UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
| | | | | |
| ☒ | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2024
or
| | | | | |
| ☐ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from ___________ to ___________
Commission File Number: 1-14106
DAVITA INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in charter)
| | | | | | | | |
| Delaware | | 51-0354549 |
| (State of incorporation) | | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
| | | | | | | | |
| 2000 16th Street |
| Denver, | CO | 80202 |
Telephone number (720) 631-2100
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Title of each class: | | Trading symbol(s): | | Name of each exchange on which registered: |
| Common Stock, $0.001 par value | | DVA | | New York Stock Exchange |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act:
None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Exchange Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports) and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ☒ No
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files). Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See the definitions of "large accelerated filer," "accelerated filer," "smaller reporting company" and "emerging growth company" in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Large accelerated filer | ☒ | | | Accelerated filer | ☐ |
| Non-accelerated filer | ☐ | | Smaller reporting company | ☐ |
| | | | Emerging growth company | ☐ |
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has filed a report on and attestation to its management's assessment of the effectiveness of its internal control over financial reporting under Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (15 U.S.C. 7262(b)) by the registered public accounting firm that prepared or issued its final report. ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes ☐ No ☒
If securities are registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act, indicate by check mark whether financial statements of the registrant included in the filing reflect the correction of an error to previously issued financial statements. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether any of those error corrections are restatements that required a recovery analysis of incentive-based compensation received by any of the registrant’s executive officers during the relevant recovery period pursuant to §240.10D-1(b). ☐
As of June 30, 2024, the aggregate market value of the registrant's common stock outstanding held by non-affiliates based upon the closing price on the New York Stock Exchange was approximately $11.8 billion.
As of January 31, 2025, the number of shares of the registrant’s common stock outstanding was approximately 80.0 million shares.
Documents incorporated by reference
Portions of the registrant’s proxy statement for its 2025 annual meeting of stockholders are incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K.
DAVITA INC.
INDEX
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | Page No. |
| | | PART I. | | |
| Item 1. | | | | |
| Item 1A. | | | | |
| Item 1B. | | | | |
| Item 1C. | | | | |
| Item 2. | | | | |
| Item 3. | | | | |
| Item 4. | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | PART II. | | |
| Item 5. | | | | |
| Item 6. | | | | |
| Item 7. | | | | |
| Item 7A. | | | | |
| Item 8. | | | | |
| Item 9. | | | | |
| Item 9A. | | | | |
| Item 9B. | | | | |
| Item 9C. | | | | |
| | | | |
| | PART III. | | |
| Item 10. | | | | |
| Item 11. | | | | |
| Item 12. | | | | |
| Item 13. | | | | |
| Item 14. | | | | |
| | | | |
| | PART IV. | | |
| Item 15. | | | | |
| Item 16. | | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
PART I
Item 1. Business
Unless otherwise indicated in this report "DaVita", "the Company" "we", "us", "our" and other similar terms refer to DaVita Inc. and its consolidated subsidiaries. Our annual report on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K and amendments to those reports filed or furnished pursuant to section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, are made available free of charge through our website, located at http://www.davita.com, as soon as reasonably practicable after the reports are filed with or furnished to the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). The SEC also maintains a website at http://www.sec.gov where these reports and other information about us can be obtained. The contents of our website are not incorporated by reference into this report.
Overview of DaVita Inc.
DaVita is a leading healthcare provider focused on transforming care delivery to improve quality of life for patients globally. As a comprehensive kidney care provider, we have been a leader in clinical quality and innovation for 25 years. We care for patients at every stage and setting along their kidney health journey–from earlier diagnosis and prevention through supporting the transplant process. This includes ensuring they are supported at home, in our dialysis centers, in the hospital and/or skilled nursing facilities. In our unwavering pursuit of a healthier tomorrow, we strive to reimagine what high quality care looks like: more preventative, better integrated, improved outcomes at the lowest total cost, and personalized at scale to deliver a better tomorrow regardless of location, insurance status or other factors. Our caring culture fuels our continuous drive toward achieving our mission to be the provider, partner and employer of choice.
Defining chronic kidney disease
There are five stages of chronic kidney disease (CKD). These stages are generally based on how well the kidneys work to filter waste and extra fluid out of the blood–with higher stages of CKD corresponding to progressing levels of kidney disease. Stage 1 CKD is the closest to healthy kidney function. Stage 5 CKD indicates that a patient has severe kidney damage.
A patient diagnosed with Stage 5 CKD has kidneys that have lost nearly all functionality or have failed. If an individual's kidneys fail, the person is then diagnosed with end stage renal disease (ESRD), also known as end stage kidney disease (ESKD). Because kidney function is essential for survival and the loss of kidney function is normally irreversible, ESKD patients require continued dialysis treatments or a kidney transplant to sustain life. Dialysis is the removal of toxins, fluids and salt from the blood of patients by artificial means. Patients suffering from ESKD generally require regular life-sustaining dialysis therapy for the rest of their lives or until they receive a kidney transplant.
The treatment goal for CKD patients prior to Stage 5 is to manage and slow the progression of the disease to preserve kidney functionality. Because kidney failure is typically caused by one or more comorbidities such as Type I and Type II diabetes, hypertension, polycystic kidney disease, long-term autoimmune attack on the kidneys or prolonged urinary tract obstruction, slowing the progression generally involves working with nephrologists and dieticians to help control blood pressure, monitor blood glucose and maintain healthy diet and exercise routines, among other things. If the kidney disease continues to progress, the goal is to support efforts for kidney transplantation where available and medically appropriate, and in the event transplantation is not possible, to work with the patient and his or her nephrologist to safely transition the patient to the dialysis treatment and modality of their choice.
Our businesses
We are a leading dialysis provider in the United States. Our U.S. dialysis and related lab services (U.S. dialysis) business treats patients with chronic kidney failure, ESKD, in the United States, and is our largest line of business. Our robust platform to deliver kidney care services also includes established nephrology and payor relationships.
In addition, as of December 31, 2024, our international operations provided dialysis and administrative services to a total of 509 outpatient dialysis centers located in 13 countries outside of the U.S., serving approximately 80,300 patients.
Finally, our U.S. integrated kidney care (IKC) business provided integrated care and disease management services to 70,400 patients in risk-based integrated care arrangements and to an additional 11,600 patients in other integrated care arrangements across the United States as of December 31, 2024.
We also maintain a few other ancillary services and investments outside of our U.S. dialysis, U.S. IKC, or international operations, which we refer to as our U.S. other ancillary services. We refer to our U.S. integrated kidney care business, U.S. other ancillary services and international operations as, collectively, our "ancillary services." We also have a separate corporate
administrative support function that supports our U.S. dialysis business and these ancillary services. Each of our businesses are described in greater detail in the sections that follow.
Our care model
Our patient-centric care model leverages our platform of kidney care services to maximize patient choice in both models and modalities of care. We believe that the flexibility we offer coupled with a focus on comprehensive kidney care supports our commitments to help improve equitable clinical outcomes and quality of life for our patients. According to the most recently published data, for the ten most recently reported years, we have continued as an industry leader in the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services’ (CMS) Quality Incentive Program (QIP), which promotes high quality services in outpatient dialysis facilities treating patients with ESKD. In addition, according to the most recently published data, for the nine most recently reported years, we have also continued as an industry leader under CMS’ Five-Star Quality Rating System (Star Rating), which rates eligible dialysis centers based on the quality of outcomes to help patients, their families, and caregivers make more informed decisions about where patients receive care. Following a pause in refreshed Star Ratings in October 2020 and October 2021 due to the COVID-19 pandemic, CMS reset the baseline with the October 2023 Star Rating release to reflect current performance and provide clinical differentiation through newly defined cutoff values. Under the new baseline, the lowest scoring 10% of facilities receive one star, the next 20% receive two stars, the next 40% receive three stars, the next 20% receive four stars and the highest 10% of facilities receive five stars in the baseline period for each subsequent evaluation period.
Our clinical outcomes are driven by our experienced and knowledgeable caregivers. We employ registered nurses, licensed practical or vocational nurses, patient care technicians, social workers, registered dietitians, biomedical technicians and other administrative and support teammates who strive to achieve superior clinical outcomes at our dialysis facilities. In addition to our teammates at our dialysis facilities, as of December 31, 2024, our domestic Chief Medical Officer leads a team of 23 nephrologists in our physician leadership team as part of our domestic Office of the Chief Medical Officer (OCMO). Our international Chief Medical Officer leads a team of 11 nephrologists in our physician leadership team as part of our international OCMO as of December 31, 2024. Our OCMO teammates represent a variety of academic, clinical practice, and clinical research backgrounds. We also have a Physician Council that serves as an advisory body to senior management, which was composed of 10 physicians with extensive experience in clinical practice and five Group Medical Directors as of December 31, 2024.
Value-based care arrangements continue to impact the kidney health space. These arrangements are fostering a much larger degree of collaboration between nephrologists and other providers, including transplant programs, resulting in a more complete understanding of each patient’s clinical needs. We believe this more complete understanding allows for better care coordination and earlier intervention, which we believe ultimately leads to improved clinical outcomes, lower overall costs and improved patient experiences. Our IKC business provides comprehensive care management for complex CKD patients nationwide, with payment models that include a variety of structures to advance and encourage integrated and value-based care. Among other arrangements, our IKC business has percent-of-premium arrangements in several Medicare Advantage ESRD Chronic Special Needs Plans and is an active participant in CMMI’s Comprehensive Kidney Care Contracting (CKCC) model that seeks to manage the care of late stage CKD and ESKD patients to delay the progression of kidney disease, promote home dialysis when appropriate, and incentivize transplants. Our IKC business also utilizes other value-based payment methodologies in its care coordination and disease management contracts, which include two-sided shared savings/shared losses and outcomes-based pay-for-performance compensation arrangements.
U.S. dialysis business
Our U.S. dialysis business is a leading provider of kidney dialysis services for patients suffering from ESKD. As of December 31, 2024, we provided dialysis, administrative and related laboratory services in the U.S. through a network of 2,657 outpatient dialysis centers in 46 states and the District of Columbia, serving a total of approximately 200,800 patients. We also have contracts to provide hospital inpatient dialysis services in approximately 760 hospitals throughout the U.S.
Based on the most recent 2024 annual data report from the United States Renal Data System (USRDS), there were over 554,000 ESKD dialysis patients in the U.S. in 2022. The underlying ESKD dialysis patient population grew at an approximate compound annual rate of 3.3% from 2012 to 2022 and 3.4% from 2017 to 2022 as compared to a decline in annual growth of 0.4% from 2021 to 2022. Despite this near term slowdown, which, among other things, included impacts from the COVID-19 pandemic on mortality rates amongst the ESKD dialysis patient population, the rate of growth has been relatively consistent over time. In general, a number of factors may impact ESKD growth rates, including, among others, mortality rates for dialysis patients or CKD patients, the growth and aging of the U.S. population, limitations on immigration in the U.S., transplant rates, incidence rates for diseases that cause kidney failure such as diabetes and hypertension, growth rates of minority populations with higher than average incidence rates of ESKD or other changes in demand for dialysis treatments over time, including for
example, as a result of the development and application of certain innovative technologies, drugs or other treatments. Certain of these factors, in particular mortality rates for dialysis or CKD patients, have been impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Treatment options for ESKD
Treatment options for ESKD are dialysis and kidney transplantation.
Dialysis options
•Hemodialysis
Hemodialysis is the most common form of ESKD treatment. The hemodialysis machine uses a filter, called a dialyzer, to remove toxins, fluids and salt from the patient’s blood. The dialysis process occurs across a semi-permeable membrane that divides the dialyzer into two distinct chambers. While blood is circulated through one chamber, a pre-mixed fluid is circulated through the other chamber. The toxins, salt and excess fluids from the blood cross the membrane into the fluid, allowing cleansed blood to return back into the patient’s body.
Hemodialysis is usually performed at a freestanding outpatient dialysis center, at a hospital-based outpatient center, in a skilled nursing facility or at the patient's home. Our freestanding outpatient dialysis centers are staffed with members of our care team and store the supplies necessary for treatment. Treatments are usually performed three times per week.
Hospital inpatient hemodialysis services are required for patients with acute kidney failure primarily resulting from acute medical illness or trauma, patients in early stages of ESKD and ESKD patients who require hospitalization for other reasons. Hospital inpatient hemodialysis is generally performed at the patient’s bedside or in a dedicated treatment room in the hospital, as needed.
Some ESKD patients may perform hemodialysis with the help of a care partner in their home or residence through the use of a hemodialysis machine designed specifically for home therapy that is portable, smaller and easier to use. This is referred to as home hemodialysis (HHD). Patients receive training, support and monitoring from registered nurses, usually in our outpatient dialysis centers, in connection with their HHD treatment. HHD is typically performed with greater frequency than dialysis treatments performed in outpatient dialysis centers and on varying schedules.
•Peritoneal dialysis
Peritoneal dialysis uses the patient’s peritoneal or abdominal cavity to eliminate fluid and toxins and is typically performed at home. The most common methods of peritoneal dialysis are continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD) and continuous cycling peritoneal dialysis (CCPD). Because it does not involve going to an outpatient dialysis center three times a week for treatment, peritoneal dialysis is generally an alternative to hemodialysis for patients who are healthier, more independent and desire more flexibility in their lifestyle.
CAPD introduces dialysis solution into the patient’s peritoneal cavity through a surgically placed catheter. Toxins in the blood continuously cross the peritoneal membrane into the dialysis solution. After several hours, the patient drains the used dialysis solution and replaces it with fresh solution. This procedure is usually repeated four times per day.
CCPD is performed in a manner similar to CAPD, but uses a mechanical device to cycle dialysis solution through the patient’s peritoneal cavity while the patient is sleeping or at rest.
•Kidney transplantation
Kidney transplantation, when successful, is considered the most desirable form of therapeutic intervention. However, in light of the shortage of suitable donors, side effects of immunosuppressive pharmaceuticals given to transplant recipients and dangers associated with transplant surgery, some patient populations have generally limited the use of this treatment option. In accordance with an executive order signed in July 2019 (the 2019 Executive Order), the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) developed policies addressing, among other things, the goal of making more kidneys available for transplant. CMS, through CMMI, also subsequently released the framework for certain proposed and existing voluntary and mandatory payment models, including ESRD Treatment Choices Model (ETC) model, which would adjust payment incentives to encourage kidney transplants. For more information about these payment models, please see the discussion below under the heading "—Integrated Kidney Care, Medicare and Medicaid program reforms and Other Healthcare Regulations."
•Hemodiafiltration
Hemodiafiltration (HDF) is a form of augmented hemodialysis that includes a component of convection to remove additional molecules from the blood. Like hemodialysis, HDF can be performed at certain freestanding outpatient dialysis
centers and may also be performed in hospital in-patient centers. HDF usage varies by country, and the efficacy of this modality is still being assessed in the U.S.
U.S. dialysis services we provide
Outpatient hemodialysis services
The majority of services we provide to patients are outpatient hemodialysis treatments. As a condition of our enrollment in Medicare for the provision of dialysis services, we contract with a nephrologist or a group of associated nephrologists to provide medical director services at each of our dialysis centers. In addition, other nephrologists may apply for practice privileges to treat their patients at our centers. Each center has an administrator, often a registered nurse, who supervises the day-to-day operations of the center and its staff. The staff of each center typically consists of registered nurses, licensed practical or vocational nurses, patient care technicians, a social worker, a registered dietician, biomedical technician support and other administrative and support personnel.
The overall number of patients to whom we provided services in the U.S. in 2024 was relatively flat compared to 2023, primarily due to growth in new admits partially offset by elevated mortality rates, which continue to be elevated relative to our pre-COVID-19 mortality rates.
Hospital inpatient hemodialysis services
As of December 31, 2024, we have contracts to provide hospital inpatient dialysis services to patients in approximately 760 hospitals throughout the U.S. We render these services based on a contracted per-treatment fee that is individually negotiated with each hospital. When a hospital requests our services, we typically administer the dialysis treatment at the patient’s bedside or in a dedicated treatment room in the hospital, as needed.
Home-based dialysis services
Home-based dialysis services includes HHD and peritoneal dialysis. Many of our outpatient dialysis centers offer certain support services for dialysis patients who prefer and are able to perform either HHD or peritoneal dialysis in their homes. Home-based hemodialysis support services consist of providing equipment and supplies, training, patient monitoring, on-call support services and follow-up assistance. Registered nurses train patients and their families or other caregivers to perform either HHD or peritoneal dialysis. The 2019 Executive Order and related HHS guidance described above also included a stated goal of increasing the relative number of new ESKD patients that receive dialysis at home.
According to the most recent annual data report from the USRDS, in 2022 approximately 14% of ESKD dialysis patients in the U.S. utilized home-based dialysis.
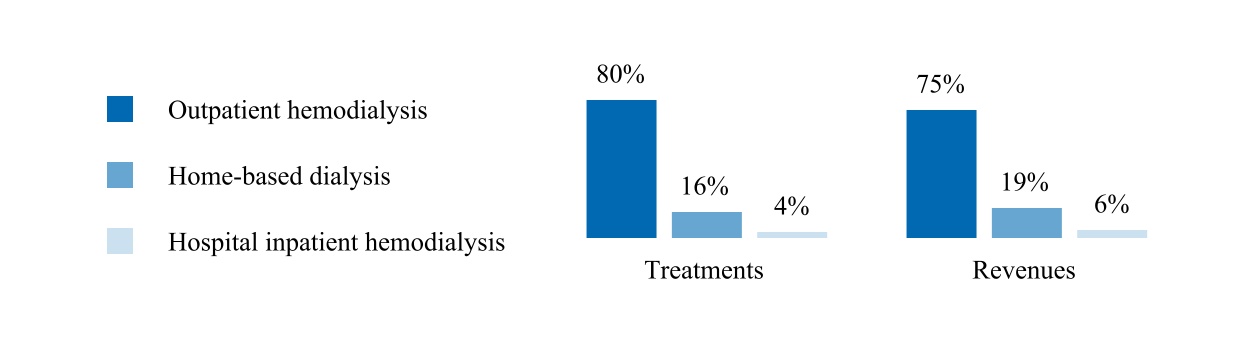
Treatments and revenues by modality:
The following graph summarizes our U.S. dialysis treatments by modality and U.S. dialysis patient service revenues by modality for the year ended December 31, 2024.
Other
ESKD laboratory services
We operate a separately licensed and highly automated clinical laboratory that specializes in ESKD patient testing. This specialized laboratory provides routine laboratory tests for dialysis and other physician-prescribed laboratory tests for ESKD patients. The vast majority of these tests are performed for our ESKD patients throughout the U.S. These tests are performed for
a variety of reasons, including to monitor a patient’s ESKD condition, including the adequacy of dialysis, as well as other medical conditions of the patient. Our laboratory utilizes information systems that provide information to certain members of the dialysis centers’ staff and medical directors regarding critical outcome indicators.
Management services
We currently operate or provide management and administrative services pursuant to management and administrative services agreements to 52 outpatient dialysis centers located in the U.S. in which we either own a noncontrolling interest or which are wholly-owned by third parties. Management fees are established by contract and are recognized as earned typically based on a percentage of revenues or cash collections generated by the outpatient dialysis centers.
Sources of revenue—concentrations and risks
Our U.S. dialysis revenues represent approximately 88% of our consolidated revenues for the year ended December 31, 2024. Our U.S. dialysis revenues are derived primarily from our core business of providing dialysis services and related laboratory services and, to a lesser extent, the administration of pharmaceuticals and management fees generated from providing management and administrative services to certain outpatient dialysis centers, as discussed above.
The sources of our U.S. dialysis revenues are principally from government-based programs, including Medicare and Medicare Advantage plans, Medicaid and managed Medicaid plans, other government-based programs including our agreement with the Veterans Administration, and commercial insurance plans. The following table summarizes our U.S. dialysis revenues by payor source for U.S. dialysis patient service revenues for the year ended December 31, 2024:
| | | | | | |
| Medicare and Medicare Advantage plans | 56 | % | |
| Medicaid and managed Medicaid plans | 8 | % | |
| Other government-based programs | 3 | % | |
| Total government-based programs | 67 | % | |
| Commercial (including hospital dialysis services) | 33 | % | |
| Total U.S. dialysis patient service revenues | 100 | % | |
Medicare revenue
Medicare fee for service
Since 1972, the federal government has provided healthcare coverage for qualified ESRD patients under the Medicare ESRD program regardless of age or financial circumstances. ESRD is the first and only disease state eligible for Medicare coverage both for dialysis and dialysis-related services and for all benefits available under the Medicare program.
Government dialysis related payment rates in the U.S. are principally determined by federal Medicare and state Medicaid policy. For patients with Medicare coverage, all ESRD payments for dialysis treatments are made under a single bundled payment rate that provides a fixed payment rate to encompass all goods and services provided during the dialysis treatment that are related to the dialysis treatment, including certain pharmaceuticals, such as erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESAs), calcimimetics, vitamin D analogs, oral-only renal phosphate binders and iron supplements, irrespective of the level of pharmaceuticals administered to the patient or additional services performed. Most lab services are also included in the bundled payment.
Although Medicare reimbursement limits the allowable charge per treatment, it provides industry participants with a relatively predictable and recurring revenue stream for dialysis services provided to patients without commercial insurance. For the year ended December 31, 2024, approximately 89% of our total U.S. dialysis patients were covered under some form of government-based program, with approximately 74% of our total U.S. dialysis patients covered under Medicare and Medicare Advantage plans.
Under this bundled payment rate system, known as the ESRD Prospective Payment System (PPS), the payments to a dialysis facility may be reduced by as much as 2% based on the facility’s performance in specified quality measures set annually by CMS through its QIP. CMS established QIP through the Medicare Improvements for Patients and Providers Act of 2008 to promote high quality services in outpatient dialysis facilities treating patients with ESRD. QIP associates a portion of Medicare reimbursement directly with a facility’s performance on quality of care measures. Reductions in Medicare reimbursement result when a facility’s overall score on applicable measures does not meet established standards.
Uncertainty about future payment rates remains a material risk to our business, as well as the potential implementation of or changes in coverage determinations or other rules or regulations by CMS or Medicare Administrative Contractors that may impact reimbursement. An important provision in the Medicare ESRD statute is an annual adjustment, or market basket update, to the ESRD PPS base rate. Absent action by Congress, the ESRD PPS base rate is updated annually by an inflation adjustment based on historical data and forecasts that may create a lag between these adjustments and actual inflationary increase. As a result, an inflation adjustment may not always cover the actual inflationary increase experienced. Due in part to continued higher than expected inflation rates, the annual update for the 2024 ESRD PPS base rate did not accurately forecast the cost increase experienced by providers.
In November 2024, CMS issued a final rule to update the Medicare ESRD PPS payment rate and policies for calendar year 2025. Among other things, the final rule updated both the ESRD and Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) dialysis payment rate for renal dialysis services furnished by ESRD facilities, extended payment for dialysis in a home setting for AKI, and outlined requirements for the ESRD QIP. CMS estimates that the overall impact of the rule will increase ESRD facilities' average reimbursement by a productivity-adjusted market basket increase of 2.2%. On January 1, 2025, phosphate binders, a drug class taken orally by many ESKD patients to reduce absorption of dietary phosphate, were incorporated into the ESRD PPS bundled payment rate. Phosphate binders are not considered accounted for in the ESRD PPS base rate at this time and will be reimbursed through a Transitional Drug Add-on Payment Adjustment (TDAPA). The TDAPA period is expected to continue for a period of at least two years.
As a result of the Budget Control Act of 2011 (BCA) and subsequent activity in Congress, a $1.2 trillion sequester (across-the-board spending cuts) in discretionary programs took effect in 2013 reducing Medicare payments (currently by 2%), which was subsequently extended into fiscal year 2032.
Most ESRD patients receiving dialysis services become eligible for primary Medicare coverage at various times, depending on their age or disability status, as well as whether they are covered by a commercial insurance plan. Generally, for a patient not covered by a commercial insurance plan, Medicare can become the primary payor for qualified ESRD patients receiving dialysis services either immediately or after a three-month waiting period. In most cases, for a patient covered by a commercial insurance plan, Medicare will either become the primary payor after 33 months, which includes the three-month waiting period, or earlier if the patient’s commercial insurance plan coverage terminates or if the patient chooses Medicare over the commercial plan. When Medicare becomes the primary payor, the payment rates we receive for that patient shift from the commercial insurance plan rates to Medicare payment rates, which are on average significantly lower than commercial insurance rates.
Medicare pays 80% of the amount set by the Medicare system for each covered dialysis treatment. The patient is responsible for the remaining 20%. In many cases, a secondary payor, such as Medicare supplemental insurance, a state Medicaid program or a commercial health plan, covers all or part of these balances. If a patient does not have secondary insurance coverage, we are generally unsuccessful in our efforts to collect from the patient the remaining 20% portion of the ESRD composite rate that Medicare does not pay. In those instances, however, we are able to recover some portion of this unpaid patient balance from Medicare through an established cost reporting process by identifying these Medicare bad debts on each center’s Medicare cost report. For additional detail on the associated risks, see the risk factor in Part I Item 1A. "Risk Factors" under the heading "Changes in federal and state legislation or regulations..."
Medicare Advantage revenue
Medicare Advantage (MA, managed Medicare or Medicare Part C) plans are offered by private health insurers who contract with CMS to provide their members with Medicare Part A, Part B and/or Part D benefits. These MA plans include health maintenance organizations, preferred provider organizations, private fee-for-service (FFS) organizations, special needs plans (SNPs) or Medicare medical savings account plans. Since January 1, 2021, under the 21st Century Cures Act (the Cures Act) Medicare-eligible beneficiaries with ESRD can choose coverage under an MA plan. MA plans usually provide reimbursement to us at a negotiated rate that is generally higher than Medicare FFS rates. CMS releases an annual MA notice that includes, among other things, a MA payment rate for MA plans and updates certain policies associated with risk adjustments. We continue to monitor MA notices, regulatory updates and guidance, as well as enforcement for impact on our business.
Medicaid revenue
Medicaid programs are state-administered programs partially funded by the federal government. These programs are intended to provide health coverage for patients whose income and assets fall below state-defined levels and who are otherwise uninsured. These programs also serve as supplemental insurance programs for co-insurance payments due from Medicaid-eligible patients with primary coverage under the Medicare program. Some Medicaid programs also pay for additional services,
including some oral medications that are not covered by Medicare. We are enrolled in the Medicaid programs in the states in which we conduct our business.
Commercial revenue
As discussed above, if a patient has commercial insurance, then that commercial insurance plan is generally responsible for payment of dialysis services for up to the first 33 months before that patient becomes eligible to elect to have Medicare as their primary payor for dialysis services. Although commercial payment rates vary, average commercial payment rates negotiated with commercial payors are generally significantly higher than Medicare rates. The payments we receive from commercial payors generate nearly all of our profits and all of our non-hospital dialysis profits come from commercial payors. Payment methods from commercial payors can include a single per treatment rate, referred to as bundled rates, or in other cases separate payments for dialysis treatments and pharmaceuticals, if used as part of the treatment, referred to as FFS rates. Commercial payment rates are the result of negotiations between us and commercial payors or third party administrators. Our commercial contracts sometimes contain annual price escalator provisions. We are comprehensively contracted, and the vast majority of patients insured through commercial health plans are covered by one of our commercial contracts, though we also receive payments for a limited set of commercial patients that are covered by a health plan that considers us out-of-network. While our out-of-network payment rates are on average higher than in-network commercial contract payment rates, we have made efforts to be contracted with the majority of commercial payors offering health plans.
Approximately 27% of our U.S. dialysis patient service revenues and approximately 11% of our U.S. dialysis patients are associated with non-hospital commercial payors for the year ended December 31, 2024. Non-hospital commercial patients as a percentage of our total U.S. dialysis patients for 2024 increased slightly compared to 2023. Less than 1% of our U.S. dialysis revenues are due directly from patients. No single commercial payor accounted for more than 10% of total U.S. dialysis revenues for the year ended December 31, 2024. See Note 2 to the consolidated financial statements included in this report for disclosure on our concentration related to our commercial payors on a total consolidated revenue basis.
Both the number of our patients under commercial plans and the rates under these commercial plans are subject to change based on a number of factors. For additional detail on these factors and other risks associated with our commercial revenue, see the risk factors in Part I Item 1A. "Risk Factors" under the headings "Our business is subject to a complex set of governmental laws, regulations and other requirements...;" "Changes in federal and state legislation or regulations...;" "If the number or percentage of patients with higher-paying commercial insurance declines...;" and "External conditions, including those related to general economic, marketplace and global health conditions..."
Physician relationships
Joint venture partners
We own and operate certain of our dialysis centers through entities that are structured as joint ventures. We generally hold controlling interests in these joint ventures, with nephrologists, hospitals, management services organizations, and/or other healthcare providers holding minority equity interests. These joint ventures are typically formed as limited liability companies. For the year ended December 31, 2024, revenues from joint ventures in which we have a controlling interest represented approximately 30% of our U.S. dialysis revenues. We expect to continue to enter into new U.S. dialysis-related joint ventures in the ordinary course of business.
Community physicians
An ESKD patient generally seeks treatment or support for their home treatment at an outpatient dialysis center near their home where their treating nephrologist has practice privileges. Our relationships with local nephrologists and our ability to provide quality dialysis services and to meet the needs of their patients are key factors in the success of our dialysis operations. Nearly 5,300 nephrologists currently refer patients to our outpatient dialysis centers.
Medical directors
Participation in the Medicare ESRD program requires that dialysis services at an outpatient dialysis center be under the general supervision of a medical director. Per these requirements, this individual is usually a board certified nephrologist. We engage physicians or groups of physicians to serve as medical directors for each of our outpatient dialysis centers. At some outpatient dialysis centers, we also separately contract with one or more other physicians or groups to serve as assistant or associate medical directors over other modalities such as home dialysis. We have over 900 individual physicians and physician groups under contract to provide medical director services.
Medical directors for our dialysis centers enter into written contracts with us that specify their duties and fix their compensation. These agreements range in duration, but generally are for periods of ten years. The compensation of our medical
directors is the result of arm’s length negotiations, consistent with fair market value, and generally depends upon an analysis of various factors such as the physician’s duties, responsibilities, professional qualifications and experience, as well as the time and effort required to provide such services.
Our medical director contracts and joint venture operating agreements generally include covenants not to compete or own interests in dialysis centers operated by other providers within a defined geographic area for various time periods, as applicable. These non-compete agreements do not restrict or limit the physicians from practicing medicine or prohibit the physicians from referring patients to any outpatient dialysis center, including dialysis centers operated by other providers.
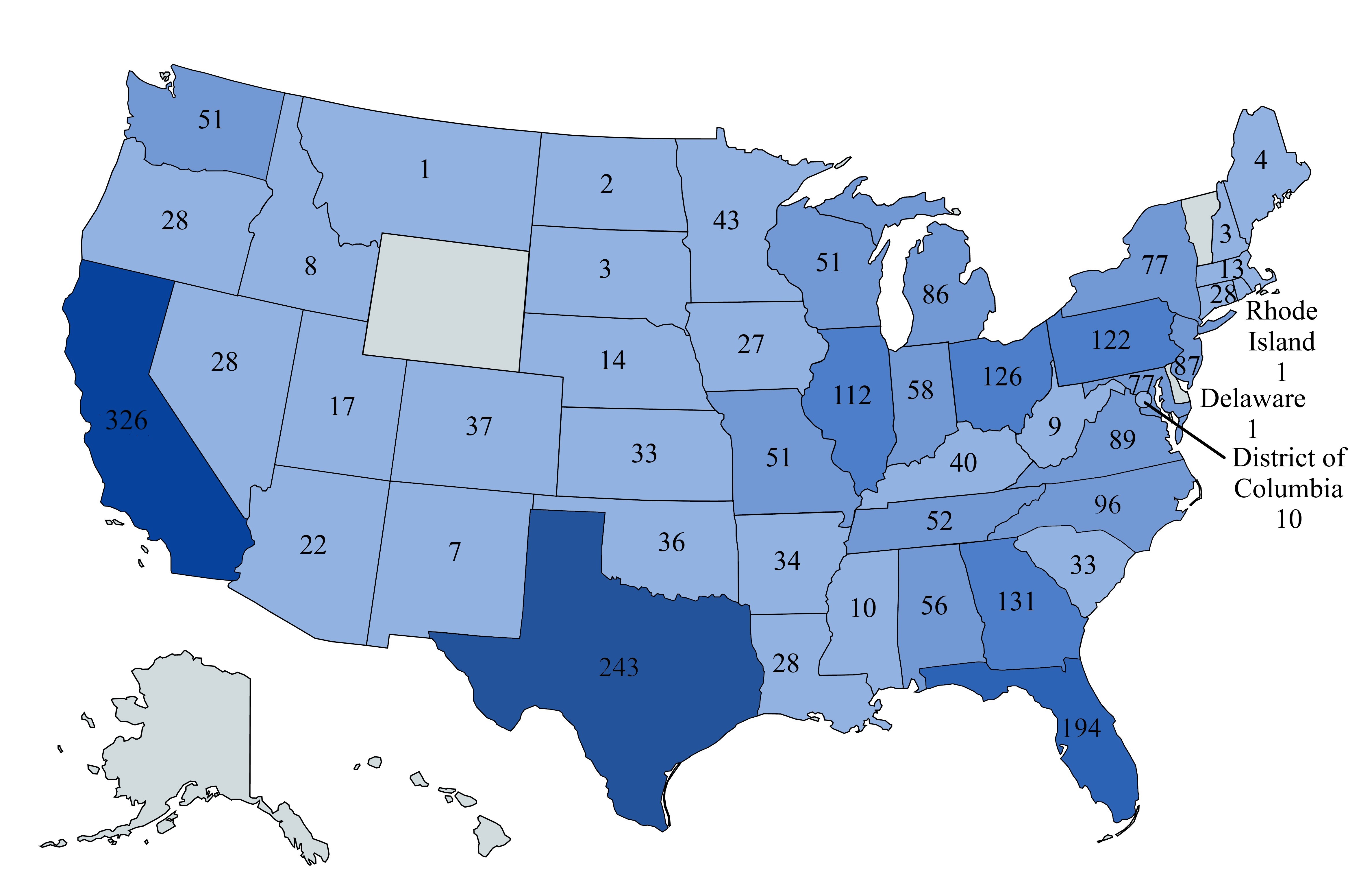
Location of our U.S. dialysis centers
We operated 2,657 outpatient dialysis centers in the U.S. as of December 31, 2024 and 2,605 of these centers are consolidated in our financial statements. Of the remaining 52 nonconsolidated U.S. outpatient dialysis centers, we own noncontrolling interests in 49 centers and provide management and administrative services to three centers that are wholly-owned by third parties. The locations of the 2,605 U.S. outpatient dialysis centers consolidated in our financial statements at December 31, 2024, were as follows:
Ancillary services, including our international operations
Our ancillary services relate primarily to our core business of providing kidney care services. As of December 31, 2024, these consisted primarily of our U.S. integrated kidney care (IKC) business, certain U.S. other ancillary businesses (including our clinical research programs, transplant software business, and venture investment group), and our international operations.
We have made and continue to make investments in building our integrated care capabilities, including the operation of certain strategic business initiatives that are intended to integrate and coordinate care among healthcare participants across the renal care continuum from CKD to ESKD to kidney transplant. Through improved technology and data sharing, as well as an increasing focus on value-based contracting and care, these initiatives seek to bring together physicians, nurses, dieticians, pharmacists, hospitals, dialysis clinics, transplant centers, payors and other specialists with a view towards improving clinical outcomes for our patients and reducing the overall cost of comprehensive kidney care. Certain of our ancillary services are described below.
U.S. Integrated Kidney Care
•Integrated Kidney Care. DaVita Integrated Kidney Care (DaVita IKC), provides advanced integrated care management services to health plans and government programs for members/beneficiaries diagnosed with ESKD and CKD. Through a combination of health monitoring, clinical coordination, innovative interventions, predictive analytics, medical claims analysis and information technology, we endeavor to assist our health plan and government program customers and patients in obtaining superior renal healthcare and improved clinical outcomes, as well as helping to reduce overall medical costs. Integrated kidney care management revenues from commercial and Medicare Advantage insurers can be based upon either an established contract fee recognized as earned for services provided over the contract period, or related to the operation of risk-based and value-based care programs, including shared savings, pay-for-performance, and capitation contracts. DaVita IKC also contracts with payors to support MA ESKD chronic condition special needs plans (C-SNPs) to provide ESKD patients full service healthcare and integrated care management services. DaVita IKC currently participates in both the involuntary and certain voluntary payment models administered by CMMI. As described below under the heading "—Government regulation—CMMI Payment Models", we have invested resources, and expect to continue to invest substantial resources in these models as part of our overall plan to grow our integrated kidney care business and value-based care initiatives. See Note 1, Other revenues, in the Company's consolidated financial statements for more information on how the Company accounts for its integrated care arrangements.
The Company is also developing, and has entered into, various forms of technology-based, administrative, financial and other collaboration and incentive arrangements with physician partners and other providers in support of our innovative care model, developing and expanding IKC programs and arrangements.
U.S. Other Ancillary services
•Clinical research programs. DaVita Clinical Research (DCR) is a provider-based specialty clinical research organization with a wide spectrum of services for clinical drug research and device development. DCR uses its extensive real-world healthcare expertise to assist in the design, recruitment and completion of retrospective and prospective studies. Revenues are based upon study generated fees, as determined by contract with drug companies and other sponsors, and are recognized as earned according to the contract terms.
•Transplant software business. DaVita's transplant software business, MedSleuth, works with transplant centers across the U.S. to provide greater connectivity among transplant candidates, transplant centers, physicians and care teams to help improve the experience and outcomes for kidney and liver transplant patients.
•Venture group. DaVita Venture Group (DVG) focuses on innovative products, solutions and businesses that improve care for patients with kidney disease and related conditions. DVG identifies companies and products for acquisitions, strategic partnerships, and venture investment opportunities. DVG’s focus includes innovation in digital health, pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and care delivery models.
For additional discussion of our ancillary services, see Part II Item 7, "Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations."
International dialysis operations
We operated, managed or administered 509 outpatient dialysis centers located in 13 countries outside of the U.S. serving approximately 80,300 patients as of December 31, 2024. Our international dialysis operations have continued to grow steadily and expand as a result of acquiring and developing outpatient dialysis centers in various strategic markets. Our international operations are included in our ancillary services.
As of December 31, 2024, the international outpatient dialysis centers we operate or provide administrative services to were located as follows:
| | | | | |
| Brazil | 100 | |
| Colombia | 72 | |
| Chile | 63 | |
| Poland | 63 | |
| Germany | 49 | |
| Malaysia | 44 | |
| United Kingdom | 27 | |
| Saudi Arabia | 26 | |
| Ecuador | 22 | |
| China | 12 | |
| Japan | 12 | |
| Portugal | 12 | |
| Singapore | 7 | |
| | 509 | |
For additional discussion of our international business, see Part II Item 7, "Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations."
Corporate administrative support
Corporate administrative support consists primarily of labor, benefits and long-term incentive compensation costs, as well as professional fees for departments which provide support to more than one of our different operating lines of business. These expenses are included in our consolidated general and administrative expenses.
Government regulation
We operate in a complex regulatory environment with an extensive and evolving set of federal, state, local and international governmental laws, regulations and other requirements. These laws, regulations and other requirements are promulgated and overseen by a number of different legislative, regulatory, administrative and quasi-regulatory bodies, each of which may have varying interpretations, judgments or related guidance. As such, we utilize considerable resources on an ongoing basis to monitor, assess and respond to applicable legislative, regulatory and administrative requirements, but there is no guarantee that we will be successful in our efforts to adhere to all of these requirements.
If any of our personnel, representatives, third party vendors or operations are alleged to have violated these or other laws, regulations or requirements, we could experience material harm to our reputation and stock price, and it could impact our relationships and/or contracts related to our business, among other things. If any of our personnel, representatives, third party vendors or operations are found to violate these or other laws, regulations or requirements, we could suffer additional severe consequences that could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows. Additional discussion on certain of these laws, regulations and other requirements is set forth below in this section.
Our business is and we expect that our industry will continue to be subject to extensive and complex federal, state, local and international laws, regulations and other requirements, the scope and effect of which are difficult to predict. We are also currently subject to various legal proceedings, such as lawsuits, investigations, audits and inquiries by various government and regulatory agencies, as described in Note 15 to the consolidated financial statements, and our operations and activities could be reviewed or challenged by regulatory authorities at any time in the future. In addition, each of the laws, regulations and other requirements, including interpretations thereof, that govern our business may continue to change over time, and there is no assurance that we will be able to accurately predict the nature, timing or extent of such changes or the impact of such changes on the markets in which we conduct business or on the other participants that operate in those markets. For additional detail on risks related to each of the foregoing, as well as the consequences of any violation of applicable laws, regulations or other requirements, see the discussion in Part I Item 1A. "Risk Factors" under the headings, "Our business is subject to a complex set of governmental laws, regulations and other requirements...;" and "We are, and may in the future be, a party to various lawsuits, demands, claims, qui tam suits, governmental investigations and audits and other legal matters..."
Licensure and Certification
Our dialysis centers are certified by CMS, as required for the receipt of Medicare payments. Certain of our payor contracts also condition payment on Medicare certification. In some states, our outpatient dialysis centers also are required to
secure additional state licenses and permits. Governmental authorities, primarily state departments of health, periodically inspect our centers to determine if we satisfy applicable federal and state standards and requirements, including the conditions for coverage in the Medicare ESRD program.
We have experienced some delays in obtaining Medicare certifications from CMS, though changes by CMS in the prioritizing of dialysis providers as well as legislation allowing private entities to perform initial dialysis facility surveys for certification has helped to decrease or limit certain delays.
In addition, pursuant to the Provider Enrollment Rule, CMS has authority to revoke provider enrollment and to impose a Medicare reapplication bar where a prospective provider's Medicare enrollment application is denied because the provider submitted incomplete, false, or misleading information for providers who are terminated from the Medicare program. CMS may also deny enrollment to providers who have affiliations with other providers that CMS has determined pose undue risk of fraud, waste or abuse. If we fail to comply with these and other applicable requirements on our licensure and certification programs, particularly in light of increased penalties that include a 10-year bar to Medicare re-enrollment, under certain circumstances it could have a material adverse impact on our business, results of operations, financial condition, cash flows and reputation.
In addition to certification by CMS, our dialysis centers are also certified by each state Medicaid program, are licensed in those states that require licensing for dialysis clinics, and are required to obtain licenses, permits and certificates, including for such areas as biomedical waste. Failure to obtain the correct certifications, permits and certificates as well as a failure to adhere to the requirements thereunder, may result in penalties, fines, and the loss of the right to operate, any of which could have a material adverse impact on our business, results of operations, financial condition, cash flows and reputation.
Federal Anti-Kickback Statute
The federal Anti-Kickback Statute prohibits, among other things, knowingly and willfully offering, paying, soliciting or receiving remuneration, directly or indirectly, in cash or kind, to induce or reward either the referral of an individual for, or the purchase, or order or recommendation of, any good or service, for which payment may be made under federal and state healthcare programs such as Medicare and Medicaid.
Federal criminal penalties for the violation of the federal Anti-Kickback Statute include imprisonment, fines and exclusion of the provider from future participation in the federal healthcare programs, including Medicare and Medicaid. Violations of the federal Anti-Kickback Statute are punishable by imprisonment for up to ten years and statutory fines of up to $100,000 or both. Larger criminal fines can be imposed under the provisions of the U.S. Sentencing Guidelines and the Alternate Fines Statute. Individuals and entities convicted of violating the federal Anti-Kickback Statute are subject to mandatory exclusion from participation in Medicare, Medicaid and other federal healthcare programs for a minimum of five years. Civil penalties for violation of this law include statutory amounts of up to $100,000 (adjusted for inflation) in monetary penalties per violation, assessments of up to three times the total payments between the parties to the arrangement, and permissive exclusion from participation in the federal healthcare programs or suspension from future participation in Medicare and Medicaid. The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act and the Health Care Reconciliation Act of 2010, as amended (collectively, the ACA), amended the federal Anti-Kickback Statute to clarify that the defendant may not need to have actual knowledge of the federal Anti-Kickback Statute or have the specific intent to violate it and to provide that any claims for items or services resulting from a violation of the federal Anti-Kickback Statute are considered false or fraudulent for purposes of the False Claims Act (FCA) and can result in treble damages and other penalties under the FCA.
The federal Anti-Kickback Statute includes statutory exceptions and regulatory safe harbors that protect certain arrangements. Business transactions and arrangements that are structured fully within an applicable safe harbor do not violate the federal Anti-Kickback Statute. When an arrangement is not structured fully within a safe harbor, the arrangement must be evaluated on a case-by-case basis in light of the parties’ intent and the arrangement’s potential for abuse, and may be subject to greater scrutiny by enforcement agencies.
In the ordinary course of our business operations, DaVita and its ancillary businesses and subsidiaries enter into numerous arrangements with physicians and other potential referral sources, that potentially implicate the Anti-Kickback Statute. Examples of such arrangements include, among other things, medical director agreements, joint ventures, leases and subleases with entities in which physicians, hospitals or medical groups hold ownership interests, consulting agreements, hospital services agreements, discharge planning services agreements, acute dialysis services agreements, value-based care arrangements, employment and coverage agreements, and incentive performance arrangements. In addition, some referring physicians may own DaVita Inc. common stock. Furthermore, our dialysis centers and subsidiaries sometimes enter into certain rebate, pricing, or other contracts to acquire certain discounted items and services that may be reimbursed by a federal healthcare program.
Agreements and other arrangements can still be appropriate under the federal Anti-Kickback Statute even if they fail to meet all parameters of a relevant safe harbor provision; and we endeavor to structure our arrangements within applicable safe harbors, although some arrangements are not structured fully within a safe harbor.
If any of our current or previous business transactions or arrangements, including but not limited to those described above, were found to violate the federal Anti-Kickback Statute, we, among other things, could face criminal, civil or administrative sanctions, including possible exclusion from participation in Medicare, Medicaid and other state and federal healthcare programs.
Stark Law
The Stark Law is a strict liability civil law that prohibits a physician who has a financial relationship, or who has an immediate family member who has a financial relationship, with entities providing Designated Health Services (DHS), from referring Medicare and Medicaid patients to such entities for the furnishing of DHS, unless an exception applies. The types of financial arrangements between a physician and a DHS entity that trigger the self-referral prohibitions of the Stark Law are broad and include direct and indirect ownership and investment interests and compensation arrangements. The Stark Law also prohibits the DHS entity receiving a prohibited referral from presenting, or causing to be presented, a claim or billing for the services arising out of the prohibited referral. If the Stark Law is implicated, the financial relationship must fully satisfy a Stark Law exception. If an exception to the Stark Law is not satisfied, then the parties to the arrangement could be subject to sanctions. Sanctions for violation of the Stark Law include denial of payment for claims for services provided in violation of the prohibition, refunds of amounts collected in violation of the prohibition, a civil penalty of up to $15,000 (adjusted for inflation) for each service arising out of the prohibited referral, a statutory civil penalty of up to $100,000 (adjusted for inflation) against parties that enter into a scheme to circumvent the Stark Law prohibition, civil assessment of up to three times the amount claimed, and potential exclusion from the federal healthcare programs, including Medicare and Medicaid. Furthermore, Stark Law violations and failure to return overpayments timely can form the basis for FCA liability as discussed below.
The definition of DHS under the Stark Law excludes services paid under a composite rate, even if some of the components bundled in the composite rate are DHS. Although the ESRD bundled payment system is no longer titled a composite rate, we believe that the former composite rate payment system and the current bundled system are both composite systems excluded from the Stark Law. Since most services furnished to Medicare beneficiaries provided in our dialysis centers are reimbursed through a bundled rate, we believe that the services performed in our facilities generally are not DHS. Certain separately billable drugs (drugs furnished to an ESRD patient that are not for the treatment of ESRD that CMS allows our centers to bill for using the so-called AY modifier) may be considered DHS. However, we have implemented certain billing controls designed to limit DHS being billed out of our dialysis clinics. Likewise, the definition of inpatient hospital services, for purposes of the Stark Law, also excludes inpatient dialysis performed in hospitals that are not certified to provide ESRD services. Consequently, we believe that our arrangements with such hospitals for the provision of dialysis services to hospital inpatients should not trigger the Stark Law referral prohibition.
In addition, although prescription drugs are DHS, there is an exception in the Stark Law for calcimimetics, ESAs and other specifically enumerated dialysis drugs when furnished in or by an ESRD facility such that the arrangement for the furnishing of the drugs does not violate the Stark Law.
In the ordinary course of business operations, DaVita and its ancillary businesses and subsidiaries have many different types of financial arrangements with referring physicians that potentially implicate the Stark Law, including, but not limited to, medical director agreements, joint ventures, leases and subleases with entities in which physicians, hospitals or medical groups hold ownership interests, consulting agreements, hospital services agreements, discharge planning services agreements, acute dialysis services agreements, value-based care arrangements, employment agreements and incentive performance arrangements. In addition, some referring physicians may own our common stock in reliance on the Stark Law exception for investment interests in large publicly traded companies.
If our interpretation of the applicability of the Stark Law to our operations is incorrect, the controls we have implemented fail, an arrangement is entered into outside of our processes, or we were to fail to satisfy an applicable exception to the Stark Law, we could be found to be in violation of the Stark Law and required to change our practices, face civil penalties, pay substantial fines, return certain payments received from Medicare and beneficiaries or otherwise experience a material adverse effect.
In addition, it might be necessary to restructure existing compensation agreements with our medical directors and to repurchase or to request the sale of ownership interests in subsidiaries and partnerships held by referring physicians or, alternatively, to refuse to accept referrals for DHS from these physicians, or take other actions to modify our operations. Any finding by CMS or other regulatory or enforcement authorities that we have violated the Stark Law or related penalties and
restructuring or other required actions could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition, cash flows, stock price and reputation.
False Claims Act
The federal FCA is a means of policing false claims, false bills or false requests for payment in the healthcare delivery system. In part, the FCA authorizes the imposition of up to three times the government’s damages and civil penalties, plus up to approximately $28,000 per claim, on any person who, among other acts:
•Knowingly presents or causes to be presented to the federal government, a false or fraudulent claim for payment or approval;
•Knowingly makes, uses or causes to be made or used, a false record or statement material to a false or fraudulent claim;
•Knowingly makes, uses, or causes to be made or used, a false record or statement material to an obligation to pay the government, or knowingly conceals or knowingly and improperly, avoids or decreases an obligation to pay or transmit money or property to the federal government; or
•Conspires to commit the above acts.
In addition, the FCA imposes severe penalties for the knowing and improper retention of overpayments collected from government payors. Under these provisions, a provider is required to refund overpayments within 60 days of obtaining knowledge of the overpayment. A provider is deemed to have knowledge of the overpayment if it has actual knowledge, or if it acts with reckless disregard or deliberate ignorance of the overpayment. An overpayment impermissibly retained could subject us to liability under the FCA, exclusion from government healthcare programs, and penalties under the federal Civil Monetary Penalty statute. As a result of these provisions, our procedures for identifying and processing overpayments may be subject to greater scrutiny.
The federal government has used the FCA to prosecute a wide variety of alleged false claims and fraud allegedly perpetrated against Medicare and state healthcare programs, including coding errors, billing for services not rendered, the submission of false cost reports, billing for services at a higher payment rate than appropriate, billing under a comprehensive code as well as under one or more component codes included in the comprehensive code and billing for care that is not considered medically necessary. The ACA provides that claims tainted by a violation of the federal Anti-Kickback Statute are false for purposes of the FCA. Some courts have held that filing claims or failing to refund amounts collected in violation of the Stark Law can form the basis for liability under the FCA. In addition to the provisions of the FCA, which provide for civil enforcement, the federal government can use several criminal statutes to prosecute persons who are alleged to have submitted false or fraudulent claims for payment to the federal government.
Fraud and abuse under state law
State fraud and abuse laws related to anti-kickback, physician self-referral, beneficiary inducement and false claims often mirror those requirements of the applicable federal laws, or, in some instances contain additional or different requirements. If we were found to violate these state laws and regulations, we, among other things, could face criminal, civil or administrative sanctions, including loss of licensure or possible exclusion from Medicaid and other state and federal healthcare programs.
In addition to these fraud waste and abuse laws, some states in which we operate dialysis centers have laws prohibiting physicians from holding financial interests in various types of medical facilities to which they refer patients. Some of these laws could potentially be interpreted broadly as prohibiting physicians who hold shares of our publicly traded stock or are physician owners from referring patients to our dialysis centers if the centers use our laboratory subsidiary to perform laboratory services for their patients or do not otherwise satisfy an exception to the law. States also have laws similar to or stricter than the federal Anti-Kickback Statute that may affect our ability to receive referrals from physicians with whom we have financial relationships, such as our medical directors and value-based care partners, or with other referral sources, including hospitals. Some state anti-kickback laws also include civil and criminal penalties. Some of these laws include exemptions that may be applicable to our medical directors, value-based care partners and other physician and referral source relationships or for financial interests limited to shares of publicly traded stock. Some, however, may include no explicit exemption for certain types of agreements and/or relationships entered into with referral sources such as physicians and hospitals. If these laws are interpreted to apply to referring sources with whom we contract for items or services, including medical directors, value-based care partners, and hospitals, to referring physicians or hospitals with whom we hold joint ownership interests, or to referring entities or individuals who hold interests in DaVita Inc. limited solely to our publicly traded stock, and for which no applicable exception exists, we may be required to terminate or restructure our relationships with or refuse referrals from these referring
entities or individuals and could be subject to criminal, civil and administrative sanctions, refund requirements and exclusions from participation in government healthcare programs, including Medicare and Medicaid.
Corporate Practice of Medicine and Fee-Splitting
There are states in which we operate that have laws that prohibit business entities not owned by health care providers, such as our Company and our subsidiaries, from practicing medicine, employing physicians and other licensed health care providers providing certain clinical services or exercising control over medical or clinical decisions by physicians and potentially other types of licensed health care providers (known collectively as the corporate practice of medicine). These states may also prohibit entities from engaging in certain financial arrangements, such as fee-splitting, with physicians and potentially other types of licensed health care providers. Violations of the corporate practice of medicine, fee-splitting and related laws vary by state and may result in physicians and potentially other types of licensed health care providers being subject to disciplinary action, as well as to forfeiture of revenues from payors for services rendered. Violations may also bring both civil and, in more extreme cases, criminal liability for engaging in medical practice without a license and violating the corporate practice of medicine, fee-splitting and related laws. Some of the relevant laws, regulations, and agency interpretations in states with corporate practice of medicine restrictions have been subject to limited judicial and regulatory interpretation.
Civil Monetary Penalties Statute
The Civil Monetary Penalties Statute, 42 U.S.C. § 1320a-7a, authorizes the imposition of civil money penalties, assessments, and exclusion against an individual or entity based on a variety of prohibited conduct, including, but not limited to:
•Presenting, or causing to be presented, claims for payment to Medicare, Medicaid, or other third-party payors that the individual or entity knows or should know are for an item or service that was not provided as claimed or is false or fraudulent;
•Offering remuneration to a federal healthcare program beneficiary that the individual or entity knows or should know is likely to influence the beneficiary to order or receive healthcare items or services from a particular provider;
•Arranging contracts with an entity or individual excluded from participation in the federal healthcare programs;
•Violating the federal Anti-Kickback Statute;
•Making, using, or causing to be made or used, a false record or statement material to a false or fraudulent claim for payment for items and services furnished under a federal healthcare program;
•Making, using, or causing to be made any false statement, omission, or misrepresentation of a material fact in any application, bid, or contract to participate or enroll as a provider of services or a supplier under a federal healthcare program; and
•Failing to report and return an overpayment owed to the federal government.
Substantial civil monetary penalties may be imposed under the federal Civil Monetary Penalty Statute and vary, depending on the underlying violation. In addition, an assessment of not more than three times the total amount claimed for each item or service may also apply, and a violator may be subject to exclusion from participation in federal and state healthcare programs.
Foreign Corrupt Practices Act
We are subject to the provisions of the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA) in the United States and similar laws in other countries, which generally prohibit companies and those acting on their behalf from making improper payments to foreign government officials and others for the purpose of obtaining or retaining business. A violation of the FCPA or other similar laws by us and/or our agents or representatives could result in, among other things, the imposition of fines and penalties, changes to our business practices, the termination of or other adverse impacts under our debt arrangements and contracts or debarment from bidding on contracts, and/or harm to our reputation.
Privacy and Security
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 and its implementing privacy and security regulations, as amended by the federal Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act (HITECH Act) (collectively referred to as HIPAA), require us to provide certain protections to patients and their health information. The HIPAA privacy and security regulations extensively regulate the use and disclosure of PHI and require covered entities, which include
healthcare providers, to implement and maintain administrative, physical and technical safeguards to protect the security of such information. Additional security requirements apply to electronic PHI. These regulations also provide patients with substantive rights with respect to their health information.
The HIPAA privacy and security regulations also require us to enter into written agreements with certain contractors, known as business associates, to whom we disclose PHI. Covered entities may be subject to penalties for, among other activities, failing to enter into a business associate agreement where required by law or as a result of a business associate violating HIPAA if the business associate is found to be an agent of the covered entity and acting within the scope of the agency. Business associates are also directly subject to liability under the HIPAA privacy and security regulations. In instances where we act as a business associate to a covered entity, there is the potential for additional liability beyond our status as a covered entity.
Covered entities must report breaches of unsecured PHI to affected individuals without unreasonable delay but not to exceed 60 days of discovery of the breach by a covered entity or its agents. Notification must also be made to the HHS and, for breaches of unsecured PHI involving more than 500 residents of a state or jurisdiction, to the media. All non-permitted uses or disclosures of unsecured PHI are presumed to be breaches unless the covered entity or business associate establishes that there is a low probability the information has been compromised. Various state laws and regulations may also require us to notify affected individuals, and U.S. state attorneys general, or other regulators or law enforcement, in the event of a data breach involving individually identifiable information without regard to whether there is a low probability of the information being compromised.
Penalties for impermissible use or disclosure of PHI were increased by the HITECH Act by imposing tiered penalties of more than $50,000 per violation and up to $1.5 million per year for identical violations. In addition, HIPAA provides for criminal penalties of up to $250,000 and ten years in prison, with the severest penalties for obtaining and disclosing PHI with the intent to sell, transfer or use such information for commercial advantage, personal gain or malicious harm. Further, state attorneys general may bring civil actions seeking either injunction or damages in response to violations of the HIPAA privacy and security regulations that threaten the privacy of state residents.
In addition to the protection of PHI, healthcare companies must meet privacy and security requirements applicable to other categories of personal information. Companies may process consumer information in conjunction with website and corporate operations. They may also handle employee information, including Social Security Numbers, payroll information, and other categories of sensitive information, to further their employment practices. In processing this additional information, companies must comply with the applicable privacy and security requirements of comprehensive privacy and data protection laws, consumer protection laws, labor and employment laws, and its publicly-available notices. In addition, federal and state laws governing the use of artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies are evolving. As the regulation of these technologies matures, we may face additional compliance costs and legal risk to our operations.
Outside of the United States, the requirements of applicable privacy and data protection laws and regulations, and any related implementation guidance from and enforcement postures of local country regulators, may present varying implementation and compliance considerations for our local country operations. These include the European Union General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), the United Kingdom General Data Protection Regulation (UK GDPR), and other non-GDPR laws, such as the Brazilian Lei Geral de Proteção de Dados (LGPD), the Saudi Arabia Personal Data Protection Law and the Data Security Law of the People's Republic of China (DSL), among others. This variation presents compliance costs and legal risks to our international operations. When providing services or using personal data, we must ensure compliance with the applicable legislation and local legal requirements.
The GDPR imposes a comprehensive data protection regime with the potential for regulatory fines as well as data breach litigation by impacted data subjects. Under the GDPR, regulatory penalties may be passed by data protection authorities for up to the greater of 4% of worldwide turnover or €20 million. The UK GDPR carries similar compliance and operational costs, and carries similar fines of up to the greater of £17.5 million or 4% of global turnover. In non-GDPR countries, the cost of non-compliance varies but can also be just as significant as those under the GDPR. For example, the maximum fine for non-compliance with the LGPD is 50 million Brazilian real (approximately $8 million) or 2% of the company’s annual revenue, while the maximum fine for non-compliance with the DSL is RMB 50 million (approximately $7 million) or 5% of the previous year's turnover. In addition to fines, data protection authorities in non-GDPR countries may also impose criminal sanctions as well as other penalties, such as orders to cease processing personal data, orders to delete personal data, or warnings and reprimands.
Privacy and data protection laws are also evolving nationally, providing for enhanced state privacy rights that are broader than the current federal privacy rights, and may add additional compliance costs and legal risks to our U.S. operations. For example, the California Consumer Privacy Act of 2018 (CCPA), which was significantly amended by the California Privacy
Rights Act (CPRA), the Colorado Privacy Act, as well as multiple other states, afford consumers expanded privacy protections. These provide for civil penalties for violations, and the CCPA and CPRA provide for a private right of action for data breaches. Additionally, several privacy bills have been proposed both at the federal and state level that may result in additional legal requirements that impact our business. On a related front, states continue to enact laws focusing on consumer health data that are similar to other comprehensive data laws, but impose more stringent consent requirements (e.g., opt-in consent for certain types of processing) for consumer health data. These laws carry statutory damages and in some cases allow for a private right of action. These state data protection laws (both the comprehensive laws and the health-focused laws) will likely result in broader increased regulatory scrutiny in applicable states of businesses' privacy and security practices, could lead to a further rise in data protection litigation, and will require additional compliance investment and potential business process changes.
In addition to the breach reporting requirements under HIPAA, companies are subject to state breach notification laws. Each state enforces a law requiring companies to provide notice of a breach of certain categories of sensitive personal information, e.g. Social Security Number, financial account information, or username and password. A company impacted by a breach must notify affected individuals, attorney’s general or other agencies within a certain time frame. If a company does not provide timely notice with the required content, it may be subject to civil penalties brought by attorneys general or affected individuals.
Companies must also safeguard personal information in accordance with federal and state data security laws and requirements. These requirements are akin to the HIPAA requirements to safeguard PHI, described above. The FTC, for example, requires companies to implement reasonable data security measures relative to its operations and the volume and complexity of the information it processes. Also, various state data security laws require companies to safeguard data with technical security controls and underlying policies and processes. Due to the constant changes in the data security space, companies must continuously review and update data security practices to seek to mitigate any potential operational or legal liabilities stemming from data security risks. For additional details on the risks of compliance with applicable privacy and security laws, regulations and standards, see the discussion in Part I Item 1A. "Risk Factors" under the heading "Privacy and information security laws are complex..." For additional information about our assessment of our cybersecurity risks, see the discussion in Part I Item 1C. "Cybersecurity."
Integrated Kidney Care, Medicare and Medicaid program reforms and Other Healthcare Regulations
The regulatory framework of the healthcare marketplace continues to evolve as a result of executive, legislative, regulatory and administrative developments and judicial proceedings. These changes shape the landscape for our current dialysis business as well as for emerging comprehensive and integrated kidney care programs. The following discussion describes certain of these changes in further detail.
CMMI Payment Models: As described above, CMS has launched payment models through CMMI to evaluate the effects of creating payment incentives for the greater use of home-based dialysis and kidney transplants for those already on dialysis, improve quality of care for kidney patients and reduce expenditures. The first of these, the ETC mandatory payment model, launched in approximately 30% of dialysis clinics across the country on January 1, 2021. CMS subsequently issued several clarifying rules and continues to evaluate the model. CMS has also implemented two voluntary kidney care payment models, Kidney Care First (KCF) and Comprehensive Kidney Care Contracting (CKCC), with the stated goal of helping healthcare providers reduce the cost and improve the quality of care for patients with late-stage chronic kidney disease and ESRD. CMS has stated these payment models are aimed to prevent or delay the need for dialysis and encourage kidney transplantation. As described above, we have invested substantial resources, and expect to continue to invest substantial resources in these models as part of our overall plan to grow our integrated kidney care business and value-based care initiatives.
For additional details on the risks related to integrated kidney care and Medicare and Medicaid program reforms, see the discussion in Part I Item 1A. "Risk Factors" under the headings "If we are not able to successfully implement our strategy with respect to our integrated kidney care and value-based care initiatives...;" and "If we are unable to compete successfully..."
Healthcare Reform, ACA and Related Regulatory and Legal Developments: The ACA regulatory framework of the healthcare marketplace continues to evolve as a result of executive, legislative, regulatory and administrative developments and judicial proceedings. For example, the expanded access to healthcare developed under the ACA has been both positively and negatively impacted over time by subsequent legal, regulatory and judicial action. In 2021 and 2022, respectively, the American Rescue Plan and Inflation Reduction Act of 2022 included several provisions designed to expand health coverage, including the expansion and extension of premium tax credits that assist consumers who purchase health insurance on marketplaces developed under the ACA and temporarily offering incentives to expand Medicaid coverage for states that have not yet done so. Our revenue and operating income levels are highly sensitive to the percentage of our patients with higher-paying commercial health insurance and any legislative, regulatory or other changes that decrease the accessibility and availability, including the
duration, of commercial insurance, such as the potential expiration at the end of 2025 of the premium tax credits described above, is likely to have a material adverse impact on our business.
Changes to the political environment may increase the likelihood of legislative or regulatory changes that would impact us, such as changes to the healthcare regulatory landscape. Examples of such potential changes also could include, among other things, legislative, regulatory, or executive development, including those that may impact the availability of certain premium tax credits under the ACA exchanges or may impact the eligibility age for Medicare beneficiaries. Some of these or other changes could in turn impact the percentage of our patients with higher-paying commercial health insurance, impact the scope or terms of coverage under commercial health plans and/or increase our expenses, among other things. The timing of legislative, regulatory or executive action related to these potential initiatives, if any, remains uncertain, particularly in light of the current economic and political environment, and as such, considerable uncertainty exists surrounding the continued development of the ACA and related regulations, programs and models, as well as similar healthcare reform measures and/or other potential changes at the federal and/or state level to laws, regulations and other requirements that govern our business.
21st Century Cures Act: As described above under the heading "—Medicare Advantage revenue," the Cures Act broadened patient access to certain enhanced benefits offered by MA plans. This change in benefit eligibility has increased the percentage of our patients on MA plans as compared to Medicare Part B plans. In addition, the Cures Act also includes provisions related to data interoperability, information blocking and patient access. For details on the risks associated with these provisions of the Cures Act, see the risk factors in Part I Item 1A. "Risk Factors" under the headings, "Our business is subject to a complex set of governmental laws, regulations and other requirements...;" "If the number or percentage of patients with higher-paying commercial insurance declines...;" and "Failing to effectively maintain, operate or upgrade our information systems or those of third-party service providers upon which we rely..."
Health Plan Price Transparency Rules: In addition, recent price transparency regulations require most group health plans, and health insurance issuers in the group and individual markets, to make certain pricing and patient responsibility information publicly available. On July 1, 2022, most group health plans and issuers of group or individual health insurance were required to begin publishing machine-readable files that include negotiated rates for all covered items and services with all providers and out-of-network allowed amounts. For plan years that begin on or after January 1, 2023, most group health plans, and health insurance issuers in the group and individual markets, must provide enrollees with out-of-pocket cost and underlying provider negotiated rate information in a consumer-friendly format for an initial list of 500 designated services (which do not include dialysis). A plan or issuer may choose to include more than these 500 services, and for plan years that begin on or after January 1, 2024, most group health plans, and health insurance issuers in the group and individual markets, must provide enrollees with this information for all covered items and services.
In addition to the aforementioned pricing transparency rules, the government has also implemented certain additional pricing transparency requirements that apply to certain types of providers, including DaVita. Under the No Surprises Act, which went into effect January 1, 2022, certain providers, including DaVita, are required to develop and disclose a "Good Faith Estimate" (GFE) that details the expected charges for furnishing certain items or services, although the government is currently only enforcing portions of this requirement with respect to uninsured or self-pay patients. The GFE is currently required to include specific information regarding the service provided and diagnostic codes, among other things, and is subject to formatting requirements, notice requirements, availability and dispute resolution procedures; in the future, GFEs will be required to include additional information, including co-provider service estimates. Similar to the aforementioned pricing transparency rules, the impact of the GFE requirements on DaVita remains uncertain at this time, in part due to ongoing rulemaking around the No Surprises Act as well as the delayed effective date of certain provisions of the GFE framework, uncertainty around operational timeframes, potential penalties and patient reaction, among other things. For additional details about the risks associated with these requirements, see the discussion in the risk factor in Part I Item 1A. "Risk Factors" under the heading, "If the number or percentage of patients with higher-paying commercial insurance declines..."
Other regulations
Our U.S. dialysis and related lab services operations are subject to various state hazardous waste and non-hazardous medical waste disposal laws at both the state and federal level. In addition, OSHA regulations require employers to provide workers who are occupationally subject to blood or other potentially infectious materials with prescribed protections. These regulatory requirements apply to all healthcare facilities, including dialysis centers, and require employers to make a determination as to which employees may be exposed to blood or other potentially infectious materials and to have in effect a written exposure control plan. In addition, employers are required to provide or employ hepatitis B vaccinations, personal protective equipment and other safety devices, infection control training, post-exposure evaluation and follow-up, waste disposal techniques and procedures and work practice controls. Employers are also required to comply with various record-keeping requirements.
In addition, certain states in which we do business have certificate of need programs regulating the establishment or expansion of healthcare facilities, including dialysis centers. Furthermore, given the evolving nature of our business, agencies, including but not limited to the Food and Drug Administration, FTC, and HHS's Office of Civil Rights, will continue to introduce and/or enforce existing laws and regulations that we may need to comply with. For additional information of the risks to our business associated with the impact of these and other laws and regulations, see the risk factors in Part I Item 1A. "Risk Factors" under the headings, "Our business is subject to a complex set of governmental laws, regulations, and other requirements..." and "Changes in federal and state legislation or regulations..."
State laws and initiatives
There have been several state-based policy initiatives to limit payments to dialysis providers or impose other burdensome operational requirements, which, if passed, could have a material adverse impact on our business, results of operation, financial condition and cash flows. For example, in October 2019, a California bill (AB 290) was signed into law that limits the amount of reimbursement paid to certain providers for services provided to patients with commercial insurance who receive charitable premium assistance (reimbursement cap). The implementation of AB 290 has been stayed pending resolution of legal challenges. The trial court has issued a decision relating to these challenges to AB 290, which is currently on appeal. In addition, California passed into law California Senate Bill No. 525 (SB 525), which raises minimum wage for many California healthcare workers and went into effect in October 2024.
For additional discussion on the risks associated with the evolving payment and regulatory landscape for kidney care, see the discussion in Part I Item 1A. "Risk Factors," including the discussion under the headings, "Our business is subject to a complex set of governmental laws, regulations and other requirements..." and "Changes in federal and state legislation or regulations..."
Corporate compliance program
Management has designed and implemented a corporate compliance program as part of our commitment to comply fully with applicable criminal, civil and administrative laws and regulations and to maintain the high standards of conduct we expect from all of our teammates, physician partners, and certain other third parties. We continuously review this program and work to enhance and evolve it as appropriate. The primary purposes of the program include:
•Assessing and identifying health care regulatory risks for existing and new businesses;
•Training and educating our teammates, physician partners, and certain other third parties to promote awareness of legal and regulatory requirements, a culture of compliance, and the necessity of complying with all applicable laws, regulations and requirements;
•Developing and implementing compliance policies and procedures and creating controls to support compliance with applicable laws, regulations and requirements and our policies and procedures;
•Auditing and monitoring the activities of our operating units and business support functions to identify and mitigate risks and potential instances of noncompliance in a timely manner; and
•Ensuring that we promptly take steps to resolve any instances of noncompliance and address areas of weakness or potential noncompliance.
We have a code of conduct that each of our teammates, members of our Board of Directors (Board), physician partners, and certain other third parties must follow, and we have an anonymous compliance hotline for teammates, physician partners, patients and other third parties to report potential instances of noncompliance that is managed by a third party. Our Chief Compliance Officer administers the compliance program. The Chief Compliance Officer reports directly to our Chief Executive Officer (CEO) and the Chair of the Compliance and Quality Committee of our Board.
We could be subject to penalties or other consequences if the OIG or a similar regulatory authority determines that we failed to comply with applicable laws, regulations or requirements, including, among other things substantial monetary penalties and exclusion from participation in federal healthcare programs that could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition, cash flows, reputation and stock price.
Competition
The U.S. dialysis industry remains highly competitive, with many new and emerging entrants entering the kidney healthcare business space. In our U.S. dialysis business, we continue to face intense competition from large and medium-sized providers, among others, which compete directly with us for limited acquisition targets, for individual patients who may choose
to dialyze with us and to engage physicians qualified to provide required medical director services. In addition to these large and medium sized dialysis providers with substantial financial resources and other established participants in the dialysis space, we also compete with new dialysis providers, individual nephrologists and former medical directors or physicians that have opened their own dialysis units or facilities. Moreover, as we continue our international dialysis expansion into various international markets, we face competition from large and medium-sized providers, among others, for acquisition targets as well as physician relationships. We also experience competitive pressures from other dialysis and healthcare providers in recruiting and retaining qualified skilled clinical personnel as well as in connection with negotiating contracts with commercial healthcare payors and inpatient dialysis service agreements with hospitals. Acquisitions, developing new outpatient dialysis centers, patient retention and referrals, and referral source relationships, in which such sources understand us to be the clinical and operational leaders in the market are significant components of our growth strategy and our business could be adversely affected if we are not able to continue to make dialysis acquisitions on reasonable and acceptable terms, continue to develop new outpatient dialysis centers, maintain our referral sources' trust in our capabilities or if we experience significant patient attrition or lack of new patient growth relative to our competitors.
Our largest competitor, Fresenius Medical Care (FMC), manufactures a full line of dialysis supplies and equipment in addition to owning and operating outpatient dialysis centers worldwide. This may, among other things, give FMC cost advantages over us because of its ability to manufacture its own products. Additionally, FMC is one of our largest suppliers of dialysis products and equipment. Our agreement with FMC typically requires us to purchase a certain amount of dialysis equipment, parts and supplies from FMC based upon a number of factors, including the operating requirements of our centers, the number of centers we acquire, and growth of our existing centers.
As we continue to expand our efforts to grow across the full continuum of kidney care from CKD care to dialysis treatment to transplant facilitation, we also face competition outside dialysis. In the integrated care market, we face competition from other dialysis providers who, similar to DaVita, may be seeking to expand arrangements with payors, physicians and hospitals. We also face competition from non-traditional providers and others in this space, who have made a number of announcements, initiatives and capital raises in areas along the full continuum of kidney care from CKD to dialysis to transplant. These business entities, certain of which command considerable resources and capital, increasingly compete with us in the integrated kidney care market, and they may also focus their efforts on the development of more traditional dialysis competition or the commencement of other new business activities or the development of innovative technologies, drugs or other treatments that could impact the rate of growth of the kidney care patient population or otherwise be transformative to the industry. For additional discussion on these developments and associated risks, see the risk factors in Part I Item 1A. "Risk Factors" under the headings, "If we are unable to compete successfully..." and "If we are not able to successfully implement our strategy with respect to our integrated kidney care and value-based care initiatives..."
Insurance
We are primarily self-insured with respect to professional and general liability, workers' compensation and automobile risks, and a portion of our employment liability practice risks, through wholly-owned captive insurance companies. We are also predominantly self-insured with respect to employee medical and other health benefits. We also maintain insurance, excess coverage, or reinsurance for property and general liability, professional liability, directors’ and officers’ liability, workers' compensation, cybersecurity and other coverage in amounts and on terms deemed appropriate by management, based on our actual claims experience and expectations for future claims. Future claims could, however, exceed our applicable insurance coverage. Physicians practicing at our dialysis centers are required to maintain their own malpractice insurance, and our medical directors are required to maintain coverage for their individual private medical practices. Our liability policies cover our medical directors for the performance of their duties as medical directors at our outpatient dialysis centers.
Human capital management
Overview
At DaVita, we are guided by our Mission—to be the provider, partner and employer of choice—and our Core Values—Service Excellence, Integrity, Team, Continuous Improvement, Accountability, Fulfillment and Fun—which are reinforced at all levels of the organization. Our teammates share a common passion for equitably improving patients' lives and are the cornerstone for the health of DaVita.
We strive to be a community first and a company second, and affectionately call ourselves a Village. To be a healthy Village, we need to attract, develop and retain top talent that reflect the communities we serve. To do so, we have implemented strategies that support our mission to be the employer of choice, such as:
•Designing programs and processes to cultivate a talent pipeline that can allow us to hire ahead of needs;
•Providing development and professional growth opportunities; and
•Offering a robust and competitive total rewards program.
We believe that this intentional investment of time and resources fosters a special community of teammates that, in turn, leads to better care for our patients and the communities we serve.
As of December 31, 2024, we employed approximately 76,000 teammates, including our international teammates, with approximately 75% of our teammates located within the U.S.
Oversight & Management
Our Board provides oversight on human capital matters, receiving regular updates from our Chief People Officer about People Services’ activities, strategies and initiatives, and through the Board’s annual work with our CEO on management development and succession planning. Among other things, our Board and/or its committees also receive reports related to pay equity, risks and trends related to labor and human capital management issues and other issues generally pertaining to our teammates. The Board, in conjunction with its committees, also oversees the Company's activities, policies and programs related to corporate environmental and social responsibility, including considering the impact of such activities, policies and programs on the Company, teammates, patients and communities, among others.
These reports and recommendations to the Board and its committees are part of our broader People Services leadership and oversight framework, which includes guidance from various stakeholders across the business and benefits from the broad participation of senior leadership.
Connection & Belonging
Our investment in our teammates is anchored by our commitment to building a team of high performing teammates that reflect the communities we serve. We take a collaborative, leader-led approach, with everyone from our front-line patient care technicians and nurses to our divisional vice presidents, our CEO, and our Board playing a role in implementing our strategy. It truly does take a Village to bring our vision to life.
To help achieve this vision, we empower all leaders and teammates to cultivate connection and belonging in their centers and on their teams. We offer a suite of training to ensure our leaders are well-versed in how to cultivate belonging on their teams, reduce bias in hiring and talent reviews, and more. Leaders may also go deeper into more complex topics to understand how to create trust and safety, respect and value others and provide fair and consistent support. Finally, the fundamentals of creating a culture of belonging are integrated into new teammate onboarding to ensure all teammates understand their role in bringing our vision to life.
Over the past several years, our efforts to build culture have focused primarily on ensuring that we are creating a welcoming, open environment where all teammates, patients, physicians and care partners belong. Based on our most recent internal engagement surveys, 84% of our U.S. teammates indicated that they feel a sense of belonging within the DaVita community. We also celebrate a Week of Belonging each year, engaging teammates globally with activities and education designed to further create a sense of belonging.
As of December 31, 2024, DaVita in the U.S. was composed of 78% women and 58% people of color. As of December 31, 2024, in the U.S. 73% of our managers and 62% of our directors are women and that leaders with profit and loss responsibility are 52% women and 27% people of color. Our Board is composed of 40% women and 20% people of color.
Talent Pipeline and Career Development
Helping teammates and leaders grow and increase their earning potential are important tenets of our Employer of Choice strategy. We have a robust set of career development offerings to support teammates in reaching their professional ambitions. We have invested in an end-to-end career development pipeline that includes programs and initiatives that provide financial, educational and social support to our clinical and operations personnel to help achieve their higher education and leadership goals.
Our DaVita Ladders program – which currently includes Clinical Ladders for our clinical teammates – is designed to unlock clarity, competitive pay and transparent career journeys to systematically create more effective teammates and leaders. Through Clinical Ladders, the Village offers clinical teammates and leaders:
•Clarity around role expectations;
•A shared language to describe and understand career progression across the business units and regions;
•More structured talent mobility efforts to empower teammates to explore alternative career pathways based on interest, competency, and skill;
•A tool to support all aspects of the talent lifecycle through selection practices, professional development review (PDR) discussions, and succession planning, among other things;
•Standardization in how we execute performance and talent conversations that are aligned to factors for role success; and
•Market informed pay structure, pay design and guidance to consistently execute our pay for performance philosophy.
Our goal is to make resources available to teammates at each step of a possible career path to enable teammates to increase their earnings potential. For example, our Bridge to Your Dreams program supports high performing teammates pursuing an associate's degree in nursing with financial assistance, resources and role placement support to become a DaVita nurse. We currently have 2,400 teammates going through the program and on the way to becoming registered nurses. We also offer programs that help develop high potential nurses, clinical coordinators and clinic nurse managers into operational managers, along with programs that prepare and coach operational managers for regional operations director roles. These are just some of the many other career development opportunities we have in place for our teammates.
We are proud of the work we have done in this area. In 2024 approximately 58% of our managers in the U.S. were promoted from within. We will continue to lean into our teammates' growth and help them achieve their career objectives.
Total Rewards Program
Our total rewards philosophy and practices are designed to be competitive in the local market and reward strong team and individual performance. We believe merit-driven pay encourages teammates to do their best work, including in caring for our patients, and we strive to link pay to performance so we can continue to incentivize the provision of extraordinary care to our patients and grow our Village.
To attract, retain and grow our teammates, we have a holistic approach to total rewards that includes financial, physical and emotional support. Highlights include, among other things:
•Healthcare benefits including a menu of plan designs and health savings accounts.
•Free health programs in support of the most prevalent health conditions affecting our teammates, including hypertension, diabetes prevention/maintenance, musculoskeletal issues and weight loss/management.
•Financial wellness elements including 401(k) match, employee stock purchase plan (ESPP), a deferred compensation plan, financial planning support and access to free banking services. Additionally, DailyPay is a service that provides teammates with financial flexibility by allowing them to access earned but unpaid wages before payday.
•Family support programs to our teammates and their families that include family care programs for back-up child and elder care, family planning support for fertility, adoption and surrogacy, parental support for children’s educational and special needs and parental leave programs. We also offer a number of scholarships for teammates' children and grandchildren.
•Teammate Assistance Program that offers counseling sessions to all teammates and their household members, along with critical incident support for work related trauma, on both a personal and group level, with access to ten free sessions annually for each household member.
•Free access to Headspace, an application for digital meditation and mindfulness, and referrals/consultations on everyday issues such as dependent care, auto repair, pet care and home improvement.
•Vitality Points, a voluntary wellness incentive program that encourages teammates and their spouses/domestic partners to engage with their provider to manage their overall health. In addition, it allows participating teammates and spouses/domestic partners to earn credits toward their medical premium for getting a biometric screening with a primary care provider.
•Short & Long term disability for full time teammates and Life/AD&D coverage at both the basic and supplemental levels. Our voluntary Whole Life plan also includes long-term care coverage.
•Our DaVita Village Network, which provides financial support to eligible teammates experiencing a specific tragedy or hardship and helps cover additional costs that insurance does not fully cover.
Pay Equity
At DaVita, we are committed to equal pay for equal work; meaning, teammates in the same position, performing at the same level, and in similar geographies, are paid equitably relative to one another, regardless of their gender, race or ethnicity. We believe that equitable pay is a critical component of establishing a work environment where all teammates are valued and feel like they belong. Equitable pay is essential to our ability to attract, motivate and retain the top talent that reflect the communities we serve who are at the center of our current and future success.
Teammate Health and Safety
We are committed to promoting a safe and compliant environment for our teammates, particularly in our clinical settings. Our safety programs are designed to proactively identify, prevent and mitigate risk in these settings, prioritizing the health, safety and well-being of both our teammates and patients. We routinely assess facilities to closely monitor adherence to established security and safety standards. We have an electronic audit system that includes monthly OSHA and infection control audits, and survey preparedness and biomedical audits are performed every six months. The audits are tracked for timely completion and correction of issues found in the audit. In the spirit of our safety culture, we also have an electronic system for capturing adverse clinical events. These events are tracked and trended to identify opportunity to improve our teammate trainings and enhance our clinical safety systems. Our teammates complete mandatory annual compliance trainings focused on key areas, reflecting our dedication to ensuring the health and safety of our teammates and patients.
For additional information about certain risks associated with our human capital management, see the risk factors in Part I Item 1A. "Risk Factors" under the headings, "Our business is labor intensive and if our labor costs continue to rise...;" and "External conditions, including those related to general economic, marketplace and global health conditions..."
Item 1A. Risk Factors
This Annual Report on Form 10-K contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of the federal securities laws. Please read the cautionary notice regarding forward-looking statements in Item 7 of Part II of this Annual Report on Form 10-K under the heading "Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations." These forward-looking statements involve risks and uncertainties, including those discussed below, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, cash flows, financial condition, results of operations and/or reputation. The risks and uncertainties discussed below are not the only ones facing our business. Additional risks and uncertainties not currently known to us or that we currently deem to be immaterial could also have a material adverse effect on our business, cash flows, financial condition, results of operations and/or reputation.
Summary Risk Factors
The following is a summary of the principal risks and uncertainties that could adversely affect our business, cash flows, financial condition and/or results of operations, and these adverse impacts may be material. This summary is qualified in its entirety by reference to the more detailed descriptions of the risks and uncertainties included in this Item 1A. below and you should read this summary together with those more detailed descriptions.
These principal risk and uncertainties relate to, among other things:
Risks Related to the Operation of our Business
General Risks
Risks Related to the Operation of our Business
External conditions, including those related to general economic, marketplace and global health conditions, have impacted and will continue to impact our business and cost structure in a variety of ways, and these and other uncontrollable events may in the future impact the rate of growth of our patient population and our ability to grow the business. There can be no assurance that we will be able to successfully execute cost savings or other initiatives in a manner that will offset the impact of these conditions, which could result in a material adverse impact on us.
We continue to be impacted by external conditions, including those related to general economic, marketplace and global health conditions, many of which are interrelated, including, among other things, inflation, interest rate volatility, labor market conditions, wage pressure, supply chain challenges, increased mortality rates of our patients and other ESKD and CKD patients, and the potential application of innovative technologies, drugs or other treatments. Certain of these impacts could be further intensified by concurrent global events such as the ongoing conflicts between Russia and Ukraine and in Israel, Gaza and the surrounding areas, severe weather events and other natural disasters, such as Hurricane Helene, Hurricane Milton and the recent wildfires in California, and the impact of policies implemented by the new administration in the United States. These global events continue to drive sociopolitical and economic uncertainty across the globe and may further impact supply chain challenges and macroeconomic conditions and trade relationships, among other things. The ultimate impact of these and other conditions on our business over time depends on future developments that are highly uncertain and difficult to predict.
We have experienced and expect to continue to experience a negative impact on revenue and treatment volume due to, among other things, elevated mortality rates of our patients in comparison to the periods prior to the COVID-19 pandemic and the associated impact on our patient census. Treatment volumes during the year have been and we expect may continue to be adversely impacted by higher than expected missed treatment rates, which during the second half of 2024 were driven primarily by severe weather events. In addition, new-to-dialysis admission rates, treatment volumes, future revenues and non-acquired growth, among other things, could continue to be negatively impacted over time to the extent that the ESKD and CKD populations experience sustained elevated mortality levels, including, among other things, due to the availability and use of vaccines, treatments and therapies. As described below in the risk factor under the heading, "If we are unable to compete successfully...", certain other events beyond our control could also impact the rate of growth of our ESKD patient population.
Any decrease in growth rates for the ESKD or CKD patient population, higher mortality rates for dialysis patients or other reductions in demand for dialysis treatments, if sustained or significant, could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows. Any such impact would be magnified to the extent it also resulted in a lower number of patients with commercial insurance or a lower percentage of patients under commercial insurance relative to government-based programs.
Ongoing global economic conditions and political and regulatory developments, such as general labor, supply chain and inflationary pressures have also increased, and will likely continue to increase, our expenses, including among other things, staffing, labor and supply costs. Our business is labor intensive and our financial and operating results have been and continue to be sensitive to variations in labor-related costs and productivity. We have historically faced and expect to continue to face difficulties in hiring and retaining caregivers due in part to a nationwide shortage of clinical personnel, which may be exacerbated with more limitations on immigration in the United States. We expect certain of these increased staffing and labor costs to continue, due to, among other factors, the continuation of a challenging labor market. The cumulative impact of these increased costs could be material. In addition, potential staffing shortages or other potential developments or disruptions related to our teammates, if material, could ultimately lead to the unplanned closures of certain centers or adversely impact clinical operations, or may otherwise have a material adverse impact on our ability to provide dialysis services or the cost of providing those services, among other things. Our industry has also experienced increased union organizing activities. For example, union petitions have been filed in nine of our clinics in California and eight of these are in different stages of the voting process and have been subject to legal challenges. For further discussion of the risks related to rising labor costs and union organizing activities, see the risk factor under the heading, "Our business is labor intensive..."
The impact of the pandemic on our patient population combined with cost inflation trends and the failure of government reimbursement rates to keep pace with these cost trends have put pressure on our existing cost structure, and we expect that certain of those increased costs will persist as inflationary and supply chain pressures and challenging labor market conditions continue. Prolonged geopolitical or global economic volatility, uncertainty, trade disputes, labor supply shortages and other challenging labor market conditions could have an adverse impact on our growth and ability to execute on our other strategic initiatives and a material adverse impact on our labor costs, among other things. Prolonged strain on global supply chains, including as a result of trade disputes, geopolitical instability, fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates or regulatory requirements may result in equipment and clinical supply shortages, disruptions, delays or associated price increases that could impact our ability to provide dialysis services or the cost of providing those services, among other things. Moreover, to the extent that monetary policies, tariffs, or other factors impacting structural costs over the long term have contributed to or may in the future contribute to inflationary pressures, this may in turn continue to increase our labor and supply costs at a rate that outpaces the Medicare or any other rate increases we may receive. In our value-based care and other programs where we assume financial accountability for total patient cost, an increase in our underlying staffing and labor expenses could have an impact on total cost of care. This increase may in turn impact the profitability of those programs relative to their respective funding.
We invested in and implemented cost savings initiatives designed to help mitigate these cost and volume pressures. These included, among other things, identified cost savings related to the achievement of general and administrative cost efficiencies through ongoing initiatives, including, among others, those that increase our use of third party service providers to perform certain activities. These opportunities and investments also included, among others, initiatives relating to clinic optimization, capacity utilization improvement and procurement opportunities, as well as investment in revenue cycle management. We incurred charges in connection with the continued implementation of these initiatives. There can be no assurance that we will be able to continue to successfully execute these initiatives or that they will achieve expectations or succeed in helping offset the impact of these challenging conditions. Any failure on our part to adjust our business and operations in this manner, to adjust to other marketplace developments or dynamics or to appropriately implement these initiatives in accordance with applicable legal, regulatory or compliance requirements could adversely impact our ability to provide dialysis services or the cost of providing those services, among other things, and ultimately could have a material adverse effect on our business, reputation, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows.
Deterioration in economic conditions, whether driven by macroeconomic conditions, global events, domestic political or governmental volatility or other events beyond our control, including the aforementioned inflationary and labor market pressures, changes in domestic policies, volatility and uncertainty, as well as potential volatility in the global trade markets or interest rates, could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows. Among other things, the potential decline in federal and state tax revenues that may result from a deterioration in economic conditions or political initiatives targeted at reducing government spending may create additional pressures to government sponsored programs. Any potential period of extended or increased job losses in the U.S. as a result of adverse economic conditions, including economic deterioration or changes in immigration regulations, could ultimately result in a smaller percentage of our patients being covered by an employer group health plan and a larger percentage being covered by lower-paying government insurance programs or being uninsured. In addition, the potential expiration at the end of 2025 of premium
tax credits available for patients who purchase health insurance on marketplaces developed under the ACA for may similarly lead to a smaller percentage of patients being covered by a commercial insurance plan. In the event a material reduction in the share of our patients covered by commercial insurance plans occurs, it would have a material adverse impact on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows. The extent of these effects will depend upon, among other things, the extent and duration of any increased unemployment levels for our patient population, any economic deterioration or potential recession; and patients’ ability to retain existing insurance and their individual choices with respect to their coverage, all of which are highly uncertain and difficult to predict. Declining economic conditions or political or other pressures that drive increased focus on healthcare costs may lead employers to select more restrictive commercial plans with lower reimbursement rates. To the extent that payors are negatively impacted by a decline in the economy, we may experience further pressure on commercial rates, a slowdown in collections and a reduction in the amounts we expect to collect. For additional information on risks regarding the potential impact of decreases to the percentage or number of our patients with commercial insurance, see the risk factor under the heading "If the number or percentage of patients with higher-paying commercial insurance declines..."
If general economic conditions or labor market conditions deteriorate or remain uncertain for an extended period of time, we may experience negative impacts on reimbursement rates or the availability of insurance coverage for our patients, which may in turn materially and unfavorably impact our revenues and financial results. These impacts could lead us to incur future charges to recognize impairment in the carrying amount of our goodwill and other intangible assets, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition. As of December 31, 2024, we had approximately $7 billion of goodwill recorded on our consolidated balance sheet. We account for impairments of goodwill in accordance with the provisions of applicable accounting guidance, and record impairment charges when and to the extent a reporting unit's carrying amount is determined to exceed its estimated fair value. We use a variety of factors to assess changes in the financial condition, future prospects and other circumstances concerning our businesses and to estimate their fair value when applicable. These assessments and the related valuations can involve significant uncertainties and require significant judgment on various matters.
The aforementioned impacts may also drive an increased need for additional liquidity funded by accessing existing credit facilities, raising new debt in the capital markets, or other sources, and we may seek to refinance existing debt, which may be more difficult or costly in an uncertain or declining economic environment. For additional information regarding the risks related to our indebtedness, see the discussion in the risk factor under the heading "The level of our current and future debt..."
Any or all of these economic conditions or developments, as well as other consequences of these conditions or developments, some of which are beyond our control and none of which we can reasonably predict, could have a material adverse effect on our patients, teammates, physician partners, suppliers, business, results of operations, financial condition and/or cash flows or materially harm our reputation. In addition, these conditions or developments each may heighten many of the other risks and uncertainties discussed herein.
Our business is subject to a complex set of governmental laws, regulations and other requirements and any failure to adhere to those requirements, or any changes in those requirements, could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows, could materially harm our stock price, and in some circumstances, could materially harm our reputation.
We operate in a complex regulatory environment with an extensive and evolving set of federal, state and local governmental laws, regulations and other requirements that apply to us. These laws, regulations and other requirements are promulgated and overseen by a number of different legislative, regulatory, administrative, and quasi-regulatory bodies, each of which may have varying interpretations, judgments or related guidance. As such, we utilize considerable resources on an ongoing basis to monitor, assess and respond to applicable legislative, regulatory and administrative requirements, but there is no guarantee that we will be successful in our efforts to adhere to all of these requirements.
Laws, regulations and other requirements that apply to or impact our business include, but are not limited to:
•Medicare and Medicaid coverage and reimbursement statutes, and other federal coverage and reimbursement statutes, rules and regulations (including, but not limited to, manual provisions, local coverage determinations, national coverage determinations, payment schedules and agency guidance);
•Medicare and Medicaid provider requirements, including, but not limited to, requirements associated with providing and updating certain information about the Medicare or Medicaid entity, as applicable, and its direct and indirect affiliates;
•Section 1115A of the Social Security Act, which, among other things, authorizes the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Innovation (CMMI) to test certain innovation models;
•Federal and state fraud waste and abuse laws;
•the 21st Century Cures Act (the Cures Act);
•Veteran Administration and other Federal Acquisition Regulations;
•executive orders and other presidential memoranda;
•the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA), the Uniting and Strengthening America by Providing Appropriate Tools Required to Intercept and Obstruct Terrorism Act of 2001, Public Law 107-56 (Patriot Act), Executive Order No. 13224 on Terrorist Financing, effective September 24, 2001, and similar laws and regulations;
•antitrust and competition laws and regulations;
•laws and regulations related to the corporate practice of medicine;
•laws and regulations regarding the collection, use and disclosure of patient health information (e.g., Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA));
•the No Surprises Act and related laws and regulations associated with transparency, interoperability, and access to data and information;
•laws and regulations regarding the storage, handling, shipment, disposal and/or dispensing of pharmaceuticals and blood products and other biological and/or patient related materials;
•laws, regulations or other guidance across jurisdictions that require enhanced disclosures and due diligence surrounding the impacts of our Company and value chain on, and the financial risks and opportunities for our Company from, environmental, social and governance (ESG) or other similar sustainability or corporate responsibility matters, as well as enhanced policies, processes and controls designed to appropriately monitor and track such information and enhanced actions to address our Company's impact on these matters; and
•individualized state laws and regulations associated with the operation of our business.
If any of our personnel, representatives, third party vendors, or operations are alleged to have violated these or other laws, regulations or requirements, we could experience material harm to our reputation and stock price, and it could impact our relationships and/or contracts related to our business, among other things. If any of our personnel, representatives, third party vendors or operations are found to violate these or other laws, regulations or requirements, we could suffer additional severe consequences that could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows, including, among others:
•Loss of required certifications or suspension or exclusion from or termination of our participation in government programs (including, without limitation, Medicare, Medicaid and CMMI demonstration programs);
•Refunds of amounts received in violation of law or applicable payment program requirements dating back to the applicable statute of limitation periods;
•Loss of licenses required to operate healthcare facilities or administer pharmaceuticals in the states in which we operate;
•Reductions in payment rates or coverage for dialysis and ancillary services and pharmaceuticals;
•Criminal or civil liability, fines, damages or monetary penalties;
•Imposition of corporate integrity agreements, corrective action plans or consent agreements;
•Enforcement actions, investigations, or audits by governmental agencies and/or state law claims for monetary damages by patients who believe their protected health information (PHI) has been used, disclosed or not properly safeguarded in violation of federal or state patient privacy laws, including, among others, HIPAA and the Privacy Act of 1974;
•Enforcement actions, investigations, or audits by government agencies related to healthcare laws and regulations inclusive of fraud and abuse laws, interoperability and related data sharing and access requirements and regulations;
•Mandated changes to our practices or procedures that significantly increase operating expenses that could subject us to ongoing audits and reporting requirements as well as increased scrutiny of our billing and business practices which could lead to potential fines, among other things;
•Termination of various relationships and/or contracts related to our business, such as joint venture arrangements, medical director agreements, hospital services and skilled nursing home agreements, real estate leases, value-based care arrangements, clinical incentive programs, payor contracts, debt agreements and consulting or participating provider agreements with physicians, among others; and
•Harm to our reputation, which could negatively impact our business relationships and stock price, our ability to attract and retain patients, physicians and teammates, our ability to obtain financing and our access to new business opportunities, among other things.
Any future penalties, sanctions or other consequences could be more severe in certain circumstances if the OIG or a similar regulatory authority determines that we knowingly or repeatedly failed to comply with laws, regulations or requirements that apply to our business. Additionally, the healthcare sector, including the dialysis industry, is regularly subject to negative publicity, including as a result of governmental investigations, adverse media coverage and political debate surrounding the U.S. healthcare system, among other things. Negative publicity, regardless of merit, regarding the dialysis industry generally, the U.S. healthcare system or DaVita in particular may adversely affect us.
See Note 15 to the consolidated financial statements included in this report for further details regarding certain pending legal proceedings and regulatory matters to which we are or may be subject from time to time, any of which may include allegations of violations of applicable laws, regulations and requirements.
Changes in federal and state legislation or regulations could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows.
Each of the laws, regulations and other requirements that govern our business may continue to change over time, and there is no assurance that we will be able to accurately predict the nature, timing or extent of such changes or the impact of such changes on the markets in which we conduct business or on the other participants that operate in those markets.
Among other things, the regulatory framework of the healthcare marketplace continues to evolve as a result of executive orders, presidential memoranda, legislative, regulatory and administrative developments and judicial proceedings. These changes shape the landscape for our current dialysis and ancillary businesses as well as for emerging comprehensive and integrated kidney care markets. For example, as described below, we have made substantial investments in and dedicated resources to our integrated care business, value-based care initiatives and home-based dialysis business to address regulatory developments that include innovative payment models, and there are risks to those investments, or additional investments may be required, in the event the regulatory environment changes and we do not adequately adapt to such changes.
In addition, access to healthcare has been both positively and negatively impacted over time by legal, regulatory and judicial action and changes to the political environment may increase the likelihood, scale and velocity of regulatory or legislative changes that would impact us. If access to healthcare is significantly altered or if other reforms limiting access to healthcare are enacted in the future, such changes could impact our business in a number of ways, some of which may be material. Considerable uncertainty exists surrounding the continued development of the healthcare regulatory and legislative environment including pilot programs and models, as well as similar healthcare reform measures and/or other changes or extensions to laws, regulations and other requirements at the federal and/or state level that govern our business. The regulatory environment may also be impacted by recent legal decisions at all levels of the federal judicial system that could have a material impact on our business. For example, the Loper Bright Enterprises v. Raimondo U.S. Supreme Court decision in June 2024 may impact current and prospective regulatory policies, including those promulgated by CMS and other agencies with significant oversight of the healthcare industry, and subject those policies to increased litigation and judicial scrutiny. Any resulting changes in regulation or enforcement may result in unexpected delays, increased costs, or other negative impacts on our business that are difficult to predict.
Changes to the continuously evolving healthcare regulatory landscape may also have the potential to generate opportunities with relative ease of entry for certain different and/or non-traditional providers and we may be competing with them for patients in an asymmetrical environment with respect to reimbursement rates, data and/or regulatory requirements or obligations given our status as an ESRD service provider and relative scale. For example, CMS may consider opening for comment its established Medicare ESRD conditions for coverage. In the event that this process results in reductions or other changes in minimum health and safety standards for the provision of dialysis services, it may change the marketplace in which we operate. If we are unable to successfully adapt to these marketplace developments in a timely and compliant manner, we may experience a material adverse reduction in our overall number of patients, among other things. For additional detail on our
evolving competitive environment, see the risk factor under the heading "If we are unable to compete successfully..." Broader changes to the regulatory landscape may also impact our business. For example, on May 7, 2024, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) published in the federal register a final rule that would generally ban all post-employment non-compete clauses with employees and prohibit employers from enforcing existing non-compete clauses in contracts with workers, with limited exceptions. On August 20, 2024, a federal court issued an injunction against the rule, preventing the FTC from enforcing it nationwide. As result, the FTC cannot implement or enforce its rule against any employer without violating the nationwide ban. The FTC has appealed this decision. Even though the rule has been enjoined, many state legislatures continue to introduce legislation that seeks to place similar limitations on restrictive covenants. While few of these states have passed legislation that has directly affected our business, it is possible that new legislation could be introduced in the future. We are continuing to assess the potential impact of the rule as well as Congressional and state legislative efforts on our business. Such efforts, if successful, could have an adverse impact on, among other things, our agreements with teammates, our arrangements with medical directors, or the terms of our existing agreements with physicians. Any failure on our part to adequately adjust to any state regulations or future federal or state regulations and the potential impact thereof could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition, cash flows, and reputation.
Although we cannot predict the short- or long-term effects of any legislative or regulatory changes, future market changes could result in, among other things, more restrictive commercial plans with lower reimbursement rates or higher deductibles and co-payments that patients may not be able to pay. Because our revenue and operating income levels are highly sensitive to the percentage and number of our patients with higher-paying commercial health insurance, any legislative, regulatory or other changes that decrease the accessibility and availability, including the duration, of commercial insurance is likely to have a material adverse impact on our business. For additional information on the impact of economic conditions or legislative or regulatory changes on the coverage and rates for our services and the percentage or number of our patients with commercial insurance, see the risk factor under the heading "If the number or percentage of patients with higher-paying commercial insurance declines..."
There have also been several state initiatives to limit payments to dialysis providers, impose other burdensome operational requirements or prescribe wage levels. Depending on the extent of the limitations, burdens or prescriptions of such initiatives, the passage of such initiatives into law could have a material adverse impact on our business, results of operation, financial condition and cash flow. For example, California Senate Bill No. 525 (SB 525), which raised the minimum wage for many California healthcare workers, went into effect in October 2024. We may continue to face other proposed regulations or legislation or ballot initiatives in various states in future years, which, if passed, could have a material adverse impact on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows.
Finally, there have also been rule making and legislative efforts at both the federal and state level regarding the use of charitable premium assistance for ESRD patients. For example, as described in Part I Item 1. "Business" under the heading "Government Regulation," certain provisions of California bill (AB 290), including the amount of reimbursement paid to certain providers for services provided to patients with commercial insurance who receive charitable premium assistance (reimbursement cap), could have negative consequences on our business if implemented in its proposed form. Depending on what provisions are implemented, organizations that provide charitable premium assistance may choose to withdraw from California, which would have an adverse impact on the ability of patients to afford Medicare premiums and Medicare supplemental and commercial coverage. We expect that such an adverse impact will in turn adversely impact our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows. In the past, bills similar to AB 290 have been introduced in other states, but none has become law. If these or similar bills are introduced and implemented in other jurisdictions, and organizations that provide charitable premium assistance in those jurisdictions are similarly impacted, it could in the aggregate have a material adverse impact on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows. For additional information on risks associated with charitable premium assistance for ESRD patients and the potential impact of decreases to the percentage or number of our patients with commercial insurance, see the risk factor under the heading "If the number or percentage of patients with higher-paying commercial insurance declines..."
Among other things, legislation, regulations, regulatory guidance, ballot initiatives and any similar initiatives could result in a reduction in the percentage of our patients with commercial insurance; limit the scope or nature of coverage through the healthcare exchanges established by the ACA or other health insurance programs or otherwise reduce reimbursement rates for our services from commercial and/or government payors; restrict or prohibit the ability of patients with access to alternative coverage from selecting a marketplace plan on or off exchange; limit the amount of revenue that a dialysis provider can retain for caring for patients with commercial insurance; impose burdensome operational requirements; affect payments made to providers for services provided to patients who receive charitable premium assistance and/or otherwise restrict or prohibit the use of charitable premium assistance; or reduce the standards for network adequacy or require disclosure of certain pricing and patient responsibility information. In turn, these potential impacts could cause us to incur substantial costs to oppose any such proposed requirements or measures, impact our dialysis center development plans, and if passed and/or implemented, could materially reduce our revenues and increase our operating and other costs, adversely impact dialysis centers across the U.S.
making certain centers economically unviable, lead to the closure of certain centers, restrict the ability of dialysis patients to obtain and maintain optimal insurance coverage and reduce the number of patients that select commercial insurance plans or Medicare Advantage (MA) plans for their dialysis care, among other things. For additional details regarding insurance coverage for dialysis services, see the discussion in the risk factor under the heading "If the number or percentage of patients with higher-paying commercial insurance declines..." The healthcare legislative and regulatory environment is dynamic and evolving, and any such proposed or issued laws, requirements, rules and guidance could impact our business, including as may be described above, and any failure on our part to adequately adjust to any resulting marketplace developments or regulatory compliance requirements, may, among other things, erode our patient base or reimbursement rates and could otherwise have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows.
To the extent that the information above describes statutory and regulatory provisions, it is qualified in its entirety by reference to the particular statutory and regulatory provisions that are referenced. For additional information related to the laws, rules and other regulations described above, see Part I Item 1. "Business" under the heading "Government Regulation."
We are, and may in the future be, a party to various lawsuits, demands, claims, qui tam suits, governmental investigations and audits and other legal matters, any of which could result in, among other things, substantial financial penalties or awards against us, mandated refunds, substantial payments made by us, required changes to our business practices, exclusion from future participation in Medicare, Medicaid and other healthcare programs and possible criminal penalties, any of which could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition, cash flows, reputation and stock price.
We are, and may in the future be, subject to investigations and audits by governmental agencies, private civil qui tam complaints filed by relators and other lawsuits, demands, claims, legal proceedings and/or other actions alleging our failure to comply with a rule, regulation, law or practice of medicine. We are, and can be in the future, subject to audits from the government concerning the billing for our patients. If, following the conclusion of any audit, the government were to require us to refund amounts and/or modify our business practices, and such amounts or changes are significant, it could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows. The healthcare industry is highly visible and politically charged, and any allegation against us, our personnel, representatives, third party vendors, or operations in such matters or matters that involve patients suffering adverse health outcomes, may, among other things harm our reputation, stock price, and it could impact our relationships and/or contracts related to our business, among other things. Each of these impacts may be material.
Responding to subpoenas, investigations and other lawsuits, claims and legal proceedings, as well as defending ourselves in such matters, will continue to require management's attention and cause us to incur significant legal expense. Negative developments, findings or terms and conditions that we might agree to accept as part of a negotiated resolution of pending or future legal or regulatory matters, or have been forced upon us, could result in, among other things, harm to our reputation, substantial financial penalties or awards against us, substantial payments made by us, required changes to our business practices, impacts on our various relationships and/or contracts related to our business, exclusion from future participation in Medicare, Medicaid and other healthcare programs and, in certain cases, criminal penalties, any of which could have a material adverse effect on us. It is possible that criminal proceedings may be initiated against us and/or individuals in our business in connection with governmental investigations. Other than as may be described in Note 15 to the consolidated financial statements included in this report, we cannot predict the ultimate outcomes of the various legal proceedings and regulatory matters to which we are or may be subject from time to time, or the timing of their resolution or the ultimate losses or impact of developments in those matters, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition, cash flows, reputation and stock price. See Note 15 to the consolidated financial statements included in this report for further details regarding these and other legal proceedings and regulatory matters.
If the number or percentage of patients with higher-paying commercial insurance declines, if the average rates that commercial payors pay us decline, if commercial plans subject patients to restriction in plan designs, or if we are unable to maintain contracts with payors with competitive terms, including, without limitation, reimbursement rates, scope and duration of coverage and in-network benefits, it could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows.
A substantial portion of our U.S. dialysis patient service revenues are generated from patients who have commercial payors as their primary payor. The majority of these patients have insurance policies that pay us on terms and at rates that are generally significantly higher than Medicare rates. As such our revenue and net income levels are sensitive to the number of our patients with higher-paying commercial insurance coverage and the percentage of our patients under higher-paying commercial plans relative to government-based programs. The payments we receive from commercial payors generate nearly all of our profit and all of our nonacute dialysis profits come from commercial payors.
When traditional or original Medicare (Medicare) becomes the primary payor for a patient, the payment rate we receive for that patient decreases from the employer group health plan or commercial plan rate to the lower Medicare payment rate. There are a number of factors that could drive a decline in the number or percentage of our patients covered under commercial insurance plans, including, among other things, improved mortality, changes in the patient's or a family member's employment status, reduced availability of commercial health plans or reduced coverage by such plans through the ACA exchanges or otherwise due to changes to the laws, marketplace, healthcare regulatory system or otherwise. For example, certain premium tax credits available to patients who purchase health insurance on marketplaces developed under the ACA are scheduled to expire at the end of 2025 unless extended or made permanent by legislative action. The potential expiration of these tax credits may significantly reduce the affordability of commercial insurance plans, leading to fewer patients covered by such plans. This may, in turn, result in more patients shifting to Medicare or other government-based program, further decreasing the percentage of patients covered under commercial insurance plans. Commercial payors could also cease paying in the primary position after providing 30 months of coverage resulting in potentially material reductions in payment as the patient moves to Medicare primary. Declining macroeconomic conditions could also negatively impact the percentage of our patients covered under commercial insurance plans. To the extent there are job losses in the U.S., we could experience a decrease in the number of patients covered under commercial plans and/or an increase in uninsured and underinsured patients independent of whether general economic conditions improve. If we experience higher numbers of uninsured or underinsured patients, it also would result in an increase in uncollectible accounts.
Our arrangements and negotiations with payors also impact the number or percentage of patients with higher-paying commercial insurance. We continuously are in the process of negotiating existing and potential new agreements with commercial payors who aggressively negotiate terms with us, and we can make no assurances about the ultimate results of these negotiations or the timing of any potential rate changes resulting from these negotiations. A material portion of both our commercial revenue and MA revenue is concentrated with a limited number of commercial payors, and any changes impacting our highest paying commercial payors or our relationships with these payors will have a disproportionate impact on us. Sometimes many significant agreements are being renegotiated at the same time. We believe payor consolidations have significantly increased the negotiating leverage of commercial payors, and ongoing consolidations may continue to increase this leverage in the future. In addition, our agreements and rates with commercial payors may be impacted by new business activities of these commercial payors as well as steps that these commercial payors have taken and may continue to take to control the cost of and/or the eligibility for access to the services that we provide, including, without limitation, relative to products on and off the healthcare exchanges. These efforts could impact the number of our patients who are eligible to enroll in commercial insurance plans, and remain on the plans, including plans offered through healthcare exchanges. We continue to experience downward pressure on some of our rates with commercial payors as a result of these and other general conditions in the market, including, among other things, as employers seek to shift to less expensive options for medical services or as commercial payors dedicate increased focus on dialysis services.
Our negotiations with commercial payors may relate to commercial fee-for-service contracts and value-based care (VBC) contracts in which we share risk with commercial payors or other structures that allow the parties to share in cost savings upon the achievement of certain outcomes, as well as contracts to provide dialysis services to MA patients. If we fail to maintain contracts with payors and other healthcare providers with competitive or favorable terms, either with respect to commercial plans, commercial VBC contracts, MA plans or otherwise, including, without limitation, with respect to reimbursement rates, scope and duration of coverage and in-network benefits, contract term or termination rights, or if we fail to accurately estimate the price for and manage our medical costs in an effective manner, whether due to inflationary pressures or otherwise, such that the profitability of our commercial or other value-based products is negatively impacted, it could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows. The ultimate result of our negotiations with payors cannot be predicted as they occur in a highly competitive environment and are influenced by changes to payment rates set by CMS and other marketplace dynamics such as those previously discussed. Among other things, these negotiations may result in termination or non-renewals of existing agreements, decreases in contracted rates, and reduction in the number of our patients that are covered by commercial plans, and we may not be able to enter into new agreements on competitive terms or at all. In the event that our ongoing negotiations with commercial payors result in overall rate reductions in excess of overall rate increases, the cumulative effect could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows. In addition, to the extent that these negotiations result in a reduction in the number of our patients covered by plans with commercial payors, it could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows.
Certain payors have been attempting to design and implement plans that restrict or limit coverage for treatment needed by ESRD patients in the commercial market. Among other things, these restrictive plan designs seek to limit the duration and/or the breadth of ESRD benefits, limit in-network providers, set arbitrary provider reimbursement rates, or otherwise restrict access to care, all of which may result in a decrease in the number of patients covered by commercial insurance or the reimbursement rate for ESRD services, among other things. Payors have also disputed the scope and duration of ESRD benefit
coverage under their plans, and, among other things, have required patients to seek Medicare coverage for ESRD treatments. On June 21, 2022, the U.S. Supreme Court issued a decision in the matter of Marietta Memorial Hospital Employee Health Benefit Plan, et al. v. DaVita Inc., et al., a case evaluating the current language of the Medicare Secondary Payor Act (MSPA), deciding that a group health plan that limits the benefits for outpatient dialysis, but does so uniformly for all plan participants, does not violate the terms of the MSPA because the plan treats all patients uniformly, regardless of whether a participant has ESRD and regardless of whether the participant is eligible for Medicare. We cannot reasonably estimate the ultimate impact of the U.S. Supreme Court’s decision at this time, as there is significant uncertainty as to, among other things, whether and to what extent payors, including, among others employer group health plans, may seek to design and implement plans to restrict access to ESRD in light of the decision; the results of proposed and pending legislative responses to the decision; how courts will interpret other anti-discriminatory provisions of the MSPA that may apply; whether there could be other potential negative impacts of the decision and any resultant plan behavior on our commercial or government mix or the number of our patients covered by commercial insurance; and the timing of each of these items. If more commercial or employer group health plans seek to implement or utilize plan designs that discourage or prevent ESRD patients from retaining their commercial coverage, during upcoming open enrollment periods or otherwise, it may lead to a decrease in the number of patients with commercial plans, the duration of benefits for patients under commercial plans and/or a decrease in the payment rates we receive, any of which could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows.
In addition, some commercial payors are pursuing or have incorporated policies into their provider manuals limiting or refusing to accept charitable premium assistance from non-profit organizations, such as the American Kidney Fund (AKF), which may impact the number of patients who are able to afford commercial plans. Paying for coverage is a significant financial burden for many patients, and ESRD disproportionately affects the low-income population. Charitable premium assistance supports continuity of coverage and access to care for patients, many of whom are unable to continue working full-time as a result of their severe health condition. Many patients with commercial and government insurance also rely on financial assistance from charitable organizations, such as the AKF. Certain payors have challenged our patients' and other providers' patients' ability to utilize assistance from charitable organizations for the payment of premiums, including, without limitation, through litigation and other legal proceedings. The use of charitable premium assistance for ESRD patients has also faced challenges and inquiries from legislators, regulators and other governmental authorities, including California AB 290 as described in the risk factor under the heading, "Changes in federal and state legislation or regulations...", and this may continue. In addition, CMS or another regulatory agency or legislative authority may issue a new rule or guidance that challenges or restricts charitable premium assistance. If any of these challenges to kidney patients' use of premium assistance is successful or restrictions are imposed on the use of financial assistance from such charitable organizations or if organizations providing such assistance are no longer available such that kidney patients are unable to obtain, or continue to receive or receive for a limited duration, such financial assistance, it may restrict the ability of dialysis patients to obtain and maintain optimal insurance coverage and could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows. In addition, if our assumptions about how kidney patients will respond to any change in financial assistance from charitable organizations are incorrect, it could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows.
Our negotiations and relationships with payors may also be impacted by legislative or regulatory developments and associated legal rulings. For example, the final rules for the Cures Act, which are described in detail in Part I Item 1. "Business" under the heading "Government Regulation," broadened ESRD patient access to certain enhanced benefits offered by MA plans. While these rules increased our MA plan enrollment for ESRD benefits in their first year, the potential ultimate impact of this change in benefit eligibility remains subject to change as market participants continue to adjust to this regulatory environment, including such changes as, for example, the overall increases in MA plan enrollment for ESRD benefits or the removal of objective time and distance standards for network adequacy for outpatient dialysis centers. In addition, the ultimate impact of the price transparency regulations and "Good Faith Estimate" (GFE) requirements described in Part I Item 1. "Business" under the heading "Government Regulation," remains uncertain at this time, in part due to ongoing rulemaking around the No Surprises Act as well as the delayed effective date of certain provisions of the GFE framework, and uncertainty around operational timeframes, potential penalties and patient reaction, among other things. While the ultimate impact of these requirements and the aforementioned price transparency rules remains uncertain, any changes by group health plans, health insurance issuers in the group and individual markets, or consumer choices resulting from these requirements could have a material adverse impact on our business, results of operations, and financial condition, and could materially harm our reputation. For additional details regarding these regulations and potential legislative or regulatory changes, the specific risks we face in connection with these regulations, and any decrease in payments we receive for services due to, for example, fewer patients being covered under commercial plans or an increase of patients covered under more restrictive commercial plans, or plans with lower reimbursement rates, see the discussion in the risk factor under the heading "Changes in federal and state legislation or regulations..."
As noted, the foregoing dynamics of our arrangements and negotiations with commercial payors each may have an impact on, among other things, our ability to enter into and maintain contracts with payors with competitive terms, including, without limitation, reimbursement rates, scope and duration of coverage and in-network benefits as well as the number or percentage of our patients with higher-paying commercial insurance. If, as a result of these or other dynamics, we experience a decline in the average rates that commercial payors pay us or a reduction in the number of patients with ESRD coverage under higher-paying commercial plans either in total or relative to the number of patients under government-based programs that pay at lower rates or an increase in the number of patients that are uninsured or underinsured, it could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows.
If we are not able to successfully implement our strategy with respect to our integrated kidney care and value-based care initiatives, including maintaining our existing business and further developing our capabilities in a complex and highly regulated environment, it could result in a loss of our investments and have a material adverse effect on our growth strategy, could adversely impact our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows, and could materially harm our reputation.
Our integrated kidney care business manages patients and coordinates their care through value-based care arrangements with commercial payors and through government programs. We have continued to grow this portion of our business both with commercial payors, including as MA has expanded, and with government programs as CMS and CMMI implement new payment models focused on comprehensive and integrated kidney care. As part of our growth strategy, we have invested and expect to continue to invest substantial resources in the further development of our integrated care business and value-based care initiatives. There can be no assurances that we will be able to successfully implement our strategies with respect to integrated kidney care and value-based care in a complex, evolving and highly competitive and regulated environment, including, among other things, executing on initiatives to reduce the overall cost of care for our IKC patients; maintaining our existing business; recovering our investments; entering into agreements with payors, physicians, third party vendors and others on competitive terms, as appropriate, that prove actuarially sound; structuring these agreements and arrangements to comply with evolving rules and regulations, including, among other things, rules and regulations related to fraud and abuse and the use of protected health information. Implementing our expanded integrated kidney care strategies and value-based care initiatives at scale also increases certain execution and compliance risks associated with developing our operational, IT, billing and telehealth systems, including our ability to accurately capture relevant patient care data, among other things. For additional details on risks associated with information systems and new technology generally, see the risk factor under the heading "Failing to effectively maintain, operate or upgrade our information systems or those of third-party service providers upon which we rely..."
Emerging entrants are pursuing opportunities to participate in the CMMI payment models as well as broader risk arrangements with other payors, and with increasing investment and funding, these emerging entrants may adopt strategies that increase our costs to participate in these payment models and/or adversely impact our ability to enter into competitive arrangements with payors, physicians and hospitals. In addition, they may have the ability to operate without regard to regulations to which we comply. For additional detail on our evolving competitive environment, see the risk factor under the heading "If we are unable to compete successfully..." If any of these or other of our integrated kidney care and value-based care initiatives are unsuccessful, it could result in a loss of our investments and have a material adverse effect on our growth strategy, could adversely impact our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows, and could materially harm our reputation.
In addition, future legislative or regulatory action related to, among other things, existing or future integrated kidney care initiatives, including among others, CMMI payment models, and/or full capitation demonstration for ESRD may impact our ability to provide a competitive and successful integrated care program at scale. There can be no assurances that any other legislation or regulation that aligns with our strategy and investments will be extended, passed into law or enacted. Additionally, the ultimate terms and conditions of any potential legislative or regulatory action impacting integrated kidney care, full capitation demonstrations or the existing CMMI payment models remain unclear. For example, the CKCC program is a 5-year demonstration that launched in 2022. CMMI continues to monitor the performance of these and other kidney care payment models, and there is no assurance that this program will be extended or modified in the future and, among other things, our costs of care could exceed our associated reimbursement rates under such legislation or regulation. Irrespective of whether such laws are passed or regulations enacted, there can be no assurances that we will be able to successfully execute on the required strategic initiatives that would allow us to maintain a competitive and successful integrated care program on a broad scale, and in the desired time frame. Any failure on our part to adequately implement strategic initiatives, including to adjust to any marketplace developments resulting from executive, legislative, regulatory or administrative changes, could have a material adverse impact on our business.
If we are not able to successfully implement our strategy with respect to home-based dialysis, including maintaining our existing business and further developing our capabilities in a complex and highly regulated environment, it could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows, and could materially harm our reputation.
Our home-based dialysis services, which include home hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis (PD), represented approximately 19% of our U.S. dialysis patient service revenues for the year ended December 31, 2024, and have increasingly become an important part of our overall strategy. In addition, home-based dialysis recently has been the subject of increased legislative, regulatory, political and industry focus. For example, in connection with the 2019 Executive Order, HHS set out specific goals related to home dialysis and CMMI’s ESRD Treatment Choices (ETC) mandatory payment model and voluntary payment models included new incentives to encourage dialysis at home. CMS subsequently finalized changes to the ETC model and other regulations to encourage dialysis facilities and healthcare providers to seek to decrease disparities in health outcomes across racial and socioeconomic status in rates of home dialysis and kidney transplants among ESRD patients. CMS also regulates home dialysis under the ESRD Prospective Payment System (PPS) rule. Under this, CMS recently finalized a proposal to allow payment for acute kidney injury (AKI) renal dialysis services furnished to beneficiaries in their home and the agency will permit ESRD facilities to bill Medicare for the home and self-dialysis training add-on payment adjustment for beneficiaries with AKI. We are a leader in home-based dialysis and have made investments in processes and infrastructure to continue to grow this modality. There are, however, risks associated with this growth, including, among other things, financial, legal, regulatory and operational risks related to our ability to design and develop infrastructure and to plan for capacity in a modality that is part of an evolving marketplace. For example, there is a limited number of available suppliers for certain critical home-based dialysis supplies, including key products provided by a supplier that was impacted by a severe weather event in 2024. As described further in the risk factor under the heading, "If certain of our suppliers and service providers…," any disruptions involving such supplies could materially impact our operations and require significant resources or operational changes in response.
We may also be subject to associated risks related to our ability to successfully manage related operational initiatives, find, train and retain appropriate staff, contract with payors for appropriate reimbursement, and maintain processes to adhere to the complex regulatory and legal requirements, including without limitation those associated with billing Medicare. For additional detail on risks associated with operating in a highly regulated environment, see the risk factor under the heading "Our business is subject to a complex set of governmental laws, regulations and other requirements..." In addition to the above risks, certain risks inherent to home-based dialysis will increase as we expand our home-based dialysis offerings, including risks related to managing transitions between in-center and home-based dialysis, billing and telehealth systems, among others. For additional detail on risks associated with information systems and new technology generally, see the risk factor under the heading "Failing to effectively maintain, operate or upgrade our information systems or those of third-party service providers upon which we rely..."
An increased focus on home-based dialysis is also indicative of the generally evolving market for kidney care. This developing market may create additional opportunities for competition with relative ease of entry, and if we are unable to successfully adapt to these or other marketplace developments, which, among other things, may include regulatory changes with respect to conditions of coverage, in a timely and compliant manner, we may experience a material adverse impact on our growth in home-based dialysis or a reduction in our overall number of patients, among other things. For additional detail on the competitive landscape in kidney care, see the risk factor under the heading "If we are unable to compete successfully..." If we are not able to successfully implement our strategy with respect to home-based dialysis, including maintaining our existing business and further developing our capabilities in a complex and highly regulated environment, it could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows, and could materially harm our reputation.
Changes in the structure of and payment rates under the Medicare ESRD or Medicare Advantage programs or changes in state Medicaid or other non-Medicare government-based programs or payment rates could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows.
A substantial portion of our dialysis revenues are generated from patients who have Medicare or MA as their primary payor. For patients with Medicare coverage, payments for dialysis treatments are currently made under a single bundled payment rate which provides a fixed payment rate to encompass all goods and services provided during the dialysis treatment that are related to the treatment of dialysis, subject to certain adjustments. Most lab services are also included in the bundled payment.
Under the ESRD PPS, bundled payments to a dialysis facility may be reduced by as much as 2% based on the facility's performance in specified quality measures set annually by CMS through the ESRD Quality Incentive Program, which was established by the Medicare Improvements for Patients and Providers Act of 2008. The bundled payment rate is also adjusted
for certain patient characteristics, a geographic usage index, a wage index and certain other factors. In addition, the ESRD PPS is subject to rebasing, which can have a positive financial effect, or a negative one if the government fails to rebase in a manner that adequately addresses the costs borne by dialysis facilities. Similarly, as new drugs, services or labs are added to the ESRD bundle, CMS' failure to adequately calculate or fund the costs associated with the drugs, services or labs could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows. In certain instances, new injectable, intravenous or oral products may be reimbursed separately from the bundled payment for a defined period of time through a transitional drug add-on payment adjustment (TDAPA). For a discussion of certain risks associated with this transitional pricing process, see the risk factor under the heading, "Changes in clinical practices, payment rates or regulations impacting pharmaceuticals and/or devices..."
The current bundled payment system presents certain operating, clinical and financial risks, which include, without limitation:
•Risk that our reimbursement rates are reduced by CMS or are otherwise inadequate. CMS publishes a final rule for the ESRD PPS each year and uncertainty about future payment rates remains a material risk to our business.
•Risk that CMS, on its own or through its contracted Medicare Administrative Contractors (MACs) or otherwise, implements Local Coverage Determinations (LCDs) or implements payment provisions, policy or regulatory mandates, including changes to the existing or future PPS, that limit our ability to either be paid for covered dialysis services or bill for treatments or other drugs and services or other rules that may impact reimbursement. Such payment rules and regulations and coverage determinations or related decisions could have an adverse impact on our operations and revenue. There is also risk that commercial insurers could seek to incorporate the requirements or limitations associated with such LCDs or CMS guidance into their contracted terms with dialysis providers, which could have an adverse impact on our revenue.
•Risk that a MAC, or multiple MACs, change their interpretations of existing regulations, manual provisions and/or guidance, or seek to implement or enforce new interpretations that are inconsistent with how we have interpreted existing regulations, manual provisions and/or guidance.
•Risk that CMS implements data and related reporting requirements that result in decreased reimbursement and/or increased technology and operational costs and/or creates brand risk.
•Risk that increases in our operating costs will outpace the Medicare rate increases we receive. We expect operating costs to continue to increase due to inflationary factors, such as increases in labor and supply costs, including, without limitation, increases in maintenance costs and capital expenditures to improve, renovate and maintain our facilities, equipment and information technology to meet changing regulatory requirements and business needs, regardless of whether there is a compensating inflation-based increase in Medicare payment rates or in payments under the bundled payment rate system.
•Risk of continued federal budget sequestration cuts or other disruptions in federal government operations and funding. As a result of the Budget Control Act of 2011, the Bipartisan Budget Act (BBA) and subsequent legislation, an annual reduction (currently 2%) to Medicare payments took effect on April 1, 2013, and has been extended into 2032. These across-the-board spending cuts have affected and will continue to adversely affect our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows. Any extended disruption in federal government operations and funding, including an extended government shutdown, U.S. government debt default and/or failure of the U.S. government to enact annual appropriations could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows. Additionally, disruptions in federal government operations may delay or negatively impact regulatory approvals and guidance that are important to our operations, and create uncertainty about the pace of upcoming regulatory developments.
•Risk that failure to adequately develop and maintain our clinical or other operational systems or failure of our clinical or operational systems to operate effectively could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows. For example, in connection with claims for which at least part of the government's payments to us is based on clinical performance or patient outcomes or co-morbidities, if our clinical systems fail to accurately capture the data we report to CMS or we otherwise have data integrity issues with respect to the reported information, we might be over-reimbursed by the government, which could, among other things, subject us to liability exclusion from participation in federal healthcare programs and penalties under the federal Civil Monetary Penalty statute, and could adversely impact our reputation.
As described above, we also contract with commercial payors that administer MA plans to provide their members with Medicare Part A, Part B and/or Part D benefits. Our MA business presents similar operating, clinical and financial risks as those related to the bundled payment system, which include, without limitation:
•Risk that reimbursement rates for the MA program are reduced by CMS or are otherwise inadequate and that payors, therefore, reduce our rates and/or fund us less for services rendered. CMS publishes a final rule for MA program rates each year and uncertainty about future payment rates remains a material risk to our business, particularly as our MA enrollment increases.
•Risk of ensuring that we remain compliant with applicable MA requirements, inclusive of MA marketing and education requirements and restrictions, as well as our contractual terms with associated plans, as our initiatives associated with MA (including chronic condition special needs and dual eligible special needs plans) continue to evolve and progress. Failure to do so could resolve in termination of agreements with plans as well as enforcement by state and federal agencies for violation of insurance, consumer protection and fraud and abuse laws and regulations.
In addition to the above risks under the current Medicare ESRD and MA programs, changing legislation and other regulatory and executive developments have led and may continue to lead to the emergence of new models of care and other initiatives in both the government and private sector that, among other things, may impact the structure of, and payment rates under, the Medicare ESRD and MA programs. Moreover, the number of our patients with primary Medicare coverage may be subject to change, particularly with the effectiveness of the Cures Act, which allows Medicare-eligible individuals with ESRD to enroll in MA managed care plans. For additional details regarding the risks we face for failing to adhere to our Medicare, MA and Medicaid regulatory compliance obligations or failing to adequately implement strategic initiatives to adjust to marketplace developments, see the risk factors above under the headings "Our business is subject to a complex set of governmental laws, regulations and other requirements...;" and "Changes in federal and state legislation or regulations..." Finally, increased political pressures to reduce government spending, including potential cuts to Medicare funding, may create additional risks to payment rates and the structure of the Medicare ESRD and MA programs. For additional information on the impact of potential reduced government spending, see the risk factor under the heading "External conditions, including those related to general economic, marketplace and global health conditions..."
Primary coverage for a significant number of our patients also comes from state Medicaid programs partially funded by the federal government and we have patients covered by other non-Medicare government-based programs, such as coverage through the Department of Veterans Affairs (VA). As state governments and other governmental organizations face increasing financial hardship and budgetary pressure, including as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic or changes in the political environment, we may in turn face reductions in payment rates, delays in the receipt of payments, limitations on enrollee eligibility or other changes to the applicable programs. For example, certain state Medicaid programs and the VA have recently considered, proposed or implemented payment rate reductions, such as the VA's proposed adoption of Medicare's bundled PPS pricing methodology for any veterans receiving treatment from non-VA providers under a national contracting initiative. Since we are a non-VA provider, these reimbursements are tied to a percentage of Medicare reimbursement, and we have exposure to any dialysis reimbursement changes made by CMS. In addition, in 2019 and subsequently renewed, we entered into a Nationwide Dialysis Services contract with the VA that includes five separate one-year renewal periods throughout the term of the contract. The term structure is similar to our prior five-year agreement with the VA, and is consistent with VA practice for similar provider agreements. With this contract award, the VA has agreed to keep our percentage of Medicare reimbursement consistent with that under our prior agreement with the VA during the term of the contract. As with that prior agreement, this agreement provides the VA with the right to terminate the agreements without cause on short notice, among other things. The current contract expires at the end of September 2025. Should the VA renegotiate, not renew or cancel these agreements for any reason, we may cease accepting patients under this program and may be forced to close centers or experience lower reimbursement rates, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows.
State Medicaid programs are increasingly adopting Medicare-like bundled payment systems, but sometimes these payment systems are poorly defined and are implemented without any claims processing infrastructure, or patient or facility adjusters. If these payment systems are implemented without any adjusters and claims processing infrastructure, Medicaid payments will be substantially reduced and the costs to submit such claims may increase, which will have a negative impact on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows. In addition, some state Medicaid program eligibility requirements mandate that citizen enrollees in such programs provide documented proof of citizenship. If our patients cannot meet these proof of citizenship documentation requirements, they may be denied coverage under these programs, resulting in decreased patient volumes and revenue. These Medicaid payment and enrollment changes, along with similar changes to other non-Medicare government programs, could reduce the rates paid by these programs for dialysis and related services, delay the
receipt of payment for services provided and further limit eligibility for coverage which could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows.
Our business is labor intensive and if our labor costs continue to rise, including due to shortages, changes in certification requirements and/or higher than normal turnover rates in skilled clinical personnel; or currently pending or future governmental laws, rules, regulations or initiatives impose additional requirements or limitations on our operations or profitability; or, if we are unable to attract and retain employees or key leadership positions; or if union organizing activities or legislative or other changes result in significant increases in our operating costs or decreases in productivity, we may experience disruptions in our business operations and increases in operating expenses, among other things, any of which could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition, cash flows and reputation.
We face increasing labor costs generally, and in particular, we continue to face increased labor costs and difficulties in hiring skilled clinical personnel, including nurses, due to a nationwide shortage of such personnel that has been exacerbated by current macroeconomic conditions and developments in the labor market. As referenced above, the current labor market is challenging and continues to experience volatility, uncertainty and labor supply shortages, particularly in healthcare. Our business is labor intensive, and our financial and operating results have been and continue to be sensitive to variations in labor-related costs, productivity and the number of pending or potential claims against us related to labor and employment practices. We have incurred and expect to continue to incur increased labor costs, including through elevated compensation levels to our teammates, the ultimate extent of which will depend on current macroeconomic conditions and ancillary impacts on the labor market, among other things. For additional discussion of the risks facing us related to the current labor environment, see the risk factor under the heading "External conditions, including those related to general economic, marketplace and global health conditions..." Additionally, to the extent that general inflationary pressures continue or further increase, this may in turn increase our labor and supply costs at a rate that outpaces the Medicare or any other rate increases we may receive.
We compete for nurses with hospitals and other healthcare providers. The ongoing nursing shortage may limit our ability to expand our operations. Furthermore, changes in certification requirements can impact our ability to maintain sufficient staff levels, including to the extent our teammates are not able to meet new requirements, among other things. In addition, if we experience a higher than normal turnover rate for our skilled clinical personnel, our operations and treatment growth may be negatively impacted, which could adversely affect our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows. For example, in 2024, we again had significant teammate turnover, particularly amongst teammates in their first year, which led to increased training costs, among other things.
We also face competition in attracting and retaining talent for key leadership positions that are responsible for developing and executing the Company's business strategy and operational initiatives. Increased competition for top leadership talent in our industry and general marketplace conditions, including recent negative publicity and events surrounding the healthcare industry, could also impact our ability to attract and retain qualified leaders. If we are unable to attract and retain qualified individuals, including with respect to our leadership team, we may experience disruptions in our business operations, including, without limitation, our ability to achieve strategic goals, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition, cash flows and reputation.
Political or other efforts at the national or local level could result in actions or proposals that increase the likelihood of success of union organizing activities at our facilities and ongoing union organizing activities at our facilities could continue or increase for other reasons. Our industry has also experienced increased union organizing activities. For example, union petitions have been filed in nine of our clinics in California and eight of these petitions are in different stages of the voting process and have been subject to legal challenges. We also have experienced a week-long attempted union-related work stoppage in these eight clinics, which concluded without impacting our ability to provide patient care. Regardless of the outcome of the ongoing elections, other teammates at other clinics may file similar petitions in the future, and these petitions, if filed, may lead to additional elections. If a significant portion of our teammates were to become unionized, we could experience, among other things, potential additional work stoppages or other business disruptions; adverse impacts to our financial results due to the costs of bargaining or implementing a grievance procedure and processing grievances; decreases in our operational flexibility and efficiency; or negative impacts on our employee culture. In addition, we are and may continue to be subject to targeted corporate campaigns by union organizers in response to which we have been and expect to continue to be required to expend substantial resources, both time and financial. Any of these events or circumstances, including our responses to such events or circumstances, could have a material adverse effect on our employee relations, treatment growth, productivity, business, results of operations, financial condition, cash flows and reputation.
Privacy and information security laws are complex, and if we fail to comply with applicable laws, regulations and standards, including with respect to third-party service providers that utilize sensitive personal information on our behalf, or if we fail to properly maintain the integrity of our data, protect our proprietary rights to our systems or defend against cybersecurity attacks, we may be subject to government or private actions due to privacy and security breaches or suffer losses to our data and information technology assets, any of which could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows or materially harm our reputation.
We must comply with numerous federal and state laws and regulations in both the U.S. and the foreign jurisdictions in which we operate governing the collection, dissemination, access, use, security and privacy of PHI. In the U.S., these regulations include, without limitation, HIPAA and its implementing privacy, security, and related regulations, as amended by the federal Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act (HITECH) and collectively referred to as HIPAA. We are also required to report known breaches of PHI and other certain personal information consistent with applicable breach reporting requirements set forth in applicable laws and regulations. From time to time, we may be subject to both federal and state inquiries or audits related to HIPAA, HITECH and other state privacy laws associated with complaints, desk audits, and data breaches. Requirements under HIPAA also continue to evolve. Globally, these regulations include, but are not limited to, European Union (EU) General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), the United Kingdom GDPR, the EU Artificial Intelligence Act, the EU Data Act and the EU Health Data Space Regulation. If we fail to comply with applicable privacy and security laws, regulations and standards, including with respect to third-party service providers that utilize sensitive personal information, including PHI, or financial information or payroll data on our behalf or with respect to the use of certain third-party digital advertising technologies, or if we fail to properly maintain the integrity of our data, protect our proprietary rights, or defend against cybersecurity attacks, it could materially harm our reputation and/or have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows. These risks may be intensified to the extent that the laws change or to the extent that we increase our use of third-party service providers that utilize sensitive personal information, including PHI, on our behalf.
Data protection laws are evolving globally, and may continue to add additional compliance costs and legal risks to our international operations. For more details on certain international data protection laws and regulations affecting our business, see Part I Item 1. "Business" under the heading "Government Regulation." The costs of compliance with, and other burdens imposed by these international data protection laws and regulations and other new laws, regulations and policies implementing these regulations may impact our international operations and may limit the ways in which we can provide services and operate, use or otherwise process personal data collected while providing services.
Privacy and data protection laws and regulations are also evolving nationally and in the states. At the federal level, this includes proposed updates to the HIPAA Security Rule, which, if enacted as proposed, could impose potentially significant compliance training costs on our operations. At the state level, legislatures around the country continue to enact state privacy laws that are broader than the current federal privacy laws, which may add additional compliance costs and legal risks to our U.S. operations. The costs of compliance with, and the burdens imposed by, these and other new federal and state laws, regulations or policies may impact our operations and/or limit the ways in which we can provide services or use personal data collected while providing services. If we fail to comply with the requirements of these and other new laws, regulations or policies, we could be subject to damage awards in private litigation or penalties that, in some cases, would have a material adverse impact on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows. For more details on the privacy and other regulations affecting our business, see Part I Item 1. "Business" under the heading "Government Regulation." In addition, laws governing the commercialization and use of artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies are evolving and as the regulation of these technologies matures, it may add additional compliance costs and legal risk to our operations. Scrutiny over cybersecurity standards in the health sector is also increasing, and ongoing developments in this area may cause us to invest additional resources in technology, personnel and programmatic cybersecurity controls as the cybersecurity risks we face continue to evolve.
Information security risks have significantly increased in recent years in part because of the proliferation of new technologies, the increasing use of the Internet and telecommunications technologies to conduct our operations, and the increased sophistication and activities of organized crime, hackers, terrorists and other external parties, including, among others, foreign state agents. Our business and operations rely on the secure and continuous processing, transmission and storage of confidential, proprietary and other information in our computer systems and networks, including sensitive personal information, such as PHI, social security numbers, and/or credit card information of our patients, teammates, physicians, business partners and others. Our business and operations also rely on certain critical IT vendors that support such processing, transmission and storage (which have become more relevant and important given the information security issues and risks that are intensified through remote work arrangements). For example, as previously reported, due to a cybersecurity breach that affected Change Healthcare (CHC), a subsidiary of UnitedHealth Group (United) that serves as an intermediary for processing the vast majority of our payment claims for domestic commercial and government payors, we temporarily suspended all claims processing activity with CHC (CHC Outage), primarily during a period of time during the first and second quarters of 2024,
which impacted our cash flows. We have since resumed claims submissions and billing processes through CHC’s information technology systems and as of the date of this filing, through a combination of CHC's platform and certain alternate billing processes, we are current on our primary claims submissions. However, the CHC Outage, and the resultant delay in claims submissions, led to a decrease in our collections and an increase in our days sales outstanding, among other things, which increase has since subsided, but we do continue to see delays in, and issues with, collections with some payors. CHC has publicly reported online and in notices to affected individuals that it identified protected health information (PHI), or personally identifiable information (PII), from users of the CHC systems, and CHC has been conducting investigations and data forensics. CHC informed the Company that a small number of patients had certain PHI exposed as a result of this breach and CHC is taking responsibility for notifying these patients. The ultimate impact of the CHC Outage remains subject to future developments and risks that are difficult to predict. These risks may include, among other things, a recurrence of system outages or service suspensions or the risk that our information technology systems or our proprietary information and sensitive or confidential data, including PHI or PII, may have been compromised through the CHC Outage, any of which may have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition, cash flows and reputation.
We regularly review, monitor and implement multiple layers of security measures through technology, processes and our people. We utilize security technologies designed to protect and maintain the integrity of our information systems and data, and our defenses are monitored and routinely tested internally and by external parties. Despite these efforts, our facilities and systems and those of our third-party service providers may be vulnerable to privacy and security incidents; security attacks and breaches; acts of vandalism or theft; computer viruses and other malicious code; coordinated attacks by a variety of actors, including, among others, activist entities or state sponsored cyberattacks; emerging cybersecurity risks; cyber risk related to connected devices; misplaced or lost data; programming and/or human errors; or other similar events that could impact the security, reliability and availability of our systems and the availability, authenticity, integrity and/or confidentiality of personal information stored on those systems. Internal or external parties have attempted to, and will continue to attempt to, circumvent our security systems, and we have in the past, and expect that we will in the future, defend against, experience, and respond to attacks on our network including, without limitation, reconnaissance probes, denial of service attempts, malicious software attacks including ransomware or other attacks intended to render our internal operating systems or data unavailable, and phishing attacks or business email compromise. Cybersecurity requires ongoing investment and diligence against evolving threats. For example, healthcare companies, including our Company and certain of our third-party service providers, strategic partners, consultants or contractors, are increasingly incorporating self-learning or "artificial intelligence" features into information technology capabilities. The use of this rapidly evolving technology may intensify the cybersecurity and reputational risks we face given its novel and untested nature, particularly to the extent such technology involves the use of PHI or PII. Emerging and advanced security threats, including, without limitation, coordinated attacks, require additional layers of security which may disrupt or impact efficiency of operations. As with any security program, there always exists the risk that employees will violate our policies despite our compliance efforts or that certain attacks may be beyond the ability of our security and other systems to detect. There can be no assurance that investments, diligence and/or our internal controls will be sufficient to prevent or timely discover an attack.
Any security breach involving the misappropriation, loss or other unauthorized disclosure or use of confidential information, including, among others, PHI, financial data, competitively sensitive information, or other proprietary data, whether by us or a third party, could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition, and cash flows and materially harm our reputation. We may be required to expend significant additional resources to modify our protective measures, to investigate and remediate vulnerabilities or other exposures, or to make required notifications. The occurrence of any of these events could, among other things, result in interruptions, delays, the loss or corruption of data, cessations in the availability of systems and liability under privacy and security laws, all of which could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows, or materially harm our reputation and trigger regulatory actions and private party litigation. If we are unable to protect the physical and electronic security and privacy of our databases and transactions, we could be subject to potential liability and regulatory action, our reputation and relationships with our patients, physicians, vendors and other business partners would be harmed, and our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows could be materially and adversely affected. Failure to adequately protect and maintain the integrity of our information systems (including our networks) and data, or to defend against cybersecurity attacks, could subject us to monetary fines, civil suits, civil penalties or criminal sanctions and requirements to disclose the breach publicly, could subject our legal representatives or senior management to liability and/or a temporary suspension during which they cannot exercise managerial duties, and could further result in a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows or harm our reputation. As malicious cyber activity escalates, including activity that originates outside of the U.S., and as we continue with certain remote work arrangements and a broadened technology footprint, the risks we face relating to transmission of data and our use of service providers outside of our network, as well as the storing or processing of data within our network, have intensified. There have been increased international, federal and state and other privacy, data protection and security enforcement efforts and we expect this trend to continue. While we plan to maintain cyber liability insurance, there can be no assurance that we will successfully be able to obtain such insurance on terms and conditions that are
favorable to us or at all. Additionally, any cyber liability insurance may not cover us for all types of losses or harms and may not be sufficient to protect us against the amount of all losses.
For additional information about our assessment of our cybersecurity risks, see discussion in Part I Item 1C. "Cybersecurity."
If certain of our suppliers and service providers do not meet our needs, if there are material price increases on supplies, if we are not reimbursed or adequately reimbursed for drugs we purchase or if we are unable to effectively access new technology or superior products, it could negatively impact our ability to effectively provide the services we offer and could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows and could materially harm our reputation. We are also subject to the risk associated with our increased reliance on third party service providers.
We have significant suppliers and service providers, with a substantial portion of our total vendor spend concentrated with a limited number of third party suppliers and service providers. These third party suppliers and service providers include, without limitation, service providers performing certain key functions for us such as claims processing, financial accounting, and information technology functions, and suppliers of pharmaceuticals or clinical products that may be the primary source of products critical to the services we provide, or to which we have committed obligations to make purchases, sometimes at particular prices.
We rely on these third-party suppliers and service providers to provide the products or services we require, and this reliance subjects us to risks arising from the loss of control over these services, changes in pricing that may affect our operating results, and potentially, termination of provisions of these services by our providers. There can be no assurance that third party suppliers and service providers will provide, or will continue to provide, the services or products that we require, or that substitute services or products, or alternate suppliers or service providers, can be identified or transitioned to on a timely or cost-effective basis or at all. In certain cases, there may be a limited number of viable alternate suppliers or service providers that have the capacity or capability to offer these supplies or services.
If our significant suppliers and service providers do not meet our needs for the products and services they supply, including, without limitation, in the event of supply chain disruptions due to global events, geopolitical instability, trade disputes, natural disasters or severe weather events, product recalls, logistical challenges, fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates, varying regulatory requirements or other shortages or disputes, and we are not able to find adequate alternative sources for these products or services on a timely or cost-effective basis; if we experience material price increases from these suppliers or otherwise in connection with our actions to secure needed products that we are unable to mitigate; if some of the drugs that we purchase from our suppliers are not reimbursed or not adequately reimbursed by commercial or government payors; or if we are unable to secure products, including pharmaceuticals at competitive rates and within the desired time frame; it could require us to make significant operational changes, could negatively impact our ability to effectively provide the services we offer or negatively impact our ability to effectively execute certain important corporate functions, and could otherwise have a material adverse impact on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows and materially harm our reputation. In addition, the technology related to the products critical to the services we provide is subject to new developments that may result in superior products, and if we are unable to incorporate these superior products into our business or otherwise find adequate alternatives on a cost-effective and timely basis, it could impact our ability to compete effectively.
We have experienced service disruptions relating to key business functions and supply chain shortages with respect to certain of our equipment and clinical supplies, including critical clinical and other supplies. For example, in September 2024, one of our suppliers notified us that a severe weather event caused extensive damage to its manufacturing plant. The damage required the supplier to close the facility and halt production of certain clinical products it supplies to us and other health care providers, including saline and peritoneal dialysate. As a result of this disruption, we worked with the supplier, other suppliers, and federal and state governmental agencies to identify alternate sources for these supplies and implemented certain operational measures that were developed to maintain continuity of care for our patients. These operational measures, including securing alternate supply and temporarily holding new starts for PD home-based dialysis resulted in increased expense and slowed growth of our home-based dialysis business in 2024 and the early portion of 2025. In general, while we have made certain operational changes in response to the foregoing, there can be no assurance that a future shortage or disruption would not require additional resources or further operational changes in the future and we are continuing to assess the balance of efficiency and resilience in evaluating the risk of future supply chain shortages or service disruptions. Separately, current macroeconomic conditions also have resulted in global supply chain challenges and have materially impacted global supply chain reliability, as described in the risk factor under the heading "External conditions, including those related to general economic, marketplace and global health conditions..."
Changes in clinical practices, payment rates or regulations impacting pharmaceuticals and/or devices could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition, and cash flows and negatively impact our ability to care for patients.
Medicare bundles certain pharmaceuticals into the ESRD PPS payment rate at industry average doses and prices. Variations above the industry average may be subject to partial reimbursement through the PPS outlier reimbursement policy. Changes to industry averages, which can be caused by, among other things, changes in physician prescribing practices, including in response to the introduction of new drugs, treatments or technologies, changes in best and/or accepted clinical practice, changes on the reliance of artificial intelligence to support clinical practices, changes in private or governmental payment criteria regarding pharmaceuticals and/or devices, or the introduction of administration policies may negatively impact our ability to obtain sufficient reimbursement levels for the care we provide, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows. Physician practice patterns, including their independent determinations as to appropriate pharmaceuticals and dosing, are subject to change, including, for example, as a result of changes in labeling of pharmaceuticals or the introduction of new pharmaceuticals. Additionally, commercial payors have increasingly examined their administration policies for pharmaceuticals and, in some cases, have modified those policies. If such policy and practice trends or other changes to private and governmental payment criteria make it more difficult to preserve our margins per treatment, it could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows. Further, increased utilization of certain pharmaceuticals whose costs are included in a bundled reimbursement rate, or decreases in reimbursement for pharmaceuticals whose costs are not included in a bundled reimbursement rate, could also have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operation, financial condition and cash flows.
Regulations and processes impacting reimbursement for pharmaceuticals and/or devices and any changes thereto could similarly affect our operating results. Among other things, as new kidney care drugs, treatments or technologies are introduced over time, we expect that the use of transitional payment adjustments to incorporate certain of these new drugs, treatments or technologies as defined by the CMS policy into the bundled Medicare Part B ESRD payment may lead to fluctuations in associated levels of operating income and risk that the reimbursement levels of such drugs, treatments or technologies may not adequately cover our cost to obtain the drug or other associated costs. Drivers of these risks include, among other things, the risk that CMS may not provide adequate funding in the Medicare Part B ESRD payment in the transitional or post-transitional period or such items are not covered by transitional add on pricing, in which case there may be less clarity on the reimbursement, either of which may in turn materially adversely impact our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows. For example, under current CMS regulation, certain oral-only drugs were paid separately under Medicare Part D until January 1, 2025, at which time they were incorporated in the ESRD bundled payment. In recent rulemaking, CMS has finalized a policy to increase TDAPA amounts for oral phosphate binders, based on 100% of Average Sales Price, increased by a fixed amount of $36.41 for certain incremental costs. We cannot predict, at this time, whether CMS' TDAPA amounts for oral phosphate binders will adequately account for the inclusion of these oral medications and the additional costs associated with dialysis providers having to supply such drugs. We have developed operational and clinical processes designed to provide the drug as may be required under the applicable regulations and as may be prescribed by physicians and have also worked to contract with manufacturers of drug(s) to establish terms and access to the product, as well as payors, as applicable, for reimbursement and/or administration of the drug. If the government or other payors implement other new requirements or protocols for patients to receive the drug and include pricing in the bundle, we could experience significant fluctuations in our associated levels of operating income and could be subject to material financial, operational and/or legal risk if we are not adequately reimbursed for the cost of the drug, if we are unable to implement effective and appropriate operational measures to distribute or bill for the drug, if we fail to implement appropriate storage and diversion controls or if we cannot obtain competitive pricing for the drug. The aggregate impact of these risks could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operation, financial condition and cash flows.
Similar operating and clinical rigor and appropriate processes will be needed for other potential new drugs, treatments or technologies that are approved and come onto the market, as well as for drugs, treatments or technologies that we contract to receive from different suppliers. Any failure to successfully contract with manufacturers for competitive pricing, failure to successfully contract with the government or other payors for appropriate reimbursement, or failure to prepare, develop and implement processes that provide for appropriate availability and use in our clinics in compliance with applicable laws, including those related to controlled substances, could have a material adverse impact on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows.
We may also be subject to increased inquiries or audits from a variety of governmental bodies or claims by third parties related to pharmaceuticals, which would require management's attention and could result in significant legal expense. Any negative findings could result in, among other things, substantial financial penalties or repayment obligations, the imposition of certain obligations on and changes to our practices and procedures as well as the attendant financial burden on us to comply with the obligations, or exclusion from future participation in the Medicare and Medicaid programs, and could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition, cash flows and reputation. For additional details, see
the risk factor under the heading "Our business is subject to a complex set of governmental laws, regulations and other requirements..."
If we are unable to compete successfully, including, without limitation, implementing our growth strategy and/or retaining patients and developing and maintaining relationships with physicians and hospitals, it could materially adversely affect our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows.
We operate in a highly competitive and continuously evolving environment across the spectrum of kidney care, and operating in this market requires us to successfully execute on strategic initiatives which, among other things, build or retain our patient population through acquisition or referrals, or that develop and maintain our relationships with physicians and hospitals in both the dialysis and pre-dialysis space.
Competition for relationships with certain referral sources, including nephrologists and hospitals, in existing and expanding geographies or areas is intense, and we continue to face intense competition from large and medium-sized providers, among others, which compete directly with us for physicians qualified to serve as medical directors, for limited acquisition targets and for individual patients. In addition to these large and medium-sized competitors with substantial financial resources and other established participants in the dialysis space, we also compete with individual nephrologists who have opened their own dialysis units or facilities. Our largest competitor, Fresenius Medical Care (FMC), manufactures a full line of dialysis supplies and equipment in addition to owning and operating dialysis centers. This may, among other things, give FMC cost advantages over us because of its ability to manufacture its own products.
We continuously compete for maintaining or developing relationships with physicians that can serve as medical directors at our centers. Physicians, including medical directors, choose where they refer their patients, and neither of our current or former medical directors have an obligation to refer their patients to our centers. Certain physicians prefer to have their patients treated at dialysis centers where they or other members of their practice supervise the overall care provided as medical director of the center. As a result, referral sources for many of our centers include the physician or physician group providing medical director services to the center. Moreover, because Medicare regulations require medical directors for each of our Medicare certified dialysis centers, our ability to operate our centers depends in part on our ability to secure medical director agreements with a sufficient number of nephrologists. Our medical director agreements range in duration, but generally are for periods of ten years, and at any given time a large number of them could be up for renewal at the same time. Medical directors have no obligation to extend their agreements with us and, under certain circumstances, our former medical directors may choose to provide medical director services for competing providers or establish their own dialysis centers in competition with ours. If we are unable to contract with nephrologists to provide medical director services, then we may be unable to satisfy the federal Medicare requirements associated with medical directors and to operate our centers. The aging of the nephrologist population and opportunities presented by our competitors or other hospitals and other healthcare providers may negatively impact a medical director's decision to enter into or extend his or her agreement with us and potential declines in the overall number of nephrologists may negatively impact our ability to enter into medical director agreements in the future. In addition, if the terms of any existing agreement are found to violate applicable laws, there can be no assurances that we would be successful in restructuring the relationship, which would lead to the early termination of the agreement. If we are unable to obtain qualified medical directors to provide supervision of the operations and care provided at our dialysis centers, it could affect not only our ability to operate the center but also the degree to which other physicians to feel confident in referring patients to our dialysis centers. If a significant number of physicians were to cease referring patients to our dialysis centers, whether due to law, rule or regulation, new competition, a perceived decrease in the quality of service levels at our centers or other reasons, it would have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows.
In addition, as we continue to expand our offerings across the kidney care continuum, our ability to enter into and maintain integrated kidney care relationships with payors, physicians and other providers may have an impact on our ability to participate in integrated kidney care. This environment is highly competitive and has been evolving. For example, there have been a number of announcements, initiatives and capital raises by non-traditional kidney care providers and others, which relate to entry into the dialysis and pre-dialysis space, the development of innovative technologies, or the commencement of new business activities that could be transformative to the industry. Some of these emerging entrants have considerable financial resources. Although these and other potential competitors may face operational or financial challenges, the evolving nature of the dialysis and pre-dialysis marketplaces have presented some opportunities for relative ease of entry for these and other potential competitors. As a result, we may compete with these smaller or non-traditional providers or others in an asymmetrical environment with respect to data and regulatory requirements that we face as an ESRD service provider, thereby negatively impacting our ability to effectively compete. These and other factors have continued to drive change in the dialysis and pre-dialysis space, and if we are unable to successfully adapt to these dynamics, it could have a material adverse impact on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows. As an example, emerging entrants are pursuing opportunities to participate in the CMMI payment models or otherwise establish value-based care programs, and increasing investment in and availability of funding to emerging entrants in the dialysis and pre-dialysis marketplace that may not be as cautious in adhering
to applicable laws and regulations and/or may not be subject to the same regulatory restrictions as the Company, could adversely impact our ability to enter into competitive arrangements.
Each of the aforementioned competitive pressures and related risks may be impacted by a continued decline in the rate of growth of the ESRD patient population, higher mortality rates for dialysis patients or other reductions in demand for dialysis treatments, whether due to population growth trends, the development and application of innovative technologies or otherwise. As described in Part I Item 1. "Business," the recent 2024 annual data report from the United States Renal Data System (USRDS) the decline in annual growth rate of ESKD dialysis patient population was 0.4% from 2021 to 2022, representing a slowdown from longer term growth. Despite this near term slowdown presented in the report, which, among other things, included impacts from the COVID-19 pandemic on mortality rates amongst the ESKD dialysis patient population, the rate of growth has been relatively consistent over time.
A number of factors may impact ESKD growth rates, including, among others, mortality rates for dialysis patients or CKD patients, the growth and aging of the U.S. population, limitation on immigration into the United States, transplant rates, incidence rates for diseases that cause kidney failure such as diabetes and hypertension, growth rates of minority populations with higher than average incidence rates of ESKD or other changes in demand for dialysis treatments over time, including for example, as a result of the development and application of certain innovative technologies, drugs or other treatments such as the glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, SGLT2 inhibitors, and other classes of drugs or new classes of drugs or other treatments that may, among other things, slow the progression of CKD. Any decrease in growth rates for the ESRD patient population, higher mortality rates for dialysis patients, increase in the availability to kidneys or replacement kidneys for transplant, or other reductions in demand for dialysis treatments, if sustained or significant, could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows. Any such impact would be magnified to the extent it also resulted in a lower number of patients with commercial insurance or a lower percentage of patients under commercial insurance relative to government-based programs. While we have continued efforts to seek growth opportunities, such as by expanding our business into various international markets, we face ongoing competition from large and medium-sized providers, among others, for acquisition targets in those markets. Providers may reduce pricing in an attempt to capture more volume in the face of declining ESRD patient growth. Any failure on our part to appropriately adjust our business and operations in light of these complicated marketplace dynamics could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows and could materially harm our reputation.
If we are not able to effectively compete in the markets in which we operate, including by implementing our growth strategy, effectively adjusting our business and operations in light of evolving marketplace dynamics, building or retaining our patient population, maintaining and developing relationships with nephrologists and hospitals, particularly medical director relationships, or making acquisitions at the desired pace or at all; if we are not able to continue to maintain the expected or desired level of non-acquired growth; or if we experience significant patient attrition either as a result of new business activities in the dialysis or pre-dialysis space by our existing competitors, other market participants, new entrants, new technology or other forms of competition, or as a result of reductions in demand for dialysis treatments, including, without limitation, due to increased mortality rates for dialysis patients resulting from COVID-19 or otherwise, reduced prevalence of ESRD, the development of innovative technologies, drugs or other treatments or an increase in the number of kidney transplants, including xenotransplants, it could materially adversely affect our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows.
The U.S. integrated kidney care, U.S. other ancillary services and international operations that we operate or invest in now or in the future may generate losses and may ultimately be unsuccessful. In the event that one or more of these activities is unsuccessful, our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows may be negatively impacted and we may have to write off our investment and incur other exit costs.
Our U.S. integrated kidney care and U.S. other ancillary services are subject to many of the same risks, regulations and laws, as described in the risk factors related to our dialysis business set forth in this Item 1A. "Risk Factors," and are also subject to additional risks, regulations and laws specific to the nature of the particular strategic initiative. We have added, and expect to continue to add additional service offerings to our business and pursue additional strategic initiatives in the future as circumstances warrant, which could include healthcare products or services not directly related to dialysis. Many of these initiatives require or would require investments of both management and financial resources and can generate significant losses for a substantial period of time and may not become profitable in the expected timeframe or at all. There can be no assurance that any such strategic initiative will ultimately be successful. Any significant change in market conditions or business performance, including, without limitation, as a result of the political, legislative or regulatory environment, may impact the performance or economic viability of any of these strategic initiatives.
If any of our U.S. integrated kidney care, U.S. other ancillary services or international operations are unsuccessful, it may have a negative impact on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows, and if we determine to exit that line of business we may incur significant termination costs. For discussion of risks and potential impacts specific to our
integrated kidney care business and related growth strategy, see the risk factor under the heading "If we are not able to successfully implement our strategy with respect to our integrated kidney care and value-based care initiatives..." In addition, we may incur material write-offs or impairments of our investments, including, without limitation, goodwill or other assets, in one or more of our U.S. integrated kidney care, U.S. other ancillary services or international operations. In that regard, we have taken, and may in the future take, impairment and restructuring charges in addition to those described above related to our U.S. integrated kidney care, U.S. other ancillary services and international operations.
Expansion of our operations to and offering our services in markets outside of the U.S., and utilizing third-party suppliers and service providers operating outside of the U.S., subjects us to political, economic, legal, operational and other risks that could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition, cash flows and reputation.
We are continuing to expand our operations by offering our services and entering new lines of business in certain markets outside of the U.S., and we have increased our utilization of third-party suppliers and service providers operating outside of the U.S., which increases our exposure to the inherent risks of doing business in international markets. Depending on the market, these risks include those relating to:
•changes in the local economic environment including, among other things, labor cost increases and other general inflationary pressures;
•political instability, armed conflicts or terrorism;
•public health crises, such as pandemics or epidemics;
•social changes;
•intellectual property legal protections and remedies;
•trade regulations;
•procedures and actions affecting approval, production, pricing, reimbursement and marketing of products and services;
•foreign currency and applicable exchange rates;
•additional U.S. and foreign taxes;
•export controls;
•antitrust and competition laws and regulations;
•lack of reliable legal systems which may affect our ability to enforce contractual rights;
•changes in local laws or regulations, or interpretation or enforcement thereof;
•potentially longer ramp-up times for starting up new operations and for payment and collection cycles;
•financial and operational, and information technology systems integration;
•failure to comply with U.S. laws, such as the FCPA, or local laws that prohibit us, our partners, or our partners' or our agents or intermediaries from making improper payments to foreign officials or any third party for the purpose of obtaining or retaining business;
•laws, regulations or other guidance that require enhanced disclosures and due diligence surrounding the impacts of our Company and value chain on, and the financial risks and opportunities for our Company from, ESG or other similar sustainability or corporate responsibility matters, as well as enhanced policies, processes and controls designed to appropriately monitor and track such information and enhanced actions to address our Company's impact on these matters; and
•data and privacy restrictions, among other things.
Issues relating to the failure to comply with applicable non-U.S. laws, requirements or restrictions may also impact our domestic business and/or raise scrutiny on our domestic practices.
Additionally, some factors that will be critical to the success of our international business and operations will be different than those affecting our domestic business and operations. For example, conducting international operations requires us to devote significant management resources to implement our controls and systems in new markets, to comply with local laws and regulations, including to fulfill financial reporting and records retention requirements among other things, and to overcome the numerous new challenges inherent in managing international operations, including, without limitation, challenges based on differing languages and cultures, challenges related to establishing clinical operations in differing regulatory and compliance environments, and challenges related to the timely hiring, integration and retention of a sufficient number of skilled personnel to carry out operations in an environment with which we are not familiar.
Any expansion of our international operations through acquisitions or through organic growth could increase these risks. Additionally, while we may invest material amounts of capital and incur significant costs in connection with the growth and development of our international operations, including to start up or acquire new operations, we may not be able to operate them profitably on the anticipated timeline, or at all.
These risks could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows and could materially harm our reputation.
Failing to effectively maintain, operate or upgrade our information systems or those of third-party service providers upon which we rely, including, without limitation, our clinical, billing and collections systems, or failure to adhere to federal and state data sharing and access requirements and regulations could materially adversely affect our business, results of operations, financial condition, cash flows and reputation.
Our business depends significantly on effective information systems. Our information systems require an ongoing commitment of significant resources to maintain, upgrade and enhance existing systems and develop or contract for new systems in order to keep pace with continuing changes in information processing technology, emerging cybersecurity risks and threats, evolving industry, legal and regulatory standards and requirements, new models of care, and other changes in our business, among other things. For example, the provisions related to data interoperability, information blocking, and patient access in the Cures Act and No Surprises Act include, among other things, changes to the Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology’s (ONC's) Health IT Certification Program and requirements that CMS-regulated payors make relevant claims/care data and provider directory information available through standardized patient access and provider directory application programming interfaces (APIs) that connect to provider electronic health records. We have made and expect to continue to make significant investments in updating and integrating our clinical IT systems and continuing to build our data interoperability capabilities. Any failure to adequately comply with these and other provisions related to data interoperability, information blocking, and patient access may, among other things, result in fines and sanctions, adversely impact our Medicare business, our ability to scale our integrated care business and our ability to compete with certain smaller and/or non-traditional providers taking advantage of an asymmetrical environment with respect to data and/or regulatory requirements given our status as an ESRD service provider; or otherwise have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows. Rulemaking in these areas is ongoing, and there can be no assurances that the implementation of planned enhancements to our systems, such as our implementation of these data interoperability provisions or our other ongoing efforts to upgrade and better integrate our clinical systems, will be successful once the regulatory environment settles or that we will ultimately realize anticipated benefits from investments in new or existing information systems. In addition, we may from time to time obtain significant portions of our systems-related support, technology or other services from third parties, which may make our operations vulnerable if such third parties fail to perform adequately.
Failure to successfully implement, operate and maintain effective and efficient information systems with adequate technological capabilities, deficiencies or defects in the systems and related technology, or our failure to efficiently and effectively implement ongoing system upgrades or consolidate our information systems to eliminate redundant or obsolete applications, could result in increased legal and compliance risks and competitive disadvantages, among other things, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results of operations and reputation. For additional information on the risks we face in a highly competitive market, see the risk factor under the heading, "If we are unable to compete successfully..." If the information we rely upon to run our business was found to be inaccurate or unreliable or if we or third parties on which we rely fail to adequately maintain information systems and data integrity effectively, whether due to software deficiencies, human coding or implementation error or otherwise, we could experience difficulty meeting clinical outcome goals, face regulatory problems, including sanctions and penalties, incur increases in operating expenses or suffer other adverse consequences, any of which could be material. Moreover, failure to adequately protect and maintain the integrity of our information systems (including our networks) and data, or information systems and data hosted by third parties upon which we rely, could subject us to severe consequences as described in the risk factor under the heading "Privacy and information security laws are complex..."
Our billing systems, among others, are critical to our billing operations. This includes our systems for our dialysis clinics as well as our systems for our hospital services and our ancillary businesses, including our international business. If there are defects in our billing systems, or billing systems or services of third parties upon which we rely, we may experience difficulties in our ability to successfully bill and collect for services rendered, including, without limitation, a delay in collections, a reduction in the amounts collected, increased risk of retractions from and refunds to commercial and government payors, an increase in our provision for uncollectible accounts receivable and noncompliance with reimbursement laws and related requirements, any or all of which could materially adversely affect our results of operations.
In the clinical environment, a failure of our clinical systems, or the systems of our third-party service providers, to operate effectively could have a material adverse effect on our business, the clinical care provided to patients, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows. For example, in connection with claims for which at least part of the government's payments to us is based on clinical performance or patient outcomes or co-morbidities, if relevant clinical systems fail to accurately capture the data we report to CMS or we otherwise have data integrity issues with respect to the reported information, this could impact our payments from government payors.
Additionally, we expect the highly competitive environment in which we operate to become increasingly more competitive as the market evolves and new technologies are introduced. This dynamic environment requires continuous investment in new technologies and clinical applications. Machine learning and artificial intelligence are increasingly driving innovations in technology, and parts of our operations may employ new technology and analytics, including artificial intelligence. If these rapidly evolving technologies or applications fail to operate as anticipated or do not perform as specified, including due to potential design defects and defects in the development of algorithms or other technologies, human error or otherwise, our clinical operations, business and reputation may be harmed. If we are unable to successfully maintain, enhance or operate our information systems, including through the implementation of such technologies or applications in our clinical operations and laboratory, or if we are unable to successfully implement adequate governance structures to manage these new technologies, we may be, among other things, unable to efficiently adapt to evolving laws and requirements, unable to remain competitive with others who successfully implement and advance this technology, subject to increased risk under existing laws, regulations and requirements that apply to our business, and our patients' safety may be adversely impacted, any of which could have a material adverse impact on our business, results of operations and financial condition and could materially harm our reputation. For additional detail, see the discussion in the risk factor under the heading "Our business is subject to a complex set of governmental laws, regulations and other requirements..."
We may engage in acquisitions, mergers, joint ventures, noncontrolling interest investments, or dispositions, which may materially affect our results of operations, debt-to-capital ratio, capital expenditures or other aspects of our business, and, under certain circumstances, could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows and could materially harm our reputation.
Our business strategy includes growth through acquisitions of dialysis centers and other businesses, as well as through entry into joint ventures. We may engage in acquisitions, mergers, joint ventures or dispositions or expand into new business lines or models, which may affect our results of operations, debt-to-capital ratio, capital expenditures or other aspects of our business. See the discussion under "Off-balance sheet arrangements and aggregate contractual obligations" in Part II Item 7. "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations."
There can be no assurance that we will be able to identify suitable acquisition or joint venture targets or merger partners or buyers for dispositions or that, if identified, we will be able to agree to acceptable terms or on the desired timetable. There can also be no assurance that we will be successful in completing any acquisitions, joint ventures, mergers or dispositions that we announce, executing new business lines or models or integrating any acquired business into our overall operations. There is no guarantee that we will be able to operate acquired businesses successfully as stand-alone businesses, or that any such acquired business will operate profitably or will not otherwise have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows or materially harm our reputation. In addition, acquisition, merger or joint venture activity conducted as part of our overall growth strategy is subject to antitrust and competition laws, and antitrust regulators can investigate future (or pending) and consummated transactions. These laws could impact our ability to pursue these transactions or our ability to consummate them on a timely basis; could require us to devote additional resources to potential transactions; and under certain circumstances, could result in mandated divestitures, among other things. If a proposed transaction or series of transactions is subject to challenge under antitrust or competition laws, we may incur substantial legal costs, management’s attention and resources may be diverted, and if we are found to have violated these or other related laws, regulations or requirements, we could suffer severe consequences that could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows and could materially harm our reputation and stock price. For additional detail, see the risk factor under the heading "Our business is subject to a complex set of governmental laws, regulations and other requirements..." Further, we cannot be certain that key talented individuals at the business being acquired will continue to work for us after the acquisition or that they will be able to continue to successfully manage or have adequate
resources to successfully operate any acquired business. In addition, certain of our acquired dialysis centers and facilities have been in service for many years, which may result in a higher level of maintenance costs. Further, our facilities, equipment and information technology may need to be improved or renovated to maintain or increase operational efficiency, compete for patients and medical directors, or meet changing regulatory requirements. Increases in maintenance costs and/or capital expenditures could have, under certain circumstances, a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows.
Businesses we acquire may have unknown or contingent liabilities or liabilities that are in excess of the amounts that we originally estimated, and may have other issues, including, without limitation, those related to internal control over financial reporting or issues that could affect our ability to comply with healthcare laws and regulations and other laws applicable to our expanded business, which could harm our reputation. As a result, we cannot make any assurances that the acquisitions we consummate will be successful. Although we generally seek indemnification from the sellers of businesses we acquire for matters that are not properly disclosed to us, we are not always successful. In addition, even in cases where we are able to obtain indemnification, we may discover liabilities greater than the contractual limits, the amounts held in escrow for our benefit (if any), or the financial resources of the indemnifying party. In the event that we are responsible for liabilities substantially in excess of any amounts recovered through rights to indemnification or alternative remedies that might be available to us, or any applicable insurance, we could suffer severe consequences that would have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows and could materially harm our reputation.
In addition, under the terms of the equity purchase agreement for the DaVita Medical Group (DMG) sale (the DMG sale agreement), we agreed to certain indemnification obligations, including claims for taxes or for which we provided the buyer with a special indemnity. As a result, we may become obligated to make payments to the buyer relating to our previous ownership and operation of the DMG business. Any such post-closing liabilities and required payments under the DMG sale agreement, or otherwise, or in connection with any other past or future disposition of material assets or businesses could individually or in the aggregate have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows and could materially harm our reputation.
Additionally, joint ventures or noncontrolling interest investments inherently involve a lesser degree of control over business operations, thereby potentially increasing the financial, legal, operational and/or compliance risks associated with the joint venture or noncontrolling interest investment. In addition, we may be dependent on joint venture partners, controlling shareholders or management who may have business interests, strategies or goals that are inconsistent with ours. Business decisions or other actions or omissions of the joint venture partner, controlling shareholders or management may require us to make capital contributions or necessitate other payments, result in litigation or regulatory action against us, result in reputational harm to us or adversely affect the value of our investment or partnership, among other things. In addition, we have potential obligations to purchase the interests held by third parties in many of our joint ventures as a result of put provisions that are exercisable at the third party's discretion within specified time periods, pursuant to the applicable agreement. If these put provisions were exercised, we would be required to purchase the third party owner's equity interest, generally at the appraised market value. There can be no assurances that these joint ventures and/or noncontrolling interest investments ultimately will be successful.
If our joint ventures were found to violate the law, we could suffer severe consequences that would have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows and could materially harm our reputation.
As of December 31, 2024, we owned a controlling interest in numerous dialysis-related joint ventures, which represented approximately 30% of our U.S. dialysis revenues for the year ended December 31, 2024. In addition, we also owned noncontrolling equity investments in several other dialysis-related joint ventures. We expect to continue to increase the number of our joint ventures. Many of our joint ventures with physicians or physician groups also have certain physician owners providing medical director services to centers we own and operate. Because our relationships with physicians are governed by the federal and state anti-kickback statutes, we have sought to structure our joint venture arrangements to satisfy as many federal safe harbor requirements as we believe are commercially reasonable. Our joint venture arrangements do not satisfy all of the elements of any safe harbor under the federal Anti-Kickback Statute, however, and therefore are susceptible to government scrutiny. Additionally, our joint ventures and minority investments inherently involve a lesser degree of control over business operations, thereby potentially increasing the financial, legal, operational and/or compliance risks associated with the joint venture or minority investment. If our joint ventures are found to violate applicable laws or regulations, we could suffer severe consequences that would have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows and could materially harm our reputation. For additional information on these risks, see the risk factors under the headings "Our business is subject to a complex set of governmental laws, regulations and other requirements...;" and "We may engage in acquisitions, mergers, joint ventures, noncontrolling interest investments, or dispositions..."
Our goals and disclosures related to ESG matters expose us to numerous risks, including without limitation risks to our reputation and stock price.
We have a longstanding program relating to environmental, social and governance (ESG) issues and have engaged with key stakeholders to develop ESG focus areas and to set ESG-related goals, many of which are aspirational. We have set and disclosed these focus areas, goals and related objectives as part of our continued commitment to ESG matters, but our goals and objectives reflect our current plans and are not guarantees that we will be able to achieve them. Our efforts to accomplish and accurately report on these goals and objectives present numerous operational, reputational, financial, legal and other risks, certain of which are outside of our control, and could have, under certain circumstances, a material adverse impact on us, including on our reputation and stock price. Examples of such risks include, among others: the availability and cost of low- or non-carbon-based energy sources and technologies for us and our vendors, evolving regulatory requirements affecting ESG standards, frameworks and disclosures, including evolving standards for measuring and reporting on related metrics, the availability of suppliers that can meet our standards, our ability to recruit, develop and retain strong talent in our labor markets, and our ability to grow our home based dialysis business.
If our ESG practices do not meet investor or other stakeholder expectations and standards, then our reputation, our ability to attract or retain employees and our attractiveness as an investment, business partner or acquirer could be negatively impacted. In addition, if there are new regulations or orders that proscribe the ability to focus on ESG programs, then there would be a risk if we continued to pursue these goals. In addition, our failure or perceived failure to adequately pursue or fulfill our goals and objectives or to satisfy various reporting standards within the timelines we announce, or at all, could also have similar negative impacts and expose us to other risks, which under certain circumstances could be material. If we are not able to adequately recognize and respond to the rapid and ongoing developments and governmental and social expectations relating to ESG matters, this failure could result in missed corporate opportunities, additional regulatory, social or other scrutiny of us, the imposition of unexpected costs, or damage to our reputation with governments, patients, teammates, third parties and the communities in which we operate, which in turn could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, cash flows and results of operations and could cause the market value of our common stock to decline.
There are significant risks associated with estimating the amount of dialysis revenues and related refund liabilities that we recognize, and if our estimates of revenues and related refund liabilities are materially inaccurate, it could impact the timing and the amount of our revenues recognition or have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows.
There are significant risks associated with estimating the amount of U.S. dialysis patient service revenues and related refund liabilities that we recognize in a reporting period. The billing and collection process is complex due to ongoing insurance coverage changes, geographic coverage differences, differing interpretations of contract coverage and other payor issues, such as ensuring appropriate documentation. Determining applicable primary and secondary coverage for approximately 200,800 U.S. patients at any point in time, together with the changes in patient coverage that occur each month, requires complex, resource-intensive processes. Errors in determining the correct coordination of benefits may result in refunds to payors. Revenues associated with Medicare and Medicaid programs are also subject to estimating risk related to the amounts not paid by the primary government payor that will ultimately be collectible from other government programs paying secondary coverage, the patient's commercial health plan secondary coverage or the patient. Collections, refunds and payor retractions typically continue to occur for up to three years and longer after services are provided. We generally expect our range of U.S. dialysis patient service revenues estimating risk to be within 1% of revenues. If our estimates of U.S. dialysis patient service revenues and related refund liabilities are materially inaccurate, it could impact the timing and the amount of our revenues recognition and have a material adverse impact on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows.
General Risk Factors
The level of our current and future debt could have an adverse impact on our business, and our ability to generate cash to service our indebtedness and for other intended purposes and our ability to maintain compliance with debt covenants depends on many factors beyond our control.
We have a substantial amount of indebtedness outstanding and we may incur substantial additional indebtedness in the future, including indebtedness incurred to finance repurchases of our common stock pursuant to our share repurchase authorization discussed under "Stock Repurchases" in Part II Item 7. "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations." As described in Note 12 to the consolidated financial statements included in this report, we are party to a senior secured credit agreement (as amended, the Credit Agreement), which consists of an up to $1.5 billion secured revolving line of credit, a secured term loan A-1 facility and a secured term loan B-1 facility. Our long-term indebtedness also includes $5.250 billion aggregate principal amount of senior notes.
Our senior secured credit facilities bear, and other indebtedness we may incur in the future may bear, interest at a variable rate. As a result, at any given time interest rates on the senior secured credit facilities and any other variable rate debt could be higher or lower than current levels. If interest rates increase, our debt service obligations on our variable rate indebtedness will increase even though the amount borrowed remains the same, and therefore net income and associated cash flows, including cash available for servicing our indebtedness, will correspondingly decrease.
The variable interest rates payable under our senior secured credit facilities have historically been linked to LIBOR as the benchmark for establishing such rates. The LIBOR rate used in our senior secured credit facilities ceased to be available starting June 30, 2023. Prior to that date, we transitioned all the debt from our senior secured credit facilities from LIBOR to Secured Overnight Financing Rate (SOFR). SOFR is a broad measure of the cost of borrowing cash overnight collateralized by U.S. Treasury securities. The SOFR rate may not perform in a manner similar to LIBOR and may result in interest rates that are higher or lower than those that would have resulted had LIBOR remained in effect, which could impact our cost of capital.
Our ability to make payments on our indebtedness, to fund planned capital expenditures and expansion efforts, including, without limitation, any strategic acquisitions or investments we may make in the future, to repurchase our stock at the levels intended or announced and to meet our other liquidity needs such as for working capital or capital expenditures, will depend on our ability to generate cash. This depends not only on the success of our business but is also subject to economic, financial, competitive, regulatory and other factors that are beyond our control. We cannot provide assurances that our business will generate sufficient cash flows from operations in the future or that future borrowings will be available to us in amounts sufficient to enable us to service our indebtedness or to fund our working capital and other liquidity needs, including those described above. If we are unable to generate sufficient funds to service our outstanding indebtedness or to meet our working capital or other liquidity needs, including those described above, we would be required to refinance, restructure, or otherwise amend some or all of such indebtedness, sell assets, change or reduce our intended or announced uses or strategy for capital deployment, including, without limitation, for stock repurchases, reduce capital expenditures, planned expansions or other strategic initiatives, or raise additional cash through the sale of our equity or equity-related securities. We cannot make any assurances that any such refinancing, restructurings, amendments, sales of assets, or issuances of equity or equity-related securities can be accomplished or, if accomplished, will be on favorable terms or would raise sufficient funds to meet these obligations or our other liquidity needs.
In addition, we may continue to incur indebtedness in the future, and the amount of that additional indebtedness may be substantial. Although the Credit Agreement includes covenants that could limit our indebtedness, we currently have, and expect to continue to have, the ability to incur substantial additional debt. The risks described in this risk factor could intensify as new debt is added to current debt levels or if we incur any new debt obligations that subject us to restrictive covenants that limit our financial and operational flexibility. Any breach or failure to comply with any of these covenants could result in a default under our indebtedness. Other risks related to our ability to generate sufficient cash to service our indebtedness and for other intended purposes, include, for example:
•increase our vulnerability to general adverse economic and industry conditions;
•limit our flexibility in planning for, or reacting to, changes in our business and the markets in which we operate;
•expose us to interest rate volatility that could adversely affect our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows, and our ability to service our indebtedness;
•place us at a competitive disadvantage compared to our competitors that have less debt; and
•limit our ability to borrow additional funds, or to refinance existing debt on favorable terms when otherwise available or at all.
Any failure to pay any of our indebtedness when due or any other default under our credit facilities or our other indebtedness could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows, and could trigger cross default or cross acceleration provisions in our other debt instruments, thereby permitting the holders of that other indebtedness to demand immediate repayment or cease to make future extensions of credit, and, in the case of secured indebtedness, to take possession of and sell the collateral securing such indebtedness to satisfy our obligations.
The borrowings under our senior secured credit facilities and senior indentures are guaranteed by certain of our domestic subsidiaries, and borrowings under our senior secured credit facilities are secured by substantially all of our and certain of our domestic subsidiaries' assets. Such guarantees and the fact that we have pledged such assets may make it more difficult and expensive for us to make, or under certain circumstances could effectively prevent us from making, additional secured and unsecured borrowings.
We could be subject to adverse changes in tax laws, regulations and interpretations or challenges to our tax positions.
We are subject to tax laws and regulations of the U.S. federal, state and local governments as well as various foreign jurisdictions. We compute our income tax provision based on enacted tax rates in the jurisdictions in which we operate. As the tax rates vary among jurisdictions, a change in earnings attributable to the various jurisdictions in which we operate could result in a change in our overall tax provision.
Changes in tax laws or regulations may be proposed or enacted that could adversely affect our overall tax liability. There can be no assurance that changes in tax laws or regulations, both within the domestic and foreign jurisdictions in which we operate, will not materially and adversely affect our effective tax rate, tax payments, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows. Similarly, changes in tax laws and regulations that impact our patients, business partners and counterparties or the economy may also impact our results of operations, financial condition and cash flows.
In addition, tax laws and regulations are complex and subject to varying interpretations, and any significant failure to comply with applicable tax laws and regulations in all relevant jurisdictions could give rise to material penalties and liabilities. We are regularly subject to audits by various tax authorities. It is possible that the final determination of any such tax audits and any related litigation could be materially different from our historical income tax provisions and accruals. Any changes in enacted tax laws, rules or regulatory or judicial interpretations; any adverse development or outcome in connection with tax audits in any jurisdiction; or any change in the pronouncements relating to accounting for income taxes could materially and adversely impact our effective tax rate, tax payments, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows.
The effects of natural or other disasters, political instability, public health crises or adverse weather events such as hurricanes, earthquakes, fires or flooding could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows.
Some of our operations, including our clinical laboratory, dialysis centers and other facilities, as well as the operations of our third party suppliers and service providers, may be adversely impacted by the effects of natural or other disasters, political instability, public health crises such as global pandemics or epidemics, or adverse weather events such as hurricanes, earthquakes, fires or flooding. Each of these effects and risks may be further intensified by the potential impact of climate change on a global scale. In addition, these risks are particularly heightened for our patients in part because individuals with chronic illness may be more susceptible to the adverse effects of epidemics or other public health crises and also because any natural or other disaster, political instability or adverse weather event that disrupts or limits the operation of any of our centers or other facilities or services may delay or otherwise impact the critical services we provide to dialysis patients. Further, any such event or other occurrence that results in a failure of the fitness of our clinical laboratory, dialysis centers and related operations and/or other facilities or the operations of our third party suppliers and service providers or otherwise adversely impacts the safety of our teammates or patients at any of those locations could lead us to face adverse consequences, including, without limitation, the potential loss of data, including PHI or PII, compliance or regulatory investigations, any of which could materially impact our business, results of operations and financial condition, and could materially harm our reputation. For example, our clinical laboratory is located in Florida, a state that has in the past experienced and may in the future experience hurricanes. Natural or other disasters or adverse weather events could significantly damage or destroy our facilities, disrupt operations, increase our costs to maintain operations and require substantial expenditures and recovery time to fully resume operations. In addition, if the frequency, intensity and widening potential geographic scope of natural or other disasters or adverse weather events increase or a number of laws or regulations adopted in response to such changes, we may face increased costs associated with operating our clinics, as well as potential interruptions to and changes in our clinical and business operations, including, without limitation, with respect to increasing costs for energy, supplies of water, or pharmaceuticals or other supplies necessary to the operations or our clinics. For additional information regarding the risks to our supply chain and third party service providers, see the discussion in the risk factor under the heading "If certain of our suppliers and service providers…"
Our presence in markets outside the U.S. may increase our exposure to these and similar risks related to natural disasters, public health crises, political instability, adverse weather or other catastrophic events outside our control. For additional information regarding the risks related to our international business, see the discussion in the risk factor under the heading "Expansion of our operations to and offering our services in markets outside of the U.S...."
Any or all of these factors, as well as other consequences of these events, none of which we can currently predict, could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows or materially harm our reputation.
We may be subject to liability claims for damages and other expenses that are not covered by insurance or exceed our existing insurance coverage that could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows and could materially harm our reputation.
Our operations and how we manage our business may subject us, as well as our officers and directors to whom we owe certain defense and indemnity obligations, to litigation and liability. Our business, profitability and growth prospects could suffer if we face negative publicity or we pay damages or defense costs in connection with a claim that is outside the scope or limits of coverage of any applicable insurance coverage, including, without limitation, claims related to adverse patient events, cybersecurity incidents, contractual disputes, antitrust and competition laws and regulations, professional and general liability and directors' and officers' duties. In addition, we have received notices of claims from commercial payors and other third parties, as well as subpoenas and civil investigative demands from the federal government, related to our business practices, including, without limitation, our historical billing practices and the historical billing practices of acquired businesses. Although the ultimate outcome of these claims cannot be predicted, an adverse result with respect to one or more of these claims could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows, and could materially harm our reputation. We maintain insurance coverage for those risks we deem are appropriate to insure against and make determinations about whether to self-insure as to other risks or layers of coverage. However, a successful claim, including, without limitation, a professional liability, malpractice or negligence claim or a claim related to antitrust and competition laws or a cybersecurity incident, which is in excess of any applicable insurance coverage, that is outside the scope or limits of any applicable insurance coverage, or that is subject to our self-insurance retentions, could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition, cash flows and reputation.
In addition, if our costs of insurance and claims increase, then our earnings could decline. Market rates for insurance premiums and deductibles have been steadily increasing. Our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows could be materially and adversely affected by any of the following:
•the collapse or insolvency of our insurance carriers;
•further increases in premiums and deductibles;
•increases in the number of liability claims against us or the cost of settling or trying cases related to those claims;
•obtaining insurance with exclusions for things such as communicable diseases; or
•an inability to obtain one or more types of insurance on acceptable terms, if at all.
If we fail to successfully maintain an effective internal control over financial reporting, the integrity of our financial reporting could be compromised, which could have a material adverse effect on our ability to accurately report our financial results, the market's perception of our business and our stock price.
The integration of acquisitions and addition of new business lines into our internal control over financial reporting has required and will continue to require significant time and resources from our management and other personnel and has increased, and is expected to continue to increase, our compliance costs. Failure to maintain an effective internal control environment could have a material adverse effect on our ability to accurately report our financial results, the market's perception of our business and our stock price. In addition, we could be required to restate our financial results in the event of a significant failure of our internal control over financial reporting or in the event of inappropriate application of accounting principles.
Provisions in our organizational documents, our compensation programs and policies and certain requirements under Delaware law may deter changes of control and may make it more difficult for our stockholders to change the composition of our Board of Directors and take other corporate actions that our stockholders would otherwise determine to be in their best interests.
Our organizational documents include provisions that may deter hostile takeovers, delay or prevent changes of control or changes in our management, or limit the ability of our stockholders to approve transactions that they may otherwise determine to be in their best interests. These include provisions prohibiting our stockholders from acting by written consent, advance notice requirements for director nominations and stockholder proposals and granting our Board of Directors the authority to issue preferred stock and to determine the rights and preferences of the preferred stock without the need for further stockholder approval.
Most of our outstanding employee stock-based compensation awards include a provision accelerating the vesting of the awards in the event of a change of control under certain circumstances. These and any other change of control provisions may affect the price an acquirer would be willing to pay for our Company.
We are also subject to Section 203 of the Delaware General Corporation Law that, subject to exceptions, prohibits us from engaging in any business combinations with any interested stockholder, as defined in that section, for a period of three years following the date on which that stockholder became an interested stockholder.
The provisions described above may discourage, delay or prevent an acquisition of our Company at a price that our stockholders may find attractive. These provisions could also make it more difficult for our stockholders to elect directors and take other corporate actions and could limit the price that investors might be willing to pay for shares of our common stock.
Item 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments
None.
Item 1C. Cybersecurity
Risk Management and Strategy
Information security risks have significantly increased in recent years in part because of the proliferation of new technologies, the increasing use of the Internet and telecommunications technologies to conduct our operations, and the increased sophistication and activities of organized crime, hackers, terrorists and other external parties, including, among others, foreign state agents. Our business and operations rely on the secure and continuous processing, transmission and storage of confidential, proprietary and other information in our computer systems and networks, including, but not limited to, sensitive personal information, such as PHI, social security numbers, and/or credit card information of our patients, teammates, physicians, business partners and others. Our business and operations also rely on certain critical IT vendors that support such processing, transmission and storage (which have become more relevant and important given the information security issues and risks that are intensified through our increased use of remote work arrangements).
To manage risks to our Company, including information and security risks, our Board oversees our enterprise-wide approach to risk management with a fundamental belief that the key components of risk management are:
•Identifying potential risks that we face;
•Assessing the likelihood and potential impact of the risks;
•Adopting strategies and controls designed to manage the risks;
•Reporting on a regular basis regarding the assessment and management of the risks;
•Monitoring these potential risks on a regular basis; and
•Evaluating whether there are new potential risks to assess.
Under our Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) process, the Company evaluates risks to the enterprise on short, intermediate and long-term bases. The ERM Committee, a group comprised of members of senior management, meet on a regular basis to oversee the performance of these risk management functions. We assess risks using a probability-magnitude lens, with shorter and intermediate term risks generally given greater weight. We prioritize mitigating activities on shorter and intermediate term risks, but also use risk analyses and oversight to proactively incorporate mitigating activities into our long-term strategy. The ERM process reflects a Company-wide effort designed to identify, assess, manage, report and monitor enterprise risks and risk areas. This effort includes the Company's Enterprise Risk Services (Internal Audit), Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX), Compliance Audit, legal and IT security teams, among others. The identification and evaluation of cybersecurity threats and risks is integrated into this ERM process.
The ERM process is incorporated into our disclosure controls and procedures. Representatives of each of our ERM, Internal Audit, legal and compliance teams sit on the Company’s management Disclosure Committee, which is responsible for, among other things, the design and establishment of disclosure controls and procedures to help ensure the timeliness, accuracy and completeness of corporate disclosure. Our IT security and privacy teams, who are responsible for assessing cybersecurity threats and risks, in turn maintain policies and procedures designed to ensure appropriate escalation of cybersecurity incidents to meet external disclosure requirements. Our Chief Information Officer (CIO) and Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) regularly meet and coordinate with our Chief Privacy Officer (CPO). Each of the CIO, CISO and CPO also advise members of the Disclosure Committee, including our Chief Legal and Public Affairs Officer (CLO), on disclosure matters on an as-needed basis.
With respect to assessing privacy, data and cybersecurity risks, the Company adopts a hybrid approach that primarily aligns with the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Cybersecurity Framework, including the guidance set
forth in the NIST HIPAA Security Rule Cybersecurity Guide, while also evaluating against certain elements of the ISO 27001 and 27005 standards that management believes provide additional levels of guidance or structure. We regularly evaluate the Company’s cybersecurity and privacy processes and procedures, both through regular audits by our Internal Audit and IT security teams, as well as regular retention of outside advisors under direction of our IT security team. Among other things, the IT security team oversees an external third party review at least every two years that evaluates the readiness of the entire Company against the NIST Cybersecurity Framework and provides an assessment that measures Capability Maturity Model Integration levels. Additionally, our CISO engages in regular consultations, typically monthly, with third-party cybersecurity advisors. Among other things, these sessions provide the Company with a broader review of the external cybersecurity environment, helping us to stay current on emerging or developing security approaches and risks. Among other initiatives, our CISO and the Company’s IT security team actively participate in industry conferences and maintain memberships to resources such as the Health Information Sharing and Analysis Center (Health-ISAC), a trusted community of critical infrastructure owners and operators within the Health Care and Public Health sector which, among other things, allows the Company to monitor email updates and alerts coordinated with the U.S. Department of Homeland Security’s Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency. In order to maintain awareness of privacy, data and cybersecurity risks, the Company incorporates these topics into its annual compliance training materials that are mandatory for all teammates and new hires, and among other things cover HIPAA privacy and security requirements.
We maintain policies and have established processes involving our IT security, privacy and legal teams that assess potential cybersecurity risks associated with our retention and use of third-party service providers. These policies and procedures are generally aligned with the NIST Cybersecurity Framework. Prior to retaining or renewing a third-party vendor, the Company policy requires a risk assessment of such potential new vendor or new engagement through a collaborative process among the Company’s IT security, privacy, insurance and legal teams, among others. Potential vendor engagements also are reviewed to assess a range of other considerations and contractual terms and conditions, including, among other things, a potential vendor’s liability insurance limits, scope and coverage of cyber insurance and privacy data protections. Our IT SOX team also conducts annual SOX reviews for those vendors that are considered in scope for SOX controls. All finalized vendor engagements are considered by Internal Audit as part of our ordinary course risk assessment and audit planning.
Cybersecurity Risks and the Impact on our Company
Due to the continuously evolving series of laws and regulations related to cybersecurity, data protection and privacy that are applicable to our business, as well as the associated risks from cybersecurity threats, we have expended significant resources in order to protect our information systems and data. We regularly review, monitor and implement multiple layers of security measures through technology, processes and our people. We utilize security technologies designed to protect and maintain the integrity of our information systems and data, and our defenses are monitored and routinely tested internally and by external parties. Despite these efforts, our facilities and systems and those of our third-party service providers may be vulnerable to privacy and security incidents; security attacks and breaches; acts of vandalism or theft; computer viruses and other malicious code; coordinated attacks by a variety of actors, including, among others, activist entities or state sponsored cyberattacks; emerging cybersecurity risks; cyber risk related to connected devices; misplaced or lost data; programming and/or human errors; or other similar events that could impact the security, reliability and availability of our systems. Internal or external parties have attempted to, and will continue to attempt to, circumvent our security systems, and we have in the past, and expect that we will in the future, defend against, experience, and respond to attacks on our network including, without limitation, reconnaissance probes, denial of service attempts, malicious software attacks including ransomware or other attacks intended to render our internal operating systems or data unavailable, and phishing attacks or business email compromise. While we have experienced cybersecurity incidents in the past, to date none have had a material impact on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows.
Cybersecurity requires ongoing investment and diligence against evolving threats and in the context of new or developing technologies. For further information regarding the risks we face from cybersecurity threats and how our business strategy, results of operations, and financial condition could be materially affected by such risks, see Part I Item IA. "Risk Factors" under the heading, "Privacy and information security laws are complex…".
Governance
Board Oversight
As part of its oversight responsibilities, the Audit Committee monitors privacy, data and cybersecurity as specific risk areas. The Audit Committee also works with the Compliance and Quality Committee to oversee enterprise risks with healthcare and anti-corruption requirements, and those requirements include certain privacy, data and cybersecurity aspects. Both Mr. Schechter, a member of the Audit Committee, and Ms. Schoppert, a member of the Audit Committee, hold a CERT Certificate in Cybersecurity Oversight. The Audit Committee engages in regular discussions with management on privacy, data, and
cybersecurity risk exposures, receiving quarterly reports from the ERM team and the CIO. On a periodic basis, the full Board of Directors also receives these reports from the ERM team and the CIO. The CPO and/or CLO periodically reports to the Audit Committee about the Company’s privacy program, and Internal Audit reports to the Audit Committee quarterly, providing the Audit Committee with results from any privacy, data, or cybersecurity audits.
Among other things, the Company’s privacy team actively develops and implements policies designed to comply with the requirements of privacy laws in the countries where the Company operates. Working with Internal Audit and the CIO, the privacy team assesses the nature and potential severity of privacy risks within DaVita and guides the organization in taking steps to help mitigate such risks. The Audit Committee also oversees the Company's negotiation of any cybersecurity insurance. Currently, the Company maintains a cybersecurity risk insurance policy providing coverage for certain cybersecurity breaches among other specified risks.
Management
As referenced above, our IT security team, in consultation with our privacy team, is primarily responsible for frontline assessments and management of day-to-day risks from cybersecurity threats, including the monitoring and detection of cybersecurity incidents and the execution of DaVita's cybersecurity and privacy incident response plans, as needed. Pursuant to the plan, the teams are responsible for assessing and classifying cybersecurity incidents and coordinating the response to such incidents, including managing both internal and external reporting obligations and remediation efforts. Our key personnel responsible for privacy and cybersecurity expertise include our CIO, CISO and CPO. Their qualifications include expertise in international privacy laws, compliance, global IT strategy, and security responsibilities, helping to ensure a comprehensive approach to risk management. Our CISO has more than two decades of experience in information technology risk and compliance and holds a Certified Chief Information Security Officer certification from EC-Council, a Certified Information Security Manager certification from ISACA and a certification from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology on AI management in healthcare. Our CPO is a Certified Information Privacy Professional and a Certified Compliance and Ethics Professional, and has more than two decades of experience in creating and implementing privacy and data protection programs that enable multinational organizations to respect and protect personal data and execute mission critical business strategies.
Our IT security team also operates a 24x7 security operations center through a managed service provider. This dedicated center, alongside active monitoring of the dark web for DaVita-related data, and our use of both internal and external tools, is designed to ensure proactive detection, prevention and remediation of cybersecurity incidents. We inform and develop this integrated approach through our ongoing internal and external evaluations and risk assessments of our IT security program as described above.
Item 2. Properties
Our corporate headquarters are located in Denver, Colorado, consisting of one owned office building and one leased office building. We lease space for our international headquarters located in the United Kingdom. Our laboratory is based in Florida where we operate our lab services out of one leased building. We also lease other administrative offices in the U.S. and worldwide.
The vast majority of our U.S. and international outpatient dialysis centers are leased. We believe that if we were unable to renew a lease of a dialysis center or administrative office, we could find alternative space at competitive market rates and relocate our operations to such new location without material disruption to our business. See Note 13 to the consolidated financial statements included in this report for information regarding our leases and "Location of our U.S. dialysis centers" under Part I Item 1. "Business" for the locations of our U.S. dialysis centers.
Item 3. Legal Proceedings
The information required by this Part I Item 3 is incorporated herein by reference to the information set forth under the caption "Contingencies" in Note 15 to the consolidated financial statements included in this report.
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures
Not applicable.
PART II
Item 5. Market for the Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of
Equity Securities
Our common stock is traded on the New York Stock Exchange under the symbol DVA. The closing price of our common stock on January 31, 2025 was $176.20 per share. According to Computershare, our registrar and transfer agent, as of January 31, 2025, there were 6,265 holders of record of our common stock. This figure does not include the indeterminate number of beneficial holders whose shares are held of record by brokerage firms and clearing agencies.
Our initial public offering was in 1994, and we have not declared or paid cash dividends to holders of our common stock since going public. We have no current plans to pay cash dividends and there are certain limitations on our ability to pay dividends under the terms of our senior secured credit facilities. See "Liquidity and capital resources" under Item 7. "Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations" and the notes to the consolidated financial statements.
Stock Repurchases
The following table summarizes our repurchases of our common stock during 2024:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Period | Total number
of shares
purchased | | Average price paid per share (1) | | Total number of shares purchased as part of publicly announced plans or programs | | Approximate dollar value
of shares that may yet be purchased under the plans or programs |
| (dollars and shares in thousands, except per share data) |
| January 1 - March 31, 2024 | 2,119 | | | $ | 112.76 | | | 2,119 | | | $ | 1,072,904 | |
| April 1 - June 30, 2024 | 2,655 | | | 140.14 | | | 2,655 | | | $ | 700,748 | |
| July 1 - September 30, 2024 | 2,734 | | | 147.20 | | | 2,734 | | | $ | 2,298,315 | |
| October 1 - December 31, 2024 | 2,325 | | | 156.46 | | | 2,325 | | | $ | 1,934,499 | |
| Total | 9,833 | | | $ | 140.06 | | | 9,833 | | | |
(1)Excludes commissions and the 1% excise tax imposed by the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022.
As of December 31, 2024, we are authorized to make share repurchases pursuant to a September 5, 2024 Board authorized repurchase plan of $2.0 billion. This authorization allows us to make purchases from time to time in the open market or in privately negotiated transactions, including without limitation, through accelerated share repurchase transactions, derivative transactions, tender offers, Rule 10b5-1 plans or any combination of the foregoing, depending upon market conditions and other considerations.
As of February 13, 2025, we have a total of $1.811 billion, excluding excise taxes, available under the current repurchase authorization for additional share repurchases. Although this share repurchase authorization does not have an expiration date, we remain subject to share repurchase limitations, including under the terms of our senior secured credit facilities.
Item 6. Reserved
Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
Forward-looking statements
This Annual Report on Form 10-K, including this Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations, contains statements that are forward-looking statements within the meaning of the federal securities laws and as such are intended to be covered by the safe harbor for "forward-looking statements" provided by the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. These forward-looking statements could include, among other things, statements about our balance sheet and liquidity, our expenses, revenues, billings and collections, patient census, availability or cost of supplies, including without limitation the impact of any reduction in clinical and other supplies due to any disruptions experienced by third party vendors, including with respect to our ability to provide home dialysis services, treatment volumes, mix expectation, such as the percentage or number of patients under commercial insurance, the effects on us and our operations of any interruptions in key functions performed by our third party service providers or suppliers, current macroeconomic, marketplace and labor market conditions, and overall impact on our patients and teammates, as well as other statements regarding our future operations, financial condition and prospects, capital allocation plans, expenses, cost saving initiatives, other strategic initiatives, use of contract labor, government and commercial payment rates, expectations related to value-based care (VBC), integrated kidney care (IKC), Medicare Advantage (MA) plan enrollment and our international operations, expectations regarding increased competition and marketplace changes, including those related to new or potential entrants in the dialysis and pre-dialysis marketplace and the potential impact of innovative technologies, drugs, or other treatments on the dialysis industry, and expectations regarding our stock repurchase program. All statements in this report, other than statements of historical fact, are forward-looking statements. Without limiting the foregoing, statements including the words "expect," "intend," "will," "could," "plan," "anticipate," "believe" and similar expressions are intended to identify forward-looking statements. These forward-looking statements are based on DaVita's current expectations and are based solely on information available as of the date of this report. DaVita undertakes no obligation to publicly update or revise any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of changed circumstances, new information, future events or otherwise, except as may be required by law. Actual future events and results could differ materially from any forward-looking statements due to numerous factors that involve substantial known and unknown risks and uncertainties. These risks and uncertainties include, among other things:
•external conditions, including those related to general economic, marketplace and global health conditions, including without limitation, the impact of global events and political or governmental volatility; the impact of the domestic political environment and related developments on the current healthcare marketplace, our patients and on our business; the continuing impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on our financial condition and the chronic kidney disease (CKD) population and our patient population; supply chain challenges and disruptions, including without limitation with respect to certain key services, critical clinical supplies and equipment we obtain from third parties, and including any impacts on our supply chain as a result of natural disasters; the potential impact of new or potential entrants in the dialysis and pre-dialysis marketplace and potential impact of innovative technologies, drugs, or other treatments on our patients and industry; elevated teammate turnover or labor costs; the impact of continued increased competition from dialysis providers and others; and our ability to respond to challenging U.S. and global economic and marketplace conditions, including, among other things, our ability to successfully identify cost saving opportunities;
•the concentration of profits generated by higher-paying commercial payor plans for which there is continued downward pressure on average realized payment rates; a reduction in the number or percentage of our patients under commercial plans, including, without limitation, as a result of continuing legislative efforts to restrict or prohibit the use and/or availability of charitable premium assistance, or as a result of payors implementing restrictive plan designs;
•risks arising from potential changes in or new laws, regulations or requirements applicable to us, including, without limitation, those related to healthcare, privacy, antitrust matters, and acquisition, merger, joint venture or similar transactions and/or labor matters, and potential impacts of changes in interpretation or enforcement thereof or related litigation impacting, among other things, coverage or reimbursement rates for our services or the number of patients enrolled in or that select higher-paying commercial plans, and the risk that we make incorrect assumptions about how our patients will respond to any such developments;
•our ability to successfully implement our strategies with respect to IKC and VBC initiatives and home based dialysis in the desired time frame and in a complex, dynamic and highly regulated environment;
•a reduction in government payment rates under the Medicare End Stage Renal Disease program, state Medicaid or other government-based programs and the impact of the MA benchmark structure;
•our reliance on significant suppliers, service providers and other third party vendors to provide key support to our business operations and enable our provision of services to patients, including, among others, suppliers of certain pharmaceuticals, administrative or other services or critical clinical products; and risks resulting from a closure,
reduction or other disruption in the services or products provided to us by such suppliers, service providers and third party vendors;
•noncompliance by us or our business associates with any privacy or security laws or any security breach by us or a third party, including, among other things, any such non-compliance or breach involving the misappropriation, loss or other unauthorized use or disclosure of confidential information;
•legal and compliance risks, such as compliance with complex, and at times, evolving government regulations and requirements, and with additional laws that may apply to our operations as we expand geographically or enter into new lines of business;
•our ability to attract, retain and motivate teammates, including key leadership personnel, and our ability to manage potential disruptions to our business and operations, including potential work stoppages, operating cost increases or productivity decreases whether due to union organizing activities, legislative or other changes, demand for labor, volatility and uncertainty in the labor market, the current challenging and highly competitive labor market conditions, including due to the ongoing nationwide shortage of skilled clinical personnel, or other reasons;
•changes in pharmaceutical practice patterns, reimbursement and payment policies and processes, or pharmaceutical pricing, including with respect to oral phosphate binders, among other things;
•our ability to develop and maintain relationships with physicians and hospitals, changing affiliation models for physicians, and the emergence of new models of care or other initiatives that, among other things, may erode our patient base and impact reimbursement rates;
•our ability to complete and successfully integrate and operate acquisitions, mergers, dispositions, joint ventures or other strategic transactions on terms favorable to us or at all; and our ability to continue to successfully expand our operations and services in markets outside the United States, or to businesses or products outside of dialysis services;
•the variability of our cash flows, including, without limitation, any extended billing or collections cycles including, without limitation, due to defects or operational issues in our billing systems or in the billing systems or services of third parties on which we rely; the risk that we may not be able to generate or access sufficient cash in the future to service our indebtedness or to fund our other liquidity needs;
•the effects on us or others of natural or other disasters, public health crises or severe adverse weather events such as hurricanes, earthquakes, fires or flooding;
•factors that may impact our ability to repurchase stock under our stock repurchase program and the timing of any such stock repurchases, as well as any use by us of a considerable amount of available funds to repurchase stock;
•our goals and disclosures related to environmental, social and governance (ESG) matters, including, among other things, evolving regulatory requirements affecting ESG standards, measurements and reporting requirements; and
•the other risk factors, trends and uncertainties set forth in Part I Item 1A. of this Annual Report on Form 10-K, and the other risks and uncertainties discussed in any subsequent reports that we file or furnish with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) from time to time.
The following should be read in conjunction with our consolidated financial statements.
Company overview
Our principal business is to provide dialysis and related lab services to patients in the United States, which we refer to as our U.S. dialysis business. We also operate our U.S. integrated kidney care (IKC) business, our U.S. other ancillary services, and our international operations, which we collectively refer to as our ancillary services, as well as our corporate administrative support functions. Our U.S. dialysis business is a leading provider of kidney dialysis services in the U.S. for patients suffering from chronic kidney failure, also known as end stage renal disease (ESRD) or end stage kidney disease (ESKD).
Operational and financial highlights for 2024 include, among other things:
•U.S. dialysis revenue growth of 4.2% from an increase in average patient services revenue per treatment of $13.88;
•revenue growth of 16.2% in our other ancillary businesses, primarily in our international operations;
•operating income of $2,090 million and adjusted operating income of $1,981 million;
•operating cash flows of $2,022 million and free cash flows of $1,162 million;
•repurchase of 9,832,705 shares of our common stock for aggregate consideration of $1,389 million, and a 9.3% reduction in our outstanding share count year-over-year;
•entered into an amendment to our senior secured credit agreement which extended the maturity date of a portion of our Term Loan B-1 in the aggregate principal amount of $1,640 million. We further amended the senior secured credit agreement to incur an incremental Term Loan A-1 tranche in the aggregate principal amount of $1,100 million and issued an aggregate principal amount of $1,000 million of 6.875% senior notes due 2032. A portion of the proceeds of these transactions was used to repay the Term Loan B-1 maturing in 2026 of approximately $950 million;
•we purchased an additional $2,500 million notional amount of forward interest rate caps to shield our exposure to significant interest rate increases through 2027; and
•leverage ratio, as a multiple of Consolidated EBITDA, each as defined by our credit agreement, remained within our target range of 3.0x to 3.5x throughout 2024.
Additional highlights include:
•a net increase in consolidated patient growth of 12.4%, with flat patient growth in U.S. dialysis and 62.6% international patient growth as of December 31, 2024;
•a net decrease of 18 U.S. dialysis centers as we continued to improve center capacity utilization, as well as a net increase of 142 international dialysis centers from acquisitions; and
•continued patient growth in IKC to 70,400 patients in risk-based integrated care arrangements and an additional 11,600 patients in other integrated care arrangements.
In 2025, we expect relatively flat year-over-year treatment volumes due to a number of factors. These include, among other things, elevated mortality levels relative to pre-pandemic levels; the continued impact of missed treatment rates, which in recent years have been impacted by increased hospitalizations and the prevalence of severe weather events; and the impact of the supply disruption affecting our home dialysis supplies. We expect operating income growth resulting from revenue per treatment improvements, primarily driven by rate increases, the net impact of our continued improvements in our billing and collections process, mix improvement and the incorporation of oral phosphate binder reimbursement into the bundle, as described below. We expect an increase in costs per treatment due to the oral phosphate binders and inflationary increases in labor and other costs, partially offset by a decline in center closure costs. In 2025, we also expect operating growth in our international business as we continue our expansion in international markets and we expect results in our 2025 integrated kidney care business to be consistent with 2024. We expect a continued increase in debt expense in 2025 due in part to the financing transactions announced in 2024 and the expiration of our 2019 interest cap agreements in 2024 as described below. Finally, considerable uncertainty remains surrounding the continued implementation and development of the various governmental laws, regulations and other requirements that may impact our business, including the extent to the which such developments impact the behavior of other health care market participants such as payors, employers, charitable organizations and government agencies.
The discussion below includes analysis of our financial condition and results of operations for the years ended December 31, 2024 compared to December 31, 2023. Our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2023,
includes a discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations for the year ended December 31, 2022, in its Part II Item 7, "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations."
References to the "Notes" in the discussion below refer to the notes to the Company's consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K at Part IV Item 15, "Exhibits, Financial Statement Schedules" as referred from Part II Item 8, "Financial Statements and Supplementary Data."
General Economic, Marketplace and Global Health Conditions; Legal and Regulatory Developments
As noted above and described below, developments in general economic, marketplace and global health conditions have directly and indirectly impacted the Company and in the future could have a material adverse impact on our patients, teammates, physician partners, suppliers, business, operations, reputation, financial condition, results of operations, share price, cash flows and/or liquidity. Many of these external factors and conditions are interrelated, including, among other things, inflation, interest rate volatility, and other economic conditions, labor market conditions, wage pressure, the increased mortality rates of our patients and other ESKD or CKD patients, supply chain challenges and the potential impact and application of innovative technologies, drugs or other treatments. Certain of these impacts could be further intensified by concurrent global events, which have continued to drive sociopolitical, geopolitical and economic uncertainty; severe weather events and other natural disasters, which have impacted national supply chain challenges; the impact of new policies implemented by the new administration in the United States, which have affected certain government sponsored programs, among other things. For additional discussion of general economic, marketplace and global health conditions that could impact our business, see Part I Item 1. "Business" and Part I Item 1A. "Risk Factors."
Operational and Financial Impacts
On a full year basis, we experienced a negative impact on revenue and treatment volume due to, among other things, continued elevated mortality rates of our patients in comparison to the periods prior to the COVID-19 pandemic and the associated impact on our patient census, missed treatments driven by severe weather events and the impact of a temporary pause in home dialysis starts that resulted from the closure of one of our supplier's facilities. Treatment volumes during the year were also adversely impacted by continued elevated missed treatment rates, which during 2024 were driven primarily by severe weather events. New-to-dialysis admission rates, treatment volumes, future revenues and non-acquired growth, among other things, could continue to be negatively impacted over time to the extent that the ESKD and CKD populations experience sustained elevated mortality levels. These mortality levels could be influenced by, among other things, the availability and use of vaccines, treatments and therapies. As described in Part I Item 1A. "Risk Factors," the magnitude of these cumulative impacts could have a material adverse impact on our results of operations, financial condition and cash flows.
Ongoing global economic conditions and political and regulatory developments, such as general labor, supply chain and inflationary pressures have increased, and will likely continue to increase, our expenses, including, among others, staffing, labor and supply costs. We have also experienced service disruptions relating to key business functions and supply chain shortages with respect to certain of our equipment and clinical supplies, including critical clinical and other supplies. Certain of these disruptions related to external conditions, such as the aforementioned severe weather event that impacted our supply chain for key products as well as the cybersecurity incident at Change Healthcare (CHC) that impacted our billing operations. As described in Part I Item 1A. "Risk Factors" under the heading, "If certain of our supplier and service providers…", any disruption involving such suppliers could materially impact our operations and require significant resources or operational changes in response.
We expect certain of these increased staffing and labor costs to continue into 2025, due to, among other factors, the continuation of inflationary conditions and a challenging healthcare labor market. The cumulative impact of these increased costs could be material. During 2024, our industry also continued to experience increased union organizing activities. For example, union petitions have been filed in nine of our clinics in California and eight of these petitions are in different stages of the voting process and have been subject to legal challenges. For additional details on the risks related to rising labor costs and union organizing activities, see the discussion in Part I Item 1A. "Risk Factors" under the headings, "Our business is labor intensive..." and "External conditions, including those related to general economic, marketplace and global health conditions..."
Legal and Regulatory Developments
As noted above, the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) published in the federal register a final rule that would generally ban all post-employment personal service non-compete clauses with employees and prohibit employers from enforcing existing non-compete clauses in contracts with workers, with limited exceptions. Even though the rule has been enjoined, many state legislatures continue to introduce legislation that seeks to place limitations on restrictive covenants with workers. For additional details on federal and state regulations or future federal or state regulations and the potential impact on our business, see the
discussion in Part I Item 1. "Business" under the heading "U.S. Dialysis Business" and Part I Item 1A. "Risk Factors" under the heading, "Changes in federal and state legislation and regulations..."
Change Healthcare
As noted above and previously reported, due to a cybersecurity breach that affected CHC, a subsidiary of UnitedHealth Group Incorporated (United) that serves as an intermediary for processing the vast majority of our payment claims for domestic commercial and government payors, we temporarily suspended all claims processing activity with CHC (CHC Outage), primarily during a period of time during the first and second quarters of 2024, which impacted our cash flows. We have since resumed claims submissions and billing processes through CHC’s information technology systems and as of the date of this filing, through a combination of CHC's platform and certain alternate billing processes, we are current on our primary claims submissions. However, the CHC Outage, and the resultant delay in claims submissions, led to an increase in our days sales outstanding (DSO), among other things. That DSO increase has subsided, but we do continue to see delays in, and issues with, collections with some payors. For additional details on the CHC Outage and a discussion of the risks associated with outages, disruptions or incidents at third parties on which we rely, see the discussion in Part I Item 1A. "Risk Factors" under the headings, "Failing to effectively maintain, operate or upgrade our information systems or those of third-party service providers upon which we rely..." and "Privacy and information security laws are complex…"
We believe that the aforementioned recent developments and general economic, marketplace and global health conditions will continue to impact the Company in the future. Their ultimate impact depends on future developments that are highly uncertain and difficult to predict.
Consolidated results of operations
The following table summarizes our revenues, operating income (loss) and adjusted operating income (loss) by line of business. See the discussion of our results for each line of business following this table. When multiple drivers are identified in the following discussion of results, they are listed in order of magnitude:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year ended December 31, | | Annual change |
| | 2024 | | 2023 | | Amount | | Percent |
| | (dollars in millions) |
| Revenues: | | | | | | | |
| U.S. dialysis | $ | 11,391 | | | $ | 10,937 | | | $ | 454 | | | 4.2 | % |
| Other - Ancillary services | 1,510 | | | 1,299 | | | 211 | | | 16.2 | % |
| Elimination of intersegment revenues | (86) | | | (96) | | | 10 | | | 10.4 | % |
| Total consolidated revenues | $ | 12,816 | | | $ | 12,140 | | | $ | 676 | | | 5.6 | % |
| | | | | | | |
| Operating income (loss): | | | | | | | |
| U.S. dialysis | $ | 2,121 | | | $ | 1,775 | | | $ | 346 | | | 19.5 | % |
| Other - Ancillary services | 83 | | | (9) | | | 92 | | | 1,022.2 | % |
| Corporate administrative support | (113) | | | (163) | | | 50 | | | 30.7 | % |
| Operating income | $ | 2,090 | | | $ | 1,603 | | | $ | 487 | | | 30.4 | % |
| | | | | | | |
Adjusted operating income (loss):(1) | | | | | | | |
| U.S. dialysis | $ | 2,086 | | | $ | 1,801 | | | $ | 285 | | | 15.8 | % |
| Other - Ancillary services | 8 | | | (45) | | | 53 | | | 117.8 | % |
| Corporate administrative support | (113) | | | (122) | | | 9 | | | 7.4 | % |
| Adjusted operating income | $ | 1,981 | | | $ | 1,635 | | | $ | 346 | | | 21.2 | % |
Certain columns or rows may not sum or recalculate due to the presentation of rounded numbers.
(1)For a reconciliation of adjusted operating income (loss) by reportable segment, see the "Reconciliations of non-GAAP measures" section below.
U.S. dialysis business
As of December 31, 2024, our U.S. dialysis business is a leading provider of kidney dialysis services, operating 2,657 outpatient dialysis centers serving approximately 200,800 patients, and contracted to provide hospital inpatient dialysis services in approximately 760 hospitals. We estimate that we have approximately a 36% share of the U.S. dialysis market based upon the number of patients we serve.
Approximately 88% of our 2024 consolidated revenues were derived directly from our U.S. dialysis business. The principal drivers of our U.S. dialysis revenues include :
•our number of treatments, which is primarily a function of the number of chronic patients requiring approximately three in-center treatments per week as well as, to a lesser extent, the number of treatments for home-based dialysis and hospital inpatient dialysis; and
•our average dialysis patient service revenue per treatment, including the mix of patients with commercial plans and government programs as primary payor.
Within our U.S. dialysis business, our home-based dialysis and hospital inpatient dialysis services are operationally integrated with our outpatient dialysis centers and related laboratory services. Our outpatient, home-based and hospital inpatient dialysis services comprise approximately 75%, 19% and 6% of our U.S. dialysis revenues, respectively.
In the U.S., government dialysis-related payment rates are principally determined by federal Medicare and state Medicaid policy. For 2024, approximately 67% of our total U.S. dialysis patient service revenues were generated from government-based programs for services to approximately 89% of our total U.S. patients. These government-based programs are principally Medicare and MA, Medicaid and managed Medicaid plans, and other government plans, representing approximately 56%, 8% and 3% of our U.S. dialysis patient service revenues, respectively.
In November 2024, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) issued a final rule to update the Medicare ESRD Prospective Payment System payment rate and policies for calendar year 2024. CMS has finalized ESRD facilities' average reimbursement by a productivity-adjusted market basket increase of 2.2% in 2025. In addition, from time-to-time CMS identifies drugs to be added to the ESRD PPS bundled payment. On January 1, 2025, phosphate binders, a drug class taken orally by many ESKD patients to reduce absorption of dietary phosphate, were incorporated into the ESRD PPS bundle. Phosphate binders are not considered accounted for in the ESRD PPS base rate at this time and will be reimbursed through a Transitional Drug Add-on Payment Adjustment (TDAPA). The TDAPA period is expected to continue for a period of at least two years. Currently, phosphate binders are offered in both generic and branded forms and are produced by multiple manufacturers. During this TDAPA period, our operating results could be materially impacted by certain factors, including physician prescribing patterns, the terms of supplier and other vendor contracts, the mix of branded and generic forms of the drug used by our patients, whether the drug enters into the ESRD PPS and becomes part of its bundled payment following TDAPA and, if so, at what rate and how payors will treat reimbursement of the drug at the conclusion of the TDAPA period.
Dialysis payment rates from commercial payors vary and a major portion of our commercial rates are set at contracted amounts with payors and are subject to intense negotiation pressure. On average, dialysis-related payment rates from contracted commercial payors are significantly higher than Medicare, Medicaid and other government program payment rates, and therefore the percentage of commercial patients in relation to total patients represents a significant driver of our total average dialysis patient service revenue per treatment. Commercial payors (including hospital dialysis services) represent approximately 33% of U.S. dialysis patient service revenues.
For a discussion of government reimbursement, the Medicare ESRD bundled payment system, MA and commercial reimbursement, see Part I Item 1."Business" under the heading "U.S. dialysis business – Sources of revenue-concentrations and risks." For a discussion of operational, clinical and financial risks and uncertainties that we face in connection with the Medicare ESRD bundled payment system, see the risk factor in Part I Item 1A. "Risk Factors" under the heading "Our business is subject to a complex set of governmental laws, regulations and other requirements and any failure to adhere to those requirements, or any changes in those requirements..." For a discussion of operational, clinical and financial risks and uncertainties that we face in connection with commercial payors, see the risk factor in Part I Item 1A. "Risk Factors" under the heading "If the number or percentage of patients with higher-paying commercial insurance declines, if the average rates that commercial payors pay us declines..."
We anticipate that we will continue to experience increases in our operating costs in 2025 that may outpace any net Medicare, commercial or other rate increases that we may receive, which could significantly impact our operating results. In particular, we expect to continue experiencing increases in operating costs that are subject to inflation, such as labor and supply costs, including increases in maintenance costs, regardless of whether there is a compensating inflation-based increase in Medicare, commercial or other payor payment rates. In addition, we expect to continue to incur capital expenditures and associated depreciation and amortization costs to improve, renovate and maintain our facilities, equipment and information technology to meet evolving regulatory requirements and otherwise.
U.S. dialysis patient care costs are those costs directly associated with operating and supporting our dialysis centers, home-based dialysis programs and hospital inpatient dialysis programs, and consist principally of labor, benefits, pharmaceuticals, medical supplies and other operating costs of the dialysis centers.
The principal drivers of our U.S. dialysis patient care costs include:
•clinical hours per treatment, labor rates and benefit costs;
•vendor pricing and utilization levels of pharmaceuticals;
•business infrastructure costs, which include the operating costs of our dialysis centers; and
•medical supply costs.
Other cost categories that can present significant variability include insurance costs and professional fees. In addition, proposed ballot initiatives or referendums, legislation, regulations or policy changes could cause us to incur substantial costs to prepare for, or implement changes required. Any such changes could result in, among other things, increases in our labor costs or limitations on the amount of revenue that we can retain. For additional information on risks associated with potential and proposed ballot initiatives, referendums, legislation, regulations or policy changes, see the risk factor in Part I Item 1A. "Risk Factors" under the heading, "Changes in federal and state healthcare legislation or regulations..."
Our average clinical hours per treatment decreased in 2024 compared to 2023 primarily due to a decrease in turnover as described below. We are always striving for improved productivity levels, however, changes in factors such as federal and state
policies or regulatory billing requirements can lead to increased labor costs as can increases in turnover. In 2024, the demand for skilled clinical personnel continued, exacerbated by the nationwide shortage of these resources. In 2024 and 2023, we experienced increases in our clinical labor wage rates, which includes contract labor, of approximately 3.8% and 1.3%, respectively. We expect to continue to see higher clinical labor rates in 2025 due to labor market conditions, including changes in local minimum wage laws, and the continued competition for skilled clinical personnel. In 2024, our overall clinical teammate turnover decreased from 2023, but remains elevated from historical pre-COVID levels. We also continue to experience increases in the infrastructure and operating costs of our dialysis centers and general increases in utilities and repairs and maintenance. In 2024, we continued to implement certain cost control initiatives to help manage our overall operating costs, including labor productivity, and we expect to continue these initiatives in 2025.
Our U.S. dialysis general and administrative expenses represented 10.3% and 10.1% of our U.S. dialysis revenues in 2024 and 2023, respectively. Increases in general and administrative expenses over the last several years were primarily related to strengthening our dialysis business and related compliance and operational processes, responding to certain legal and compliance matters and professional fees. We expect that these levels of general and administrative expenses will be impacted by continued investment in developing our capabilities and executing on our strategic priorities, among other things.
U.S. dialysis results of operations
Treatment volume:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year ended December 31, | | Annual change |
| | 2024 | | 2023 | | Amount | | Percent |
| Dialysis treatments | 29,046,346 | | | 28,910,177 | | | 136,169 | | | 0.5 | % |
| Average treatments per day | 92,534 | | | 92,542 | | | (8) | | | — | % |
| Treatment days | 314 | | | 312 | | | 2 | | | 0.6 | % |
Normalized non-acquired treatment growth(1) | — | % | | (0.1) | % | | | | 0.1 | % |
Certain columns or rows may not sum or recalculate due to the presentation of rounded numbers
(1)Normalized non-acquired treatment growth reflects year over year growth in treatment volume, adjusted to exclude acquisitions and other similar transactions, and further adjusted to normalize for the number and mix of treatment days in a given period versus the prior period.
Our U.S. dialysis operating revenues and expenses are directly driven by treatment volume. The increase in our U.S. dialysis treatments in 2024 was primarily driven by additional treatment days and increased treatments from acquired treatment growth partially offset by an increase in missed treatments.
Revenues:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year ended December 31, | | Annual change |
| | 2024 | | 2023 | | Amount | | Percent |
| | (dollars in millions, except per treatment data) |
| Total revenues | $ | 11,391 | | | $ | 10,937 | | | $ | 454 | | | 4.2 | % |
| Average patient service revenue per treatment | $ | 391.32 | | | $ | 377.44 | | | $ | 13.88 | | | 3.7 | % |
Certain columns or rows may not sum or recalculate due to the presentation of rounded numbers
U.S. dialysis average patient service revenue per treatment increased primarily driven by the increase in average reimbursement rates from normal annual rate increases including Medicare rate increases, revenue cycle improvements, favorable changes in mix, and an increase in hospital inpatient dialysis rates.
Operating expenses and charges:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year ended December 31, | | Annual change |
| | 2024 | | 2023 | | Amount | | Percent |
| | (dollars in millions, except per treatment data) |
| Patient care costs | $ | 7,498 | | | $ | 7,395 | | | $ | 103 | | | 1.4 | % |
| General and administrative | 1,174 | | | 1,102 | | | 72 | | | 6.5 | % |
| Depreciation and amortization | 661 | | | 696 | | | (35) | | | (5.0) | % |
| Equity investment income | (28) | | | (30) | | | 2 | | | 6.7 | % |
| Gain on changes in ownership interests | (35) | | | — | | | (35) | | | (100.0) | % |
| Total operating expenses and charges | $ | 9,270 | | | $ | 9,162 | | | $ | 107 | | | 1.2 | % |
| Patient care costs per treatment | $ | 258.12 | | | $ | 255.78 | | | $ | 2.34 | | | 0.9 | % |
Certain columns or rows may not sum or recalculate due to the presentation of rounded numbers
Charges impacting operating income
Closure costs. In the third quarter of 2022, we began a strategic review of our outpatient clinic capacity requirements and utilization, which had been significantly impacted by declines in our patient census due to the COVID-19 pandemic. This review continued through 2023, with impacts continuing into 2024, and has resulted in higher than normal charges for center capacity closures over the last several quarters. These capacity closure costs include net losses on assets retired, lease termination costs, asset impairments and accelerated depreciation and amortization.
During the year ended December 31, 2024, U.S. dialysis center closure costs were approximately $72.4 million, which impacted our patient care costs by $30.8 million, our general and administrative expenses by $25.6 million and our depreciation and amortization expense by $16.0 million. By comparison, during the year ended December 31, 2023, U.S. dialysis center closures were approximately $99.1 million, which impacted our patient care costs by $28.0 million, our general and administrative expenses by $20.6 million and our depreciation and amortization expense by $50.5 million.
In the upcoming fiscal year, we expect a decrease in our center closure costs as we expect future closures to return to pre-COVID levels.
Severance costs. During the fourth quarter of 2022, we committed to a plan to increase efficiencies and cost savings in certain general and administrative support functions. As a result of this plan, we recognized expenses related to termination and other benefit commitments in our U.S. dialysis business of $26.7 million during the twelve months ended December 31, 2023.
Patient care costs. U.S. dialysis patient care costs are those costs directly associated with operating and supporting our dialysis centers and consist principally of compensation expenses including labor and benefits, pharmaceuticals, medical supplies and other operating costs of the dialysis centers.
U.S. dialysis patient care costs per treatment increased primarily due to increased compensation expenses, including increased wage rates, as well as increases in health benefit expense and medical supply costs. Other drivers of this change include increases in utilities expense driven by lower expense in 2023 related to our virtual power purchase arrangements, insurance costs and routine repairs and maintenance. These increases were partially offset by decreases in contributions to charitable organizations, other direct operating expenses associated with our dialysis centers, contract wages and a gain on settlement received in the fourth quarter of 2024.
General and administrative expenses. U.S. dialysis general and administrative expenses increased primarily due to increases in compensation expense, including increased wage rates and headcount, as well as IT-related costs and advocacy costs, including a refund received in 2023 related to 2022 advocacy costs. Other drivers of this change include increased professional fees, center closure costs, as described above, and health benefit expense. These increases were partially offset by decreases in severance costs, as described above, and contributions to our charitable foundation.
Depreciation and amortization. Depreciation and amortization expense is directly impacted by the number of our dialysis centers and the information technology that we develop and acquire as well as changes in useful lives of assets. U.S. dialysis depreciation and amortization expense decreased in 2024 primarily due to decreased accelerated depreciation related to center closures, as described above.
Equity investment income. U.S. dialysis equity investment income decreased due to the consolidation of a previously nonconsolidated dialysis partnership in the first quarter of 2024, partially offset by increased profitability at certain nonconsolidated dialysis partnerships.
Gain on changes in ownership interests. During the first quarter of 2024, we acquired a controlling interest in a previously nonconsolidated dialysis partnership for which we recognized a non-cash gain of $35.1 million on our prior investment upon consolidation.
Operating income and adjusted operating income
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year ended December 31, | | Annual change |
| | 2024 | | 2023 | | Amount | | Percent |
| (dollars in millions) |
| Operating income | $ | 2,121 | | | $ | 1,775 | | | $ | 346 | | | 19.5 | % |
Adjusted operating income(1) | $ | 2,086 | | | $ | 1,801 | | | $ | 285 | | | 15.8 | % |
Certain columns or rows may not sum or recalculate due to the presentation of rounded numbers.
(1)For a reconciliation of adjusted operating income by reportable segment, see the "Reconciliations of non-GAAP measures" section below.
U.S. dialysis operating income for 2024 compared to 2023 was positively impacted by a gain on a change in business ownership interest and severance costs, as described above. U.S. dialysis operating income and adjusted operating income increased compared to 2023 primarily due to an increase in our average patient service revenue per treatment and dialysis treatments, as described above, as well as decreases in charitable contributions, center closure costs, as described above, other direct operating expenses associated with our dialysis centers, contract wages and a gain on settlement, as described above. These increases in operating income and adjusted operating income were partially offset by increases in compensation expenses, as described above, as well as increases in health benefit expense, IT-related costs, medical supply costs, advocacy costs and utilities expense, as described above. Operating income and adjusted operating income were also negatively impacted by increased insurance costs, routine repairs and maintenance and professional fees.
Other - Ancillary services
Our other operations include ancillary services that are primarily aligned with our core business of providing dialysis services to our network of patients. As of December 31, 2024, these consisted primarily of our U.S. IKC business, certain U.S. other ancillary businesses (including our clinical research programs, transplant software business, and venture investment group), and our international operations.
These ancillary services, including our international operations, generated revenues of approximately $1.510 billion in 2024, representing approximately 12% of our consolidated revenues.
As of December 31, 2024, DaVita IKC provided integrated care and disease management services to approximately 70,400 patients in risk-based integrated care arrangements and to an additional 11,600 patients in other integrated care arrangements. We also expect to add additional service offerings to our business and pursue additional strategic initiatives in the future as circumstances warrant, which could include, among other things, healthcare services not related to kidney disease.
For a discussion of the risks related to IKC and our ancillary services, see the discussion in the risk factors in Part I Item 1A. "Risk Factors" under the headings, "The U.S. integrated kidney care, U.S. other ancillary services and international operations that we operate or invest in now or in the future..." and "If we are not able to successfully implement our strategy with respect to our integrated kidney care and value-based care initiatives..."
As of December 31, 2024, our international dialysis business owned or operated 509 outpatient dialysis centers located in 13 countries outside of the U.S. For 2024, total revenues generated from our international operations were approximately 8% of our consolidated revenues.
Ancillary services results of operations
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year ended December 31, | | Annual change |
| | 2024 | | 2023 | | Amount | | Percent |
| (dollars in millions) |
| Revenues: | | | | | | | |
| U.S. IKC | $ | 508 | | | $ | 511 | | | $ | (3) | | | (0.6) | % |
| U.S. other ancillary | 25 | | | 25 | | | — | | | — | % |
| International | 977 | | | 763 | | | 214 | | | 28.0 | % |
| Total ancillary services revenues | $ | 1,510 | | | $ | 1,299 | | | $ | 211 | | | 16.2 | % |
| | | | | | | |
| Operating (loss) income: | | | | | | | |
| U.S. IKC | $ | (35) | | | $ | (39) | | | $ | 4 | | | 10.3 | % |
| U.S. other ancillary | (9) | | | (25) | | | 16 | | | 64.0 | % |
International(1) | 127 | | | 55 | | | 72 | | | 130.9 | % |
| Total ancillary services operating income (loss) | $ | 83 | | | $ | (9) | | | $ | 92 | | | 1,022.2 | % |
| | | | | | | |
Adjusted operating (loss) income(2): | | | | | | | |
| U.S. IKC | $ | (35) | | | $ | (93) | | | $ | 58 | | | 62.4 | % |
| U.S. other ancillary | (9) | | | (7) | | | (2) | | | (28.6) | % |
International(1) | 52 | | | 55 | | | (3) | | | (5.5) | % |
| Total adjusted operating income (loss): | $ | 8 | | | $ | (45) | | | $ | 53 | | | 117.8 | % |
Certain columns or rows may not sum or recalculate due to the presentation of rounded numbers.
(1)The reported operating income and adjusted operating income for the years ended December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023, includes foreign currency gains (losses) embedded in equity method income recognized from our APAC joint venture, which was consolidated in the fourth quarter of 2024, of approximately $0.6 million and $(1.6) million, respectively.
(2)For a reconciliation of adjusted operating (loss) income by reportable segment, see the "Reconciliations of non-GAAP measures" section below.
Revenues:
Our IKC revenues were impacted by decreased revenues from our special needs plans and the divestiture of our physician services business, partially offset by a net increase in shared savings. Our U.S. other ancillary services revenues were impacted by increased revenues from our transplant software business, offset by decreased revenues in our clinical research programs. Our international revenues increased due to acquired and non-acquired treatment growth and average reimbursement rate increases in certain countries, partially offset by charges for balances deemed uncollectible.
Items impacting operating income
IKC adjustment. The decrease in IKC revenues for 2024, as described above, was impacted by the lifting of certain revenue recognition constraints for some of our value-based care contracts with health plans in 2023, which allowed us to recognize approximately $55 million in incremental shared savings revenues during 2023 compared to what we would have recognized under previous years' constraints.
Since we launched our IKC VBC business, the COVID-19 pandemic and its distorting effects on medical utilization have subsided, our VBC contracts have continued to mature, we have begun to receive more timely and granular data from our health plan partners and we have gained more experience making total medical cost estimates for this population. These changes and refinements have helped to mitigate or alleviate a number of the information and measurement limitations that constrained our revenue recognition in the past, allowing us to recognize a greater share of expected shared savings revenues for our VBC plans sooner than we had in previous periods. As a result, we recognized a majority of the VBC shared savings revenues we expected to earn for 2023 in 2023, while in previous years a substantial majority of the shared savings earned for a VBC plan year were recognized in a subsequent year.
Our fiscal year 2023 therefore included a general shift in the timing of our revenue recognition for shared savings under our VBC contracts with health plans, as it included a majority of shared savings revenues earned for both 2022 and 2023.
Severance and other costs. During the fourth quarter of 2022, similar to U.S. dialysis, we committed to a plan to increase efficiencies and cost savings in certain general and administrative support functions and other overhead costs. As a result of this plan, we recognized expenses related to termination and other benefit commitments in our IKC business of $0.5 million during the year ended December 31, 2023.
Goodwill impairment charge and related items. During the fourth quarter of 2023, we recognized a goodwill impairment charge of $26.1 million in our transplant software business. We also recognized a gain of $7.7 million due to a reduction in the estimated value of earn-out obligations from our original acquisition of this business. This impairment charge and related gain resulted from a reduction in estimated fair value for the business driven primarily from the business not achieving its revenue targets, with reduced revenue expectations for future years, as well as an increase in the risk-free rate.
Gain on changes in ownership interests. During the fourth quarter of 2024, we acquired a controlling interest in the previously nonconsolidated partnership known as the Company's APAC joint venture, for which we recognized a non-cash gain of $74.3 million on our prior investment upon consolidation.
Operating income (loss) and adjusted operating income (loss):
Our IKC operating loss for 2024 compared to 2023 was impacted by the IKC adjustment, as described above. Our IKC operating loss and adjusted operating loss decreased primarily due to a net increase in shared savings, decreased medical costs for our special needs plans and the divestiture of our physician services business. These increases were partially offset by decreased revenues from our special needs plans and continued investments in our integrated care support functions. Our U.S. other ancillary services operating loss for 2024 compared to 2023 was impacted by a goodwill impairment charge and related gain, as described above. Our U.S. other ancillary services operating loss and adjusted operating loss was impacted by decreased revenues in our clinical research programs and increased expenses in our transplant software business, partially offset by increased revenues from our transplant software business. Our international operating income was impacted by a gain on a change in business ownership interests, as described above. International operating income and adjusted operating income were impacted by increased revenues, as described above, partially offset by increases in operating and deal costs from acquisition-related growth.
Corporate administrative support
Corporate administrative support consists primarily of labor, benefits and long-term incentive compensation expense, as well as professional fees, for departments which provide support to more than one of our various operating lines of business. Corporate administrative support expenses are included in general and administrative expenses on our consolidated income statement.
Accruals for legal matters. During 2023, we recorded a charge of $40 million for a legal matter within corporate administrative support.
Corporate administrative support expenses decreased $50 million due to the absence in 2024 of the legal charge described above, and decreased long-term incentive compensation costs, partially offset by increased compensation expenses in 2024.
Corporate-level charges
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year ended December 31, | | Annual change |
| | 2024 | | 2023 | | Amount | | Percent |
| (dollars in millions) |
| Debt expense | $ | 470 | | | $ | 399 | | | $ | 71 | | | 17.8 | % |
| Debt prepayment, extinguishment and modification costs | $ | 20 | | | $ | 8 | | | $ | 12 | | | 150.0 | % |
Weighted average effective interest rate(1) | 5.07 | % | | 4.52 | % | | | | 0.55 | % |
| Other loss, net | $ | (70) | | | $ | (19) | | | $ | (51) | | | (268.4) | % |
| Effective income tax rate | 18.3 | % | | 18.7 | % | | | | (0.4) | % |
Effective income tax rate attributable to DaVita Inc.(2) | 22.9 | % | | 24.3 | % | | | | (1.4) | % |
| Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests | $ | 314 | | | $ | 265 | | | $ | 49 | | | 18.5 | % |
Certain columns or rows may not sum or recalculate due to the presentation of rounded numbers.
(1)Represents our overall weighted average effective interest rate on all debt, including the effect of interest rate caps and amortization of debt discount, premium and deferred financing charges.
(2)For a reconciliation of our effective income tax rate attributable to DaVita Inc., see the "Reconciliations of non-GAAP measures" section below.
Debt expense
Debt expense increased primarily due to an increase in overall weighted average effective interest rate principally related to the expiration of our 2019 interest rate cap agreements on June 30, 2024, which had lower rates than our currently effective interest rate caps, as well as an increase in our our long-term debt balance related to the issuance of 6.875% senior notes due 2032 and incremental borrowing on our Term Loan A-1, partially offset by the repayment of the non-extended Term Loan B-1. See Note 12 to the consolidated financial statements for further information on the components of our debt and changes in them since 2023.
Debt extinguishment and modification costs
Debt prepayment, extinguishment and modification costs were $20 million in 2024 composed of fees incurred in connection with the additional incremental borrowing on our Term Loan A-1 (Incremental Term Loan A-1), the extension of the maturity date of a portion of our Term Loan B-1 from August 2026 to May 2031 (Extended Term Loan B-1), and deferred financing costs and original issue discount written off for the extinguishment of the non-extended Term Loan B-1. Comparatively, debt extinguishment and modification costs were $8 million in 2023 related to the refinancing of our prior Term Loan A and prior revolving line of credit. These costs were composed of deferred financing costs written off for the portion of this debt considered extinguished and reborrowed and fees incurred as part of this debt refinancing. See Note 12 to the condensed consolidated financial statements for further information on the Incremental Term Loan A-1, Extended Term Loan B-1 and the components of our debt.
Other loss
Other loss consists primarily of interest income on cash and cash equivalents and short- and long-term investments, equity investment (loss) income on equity method investments other than dialysis partnerships, realized and unrealized gains and losses recognized on other investments, impairments on investments, and foreign currency transaction gains and losses. Other loss increased primarily due to equity investment losses on our investment in Mozarc Medical Holding LLC (Mozarc), including the $14 million gain recognized in 2023 on the non-cash assets contributed to Mozarc, partially offset by decreased losses recognized on other investments, decreased losses on foreign currency transactions and an increase in interest income.
Provision for income taxes
Our effective income tax rate and effective income tax rate attributable to DaVita Inc. decreased in 2024 primarily due to the tax impact of non-taxable non-cash gains related to previously nonconsolidated businesses and a decrease in nondeductible executive compensation. This benefit was partially offset by additional expense recognized in 2024 for finalized tax returns and a decrease in benefits recognized for uncertain tax positions.
Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests
The increase in income attributable to noncontrolling interests was due to an increase in earnings at certain U.S. dialysis partnerships.
U.S. dialysis accounts receivable
Our U.S. dialysis accounts receivable balances at December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023 were $1.615 billion and $1.632 billion, respectively, representing approximately 52 days and 54 days of revenue (DSO), respectively. The decrease in DSO was primarily due to continued collections improvements. Our DSO calculation is based on the most recent quarter’s average revenues per day. There were no significant changes during 2024 from 2023 in the carrying amount of accounts receivable outstanding over one year old or in the amounts pending approval from third-party payors.
As of December 31, 2024 and 2023, our U.S. dialysis accounts receivable balances that are more than six months old represented approximately 23% and 19% of our U.S. dialysis accounts receivable balances outstanding, respectively. Substantially all revenue realized for patient services is received from government and commercial payors, as discussed above. Less than 1% of our revenues in both periods were classified as patient pay.
Amounts pending approval from third-party payors associated with Medicare bad debt claims as of December 31, 2024 and 2023, other than the standard monthly billing, were approximately $107 million, and are classified within other receivables. A significant portion of our Medicare bad debt claims are typically paid to us before the Medicare fiscal intermediary audits the claims but are subject to subsequent adjustment based upon the actual results of those audits. Such audits typically occur one to four years after the claims are filed.
Liquidity and capital resources
The following table summarizes our major sources and uses of cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year ended December 31, | | Annual change |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | Amount | | Percent |
| (dollars in millions) |
| Net cash provided by operating activities: | | | | | | | |
| Net income | $ | 1,251 | | | $ | 957 | | | $ | 294 | | | 30.7 | % |
| Non-cash items in net income | 801 | | | 908 | | | (107) | | | (11.8) | % |
| Other working capital changes | 44 | | | 209 | | | (165) | | | (78.9) | % |
| Other | (74) | | | (14) | | | (60) | | | (428.6) | % |
| $ | 2,022 | | | $ | 2,059 | | | $ | (37) | | | (1.8) | % |
| | | | | | | |
| Net cash used in investing activities: | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
Maintenance capital expenditures(1) | $ | (394) | | | $ | (406) | | | $ | 12 | | | 3.0 | % |
Development capital expenditures(2) | (162) | | | (162) | | | — | | | — | % |
| Acquisition expenditures | (246) | | | (26) | | | (220) | | | (846.2) | % |
| Proceeds from sale of self-developed properties | 18 | | | 11 | | | 7 | | | 63.6 | % |
| | | | | | | |
| Other | 12 | | | (189) | | | 201 | | | 106.3 | % |
| $ | (771) | | | $ | (772) | | | $ | 1 | | | 0.1 | % |
| | | | | | | |
| Net cash used in financing activities: | | | | | | | |
| Debt proceeds (payments), net | $ | 1,095 | | | $ | (550) | | | $ | 1,645 | | | 299.1 | % |
| Deferred and debt related financing costs | (51) | | | (70) | | | 19 | | | 27.1 | % |
| Distributions to noncontrolling interests | (337) | | | (281) | | | (56) | | | (19.9) | % |
| Contributions from noncontrolling interests | 14 | | | 15 | | | (1) | | | (6.7) | % |
| Stock award exercises and other share issuances | (114) | | | (48) | | | (66) | | | (137.5) | % |
| Share repurchases | (1,386) | | | (272) | | | (1,114) | | | (409.6) | % |
| Other | (39) | | | 35 | | | (74) | | | (211.4) | % |
| $ | (817) | | | $ | (1,170) | | | $ | 353 | | | 30.2 | % |
| | | | | | | |
| Total number of shares repurchased | 9,832,705 | | | 2,903,832 | | | 6,928,873 | | | 238.6 | % |
| | | | | | | |
Free cash flow(3) | $ | 1,162 | | | $ | 1,236 | | | $ | (74) | | | (6.0) | % |
Certain columns or rows may not sum or recalculate due to the presentation of rounded numbers.
(1)Maintenance capital expenditures represent capital expenditures to maintain the productive capacity of the business and include those made for investments in information technology, dialysis center renovations, capital asset replacements, and any other capital expenditures that are not development or acquisition expenditures.
(2)Development capital expenditures principally represent capital expenditures (other than acquisition expenditures) made to expand the productive capacity of the business and include those for new U.S. and international dialysis center developments, dialysis center expansions and relocations, and new or expanded contracted hospital operations.
(3)For a reconciliation of our free cash flow, see the "Reconciliations of Non-GAAP measures" section below.
Consolidated cash flows
Consolidated cash flows from operating activities for 2024 and 2023 were $2,022 million and $2,059 million, respectively. The decrease in cash flows was primarily driven by increases in taxes and interest paid combined with changes in other working capital items partially offset by improved operating results.
Cash flows used for investing activities in 2024 was flat compared to 2023. An increase in acquisitions due to our international growth was largely offset by decreases in equity investments driven by our investment in Mozarc in 2023.
Cash flows used in financing activities decreased $353 million in 2024 compared to 2023. Significant sources of cash during the period included the extension of the maturity date from August 2026 to May 2031 for a portion of our Term Loan B-1 (the Extended Term Loan B-1 transaction) in the aggregate principal amount of approximately $1,640 million, (such portion referred to as the Extended Term Loan B-1), the incurrence of an incremental Term Loan A-1 tranche in the aggregate principal amount of $1,100 million (such portion referred to as the Incremental Term Loan A-1), the issuance of 6.875% senior notes due 2032 in the amount of $1,000 million (the 6.875% Senior Notes) and Change Healthcare temporary funding assistance of $93 million, net, pursuant to the CHC Funding Arrangement during the year ended December 31, 2024. Significant uses of cash during that same period included debt prepayments on Term Loan B-1 in the aggregate amount of approximately $2,590 million as part of the Extended Term Loan B-1, Incremental Term Loan A-1 and 6.875% Senior Notes transactions, and regularly scheduled principal payments under our senior secured credit facilities totaling approximately $75 million on our Term Loan A-1, $14 million on Term Loan B-1 and $4 million on Extended Term Loan B-1, as well as additional required payments under other debt arrangements. Additionally, we recognized financing cash outflows of $36 million in deferred financing costs and discount related to the Fourth and Sixth Amendments to the Senior Secured Credit Agreement and 6.875% Senior Notes transactions, as well as $15 million in cap premium fees for our 2024 forward interest rate cap agreements. During the year ended December 31, 2024 we also used cash to repurchase 9,832,705 shares of our common stock.
By comparison, 2023 significant uses of cash included the pay-off of the remaining principal balance outstanding on our prior Term Loan A and prior revolving line of credit in the amount of $1,444 million and $150 million, respectively. Other uses of cash included regularly scheduled and other principal payments under our senior secured credit facilities totaling approximately $54 million on our prior Term Loan A, $16 million on our new Term Loan A-1, $57 million on Term Loan B-1, additional net repayments of $15 million on our revolving line of credit, as well as additional required payments under other debt arrangements. Additionally, we recognized financing cash outflows of $30 million in deferred financing costs related to the Amendments to the Senior Secured Credit Agreement and $40 million in cap premium fees for our 2023 forward interest cap agreements. Significant sources of cash during the period included the refinancing of the Term Loan A and revolving line of credit with a secured Term Loan A-1 facility in the aggregate principal amount of $1,250 million. During the year ended December 31, 2023 we also used cash to repurchase 2,903,832 shares of our common stock.
Dialysis center capacity and growth
We are typically able to increase our capacity by extending hours at our existing dialysis centers, expanding our existing dialysis centers, relocating our dialysis centers, developing new dialysis centers and by acquiring dialysis centers. The development of a typical new outpatient dialysis center generally requires approximately $2 million for leasehold improvements and other capital expenditures. Based on our experience, a new outpatient dialysis center typically opens within a year after the property lease is signed, normally achieves operating profitability in the second year after Medicare certification, and normally reaches maturity within three to five years. Acquiring an existing outpatient dialysis center requires a substantially greater initial investment, but profitability and cash flows are generally accelerated and more predictable. To a limited extent, we enter into agreements to provide management and administrative services to outpatient dialysis centers in which we own a noncontrolling interest or which are wholly-owned by third parties in return for management fees.
The table below shows the growth in our dialysis operations by number of dialysis centers owned or operated:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| U.S. | | International |
| | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2024 | | 2023 |
| Number of centers operated at beginning of year | 2,675 | | | 2,724 | | | 367 | | | 350 | |
| Acquired centers | 12 | | | — | | | 198 | | | 12 | |
| Developed centers | 13 | | | 20 | | | 5 | | | 8 | |
Net change in non-owned managed or administered centers(1) | (7) | | | 3 | | | (47) | | | 2 | |
Sold and closed centers(2) | (12) | | | (6) | | | (6) | | | (2) | |
Closed centers(3) | (24) | | | (66) | | | (8) | | | (3) | |
| Number of centers operated at end of year | 2,657 | | | 2,675 | | | 509 | | | 367 | |
(1)Represents the change in the number of dialysis centers which we manage or provide administrative services to but in which we own a noncontrolling equity interest or which are wholly-owned by third parties. For our international business, 2024 activity includes a reduction in managed centers, and an increase in acquired centers, from the consolidation of our APAC joint venture on November 1, 2024.
(2)Represents dialysis centers that were sold and/or closed for which the majority of patients were not retained.
(3)Represents dialysis centers that were closed for which the majority of patients were retained and transferred to one of our other existing outpatient dialysis centers.
Stock repurchases
The following table summarizes our common stock repurchases during the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2023:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 |
| (dollars in millions and shares in thousands, except per share data) |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| Shares | 9,833 | | | 2,904 | |
Amounts paid(1) | $ | 1,389 | | | $ | 286 | |
Average price paid per share(2) | $ | 140.06 | | | $ | 97.82 | |
(1)Includes commissions and the 1% excise tax imposed on certain stock repurchases made after December 31, 2022 by the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022. The excise tax is recorded as part of the cost basis of treasury stock repurchased and, as such, is included in stockholders’ equity.
(2)Excludes commissions and the excise tax described above
Subsequent to December 31, 2024, we have repurchased 778,746 shares of our common stock for $125 million at an average price paid of $158.48 per share through February 13, 2025, including repurchases from Berkshire Hathaway Inc. (Berkshire) pursuant to our previously disclosed share repurchase agreement.
See further discussion of our share repurchase activity, authorizations and information on our share repurchase agreement with Berkshire in Note 18 to the consolidated financial statements.
Available liquidity
As of December 31, 2024, our cash balance was $795 million and we held approximately $51 million in short-term investments. At that time we also had undrawn capacity on the revolving line of credit under our senior credit facilities of $1.5 billion. Credit available under this revolving line of credit is reduced by the amount of any letters of credit outstanding thereunder, of which there were none as of December 31, 2024. As of December 31, 2024 we separately had approximately $161 million in letters of credit outstanding under a separate bilateral secured letter of credit facility.
See Note 12 to the consolidated financial statements for components of our long-term debt and their interest rates.
We believe that our cash flows from operations and other sources of liquidity, including from amounts available under our senior secured credit facilities and our access to the capital markets, will be sufficient to fund our scheduled debt service under the terms of our debt agreements and other obligations for the foreseeable future, including the next 12 months. From time to time, depending on market conditions, our capital requirements and the availability of financing, among other things, we may seek to refinance our existing debt and may incur additional indebtedness. Our primary recurrent sources of liquidity are cash from operations and cash from borrowings, which are subject to general, economic, financial, competitive, regulatory and other factors that are beyond our control, as described in Part I Item 1A. "Risk Factors" under the heading "The level of our current and future debt..."
Reconciliations of non-GAAP measures
The following tables provide reconciliations of adjusted operating income (loss) to operating income (loss) as presented on a U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) basis for our U.S. dialysis reportable segment as well as for our U.S. IKC business, our U.S. other ancillary services, our international business, and for our total ancillary services which combines them and is disclosed as our other segments category, in addition to our corporate administrative support.
In connection with a comment letter from the Securities and Exchange Commission Staff, beginning in the second quarter of 2024, we have updated the presentation of our non-GAAP measures to no longer exclude center closure costs for all periods presented. To facilitate comparisons, the non-GAAP measures presented for prior periods have also been conformed to the presentation of non-GAAP measures for the current period.
These non-GAAP or "adjusted" measures are presented because management believes these measures are useful adjuncts to, but not alternatives for, our GAAP results. Specifically, management uses adjusted operating income (loss) to compare and evaluate our performance period over period and relative to competitors, to analyze the underlying trends in our business, to establish operational budgets and forecasts and for incentive compensation purposes. We believe this non-GAAP measure is also useful to investors and analysts in evaluating our performance over time and relative to competitors, as well as in analyzing the underlying trends in our business. We also believe this presentation enhances a user's understanding of our normal operating income by excluding certain items which we do not believe are indicative of our ordinary results of operations.
In addition, our effective income tax rate on income attributable to DaVita Inc. excludes noncontrolling owners' income, which primarily relates to non-tax paying entities. We believe this adjusted effective income tax rate is useful to management, investors and analysts in evaluating our performance and establishing expectations for income taxes incurred on our ordinary results attributable to DaVita Inc.
Finally, our free cash flow represents net cash provided by operating activities less distributions to noncontrolling interests, development capital expenditures, and maintenance capital expenditures; plus contributions from noncontrolling interests and proceeds from the sale of self-developed properties. Management uses this measure to assess our ability to fund acquisitions and meet our debt service obligations and we believe this measure is equally useful to investors and analysts as an adjunct to cash flows from operating activities and other measures under GAAP.
It is important to bear in mind that these non-GAAP "adjusted" measures are not measures of financial performance under GAAP and should not be considered in isolation from, nor as substitutes for, their most comparable GAAP measures.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year ended December 31, 2024 |
| U.S.
dialysis | | Ancillary services | | Corporate
administration | | |
| | U.S. IKC | | U.S. Other | | International | | Total | | | Consolidated |
| (dollars in millions) |
| Operating income (loss) | $ | 2,121 | | | $ | (35) | | | $ | (9) | | | $ | 127 | | | $ | 83 | | | $ | (113) | | | $ | 2,090 | |
Gain on changes in ownership interests(1) | (35) | | | — | | | — | | | (74) | | | (74) | | | — | | | (109) | |
Adjusted operating income (loss)(2) | $ | 2,086 | | | $ | (35) | | | $ | (9) | | | $ | 52 | | | $ | 8 | | | $ | (113) | | | $ | 1,981 | |
Certain columns or rows may not sum or recalculate due to the presentation of rounded numbers.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year ended December 31, 2023 |
| U.S.
dialysis | | Ancillary services | | Corporate
administration | | |
| | U.S. IKC | | U.S. Other | | International | | Total | | | Consolidated |
| (dollars in millions) |
| Operating income (loss) | $ | 1,775 | | | $ | (39) | | | $ | (25) | | | $ | 55 | | | $ | (9) | | | $ | (163) | | | $ | 1,603 | |
Severance and other costs(3) | 27 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 1 | | | 28 | |
Legal matter(4) | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 40 | | | 40 | |
IKC adjustment(5) | — | | | (55) | | | — | | | — | | | (55) | | | — | | | (55) | |
Earn-out revaluation(6) | — | | | — | | | (8) | | | — | | | (8) | | | — | | | (8) | |
Goodwill impairment(6) | — | | | — | | | 26 | | | — | | | 26 | | | — | | | 26 | |
Adjusted operating income (loss)(2) | $ | 1,801 | | | $ | (93) | | | $ | (7) | | | $ | 55 | | | $ | (45) | | | $ | (122) | | | $ | 1,635 | |
Certain columns or rows may not sum or recalculate due to the presentation of rounded numbers.
(1)Represents non-cash gains recognized on the acquisitions of controlling financial interests in previously nonconsolidated partnerships in 2024. See additional discussion above under the heading "Gain on changes in ownership interests" within "U.S. dialysis results of operations" and "Ancillary services results of operation" for the $35 million and $74 million, respectively. These gains were to mark our prior investments in these businesses to fair value before consolidation and to recognize related foreign currency gains from translation adjustments previously deferred in accumulated other comprehensive loss. Gains on changes in business ownership interests do not represent a normal and recurring requirement of operating our business or generating revenues and may obscure analysis of underlying trends and financial performance.
(2)In connection with the conclusion of a comment letter from the Securities and Exchange Commission Staff in July 2024, beginning in the second quarter 2024, we have updated the presentation of our non-GAAP measures to no longer exclude center closure costs for all periods presented. To facilitate comparisons, the non-GAAP measures presented for prior periods also have been conformed to the presentation of the non-GAAP measures for the current period.
(3)Includes severance and other termination costs related to a prior strategic restructuring initiative and associated transition of certain general and administrative support functions to a third party. See additional discussion above under the heading "Severance costs" within "U.S. dialysis results of operations" and "Severance and other costs" within "Ancillary services results of operations".
(4)Represents an amount that was accrued for costs prior to agreement on a third-party settlement for the matter further described in Note 15 to our consolidated financial statements under the heading "2017 U.S. Attorney Colorado Investigation". We have excluded this charge, which had been previously disclosed, from our non-GAAP metrics because, among other things, we do not believe it is indicative of our ordinary results of operations. In this instance, among the factors considered were that the claim relates to prior ancillary operations or activities that we sold or closed (or otherwise ceased) prior to June 2020, and the charge is significant and may obscure analysis of underlying trends and financial performance of our current business.
(5)Our fiscal year 2023 results included a majority of shared savings revenues earned for both 2022 and 2023 as a result of a general shift in the timing of recognition for shared savings under our VBC contracts with health plans due to the lifting of certain revenue recognition constraints in 2023. This amount represents the effect of shared savings revenues recognized in 2023 incremental to what we would have recognized in 2023 under prior year constraints. We have excluded this benefit to operating income because it is both unusual to our business and significant in size, and may obscure analysis of underlying trends and financial performance. See additional discussion above under "IKC adjustment" within "Ancillary services results of operations".
(6)Represents a goodwill impairment charge, and related gain from a reduction in earn-out obligation values, for our transplant software business. See additional discussion above under the heading "Goodwill impairment charge and related items" within "Ancillary services results of operations". This charge and this gain are excluded from our non-GAAP metrics because they do not occur in or reflect the ordinary course of our ongoing business operations, are inherently unpredictable and, in the case of impairments, are non-cash amounts, the exclusion of which facilitates comparison of historical, current, and forecasted financial results.
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 |
| (dollars in millions) |
| Income before income taxes | $ | 1,530 | | | $ | 1,177 | |
| Less: Noncontrolling owners’ income primarily attributable to non-tax paying entities | (315) | | | (263) | |
| Income before income taxes attributable to DaVita Inc. | $ | 1,215 | | | $ | 914 | |
| | | |
| Income tax expense | $ | 280 | | | $ | 220 | |
| Income tax attributable to noncontrolling interests | (1) | | | 2 | |
| Income tax expense attributable to DaVita Inc. | $ | 279 | | | $ | 222 | |
| | | |
| Effective income tax rate on income attributable to DaVita Inc. | 22.9 | % | | 24.3 | % |
Certain columns or rows may not sum or recalculate due to the presentation of rounded numbers.
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 |
| (dollars in millions) |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | $ | 2,022 | | | $ | 2,059 | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net cash provided by operating activities to free cash flow: | | | |
| Distributions to noncontrolling interests | (337) | | | (281) | |
| Contributions from noncontrolling interests | 14 | | | 15 | |
| Maintenance capital expenditures | (394) | | | (406) | |
| Development capital expenditures | (162) | | | (162) | |
| Proceeds from sale of self-developed properties | 18 | | | 11 | |
| Free cash flow | $ | 1,162 | | | $ | 1,236 | |
Certain columns or rows may not sum or recalculate due to the presentation of rounded numbers.
Off-balance sheet arrangements and aggregate contractual obligations
In addition to the debt obligations and operating lease liabilities reflected on our balance sheet, we have commitments associated with letters of credit as well as certain working capital funding obligations associated with our equity investments in nonconsolidated dialysis ventures that we manage and some we manage that are wholly-owned by third parties.
We also have potential obligations to purchase the noncontrolling interests held by third parties in many of our majority-owned dialysis partnerships and other nonconsolidated entities. These obligations are in the form of put provisions that are exercisable at the third-party owners’ discretion within specified periods as outlined in each specific put provision. For additional information see Notes 16 and 23 to the consolidated financial statements.
The following is a summary of these cash contractual obligations and commitments as of December 31, 2024:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2025 | | 2026-2027 | | 2028-2029 | | Thereafter | | Total |
| (dollars in millions) |
| Debt and leases: | | | | | | | | | |
Long-term debt(1): | | | | | | | | | |
| Principal payments | $ | 243 | | | $ | 315 | | | $ | 1,911 | | | $ | 6,826 | | | $ | 9,295 | |
| Interest payments on credit facilities and senior notes | 500 | | | 967 | | | 746 | | | 489 | | | 2,702 | |
Financing leases(2) | 28 | | | 62 | | | 51 | | | 75 | | | 216 | |
Operating leases, including imputed interest(2) | 508 | | | 971 | | | 696 | | | 864 | | | 3,039 | |
| | $ | 1,279 | | | $ | 2,315 | | | $ | 3,404 | | | $ | 8,254 | | | $ | 15,252 | |
Partnership interests subject to put provisions:(3) | | | | | | | | | |
| On-balance sheet: | | | | | | | | | |
| Noncontrolling interests subject to put provisions | 1,527 | | | 84 | | | 44 | | | 40 | | | 1,695 | |
| Off-balance sheet: | | | | | | | | | |
| Non-owned and minority owned put provisions | 57 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 57 | |
| | $ | 1,584 | | | $ | 84 | | | $ | 44 | | | $ | 40 | | | $ | 1,752 | |
(1)See Note 12 to the consolidated financial statements for components of our long-term debt and related interest rates.
(2)See Note 13 to the consolidated financial statements for components of our leases and related interest rates.
(3)Represents amounts for which we are contractually committed, should the outside partner exercise its put option.
As of December 31, 2024 we had outstanding letters of credit in the aggregate amount of approximately $161 million under a separate bilateral secured letter of credit facility.
As of December 31, 2024 we have outstanding purchase agreements with various suppliers to purchase set amounts of dialysis equipment, parts, pharmaceuticals, and supplies. If we fail to meet the minimum purchase commitments under these contracts during any year, we are required to pay the difference to the supplier. For additional information see Note 16 to the consolidated financial statements.
We also have certain potential commitments to provide working capital funding, if necessary, to certain nonconsolidated dialysis businesses that we manage and in which we own a noncontrolling equity interest or which are wholly-owned by third parties. For additional information see Note 16 to the consolidated financial statements.
Additionally, we expect our 2025 capital expenditures to be consistent with our 2024 capital expenditures.
In addition, we have approximately $39 million of existing long-term income tax liabilities for unrecognized tax benefits, including interest and penalties, which are excluded from the table above as reasonably reliable estimates of their timing cannot be made.
On March 5, 2024, we entered into four separate purchase agreements with Fresenius Medical Care AG and its affiliates to acquire their dialysis service operations in Chile, Ecuador, Colombia and Brazil. The Chile, Ecuador and Colombia transactions closed during 2024. The Brazil transaction is expected to close mid-year 2025 and remains subject to customary closing conditions and regulatory approval. The expected cash payment for this remaining transaction is approximately $100 million, subject to certain customary adjustments.
Contingencies
The information in Note 15 to the consolidated financial statements included in this report is incorporated by reference in response to this item.
Critical accounting policies, estimates and judgments
Our consolidated financial statements and accompanying notes are prepared in accordance with United States generally accepted accounting principles. These accounting principles require us to make estimates, judgments and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of revenues, expenses, assets, liabilities, contingencies and noncontrolling interests subject to put provisions (redeemable equity interests). All significant estimates, judgments and assumptions are developed based on the best information available to us at the time made and are regularly reviewed and updated when necessary. Actual results will generally differ from these estimates, and such differences may be material. Changes in estimates are reflected in our financial statements in the period of change based upon on-going actual experience trends or subsequent settlements and realizations depending on the nature and predictability of the estimates and contingencies. Certain accounting estimates, including those concerning revenue recognition and accounts receivable, fair value estimates for goodwill and noncontrolling interests, accounting for income taxes, and loss contingencies are considered to be critical to evaluating and understanding our financial results because they involve inherently uncertain matters and their application requires the most difficult and complex judgments and estimates. For additional information, see Part IV Item 15, "Exhibits, Financial Statement Schedules" – Note 1 – "Organization and summary of significant accounting policies" as referred from Part II Item 8, "Financial Statements and Supplementary Data."
Revenue recognition and accounts receivable for our U.S. dialysis patient services. There are significant estimating risks associated with the amount of U.S. dialysis patient service revenue that we recognize in a given reporting period. Payment rates are often subject to significant uncertainties related to wide variations in the coverage terms of the commercial healthcare plans under which we receive payments. In addition, ongoing insurance coverage changes, geographic coverage differences, differing interpretations of contract coverage, and other payor issues complicate the billing and collection process. The measurement and recognition of revenue requires the use of estimates of the amounts that will ultimately be realized considering, among other items, retroactive adjustments that may be associated with regulatory reviews, audits, billing reviews and other matters.
Revenues associated with Medicare and Medicaid programs are recognized based on (a) the payment rates that are established by statute or regulation for the portion of the payment rates paid by the government payor (e.g., 80% for Medicare patients) and (b) for the portion not paid by the primary government payor, the estimated amounts that will ultimately be collectible from other government programs providing secondary coverage (e.g., Medicaid secondary coverage), the patient’s commercial health plan secondary coverage, or the patient. Our dialysis-related reimbursements from Medicare are subject to certain variations under Medicare’s single bundled payment rate system whereby our reimbursements can be adjusted for certain patient characteristics and other variable factors. Our revenue recognition depends upon our ability to effectively capture, document and bill for Medicare’s base payment rate and these other factors. In addition, as a result of the potential range of variations that can occur in our dialysis-related reimbursements from Medicare under the single bundled payment rate system, our revenue recognition is subject to a greater degree of estimating risk.
Commercial healthcare plans, including contracted managed-care payors, are billed at our usual and customary rates; however, revenue is recognized based on estimated net realizable revenue for the services provided. Net realizable revenue is estimated based on contractual terms for the patients covered under commercial healthcare plans with which we have formal agreements, non-contracted commercial healthcare plan coverage terms if known, estimated secondary collections, historical collection experience, historical trends of refunds and payor payment adjustments (retractions), inefficiencies in our billing and collection processes that can result in denied claims for payments, the estimated timing of collections, changes in our expectations of the amounts that we expect to collect and regulatory compliance matters. Determining applicable primary and secondary coverage for our approximately 200,800 U.S. dialysis patients at any given point in time, together with the changes in patient coverages that occur each month, requires complex, resource-intensive processes. Collections, refunds and payor retractions typically continue to occur for up to three years or longer after services are provided.
We generally expect the range of our U.S. dialysis revenue estimating risk to be within 1% of revenue, which can represent as much as approximately 5% of our U.S. dialysis business’s operating income and adjusted operating income. Changes in estimates are reflected in the then-current financial statements based on on-going actual experience trends, or subsequent settlements and realizations depending on the nature and predictability of the estimates and contingencies. Changes in revenue estimates for prior periods are separately disclosed and reported if material to the current reporting period and longer term trend analyses, and have not been significant.
Revenues for laboratory services, which are integrally related to our dialysis services, are recognized in the period services are provided at the estimated net realizable amounts to be received.
Certain fair value estimates. Fair value measurements and estimates affect, or potentially affect, a variety of elements in the Company's financial statements. Two of the elements most significantly impacted by fair value estimates are the Company's goodwill impairment assessments and remeasurements of its noncontrolling interests subject to put provisions balance.
Goodwill is not amortized, but is assessed for impairment at least annually, or when changes in circumstances warrant. An impairment charge is recorded when and to the extent a reporting unit's carrying amount is determined to exceed its estimated fair value. Changes in circumstance that may trigger a goodwill impairment assessment for one of our business units can include, among others, changes in the legal environment, addressable market, business strategy, development or business plans, reimbursement structure or rates, operating performance, future prospects, relationships with partners, interest rates and/or market value indications for the subject business. We use a variety of factors to assess changes in the financial condition, future prospects and other circumstances for businesses subject to goodwill impairment assessment. However, these assessments and the related valuations can involve significant uncertainties and require significant judgment on various matters.
The Company is also required to remeasure its noncontrolling interests subject to put provisions to estimated fair value each reporting period. These estimates also require substantive judgment on meaningful uncertainties concerning this significant balance. See Notes 16 and 23 to the consolidated financial statements for a summary of the Company's approach to these valuations, the variables and uncertainties involved, and the sensitivity of these valuations to changes in a primary aggregate valuation metric.
Accounting for income taxes. Our income tax expense, deferred tax assets and liabilities, and liabilities for unrecognized tax benefits reflect management’s best assessment of estimated current and future taxes to be paid. We are subject to income taxes in the United States and numerous state and foreign jurisdictions, and changes in tax laws or regulations may be proposed or enacted that could adversely affect our overall tax liability. The actual impact of any such laws or regulations could be materially different from our current estimates.
Significant judgments and estimates are required in determining our consolidated income tax expense. Deferred income taxes arise from temporary differences between the tax basis of assets and liabilities and their reported amounts in the financial statements, which will result in taxable or deductible amounts in the future. In evaluating our ability to recover our deferred tax assets within the jurisdictions from which they arise, we consider all available positive and negative evidence, including scheduled reversals of deferred tax liabilities, projected future taxable income, tax planning strategies, results of recent operations, and assumptions about the amount of future federal, state, and foreign pre-tax operating income adjusted for items that do not have tax consequences. The assumptions about future taxable income require significant judgments and are consistent with the plans and estimates we use to manage the underlying businesses. To the extent that recovery is not likely, a valuation allowance is established. The allowance is regularly reviewed and updated for changes in circumstances that would cause a change in judgment about the realizability of the related deferred tax assets.
Loss contingencies. As discussed in Notes 1 and 15 to the consolidated financial statements, we operate in a highly regulated industry and are party to various lawsuits, claims, qui tam suits, governmental investigations and audits (including, without limitation, investigations or other actions resulting from our obligation to self-report suspected violations of law), contract disputes and other legal proceedings. Assessments of such matters can involve a series of complex judgments about future events and can rely heavily on estimates and assumptions. We record accruals for loss contingencies on such matters to the extent that we determine an unfavorable outcome is probable and the amount of the loss can be reasonably estimated. See Note 15 to the consolidated financial statements included in this report for further discussion.
Significant new accounting standards
See Note 1 to the consolidated financial statements included in this report for information regarding certain recent financial accounting standards that have been issued by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB).
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk
Market risk is the potential loss arising from adverse changes in market rates and prices, such as foreign currency exchange rates, interest rates and other relevant market rate or price changes. In the ordinary course of business, the Company is exposed to various market risks, including changes in foreign currency exchange and interest rates, and the Company regularly evaluates the exposure to such changes. The Company addresses its exposure to market risks, principally the market risks associated with changes in interest rates, through a controlled program of risk management that includes, from time to time, the use of derivative financial instruments such as interest rate cap agreements. The Company does not hold or issue derivative financial instruments for trading purposes.
Interest rate sensitivity
We believe that our cash flows from operations and other sources of liquidity, including from amounts available under our current credit facilities and our access to the capital markets, will be sufficient to fund our scheduled debt service under the terms of our debt agreements and other obligations for the foreseeable future, including the next 12 months. Our primary recurrent sources of liquidity are cash from operations and cash from borrowings.
One means of assessing exposure to debt-related interest rate changes is a duration-based analysis that measures the potential loss in net income resulting from a hypothetical increase in interest rates of 100 basis points across all variable rate maturities (referred to as a parallel shift in the yield curve). Under this model, with all else held constant, it is estimated that such an increase would have reduced net income by approximately $4.2 million, $4.8 million, and $21.4 million, net of tax and the effect of our interest rate caps, for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023, and 2022, respectively.
For a further discussion of our debt and interest rate cap agreements, see Note 12 to our consolidated financial statements at Part IV Item 15, "Exhibits, Financial Statement Schedules" – Note 12 as referred from Part II Item 8, "Financial Statements and Supplementary Data."
Exchange rate sensitivity
While our business is predominantly conducted in the U.S., we have developing operations in 13 other countries as well. For financial reporting purposes, the U.S. dollar is our reporting currency. However, the functional currencies of our operating businesses in other countries are typically those of the countries in which they operate. Therefore, changes in the rate of exchange between the U.S. dollar and the local currencies in which our international operations are conducted affect our results of operations and financial position as reported in our consolidated financial statements.
We have consolidated the balance sheets of our non-U.S. dollar denominated operations into U.S. dollars at the exchange rates prevailing at the balance sheet dates and have translated their revenues and expenses at average exchange rates during each period. Additionally, our individual subsidiaries are exposed to transactional risks mainly resulting from intercompany transactions between and among subsidiaries with different functional currencies. This exposes the subsidiaries to fluctuations in the rate of exchange between the invoicing or obligation currencies and the currency in which their local operations are conducted.
We evaluate our exposure to foreign exchange risk through the judgment of our international and corporate management teams. Our international operations constitute approximately 14% of our consolidated assets and approximately 8% of our consolidated revenues for the year ended December 31, 2024, with no single country constituting more than 4% of consolidated assets. In addition, our unrealized foreign currency translation (losses) gains were approximately 9.9%, 5.5%, and 2.2% of our consolidated operating income for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively.
Given the relatively small size of our international operations, management does not consider our exposure to foreign exchange risk to be significant to the consolidated enterprise. As such, through December 31, 2024, we have not engaged in transactions to hedge the exposure of our international transactions or net investments to foreign currency risk.
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data
See the Index to Financial Statements and Index to Financial Statement Schedules included at Part IV Item 15, "Exhibits, Financial Statement Schedules."
Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure
None.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures
Management has established and maintains disclosure controls and procedures designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed in the reports that it files or submits pursuant to the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 (Exchange Act) as amended is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms, and that such information is accumulated and communicated to our management including our Chief Executive Officer (CEO) and Chief Financial Officer (CFO) as appropriate to allow for timely decisions regarding required disclosures.
At the end of the period covered by this report, we carried out an evaluation, under the supervision and with the participation of our CEO and CFO, of the effectiveness of the design and operation of the Company's disclosure controls and procedures in accordance with the Exchange Act requirements as of December 31, 2024. Based upon that evaluation, the CEO and CFO concluded that the Company's disclosure controls and procedures were effective as required by the Exchange Act as of such date for our Exchange Act reports, including this report. Management recognizes that these controls and procedures can provide only reasonable assurance of desired outcomes, and that estimates and judgments are still inherent in the process of maintaining effective controls and procedures.
There was no change in the Company's internal control over financial reporting that was identified during the evaluation that occurred during the fourth fiscal quarter of 2024 that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, the Company's internal control over financial reporting.
Item 9B. Other Information
None of our directors or executive officers adopted or terminated a Rule 10b5-1 trading arrangement or adopted or terminated a non-Rule 10b5-1 trading arrangement (as defined in Item 408(c) of Regulation S-K) during the quarter ended December 31, 2024.
Item 9C. Disclosure Regarding Foreign Jurisdictions that Prevent Inspections
Not applicable.
PART III
Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance
We intend to disclose any amendments or waivers to the Code of Ethics applicable to our principal executive officer, principal financial officer, principal accounting officer or controller or persons performing similar functions, on our website located at http://www.davita.com. In 2002, we adopted a Corporate Governance Code of Ethics that applies to our principal executive officer, principal financial officer, principal accounting officer or controller, and to all of our financial accounting and legal professionals who are directly or indirectly involved in the preparation, reporting and fair presentation of our financial statements and Exchange Act reports. The Code of Ethics is posted on our website, located at http://www.davita.com. We also maintain a Corporate Code of Conduct that applies to all of our employees, officers and directors, which is posted on our website.
Under our Corporate Governance Guidelines all Board Committees including the Audit Committee, Nominating and Governance Committee and the Compensation Committee, which are composed solely of independent directors as defined within the listing standards of the New York Stock Exchange, have written charters that outline the committee’s purpose, goals, membership requirements and responsibilities. These charters are regularly reviewed and updated as necessary by our Board of Directors. All Board Committee charters as well as the Corporate Governance Guidelines are posted on our website located at http://www.davita.com.
The other information required to be disclosed by this item will appear in, and is incorporated by reference from, the sections entitled "Proposal 1 Election of Directors", "Corporate Governance", and "Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management" to be included in our definitive proxy statement relating to our 2025 annual stockholder meeting.
Item 11. Executive Compensation
The information required by this item will appear in, and is incorporated by reference from, the sections entitled "Executive Compensation", "Pay Ratio Disclosure", "Compensation of Directors" and "Compensation Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation" included in our definitive proxy statement relating to our 2025 annual stockholder meeting. The information required by Item 407(e)(5) of Regulation S-K will appear in and is incorporated by reference from the section entitled "Compensation Committee Report" to be included in our definitive proxy statement relating to our 2025 annual stockholder meeting; however, this information shall not be deemed to be filed.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters
The following table provides information about our common stock that may be issued upon the exercise of stock-settled stock appreciation rights, restricted stock units, performance stock units and other rights under all of our existing equity compensation plans as of December 31, 2024, which consist of our DaVita Inc. 2020 Incentive Award Plan, DaVita Healthcare Partners Inc. 2011 Incentive Award Plan and our DaVita Inc. Employee Stock Purchase Plan. The material terms of these plans are described in Note 17 to the consolidated financial statements.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Plan category (shares in thousands) | | Number of shares to be issued upon exercise of outstanding options, warrants and rights(1) | | Weighted average exercise price of outstanding options, warrants and rights(2) | | Number of shares remaining
available for future issuance under equity
compensation plans (excluding securities reflected in
column (a)) | | Total of shares reflected in columns (a) and (c) |
| | | (a) | | (b) | | (c) | | (d) |
| Equity compensation plans approved by shareholders | | 3,751 | | | $ | 108.02 | | | 10,256 | | | 14,007 | |
| Equity compensation plans not requiring shareholder approval | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
| Total | | 3,751 | | | $ | 108.02 | | | 10,256 | | | 14,007 | |
(1) Includes 673 shares of common stock reserved for issuance in connection with performance share units at the maximum number of shares issuable thereunder.
(2) This weighted average excludes full value awards such as restricted stock units and performance share units.
Other information required to be disclosed by Item 12 will appear in, and is incorporated by reference from, the section entitled "Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management" to be included in our definitive proxy statement relating to our 2025 annual stockholder meeting.
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence
The information required by this item will appear in, and is incorporated by reference from, the section entitled "Certain Relationships and Related Transactions" and the section entitled "Corporate Governance" to be included in our definitive proxy statement relating to our 2025 annual stockholder meeting.
Item 14. Principal Accounting Fees and Services
The information required by this item will appear in, and is incorporated by reference from, the section entitled "Proposal 2 Ratification of the Appointment of our Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm" to be included in our definitive proxy statement relating to our 2025 annual stockholder meeting. Our independent registered public accounting firm is KPMG LLP, Seattle, WA, USA PCAOB ID: 185.
PART IV
Item 15. Exhibits, Financial Statement Schedules
(a) Documents filed as part of this Report:
(1) Index to Financial Statements: (2) Exhibits
The information required by this Item is set forth in the Exhibit Index that precedes the signature pages of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Item 16. Form 10-K Summary
None.
DAVITA INC.
MANAGEMENT’S REPORT ON INTERNAL CONTROL OVER FINANCIAL REPORTING
Management is responsible for establishing and maintaining an adequate system of internal control over financial reporting designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles and which includes those policies and procedures that (i) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the Company; (ii) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the Company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the Company; and (iii) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the Company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
During the last fiscal year, the Company conducted an evaluation, under the oversight of the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, of the effectiveness of the design and operation of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. This evaluation was completed based on the criteria established in the report titled "Internal Control—Integrated Framework (2013)" issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO).
Based upon our evaluation under the COSO framework, we have concluded that the Company’s internal control over financial reporting was effective as of December 31, 2024.
The Company’s independent registered public accounting firm, KPMG LLP, has issued an attestation report on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting, which report is included in this Annual Report.
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Stockholders and the Board of Directors
DaVita Inc.:
Opinion on the Consolidated Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of DaVita Inc. and subsidiaries (the Company) as of December 31, 2024 and 2023, the related consolidated statements of income, comprehensive income, cash flows, and equity for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2024, and the related notes (collectively, the consolidated financial statements). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2024 and 2023, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2024, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2024, based on criteria established in Internal Control – Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission, and our report dated February 13, 2025 expressed an unqualified opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
Basis for Opinion
These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these consolidated financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the consolidated financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the consolidated financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the consolidated financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Critical Audit Matters
The critical audit matters communicated below are matters arising from the current period audit of the consolidated financial statements that were communicated or required to be communicated to the audit committee and that: (1) relate to accounts or disclosures that are material to the consolidated financial statements and (2) involved our especially challenging, subjective, or complex judgments. The communication of critical audit matters does not alter in any way our opinion on the consolidated financial statements, taken as a whole, and we are not, by communicating the critical audit matters below, providing separate opinions on the critical audit matters or on the accounts or disclosures to which they relate.
U.S. dialysis patient service revenue recognition
As discussed in Notes 1 and 2 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company recognized $11,366 million in U.S. dialysis patient service revenue for the year ended December 31, 2024. There are uncertainties associated with estimating U.S. dialysis patient service revenue, which generally take several years to resolve. As these estimates are refined over time, both positive and negative adjustments are recognized in the current period.
We identified the recognition of the transaction price the Company expects to collect as a result of satisfying its performance obligations related to U.S. dialysis patient service revenue as a critical audit matter because it involves estimation that requires complex auditor judgment. The key assumptions and inputs used to estimate the transaction price relate to ongoing insurance coverage changes, differing interpretations of contract coverage, determination of applicable primary and secondary coverage, coordination of benefits, and varying patient characteristics impacting Medicare reimbursements. Changes to the key assumptions and inputs used in the application of the methodology may have a significant effect on the Company’s determination of the estimate.
The following are the primary procedures we performed to address this critical audit matter. We evaluated the design and tested the operating effectiveness of certain internal controls over the Company’s U.S. dialysis patient service revenue recognition process, including controls related to the application of the methodology used to estimate the transaction price, and the key assumptions and inputs. We evaluated the Company’s key assumptions and inputs to estimate the transaction price the Company expects to collect as a result of satisfying its performance obligation by comparing key assumptions to historical collection experience, trends of refunds and payor payment adjustments, delays in the Company’s billing and collection process and regulatory compliance matters. Additionally, we compared U.S. dialysis patient service revenue related to the transaction price estimates recognized in prior periods to actual cash collections related to performance obligations satisfied in prior periods to analyze the Company’s ability to estimate the transaction price the Company expects to collect as a result of satisfying its performance obligations. We developed an estimate of U.S. dialysis patient service revenue recorded by the Company for the year ended December 31, 2024.
Evaluation of legal proceedings and regulatory matters
As discussed in Note 15 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company operates in a highly regulated industry and is a party to various lawsuits, demands, claims, qui tam suits, governmental investigations, audits (including, without limitation, investigations or other actions resulting from its obligation to self-report suspected violation of law) and other legal proceedings. The Company records accruals for certain legal proceedings and regulatory matters to the extent an unfavorable outcome is probable, and the amount of the loss can be reasonably estimated.
We identified the evaluation of legal proceedings and regulatory matters as a critical audit matter. Due to the nature of the legal proceedings and regulatory matters, a high degree of subjectivity was required in evaluating the completeness of the Company’s population of legal proceedings and regulatory matters. Additionally, complex auditor judgment was required in evaluating the Company’s probability of outcome assessment, and related disclosures.
The following are the primary procedures we performed to address this critical audit matter. We evaluated the design and tested the operating effectiveness of certain internal controls over the Company’s legal proceedings and regulatory matters process. This includes controls over the Company’s determination of the completeness of the population of legal proceedings and regulatory matters, as well as controls over the Company’s probability of outcome assessment, and related disclosures. We tested existing legal proceedings and regulatory matters by reading certain written correspondence received from outside parties as well as reading certain written responses provided to outside parties. We read letters received directly from the Company’s external and internal legal counsel that described certain legal proceedings and regulatory matters. We involved forensic professionals with specialized skills and knowledge who inspected the Company’s compliance case log. Additionally, we assessed the completeness of the population of legal proceedings and regulatory matters and related disclosures by 1) inquiring of certain key executives and directors and 2) evaluating information received through procedures described above and through publicly available information about the Company, its competitors, and the industry.
/s/ KPMG LLP
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2000.
Seattle, Washington
February 13, 2025
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Stockholders and the Board of Directors
DaVita Inc.:
Opinion on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
We have audited DaVita Inc. and subsidiaries' (the Company) internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2024, based on criteria established in Internal Control – Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. In our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2024, based on criteria established in Internal Control – Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the consolidated balance sheets of the Company as of December 31, 2024 and 2023, the related consolidated statements of income, comprehensive income, cash flows, and equity for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2024, and the related notes (collectively, the consolidated financial statements), and our report dated February 13, 2025 expressed an unqualified opinion on those consolidated financial statements.
Basis for Opinion
The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Management's Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audit also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
/s/ KPMG LLP
Seattle, Washington
February 13, 2025
DAVITA INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF INCOME
(dollars and shares in thousands, except per share data)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year ended December 31, |
| | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| Dialysis patient service revenues | $ | 12,260,375 | | | $ | 11,574,941 | | | $ | 11,176,464 | |
| Other revenues | 555,175 | | | 565,206 | | | 433,430 | |
| Total revenues | 12,815,550 | | | 12,140,147 | | | 11,609,894 | |
| Operating expenses: | | | | | |
| Patient care costs | 8,598,521 | | | 8,319,717 | | | 8,209,553 | |
| General and administrative | 1,538,341 | | | 1,473,984 | | | 1,355,197 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | 723,860 | | | 745,443 | | | 732,602 | |
| | | | | |
| Equity investment income, net | (26,189) | | | (27,864) | | | (26,520) | |
| | | | | |
| Goodwill impairment charges | — | | | 26,083 | | | — | |
| Gain on changes in ownership interests | (109,466) | | | — | | | — | |
| | | | | |
| Total operating expenses | 10,725,067 | | | 10,537,363 | | | 10,270,832 | |
| Operating income | 2,090,483 | | | 1,602,784 | | | 1,339,062 | |
| Debt expense | (470,469) | | | (398,551) | | | (357,019) | |
| Debt prepayment, extinguishment and modification costs | (19,813) | | | (7,962) | | | — | |
| Other loss, net | (69,808) | | | (19,177) | | | (15,765) | |
| Income from continuing operations before income taxes | 1,530,393 | | | 1,177,094 | | | 966,278 | |
| Income tax expense | 279,656 | | | 220,116 | | | 198,087 | |
| Net income from continuing operations | 1,250,737 | | | 956,978 | | | 768,191 | |
| Net income from discontinued operations, net of tax | — | | | — | | | 13,452 | |
| Net income | 1,250,737 | | | 956,978 | | | 781,643 | |
| Less: Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests | (314,395) | | | (265,443) | | | (221,243) | |
| Net income attributable to DaVita Inc. | $ | 936,342 | | | $ | 691,535 | | | $ | 560,400 | |
| | | | | |
| Earnings per share attributable to DaVita Inc.: | | | | | |
| Basic net income from continuing operations | $ | 11.02 | | | $ | 7.62 | | | $ | 5.88 | |
| Basic net income | $ | 11.02 | | | $ | 7.62 | | | $ | 6.03 | |
| Diluted net income from continuing operations | $ | 10.73 | | | $ | 7.42 | | | $ | 5.71 | |
| Diluted net income | $ | 10.73 | | | $ | 7.42 | | | $ | 5.85 | |
| | | | | |
| Weighted average shares for earnings per share: | | | | | |
| Basic shares | 84,991 | | | 90,790 | | | 92,992 | |
| Diluted shares | 87,274 | | | 93,182 | | | 95,834 | |
| | | | | |
| Amounts attributable to DaVita Inc.: | | | | | |
| Net income from continuing operations | $ | 936,342 | | | $ | 691,535 | | | $ | 546,948 | |
| Net income from discontinued operations | — | | | — | | | 13,452 | |
| Net income attributable to DaVita Inc. | $ | 936,342 | | | $ | 691,535 | | | $ | 560,400 | |
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
DAVITA INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
(dollars in thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year ended December 31, |
| | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Net income | $ | 1,250,737 | | | $ | 956,978 | | | $ | 781,643 | |
| Other comprehensive loss, net of tax: | | | | | |
| Unrealized gains on interest rate cap agreements: | | | | | |
| Unrealized gains | 7,250 | | | 6,895 | | | 108,669 | |
| Reclassification of net realized gains into net income | (43,660) | | | (77,727) | | | (8,806) | |
| Unrealized gains on defined benefit plans | 46 | | | — | | | — | |
| Unrealized (losses) gains on foreign currency translation: | | | | | |
| Unrealized (losses) gains | (207,861) | | | 87,934 | | | (29,802) | |
| Reclassification of net realized gains into net income | (14,487) | | | — | | | — | |
| Other comprehensive (loss) income | (258,712) | | | 17,102 | | | 70,061 | |
| Total comprehensive income | 992,025 | | | 974,080 | | | 851,704 | |
| Less: Comprehensive income attributable to noncontrolling interests | (314,395) | | | (265,443) | | | (221,243) | |
| Comprehensive income attributable to DaVita Inc. | $ | 677,630 | | | $ | 708,637 | | | $ | 630,461 | |
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
DAVITA INC.
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(dollars and shares in thousands, except per share data)
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 |
| ASSETS | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 794,933 | | | $ | 380,063 | |
| Restricted cash and equivalents | 84,892 | | | 84,571 | |
| Short-term investments | 51,064 | | | 11,610 | |
| Accounts receivable | 2,146,975 | | | 1,986,856 | |
| Inventories | 134,559 | | | 143,105 | |
| Other receivables | 383,166 | | | 422,669 | |
| Prepaid and other current assets | 122,948 | | | 102,645 | |
| Income tax receivable | 27,535 | | | 6,387 | |
| Total current assets | 3,746,072 | | | 3,137,906 | |
| Property and equipment, net of accumulated depreciation | 2,940,916 | | | 3,073,533 | |
| Operating lease right-of-use assets | 2,393,558 | | | 2,501,364 | |
| Intangible assets, net of accumulated amortization | 197,431 | | | 203,224 | |
| Equity method and other investments | 336,684 | | | 545,848 | |
| Long-term investments | 33,660 | | | 47,890 | |
| Other long-term assets | 261,731 | | | 271,253 | |
| Goodwill | 7,375,216 | | | 7,112,560 | |
| | $ | 17,285,268 | | | $ | 16,893,578 | |
| LIABILITIES AND EQUITY | | | |
| Accounts payable | $ | 547,200 | | | $ | 514,533 | |
| Other liabilities | 934,145 | | | 828,878 | |
| Accrued compensation and benefits | 800,484 | | | 752,598 | |
| Current portion of operating lease liabilities | 410,411 | | | 394,399 | |
| Current portion of long-term debt | 270,867 | | | 123,299 | |
| Income tax payable | 10,303 | | | 28,507 | |
| Total current liabilities | 2,973,410 | | | 2,642,214 | |
| Long-term operating lease liabilities | 2,209,655 | | | 2,330,389 | |
| Long-term debt | 9,175,903 | | | 8,268,334 | |
| Other long-term liabilities | 169,588 | | | 183,074 | |
| Deferred income taxes | 665,361 | | | 726,217 | |
| Total liabilities | 15,193,917 | | | 14,150,228 | |
| Commitments and contingencies | | | |
| Noncontrolling interests subject to put provisions | 1,695,483 | | | 1,499,288 | |
| Equity: | | | |
| Preferred stock ($0.001 par value, 5,000 shares authorized; none issued) | — | | | — | |
Common stock ($0.001 par value, 450,000 shares authorized; 90,369 and 80,536 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2024, respectively, and 88,824 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2023) | 90 | | | 89 | |
| Additional paid-in capital | 286,270 | | | 509,804 | |
| Retained earnings | 1,534,630 | | | 598,288 | |
| Treasury stock (9,833 and zero shares, respectively) | (1,389,072) | | | — | |
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss | (310,796) | | | (52,084) | |
| Total DaVita Inc. shareholders' equity | 121,122 | | | 1,056,097 | |
| Noncontrolling interests not subject to put provisions | 274,746 | | | 187,965 | |
| Total equity | 395,868 | | | 1,244,062 | |
| | $ | 17,285,268 | | | $ | 16,893,578 | |
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
DAVITA INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(dollars in thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year ended December 31, |
| | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Cash flows from operating activities: | | | | | |
| Net income | $ | 1,250,737 | | | $ | 956,978 | | | $ | 781,643 | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | | | | | |
| Depreciation and amortization | 723,860 | | | 745,443 | | | 732,602 | |
| Impairment charges | — | | | 26,083 | | | — | |
| Loss on extinguishment of debt | 12,527 | | | 7,132 | | | — | |
| Stock-based compensation expense | 102,788 | | | 112,375 | | | 95,427 | |
| Deferred income taxes | (57,840) | | | (39,354) | | | (75,669) | |
| Equity investment loss, net | 115,839 | | | 64,777 | | | 8,773 | |
| Gain on changes in ownership interests | (109,466) | | | — | | | — | |
| Other non-cash losses and (gains), net | 13,414 | | | (8,938) | | | 21,693 | |
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities, net of effect of acquisitions and divestitures: | | | | | |
| Accounts receivable | (29,766) | | | 172,361 | | | (148,394) | |
| Inventories | 17,942 | | | (32,132) | | | (757) | |
| Other current assets | 36,801 | | | (43,437) | | | 27,533 | |
| Other long-term assets | (67,031) | | | (5,792) | | | (50,549) | |
| Accounts payable | 1,699 | | | 26,890 | | | 87,481 | |
| Accrued compensation and benefits | 14,687 | | | 56,209 | | | 34,536 | |
| Other current liabilities | 46,733 | | | 27,082 | | | 89,955 | |
| Income taxes | (44,214) | | | 1,570 | | | (24,103) | |
| Other long-term liabilities | (6,672) | | | (8,216) | | | (15,601) | |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | 2,022,038 | | | 2,059,031 | | | 1,564,570 | |
| Cash flows from investing activities: | | | | | |
| Additions of property and equipment | (555,443) | | | (567,985) | | | (603,429) | |
| Acquisitions | (246,068) | | | (26,394) | | | (57,308) | |
| Proceeds from asset and business sales | 25,862 | | | 30,610 | | | 117,582 | |
| Purchase of debt investments held-to-maturity | (15,319) | | | (37,180) | | | (129,803) | |
| Purchase of other debt and equity investments | (9,140) | | | (9,566) | | | (3,590) | |
| Proceeds from debt investments held-to-maturity | 22,638 | | | 99,639 | | | 71,125 | |
| Proceeds from sale of other debt and equity investments | 4,566 | | | 10,365 | | | 3,781 | |
| Purchase of equity method investments | (5,205) | | | (276,202) | | | (31,885) | |
| Distributions from equity method investments | 6,680 | | | 4,913 | | | 3,962 | |
| Other | — | | | — | | | (782) | |
| Net cash used in investing activities | (771,429) | | | (771,800) | | | (630,347) | |
| Cash flows from financing activities: | | | | | |
| Borrowings | 6,624,310 | | | 2,468,341 | | | 2,393,116 | |
| Payments on long-term debt | (5,515,213) | | | (3,020,956) | | | (2,404,395) | |
| Deferred and debt related financing costs | (50,874) | | | (69,791) | | | (3) | |
| Purchase of treasury stock | (1,385,932) | | | (272,219) | | | (802,228) | |
| Distributions to noncontrolling interests | (337,042) | | | (280,938) | | | (267,946) | |
| Net proceeds from issuance of common stock under employee stock plans | 20,453 | | | 16,900 | | | 18,577 | |
| Payment of tax withholdings on net share settlements of equity awards | (134,040) | | | (65,012) | | | (55,944) | |
| Contributions from noncontrolling interests | 14,499 | | | 14,773 | | | 14,797 | |
| Proceeds from sales of additional noncontrolling interests | 860 | | | 50,962 | | | 3,673 | |
| Purchases of noncontrolling interests | (53,958) | | | (12,555) | | | (20,775) | |
| Net cash used in financing activities | (816,937) | | | (1,170,495) | | | (1,121,128) | |
| Effect of exchange rate changes on cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash | (18,481) | | | 8,909 | | | (29,066) | |
| Net increase (decrease) in cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash | 415,191 | | | 125,645 | | | (215,971) | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| Cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash at beginning of the year | 464,634 | | | 338,989 | | | 554,960 | |
| Cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash at end of the year | $ | 879,825 | | | $ | 464,634 | | | $ | 338,989 | |
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
DAVITA INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF EQUITY
(dollars and shares in thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Non-controlling
interests
subject to put
provisions | | DaVita Inc. Shareholders' Equity | | Non-controlling interests not
subject to
put provisions |
| | | | Additional
paid-in
capital | | Retained
earnings | | | | Accumulated
other
comprehensive
income (loss) | | | |
| | Common stock | | | | Treasury stock | | | | |
| | Shares | | Amount | | | | Shares | | Amount | | | Total | |
| Balance at December 31, 2021 | $ | 1,434,832 | | | 97,289 | | | $ | 97 | | | $ | 540,321 | | | $ | 354,337 | | | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | (139,247) | | | $ | 755,508 | | | $ | 180,640 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Comprehensive income: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income | 151,379 | | | | | | | | | 560,400 | | | | | | | | | 560,400 | | | 69,864 | |
| Other comprehensive income | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 70,061 | | | 70,061 | | | |
| Stock purchase plan | | | 285 | | | — | | | 18,061 | | | | | | | | | | | 18,061 | | | |
| Stock award plans | | | 932 | | | 1 | | | (55,921) | | | | | | | | | | | (55,920) | | | |
Stock-settled stock-based
compensation expense | | | | | | | 95,230 | | | | | | | | | | | 95,230 | | | |
Changes in noncontrolling
interest from: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Distributions | (176,957) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (90,989) | |
| Contributions | 10,962 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 3,835 | |
| Acquisitions and divestitures | 2,392 | | | | | | | 939 | | | | | | | | | | | 939 | | | 866 | |
| Partial purchases | (11,670) | | | | | | | (6,586) | | | | | | | | | | | (6,586) | | | (193) | |
| Fair value remeasurements | (62,487) | | | | | | | 62,487 | | | | | | | | | | | 62,487 | | | |
| Other | 457 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | — | | | (457) | |
| Purchase of treasury stock | | | | | | | | | | | (8,095) | | | (787,854) | | | | | (787,854) | | | |
| Retirement of treasury stock | | | (8,095) | | | (8) | | | (47,596) | | | (740,250) | | | 8,095 | | | 787,854 | | | | | — | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Balance at December 31, 2022 | $ | 1,348,908 | | | 90,411 | | | $ | 90 | | | $ | 606,935 | | | $ | 174,487 | | | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | (69,186) | | | $ | 712,326 | | | $ | 163,566 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Comprehensive income: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income | 176,789 | | | | | | | | | 691,535 | | | | | | | | | 691,535 | | | 88,654 | |
| Other comprehensive income | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 17,102 | | | 17,102 | | | |
| Stock purchase plan | | | 231 | | | — | | | 18,213 | | | | | | | | | | | 18,213 | | | |
| Stock award plans | | | 1,086 | | | 2 | | | (65,014) | | | | | | | | | | | (65,012) | | | |
Stock-settled stock-based
compensation expense | | | | | | | 109,813 | | | | | | | | | | | 109,813 | | | |
Changes in noncontrolling
interest from: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Distributions | (184,044) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (96,894) | |
| Contributions | 12,878 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 1,895 | |
| Acquisitions and divestitures | 181 | | | | | | | 13,077 | | | | | | | | | | | 13,077 | | | 30,776 | |
| Partial purchases | (5,296) | | | | | | | (5,375) | | | | | | | | | | | (5,375) | | | (32) | |
| Fair value remeasurements | 149,872 | | | | | | | (149,872) | | | | | | | | | | | (149,872) | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Purchase of treasury stock | | | | | | | | | | | (2,904) | | | (285,710) | | | | | (285,710) | | | |
| Retirement of treasury stock | | | (2,904) | | | (3) | | | (17,973) | | | (267,734) | | | 2,904 | | | 285,710 | | | | | — | | | |
| Balance at December 31, 2023 | $ | 1,499,288 | | | 88,824 | | | $ | 89 | | | $ | 509,804 | | | $ | 598,288 | | | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | (52,084) | | | $ | 1,056,097 | | | $ | 187,965 | |
DAVITA INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF EQUITY - continued
(dollars and shares in thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Non-controlling
interests
subject to put
provisions | | DaVita Inc. Shareholders' Equity | | Non-controlling interests not
subject to
put provisions |
| | | Additional
paid-in
capital | | Retained
earnings | | | | Accumulated
other
comprehensive
income (loss) | | | |
| Common stock | | | | Treasury stock | | | | |
| Shares | | Amount | | | | Shares | | Amount | | | Total | |
| Balance at December 31, 2023 | $ | 1,499,288 | | | 88,824 | | | $ | 89 | | | $ | 509,804 | | | $ | 598,288 | | | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | (52,084) | | | $ | 1,056,097 | | | $ | 187,965 | |
| Comprehensive income: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income | 214,986 | | | | | | | | | 936,342 | | | | | | | | | 936,342 | | | 99,409 | |
| Other comprehensive loss | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (258,712) | | | (258,712) | | | |
| Stock purchase plan | | | 184 | | | | | 20,441 | | | | | | | | | | | 20,441 | | | |
| Stock award plans | | | 1,361 | | | 1 | | | (134,041) | | | | | | | | | | | (134,040) | | | |
Stock-settled stock-based
compensation expense | | | | | | | 99,095 | | | | | | | | | | | 99,095 | | | |
Changes in noncontrolling
interest from: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Distributions | (226,389) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (110,653) | |
| Contributions | 11,639 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 2,860 | |
| Acquisitions and divestitures | 38,806 | | | | | | | 491 | | | | | | | | | | | 491 | | | 95,024 | |
| Partial purchases | (49,265) | | | | | | | (3,102) | | | | | | | | | | | (3,102) | | | 141 | |
| Fair value remeasurements | 206,418 | | | | | | | (206,418) | | | | | | | | | | | (206,418) | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Purchase of treasury stock | | | | | | | | | | | (9,833) | | | (1,389,072) | | | | | (1,389,072) | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Balance at December 31, 2024 | $ | 1,695,483 | | | 90,369 | | | $ | 90 | | | $ | 286,270 | | | $ | 1,534,630 | | | (9,833) | | | $ | (1,389,072) | | | $ | (310,796) | | | $ | 121,122 | | | $ | 274,746 | |
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
DAVITA INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(dollars in thousands, except per share data)
1. Organization and summary of significant accounting policies
Organization
The Company's operations are composed of its dialysis and related lab services to patients in the United States (its U.S. dialysis business), its U.S. integrated kidney care (IKC) business, its U.S. other ancillary services and its international operations (collectively, its ancillary services), as well as its corporate administrative support functions.
The Company’s largest line of business is its U.S. dialysis business, which operates kidney dialysis centers in the U.S. for patients suffering from chronic kidney failure, also known as end stage renal disease or end stage kidney disease (ESRD or ESKD). As of December 31, 2024, the Company operated or provided administrative services through a network of 2,657 U.S. outpatient dialysis centers in 46 states and the District of Columbia, serving a total of approximately 200,800 patients. In addition, as of December 31, 2024, the Company operated or provided administrative services to a total of 509 outpatient dialysis centers serving approximately 80,300 patients located in 13 countries outside of the U.S.
The Company’s U.S. dialysis and related lab services business qualifies as a separately reportable segment, and all other operating segments have been combined and disclosed in the other segments category.
Basis of presentation
These consolidated financial statements are prepared in accordance with United States generally accepted accounting principles (U.S. GAAP). The financial statements include DaVita Inc. and its subsidiaries, partnerships and other entities in which it maintains a majority voting or other controlling financial interest (collectively, the Company). All significant intercompany transactions and balances have been eliminated. Equity investments in investees over which the Company has significant influence are recorded on the equity method, while investments in other equity securities are recorded at fair value or on the adjusted cost method, as applicable. For the Company’s international subsidiaries, local currencies are considered their functional currencies. Translation adjustments result from translating the financial statements of the Company’s international subsidiaries from their functional currencies into the Company’s reporting currency (the U.S. dollar, or USD).
The Company has evaluated subsequent events through the date these consolidated financial statements were issued and has included all necessary adjustments and disclosures.
Use of estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with U.S. GAAP requires the use of estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of revenues, expenses, assets, liabilities, contingencies and noncontrolling interests subject to put provisions. Although actual results in subsequent periods will differ from these estimates, such estimates are developed based on the best information available to management and management’s best judgments at the time. All significant assumptions and estimates underlying the amounts reported in the financial statements and accompanying notes are regularly reviewed and updated when necessary. Changes in estimates are reflected in the financial statements based upon on-going actual experience trends or subsequent settlements and realizations depending on the nature and predictability of the estimates and contingencies.
The most significant assumptions and estimates underlying these consolidated financial statements and accompanying notes involve revenue recognition and accounts receivable, certain fair value estimates, accounting for income taxes and loss contingencies. Specific estimating risks and contingencies are further addressed within these notes to the consolidated financial statements.
Revenues
Dialysis patient service revenues
Revenues are recognized based on the Company’s estimate of the transaction price the Company expects to collect as a result of satisfying its performance obligations. Dialysis patient service revenues are recognized in the period services are provided based on these estimates. Revenues consist primarily of payments from government and commercial health plans for dialysis services provided to patients. The Company maintains a usual and customary fee schedule for its dialysis treatments and related lab services; however, actual collectible revenue is normally recognized at a discount from this fee schedule.
The majority of the Company's revenues are paid from government programs, principally Medicare, Medicare Advantage and Medicaid. Revenues associated with Medicare and Medicaid programs are estimated based on: (a) the payment
DAVITA INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (continued)
(dollars and shares in thousands, except per share data)
rates that are established by statute or regulation for the portion of payment rates paid by the government payor (e.g., 80% for Medicare patients) and (b) for the portion not paid by the primary government payor, estimates of the amounts ultimately collectible from other government programs providing secondary coverage (e.g., Medicaid secondary coverage), the patient’s commercial health plan secondary coverage, or the patient.
Under Medicare’s bundled payment rate system, services covered by Medicare are subject to estimating risk, whereby reimbursements from Medicare can vary significantly depending upon certain patient characteristics and other variable factors. Even with the bundled payment rate system, Medicare payments for bad debt claims as established by cost reports require evidence of collection efforts. As a result, billing and collection of Medicare bad debt claims can be delayed significantly and final payment is subject to audit. The Company’s revenue recognition is estimated based on its judgment regarding its ability to collect, which depends upon its ability to effectively capture, document and bill for Medicare’s base payment rate as well as these other variable factors.
Medicare Advantage revenues are reimbursed at negotiated contract rates that are generally higher than Medicare fee-for-service rates, but which generally have a slower payment cycle than Medicare fee-for-service payments, and some of which are subject to certain quality or performance adjustments. Medicare Advantage revenues are subject to meaningful estimating risk based on factors similar to those described for commercial health plans below.
Medicaid payments, when Medicaid coverage is secondary, can also be difficult to estimate. For many states, Medicaid payment terms and methods differ from Medicare, and may prevent accurate estimation of individual payment amounts prior to billing.
Revenues earned under government programs are subject to significant estimating risk, as they can be subject to adjustment as a result of examination by government agencies or contractors, differing interpretations of applicable regulations by different Medicare contractors or regulatory authorities, differing opinions regarding a patient's diagnosis or the medical necessity of patient services, or retroactive applications or interpretations of governmental requirements.
In addition to government programs, the Company also earns revenues that are paid by commercial health plans. Revenues associated with commercial health plans are estimated based on contractual terms for the patients under healthcare plans with which the Company has formal agreements, non-contracted health plan coverage terms if known, estimated secondary collections, historical collection experience, historical trends of refunds and payor payment adjustments (retractions), inefficiencies in the Company’s billing and collection processes that can result in denied claims for payments, delays in collections due to payor payment inefficiencies, and regulatory compliance matters.
Commercial revenue recognition also involves significant estimating risks. With many larger commercial insurers, the Company has several different contracts and payment arrangements, and these contracts often include only a subset of the Company’s centers. Some of the Company's commercial revenue contracts are also subject to certain quality or performance adjustments. In certain circumstances, it may not be possible to determine which contract, if any, should be applied prior to billing. In addition, for services provided by non-contracted centers, final collection may require specific negotiation of a payment amount, typically at a significant discount from the Company’s usual and customary rates.
As described above, there are significant risks associated with estimating dialysis patient service revenue, whether paid from governmental or commercial sources, many of which take several years to resolve. These estimates are subject to examinations by or differing interpretations among government contractors or agencies or other regulatory authorities, retroactive application of interpretations, commercial insurance coverage changes, geographic coverage differences, differing interpretations of commercial contract coverage and other payor- and patient-specific issues, including determination of applicable primary and secondary coverage, changes in patient insurance coverage and coordination of benefits. As the Company's revenue estimates are refined over time, both positive and negative adjustments to revenue are recognized in the current period.
Other revenues
Other revenues consist of revenues earned by the Company's non-dialysis ancillary services as well as fees for management and administrative services to outpatient dialysis businesses that the Company does not consolidate. Other revenues are estimated and recognized in the period the Company's performance obligations are met, subject to applicable measurement constraints.
The Company's IKC revenues include revenues earned under risk-based arrangements, including value-based care (VBC) arrangements. Under its VBC arrangements, the Company assumes full or shared financial risk for the total medical cost of care for patients below or above a benchmark. The benchmarks against which the Company incurs profit or loss on these
DAVITA INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (continued)
(dollars and shares in thousands, except per share data)
contracts are typically based on the underlying premiums paid to the insuring entity (the Company's counterparty), with adjustments where applicable, or on trended and adjusted medical cost targets.
For some of the Company's risk-based arrangements (such as its special needs plans), the Company acts as a principal with respect to all medical services provided to the patient by effectively hosting or sponsoring the entire arrangement, and as a result recognizes revenue and expense for all medical services provided to covered patients. However, under its VBC arrangements (including VBC contracts with health plans and via direct government programs), the Company provides health monitoring and care coordination services to patients but does not control or direct the medical services that patients receive from third party providers. As a result, the Company does not include third party medical costs in its reported revenues and expenses for its VBC arrangements, but rather recognizes revenue only for the estimated amount of shared savings or shared losses or related revenues that are directly earned or incurred by the Company, and ultimately paid to or by the Company, under the arrangement.
Measurements of revenue for the Company's IKC risk-based arrangements are complex, sensitive to a number of key inputs, and require meaningful estimates for a number of factors, including but not limited to member alignment data, third-party medical claims expense, outcomes on various quality metrics, and ultimate risk adjustment factor (RAF) scores. Information and other measurement limitations on these factors may constrain revenue recognition for a risk-based arrangement until a period after the Company's performance obligations have been met.
Other (loss) income, net
Other (loss) income includes interest income on cash and cash equivalents and short- and long-term investments, equity investment (loss) income on equity method investments other than dialysis partnerships, realized and unrealized gains and losses recognized on other investments, impairments on investments, and foreign currency transaction gains and losses.
Cash and cash equivalents
Cash equivalents are short-term highly liquid investments readily convertible to known amounts of cash that typically mature within three months or less at date of purchase.
Restricted cash and equivalents
Restricted cash and cash equivalents include funds held in trust to satisfy insurer and state regulatory requirements related to wholly-owned captive insurance companies that bear professional and general liability and workers' compensation risks for the Company as well as funds held in escrow.
Investments in debt and equity securities
The Company classifies certain debt securities as held-to-maturity and records them at amortized cost based on the Company’s intentions and strategies concerning those investments. Equity securities that have readily determinable fair values or redemption values are recorded at estimated fair value with changes in fair value recognized in current earnings within other (loss) income, net. These debt and equity investments are classified as short-term investments or long-term investments on the Company's consolidated balance sheet. See Note 4 for further details.
Inventories
Inventories are stated at the lower of cost (first-in, first-out) or net realizable value and consist principally of pharmaceuticals and dialysis-related supplies. Rebates related to inventory purchases are recorded when earned and are based on certain qualification requirements which are dependent on a variety of factors including future pricing levels and purchase volume levels from the manufacturer and related data submission.
Property and equipment
The Company capitalizes expenditures to purchase property and equipment, improvements thereon, leasehold improvements, and qualifying software costs, as well as costs to replace, extend the life of or improve the functionality of existing capital assets, where such purchases and costs have an expected benefit period of more than one year. All other expenditures related to capital assets are expensed as incurred (i.e., as repairs and maintenance expense).
Property and equipment is stated at cost less accumulated depreciation and amortization and is further reduced by any impairments. Maintenance and repairs are charged to expense as incurred. Property and equipment assets are reviewed for possible impairment whenever significant events or changes in circumstances indicate that an impairment may have occurred.
DAVITA INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (continued)
(dollars and shares in thousands, except per share data)
Property and equipment impairment assessments are performed at a location or market level, as applicable, based on the specific cash flows they support or protect. If the Company commits to a plan to dispose of a long-lived asset before the end of its previously estimated useful life, cash flow estimates are revised accordingly, and the Company records an asset impairment, if applicable, or accelerates depreciation over the revised estimated useful life. Upon sale or retirement of long-lived assets, the cost and related accumulated depreciation or amortization are removed from the balance sheet and any resulting gain or loss is included in current operating expenses.
Leases
The Company leases substantially all of its dialysis facilities. The majority of the Company’s facilities are leased under non-cancellable operating leases which contain renewal options. These renewal options are included in the Company's determination of lease right-of-use assets and related lease liabilities when renewal is considered reasonably certain at the commencement date. The Company's leases are generally subject to fixed escalation clauses or contain consumer price index increases.
The Company categorizes leases with contractual terms longer than twelve months as either operating or finance leases. Finance leases are generally those leases that allow the Company to substantially utilize or pay for the entire asset over its estimated life. All other leases are categorized as operating leases. The Company has elected the practical expedient to not separate lease components from non-lease components for its financing and operating leases. For short-term leases with a term of less than 12 months, the Company does not recognize lease right-of-use assets or lease liabilities and instead recognizes short-term lease costs as rent expense directly as incurred.
Financing and operating lease liabilities are measured at the net present value of lease payments over the lease term as of the commencement date. Since most of the Company's leases do not provide an implicit rate of return, the Company uses its incremental borrowing rate based on information available at the commencement date or remeasurement date in determining the present value of lease payments.
Assets acquired under finance leases are recorded on the balance sheet within property and equipment, net and liabilities for finance lease obligations are recorded within long-term debt. Finance lease assets are amortized to depreciation expense on a straight-line basis over the shorter of their estimated useful lives or the expected lease term. Accretion of interest on finance lease liabilities is included in debt expense.
Rights to use assets under operating leases are recorded on the balance sheet as operating lease right-of-use assets and liabilities for operating lease obligations are recorded as operating lease liabilities. Both amortization of operating lease right-of-use assets and interest accretion on operating lease liabilities are recorded to rent expense over the lease term. Rent expenses are included in patient care costs or general and administrative expense, as applicable, based on the business unit or corporate function for which the space is leased. The Company evaluates its lease right-of-use assets for impairments in a similar manner to long-lived assets, as described above in Property and equipment.
Amortizable intangibles
Amortizable intangible assets include noncompetition agreements, hospital service contracts, and customer relationships arising from other service contracts, each of which have finite useful lives. Amortization expense is computed using the straight-line method over the useful lives of the assets estimated as follows: noncompetition agreements and hospital acute service contracts over the contract term, and customer relationships from other service contracts over the remaining contract term plus expected renewal periods. Amortizable intangible assets are reviewed for possible impairment whenever significant events or changes in circumstances indicate that an impairment may have occurred. Amortizable intangible asset impairment assessments are performed on a location, market or business unit basis, as applicable, based on the specific cash flows they support or protect.
Indefinite-lived intangibles
Indefinite-lived intangible assets include international licenses and accreditations that allow the Company to be reimbursed for providing dialysis services to patients, each of which has an indefinite useful life. Indefinite-lived intangibles are not amortized, but are assessed for impairment at least annually and whenever significant events or changes in circumstances indicate that an impairment may have occurred. Costs to renew indefinite-lived intangible assets are expensed as incurred.
DAVITA INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (continued)
(dollars and shares in thousands, except per share data)
Equity method and other investments
Equity investments that do not have readily determinable fair values are carried on the equity method if the Company maintains significant influence over the investee unless the fair value option is elected. Equity investments without readily determinable fair values for which the Company does not maintain significant influence over the investee are carried either on the adjusted cost method or at estimated fair value, as determined on an investment-specific basis. The adjusted cost method represents the Company's cost for an investment, net of any impairments, as adjusted for any subsequent observable price changes. These equity investments are classified as equity method and other investments on the Company's consolidated balance sheet. See Note 8 for further details.
Equity method investments are assessed for other-than-temporary impairment when significant events or changes in circumstances indicate that an other-than-temporary impairment may have occurred. An other-than-temporary impairment charge is recorded when the fair value of an investment has fallen below its carrying amount and the shortfall is expected to be indefinitely or permanently unrecoverable.
Income and expense from nonconsolidated dialysis partnerships accounted for as equity method investments are recorded within equity investment income, net. For ownership interests accounted for as equity method investments other than dialysis partnerships, income and expense are included on up to a one quarter lag in other (loss) income, net.
Goodwill
Goodwill represents the difference between the fair value of businesses acquired and the fair value of the identifiable tangible and intangible net assets acquired. Goodwill is not amortized, but is assessed by individual reporting unit for impairment as circumstances warrant and at least annually.
The Company operates multiple reporting units. The Company's annual impairment assessment is performed in the third quarter for its U.S. dialysis reporting unit and at various points throughout the year for its other reporting units. In addition to these annual impairment assessments, the Company performs impairment assessments at intervening periods when a reporting unit is considered at risk of significant goodwill impairment.
In performing these assessments, the Company may first assess goodwill for impairment qualitatively as determined appropriate. If goodwill is more likely than not impaired, the Company is required to perform a quantitative assessment. When performing quantitative goodwill impairment assessments, the Company estimates fair value using either appraisals developed with an independent third party valuation firm, which consider both discounted cash flow estimates for the subject business and observed market multiples for similar businesses, or recent good-faith offer prices received for the subject business that would be acceptable to the Company. An impairment charge is recognized when and to the extent a reporting unit's carrying amount is determined to exceed its fair value after taking into account the effect of deferred taxes arising from the impairment. See Note 9 for further details.
Self-insurance
The Company predominantly self-insures its professional and general liability, workers' compensation and automobile risks, and a portion of its employment liability practice risks, through its wholly-owned captive insurance companies, with excess or reinsurance coverage for additional protection. The Company is also predominantly self-insured with respect to employee medical and other health benefits. The Company records insurance liabilities for the professional and general liability, workers’ compensation, automobile, employee health benefit and portion of employment liability practice risks that it retains and estimates its liability for those risks using third party actuarial calculations that are based upon historical claims experience and expectations for future claims.
Income taxes
Federal, state and foreign income taxes are computed at currently enacted tax rates less tax credits using the asset and liability method. Deferred taxes are adjusted both for items that do not currently have tax consequences and for the cumulative effect of any changes in tax rates from those previously used to determine deferred tax assets or liabilities. Tax provisions include amounts that are currently payable, changes in deferred tax assets and liabilities that arise because of temporary differences between the timing of when items of income and expense are recognized for financial reporting and income tax purposes, changes in the recognition of tax positions and any changes in the valuation allowance caused by a change in judgment about the realizability of the related deferred tax assets. A valuation allowance is established when necessary to reduce deferred tax assets to amounts expected to be realized.
DAVITA INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (continued)
(dollars and shares in thousands, except per share data)
The Company uses a recognition threshold of more-likely-than-not and a measurement attribute on all tax positions taken or expected to be taken in a tax return in order to be recognized in the financial statements. Once the recognition threshold is met, the tax position is then measured to determine the actual amount of benefit to recognize in the financial statements.
Stock-based compensation
The Company’s stock-based compensation expense for stock-settled awards is measured at the estimated fair value of awards on the date of grant and recognized on a cumulative straight-line basis over the vesting terms of the awards, unless the stock awards are based on non-market-based performance metrics, in which case expense is adjusted for the ultimate number of shares expected to be issued as of the end of each reporting period. Stock-based compensation expense for cash-settled awards is based on their estimated fair values as of the end of each reporting period. The expense for all stock-based awards is recognized net of expected forfeitures.
Stock-based compensation to be settled in shares is recorded to the Company’s shareholders’ contributed capital, while stock-based compensation to be settled in cash is recorded as a liability. Shares issued upon exercise or, when applicable, vesting of stock awards, are issued from authorized but unissued shares.
Interest rate cap agreements
The Company often carries a combination of current or forward interest rate caps on portions of its variable rate debt as a means of hedging its exposure to changes in Secured Overnight Financing Rate (SOFR) interest rates as part of its overall interest rate risk management strategy. These interest rate caps are not held for trading or speculative purposes and are designated as qualifying cash flow hedges. See Note 12 for further details.
Noncontrolling interests
Noncontrolling interests represent third-party equity interests in entities which are consolidated by the Company for financial statement reporting purposes. As of December 31, 2024, third parties held direct or indirect noncontrolling equity interests in 728 consolidated legal entities.
Fair value estimates
Fair value is defined as the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. Fair value measurements are determined based on the principal or most advantageous market for the item being measured, assume that buyers and sellers are independent, willing and able to transact, and knowledgeable, with access to all information customarily available in such a transaction, and are based on assumptions that market participants would use in pricing the item, not assumptions specific to the reporting entity. The criticality of a particular fair value estimate to the Company's consolidated financial statements depends upon the nature and size of the item being measured, the extent of uncertainties involved and the nature and magnitude or potential effect of assumptions and judgments required. Certain fair value estimates can involve significant uncertainties and require significant judgment on various matters, some of which could be subject to reasonable disagreement.
The Company relies on fair value measurements and estimates for purposes that require the recording, reassessment, or adjustment of the carrying amounts of certain assets, liabilities, and noncontrolling interests subject to put provisions (redeemable equity interests classified as temporary equity). These purposes can include the accounting for business combination transactions; impairment assessments for goodwill, other intangible assets, or other long-lived assets; recurrent revaluation of investments in debt and equity securities, contingent earn-out obligations, interest rate cap agreements, and noncontrolling interests subject to put provisions; and the accounting for equity method and other investments and stock-based compensation, as applicable. The Company has classified its assets, liabilities and temporary equity into the fair value hierarchy levels defined by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) reflecting their differing degrees of uncertainty. See Note 23 for further details.
New accounting standards
New standards recently adopted
In November 2023, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update (ASU) 2023-07, Segment Reporting (Topic 280): Improvements to Reportable Segment Disclosures, which expands reportable segment disclosure requirements, primarily through enhanced disclosures about significant segment expenses. The guidance also requires disclosure of the chief operating decision maker's (CODM) position for each segment and detail of how the CODM uses financial reporting to assess their
DAVITA INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (continued)
(dollars and shares in thousands, except per share data)
segment’s performance. The amendments in this ASU became effective for the Company beginning January 1, 2024. See Note 24 for further discussion of the Company's reportable segments.
New standards not yet adopted
In December 2023, the Financial Accounting Standards Board issued ASU 2023-09, Income Taxes (Topic 740): Improvements to Income Tax Disclosures, which expands income tax disclosure requirements to include additional information related to the rate reconciliation of effective tax rates to statutory rates, as well as additional disaggregation of taxes paid in both U.S. and foreign jurisdictions. The amendments in the ASU also remove disclosures related to certain unrecognized tax benefits and deferred taxes. ASU 2023-09 is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2024. The amendments may be applied prospectively or retrospectively, and early adoption is permitted. The Company intends to adopt this ASU for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2025 and is still assessing the effect this guidance may have on its consolidated financial statement disclosures.
In November 2024, the Financial Accounting Standards Board issued ASU 2024-03, Income Statement—Reporting Comprehensive Income—Expense Disaggregation Disclosures, which requires disaggregated disclosure of income statement expenses, including purchases of inventory, employee compensation, depreciation, and amortization. The amendments in this ASU are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2026. The amendments in this ASU may be applied prospectively or retrospectively, and early adoption is permitted. The Company is currently assessing the effect this guidance may have on its consolidated financial statements.
DAVITA INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (continued)
(dollars and shares in thousands, except per share data)
2. Revenue recognition and accounts receivable
The Company's revenues by segment and primary payor source were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year ended December 31, 2024 |
| U.S. dialysis | | Other - Ancillary services | | Consolidated |
| Patient service revenues: | | | | | |
| Medicare and Medicare Advantage | $ | 6,374,882 | | | $ | | $ | 6,374,882 | |
| Medicaid and Managed Medicaid | 863,947 | | | | | 863,947 | |
| Other government | 343,705 | | | 717,735 | | | 1,061,440 | |
| Commercial | 3,783,827 | | | 248,026 | | | 4,031,853 | |
| Other revenues: | | | | | |
| Medicare and Medicare Advantage | | | 463,731 | | | 463,731 | |
| Medicaid and Managed Medicaid | | | 740 | | | 740 | |
| Commercial | | | 21,396 | | | 21,396 | |
Other(1) | 24,356 | | | 58,862 | | | 83,218 | |
| Eliminations of intersegment revenues | (71,747) | | | (13,910) | | | (85,657) | |
| Total | $ | 11,318,970 | | | $ | 1,496,580 | | | $ | 12,815,550 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year ended December 31, 2023 |
| U.S. dialysis | | Other - Ancillary services | | Consolidated |
| Patient service revenues: | | | | | |
| Medicare and Medicare Advantage | $ | 6,100,183 | | | $ | | $ | 6,100,183 | |
| Medicaid and Managed Medicaid | 833,744 | | | | | 833,744 | |
| Other government | 354,304 | | | 500,137 | | | 854,441 | |
| Commercial | 3,623,516 | | | 251,279 | | | 3,874,795 | |
| Other revenues: | | | | | |
| Medicare and Medicare Advantage | | | 460,991 | | | 460,991 | |
| Medicaid and Managed Medicaid | | | 1,733 | | | 1,733 | |
| Commercial | | | 32,329 | | | 32,329 | |
Other(1) | 25,251 | | | 52,754 | | | 78,005 | |
| Eliminations of intersegment revenues | (88,222) | | | (7,852) | | | (96,074) | |
| Total | $ | 10,848,776 | | | $ | 1,291,371 | | | $ | 12,140,147 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year ended December 31, 2022 |
| U.S. dialysis | | Other - Ancillary services | | Consolidated |
| Patient service revenues: | | | | | |
| Medicare and Medicare Advantage | $ | 6,041,496 | | | $ | | $ | 6,041,496 | |
| Medicaid and Managed Medicaid | 759,579 | | | | | 759,579 | |
| Other government | 336,991 | | | 464,921 | | | 801,912 | |
| Commercial | 3,437,306 | | | 223,216 | | | 3,660,522 | |
| Other revenues: | | | | | |
| Medicare and Medicare Advantage | | | 345,340 | | | 345,340 | |
| Medicaid and Managed Medicaid | | | 1,546 | | | 1,546 | |
| Commercial | | | 22,211 | | | 22,211 | |
Other(1) | 24,437 | | | 44,092 | | | 68,529 | |
| Eliminations of intersegment revenues | (87,035) | | | (4,206) | | | (91,241) | |
| Total | $ | 10,512,774 | | | $ | 1,097,120 | | | $ | 11,609,894 | |
(1)Consists primarily of management service fees in the Company's U.S. dialysis business and research fees, management fees, and other non-patient service revenues in the Other - ancillary services businesses.
DAVITA INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (continued)
(dollars and shares in thousands, except per share data)
The majority of the Company's non-patient service revenues from Medicare and Medicare Advantage, Medicaid and Managed Medicaid, and commercial sources represent risk-based revenues earned by the Company's U.S. IKC business.
For its IKC business, the Company recognized revenues for performance obligations satisfied in previous years of $116,336, $94,361, and $34,600 during the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively. The delay in recognition of these amounts resulted predominantly from measurement limitations and recognition constraints on both the Company's VBC contracts with health plans, many of which are complex and relatively new arrangements, as well as its government Comprehensive Kidney Care Contracting (CKCC) program. The Company's revenue recognition for its government CKCC program also remains heavily constrained for plan year 2024. See Note 1 "Other revenues" for a description of the Company's accounting for these value-based care arrangements.
No single commercial payor accounted for more than 10% of consolidated revenues or consolidated accounts receivable for the periods presented in these consolidated financial statements or at their period-ends, respectively.
Dialysis services accounts receivable and other receivables from Medicare, including Medicare Advantage plans, and Medicaid, including managed Medicaid plans, were approximately $833,464 and $817,045 as of December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively. Approximately 23% and 19% of the Company’s U.S. dialysis accounts receivable balances as of December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively, were more than six months old. There were no significant balances over one year old at December 31, 2024. The Company's accounts receivable are principally due from Medicare and Medicaid programs and commercial insurance plans.
3. Earnings per share
Basic earnings per share is calculated by dividing net income attributable to the Company by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding. Weighted average common shares outstanding include restricted stock unit awards that are no longer subject to forfeiture because the recipients have satisfied either their explicit vesting terms or retirement eligibility requirements.
Diluted earnings per share includes the dilutive effect of outstanding stock-settled stock appreciation rights and unvested stock units as computed under the treasury stock method.
The reconciliations of the numerators and denominators used to calculate basic and diluted earnings per share were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year ended December 31, |
| | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Net income attributable to DaVita Inc.: | | | | | |
| Continuing operations | $ | 936,342 | | | $ | 691,535 | | | $ | 546,948 | |
| Discontinued operations | — | | | — | | | 13,452 | |
| Net income attributable to DaVita Inc. | $ | 936,342 | | | $ | 691,535 | | | $ | 560,400 | |
| | | | | |
| Weighted average shares outstanding: | | | | | |
| Basic shares | 84,991 | | | 90,790 | | | 92,992 | |
| Assumed incremental from stock plans | 2,283 | | | 2,392 | | | 2,842 | |
| Diluted shares | 87,274 | | | 93,182 | | | 95,834 | |
| | | | | |
| Basic net income attributable to DaVita Inc.: | | | | | |
| Continuing operations per share | $ | 11.02 | | | $ | 7.62 | | | $ | 5.88 | |
| Discontinued operations per share | — | | | — | | | 0.15 | |
| Basic net income per share attributable to DaVita Inc. | $ | 11.02 | | | $ | 7.62 | | | $ | 6.03 | |
| | | | | |
| Diluted net income attributable to DaVita Inc.: | | | | | |
| Continuing operations per share | $ | 10.73 | | | $ | 7.42 | | | $ | 5.71 | |
| Discontinued operations per share | — | | | — | | | 0.14 | |
| Diluted net income per share attributable to DaVita Inc. | $ | 10.73 | | | $ | 7.42 | | | $ | 5.85 | |
| | | | | |
Anti-dilutive stock-settled awards excluded from calculation(1) | 103 | | | 531 | | | 1,058 | |
(1)Shares associated with stock awards excluded from the diluted denominator calculation because they were anti-dilutive under the treasury stock method.
DAVITA INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (continued)
(dollars and shares in thousands, except per share data)
4. Short-term and long-term investments
The Company’s short-term and long-term investments, consisting of debt instruments classified as held-to-maturity and equity investments with readily determinable fair values or redemption values, were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, 2024 | | December 31, 2023 |
| | Debt
securities | | Equity
securities | | Total | | Debt
securities | | Equity
securities | | Total |
| Certificates of deposit and other time deposits | $ | 44,158 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 44,158 | | | $ | 22,109 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 22,109 | |
| Investments in mutual funds and common stock | — | | | 40,566 | | | 40,566 | | | — | | | 37,391 | | | 37,391 | |
| | $ | 44,158 | | | $ | 40,566 | | | $ | 84,724 | | | $ | 22,109 | | | $ | 37,391 | | | $ | 59,500 | |
| Short-term investments | $ | 44,158 | | | $ | 6,906 | | | $ | 51,064 | | | $ | 7,110 | | | $ | 4,500 | | | $ | 11,610 | |
| Long-term investments | — | | | 33,660 | | | 33,660 | | | 14,999 | | | 32,891 | | | 47,890 | |
| | $ | 44,158 | | | $ | 40,566 | | | $ | 84,724 | | | $ | 22,109 | | | $ | 37,391 | | | $ | 59,500 | |
Debt securities: The Company's short-term debt investments are principally bank certificates of deposit with contractual maturities longer than three months but shorter than one year. Typically, the Company's long-term debt investments are bank time deposits with contractual maturities longer than one year. These debt securities are accounted for as held-to-maturity and recorded at amortized cost, which approximated their fair values at December 31, 2024 and 2023.
Equity securities: Substantially all of the Company's short-term and long-term equity investments are held within a trust to fund existing obligations associated with the Company’s non-qualified deferred compensation plans.
5. Other receivables
Other receivables comprised the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, |
| | 2024 | | 2023 |
| Customer contract assets: | | | |
| Medicare bad debt claims | $ | 107,129 | | | $ | 107,444 | |
| IKC risk-based arrangements | 143,942 | | | 127,442 | |
| Supplier rebates and non-trade receivables | 132,095 | | | 187,783 | |
| | 383,166 | | | $ | 422,669 | |
6. Property and equipment
Property and equipment comprised the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, |
| | 2024 | | 2023 |
| Land | $ | 50,172 | | | $ | 35,216 | |
| Buildings | 428,994 | | | 436,460 | |
| Leasehold improvements | 4,180,747 | | | 4,058,987 | |
| Equipment and information systems, including internally developed software | 4,410,395 | | | 4,125,235 | |
| New center and capital asset projects in progress | 133,311 | | | 177,149 | |
| | 9,203,619 | | | 8,833,047 | |
| Less accumulated depreciation | (6,262,703) | | | (5,759,514) | |
| | $ | 2,940,916 | | | $ | 3,073,533 | |
Depreciation and amortization expenses are computed using the straight-line method over the useful lives of the assets estimated as follows: buildings, 25 years to 40 years; leasehold improvements, the shorter of ten years or the expected lease term; and equipment and information systems, including internally developed software, principally three years to 15 years. Depreciation expense on property and equipment was $716,396, $736,474 and $721,133 for 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively.
Interest on debt incurred during the development of new centers and other capital asset projects is capitalized as a component of the asset cost based on the respective in-process capital asset balances. Interest capitalized was $7,978, $9,178 and $12,677 for 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively.
7. Intangible assets
Intangible assets other than goodwill comprised the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, |
| | 2024 | | 2023 |
| Indefinite-lived licenses | $ | 146,025 | | | $ | 153,983 | |
| Noncompetition agreements | 22,234 | | | 31,090 | |
| Customer relationships and other | 61,580 | | | 56,596 | |
| | 229,839 | | | 241,669 | |
| Accumulated amortization: | | | |
| Noncompetition agreements | (13,982) | | | (23,680) | |
| Customer relationships and other | (18,426) | | | (14,765) | |
| | $ | 197,431 | | | $ | 203,224 | |
Noncompetition agreements are generally amortized over four years to 10 years and customer relationships are principally amortized over 10 years to 20 years. The weighted average renewal or extension period of customer relationships was three years and two years as of December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively. Amortization expense from amortizable intangible assets was $7,464, $8,969, and $11,469 for 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively.
For the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, the Company recognized no impairment charges on any intangible assets other than goodwill. See Note 9 for further information regarding goodwill.
Scheduled amortization expenses from amortizable intangible assets as of December 31, 2024 were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Noncompetition
agreements | | Customer relationships and other |
| 2025 | $ | 2,301 | | | $ | 4,031 | |
| 2026 | 1,598 | | | 4,047 | |
| 2027 | 1,157 | | | 3,871 | |
| 2028 | 956 | | | 3,784 | |
| 2029 | 427 | | | 3,780 | |
| Thereafter | 1,813 | | | 23,641 | |
| Total | $ | 8,252 | | | $ | 43,154 | |
8. Equity method and other investments
The Company maintains equity method and other minor investments in the private securities of certain other healthcare and healthcare-related businesses as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, |
| | 2024 | | 2023 |
| Mozarc Medical Holding LLC | $ | 215,706 | | | $ | 324,711 | |
| APAC joint venture | — | | | 98,865 | |
| Other equity method partnerships | 99,246 | | | 107,282 | |
| Adjusted cost method and other investments | 21,732 | | | 14,990 | |
| $ | 336,684 | | | $ | 545,848 | |
During 2024, 2023 and 2022, the Company recognized equity investment income of $26,189, $27,864 and $26,520, respectively, from its equity method investments in nonconsolidated dialysis partnerships. The Company also recognized equity investment losses from other equity method investments of $112,696, $59,508 and $4,703 in other loss, net during 2024, 2023
DAVITA INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (continued)
(dollars and shares in thousands, except per share data)
and 2022, respectively.
Effective April 1, 2023, the Company formed a new, independent kidney care-focused medical device company (Mozarc Medical Holding LLC, or Mozarc) with Medtronic, Inc. (Medtronic). The Company holds a 50% voting equity interest in Mozarc and Medtronic holds the other 50% voting equity interest. The Company does not maintain a controlling financial interest in Mozarc and accounts for this investment on the equity method, with equity method income or loss recognized in other loss, net, on a one-month lag.
The Company's investment in Mozarc was recorded at a cumulative measured cost of $370,740, which includes the value of contingent consideration payable to Medtronic of $86,200. As of December 31, 2024, the book value of the Company's contingent consideration payable to Medtronic approximates its estimated fair value, which is based on level 3 inputs.
The Company also holds a 75% voting and economic interest in DaVita Care Pte. Ltd. (the APAC joint venture, or APAC JV) and an unrelated noncontrolling investor holds the other 25% voting and economic interest in the joint venture.
Prior to November 1, 2024, the Company did not control or consolidate the APAC JV as a result of substantive participating rights retained by the unrelated investor over certain key operating decisions for the joint venture. Effective November 1, 2024, the third-party rights that blocked the Company's ultimate unilateral operating control of this business were removed, resulting in the Company's consolidation of this business. See Note 20 for further information.
The Company's other equity method investments include 17 legal entities over which the Company has significant influence but in which it does not maintain a controlling financial interest. Almost all of these are U.S. dialysis partnerships in the form of limited liability companies. The Company's ownership interests in these partnerships vary, and are often subject to blocking rights on certain key operating decisions held by outside investors, but mostly range from 30% to 65%.
There were no significant investment impairments or other valuation adjustments for the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2023. For the year ended December 31, 2022, the Company recognized impairments and other valuation adjustments on the Company's adjusted cost method and other investments of $20,154 in other loss, net.
9. Goodwill
Changes in the carrying amount of goodwill by reportable segment were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | U.S. dialysis | | Other - Ancillary
services | | Consolidated |
| Balance at December 31, 2022 | $ | 6,416,825 | | | $ | 659,785 | | | $ | 7,076,610 | |
| Acquisitions | — | | | 25,723 | | | 25,723 | |
| Impairment charges | — | | | (26,083) | | | (26,083) | |
| Foreign currency and other adjustments | — | | | 36,310 | | | 36,310 | |
| Balance at December 31, 2023 | $ | 6,416,825 | | | $ | 695,735 | | | $ | 7,112,560 | |
| Acquisitions | 102,082 | | | 246,987 | | | 349,069 | |
| Divestitures | (1,687) | | | (1,506) | | | (3,193) | |
| | | | | |
| Foreign currency and other adjustments | — | | | (83,220) | | | (83,220) | |
| Balance at December 31, 2024 | $ | 6,517,220 | | | $ | 857,996 | | | $ | 7,375,216 | |
| | | | | |
| Balance at December 31, 2024: | | | | | |
| Goodwill | $ | 6,517,220 | | | $ | 999,817 | | | $ | 7,517,037 | |
| Accumulated impairment charges | — | | | (141,821) | | | (141,821) | |
| $ | 6,517,220 | | | $ | 857,996 | | | $ | 7,375,216 | |
Substantially all of the Company’s operating segments described in Note 24 to these consolidated financial statements represents an individual reporting unit for goodwill impairment assessment purposes.
Within the U.S. dialysis operating segment, the Company considers each of its dialysis centers to constitute an individual business for which discrete financial information is available. However, since these dialysis centers have similar operating and economic characteristics, and the allocation of resources and significant investment decisions concerning these businesses are highly centralized and the benefits broadly distributed, the Company has aggregated these centers and deemed them to constitute a single reporting unit.
DAVITA INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (continued)
(dollars and shares in thousands, except per share data)
The Company has applied a similar aggregation to the dialysis centers within each of its international reporting units. For the Company’s other operating segments, discrete business components below the operating segment level constitute individual reporting units.
The Company performed various annual impairment assessments during the year ended December 31, 2024, with no impairment indicated. None of the Company’s reporting units were considered at risk of significant goodwill impairment as of December 31, 2024.
During the year ended December 31, 2023, the Company performed its annual impairment assessment of its transplant software reporting unit and recognized a goodwill impairment charge of $26,083 in that reporting unit, or $19,575 net of tax. This charge resulted from a reduction in estimated fair value for the business driven primarily from the business not achieving its revenue targets, with reduced revenue expectations for future years, as well as an increase in the risk-free rate. After this impairment charge, the transplant software reporting unit had a goodwill balance of $14,424 remaining.
10. Other liabilities
Other liabilities comprised the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, |
| | 2024 | | 2023 |
| Payor refunds and retractions | $ | 484,459 | | | $ | 448,589 | |
| Insurance and self-insurance accruals | 83,038 | | | 74,337 | |
| Accrued interest | 60,541 | | | 35,914 | |
| Accrued non-income tax liabilities | 59,007 | | | 47,391 | |
| Other | 247,100 | | | 222,647 | |
| | $ | 934,145 | | | $ | 828,878 | |
11. Income taxes
The Company accounts for income taxes under the asset and liability method, which requires the recognition of deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future tax consequences of events that have been included in the consolidated financial statements. Under this method, deferred tax assets and liabilities are determined on the basis of the differences between the financial statement and tax basis of assets and liabilities using enacted tax rates in effect for the year in which the differences are expected to reverse.
Income before income taxes from continuing operations consisted of the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year ended December 31, |
| | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Domestic | $ | 1,374,571 | | | $ | 1,100,420 | | | $ | 926,604 | |
| International | 155,822 | | | 76,674 | | | 39,674 | |
| | $ | 1,530,393 | | | $ | 1,177,094 | | | $ | 966,278 | |
DAVITA INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (continued)
(dollars and shares in thousands, except per share data)
Income tax expense for continuing operations consisted of the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year ended December 31, |
| | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Current: | | | | | |
| Federal | $ | 253,504 | | | $ | 200,070 | | | $ | 201,932 | |
| State | 52,410 | | | 38,370 | | | 55,593 | |
| International | 31,532 | | | 21,008 | | | 16,253 | |
| Total current income tax | 337,446 | | | 259,448 | | | 273,778 | |
| Deferred: | | | | | |
| Federal | (47,715) | | | (40,234) | | | (66,400) | |
| State | (2,855) | | | 367 | | | (12,289) | |
| International | (7,220) | | | 535 | | | 2,998 | |
| Total deferred income tax | (57,790) | | | (39,332) | | | (75,691) | |
| | $ | 279,656 | | | $ | 220,116 | | | $ | 198,087 | |
The reconciliation between the Company’s effective tax rate from continuing operations and the U.S. federal income tax rate is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year ended December 31, |
| | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Federal income tax rate | 21.0 | % | | 21.0 | % | | 21.0 | % |
| State income taxes, net of federal benefit | 3.4 | | | 2.6 | | | 3.8 | |
| Equity compensation | (1.1) | | | (1.1) | | | (1.6) | |
| | | | | |
| Nondeductible executive compensation | 0.7 | | | 1.2 | | | 1.1 | |
| Political advocacy costs | 0.3 | | | 0.2 | | | 2.2 | |
| Unrecognized tax benefits | (0.5) | | | (1.1) | | | (1.1) | |
| Change in international valuation allowance | 0.1 | | | 0.8 | | | 1.2 | |
| Credits | (1.2) | | | (1.2) | | | (1.2) | |
| Other | 0.3 | | | 1.9 | | | 1.1 | |
Impact of noncontrolling interests primarily
attributable to non-tax paying entities | (4.7) | | | (5.6) | | | (6.0) | |
| Effective tax rate | 18.3 | % | | 18.7 | % | | 20.5 | % |
DAVITA INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (continued)
(dollars and shares in thousands, except per share data)
Deferred tax assets and liabilities arising from temporary differences for continuing operations were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, |
| | 2024 | | 2023 |
| Receivables | $ | 37,630 | | | $ | 23,075 | |
| Accrued liabilities | 74,419 | | | 81,281 | |
| Operating lease liabilities | 508,729 | | | 533,859 | |
| Net operating loss carryforwards | 161,371 | | | 183,216 | |
| Investments in partnerships | 4,108 | | | — | |
| Other | 54,600 | | | 52,142 | |
| Deferred tax assets | 840,857 | | | 873,573 | |
| Valuation allowance | (107,952) | | | (113,237) | |
| Net deferred tax assets | 732,905 | | | 760,336 | |
| Intangible assets | (757,797) | | | (731,024) | |
| Property and equipment | (63,726) | | | (127,191) | |
| Operating lease assets | (464,455) | | | (486,864) | |
| Investments in partnerships | — | | | (19,119) | |
| Other | (66,035) | | | (87,918) | |
| Deferred tax liabilities | (1,352,013) | | | (1,452,116) | |
| Net deferred tax liabilities | $ | (619,108) | | | $ | (691,780) | |
| Reported as: | | | |
| Deferred tax liabilities | $ | (665,361) | | | $ | (726,217) | |
| Deferred tax assets (included in Other long-term assets) | 46,253 | | | 34,437 | |
| $ | (619,108) | | | $ | (691,780) | |
At December 31, 2024, the Company had federal net operating loss carryforwards of approximately $44,248 that expire through 2036, although a substantial amount expire by 2029. The Company also had state net operating loss carryforwards of $555,691, some of which have an indefinite life, while a substantial amount expire by 2044. Additionally, the Company had international net operating loss carryforwards of $410,313, some of which will begin to expire in 2026, though the majority have an indefinite life. The Company has a state capital loss carryover of $9,653, the majority of which will expire in 2025. The utilization of a portion of these losses may be limited in future years based on the profitability of certain entities. A valuation allowance is recorded to account for the unrealizable balances in the table above. The net decrease of $5,285 in the valuation allowance is primarily due to unutilized state capital losses that expired in the current year.
The Company remains indefinitely reinvested in several of the foreign jurisdictions in which it operates as of December 31, 2024. As a result of the passage of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (2017 Tax Act), the Company does not expect any significant taxes to be incurred if such earnings were remitted.
Unrecognized tax benefits
A reconciliation of the beginning and ending liability for unrecognized tax benefits that do not meet the more-likely-than-not threshold is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year ended December 31, |
| | 2024 | | 2023 |
| Beginning balance | $ | 47,379 | | | $ | 63,985 | |
| Additions for tax positions related to current year | 3,866 | | | 4,088 | |
| Adjustments for tax positions related to prior years | (1,452) | | | (7,273) | |
| Reductions related to lapse of applicable statute | (8,309) | | | (5,428) | |
| Reductions related to settlements with taxing authorities | — | | | (7,993) | |
| Ending balance | $ | 41,484 | | | $ | 47,379 | |
DAVITA INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (continued)
(dollars and shares in thousands, except per share data)
As of December 31, 2024, the Company’s total liability for unrecognized tax benefits relating to tax positions that do not meet the more-likely-than-not threshold is $41,484. Of this balance, $27,336 would impact the Company’s effective tax rate if recognized.
The Company recognizes accrued interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits in its income tax expense. We recognized a benefit of $679 and $138 related to interest and penalties net of federal tax benefit within tax expense in 2024 and 2023, respectively. At December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023, the Company had approximately $5,846 and $6,525, respectively, accrued for interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits, net of federal tax benefit.
The Company and its subsidiaries are under examination in various state, local and foreign tax jurisdictions. In 2022, the Company was able to reach a settlement with the IRS for tax years 2014-2015. Subsequent to the settlement, the Company filed a 2014 refund claim with respect to a contested issue that was included in the IRS examination. During 2023 the IRS denied the refund claim and the Company has until September 2025 to appeal. Except for the 2014 refund claim, the Company is no longer subject to U.S. federal examinations prior to 2021.
12. Long-term debt
Long-term debt comprised the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, | | | | As of December 31, 2024 |
| | 2024 | | 2023 | | Maturity date | | Interest rate | | Estimated fair value(1) |
| Senior Secured Credit Facilities: | | | | | | | | | |
| Term Loan A-1 | $ | 2,259,295 | | | $ | 1,234,375 | | | 4/28/2028 | | Base +1.75%(2) | | $ | 2,256,471 | |
| Term Loan B-1 | — | | | 2,603,786 | | | | | | | $ | — | |
| Extended Term Loan B-1 | 1,636,150 | | | | | 5/9/2031 | | SOFR + 2.00% | | $ | 1,638,195 | |
| Revolving line of credit | — | | | — | | | 4/28/2028 | | Base +1.75%(2) | | $ | — | |
| Senior Notes: | | | | | | | | | |
| 4.625% Senior Notes | 2,750,000 | | | 2,750,000 | | | 6/1/2030 | | 4.625 | % | | $ | 2,533,438 | |
| 3.75% Senior Notes | 1,500,000 | | | 1,500,000 | | | 2/15/2031 | | 3.75 | % | | $ | 1,301,250 | |
| 6.875% Senior Notes | 1,000,000 | | | | | 9/1/2032 | | 6.875 | % | | $ | 1,007,500 | |
Acquisition obligations and other notes payable(3) | 56,483 | | | 102,328 | | | 2025-2038 | | 5.58 | % | | $ | 56,483 | |
Financing lease obligations(4) | 216,401 | | | 255,491 | | | 2025-2039 | | 4.58 | % | | |
CHC temporary funding assistance(5) | 92,777 | | | | | | | — | % | | $ | 92,777 | |
| Total debt principal outstanding | 9,511,106 | | | 8,445,980 | | | | | | | |
Discount, premium and deferred financing costs(6) | (64,336) | | | (54,347) | | | | | | | |
| | 9,446,770 | | | 8,391,633 | | | | | | | |
| Less current portion | (270,867) | | | (123,299) | | | | | | | |
| | $ | 9,175,903 | | | $ | 8,268,334 | | | | | | | |
(1)For the Company's senior secured credit facilities, fair value estimates are based on bid and ask quotes, a level 2 input. For the Company's senior notes, fair value estimates are based on market level 1 inputs. For acquisition obligations and other notes payable, the carrying values presented here approximate their estimated fair values, based on estimates of their present values typically using level 2 interest rate inputs. For the CHC temporary funding assistance, the carrying value presented here approximates the estimated fair value based on the short-term nature of settlement.
(2)The Company's senior secured credit facilities bear interest at Term SOFR, plus an interest rate margin, with certain portions also subject to a credit spread adjustment (CSA). Term SOFR plus CSA is referred to as "Base" in the table above. The Term Loan A-1 and revolving line of credit bear a CSA of 0.10%.
(3)The interest rate presented for acquisition obligations and other notes payable is their weighted average interest rate based on the current fixed and variable interest rate components in effect as of December 31, 2024.
(4)Financing lease obligations are measured at their approximate present values at inception. The interest rate presented is the weighted average discount rate embedded in financing leases outstanding.
(5)The Change Healthcare (CHC) temporary funding assistance, as described below, is interest-free and amounts provided under this program are subject to repayment at a future date to be mutually agreed to by the parties. The balance is included in the Company's current portion of long-term debt as of December 31, 2024.
DAVITA INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (continued)
(dollars and shares in thousands, except per share data)
(6)As of December 31, 2024, the carrying amount of the Company's senior secured credit facilities has been reduced by a discount of $8,084 and deferred financing costs of $28,879, and the carrying amount of the Company's senior notes has been reduced by deferred financing costs of $37,612 and increased by a debt premium of $10,239. As of December 31, 2023, the carrying amount of the Company's senior secured credit facilities was reduced by a discount of $2,487 and deferred financing costs of $32,498, and the carrying amounts of the Company's senior notes was reduced by deferred financing costs of $31,491 and increased by a debt premium of $12,129.
Scheduled maturities of long-term debt at December 31, 2024 were as follows:
| | | | | |
| 2025 | $ | 270,867 | |
| 2026 | $ | 174,693 | |
| 2027 | $ | 202,674 | |
| 2028 | $ | 1,922,275 | |
| 2029 | $ | 39,993 | |
| Thereafter | $ | 6,900,604 | |
Senior Secured Credit Facilities
On May 9, 2024 (the Fourth Amendment Effective Date), the Company entered into the Fourth Amendment (the Fourth Amendment) to its senior secured credit agreement dated as of August 12, 2019 (as amended, restated, supplemented or otherwise modified from time to time, the Credit Agreement). The Fourth Amendment modified the Credit Agreement to, among other things, extend the maturity date for a portion of its Term Loan B-1 in the aggregate principal amount of $911,598 and extend an additional incremental principal amount of $728,653 (together, referred to as the Extended Term Loan B-1). The Company used the incremental proceeds from the Extended Term Loan B-1 to prepay a proportionate amount of the principal balance still outstanding on its Term Loan B-1.
The Extended Term Loan B-1 bears interest at the Company’s option, based on (i) the Base Rate (as defined below) plus the Applicable Margin (as defined below), or (ii) the forward-looking term rate based on the secured overnight financing rate that is published by CME Group Benchmark Administration Limited (Term SOFR) plus the Applicable Margin. The "Base Rate" is defined as the highest of (i) the Federal Funds Rate, as published by the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, plus 0.50%, (ii) the prime commercial lending rate of Wells Fargo as established from time to time and (iii) Term SOFR for an interest period of one month plus 1.00%; provided that if Term SOFR or the Base Rate is less than 0.00% such rate shall be deemed to be 0.00% for purposes of the Credit Agreement. The "Applicable Margin" for the Extended Term Loan B-1 is 2.00% in the case of Term SOFR loans, and 1.00% in the case of Base Rate loans. The Extended Term Loan B-1 requires quarterly principal payments beginning on December 31, 2024 of 0.25% of the aggregate principal amount of the Extended Term Loan B-1 outstanding on the Fourth Amendment Effective Date, with the balance due on May 9, 2031.
As a result of the Fourth Amendment transaction described above, the Company recognized debt prepayment, extinguishment and modification costs of $9,732 in the second quarter of 2024 composed partially of fees incurred for this transaction and partially of deferred financing costs and original issue discount written off for the portion of debt considered extinguished and reborrowed as a result of the Fourth Amendment. For the portion of the debt that was considered extinguished and reborrowed, the Company recognized constructive financing cash outflows and financing cash inflows on the statement of cash flows of $6,302 and $728,653 for the Extended Term Loan B-1, respectively, and constructive financing cash outflows of $722,351 for the prepayment of a portion of Term Loan B-1, even though no funds were actually paid or received. Another $13,282 of the debt considered extinguished related to the Extended Term Loan B-1 represented a non-cash financing activity.
On August 13, 2024, the Company entered into the Sixth Amendment (the Sixth Amendment) to the Credit Agreement. The Sixth Amendment modified the Credit Agreement to extend an additional incremental principal amount of $1,100,000 on its Term Loan A-1 (together with the existing Term Loan A-1 balance, referred to as the Increased Term Loan A-1). The Sixth Amendment also incorporated the provisions of the Fifth Amendment to the Credit Agreement, dated as of August 7, 2024, which removed a cap on the amount of incremental term "A" loans the Company can incur under the Credit Agreement. The Company used a portion of the net proceeds from this transaction along with the net proceeds from the issuance of 6.875% Senior Notes due 2032, described below, to prepay the remainder of the balance outstanding on its Term Loan B-1 maturing 2026 in the amount of $949,819, the balance outstanding on its revolving line of credit and related accrued interest and fees. The remaining borrowings added cash to the balance sheet for general corporate purposes.
The Increased Term Loan A-1 bears interest at Term SOFR, plus a CSA of 0.10% and an interest rate margin which is subject to adjustment depending upon the Company's leverage ratio under the Credit Agreement, and which can range from
DAVITA INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (continued)
(dollars and shares in thousands, except per share data)
1.25% to 2.25%, provided that this adjusted rate shall never be less than 0.00%. The Increased Term Loan A-1 requires amortizing quarterly principal payments that began on September 30, 2024 of $29,728 per quarter through June 30, 2027, and $44,591 per quarter from September 30, 2027 through March 31, 2028, with the balance due on April 28, 2028.
As a result of the Sixth Amendment transaction described above, the Company recognized debt prepayment, extinguishment and modification costs of $10,081 in the third quarter of 2024 composed partially of fees incurred for this transaction and partially of deferred financing costs and original issue discount written off for the extinguishment of the Term Loan B-1. Additionally, $861,282 of the debt considered extinguished and reborrowed related to the Increased Term Loan A-1 represented a non-cash financing activity.
Borrowings under the Company's senior secured credit facilities are guaranteed and secured by substantially all of DaVita Inc.'s and certain of the Company’s domestic subsidiaries' assets and rank senior to all unsecured indebtedness. Borrowings under the Term Loan A-1, Extended Term Loan B-1 and revolving line of credit rank equal in priority for that security and related subsidiary guarantees. The Credit Agreement contains certain customary affirmative and negative covenants such as various restrictions or limitations on permitted amounts of investments (including acquisitions), share repurchases, payment of dividends, and redemptions and incurrence of other indebtedness. Many of these restrictions and limitations will not apply as long as the Company’s leverage ratio calculated in accordance with the Credit Agreement is below 4.00:1.00. In addition, the Credit Agreement requires compliance with a maximum leverage ratio covenant, tested quarterly, of 5.00:1.00 through June 30, 2026 and 4.50:1.00 thereafter (subject to an increase to 5.00:1.00 during the four fiscal quarters following a material acquisition).
In addition to the prepayments described above, during 2024, the Company made regularly scheduled and other principal payments under its senior secured credit facilities totaling $75,080 on Term Loan A-1, $13,716 on Term Loan B-1 and $4,101 on Extended Term Loan B-1.
As of December 31, 2024, the Company had undrawn capacity on the revolving line of credit under its senior secured credit facilities of $1,500,000. Credit available under this revolving line of credit is reduced by the amount of any letters of credit outstanding thereunder, of which there were none as of December 31, 2024. The Company also had letters of credit of approximately $161,496 outstanding under a separate bilateral secured letter of credit facility as of December 31, 2024.
The Company's 2019 interest rate cap agreements expired on June 30, 2024 and a portion of the Company's 2023 cap agreements became effective on or prior to June 30, 2024. As of December 31, 2024, the effective portion of the Company's 2023 interest rate cap agreements had the economic effect of capping the Company's maximum exposure to SOFR variable interest rate changes on equivalent amounts of the Company's floating rate debt, including all of Extended Term Loan B-1 and a portion of Term Loan A-1. The remaining $395,445 outstanding principal balance of Term Loan A-1 is subject to SOFR-based interest rate volatility. These cap agreements are designated as cash flow hedges and, as a result, changes in their fair values are reported in other comprehensive income. The original premiums paid for the caps are amortized to debt expense utilizing the effective interest rate method over the term of each cap agreement starting from its effective date. These cap agreements do not contain credit risk-contingent features.
Senior Notes
On August 13, 2024, the Company issued $1,000,000 aggregate principal amount of 6.875% senior notes due 2032 (the 6.875% Senior Notes) in a private offering pursuant to Rule 144A and Regulation S under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended. The 6.875% Senior Notes pay interest on March 1 and September 1 of each year beginning March 1, 2025 and mature on September 1, 2032. The 6.875% Senior Notes are unsecured senior obligations and rank equally in right of payment with the Company's existing and future unsecured senior indebtedness. The 6.875% Senior Notes are guaranteed by each of the Company’s domestic subsidiaries that guarantee its senior secured credit facilities. The Company may redeem up to 40% of the aggregate principal amount of the 6.875% Senior Notes at any time prior to September 1, 2027 at 106.875% of the aggregate principal amount from the proceeds of one or more equity offerings, plus accrued and unpaid interest. On and after September 1, 2027, the Company may at its option redeem the 6.875% Senior Notes, in whole or from time to time in part, at certain redemption prices specified in the indenture governing these notes plus accrued and unpaid interest. If the Company experiences certain change of control events, the Company must offer to repurchase all of the 6.875% Senior Notes (unless otherwise redeemed) at a price equal to 101% of the principal amount thereof, plus accrued and unpaid interest. The 6.875% Senior Notes contain restrictive covenants that limit the ability of the Company and the subsidiary guarantors of the 6.875% Senior Notes to, among other things and subject to certain exceptions and qualifications, create certain liens, enter into certain sale/leaseback transactions, or merge with or into, or convey, transfer or lease all or substantially all of their assets. The 6.875% Senior Notes and related subsidiary guarantees do not have any registration or similar rights and are not expected to be registered for exchange on public markets. As of December 31, 2024, the Company incurred $11,421 in fees and other
DAVITA INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (continued)
(dollars and shares in thousands, except per share data)
professional expenses associated with this transaction that were capitalized and will amortize over the term of the 6.875% Senior Notes.
All of the Company's outstanding senior notes, including the 6.875% Senior Notes (collectively, the Senior Notes), are unsecured obligations, rank equally in right of payment with the Company’s existing and future unsecured senior indebtedness and require semi-annual interest payments. The Company may redeem some or all of the Senior Notes at any time on or after certain specific dates and at certain specific redemption prices as outlined in the indenture governing each series of Senior Notes. Interest rates on the Senior Notes are fixed by their terms.
Change Healthcare
On March 1, 2024, Change Healthcare (CHC), a subsidiary of UnitedHealth Group, launched a temporary assistance funding program (CHC Funding) to help bridge the gap in short-term cash flow needs for providers impacted by the disruption of CHC's services. Under the program, CHC provides funding to providers for amounts that would otherwise have been received (with certain limitations), but for the disruption in processing electronic claims as a result of the outage. Amounts provided under this program are subject to repayment at a future date to be mutually agreed to by CHC and the Company.
CHC has restored claims submission functionality and the Company has resumed claims submissions and billing processes through CHC’s information technology systems. Through a combination of CHC's platform and certain alternate billing processes, the Company is current on its primary claims submissions, but does continue to see delays in collections with some payors. As of December 31, 2024, the remaining CHC Funding amount outstanding was $92,777. Subsequent to December 31, 2024, the Company made a payment for a portion of the CHC Funding amount, leaving a remaining balance outstanding of $70,000 as of February 13, 2025.
Interest rate cap agreements
During 2024 the Company entered into several forward interest rate cap agreements, described below, that have the economic effect of capping the Company's exposure to SOFR variable interest rate changes on specific portions of the Company's floating rate debt (2024 cap agreements). These 2024 cap agreements are designated as cash flow hedges and, as a result, changes in their fair values will be reported in other comprehensive income. These 2024 cap agreements do not contain credit-risk contingent features, and become effective and expire as described in the table below.
The following table summarizes the Company’s interest rate cap agreements outstanding as of December 31, 2024:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | Notional amount effective
through December 31 unless noted |
| Year cap agreements executed | | Initial notional amount | | SOFR maximum rate | | Approximate effective date | | Maturity date | |
| | | | | 2024 | | 2025 | | 2026 | | 2027 |
| 2023 | | $ | 1,000,000 | | | 3.75% | | 6/30/2024 | | 12/31/2025 | | $ | 1,000,000 | | $ | 500,000 | | | | |
| 2023 | | $ | 1,000,000 | | | 4.00%(1) | | 6/30/2024 | | 12/31/2025 | | $ | 1,000,000 | | $ | 750,000 | | | | |
| 2023 | | $ | 1,000,000 | | | 4.75%(2) | | 6/30/2024 | | 12/31/2025 | | $ | 1,000,000 | | $ | 750,000 | | | | |
| 2023 | | $ | 500,000 | | | 5.00%(3) | | 6/30/2024 | | 12/31/2026 | | $ | 500,000 | | $ | 500,000 | | $ | 500,000 | | |
| 2023 | | $ | 250,000 | | | 4.50% | | 12/31/2024 | | 12/31/2025 | | | | $ | 250,000 | | | | |
| 2023 | | $ | 750,000 | | | 4.00% | | 12/31/2024 | | 12/31/2026 | | | | $ | 750,000 | | $ | 500,000 | | |
| 2024 | | $ | 1,750,000 | | | 4.50%(4) | | 12/31/2025 | | 12/31/2027 | | | | | | $ | 1,750,000 | | $ | 1,000,000 |
| 2024 | | $ | 750,000 | | | 4.00%(5) | | 12/31/2025 | | 12/31/2027 | | | | | | $ | 750,000 | | $ | 500,000 |
| Total notional coverage | | $ | 3,500,000 | | $ | 3,500,000 | | $ | 3,500,000 | | $ | 1,500,000 |
| Weighted average strike rate | | 4.29 | % | | 4.02 | % | | 4.32 | % | | 4.58 | % |
(1)Effective January 1, 2025, the maximum rate of 4.00% decreased to 3.75% for these interest rate caps.
(2)Effective January 1, 2025, the maximum rate of 4.75% decreased to 4.00% for these interest rate caps.
(3)Effective January 1, 2025, the maximum rate of 5.00% decreased to 4.50% for these interest rate caps.
(4)Effective December 31, 2026, the maximum rate of 4.50% increases to 4.75% for these interest rate caps.
(5)Effective December 31, 2026, the maximum rate of 4.00% increases to 4.25% for these interest rate caps.
DAVITA INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (continued)
(dollars and shares in thousands, except per share data)
The following table summarizes the effects of the Company’s interest rate cap agreements for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Amount of unrealized gains (losses) in OCI on interest rate cap agreements | | Location in Consolidated Statements of Income | | Reclassification from accumulated other comprehensive income into net income |
| | | Year ended December 31, | | | Year ended December 31, |
| Derivatives designated as cash flow hedges | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 | | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Interest rate cap agreements | | $ | 9,662 | | | $ | 9,186 | | | $ | 144,793 | | | Debt expense | | $ | (58,175) | | | $ | (103,567) | | | $ | (11,732) | |
| Related income tax | | (2,412) | | | (2,291) | | | (36,124) | | | Related income tax | | 14,515 | | | 25,840 | | | 2,926 | |
| Total | | $ | 7,250 | | | $ | 6,895 | | | $ | 108,669 | | | | | $ | (43,660) | | | $ | (77,727) | | | $ | (8,806) | |
The fair value of the Company's interest rate cap agreements, which are classified in other long-term assets on its consolidated balance sheet, were $30,062 and $79,805 for the years ended December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023, respectively.
See Note 19 for further details on amounts recorded and reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive (loss) income and recorded as debt expense (offset) related to the Company’s interest rate cap agreements for the year ended December 31, 2024.
As a result of the variable rate cap from the Company's 2023 interest rate cap agreements, the Company’s weighted average effective interest rate on its senior secured credit facilities at the end of December 31, 2024 was 6.91%, based on the current margins in effect for its senior secured credit facilities as of December 31, 2024, as detailed in the table above.
The Company’s weighted average effective interest rate on all debt, including the effect of interest rate caps and amortization of debt discount, was 5.07% for the year ended December 31, 2024 and 5.68% as of December 31, 2024.
As of December 31, 2024, the Company’s interest rates were fixed and economically fixed on approximately 59% and 96% of its total debt, respectively.
Debt expense
Debt expense consisted of interest expense of $435,203, $373,951 and $339,247 and the amortization and accretion of debt discounts and premiums, amortization of deferred financing costs, costs for the undrawn portion of the revolving line of credit and the amortization of interest rate cap agreements of $35,266, $24,600 and $17,772 for 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively. These interest expense amounts are net of capitalized interest.
13. Leases
The Company leases substantially all of its dialysis facilities. The majority of the Company’s facilities are leased under non-cancellable operating leases which range in terms from five years to 15 years and which contain renewal options of five years to 10 years at the fair rental value at the time of renewal. The Company's leases are generally subject to fixed escalation clauses or contain consumer price index increases. See Note 1 for further information on how the Company accounts for leases.
As of December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023, assets recorded under finance leases were $309,363 and $322,844, respectively, and accumulated amortization associated with finance leases was $139,071 and $122,286, respectively, included in property and equipment, net, on the Company's consolidated balance sheet.
In certain markets, the Company acquires and develops dialysis centers. Upon completion, the Company sells the center to a third party and leases the space back with the intent of operating the center on a long-term basis. Both the sale and leaseback terms are generally market terms. Substantially all of the lease terms are consistent with the Company's other operating leases with the majority of the leases under non-cancellable operating leases ranging in terms from 10 years to 15 years and containing renewal options of five years to 15 years at the fair rental value at the time of renewal.
DAVITA INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (continued)
(dollars and shares in thousands, except per share data)
The components of lease expense were as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year ended December 31, |
| Lease cost | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
Operating lease cost(1): | | | | | | |
| Fixed lease expense | | $ | 557,591 | | | $ | 556,844 | | | $ | 552,194 | |
| Variable lease expense | | 131,539 | | | 135,990 | | | 127,621 | |
| Financing lease cost: | | | | | | |
| Amortization of leased assets | | 28,262 | | | 26,964 | | | 27,079 | |
| Interest on lease liabilities | | 10,885 | | | 11,724 | | | 12,776 | |
| Net lease cost | | $ | 728,277 | | | $ | 731,522 | | | $ | 719,670 | |
(1)Includes short-term lease expense and sublease income, which are immaterial.
Other information related to leases was as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year ended December 31, |
| Lease term and discount rate | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Weighted average remaining lease term (years): | | | | | | |
| Operating leases | | 7.2 | | 7.6 | | 8.2 |
| Finance leases | | 7.9 | | 8.5 | | 9.4 |
| Weighted average discount rate: | | | | | | |
| Operating leases | | 4.1 | % | | 4.0 | % | | 3.6 | % |
| Finance leases | | 4.6 | % | | 4.6 | % | | 4.5 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year ended December 31, |
| Other information | | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Gains on sale leasebacks, net | | $ | 2,260 | | | $ | 3,387 | | | $ | 28,005 | |
Cash paid for amounts included in the
measurement of lease liabilities: | | | | | | |
| Operating cash flows for operating leases | | $ | 719,339 | | | $ | 708,162 | | | $ | 696,291 | |
| Operating cash flows for finance leases | | $ | 18,599 | | | $ | 19,246 | | | $ | 20,103 | |
| Financing cash flows for finance leases | | $ | 29,592 | | | $ | 26,455 | | | $ | 24,329 | |
Net operating lease assets obtained in exchange
for new or modified operating lease liabilities | | $ | 286,022 | | | $ | 269,564 | | | $ | 278,108 | |
Future minimum lease payments under non-cancellable leases as of December 31, 2024 are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Operating leases | | Finance leases |
| 2025 | | $ | 508,420 | | | $ | 36,557 | |
| 2026 | | 517,309 | | | 38,694 | |
| 2027 | | 453,895 | | | 37,421 | |
| 2028 | | 385,211 | | | 33,854 | |
| 2029 | | 310,332 | | | 24,862 | |
| Thereafter | | 863,739 | | | 82,400 | |
| Total future minimum lease payments | | 3,038,906 | | | 253,788 | |
| Less portion representing interest | | (418,840) | | | (37,387) | |
| Present value of lease liabilities | | $ | 2,620,066 | | | $ | 216,401 | |
Rent expense under all operating leases for 2024, 2023 and 2022 was $689,130, $692,834 and $679,815, respectively. Rent expense is recorded on a straight-line basis over the term of the lease, including leases that contain fixed escalation clauses or include abatement provisions. Leasehold improvement incentives reduce the carrying value of right-of-use assets and are amortized to rent expense over the term of the lease. Finance lease obligations are included in long-term debt. See Note 12 for further details on long-term debt.
DAVITA INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (continued)
(dollars and shares in thousands, except per share data)
14. Employee benefit plans
The Company has a 401(k) retirement savings plan for substantially all of its U.S. employees which has been established pursuant to applicable provisions of the Internal Revenue Code (IRC). The plan allows for employees to contribute a percentage of their base annual salaries on a tax-deferred basis not to exceed IRC limitations. The Company maintains a 401(k) matching program under which the Company matches 50% of the employee's contribution up to 6% of the employee's salary, subject to certain limitations. The matching contributions are subject to certain eligibility and vesting conditions. For the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, the Company accrued matching contributions totaling approximately $79,006, $73,725 and $70,084, respectively.
The Company also maintains a voluntary compensation deferral plan, the Deferred Compensation Plan. The Deferred Compensation Plan is non-qualified and permits certain employees whose annualized base salary equals or exceeds a minimum annual threshold amount as set by the Company to elect to defer all or a portion of their annual bonus payment and up to 50% of their base salary into a deferral account maintained by the Company. Total contributions to this plan in 2024, 2023 and 2022 were $2,521, $2,695 and $3,573, respectively. Deferred amounts are generally paid out in cash at the participant’s election either in the first or second year following retirement or in a specified future period at least three to four years after the deferral election was effective. During 2024, 2023 and 2022 the Company distributed $4,511, $3,899 and $3,731, respectively, to participants from its deferred compensation plans. Participants are credited with their proportional amount of annual earnings from the plans. The assets of these plans are held in rabbi trusts subject to the claims of the Company’s general creditors in the event of its bankruptcy. As of December 31, 2024 and 2023, the total fair value of assets held in these plans' trusts was $39,527 and $36,936, respectively. The assets of these plans are recorded at fair value with changes in fair value recorded in other loss, net. See Note 4 for further details. Any fair value changes to the corresponding liability balance are recorded as compensation expense.
15. Contingencies
The Company operates in a highly regulated industry and is a party to, or has the potential to be a party to, various lawsuits, demands, claims, qui tam suits, governmental investigations and audits (including, without limitation, investigations or other actions resulting from its obligation to self-report suspected violations of law) and other legal proceedings, including, without limitation, those described below. The Company records accruals for certain legal proceedings and regulatory matters to the extent that the Company determines an unfavorable outcome is probable and the amount of the loss can be reasonably estimated. Excluding amounts stated below, as of December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023, the Company’s total recorded accruals with respect to legal proceedings and regulatory matters, net of anticipated third party recoveries, were immaterial. While these accruals reflect the Company’s best estimate of the probable loss for those matters as of the dates of those accruals, the recorded amounts may differ materially from the actual amount of the losses for those matters, and any anticipated third party recoveries for any such losses may not ultimately be recoverable. Additionally, in some cases, no estimate of the possible loss or range of loss in excess of amounts accrued, if any, can be made because of the inherently unpredictable nature of legal proceedings and regulatory matters, which also may be impacted by various factors, including, without limitation, that they may involve indeterminate claims for monetary damages or may involve fines, penalties or non-monetary remedies; present novel legal theories or legal uncertainties; involve disputed facts; represent a shift in regulatory policy; are in the early stages of the proceedings; or may result in a change of business practices. Further, there may be various levels of judicial review available to the Company in connection with any such proceeding.
The following is a description of certain lawsuits, claims, governmental investigations and audits and other legal proceedings to which the Company is subject.
Certain Governmental Inquiries and Related Proceedings
2017 U.S. Attorney Colorado Investigation: In November 2017, the U.S. Attorney’s Office, District of Colorado informed the Company of an investigation it was conducting into possible federal healthcare offenses involving DaVita Kidney Care, as well as several of the Company’s wholly-owned subsidiaries. In addition to DaVita Kidney Care, the matter included an investigation into DaVita Rx, DaVita Laboratory Services, Inc. (DaVita Labs), and RMS Lifeline Inc. (Lifeline). In each of August 2018, May 2019, and July 2021, the Company received a Civil Investigative Demand (CID) pursuant to the False Claims Act from the U.S. Attorney's Office relating to this investigation. On May 6, 2024, the Company finalized and executed a settlement agreement with the government and the relator in a qui tam matter that included a settlement amount of $34,487 for this matter. On May 7, 2024, the government notified the U.S. District Court, District of Colorado of its decision to intervene for purposes of settlement in the matter of U.S. ex rel. Kogod v. DaVita Inc., et al. The government and the relator agreed to voluntarily dismiss all substantive claims in the matter, and, on July 18, 2024, the District Court dismissed all claims except for the relator’s statutory claim for expenses, attorney’s fees, and costs. On December 10, 2024, the parties signed an agreement to
DAVITA INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (continued)
(dollars and shares in thousands, except per share data)
resolve the remaining claim for relator’s statutory claim for expenses, attorney’s fees, and costs for an immaterial amount. On December 20, 2024, the parties filed a stipulation of dismissal with the District Court on the remaining claim and the District Court ordered the relator’s claim withdrawn.
2020 U.S. Attorney New Jersey Investigation: In March 2020, the U.S. Attorney’s Office, District of New Jersey served the Company with a subpoena and a CID relating to an investigation being conducted by that office and the U.S. Attorney’s Office, Eastern District of Pennsylvania. The subpoena and CID request information on several topics, including certain of the Company’s joint venture arrangements with physicians and physician groups, medical director agreements, and compliance with its five-year Corporate Integrity Agreement, the term of which expired October 22, 2019. In November 2022, the Company learned that, on April 1, 2022, the U.S. Attorney’s Office for the District of New Jersey notified the U.S. District Court for the District of New Jersey of its decision not to elect to intervene in the matter of U.S. ex rel. Doe v. DaVita Inc. and filed a Stipulation of Dismissal. On April 13, 2022, the U.S. District Court for the District of New Jersey dismissed the case without prejudice. On October 12, 2022, the U.S. Attorney’s Office for the Eastern District of Pennsylvania notified the U.S. District Court, Eastern District of Pennsylvania, of its decision not to elect to intervene at this time in the matter of U.S. ex rel. Bayne v. DaVita Inc., et al. The court then unsealed an amended complaint, which alleges violations of federal and state False Claims Acts, by order dated October 14, 2022. On November 8, 2023, the private party relator filed a fourth amended complaint. On November 29, 2023, the Company filed a motion to dismiss the fourth amended complaint.
2020 California Department of Insurance Investigation: In April 2020, the California Department of Insurance (CDI) sent the Company an Investigative Subpoena relating to an investigation being conducted by that office. CDI issued a superseding subpoena in September 2020 and an additional subpoena in September 2021. Those subpoenas request information on a number of topics, including but not limited to the Company’s communications with patients about insurance plans and financial assistance from the American Kidney Fund (AKF), analyses of the potential impact of patients’ decisions to change insurance providers, and documents relating to donations or contributions to the AKF. The Company is continuing to cooperate with CDI in this investigation.
2023 District of Columbia Office of Attorney General Investigation: In January 2023, the Office of the Attorney General for the District of Columbia issued a CID to the Company in connection with an antitrust investigation into the AKF. The CID covers the period from January 1, 2016 to the present. The CID requests information on a number of topics, including but not limited to the Company’s communications with the AKF, documents relating to donations to the AKF, and communications with patients, providers, and insurers regarding the AKF. The Company is cooperating with the government in this investigation.
2024 Federal Trade Commission Investigation: In April 2024, the Company received from the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) two CIDs in connection with an industry investigation under Section 5 of the Federal Trade Commission Act regarding the acquisition of medical director services and provision of dialysis services. The CIDs cover the period from January 1, 2016 to the present and generally seek information relating to restrictive covenants, such as non-competes, with physicians. The Company is cooperating with the government in this investigation.
* * *
Although the Company cannot predict whether or when proceedings might be initiated or when these matters may be resolved (other than as may be described above), it is not unusual for inquiries such as these to continue for a considerable period of time through the various phases of document and witness requests and ongoing discussions with regulators and to develop over the course of time. In addition to the inquiries and proceedings specifically identified above, the Company frequently is subject to other inquiries by state or federal government agencies. Negative findings or terms and conditions that the Company might agree to accept could result in, among other things, substantial financial penalties or awards against the Company, substantial payments made by the Company, harm to the Company’s reputation, required changes to the Company’s business practices, an impact on the Company's various relationships and/or contracts related to the Company's business, exclusion from future participation in the Medicare, Medicaid and other federal health care programs and, if criminal proceedings were initiated against the Company, members of its board of directors or management, possible criminal penalties, any of which could have a material adverse effect on the Company.
Other Proceedings
2021 Antitrust Indictment and Putative Class Action Suit: On July 14, 2021, an indictment was returned by a grand jury in the U.S. District Court, District of Colorado against the Company and its former chief executive officer in the matter of U.S. v. DaVita Inc., et al. alleging that purported agreements entered into by DaVita's former chief executive officer not to solicit senior-level employees violated Section 1 of the Sherman Act. On April 15, 2022, a jury returned a verdict in the Company’s
DAVITA INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (continued)
(dollars and shares in thousands, except per share data)
favor, acquitting both the Company and its former chief executive officer on all counts. On April 20, 2022, the court entered judgments of acquittal and closed the case. On August 9, 2021, DaVita Inc. and its former chief executive officer were added as defendants in a consolidated putative class action complaint in the matter of In re Outpatient Medical Center Employee Antitrust Litigation in the U.S. District Court, Northern District of Illinois. This class action complaint asserts that the defendants violated Section 1 of the Sherman Act and seeks to bring an action on behalf of certain groups of individuals employed by the Company. On October 27, 2024, the plaintiffs filed a Third Amended Complaint, seeking to bring an action on behalf of certain groups of individuals employed by the Company between March 2008 and January 2021, to which the Company responded on December 20, 2024. The Company disputes the allegations in the class action complaint, as well as the asserted violations of the Sherman Act, and intends to defend this action accordingly.
Additionally, from time to time the Company is subject to other lawsuits, demands, claims, governmental investigations and audits and legal proceedings that arise due to the nature of its business, including, without limitation, contractual disputes, such as with payors, suppliers and others, employee-related matters and professional and general liability claims. From time to time, the Company also initiates litigation or other legal proceedings as a plaintiff arising out of contracts or other matters.
* * *
Other than as may be described above, the Company cannot predict the ultimate outcomes of the various legal proceedings and regulatory matters to which the Company is or may be subject from time to time, including those described in this Note 15, or the timing of their resolution or the ultimate losses or impact of developments in those matters, which could have a material adverse effect on the Company’s revenues, earnings and cash flows. Further, any legal proceedings or regulatory matters involving the Company, whether meritorious or not, are time consuming, and often require management’s attention and result in significant legal expense, and may result in the diversion of significant operational resources, may impact the Company's various relationships and/or contracts related to the Company's business or otherwise harm the Company’s business, results of operations, financial condition, cash flows or reputation.
16. Noncontrolling interests subject to put provisions and other commitments
Noncontrolling interests subject to put provisions
The Company has potential obligations to purchase the equity interests held by third parties in many of its majority-owned dialysis partnerships and other nonconsolidated entities. These noncontrolling interests subject to put provisions constitute redeemable equity interests and are therefore classified as temporary equity and carried at estimated fair value on the Company's balance sheet.
Specifically, these obligations are in the form of put provisions that are exercisable at the third-party owners’ discretion within specified periods outlined in each specific put provision. If these put provisions were exercised, the Company would be required to purchase the third-party owners’ equity interests, generally at the appraised fair market value of the equity interests or in certain cases at a predetermined multiple of earnings or cash flows attributable to the equity interests put to the Company, intended to approximate fair value. The methodology the Company uses to estimate the fair values of noncontrolling interests subject to put provisions assumes the higher of either a liquidation value of net assets or an average multiple of earnings, based on historical earnings, patient mix and other performance indicators that can affect future results, as well as other factors. The estimated fair values of noncontrolling interests subject to put provisions are a critical accounting estimate that involves significant judgments and assumptions and may not be indicative of the actual values at which the noncontrolling interests may ultimately be settled, which could vary significantly from the Company’s current estimates. The estimated fair values of noncontrolling interests subject to put provisions can fluctuate and the implicit multiple of earnings at which these noncontrolling interests obligations may be settled will vary significantly depending upon market conditions including potential purchasers’ access to the capital markets, which can impact the level of competition for dialysis and non-dialysis related businesses, the economic performance of these businesses and the restricted marketability of the third-party owners’ equity interests. The amount of noncontrolling interests subject to put provisions that employ a contractually predetermined multiple of earnings rather than fair value is immaterial.
Certain consolidated dialysis partnerships are originally contractually scheduled to dissolve after terms ranging from ten years to 50 years. While noncontrolling interests in these limited life entities qualify as mandatorily redeemable financial instruments, they are subject to a classification and measurement scope exception from the accounting guidance generally applicable to other mandatorily redeemable financial instruments. Future distributions upon dissolution of these entities would be valued below the related noncontrolling interest carrying balances in the consolidated balance sheet.
DAVITA INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (continued)
(dollars and shares in thousands, except per share data)
Other commitments
The Company has agreements with various suppliers to purchase established amounts of dialysis equipment, parts, pharmaceuticals and supplies. As of December 31, 2024, the remaining minimum purchase commitments under these arrangements were approximately $559,952, $547,079, $547,031, $564,134 and $414,491 for the years 2025, 2026, 2027, 2028 and 2029, respectively. If the Company fails to meet the minimum purchase commitments under these contracts during any year, it is required to pay the difference to the supplier.
The Company also has certain potential commitments to provide working capital funding, if necessary, to certain nonconsolidated dialysis businesses that the Company manages and in which the Company owns a noncontrolling equity interest or which are wholly-owned by third parties of approximately $7,131.
Other than the letters of credit disclosed in Note 12 to these consolidated financial statements, and the arrangements as described above, the Company has no off balance sheet financing arrangements as of December 31, 2024.
17. Stock-based compensation
Stock-based compensation
Stock-based compensation consists primarily of stock-settled stock appreciation rights, restricted stock units and performance stock units. Stock-based compensation, which is primarily general and administrative in nature, is attributed to the Company’s U.S. dialysis business, its corporate administrative support, and its ancillary services. See Note 1 "Organization and summary of significant accounting policies" for more information on how the Company measures and recognizes stock-based compensation expense.
Long-term incentive compensation plans
The DaVita Inc. 2020 Incentive Award Plan (the 2020 Plan) is the Company’s current omnibus equity compensation plan and provides for grants of stock-based awards to employees, directors and other individuals providing services to the Company, except that incentive stock options may only be awarded to employees. The 2020 Plan provides for the grant of stock appreciation rights, nonqualified stock options, incentive stock options, restricted stock units, restricted stock, performance stock awards, dividend equivalents, stock payments, deferred stock unit awards, deferred stock awards and performance cash awards. The 2020 Plan mandates a maximum award term of 10 years for stock appreciation rights and stock options and stipulates that awards of these types be granted with a base or exercise price per share of not less than the fair market value of the Company's common stock on the date of grant. Shares available under the 2020 Plan are stated on a full value share basis. The 2020 Plan therefore provides that shares available for issuance under the plan are reduced by one share available for every four shares underlying stock appreciation rights and stock options, and are reduced by one share available for every one share underlying stock-based awards other than stock appreciation rights and stock options. At December 31, 2024, there were 4,969 shares available for future grants under the 2020 Plan. The Company’s stock awards granted under the 2020 Plan generally vest over 36 months to 48 months from the date of grant.
DAVITA INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (continued)
(dollars and shares in thousands, except per share data)
A summary of the status of the Company’s stock-settled awards, including base shares for stock-settled stock appreciation rights (SSARs) and stock-settled stock unit awards is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year ended December 31, 2024 |
| | Stock appreciation rights | | Stock units |
| Awards | | Weighted
average
exercise
price | | Weighted
average
remaining
contractual life | | Awards | | Weighted
average
remaining
contractual life |
| Outstanding at beginning of year | 3,471 | | | $ | 67.40 | | | | | 3,223 | | | |
| Granted | — | | | | | | | 827 | | | |
| Added by performance factor | | | | | | | 16 | | | |
| Exercised/Vested | (3,200) | | | $ | 63.99 | | | | | (628) | | | |
| Canceled | (3) | | | $ | 75.95 | | | | | (292) | | | |
| Outstanding at end of period | 268 | | | $ | 108.02 | | | 1.63 | | 3,146 | | | 1.96 |
| Exercisable at end of period | 72 | | | $ | 102.48 | | | 1.01 | | — | | | — | |
| Weighted-average fair value of grants: | | | | | | | | | |
| 2024 | | | | | | | $ | 142.36 | | | |
| 2023 | | | | | | | $ | 77.61 | | | |
| 2022 | $ | 35.13 | | | | | | | $ | 107.60 | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Awards Outstanding | | Weighted average exercise price | | Awards exercisable | | Weighted average exercise price |
| Range of SSARs base prices | |
| $70.01–$80.00 | | 14 | | | $ | 75.95 | | | 14 | | | $ | 75.95 | |
| $100.01–$110.00 | | 124 | | | $ | 108.93 | | | 58 | | | $ | 108.93 | |
| $110.01–$120.00 | | 130 | | | $ | 110.63 | | | — | | | |
| Total | | 268 | | | $ | 108.02 | | | 72 | | | $ | 102.48 | |
For the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, the aggregate intrinsic value of stock-based awards exercised was $323,681, $168,500 and $149,442, respectively. At December 31, 2024, the aggregate intrinsic value of stock-based awards outstanding was $490,209 and the aggregate intrinsic value of stock awards exercisable was $3,394.
Estimated fair value of stock-based compensation awards
The Company has estimated the grant-date fair value of stock-settled stock appreciation rights awards using the Black-Scholes-Merton valuation model and stock-settled stock unit awards at intrinsic value on the date of grant, except for portions of the Company’s performance stock unit awards for which a Monte Carlo simulation was used to estimate the grant-date fair value. The following assumptions were used in estimating these values and determining the related stock-based compensation expense attributable to the current period:
Expected term of the awards: The expected term of awards granted represents the period of time that they are expected to remain outstanding from the date of grant. The Company determines the expected term of its stock awards based on its historical experience with similar awards, considering the Company’s historical exercise and post-vesting termination patterns.
Expected volatility: Expected volatility represents the volatility anticipated over the expected term of the award. The Company determines the expected volatility for its awards based on the volatility of the price of its common stock over the most recent retrospective period commensurate with the expected term of the award, considering the volatilities expected by peer companies in near industries.
Expected dividend yield: The Company has not paid dividends on its common stock and does not currently expect to pay dividends during the term of stock awards granted.
Risk-free interest rate: The Company bases the expected risk-free interest rate on the implied yield currently available on stripped interest coupons of U.S. Treasury issues with a remaining term equivalent to the expected term of the award.
DAVITA INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (continued)
(dollars and shares in thousands, except per share data)
No SSAR awards were granted during the years ended December 31, 2024 or 2023. A summary of the weighted average valuation inputs described above used for estimating the grant-date fair value of SSAR awards granted during the year end December 31, 2022 were as follows:
| | | | | |
| |
| Expected term | 4.5 |
| Expected volatility | 34.3 | % |
| Expected dividend yield | — | % |
| Risk-free interest rate | 2.1 | % |
The Company estimates expected forfeitures based upon historical experience with separate groups of employees that have exhibited similar forfeiture behavior in the past. Stock-based compensation expense is recorded only for awards that are expected to vest.
Employee stock purchase plan
The Employee Stock Purchase Plan entitles qualifying employees to purchase up to $25 of the Company’s common stock during each calendar year. The amounts used to purchase stock are accumulated through payroll withholdings or through optional lump sum payments made in advance of the first day of the purchase right period. This compensatory plan allows employees to purchase stock for the lesser of 100% of its fair market value on the first day of the purchase right period or 85% of its fair market value on the last day of the purchase right period. Purchase right periods begin on January 1 and July 1, and end on December 31. Contributions used to purchase the Company’s common stock under this plan for the 2024, 2023 and 2022 purchase periods were $20,441, $18,213 and $18,061, respectively. Shares purchased pursuant to the plan’s 2024, 2023 and 2022 purchase periods were 184, 231 and 285, respectively. At December 31, 2024, there were 5,286 shares remaining available for future grants under this plan.
The fair value of participants’ purchase rights was estimated as of the beginning dates of the purchase right periods using the Black-Scholes-Merton valuation model with the following weighted average assumptions for purchase right periods in 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively: expected volatility of 32.6%, 41.3% and 31.7%; risk-free interest rates of 4.8%, 4.9% and 1.3%; and no dividends. Using these assumptions, the weighted average estimated per share fair value of each purchase right was $31.78, $25.25 and $26.50 for 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively.
Stock-based compensation expense and proceeds
For the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, the Company recognized $102,788, $112,375 and $95,427 in stock-based compensation expense for stock appreciation rights, stock units and discounted employee stock purchase plan purchases, which are primarily included in general and administrative expenses. The estimated tax benefits recorded for stock-based compensation in 2024, 2023 and 2022 were $16,398, $16,536 and $14,723, respectively. As of December 31, 2024, there was $146,350 of total estimated but unrecognized stock-based compensation expense under the Company’s equity compensation plans. The Company expects to recognize this expense over a weighted average remaining period of 1.2 years.
For the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, the Company received $27,531, $25,629 and $24,805, respectively, in actual tax benefits upon the exercise or vesting of stock awards. Since the Company issues stock-settled stock appreciation rights rather than stock options, there were no cash proceeds from stock option exercises.
DAVITA INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (continued)
(dollars and shares in thousands, except per share data)
18. Shareholders’ equity
Stock repurchases
The following table summarizes the Company's repurchases of its common stock during the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Open market repurchases | | | | | |
| Shares | 9,833 | | | 2,904 | | | 8,095 | |
Amounts paid(1) | $ | 1,389,072 | | | $ | 285,710 | | | $ | 787,854 | |
Average price paid per share(2) | $ | 140.06 | | | $ | 97.82 | | | $ | 97.30 | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
(1)Includes commissions and the 1% excise tax imposed on certain stock repurchases made after December 31, 2022 by the Inflation Reduction Act of 2022. The excise tax is recorded as part of the cost basis of treasury stock repurchased and, as such, is included in stockholders’ equity.
(2)Excludes commissions and the excise tax described above.
The Company repurchased 779 shares of its common stock for $124,665 at an average price paid of $158.48 per share subsequent to December 31, 2024 through February 13, 2025, inclusive of the shares repurchased from Berkshire Inc. as discussed below.
As of December 31, 2024, the Company is authorized to make share repurchases pursuant to a September 5, 2024 Board authorized repurchase plan of $2,000,000. This authorization allows the Company to make purchases from time to time in the open market or in privately negotiated transactions, including without limitation, through accelerated share repurchase transactions, derivative transactions, tender offers, trading plans pursuant to Rule 10b5-1 or Rule 10b-18, or any combination of the foregoing, depending upon market conditions and other considerations.
As of February 13, 2025, the Company has a total of $1,811,069, excluding excise taxes, available under the current authorization for additional share repurchases. Although this share repurchase authorization does not have an expiration date, the Company remains subject to share repurchase limitations, including under the terms of its senior secured credit facilities.
Berkshire share repurchase agreement
On April 30, 2024, the Company entered into an agreement (the share repurchase agreement) with Berkshire Hathaway Inc. on behalf of itself and its affiliates (collectively, Berkshire). Under the share repurchase agreement, at any time Berkshire beneficially owns at least 45.0% of the issued and outstanding common stock of the Company in the aggregate, the Company will repurchase from Berkshire, and Berkshire will sell to the Company, on a quarterly basis, a number of shares of common stock sufficient to return Berkshire’s aggregate beneficial ownership to 45.0% of the Company's issued and outstanding common stock. The per share price the Company will pay Berkshire for any such share repurchase will be the volume-weighted average price per share paid by the Company for any shares of common stock repurchased by the Company from public stockholders pursuant to the Company’s share repurchase program during the applicable repurchase period.
Under this agreement, repurchases of common stock by the Company from Berkshire will occur on the date that is two business days prior to the date of the Company’s regular quarterly or annual investor call to publicly report earnings; however, if at any time the Company determines that Berkshire beneficially owns or will beneficially own shares of common stock representing more than 49.5% of the issued and outstanding common stock in the aggregate, such determination will trigger immediate share repurchases under this agreement.
As of December 31, 2024, Berkshire beneficially owned less than 45.0% of the issued and outstanding common stock of the Company and, as a result, no repurchase obligation existed at such date. Subsequent to December 31, 2024, through February 13, 2025, the Company's open market share repurchases caused Berkshire to beneficially own greater then 45.0%. As such, on February 11, 2025 the Company repurchased 203 shares of common stock from Berkshire for $32,001 at an average price paid of $156.01 per share.
Berkshire standstill agreement
Berkshire remains subject to a standstill agreement with the Company, as amended and restated as of February 9, 2022 (the standstill agreement). The standstill agreement currently restricts Berkshire’s actions with respect to acquiring additional
DAVITA INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (continued)
(dollars and shares in thousands, except per share data)
shares of the Company’s common stock, and for any matter presented to Company stockholders, the standstill agreement requires Berkshire to vote any shares it beneficially holds in excess of 40% of the then-outstanding voting stock of the Company in accordance with the recommendation of the Board of Directors of the Company (Board). The standstill agreement also restricts Berkshire from taking certain actions, including, among other things, actions relating to stockholder proposals and actions seeking to control or influence the Board, management or policies of the Company. The standstill agreement provisions vary depending on Berkshire’s ownership levels and in the event of certain specified leadership changes at Berkshire.
The standstill agreement may be terminated by Berkshire at any time it ceases to beneficially own more than 15% of the Company's then-outstanding common stock, and terminates automatically if the Company enters into or publicly announces a plan to enter into a definitive agreement concerning a transaction involving all or a controlling portion of the Company's equity securities or all, or substantially all, of the Company's assets.
Charter documents & Delaware law
The Company’s charter documents include provisions that may deter hostile takeovers, delay or prevent changes of control or changes in management, or limit the ability of stockholders to approve transactions that they may otherwise determine to be in their best interests. These include provisions prohibiting stockholders from acting by written consent, requiring 90 days advance notice for director nominations and stockholder proposals and granting the Company's Board of Directors the authority to issue up to 5,000 shares of preferred stock and to determine the rights and preferences of the preferred stock without the need for further stockholder approval.
The Company is also subject to Section 203 of the Delaware General Corporation Law which, subject to exceptions, prohibits the Company from engaging in any business combinations with any interested stockholder, as defined in that section, for a period of three years following the date on which that stockholder became an interested stockholder. The provisions described above may discourage, delay or prevent an acquisition of the Company at a price that stockholders may find attractive.
Changes in DaVita Inc.’s ownership interests in consolidated subsidiaries
The effects of changes in DaVita Inc.’s ownership interests in consolidated subsidiaries on the Company’s consolidated equity were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year ended December 31, |
| | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Net income attributable to DaVita Inc. | $ | 936,342 | | | $ | 691,535 | | | $ | 560,400 | |
| Changes in paid-in capital for: | | | | | |
| Purchases of noncontrolling interests | (3,102) | | | (5,375) | | | (6,586) | |
| Sales of noncontrolling interest | 491 | | | 13,077 | | | 939 | |
| Net transfers in noncontrolling interests | (2,611) | | | 7,702 | | | (5,647) | |
Net income attributable to DaVita Inc. net of transfers in
noncontrolling interests | $ | 933,731 | | | $ | 699,237 | | | $ | 554,753 | |
The Company acquired additional ownership interests in several existing majority-owned partnerships for $53,958, $12,555 and $20,775 in 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively.
DAVITA INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (continued)
(dollars and shares in thousands, except per share data)
19. Accumulated other comprehensive loss
Charges and credits to other comprehensive (loss) income have been as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Interest rate cap agreements(1) | | Defined benefit plans | | | | Foreign currency
translation
adjustments | | Accumulated other
comprehensive
(loss) income |
| Balance at December 31, 2021 | $ | (1,178) | | | $ | — | | | | | $ | (138,069) | | | $ | (139,247) | |
| Unrealized gains (losses) | 144,793 | | | — | | | | | (30,554) | | | 114,239 | |
| Related income tax | (36,124) | | | — | | | | | 752 | | | (35,372) | |
| | 108,669 | | | — | | | | | (29,802) | | | 78,867 | |
| Reclassification of income into net income | (11,732) | | | — | | | | | — | | | (11,732) | |
| Related income tax | 2,926 | | | — | | | | | — | | | 2,926 | |
| | (8,806) | | | — | | | | | — | | | (8,806) | |
| Balance at December 31, 2022 | $ | 98,685 | | | $ | — | | | | | $ | (167,871) | | | $ | (69,186) | |
| Unrealized gains | 9,186 | | | — | | | | | 89,055 | | | 98,241 | |
| Related income tax | (2,291) | | | — | | | | | (1,121) | | | (3,412) | |
| | 6,895 | | | — | | | | | 87,934 | | | 94,829 | |
| Reclassification of income into net income | (103,567) | | | — | | | | | — | | | (103,567) | |
| Related income tax | 25,840 | | | — | | | | | — | | | 25,840 | |
| | (77,727) | | | — | | | | | — | | | (77,727) | |
| Balance at December 31, 2023 | $ | 27,853 | | | $ | — | | | | | $ | (79,937) | | | $ | (52,084) | |
| Unrealized gains (losses) | 9,662 | | | 46 | | | | | (207,906) | | | (198,198) | |
| Related income tax | (2,412) | | | — | | | | | 45 | | | (2,367) | |
| | 7,250 | | | 46 | | | | | (207,861) | | | (200,565) | |
| Reclassification of income into net income | (58,175) | | | — | | | | | (15,252) | | | (73,427) | |
| Related income tax | 14,515 | | | — | | | | | 765 | | | 15,280 | |
| | (43,660) | | | — | | | | | (14,487) | | | (58,147) | |
| Balance at December 31, 2024 | $ | (8,557) | | | $ | 46 | | | | | $ | (302,285) | | | $ | (310,796) | |
(1)The reclassification of net interest rate cap realized losses into income are recorded as debt expense in the corresponding consolidated statements of income. See Note 12 for further details.
DAVITA INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (continued)
(dollars and shares in thousands, except per share data)
20. Acquisitions and divestitures
Acquisition of DaVita Care Pte. Ltd.
Effective November 1, 2024, the Company acquired control of DaVita Care Pte. Ltd. (DVC), previously referred to as the Company's APAC joint venture, through a change in control rights for no cash consideration. See Note 8 for more information.
In connection with this acquisition, the Company recognized a non-cash gain of $59,067 on its previously held equity interests in the acquiree and realized a related foreign currency gain of $15,252 from foreign currency translation adjustments on this investment which were previously classified in accumulated other comprehensive loss. The Company estimated the fair value of its previously held equity interests of $114,744 using appraisals developed with an independent third party valuation firm.
The following table summarizes the assets acquired and liabilities assumed in this transaction and recognized at the acquisition date at estimated fair values, as well as the estimated fair value of noncontrolling interests assumed in this transaction:
| | | | | |
| | Year ended December 31, 2024 |
| Cash | $ | 34,818 | |
| Other current assets | $ | 44,810 | |
| Property and equipment | 22,651 | |
| |
| Other long-term assets | 37,682 | |
| Indefinite-lived licenses | 15,114 | |
| Goodwill | 127,207 | |
| |
| Liabilities assumed | (54,708) | |
| Noncontrolling interests assumed | (112,830) | |
| $ | 114,744 | |
Other international and routine acquisitions
During 2024, 2023 and 2022, the Company acquired other dialysis and related businesses for consideration paid in cash.
As part of these other international and routine transactions in 2024, the Company acquired a controlling interest in a previously nonconsolidated U.S. dialysis partnership for which it recognized a non-cash gain of $35,147 on its prior investment upon consolidation. The Company estimated the fair value of its previously held equity interest in this business using appraisals developed with independent third party valuation firms.
Aggregate consideration – DVC and all other acquisitions
Aggregate consideration for both the DaVita Care Pte. Ltd. acquisition and all other international and routine acquisitions described above has been as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year ended December 31, |
| 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Cash paid | $ | 329,187 | | | $ | 27,648 | | | $ | 59,271 | |
| | | | | |
| Contingent purchase price and liabilities assumed | 50,384 | | | 19,801 | | | 19,337 | |
| Fair value of previously held equity interests | 182,270 | | | — | | | — | |
| | | | | |
| Aggregate consideration | $ | 561,841 | | | $ | 47,449 | | | $ | 78,608 | |
| Number of dialysis centers acquired — U.S. | 12 | | — | | 5 |
| Number of dialysis centers acquired — International | 198 | | 12 | | 11 |
Purchase price allocations — DVC and all other acquisitions
The assets and liabilities for these acquisitions were recorded at their estimated fair values at the dates of the acquisitions and are included in the Company’s consolidated financial statements, as are their operating results, from the designated effective dates of the acquisitions.
DAVITA INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (continued)
(dollars and shares in thousands, except per share data)
The initial purchase price allocations for these transactions have been recorded at estimated fair values based on information available to management and will be finalized when certain information arranged to be obtained has been received. For several of the 2024 acquisitions, certain income tax amounts are pending final evaluation and quantification of any pre-acquisition tax contingencies. In addition, valuation of contingent earn-outs, intangibles, fixed assets, leases and certain working capital items relating to several of these acquisitions are pending final quantification.
The following table summarizes the assets acquired and liabilities assumed in these transactions and recognized at their acquisition dates at estimated fair values, as well as the estimated fair value of noncontrolling interests assumed in these transactions:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year ended December 31, |
| | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Cash | $ | 83,119 | | | $ | 1,254 | | | $ | 1,963 | |
| Other current assets | 249,738 | | | 6,128 | | | 6,389 | |
| Property and equipment | 94,951 | | | 4,130 | | | 7,481 | |
| | | | | |
| Right-of-use lease assets and other long-term assets | 97,591 | | | 785 | | | 1,066 | |
| Indefinite-lived licenses | 22,725 | | | 15,789 | | | 19,610 | |
| Goodwill | 349,069 | | | 25,723 | | | 49,047 | |
| | | | | |
| Liabilities assumed | (201,704) | | | (6,179) | | | (6,081) | |
| Noncontrolling interests assumed | (133,648) | | | (181) | | | (867) | |
| $ | 561,841 | | | $ | 47,449 | | | $ | 78,608 | |
The amount of goodwill related to these acquisitions recognized or adjusted in 2024, 2023 and 2022 that is deductible for local tax purposes was $54,810, $17,836 and $49,047, respectively.
Pro forma financial information (unaudited)
The following summary, prepared on a pro forma basis, combines the results of operations as if all acquisitions in 2024 and 2023 had been consummated as of the beginning of 2023, including the impact of certain adjustments such as amortization of intangibles, interest expense on acquisition financing and income tax effects.
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year ended December 31, |
| | 2024 | | 2023 |
| | (unaudited) |
| Pro forma total revenues | $ | 13,073,083 | | | $ | 12,625,223 | |
| Pro forma net income attributable to DaVita Inc. | $ | 952,836 | | | $ | 732,265 | |
| Pro forma basic net income per share attributable to DaVita Inc. | $ | 11.21 | | | $ | 8.07 | |
| Pro forma diluted net income per share attributable to DaVita Inc. | $ | 10.92 | | | $ | 7.86 | |
21. Discontinued operations previously held for sale
DaVita Medical Group (DMG)
On June 19, 2019, the Company completed the sale of its prior DMG business to Optum, a subsidiary of UnitedHealth Group Inc. At close, the Company's ultimate net proceeds from this sale remained subject to resolution of certain post-closing adjustments.
Shortly after December 31, 2022, Optum made an additional purchase price payment of $13,452 to the Company after resolution of one such post-closing matter, which represented a contingent gain to the Company for the fourth quarter of 2022.
The Company recognized no DMG operating, financing or investing cash flows for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022.
Under the equity purchase agreement, the Company also has certain continuing indemnification obligations that could require payments to the buyer relating to the Company's previous ownership and operation of the DMG business. Potential payments under these provisions, if any, remain subject to continuing uncertainties and the amounts of such payments could be significant to the Company.
DAVITA INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (continued)
(dollars and shares in thousands, except per share data)
22. Variable interest entities
The Company manages or maintains an ownership interest in certain legal entities subject to the consolidation guidance applicable to variable interest entities (VIEs). Almost all of the VIEs the Company consolidates are either U.S. dialysis partnerships encumbered by guaranteed debt, U.S. dialysis limited partnerships, U.S. integrated kidney care subsidiaries, non-U.S. subsidiaries that are structurally dependent on subordinated debt, or other legal entities subject to nominee ownership arrangements.
Under U.S. GAAP, VIEs typically include entities for which (i) the entity’s equity is not sufficient to finance its activities without additional subordinated financial support; (ii) the equity holders as a group lack the power to direct the activities that most significantly influence the entity’s economic performance, the obligation to absorb the entity’s expected losses, or the right to receive the entity’s expected returns; or (iii) the voting rights of some investors are not proportional to their obligations to absorb the entity’s losses.
The substantial majority of VIEs the Company is associated with are U.S. dialysis partnerships which the Company manages and in which it maintains a controlling majority ownership interest. These U.S. dialysis partnerships are considered VIEs either because they are (i) encumbered by debt guaranteed proportionately by the partners that is considered necessary to finance the partnership's activities, or (ii) in the form of limited partnerships for which the limited partners are not considered to have substantive kick-out or participating rights. The Company consolidates virtually all such U.S. dialysis partnerships.
Also, certain wholly-owned entities employed in the Company's integrated kidney care business constitute VIEs since by design these entities require additional subordinated financial support. The Company believes it has the most power over these entities' most significant activities and the Company is fully exposed to all or almost all of their expected losses. The Company therefore consolidates these wholly-owned entities as its subsidiaries.
Finally, some of the Company's business units rely on the operating activities of certain nominee-owned legal entities in which it does not maintain a controlling ownership interest but over which it has indirect influence and of which it is considered the primary beneficiary. These entities are subject to transfer restriction, management and other agreements that effectively transfer substantial ultimate powers over, and economic responsibility for, these entities to the Company. The Company consolidates all of the nominee-owned entities with which it is most closely associated.
In addition to the consolidated entities described above, the Company maintains minor equity method or other venture capital investments in certain development-stage investees which qualify as VIEs based on their capitalization. The Company has concluded that it is not the primary beneficiary of any of these investees.
For the VIEs described above, these consolidated financial statements include total assets of $577,585 and total liabilities and noncontrolling interests to third parties of $249,900 at December 31, 2024.
The Company also sponsors certain non-qualified deferred compensation plans whose trusts qualify as VIEs and the Company consolidates these plans as their primary beneficiary. The assets of these plans are recorded in short-term or long-term investments with related liabilities recorded in accrued compensation and benefits and other long-term liabilities. See Notes 4 and 14 for disclosures concerning the assets of these consolidated non-qualified deferred compensation plans.
23. Fair values of financial instruments
The Company measures the fair value of certain assets, liabilities, and noncontrolling interests subject to put provisions (redeemable equity interests classified as temporary equity) based upon certain valuation techniques that include observable or unobservable inputs and assumptions that market participants would use in pricing these assets, liabilities, temporary equity and commitments. The Company has also classified assets, liabilities and temporary equity that are measured at fair value on a recurring basis into the appropriate fair value hierarchy levels as defined by the FASB.
DAVITA INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (continued)
(dollars and shares in thousands, except per share data)
The following table summarizes the Company’s assets, liabilities and temporary equity measured at fair value on a recurring basis as of December 31, 2024 and 2023:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2024 | Total | | Quoted prices in
active markets for
identical assets
(Level 1) | | Significant other
observable inputs
(Level 2) | | Significant
unobservable
inputs
(Level 3) |
| Assets | | | | | | | |
| Investments in equity securities | $ | 40,566 | | | $ | 40,566 | | | | | |
| Interest rate cap agreements | $ | 30,062 | | | | | $ | 30,062 | | | |
| Liabilities | | | | | | | |
| Contingent earn-out obligations for acquisitions | $ | 13,542 | | | | | | | $ | 13,542 | |
| Temporary equity | | | | | | | |
| Noncontrolling interests subject to put provisions | $ | 1,695,483 | | | | | | | $ | 1,695,483 | |
| December 31, 2023 | | | | | | | |
| Assets | | | | | | | |
| Investments in equity securities | $ | 37,391 | | | $ | 37,391 | | | | | |
| Interest rate cap agreements | $ | 79,805 | | | | | $ | 79,805 | | | |
| Liabilities | | | | | | | |
| Contingent earn-out obligations for acquisitions | $ | 23,088 | | | | | | | $ | 23,088 | |
| Temporary equity | | | | | | | |
| Noncontrolling interests subject to put provisions | $ | 1,499,288 | | | | | | | $ | 1,499,288 | |
Investments in equity securities represent investments in various open-ended registered investment companies (mutual funds) and common stocks and are recorded at fair value estimated based on reported market prices or redemption prices, as applicable. See Note 4 for further discussion.
Interest rate cap agreements are recorded at fair value estimated from valuation models utilizing the income approach and commonly accepted valuation techniques that use inputs from closing prices for similar assets and liabilities in active markets as well as other relevant observable market inputs at quoted intervals such as current interest rates, forward yield curves, implied volatility and credit default swap pricing. The Company does not believe the ultimate amount that could be realized upon settlement of these interest rate cap agreements would be materially different from the fair value estimates currently reported. See Note 12 for further discussion.
As of December 31, 2024, the Company had contingent earn-out obligations associated with business acquisitions that could result in the Company paying the former owners a total of up to approximately $24,580 if certain performance targets or quality margins are met over the next one year to five years. The estimated fair value measurements of these contingent earn-out obligations are primarily based on unobservable inputs, including projected earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA), revenue and key performance indicators. The estimated fair value of these contingent earn-out obligations is remeasured as of each reporting date and could fluctuate based upon any significant changes in key assumptions, such as changes in the Company credit risk adjusted rate that is used to discount obligations to present value.
The estimated fair value of noncontrolling interests subject to put provisions is based principally on the higher of either estimated liquidation value of net assets or a multiple of earnings for each subject dialysis partnership, based on historical earnings, revenue mix, and other performance indicators that can affect future results. The multiples used for these valuations are derived from observed ownership transactions for dialysis businesses between unrelated parties in the U.S. in recent years, and the specific valuation multiple applied to each dialysis partnership is principally determined by its recent and expected revenue mix and contribution margin. As of December 31, 2024, an increase or decrease in the weighted average multiple used in these valuations of one times EBITDA would change the estimated fair value of these noncontrolling interests by approximately $225,000. See Note 16 for a discussion of the Company’s methodology for estimating the fair values of noncontrolling interests subject to put obligations and the reconciliation of changes on the consolidated statements of equity.
The Company's fair value estimates for its senior secured credit facilities are based upon quoted bid and ask prices for these instruments, a level 2 input. For the Company's senior notes, fair value estimates are based on level 1 market inputs. See Note 12 for further discussion of the Company's debt.
DAVITA INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (continued)
(dollars and shares in thousands, except per share data)
Other financial instruments consist primarily of cash and cash equivalents, restricted cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable, accounts payable, other accrued liabilities, lease liabilities and debt. The balances of financial instruments other than debt and lease liabilities are presented in the consolidated financial statements at December 31, 2024 and 2023 at their approximate fair values due to the short-term nature of their settlements.
24. Segment reporting
The Company's operating divisions are composed of its U.S. dialysis and related lab services business (its U.S. dialysis business), its U.S. integrated kidney care business, its U.S. other ancillary services and its international operations (collectively, its ancillary services), as well as its corporate administrative support functions. See Note 1 "Organization" for a summary description of the Company's businesses.
The Company’s operating segments have been defined based on the separate financial information that is regularly produced and reviewed by the Company’s chief operating decision maker in making decisions about allocating resources to and assessing the financial performance of the Company’s various operating lines of business. The chief operating decision maker for the Company is its Chief Executive Officer.
The Company’s separate operating segments include its U.S. dialysis and related lab services business, its U.S. integrated kidney care business, its U.S. other ancillary services, its operations in each foreign sovereign jurisdiction, and, until its reconsolidation in the fourth quarter of 2024, the Company's equity method investment in its Asia Pacific joint venture (APAC JV). The U.S. dialysis and related lab services business qualifies as a separately reportable segment, and all other operating segments have been combined and disclosed in the other segments category.
The Company’s operating segment financial information included in this report is prepared on the internal management reporting basis that the chief operating decision maker uses to assess the financial performance of and allocate resources among the Company's operating segments. For internal management reporting, segment operations include direct segment operating expenses but generally exclude corporate administrative support costs, which consist primarily of indirect labor, benefits and long-term incentive compensation expenses of certain departments which provide support to more than one of the Company’s various operating lines of business. The chief operating decision maker uses segment operating margin to assess segment profitability and resource allocation. The chief operating decision maker does not review total assets by segment to make decisions regarding resources; therefore, the total assets by segment disclosure has not been included.
DAVITA INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (continued)
(dollars and shares in thousands, except per share data)
The following is a summary of segment revenues, segment operating margin, and a reconciliation of segment operating margin to consolidated income from continuing operations before income taxes:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year ended December 31, |
| | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Segment revenues: | | | | | |
| U.S. dialysis | | | | | |
| Patient service revenues: | | | | | |
| External sources | $ | 11,294,614 | | | $ | 10,823,525 | | | $ | 10,488,327 | |
| Intersegment revenues | 71,747 | | | 88,222 | | | 87,045 | |
| U.S. dialysis patient service revenues | 11,366,361 | | | 10,911,747 | | | 10,575,372 | |
| Other revenues | | | | | |
| External sources | 24,356 | | | 25,251 | | | 24,447 | |
| Intersegment revenues | — | | | — | | | (10) | |
| Total U.S. dialysis revenues | 11,390,717 | | | 10,936,998 | | | 10,599,809 | |
| Other - Ancillary services | | | | | |
| Patient service revenues | 965,761 | | | 751,416 | | | 688,137 | |
| Other external sources | 530,819 | | | 539,955 | | | 408,983 | |
| Intersegment revenues | 13,910 | | | 7,852 | | | 4,206 | |
| Total ancillary services | 1,510,490 | | | 1,299,223 | | | 1,101,326 | |
| Total net segment revenues | 12,901,207 | | | 12,236,221 | | | 11,701,135 | |
| Elimination of intersegment revenues | (85,657) | | | (96,074) | | | (91,241) | |
| Consolidated revenues | $ | 12,815,550 | | | $ | 12,140,147 | | | $ | 11,609,894 | |
| Significant segment expenses: | | | | | |
| U.S. dialysis | | | | | |
| Patient care costs | $ | 7,497,576 | | | $ | 7,394,640 | | | $ | 7,334,415 | |
| General and administrative | 1,173,990 | | | 1,102,072 | | | 1,037,552 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | 661,181 | | | 695,674 | | | 690,949 | |
Other segment items(1) | (63,037) | | | (29,966) | | | (28,417) | |
| U.S. dialysis segment expenses | 9,269,710 | | | 9,162,420 | | | 9,034,499 | |
| Other - Ancillary services expenses | 1,427,833 | | | 1,307,970 | | | 1,197,905 | |
| | | | | |
| Segment operating margin: | | | | | |
| U.S. dialysis | $ | 2,121,007 | | | 1,774,578 | | | 1,565,310 | |
Other - Ancillary services(2) | 82,657 | | | (8,747) | | | (96,579) | |
| Total segment margin | 2,203,664 | | | 1,765,831 | | | 1,468,731 | |
| Reconciliation of segment operating margin to consolidated income from continuing operations before income taxes: | | | | | |
| Corporate administrative support | (113,181) | | | (163,047) | | | (129,669) | |
| Consolidated operating income | 2,090,483 | | | 1,602,784 | | | 1,339,062 | |
| Debt expense | (470,469) | | | (398,551) | | | (357,019) | |
| Debt prepayment, extinguishment and modification costs | (19,813) | | | (7,962) | | | — | |
| Other loss, net | (69,808) | | | (19,177) | | | (15,765) | |
| Income from continuing operations before income taxes | $ | 1,530,393 | | | $ | 1,177,094 | | | $ | 966,278 | |
(1)Other segment items for our U.S. dialysis segment include equity income from nonconsolidated joint ventures and a gain on changes in ownership interest.
(2)Segment operating margin (loss) for Other - Ancillary services includes equity investment loss of $1,701, $2,103 and $1,898 in 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively.
DAVITA INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS - (continued)
(dollars and shares in thousands, except per share data)
Depreciation and amortization expense by reportable segment was as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year ended December 31, |
| | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| U.S. dialysis | $ | 661,181 | | | $ | 695,674 | | | $ | 690,949 | |
| Other - Ancillary services | 62,679 | | | 49,769 | | | 41,653 | |
| | $ | 723,860 | | | $ | 745,443 | | | $ | 732,602 | |
Expenditures for property and equipment by reportable segment were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year ended December 31, |
| | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| U.S. dialysis | $ | 469,799 | | | $ | 501,149 | | | $ | 533,600 | |
| Other - Ancillary services | 85,644 | | | 66,836 | | | 69,829 | |
| | | | | |
| | $ | 555,443 | | | $ | 567,985 | | | $ | 603,429 | |
The Company's international operations include approximately $317,488 and $240,742 in 2024 and 2023, respectively, of net property and equipment.
25. Supplemental cash flow information
The table below provides supplemental cash flow information:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Year ended December 31, |
| | 2024 | | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Cash paid: | | | | | |
| Income taxes, net | $ | 387,940 | | | $ | 268,091 | | | $ | 344,430 | |
| Interest, net | $ | 423,360 | | | $ | 387,661 | | | $ | 350,999 | |
| Non-cash investing and financing activities: | | | | | |
| Fixed assets under financing lease obligations | $ | 11,327 | | | $ | 13,269 | | | $ | 1,928 | |
EXHIBIT INDEX
| | | | | | | | |
| | Equity Purchase Agreement, dated as of December 5, 2017, by and among DaVita Inc., Collaborative Care Holdings, LLC, and solely with respect to Section 9.3 and Section 9.18 thereto, UnitedHealth Group Incorporated.(2) |
| | |
| | Amendment No. 1 dated as of September 20, 2018, to that certain Equity Purchase Agreement, dated as of December 5, 2017, by and among DaVita Inc., a Delaware corporation, Collaborative Care Holdings, LLC, a Delaware limited liability company and a wholly owned subsidiary of Optum, Inc., and solely with respect to Section 9.3 and Section 9.18 thereto, UnitedHealth Group Incorporated, a Delaware corporation.(14) |
| | |
| | Second Amendment to Equity Purchase Agreement by and between DaVita Inc., a Delaware corporation, and Collaborative Care Holdings, LLC, a Delaware limited liability company, dated as of December 11, 2018, amending that certain Equity Purchase Agreement, dated as of December 5, 2017, by and among DaVita Inc., Collaborative Care Holdings, LLC, and, solely with respect to Section 9.3 and Section 9.18 thereto, UnitedHealth Group Incorporated (as previously amended).(9) |
| | |
| | Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation of DaVita Inc.(1) |
| | |
| | Amended and Restated Bylaws for DaVita Inc. adopted on September 5, 2024.(23) |
| | |
| | Indenture for the 4.625% Senior Notes due 2030, dated as of June 9, 2020, by and among DaVita Inc., the subsidiary guarantors party thereto and The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A., as Trustee.(13) |
| | |
| | Form of 4.625% Senior Notes due 2030 and related Guarantee (included in Exhibit 4.1).(13) |
| | |
| | Indenture for the 3.750% Senior Notes due 2031, dated August 11, 2020, by and among DaVita Inc., the subsidiary guarantors party thereto and The Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A., as Trustee.(11) |
| | | |
| | Form of 3.750% Senior Notes due 2031 and related Guarantee (included in Exhibit 4.3).(11) |
| | |
| | Indenture for 6.785% Senior Notes due 2032, dated as of August 13, 2024, by and among DaVita Inc., the subsidiary guarantors party thereto and the Bank of New York Mellon Trust Company, N.A., as Trustee.(26) |
| | |
| | Form of 6.875% Senior Notes due 2032 and related Guarantee (included in Exhibit 4.5).(26) |
| | |
| | Description of Securities.(20) |
| | |
| | Credit Agreement, dated August 12, 2019, by and among DaVita Inc., certain subsidiary guarantors party thereto, the lenders party thereto, Credit Agricole Corporate and Investment Bank, JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A. and MUFG Bank Ltd., as co-syndication agents, Bank of America, N.A., Barclays Bank PLC, Credit Suisse Loan Funding LLC, Goldman Sachs Bank USA, Morgan Stanley Senior Funding, Inc. and Suntrust Bank, as co-documentation agents, and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as administrative agent, collateral agent and swingline lender.(16) |
| | |
| | First Amendment, dated as of February 13, 2020, to that certain Credit Agreement, dated as of August 12, 2019, by and among DaVita Inc., certain subsidiary guarantors party thereto, the lenders party thereto, and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as administrative agent, collateral agent and swingline lender.(20) |
| | |
| | Second Amendment, dated as of April 3, 2023, to that certain Credit Agreement, dated as of August 12, 2019, by and among DaVita Inc., certain subsidiary guarantors party thereto, the lenders party thereto, and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as administrative agent, collateral agent and swingline lender.(25) |
| | |
| | Third Amendment, dated as of April 28, 2023, to that certain Credit Agreement, dated as of August 12, 2019, by and among DaVita Inc., certain subsidiary guarantors party thereto, the lenders party thereto, and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as administrative agent, collateral agent and swingline lender.(24) |
| | | | | | | | |
| | Fourth Amendment, dated as of May 9, 2024, to that certain Credit Agreement, dated as of August 12, 2019, by and among DaVita Inc., certain subsidiary guarantors party thereto, the lenders party thereto, and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as administrative agent, collateral agent and swingline lender.(28) |
| | |
| | Fifth Amendment, dated as of August 7, 2024, to that certain Credit Agreement, dated as of August 12, 2019, by and among DaVita Inc., certain subsidiary guarantors party thereto, the lenders party thereto, and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as administrative agent, collateral agent and swingline lender.ü |
| | |
| | Sixth Amendment, dated as of August 13, 2024, to that certain Credit Agreement, dated as of August 12, 2019, by and among DaVita Inc., certain subsidiary guarantors party thereto, the lenders party thereto, and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as administrative agent, collateral agent and swingline lender (including a conformed copy of the Credit Agreement, reflecting all amendments through the Sixth Amendment, attached as Annex A thereto).(26) |
| | |
| | Restated Standstill Agreement, dated February 9, 2022, by and between DaVita inc. and Berkshire Hathaway Inc.(27) |
| | |
| | Share Repurchase Agreement, dated as of April 30, 2024, by and between DaVita Inc. and Berkshire Hathaway Inc.(29) |
| | |
| | Employment Agreement, dated as of April 29, 2019, by and between Javier J. Rodriguez and DaVita Inc.(10)* |
| | |
| | Stock Appreciation Rights Agreement, effective November 4, 2019, by and between Javier J. Rodriguez and DaVita Inc.(19)* |
| | |
| | Employment Agreement, effective February 21, 2017, by and between DaVita Inc. and Joel Ackerman.(6)* |
| | |
| | Employment Agreement, effective April 27, 2016, by and between DaVita HealthCare Partners Inc. and Kathleen A. Waters.(4)* |
| | |
| | Employment Agreement, effective April 29, 2015, by and between DaVita HealthCare Partners Inc. and Michael Staffieri.(20)* |
| | |
| | Employment Agreement, effective September 15, 2024, by and between DaVita Inc. and David Maughan.(31)* |
| | |
| | Form of Indemnity Agreement.(8)* |
| | |
| | Form of Indemnity Agreement.(5)* |
| | |
| | DaVita Inc. Deferred Compensation Plan.(6)* |
| | |
| | Amended and Restated Employee Stock Purchase Plan.(18)* |
| | |
| | DaVita Inc. Severance Plan for Directors and Above.(3)* |
| | |
| | DaVita Inc. Non-Employee Director Compensation Policy.(15)* |
| | |
| | Amended and Restated DaVita Inc. 2011 Incentive Award Plan.(7)* |
| | |
| | Amendment No. 1 to the Amended and Restated DaVita Inc. 2011 Incentive Award Plan.(19)* |
| | |
| | DaVita Inc. 2020 Incentive Award Plan.(21)* |
| | |
| | Form of Stock Appreciation Rights Agreement-Executives (DaVita Inc. 2011 Incentive Award Plan).(17)* |
| | | | | | | | |
| | |
| | Form of Stock Appreciation Rights Agreement (DaVita Inc. 2020 Incentive Award Plan).(22)* |
| | |
| | Form of Performance-Based Restricted Stock Unit Agreement (DaVita Inc. 2020 Incentive Award Plan).(22)* |
| | |
| | Form of Restricted Stock Unit Agreement (DaVita Inc. 2020 Incentive Award Plan).(22)* |
| | |
| | Form of Stock Appreciation Rights Agreement (DaVita Inc. 2020 Incentive Award Plan).(25)* |
| | |
| | Form of Performance-Based Restricted Stock Unit Agreement (DaVita Inc. 2020 Incentive Award Plan).(25)* |
| | |
| | Form of Restricted Stock Unit Agreement (DaVita Inc. 2020 Incentive Award Plan).(25)* |
| | |
| | Form of Performance-Based Restricted Stock Unit Agreement (DaVita Inc. 2020 Incentive Award Plan).(30)* |
| | |
| | Form of Restricted Stock Unit Agreement (DaVita Inc. 2020 Incentive Award Plan).(30)* |
| | |
| | Form of Stock Appreciation Rights Agreement (DaVita Inc. 2020 Incentive Award Plan).(30)* |
| | |
| | DaVita Inc. Insider Trading Policy.ü |
| | |
| | List of our subsidiaries.ü |
| | |
| | Consent of KPMG LLP, independent registered public accounting firm.ü |
| | |
| | Powers of Attorney with respect to DaVita Inc. (Included on Page S-1). |
| | |
| | Certification of the Chief Executive Officer, dated February 13, 2025, pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a) or 15d-14(a), as adopted pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002.ü |
| | |
| | Certification of the Chief Financial Officer, dated February 13, 2025, pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a) or 15d-14(a), as adopted pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002.ü |
| | |
| | Certification of the Chief Executive Officer, dated February 13, 2025, pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002.ü |
| | | |
| | Certification of the Chief Financial Officer, dated February 13, 2025, pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002.ü |
| | |
| | DaVita Inc. Dodd-Frank Policy on Recoupment of Incentive Compensation.(12)* |
| | |
| 101.INS | | XBRL Instance Document - the Instance Document does not appear in the Interactive Data File because its XBRL tags are embedded within the Inline XBRL document.ü |
| | | |
| 101.SCH | | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document.ü |
| | |
| 101.CAL | | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document.ü |
| | | |
| 101.DEF | | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document.ü |
| | | |
| 101.LAB | | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document.ü |
| | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| 101.PRE | | Inline XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document.ü |
| | |
| 104 | | Cover Page Interactive Data File (formatted as Inline XBRL and contained in Exhibit 101).ü |
| | | | | |
| ü | Included in this filing. |
| * | Management contract or executive compensation plan or arrangement. |
(1)Filed on June 8, 2023 as an exhibit to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K.
(2)Filed on December 6, 2017 as an exhibit to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K.
(3)Filed on October 28, 2021 as an exhibit to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2021.
(4)Filed on May 2, 2017 as an exhibit to the Company’s Quarterly Report on 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2017.
(5)Filed on March 3, 2005 as an exhibit to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2004.
(6)Filed on February 24, 2017 as an exhibit to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2016.
(7)Filed on April 28, 2014 as an appendix to the Company's Definitive Proxy Statement on Schedule 14A.
(8)Filed on December 20, 2006 as an exhibit to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K.
(9)Filed on December 17, 2018 as an exhibit to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K.
(10)Filed on April 29, 2019 as an exhibit to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K.
(11)Filed on August 11, 2020 as an exhibit to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K.
(12)Filed on February 14, 2024 as an exhibit to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2023.
(13)Filed on June 9, 2020 as an exhibit to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K.
(14)Filed on September 24, 2018 as an exhibit to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K.
(15)Filed on February 22, 2023 as an exhibit to the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2022.
(16)Filed on August 14, 2019 as an exhibit to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K.
(17)Filed on July 22, 2019 as an exhibit to the Company’s Tender Offer Statement on Schedule TO-I.
(18)Filed on May 10, 2016 as an appendix to the Company's Proxy Statement on DEF 14A.
(19)Filed on December 6, 2019 as an appendix to the Company's Proxy Statement on DEF 14A.
(20)Filed on February 21, 2020 as an exhibit to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2019.
(21)Filed on April 27, 2020 as an appendix to the Company's Proxy Statement on DEF 14A.
(22)Filed on August 17, 2020 as an exhibit to the Company’s Tender Offer Statement on Schedule TO-I.
(23)Filed on September 5, 2024 as an exhibit to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K.
(24)Filed on May 1, 2023 as an exhibit to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K.
(25)Filed on May 8, 2023 as an exhibit to the Company's Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2023.
(26)Filed on August 14, 2024 as an exhibit to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K.
(27)Filed on February 9, 2022 as an exhibit to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K.
(28)Filed on May 13, 2024 as an exhibit to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K.
(29)Filed on May 1, 2024 as an exhibit to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K.
(30)Filed on May 2, 2024 as an exhibit to the Company’s Quarterly Report on 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2024.
(31)Filed on September 13, 2024 as an exhibit to the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K.
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, we have duly caused this Annual Report on Form 10-K to be signed on our behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized, in the City of Denver, State of Colorado, on February 13, 2025.
| | | | | | | | |
| DAVITA INC. |
| | | |
| By: | | /S/ JAVIER J. RODRIGUEZ |
| | | Javier J. Rodriguez
Chief Executive Officer |
KNOW ALL MEN BY THESE PRESENT, that each person whose signature appears below constitutes and appoints Javier J. Rodriguez, Joel Ackerman, and Kathleen Waters, and each of them his or her true and lawful attorneys-in-fact and agents with full power of substitution and resubstitution, for him or her and in his or her name, place and stead, in any and all capacities, to sign any and all amendments to this Annual Report on Form 10-K, and to file the same, with all exhibits thereto, and other documents in connection therewith, with the Securities and Exchange Commission, granting unto said attorneys-in-fact and agents, and each of them, full power and authority to do and perform each and every act and thing requisite or necessary to be done in and about the premises, as fully to all intents and purposes as he or she might or could do in person, hereby ratifying and confirming all that said attorneys-in-fact and agents or any of them, or their or his or her substitute or substitutes, may lawfully do or cause to be done by virtue hereof.
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this Annual Report on Form 10-K has been signed by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Signature | | Title | | Date |
| | | |
/S/ JAVIER J. RODRIGUEZ | | Chief Executive Officer and Director | | February 13, 2025 |
| Javier J. Rodriguez | | (Principal Executive Officer) | | |
| | | |
/S/ JOEL ACKERMAN | | Chief Financial Officer and Treasurer | | February 13, 2025 |
| Joel Ackerman | | (Principal Financial Officer) | | |
| | | |
/S/ CHRISTOPHER M. BERRY | | Chief Accounting Officer | | February 13, 2025 |
| Christopher M. Berry | | (Principal Accounting Officer) | | |
| | | | | |
/S/ PAMELA M. ARWAY | | Director | | February 13, 2025 |
| Pamela M. Arway | | | | |
| | | |
/S/ CHARLES G. BERG | | Director | | February 13, 2025 |
| Charles G. Berg | | | | |
| | | |
/S/ BARBARA J. DESOER | | Director | | February 13, 2025 |
| Barbara J. Desoer | | | | |
| | | |
/S/ JASON M. HOLLAR | | Director | | February 13, 2025 |
| Jason M. Hollar | | | | |
| | | | |
/S/ GREGORY J. MOORE | | Director | | February 13, 2025 |
| Gregory J. Moore | | | | |
| | | |
/S/ DENNIS W. PULLIN | | Director | | February 13, 2025 |
| Dennis W. Pullin | | | | |
| | | | | |
/S/ ADAM H. SCHECHTER | | Director | | February 13, 2025 |
| Adam H. Schechter | | | | |
| | | | |
/S/ WENDY L. SCHOPPERT | | Director | | February 13, 2025 |
| Wendy L. Schoppert | | | | |
| | | | |
/S/ PHYLLIS R. YALE | | Director | | February 13, 2025 |
| Phyllis R. Yale | | | | |