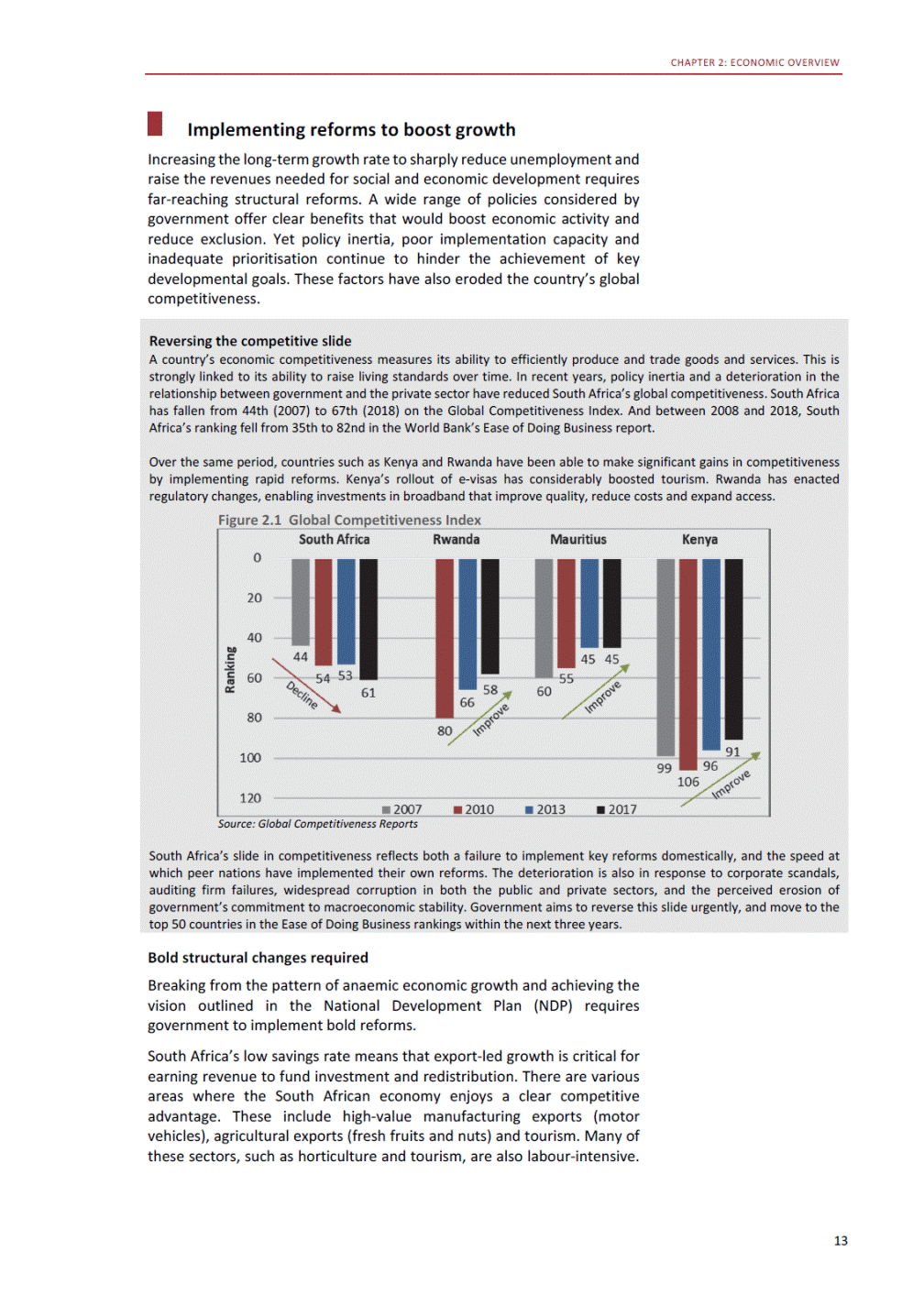
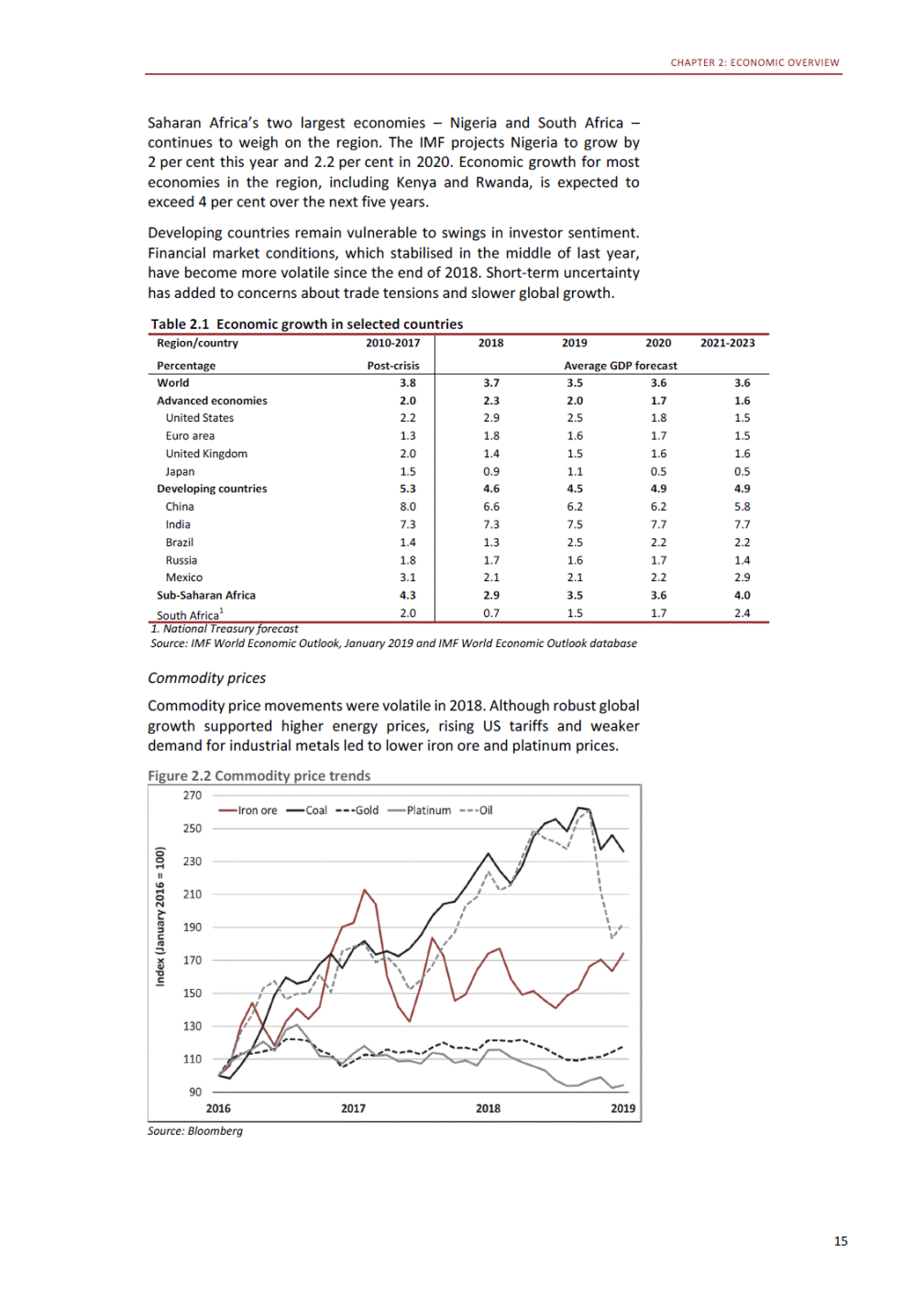
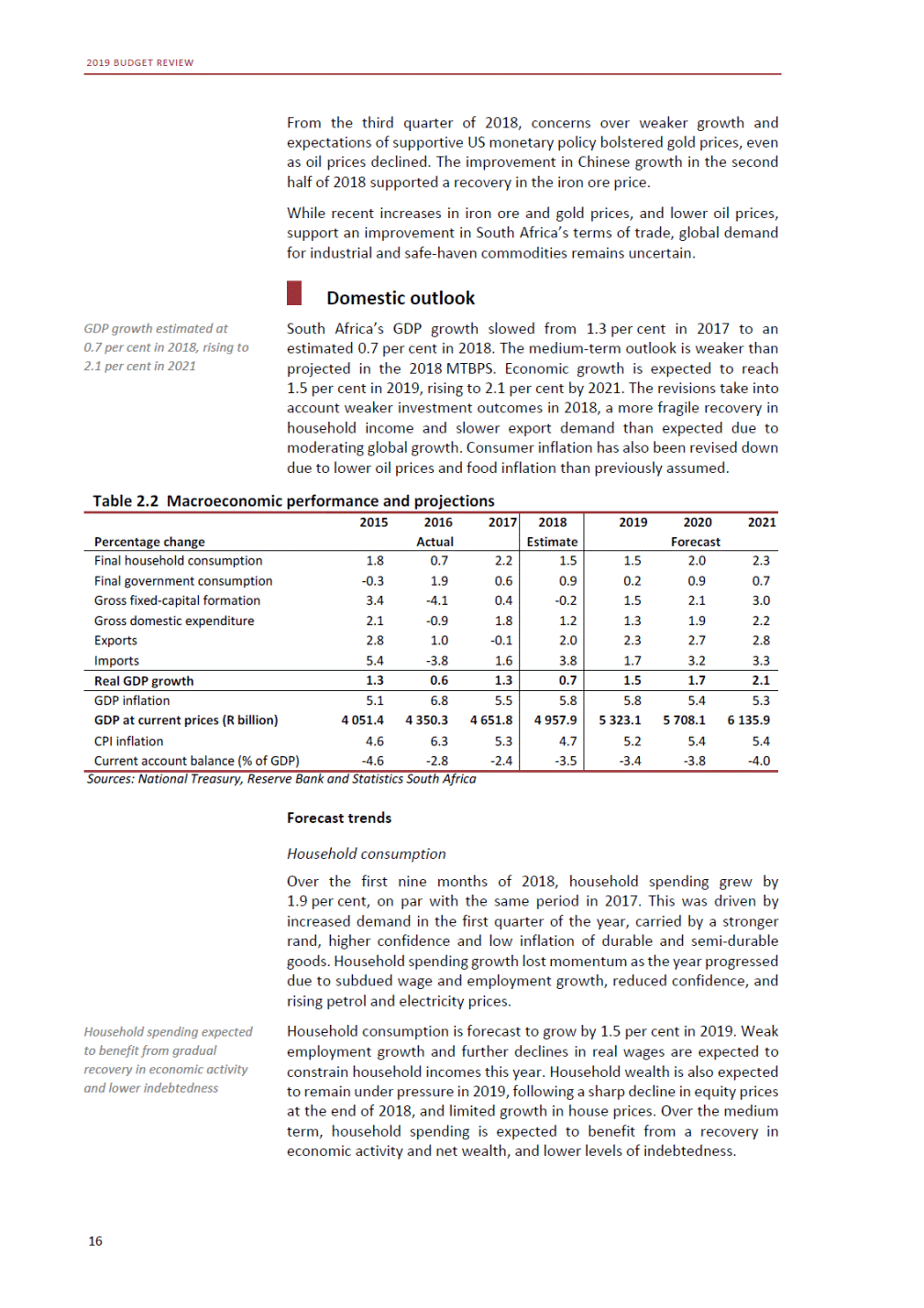
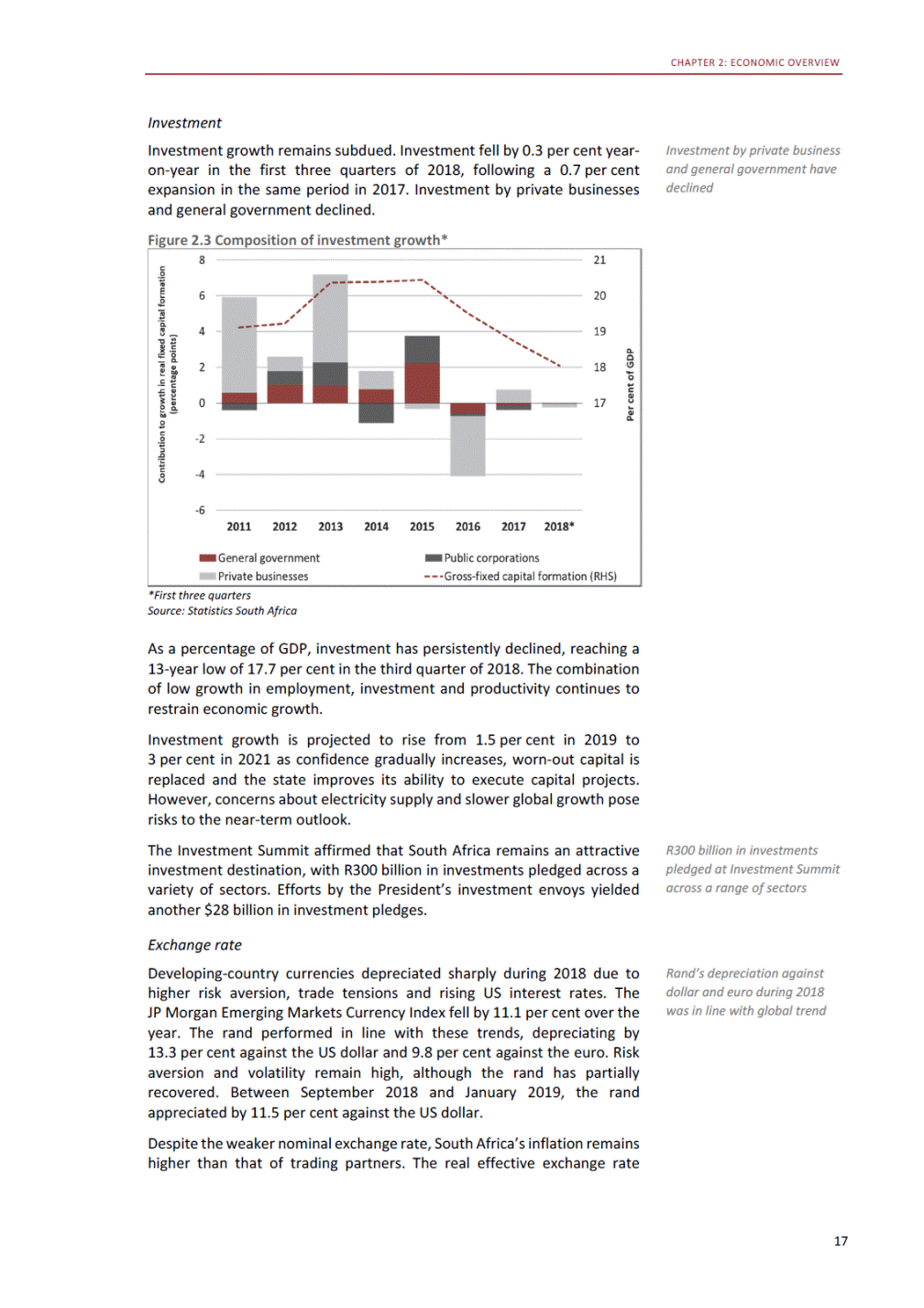
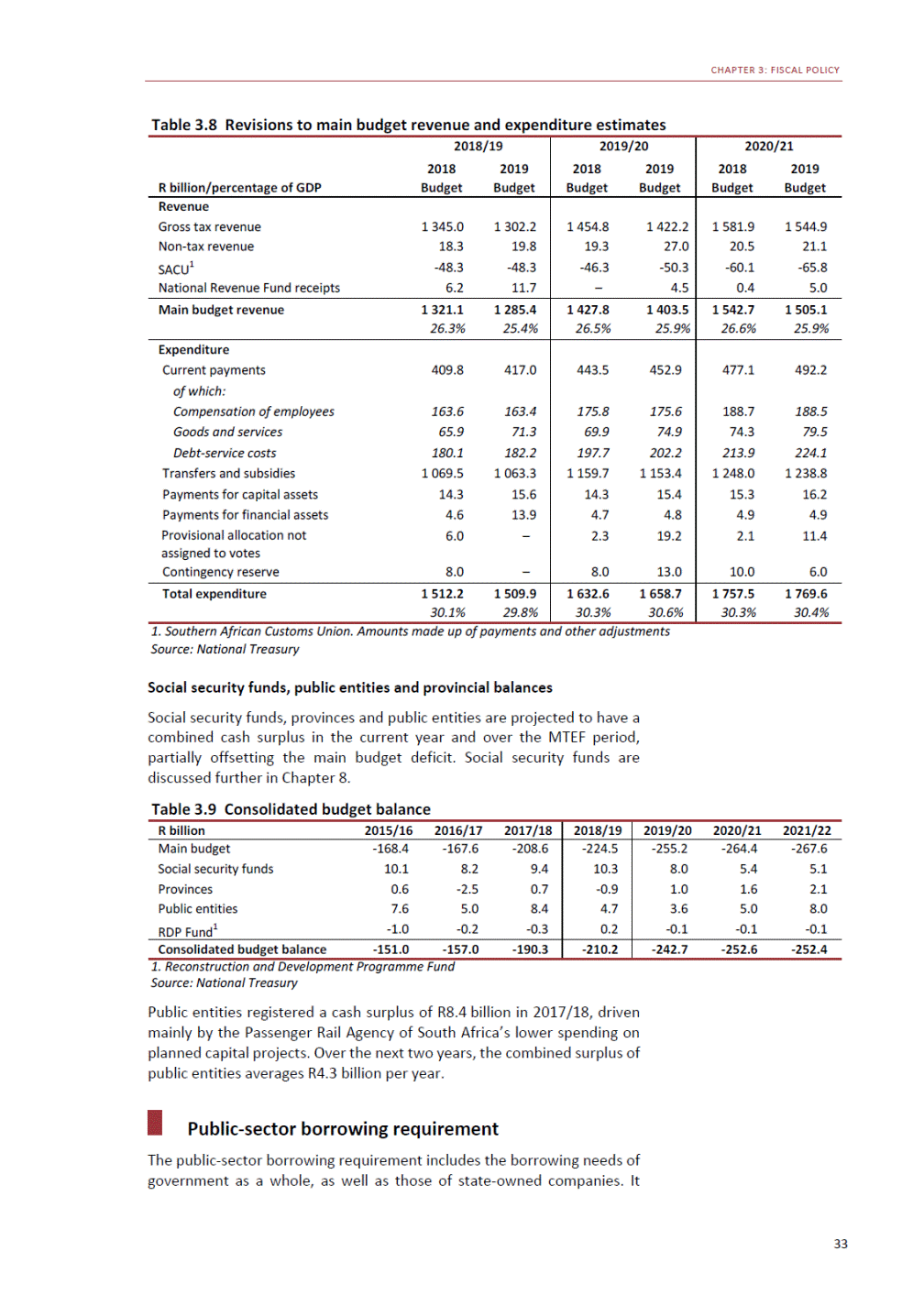
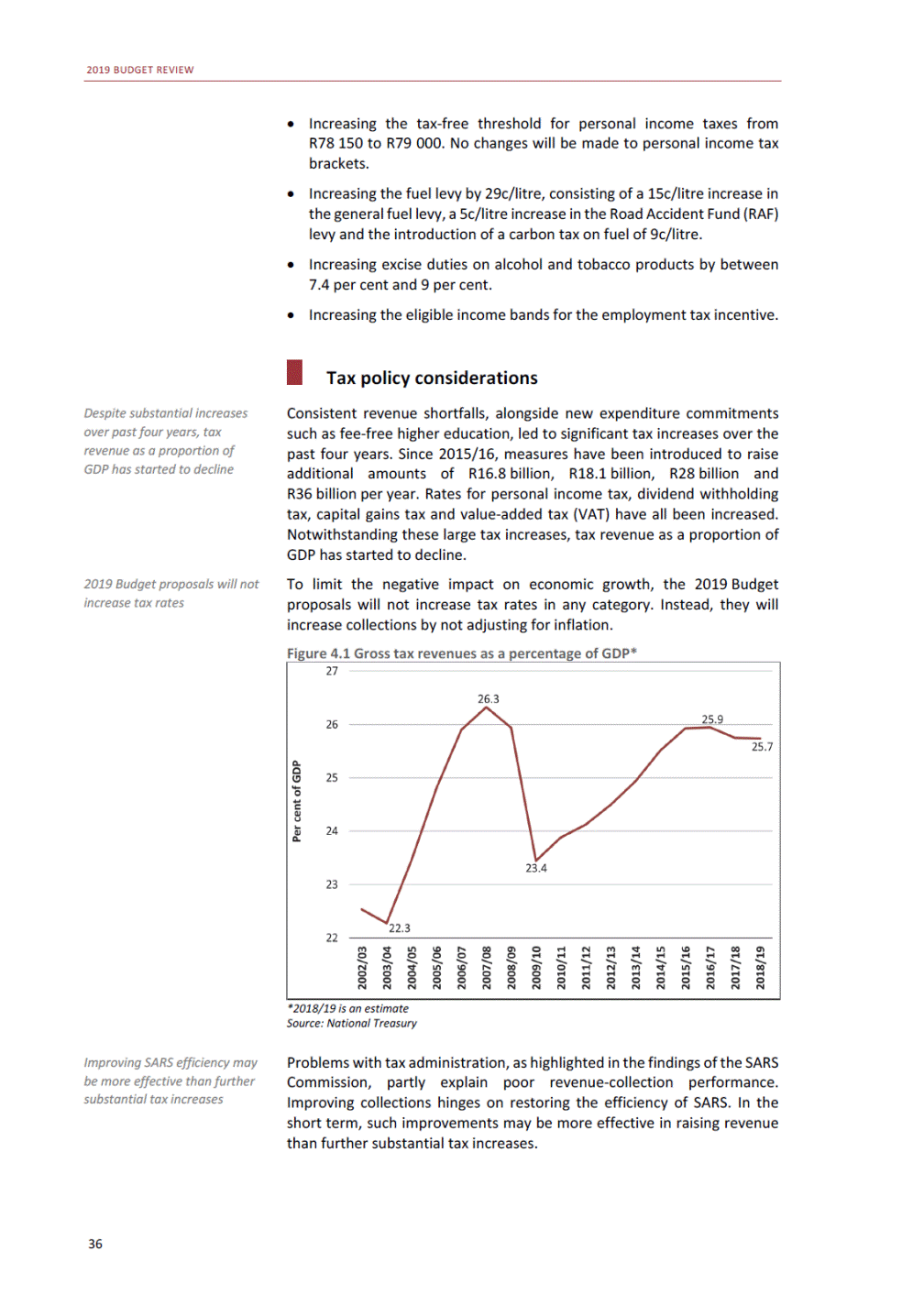
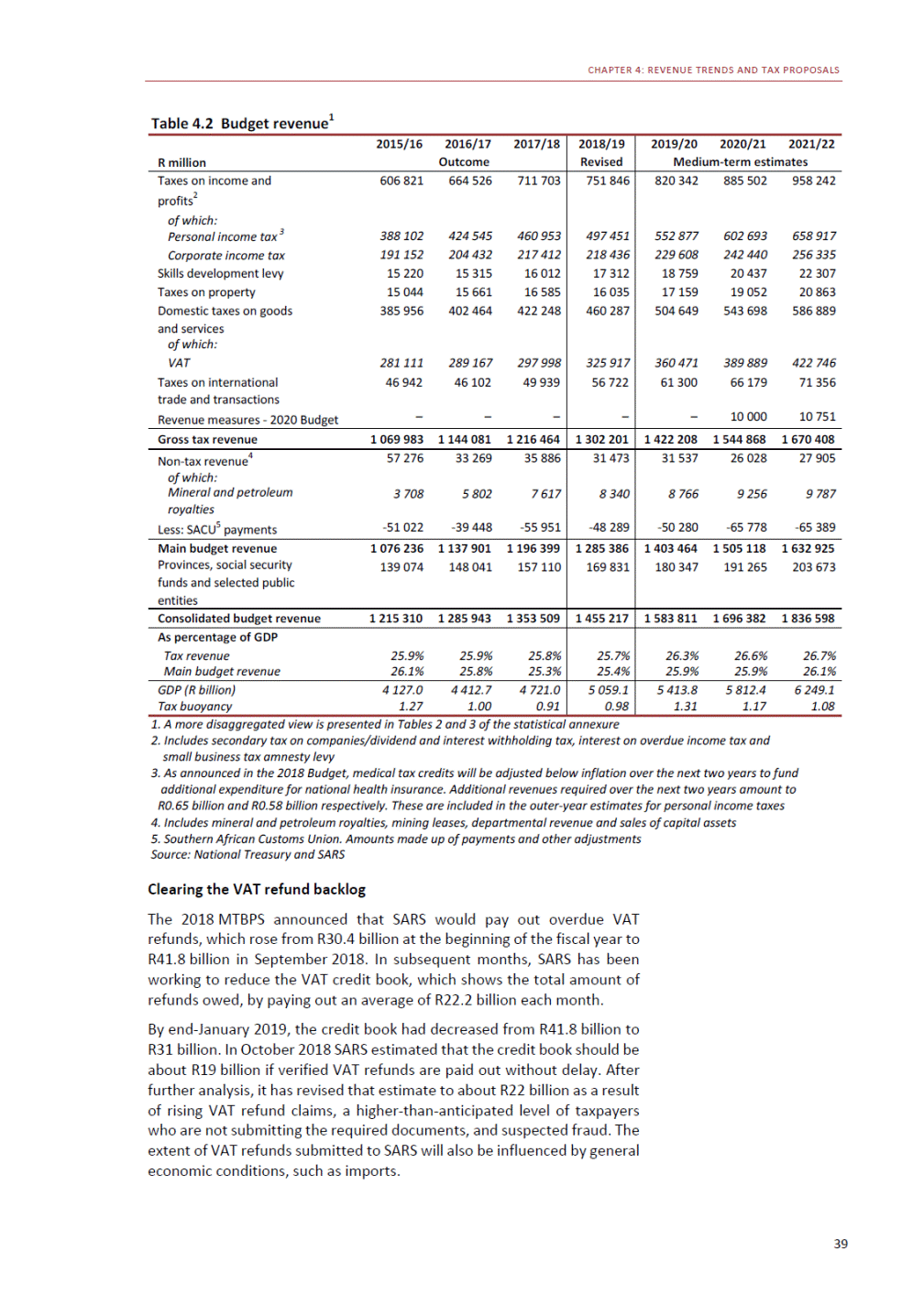
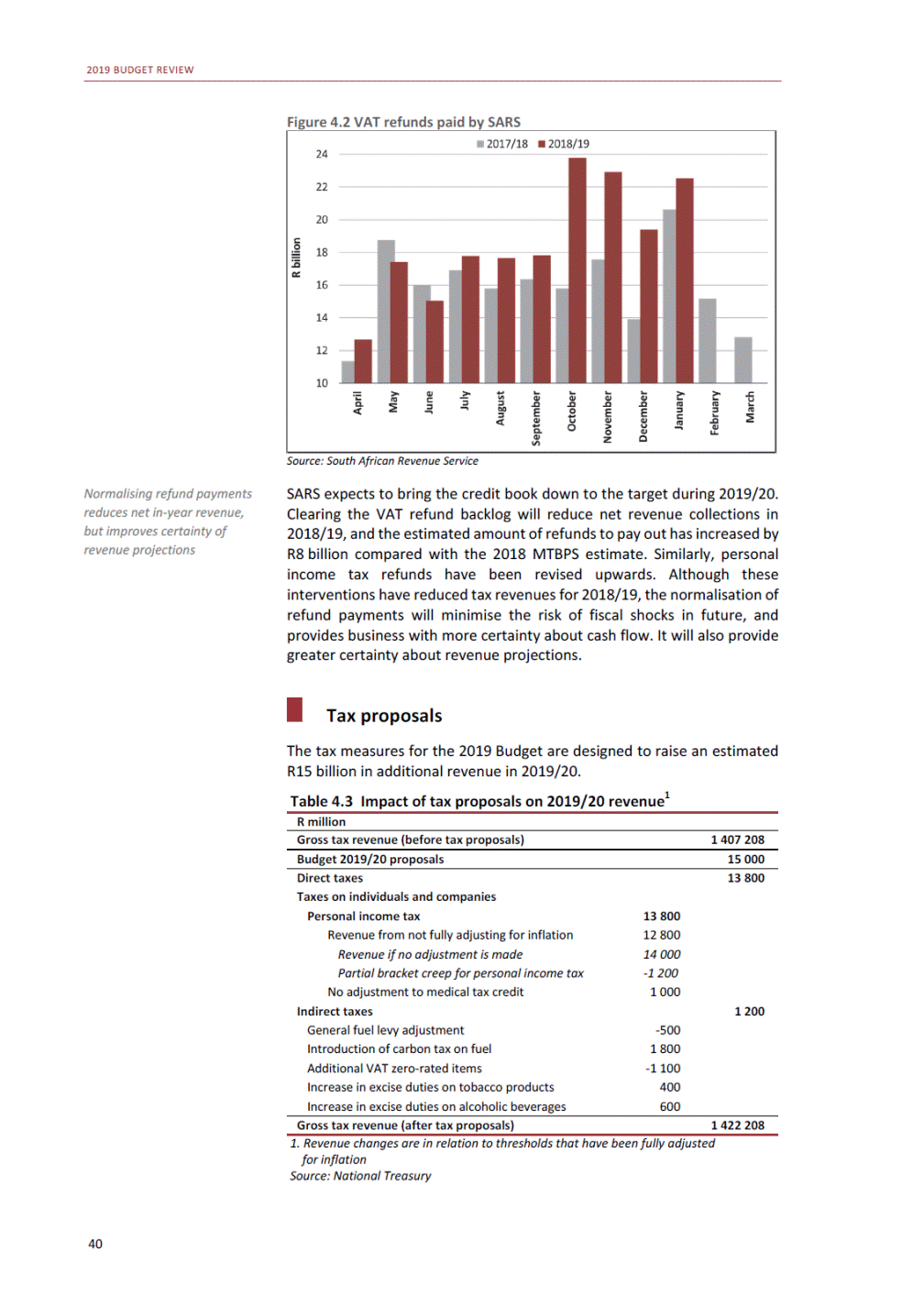
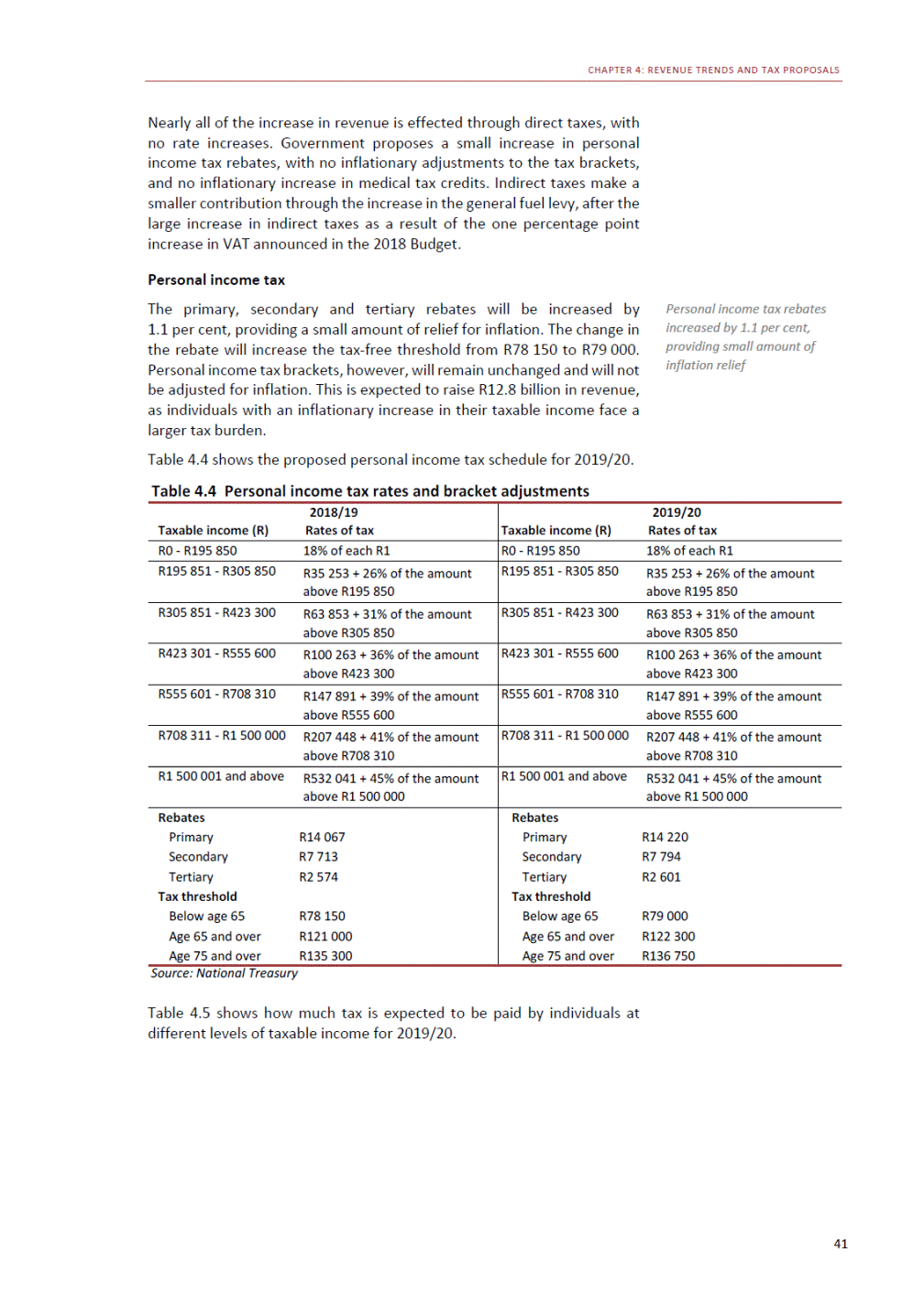
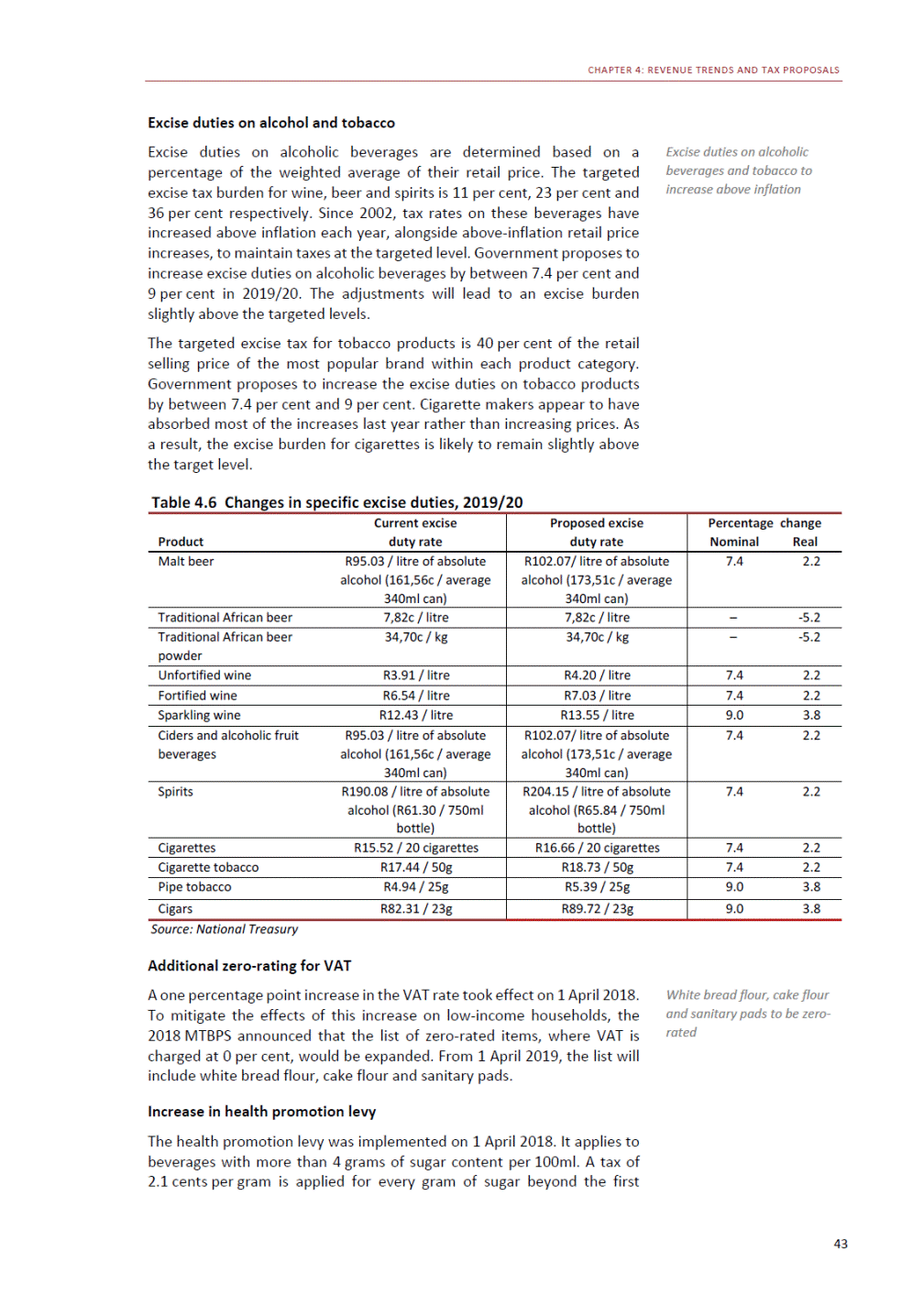
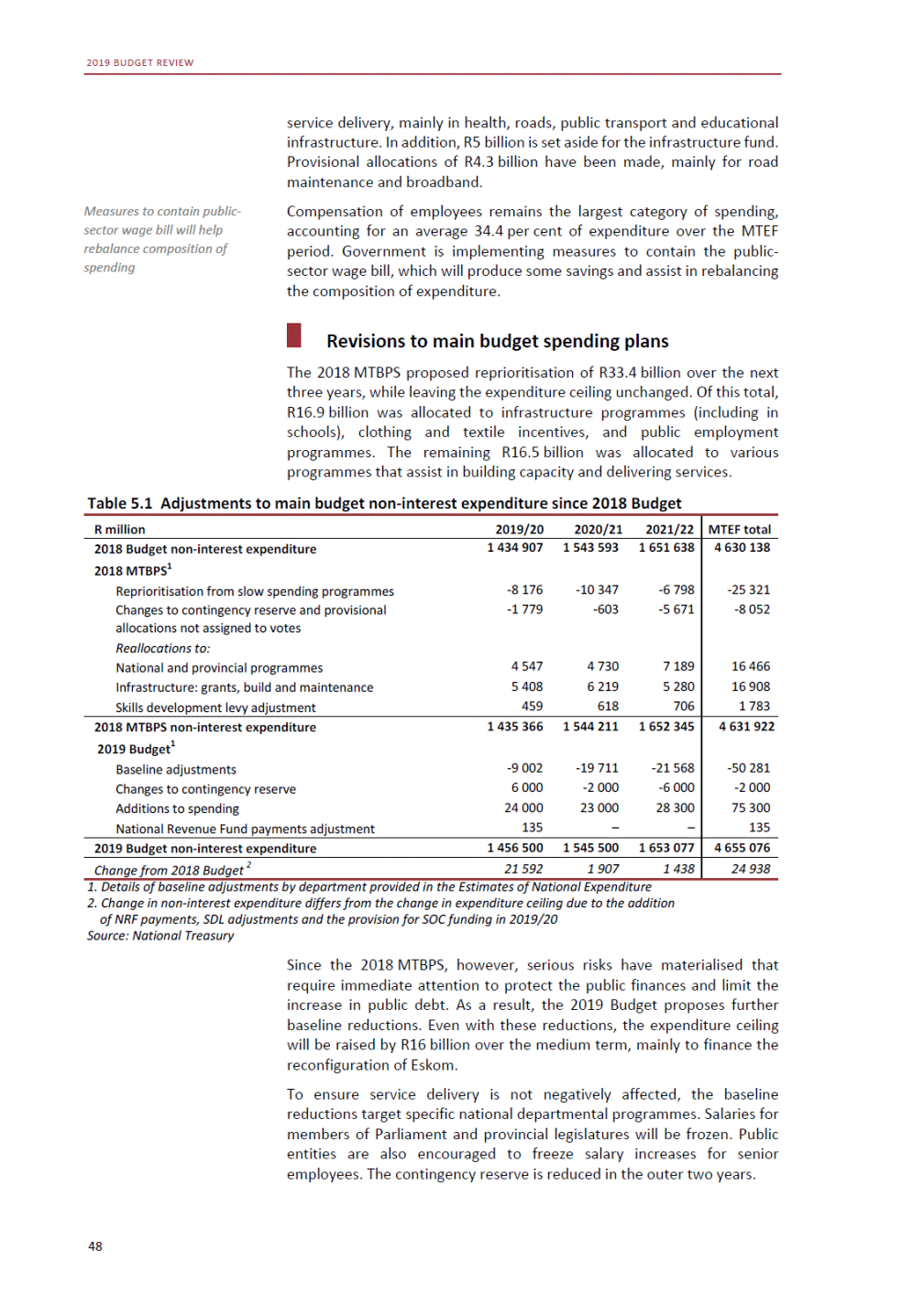
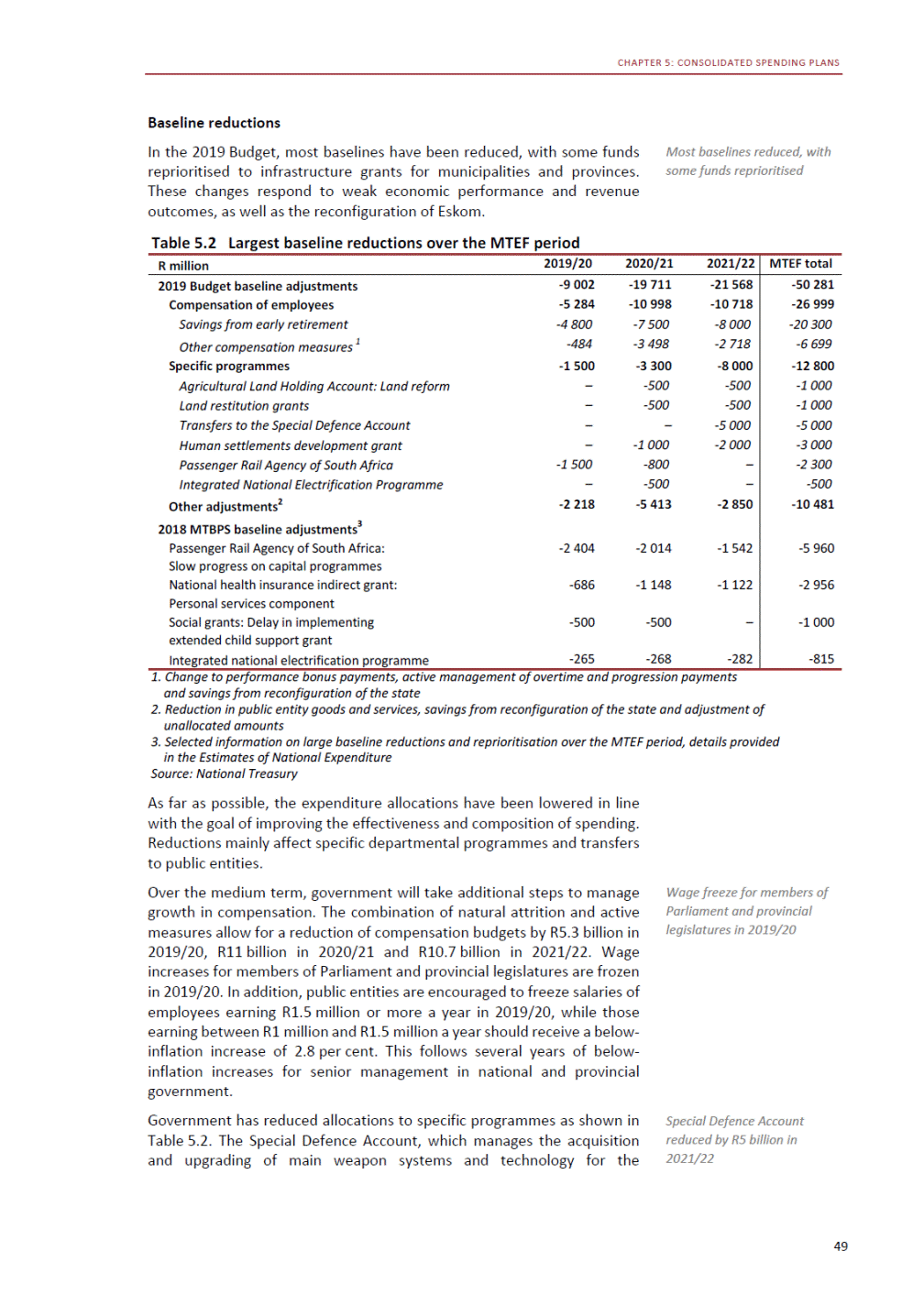
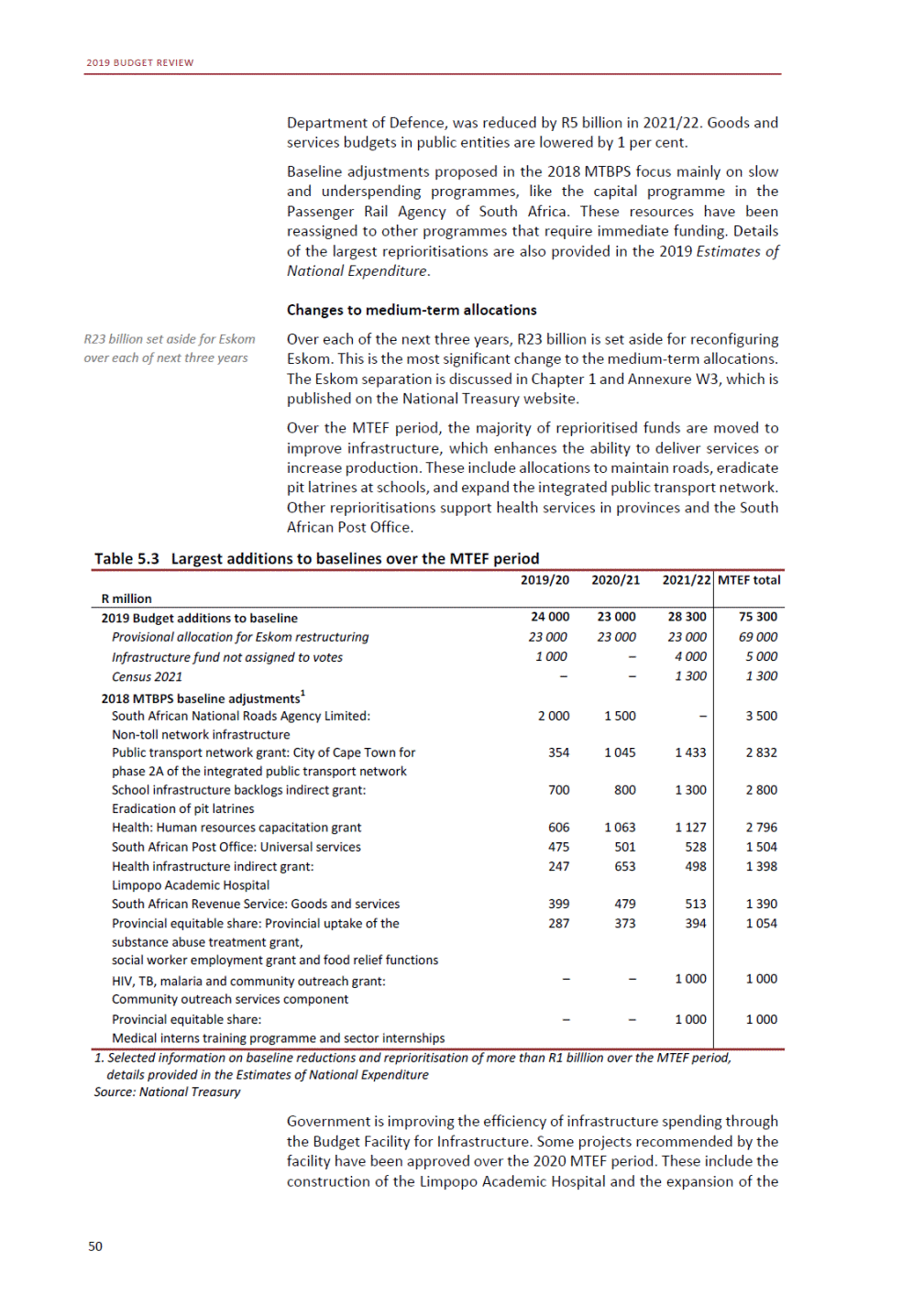
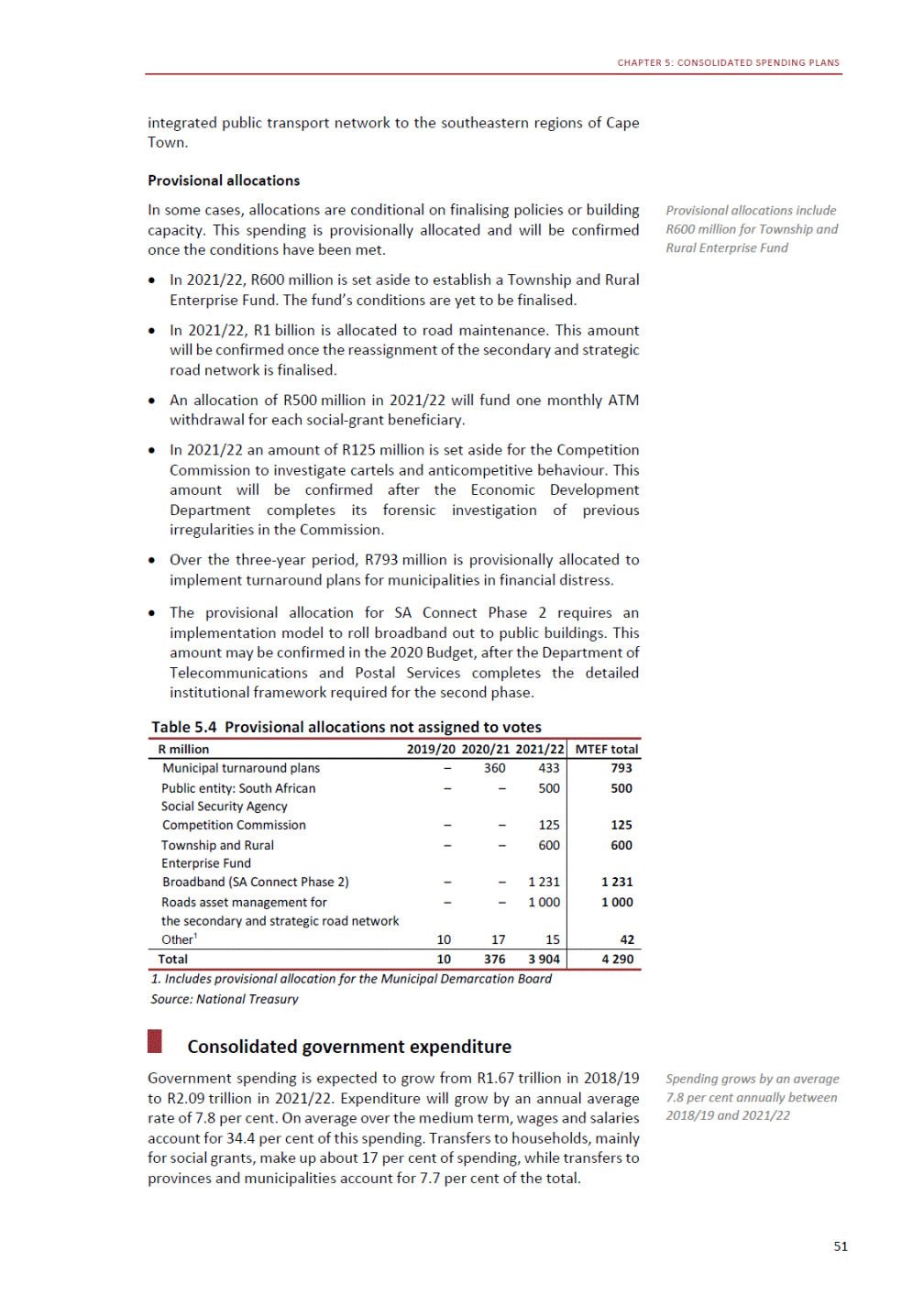
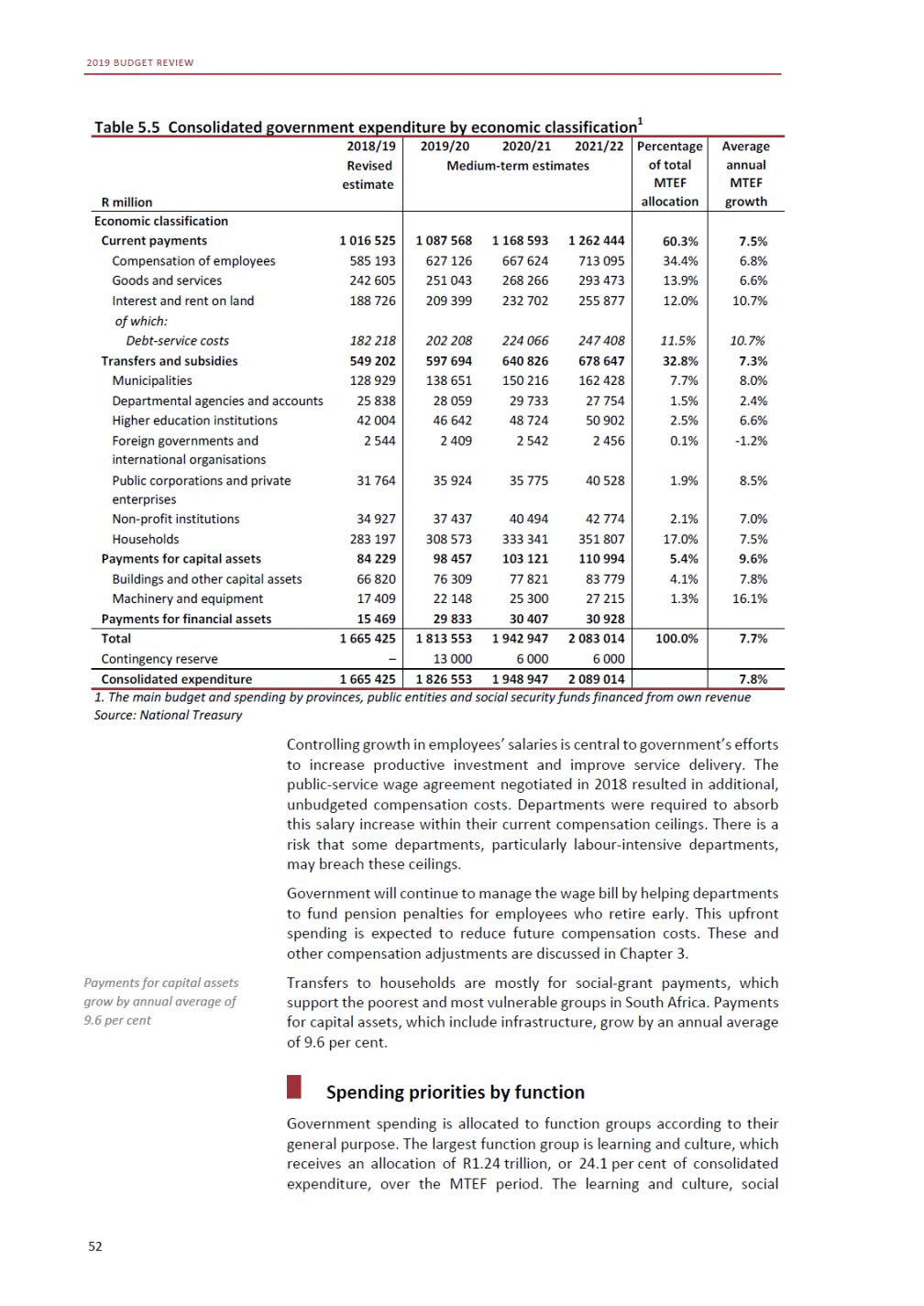
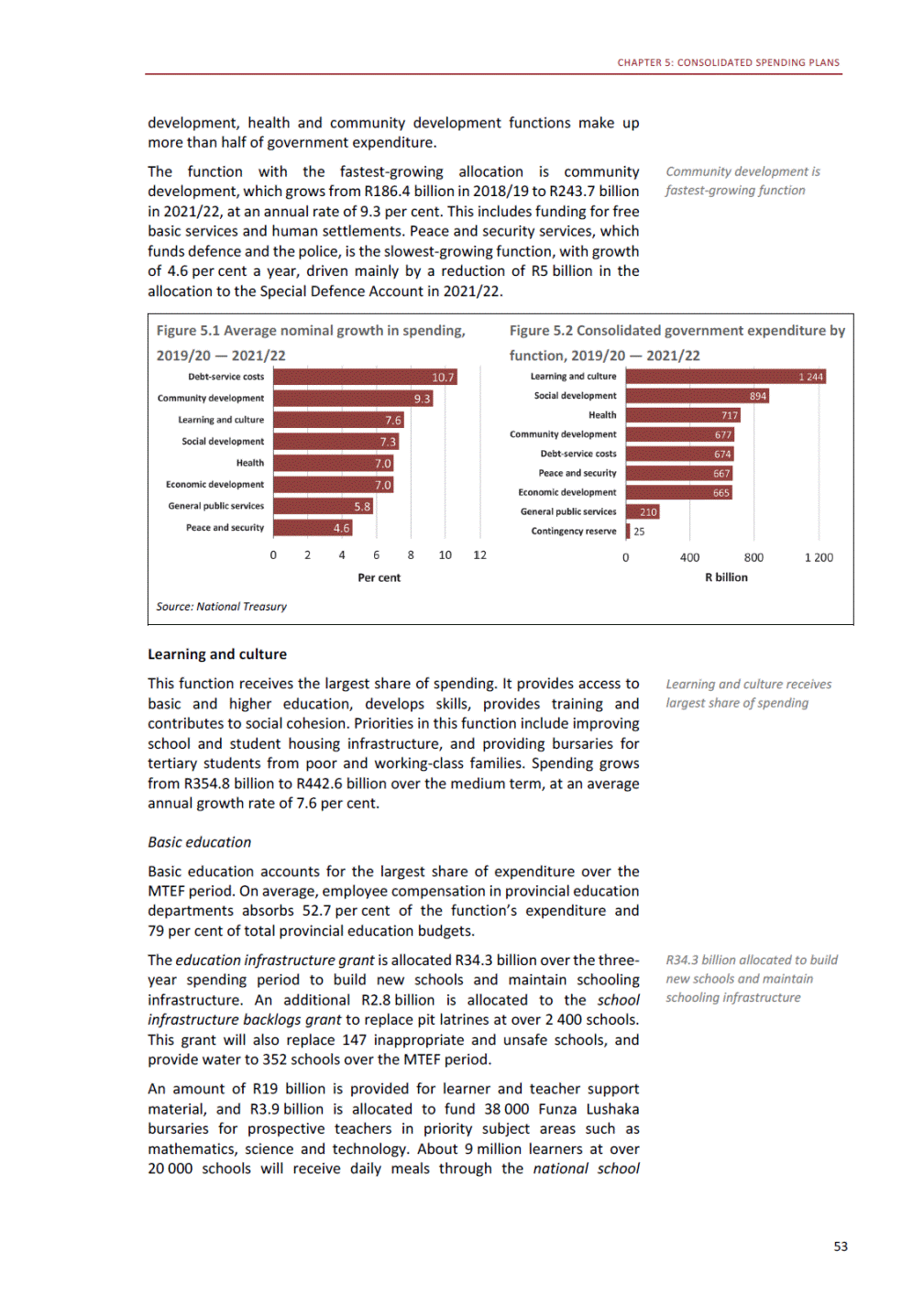
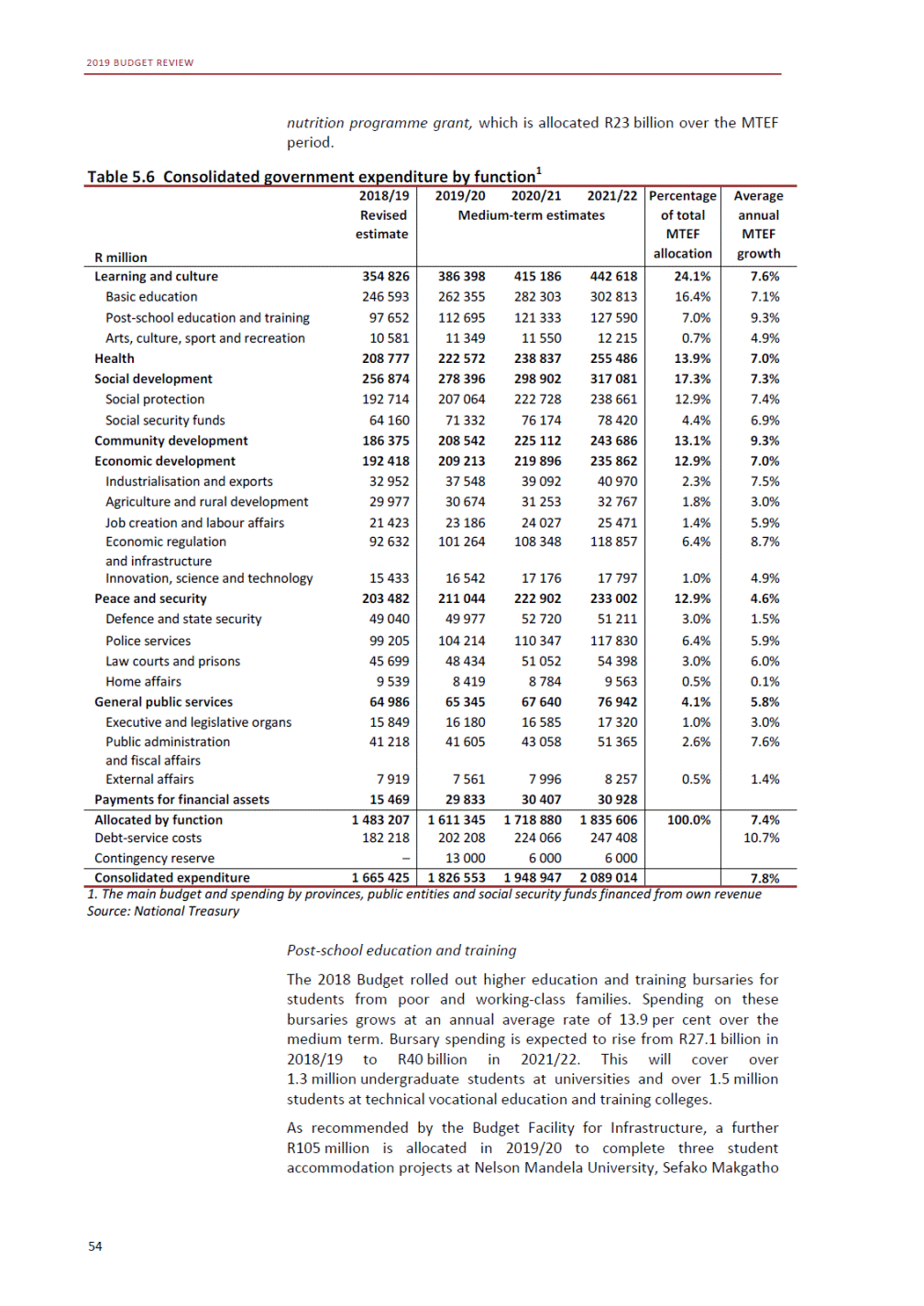
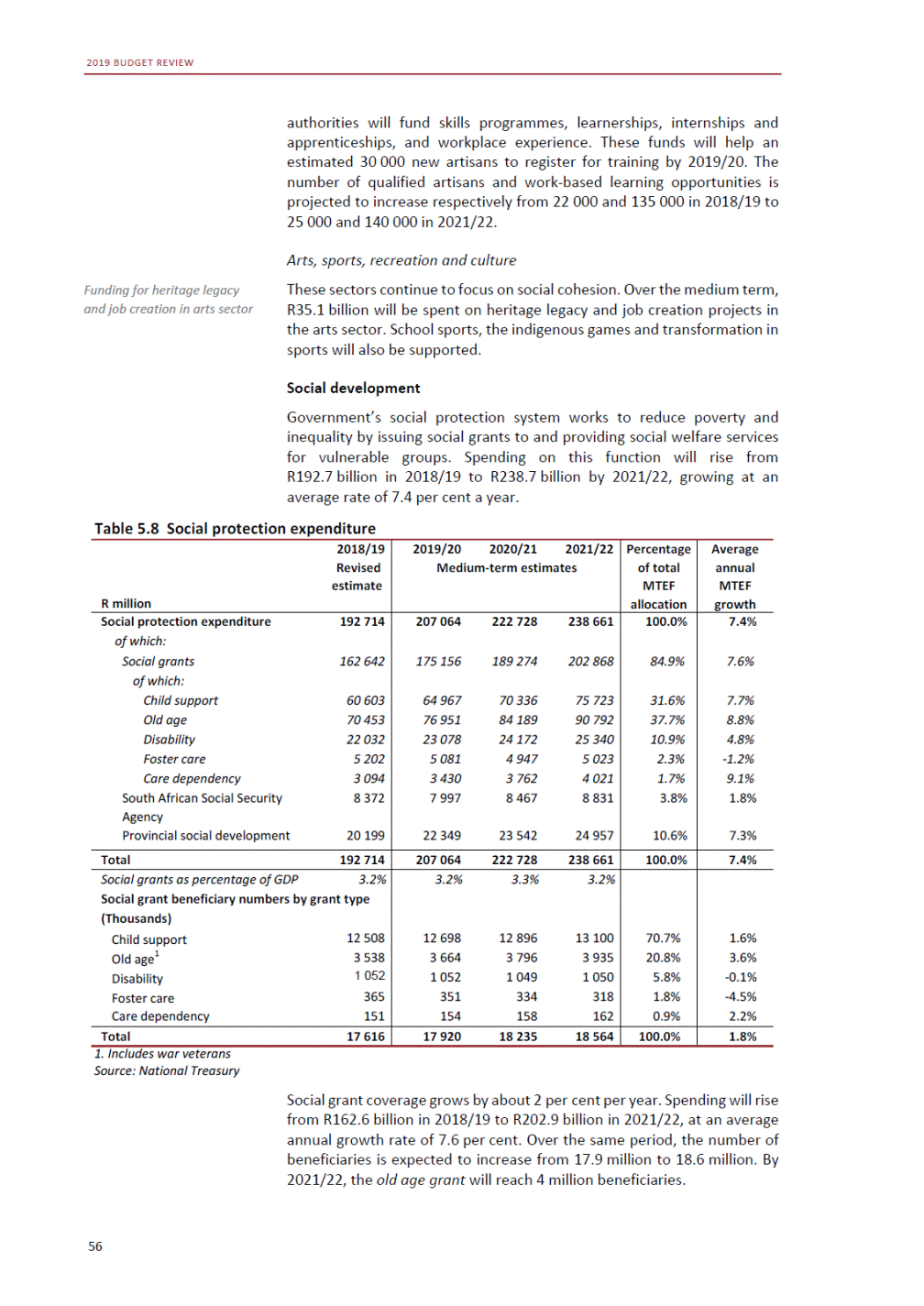
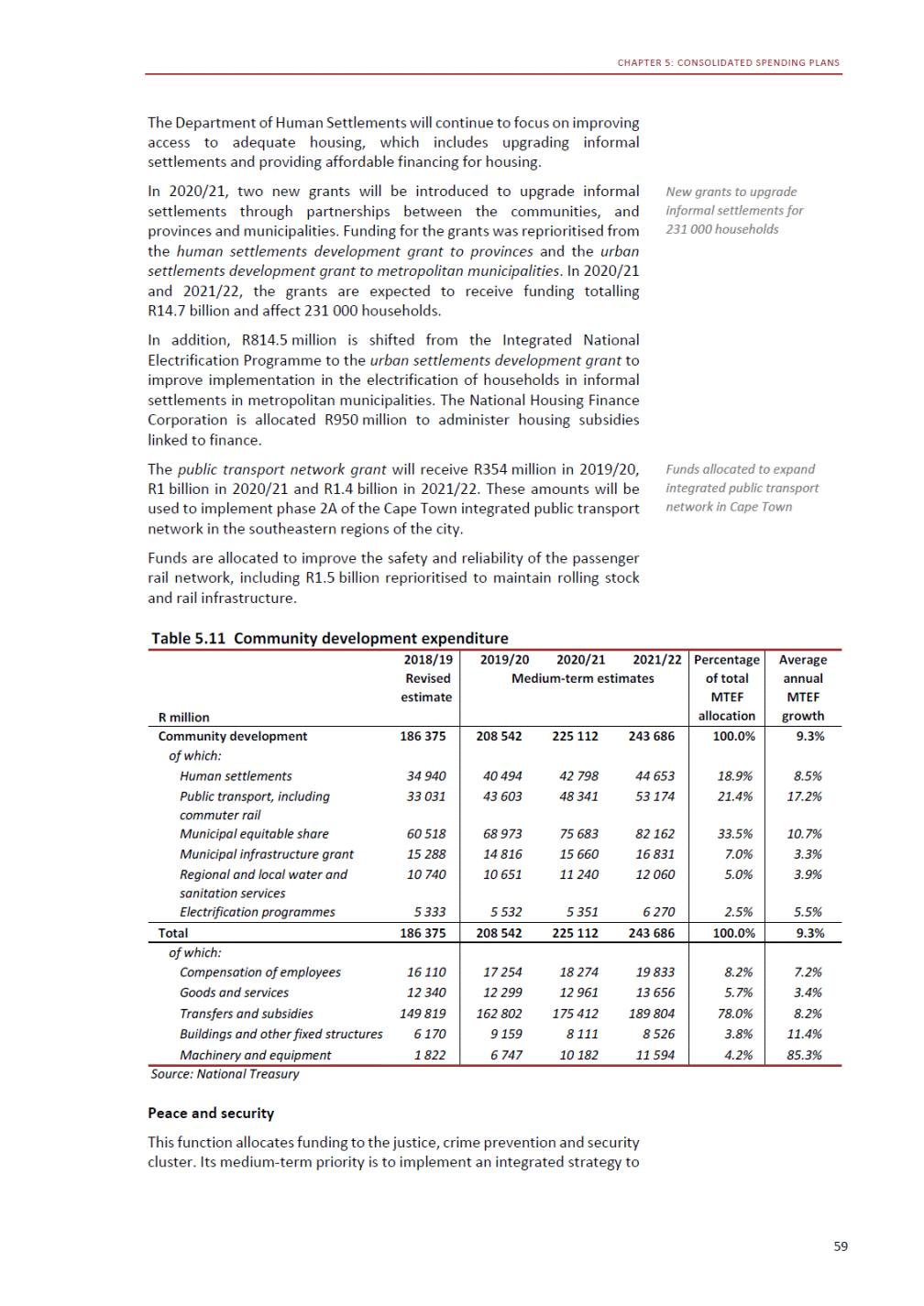
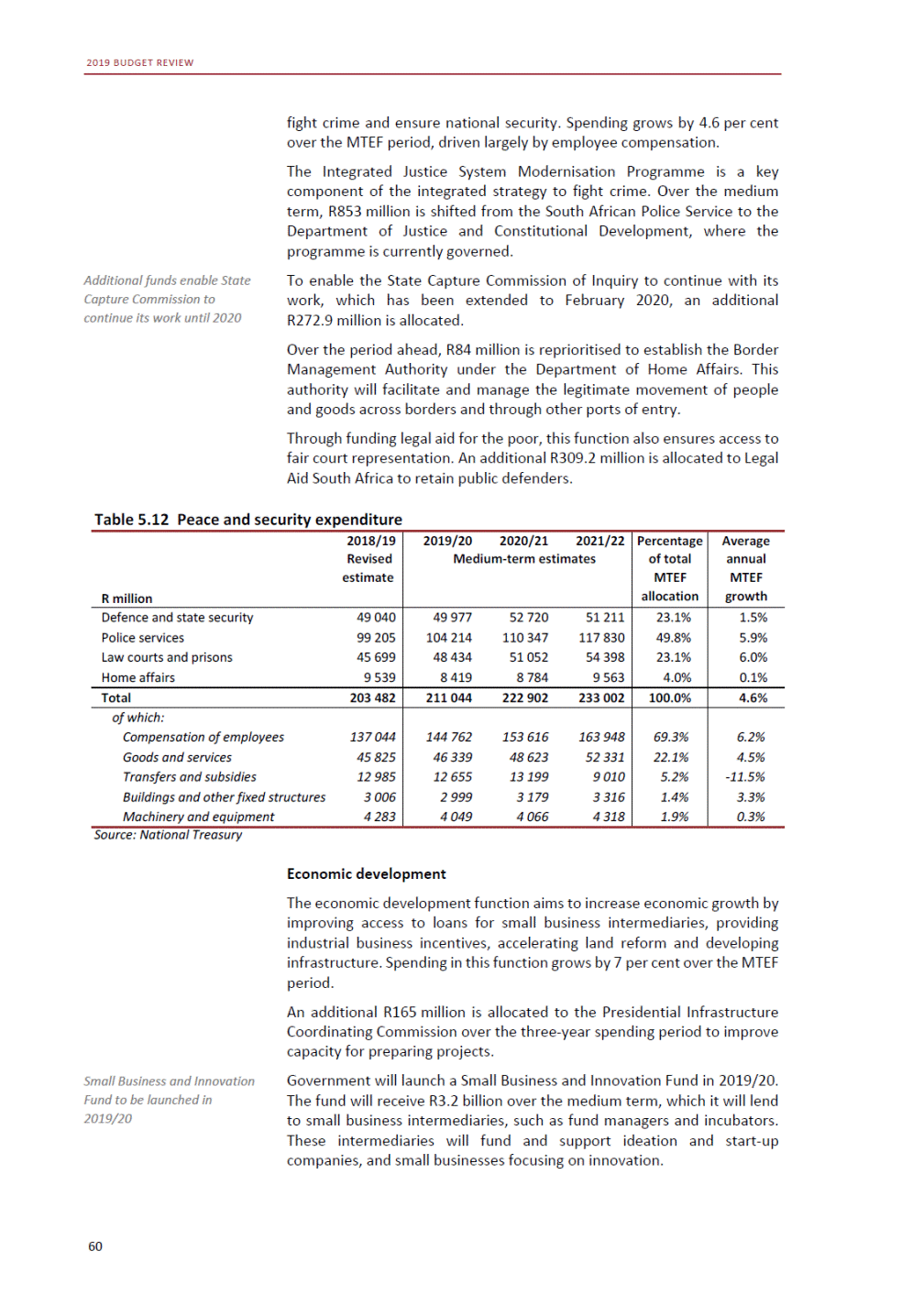
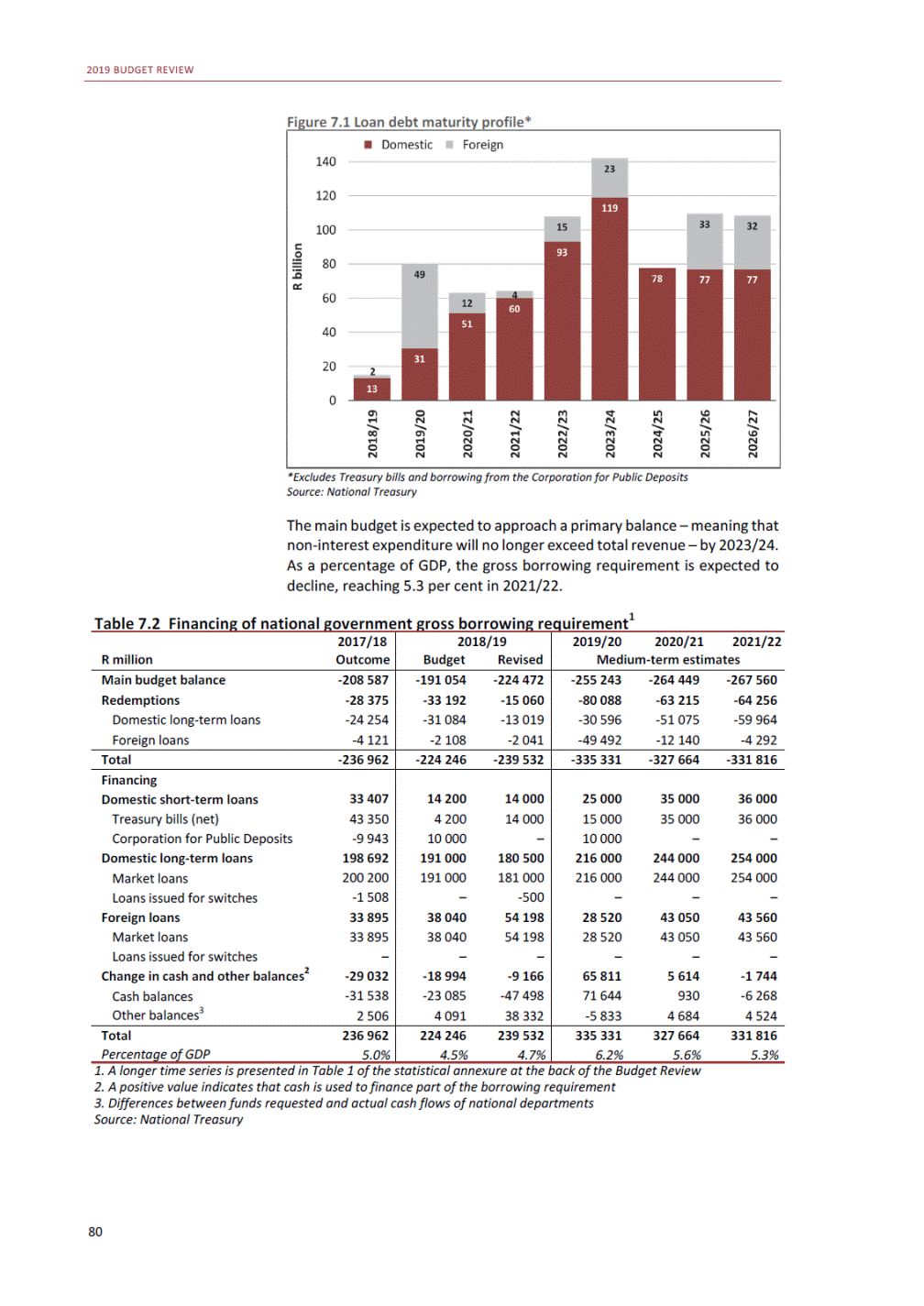
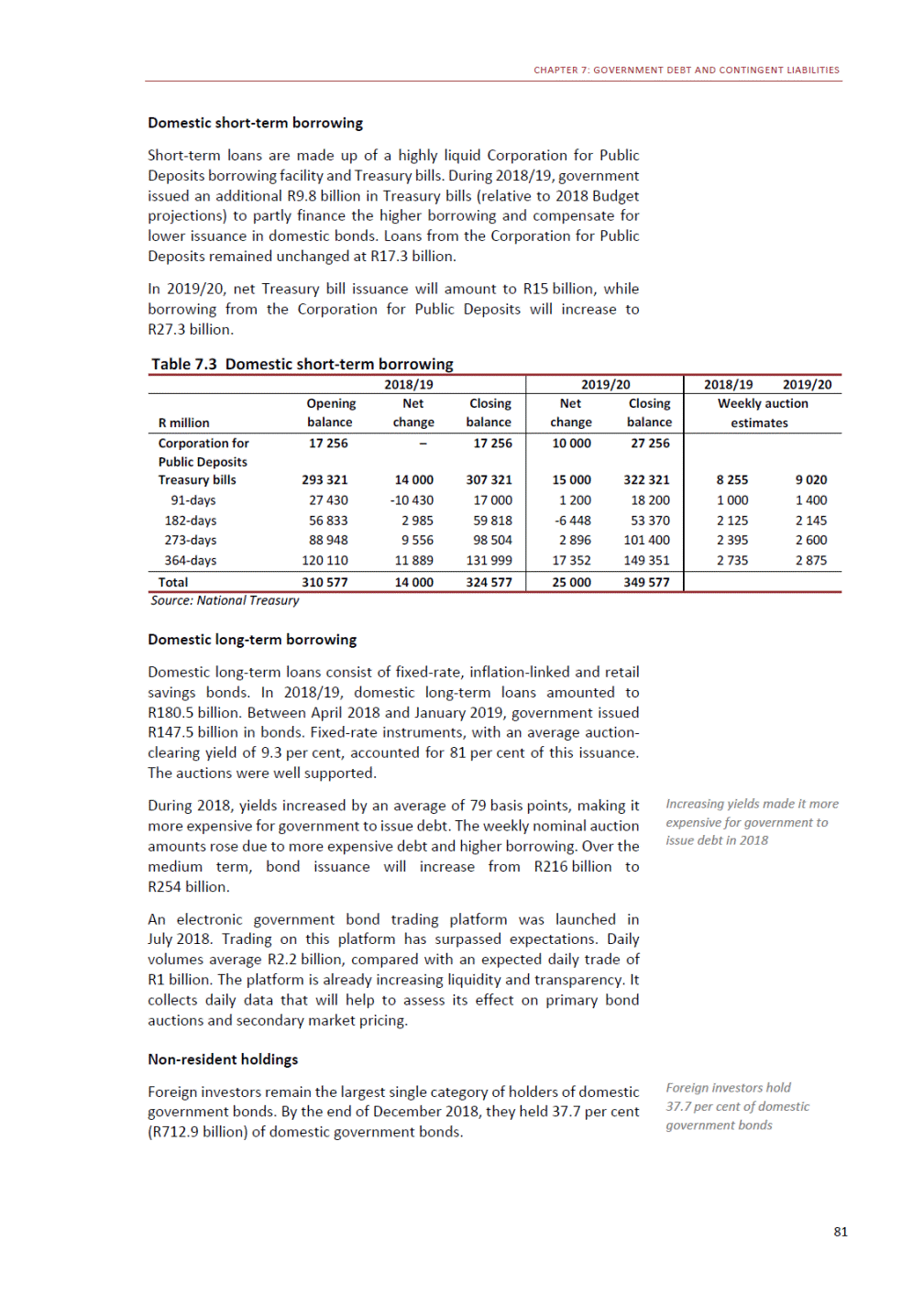
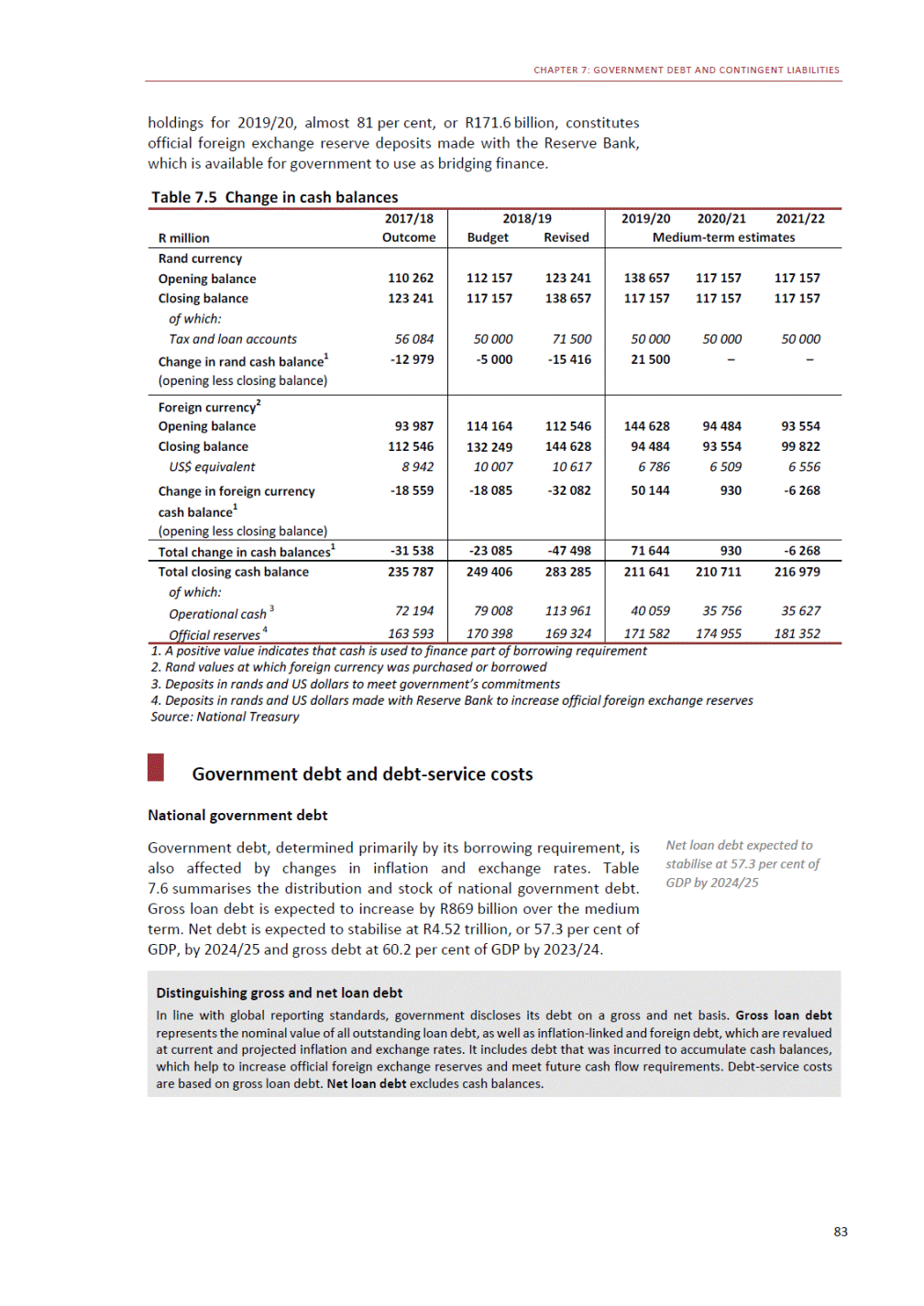
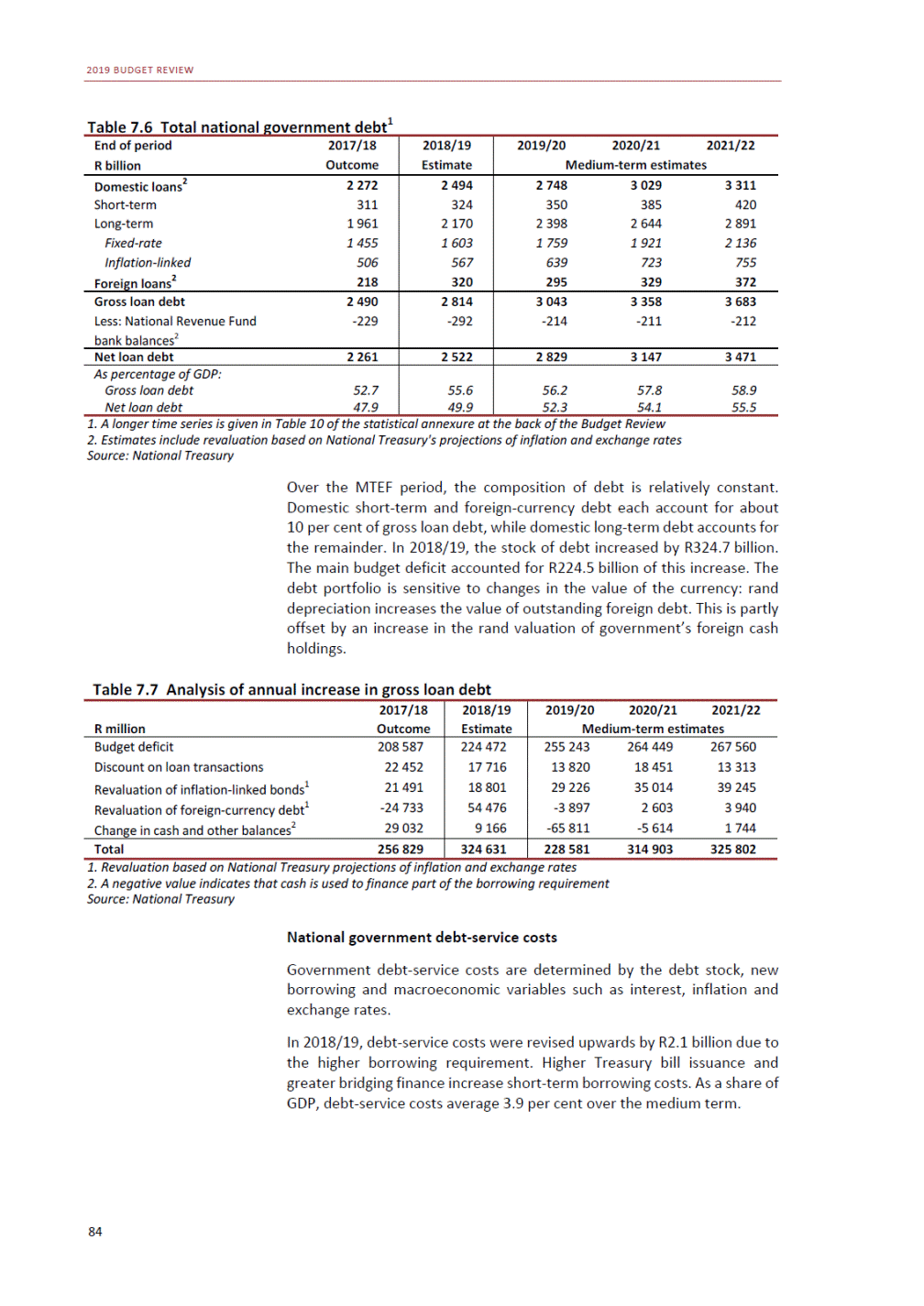
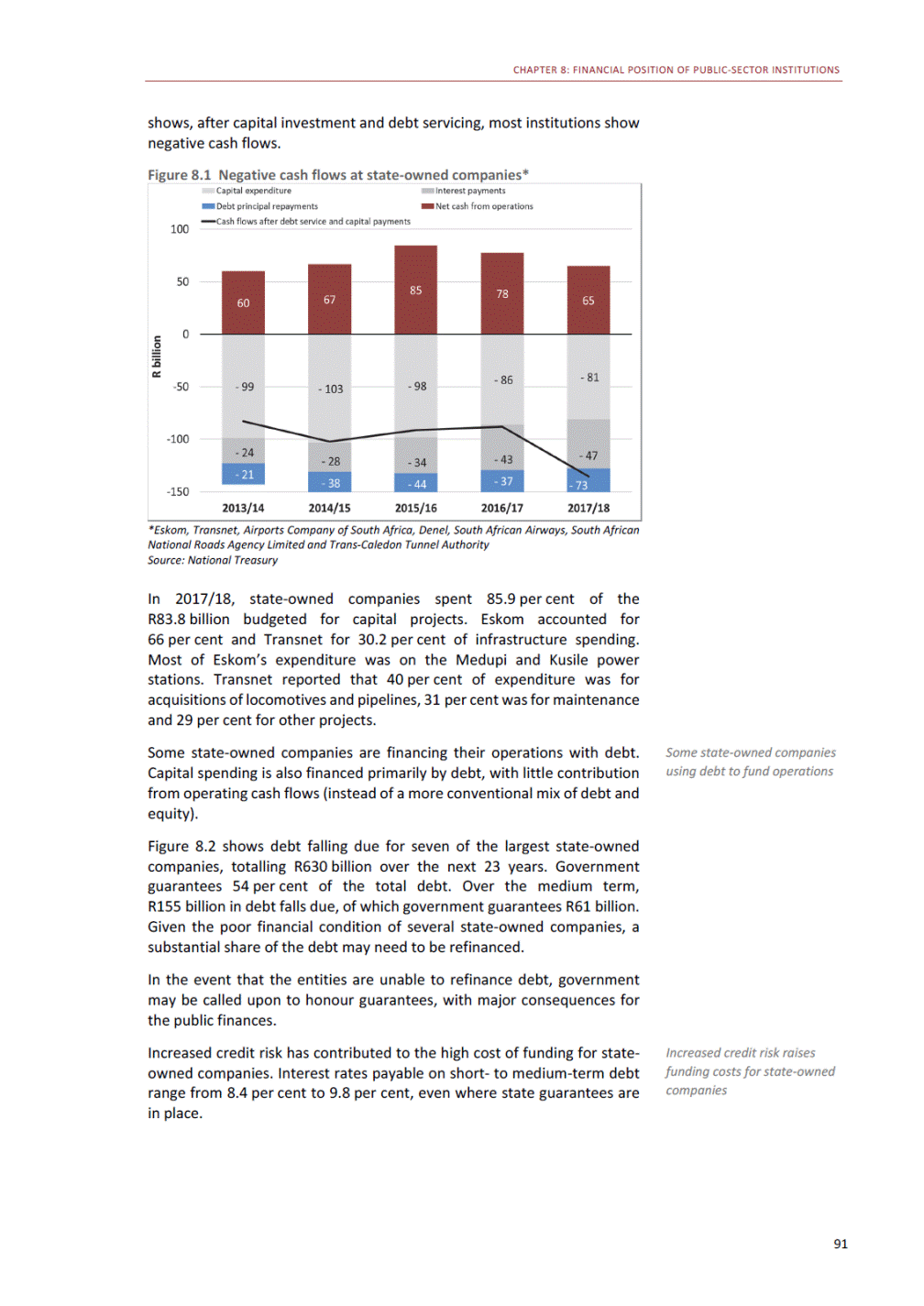
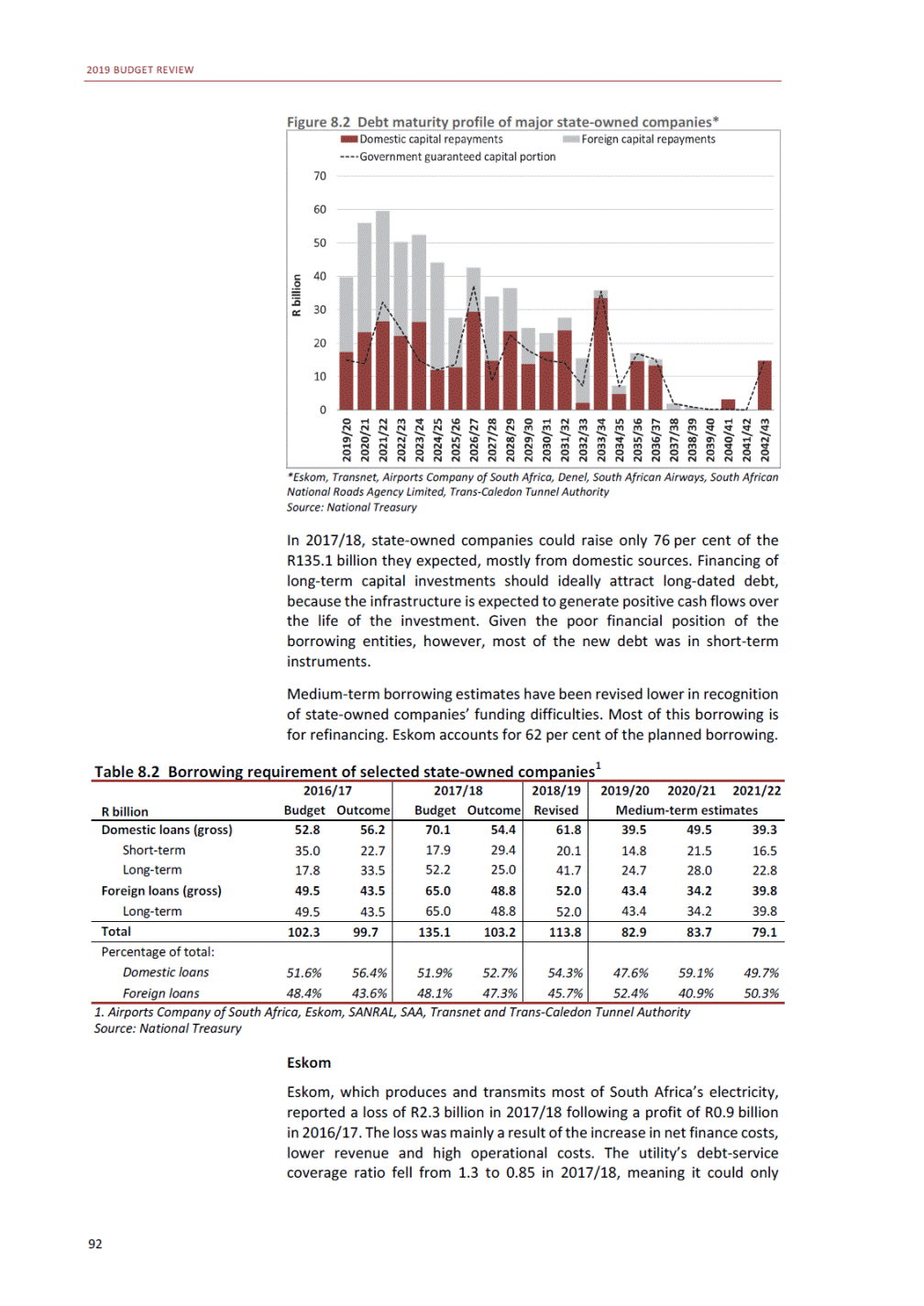
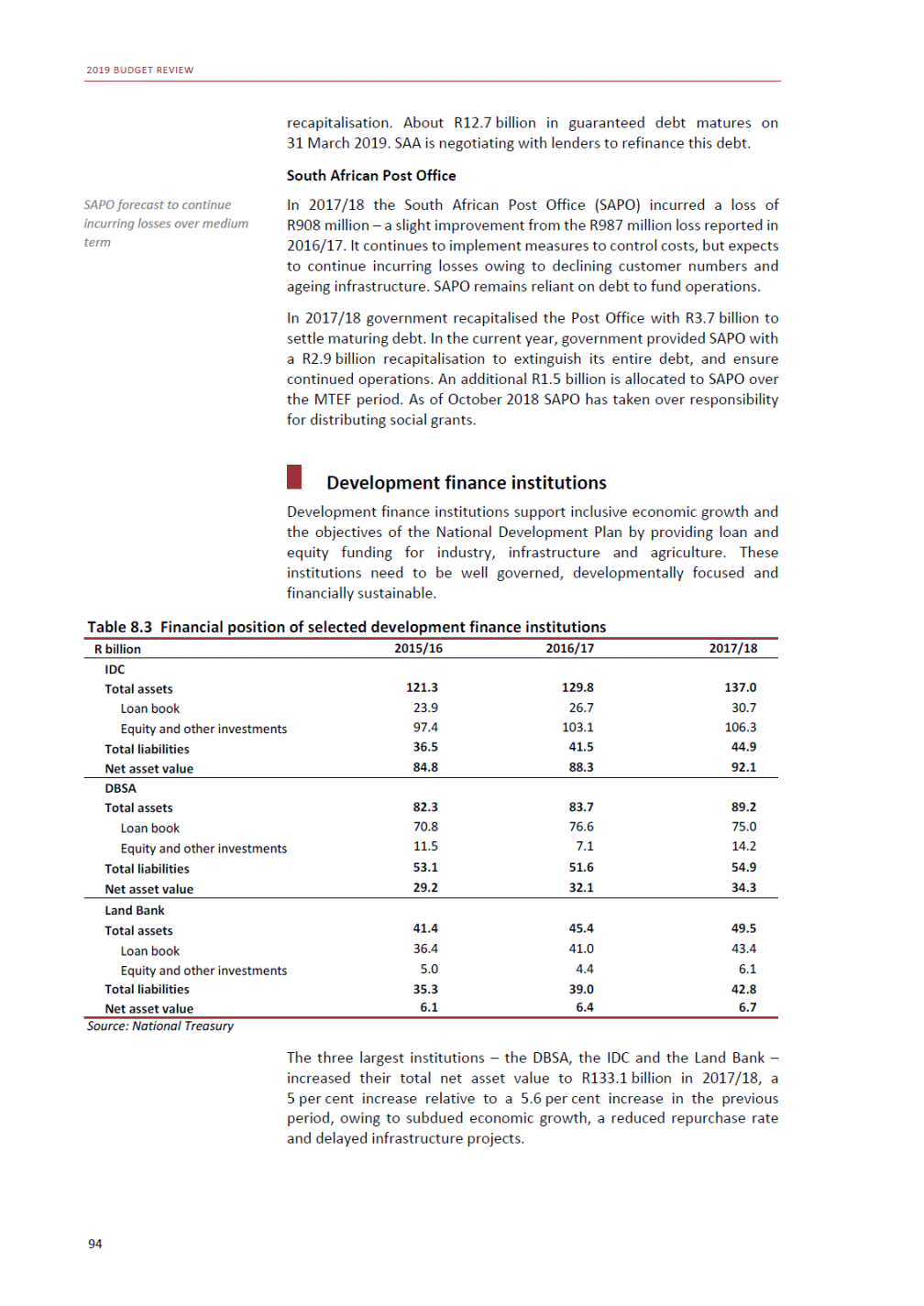
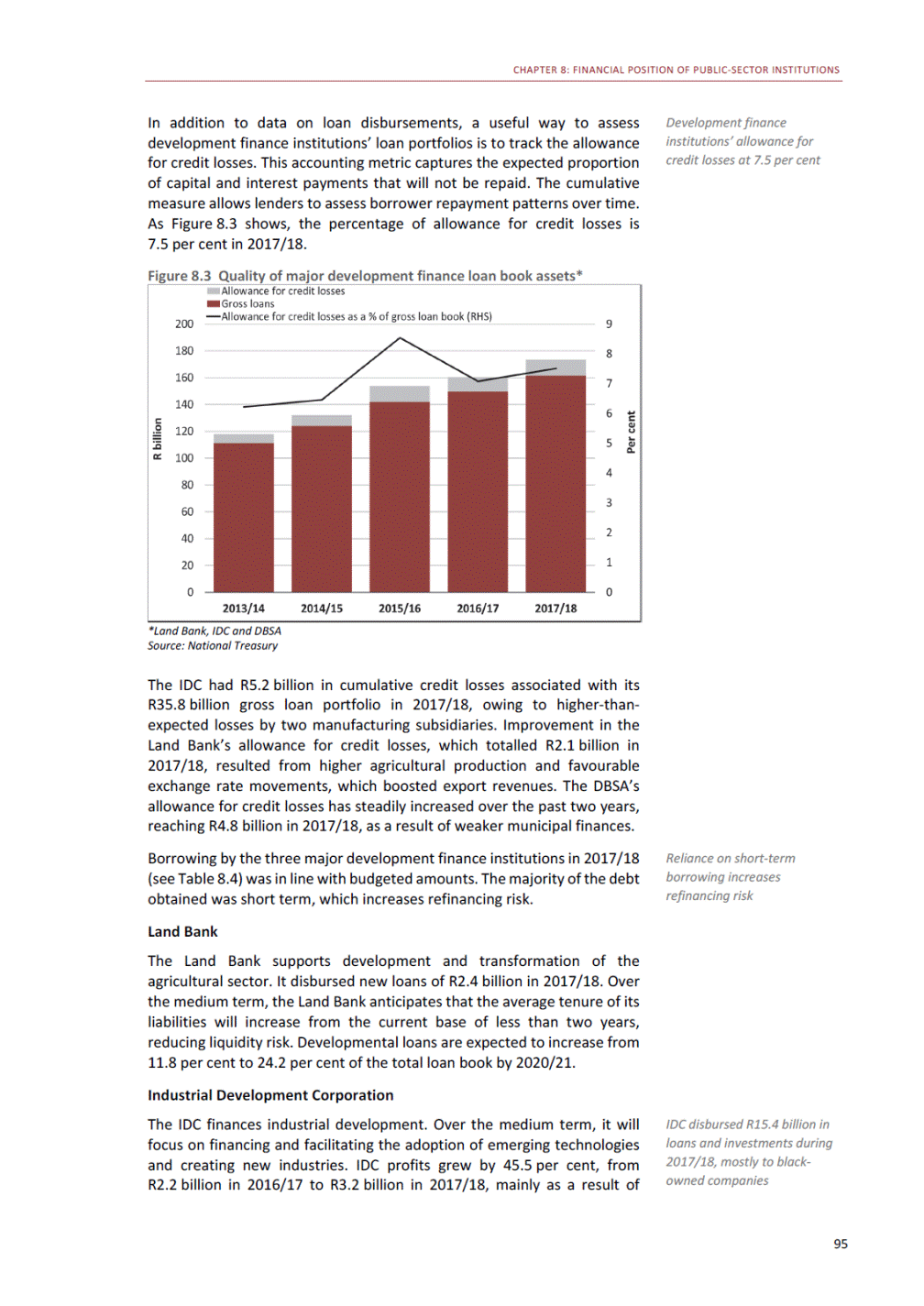
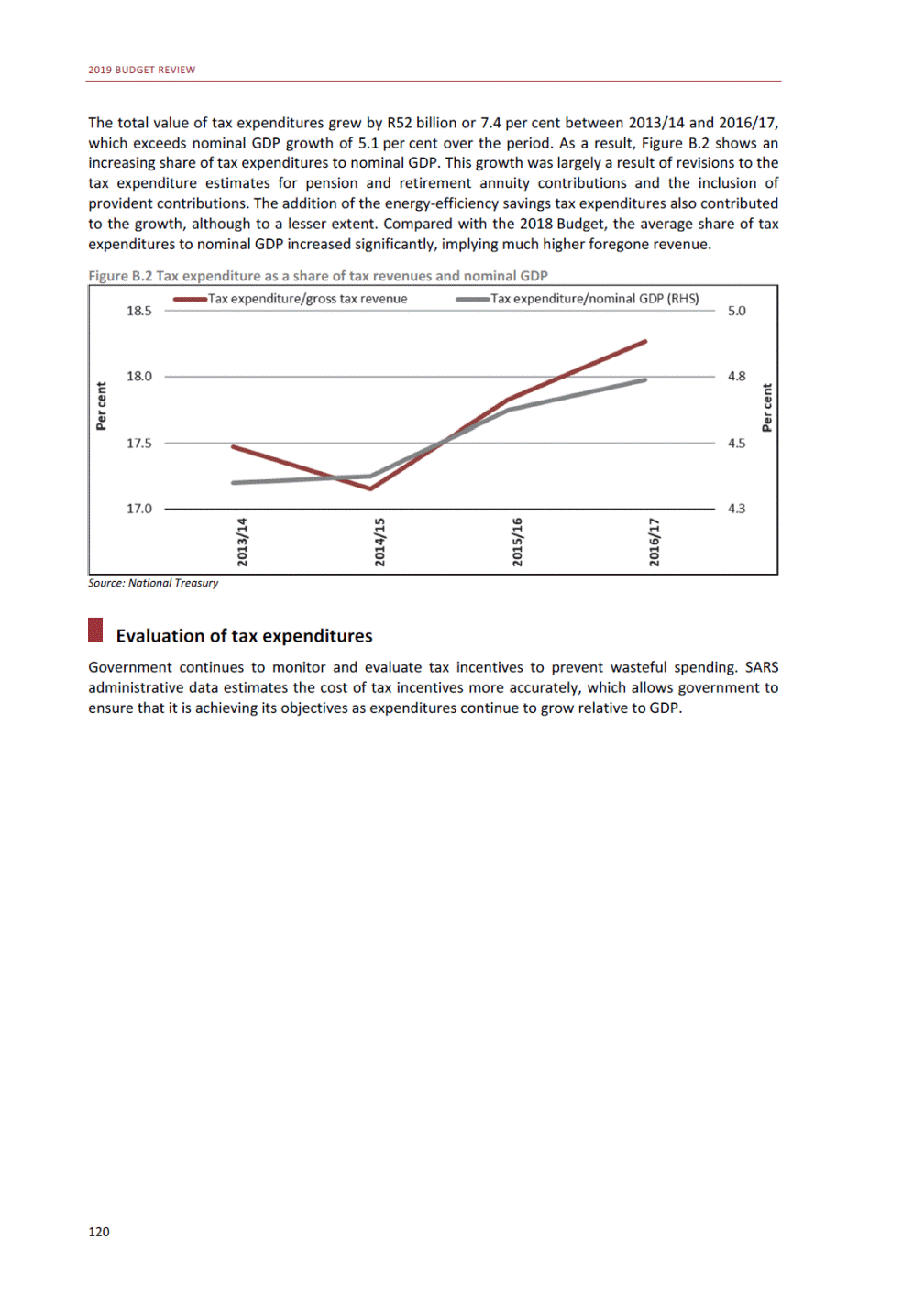
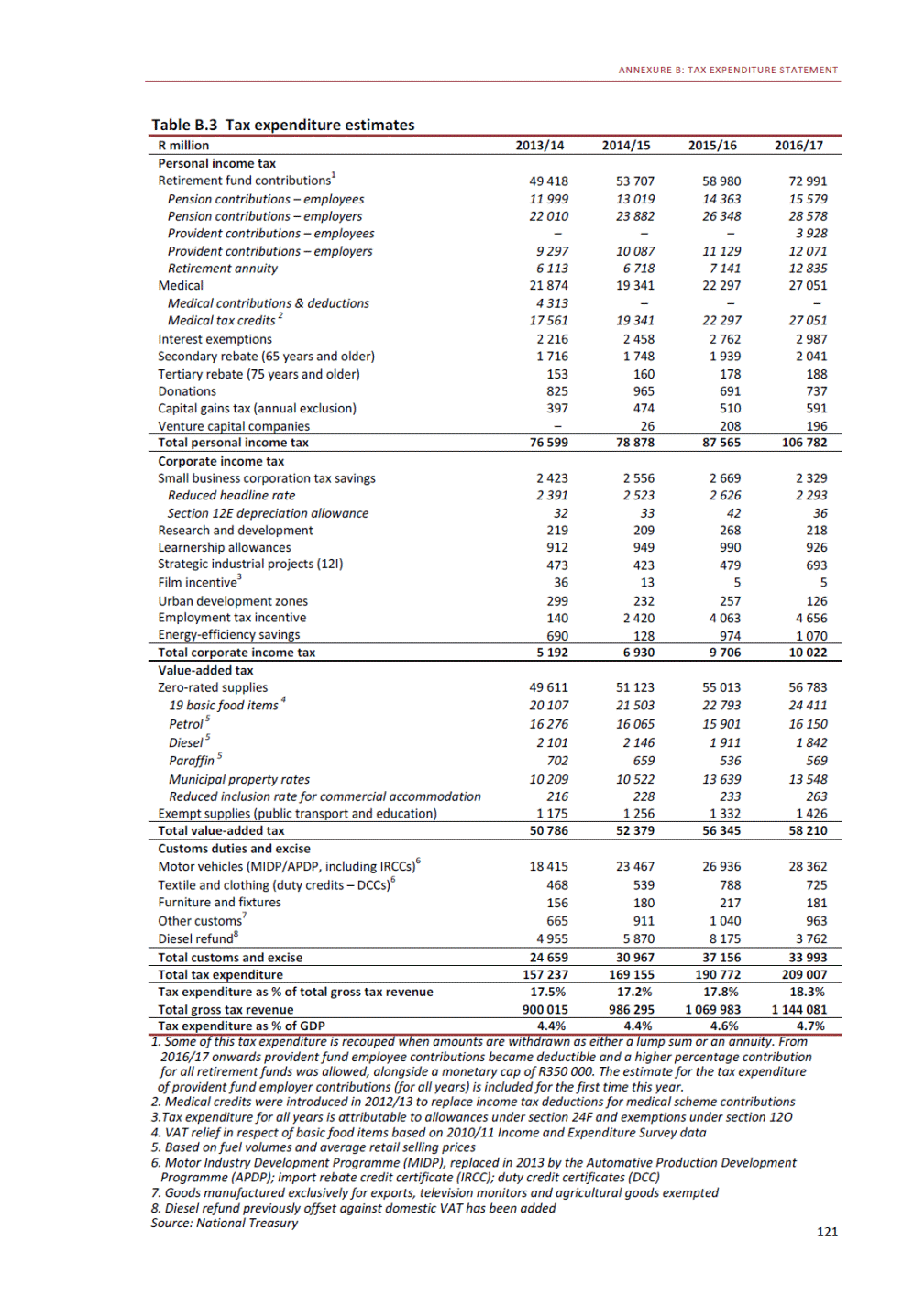
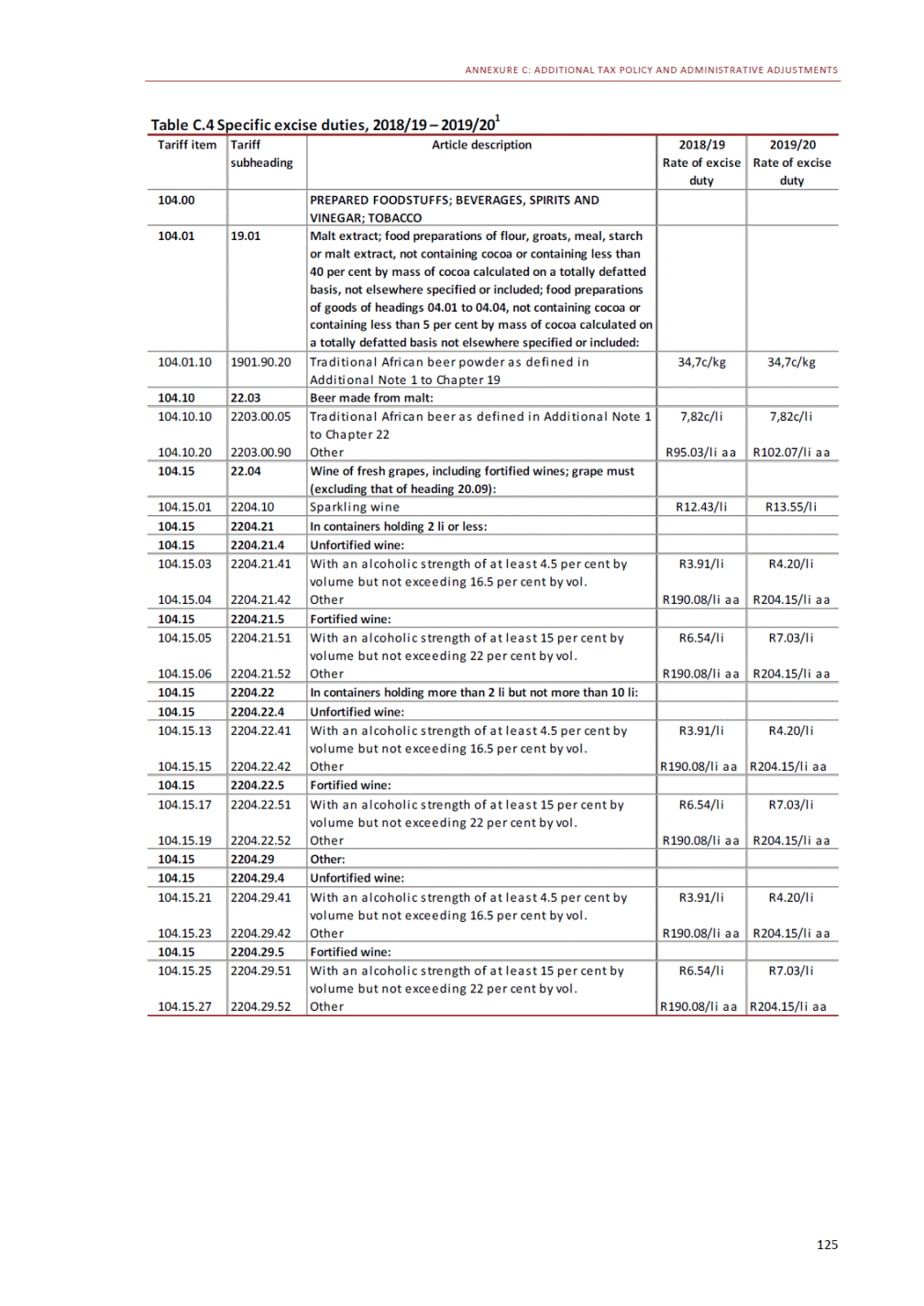
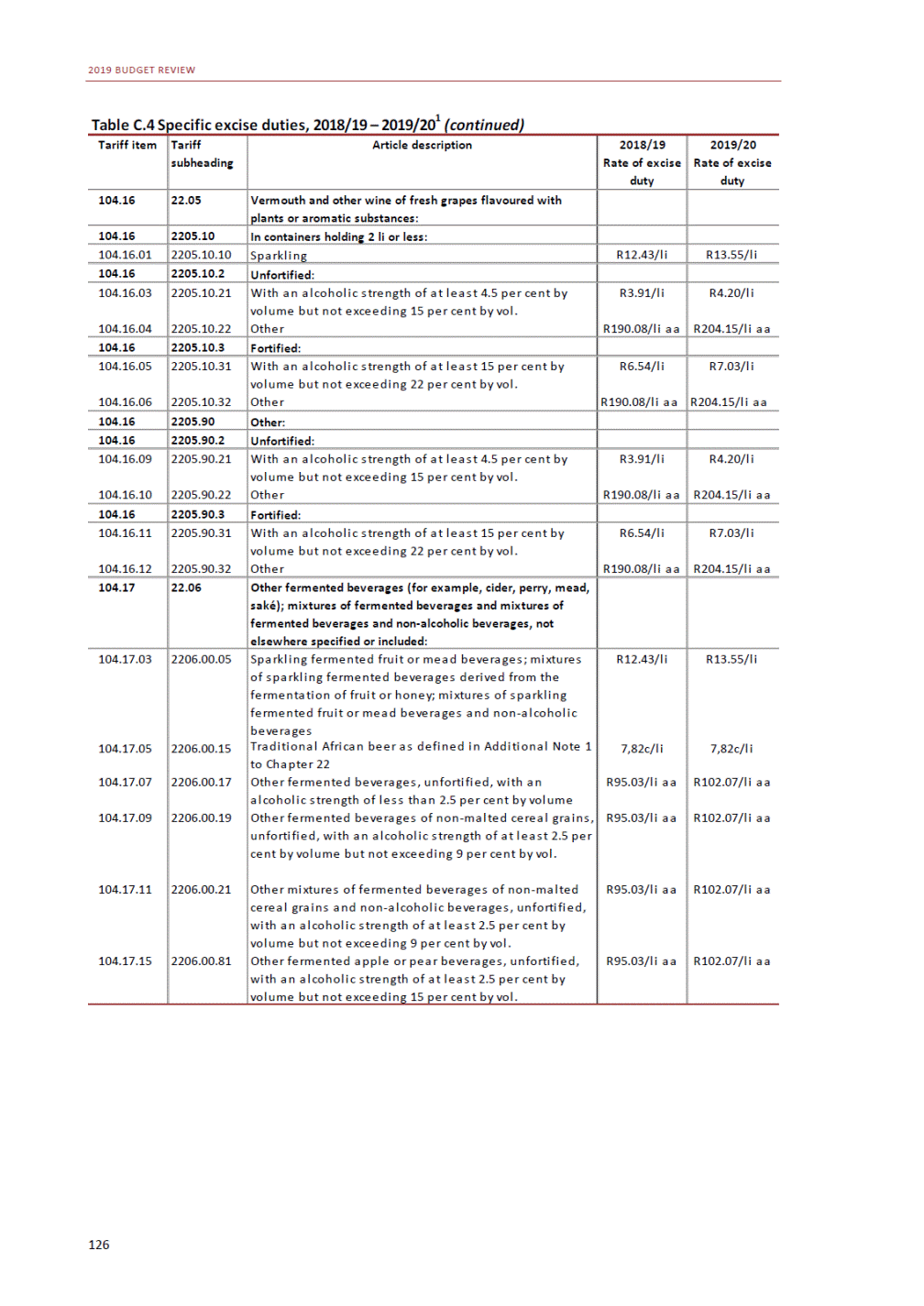
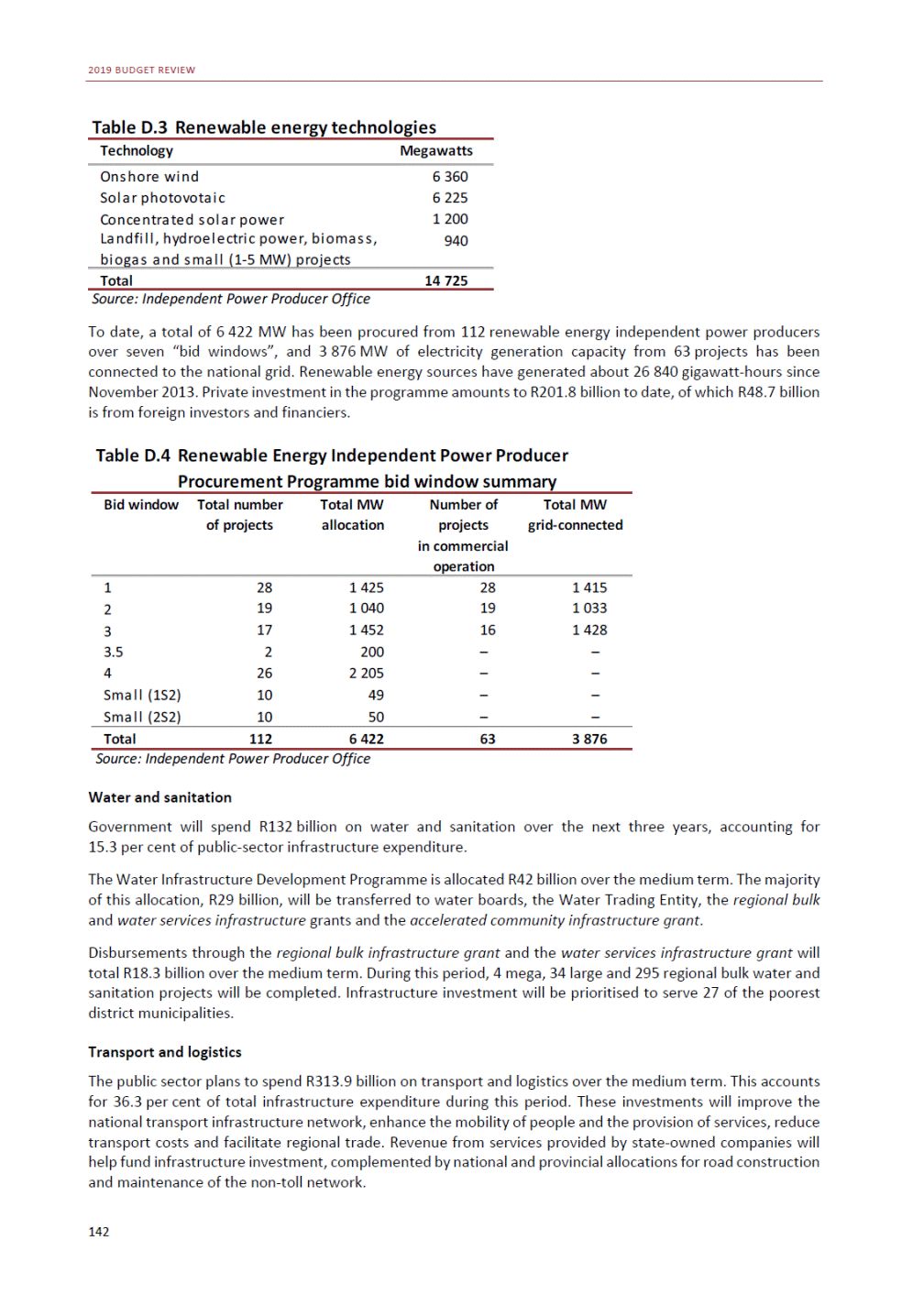
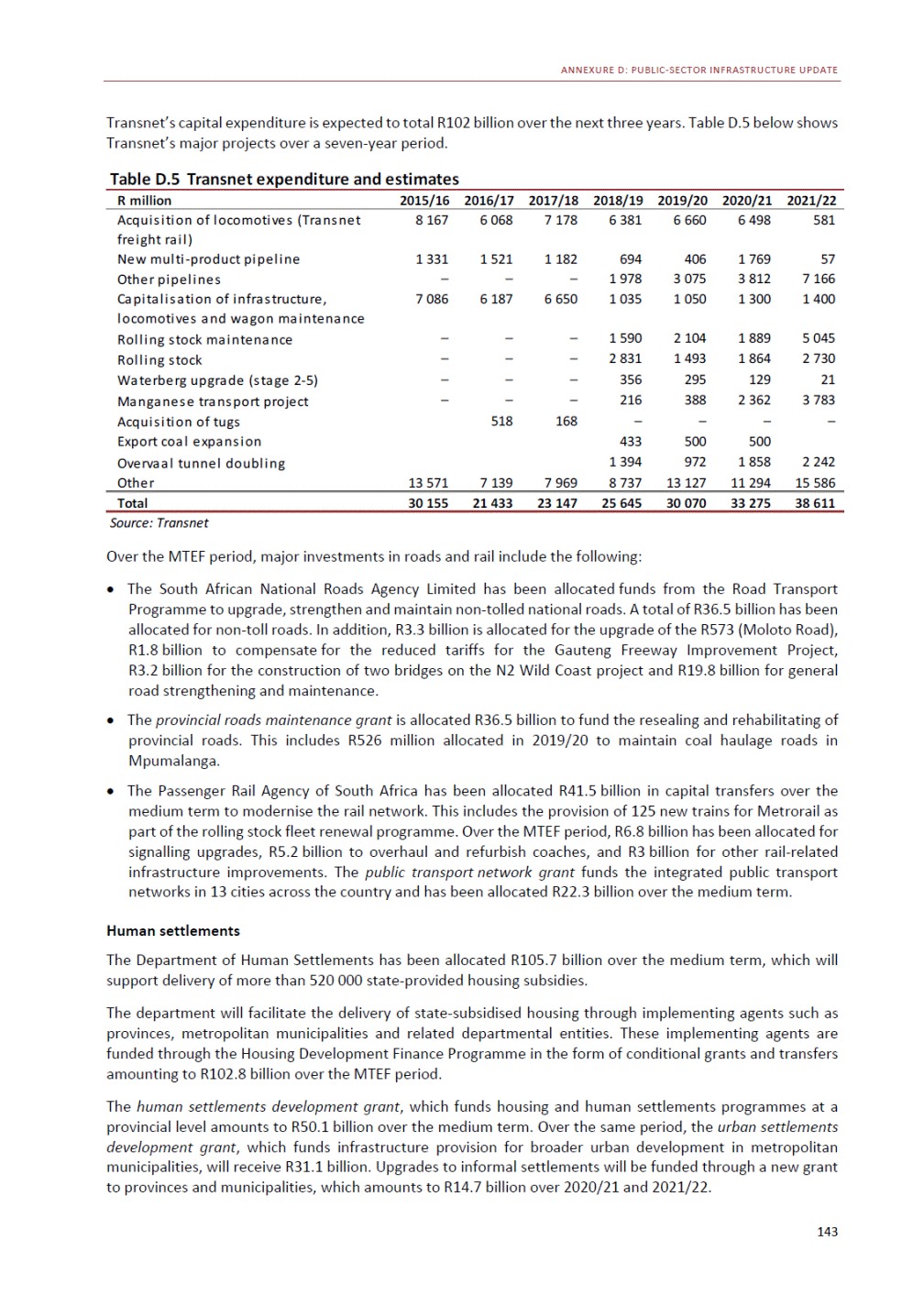
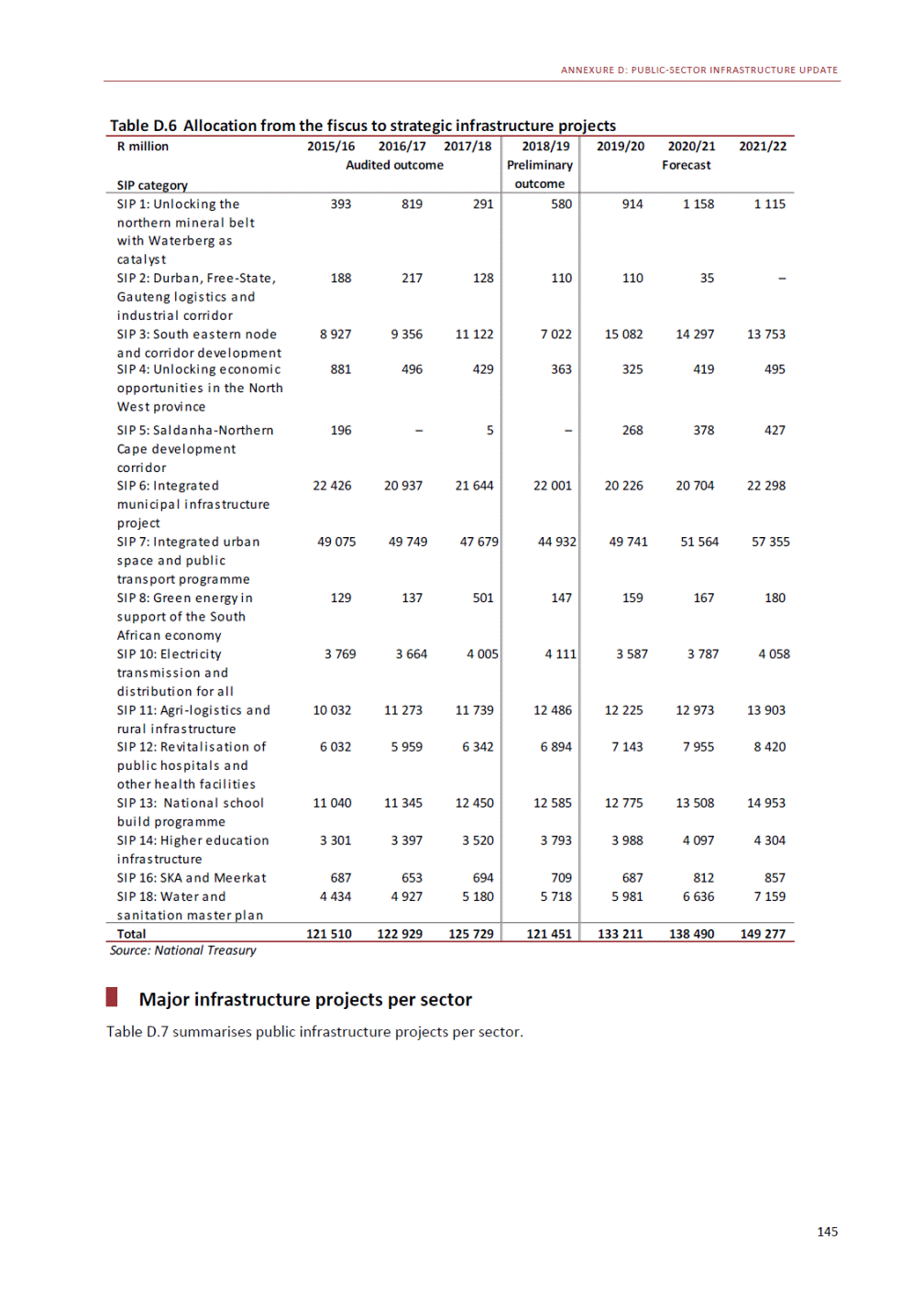
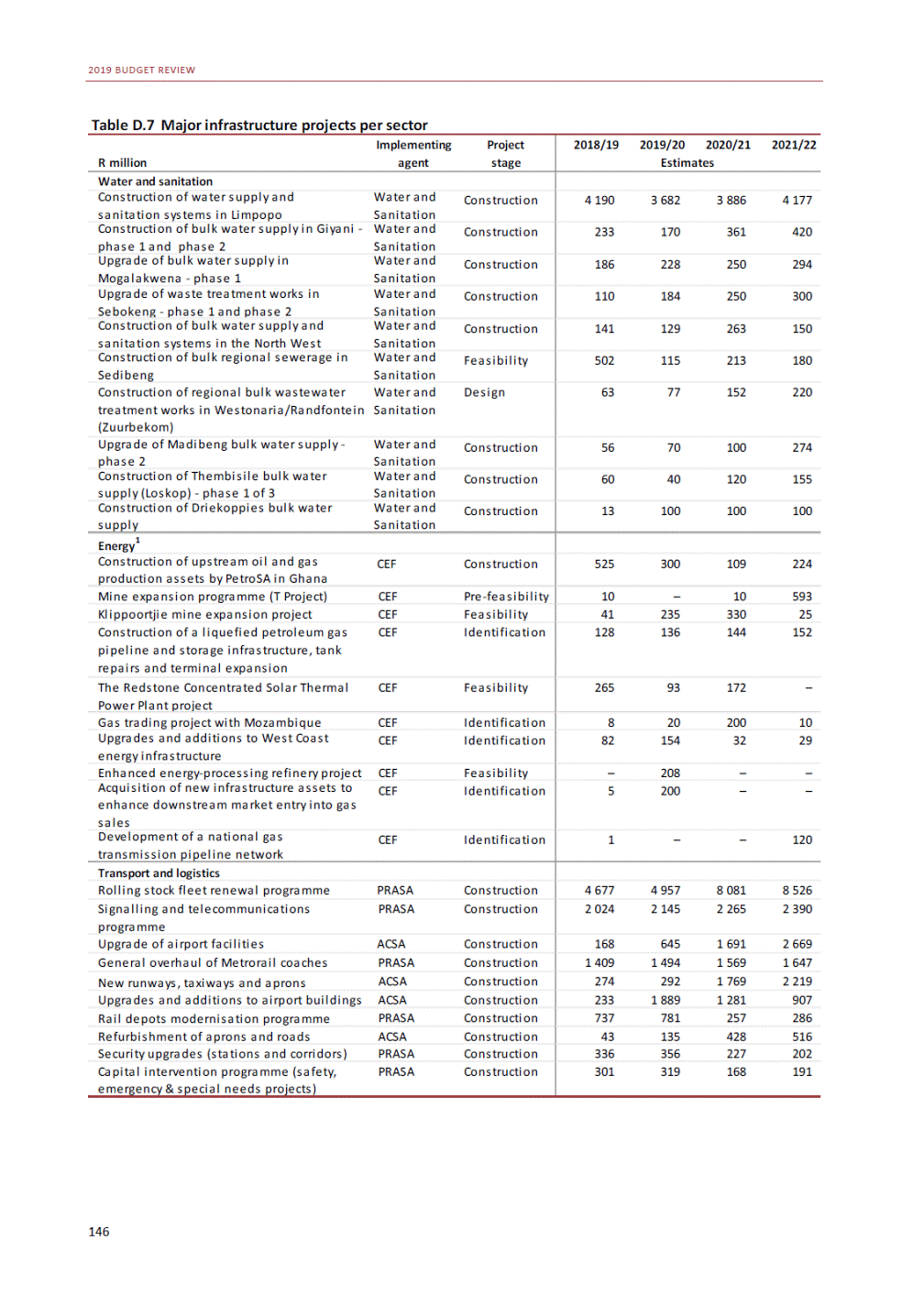
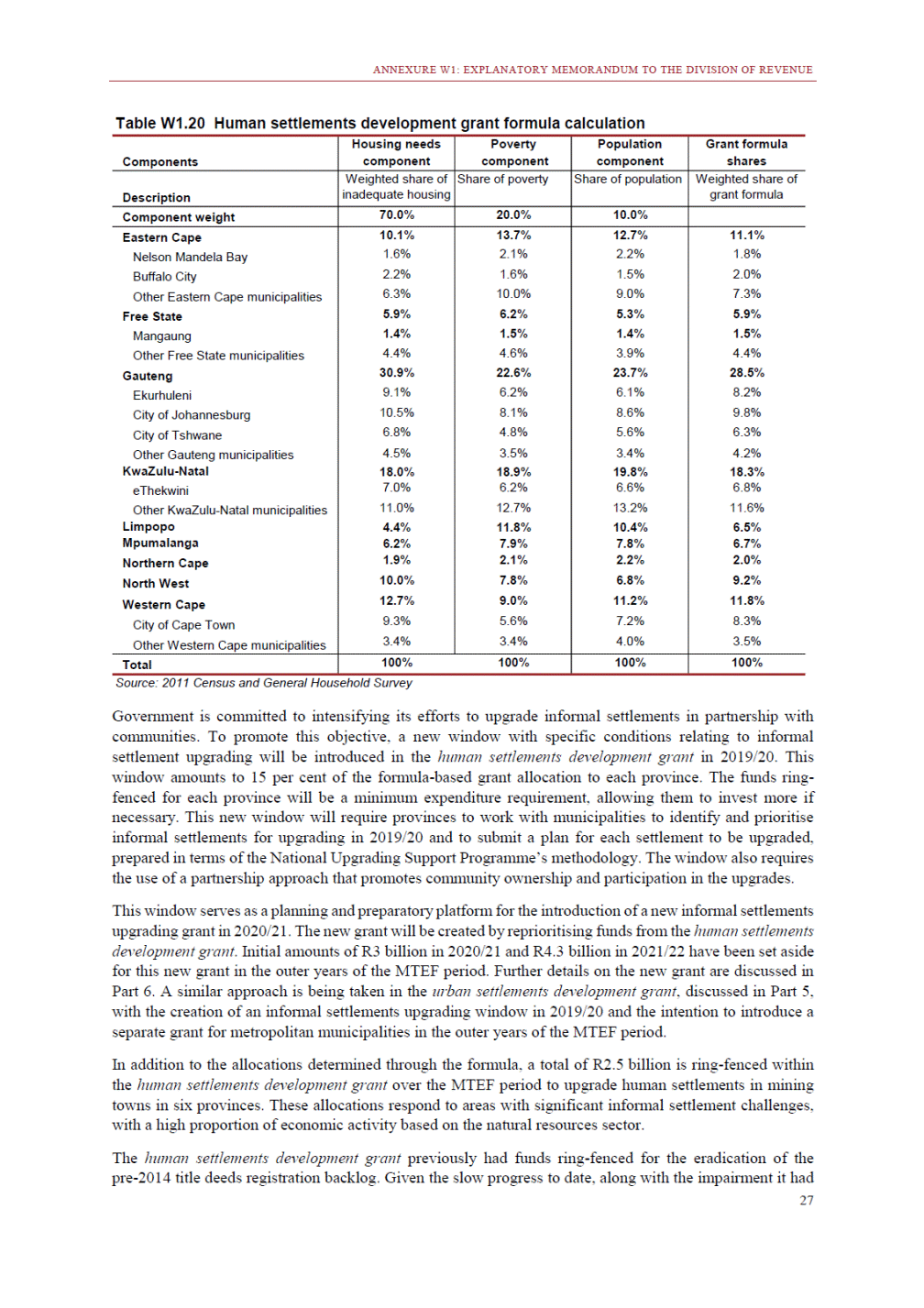
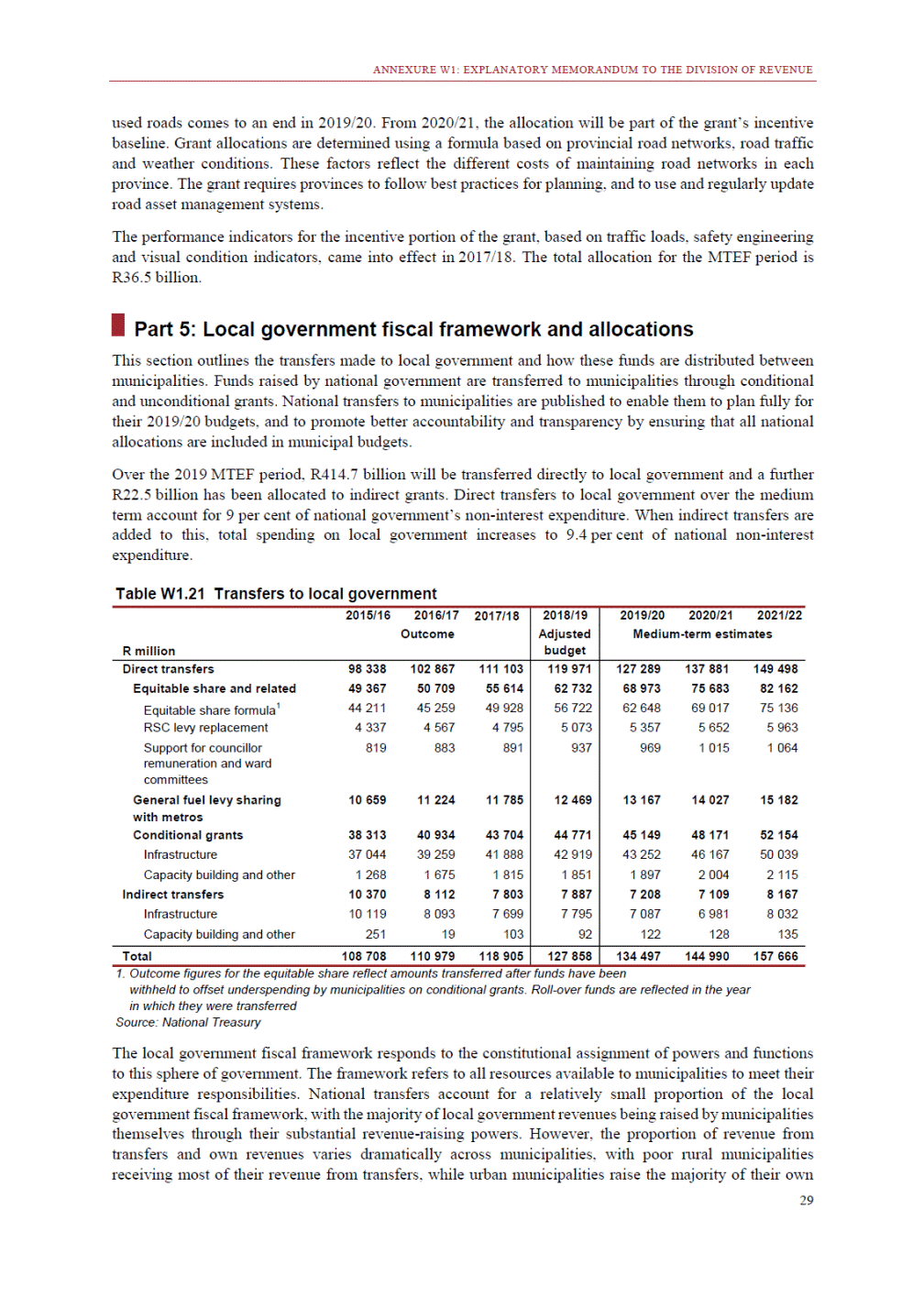
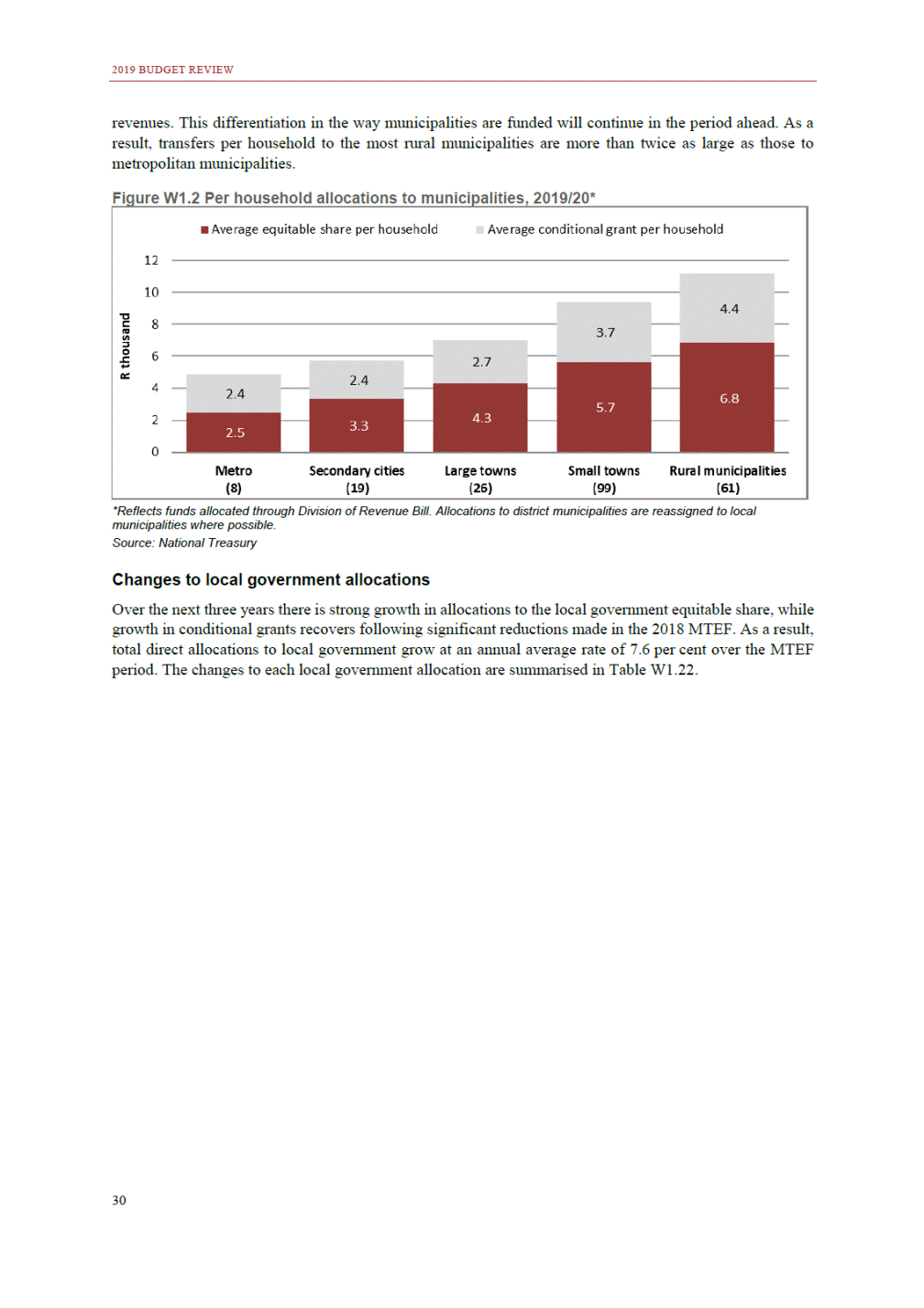
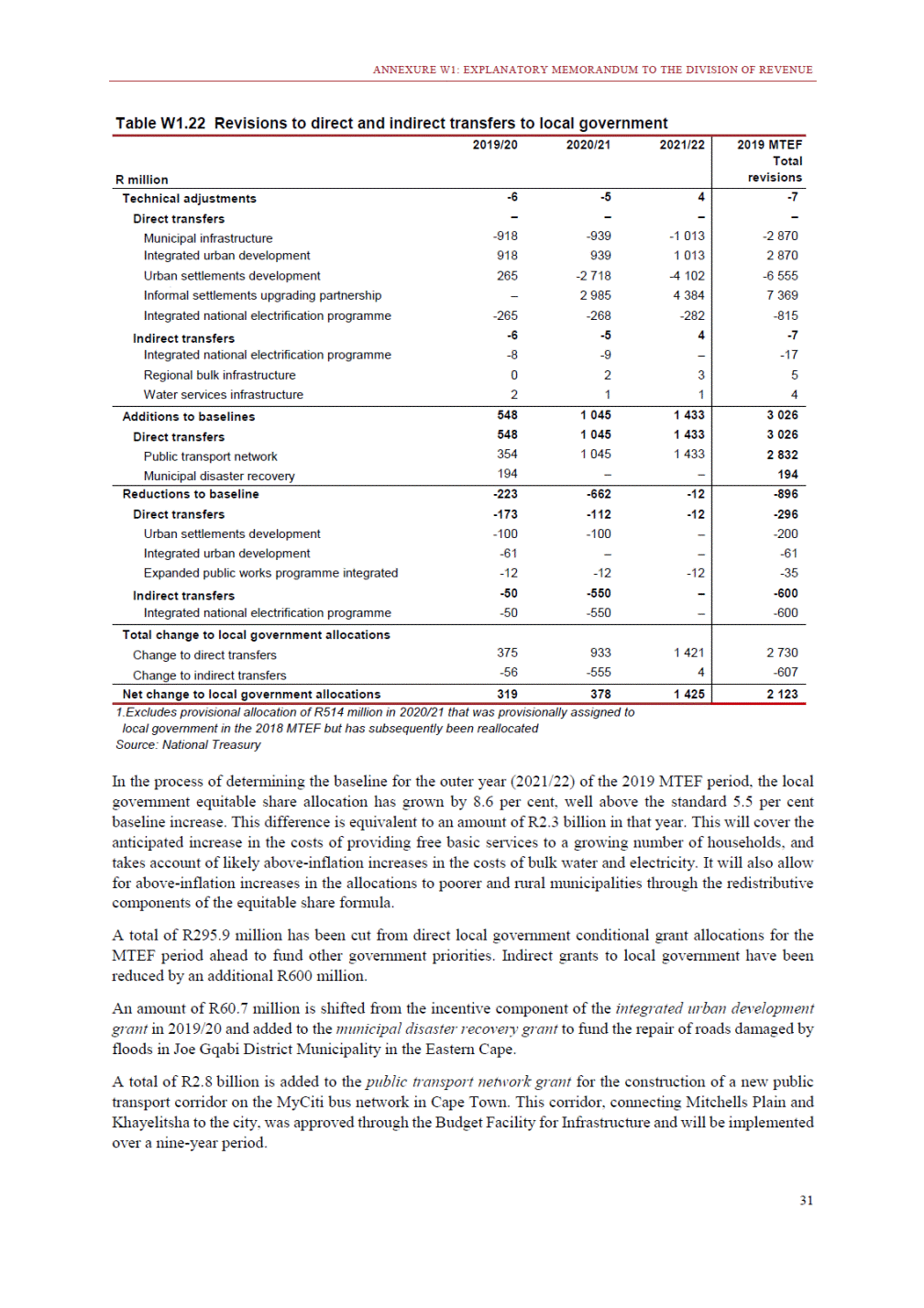
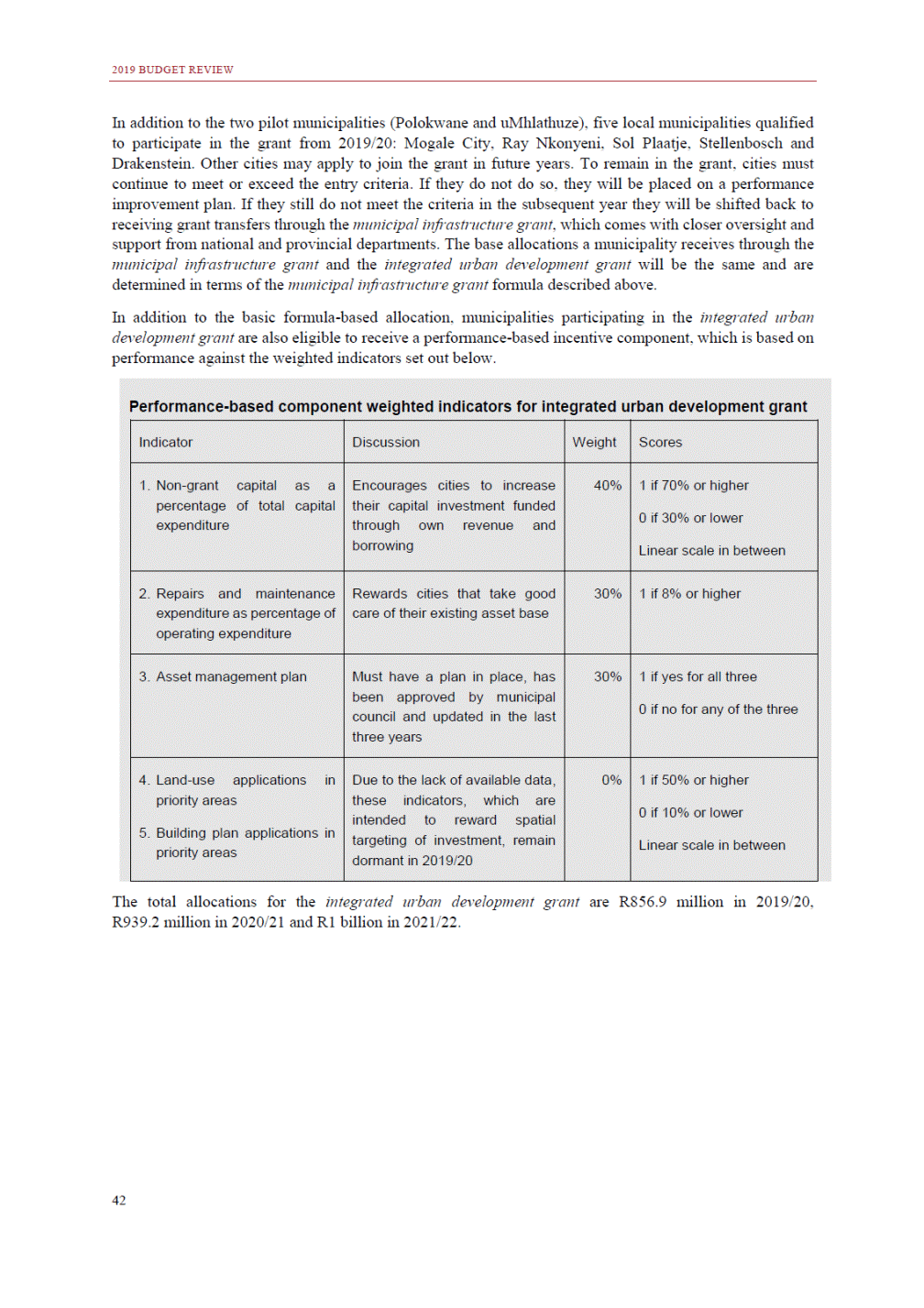
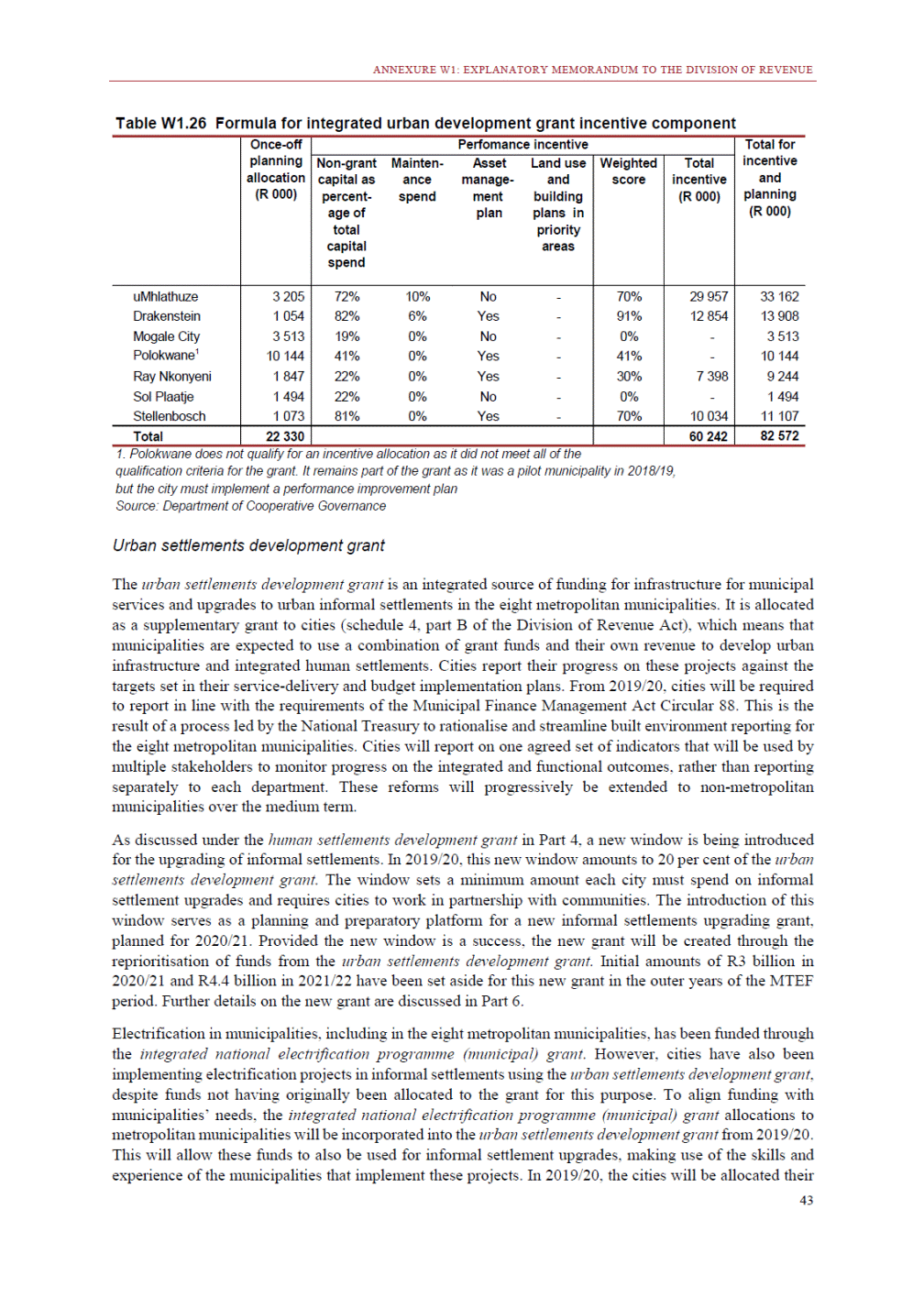
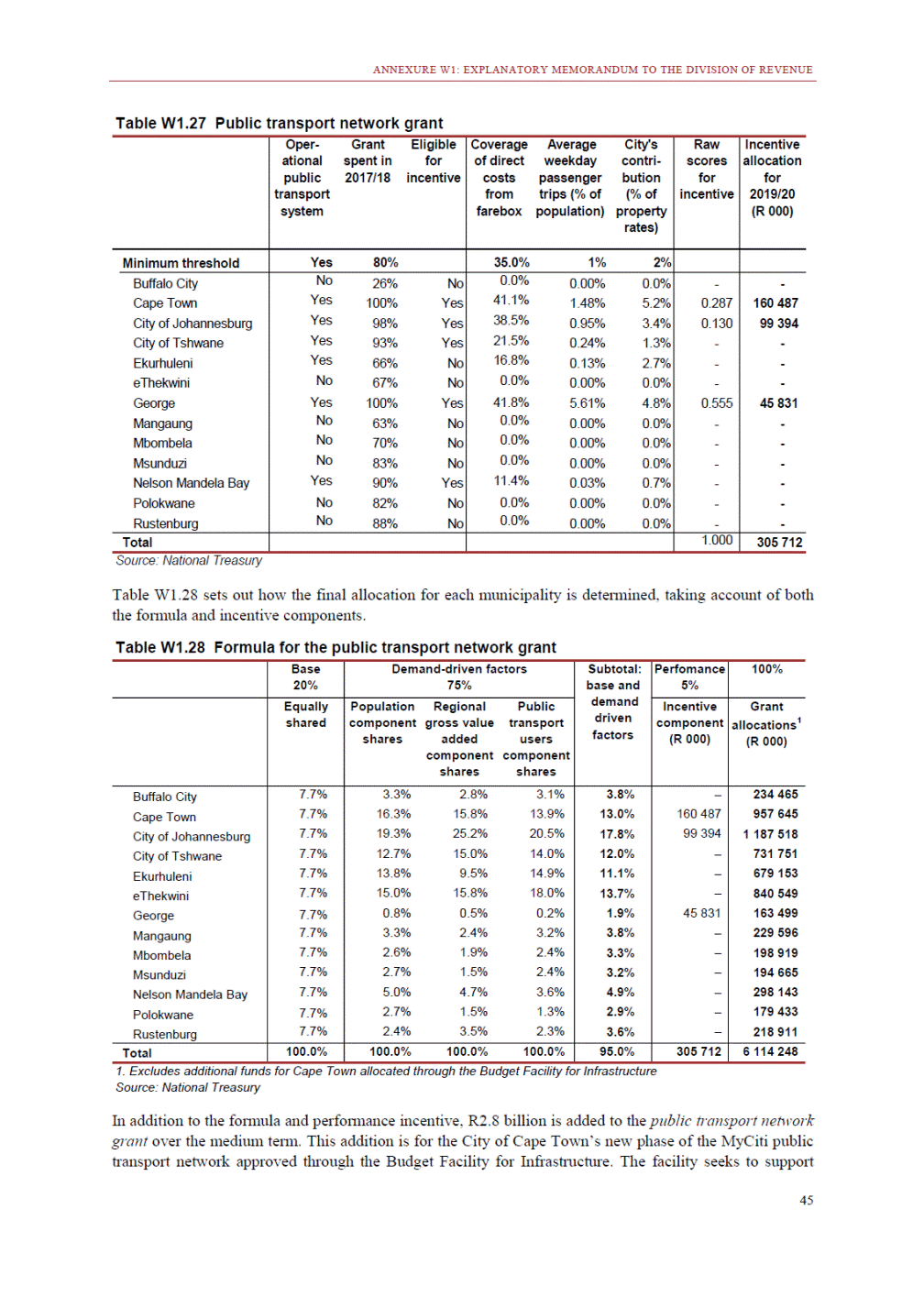
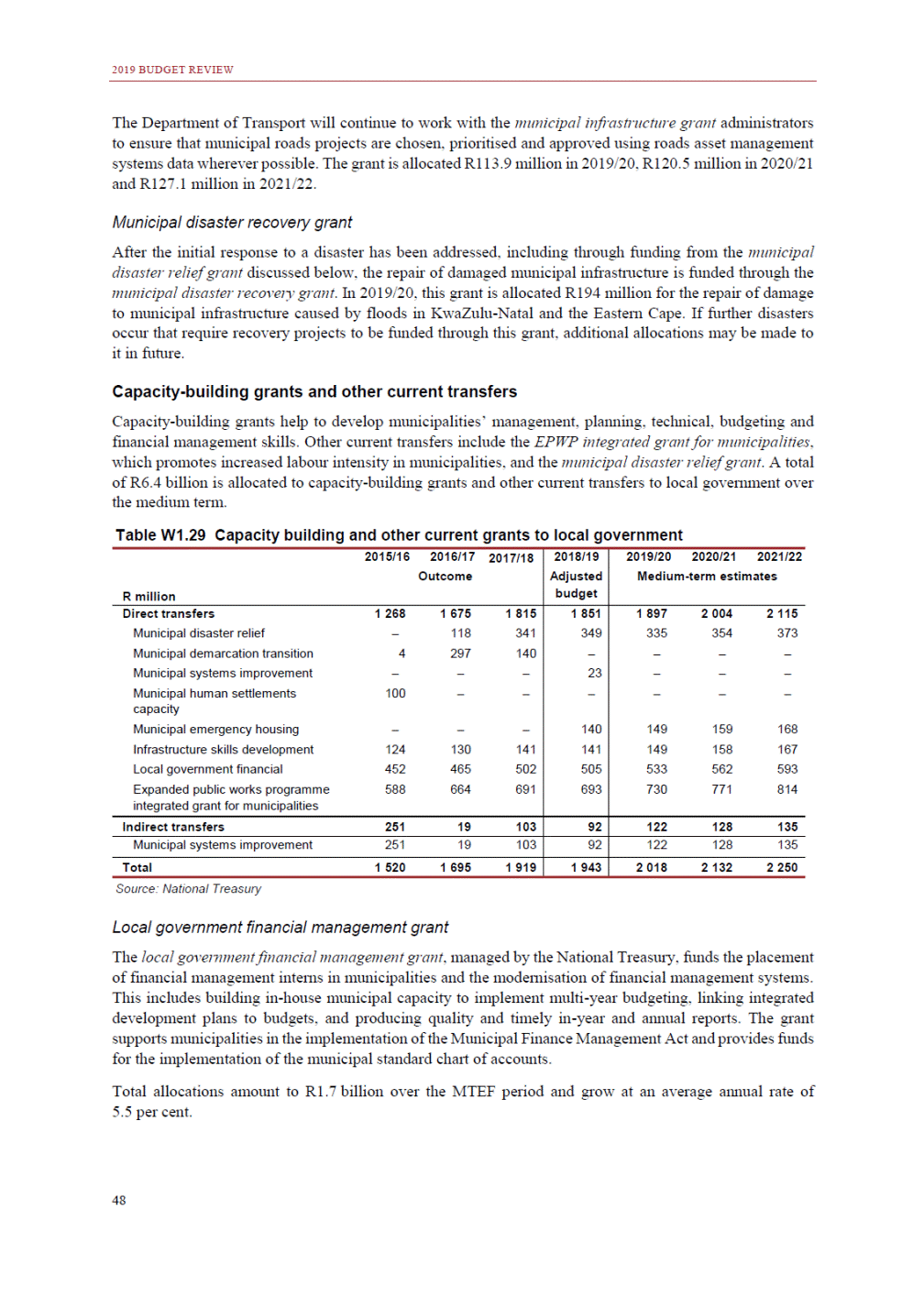
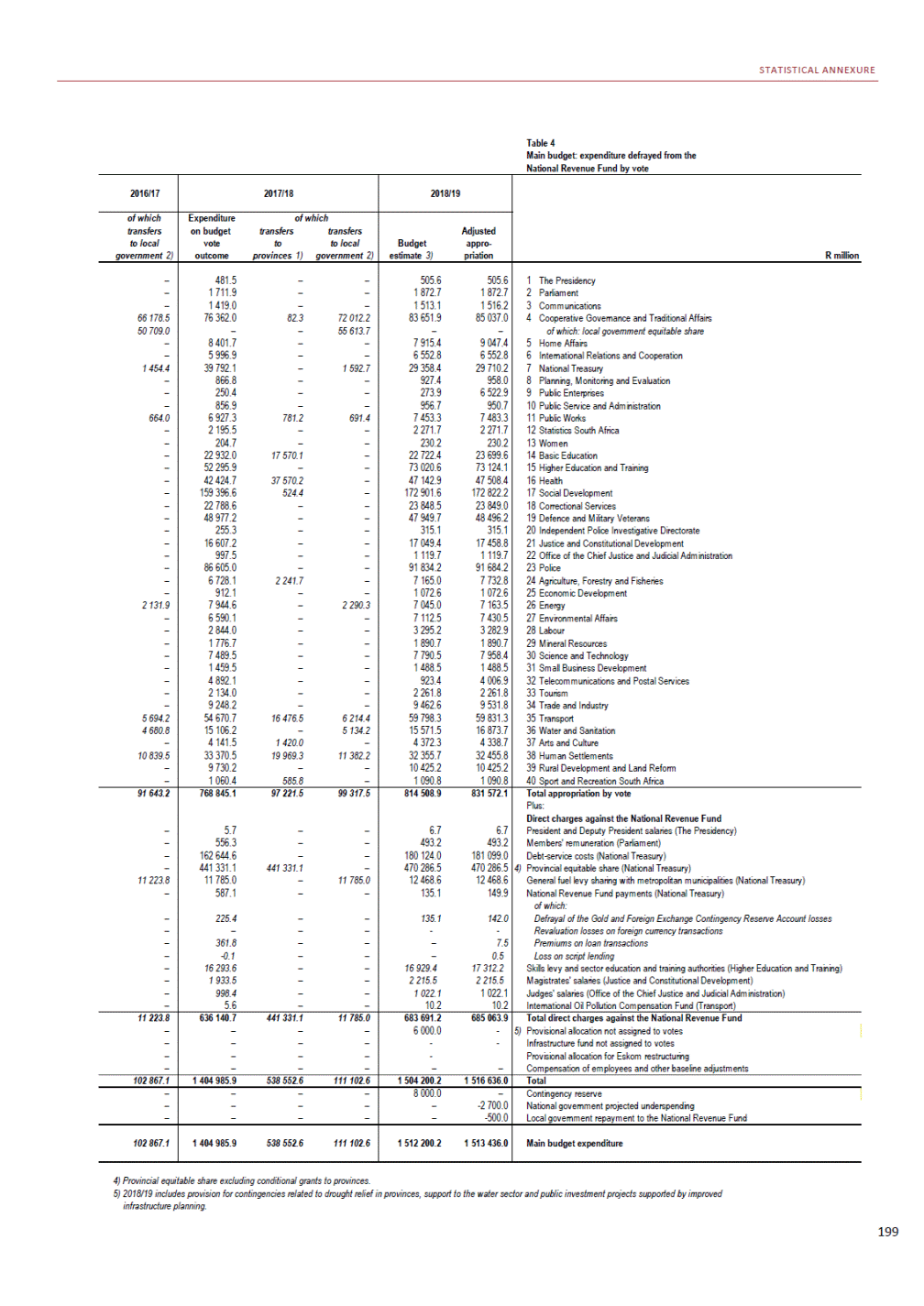
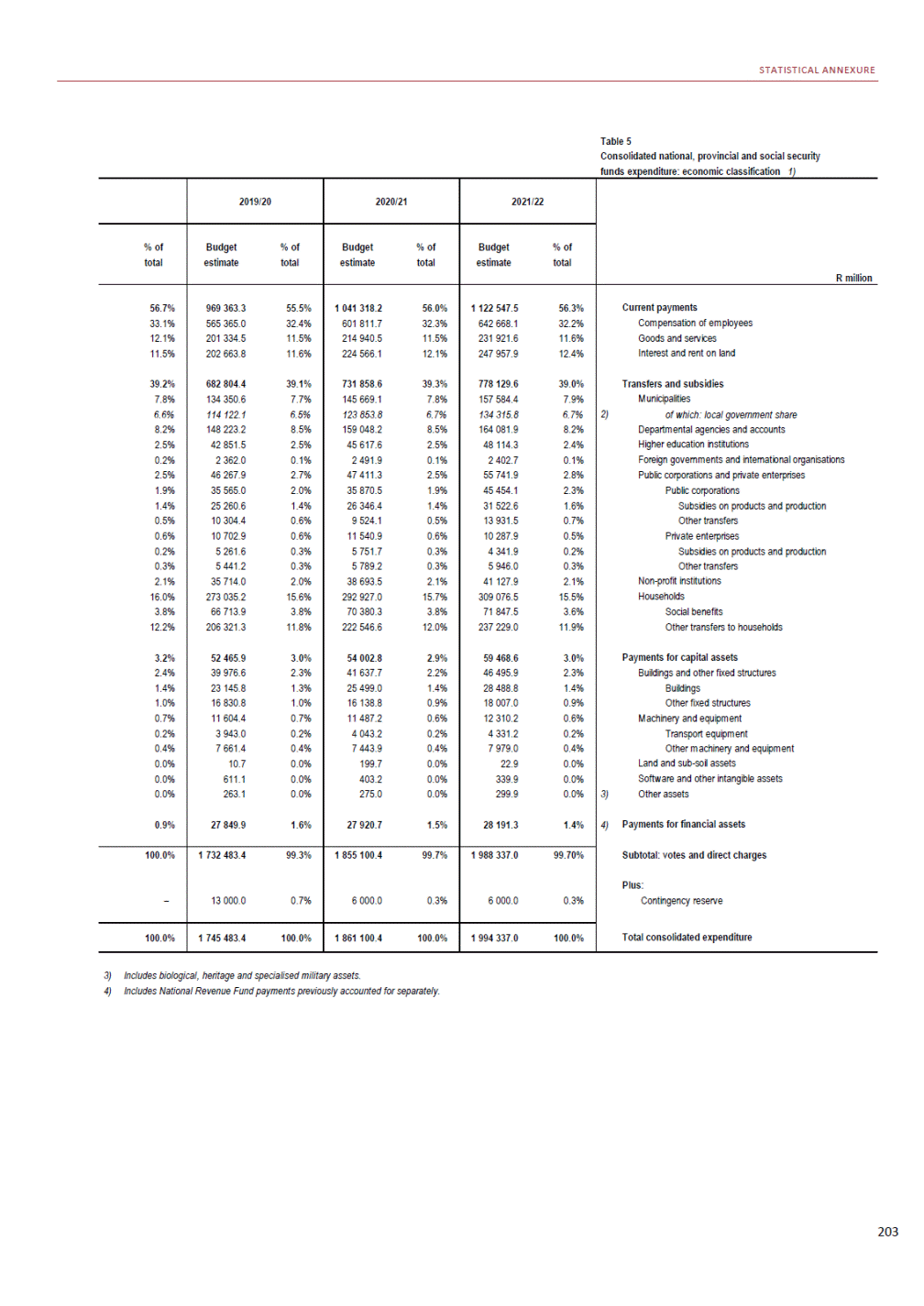
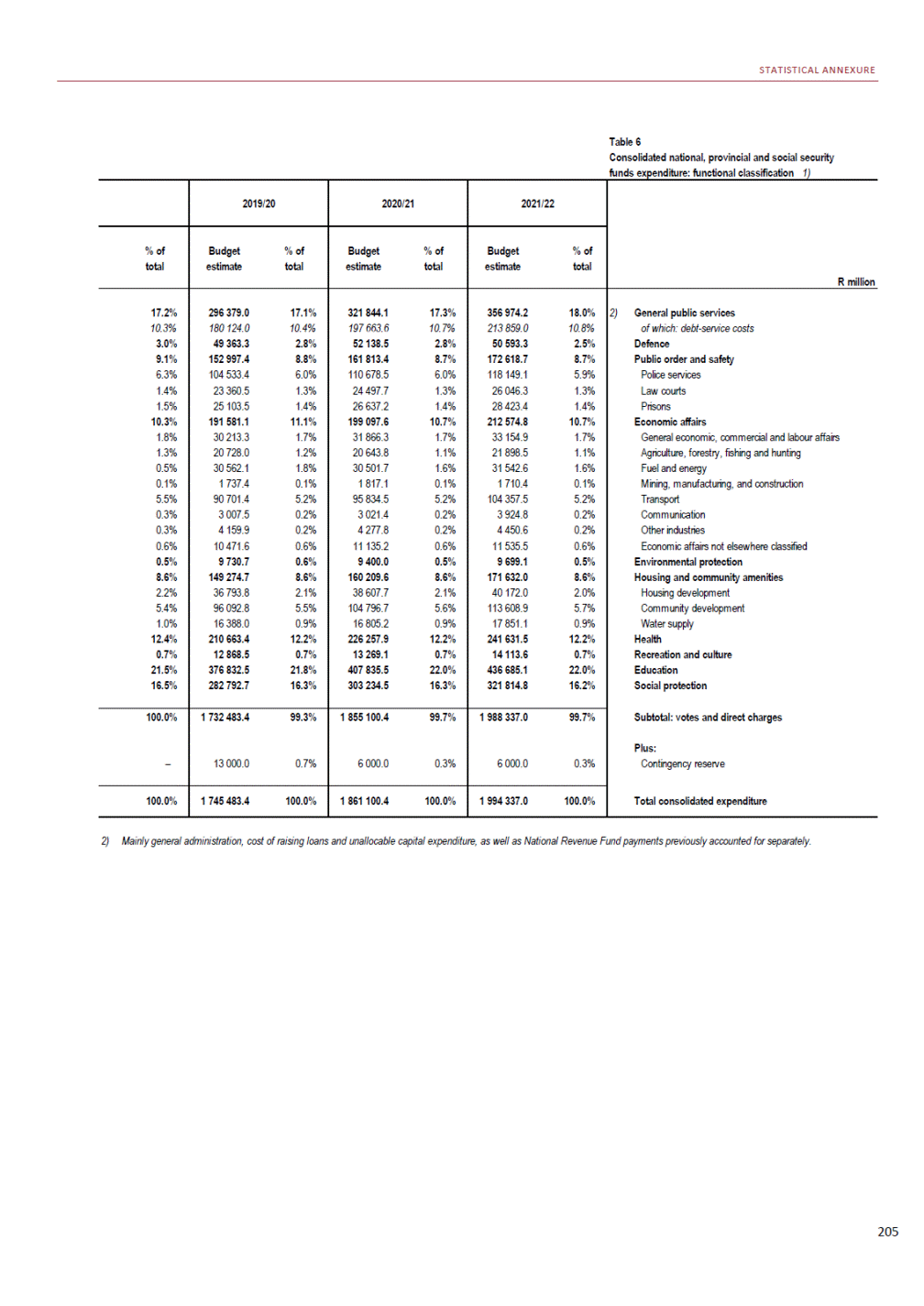
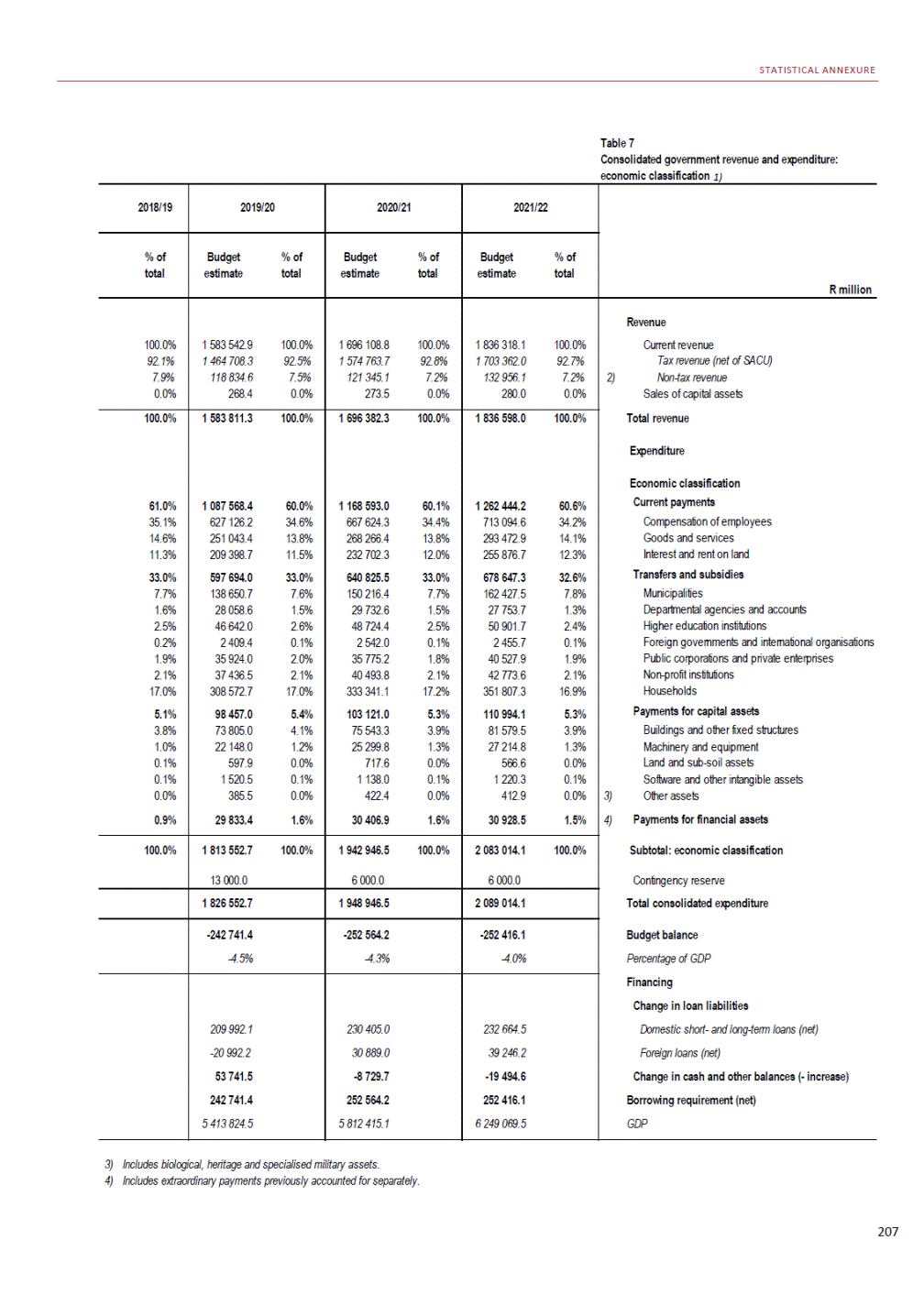
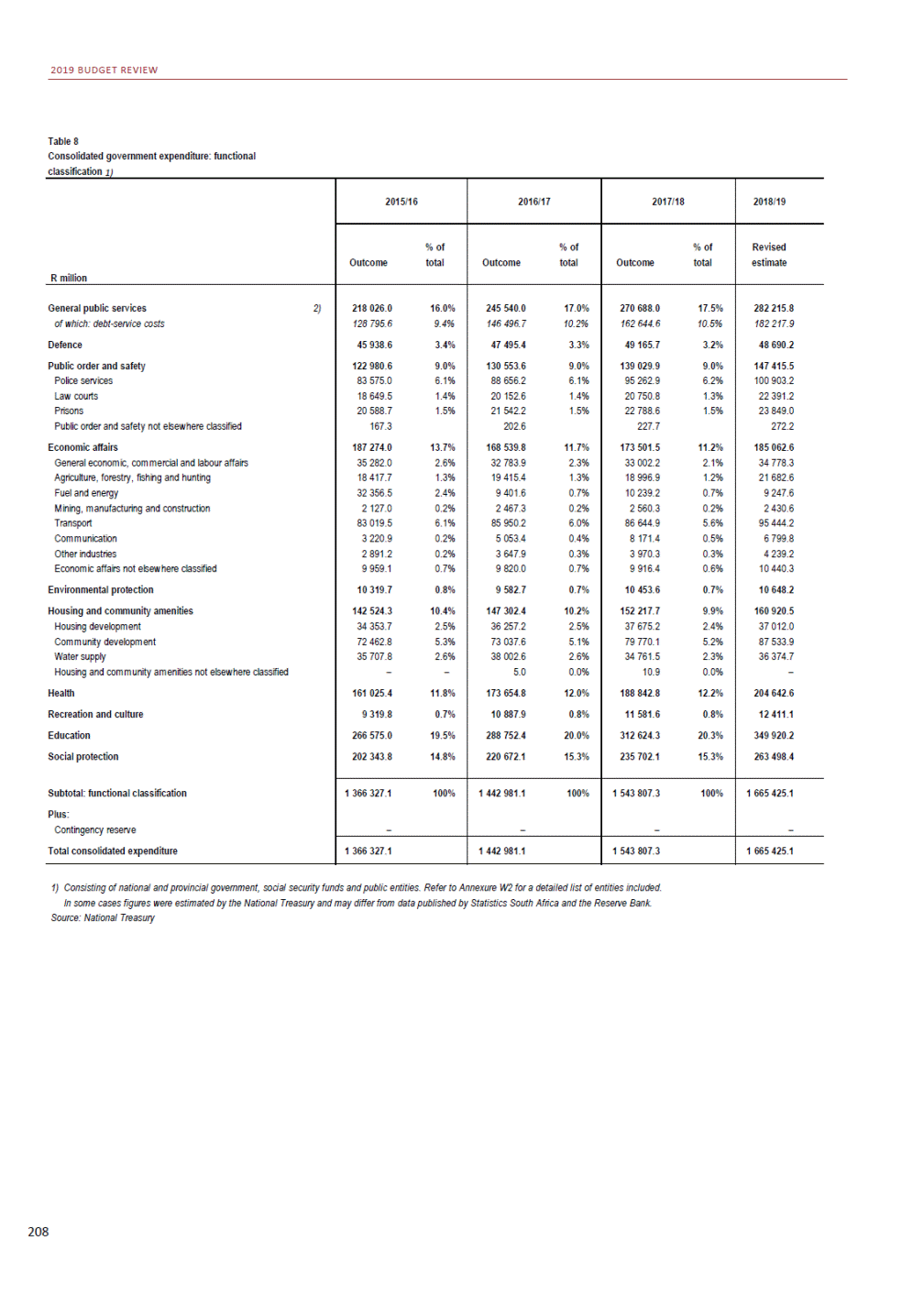
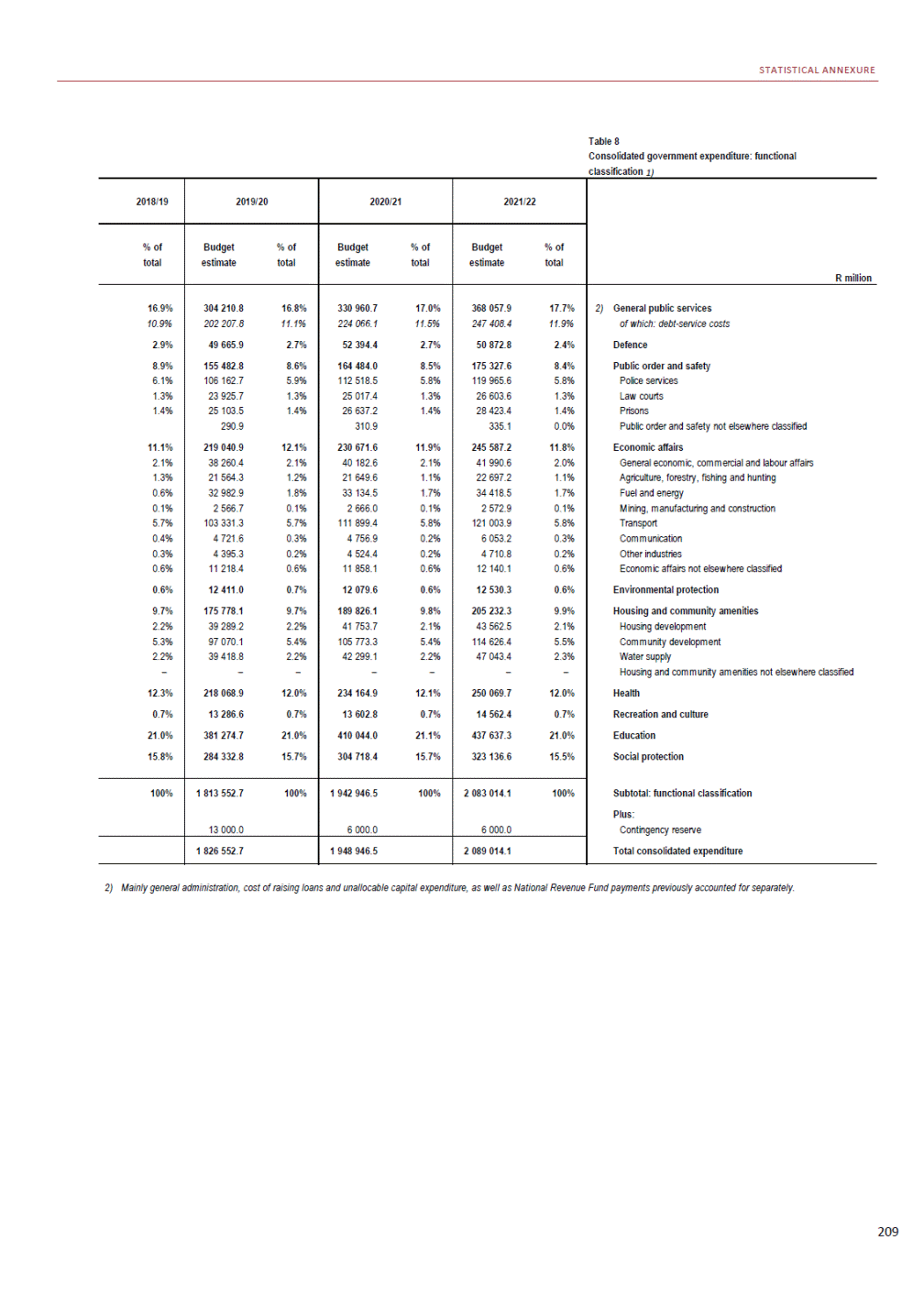
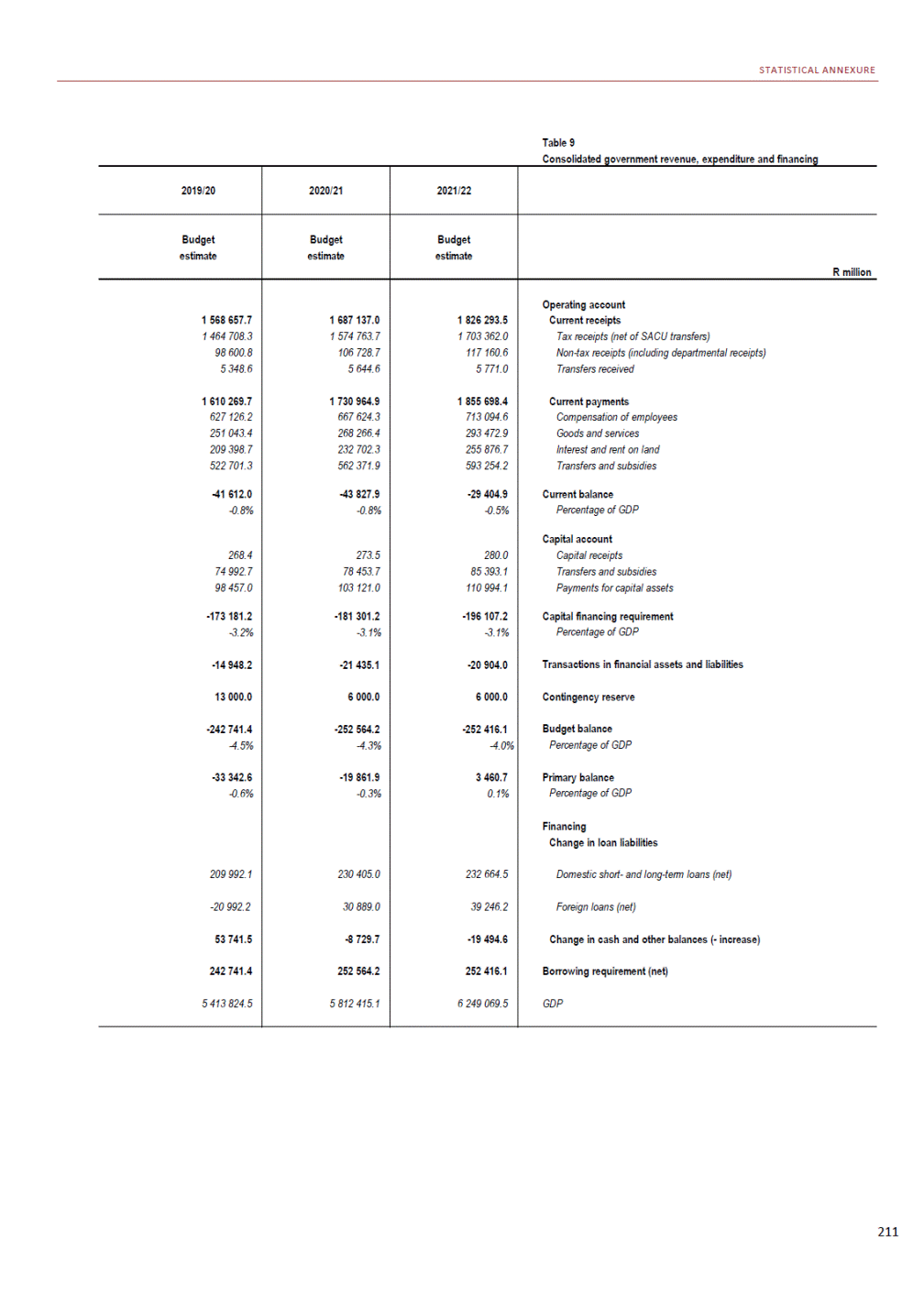
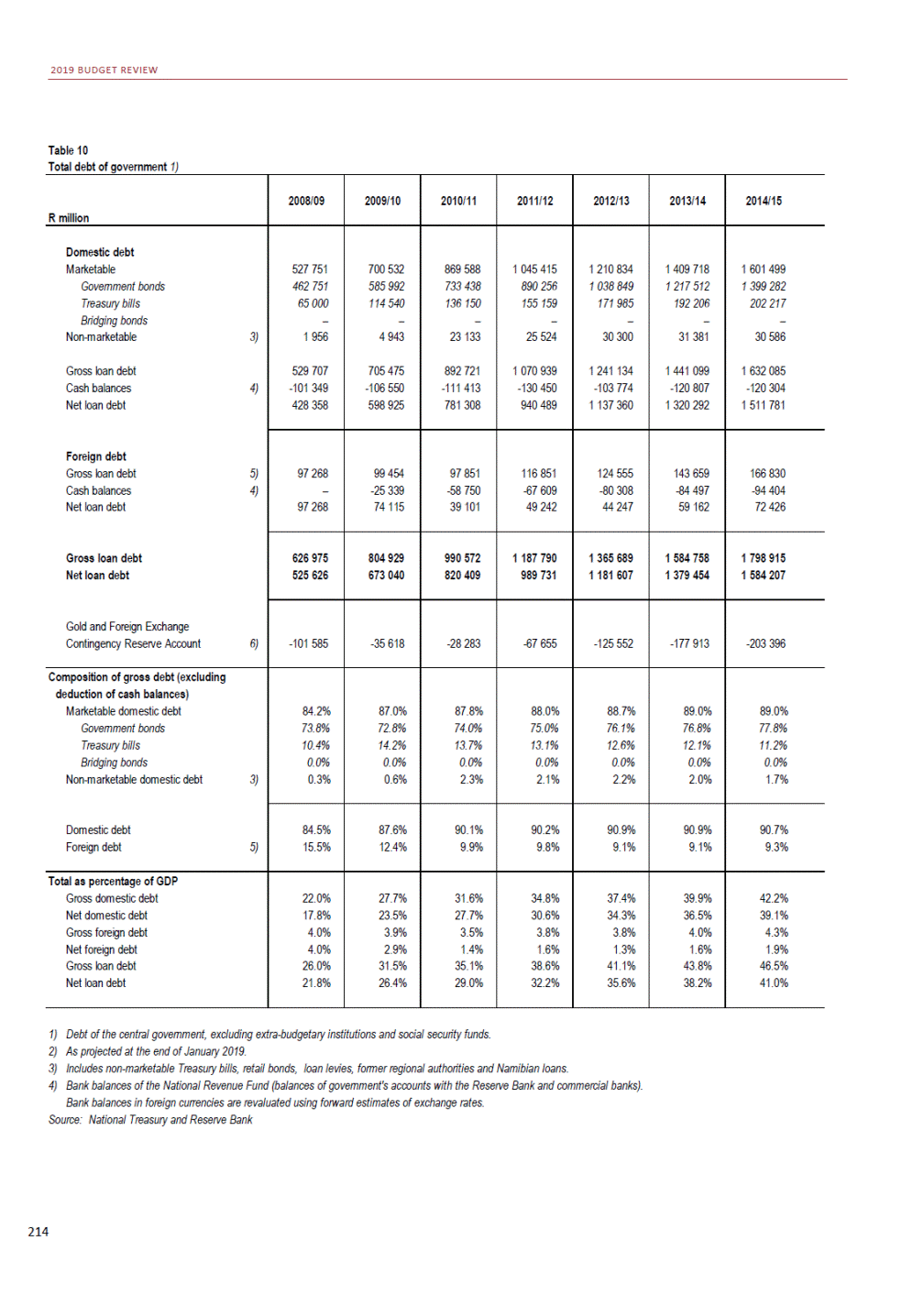
ANNEXURE W2: STRUCTURE OF THE GOVERNMENT ACCOUNTS to calculate the surplus or deficit, as well as government’s contribution to the economy in the form of output, value added and final consumption. The functional classification complements the economic classification. It serves to distinguish transactions by policy purpose or type of outlay. This is also referred to as expense by output. Its main purpose is to facilitate understanding of how funds available to government have been spent on health, education, general public services, public order and safety, and so on. The broad categories in the functional classification are listed below: General public services refers to the administration, operation or support of executive and legislative organs, financial and fiscal affairs, and external affairs. It includes foreign economic aid to developing countries and economic aid through international organisations. The category also covers general services, such as personnel services, overall planning and statistical services, and basic research in the general public service. The cost of state debt is included in this category. Defence includes administration, operation and support of military and civil defence, and the operation of military aid missions accredited to foreign governments or attached to international military organisations. Applied research and development (R&D) related to defence is also included. Public order and safety covers police services, fire protection services, justice and law courts, prisons and related R&D. Economic affairs includes government spending associated with the regulation and more efficient operation of the business sector. This category incorporates general economic affairs; commercial and labour affairs; agriculture, forestry, fishing and hunting; fuel and energy; mining; manufacturing and construction; transport; communication and related R&D. Environmental protection relates to the conservation of biodiversity and landscape – the protection of habitats, including the management of natural parks and reserves, waste management, wastewater management, pollution abatement and related R&D. Housing and community amenities includes the administration of housing and community development affairs and services, water supply, street lighting and related R&D. Health covers spending on services provided to individuals and on a collective basis, including medical products, appliances and equipment, outpatient services, hospital services, public health services and related R&D. Recreation and culture includes recreational and sporting services, cultural services, broadcasting and publishing services, religious and other community services, as well as related R&D. Education includes spending on services provided to individual learners and students, as well as those provided collectively. It includes pre-primary, primary, secondary and tertiary education, as well as subsidiary education services and related R&D. Social protection covers services supplied directly to communities, households or individuals, including transfers for sickness and disability, old age, families and children, unemployment, support to households to meet the cost of housing and related R&D. Expenditure in a particular budget vote may cover more than one function. For example, health expenditure may include spending on education for medical training. The consolidated government account The consolidated government account presents the accounts of national and provincial government, and social security funds. In this account, the National Treasury calculates estimates of general government revenue and expenditure over the medium term. In the 2019 Budget Review, a total of 163 national and provincial departments and 186 central government entities, classified as extra-budgetary agencies, are 5