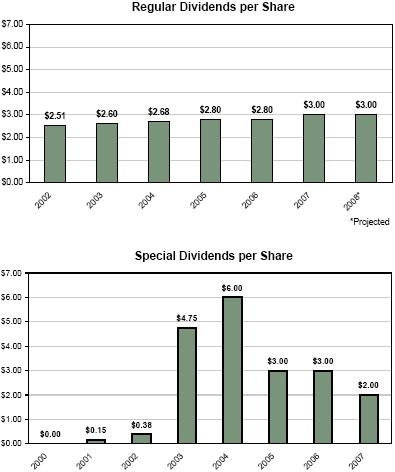
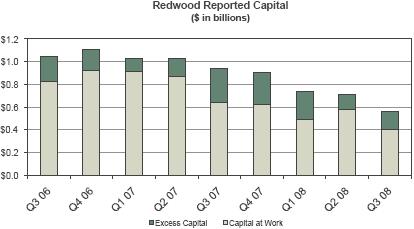
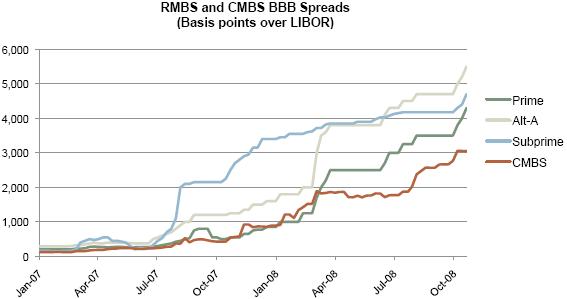
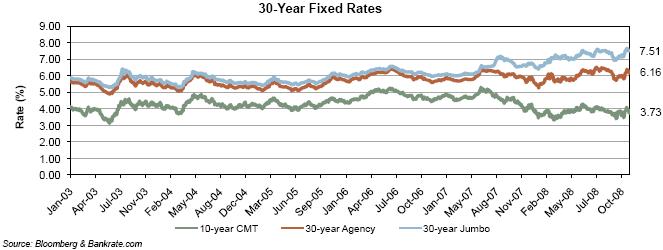
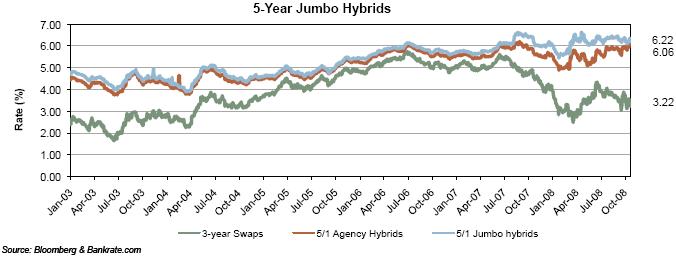
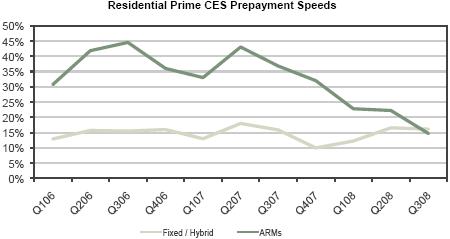
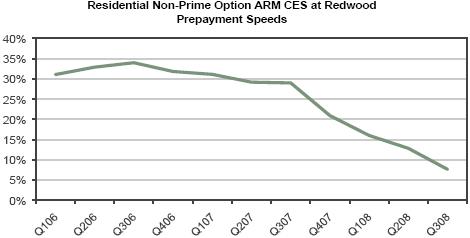
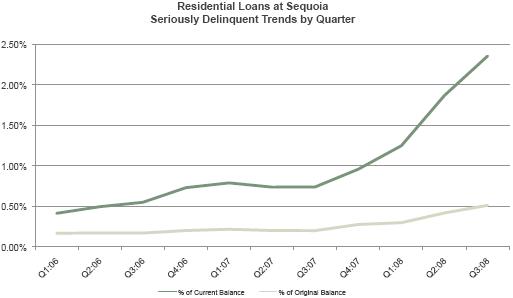
BOOK VALUE
Book value is the value of our common equity. As measured for GAAP, through December 31, 2007, reported book value generally incorporated mark-to-market adjustments for securities and interest rate agreements, but not for loans or liabilities. Beginning January 1, 2008, book value as measured for GAAP includes mark-to-market adjustments on certain assets and liabilities. We may also report management’s estimate of economic value, which is management’s estimate of the fair value of its investments net of liabilities.
COLLATERALIZED DEBT OBLIGATION (CDO) SECURITIZATIONS
The securitization of a diverse pool of assets. See “Acacia.”
CDO EQUITY SECURITIES
CDO equity securities (or CDO CES) are credit-enhancement securities that bear the initial credit losses of the assets owned by CDO securitization entities.
COMMERCIAL WHOLE LOANS
Commercial whole loans are unsecuritized first-lien loans that are secured by commercial real estate.
CONDUIT
A conduit is an entity that acquires closed loans from originators, accumulates loans over a period, and sells these loans, seeking to generate a gain on sale. Sales are usually made via securitization, but also can be made through bulk whole loan sales.
CORE EQUITY (CORE BOOK VALUE)
Core equity is not a measure calculated in accordance with GAAP. GAAP equity includes unrealized mark-to-market adjustments for some of our assets and interest rate agreements (“accumulated other comprehensive income”). Core equity excludes these mark-to-market adjustments. Core equity in some ways approximates what our equity value would be if we used historical amortized cost accounting exclusively. A reconciliation of core equity to GAAP equity appears in Table 2 of the Appendix.
CONSTANT (OR CONDITIONAL) PREPAYMENT RATE (CPR)
Constant (or conditional) prepayment rate (CPR) is an industry-standard measure of the speed at which mortgage loans prepay. It approximates the annual percentage rate at which a pool of loans is paying down due to principal prepayments.
CREDIT-ENHANCEMENT SECURITIES (CES)
Credit-enhancement securities (CES) absorb the initial credit losses generated by a pool of securitized assets. As a result, the more senior securities issued from that securitization are credit-enhanced because they carry less credit risk. Our definition of CES includes all the below investment-grade rated bonds issued from a securitization. These securities are also referred to as subordinated securities or B-pieces. For a typical securitization of prime residential loans, there are three CES: the first-loss, second-loss, and third-loss bonds. The first-loss security takes the initial risk of credit loss. If credit losses within the securitized asset pool exceed the principal value of the first-loss security, the second-loss security is at risk. If cumulative losses exceed the principal value of the first- and second-loss securities, then the third-loss security is at risk. Generally, for these securitizations, the third-loss security has a credit rating of BB, the second-loss security has a credit rating of B, and the first-loss security is unrated. Other types of securitizations, such as commercial, CDO, subprime residential, and some alt-a residential transactions, may be structured differently. Nevertheless, the non-investment grade rated securities issued from these securitizations function as credit-enhancement securities in these transactions.
GAAP
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles in the United States.
GSEs (GOVERNMENT-SPONSORED ENTERPRISES)
Government-sponsored enterprises (GSEs), include the Federal National Mortgage Association (Fannie Mae) and the Federal Home Loan and Mortgage Corporation (Freddie Mac).
INTEREST-ONLY SECURITIES (IOs)
Interest-only securities (IOs) are specialized securities created by securitization entities where the projected cash flows generated by the underlying assets exceed the cash flows projected to be paid to the ABS issued that have principal balances. They receive interest payments calculated by a formula wherein cash flows on IOs vary as a function of interest payments generated by the underlying assets within a securitization or as a function of the spread between the yield on the loans owned by a securitization entity and the cost of funds of the securities issued by that entity. Typically, IOs do not have a principal balance and they will not receive principal payments. Interest payments to IOs usually equal an interest rate formula multiplied by a “notional” principal balance. The notional principal balances for IOs are typically reduced over time as the actual principal balances of the underlying pools of assets pay down, thus reducing the cash flows to the IOs over time. Cash flows on IOs are typically reduced more quickly when asset prepayments accelerate.
INVESTMENT GRADE SECURITIES (IGS)
Investment grade securities (IGS) are securities that are rated AAA, AA, A, or BBB.
LEVERAGE RATIOS
We use collateralized debt to finance the accumulation of assets prior to sale to a securitization entity and to finance investments in high-quality loans and IGS. We currently have very low levels of short-term recourse debt. However, because of the consolidation of independent securitization entities, it appears on our GAAP consolidated financial statements that Redwood is highly leveraged, with total consolidated liabilities significantly greater than equity. The obligations of these securitization entities are not obligations of Redwood. When determining Redwood’s financial leverage, traditional leverage ratios may be misleading in some respects if consolidated ABS issued from securitization entities are included as part of Redwood’s obligations when calculating this or similar ratios.
LONG-TERM DEBT AT REDWOOD
Long-term debt at Redwood is debt that is an obligation of Redwood that is not payable within a year and includes junior subordinated notes and trust preferred securities. We generally treat long-term debt as part of our capital base when it is not payable in the near future. We may issue other forms of long-term debt in the future.
MARK-TO-MARKET ACCOUNTING
Mark-to-market accounting uses estimated fair values of assets, liabilities, and hedges. Many of our assets are carried on our balance sheet at their fair value rather than historical amortized cost. Through December 31, 2007 changes in the fair value of some of our assets and hedges are reported through our income statement. Beginning January 1, 2008 we began to use mark-to-market accounting for income statement purposes for a wider variety of assets and liabilities. This likely makes quarter-to-quarter GAAP income trends more volatile. Taxable income is generally not affected by market valuation adjustments.
THE REDWOOD REVIEW 3RD QUARTER 2008 55
MARKET VALUE ADJUSTMENTS (MVA)
Market value adjustments (MVA) are those changes in market values reported through our GAAP income statement. They reflect all changes in market values on assets and liabilities accounted for at fair value and impairments on securities accounted for as AFS.
NEGATIVE AMORTIZATION ADJUSTABLE-RATE MORTGAGES
(NEG AM ARMs, OPTION ARMs, OR MTA ARMs)
Negative amortization ARMs (neg am ARMs, option ARMs, pay option ARMs, or monthly treasury average (MTA) ARMs) are adjustable-rate mortgages that allow the borrower to choose between different payment options. These options allow the borrower to make minimum payments, or other payments that are less than the interest accrued on the mortgage during that period. As a result of this feature, the borrower’s loan balance may increase, causing negative amortization of the loan balance.
NON-PRIME SECURITIES
Non-prime securities are alt-a and subprime securities. See definitions of alt-a and subprime securities.
OPTION ARMs
See negative amortization adjustable-rate mortgages.
PRIME RESIDENTIAL REAL ESTATE LOANS
Prime loans are residential loans with high quality credit characteristics, such as borrowers with high FICO credit scores, lower loan-to-value ratios, lower debt-to-income ratios, greater levels of other assets, and more documentation.
PRIME SECURITIES
Prime securities are residential mortgage-backed securities backed by high credit-quality loans, generally with balances greater than conforming loan limits. Prime securities are typically backed by loans that have relatively high weighted average FICO scores (700 or higher), low weighted average LTVs (75% or less), limited concentrations of investor properties, and low percentages of loans with low FICO or high LTV.
PROFITABILITY RATIOS
Many financial institution analysts use asset-based profitability ratios such as interest rate spread and interest rate margin when analyzing financial institutions. These are asset-based measures. Because we consolidate the assets and liabilities of securitization entities for GAAP purposes, our total GAAP assets and liabilities may vary over time, and may not be comparable in economic reality to assets typically used in profitability calculations for other financial institutions. As a result, we believe equity-based profitability ratios may be more appropriate than asset-based measures for analyzing Redwood’s operations. We believe, for example, that net interest income as a percentage of equity is a useful measure of profitability. For operating expenses, we believe useful measures are operating efficiency ratio (operating expenses as a percentage of net interest income) and operating expenses as a percentage of equity.
56 THE REDWOOD REVIEW 3RD QUARTER 2008
REAL ESTATE INVESTMENT TRUST (REIT)
A real estate investment trust (REIT) is an entity that makes a tax election to be taxed as a REIT, invests in real estate assets, and meets other REIT qualifications, including the distribution as dividends of at least 90% of REIT taxable income. A REIT’s profits are not taxed at the corporate level to the extent that these profits are distributed as dividends to stockholders, providing an operating cost savings. On the other hand, the requirement to pay out as dividends most of the REIT profits means it can be harder for a REIT to grow if using only internally-generated funds (as opposed to issuing new stock).
REAL ESTATE OWNED (REO)
Real estate owned (REO) refers to real property owned by the lender that has been acquired through foreclosure.
REDWOOD DEBT
Redwood debt is an obligation of Redwood. See Long-term debt at Redwood and Short-term debt at Redwood.
REIT RETAINED TAXABLE INCOME
REIT retained taxable income is not a measure calculated in accordance with GAAP. REIT retained taxable income is the taxable income earned at the REIT after dividend distributions to our shareholders, less corporate income taxes paid at the REIT level. A reconciliation of REIT retained taxable income to GAAP income appears in Table 3 in the Appendix.
REIT SUBSIDIARY
A REIT subsidiary is a subsidiary of a REIT that is taxed as a REIT.
REIT TAXABLE INCOME
REIT taxable income is not a measure calculated in accordance with GAAP. REIT taxable income is pre-tax income calculated for tax purposes at Redwood including only its REIT subsidiaries (i.e., excluding its taxable subsidiaries). REIT taxable income is an important measure as it is the basis of our dividend distribution requirements. We must distribute at least 90% of REIT taxable income as dividends to shareholders over time. As a REIT, we are not subject to corporate income taxes on the REIT taxable income we distribute. We pay income tax on the REIT taxable income we retain (up to 10% of total REIT taxable income). A reconciliation of REIT taxable income to GAAP income appears in Table 3 in the Appendix.
RETURN ON EQUITY (ROE) AND ADJUSTED RETURN ON EQUITY
ROE is the amount of profit we generate each year per dollar of equity capital and equals GAAP income divided by GAAP equity. Adjusted ROE is GAAP income divided by core equity. Core equity excludes balance sheet mark-to-market adjustments. Thus, only those market value changes that are included in our income statement will affect adjusted ROE.
SEQUOIA
Sequoia is the brand name for securitizations of residential real estate loans Redwood sponsors.
SHORT-TERM DEBT AT REDWOOD
Short-term debt at Redwood is debt that is an obligation of Redwood and payable within a year. We obtain this debt from a variety of Wall Street firms, banks, and other institutions. As another form of short-term debt, we have issued collateralized commercial paper in the past and may issue other forms of short-term debt in the future.
THE REDWOOD REVIEW 3RD QUARTER 2008 57
SUBPRIME SECURITIES
Subprime securities are residential mortgage-backed securities backed by loans to borrowers who typically have lower credit scores and/or other credit deficiencies that prevent them from qualifying for prime or alt-a mortgages and may have experienced credit problems in the past, such as late payments or bankruptcies. To compensate for the greater risks and higher costs to service the loans, subprime borrowers pay higher interest rates, points, and origination fees.
Typical characteristics of subprime loan pools include more than 60% of loans with FICO scores below 680, weighted average LTVs over 85%, more than 70% of loans with LTVs over 75%, and loans with LTVs over 80% with no mortgage insurance.
TAXABLE SUBSIDIARY
A taxable subsidiary is a subsidiary of a REIT that is not taxed as a REIT and thus pays taxes on its income. A taxable subsidiary is not limited to investing in real estate and it can choose to retain all of its after-tax profits.
TOTAL RETAINED TAXABLE INCOME
Total retained taxable income is not a measure calculated in accordance with GAAP. Total retained taxable income is the taxable income earned at the REIT after dividend distributions to shareholders and taxes. It also includes all of the taxable income earned at our taxable subsidiaries, less corporate income taxes paid, as we generally retain the after-tax income at our taxable subsidiaries. A reconciliation of total retained taxable income to GAAP income appears in Table 3 in the Appendix.
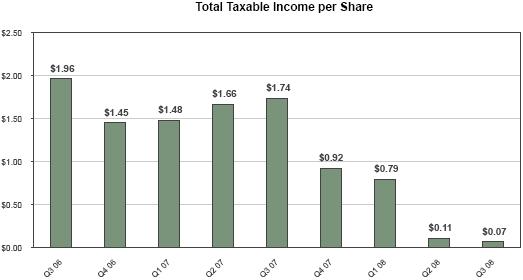
TOTAL TAXABLE INCOME
Total taxable income is not a measure calculated in accordance with GAAP. Total taxable income is pre-tax income for Redwood and all its subsidiaries as calculated for tax purposes. Taxable income calculations differ significantly from GAAP income calculations. A reconciliation of total taxable income to GAAP income appears in Table 3 in the Appendix.
58 THE REDWOOD REVIEW 3RD QUARTER 2008