
Public Marco Pieters ASML Investor Day Veldhoven, The Netherlands November 14, 2024 Executive Vice President and Head of Business Line Applications Small Talk 2024 Holistic Lithography Solutions and business opportunity Exhibit 99.6

Public Holistic Lithography Opportunity & Growth Drivers • Holistic Lithography focuses on improving Accuracy and Patterning Yield for our customers. • Accuracy: drive improvements in Overlay and Edge Placement Error (EPE) via Computational Lithography (physical models & AI), Metrology & Inspection and Scanner Optimization. • Patterning Yield: drive cost effective metrology and inspection solutions for both 2D and 3D structures enabling early yield ramp and holistic lithography control • Significant progress on multi e-beam inspection and the opportunity for HVM, first application will be Voltage Contrast inspection • Followed by smaller 2D features and 3D structures requiring buried defect inspection • Enable front end 3D integration (wafer bonding) with metrology and control solutions to meet customer overlay requirements. • The Holistic Lithography business is expected to grow at >15% CAGR with strong gross margins from 2025 to 2030. Computational lithography and metrology Metrology and inspection Lithography scanner with advanced control capability EUV DUV
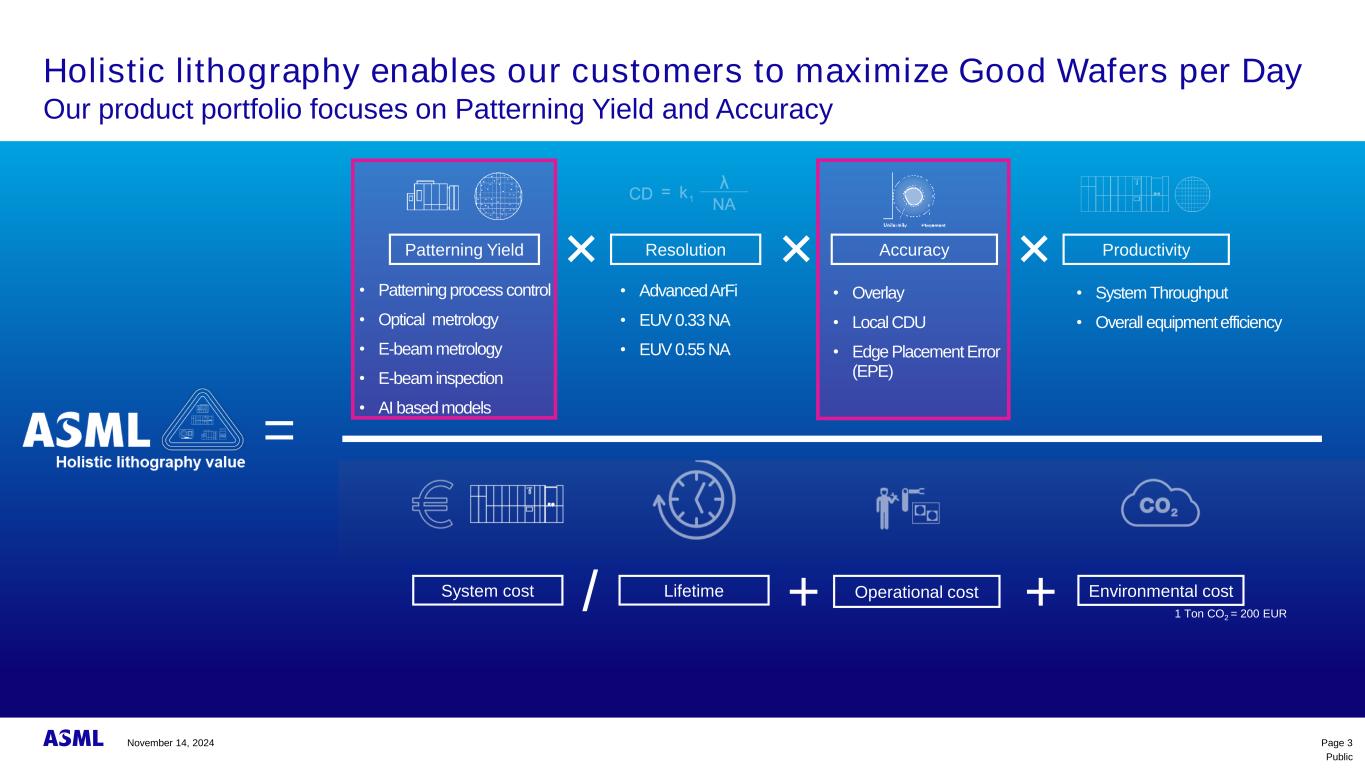
Public • Patterning process control • Optical metrology • E-beam metrology • E-beam inspection • AI based models • Overlay • Local CDU • Edge Placement Error (EPE) Holistic lithography enables our customers to maximize Good Wafers per Day Our product portfolio focuses on Patterning Yield and Accuracy Resolution Productivity× × × • Advanced ArFi • EUV 0.33 NA • EUV 0.55 NA • System Throughput • Overall equipment efficiency Operational cost Environmental costSystem cost Lifetime/ + 1 Ton CO2 = 200 EUR + = Patterning Yield Accuracy Page 3November 14, 2024
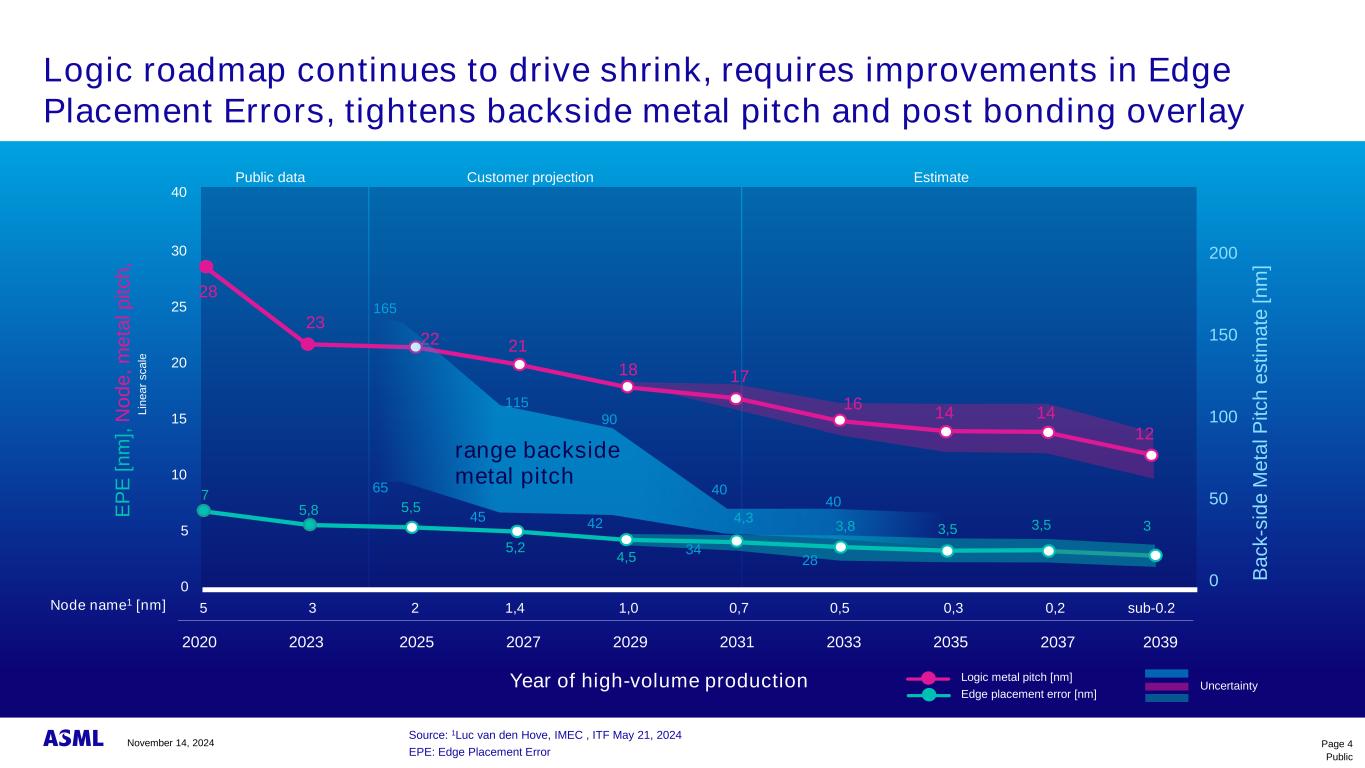
EPE: Edge Placement Error Source: 1Luc van den Hove, IMEC , ITF May 21, 2024 0 5 10 15 30 20 25 21 18 16 14 28 4,3 3,5 3,5 Public data Customer projection 2020 2023 2025 2027 2029 2031 2033 2035 17 14 3,8 22 23 E P E [ n m ], N o d e , m e ta l p it c h , L in e a r s c a le Year of high-volume production 7 20392037 12 3 5 3 2 1,4 1,0 0,7 0,20,5 0,3 sub-0.2 Logic metal pitch [nm] Edge placement error [nm] Uncertainty 5,5 4,5 5,8 Node name1 [nm] 40 Estimate Public Page 4 0 50 200 100 150 B a c k -s id e M e ta l P it c h e s ti m a te [ n m ] range backside metal pitch 165 65 115 45 42 40 34 40 28 90 5,2 Logic roadmap continues to drive shrink, requires improvements in Edge Placement Errors, tightens backside metal pitch and post bonding overlay November 14, 2024
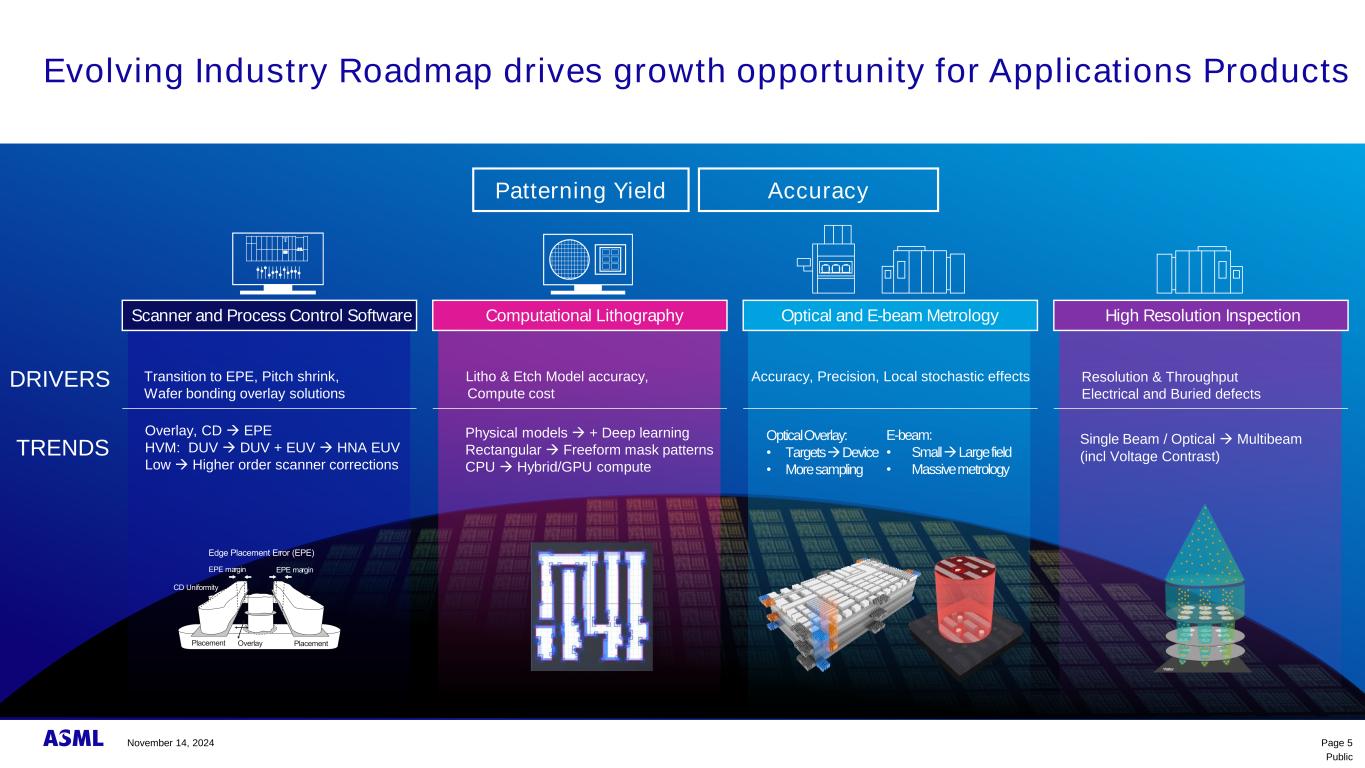
Public Evolving Industry Roadmap drives growth opportunity for Applications Products Patterning Yield Accuracy DRIVERS TRENDS Computational Lithography Litho & Etch Model accuracy, Compute cost Physical models → + Deep learning Rectangular → Freeform mask patterns CPU → Hybrid/GPU compute Scanner and Process Control Software Transition to EPE, Pitch shrink, Wafer bonding overlay solutions Overlay, CD → EPE HVM: DUV → DUV + EUV → HNA EUV Low → Higher order scanner corrections Page 5November 14, 2024 High Resolution Inspection Resolution & Throughput Electrical and Buried defects Single Beam / Optical → Multibeam (incl Voltage Contrast) Optical and E-beam Metrology Accuracy, Precision, Local stochastic effects Optical Overlay: • Targets → Device • More sampling E-beam: • Small → Large field • Massive metrology

Public Evolving Industry Roadmap drives growth opportunity for Applications Products Page 6 2023 2026 2030 Scanner and Process Control Software Computational Lithography Optical and E-beam Metrology High Resolution Inspection (optical & E-beam) 5.4 B€ 7.6 B€ 11 B€ Total Addressable Market EUV DUV Metrology and inspection November 14, 2024 Computational lithography and metrology
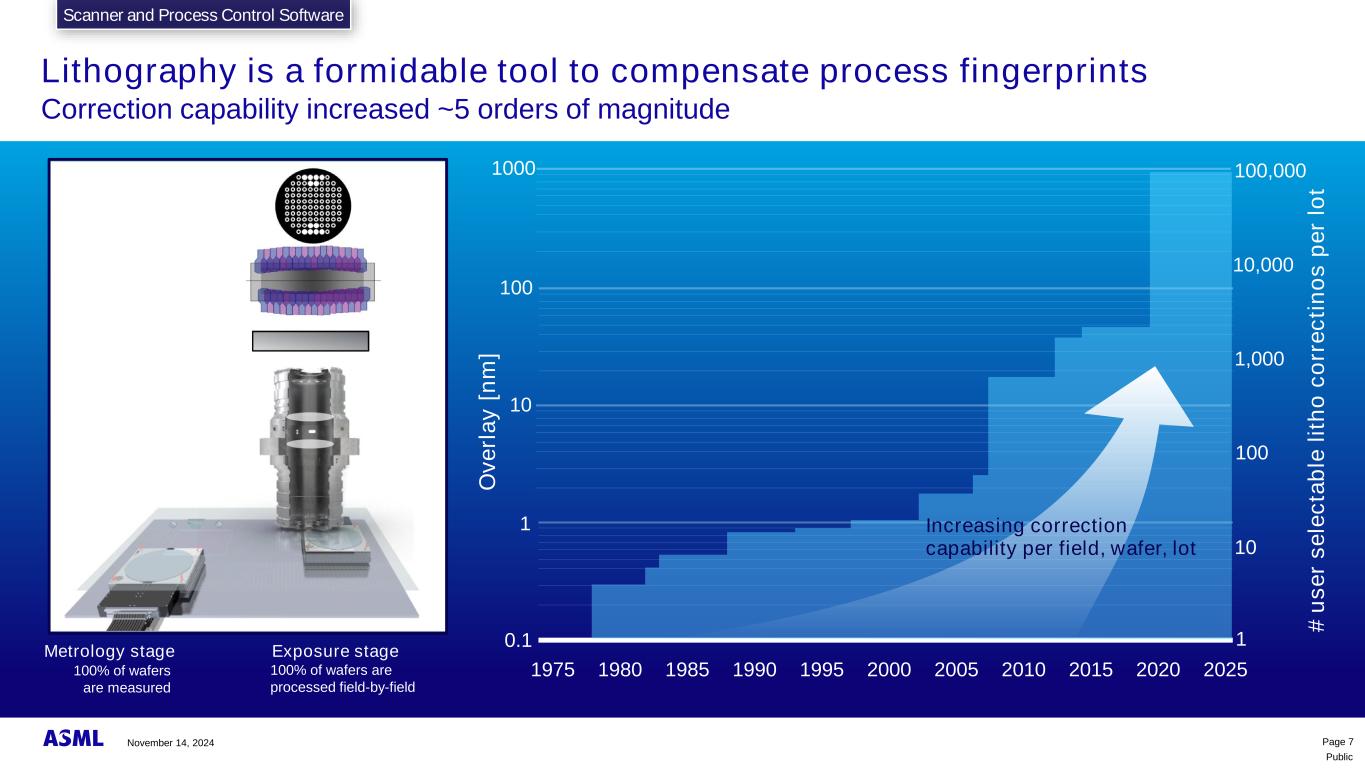
Public Lithography is a formidable tool to compensate process fingerprints Correction capability increased ~5 orders of magnitude Exposure stage 100% of wafers are measured 100% of wafers are processed field-by-field Metrology stage Even Fingers Odd Fingers Grey Filter X Y Z Optical Centerline Dose manipulator Flexible Illuminator Reticle stage 1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 2015 2020 2025 1000 100 10 1 0.1 O v e rl a y [ n m ] Page 7 1,000 100 10 1 10,000 # u s e r s e le c ta b le l it h o c o rr e c ti n o s p e r lo t 100,000 Increasing correction capability per field, wafer, lot Scanner and Process Control SoftwareScanner and Process Control Software November 14, 2024
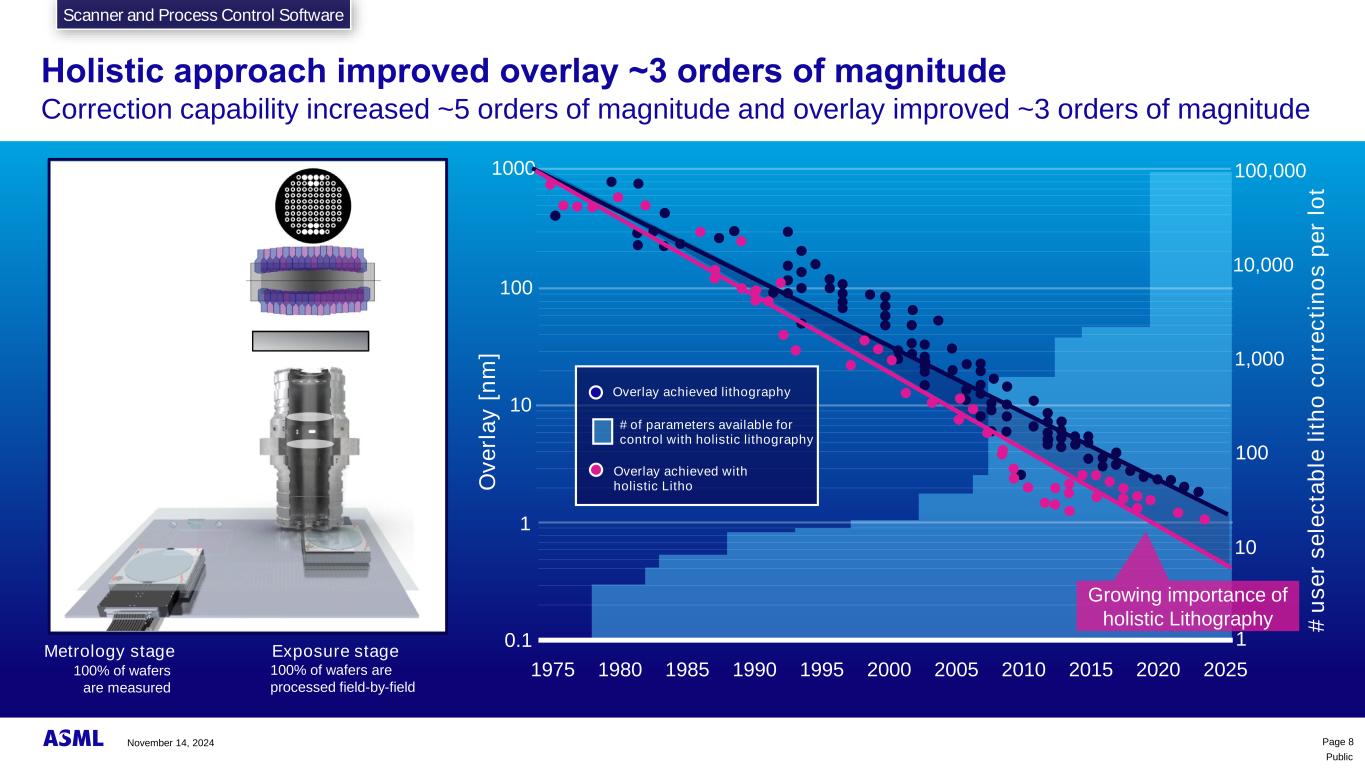
Public Holistic approach improved overlay ~3 orders of magnitude Correction capability increased ~5 orders of magnitude and overlay improved ~3 orders of magnitude Exposure stage 100% of wafers are measured 100% of wafers are processed field-by-field Metrology stage Even Fingers Odd Fingers Grey Filter X Y Z Optical Centerline Dose manipulator Flexible Illuminator Reticle stage 1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 2015 2020 2025 1000 100 10 1 0.1 Overlay achieved lithography O v e rl a y [ n m ] Page 8 # of parameters available for control with holistic lithography Growing importance of holistic Lithography Overlay achieved with holistic Litho 1,000 100 10 1 10,000 100,000 Scanner and Process Control Software November 14, 2024 # u s e r s e le c ta b le l it h o c o rr e c ti n o s p e r lo t

Public # u s e r s e le c ta b le l it h o c o rr e c ti n o s p e r lo t Holistic approach improved overlay ~3 orders of magnitude and extending to EPE gives another opportunity to improve Yield 1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 2015 2020 2025 1000 100 10 1 0.1 Overlay achieved lithography O v e rl a y [ n m ] Page 9 # of parameters available for control with holistic lithography Growing importance of holistic Lithography Overlay achieved with holistic Litho 1,000 100 10 1 10,000 100,000 Correlation to yield EPE OVL CD Scanner and Process Control SoftwareScanner and Process Control Software November 14, 2024

Public DUV EUV insertion High-NA EUV insertion Page 10 2010 2012 2014 2020 2022 2024 2026 2028 2030 10000 1 2016 2018 100 10 1000 Metrology # Parameters in model # of metrology gauges Physical models + Metrology + AIPhysical Models Accuracy Cost Ai Computational Lithography Computational litho: optical proximity correction accuracy has improved rapidly thanks to the introduction of machine learning and massive metrology a .u . November 14, 2024
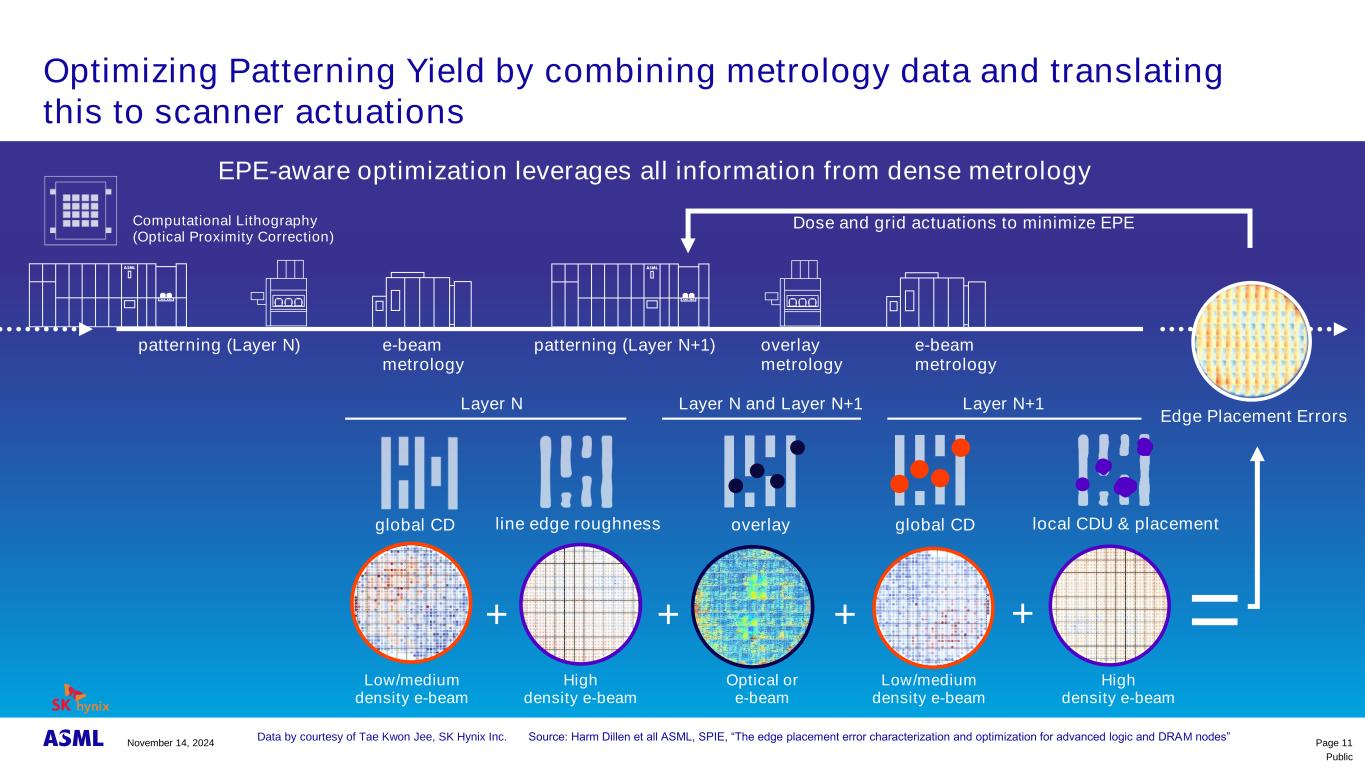
Public Optimizing Patterning Yield by combining metrology data and translating this to scanner actuations Page 11 patterning (Layer N+1) overlay metrology e-beam metrology e-beam metrology patterning (Layer N) global CD Layer N Layer N and Layer N+1 overlay Layer N+1 global CD local CDU & placementline edge roughness =+ + + + Dose and grid actuations to minimize EPE Low/medium density e-beam Low/medium density e-beam High density e-beam High density e-beam Optical or e-beam Edge Placement Errors Computational Lithography (Optical Proximity Correction) EPE-aware optimization leverages all information from dense metrology Data by courtesy of Tae Kwon Jee, SK Hynix Inc. S u : H ASML, S I , “Th p h z p z RAM n s” November 14, 2024

Public Massive overlay metrology is needed to drive those scanner corrections YieldStar platform enables increase of sampling by 80% while cost effectiveness is improved by 30~45% every 4 years Page 12 100% 90% 80% 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 0% 14000 13000 12000 11000 10000 9000 8000 7000 6000 5000 4000 3000 2000 1000 0 2010 2014 2018 2022 2026 2030 M e tr o lo g y c o s t p e r p o in t P o in ts m e a s u re d p e r lo t 40% 20% 40% 45% 800 1400 2400 5200 7000 14000 Opportunity driven by tighter resolution and wafer bonding requirement of >2000 point per wafer. Optical and E-beam Metrology 30% November 14, 2024

Public YieldStar installed base reached >1000 systems in H1’24 Page 13 Optical and E-beam Metrology 2010 2015 2020 2024 1200 1000 800 600 400 200 0 N u m b e r o f s h ip m e n ts [ c u m u la ti v e ] ’23’22’21’19’18’17’16’14’13’12’11’09’08 November 14, 2024
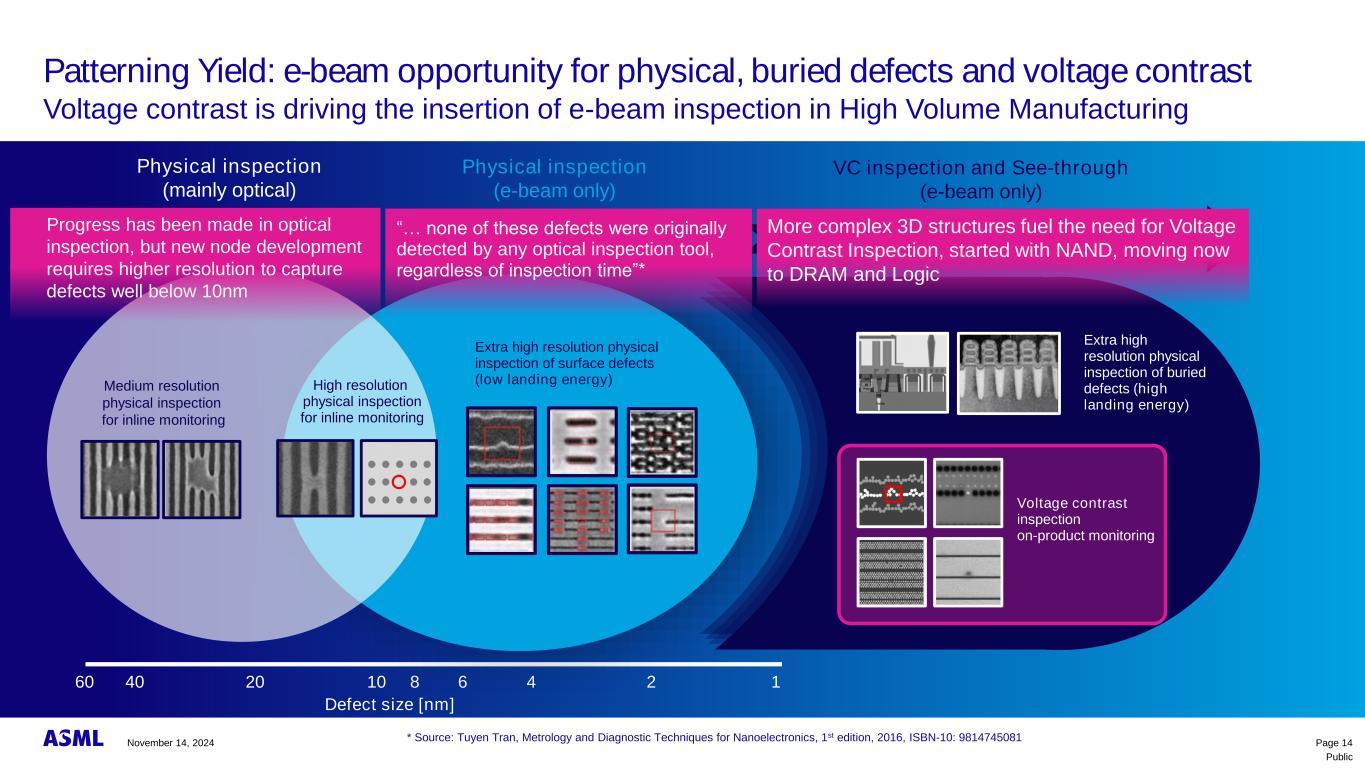
Public Patterning Yield: e-beam opportunity for physical, buried defects and voltage contrast Voltage contrast is driving the insertion of e-beam inspection in High Volume Manufacturing Page 14 160 1040 20 8 6 4 2 Defect size [nm] Buried and electric defects Extra high resolution physical inspection of buried defects (high landing energy) VC inspection and See-through (e-beam only) * Source: Tuyen Tran, Metrology and Diagnostic Techniques for Nanoelectronics, 1st edition, 2016, ISBN-10: 9814745081 <10nm defects Extra high resolution physical inspection of surface defects (low landing energy) Physical inspection (e-beam only) >10nm defects Medium resolution physical inspection for inline monitoring Physical inspection (mainly optical) High resolution physical inspection for inline monitoring Progress has been made in optical inspection, but new node development requires higher resolution to capture defects well below 10nm More complex 3D structures fuel the need for Voltage Contrast Inspection, started with NAND, moving now to DRAM and Logic “… h s s w detected by any optical inspection tool, ss sp ”* Voltage contrast inspection on-product monitoring November 14, 2024
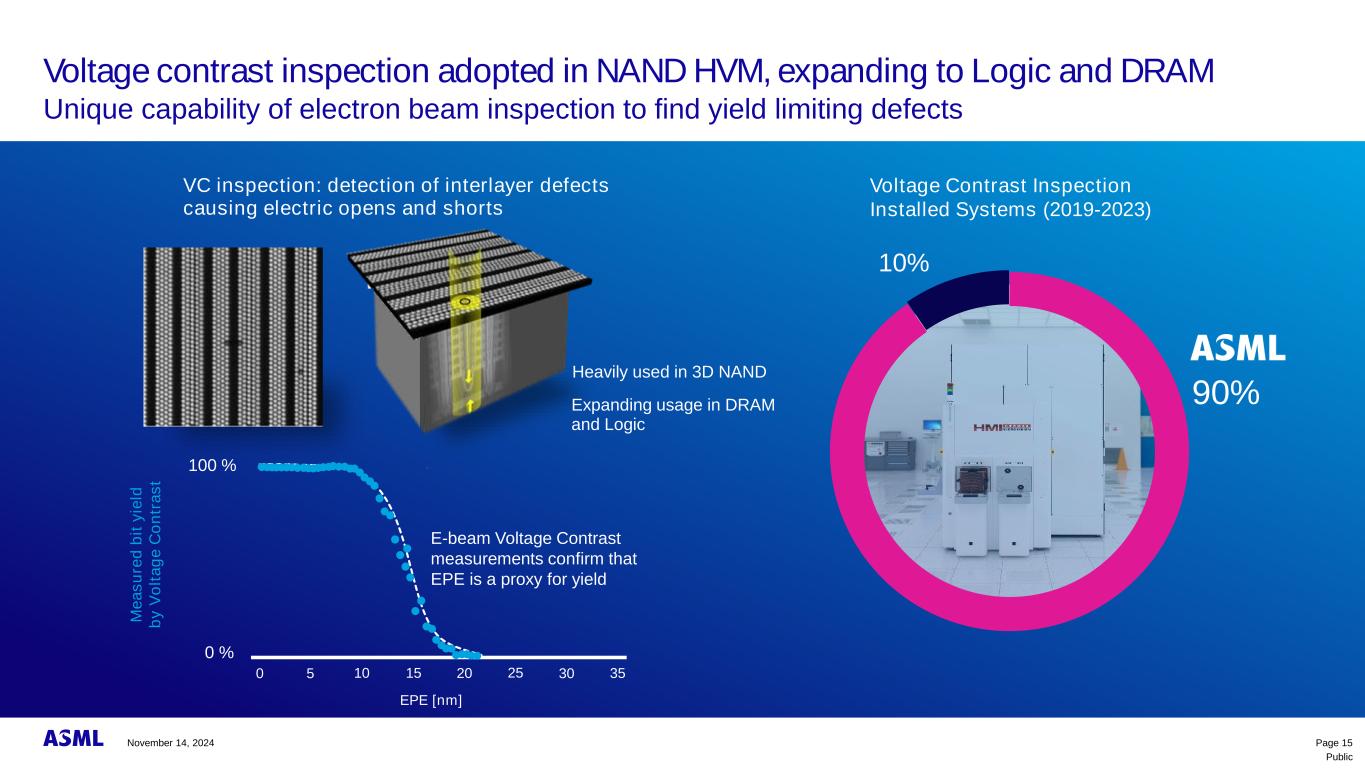
Public Voltage contrast inspection adopted in NAND HVM, expanding to Logic and DRAM Unique capability of electron beam inspection to find yield limiting defects Page 15 100 % 0 % 0 5 10 15 20 25 3530 EPE [nm] E-beam Voltage Contrast measurements confirm that EPE is a proxy for yield M e a s u re d b it y ie ld b y V o lt a g e C o n tr a s t VC inspection: detection of interlayer defects causing electric opens and shorts Heavily used in 3D NAND Expanding usage in DRAM and Logic Voltage Contrast Inspection Installed Systems (2019-2023) 10% 90% November 14, 2024
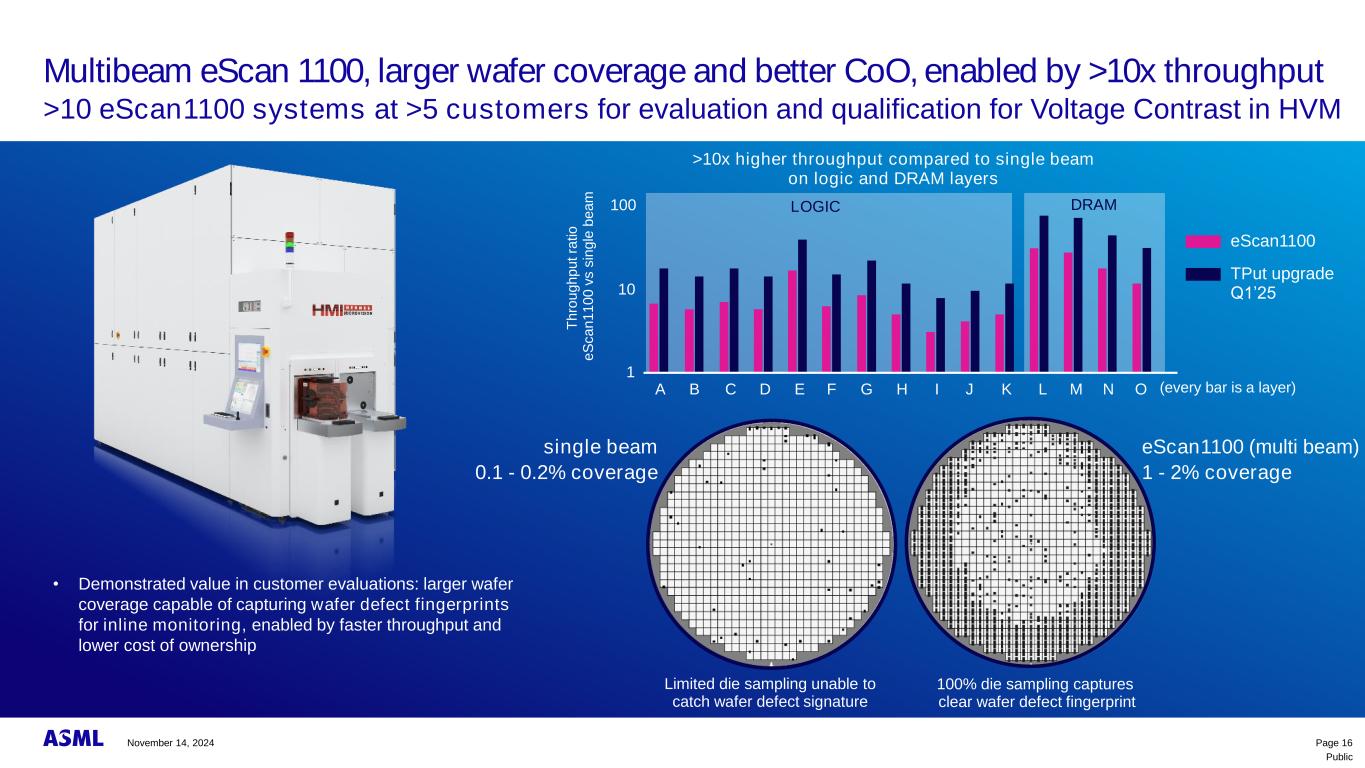
Public Multibeam eScan 1100, larger wafer coverage and better CoO, enabled by >10x throughput >10 eScan1100 systems at >5 customers for evaluation and qualification for Voltage Contrast in HVM • Demonstrated value in customer evaluations: larger wafer coverage capable of capturing wafer defect fingerprints for inline monitoring, enabled by faster throughput and lower cost of ownership >10x higher throughput compared to single beam on logic and DRAM layers Limited die sampling unable to catch wafer defect signature 100% die sampling captures clear wafer defect fingerprint single beam eScan1100 (multi beam) 0.1 - 0.2% coverage 1 - 2% coverage 100 10 1 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O T h ro u g h p u t ra ti o e S c a n 1 1 0 0 v s s in g le b e a m DRAMLOGIC eScan1100 TPut upgrade Q1’25 (every bar is a layer) Page 16November 14, 2024

Public Customer data shows eScan1100 capturing clear defect signature with higher throughput 7~8x larger wafer coverage and ~60% shorter cycle time * based on full wafer area size as 707cm² Page 17 Single Beam Inspection eScan1100 Wafer coverage: 0.2% Wafer coverage: 1.5%* Inspection time: 100% Inspection time: ~40% Miss the signature Clear defect signature November 14, 2024
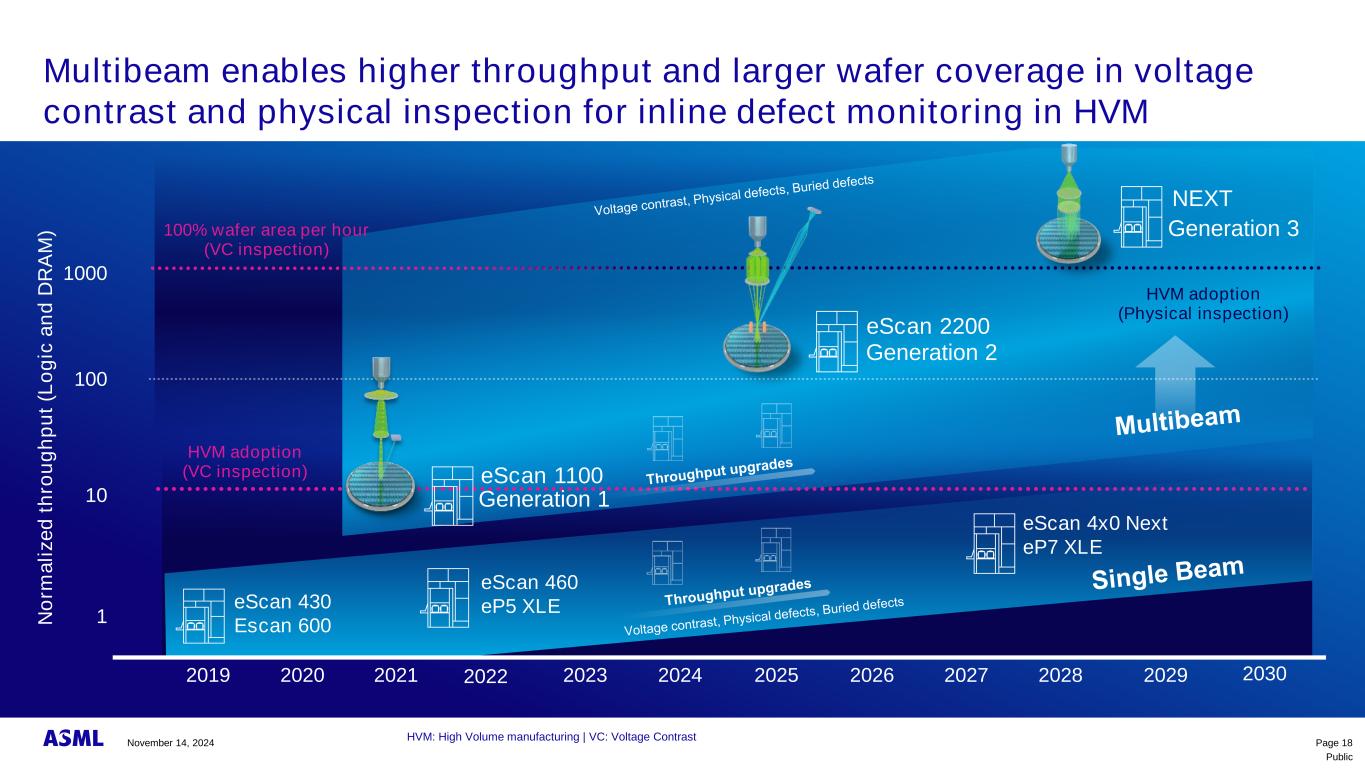
Public Multibeam enables higher throughput and larger wafer coverage in voltage contrast and physical inspection for inline defect monitoring in HVM Page 18 2019 2020 2021 2023 2024 2025 2026 2027 2028 2029 100 1000 10 1N o rm a li z e d t h ro u g h p u t (L o g ic a n d D R A M ) 100% wafer area per hour (VC inspection) eScan 430 Escan 600 eScan 460 eP5 XLE eScan 4x0 Next eP7 XLE HVM adoption (Physical inspection) 2022 2030 eScan 1100 Generation 1 Generation 2 Generation 3 eScan 2200 NEXT HVM: High Volume manufacturing | VC: Voltage Contrast HVM adoption (VC inspection) November 14, 2024

Public Next step in multibeam: from 25 to >2700 beams Technology demonstration ongoing, working towards customer early access in 2025 Focal plane verification Through focus measurement >2700 beams on scintillator screen All of >2700 beams on scintillator screen are functional Detector functionality and resolution verification Sample image Page 19November 14, 2024

Public We expect front end 3D integration to complement 2D shrink in driving density Front end 3D integration challenges will trigger new litho opportunities for all semiconductor products Page 20 Stack LOGIC W-W hybrid W-W Fusion W-W | D-W Fusion Overlay 3D NAND BSPN CFET HVM 2026 >2032 Array CMOS Logic Bare-Si Logic Logic Bonding 5nm → 2nm50nm → 25nm 2.5nm → 1.6nm Litho KrF NXE/EXE NXE/EXE Array W-W / D-W hybrid Array CMOS 50nm → 25nm KrF NAND DRAM W-W hybrid W-W hybrid W-W / D-W hybrid 3D ARRAY4F2 2D ARRAY >2027 >2032 >2032 Array CMOS Array CMOS Array CMOS Array >4.5nm6nm → 3nm 6nm → 3nm ArFiArFi ArFi >2030 November 14, 2024

Public Holistic Lithography will enable 3D integration Metrology and scanner control at pre and post bonding critical process points needed for overlay Page 21 < 5 nm overlay error Both wafers have separate patterning and processes but overlay needs to be matched between them prior to bonding Pre-bonding ARRAY CMOS Bonder creates a massive deformation on the wafer CMOS Scanner correction and control2 ARRAY Scanner and offline metrology1 Actuators Bonding November 14, 2024

Public Holistic Lithography will enable 3D integration Metrology and scanner control at pre and post bonding critical process points needed for overlay Page 22 Actuators Holistically bringing the overlay after bonding back to customer requirements Post-bonding >2000 measurements/wafer < 5 nm overlay error 3 Bonder creates a massive deformation on the wafer Bonding >5000 measurements/wafer >50nm overlay error Standard bonding recipe, optimizing post bonding grid Co-optimized bonding recipe, optimizing post bonding litho Wafer deformation directly after bonding Overlay error after litho correction Wafer deformation directly after bonding Overlay error after litho correctionRequires massive metrology on every wafer to categorize the large (local) variety in fingerprint Richard van Haren, at all, ASML, EVG, Leti:, “Characterization and mitigation of local wafer deformations introduced by direct wafer-to-wafer bonding”, SPIE Advanced Lithography + Patterning, 2024 November 14, 2024
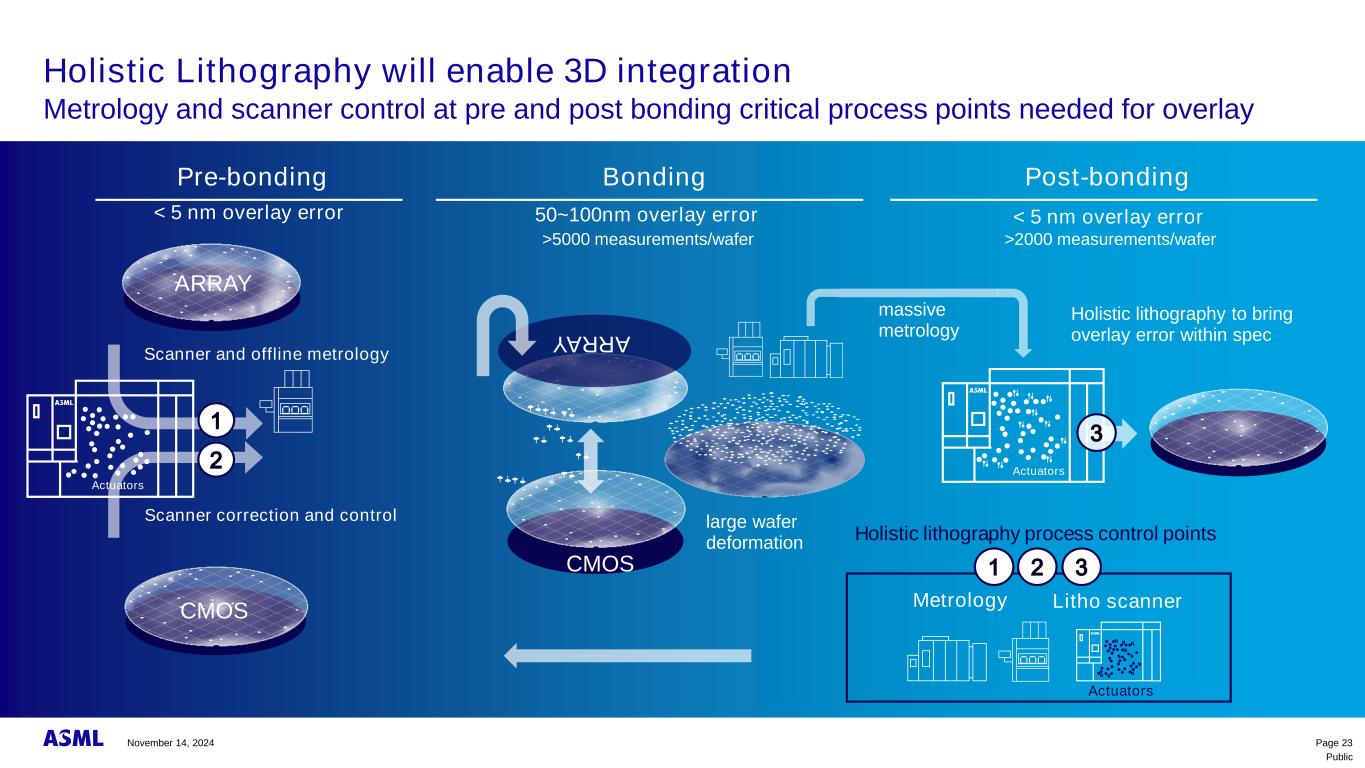
Public Holistic Lithography will enable 3D integration Metrology and scanner control at pre and post bonding critical process points needed for overlay Page 23 Pre-bonding CMOS Scanner correction and control ARRAY Scanner and offline metrology 2 1 Actuators Post-bondingBonding ARRAY CMOS massive metrology Actuators large wafer deformation 3 Metrology Litho scanner Holistic lithography process control points Actuators 321 >5000 measurements/wafer 50~100nm overlay error >2000 measurements/wafer < 5 nm overlay error< 5 nm overlay error Holistic lithography to bring overlay error within spec November 14, 2024

Public Holistic Lithography Opportunity & Growth Drivers • Holistic Lithography focuses on improving Accuracy and Patterning Yield for our customers. • Accuracy: drive improvements in Overlay and Edge Placement Error (EPE) via Computational Lithography (physical models & AI), Metrology & Inspection and Scanner Optimization. • Patterning Yield: drive cost effective metrology and inspection solutions for both 2D and 3D structures enabling early yield ramp and holistic lithography control • Significant progress on multi e-beam inspection and the opportunity for HVM, first application will be Voltage Contrast inspection • Followed by smaller 2D features and 3D structures requiring buried defect inspection • Enable front end 3D integration (wafer bonding) with metrology and control solutions to meet customer overlay requirements. • The Holistic Lithography business is expected to grow at >15% CAGR with strong gross margins from 2025 to 2030. Computational lithography and metrology Metrology and inspection Lithography scanner with advanced control capability EUV DUV

Public Forward Looking Statements This document and related discussions contain statements that are forward-looking within the meaning of the U.S. Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995, including statements with respect to our strategy, plans and expected trends, including trends in end markets and the technology industry and business environment trends, including the emergence of AI and its potential opportunities and expectations for the semiconductor industry, including pu p w , s RAM , s s w h sp M ’s w xp s s w h and aspirations by 2030, global market trends and technology, product and customer roadmaps, long term outlook and expected lithography and semiconductor industry growth and trends and expected growth in semiconductor sales and semiconductor market opportunity through to 2030 and beyond, expected growth in wafer demand and capacity and additional wafer capacity requirements, expected investments by our customers, including investments in our technology and in wafer capacity, plans to increase capacity, expected growth in lithography spend, growth opportunities including opportunities for growth in service and upgrades and opportunities for growth in Installed Base Management sales, expected growth and gross margins in the holistic lithography business and xp ss b k App s p u s, xp s b s w s b s , ASML’s s supp ’s p , xp p u s s s, s s h up 2030, including annual revenue and gross margin opportunity and development potential for 2030, outlook and expected, modelled or potential financial results, including revenue opportunity, gross margin, R&D costs, SG&A costs, capital expenditure, cash conversion cycle and annualized effective tax rate for 2030 and assumptions and drivers underlying such expected, modelled or potential amounts, and other assumptions underlying our business and financial models, expected trends, outlook and growth in semiconductor end markets and long term growth opportunities, demand and demand drivers, expected opportunities and growth drivers for and technological innovation of our products including DUV EUV, High NA, Hyper NA, Applications, and other products impacting productivity and costs, transistor dimensions, logic and DRAM shrink, foundry competition, statements with respect to dividends and share buybacks and our capital return policy, including expectation to return significant amounts of cash to shareholders through growing dividends and buybacks and statements with respect to energy generation and consumption trends and the drive toward energy efficiency, emissions reduction and greenhouse gas neutrality goals and target dates to achieve greenhouse gas neutrality, zero waste from operations and other ESG targets and ambitions and plans to maintain a leadership position in ESG, increasing technological sovereignty across the world and the expected impact on semiconductor sales, including specific goals of countries across the world, increasing competition in the foundry business, estimates for 2024 and other non-historical statements. You can generally identify these statements by the use of words like "may", "will", "could", "should", "project", "believe", "anticipate", "expect", "plan", " s ", " s ", "p ", “ pp u ”, “s ”, “ u ,” " ", " u ", " ", " u u ", "p ss", "goal" and variations of these words or comparable words. These statements are not historical facts, but rather are based on current expectations, estimates, assumptions, models, opportunities and projections about our business and our future and potential financial results and readers should not place undue reliance on them. Forward- looking statements do not guarantee future performance and involve a number of substantial known and unknown risks and uncertainties. These risks and uncertainties include, without limitation, customer demand, semiconductor equipment industry capacity, worldwide demand for semiconductors and semiconductor manufacturing capacity, lithography tool utilization and semiconductor inventory levels, general trends and consumer confidence in the semiconductor industry and end markets, the impact of general economic conditions, including the impact of the current macroeconomic environment on the semiconductor industry, uncertainty around a market recovery including the timing thereof, the impact of inflation, interest rates, wars and geopolitical developments, the impact of pandemics, the performance of our systems, the success of technology advances and the pace of new product development and customer acceptance of and demand for new products, our production capacity and ability to adjust capacity to meet demand, supply chain capacity, timely availability of parts and components, raw materials, critical manufacturing equipment and qualified employees, our ability to produce systems to meet demand, the number and timing of systems ordered, shipped and recognized in revenue, risks relating to fluctuations in net bookings and our ability to convert bookings into sales, the risk of order cancellation or push outs and restrictions on shipments of ordered sys s u xp s, sks h , p u us ps M ’s w, risks relating to the trade environment, import/export and national security regulations and orders and their impact on us, including the impact of changes in export regulations and the impact of such regulations on our ability to obtain necessary licenses and to sell our systems and provide services to certain customers, exchange rate fluctuations, changes in tax rates, available liquidity and free cash flow and liquidity requirements, our ability to refinance our indebtedness, available cash and distributable reserves for, and other factors impacting, dividend payments and share repurchases, the number of shares that we repurchase under our share repurchase programs, our ability to enforce patents and protect intellectual property rights and the outcome of intellectual property disputes and litigation, our ab SG s x u u SG s , h s h p ASML’s bus ss financial results including the risk that actual results may differ materially from the models, potential and opportunity we pres 2030 h u u p s, h sks h sk s u ASML’s A u Report on Form 20-F for the year ended December 31, 2023 and other filings with and submissions to the US Securities and Exchange Commission. These forward-looking statements are made only as of the date of this document. We undertake no obligation to update any forward-looking statements after the date of this report or to conform such statements to actual results or revised expectations, except as required by law. This document and related discussions contain statements relating to our approach to and interim progress on achieving certain energy efficiency and greenhouse gas emissions reduction targets, including our ambition to achieve h us s u . R s “ h us s u ” s ss s, ASML’s s h s GHG emission reduction targets, compensated by the same amount of metric tons of carbon credits that are verified against recognised quality standards. Page 25November 14, 2024

Public THANK YOU

























