immaterial.
Natural Gas Storage Projects
Sempra Pipelines & Storage’s Sempra Midstream owned 60 percent of Mississippi Hub, LLC (Mississippi Hub) through December 31, 2008 and on January 16, 2009, purchased the remaining 40-percent ownership interest for $94 million in cash.
NOTE 4. INVESTMENTS IN UNCONSOLIDATED ENTITIES
SEMPRA ENERGY AND SDG&E
Available-for-Sale Securities
In June 2009, SDG&E remarketed $176 million of its industrial development bonds at a fixed rate of 5.875 percent, maturing in 2034. Prior to SDG&E's remarketing, SDG&E purchased $152 million of the bonds from Sempra Energy. We discuss these bonds further in Note 6 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in the Annual Report.
SEMPRA COMMODITIES
RBS Sempra Commodities LLP (RBS Sempra Commodities) is a limited liability partnership formed in the United Kingdom to own and operate the commodities-marketing businesses previously operated through wholly owned subsidiaries of Sempra Energy. We account for our investment in RBS Sempra Commodities under the equity method, and report our share of partnership earnings in the Sempra Commodities segment.
Excluding the impairment charge discussed below, for the three months and nine months ended September 30, 2010, we recorded pretax equity earnings of $24 million and $15 million, respectively, from RBS Sempra Commodities. Pretax equity earnings from RBS Sempra Commodities were $105 million and $384 million for the three months and nine months ended September 30, 2009, respectively. The partnership income that is distributable to us on an annual basis is computed on the partnership's basis of accounting, International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), as adopted by the European Union. For the three months and nine months ended September 30, 2010, our share of distributable income, on an IFRS basis, was $22 million and $53 million, respectively. In the three months and nine months ended September 30, 2009, our share of distributable income, on an IFRS basis, was $60 million and $276 million, respectively. In the second quarter of 2010, we received the remaining distribution of 2009 partnership income of $198 million. In the first nine months of 2009, we received cash distributions from the partnership of $407 million. We discuss the equity method investment in RBS Sempra Commodities further in Note 4 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in the Annual Report.
In November 2009, our partner in the joint venture, The Royal Bank of Scotland (RB S), announced its intention to divest its interest in RBS Sempra Commodities in connection with a directive from the European Commission to dispose of certain assets. In February 2010, Sempra Energy, RBS and the partnership entered into an agreement with J.P. Morgan Ventures Energy Corporation (J.P. Morgan Ventures), a unit of J.P. Morgan Chase & Co. (JP Morgan), for J.P. Morgan Ventures to purchase the global metals and oil businesses and the European natural gas and power business from the joint venture. This transaction was completed on July 1, 2010, and we received the majority of the proceeds in early July 2010 and the remainder in September 2010. The purchase price was $1.6 billion, and our share of the proceeds was approximately $1 billion, including distributions of 2009 partnership income attributable to the businesses sold, which were $134 million of the $198 million in distributions we received in April 2010.
This sale to J.P. Morgan Ventures did not include RBS Sempra Commodities' North American power and natural gas trading businesses and its retail energy solutions business. In September 2010, Noble Group Ltd. (Noble Group) agreed to acquire the U.S. retail commodity marketing business of the RBS Sempra Commodities joint venture for $318 million in cash, plus assumption of all debt, and the transaction closed on November 1, 2010. In October 2010, J.P. Morgan Ventures agreed to purchase, subject to regulatory approval, most of the remaining assets of RBS Sempra Commodities for approximately $220 million. The assets to be sold include the joint venture’s wholesale natural gas and power trading agreements, as well as over-the-counter and exchange-traded transactions, with counterparties across North America. The counterparties include natural gas producers, pipeline and storage providers, power plants, regasification facilities, utilities and municipal customers. The sale is expected to close before year-end and will complete the divestiture of the remaining principal assets of RBS Sempra Commodities.
We expect our share of the proceeds from the sales of all of the partnership businesses and related cash distributions to total $1.8 billion to $1.9 billion. This includes approximately $1.3 billion expected from the announced transactions, plus $500 million to $600 million consisting primarily of cash and accounts receivable, as well as net margin that is expected to be collected as customers are transferred to JP Morgan. The transfer of all accounts to JP Morgan will be done as soon as possible following closing, but is expected to continue into 2011.
Projected cash distributions from RBS Sempra Commodities are net of expected transition costs and are not expected to fully recover the goodwill included in the carrying value of our investment in the partnership. Accordingly, we recorded a pretax non-cash charge of $305 million ($139 millio n after-tax) for the three months and nine months ended September 30, 2010 to reduce our investment in RBS Sempra Commodities. This charge is included in Equity Earnings (Losses) from RBS Sempra Commodities LLP on the Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations. The fair value of our investment in RBS Sempra Commodities was significantly impacted by unobservable inputs (i.e., Level 3 inputs) as defined by the accounting guidance for fair value measurements, which we discuss below in Note 8. The inputs included estimated future cash distributions expected from the partnership, excluding the impact of costs anticipated for transactions that have not closed as of September 30, 2010. The investment balance of $825 million at September 30, 2010 reflects our portion of the partnership’s earnings, distributions received from the partnership and the non-cash charge to bring the investment to fair value.
The following table shows summarized financial info rmation for RBS Sempra Commodities (on a GAAP basis):
| Three months ended September 30, | Nine months ended September 30, |
(Dollars in millions) | 2010 | 2009 | 2010 | 2009 |
Gross revenues and fee income | $ | 72 | $ | 291 | $ | 466 | $ | 1,167 |
Gros s profit | | 74 | | 268 | | 446 | | 1,096 |
Income (loss) from continuing operations | | (7) | | 115 | | (20) | | 504 |
Partnership net income (loss) | | (7) | | 115 | | (20) | | 504 |
We provide information regarding the Sempra Commodities segment in Note 11.
SEMPRA PIPELINES & STORAGE
In the first quarter 2010, Sempra Pipelines & Storage contributed $65 million to Rockies Express, a joint venture to own and operate the Rockies Express Pipeline, to complete the construction phase of the project. Sempra Pipelines & Storage contributed $315 million and $527 million in the three months and nine months ended September 30, 2009, respectively. We discuss this investment in Note 4 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements i n the Annual Report.
Sempra Pipelines & Storage owns 43 percent of two Argentine natural gas utility holding companies, Sodigas Pampeana and Sodigas Sur. The Argentine economic decline and government responses (including Argentina’s unilateral, retroactive abrogation of utility agreements early in 2002) continue to adversely affect the operations of these Argentine utilities. In 2002, Sempra Pipelines & Storage initiated arbitration proceedings at the International Center for the Settlement of Investment Disputes (ICSID) under the 1994 Bilateral Investment Treaty between the United States and Argentina for recovery of the diminution of the value of its investments that has resulted from Argentine governmental actions. In September 2007, the tribunal awarded us compensation of $172 million, which included interest up to the award date. In January 2008, Argentina filed an action at the ICSID seeking to annul the award. In June 2010, the Annulment Commi ttee granted Argentina’s petition for annulment of the award. This action did not impact our earnings, as we did not record the original award pending assurance of collectability. On November 3, 2010, Sempra Pipelines & Storage resubmitted arbitration proceedings against Argentina before the ICSID on the same and similar grounds as the 2002 filing.
In a separate but related proceeding related to our political risk insurance policy, we negotiated a $48 million settlement that was collected in September 2010. The proceeds from the settlement are reported in Other Income, Net, on the Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations for the three months and nine months ended September 30, 2010.
We continue to actively pursue the sale of our investments in the two Argentine companies. In September 2010, we concluded that, although the ICSID claim had been annulled as discussed above, rate increases soug ht in Argentina would continue to be delayed. We believe this continued uncertainty has impacted the fair value of our net investment in the two Argentine companies, and recorded a non-cash impairment charge of $24 million, which is reported in Equity Earnings (Losses), Net of Income Tax, on the Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations for the three months and nine months ended September 30, 2010. The Sodigas Pampeana and Sodigas Sur fair value was significantly impacted by unobservable inputs (i.e., Level 3 inputs) as defined by the accounting guidance for fair value measurements, which we discuss below in Note 8. The inputs included discount rates and estimated future cash flows. Such cash flows considered the value of those businesses with positive cash flows, the value of the non-operating assets, and the probability-weighted value of anticipated rate increases, considering both the timing and magnitude of such increases.
SEMPRA GENERATION
Sempra Generation and BP Wind Energy currently hold 50-percent ownership interests in Fowler Ridge II Wind Farm LLC (Fowler Ridge), a joint venture which operates a 200-MW wind farm project located in Benton County, Indiana. As of December 2009, Sempra Generation had invested $235 million in the joint venture. In August 2010, Sempra Generation received a $180 million return of capital from Fowler Ridge. We discuss this further in Note 6 below and provide additional information in Note 4 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in the Annual Report.
NOTE 5. OTHER FINANCIAL DATA
VARIABLE INTEREST ENTITIES
We consolidate a VIE if we are the primary beneficiary of the VIE’s activities. Our determination of whether we are the primary beneficiary is based upon qualitative and quantitative analyses, which assess
§the purpose and design of the VIE;
§the nature of the VIE's risks and the risks we absorb;
§the power to direct activities that most significantly impact the economic performance of the VIE; and
§the obligation to absorb losses or right to receive benefits that could be significant to the VIE.
SDG&E has agreements under which it purchases power generated by facilities for which it supplies all of the natural gas to fuel the power plant (i.e., tolling agreements). SDG&E’s obligation to absorb natural gas costs may be a significant variable interest. In addition, SDG&E has the power to direct the dispatch of electricity generated by these facilities. Based upon our analysis, the ability to direct the dispatch of electricity may have the most significant impacts on the economic performance of the entity owning the generating facility because of the associated exposure to the cost of natural gas, which fuels the plants, and the value of electricity produced. To the extent that SDG&E 1) is obligated t o purchase and provide fuel to operate the facility, 2) has the power to direct the dispatch, and 3) purchases all of the output from the facility for a substantial portion of the facility’s useful life, SDG&E may be the primary beneficiary of the entity owning the generating facility. SDG&E determines if it is the primary beneficiary in these cases based on the operational characteristics of the facility, including its expected power generation output relative to its capacity to generate and the financial structure of the entity, among other factors. If we determine that SDG&E is the primary beneficiary, Sempra Energy and SDG&E consolidate the entity that owns the facility as a VIE, as we discuss below.
Otay Mesa VIE
SDG&E has a 10-year agreement to purchase power generated at the Otay Mesa Energy Center (OMEC), a 605-MW generating facility that began commercia l operations in October 2009. In addition to tolling, the agreement provides SDG&E with the option to purchase the power plant at the end of the contract term in 2019, or upon earlier termination of the purchased-power agreement, at a predetermined price subject to adjustments based on performance of the facility. If SDG&E does not exercise its option, under certain circumstances, it may be required to purchase the power plant at a predetermined price.
The facility owner, Otay Mesa Energy Center LLC (OMEC LLC), is a VIE (Otay Mesa VIE), of which SDG&E is the primary beneficiary. SDG&E has no OMEC LLC voting rights and does not operate OMEC. In addition to the risks absorbed under the tolling agreement, SDG&E absorbs separately through the put option a significant portion of the risk that the value of Otay Mesa VIE could decline. Sempra Energy and SDG&E have consolidated Otay Mesa VIE since the second quarter of 2007, and have continued to con solidate it through the third quarter of 2010. Otay Mesa VIE's equity of $107 million at September 30, 2010 and $146 million at December 31, 2009 is included on the Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheets in Other Noncontrolling Interests for Sempra Energy and in Noncontrolling Interest for SDG&E.
OMEC LLC has a loan outstanding of $367 million at September 30, 2010, the proceeds of which were used for the construction of OMEC. The loan is with third party lenders and is secured by OMEC's property, plant and equipment. SDG&E is not a party to the loan agreement and does not have any additional implicit or explicit financial responsibility to OMEC LLC. The loan fully matures in April 2019 and bears interest at rates varying with market rates. In addition, OMEC LLC has entered into interest rate swap agreements to moderate its exposure to interest rate changes. We provide additional information concerning the interest rate swaps in Note 7.
Other Variable Interest Entities
SDG&E's power procurement is subject to reliability requirements that may require SDG&E to enter into various power purchase arrangements which include variable interests. SDG&E evaluates these contracts to determine if variable interests exist and, based on the qualitative and quantitative analyses described above, if SDG&E, and thereby Sempra Energy, is the primary beneficiary. SDG&E has determined that no contracts other than that relating to Otay Mesa VIE mentioned above result in SDG&E being the primary beneficiary. In addition to the tolling agreements described above, other variable interests involve various elements of fuel and power costs, including certain construction costs, tax credits, and other components of cash flow expected to be paid to or received by our counterparties. In most of these cases, the expectation of variability is not subs tantial, and SDG&E generally does not have the power to direct activities that most significantly impact the economic performance of the other VIEs. If our ongoing evaluation of these VIEs were to conclude that SDG&E becomes the primary beneficiary and consolidation by SDG&E becomes necessary, the effects are not expected to significantly affect the financial position, results of operations, or liquidity of SDG&E. SDG&E is not exposed to losses or gains as a result of these other VIEs, because all such variability would be recovered in rates.
Sempra Energy’s other business units also enter into arrangements which could include variable interests. We evaluate these contracts based upon the qualitative and quantitative analyses described above. We have determined that these contracts are not variable interests in a VIE and therefore are not subject to the requirements of ASU 2009-17.
PENSION AND OTHER POSTRETIREMENT BENEFITS
Net Periodic Benefit Cost
The following three tables provide the components of net periodic benefit cost:
NET PERIODIC BENEFIT COST -- SEMPRA ENERGY CONSOLIDATED |
(Dollars in millions) |
| Pension Benefits | Other Postretirement Benefits |
| Three months ended September 30, | Three months ended September 30, |
| 2010 | 2009 | 2010 | 2009 |
Service cost | $ | 20 | $ | 17 | $ | 5 | $ | 7 |
Interest cost | | 41 | | 42 | | 14 | | 14 |
Expected return on assets | | (36) | | (34) | | (12) | | (11) |
Amortization of: | | | | | | | | |
Prior service cost | | 1 | | 1 | | - | | - |
Actuarial loss | | 8 | | 6 | | 2 | | 1 |
Regulatory adjustment | | 5 | | (14) | | 1 | | 1 |
Total net periodic benefit cost | $ | 39 | $ | 18 | $ | 10 | $ | 12 |
| Nine months ended September 30, | Nine months ended September 30, |
| 2010 | 2009 | 2010 | 2009 |
Service cost | $ | 62 | $ | 56 | $ | 20 | $ | 21 |
Interest cost | | 125 | | 127 | | 43 | | 43 |
Expected return on assets | | (108) | | (104) | | (35) | | (35) |
Amortization of: | | | | | | | | |
Prior service cost (credit) | | 3 | | 3 | | (1) | | (1) |
Ac tuarial loss | | 23 | | 18 | | 6 | | 3 |
Regulatory adjustment | | (14) | | (53) | | 5 | | 5 |
Total net periodic benefit cost | $ | 91 | $ | 47 | $ | 38 | $ | 36 |
NET PERIODIC BENE FIT COST -- SDG&E |
(Dollars in millions) |
| Pension Benefits | Other Postretirement Benefits |
| Three months ended September 30, | Three months ended September 30, |
| 2010&nb sp; | 2009 | 2010 | 2009 |
Service cost | $ | 7 | $ | 5 | $ | 2 | $ | 2 |
Interest cost | | 12 | | 12 | | 2 | | 3 |
Expected return on assets | | (11) | | (8) | | (2) | | (1) |
Amortization of: | | | | | | | | |
Prior service cost | | - | | - | | 1 | | 1 |
Actuarial loss | | 3 | | 4 | | - | | - ; |
Regulatory adjustment | | 3 | | (2) | | - | | - |
Total net periodic benefit cost | $ | 14 | $ | 11 | $ | 3 | $ | 5 |
| Nine months ended September 30, | Nine months ended September 30, |
| 2010 | 2009 | 2010 | 2009 |
Service cost | $ | 21 | $ | 17 | $ | 5 | $ | 5 |
Interest cost | | 36 | | 36 | | 7 | | 7 |
Expected return on assets | | (32) | | (24) | | (5) | | (3) |
Amortization of: | | | | | | | | |
Prior service cost | | 1 | | 1 | | 3 | | 3 |
Actuarial loss | | 9 | | 12 | | - | | - |
Regulatory adjustment | | (2) | | (16) | | 1 | | 1 |
Total net periodic benefit cost | $ | 33 | $ | 26 | $ | 11 | $ | 13 |
NET PERIODIC BENEFIT COST -- SOCALGAS |
(Dollars in millions) |
| Pension Benefits | Other Postretirement Benefits |
| Three months ended September 30, | Th ree months ended September 30, |
| 2010 | 2009 | 2010 | 2009 |
Service cost | $ | 11 | $ | 9 | $ | 3 | $ | 6 |
Interest cost | | 25 | | 25 | | 11 | | 11 |
Expected return on assets | | (23) | | (24) | | (9) | | (10) |
Amortization of: | | | | | | | | |
Prior service cost (credit) | | 1 | &n bsp; | 1 | | (1) | | (1) |
Actuarial loss | | 2 | | - | | 2 | | 1 |
Regulatory adjustment | | 2 | | (10) | | 1 | | 1 |
Total net periodic benefit cost | $ | 18 | $ | 1 | $ | 7 | $ | 8 |
| Nine months ended September 30, | Nine months ended September 30, |
| 2010 | 2009 | 2010 | 2009 |
Service cost | $ | 34 | $ | 31 | $ | 13 | $ | 15 |
Interest cost | | 74 | | 74 | | 34 | | 34 |
Expected return on assets | | (68) | | (70) | | (29) | | (31) |
Amortization of: | | | | | | | | |
Prior service cost (credit) | | 2 | | 2 | | (3) | | (3) |
Actuarial loss | | 7 | | - | | 6 | | 3 |
Regulatory adjustment | | (12) | | (35) | | 4 | | 4 |
Total net periodic benefit cost | $ | 37 | $ | 2 | $ | 25 | $ | 22 |
Benefit Plan Contributions
The following table shows our year-to-date contributions to our pension and other postretirement benefit plans and the amounts we expect to contribute in 2010:
| Sempra Energy | | |
(Dollars in millions) | Consolidated | SDG&E | SoCalGas |
Contributions through September 30, 2010: | | | | | | |
Pension plans | $ | 91 | $ | 35 | $ | 37 |
Other postretirement benefit plans | | 39 | | 12 | | 26 |
Total expected contributions in 2010: | | | | | | |
Pension plans | $ | 163 | $ | 62 | $ | 72 |
Other postretirement benefit plans | | 52 | | 15 | | 33 |
EARNINGS PER SHARE
The following table pr ovides the per share computations for our earnings for the three months and nine months ended September 30, 2010 and 2009. Basic earnings per common share (EPS) is calculated by dividing earnings attributable to common stock by the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding for the period. Diluted EPS includes the potential dilution of common stock equivalent shares that could occur if securities or other contracts to issue common stock were exercised or converted into common stock.
EARNINGS PER SHARE COMPUTATIONS |
(Dollars in millions, except per share amounts; shares in thousands) |
| Three months ended September 30, | Nine months ended September 30, |
| 2010 | 2009 | 2010 | 2009 |
Numerator: | | | | | | | | |
Earnings | $ | 131 | $ | 317 | $ | 459 | $ | 831 |
| | | | | | | | |
Denominator: | | | | &n bsp; | | | | |
Weighted-average common shares | | | | | | | | |
outstanding for basic EPS | | 246,668 | | 243,925 | | 246,513 | | 242,806 |
Dilutive effect of stock options, res tricted | | | | | | | | |
& nbsp; stock awards and restricted stock units | | 3,143 | | 4,536 | | 3,260 | | 4,069 |
Weighted-average common shares | | | | | | | | |
outstanding for diluted EPS | | 249,811 | | 248,461 | | 249,773 | | 246,875 |
| | | | | | | | |
Earnings per share: | | | | | | | | |
Basic | $ | 0.53 | $ | 1.30 | $ | 1.86 | $ | 3.42 |
Diluted | $ | 0.53 | $ | 1.27 | $ | 1.84 | $ | 3.37 |
The dilution from common stock options is based on the treasury stock method. Under this method, proceeds based on the exercise price plus unearned compensation and windfall tax benefits or minus tax shortfalls related to the options are assumed to be used to repurchase shares on the open market at the average market price for the period. The windfall tax benefits are tax deductions we would receive upon the assumed exercise of stock options in e xcess of the deferred income taxes we recorded related to the compensation expense on the stock options. Tax shortfalls occur when the assumed tax deductions are less than recorded deferred income taxes. The calculation excludes options for which the exercise price on common stock was greater than the average market price during the period. We had 2,132,975 and 2,158,528 such stock options outstanding during the three months and nine months ended September 30, 2010, respectively. We had 1,505,096 and 1,507,361 such stock options outstanding during the three months and nine months ended September 30, 2009, respectively.
We had 10,800 and 8,407 stock options outstanding during the three months and nine months ended September 30, 2010, respectively, that were anti-dilutive because of the unearned compensation and windfall tax benefits included in the assumed proceeds under the treasury stock method. We had 890,781 such anti-dilutive stock options during the nine months ended September 30, 2009 and none for the three months ended September 30, 2009.
The dilution from unvested restricted stock awards and units is also based on the treasury stock method. Assumed proceeds equal to the unearned compensation and windfall tax benefits or minus tax shortfalls related to the awards and units are assumed to be used to repurchase shares on the open market at the average market price for the period. The windfall tax benefits or tax shortfalls are the difference between tax deductions we would receive upon the assumed vesting of restricted stock awards and units and the deferred income taxes we recorded related to the compensation expense on the restricted stock awards and units. There were no such anti-dilutive restricted stock awards or units during any period presented.
COMMON STOCK REPURCHASE PROGRAM
In September 2010, we entered into a Collared Accelerated Share Acquisition Program under which we prepaid $500 million to repurchase shares of our common stock in a share forward transaction. The total number of shares purchased (subject to a minimum of 8,078,000 shares and maximum of 10,321,889 shares) will be determined by dividing the $500 million purchase price by the volume-weighted average trading prices of shares of our common stock during a valuation period, minus a fixed discount and subject to a minimum and maximum price set during a hedging period. The program may extend into the first quarter of 2011.
Our outstanding shares used to calculate earnings per share are reduced by the number of shares repurchased when they are delivered to us, and the $500 million purchase price was recorded as a reduction in shareholders’ equity upon its prepayme nt. We received 5,670,006 shares during the quarter ended September 30, 2010, and 2,407,994 shares on October 4, 2010. We will receive any additional repurchased shares above the minimum at the end of the valuation period, which will continue until the program is completed.
SHARE-BASED COMPENSATION
We discuss our share-based compensation plans in Note 10 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in the Annual Report. We recorded share-based compensation expense, net of income taxes, of $4 million for both the three months ended September 30, 2010 and 2009, and $17 million and $15 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2010 and 2009, respectively. Pursuant to our share-based compensation plans, we granted 687,600 non-qualified stock options and 773,616 restricted stock units during the nine months ended September 30, 2010, primarily in Jan uary 2010.
CAPITALIZED FINANCING COSTS
Capitalized financing costs include capitalized interest costs and, at the Sempra Utilities, an allowance for funds used during construction (AFUDC) related to both debt and equity financing of construction projects. The following table shows capitalized financing costs for the three months and nine months ended September 30, 2010 and 2009.
CAPITALIZED FINANCING COSTS | | | | |
(Dollars in millions) | | | | |
| Three months ended September 30, | Nine months ended September 30, |
| 2010 | 2009 | 2010 | 2009 |
Sempra Energy Consolidated: | | | | | | | | |
AFUDC related to debt | $ | 6 | $ | 4 | $ | 16 | $ | 11 |
AFUDC related to equity | | 13 | | 10 | | 40 | | 28 |
Other capitalized financing costs | | 9 | | 15 | | 27 | | 62 |
Total Sempra Energy Consolidated | $ | 28 | $ | 29 | $ | 83 | $ | 101 |
SDG&E: | | | | | | | | |
AFUDC related to debt | $ | 5 | $ | 3 | $ | 12 | $ | 7 |
AFUDC related to equity | | 11 | | 8 | | 30 | | 21 |
Other capitalized financing costs | | - | | &nbs p;2 | | - | | 4 |
Total SDG&E | $ | 16 | $ | 13 | $ | 42&n bsp; | $ | 32 |
SoCalGas: | | | | | | | | |
AFUDC related to debt | $ | 1 | $ | 1 | $ | 4 | $ | 4 |
AFUDC related to equity | | 2 | | 2 | | 10 | | 7 |
Other capitalized financing costs | | - | | 1 | | - | | 1 |
Total SoCalGas | $ | 3 | $ | 4 | $ | 14 | $ | 12 |
COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
The following table provides a reconc iliation of net income to comprehensive income.
COMPREHENSIVE INCOME |
(Dollars in millions) |
| | Three months ended September 30, |
| | 2010 | | 2009 |
| | Share- | Non- | | | Share- | Non- | |
| | holders' | controlling | Total | | holders' | controlling | Total |
| | Equity(1) | Interests | Equity | | Equity(1) | Interests | Equity |
Sempra Energy Consolidated: | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income (loss)(2) | $ | 133 | $ | (6) | $ | 127 | | $ | 319 | $ | (17) | $ | 302 |
| Foreign currency translation | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| adjustments | | 53 | | - | | 53 | | | (11) | | - | | (11) |
| Financial instruments | | (3) | | 1 | | (2) | | | (5) | | - | | (5) |
| Available-for-sale securities | | 4 | | - | | 4 | | | 8 | | - | | 8 |
| Net actuarial gain | | 1 | | - | | 1 | | | 2 | | - | | 2 |
| Comprehensive income (loss) | $ | 188 | $ | (5) | $ | 183 | | $ | 313 | $ | (17) | $ | 296 |
SDG&E: | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income (loss) | $ | 108 | $ | (5) | $ | 103 | | $ | 110 | $ | (18) | $ | 92 |
| Financial instruments | | - | | 1 | | 1 | | | - | | - | | -& nbsp; |
| Comprehensive income (loss) | $ | 108 | $ | (4) | $ | 104 | | $ | 110 | $ | (18) | $ | 92 |
PE: | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income(2) | $ | 79 | $ | - | $ | 79 | | $ | 73 | $ | - | $ | 73 |
| Financial instruments | | 1 | | - | | 1 | | | - | | - | | - |
| Comprehensive income | $ | 80 | $ | - | $ | 80 | | $ | 73 | $ | - | $ | 73 |
SoCalGas: | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income | $ | 78 | $ | - | $ | 78 | | $ | 74 | $ | - | $ | 74 |
| Financial instruments | | 1 | | - | | 1 | | | - | | - | | - |
| Comprehensive income | $ | 79 | $ | - | $ | 79 | | $ | 74 | $ | - | $ | 74 |
COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (Continued) |
(Dollars in millions) |
| | Nine months ended September 30, |
| | 2010 | | 2009 |
| | Share- | Non- | | | Share- | Non- | |
| | holders' | controlling | Total | | holders' | controlling | Total |
| | Equity(1) | Interests | Equity | | Equity(1) | Interests | Equity |
Sempra Energy Consolidated: | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income (loss)(2) | $ | 466 | $ | (34) | $ | 432 | | $ | 838 | $ | (22) | $ | 816 |
| Foreign currency translation | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| adjustments | | 32 | | - | | 32 | | | 69 | | - | | 69 |
| Financial instruments | | (12) | | 5 | | (7) | | | 18 | | (3) | | 15 |
| Available-for-sale securities | | 1 | | - | | 1 | | | 21 | | - | | 21 |
| Net actuarial gain | | 4 | | - | | 4 | | | 4 | | - | | 4 |
| Comprehensive income (loss) | $ | 491 | $ | (29) | $ | 462 | | $ | 950 | $ | (25) | $ | 925 |
SDG&E: | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income (loss) | $ | 268 | $ | (34) | $ | 234 | | $ | 281 | $ | 9 | $ | 290 |
| Financial instruments | | - | | 5 | | 5 | | | 2 | | (3) | | (1) |
| Net actuarial gain | | 1 | | - | | 1 | | | 1 | | - | | 1 |
| Comprehensive income (loss) | $ | 269 | $ | (29) | $ | 240 | | $ | 284 | $ | 6 | $ | 290 |
PE: | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income(2) | $ | 215 | $ | - | $ | 215 | | $ | 195 | $ | - | $ | 195 |
| Financial instruments | | 2 | | - | | 2 | | | 2 | | - | | 2 |
| Comprehensive income | $ | 217 | $ | - | $ | 217 | | $ | 197 | $ | - | $ | 197 |
SoCalGas: | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income | $ | 213 | $ | - | $ | 213 | | $ | 199 | $ | - | $ | 199 |
| Financial instruments | | 2 | | - | | 2 | | | 2 | | - | | 2 |
| Comprehensive income | $ | 215 | $ | - | $ | 215 | | $ | 201 | $ | - | $ | 201 |
(1) | Shareholders' equity of Sempra Energy Consolidated, SDG&E, PE or SoCalGas as indicated in left margin. |
(2) | Before preferred dividends of subsidiaries. |
The amounts for comprehensive income in the table above are net of income tax expense (benefit) as follows:
INCOME TAX EXPENSE (BENEFIT) ASSOCIATED WITH OTHER COMPREHENSIVE INCOME |
(Dollars in millions) |
| | Three months ended September 30, |
| | 2010 | | 2009 |
| | Share- | Non- | | | Share- | Non- | |
| | holders' | controlling | Total | | holders' | controlling | Total |
| | Equity(1) | Interests | Equity | | Equity( 1) | Interests | Equity |
Sempra Energy Consolidated: | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Financial instruments | $ | (1) | $ | - | $ | (1) | | $ | (2) | $ | - | $ | (2) |
| Available-for-sale securities | | - | | - | | - | | | 6 | | - | | 6 |
| Net actuarial gain | | 1 | | - | | 1 | | | - | | - | | - |
SDG&E: | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Financial instruments | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - |
PE: | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Financial instruments | $ | 1 | $ | - | $ | 1 | | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - |
SoCalGas: | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Financial instruments | $ | 1 | $ | - | $ | 1 | | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Nine months ended September 30, |
| | 2010 | | 2009 |
| | Share- | Non- | | | Share- | Non- | |
| | holders' | controlling | Total | | holders' | controlling | Total |
| | Equity(1) | Interests | Equity | | Equity(1) | Interests | Equity |
Sempra Energy Consolidated: | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Financial instruments | $ | (7) | $ | - | $ | (7) | | $ | 12 | $ | - | $ | 12 |
| Available-for-sale securities | | (1) | | - | | (1) | | | 10 | | - | | 10 |
| Net actuarial gain | | 3 | | - | | 3 | | | 2 | | - | | 2 |
SDG&E: | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Financial instruments | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | | $ | 1 | $ | - | $ | 1 |
PE: | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Financial instruments | $ | 2 | $ | - | $ | 2 | | $ | 1 | $ | - | $ | 1 |
SoCalGas: | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Financial instruments | $ | 2 | $ | - | $ | ;2 | | $ | 1 | $ | - | $ | 1 |
(1) | Shareholders' equity of Sempra Energy Consolidated, SDG&E, PE or SoCalGas as indicated in left margin. |
SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY AND NONCONTROLLING INTERESTS
The following two tables provide a reconciliation of Sempra Energy and SDG&E shareholders’ equity and noncontrolling interests for the nine months ended S eptember 30, 2010 and 2009. There were no changes in the equity of PE's noncontrolling interests for the three months or nine months ended September 30, 2010 or 2009.
SHAREHOLDERS' EQUITY AND NONCONTROLLING INTERESTS |
(Dollars in millions) |
| | Sempra | | | | |
| | Energy | | Non- | | |
| | Shareholders' | | controlling | | Total |
| | Equity | | Interests | | Equity |
Balance at December 31, 2009 | $ | 9,007 | $ | 244 | $ | 9,251 |
Comprehensive income (loss) | | 491 | | (29) | | 462 |
Share-based compensation expense | | 31 | | - | | 31 |
Common stock dividends decl ared | | (287) | | - | | (287) |
Preferred dividends of subsidiaries | | (7) | | - | | (7) |
Issuance of common stock | | 53 | | - | | 53 |
Tax benefit related to share-based compensation | | 3 | | - | | 3 |
Repurchase of common stock | | (502) | | - | | (502) |
Common stock released from ESOP | | 13 | | - | | 13 |
Distributions to noncontrolling interests | | - | | (10) | | (10) |
Balance at September 30, 2010 | $ | 8,802 | $ | 205 | $ | 9,007 |
Balance at December 31, 2008 | $ | 7,969 | $ | 340 | $ | &n bsp;8,309 |
Comprehensive income (loss) | | 950 | | (25) | | 925 |
Purchase of noncontrolling interest in subsidiary | | (10) | | (84) | | (94) |
Share-based compensation expense | | &nbs p;28 | | - | | 28 |
Common stock dividends declared | | (287) | | - | | (287) |
Preferred dividends of subsidiaries | | (7) | | - | | (7) |
Issuance of common stock | | 81 | | - | | 81 |
Tax benefit related to share-based compensation | | 10 | | - | | 10 |
Common stock released from ESOP | | 11 | | - | | 11 |
Equity contributed by noncontrolling interests | | - | | 7 | | 7 |
Balance at September 30, 2009 | $ | 8,745 | $ | 238 | $ | 8,983 |
SHAREHOLDERS' EQUITY AND NONCONTROLLING INTEREST |
(Dollars in millions) |
| | SDG&E | | Non- | | |
| | Shareholders' | | controlling | | Total |
| | Equity | | Interest | | Equity |
Balance at December 31, 2009 | $ | 2,739 | $ | 146 | $ | 2,885 |
Comprehen sive income (loss) | | 269 | | (29) | | 240 |
Preferred stock dividends declared | | (4) | | - | | (4) |
Distributions to noncontrolling interest | | - | | (10) | | (10) |
Balance at September 30, 2010 | $ | 3,004 | $ | 107 | $ | 3,111 |
Balance at December 31, 2008 | $ | 2,542 | $ | 128 | $ | 2,670 |
Comprehensive income | | 284 | | 6 | | 290 |
Common stock dividends declared | | (150) | | - | | (150) |
Preferred stock dividends declared | | (4) | | - | | (4) |
Equity contributed by noncontrolling interest | | - | | 7 | | 7 |
Balance at September 30, 2009 | $ | 2,672 | $ | 141 | $ | 2,813 |
TRANSACTIONS WITH AFFILIATES
Loans to Unconsolidated Affiliates
S empra Pipelines & Storage has a U.S. dollar-denominated loan to Camuzzi Gas del Sur S.A., an affiliate of Sempra Pipelines & Storage’s Argentine investments, which we discuss in Note 1 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in the Annual Report. The loan to Camuzzi Gas del Sur S.A. has a $28 million balance outstanding at a variable interest rate (7.29 percent as ofSeptember 30, 2010). In May 2010, the maturity date of the loan was extended from June 2010 to June 30, 2011. The loan is fully reserved at September 30, 2010.
Investments
In November 2009, Sempra Pipelines & Storage purchased $50 million of 2.75-percent bonds issued by Chilquinta Energía S.A., an unconsolidated affiliate, that are adjusted for Chilean inflation. The bonds mature on October 30, 2014. The carrying value of the bonds after the effect of foreign currency translation was $55 million at Septembe r 30, 2010. We discuss this investment in Note 4 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in the Annual Report.
Other Affiliate Transactions
Sempra Energy, SDG&E and SoCalGas provide certain services to each other and are charged an allocable share of the cost of such services. Amounts due to/from affiliates are as follows:
AMOUNTS DUE TO AND FROM AFFILIATES AT SDG&E, PE AND SOCALGAS |
(Dollars in millions) |
| | September 30, | | December 31, |
| 2010 | | 2009 |
SDG&E | | | | | |
Current: | | | | | |
Due from Sempra Energy | $ | - | | $ | 2 |
Due from SoCalGas | | 3 | | | 3 |
Due from various affiliates | | 1 | | | 3 |
| $ | 4 | | $ | 8 |
| | | | | |
Due to Sempra Energy | $ | 21 | | $ | - |
| | | | | |
Income taxes due from Sempra Energy(1) | $ | (92) | | $ | (37 ) |
| | | | | |
Noncurrent: | | | | | |
Promissory note due from Sempra Energy, variable rate based on | | | | | |
short-term commercial paper rates (0.13% at December 31, 2009) | $ | - | | $ | 2 |
| | | | | |
Pacific Enterprises | | | | | |
Current: | | | | | |
Due from Sempra Energy | $ | 113 | | $ | 7 |
Due from various affiliates | | 5 | | | 5 |
| $ | 118 | | $ | 12 |
| | | | | |
Due to affiliate | $ | 84 | | $ | 84 |
Due to SDG&E | | 3 | | | 3 |
| $ | 87 | | $ | 87 |
| | | | | |
Income taxes due to (from) Sempra Energy(1) | $ | 1 | | $ | (2) |
| | | | | |
Noncurrent: | | | | | |
Promissory note due from Sempra Energy, variable rate based on | | | | | |
short-term commercial paper rates (0.17% at September 30, 2010) | $ | 504 | | $ | 513 |
| | | | | |
SoCalGas | | | | | |
Current: | | | | | |
Due from Sempra Energy | $ | 118 | | $ | 6 |
| | | | | |
Due to SDG&E | $ | 3 | | $ | 3 |
| | | | | | |
Income taxes due to (from) Sempra Energy(1) | $ | 5 | | $ | (2) |
(1) | SDG&E, PE and SoCalGas are included in the consolidated income tax return of Sempra Energy and are allocated income tax expense from Sempra Energy in an amount equal to that which would result from the companies' having always filed a separate return. |
Revenues from unconsolidated affiliates at the Sempra Utilities are as follows:
REVENUES FROM UNCONSOLIDATED AFFILIATES AT THE SEMPRA UTILITIES |
(Dollars in millions) |
| Three months ended | Nine months ended |
| September 30, | September 30, |
| 2010 | 2009 | 2010 | 2009 |
SDG&E | $ | 1 | $ | 2 | $ | 6 | $ | 6 |
SoCalGas | | 11 | | 9 | | 32 | | 24 |
Transactions with RBS Sempra Commodities
Several of our business units engage in transactions with RBS Sempra Commodities. Amounts in our Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements related to these transactions are as follows:
AMOUNTS RECORDED FOR TRANSACTIONS WITH RBS SEMPRA COMMODITIES |
(Dollars in millions) |
| | Three months ended | Nine months ended |
| | September 30, | September 30, |
| 2010 | 2009 | 2010 | 2009 |
Revenues: | | | | | | | | |
Sempra LNG(1) | $ | 60 | $ | 16 | $ | 199 | $ | 21 |
Sempra Commodities | | 6 | | 7 | | 19 | | 11 |
SDG&E | | - | | 2 | | - | | 2 |
SoCalGas | &n bsp; | 1 | | 3 | | 8 | | 6 |
Sempra Generation | | 4 | | (15) | | - | | (6) |
Total revenues | $ | 71 | $ | 13 | $ | 226 | $ | 34 |
| | | | | | | | | |
Cost of natural gas: | | | | | | | | |
Sempra LNG | $ | 63 | $ | - | $ | 208 | $ | - |
Sempra Generation | | 30 | | - | | 58 | | - |
SoCalGas | | 10 | | 1 | | 33 | | 6 |
Sempra Pipelines & Storage | | 6 | | 5 | | 22 | | 15 |
SDG&E | | 1 | | - | | 2 | | - |
Total cost of natural gas | $ | 110 | $ | 6 | $ | 323 | $ | 21 |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | September 30, | December 31, |
| | | | | 2010 | 2009 |
Fixed-price contracts and other derivatives - Net Asset (Liability): | | | | | | | | |
Sempra Generation | | | | | $ | 28 | $ | 7 |
Sempra LNG | | | | | | (36) | | (47) |
Total | | | | | $ | (8) | $ | (40) |
| | | | | | | | |
Due to unconsolidated affiliates: | | | | | | | | |
Sempra Generation | | | | | $ | 8 | $ | 13 |
Sempra LNG | | | | | | - | | 13 |
Sempra Pipelines & Storage | | | | | | 2 | | 3 |
Total | | | | | $ | 10 | $ | 29 |
| | | | | | | | |
Due from unconsolidated affiliates: | | | | | | | | |
Sempra Commodities | | | | | $ | 1 | $ | 1 |
Sempra Generation | | | | | | 7 | | 22 |
Sempra LNG | | | | | | 17 | | 15 |
Parent and other | | | | | | 5 | | 3 |
Total | | | | | $ | 30 | $ | 41 |
(1) | Includes (losses) gains of $(3) million and $11 million for the three mo nths and nine months ended September 30, 2010, respectively, and losses of $6 million and $5 million for the three months and nine months ended September 30, 2009, respectively, related to a natural gas sales agreement with RBS Sempra Commodities which is subject to mark-to-market accounting. Under this agreement, which extends for five years beginning September 1, 2009, RBS Sempra Commodities will market natural gas that Sempra LNG purchases and does not sell under other contracts. |
WRITE-OFF OF LONG-LIVED ASSETS
In the second quarter of 2009, we recorded a pretax write-off of $132 million related to certain assets at one of Sempra Pipelines & Storage’s Liberty Gas Storage natural gas storage projects. Sempra Pipelines & Storage owns a 75-percent interest in the partnership that is developing the project. Our partner’ s 25-percent share of the pretax charge was $33 million, which is included in Losses Attributable to Noncontrolling Interests on our Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations for the nine months ended September 30, 2009. The impact to our net income and to our earnings was $97 million and $64 million, respectively, for the nine months ended September 30, 2009. We discuss this write-off further in Note 1 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in the Annual Report.
OTHER INCOME (EXPENSE), NET
Other Income (Expense), Net on the Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations consists of the following:
OTHER INCOME (EXPENSE), NET |
(Dollars in millions) |
| | Three months ended Se ptember 30, | Nine months ended September 30, |
| | 2010 | 2009 | 2010 | 2009 |
Sempra Energy Consolidated: | | | | | | | | |
Allowance for equity funds used during construction | $ | 13 | $ | 10 | $ | 40 | $ | 28 |
Investment gains(1) | | 10 | | 20 | | 15 | ; | 40 |
Gains (losses) on interest rate instruments(2) | | (17) | | (10) | | (40) | | 19 |
Regulatory interest, net | | 1 | | 4 | | - | | 4 |
Sundry, net(3) | | 59 | | - | | 67 | | 6 |
| Total | $ | 66 | $ | 24 | $ | 82 | $ | 97 |
SDG&E: | | | | | | | | |
Allowance for equity funds used during construction | $ | 11 | $ | 8 | $ | 30 | $ | ;21 |
Gains (losses) on interest rate instruments(2) | | (17) | | (11) | | (51) | | 19 |
Regulatory interest, net | | - | | 5 | | - | | 5 |
Sundry, net | | 4 | | (1) | | 3 | | - |
| Total | $ | (2) | $ | 1 | $ | (18) | $ | 45 |
SoCalGas and PE: | | | | | | | | |
Allowance for equity funds used during construction | $ | 2 | $ | 2 | $ | 10 | $ | 7 |
Regulatory interest, net | | - | | (1) | | - | | (1) |
Sundry, net | | - | | (2) | | (2) | | (2) |
| Total at SoCalGas | | 2 | | (1) | | 8 | | 4 |
Additional at PE: | | | | | | | | |
Sundry, net | | - | | (3) | | - | | (3) |
| Total at PE | $ | 2 | $ | (4) | $ | 8 | $ | 1 |
(1) | Represents investment gains on dedicated assets in support of our executive retirement and deferred compensation plans. These amounts are partially offset by corresponding changes in compensation expense related to the plans. |
(2) | Related to Otay Mesa VIE. Sempra Energy Consolidated also includes additional instruments. |
(3) | Amounts in 2010 include proceeds from a legal settlement of $48 million, as we discuss in Note 4. | | |
INCOME TAXES
INCOME TAX EXPENSE (BENEFIT) AND EFFECTIVE INCOME TAX RATES |
(Dollars in millions) |
| | | Three months ended September 30, |
| | | 2010 | | 2009 |
| | | Income Tax Expense | | Effective Income | | | Income Tax | | Effective Income | |
| | | (Benefit) | | Tax Rate | | | Expense | | Tax Rate | |
Sempra Energy Consolidated | $ | (32) | | (32) | % | $ | 128 | | 31 | % |
SDG&E | | 56 | | 35 | | | 53 | | 37 | |
PE | | 42 | | 35 | | | 41 | | 36 | |
SoCalGas | | 42 | | 35 | | | 42 | | 36 | |
| | | Nine months ended September 30, |
| | | 2010 | | 2009 |
| | | Income Tax | | Effective Income | | | Income Tax | | Effective Income | |
| | | Expense | | Tax Rate | | | Expense | | Tax Rate | |
Sempra Energy Consolidated | $ | 85 | | 18 | % | $ | 327 | | 30 | % |
SDG&E | | 131 | | 36 | | | 141 | | 33 | |
PE | | 132 | | 38 | | | 117 | | 38 | |
SoCalGas | | 132 | | 38 | | | 115 | | 37 | |
Changes in Effective Income Tax Rates
Sempra Energy Consolidated
The change in effective income tax rate for the three months ended September 30, 2010 was primarily due to:
§higher planned investment tax credits;
§higher exclusions from taxable income of the equity portion of AFUDC; and
§higher pretax income (including a $175 million gain related to our share of the RBS Sempra Commodities sale to J.P. Morgan Ventures on July 1, 2010) in countries with lower statutory rates; offset by
§$11 million state income tax expense related to our exit from the RBS Sempra Commodities business;
§lower favorable impact from the resolution of prior years' income tax issues;
§an increase in the amount by which book depreciation exceeds normalized tax depreciation, which is not treated as a deferred tax asset for ratemaking purposes; and
§$5 million tax expense in 2010 compared to $3 million tax benefit in 2009 due to Mexican currency translation and inflation adjustments.
For the nine months ended September 30, 2010, the effective income tax rate decreased primarily due to:
§higher planned investment tax credits;
§higher deductions for self-developed software costs;
§higher pretax income (including a $175 million gain related to our share of the RBS Sempra Commodities sale to J.P. Morgan Ventures on July 1, 2010) in countries with lower statutory rates; and
§higher exclusions from taxable income of the equity portion of AFUDC; offset by
§$11 million state income tax expense related to our exit from the RBS Sempra Commodities business;
§lower favorable impact from the resolution of prior years' in come tax issues;
§a $16 million write-down of the deferred tax assets related to other postretirement benefits, as a result of a change in U.S. tax law that eliminates a future deduction, starting in 2013, for retiree healthcare funded by the Medicare Part D subsidy;
§an increase in the amount by which book depreciation exceeds normalized tax depreciation, which is not treated as a deferred tax asset for ratemaking purposes; and
§$4 million higher tax expense in 2010 due to Mexican currency translation and inflation adjustments.
SDG&E
The decrease in SDG&E's effective income tax rate for the three months ended September 30, 2010 was primarily due to:
§the impact of Otay Mesa VIE;
§a decrease in the amount by which book depreciation exceeds normalized tax depreciation, which is not treated as a deferred tax asset for ratemaking purposes;
§higher exclusions from taxable income of the equity portion of AFUDC; and
§higher favorable impact from the resolution of prior years' income tax issues; offset by
§lower deductions for self-developed software costs;
§lower deductions for other postretirement benefits; and
§lower utility repair allowance.
For the nine months ended September 30, 2010, the increase in SDG&E's effective income tax rate was primarily due to:
§the impact of Otay Mesa VIE;
§a $3 million write-down of the deferred t ax assets related to other postretirement benefits as a result of a change in U.S. tax law, as we discuss above;
§an increase in the amount by which book depreciation exceeds normalized tax depreciation, which is not treated as a deferred tax asset for ratemaking purposes;
§lower deductions for other postretirement benefits; and
§lower utility repair allowance; offset by
§higher exclusions from taxable income of the equity portion of AFUDC; and
§higher favorable impact from the resolution of prior years' income tax issues.
SDG&E's results include Otay Mesa VIE, which is consolidated, and therefore, SDG&E's effective income tax rate is impacted by the VIE’s stand-alone effective income tax rate.
PE and SoCalGas
The decrease in PE's and SoCalGas' effective income tax rates for the three months ended September 30, 2010 was primarily due to:
§higher deductions for self-developed software costs; offset by
§lower deductions for other postretirement benefits; and
§an increase in the amount by which book depreciation exceeds normalized tax depreciation, which is not treated as a deferred tax asset for ratemaking purposes.
For the nine months ended September 30, 2010, the increase in SoCalGas’ effective income tax rate was primarily due to:
§a $13 million write-down of the deferred tax assets related to other postretirement benefits as a result of a change in U.S. tax law, as we discuss above;
§lower deductions for other postretirement benefits; and
§an increase in the amount by which book depreciation exceeds normalized tax depreciation, which is not treated as a deferred tax asset for ratemaking purposes; offset by
§higher deductions for self-developed software costs; and
§higher exclusions from taxable income of the equity portion of AFUDC.
Although it did not change year-over-year, these fluctuations are also reflected in PE’s effective income tax rate.
NOTE 6. DEBT AND CREDIT FACILITIES
COMMITTED LINES OF CREDIT
At September 30, 2010, Sempra Energy Consolidated had $4.3 billion in committed lines of credit to provide liquidity and to support commercial paper and variable-rate demand notes, the major components of which we detail below. Available unused credit on these lines at September 30, 2010 was $3.4 billion. In October 2010, we entered into new credit agreements to replace our previous principal credit agreements. The new agreements have a longer term and, in light of our exit from the commodities joint venture which we discuss in Note 4, a lower credit commitment by $500 million (at Sempra Global).
Sempra Energy
In October 2010, Sempra Energy entered into a new $1 billion, four-year syndicated revolving credit agreement expiring in October 2014, replacing the previous $1 billion three-year credit agreement scheduled to expire in 2011. Citibank, N.A. serves as administrative agent for the syndicate of 23 lenders. No single lender has greater than a 7-percent share.
Borrowings bear interest at benchmark rates plus a margin that varies with market index rates and Sempra Energy's credit ratings. The facility requires Sempra Energy to maintain a ratio of total indebtedness to total capitalization (as defined in the agreement) of no more than 65 percent at the end of each quarter. The facility also provides for issuance of up to $400 million of letters of credit on behalf of Sempra Energy with the amount of borrowings otherwise available under the facility reduced by the amount of outstanding letters of credit.
Under the previous credit agreement at September 30, 2010, Sempra Energy had no outstanding borrowings supported by the facility.
Sempra Global
In October 2010, Sempra Global entered into a new $2 billion, four-year syndicated revolving credit agreement expiring in October 2014, replacing the previous $2.5 billion three-year credit agreement scheduled to expire in 2011. Citibank, N.A. serves as administrative agent for the syndicate of 23 lenders. No single lender has greater than a 7-percent share.
Sempra Energy guarantees Sempra Global’s obligations under the credit facility. Borrowings bear interest at benchmark rates plus a margin that varies with market index rates and Sempra Energy’s credit ratings. The facility requires Sempra Energy to maintain a ratio of total indebt edness to total capitalization (as defined in the agreement) of no more than 65 percent at the end of each quarter.
Under the previous credit agreement at September 30, 2010, Sempra Global had $7 million of letters of credit outstanding, $38 million of variable-rate demand notes outstanding, and $574 million of commercial paper outstanding supported by the facility.
Sempra Utilities
In October 2010, SDG&E and SoCalGas entered into a new combined $800 million, four-year syndicated revolving credit agreement expiring in October 2014, replacing the previous $800 million three-year credit agreement scheduled to expire in 2011. JPMorgan Chase Bank serves as administrative agent for the syndicate of 22 lenders. No single lender has greater than a 7-percent share. The agreement permits each utility to individually borrow up to $600 million, subject to a combined limit of $800 million for both utilities. It also provides for the issuance of letters of credit on behalf of each utility subject to a combined letter of credit commitment of $200 million for both utilities. The amount of borrowings otherwise available under the facility is reduced by the amount of outstanding letters of credit.
Borrowings under the facility bear interest at benchmark rates plus a margin that varies with market index rates and the borrowing utility's credit rating. The agreement requires each utility to maintain a ratio of total indebtedness to total capitalization (as defined in the agreement) of no more than 65 percent at the end of each quarter.
Each utility’s obligations under the agreement are individual obligations, and a default by one utility would not constitute a default by the other utility or preclude borrowings by, or the issuance of letters o f credit on behalf of, the other utility.
Under the previous credit agreement at September 30, 2010, SDG&E and SoCalGas had no outstanding borrowings and SDG&E had $25 million of letters of credit outstanding and $237 million variable-rate demand notes outstanding supported by the facility. Available unused credit on the lines at September 30, 2010 was $338 million at SDG&E and $538 million at SoCalGas; SoCalGas' availability reflects the impact of SDG&E's use of the combined credit available on the line.
GUARANTEES
RBS Sempra Commodities
As we discuss in Note 4, Sempra Energy, RBS and RBS Sempra Commodities have completed the sale of certain businesses within the partnership, and there is one pending transaction for the sale of the remaining pri ncipal assets expected to close before year-end. In connection with each of these transactions, the buyers are, subject to certain qualifications, obligated to replace any guarantees that we have issued in connection with the applicable businesses sold with guarantees of their own. During the process of replacing the guarantees, they are obligated to indemnify us in accordance with the applicable transaction documents for any claims or losses in connection with the guarantees that we issued in connection with the businesses sold. With respect to the transaction with Noble Group, for those guarantees that Noble Group is not able to replace, we have agreed to allow Noble Group to continue trading under such guarantees until June 1, 2011.
We have indemnified the partnership for certain litigation and tax liabilities related to the businesses purchased by the partnership. We recorded these obligations at a fair value of $5 million on April 1, 2008, the date we formed the partnership. This liability is being amortized over its expected life. Certain of these obligations may be remeasured when the indemnity is reissued to the buyers of the Sempra Commodities businesses.
RBS is obligated to provide RBS Sempra Commodities with all working-capital requirements and credit support. However, as a transitional measure, we continue to provide back-up guarantees for a portion of RBS Sempra Commodities’ trading obligations. Some of these back-up guarantees may continue for a prolonged period of time. RBS, which is controlled by the government of the United Kingdom, has fully indemnified us for any claims or losses in connection with these arrangements.
RBS Sempra Commodities’ net trading liabilities supported by Sempra Energy’s guarantees at September 30, 2010 were $561 million, consisting of guaranteed trading obligations net of collateral. Th e amount of guaranteed net trading liabilities varies from day to day with the value of the trading obligations and related collateral.
Other Guarantees
Sempra Energy, Conoco Phillips (Conoco) and Kinder Morgan Energy Partners, L.P. (KMP) currently hold 25-percent, 25-percent and 50-percent ownership interests, respectively, in Rockies Express. Rockies Express operates a natural gas pipeline linking natural gas producing areas in the Rocky Mountain region to the upper Midwest and the eastern United States. In April 2010, Rockies Express’ $2 billion, five-year credit facility expiring in May 2011 that provided for revolving extensions of credit guaranteed by Sempra Energy, Conoco and KMP in proportion to their respective ownership percentages was reduced to $200 million, and Sempra Energy, Conoco and KMP were released from their guarantor obligations. Long-term debt of $1.7 billion i ssued in March 2010 was used to pay down the credit facility; this new debt is not separately guaranteed by the partners.
Sempra Generation and BP Wind Energy currently hold 50-percent ownership interests in Fowler Ridge. In August 2010, Fowler Ridge obtained a $348 million term loan expiring in August 2022. The proceeds were used to return $180 million of each owner’s investment in the joint venture. The loan agreement requires Sempra Generation and BP Wind Energy to return cash to the project in the event that the project does not meet certain cash flow criteria or in the event that the project’s debt service and operation and maintenance reserve accounts are not maintained at specific thresholds. Sempra Generation recorded a liability of $9 million for its obligation associated with the cash flow requirements, which constitutes a guarantee. The outstanding loan is not separately guaranteed by the partners. We provide additional information a bout the investment in Note 4 above and in Note 4 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in the Annual Report.
WEIGHTED AVERAGE INTEREST RATES
The weighted average interest rates on the total short-term debt outstanding at Sempra Energy were 0.39 percent and 0.79 percent at September 30, 2010 and December 31, 2009, respectively. The short-term debt outstanding at SDG&E at December 31, 2009 was a non-interest bearing loan at Orange Grove.
LONG-TERM DEBT
In August 2010, SDG&E publicly offered and sold $500 million of 4.50-percent first mortgage bonds, maturing in 2040.
In May 2010, SDG&E publicly offered and sold $250 million of 5.35-percent first mortgage bonds, maturing in 2040.
SDG&E has two power purchase agreements with peaker plant facilities that went into commercial operation in June 2010 and are accounted for as capital leases. As of September 30, 2010, capital lease obligations for these leases, each with a 25-year term, were $181 million.
INTEREST RATE SWAPS
We discuss our fair value interest rate swaps and interest rate swaps to hedge cash flows in Note 7.
NOTE 7. DERIVATIVE FI NANCIAL INSTRUMENTS
We use derivative instruments primarily to manage exposures arising in the normal course of business. These exposures are commodity market risk and benchmark interest rate risk. Our use of derivatives for these risks is integrated into the economic management of our anticipated revenues, anticipated expenses, assets and liabilities. Derivatives may be effective in mitigating these risks that could lead to declines in anticipated revenues or increases in anticipated expenses, or that our asset values may fall or our liabilities increase. Accordingly, our derivative activity summarized below generally represents an impact that is intended to offset associated revenues, expenses, assets or liabilities that are not presented below.
We record all derivatives at fair value on the Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheets. We designate each derivative as 1) a cash flow hedge, 2) a fair value hedge, or 3) undesignated. Depending on the applicability of hedge accounting and, for the Sempra Utilities and other operations subject to regulatory accounting, the requirement to pass impacts through to customers, the impact of derivative instruments may be offset in other comprehensive income (cash flow hedge), on the balance sheet (fair value hedges and regulatory offsets), or recognized in earnings. We classify cash flows from the settlements of derivative instruments as operating activities on the Condensed Statements of Consolidated Cash Flows.
In certain cases, we apply the normal purchase or sale exception to derivative accounting and have other commodity contracts that are not derivatives. These contracts are not recorded at fair value and are therefore excluded from the disclosures below.
HEDGE ACCOUNTING
We may designate a derivative as a cash flow hedging instrument if it effectively converts anticipated revenues or expenses to a fixed dollar amount. We may utilize cash flow hedge accounting for derivative commodity instruments and interest rate instruments. Designating cash flow hedges is dependent on the business context in which the instrument is being used, the effectiveness of the instrument in offsetting the risk that a given future revenue or expense item may vary, and other criteria.
We may designate an interest rate derivative as a fair value hedging instrument if it effectively converts our own debt from a fixed interest rate to a variable rate. The combination of the derivative and debt instruments results in fixing that portion of the fair value of the debt that is related to benchmark interest rates. Designating fair value hedges is dependent on the instrument being used, the effectiveness of the instrument in offsetti ng changes in the fair value of our debt instruments, and other criteria.
ENERGY DERIVATIVES
Our market risk is primarily related to natural gas and electricity price volatility and the specific physical locations where we transact. We use energy derivatives to market energy products and manage these risks. The use of energy derivatives in our various businesses depends on the particular energy market, and the operating and regulatory environments applicable to the business.
§The Sempra Utilities use natural gas energy derivatives, on their customers' behalf, with the objective of managing price and basis risks and lowering natural gas costs. These derivatives include fixed price natural gas positions, options, and basis risk instruments, whi ch are either exchange-traded or over-the-counter financial instruments. This activity is governed by risk management and transacting activity plans that have been filed with and approved by the California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC). Natural gas derivative activities are recorded as commodity costs that are offset by regulatory account balances and are recovered in rates. Net commodity cost impacts on the Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations are reflected in Cost of Electric Fuel and Purchased Power or in Cost of Natural Gas.
§SDG&E is allocated and may purchase congestion revenue rights (CRRs), which serve to reduce the regional electricity price volatility risk which may result from local transmission capacity constraints. Unrealized gains and losses do not impact earnings, as they are offset by regulatory account balances . Realized gains and losses associated with CRRs are recorded in Cost of Electric Fuel and Purchased Power on the Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations.
§Sempra Generation uses natural gas and electricity instruments to market energy products and optimize the earnings of its power generation fleet. Gains and losses associated with these derivatives are recognized in Sempra Global and Parent Revenues or in Cost of Natural Gas, Electric Fuel and Purchased Power on the Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations.
§Sempra LNG and Sempra Pipelines & Storage use natural gas derivatives to market energy products and optimize the earnings of the liquefied natural gas business and Sempra Pipelines & Storage's natural gas storage and transportation asse ts. Sempra Pipelines & Storage also uses natural gas energy derivatives with the objective of managing price risk and lowering natural gas prices at its Mexican distribution operations. Sempra Pipelines & Storage’s derivatives are either undesignated or are recorded as commodity costs that are offset by regulatory account balances and are recovered in rates. The impacts on earnings are recognized in Sempra Global and Parent Revenues or in Cost of Natural Gas, Electric Fuel and Purchased Power on the Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations. Sempra LNG’s derivatives are undesignated and their impact on earnings is recorded in Sempra Global and Parent Revenues on the Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations.
§From time to time, our various businesses, including the Sempra Utilities, may use other energy derivatives to hedge exposures such as the price of vehicl e fuel.
We summarize net energy derivative volumes as of September 30, 2010 as follows:
Business Unit and Commodity | Volume | |
Sempra Utilities: | | |
| SDG&E: | | |
| | Natural gas | 48 million MMBtu | (1) |
| | Congestion revenue rights | 19 million MWh | (2) |
| | | |
Sempra Global: | | |
| Sempra LNG - natural gas | 7 million MMBtu | |
| Sempra Pipelines & Storage - natural gas | 1 million MMBtu | |
| Sempra Generation - electric power | 1 million MWh | |
(1) | Million British thermal units | |
(2) | Mega watt hours | |
In addition to the amounts noted above, we frequently use commodity derivatives to manage risks associated with the physical locations of our customers, assets and other contractual obligations, such as natural gas purchases.
INTEREST RATE DERIVATIVES
We are exposed to interest rates primarily as a result of our current and expected use of financing. We periodically enter into interest rate derivative agre ements intended to moderate our exposure to interest rates and to lower our overall costs of borrowing. We utilize interest rate swaps typically designated as fair value hedges, as a means to achieve our targeted level of variable rate debt as a percent of total debt. In addition, we may utilize interest rate swaps, which are typically designated as cash flow hedges, to lock in interest rates in anticipation of future financings.
Interest rate derivatives are utilized by the Sempra Utilities as well as by other Sempra Energy subsidiaries. Although the Sempra Utilities generally recover borrowing costs in rates over time, the use of interest rate derivatives is subject to certain regulatory constraints, and the impact of interest rate derivatives may not be recovered from customers as timely as described above with regard to natural gas derivatives. Accordingly, interest rate derivatives are generally accounte d for as hedges at the Sempra Utilities, as at the rest of Sempra Energy's subsidiaries. Separately, Otay Mesa VIE has entered into interest rate swap agreements to moderate their exposure to interest rate changes.
The net notional amounts of our interest rate derivatives as of September 30, 2010 were:
| | September 30, 2010 |
(Dollars in millions) | Notional Debt | Maturities |
Sempra Energy Consolidated(1) | $ | 215-355 | 2011-2019 |
SDG&E(1) | | 285-372 | 2019 |
SoCalGas | | 150 | 2011 |
(1) | Includes Otay Mesa VIE. All of SDG&E's interest rate derivatives relate to Otay Mesa VIE. |
FINANCIAL STATEMENT PRESENTATION
The following table provides the fair values of derivative instruments, without consideration of margin deposits held or posted, on the Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheets as of September 30, 2010 and December 31, 2009:
DERIVATIVE INSTRUMENTS ON THE CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS |
(Dollars in millions) |
| | September 30, 2010 |
| | | | | | | | | Deferred |
| | | | | | | | | credits |
| | | Current | | | | Current | | and other |
| | | asse ts: | | | | liabilities: | | liabilities: |
| | | Fixed-price | | Investments | | Fixed-price | | Fixed-price |
| | | contracts | | and other | | contracts | | contracts |
| | | and other | | assets: | | and other | | and other |
Derivatives designated as hedging instruments | | derivatives(1) | | Sundry | | derivatives(2) | | derivatives |
Sempra Energy Consolidated: | | | | | | | | |
| Interest rate instruments | $ | 3 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - |
SoCalGas: | | | | | | | | |
| Interest rate instruments | $ | 3 | $ | - | $ | -&nb sp; | $ | - |
| | | | | | | | | |
Derivatives not designated as hedging instruments | | | | | | | | |
Sempra Energy Consolidated: | | | | | | | | |
| Interest rate instruments(3) | $ | 9 | $ | 36 | $ | (26) | $ | (92) |
| Commodity contracts not subject to rate recovery | | 90 | | 34 | | (70) | | (41) |
| Associated offsetting commodity contracts | | (29) | | (13) | | 29 | | 13 |
| Commodity contracts subject to rate recovery | | 12 | | 5 | | (61) | | (32) |
| Associated offsetting commodity contracts | | (53) | | (30) | | 53 | | 30 |
| Total | $ | 29 | $ | 32 | $ | (75) | $ | (122) |
SDG&E: | | | | | | | | |
| Interest rate instruments(3) | $ | - | $ | - | $ | (17) | $ | (62) |
| Commodity contracts subject to rate recovery | | 8 | | 5 | | (48) | | (32) |
| Associated offsetting commodity contracts | | (48) | | (30) | | 48 | | 30 |
| Total | $ | (40) | $ | (25) | $ | (17) | $ | (64) |
SoCalGas: | | | | | | | | |
| Commodity contracts subject to rate recovery | $ | 4 | $ | - | $ | (5) | $ | - |
| Associated offsetting commodity contracts | | (5) | | - | ; | 5 | | - |
| Total | $ | (1) | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, 2009 |
| | | | | | | | | Deferred |
| | | �� | | | | | | credits |
| | | Current | | | | Current | | and other |
| | | assets: | | | | liabilities: | | liabilities: |
| | | Fixed-price | | Investments | | Fixed - -price | | Fixed-price |
| | | contracts | | and other | | contracts | | contracts |
| | | and other | | assets: | | and other | | and other |
Derivatives designated as hedging instruments | | derivatives(1) | | Sundry | | derivatives(2) | | derivatives |
Sempra Energy Consolidated: | | | | | | ; | | |
| Interest rate instruments | $ | 12 | $ | 2 | $ | - | $ | - |
| Commodity contracts not subject to rate recovery | | 1 | | - | | - | | - |
| Total | $ | 13 | $ | 2 | $ | - | $ | - |
SoCalGas: | | | | | | | | |
| Interest rate instruments | $ | 6 | $ | 2 | $ | - | $ | - |
| | | | | | | | | |
Derivatives not designated as hedging instruments | | | | | | | | |
Sempra Energy Consolidated: | | | | | | | | |
| Interest rate instruments(3) | $ | 9 | $ | 15 | $ | (25) | $ | (33) |
| Commodity contracts not subject to rate recovery | | 74 | | 30 | | (64) | | (42) |
| Associated offsetting commodity contracts | | (34) | | (6) | | 34 | | 6 |
| Commodity contracts subject to rate recovery | | 20 | | 7 | | (20) | | (13) |
| Associated offsetting commodity contracts | | (14) | | (9) | | 14 | | 9 |
| Total | $ | 55 | $ | 37 | $ | (61) | $ | (73) |
SDG&E: | | | | | | | | |
| Interest rate instruments(3) | $ | - | $ | - | $ | (17) | $ | (26) |
| Commodity contracts subject to rate recovery | | 18 | | 7 | | (13) | | (9) |
| Associated offsetting commodity contracts | | (13) | | (9) | | 13 | | 9 |
| Total | $ | 5 | $ | (2) | $ | (17) | $ | (26) |
SoCalGas: | | | | | | | | |
| Commodity contracts subject to rate recovery | $ | 2 | $ | ;- | $ | (1) | $ | - |
| Associated offsetting commodity contracts | | (1) | | - | | 1 | | - |
| Total | $ | 1 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - |
(1) | Included in Current Assets: Other for SoCalGas. |
(2) | Included in Current Liabilities: Other for SoCalGas. |
(3) | Includes Otay Mesa VIE. All of SDG&E's amounts relate to Otay Mesa VIE. |
The effects of derivative instruments designated as hedges on the Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations for the three months and nine months ended September 30, 2010 and 2009 were:
FAIR VALUE HEDGE IMPACT ON THE CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS |
(Dollars in millions) |
| | | Gain (loss) on derivative recognized in earnings |
| | | Three months ended September 30, | Nine months ended September 30, |
| Location | 2010 | 2009 | 2010 | 2009 |
Sempra Energy Consolidated: | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest rate instruments | Interest Expense | $ | 2 | $ | 5 | $ | 9 | $ | 5 |
| Interest rate instruments | Other Income, Net | | (2) | | (5) | | (11) | | (12) |
| Total(1) | | $ | - | $ | - | $ | (2) | $ | (7) |
SoCalGas: | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest rate instrument | Interest Expense | $ | 2 | $ | (5) | $ | 5 | $ | (5) |
| Interest rate instrument | Other Income, Net | | (2) | | (1) | | (4) | | (3) |
| Total(1) | | $ | &nb sp;- | $ | (6) | $ | 1 | $ | (8) |
(1) | There has been no hedge ineffectiveness on these swaps. Changes in the fair values of the interest rate swap agreements are exactly offset by changes in the fair value of the underlying long-term debt. |
CASH FLOW HED GE IMPACT ON THE CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS | | |
(Dollars in millions) | | |
| | Pretax gain (loss) recognized | | | Gain (loss) reclassified from AOCI |
| | in OCI (effective portion) | | | into earnings (effective portion) |
| | Three months ended September 30, | | | Three months ended September 30, |
| 2010 | 2009 | | Location | 2010 | 2009 |
Se mpra Energy Consolidated: | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest rate instruments(1) | $ | - | $ | (8) | | Interest Expense | $ | (2) | $ | 4&n bsp; |
| Commodity contracts not | | | | | | Revenues: Sempra Global | | | | |
| subject to rate recovery | | - | | - | | and Parent | | - | | 2 |
| Commodity contracts not | | | | | | Cost of Natural Gas, Electric | | | | |
| subject to rate recovery | | - | | (3) | | Fuel and Purchased Power | | - | | (1) |
| Commodity contracts not | | | | | | Equity Earnings (Losses): RBS | | | | |
| subject to rate recovery | | 1 | | - | | Sempra Commodities LLP | | 7 | | - |
| Total | $ | 1 | $ | (11) | | | $ | 5 | $ | 5 |
SDG&E: | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest rate instruments(1) | $ | - | $ | - | | Interest Expense | $ | (1) | $ | 6 |
SoCalGas: | | & nbsp; | | | | | | | | |
| Interest rate instruments | $ | - | $ | - | | Interest Expense | $ | (1) | $ | (1) |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Pretax gain (loss) recognized | | | Gain (loss) reclassified from AOCI |
| | in OCI (effective portion) | | | into earnings (effective portion) |
| | Nine months ended September 30, | | | Nine months ended September 30, |
| 2010 | 2009 | | Location | 2010 | 2009 |
Sempra Energy Consolidated: | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest rate instruments(1) | $ | - | $ | 13 | | Interest Expense | $ | (9) | $ | - |
| Interest rate instruments | | - | | - | | Other Income, Net(2) | | 10 | | - |
| Commodity contracts not | | | | | | Revenues: Sempra Global | | | | |
| subject to rate recovery | | - | | 11 | | and Parent | | - | | 18 |
| Commodity contracts not | | | | | | Cost of Natural Gas, Electric | | | | |
| subject to rate recovery | | - | | (5) | | Fuel and Purchased Power | | - | | (9) |
| Commodity contracts not | | | | | | Equity Earnings (Losses): RBS | | | | |
| subject to rate recovery | | 1 | | - | | Sempra Commodities LLP | | 14 | | (9) |
| Total | $ | 1 | $ | 19 | | | $ | 15 | $ | - |
SDG&E: | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest ra te instruments(1) | $ | - | $ | - | | Interest Expense | $ | (5) | $ | 4 |
SoCalGas: | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest rate instruments | $ | - | $ | - | | Interest Expense | $ | (4) | $ | (3) |
(1) | Amounts in 2010 include Otay Mesa VIE. All of SDG&E's 2010 interest rate derivative act ivity relates to Otay Mesa VIE. |
(2) | Gains reclassified into earnings due to changes in cash requirements and associated impacts on forecasted interest payments, primarily related to proceeds received from RBS Sempra Commodities. See Note 4. |
Sempra Energy expects that losses of $5 million, which are net of income tax benefit, that are currently recorded in Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) related to cash flow hedges will be reclassified into earnings during the next twelve months as the hedged items affect earnings. Actual amounts ultimately reclassified to earnings depend on the commodity prices and interest rates in effect when derivative contracts that are currently outstanding mature. The maximum term over which RBS Sempra Commodities hedges forecasted natural gas purchases and sales is 63 months.
SDG&E and SoCalGas expect that losses of $6 million and $2 million, respectively, which are net of income tax benefit, that are currently recorded in Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) related to these cash flow hedges will be reclassified into earnings during the next twelve months as the hedged items affect earnings.
The effects of derivative instruments not designated as hedging instruments on the Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations for the three months and nine months ended September 30, 2010 and 2009 were:
UNDESIGNATED DERIVATIVE IMPACT ON THE CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS |
(Dollars in millions) |
| | | Gain (loss) on derivative recognized in earnings |
| | | Three months ended September 30, | Nine months ended September 30, |
| Location | 2010 | 2009 | 2010 | 2009 |
Sempra Energy Consolidated: | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest rate instruments(1) | Other Income, Net | $ | (17) | $ | (10) | $ | (50) | $ | 19 |
| Commodity contracts not subject | | | | | | | | | |
| to rate recovery | Revenues: Sempra Global and Parent | | 15 | | 60 | | 45 | | 35 |
| Commodity contracts not subject | Cost of Natural Gas, Electric | | | | | | | | |
| to rate recovery | Fuel and Purchased Power | | (7) | | (49) | | & nbsp;(22) | | (30) |
| Commodity contracts subject | Cost of Electric Fuel | | | | | | | | |
| to rate recovery | and Purchased Power | | (39) | | (18) | | (100) | | (24) |
| Commodity contracts subject | | &n bsp; | | | | | | | |
| to rate recovery | Cost of Natural Gas | | (4) | | - | | (5) | | (3) |
| Commodity contracts subject | Cost of Natural Gas, Electric | | | | | | | | |
| to rate recovery | Fuel and Purchased Power | | (1) | | - | | (4) | | - |
| Total | | $ | (53) | $ | (17) | $ | (136) | $ | (3) |
SDG&E: | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest rate instruments(1) | Other Income (Expense), Net | $ | (17) | $ | (11) | $ | (51) | $ | 19 |
| Commodity contracts subject | Cost of Electric Fuel | | | | | | | | |
| to rate recovery | and Purchased Power | | (39) | | (18) | | (100) | | (24) |
| Total | | $ | (56) | $ | (29) | $ | (151) | $ | (5) |
SoCalGas: | | | | | | | | | |
| Commodity contracts subject | | | | | | | | | |
| to rate recovery | Cost of Natural Gas | $ | (4) | $ | - | $ | (5) | $ | (3) |
(1) | Related to Otay Mesa VIE. Sempra Energy Consolidated also includes additional instruments. |
CONTINGENT FEATURES
For Sempra Energy and SDG&E , certain of our derivative instruments contain credit limits which vary depending upon our credit ratings. Generally, these provisions, if applicable, may reduce our credit limit if a specified credit rating agency reduces our rating. In certain cases, if our credit ratings were to fall below investment grade, the counterparty to these derivative liability instruments could request immediate payment or demand immediate and ongoing full collateralization.
For Sempra Energy, the total fair value of this group of derivative instruments in a net liability position at September 30, 2010 is $5 million. As of September 30, 2010, if the credit ratings of Sempra Energy and SDG&E were both reduced below investment grade, $5 million of additional assets could be required to be posted as collateral for these derivative contracts.
For SDG&E, the total fair value of this group of derivative instruments in a net liability position at September 30, 2010 is $2 million. As of September 30, 2010, if the credit ratings of SDG&E were reduced below investment grade, $2 million of additional assets could be required to be posted as collateral for these derivative contracts.
For Sempra Energy, SDG&E, PE and SoCalGas, some of our derivative contracts contain a provision that would permit the counterparty, in certain circumstances, to request adequate assurance of our performance under the contract. Such additional assurance, if needed, is not material and is not included in the amounts above.
NOTE 8. FAIR VALUE MEASUREMENTS
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
The fair values of certain of our financial instruments (cash, temporary investments, accounts and notes receivable, dividends and accounts payable, short-term debt and customer deposits) approximate their carrying amounts. The following table provides the carrying amounts and fair values of the remaining financial instruments at September 30, 2010 and December 31, 2009:
FAIR VALUE OF FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS |
(Dollars in millions) |
| | September 30, 2010 | December 31, 2009 |
| | Carrying | Fair | Carrying | Fair |
| | Amount | Value | Amount | Value |
Sempra Energy Consolidated: | | | | | | | | |
Investments in affordable housing partnerships(1) | $ | 29 | $ | 58 | $ | 34 | $ | 59 |
Total long-term debt(2) | | 8,152 | | 9,288 | | 8,004 | | 8,572 |
Due to unconsolidated affiliate | | 2 | | 2 | | 2 | | 2 |
Preferred stock of subsidiaries | | 179 | | 171 | | 179 | | 156 |
SDG&E: | | | | | | | | |
Total long-term debt(3) | $ | 3,308 | $ | 3,594 | $ | 2,652 | $ | 2,808 |
Contingently redeemable preferred stock | | 79 | | 82 | | 79 ; | | 76 |
PE and SoCalGas: | | | | | | | | |
Total long-term debt(4) | $ | 1,266 | $ | 1,396 | $ | 1,270 | $ | 1,356 |
| | | | | | | | |
PE: | | | | | | | | |
Preferred stock | $ | 80 | $ | 69 | $ | 80 | $ | 61 |
Preferred stock of subsidiary | | 20 | | 20 | | 20 | | 19 |
| | | | | | | | | |
SoCalGas: | | | | | | | | |
Preferred stock | $ | 22 | $ | 21 | $ | 22 | $ | 20 |
(1) | We discuss our investments in affordable housing partnerships in Note 4 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in the Annual Report. |
(2) | Before reductions for unamortized discount of $21 million at September 30, 2010 and $17 million at December 31, 2009, and excluding capital leases of $214 mill ion at September 30, 2010 and $46 million at December 31, 2009. |
(3) | Before reductions for unamortized discount of $10 million at September 30, 2010 and $4 million at December 31, 2009, and excluding capital leases of $197 million at September 30, 2010 and $20 million at Decemb er 31, 2009. |
(4) | Before reductions for unamortized discount of $2 million at September 30, 2010 and $2 million at December 31, 2009, and excluding capital leases of $17 million at September 30, 2010 and $26 million at December 31, 2009. |
Sempra Energy based the fair values of investments in affordable housing partnerships on the present value of estimated future cash flows, discounted at rates available for similar investments. All entities based the fair values of long-term debt and preferred stock on their quoted market prices or quoted market prices for similar securities.
Nuclear Decommissioning Trusts
We discuss SDG&E's investments in nuclear decommissioning trust funds in Note 7 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in the Annual Report. The following table shows the fair values and gross unrealized gains and losses for the securities held in the trust funds:
NUCLEAR DECOMMISSIONING TRUSTS |
(Dollars in millions) |
| | | | | Gross | | Gross | | Estimated |
| | | | | Unrealized | | Unrealized | | Fair |
| | | Cost | | Gains | | Losses | | Value |
As of September 30, 2010: | | | | | | | | |
Debt securities | | | | | | | | |
Debt securities issued by the U.S. Treasury and other | | | | | | | | |
U.S. government corporations and agencies(1) | $ | 141 | $ | 24 | $ | - | $ | 165 |
Municipa l bonds(2) | | 85 | | 5 | | (1) | | 89 |
Other securities(3) | | 22 | | 4 | | - | | 26 |
Total debt securities | | 248 | | 33 | | (1) | | 280 |
Equity securities | | 240 | | 201 | | (2) | | 439 |
Cash and cash equivalents | | 18 | | - | | - | | 18 |
Total available-for-sale securities | $ | 506 | $ | 234 | $ | (3) | $ | 737 |
As of December 31, 2009: | | | | | | | | |
Debt securities | | | | | | | | |
Debt securities issued by the U.S. Treasury and other | | | | | | | | |
U.S. government corporations and agencies | $ | 141 | $ | 12 | $ | (3) | $ | 150 |
Municipal bonds | | 85 | | 3 | | (3) | | 85 |
Other securities | | 12 | | 1 | | - | | 13 |
Total debt securities | | 238 | | 16 | | (6) | | 248 |
Equity securities | | 238 | | 188 | | (5) | | 421 |
Cash and cash equivalents | | 9 | | - | | - | | 9 |
Total available-for-sale securities | $ | 485 | $ | 204 | $ | (11) | $ | 678 |
(1) | Maturity dates are 2011-2040. |
(2) | Maturity dates are 2012-2057. |
(3) | Maturity dates are 2011-2049. |
The following table shows the proceeds from sales of securities in the trusts and gross realized gains and losses on those sales:
SALES OF SECURITIES |
(Dollars in millions) |
| Three months ended September 30, | Nine months ended September 30, |
| 2010 | 2009 | 2010 | 2009 |
Proceeds from sales | $ | 97 | $ | 62 | $ | 247 | $ | 150 |
Gross realized gains | | 4 | | - | | 7 | | 4 |
Gross realized losses | | (2) | | (6) | | (9) | | (30) |
Net unrealized gains (losses) are included in Regulatory Liabilities Arising from Removal Obligations on the Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheets. We determine the cost of securities in the trusts on the basis of specific identification.
Derivative Positions Net of Cash Collateral
Each Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheet reflects the offsetting of net derivative positions with fair value amounts for cash collateral with the same counterparty when management believes a legal right of offset exists.
The following table provides the amount of fair value of cash collateral receivables that were not offset in the Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheets as of September 30, 2010 and December 31, 2009:
| September 30, | December 31, |
(Dollars in millions) | 2010 | 2009 |
Sempra Energy Consolidated | $ | 24 | $ | 36 |
SDG&E | | 21 | | 30 |
SoCalGas | | 3 | | 5 |
Fair Value Hierarchy
We discuss the valuation techniques and inputs we use to measure fair value and the definition of the three levels of the fair value hierarchy in Notes 1 and 2 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in the Annual Report. We have not changed the valuation techniques or inputs we use to measure fair value during the nine months ended September 30, 2010.
The three tables below, by level within the fair value hierarchy, set forth our financial assets and liabilities that were accounted for at fair value on a recurring basis as of September 30, 2010 and December 31, 2009. We also discuss our financial assets and liabilities recorded at fair value on a non-recurring basis. We classify financial assets and liabilities in their entirety based on the lowest level of input that is significant to the fair value measurement. Our asses sment of the significance of a particular input to the fair value measurement requires judgment, and may affect the valuation of fair value assets and liabilities, and their placement within the fair value hierarchy levels.
The fair value of commodity derivative assets and liabilities is determined in accordance with our netting policy, as discussed above under "Derivative Positions Net of Cash Collateral."
The determination of fair values, shown in the tables below, incorporates various factors, including but not limited to, the credit standing of the counterparties involved and the impact of credit enhancements (such as cash deposits, letters of credit and priority interests).
We discuss our financial assets and liabilities that were accounted for at fair value on a recurring basis further in Note 12 of the Notes to Consolida ted Financial Statements in the Annual Report.
RECURRING FAIR VALUE MEASURES -- SEMPRA ENERGY CONSOLIDATED |
(Dollars in millions) |
| At fair value as of September 30, 2010 |
| | | | | | | | Collateral | | |
| | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 | | netted | | Total |
Assets: | | | | | | | | | | |
&n bsp; Nuclear decommissioning trusts(1) | | | | | | | | | | |
Equity securities | $ | 439 | $ | - | $ | -&n bsp; | $ | - | $ | 439 |
Debt securities: | | | | | | | | | | |
Debt securities issued by the U.S. Treasury and other | | | | | | | | | | |
U.S. government corporations and agencies | | 132 | | 33 | | - | | - | | 165 |
Municipal bonds | | - | | 89 | | - | | - | | 89 |
Other securities | | - | | 26 | | - | | - | | 26 |
Tota l debt securities | | 132 | | 148 | | - | | - | | 280 |
Total nuclear decommissioning trusts(1) | | 571 | | 148 | | - | | - | | 719 |
Interest rate instruments | | -& nbsp; | | 49 | | - | | - | | 49 |
Commodity contracts subject to rate recovery | | 21 | | - | | 12 | | - | | 33 |
Commodity contracts not subject to rate recovery | | 5 | | 79 | | - | | (20) | | 64 |
Investments | | 9 | | - | | - | | - | | 9 |
Total | $ | 606 | $ | 276 | $ | 12 | $ | (20) | $ | 874 |
Liabilities: | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest rate instruments | $ | - | $ | 117 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 117 |
Commodity contracts subject to rate recovery | | 79 | | 10 | | - | | (79) | | 10 |
Commodity contracts not subject to rate recovery | | - | | 69 | | - | | - | | 69 |
Total | $ | 79 | $ | 196 | $ | - | $ | (79) | $ | 196 |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| At fair value as of December 31, 2009 |
| | | | | | | | Collateral | | |
| | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 | | netted | | Total |
Assets: | | | | | | | | | | |
Nuclear decommissioning trusts(1) | | | | | | | | & nbsp; | | |
�� Equity securities | $ | 421 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 421 |
Debt securities: | | | | | | | | | | |
Debt securities issued by the U.S. Treasury and other | | | | | | | | | | |
U.S. government corporations and agencies | | 111 | | 39 | | - | | - | | 150 |
Municipal bonds | | - | | 85 | | - | | - | | 85 |
Other securities | | - | | 13 | | - | | - | | 13 |
Total debt securities | | 111 | | 137 | | - | | - | | 248 |
Total nuclear decommissioning trusts(1) | | 532 | | 137 | | - | | - | | 669 |
Interest rate instruments | | - | | 38 | | - | | - | | 38 |
Commodity contracts subject to rate recovery | | 32 | | 3 | | 10 | | - | | 45 |
Commodity contracts not subject to rate recovery | | 7 | | 62 | | - | | (40) | | 29 |
Investments | | 1 | | - | | - | | - | | 1 |
Total | $ | 572 | $ | 240 | $ | 10 | $ | (40) | $ | 782 |
Liabilities: | | | | | | | | | | |
; Interest rate instruments | $ | - | $ | 59 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 59 |
Commodity contracts subject to rate recovery | | 9 | | 9 | | - | | (9) | | 9 |
Commodity contracts not subject to rate recovery | | - | | 65 | | - | | - | | 65 |
Total | $ | 9 | $ | 133 | $ | - | $ | (9) | $ | 133&nbs p; |
(1) | Excludes cash balances and cash equivalents. | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
RECURRING FAIR VALUE MEASURES -- SDG&E |
(Dollars in millions) |
| At fair value as of September 30, 2010 |
| | | | | | | | Collateral | | |
| | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 | | netted | | Total |
Assets: | | | | | | | | | | |
Nuclear decommissioning trusts(1) | | | | | | | | | | |
Equity securities | $ | 439 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 439 |
Debt securities: | | &n bsp; | | | | | | | | |
Debt securities issued by the U.S. Treasury and other | | | | | | | | | | |
U.S. government corporations and agencies | | 132 | | 33 | | - | | - | | 165 |
Municipal bonds | | - | | 89 | | - | | - | | 89 |
Other securities | | - | | 26 | | - | | - | | 26 |
Total debt securities | | 132 | | 148 | | - | | - | | 280 |
Total nuclear decommissioning trusts(1) | | 571 | | 148 | | - | | - | | 719 |
Commodity contracts subject to rate recovery | | 20 | | - | | 12 | | - | | 32 |
Commodity contracts not subject to rate recovery | | 1 | | - | | - | | - | | 1 |
Total | $ | 592 | $ | 148 | $ | 12 | $ | - | $ | 752 |
| | | | | | | | | | |
Liabilities: | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest rate instruments | $ | - | $ | 79 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 79 |
Commodity contracts subject to rate recovery | | 78 | | 2 | | - | | (78) | | 2 |
Total | $ | 78 | $ | 81 | $ | - | $ | (78) | $ | 81 |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| At fair value as of December 31, 2009 |
| | | | | | | | Collateral | | |
| | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 | | netted | | Total |
Assets: | | | | | | | | | | |
Nuclear decommissioning trusts(1) | | | | | | | | | | |
Equity securities | $ | 421 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 421 |
Debt securities: | | | | | | | | | | |
Debt securities issued by the U.S. Treasury and other | | | | | | | | | | |
U.S. government corporations and agencies | | 111 | | 39 | | - | | - | | 150 |
Municipal bonds | | - | | 85 | | - | | - | | 85 |
Other securities | | - | | 13 | | - | | - | | 13 |
Total debt securities | | 111 | | 137 | | - | | - | | 248 |
Total nuclear decommissioning trusts(1) | | 532 | | 137 | | - | | - | | 669 |
Commodity contracts subject to rate recovery | | 29 | | 2 | | 10 | | - | | 41 |
Commodity contracts not subject to rate recovery | | 1 | | - | | - | | - | | 1 |
Total | $ | 562 | $ | 139 | $ | 10 | $ | - | $ | 711 |
| | | | | | | | | | |
Liabilities: | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest rate instruments | $ | - | $ | 43 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 43 |
Commodity contracts subject to rate recovery | | 9 | | - | | - | | (9) | | - |
Total | $ | 9 | $ | 43 | $ | - | $ | (9) | $ | 43 |
(1) | Excludes cash balances and cash equivalents. | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
RECURRING FAIR VALUE MEASURES -- SOCALGAS |
(Dollars in millions) |
| At fair value as of September 30, 2010 |
| | | | | | | | Collateral | | |
| | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 | | netted | | Total |
Assets: | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest rate instruments | $ | - | $ | 3 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 3 |
Commodity contracts subject to rate recovery | | 1 | | - | | - | | - | | 1 |
Commodity contracts not subject to rate recovery | | 2 | | - | | & nbsp;- | | - | | 2 |
Total | $ | 3 | $ | 3 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 6 |
Liabilities: | | | | | | | | | | |
Commodity contracts subject to rate recovery | $ | 1 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | (1) | $ | - |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| At fair value as of December 31, 2009 |
| | | | | | | | Collateral | | |
| | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 | | netted | | Total |
Assets: | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest rate instruments | $ | - | $ | 8 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 8 |
Commodity contracts subject to rate recovery | | 3 | | 1 | | - | | - | | 4 |
Commodity contracts not subject to rate recovery | | 3 | | - | | - | | - | | 3 |
Total | $ | 6 | $ | 9 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 15 |
There were no transfers into or out of Level 1 or Level 2 for Sempra Energy Consolidated, SDG&E or SoCalGas during the periods presented.
Level 3 Information
The following table sets forth reconciliations of changes in the fair value of net trading and other derivatives classified as Level 3 in the fair value hierarchy for Sempra Energy Consolidated and SDG&E:
| Three months ended September 30, |
(Dollars in millions) | 2010 | 2009 |
Balance as of July 1 | $ | 7 | $ | 25 |
Realized and unrealized losses | | (1) | | (8) |
Allocated transmission instruments | | 7 | | 15 |
Settlements | | (1) | | - |
Balance as of September 30 | $ | 12 | $ | 32 |
Change in unrealized gains relating to | | | | |
instruments still held at September 30 | $ | - | $ | - |
| Nine months ended September 30, |
(Dollars in millions) | 2010 | 2009 |
Balance as of January 1 | $ | 10 | $ | 27 |
Realized and unrealized losses | | (5) | | (7) |
Allocated transmission instruments | | 7 | | 15 |
Settlements | | - | | (3) |
Balance as of September 30 | $ | 12 | $ | 32 |
Change in unrealized gains relating to | | | | |
instruments still held at September 30 | $ | - | $ | - |
There were no transfers into or out of Level 3 during the periods presented.
Gains and losses (realized and unrealized) for Level 3 recurring items are primarily related to SDG&E's congestion revenue rights and were included in Cost of Electric Fuel and Purchased Power on the Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations for the three months and nine months ended September 30, 2010 and 2009.
Non-Recurring Fair Value Measures – Sempra Energy Consolidated
We discuss non-recurring fair value measures and the associated accounting impact in Note 4.
NOTE 9. SEMPRA UTILITIES' REGULATORY MATTERS
POWER PROCUREMENT AND RESOURCE PLANNING
Sunrise Powerlink Electric Transmission Line
In December 2008, the CPUC issued a final decision authorizing SDG&E to construct a 500-kilovolt (kV) electric transmission line between the Imperial Valley and the San Die go region (Sunrise Powerlink). This line is designed to provide 1,000 MW of increased import capability into the San Diego area. This CPUC decision approved SDG&E’s request to construct the Sunrise Powerlink along a route that would generally run south of the Anza-Borrego Desert State Park. The decision also approves the environmental impact review conducted jointly by the CPUC and the Bureau of Land Management (BLM) and establishes a total project cost cap of $1.9 billion, including approximately $190 million for environmental mitigation costs. In January 2009, the BLM issued its decision approving the project, route and environmental review.
The CPUC decision requires SDG&E to adhere to certain commitments it made during the application process, as follows:
§not to contract, for any length of term, with conventional coal g enerators to deliver power via the Sunrise Powerlink;
§if any currently approved renewable energy contract that is deliverable via the Sunrise Powerlink fails, to replace it with a viable contract with a renewable generator located in the Imperial Valley region; and
§voluntarily raise SDG&E's Renewables Portfolio Standard Program goal (discussed below under "Renewable Energy") to 33 percent by 2020.
After the issuance by the CPUC of its final decision, the Utility Consumers Action Network (UCAN) and the Center for Biological Diversity/Sierra Club (CBD) applied for rehearing of the final decision. After the CPUC denied t hese rehearing applications, in August 2009, UCAN and the CBD jointly filed a petition with the California Supreme Court challenging the CPUC's decision with regard to implementation of the California Environmental Quality Act (CEQA). UCAN also filed a petition with the California Court of Appeal (Court of Appeal) challenging the decision on other legal grounds, which the Court of Appeal denied in August 2010. The UCAN/CBD appeal will be addressed by the California Supreme Court now that the Court of Appeal has dismissed UCAN's first petition.
In addition, three appeals of the BLM decision were filed with the Interior Board of Land Appeals (IBLA) by individuals, a community organization, and the Viejas Indian tribe. The Viejas Indian tribe withdrew its appeal and the IBLA denied the other two appeals.
Opponents who filed the BLM appeals also filed a lawsuit in Federal District Court for declarato ry and injunctive relief regarding Sunrise Powerlink. The complaint alleges that the BLM failed to properly assess the environmental impacts of the approved Sunrise Powerlink route and the related potential development of renewable resources in east San Diego County and Imperial County. The complaint requests a declaration that the BLM violated federal law in approving Sunrise Powerlink and an injunction against any construction activities. On October 25, 2010, the court granted SDG&E's motion to dismiss the complaint in its entirety for want of standing; the plaintiffs filed an amended complaint on November 5, 2010.
In September 2010, the CPUC and BLM jointly approved the final Project Modification Report, accepting all of the proposed modifications to the approved route and finding that no additional environmental studies are required. In October 2010, the United States Forest Service (USFS) issued a decision rejecting all pending appeals and rea ffirming its July 2010 decision approving the segment of Sunrise Powerlink's route within its jurisdiction. The USFS is expected to issue a special use permit to SDG&E by year-end, which will allow SDG&E to begin construction on USFS land. On October 22, 2010, the CBD and the plaintiffs in the Federal District Court suit against BLM filed an application for rehearing with the CPUC challenging its approval of the Project Modification Report. The CPUC summarily rejected this application for rehearing as contrary to the CPUC's rules. On October 25, 2010, the BLM federal court plaintiffs filed an appeal with the IBLA challenging the BLM's approval of the Project Modification Report. This appeal was accompanied by a motion for a stay of construction of the project, which SDG&E opposed on November 4, 2010. SDG&E will also oppose the IBLA appeal.
Sunrise Powerlink costs will be recovered in SDG&E's Electric Transmission Formula Rate, where SDG&E must demonstrate to the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) that such costs were prudently incurred.
The total amount invested by SDG&E in the Sunrise Powerlink project as of September 30, 2010 was $447 million, which is included in Property, Plant and Equipment on the Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheets of Sempra Energy and SDG&E. SDG&E expects the Sunrise Powerlink to be in commercial operation in the second half of 2012.
We provide additional information concerning Sunrise Powerlink in Note 15 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in the Annual Report.
Renewable Energy
Certain California electric retail sellers, including SDG&E, are required to deliver 20 percent of their retail energy sales from renewable energy sources beginning in 2010. The rules governing this requirem ent, administered by both the CPUC and the California Energy Commission (CEC), are generally known as the Renewables Portfolio Standard (RPS) Program. In September 2009, the Governor of California issued an Executive Order which set a target for each California utility to procure 33 percent of their annual electric energy requirements from renewable energy sources by 2020. This Executive Order designates the California Air Resources Board (CARB) as the agency responsible for establishing the compliance rules and regulations under CARB's Assembly Bill 32 authority to regulate greenhouse gas emissions. In September 2010, CARB adopted a requirement known as the California Renewable Energy Standard (RES), which obligates California utilities to procure 33 percent of their annual electric energy requirements from renewable energy sources by 2020. CARB has not yet issued the final version of formal regulations articulating the requirement or detailing how the RES will be implemented.
In 2008, the CPUC issued a decision defining flexible compliance mechanisms that can be used to defer compliance with or meet the RPS Program mandates in 2010 and beyond. The decision established that a finding by the CPUC of insufficient transmission is a permissible reason to defer compliance with the RPS Program mandates. This decision also confirmed that any renewable energy procured in excess of the established targets for prior years, currently and in the future, could be applied to any procurement shortfalls in the years 2010 and beyond.
SDG&E continues to procure renewable energy supplies to achieve the RPS Program goals and the Executive Order/RES requirements. A substantial number of these supply contracts, however, are contingent upon many factors, including:
§access to electric transmission inf rastructure (including SDG&E's Sunrise Powerlink transmission line);
§timely regulatory approval of contracted renewable energy projects;
§the renewable energy project developers' ability to obtain project financing and permitting; and
§successful development and implementation of the renewable energy technologies.
SDG&E believes it will be able to comply with the RPS Program requirements based on its contracting activity and application of the flexible compliance mechanisms. SDG&E's failure to comply with the RPS Program requir ements in 2010, or in any subsequent years, could subject it to a CPUC-imposed penalty of 5 cents per kilowatt hour of renewable energy under-delivery up to a maximum penalty of $25 million per year. A determination regarding RES compliance is not possible at this time, as program details are not yet known.
Solar Photovoltaic Program
The CPUC issued a decision in September 2010 approving a new solar photovoltaic (PV) program for SDG&E. Under the adopted program, SDG&E may develop up to 100 MW of solar PV in its service area, consisting of up to 26 MW of utility owned generation and up to 74 MW of purchased power from independent producers. Individual project size may range up to 5 MW. Over the 5-year program, SDG&E will be allowed to spend up to $100 million in capital costs for the systems it owns, based on an overall cost cap of $3.50 per watt, including a 10-percent contingency factor. A cost cap of $235 per MWh will apply to purchased power under the program.
East County Substation
In August 2009, SDG&E filed an application with the CPUC for authorization to proceed with the East County Substation Project, which will include construction of a new 500/230/138-kV substation, rebuilding of the existing Boulevard Substation and construction of a new 138-kV transmission line connecting the two substations. The project, estimated to cost approximately $280 million, would allow interconnections from new renewable-generation sources and enhance the reliability of electric service to a number of communities. The CPUC and BLM have agreed to prepare a joint environmental impact report and environmental impact statement. A CPUC decision on this project is expected in 2011.
GENERAL RATE CASE (GRC)
The CPUC uses a general rate case proceeding to prospectively set rates sufficient to allow the Sempra Utilities to recover their reasonable cost of operations and to provide the opportunity to realize an acceptable rate of return on their investments. The Sempra Utilities filed their Notices of Intent (NOI) for the 2012 General Rate Case (2012 GRC) in August 2010. These NOIs are preliminary applications that propose revenue requirement increases of $246 million for SDG&E and $282 million for SoCalGas over their respective 2011 authorized revenue. These increases would equate to increases in rates of 7 percent for SDG&E and 7.4 percent for SoCalGas over their 2010 rates. In October 2010, the CPUC staff completed its review of the NOIs and accepted the proposed filings, enabling both SDG&E and SoCalGas to file their final applications in mid-December 2010. The CPUC is scheduled to issue a decision on each of the final applications in late 2011, with changes in rates to become effective on January 1, 2012.
A number of parties have asked the CPUC to delay the filing of SDG&E's and SoCalGas' next GRC applications for at least a year. To date, the CPUC has denied all such requests and has ordered SDG&E and SoCalGas to follow their original GRC schedules.
UTILITY INCENTIVE MECHANISMS
The CPUC applies performance-based measures and incentive mechanisms to all California utilities, under which the Sempra Utilities have earnings potential above authorized base margins if they achieve or exceed specific performance and operating goals.
We provide additional information regarding these incentive mechanisms in Note 16 of the Notes to Consolidat ed Financial Statements in the Annual Report, and updates below.
Natural Gas Procurement
In January 2010, the CPUC approved a Gas Cost Incentive Mechanism (GCIM) award of $12 million for SoCalGas' procurement activities during the 12-month period ending March 31, 2009. In June 2010, SoCalGas applied to the CPUC for approval of a GCIM award of $6 million for SoCalGas' procurement activities during the 12-month period ending March 31, 2010. SoCalGas expects a CPUC decision in 2011.
Energy Efficiency
In December 2009, the CPUC awarded $0.3 million and $2.1 million, net of a 35 percent holdback pending a final true-up in 2010, to SDG&E and SoCalGas, respectively, for their performance during the 2006 – 2008 program period. In February 2010, the Sempra Utilities filed a petition with the CPUC to correct errors in the computation of the awards. If adopted, the changes would increase the awards by $0.4 million for SDG&E and $1.3 million for SoCalGas, net of the 35 percent holdback.
An Administrative Law Judge draft decision and a Commissioner alternate decision were issued in September 2010 regarding the final true-up of the energy efficiency incentive earnings for the 2006 – 2008 program period. The draft decision rules that no additional incentive payments are warranted for the final true-up of incentive earnings. The alternate decision approves additional incentive awards of $6 million for SDG&E and $3.9 million for SoCalGas for the final true-up of the amounts held back for prior years' awards, but makes no determination on the petition to correct errors. A final decision is expected by the end of 2010.
COST OF CAPITAL
A cost of capital proceeding determines the Sempra Utilities' authorized capital structure and the authorized rate of return that the Sempra Utilities may earn on their electric and natural gas distribution and electric generation assets.
In January 2010, the CPUC approved SDG&E's and the Division of Ratepayer Advocates' (DRA) joint petition to delay SDG&E's next scheduled cost of capital proceeding for two years. With this approval, SDG&E's next cost of capital application is scheduled to be filed in April 2012 for a 2013 test year, consistent with the schedule for cost of capital applications for each of Southern California Edison (Edison) and Pacific Gas and Electric (PG&E).
In addition to establishing the authorized rate of return, a cost of capital proceeding also addresses market-based benchmarks to be monitored to determine whether an adjustment to the established authorized rate of return is required during the interim years between cost of capital proceedings. SDG&E’s cost of capital benchmark is based on the 12-month average monthly A-rated utility bond yield as published by Moody’s for the 12-month period October through September of each fiscal year. If this 12-month average falls outside of the range of 5.02 percent to 7.02 percent, SDG&E’s authorized rate of return would be adjusted, upward or downward, by one-half of the difference between the 12-month average and 6.02 percent (SDG&E’s benchmark interest rate), effective January 1 following the year in which the benchmark range was exceeded.
SoCalGas’ cost of capital trigger mechanism identifies two conditions for determining whether a change in the authorized rate of return is required. Both conditions are based on the 30-year Treasury Bond Yields – one being the most recent 12-month rolling average yield and the second being the corresponding 12-month forecasted rolling yield on 30-year Treasury Bonds as published by Global Insights. If both interest rates fall outside a range of 3.88 percent to 6.88 percent, SoCalGas’ authorized rate of return would be adjusted, upward or downward, by one-half of the difference between the historical 12-month rolling average yield and 5.38 percent (SoCalGas' benchmark interest rate), effective January 1 following the year in which both conditions were exceeded.
At September 30, 2010, neither SDG&E’s nor SoCalGas’ benchmark ranges have been exceeded.
ADVANCED METERING INFRASTRUCTURE
In April 2010, the C PUC issued a decision approving SoCalGas' application to upgrade approximately six million natural gas meters with an advanced metering infrastructure (AMI), subject to certain safeguards to better ensure its cost effectiveness for ratepayers. The approved cost of the project is $1.05 billion (including approximately $900 million in capital investment), with SoCalGas being subject to risk/reward sharing for costs above or below this amount. Installation of the meters is expected to begin in late 2012 and continue through 2017.
In May 2010, The Utility Reform Network (TURN) and the Utility Workers Union of America (UWUA) Local 132, parties opposing SoCalGas' AMI application, filed an application for rehearing of the CPUC's decision. The application for rehearing is still pending.
SDG&E REQUEST FOR AUTHORITY TO INVEST IN WIND FARM
In July 2010, SDG&E filed a request with the CPUC seeking authority to make a tax equity investment in the holding company of a wind farm project in an amount not to exceed $600 million. SDG&E is seeking to treat the investment as a rate-based asset for which it would earn its authorized rate of return. A CPUC decision is expected in 2011.
If approved by the CPUC, and after the wind farm project has met all of the conditions precedent set forth in the definitive documents, SDG&E would invest in one or more project holding companies in an amount not to exceed 80% of the project costs (not to exceed an aggregate amount of $600 million) upon the initiation of commercial operation of the project. SDG&E expects the project to be in commercial operation in the second half of 2012.
2007 WILDFIRES COST RECOVERY FOR COMPANY FACILITIES
In October 2010, the CPUC issued a decision approving a settlement agreement between SDG&E and the DRA, authorizing SDG&E to recover $43 million of capital costs incurred to replace and repair company facilities under CPUC jurisdiction damaged by the October 2007 wildfires. This decision was in response to an application that SDG&E filed with the CPUC in March 2009 seeking to recover $49.8 million of incremental costs ($43 million of capital costs and $6.8 million of operation and maintenance costs), which application was protested by the DRA.
SDG&E also incurred $30.1 million of incremental costs for the replacement and repair of company facilities under FERC jurisdiction, which are currently being recovered in SDG&E's electric transmission rates.
We discuss recovery of 2007 wildfire litigation costs in Note 10.
INSURANCE COST RECOVERY
SDG&E filed an application with the CPUC in August 2009 seeking authorization to recover higher liability insurance premiums, which SDG&E began incurring commencing July 1, 2009, and any losses realized due to higher deductibles associated with the new policies. Evidentiary hearings were held in April 2010 and a final CPUC decision is expected by the end of 2010. SDG&E made the filing under the CPUC’s rules allowing utilities to seek recovery of significant cost increases incurred between GRC filings resulting from unforeseen circumstances. SDG&E is requesting a $29 million revenue requirement for the 2009/2010 policy period for the incremental increase in its liability and wildfire insurance premium costs above what is currently authorized in rates and proposes a mechanism for recovery of future liability insurance costs incurred in the 2010/2011 policy period and the first six months of the 2011/2012 policy period. The CPUC's rules allow a utility to seek recovery of incurred costs that meet certain criteria, subject to a $5 million deductible per event. SDG&E has asked that the increase in liability insurance costs for the 2009/2010, 2010/2011 and the first six months of the 2011/2012 policy periods be deemed a single event subject to one $5 million deductible. In the nine months ended September 30, 2010 and 2009, SDG&E's after-tax earnings were adversely impacted by $20 million and $5 million, respectively, due to the incremental insurance premiums associated with its wildfire coverage.
EXCESS WILDFIRE CLAIMS COST RECOVERY
SDG&E and SoCalGas filed an application, along with other related filings, with the CPUC in August 2009 proposing a new mechanism for the future recovery of all wildfire-related expenses for claims, litigation expenses and insu rance premiums that are in excess of amounts authorized by the CPUC for recovery in rates. In connection with these filings, SDG&E is seeking the recovery of costs incurred by SDG&E for the 2007 wildfire losses that are in excess of amounts recovered from its insurance coverage and other potentially responsible third parties, as well as similar costs for future wildfires, if and when incurred. The application for a new mechanism for recovery of costs incurred for future wildfires was made jointly with Edison and PG&E. In July 2010, the CPUC approved the utilities' requests for separate regulatory accounts to record the subject expenses while the joint utility application is pending before the CPUC. Several parties protested the original application and, in response, the utilities submitted an amended application in July 2010. A proceeding schedule has not yet been established.
We provide additional information about 2007 wildfire litigation costs and thei r recovery in Note 10.
NOTE 10. COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
LEGAL PROCEEDINGS
We record loss reserves for legal proceedings when it is probable that a loss has been incurred and the amounts of the loss can be reasonably estimated. However, the uncertainties inherent in legal proceedings make it difficult to estimate with reasonable certainty the costs and effects of resolving these matters. Accordingly, actual costs incurred may differ materially from reserved amounts, may exceed applicab le insurance coverages and could materially adversely affect our business, cash flows, results of operations, and financial condition.
At September 30, 2010, Sempra Energy’s reserves for material legal proceedings, on a consolidated basis, were $619 million, of which $150 million is offset by an insurance receivable for wildfire litigation and $102 million is for previously resolved matters. At September 30, 2010, these reserves for SDG&E and SoCalGas were $345 million (also offset by the $150 million insurance receivable) and $13 million, respectively. We provide additional information about previously resolved matters in Note 17 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in the Annual Report.
SDG&E 2007 Wildfire Litigation
In October 2007, San Diego County experienced several catastrophic wildfires. Reports issued by the California Department of Forestry and Fire Protection (Cal Fire) concluded that two of these fires (the Witch and Rice fires) were SDG&E "power line caused" and that a third fire (the Guejito fire) occurred when a wire securing a Cox Communications' fiber optic cable came into contact with an SDG&E power line "causing an arc and starting the fire." Cal Fire reported that the Rice fire burned approximately 9,500 acres and damaged 206 homes and two commercial properties, and the Witch and Guejito fires merged and eventually burned approximately 198,000 acres, resulting in two fatalities, approximately 40 firefighters injured and approximately 1,141 homes destroyed.
A September 2008 staff report issued by the CPUC's Consumer Protection and Safety Division reached substantially the same conclusions as the Cal Fire reports, but also contended that the power lines involved in the Witch and Rice fires and the lashing wire involv ed in the Guejito fire were not properly designed, constructed and maintained. In November 2008, the CPUC initiated proceedings to determine if any of its rules were violated and in October 2009, SDG&E and the Consumer Protection and Safety Division entered into a settlement agreement, approved by the CPUC in April 2010, that resolves these proceedings by SDG&E's payment of $14.75 million.
Numerous parties have sued SDG&E and Sempra Energy in San Diego County Superior Court seeking recovery of unspecified amounts of damages, including punitive damages, from the three fires. These include owners and insurers of properties that were destroyed or damaged in the fires and public entities seeking recovery of firefighting, emergency response, and environmental costs. They assert various bases for recovery, including inverse condemnation based upon a California Court of Appeal decision finding that another California investor-owned utility was subject to strict liability, without regard to foreseeability or negligence, for property damages resulting from a wildfire ignited by power lines. In October 2010, the court of appeal affirmed the trial court's ruling that these claims must be pursued in individual lawsuits (rather than as class actions on behalf of all persons who incurred wildfire damages). SDG&E has filed cross-complaints against Cox Communications seeking indemnification for any liability that SDG&E may incur that relates to the Guejito fire, two SDG&E contractors seeking indemnification in connection with the Witch fire, and one SDG&E contractor seeking indemnification in connection with the Rice fire. The court has scheduled a Guejito fire trial for two individual plaintiffs to begin in March 2011.
SDG&E has settled substantially all of the 19,000 claims of homeowner insurers relating to the three fires, including claims for payment by the insurers to their policyholders for approximately 1,000 of the 1,300 houses, mobile homes, and apartment units identified in public records as having been destroyed. Under the settlement agreements, SDG&E has paid or will pay 57.5 percent of the approximately $1.6 billion paid or reserved for payment by the insurers to their policyholders and received an assignment of the insurers’ claims against Cox Communications and other parties potentially responsible for the fires.
The wildfire litigation also includes claims of non-insurer plaintiffs for damage to uninsured and underinsured structures, business interruption, evacuation expenses, agricultural damage, emotional harm, personal injuries and other losses. SDG&E has settled the claims of approximately 450 of these plaintiffs. Of the approximately 2,500 remaining plaintiffs, approximately 1,200 have thus far submitted settlement demands or damage information. Individual and business claims total approximately $825 million and government entity claims total approximately $150 million. SDG&E expects to receive additional settlement demands and damage estimates as settlement negotiations continue.
SDG&E's settlements and defense costs have exceeded its $1.1 billion of liability insurance coverage. SDG&E has established reserves for its estimated cost of resolving the remaining claims for damages of approximately 1,300 plaintiffs. It expects that its wildfire reserves and amounts paid to resolve wildfire claims will continue to increase as it obtains additional information and is unable to reasonably estimate the amount or timing of recoveries from other potentially responsible parties.
SDG&E has concluded, however, that it is probable that it will be permitted to recover from its utility customers substantially all reasonably incurred costs of resolving wildfire claims in excess of its liability insurance coverage and any amounts recovered from other potent ially responsible parties. Accordingly, although recovery from utility customers will require future regulatory actions as we discuss in Note 9, SDG&E has recorded a regulatory asset in an amount substantially equal to the aggregate amount it has paid or reserved for payment for the resolution of wildfire claims and related costs in excess of its liability insurance coverage. SDG&E will increase the amount of the regulatory asset as additional amounts are paid or reserves are recorded and reduce it by any amounts recovered from other potentially responsible parties. As of September 30, 2010, the amount of the regulatory asset was $311 million.
Consequently, Sempra Energy and SDG&E expect no significant earnings impact from the resolution of the remaining wildfire claims. However, SDG&E’s cash flow will be adversely affected by timing differences between the resolution of claims and recoveries from other potentially responsible parties and utility cus tomers, which may extend over a number of years. Also, recovery from customers will require future regulatory actions, and a failure to obtain recovery, or any negative assessment of the likelihood of recovery, would likely have a material adverse effect on Sempra Energy's and SDG&E's cash flows and results of operations.
SDG&E will continue to gather information to evaluate and assess the remaining wildfire claims and the likelihood, amount and timing of related recoveries from other potentially responsible parties and utility customers and will make appropriate adjustments to wildfire reserves and the related regulatory asset as additional information becomes available.
Sempra LNG
Sempra LNG has been engaged in a long-running land dispute relating to property adjacent to its Energía Costa Azul liquefied natural gas (LNG) receipt terminal near Ensenada, Mexico. The adjacent property is not required by environmental or other regulatory permits for the operation of the terminal. A claimant to the adjacent property has nonetheless asserted that his health and safety are endangered by the operation of the facility. In June 2010, a Mexican federal appeals court revoked a district court order, issued at the behest of the claimant, directing Mexican regulatory authorities to provisionally suspend authorizations for the operation of the LNG terminal. No terminal permits were affected as a result of these proceedings and the terminal has continued to operate normally. The Mexican district court is expected to conduct additional proceedings regarding the claimant’s assertions and whether the terminal’s permits should be modified or revoked.
The property claimant has also filed a lawsuit in U.S. district court in San Diego seeking compensatory and punitive damages and earnings from the Energía Costa Azul LNG terminal based on his allegations that he was wrongfully evicted from the adjacent property and that he has been harmed by other allegedly improper actions.
Energy Crisis Litigation Settlement
Sempra Energy, RBS Sempra Commodities and Sempra Generation have reached a comprehensive settlement to resolve substantially all of their remaining energy crisis litigation for a total payment of $410 million. Described in more detail below, the matters resolved by the settlement include the multiple actions brought by the California Department of Water Resources (DWR) and other parties with respect to the validity, pricing and operation of Sempra Generation’s contract with the DWR and the FERC refu nd and manipulation proceedings against RBS Sempra Commodities. Two settlement agreements were submitted in October 2010 to the FERC for its approval. We anticipate that the FERC will act on the settlements in the first quarter of 2011.
We expect the settlement of $410 million to be funded largely from previously recorded reserves and receivables at RBS Sempra Commodities. Sempra Energy has also recorded an additional pretax charge of $159 million in the first quarter of 2010 to provide for the remainder of the settlement, including $139 million at Sempra Generation and $20 million at Sempra Commodities.
DWR Contract
Among other relief from existing and potential disputes, under the terms of the settlement reached on the DWR contract, all claims, appeals and proceedings related to the DWR contract will be dismissed. These matters include the 2002 challenge bro ught by the California Energy Oversight Board (CEOB) and the CPUC at the FERC asserting that the DWR contract with Sempra Generation contained unjust and unreasonable rates; the DWR’s appeal in response to the denial of its 2002 claims for misrepresentation and breach of contract in San Diego Superior Court; and the 2008 arbitration proceedings in which the DWR asserted that Sempra Generation had breached the parties' agreement in various operational respects, and violated the order issued by an earlier arbitration panel relating to the amount refunded to the DWR and the manner in which Sempra Generation operates.
FERC Refund Proceedings
The settlement involving RBS Sempra Commodities includes, among other things, resolution of the following matters: the FERC's investigation of prices charged by various electric suppliers to buyers in the California Power Exchange (PX) and Independent System Operator (ISO) m arkets; a complaint involving short-term bilateral sales up to one month in the Pacific Northwest (the settlement resolves the sales between the DWR and Sempra Commodities); the California Attorney General's complaint that electricity sellers had failed to comply with the FERC's quarterly reporting requirements; and the California Attorney General's complaint seeking to collect for alleged overcharges related to all short-term bilateral transactions between sellers and the DWR from January 18, 2001 through June 20, 2001.
FERC Manipulation Investigation
The settlement involving RBS Sempra Commodities also includes resolution of the FERC's separate investigation into whether there was manipulation of short-term energy markets in the western United States that would constitute violations of applicable tariffs and warrant disgorgement of associated profits.
Sempra Energy and RBS Sempra Commodities have recorded reserves for the full amount of the settlement and other litigation. Pursuant to the agreements related to the formation of RBS Sempra Commodities, we have indemnified RBS should the liability from the final resolution of these matters be greater than the reserves related to Sempra Commodities. Pursuant to our agreement with the Noble Group as we discuss in Note 4, we have also indemnified Noble Americas Gas & Power Corp. and its affiliates for all losses incurred by such parties resulting from these proceedings as related to Sempra Commodities.
Other Litigation
Sempra Energy and several subsidiaries, along with three oil and natural gas companies, the City of Beverly Hills, and the Beverly Hills Unified School District, are defendants in a toxic tort lawsuit filed in Los Angeles County Superior Court by approxima tely 1,000 plaintiffs. This lawsuit claims that various emissions resulted in cancer or fear of cancer. We have submitted the case to our insurers, who have reserved their rights with respect to coverage. In November 2006, the court granted the defendants' summary judgment motions based on lack of medical causation for the 12 initial plaintiffs scheduled to go to trial first. The court also granted summary judgment excluding punitive damages. The court has stayed the case as to the remaining plaintiffs pending the appeal of the rulings. A mediation occurred in June 2010, after which the plaintiffs’ counsel agreed to recommend a settlement of the lawsuits as to Sempra Energy and its subsidiaries for an amount that is not significant. Any such settlement will require approval by each of the plaintiffs. If approval is obtained, finalization of the settlement is expected to occur within six months.
We are also defendants in ordinary routine lit igation incidental to our businesses, including personal injury, product liability, property damage and other claims. California juries have demonstrated an increasing willingness to grant large awards, including punitive damages, in these cases.
Wildfire Reserves and Insurance Receivables
In 2009 and 2010, as liabilities for wildfire litigation have become reasonably estimable, SDG&E has recorded related reserves as a current liability. The impact of this liability is offset by a current receivable resulting from SDG&E’s liability insurance and, for reserves in excess of the insurance coverage, the recognition of a regulatory asset, as discussed above. There was no effect on SDG&E's or Sempra Energy's 2009 earnings from the recording of the reserves. The impact on their 2010 earnings was $7 million and $17 million in the three months and nine months ended September 30, 2010, respect ively. At September 30, 2010, wildfire litigation reserves were $344 million and the receivable from SDG&E's insurers was $150 million.
NUCLEAR INSURANCE
SDG&E and the other owners of San Onofre Nuclear Generating Station (SONGS) have insurance to cover claims from nuclear liability incidents arising at SONGS. This insurance provides $375 million in coverage limits, the maximum amount available, including coverage for acts of terrorism. In addition, the Price-Anderson Act provides for up to $12.2 billion of secondary financial protection (SFP). If a nuclear liability loss occurring at any U.S. licensed/commercial reactor exceeds the $375 million insurance limit, all nuclear reactor owners could be required to contribute to the SFP. SDG&E's contribution would be up to $47 million. This amount is subject to an annual maximu m of $7 million, unless a default occurs by any other SONGS owner. If the SFP is insufficient to cover the liability loss, SDG&E could be subject to an additional assessment.
The SONGS owners, including SDG&E, also have $2.75 billion of nuclear property, decontamination, and debris removal insurance. In addition, the SONGS owners have up to $490 million insurance coverage for outage expenses and replacement power costs due to accidental property damage. This coverage is limited to $3.5 million per week for the first 52 weeks, then $2.8 million per week for up to 110 additional weeks. There is a 12-week waiting period deductible. These insurance coverages are provided through a mutual insurance company. Insured members are subject to retrospective premium assessments. SDG&E could be assessed up to $8.5 million.
The nuclear property insurance program includes an industry aggregate loss limit for non-cert ified acts of terrorism (as defined by the Terrorism Risk Insurance Act). The industry aggregate loss limit for property claims arising from non-certified acts of terrorism is $3.24 billion. This is the maximum amount that will be paid to insured members who suffer losses or damages from these non-certified terrorist acts.
CONTRACTUAL COMMITMENTS
Sempra Energy Consolidated
In the first nine months of 2010, significant increases in commitments at Sempra Energy were
§the issuance of $250 million of 5.35-percent first mortgage bonds and $500 million of 4.50-percent first mortgage bonds maturing in 2040 at SDG&E;
§$453 million for purchased-power contracts at SDG&E;
§$223 million for costs associated with nuclear fuel fabrication at SONGS;
§$133 million at SDG&E for engineering, material procurement and construction costs associated with the Sunrise Powerlink project;
§$54 million at SDG&E for electric distribution systems, advanced metering infrastructure, and electric generation plant and equipment;
§$52 million for construction and infrastructure improvemen ts for gas transmission and distribution operations at SoCalGas; and
§$315 million at Sempra Pipelines & Storage and Sempra LNG for natural gas contracts.
The future payments for the contractual commitments listed above are expected to be $280 million for 2010, $187 million for 2011, $151 million for 2012, $135 million for 2013, $112 million for 2014 and $2.2 billion thereafter. These amounts include expected interest payments on the first mortgage bonds using the stated interest rates.
Reserves for Sempra Energy and SDG&E related to wildfire litigation are discussed above in “SDG&E 2007 Wildfire Litigation.” Reserves for Sempra Energy related to the FERC and DWR contract settlement litigation are discussed above in “Energy Crisis Litigation Settlement.”
Changes to SoCalGas’ natural gas purchase and pipeline capacity commitments and Sempra LNG’s natural gas purchase and transportation commitments are discussed below.
At December 31, 2009, Sempra LNG had LNG purchase agreements with Tangguh PSC Contractors and Ras Laffan Liquefied Natural Gas Company. We discuss these agreements further in Note 17 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in the Annual Report.
In April 2010, Sempra LNG entered into an LNG supply option agreement with Gazprom Global LNG Limited (GGLNG), a subsidiary of OAO Gazprom. The multi-year agreement, which commenced in June 2010, allows GGLNG to deliver and sell up to two LNG cargoes per month to Sempra LNG at its Cameron receipt terminal. GGLNG pays Sempra LNG a fee for the right to deliver and sell the LNG cargoes using a predetermined pricing formula based on a market index.
Sempra LNG’s commitments under all LNG purchase agreements, reflecting the additional recent agreement with GGLNG, changes in forward prices since December 31, 2009, and actual transactions for the first nine months of 2010, are expected to decrease by $1.4 billion in 2010 and $2 million in 2011, to increase by $121 million in 2012, and to decrease by $81 million in 2013, $254 million in 2014 and $4.4 billion thereafter compared to December 31, 2009.
The LNG commitment amounts above are based on Sempra LNG’s commitment to accept the maximum possible delivery of cargoes under the agreements. Actual LNG purchases for the nine months ended September 30, 2010 have been significantly lower than the maximum amounts possible.
Sempra LNG has a natural gas transportation agreement to provide service from the U.S./Mexico border to Southern California and Arizona. At September 30, 2010, Sempra LNG’s remaining commitment on this contract, which runs through August 2022, is $226 million.
SDG&E
In the first nine months of 2010, significant increases to contractual commitments at SDG&E were the issuance of $250 million of 5.35-percent first mortgage bonds maturing in 2040, the issuance of $500 million of 4.50-percent first mortgage bonds maturing in 2040, $453 million for purchased-power contracts, $223 million for costs associated with nuclear fuel fabrication at SONGS, $133 million for engineering, material procurement and construction costs associated with the Sunrise Powerlink project and $54 million for electric distribution systems, advanced metering infrastructure, and electric generation plant and equipment.
The future payments for these contractual com mitments are expected to be $180 million for 2010, $143 million for 2011, $120 million for 2012, $107 million for 2013, $93 million for 2014 and $2 billion thereafter. These amounts include expected interest payments on the first mortgage bonds using the stated interest rates.
SoCalGas
In the first nine months of 2010, significant increases to contractual commitments at SoCalGas were $52 million for construction and infrastructure improvements for gas transmission and distribution operations. The future payments for these contractual commitments are expected to be $39 million for 2010 and $13 million for 2011.
SoCalGas’ natural gas purchase and pipeline capacity commitments have decreased by $682 million since December 31, 2009. The decrease, primarily due to a reduction of $1.1 billion based on lower natural gas forward p rices and actual transactions for the first nine months of 2010, is offset by new natural gas purchase and pipeline capacity contracts of $415 million. Net future payments are therefore expected to decrease by $903 million for 2010 and to increase by $124 million for 2011, $52 million for 2012, $29 million for 2013, $14 million for 2014 and $2 million thereafter compared to December 31, 2009.
CAPITAL LEASES
SDG&E has two power purchase agreements with peaker plant facilities that went into commercial operation in June 2010 and are accounted for as capital leases. As of September 30, 2010, capital lease obligations for these leases, each with a 25-year term, were $181 million.
At September 30, 2010, the future minimum lease payments and present value of the net minimum lease payments under these capital leases for both Sempra Energy Consolidated and SDG&E were as follows:
(Dollars in millions) | |
| 2010 | $ | 6 |
| 2011 | | 24 |
| 2012 | | 24 |
| 2013 | | 24 |
| 2014 | | 24 |
| Thereafter | | 489 |
| Total minimum lease payments(1) | | 591 |
| Less: estimated executory costs | | (97) |
| Less: interest(2) | | (313) |
| Present value of net minimum lease payments(3) | $ | 181 |
(1) | This amount will be recorded over the lives of the leases as Cost of Electric Fuel and Purchased Power on Sempra Energy's and SDG&E's Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations. This expense will receive ratemaking treatment consistent with purchased-power costs. |
(2) | Amount necessary to reduce net minimum lease payments to present value at the inception of the leases. |
(3) | Includes $7 million in Current Portion of Long-term Debt and $174 million in Long-term Debt on Sempra Energy's and SDG&E's Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheets at September 30, 2010. |
NOTE 11. SEGMENT INFORMATION
We have six separately managed reportable segments, as follows:
1. &nbs p; SDG&E provides electric service to San Diego and southern Orange counties and natural gas service to San Diego County.
2. SoCalGas is a natural gas distribution utility, serving customers throughout most of Southern California and part of central California.
3. Sempra Commodities holds our investment in RBS Semp ra Commodities, a joint venture with RBS. The partnership was formed fromour commodities-marketing businesses previously reported in this segment. The partnership's commodity trading businesses serve customers in natural gas and electricity, and prior to July 1, 2010, also in petroleum and petroleum products, and base metals. Sempra Commodities also includes the operating results of Sempra Rockies Marketing, which holds firm service capacity on the Rockies Express Pipeline.
In February 2010, Sempra Energy, RBS and the partnership entered into an agreement to sell certain businesses within the partnership, which agreement was consummated on July 1, 2010. In September and October of 2010, the partnership entered into two additional agreements for transactions which will complete the divestiture of the last of the joint venture’s principal assets. One of these transactions was compl eted on November 1, 2010, and the second transaction is expected to be completed by year-end. We discuss these transactions and other matters concerning the partnership in Note 4 above and in Notes 4 and 20 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in the Annual Report.
4. Sempra Generation develops, owns and operates, or holds interests in, electric power plants and energy projects in Arizona, California, Colorado, Nevada, Indiana, Hawaii and Mexico to serve wholesale electricity markets in the United States and Mexico.
5. Sempra Pipelines & Storage develops, owns and operates, or holds interests in, natural gas and propane pipelines and natural gas storage facilities in the United States and Mexico, and companies that provide natural gas or electricity services in Argentina, Chile, Mexico and Peru. We are currently pursuing the sale of our interests in the Argentine utilities, which we discuss further in Note 4 above and in Note 4 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in the Annual Report. Sempra Pipelines & Storage also operates a natural gas distribution utility in Alabama.
6. Sempra LNG develops , owns and operates receipt terminals for importing LNG in the U.S. and Mexico, and has supply and marketing agreements to purchase LNG and sell natural gas.
We evaluate each segment's performance based on its contribution to Sempra Energy's reported earnings. The Sempra Utilities operate in essentially separate service territories, under separate regulatory frameworks and rate structures set by the CPUC. The Sempra Utilities' operations are based on rates set by the CPUC and the FERC. We describe the accounting policies of our segments in Note 1 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in the Annual Report.
In the first quarter of 2010, Sempra LNG became a reportable segment. We have revised segment disclosures for 2009 to reflect this.
The following ta bles show selected information by segment from our Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations and Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheets.
Amounts labeled as "all other" in the following tables consist primarily of parent organizations.
SEGMENT INFORMATION | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
(Dollars in millions) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Three months ended September 30, | Nine months ended September 30, |
| 2010 | 2009 | 2010 | 2009 |
REVENUES | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
SDG&E | $ | 811 | 38 | % | $ | 773 | 42 | % | $ | 2,245 | 34 | % | $ | 2,136 | 38 | % |
SoCalGas | | 776 | 37 | | | 662 | 36 | | | 2,792 | 42 | | | 2,276 | 40 | |
Sempra Commodities | | 24 | 1 | | | 24 | 1 | | | 73 | 1 | | | 50 | 1 | |
Sempra Generation | | 269 | 13 | | | 250 | 13 | | | &nb sp;806 | 12 | | | 792 | 14 | |
Sempra Pipelines & Storage | | 77 | 3 | | | 98 | 5 | | | 262 | 4 | | | 328 | 6 | |
Sempra LNG | | 183 | 9 | | | 68 | 4 | | | 554 | 8 | | | 125 | 2 | |
Adjustments and eliminations | | 2 | - | | | (2) | - | | | 3 | - | &nb sp; | | (2) | - | |
Intersegment revenues | | (26) | (1) | | | (20) | (1) | | | (77) | (1) | | | (55) | (1) | |
Total | $ | 2,116 | 100 | % | $ | 1,853 | 100 | % | $ | 6,658 | 100 | % | $ | 5,650 | 100 | % |
INTEREST EXPENSE | | &nbs p; | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
SDG&E | $ | 37 | | | $ | 29 | | | $ | 99 | | | $ | 75 | | |
SoCalGas | | 17 | | | | 16 | | | | 50 | | | | 51 | | |
Sempra Commodities | | 2 | | | | 1 | | | | 3 | | | | 7 | | |
Sempra Generation | | 4 | | | | 3 | | | | 11 | | | | 11 | | |
Sempra Pipelines & Storage | | 10 | | | | 9 | | | | 25 | | &n bsp; | | 23 | | |
Sempra LNG | | 13 | | | | 8 | | | | 37 | | | | 12 | | |
All other | | 73 | | | | 70 | | | | 239 | | | | 190 | | |
Intercompany eliminations | | (45) | | | | (40) | | | | (141) | | | | (112) | | |
Total | $ | 111 | | | $ | 96 | | | $ | 323 | | | $ | 257 | | |
INTEREST INCOME | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
SDG&E | $ | - | | | $ | 1 | | | $ | - | | | $ | 1 | | |
SoCalGas | | 1 | | | | ;1 | | | | 1 | | | | 3 | | |
Sempra Commodities | | 6 | | | | - | &n bsp; | | | 6 | | | | - | | |
Sempra Generation | | 6 | | | | 4 | | | | 11 | | | | 10 | | |
Sempra Pipelines & Storage | | 4 | | | | 5 | | | | 12 | | | | 13 | | |
Sempra LNG | | 1 | | | | - | | | | 1 | | | | - | | |
All other | | 32 | | | | 34 | | | | 123 | | | | 101 | | |
Intercompany eliminations | | (45) | | | | (40) | | | | (141) | | | | (112) | | |
Total | $ | 5 | | | $ | &nbs p;5 | | | $ | 13 | | | $ | 16 | | |
DEPRECIATION AND AMORTIZATION | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
SDG&E | $ | 96 | 44 | % | $ | 81 | 41 | % | $ | 283 | 44 | % | $ | 239 | 42 | % |
SoCalGas | | 78 | 36 | | | 73 | 37 | | | 230 | 36 | | | 220 | 39 | |
Sempra Generation | | 16 | 7 | | | 14 | 7 | | | 47 | 7 | | | 43 | 7 | |
Sempra Pipelines & Storage | | 11 | 5 | | | 13 | 7 | | | 32 | 5 | | | 32 | 6 | |
Sempra LNG | | 13 | 6 | | | 10 | 5 | | | 38 | 6 | | | 23 | 4 | |
All other | | 4 | 2 | | | 5 | 3 | | | 13 | 2 | | | 11 | 2 | |
Total | $ | 218 | 100 | % | $ | 196 | 100 | % | $ | 643 | 100 | % | $ | 568 | 100 | % |
INCOME TAX EXPENSE (BENEFIT) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
SDG&E | $ | 56 | | | $ | 53 | | | $ | 131 | | | $ | 141 | | |
SoCalGas | | 42 | | | | 42 | | | | 132 | | | | 115 | | |
Sempra Commodities | | (147) | | | | 30 | | | | (167) | | | | 104 | | |
Sempra Generation | | 18 | | | | 30 | | | | (19) | | | | 76 | | |
Sempra Pipelines & Storage | | 23 | | | | (9) | | | | 36 | | | | (26) | | |
Sempra LNG | | 3 | | | | (10) | | | | 19 | | | | (32 ) | | |
All other | | (27) | | | | (8) | | | | (47) | | | | (51) | | |
Total | $ | (32) | | | $ | 128 | | | $ | 85 | | | $ | 327 | | |
SEGMENT INFORMATION (Continued) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
(Dollars in millions) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Three months ended September 30, | Nine months ended September 30, |
| 2010 | 2009 | 2010 | 2009 |
EQUITY EARNINGS (LOSSES) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Earnings (losses) recorded before tax: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Sempra Commodities | $ | (281) | | | $ | 105 | | | $ | (290) | | | $ | 384 | | |
Sempra Generation | | (1) | | | | 4 | | | | (2) | | | | (2) | | |
Sempra Pipelines & Storage | | 10 | | | | 18 | | | | 32 | | | | 39 | | |
All other | | (1) | | | | (4) | | | | (6) | | &nbs p; | | (10) | | |
Total | $ | (273) | | | $ | 123 | | | $ | (266) | | | $ | 411 | | |
Earnings (losses) recorded net of tax: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Sempra Pipelines & Storage | $ | (4) | | | $ | 20 | | | $ | 42 | | | $ | 59 | | |
EARNINGS (LOSSES) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
SDG&E(1) | $ | 106 | 81 | % | $ | 108 | 34 | % | $ | 264 | 58 | % | $ | 277 | 33 | % |
SoCalGas(1) | | 78 | 59 | | | 74 | 23 | | | 212 | 46 | | | 198 | 24 | |
Sempra Commodities | | (134) | (102) | | | 75 | 24 | | | (139) | (30) | | | 274 | 33 | |
Sempra Generation | | 56 | 43 | | | 43 | 14 | | | 51 | 11 | | | 119 | 14 | |
Sempra Pipelines & Storage | | 43 | 33 | | | 54 | 17 | | | 120 | 26 | | | 64 | 8 | |
Sempra LNG | | 5 | 4 | | | - | - | | | 50 | 11 | | | (19) | (2) | |
All other | | (23) | (18) | | | (37) | (12) | | | (99) | (22) | | | (82) | (10) | |
Total | $ | 131 | 100 | % | $ | 317 | 100 | % | $ | 459 | 100 | % | $ | 831 | 100 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | Nine months ended September 30, |
| | | | | | | | | 2010 | 2009 |
EXPENDITURES FOR PROPERTY PLANT & EQUIPMENT | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
SDG&E | | | | | | | | | $ | 822 | 61 | % | $ | 633 | 46 | % |
SoCalGas | | | | | | | | | | 337 | 25 | | | 336 | 24 | |
Sempra Generation | | | | | | | | | | 32 | 2 | | | 21 | 2 | |
Sempra Pipelines & Storage | | | | | | | | | | 151 | 11 | | | 149 | 11 | |
Sempra LNG | | | | | | | | | | 9 | 1 | | | 230 | 17 | |
All other | | | | | | &nb sp; | | | | 3 | - | | | 2 | - | |
Total | | | | | | | | | $ | 1,354 | 100 | % | $ | 1,371 | 100 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | September 30, 2010 | December 31, 2009 |
ASSETS | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
SDG&E | | | | | | | | | $ | 11,496 | 40 | % | $ | 10,229 | 36 | % |
SoCalGas | | | | | | | | | | 7,350 | 25 | | | 7,287 | 25 | |
Sempra Commodities | | | | | | | | | | 1,963 | 7 | | | 2,255 | 8 | |
Sempra Generation | | | | | | | | | | 2,383 | 8 | | | 2,048 | 7 | |
Sempra Pipelines & Storage | | | | | | | | | | 5,108 | 18 | | | 4,485 | 16 | |
Sempra LNG | | | | | | | | | | 2,329 | 8 | | | 2,277 | 8 | |
All other | | | | | | | | | | 492 | 2 | | | 596 | 2 | |
Intersegment receivables | | | | | &nbs p; | | | | | (2,172) | (8) | | | (665) | (2) | |
Total | | | | | | | | | $ | 28,949 | 100 | % | $ | 28,512 | 100 | % |
INVESTMENTS IN EQUITY METHOD INVESTEES | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Sempra Commodities | | | | | | | | | $ | 825 | | | $ | 2,172 | | |
Sempra Generation | | | | | | | | | | 256 | | | | 434 | | |
Sempra Pipelines & Storage | | | | | | | | | | 1,746 | | | | 1,429 | | |
All other | | | | | | | | | | 18 | | | | 21 | | |
Total | | | | | | | | | $ | 2,845 | | | $ | 4,056 | | |
(1) | After preferred dividends. | | | | | | �� | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
ITEM 2. MANAGEMENT'S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
You should read the following discussion in conjunction with the financial statements contained in this Form 10-Q, "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations" contained in our 2009 Annual Report on Form 10-K (Annual Report), and "Risk Factors" contained in our Annual Report and Part II of this Form 10-Q.
Sempra Energy is a Fortune 500 energy services holding company whose business units provide electric, natural gas and other energy products and services to their customers. Our operations are divided principally between the Sempra Utilities and Sempra Global. The Sempra Utilities consist of two California regulated public utility companies, 1) San Diego Gas & Electric Company (SDG&E) and 2) Southern Californi a Gas Company (SoCalGas). Sempra Global consists of businesses engaged in providing energy products and services.
This report includes information for the following separate registrants:
§Sempra Energy and its consolidated entities
§SDG&E
§Pacific Enterprises (PE), the holding company for SoCalGas
§SoCalGas
References in this report to "we," "our" and "Sempra Energy Consolidated" are to Sempra Energy and its consolidated entities, collectively, unless otherwise indicated by the context.
PE's operations consist solely of those of SoCalGas and additional items (e.g., cash, intercompany accounts and equity) attributable to serving as a holding company for SoCalGas.
Below are the summary descriptions of our operating business units.
SEMPRA ENERGY BUSINESS UNITS
The Sempra Utilities consist of SDG&E and SoCalGas.
SEMPRA UTILITIES | | |
| Market | service territory |
SAN DIEGO GAS & ELECTRIC COMPANY (SDG&E) A regulated public utility; infrastructure supports electric generation, transmission and distribution, and natural gas distribution | §Provides electricity to 3.5 million consumers (1.4 million meters) §Provides natural gas to 3.2 million consumers (845,000 meters) | Serves the county of San Diego, CA and an adjacent portion of southern Orange County covering 4,100 square miles |
SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA GAS COMPANY (SOCALGAS) A regulated public utility; infrastructure supports natural gas distribution, transmission and storage | §Residential, commercial, industrial, utility electric generation and wholesale customers §Covers a population of 20.7 million (5.8 million meters) | Southern California and portions of Central California (excluding San Diego County, the city of Long Beach and the desert area of San Bernardino County) coveri ng 20,000 square miles |
Sempra Global is a holding company for most of our subsidiaries that are not subject to California utility regulation. Sempra Global's principal business units, which provide energy-related products and services, are
§Sempra Commodities
§Sempra Generation
§Sempra Pipelines & Storage
§Sempra LNG
SEMPRA GLOBAL | | |
| Market | Geographic Region |
SEMPRA COMMODITIES Holds an interest in RBS Sempra Commodities LLP, a commodities-marketing business joint venture with The Royal Bank of Scotland (RBS) | §Natural gas; natural gas liquids §Power Prior to July 1, 2010: §Petroleum and petroleum products §Coal §Emissions §Ethanol §Base metals | §North America Prior to July 1, 2010: §Global |
SEMPRA GENERATION Develops, owns and operates, or holds interests in, electric power plants and energy projects | §Wholesale electricity | §U.S.A. §Mexico |
SEMPRA PIPELINES & STORAGE Develops, owns and operates, or holds interests in, natural gas and propane pipelines and natural gas storage facilities, and natural gas and electric service providers | §Natural gas §Electricity | §U.S.A. §Mexico §Argentina §Chile §Peru |
SEMPRA LNG Develops, owns and operates receipt terminals for importation of liquefied natural gas (LNG) and sale of natural gas | §Liquefied natural gas §Natural gas | §U.S.A. §Mexico |
In February 2010, we, RBS and our joint-venture partnership, RBS Sempra Commodities LLP (RBS Sempra Commodities), entered into an agreement to sell certain businesses within the joint venture, which agreement was consummated on July 1, 2010. In September and October of 2010, the partnership entered into two additional agreements which will complete the divestiture of the last of the joint venture’s principal assets. One of these transactions was completed on November 1, 2010, and the second transaction is expected to be completed by year-end. We discuss these transactions and other matters concerning the partnership in Note 4 of the Notes to Condensed Consoli dated Financial Statements herein and in Notes 4 and 20 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in the Annual Report.
We discuss the following in Results of Operations:
§Overall results of our operations and factors affecting those results
§Our business unit results
§Significant changes in revenues, costs and earnings between periods
In the three months ended September 30, 2010, our earnings decreased by $186 million (59%) to $131 million primarily due to a $139 million after-tax write-down of our investment in RBS Sempra Commodities in the Sempra Commodities segment and lower earnings from the joint venture, as we discuss in Note 4 of the Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements herein. Diluted earnings per share for the three-month period decreased by $0.74 (58%) per share to $0.53 per share, primarily from the write-down and lower earnings at Sempra Commodities.
In the nine months ended September 30, 2010, our earnings decreased by $372 million (45%) to $459 million primarily due to lower joint-venture earnings and the investment write-down at Sempra Commodi ties and lower earnings at Sempra Generation, partially offset by improved results at Sempra LNG and Sempra Pipelines & Storage. In the first quarter of 2010, Sempra Generation and Sempra Commodities recorded after-tax litigation expense of $84 million and $12 million, respectively, related to the agreement to settle certain energy crisis litigation, as we discuss in Note 10 of the Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements herein. Diluted earnings per share for the nine months decreased by $1.53 (45%) per share to $1.84 per share, primarily from the write-down at Sempra Commodities and net lower earnings.
Earnings in the nine-month period of 2009 were negatively impacted by an after-tax asset write-off of $64 million related to assets at Sempra Pipelines & Storage’s Liberty Gas Storage (Liberty) project.
The following table shows our earnings by business unit, which we discuss below in "Business Unit Results."
SEMPRA ENERGY EARNINGS (LOSSES) BY BUSINESS UNIT |
(Dollars in millions) |
| | Three months ended September 30, |
| | 2010 | 2009 |
Sempra Utilities: | | | | | | | | |
SDG&E(1) | $ | 106 | 81 | % | $ | 108 | 34 | % |
SoCalGas(1) | | 78 | 59 | | | 74 | 23 | |
Sempra Global: | | | | | | | | |
Sempra Commodities | | (134) | (102) | | | 75 | 24 | |
Sempra Generation | | 56 | 43 | | | 43 | 14 | |
Sempra Pipelines & Storage | | 43 | 33 | | | 54 | 17 | |
Sempra LNG | | 5 | 4 | | | - | - | |
Parent and other(2) | | (23) | (18) | | | (37) | (12) | |
Earnings | $ | 131 | 100 | % | $ | 317 | 100 | % |
| | Nine months ended September 30, |
| | 2010 | 2009 |
Sempra Utilities: | | | ; | | | | | |
&nb sp; SDG&E(1) | $ | 264 | 58 | % | $ | 277 | 33 | % |
SoCalGas(1) | | 212 | 46 | | | 198 | 24 | |
Sempra Global: | | | | | | | | |
Sempra Commodities | | (139) | (30) | | | 274 | 33 | |
Sempra Generation | | 51 | 11 | | | 119 | 14 | |
Sempra Pipelines & Storage | | 120 | 26 | | | 64 | 8 | |
Sempra LNG | | 50 | 11 | | | (19) | (2) | |
Parent and other(2) | | (99) | (22) | | | (82) | (10) | |
Earnings | $ | 459 | 100 | % | $ | 831 | 100 | % |
(1) | After preferred dividends. |
(2) | Includes after-tax interest expense ($35 million and $33 million for the three months ended September 30, 2010 and 2009, respectively, and $110 million and $100 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2010 and 2009, respectively), intercompany eliminations recorded in consolidation and certain corporate costs. |
BUSINESS UNIT RESULTS
The following section is a discussion of earnings by business unit, as it appears in the table above.
EARNINGS BY BUSINESS UNIT -- SEMPRA UTILITIES |
(Dollars in millions) |


SDG&E
SDG&E business unit earnings were
§$106 million in the three months ended September 30, 2010 ($108 million before preferred dividends)
§$108 million in the three months ended September 30, 2009 ($110 million before preferred dividends)
§$264 million in the nine months ended September 30, 2010 ($268 million before preferred dividends)
§$277 million in the nine months ended September 30, 2009 ($281 million before preferre d dividends)
The decrease of $2 million (2%) in the three months ended September 30, 2010 was due to:
§$9 million from the resolution of regulatory matters that favorably impacted 2009 earnings;
§$6 million increase in litigation reserves in 2010; and
§$5 million higher liability insurance premiums for wildfire coverage; offset by
§$12 million higher authorized margin for operations regulated by the California Public Utilities Commission (CPUC) and lower operation and maintenance expenses (excluding insurance premiums for wildfire coverage); and
§$4 million higher electric transmission margin.
The decrease of $13 million (5%) in the nine months ended September 30, 2010 was due to:
§$16 million higher liability insurance premiums for wildfire coverage;
§$11 million lower favorable impact from the resolution of prior years’ income tax issues;
§$11 million net unfavorable impact from an increase in litigation reserves in 2010 compared to the favorable resolution of litigation in 2009; and
§$3 million due to the write-down of deferred tax assets as a result of the change to U.S. tax law regarding the Medicare Part D subsidy; offset by
§$12 million higher authorized margin for CPUC-regulated operations in excess of higher operation and maintenance expenses (excluding insurance premiums for wildfire coverage);
§$9 million higher electric transmission margin; and
§$6 million lower income taxes as a result of higher software development costs and incremental depreciation expense deductions for tax purposes which, for ratemaking purposes, are not treated as deferred taxes.
SoCalGas
SoCalGas business unit earnings were
§$78 million in the three months ended September 30, 2010 (both before and after preferred dividends)
§$74 million in the three months ended September 30, 2009 (both before and after preferred dividends)
§$212 million in the nine months ended September 30, 2010 ($213 million before preferred dividends)
§$198 million in the nine months ended September 30, 2009 ($199 million before preferred dividends)
The increase of $4 million (5%) in the three months ended September 30, 2010 was primarily due to higher authorized margin for CPUC-regulated operations in excess of higher operation and maintenance expenses.
The increase of $14 million (7%) in the nine months ended September 30, 2010 was due to:
§$12 million higher authorized margin for CPUC-regulated operations in excess of hig her operation and maintenance expenses;
§$5 million net favorable earnings impact primarily due to the effect of self-developed software costs on the effective income tax rate; and
§$3 million higher regulatory awards; offset by
§$13 million due to the write-off of deferred tax assets as a result of the change in U.S. tax law regarding the Medicare Part D subsidy.
EARNINGS (LOSSES) BY BUSINESS UNIT – SEMPRA GLOBAL |
(Dollars in millions) |
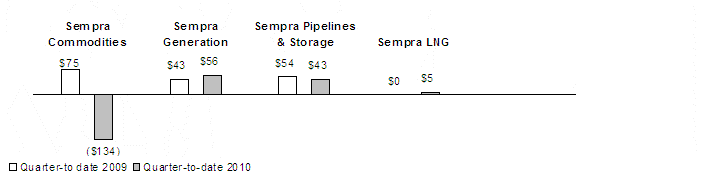
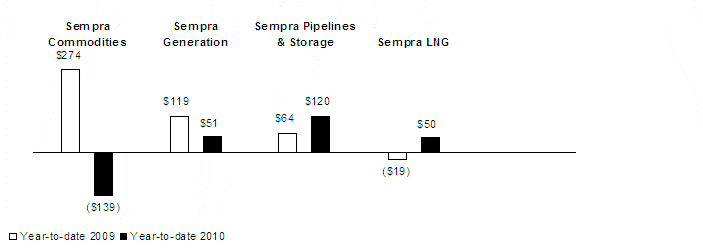
Sempra Commodities
Sempra Commodities recorded business unit earnings (losses) of:
§$(134) million in the three months ended September 30, 2010
§$75 million in the three months ended September 30, 2009
§$(139) million in the nine months ended September 30, 2010
§$274 million in the nine months ended September 30, 2009
The change in earnings for the three months ended September 30, 2010 was due to:
§a $139 million write-down of our investment in the RBS Sempra Commodities joint venture (as we discuss in Note 4 of the Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements herein);
§equity earnings from RBS Sempra Commodities of $18 million in 2010 compared to $75 million in 2009; and
§$11 million state income tax expense related to our exit from the RBS Sempra Commodities business.
The change in earnings for the nine months ended September 30, 2010 was due to:
§the $139 million write-down of our investment in the RBS Sempra Commodities joint venture;
§equity earnings from RBS Sempra Commodities of $24 million in 2010 compared to $278 million in 2009;
§$12 million litigation expense related to an agreement to settle energy crisis litigation associated with the DWR contract, as we discuss in Note 10 of the Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements herein; and
§$11 million state income tax expense related to our exit from the RBS Sempra Commodities business.
The equity earnings from the joint venture were adversely impacted by the sale on July 1, 2010 of the global metals and oil businesses and the European natural gas and power business; lower volatility in the U.S. natural gas and power business; and the disruptions caused by the process to sell the partnership’s businesses.
Sempra Generation
Sempra Generation recorded business unit earnings of:
§$56 million in the three months ended September 30, 2010
§$43 million in the three months ended September 30, 2009
§$51 million in the nine months ended September 30, 2010
§$119 million in the nine months ended September 30, 2009
The increase in earnings of $13 million (30%) in the three months ended September 30, 2010 was due to:
§$12 million renewable energy tax credits primarily due to additional investments in the Copper Mountain Solar project; and
§$6 million mark-to-market gains on forward contracts with RBS Sempra Commodities and other counterparties in 2010 compared to $2 million mark-to-market losses in 2009; offset by
§$9 million lower earnings from operations, primarily due to less favorable market pricing in 2010.
The decrease in earnings of $68 million (57%) in the nine months ended September 30, 2010 was primarily due to:
§$86 million in litigation expense related to an agreement to settle energy crisis litigation associated with the DWR contract, as we discuss in Note 10 of the Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements herein;and
§$26 million lower earnings from operations, primarily from increased scheduled plant maintenance and associated down time in 2010, less favorable market pricing, and expenses and associated down time from earthquake damage to our Mexicali power plant in the second quarter of 2010; offset by
§$37 million renewable energy tax credits in 2010.
Sempra Pipelines & Storage
Sempra Pipelines & Storage recorded business unit earnings of:
§$43 million in the three months ended September 30, 2010
§$54 million in the three months ended September 30, 2009
§$120 million in the nine months ended September 30, 2010
§$64 million in the nine months ended September 30, 2009
The decrease of $11 million (20%) in the three months ended September 30, 2010 was due to:
§a $24 million write-down of our investment in Argentina; and
§$15 million from the favorable resolution of prior years’ income tax issues in 2009; offset by
§$48 million in proceeds received from a legal settlement in 2010, less a related income tax effect of $17 million.
The improvement in earnings of $56 million (88%) in the nine months ended September 30, 2010 was primarily due to:
§$64 million lower earnings in 2009 from a write-off of assets at Liberty; and
§$48 million in proceeds received from a legal settlement in 2010, less a related income tax effect of $17 million; offset by
§a $24 million write-down of our investment in Argentina; and
§$15 million from the favorable resolution of prior years’ income tax issues in 2009.
We discuss the investment write-down and legal settlement in Note 4 of the Notes to Condensed Consolidated Statements herein.
Sempra LNG
Sempra LNG recorded earnings (losses) of:
§$5 million in the three months ended September 30, 2010
§$0 million in the three months ended September 30, 2009
§$50 million in the nine months ended September 30, 2010
§$(19) million in the nine months ended September 30, 2009
The improvement in earnings of $5 million and $69 million in the three months and nine months ended September 30, 2010, respectively, was primarily from higher earnings from the start-up in 2009 of marketing operations, the Cameron receipt terminal and the nitrogen-injection facility at the Energía Costa Azul receipt terminal.
Parent and Other
Losses for Parent and Other were
§$23 million in the three months ended September 30, 2010
§$37 million in the three months ended September 30, 2009
§$99 million in the nine months ended September 30, 2010
§$82 million in the nine months ended September 30, 2009
The decrease in losses of $14 million (38%) in the three months ended September 30, 2010 was primarily due to lower income tax expense.
The increase in losses of $17 million (21%) in the nine months ended September 30, 2010 was primarily due to higher net interest expense.
CHANGES IN REVENUES, COSTS AND EARNINGS
This section contains a discussion of the differences between periods in specific line items of the Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations for Sempra Energy, SDG&E, PE and SoCalGas.
Sempra Utilities Revenues
The current regulatory framework permits the cost of natural gas purchased for core customers (primarily residential and small commercial and industrial customers) to be passed on to customers substantially as incurred. However, SoCalGas' Gas Cost Incentive Mechanism (GCIM) provides SoCalGas the opportunity to share in the savings and/or costs from buying natural gas for its core customers at prices below or above market-based monthly benchmarks. This mechanism permits full recovery of costs incurred when average purchase costs are within a price range around a monthly benchmark price. Any higher costs or savings realized outside thi s range are shared between the core customers and SoCalGas. We provide further discussion in Note 9 of the Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements herein.
The regulatory framework also permits SDG&E to recover the actual cost incurred to generate or procure electricity based on annual estimates of the cost of electricity supplied to customers. The differences in cost between estimates and actual are recovered in the next year through rates.
Sempra Utilities: Natural Gas Revenues and Cost of Natural Gas
The tables below show natural gas revenues for Sempra Energy, SDG&E and SoCalGas for the nine-month periods ended September 30. The Sempra Energy Consolidated amounts reflect SDG&E and SoCalGas revenues, net of intercompany transactions. Because the cost of natural gas is recovered in rates, changes in the cost are reflecte d in the changes in revenues. In addition to the change in market prices, the average cost of natural gas recorded during a period is impacted by the difference between customer billings and recorded or CPUC-authorized costs. These differences are required to be balanced over time, resulting in over- and undercollected regulatory balancing accounts.
SEMPRA ENERGY CONSOLIDATED |
NATURAL GAS SALES AND TRANSPORTATION |
(Volumes in billion cubic feet, dollars in millions) |
| Natural Gas Sales | Transportation | Total |
Customer class | Volumes | Revenue | Volumes | Revenue | Volumes | Revenue |
2010: | | | | | | | | | |
Residential | 195 | $ | 1,943 | 1 | $ | 2 | 196 | $ | 1,945 |
Commercial and industrial | 86 | | 657 | 203 | | 177 | 289 | | 834 |
Electric generation plants | - | | - | 153 | | 36 | 153 | | 36 |
Wholesale | - | | - | 17 | | 3 | 17 | | 3 |
| 281 | $ | 2,600 | 374 | $ | 218 | 655 | | 2,818 |
Other revenues | | | | | | | | | 70 |
Balancing accounts(1) | | | | | | | | | 246 |
Total | | | | | | | | $ | 3,134 |
2009: | | | | | | | | | |
Residential | 187 | $ | 1,624 | 1 | $ | 2 | 188 | $ | 1,626 |
Commercial and industrial | 85 | | 553 | 205 | | 163 | 290 | | 716 |
Electric generation plants | - | | - | 203 | | 51 | 203 | | 51 |
Wholesale | - | | - | 12 | | 3 | 12 | | 3 |
| 272 | $ | 2,177 | 421 | $ | 219 | 693 | | 2,396 |
Other revenues | | | | | | | | | 75 |
Balancing accounts(1) | | | | | | | | | 133 |
Total | | | | | | | | $ | 2,604 |
(1) We discuss balancing accounts and their effects in Note 1 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in the Annual Report. |
During the three months ended September 30, 2010, our natural gas revenues increased by $127 million (17%) to $858 million, and the cost of natural gas increased by $77 million (37%) to $285 million. During the nine months ended September 30, 2010, our natural gas revenues increased by $530 million (20%) to $3.1 billion, and the cost of natural gas increased by $405 million (41%) to $1.4 billion. The primary factor contributing to the increased natural gas revenues and cost of natural gas in both the third-quarter and year-to-date periods was higher natural gas pr ices in 2010. We discuss the increase in the cost of natural gas individually for SDG&E and SoCalGas below.
SDG&E |
NATURAL GAS SALES AND TRANSPORTATION |
(Volumes in billion cubic feet, dollars in millions) |
| Natural Gas Sales | Transportation | Total |
Customer class | Volumes | Revenue | Volumes | Revenue | Volumes | Revenue |
2010: | | | | | | | | | |
Residential | 23 | $ | 260 | - | $ | - | 23 | $ | 260 |
Commercial and industrial | 11 | | 82 | 6 | | 9 | 17 | | 91 |
Electric generation plants | - | | - | 21 | | 5 | 21 | | 5 |
| 34 | $ | 342 | 27 | $ | 14 | 61 | | 356 |
Other revenues | | | | | | | | | 27 |
Balancing accounts | | | | | | | | | (8) |
Total(1) | | | | | | | | $ | 375 |
2009: | | | | | | | | | |
Residential | 23 | $ | 230 | - | $ | - | 23 | $ | 230 |
Commercial and industrial | 11 | | 76 | 5 | | 7 | 16 | | 83 |
Electric generation plants | - | | - | 45 | | 13 | 45 | | 13 |
| 34 | $ | 306 | 50 | $ | 20 | 84 | | 326 |
Other revenues | | | | | | | | | 25 |
Balancing accounts | | | | | | | | | 2 |
Total(1) | | | | | | | | $ | 353 |
(1) Includes sales to affiliates of $1 million in each of 2010 and 2009. |
| | | | | | | | | |
During the three months ended September 30, 2010, SDG&E's natural gas revenues increased by $15 million (19%) to $93 million, and the cost of natural gas increased by $7 million (23%) to $37 million. During the nine months ended September 30, 2010, SDG&E's natural gas revenues increased by $22 million (6%) to $375 million, and the cost of natural gas increased by $16 million (10%) to $170 million. The average cost of natural gas for the three months ended September 30, 2010 was $4.86 per thousand cubic feet (Mcf) compared to $4.27 per Mcf for the corresponding period in 2009, a 14-percent increase of $0.59 per Mcf, resulting in higher revenues and cost of $5 million. For the nine months ended September 30 , 2010, SDG&E’s average cost of natural gas was $4.98 per Mcf compared to $4.52 per Mcf for the corresponding period in 2009, a 10-percent increase of $0.46 per Mcf, resulting in higher revenues and cost of $16 million.
SOCALGAS |
NATURAL GAS SALES AND TRANSPORTATION |
(Volumes in billion cubic feet, dollars in millions) |
| Natural Gas Sales | Transportation | Total |
Customer class | Volumes | Revenue | Volumes | Revenue | Volumes | Revenue |
2010: | | | | | | | & nbsp; | | |
Residential | 172 | $ | 1,683 | 1 | $ | 2 | 173 | $ | 1,685 |
Commercial and industrial | 75 | | 575 | 197 | | 169 | 272 | | 744 |
Electric generation plants | - | | - | 132 | | 31 | 132 | | 31 |
Wholesale | - | | - | 108 | | 11 | 108 | | 11 |
| 247 | $ | 2,258 | 438 | $ | 213 | 685 | | 2,471 |
Other revenues | | | | | | | | | 67 |
Balancing accounts | | | | | | | | | 254 |
Total(1) | | | | | | | | $ | 2,792 |
2009: | | | | | | | | | |
Residential | 164 | $ | 1,394 | 1 | $ | 2 | 165 | $ | 1,396 |
Commercial and industrial | 74 | | 477 | 200 | | 157 | 274 | | 634 |
Electric generation plants | - | | - | 158 | | 38 | 158 | | 38 |
Wholesale | - | | - | 99 | | 10 | 99 | | 10 |
| 238 | $ | 1,871 | 458 | $ | 207 | 696 | | 2,078 |
Other revenues | | | | | | | | | 67 |
Balancing accounts | | | | | | | | | 131 |
Total(1) | | | | | | | | $ | 2,276 |
(1) Includes sales to affiliates of $32 million i n 2010 and $24 million in 2009. |
During the three months ended September 30, 2010, SoCalGas' revenues increased by $114 million (17%) to $776 million, and the cost of natural gas increased by $72 million (40%) to $252 million. The increase in revenues was primarily due to:
§the increase in cost of natural gas, which was caused primarily by higher natural gas prices, as we discuss below;
§$25 million higher CPUC-authorized cost recovery, for which revenues are fully offset in operation and maintenance expenses; and
§$13 million higher authorized base margin in accordance with the CPUC's 2008 General Rate Case (GRC) decision.
During the nine months ended September 30, 2010, SoCalGas’ revenues increased by $516 million (23%) to $2.8 billion, and the cost of natural gas increased by $395 million (47%) to $1.2 billion. The increase in revenues was primarily due to:
§the increase in cost of natural gas, which was caused primarily by higher natural gas prices, as we discuss below;
§$60 million higher CPUC-authorized cost recovery, for which revenues are fully offset in operation and maintenance expenses; and
§$39 million higher authorized base margin in accordance with the CPUC's 2008 GRC decision.
SoCalGas' average cost of natural gas for the three months ended September 30, 2010 was $4.40 per Mcf compared to $3.36 per Mcf for the corresponding period in 2009, a 31-percent increase of $1.04 per Mcf, resulting in higher revenues and cost of $59 million. For the nine months ended September 30, 2010, SoCalGas' average cost of natural gas was $5.04 per Mcf compared to $3.57 per Mcf for the corresponding period in 2009, a 41-percent increase of $1.47 per Mcf, resulting in higher revenues and cost of $362 million.
Sempra Energy and SDG&E: Electric Revenues and Cost of Electric Fuel and Purchased Power
The table below shows electric revenues for Sempra Energy and SDG&E. Sempra Energy amounts are shown after eliminating intercompany transactions. Because the cost of electricity is substantially recovered in rates, changes in the cost are reflected in the changes in revenues.
During the three months ended September 30, 2010, electric revenues increased by $24 million (3%) to $717 million at Sempra Energy and by $23 million (3%) to $718 million at SDG&E. The increase in revenues was primarily due to:
§$16 million increase due to tolling payments and natural gas supply costs in 2010 associated with the power generated by Otay Mesa VIE in excess of purchased power costs in 2009 for the equivalent amount of power;
§$15 million higher authorized transmission and electric generation margins;
§$9 million higher authorized base margin on electric distribution; and
§$6 million increase in the cost of electric fuel and purchased power excluding Otay Mesa VIE; offset by
§$16 million lower recoverable expenses that are fully offset in operation and maintenance expenses; and
§$9 million resolution of regulat ory matters in 2009 that favorably impacted earnings.
During the nine months ended September 30, 2010, electric revenues increased by $87 million (5%) at both Sempra Energy and SDG&E to $1.9 billion. The increase in revenues was primarily due to:
§$22 million increase due to tolling payments and natural gas supply costs in 2010 associated with the power generated by Otay Mesa VIE in excess of purchased power costs in 2009 for the equivalent amount of power;
§$38 million higher authorized transmission and electric generation margins;
§$22 million higher authorized base margin on el ectric distribution; and
§$12 million increase in the cost of electric fuel and purchased power excluding Otay Mesa VIE; offset by
§$9 million resolution of regulatory matters in 2009 that favorably impacted earnings.
The cost of electric fuel and purchased power at both Sempra Energy and SDG&E decreased in the three months ended September 30, 2010 primarily due to an $11 million decrease in the cost of power purchased from third-party generators as a result of the start up of new power generation at Otay Mesa VIE, which commenced commercial operations in the fourth quarter of 2009, offset by a $6 million increase in other fuel and purchased power costs. Associated with this decrease, SDG&E’s o perating costs increased by $11 million from Otay Mesa VIE’s operations.
At both Sempra Energy and SDG&E, the cost of electric fuel and purchased power decreased by $28 million (6%) to $480 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2010 primarily due to a $40 million decrease in the cost of power purchased from third-party generators as a result of the start up of new power generation at Otay Mesa VIE, which commenced commercial operations in the fourth quarter of 2009, offset by a $12 million increase in other fuel and purchased power costs. Associated with this decrease, SDG&E’s operating costs increased by $31 million from Otay Mesa VIE’s operations.
ELECTRIC DISTRIBUTION AND TRANSMISSION |
(Volumes in millions of kilowatt-hours, dollars in millions) |
| 2010 | 2009 |
Customer class | Volumes | Revenue | Volumes | Revenue |
Sempra Energy Consolidated: | | | | | | |
Residential | 5,406 | $ | 756 | 5,671 | $ | 831 |
Commercial | 5,017 | | 651 | 5,302 | | 725 |
Industrial | 1,598 | | 167 | 1,716 | | 194 |
Direct access | 2,365 | | 90 | 2,290 | | 80 |
Street and highway lighting | 76 | | 9 | 79 | | 10 |
| 14,462 | | 1,673 | 15,058 | | 1,840 |
Other revenues | | | 77 | | | 102 |
Balancing accounts | | | 115 | | | (164) |
Tot al | | $ | 1,865 | | $ | 1,778 |
SDG&E: | | | | | | |
Residential | 5,406 | $ | 756 | 5,671 | $ | 831 |
Commercial | 5,017 | | 651 | 5,302 | | 725 |
Industrial | 1,612 | | 169 | 1,724 | | 195 |
Direct access | 2,365 | | 90 | 2,290 | | 80 |
Street and highway lighting | 76 | | 9 | 79 | | 10 |
| 14,476 | | 1,675 | 15,066 | | 1,841 |
Other revenues | | | 80 | | | 106 |
Balancing accounts | | | 115 | | | (164) |
Total(1) | | $ | 1,870 | | $ | 1,783 |
(1) Includes sales to affiliates of $5 million in each of 2010 and 2009. |
We do not include in the Condensed Consolidated Statements of Operations the commodity costs (and the revenues to recover those costs) associated with long-term contracts that are allocated to SDG&E by the California Department of Water Resources (DWR). However, we do include the associated volumes and distribution re venues in the table above. We provide further discussion of these contracts in Note 1 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in the Annual Report.
Sempra Global and Parent Revenues and Cost of Sales
In the three months ended September 30, 2010, our Sempra Global and Parent revenues increased by $112 million (26%) to $541 million. During the nine months ended September 30, 2010, our Sempra Global and Parent revenues increased by $391 million (31%) to $1.7 billion. The increases in both the three months and nine months ended September 30, 2010 were due to higher revenues at Sempra LNG, primarily due to increased marketing operations and the start up of operations at its Cameron LNG receipt terminal and the nitrogen-injection facility at the Energía Costa Azul receipt terminal, partially offset by lower revenues at Sempra Pipelines & Storage due to the expiration of the Comis ión Federal de Electricidad (CFE) natural gas supply contract in 2009. At the expiration of the contract, Sempra LNG began supplying the CFE under a separate contract ending December 2022.
In the three months ended September 30, 2010, our cost of natural gas, electric fuel and purchased power increased by $72 million (33%) to $292 million. During the nine months ended September 30, 2010, our cost of natural gas, electric fuel and purchased power increased by $212 million (31%) to $887 million. The increases in both periods were primarily associated with the higher revenues at Sempra LNG, offset partially by lower costs at Sempra Pipelines & Storage resulting primarily from the expiration of the CFE contract.
Litigation Expense
Sempra Energy Consolidated
We recorded $184 million in litigation expense in the nine months ended September 30, 2010, which included $163 million related to the agreement to settle certain energy crisis litigation. We discuss this settlement agreement in Note 10 of the Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements herein.
Other Operation and Maintenance
Sempra Energy Consolidated
For the three months ended September 30, 2010, our other operation and maintenance expenses increased by $22 million (4%) to $590 million, primarily due to an increase at SoCalGas. For the nine months ended September 30, 2010, our other operation and maintenance expenses increased by $109 million (7%) to $1.8 billion, primarily due to higher operation an d maintenance expenses at both SDG&E and SoCalGas.
We discuss the changes in operation and maintenance expenses at SDG&E and SoCalGas below.
Operation and Maintenance
SDG&E
For the three months ended September 30, 2010, SDG&E's operation and maintenance expenses decreased by $1 million to $235 million, primarily due to $12 million lower expenses recoverable in revenues as incurred, offset by $10 million higher litigation expense in 2010.
For the nine months ended September 30, 2010, SDG&E's operation and maintenance expenses increased by $55 million (8%) to $704 million. The increase was due to:
§$21 million higher other operational and maintenance costs (including $22 million of higher liability insurance premiums for wildfire coverage and $12 million at Otay Mesa VIE due to commencement of plant operation in October 2009, offset by $13 million lower other operational and maintenance costs);
§$18 million net unfavorable impact from an increase in litigation reserves in 2010 compared to the favorable resolution of litigation in 2009; and
§$15 million higher expenses recoverable in revenues as incurred.
SoCalGas
For the three months ended September 30, 2010, SoCalGas' operation and maintenance expenses increased by $33 million (13%) to $285 million. The increase was d ue primarily to $25 million higher expenses recoverable in revenues as incurred.
For the nine months ended September 30, 2010, SoCalGas’ operation and maintenance expenses increased by $72 million (9%) to $840 million due primarily to $60 million higher expenses recoverable in revenues as incurred.
Write-off of Long-lived Assets
In the second quarter of 2009, we recorded a $132 million write-off related to certain assets at one of Sempra Pipelines & Storage’s Liberty natural gas storage projects. Sempra Energy's after-tax share of this write-off was $64 million. We discuss the write-off of the assets in Note 1 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in the Annual Report.
Equity Earnings (Losses) Before Income Taxes
Sempra Energy Consolidated
For the three months ended September 30, 2010, equity losses from our investment in RBS Sempra Commodities were $281 million compared to equity earnings of $105 million in the corresponding period of 2009. For the nine months ended September 30, 2010, equity losses from our investment in RBS Sempra Commodities were $290 million compared to equity earnings of $384 million in the corresponding period of 2009. Equity earnings were adversely impacted by several factors, as we discuss above in “Business Unit Results – Sempra Commodities.” Results for both periods in 2010 include a $305 million pretax write-down of our investment in RBS Sempra Commodities. We discuss the write-down further in Note 4 of the Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements herein.
We provide additional information about the determination and allocation of this investment' s earnings in Note 4 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in the Annual Report.
Other Income (Expense), Net
Sempra Energy Consolidated
In the three months ended September 30, 2010, other income, net, increased by $42 million (175%) to $66 million primarily due to:
§proceeds of $48 million from a legal settlement at Sempra Pipelines & Storage; offset by
§$17 million in losses on interest rate instruments in 2010 at Otay Mesa VIE compared to $11 m illion in 2009; and
§a $10 million decrease in gains from investment activity related to our executive retirement and deferred compensation plans in 2010.
For the nine months ended September 30, 2010, other income, net, decreased by $15 million (15%) to $82 million primarily due to:
§$51 million in losses on interest rate instruments in 2010 at Otay Mesa VIE compared to $19 million in gains in 2009; and
§a $25 million decrease in gains from investment activity related to our executive retirement and deferred compensation plans in 2010; offset by
§proceeds of $48 million from a legal settlement at Sempra Pipelines & Storage;
§$12 million increase in allowance for equity funds used during construction; and
§a $10 million gain recognized on an interest rate instrument at Parent and Other.
SDG&E
The changes in SDG&E’s other income (expense), net, in the three months and nine months ended September 30, 2010, were primarily due to the losses and gains from interest rate instruments at Otay Mesa VIE, as we discuss above.
Interest Expense
Sempra Energy Consolidated
For the three months ended September 30, 2010, our interest expense increased by $15 million (16%) to $111 million. The increase included:
§$17 million higher interest expense, primarily from long-term debt issued in 2009 and 2010 at Parent and Other and SDG&E; offset by
§$5 million lower interest expense from maturities of debt at Parent and Other.
During the nine months ended September 30, 2010, our interest expense increased by $66 million (26%) to $323 million. The increase was primarily due to:
§$70 million higher interest expense, primarily from long-term debt issued in 2009 and 2010 at Parent and Other and SDG&E; and
§$26 million lower capitalized interest, primarily at Sempra LNG due to completion of construction projects; offset by
§$22 million lower interest expense from maturities of debt at Parent and Other; and
§$14 million lower short-term debt interest expense, primarily from lower average commercial paper borrowings and interest rates, and reduced interest expense related to energy crisis litigation reserves at Parent and Other.
Income Taxes
The table below shows the income tax expense (benefit) and effective income tax rates for Sempra Energy, SDG&E, PE and SoCalGas.
INCOME TAX EXPENSE (BENEFIT) AND EFFECTIVE INCOME TAX RATES |
(Dollars in millions) |
| | | Three months ended Septe mber 30, |
| | | 2010 | | 2009 |
| | | Income Tax Expense | | Effective Income | | | Income Tax | | Effective Income | |
| | | (Benefit) | | Tax Rate | | | Expense | | Tax Rate | |
Sempra Energy Consolidated | $ | (32) | | (32) | % | $ | 128 | | 31 | % |
SDG&E | | 56 | | 35 | | | 53 | | 37 | |
PE | | 42 | | 35 | | | 41 | | 36 | |
SoCalGas | | 42 | | 35 | | | 42 | | 36 | |
| | | Nine months ended September 30, |
| | | 2010 | | 2009 |
| | | Income Tax | | Effective Income | | | Income Tax | | Effective Income | |
| | | Expense | | Tax Rate | | | Expense | | Tax Rate | |
Sempra Energy Consolidated | $ | 85 | | 18 | % | $ | 327 | | 30 | % |
SDG&E | | 131 | | 36 | | | 141 | | 33 | |
PE | | 132 | | 38 | | | 117 | | 38 | |
SoCalGas | | 132 | | 38 | | | 115 | | 37 | |
Sempra Energy Consolidated
The change in income tax expense in the three months ended September 30, 2010 was due to lower pretax income and a lower effective income tax rate primarily resulting from:
§higher planned investment tax credits;
§higher exclusions from taxable income of the equity portion of AFUDC; and
§higher pretax income (including a $175 million gain related to our share of the RBS Sempra Commodities sale to J.P. Morgan Ventures Energy Corporation on July 1, 2010) in countries with lower statutory rates; offset by
§$11 million state income tax expense related to our exit from the RBS Sempra Commodities business;
§lower favorable impact from the resolution of prior years' income tax issues;
§an increase in the amount by which book depreciation exceeds normalized tax depreciation, which is not treated as a deferred tax asset for ratemaking purposes; and
§$5 million tax expense in 2010 compared to $3 million tax benefit in 2009 due to Mexican currency translation and inflatio n adjustments.
In the nine months ended September 30, 2010, Sempra Energy's income tax expense decreased due to lower pretax income and a lower effective income tax rate. The lower effective income tax rate was primarily due to:
§higher planned investment tax credits;
§higher deductions for self-developed software costs;
§higher pretax income (including a $175 million gain related to our share of the RBS Sempra Commodities sale to J.P. Morgan Ventures Energy Corporation on July 1, 2010) in countries with lower statutory rates; and
§higher exclusions from taxable income of the equity portion of AFUDC; offset by
§$11 million state income tax expense related to our exit from the RBS Sempra Commodities business;
§lower favorable impact from the resolution of prior years' income tax issues;
§a $16 million write-down of the deferred tax assets related to other postretirement benefits, as a result of a change in U.S. tax law that eliminates a future deduction, starting in 2013, for retiree healthcare funded by the Medicare Part D subs idy;
§an increase in the amount by which book depreciation exceeds normalized tax depreciation, which is not treated as a deferred tax asset for ratemaking purposes; and
§$4 million higher tax expense in 2010 due to Mexican currency translation and inflation adjustments.
SDG&E
The increase in SDG&E's income tax expense in the three months ended September 30, 2010 was primarily due to higher pretax income, offset by a lower effective income tax rate. The lower effective income tax rate was primarily due to:
§the impact of Otay Mesa VIE;
§a decrease in the amount by which book depreciation exceeds normalized tax depreciation, which is not treated as a deferred tax asset for ratemaking purposes;
§higher exclusions from taxable income of the equity portion of AFUDC; and
§higher favorable impact from the resolution of prior years' income tax issues; offset by
§lower deductions for self-developed software costs;
§ lower deductions for other postretirement benefits; and
§lower utility repair allowance.
In the nine months ended September 30, 2010, SDG&E's income tax expense decreased primarily from lower pretax income, partially offset by a higher effective income tax rate resulting primarily from:
§the impact of Otay Mesa VIE;
§a $3 million write-down of the deferred tax assets related to other postretirement benefits as a result of a change in U.S. tax law, as we discuss above;
§an increase in the amount by which book depreciation exceeds normalized tax depreciation, which is not treated as a deferred tax asset for ratemaking purposes;
§lower deductions for other postretirement benefits; and
§lower utility repair allowance; offset by
§higher exclusions from taxable income of the equity portion of AFUDC; and
§higher favorable impact from the resolution of prior years' income tax issues.
SDG&E's results include Otay Mesa VIE, which is consolidated, and therefore, SDG&E's effective income tax rate is impacted by the VIE’s stand-alone effective income tax rate.
PE and SoCalGas
The decrease in PE’s and SoCalGas’ effective income tax rates in the three months ended September 30, 2010 was primarily due to:
§higher deductions for self-developed software costs; offset by
§lower deductions for other postretirement benefits; and
§an increase in the amount by which book depreciation exceeds no rmalized tax depreciation, which is not treated as a deferred tax asset for ratemaking purposes.
In the nine months ended September 30, 2010, income tax expense increased at PE and SoCalGas primarily due to higher pretax income. The effective income tax rate at SoCalGas increased slightly primarily due to:
§a $13 million write-down of the deferred tax assets related to other postretirement benefits as a result of a change in U.S. tax law, as we discuss above;
§lower deductions for other postretirement benefits; and
§an increase in the amount by which book depreciation exceeds no rmalized tax depreciation, which is not treated as a deferred tax asset for ratemaking purposes; offset by
§higher deductions for self-developed software costs; and
§higher exclusions from taxable income of the equity portion of AFUDC.
Although it did not change year-over-year, these fluctuations are also reflected in PE’s effective income tax rate.
Equity Earnings (Losses), Net of Income Tax
Equity losses, net of income tax, were $4 million i n the three months ended September 30, 2010 compared to equity earnings of $20 million for the corresponding period in 2009. Equity earnings, net of income tax, decreased by $17 million (29%) to $42 million in the nine months ended September 30, 2010. The change in both the three months and nine months was primarily due to a $24 million write-down of Sempra Pipelines & Storage’s investment in Argentina.
Losses (Earnings) Attributable to Noncontrolling Interests
Sempra Energy Consolidated
Losses attributable to noncontrolling interests decreased by $11 million (65%) in the three months ended September 30, 2010. The decrease was primarily due to a $13 million decrease in losses attributable to noncontrolling interests at SDG&E, which we discuss below.
Losses attributable to noncontrol ling interests increased by $12 million (55%) in the nine months ended September 30, 2010. The change was primarily due to:
§$43 million increase in losses attributable to noncontrolling interests at SDG&E, which we discuss below; offset by
§$33 million associated with the write-off of assets at Liberty in 2009.
SDG&E
Losses attributable to noncontrolling interests, all related to Otay Mesa VIE, were $5 million in the three months ended September 30, 2010 compared to $18 million in the corresponding period of 2009. The change was primarily due to:
§a $20 million increase in operating income; offset by
§a $6 million increase in losses on interest rate instruments in 2010.
Losses attributable to noncontrolling interests, all related to Otay Mesa VIE, were $34 million in the nine months ended September 30, 2010 compared to earnings of $9 million in the corresponding period of 2009. The change was primarily due to:
§$51 million in losses on interest rate instruments in 2010 compared to $19 million in gains in 2009; offset by
§a $36 million increase in operating income.
Earnings
We discuss variations in Sempra Energy's earnings by business unit above in "Business Unit Results."
CAPITAL RESOURCES AND LIQUIDITY
We expect our cash flows from operations to fund a substantial portion of our capital expenditures and dividends. In addition, we may meet our cash requirements through the issuance of short-term and long-term debt and the proceeds from the transactions to sell the businesses within RBS Sempra Commodities, as we discuss below.
Our committed lines of credit provide liquidity and support commercial paper. As we discuss in Note 6 of the Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements herein, in October 2010, Sempra Energy, Sempra Global and the Sempra Utilities entered into agreements for new credit facilities, to replace the previous principal credit agreements that were scheduled to expire in 2011. The new agreements have a longer term (four years) and, in light of our exit from the commodities joint venture, a lower total credit commitment by $500 million at Sempra Global. At Sempra Energy and Sempra Global, the new agreements are syndicated broadly among 23 different lenders and at the Sempra Utilities, among 22 different lenders. No single lender has greater than a 7-percent share in any agreement.
The table below shows the amount of available funds at September 30, 2010:
AVAILABLE FUNDS AT SEPTEMBER 30, 2010 |
(Dollars in millions) |
| | Sempra Energy | | |
| | Consolidated | SDG&E | PE/SoCalGas |
Unrestricted cash and cash equivalents | $ | 547 | $ | 332 | $ | 72 |
Available unused credit(1) | | 3,419 | | 338 | | 538 |
(1) | Borrowings on the shared line of credit at SDG&E and SoCalGas are limited to $600 million for each utility and $800 million in total. SDG&E's available funds reflect letters of credit outstanding of $25 million and variable-rate demand notes outstanding of $237 million supported by the line. SoCalGas' availability reflects the impact of SDG&E's use of the combined credit available on the line. |
Sempra Energy Consolidated
We believe that these available funds and cash flows from operations, distributions from equity method investments and security issuances, combined with current cash balances, will be adequate to:
§finance capital expenditur es
§meet liquidity requirements
§fund shareholder dividends and common stock repurchases
§fund new business acquisitions or start-ups
As we discuss in Note 4 of the Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements herein, in July 2010, RBS Sempra Commodities sold its global metals and oil businesses, as well as the European natural gas and power business. Our share of the proceeds from this transaction approximated $1 billion, including a $134 million distribution of 2009 partnership earnings related to the businesses sold. In September 2010, Noble Group Ltd. agreed to acquire the U.S. retail commodity marketing business of RBS Sempra Commodities for $318 million in cash, plus assumption of all debt, which agreement was consummated on November 1, 2010. In October 2010, the joint venture entered into an agreement to sell most of its remaining assets to J.P. Morgan Ventures Energy Corporation (J.P. Morgan Ventures), a unit of J.P. Morgan Chase & Co. (JP Morgan), for approximately $220 million. This transaction is expected to close by year-end.
We expect our share of the proceeds from the sales of all of the partnership’s businesses and related cash distributions to total $1.8 billion to $1.9 billion. This includes approximately $1.3 billion expected from the announced transactions, plus $500 million to $600 million consisting primarily of cash and accounts receivable, as well as net margin that is expected to be collected as customers are transferred to JP Morgan. The transfer of all accounts to JP Morgan will be done as soo n as possible, but is expected to continue into 2011. We are using $500 million of the proceeds to repurchase shares of our common stock under a Collared Accelerated Share Acquisition Program, which began in September 2010. We discuss the share repurchase program further in Note 5 of the Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements herein.
SDG&E has issued long-term debt in 2010 and both Sempra Energy and SDG&E issued long-term debt in 2009. Changing economic conditions could affect the availability and cost of both short-term and long-term financing. If cash flows from operations were to be significantly reduced or we were to be unable to borrow under acceptable terms, we would reduce or postpone discretionary capital expenditures and investments in new businesses. If these measures were necessary, they would primarily impact our Sempra Global businesses, as credit availability for the Sempra Utilities has not been significantly impacted by the credit crisis. Discretionary expenditures at Sempra Global include projects that we have not yet made firm commitments to build, primarily renewable generation facilities. We continuously monitor our ability to finance the needs of our operating, investing and financing activities in a manner consistent with our intention to maintain strong, investment-quality ratings.
We have significant investments in several trusts to provide for future payments of pensions and other postretirement benefits, and nuclear decommissioning. The value of the trust funds’ investments declined in 2008 and the first quarter of 2009 due to a decrease in the equity market and volatility in the fixed income market. Values increased from favorable market activity later in 2009 and in 2010. However, these markets continue to be volatile. The changes in asset values have not affected the funds’ abilities to make required payments, but may impact funding requirem ents for pension and other postretirement benefit plans. At the Sempra Utilities, funding requirements are generally recoverable in rates.
We discuss our principal credit agreements more fully in Note 6 of the Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements herein and in Note 6 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in the Annual Report.
Sempra Utilities
The Sempra Utilities expect that cash flows from operations and debt issuances will continue to be adequate to meet operating and capital expenditure requirements. Due to the extended review period associated with the Sunrise Powerlink project and the resultant delay in initiating construction activities, SDG&E declared and paid a $150 million common dividend to Sempra Energy in the first quarter of 2009. However, the level of future common dividends from SDG&E and SoCa lGas may be reduced or eliminated during periods of increased capital expenditures. The level of future common dividends from PE is dependent upon common dividends paid by SoCalGas. Sempra Energy may from time to time make additional equity contributions to SDG&E or SoCalGas to support the Sempra Utilities' capital expenditure programs.
As we discuss in Note 10 of the Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements herein, SDG&E’s and therefore Sempra Energy’s cash flows are likely to be adversely impacted by cash flows related to the 2007 wildfire litigation.
Sempra Commodities
We discuss above the completed and pending transactions and anticipated cash flows related to the dissolution of the RBS Sempra Commodities joint venture, which generally comprises the Sempra Commodities business unit. The impact of the sale transactions on cash flow will depend on many factors, including the final proceeds received from the transactions, potential changes to the partnership agreement, and any sales of residual assets. Our partner in the joint venture, RBS, is obligated to provide the joint venture with all working-capital requirements and credit support. However, we are providing transitional back-up guarantees, some of which may continue for a prolonged period of time. RBS or JP Morgan have fully indemnified us for any claims or losses in connection with these arrangements.
We account for our investment in the partnership under the equity method. RBS Sempra Commodities intends to distribute all of its net income on an annual basis, although the distributions are within the discretion of the board of directors of the partnership. In limited cases, the partnership may retain earnings allocable to the partners to replenish capital depleted through losses. In the first nine months of 2010, we received cash distributions from the partnership of $1 billion, which includes our share of proceeds from the transaction with J.P. Morgan Ventures. In the first nine months of 2009, we received cash distributions from the partnership of $407 million. Based on the joint venture’s results through the third quarter of 2010, we currently do not expect distributions for 2010 results to be material.
We provide additional information about RBS Sempra Commodities and the sales transactions in Notes 4 and 6 of the Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements herein and in Notes 3, 4, 6 and 20 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in the Annual Report.
Sempra Generation
We expect Sempra Generation to require funds for the development of electric generation facilities, primarily renewable energy projects. Projects at Sempra Generation may be financed through a combination of operating cash flow, project financing, funds from the parent and external borrowings. Cash flows from operations at Sempra Generation are expected to decrease upon the expiration of their contract with the DWR in late 2011 due to less favorable pricing on replacement contracts. Also, Sempra Generation may not be able to replace all of the lost revenue. We expect the litigation settlement recorded in the first quarter of 2010 related to the DWR litigation to be funded from operations.
Sempra Generation's long-term power sale contracts may contain collateral requirements, although the DWR contract does not contain such requirements. The collateral arrangements require Sempra Generation and/or the counterparty to post cash, guarantees or letters of credit to the other party for exposure in excess of established thresholds. Sempra Generation may be required t o provide collateral when market price movements adversely affect the counterparty's cost of replacement energy supplies if Sempra Generation fails to deliver the contracted amounts. Sempra Generation had no outstanding collateral requirements under such contracts at September 30, 2010.
Sempra Pipelines & Storage
Sempra Pipelines & Storage is expected to require funding from the parent or from external sources to fund projects, including the development and expansion of its natural gas storage projects.
Also, on April 30, 2010, Sempra Pipelines & Storage completed an acquisition resulting in the purchase of the Mexican pipeline and natural gas infrastructure assets of El Paso Corporation for $307 million ($292 million, net of cash acquired). We discuss the acquisition further in Note 3 o f the Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements herein.
Sempra LNG
Sempra LNG required funding from 2004 through 2009 for its development of the Energía Costa Azul and Cameron LNG receipt terminals. As both of these facilities are now in service, Sempra LNG is expected to provide operating cash flow for further development within Sempra Global.
CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES
CASH PROVIDED BY OPERATING ACTIVITIES |
(Dollars in millions) |
| 2010 | 2010 Change | 2009 |
Sempra Energy Consolidated | $ | 1,602 | $ | (282) | (15) | % | $ | 1,884 |
SDG&E | | 416 | | (203) | (33) | | | 619 |
PE | | 562 | | 17 | 3 | | | 545 |
SoCalGas | | 569 | | 20 | 4 | | | 549 |
Sempra Energy Consolidated
Cash provided by operating activities at Sempra Energy decreased in 2010 primarily due to $209 million lower distributions received from RBS Sempra Commodities.
SDG&E
Cash provided by operating activities at SDG&E decreased in 2010 primarily due to $117 million of settlement payments in 2010, net of cash received from liability insurance, compared to $36 million of cash received from liability insurance in 2 009, net of settlement payments, related to the 2007 wildfire litigation.
PE and SoCalGas
Cash provided by operating activities at PE and SoCalGas increased in 2010 primarily due to:
§$60 million higher net income, net of noncash adjustments, at SoCalGas; and
§a $71 million accounts payable decrease in 2010 compared to a $185 million decrease in 2009, primarily due to higher natural gas prices in 2010 compared to 2009; offset by
§a $66 million decrease in regulatory balancing accounts in 2010 compared to a $52 million increase in 2009. Over- and undercollected regulatory balancing accounts reflect the difference between billings and recorded or CPUC-authorized costs. These differences are required to be balanced over time; and
§a $272 million accounts receivable decrease in 2010 compared to a $306 million decrease in 2009, primarily due to higher natural gas volumes and cost of natural gas in 2010 compared to 2009.
The table below shows the contributions to pension and other postretirement benefit plans for the nine months ended September 30, 2010.
| | Other |
| Pension | Postretirement |
(Dollars in millions) | Benefits | Benefits |
Sempra Energy Consolida ted | $ | 91 | $ | 39 |
SDG&E | | 35 | | 12 |
PE/SoCalGas | | 37 | | 26 |
CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES
CASH USED IN INVESTING ACTIVITIES |
(Dollars in millions) |
| 2010 | 2010 Change | 2009 |
Sempra Energy Consolidated | $ | (633) | $ | (1,337) | (68) | % | $ | (1,970) |
SDG&E | | (813) | | 233 | 40 | | | (580) |
PE | | (435) | | 106 | 32 | | | (329) |
SoCalGas | | (445) | | 109 | 32 | | | (336) |
SempraEnergy Consolidated
Cash used in investing activities at Sempra Energy decreased in 2010 primarily due to:
§$849 million of distributions from RBS Sempra Commodities LLP at Sempra Commodities in 2010 related to the sale of businesses within the joint venture, as we discuss in Note 4 of the Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements herein;
§$180 million of distributions from Fowler Ridge II Wind Farm (Fowler Ridge) at Sempra Generation in 2010;
§a $182 million investment in Fowler Ridge b y Sempra Generation in 2009; and
§$462 million lower contributions to Rockies Express. The $65 million contribution in the first quarter of 2010 was the last required for the construction phase of the project; offset by
§$176 million proceeds from remarketing of industrial development bonds in 2009; and
§Sempra Pipelines & Storage’s $292 million acquisition (net of cash acquired) resulting in the purchase of Mexican pipeline and natural gas infrastructure assets.
SDG&E
The increase in cash used in investing activities at SDG&E in 2010 was due to:
§a $189 million net increase in capital expenditures (a $265 million increase at SDG&E, offset by a decrease of $76 million at Otay Mesa VIE);
§net proceeds of $24 million related to industrial development bonds in 2009; and
§$20 million lower decrease in loans to affiliates.
PE and SoCalGas
Cash used in investing activities at PE and SoCalGas increased in 2010 primarily due to a $108 millio n increase in advances from SoCalGas to Sempra Energy in 2010.
FUTURE CONSTRUCTION EXPENDITURES AND INVESTMENTS
The amounts and timing of capital expenditures are generally subject to approvals by the CPUC, the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) and other regulatory bodies. However, in 2010, we expect to make capital expenditures and investments of $3 billion, including:
§$1.9 billion at the Sempra Utilities (excluding Otay Mesa VIE) for capital projects and plant improvements ($1.4 billion at SDG&E and $500 million at SoCalGas)
§$1.1 billion at our other subsidiaries for the development of natural gas stor age facilities and pipelines, and renewable generation projects
The Sempra Utilities expect the capital expenditures to include:
§$780 million for additions to SDG&E’s natural gas and electric distribution systems, advanced metering infrastructure, and electric generation plant and equipment
§$500 million at SoCalGas for improvements to distribution and transmission systems, and for advanced metering infrastructure
§$400 million at SDG&E for the Sunrise Powerlink transmission line
&# 167;$190 million for improvements to SDG&E’s electric transmission infrastructure
The Sempra Utilities expect to finance these expenditures and investments with cash flows from operations, cash on hand and debt issuances.
The expected capital expenditures of $1.1 billion at our other subsidiaries include:
§approximately $150 million to $250 million for Copper Mountain Solar (a 48-megawatt (MW) solar generation facility under construction by Sempra Generation in Boulder City, Nevada);
§approximately $230 million for investments in Cedar Creek II Wind Farm, a 250-MW project in northern Colorado;
§approximately $250 million to $300 million for Sempra Pipelines & Storage’s contribution to Rockies Express and the development of natural gas storage projects at Bay Gas and Mississippi Hub; and
§$307 million for Sempra Pipelines & Storage’s acquisition resulting in the purchase of Mexican pipeline and natural gas infrastructure assets which closed in April 2010 and that we discuss in Note 3 of the Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements herein.
Our level of capital expenditures and investments in the next few years may vary substantially and will depend on the cost and availability of financing, regulatory approvals and business opportunities providing desirable rates of return. We intend to finance our capital expenditures in a manner that will maintain our strong investment-grade ratings and capital structure.
CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES
CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES |
(Dollars in millions) |
| 2010 | 2010 Change | 2009 |
Sempra Energy Consolidated | $ | (532) | $ | (1,043) | 204 | % | $ | 511 |
SDG&E | | 716 | | 483 | 207 | | | 233 |
PE | | (104) | | (100) | (2,500) | | | (4) |
SoCalGas | | (101) | | (100) | (10,000) | | | (1) |
Sempra Energy Consolidated
At Sempra Energy, financing acti vities used cash in 2010 compared to providing cash in 2009, primarily due to:
§$502 million repurchases of common stock in 2010;
§$410 million lower issuances of debt; and
§$402 million higher debt payments; offset by
§$94 million for the purchase of the remaining 40-percent ownership interest in Mississippi Hub in 2009; and
§$184 million increase in short-term debt in 2010 co mpared to a $52 million decrease in 2009.
SDG&E
Cash provided by financing activities at SDG&E increased primarily due to:
§$150 million common dividends paid to Sempra Energy in 2009; and
§$358 million higher issuances of long-term debt.
PE and SoCalGas
Cash used in financing activities at PE and SoCalGas in 2010 increased due to $100 million common dividends paid to Sempra Energy and PE, respectively.
COMMITMENTS
We discuss significant changes to contractual commitments at Sempra Energy, SDG&E, PE and SoCalGas in Note 10 of the Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements herein.
FACTORS INFLUENCING FUTURE PERFORMANCE
SEMPRA ENERGY OVERVIEW
The Sempra Utilities' operations generally provide relatively stable earnings and liquidity. However, for the next few years, SDG&E and SoCalGas intend to limit their common stock dividends to reinvest their earnings in significant capital projects.
Sempra Global's long-term contracts also generally provide relatively stable earnings and liquidity, but are subject to variability due to fluctuations in commodity prices. Also, Sempra Generation's contract with the DWR, which provides a significant portion of Sempra Generation's revenues, ends in late 2011. Because it is unable to forecast with certainty future electricity prices and the cost of natural gas, contracts it enters into to replace the DWR contract, if obtained, or merchant (daily) sales may provide substantially lower earnings. Sempra Generation is also undertaking several projects for the construction of renewable generation facilities, with planned in-service dates ranging from late 2010 to 2012.
Sempra Pipelines & Storage is also expected to provide earnings from construction programs when completed and other investments, but will require substantial funding for these investments. At Sempra LNG, until there are firm LNG supply or capacity services contracts from third parties that would subscribe to 100 percent of the capacity of Sempra LNG's Cameron receipt terminal, Sempra LNG will seek to purchase and market short-term LNG supplies and sell short-term capacity, which may result in greater variability in revenues and earnings.
The Sempra Utilities' performance will depend primarily on the ratemaking and regulatory process, environmental regulations, economic conditions, actions by the California legislature to address the state budget crisis and the changing energy marketplace. Their performance will also depend on the successful completion of capital projects that we discuss in various sections of this report. As the 2008 General Rate Case provides for fixed annual increases through 2011 rather than adjustments based on inflation indices as in the past, performance will depend on the Sempra Utilit ies' ability to manage costs, including bad debts. Starting in the third quarter of 2009, SDG&E's liability insurance premiums increased significantly, by approximately $40 million annually, due to the increased costs of wildfire coverage as compared to the previous policy year. Starting in the third quarter of 2010, SDG&E has secured additional insurance coverage of approximately $560 million with respect to any future wildfire liabilities. SDG&E's maximum loss recovery due to a wildfire incident from insurance carriers is now approximately $960 million, with the remainder of Sempra Energy's business units' maximum coverage for a wildfire incident remaining at $400 million, the same as in the previous policy year. Starting in the third quarter of 2010, SDG&E's insurance premiums increase by approximately $30 million (pretax) annually for the increased coverage.
In regard to the 2007 wildfire litigation, SDG&E has exceeded its $1.1 billion of liability in surance coverage in settling wildfire claims. However, it has concluded that it is probable that it will be permitted to recover from its utility customers substantially all reasonably incurred costs of resolving wildfire claims in excess of its liability insurance coverage and any amounts recovered from other potentially responsible parties. Consequently, Sempra Energy and SDG&E expect no significant earnings impact from the resolution of the remaining wildfire claims. However, SDG&E’s cash flow will be adversely affected by timing differences between the resolution of claims and recoveries from other potentially responsible parties and utility customers, which may extend over a number of years. In addition, recovery from customers will require future regulatory actions, and a failure to obtain recovery, or any negative assessment of the likelihood of recovery, would likely have a material adverse effect on Sempra Energy's and SDG&E's cash flows and results of operations.
SDG&E will continue to gather information to evaluate and assess the remaining wildfire claims and the likelihood, amount and timing of related recoveries from other potentially responsible parties and utility customers and will make appropriate adjustments to wildfire reserves and the related regulatory asset as additional information becomes available. We provide additional information concerning these matters in Notes 9 and 10 of the Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements herein.
SDG&E has a 20-percent ownership interest in San Onofre Nuclear Generating Station (SONGS), a 2,150-MW nuclear generating facility near San Clemente, California. SONGS is operated by Southern California Edison (SCE) and is subject to the jurisdiction of the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC). SCE is currently addressing a number of regulatory and performance issues at SONGS, and the NRC has required SCE to take actions to provide greater assurance of compliance by SONGS personnel. SCE continues to implement plans and address the identified issues, however a number of these issues remain outstanding. To the extent that these issues persist, the likelihood of further required action by SCE persists, which may result in increased SONGS operating costs and/or adversely impacted operations. Currently, SDG&E is allowed to fully offset its share of SONGS operating costs in revenue. If further action is required, it may result in an increase in SDG&E’s Operation and Maintenance Expense, with any increase being fully offset in Operating Revenues – Electric or, if electric generation is adversely impacted, require SDG&E to procure additional electricity supply from other sources. We provide more information about SONGS in Notes 7, 15 and 17 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in the Annual Report, and in Items 1 and 1A of our 2009 Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Both SDG&E's an d SoCalGas' cost of capital decisions include provisions that can result in adjustments, upwards or downwards, to their return on capital in periods between cost of capital filings. As a result of the worldwide recession, interest rates have remained at relatively low levels for an extended period of time. If the cost of capital benchmark interest rates, for either company, recorded in the third quarter of 2010 were to continue at the same levels through the second quarter of 2011, one or both companies’ authorized return on capital could be adjusted downward effective January 1, 2012. It is estimated that if such a downward adjustment were to occur, it would result in an adverse impact to earnings in 2012 of $15 million at SDG&E and $23 million at SoCalGas. Both SDG&E and SoCalGas are planning to file a cost of capital application with the CPUC in April 2012. Once approved by the CPUC, the applications would establish return on capital and cost of debt recovery for both SDG&E and SoCalGas starting in J anuary 2013.
In 2008, we completed the formation of a partnership, RBS Sempra Commodities, to own and operate our commodities-marketing businesses, which generally comprised our Sempra Commodities segment. In November 2009, RBS announced its intention to divest its interest in the joint venture following a directive from the European Commission to dispose of certain assets. In February 2010, Sempra Energy, RBS and the partnership entered into an agreement to sell certain businesses within the partnership, which agreement was consummated on July 1, 2010. In September 2010, the parties announced an agreement to sell the U.S. retail commodity marketing business of RBS Sempra Commodities, which closed on November 1, 2010. In October 2010, the joint venture entered into an agreement to sell most of its remaining assets to J.P. Morgan Ventures. This transaction is expected to close by year-end. Our joint venture partner, RBS, continues to be obligated to provid e the partnership with all working-capital requirements and credit support.
We expect our share of the proceeds from the sales of all of the joint venture's businesses and related cash distributions to total $1.8 billion to $1.9 billion. These distributions are net of expected transition costs and are not expected to fully recover the goodwill included in the carrying value of our investment in the joint venture. Accordingly, in the third quarter of 2010, we recorded an after-tax charge of $139 million to reduce our investment in RBS Sempra Commodities.
Future earnings and distributions from the partnership will depend on the profitability achieved in the partnership's remaining businesses through their final disposition dates and the continued ability of RBS to provide capital and credit support for the partnership. Results of the joint venture in the first three quarters of 2010 were adversely impac ted by the sale on July 1, 2010, of the global metals and oil businesses and the European natural gas and power business; lower volatility in the U.S. natural gas and power business; and the disruptions caused by the process to sell the partnership's businesses. We provide additional information in Notes 4 and 6 of the Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements herein and in Notes 3, 4, 6 and 20 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in the Annual Report.
We may be further impacted by depressed and rapidly changing economic conditions. Moreover, the dollar has fluctuated significantly compared to some foreign currencies, especially in Mexico and South America where we have significant operations. North American natural gas prices, which affect profitability at Sempra Generation and Sempra LNG, are currently significantly below Asian and European prices. These factors could, if they remain unchanged, adversely affect profitability.
We discuss additional matters that could affect our future performance in Notes 9 and 10 of the Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements herein and in Notes 15 through 17 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in the Annual Report.
FINANCIAL DERIVATIVES REFORMS
In July 2010, federal legislation to reform financial markets was enacted that significantly alters how over-the-counter (OTC) derivatives are regulated, which may impact all of our businesses. The law increased regulatory oversight of OTC energy derivatives, including (1) requiring standardized OTC derivatives to be traded on registered exchanges regulated by the U.S. Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC), (2) imposing new and potentially higher capital and margin requirements and (3) authorizing the establishment of overall vol ume and position limits. The law gives the CFTC authority to exempt end users of energy commodities which could reduce, but not eliminate, the applicability of these measures to us and other end users. These requirements could cause our OTC transactions to be more costly and have an adverse effect on our liquidity due to additional capital requirements. In addition, as these reforms aim to standardize OTC products, they could limit the effectiveness of our hedging programs, because we would have less ability to tailor OTC derivatives to match the precise risk we are seeking to protect.
LITIGATION
We describe legal proceedings which could adversely affect our future performance in Note 10 of the Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements herein.
SEMPRA UTILITIES – INDUSTRY DEVELOPMENTS AND CAPITAL PROJECTS
We describe capital projects, electric and natural gas regulation and rates, and other pending proceedings and investigations that affect our business in Note 9 of the Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements herein and in Notes 15 and 16 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in the Annual Report.
SEMPRA GLOBAL INVESTMENTS
As we discuss in "Cash Flows From Investing Activities," our investments will significantly impact our future performance. In addition to the discussion below, we provide information about these investments in "Capital Resources and Liquidity" herein and “Capital Resources and Liquidity” and “Factors Influencing Future Performance” in the Annual Report.
Sempra Generation
Copper Mountain Solar
Pacific Gas and Electric has contracted for 48 MW of solar power from Copper Mountain Solar, a new plant under development in Boulder City, Nevada by Sempra Generation on land adjacent to the 10-MW El Dorado Energy Solar plant. Construction has begun and we expect it to be completed in late 2010.
Mesquite Solar
Mesquite Solar is a photovoltaic generation facility under development by Sempra Generation in Maricopa County, Arizona. When fully developed, the project will be capable of producing approximately 400 MW to 600 MW of solar power. Mesquite Solar will connect to the 500-kilovolt Hassayampa switchyard via our existing Mesquite Power natural gas generation plant.
Construction of the first phase (Mesquite Sola r I) of 150 MW is expected to begin in 2011 and be completed in 2013. In October 2010, Sempra Generation announced that PG&E has contracted, subject to CPUC approval, for 150 MW of solar power at Mesquite Solar I for 20 years.
Cedar Creek II Wind Farm
In October 2010, Sempra Generation invested $209 million for a 50 percent-ownership interest in Cedar Creek II Wind Farm LLC, a joint venture with BP Wind Energy for the development of a 250-MW wind farm in northern Colorado expected to be operational in mid-2011. Public Service Company of Colorado, an Xcel Energy company, has contracted for all of the power from the facility for 25 years.
Sempra Pipelines & Storage
Natural Gas Storage Projects
Currently, Sempra Pipelines & Storage has 23 billion cubic feet (Bcf) of operational working natural gas storage capacity, including approximately 12 Bcf which recently became operational at its Mississippi Hub and Bay Gas natural gas storage facilities. We plan to develop as much as 75 Bcf of total storage capacity by 2015.
Sempra Pipelines & Storage’s natural gas storage facilities and projects include
§Bay Gas Storage Company, a facility located 40 miles north of Mobile, Alabama, that provides underground storage and delivery of natural gas. Sempra Pipelines & Storage owns 91 percent of the project. It is the easternmost salt dome storage facility on the gulf coast, with direct service to the Florida market and markets across the Southeast, Mid-Atlantic and Northeast regions.
§Mississippi Hub storage facility, located in Simpson County, Mississippi, an underground salt dome natural gas storage project with access to shale basins of East Texas and Louisiana, traditional gulf supplies and LNG, with multiple interconnections to serve the Southeast and Northeast regions.
§Liberty Gas Storage Expansion, a salt cavern facility in Cameron Parish, Louisiana. Sempra Pipelines & Storage owns 75 percent of the project and ProLiance Transportation LLC owns the remaining 25 percent. The project’s location provides access to several LNG facilities in the area.
Acquisition of Mexican Pipeline and Natural Gas Infrastructure
On April 30, 2010, Sempra Pipelines & Storage completed the acquisition resulting in a purchase of the Mexican pipeline an d natural gas infrastructure assets of El Paso Corporation for $307 million ($292 million, net of cash acquired).
We discuss the acquisition more fully in Note 3 of the Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements herein.
CRITICAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES AND ESTIMATES
We view certain accounting policies as critical because their application is the most relevant, judgmental and/or material to our financial position and results of operations, and/or because they require the use of material judgments and estimates. We discus s these accounting policies in "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations" in the Annual Report.
We describe our significant accounting policies in Note 1 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in the Annual Report.
We discuss the relevant pronouncements that have recently become effective and have had or may have an impact on our financial statements in Note 2 of the Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements herein.
ITEM 3. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
We provide disclosure regarding derivative activity in Note 7 of the Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements herein. We discuss our market risk and risk policies in detail in "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations" in the Annual Report.
INTEREST RATE RISK
The table below shows the nominal amount and the one-year VaR for long-term debt, excluding capital lease obligations, at September 30, 2010 and December 31, 2009:
| Sempra Energy | | | | |
| Consolidated | SDG&E | PE/SoCalGas |
| Nominal | One-Year | Nominal | One-Year | Nominal | One-Year |
(Dollars in millions) | Debt | VaR(1) | Debt | VaR(1) | Debt | VaR(1) |
At September 30, 2010: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Utility fixed-rate | $ | 3,817 | $ | 701 | $ | & nbsp;2,704 | $ | 585 | $ | 1,113 | $ | 116 |
Utility variable-rate | | 754 | | 44 | | 604 | | 44 | | 150 | | - |
Non-util ity, fixed-rate and variable-rate | | 3,578 | | 481 | | - | | - | | - | | - |
At December 31, 2009: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Utility fixed-rate | $ | 3,067 | $ | 369 | $ | 1,954 | $ | 273 | $ | 1,113 | $ | 97&nb sp; |
Utility variable-rate | | 848 | | 43 | | 698 | | 43 | | 150 | | - |
Non-utility, fixed-rate and variable-rate | | 4,075 | | 392 | | - | | - | | - | | - |
(1) After the effects of interest rate swaps. |
At September 30, 2010, the net notional amount of intere st rate swap transactions ranged from $215 million to $355 million at Sempra Energy (ranges relate to amortizing notional amounts). We provide additional information about interest rate swap transactions in Note 7 of the Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements herein.
FOREIGN CURRENCY RATE RISK
We discuss our foreign currency rate risk in detail in "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations" in the Annual Report. At September 30, 2010, there were no significant changes to our exposure to foreign currency rate risk since December 31, 2009.
ITEM 4. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
EVALUATION OF DISCLOSURE CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
Sempra Energy, SDG&E, PE and SoCalGas have designed and maintain disclosure controls and procedures to ensure that information required to be disclosed in their respective reports is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the rules and forms of the Securities and Exchange Commission and is accumulated and communicated to the management of each company, including each respective Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, to allow timely decisions regardi ng required disclosure. In designing and evaluating these controls and procedures, the management of each company recognizes that any system of controls and procedures, no matter how well designed and operated, can provide only reasonable assurance of achieving the desired control objectives; therefore, the management of each company applies judgment in evaluating the cost-benefit relationship of other possible controls and procedures.
Under the supervision and with the participation of management, including the Chief Executive Officers and Chief Financial Officers of Sempra Energy, SDG&E, PE and SoCalGas, each company evaluated the effectiveness of the design and operation of its disclosure controls and procedures as of September 30, 2010, the end of the period covered by this report. Based on these evaluations, the Chief Executive Officers and Chief Financial Officers of Sempra Energy, SDG&E, PE and SoCalGas concluded that their respective company's dis closure controls and procedures were effective at the reasonable assurance level.
INTERNAL CONTROL OVER FINANCIAL REPORTING
There have been no changes in the companies' internal control over financial reporting during the most recent fiscal quarter that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, the companies' internal control over financial reporting.
PART II – OTHER INFORMATION
ITEM 1. LEGAL PROCEEDINGS
We are not party to, and our property is not the subject of, any material pending legal proceedings (other than ordinary routine litigation incidental to our businesses) except for the matters 1) described in Notes 9 and 10 of the Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements herein, or 2) referred to in "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations" herein and in the Annual Report.
There have not been any material changes from the risk factors previously disclosed in our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2009, except for the following additional risk that was disclosed in our Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2010:
RECOVERY OF 2007 WILDFIRE LITIGATION COSTS
As we discuss in Note 10 of the Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements herein, SDG&E is subject to numerous lawsuits arising out of the San Diego County wildfires in 2007. It expects that substantially all reasonably incurred costs of resolving 2007 wildfire claims that exceed its liability insurance coverage and any amounts recovered from other potentially responsible parties will be recovered from utility customers. However, recovery from cu stomers will require future regulatory actions, and a failure to obtain recovery, or any negative assessment of the likelihood of recovery, would likely have a material adverse effect on Sempra Energy’s and SDG&E’s cash flows and results of operations.
ITEM 2. UNREGISTERED SALES OF EQUITY SECURITIES AND USE OF PROCEEDS
Purchases of Equity Securities by the Issuer and Affiliated Purchasers
On September 21, 2010, we entered into a Collared Accelerated Share Acquisition Program with JPMorgan Chase Bank, National Association under which we prepaid $500 million to repurchase shares of our common stock, as we discuss in our Current Report on Form 8-K dated September 21, 2010 and in Note 5 of the Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements herein.
The following table sets forth information concerning purchases made by us, from the program authorized above, of our common stock during the third quarter of 2010:
| | | | | | Maximum |
| | | | | Total Number of | Dollar Value of |
| | Total | | | Shares Purchased as | Shares that May |
| | Number | Average | Part of Publicly | Yet Be Purchased |
| | of Shares | Price Paid | Announced Plans | Under the Plans |
| | Purchased (1) | Per Share (1) | or Programs (1) | or Programs |
| | | | | | |
September 2010 | 5,670,006 | | | 5,670,006 | |
| | 5,670,006 | | | 5,670,006 | $500 million remaining (2) |
(1) | All shares were purchased under the Collared Accelerated Share Acquisition Program entered into on September 21, 2010. The weighted average cost to us of shares purchased under the program will not be determinable until the completion of the program, which is expected to extend into the first quarter of 2011. Additional information regarding the program is provided in Note 5 of the Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements herein. |
(2) | Our board of directors has authorized the repurchase of shares of our common stock provided that the amounts expended for such purposes do not exceed the greater of $2 billion or amounts expended to purchase no more than 40 million shares. We prepaid $500 million under a Collared Accelerated Share Acquisition Program with JPMorgan Chase Bank, National Association on September 21, 2010 and expended an additional $1 billion pursuant to a share repurchase program completed in 2008. Therefore, approximately $500 million remains authorized by the board for the purchase of additional shares. We also may, from time to time, purchase shares of our common stock from restricted stock plan participants who elect to sell a sufficient number of vesting restricted shares to meet minimum statutory tax withholding requirements. |
EXHIBIT 10 -- MATERIAL CONTRACTS |
Sempra Energy |
10.1 | Master Confirmation for Share Purchase Agreement, dated as of September 21, 2010, between Sempra Energy and JPMorgan Chase Bank, National Association. |
EXHIBIT 12 – STATEMENTS RE: COMPUTATION OF RATIOS |
Sempra Energy |
12.1 | Sempra Energy Computation of Ratio of Earnings to Combined Fixed Charges and Preferred Stock Dividends. |
San Diego Gas & Electric Company |
12.2 | San Diego Gas & Electric Company Computation of Ratio of Earnings to Combined Fixed Charges and Preferred Stock Dividends. |
Pacific Enterprises |
12.3 | Pacific Enterprises Computation of Ratio of Earnings to Combined Fixed Charges and Preferred Stock Dividends. |
Southern California Gas Company |
12.4 | Southern California Gas Company Computation of Ratio of Earnings to Combined Fixed Charges and Preferred Stock Dividends. |
EXHIBIT 31 -- SECTION 302 CERTIFICATIONS |
Sempra Energy |
31.1 | Statement of Sempra Energy's Chief Executive Officer pursuant to Rules 13a-14 and 15d-14 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. |
| |
31.2 | Statement of Sempra Energy's Chief Financial Officer pursuant to Rules 13a-14 and 15d-14 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. |
San Diego Gas & Electric Company |
31.3 | Statement of San Diego Gas & Electric Company's Chief Executive Officer pursuant to Rules 13a-14 and 15d-14 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. |
| |
31.4 | Statement of San Diego Gas & Elec tric Company's Chief Financial Officer pursuant to Rules 13a-14 and 15d-14 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. |
Pacific Enterprises |
31.5 | Statement of Pacific Ente rprise's Chief Executive Officer pursuant to Rules 13a-14 and 15d-14 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. |
| |
31.6 | Statement of Pacific Enterprise's Chief Financial Officer pursuant to Rules 13a-14 and 15d-14 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. |
Southern California Gas Company |
31.7 | Statement of Southern California Gas Company's Chief Executive Officer pursuant to Rules 13a-14 and 15d-14 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. |
| |
31.8 | Statement of Southern California Gas Company's Chief Financial Officer pursuant to Rules 13a-14 and 15d-14 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. |
EXHIBIT 32 -- SECTION 906 CERTIFICATIONS |
Sempra Energy |
32.1 | Statement of Sempra Energy's Chief Executive Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Sec. 1350. |
| |
32.2 | Statement of Sempra Energy's Chief Financial Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Sec. 1350. |
San Diego Gas & Electric Company |
32.3 | Statement of San Diego Gas & Electric Company's Chief Executive Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Sec. 1350. |
| |
32.4 | Statement of San Diego Gas & Electric Company's Chief Financial Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Sec. 1350. |
Pacific Enterprises |
32.5 | Statement of Pacific Enterprise's Chief Executive Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Sec. 1350. |
| |
32.6 | Statement of Pacific Enterprise's Chief Financial Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Sec. 1350. |
Southern California Gas Company |
32.7 | Statement of Southern California Gas Company's Chief Executive Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Sec. 1350. |
| |
32.8 | Statement of Southern California Gas Company's Chief Financial Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Sec. 1350. |
EXHIBIT 101 -- INTERACTIVE DATA FILE |
| |
101.INS | XBRL Instance Document |
| |
101.SCH | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document |
| |
101.CAL | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document |
| |
101.DEF | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document |
| |
101.LAB | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document |
| |
101.PRE | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document |
SIGNATURES |
Sempra Energy: |
|
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized. |
|
| SEMPRA ENERGY,
(Registrant) |
| |
Date: November 9, 2010 | By: /s/ Joseph A. Householder |
| Joseph A. Householder
Senior Vice President, Controller and Chief Accounting Officer |
San Diego Gas & Electric Company: |
|
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized. |
|
| SAN DIEGO GAS & ELECTRIC COMPANY,
(Registrant) |
| |
Date: November 9, 2010 | By: /s/ Robert M. Schlax |
| Robert M. Schlax
Vice President, Controller, Chief Financial Officer and Chief Accounting Officer |
Pacific Enterprises: |
|
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized. |
|
| PACIFIC ENTERPRISES,
(Registrant) |
| |
Date: November 9, 2010 | By: /s/ Robe rt M. Schlax |
| Robert M. Schlax
Vice President, Controller, Chief Financial Officer and Chief Accounting Officer |
Southern California Gas Company: |
|
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authori zed. |
|
| SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA GAS COMPANY,
(Registrant) |
| |
Date: November 9, 2010 | By: /s/ Robert M. Schlax |
| Robert M. Schlax
Vice President, Controller, Chief Financial Officer and Chief Accounting Officer |



