UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
|
| |
| x | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2013
or
|
| |
| ¨ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from to
Commission file number: 1-16239
ATMI, Inc.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
|
| | |
| Delaware | | 06-1481060 |
(State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
| 7 Commerce Drive, Danbury, CT | | 06810 |
| (Address of principal executive offices) | | (Zip Code) |
203-794-1100
(Registrant’s telephone number, including area code)
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
|
| | |
| Title of each class | | Name of each exchange on which registered |
| Common Stock, par value $0.01 per share | | The NASDAQ Stock Market LLC (NASDAQ Global Select Market) |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act:
None
(Title of class)
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ¨ No x
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ¨ No x
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act (Check one):
|
| | | |
| Large accelerated filer | ¨ | Accelerated filer | x |
| Non-accelerated filer | ¨ | Smaller reporting company | ¨ |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes ¨ No x
The aggregate market value of the common stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant at June 30, 2013, was approximately $660,966,000 based on the closing sale price of such stock on the NASDAQ Global Select Market on that date.
The number of shares outstanding of the registrant’s common stock as of January 31, 2014 was 33,101,335.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
The information required to be included in Part III of this Annual Report on Form 10-K will be provided in accordance with Instruction G(3) to Form 10-K no later than April 30, 2014.
ATMI, INC.
Annual Report on Form 10-K
For the Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2013
TABLE OF CONTENTS
|
| | |
| | | Page |
| |
| Item 1. | | |
| Item 1A. | | |
| Item 1B. | | |
| Item 2. | | |
| Item 3. | | |
| Item 4. | | |
| | |
| |
| Item 5. | | |
| Item 6. | | |
| Item 7. | | |
| Item 7A. | | |
| Item 8. | | |
| Item 9. | | |
| Item 9A. | | |
| Item 9B. | | |
| | |
| |
| Item 10. | | |
| Item 11. | | |
| Item 12. | | |
| Item 13. | | |
| Item 14. | | |
| | |
| |
| Item 15. | | |
| | |
| |
| F-1 |
PART I
References in this annual report to “the Company,” “ATMI,” “we,” “us” and “our” refer to ATMI, Inc. and our wholly-owned subsidiaries on a consolidated basis.
Item 1. Business
Cautionary Statements Under the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995
Forward-Looking Statements
Disclosures included in this Form 10-K contain “forward-looking statements” within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. Forward-looking statements may be identified by words such as “anticipate,” “plan,” “believe,” “seek,” “estimate,” “expect,” “could,” and words of similar meanings and include, without limitation, statements about the expected future business and financial performance of ATMI such as financial projections, expectations for demand and sales of new and existing products, customer and supplier relationships, research and development programs, market and technology opportunities, international trends, business strategies, business opportunities, objectives of management for future operations, microelectronics industry (including wafer start) growth and trends in the markets in which the Company participates. Forward-looking statements are based on management’s current expectations and assumptions, which are inherently subject to uncertainties, risks and changes in circumstances that are difficult to predict. Investors and others should consider the cautionary statements and risk factors discussed in Item 1A below. Actual outcomes and results may differ materially from these expectations and assumptions because of changes in political, economic, business, competitive, market, regulatory, and other factors. ATMI undertakes no obligation to update publicly or review any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future developments or otherwise, except as required by law.
Our Business
On December 22, 2013, ATMI and certain of its subsidiaries and Pall Corporation, entered into a Share and Asset Purchase Agreement pursuant to which ATMI agreed to sell and transfer to Pall Corporation all assets and liabilities primarily related to the LifeSciences business in exchange for cash proceeds of $185 million, subject to customary working capital adjustments. The transaction closed on February 20, 2014. For purposes of this Form 10-K, we have treated the LifeSciences business as a discontinued operation.
The LifeSciences business unit sells products that address an increasing number of critical process steps for the biotechnology, laboratory and cell therapy markets, including disposable mixers and bioreactors. This unit includes our Newform™ products and Integrity™ mixers, bioreactors and bioprocess vessels.
As a result of the decision to exit the LifeSciences business, ATMI’s continuing operations are comprised of one primary business: Microelectronics.
On February 4, 2014, ATMI and Entegris, Inc. ("Entegris") entered into an Agreement and Plan of Merger pursuant to which, subject to the satisfaction or waiver of certain conditions, ATMI will merge with and into Atomic Merger Corporation, a wholly-owned subsidiary of Entegris ("Merger Sub"). Under the terms of the merger agreement, ATMI shareholders will receive $34.00 in cash, without interest or dividends, for each share of ATMI common stock they hold at the time of closing. We anticipate closing the transaction in the second quarter of 2014.
We believe we are among the leading suppliers of high performance materials, materials packaging and materials delivery systems used worldwide in the manufacture of microelectronics devices. Our products consist of “front-end” semiconductor performance materials, sub-atmospheric pressure gas delivery systems for safe handling and delivery of toxic and hazardous gases to semiconductor process equipment, and high-purity materials packaging and dispensing systems that allow for the reliable introduction of low volatility liquids and solids to microelectronics processes. ATMI targets semiconductor and flat-panel display manufacturers, whose products form the foundation of microelectronics technology rapidly proliferating through the consumer products, information technology, automotive, and communications industries. The market for microelectronics devices is continually changing, which drives demand for new products and technologies that have improved performance at lower cost. ATMI’s customers include many of the leading semiconductor manufacturers in the world who target leading-edge technologies. ATMI’s objective is to meet the demands of our microelectronics customers with solutions that maximize the efficiency and safety of their manufacturing processes, reduce capital or operating costs, and minimize the time to develop new products and integrate them into their processes.
ATMI’s core competencies include:
| |
| • | knowledge of the science and economics of process applications for customer needs in markets served; |
| |
| • | the ability to use a combinatorial science-based research approach and high-productivity development (“HPD”) capabilities to significantly shorten our new product development life cycle and develop next generation materials necessary as the semiconductor industry moves toward advanced technology generations, such as 14 and 10 nanometers; |
| |
| • | the materials science of packaging, delivery, and deposition of ultra-pure semiconductor materials; |
| |
| • | the ability to rapidly develop innovative technology and intellectual property that strengthens our competitive position; |
Our customers’ products and manufacturing processes are increasingly complex, requiring continual innovations for materials and materials handling solutions. ATMI has historically capitalized on these industry dynamics through:
| |
| • | a strategy of leveraging the combination of our performance materials and materials handling competence to provide greater process efficiency value to our customers; |
| |
| • | an extensive research and development program that has produced a stream of proprietary and patented products for these markets; |
| |
| • | a key customer focus, which has included providing applications development in order to offer materials solutions for future generation technologies and the ability to perform electrical test measurements in our development efforts to ensure our solutions meet our customers’ needs; |
| |
| • | strategic alliances and collaboration efforts that have allowed us to add complementary technologies to our product portfolio more rapidly than through internal development alone. |
The majority of ATMI’s semiconductor business generally tracks semiconductor wafer starts. Additional financial information about the Company and related geographic information can be found in Item 7: “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” of this Form 10-K.
We believe we have achieved a leadership position in certain high-performance semiconductor materials, materials packaging, and materials delivery systems for the microelectronics market by focusing on providing solutions to our customers that allow them to make faster, more advanced, or less expensive devices while improving their manufacturing asset productivity and production yields. We also focus on partnering with customers to bring new technologies into high-volume production as quickly and efficiently as possible. ATMI plans to continue to focus on leveraging our core technologies to create new high-growth product lines, including growing our leadership position in advanced interconnect applications, which today is focused on copper.
ATMI’s operations comprise one operating business segment.
ATMI’s Strategy
ATMI’s strategic intent is to be the source of process efficiency solutions to technology-driven customers by providing innovative materials and related delivery systems and technologies to:
| |
| • | Focus development and application engineering initiatives with the leading manufacturers to provide next generation performance materials and process solutions; |
| |
| • | Target high-growth, high-margin specialty markets that use ATMI’s core materials and packaging technologies and require products that are consumed in the production process; |
| |
| • | Add value through performance materials packaging, dispensing, and process technologies designed to meet the demands of users for greater levels of purity, productivity, safety, environmental responsiveness, and speed; |
| |
| • | Significantly shorten new product development time lines and facilitate the development of next generation materials through the use of a combinatorial science-based research approach and HPD capabilities; |
| |
| • | Leverage ATMI’s technology leadership and financial strength by investing extensively to develop proprietary and patented materials and process solutions, which the Company uses to quickly commercialize new offerings for customers; |
| |
| • | Form strategic alliances, including joint development programs and collaborative marketing efforts, to accelerate the introduction of ATMI’s products into existing and new markets; and |
| |
| • | Deploy existing technologies into new markets and bring sustainable solutions to emerging global issues such as the growth in electronic waste. |
In summary, ATMI’s strategy does not encompass a “traditional” materials supplier-to-customer relationship. In those relationships, suppliers tend to provide materials to customers based solely on the cost, quantity, and quality of the materials being supplied. Instead, ATMI works to develop partnerships with its customers based on our ability to improve the process efficiency of customers’ development, scale-up, manufacturing and supply chain processes, thereby reducing customers’ total cost of ownership. ATMI seeks to provide value to its customers through the use of its technical capabilities, and applications knowledge in a manner that changes its commercial relationship with those customers to one of value-sharing.
Microelectronics Products and Processes
ATMI believes it is among the most innovative suppliers of high-purity materials and related delivery systems and technologies. Products serving the integrated circuit (“IC”) fabrication market represent the largest portion of ATMI’s business and development activities. The principal drivers for this market are cost, yield, speed, utilization of capital, and risk reduction. The success of an electronic component or device is driven by the increased functionality it can deliver at a lower cost. Yield and capital utilization are significant drivers for the IC industry due to the implications on throughput and financial return, and the challenge is compounded by the requirement to manufacture devices for increasingly complex advanced technology generations. In an industry where the capital infrastructure is significant and product life cycles are short, the ability to bring the next generation technology rapidly to market can make a significant difference in our customers’ success. ATMI’s ability to shorten deployment of production-ready solutions is critical to our success.
Ion Implantation. The primary issues for IC manufacturers are production throughput, cost, and safety because of the hazardous properties of the implant gases used. ATMI’s patented Safe Delivery Source® ("SDS®") solutions use a standard gas cylinder containing a carbon-based adsorbent material. The cylinder is filled with gas under conditions such that the gas is adsorbed onto the adsorbent material at sub-atmospheric pressure. Sub-atmospheric storage of hazardous gases minimizes potential leaks of gas during transportation and use, thus providing significant safety and environmental improvements over traditional high-pressure and mechanical cylinders. In addition, SDS products allow more process gas to be stored in the cylinder, providing significantly higher rates of productivity than traditional methods of gas delivery used in ion implantation manufacturing processes. These advantages have led the majority of significant chip manufacturers to adopt this technology as the industry standard for dopant gas delivery. Materials packaged in SDS systems include primarily arsine, phosphine, germanium and boron trifluoride. The third generation of SDS products, called SDS3, maintains all the inherent safety features of previous generation SDS products, but dramatically increases the gas storage capacity by using a new adsorbent. The two to three times capacity improvement over the previous SDS products allows ion implanter users to reduce tool down time, resulting in significant cost savings for our customers. We also offer Vacuum Actuated Cylinders (“VAC®”), a complementary technology to SDS where select implant gases are stored under high pressure but delivered sub-atmospherically.
Copper Integration. ATMI believes it is a market leader in copper electroplating materials and processes in semiconductor development and manufacturing with our Viaform® product, which includes inorganic and proprietary organic molecules that provide the wiring for copper interconnects allowing manufacturers to eliminate processing steps. ATMI also focuses on the total copper integration scheme with post-chemical mechanical planarization (“CMP”) cleaning solutions developed using our HPD capability, which includes knowledge-rich, combinatorial science experiments to deliver the best possible solution.
ATMI employs combinatorial-science based methods for materials discovery, unit process development and device integration in support of our customers’ needs to develop new materials in response to the challenges of decreasing node sizes. Our experience in materials development and packaging combined with these capabilities bring the unique ability to provide massively parallel experimentation for materials screening, process window characterization, device integration and performance optimization.
Deposition. Several processes for depositing thin films such as chemical vapor deposition (“CVD”) and atomic layer deposition (“ALD”) processes are enabled by advanced liquid, gaseous and solid precursors. ATMI is well-positioned for the incorporation of ALD processes by the semiconductor industry with its ProE-Vap® ampoule. This proprietary container allows for reliable delivery of low volatility solid precursors required for processes that demand ALD, like high-k gates. ATMI has successfully adopted the carbon adsorption technology used in SDS and introduced products for semiconductor deposition processes marketed under the SAGE® brand. These applications include: low-k plasma-enhanced deposition, or “PE-CVD”, processes using low-k materials, pre-metal dielectric high-density plasma, or “HDP-CVD”, and films using phosphine gases and thermal deposition processes using germane gases.
Surface Preparation. ATMI’s ST and AP photoresist strip and post-CMP cleaning materials are proprietary chemistries used for applications such as semiconductor post-etch residue removal, wafer etching, organics removal, negative resist removal, edge bead removal, and corrosion prevention.
Materials Packaging. ATMI’s NOWPak® liner technologies and container assemblies form the basis for its high-purity liquid materials packaging and dispensing system product portfolio for applications in IC fabrication and flat-panel display. BrightPak™, our next-generation liquid containment and delivery system, addresses the requirements of advanced photolithography.
Collaborative Arrangements. ATMI works collaboratively with customers on specific projects to develop next-generation materials.
Raw Materials
We use a broad range of specialty and commodity chemicals and polymers in the development of our products, including parts and sub-assemblies that are obtained from outside suppliers. We seek, where possible, to have several sources of supply for all of these materials. Although we may, in some instances, rely on a single or a limited number of suppliers, or upon suppliers in a single country, for some of these materials, we have not experienced any sustained interruption in production or the supply of these materials and do not anticipate any significant difficulties in obtaining the materials necessary to manufacture our products.
Working Capital
In the ordinary course of our business, we maintain an adequate level of working capital at all times to support business needs. We carry adequate finished goods inventories to meet our customers’ delivery requirements. SDS related finished goods inventories increased in 2012 as a result of the transition of business activities from Matheson to us and this increase continued in 2013 as we prepared to bring our new factory in JangAn, Korea on-line. We generally do not provide customers with rights of return (with the exception of standard warranty provisions, which historically have not been material) and we generally do not provide customers extended payment terms beyond 90 days.
Customers, Sales, and Marketing
ATMI sells and distributes its products worldwide primarily through a direct global sales and service organization. For a breakdown of revenue by geography, see Note 15 in the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements (Part II, Item 8 of this Form 10-K). Also, for detail regarding revenue by product type, see Note 14 in the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements (Part II, Item 8 of this Form 10-K). ATMI markets and sells its materials products to end-use customers, chemical suppliers, and original equipment manufacturers (“OEMs”) through its direct sales force in North America, Europe, Taiwan, South Korea, Japan, China, and Singapore, with limited use of regional manufacturing representatives in certain parts of Asia and Europe. High-purity materials packaging containers are generally sold to chemical suppliers, who sell their high-purity chemicals in these containers at the request of end-users. Through October 2011, ATMI sold its SDS products for ion implant applications directly to certain end-users and through an exclusive distribution agreement with Matheson Tri-Gas, Inc. ("Matheson"). During the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011, ATMI recognized $0.2 million, $6.9 million, and $65.8 million of revenues from Matheson, which represented an immaterial percent, 1.9 percent, and 18.7 percent of our revenues for each of these years, respectively. ATMI’s 2012 revenues from Matheson are associated with transition activities in Asia during first half of the year. On October 31, 2011, ATMI entered into an agreement with Matheson which terminated their exclusive license, manufacturing and distribution rights for SDS in exchange for a $95 million cash payment by ATMI, and payments for the repurchase by ATMI of certain inventory in the Matheson distribution channel. During the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011, respectively, ATMI recognized revenues from Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Corporation (“TSMC”), of $53.8 million, $48.1 million, and $32.0 million, which represented 14.9 percent, 13.1 percent, and 9.1 percent of our revenues for these periods. During the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011, respectively, ATMI recognized revenues from Samsung, a leading global integrated circuit manufacturer, of $50.7 million, $57.3 million, and $47.6 million, which represented 14.1 percent, 15.7 percent, and 13.5 percent of our revenues for these periods. During the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011, respectively, ATMI recognized revenues from United Microelectronics Corporation (“UMC”), of $37.7 million, $44.7 million, and $48.7 million, which represented 10.4 percent, 12.2 percent, and 13.8 percent of our revenues for these periods. There are no material seasonal effects on our business. The global nature of our business and the significance of our foreign operations expose us to certain risks in the countries in which we operate, including political and economic stability, the adequacy of country infrastructure and labor resources, currency fluctuations and controls, compliance with foreign laws and intellectual property protection. Investors and others should consider the cautionary statements and risk factors discussed in Item 1A below.
Manufacturing
This table summarizes the locations, products manufactured and size of ATMI’s various manufacturing facilities as of December 31, 2013.
|
| | | | |
| Location | | Products | | Square Footage |
| Anseong, South Korea | | • CVD materials | | 13,000 |
| Anseong, South Korea | | • high-purity materials packaging systems | | 10,000 |
Bloomington, MN (2) | | • high-purity materials packaging systems | | 68,000 |
Brussels, Belgium (1) | | • high efficiency bioreactor solutions | | 22,000 |
| Burnet, TX | | • liquid materials and delivery systems | | 77,000 |
| Danbury, CT | | • gas delivery systems | | 73,000 |
Hoegaarden, Belgium (1) | | • high-purity materials packaging and mixing systems | | 74,000 |
| JangAn, South Korea | | • high-purity materials packaging and gas delivery systems | | 127,000 |
| |
| (1) | These facilities are associated with the LifeSciences business that are accounted for as discontinued operations at December 31, 2013. These facilities were sold to or the associated lease was transferred to Pall Corporation upon the completion of the closing of the Share and Asset Purchase Agreement. Refer to Note 2 for additional information. |
| |
| (2) | A portion of this facility is used for LifeSciences related manufacturing and will be sublet to Pall Corporation during the post-closing transition period. |
We use contract manufacturers for certain of our materials and delivery equipment products, both in the U.S. and Asia.
During 2013 we made significant progress in the construction of our new state-of-the-art manufacturing facility in JangAn, Gyeonggi province, South Korea. We expect to begin high volume production of certain products in 2014. The JangAn facility will manufacture a range of products for customers in the semiconductor manufacturing market, including: SDS® and VAC® gas delivery systems and materials for semiconductor and solar ion implant applications; NOWPak® liner-based liquid delivery systems used in photolithography and display applications; and advanced materials used primarily for leading-edge semiconductor thin film deposition, surface preparation and post-CMP cleaning applications.
Competition
ATMI’s primary competitors include Air Products and Chemicals (Electronics Division), DuPont Electronic Technologies, Dow Chemical Company (including Rohm and Haas), BASF and Air Liquide as well as several smaller companies that specialize in niche markets.
ATMI’s SDS products (using adsorbent-based delivery technology) face competition from Praxair, Inc., and others, who have a mechanical-based product approach to delivering gas at sub-atmospheric pressure which currently comprise a small portion of the market. Several companies compete with high-pressure gas cylinders and solid sources. There are numerous domestic and foreign companies that offer products that compete with ATMI’s materials, materials packaging and materials delivery systems.
ATMI believes that its ability to compete in the markets for containers and dispensing systems is dependent largely upon its patented high-purity material packaging technology and its proven ability to enhance and improve its products and technologies. Our NOWPak and BrightPak products primarily compete with glass and plastic bottle manufacturers.
ATMI competes in established markets based on our ability to innovate and on product performance, process efficiency, safety and price. In new and emerging markets we compete based on our ability to develop innovative products that fulfill new and changing customer needs in an efficient, cost-effective manner. Increased competition has, and may continue to, affect the prices we are able to charge for our products. In addition, our competitors could own or could obtain intellectual property rights which could restrict our ability to market our existing products and/or to innovate and develop new products.
Research and Development
The Company’s R&D expenses consist of personnel and other direct and indirect costs for internally funded project development, including the use of outside service providers. ATMI also participates in joint development efforts with several key semiconductor manufacturers, advanced technology developers, and semiconductor equipment manufacturers. Total expenses for R&D for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011 were $55.7 million, $47.3 million, and $46.8 million, respectively. Total research and development expenditures represented 15.4 percent, 12.9 percent, and 13.3 percent of revenues in 2013, 2012 and 2011, respectively.
ATMI has made significant investments to create global HPD capabilities that incorporate high-productivity screening tools to more rapidly create new materials required by our customers. These capabilities allow us to pursue a wider window of material possibilities, in a shorter time, utilizing fewer resources compared to previous methods. We are currently using our HPD capabilities to solve customers’ materials challenges in multiple applications such as post-CMP cleaning, copper post-etch residue removal and others - all areas that pose substantial development hurdles for our customers in the race to transition to the next technology nodes.
During the fourth quarter of 2013, we completed negotiations with Intermolecular, Inc., which resulted in the discontinuation of site, maintenance, and license support for certain long-lived HPD assets. In accordance with the provisions of ASC 360 “Property, Plant and Equipment”, long-lived assets held and used with a carrying amount of $10.8 million and the related prepaid support fees with a carrying amount of $0.7 million were deemed to be impaired and we recorded a charge, which is included in the caption "Research and development" in the consolidated statements of operations.
Strategic Alliances
ATMI forms strategic alliances, including joint development programs and collaborative marketing efforts, to develop new products and to accelerate the introduction of its products. These programs have led to significant technological advances, including the development of proprietary advanced materials and semiconductor manufacturing processes. In October 2011, ATMI terminated its exclusive license, manufacture, and distribution agreement with Matheson, whereby ATMI had granted licensing rights for the manufacturing and worldwide distribution of certain SDS products to Matheson. Following a transition period of two years ATMI now manufactures substantially all of its SDS products for worldwide distribution. ATMI has a strategic alliance with Enthone, Inc. (“Enthone”), a subsidiary of Alent plc, pursuant to which ATMI purchased the exclusive worldwide marketing and distribution rights to Enthone’s copper ECD products, including its ViaForm products, through 2014, subject to automatic renewal upon satisfaction of certain conditions which ATMI has met. Under the terms of the agreement, Enthone continues to manufacture the ViaForm products for ATMI. ATMI holds a minority equity interest in Intermolecular, Inc. (“Intermolecular”), has purchased HPD tools from Intermolecular, and has dedicated development resources with multiple key customers using this technology platform. ATMI has a minority equity interest in Anji Microelectronics Co., Ltd., with operations in Shanghai, China, as well as marketing and licensing agreements around advanced semiconductor post-etch cleaning materials. ATMI has a minority equity investment in Lake LED Materials, Co., LTD (“Lake LED”), a South Korean company. We have also formed a strategic alliance with Lake LED focused on providing metal organic precursors to the light emitting diode (“LED”) market for customers outside of Asia. In October 2012, ATMI acquired additional commercial rights to customers and exclusive intellectual property rights related to our eVOLV™ recycling technology in exchange for cash consideration and the return of our equity interest in Green Lyon Group, Inc. These alliances and programs enhance ATMI’s core technology base and promote the introduction of new and innovative products.
Backlog
Substantial portions of our business are conducted with open-ended supply contracts and / or consignment agreements that do not specify quantities. The Company does not believe that backlog as of any particular date is indicative of future results.
Patents and Proprietary Rights
ATMI has made, and continues to make, a significant investment in securing intellectual property protection for its technology and products. ATMI seeks to protect its technology by, among other things, filing patent applications where appropriate. The Company also relies upon trade secrets, know-how, continuing technological innovation, and licensing opportunities to help develop and maintain its competitive position.
As of December 31, 2013, ATMI owns or controls approximately 318 United States patents and has approximately 140 current United States patent applications pending. Foreign counterparts of certain of these applications have been filed, or may be filed at an appropriate time. ATMI decides on a case-by-case basis whether, and in which countries, it will file counterparts of a United States patent application. ATMI’s United States patents expire between approximately 2014 and 2031. ATMI also holds approximately 19 United States registered trademarks.
ATMI requires all employees, outside scientific collaborators, sponsored researchers, and other advisors and consultants who are provided confidential information to execute confidentiality agreements upon the commencement of employment or consulting relationships with the Company. These agreements generally provide that all confidential information developed or made known to the entity or individual during the course of the entity’s or individual’s relationship with ATMI is to be kept confidential and not disclosed to third parties except in specific circumstances. All of ATMI’s employees have entered into agreements providing for the assignment of rights to inventions made by them while employed by the Company.
Environmental and Social Considerations
Regulation. ATMI uses hazardous materials and generates regulated waste streams as part of its manufacturing, processing and R&D activities. As a result, the Company is subject to a variety of governmental regulations related to the storage, use, transportation, and disposal of these materials. ATMI’s failure to comply with present or future laws could result in fines or other liabilities being imposed on the Company, suspension of production or a cessation of operations. Investors and others should consider the cautionary statements and risk factors discussed in Item 1A below.
Sustainability. ATMI considers the environmental sustainability of our products through our development process with the objective of ensuring we provide our customers with solutions that meet their needs and, to the extent possible, minimize environmental impact.
Conflict Minerals. ATMI supports the goals and objectives of Section 1502 of the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act (the “Act”) which requires issuers to disclose their use of conflict minerals and whether their origin was the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) or adjoining countries. ATMI is committed to sourcing materials from companies that share our values around human rights, ethics and environmental responsibility. We expect our suppliers to comply with this important legislation and meet our sustainability expectations.
Refer to website (http://investor.atmi.com/governance.cfm) for a copy of our policy.
Employees and Employee Relations
As of December 31, 2013, ATMI employed 647 individuals, including 278 in sales, marketing, and administration, 238 in operations, and 131 in research and development. ATMI has never experienced any work stoppages and considers its relations with its employees to be good.
Company Information
ATMI was incorporated under the laws of Delaware in 1997, and its predecessor company was incorporated under the laws of Delaware in 1987. ATMI’s headquarters is located at 7 Commerce Drive, Danbury, Connecticut 06810, and the telephone number is (203) 794-1100.
ATMI’s website can be found on the Internet at www.atmi.com. The website contains information about the Company and its operations. We make available free of charge through our website our Annual Reports on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, and Current Reports on Form 8-K, and amendments to these reports, as soon as reasonably practicable after we electronically file such material with, or furnish such material to, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). These reports may be accessed on our website by following the link under Investor and then clicking on Financial Information.
Any of our reports filed or furnished with the SEC can also be obtained in print by any stockholder who requests them from our Investor Relations Department:
Investor Relations
ATMI, Inc.
7 Commerce Drive
Danbury, CT 06810
Item 1A. Risk Factors
Cautionary Statements Regarding Future Results of Operations
You should read the following cautionary statements in conjunction with the factors discussed elsewhere in this and other of our filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and in materials incorporated by reference in these filings. These cautionary statements are intended to highlight material factors that may affect our financial condition and results of operations. Like other companies, we are susceptible to macroeconomic downturns in the United States or abroad that may affect the general economic climate and our performance and the performance of our customers. Similarly, the price of our common stock is subject to volatility because of fluctuations in general market conditions, differences in our results of operations from estimates and projections generated by the investment community, and other factors beyond our control.
Our merger with Entegris could be delayed or fail to close, which could adversely affect our financial condition and could negatively impact our stock price.
On February 4, 2014, we entered into an agreement and plan of merger pursuant to which we agreed to be merged into a wholly owned subsidiary of Entegris. We will incur significant transaction costs relating to the merger, including legal, financial advisory, and other expenses. In general, these expenses are payable by us whether or not the merger is completed. If the merger is not completed under specific circumstances provided in the agreement and plan of merger, we may be required to pay Entergris a termination fee of $30 million. The payment of such transaction costs or termination fees could have an adverse effect on our financial condition, results of operations or cash flows. In addition, we could be subject to litigation in the event the merger is not consummated, which could subject us to significant liability for damages and result in the incurrence of substantial legal fees. The current price of our stock may reflect an assumption that the pending merger will occur and failure to complete the merger could result in a decline in our stock price.
We may encounter difficulties or unforeseen challenges supporting Pall Corporation during the Transition Services period.
We may encounter difficulty or unforeseen challenges in providing transition services to Pall Corporation in accordance with the terms of the Transition Services Agreement related to the sale of the LifeSciences business. These challenges could include ensuring proper data segregation in our systems and managing our resources effectively to ensure we adequately support both businesses.
Our profit margins may be adversely affected by a number of factors.
Our profit margins may be adversely affected in the future by a number of factors, including price reductions, decreases in our shipment volume, improvements in our customers' abilities to efficiently use our chemistries, reductions in, or obsolescence of, our inventory, shifts in our product mix and changes in foreign currency exchange rates. Many of our expenses, particularly those relating to capital equipment and manufacturing overhead, are fixed in the short term. Accordingly, reduced demand for our products and services can cause our fixed production costs to be allocated across reduced production volumes, which can adversely affect our gross margin and profitability, and reduced demand could adversely affect our performance. Our ability to reduce expenses is further constrained because we must continue to invest in research and development to maintain our competitive position and to maintain service and support for our existing global customer base.
Cyclicality in the markets we sell to may adversely affect our performance.
The semiconductor equipment market has historically been cyclical and subject to significant and often rapid increases or decreases in demand. These changes could adversely affect our results of operations and could have an adverse effect on the market price of our common stock. Our results of operations have been adversely affected, and may be further affected in the future, if demand for semiconductors, or devices that use semiconductors, or flat panels products decreases or grows at a significantly slower pace than has historically occurred. Subsequent upturns in the markets which we serve have historically been characterized by sudden increased product demand and production capacity constraints. We may have difficulty reacting quickly enough to a sudden upturn in demand for our products and may incur significant expediting and manufacturing costs to meet a rapid increase in customer demand.
Global economic crisis and uncertainty in financial markets could materially and adversely affect our business and results of operations.
On an ongoing basis, our business may be affected by economic down-turns which could impact the volatility and liquidity of financial and credit markets, the general global economy, and factors such as inflationary or deflationary pressures yielding other market or economic challenges. There can be no assurance that there will not be deterioration in credit and financial markets affecting consumer confidence in economic conditions. In addition, financial difficulties experienced by our suppliers, distributors or customers could result in product delays, increased accounts receivable defaults and inventory challenges. Similarly, the price of our common stock is subject to volatility due to fluctuations in general market conditions, differences in our results of operations from estimates and projections generated by the investment community, and other factors beyond our control.
Our business could be adversely affected if we cannot protect our proprietary technology or if we infringe on the proprietary technology of others.
Our proprietary technology supports our ability to compete effectively with other companies. Although we have been awarded, have filed applications for or have been licensed under numerous patents in the United States and other countries, these patents may not fully protect our technology or competitive position. Further, our competitors may apply for and obtain patents that will restrict our ability to make and sell our products.
Our competitors may intentionally infringe our patents. Third parties may also assert infringement claims against us in the future. Litigation may be necessary to enforce patents issued to us, to protect our trade secrets or know-how, to defend ourselves against claimed infringement of the rights of others or to determine the scope and validity of the proprietary rights of others. The defense and prosecution of patent suits are both costly and time consuming, even if the outcome is favorable to us. Outside the United States, in particular, such proceedings can be extremely expensive and their outcome very unpredictable. An adverse outcome in the defense of a patent suit could cause us to lose proprietary rights, subject us to significant liabilities to third parties or require us to license rights from third parties or to cease selling our products. Any of these events could have a material adverse effect on our business, operating results and financial condition. We also rely on unpatented proprietary technology that others may independently develop or otherwise obtain access to. Our inability to maintain the proprietary nature of our technologies could negatively affect our revenues and earnings.
The loss of or significant curtailment of purchases by any of our largest customers could adversely affect our results of operations.
While we generate revenue from hundreds of customers worldwide, in 2013, approximately 76 percent of our revenues were generated by 20 customers. The loss of or significant curtailment of purchases by one or more of our top customers, including curtailments due to a change in the design or manufacturing sourcing policies or practices of these customers or the timing of customer inventory adjustments may adversely affect our results of operations. Our customers and their customers aggressive management of inventory has already adversely affected our results of operations in the past and may continue to adversely affect future results of operations.
Customer driven pricing pressure may adversely affect our average selling prices.
We face aggressive cost-containment pressures from our customers. There can be no assurances that we will be able to maintain current prices in the face of continuing pricing pressures. Over time, the average price for our products may decline as the markets for these products become more competitive. Any material reduction in product prices could negatively affect both revenues and profits.
Our revenues and earnings could be negatively affected if we cannot anticipate market trends, enhance our existing products and processes, develop and commercialize new products and processes, and identify and consummate strategic acquisitions.
We believe that our future success will depend, in part, upon our ability to anticipate rapidly changing technologies and market trends, to enhance our existing products and processes, to develop and commercialize new products and processes, and to expand through selected acquisitions of technologies or businesses or other strategic alliances. The microelectronics industry markets we serve undergo frequent technological changes, which in turn create demand for new and improved products and process technologies. We may not be able to improve our existing products and process technologies or to develop and market new products and technologies that will be cost-effective or introduced in a timely manner or accepted in the marketplace. We may not be able to leverage our knowledge to make full use of combinatorial science and HPD capabilities as an effective market offering for our customers. Our failure to develop or introduce enhanced and new products and processes in a timely manner may negatively affect our revenues and earnings, and result in a potential impairment of assets. Management considers, on a continuing basis, potential acquisitions of technologies and businesses and other strategic alliances, some of which may be material to us. However, we cannot be assured that we will identify or succeed in consummating transactions with suitable acquisition candidates or alliance partners in the future.
We may have difficulty obtaining the resources or products we need for manufacturing or assembling our products or operating other aspects of our business, which could adversely affect our ability to meet demand for our products and may increase our costs.
We have hundreds of suppliers providing various materials that we use in the production of our products and other aspects of our business, and we seek, where possible, to have several sources of supply for all of these materials. However, we may rely on a single or a limited number of suppliers, or upon suppliers in a single country, for certain of these materials. The inability of such suppliers to deliver adequate supplies of reasonable quality production materials or other supplies could disrupt our production process. In addition, production could be disrupted by the unavailability of the resources used in production such as electricity, chemicals, and gases. The unavailability or reduced availability of the materials or resources we use in our business may require us to reduce production of products or may require us to incur additional costs in order to obtain an adequate supply of these materials or resources. The occurrence of any of these events could adversely affect our business and results of operations.
We face intense competition from a variety of sources, including larger companies.
The markets for our products are intensely competitive. A number of domestic and international companies engage in commercial activities in the markets we serve. Many of these companies have substantially greater financial, research and development, manufacturing and sales resources than we do. In addition, as these industries evolve, other competitors may emerge. To remain competitive, we must continue to invest in and focus upon research and development and product and process innovation. We may not be successful if we cannot compete on: price, technical capabilities, quality, or customer service.
Our global manufacturing and sales activities subject us to risks associated with legal, political, economic or other changes.
We have facilities in seven countries worldwide and in 2013, approximately 83 percent of our revenues came from sales to companies outside the United States. The global nature of our business and the significance of our foreign operations expose us to certain risks in the countries in which we operate, including political and economic instability, the adequacy of country infrastructure and labor resources, currency fluctuations and controls, compliance with foreign laws and intellectual property protection, changes in export controls, health conditions, and possible disruptions in transportation networks, which could result in an adverse effect on our business operations in such countries and our results of operations.
Our results of operations could be adversely affected by fluctuations in exchange rates.
Given our current operations and large customer base outside the United States, we employ the use of forward currency exchange contracts and foreign exchange contracts designated as cash flow hedges to attempt to minimize the potentially adverse earnings effect from exchange rate fluctuations on our net balance sheet exposures. Nevertheless, in periods when the U.S. dollar significantly fluctuates in relation to the non-U.S. currencies in which we transact business, such as the Euro, Japanese Yen, the South Korean Won, and the New Taiwan Dollar, fluctuations can have an adverse effect on our revenues and results of operations. Our foreign exchange contracts designed as cash flow hedges may be less effective if the forecasted notional amount hedged differs from the actual amount of cash collected.
Our results of operations could be adversely affected by climate change and natural events in the locations in which we, our customers or our suppliers operate.
We have manufacturing and other operations in locations subject to natural events such as severe weather and earthquakes that could disrupt operations. In addition, our suppliers and customers also have operations in such locations. A natural disaster that results in a prolonged disruption to our operations, or our customers’ or suppliers’ operations, may adversely affect our results of operations and financial condition. Also, climate change poses both regulatory and physical risks that could harm our results of operations or affect the way we conduct our businesses.
Incorrect forecasts of customer demand could adversely affect our results of operations.
Our ability to match inventory and production mix with the product mix needed to fill current orders and orders to be delivered may affect our ability to meet our forecasts. In addition, when responding to customers’ requests for shorter shipment lead times, we manufacture product based on forecasts of customers’ demands. These forecasts are based on multiple assumptions. If we inaccurately forecast customer demand, we may incur expedited shipping costs to deliver products to meet customer demand or hold excess or obsolete inventory that would reduce our profit margins and could adversely affect our results of operations.
We may have difficulty managing our growth and attracting and retaining highly skilled scientific, technical, managerial and marketing personnel, which could adversely affect our revenues and increase our operating expenses.
We have historically experienced periods of growth and intend to grow our business in the future. The management of our growth requires qualified personnel, systems and other resources. Our future success will depend in part on our ability to attract and retain highly skilled scientific, technical, managerial and marketing personnel. Competition for such personnel in the industries that we serve is intense, and our competitors are often larger and more established than we are. We may not be successful in attracting and retaining qualified personnel. In addition, our expansion may also significantly strain operational, management, financial, sales and marketing and other resources. To manage growth effectively, we must continue to enhance and integrate our information technology infrastructure, systems and controls and successfully expand, train and manage our employee base. We may not be able to manage this expansion effectively, including by providing satisfactory levels of customer service and technical support. Inability to manage our growth and to attract and retain skilled personnel could have a material adverse effect on our business, operating results and financial condition.
We engage in business combinations and divestitures and asset acquisitions, and may encounter difficulties integrating acquired businesses with our current operations; therefore, we may not realize the anticipated benefits of the acquisitions.
We seek to grow, in part, through strategic business combinations and asset acquisitions. In the past several years, we have made certain acquisitions intended to complement and expand our business, and may continue to do so in the future. The success of these transactions will depend on our ability to integrate assets and retain and integrate key personnel acquired in these transactions, apply our internal controls to these acquired businesses, and cooperate with our strategic partners. We may encounter difficulties in integrating acquisitions with our operations, applying our internal controls processes to these acquisitions, and in managing strategic investments. We may also have difficulty in integrating and managing new IT environments. Furthermore, we may not realize the degree or timing of benefits we anticipate when we first enter into a transaction. Any of the foregoing could adversely affect our business and results of operations.
We face the risk of product liability claims.
The manufacture and sale of our products, which include thin film and other toxic materials, involve the risk of product liability claims. In addition, a failure of one of our products at a customer site could interrupt the business operations of the customer. Our existing insurance coverage limits may not be adequate to protect us from all liabilities that we might incur in connection with the manufacture and sale of our products if a successful product liability claim or series of product liability claims were brought against us.
We may be subject to information technology system failures, network disruptions and breaches in data security.
Information technology system failures, network disruptions and breaches of data security from cyber-attacks, employee social media use on our computers or through failure of our internet service providers and other cloud computing service providers to successfully secure their own systems could disrupt our operations causing customer communication and order management issues, unintentional disclosure of customer, employee and proprietary information, and disruption in transaction processing which could affect our reputation and reporting of financial results. While management has taken steps to address these concerns by implementing sophisticated network security, hiring competent personnel and establishing prudent internal control measures, there can be no assurance that a system failure or data security breach will not have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and operating results.
Our business is potentially subject to substantial liabilities for failure to comply with environmental regulations.
We use, generate and discharge toxic or otherwise hazardous chemicals and waste in our manufacturing, processing and research and development activities. As a result, we are subject to a variety of governmental regulations related to the storage, use and disposal of these materials. Our failure to comply with present or future laws could result in fines or other liabilities being imposed on us, suspension of production or a cessation of operations.
In addition, under federal and state statutes and regulations, a government agency may seek to recover its response costs and/or require future remedial measures from both operators and owners of property where releases of hazardous substances may have occurred (including releases by prior occupants) or are ongoing, and for which only partial indemnification may be available in some cases.
Our activities may also result in our being subject to additional regulation. Such regulations could require us to acquire significant additional equipment or to incur other substantial expenses to comply with environmental laws. Our failure to control the use of hazardous substances could subject us to substantial financial liabilities.
Our financial results or financial condition could be adversely affected by changes in accounting standards and subjective assumptions, estimates and judgments by management related to complex accounting matters.
Generally accepted accounting principles and related accounting pronouncements, implementation guidelines and interpretations with regard to a wide range of matters that are relevant to our business, such as revenue recognition, business combinations, asset impairment, inventories, fair value measurements, self-insurance, tax matters and litigation, are highly complex and involve many subjective assumptions, estimates and judgments. Changes in these rules or their interpretation or changes in underlying assumptions, estimates or judgments could significantly change our reported or expected financial performance or financial condition.
Our results of operations could be adversely affected by changes in taxation.
Because we are a multi-national company, we have a business presence in many countries and, as a result, are subject to taxation and audit by a number of taxing authorities. Tax rates vary among the jurisdictions in which we operate. Our results of operations could be affected by market opportunities or decisions we make that cause us to increase or decrease operations in one or more countries, or by changes in applicable tax rates or audits by the taxing authorities in countries in which we operate. In addition, we are subject to laws and regulations in various locations that govern the determination of which is the appropriate jurisdiction to decide when and how much profit has been earned and is subject to taxation in that jurisdiction. Changes in these laws and regulations could affect the locations where we are deemed to earn income, which could in turn affect our results of operations. We have deferred tax assets on our balance sheet. Changes in applicable tax laws and regulations could affect our ability to realize those deferred tax assets, which could also affect our results of operations. Each quarter we forecast our tax liability based on our forecast of our performance for the year. If that performance forecast changes, our forecasted tax liability may change.
Compliance with changing corporate governance regulations and public disclosures may result in additional risks and exposures.
Changing laws, regulations and standards relating to corporate governance and public disclosure, and new regulations from the SEC, have created uncertainty for public companies such as ours. One such example is the current ambiguity regarding the breadth and pace of adoption of IFRS whether by convergence or SEC mandate. These laws, regulations, and standards are subject to varying interpretations in many cases and as a result, their application in practice may evolve over time as new guidance is provided by regulatory and governing bodies. This could result in continuing uncertainty regarding compliance matters and higher costs necessitated by ongoing revisions to disclosure and governance practices and our commitment to maintaining high standards with regard thereto. As a result, our efforts to comply with evolving laws, regulations, and standards have resulted in, and are likely to continue to result in, increased selling, general, and administrative expenses and significant management time and attention. We are also monitoring the evolving establishment of SEC rules in compliance with the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act (“Dodd-Frank”) to determine the potential future effect on our disclosures and shareholders rights. One example of incremental regulation is the newly promulgated provision of Dodd-Frank regarding the disclosure of Conflict Minerals beginning in 2014.
Item 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments
None.
Item 2. Properties
This table summarizes the location and size of ATMI’s significant real properties as of December 31, 2013:
|
| | | | |
| Location | | Square Footage | | Lease / Own |
| Anseong, South Korea | | 13,000 | | Own |
| Anseong, South Korea | | 10,000 | | Lease |
Bloomington, MN(3) | | 68,000 | | Lease |
Brussels, Belgium (2) | | 22,000 | | Lease |
| Burnet, TX | | 77,000 | | Own |
| Chutung Town, Taiwan | | 18,000 | | Lease |
Danbury, CT (1) | | 31,000 | | Lease |
| Danbury, CT | | 73,000 | | Lease |
Hoegaarden, Belgium (2) | | 74,000 | | Own |
| Hsin-chu, Taiwan | | 30,000 | | Lease |
| JangAn, South Korea | | 127,000 | | Own |
| Round Rock, TX | | 15,000 | | Lease |
| Shanghai, China | | 6,000 | | Lease |
| Suwon, South Korea | | 16,000 | | Lease |
| Tempe, AZ | | 10,000 | | Lease |
| Tokyo, Japan | | 6,000 | | Lease |
| |
(2) | These facilities are associated with the LifeSciences business that are accounted for as discontinued operations at December 31, 2013. These facilities were sold, or the associated lease was transferred for facilities held under lease, to Pall Corporation, in conjunction with the closing under the Share and Asset Purchase Agreement. Refer to Part I Item 1, contained herein, for additional information. |
| |
(3) | A portion of this facility is used for LifeSciences related manufacturing and will be sublet to Pall Corporation during the post-closing transition period. |
ATMI also leases other sales offices throughout the world, each one of which occupies 5,000 or fewer square feet.
Our fixed assets as of December 31, 2013 include the manufacturing facilities and non-manufacturing facilities such as sales and administrative offices, including leasehold improvements made to those facilities under non-cancelable leases, set forth in the table above and a substantial quantity of machinery and equipment. The facilities, leasehold improvements, machinery and equipment in use as of December 31, 2013 are in good operating condition, are well-maintained and substantially all are in regular use.
We believe that the fixed assets capitalized and facilities in operation at December 31, 2013 for the production of our products are suitable and adequate for the business conducted therein in the current business environment and have sufficient production capacity for their present intended purposes. We continue to assess the required amount of capital spending necessary for the incremental demand for our SDS products. In 2013, we made significant progress in the construction of our new state-of-the-art manufacturing facility in JangAn, Gyeonggi province, South Korea. We expect to begin high-volume production of certain products at this new facility in 2014. Utilization of our facilities varies based on demand for our products. We continuously review our anticipated requirements for facilities and, based on that review, may from time to time adjust our facility plans.
Item 3. Legal Proceedings
ATMI is, from time to time, involved in legal actions, governmental audits, and proceedings relating to various matters incidental to its business including contract disputes, intellectual property disputes, product liability claims, employment matters, export and trade matters, and environmental claims. While the outcome of such matters cannot be predicted with certainty, in the opinion of management, after reviewing such matters and consulting with ATMI’s counsel and considering any applicable insurance or indemnifications, any liability which may ultimately be incurred is not expected to materially affect ATMI’s consolidated financial position, cash flows or results of operations.
On or about February 7 and 28, 2014, two putative class action complaints challenging the Merger were filed in the Superior Court of the State of Connecticut, Judicial District of Danbury, captioned Andrew Pace v. ATMI, Inc., et al. and Dolores Carter v. ATMI, Inc., et al., respectively. The complaints were filed on behalf of the public shareholders of ATMI and name as defendants ATMI, the members of its Board of Directors, Entegris and Merger Sub. The complaints generally allege that ATMI’s directors breached their fiduciary duties to ATMI’s shareholders by agreeing to sell ATMI for inadequate and unfair consideration and pursuant to an inadequate and unfair process, and that ATMI, Entegris and Merger Sub aided and abetted those alleged breaches. The complaint in the Carter action also alleges purported disclosure deficiencies in the preliminary proxy statement for the Merger that ATMI filed with the SEC on February 25, 2014. The complaints seek, among other things, to enjoin the Merger. ATMI believes that the claims have no merit and no loss contingency range can be estimated at this time.
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures
Not applicable.
PART II
Item 5. Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
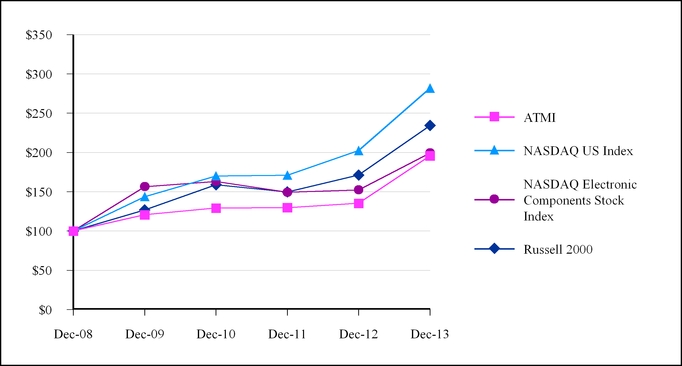
The following graph compares the cumulative total stockholder return on ATMI’s common stock with the return on the Total Return Index for the NASDAQ Global Select Market (NASDAQ US Index), the Russell 2000 Index and the NASDAQ Electronic Components Stock Index. The measurement assumes a $100 investment as of December 31, 2008 with all dividends, if any, reinvested. The data presented are on an annual basis for the five years ended December 31, 2013. The performance shown is not necessarily indicative of future performance.
|
| | | | | | | | |
| Relative Stock Performance |
| Date | | NASDAQ
US Index | | NASDAQ Electronic Components Stock Index | | ATMI | | Russell 2000 |
| 12/31/2008 | | 100.00 | | 100.00 | | 100.00 | | 100.00 |
| 12/31/2009 | | 143.74 | | 156.46 | | 120.67 | | 126.81 |
| 12/31/2010 | | 170.17 | | 163.16 | | 129.23 | | 158.90 |
| 12/31/2011 | | 171.08 | | 149.21 | | 129.81 | | 149.78 |
| 12/31/2012 | | 202.40 | | 152.30 | | 135.32 | | 171.24 |
| 12/31/2013 | | 281.91 | | 199.40 | | 195.79 | | 234.28 |
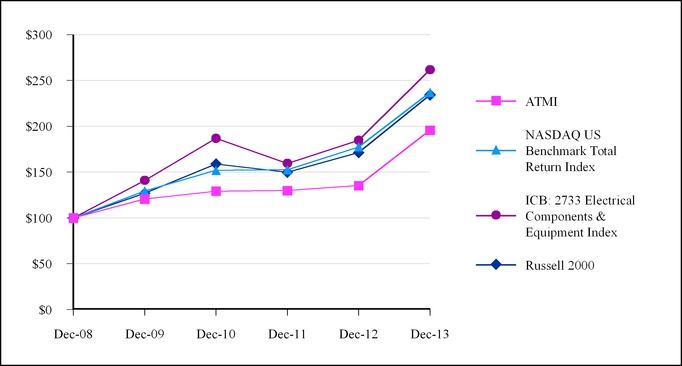
As a result of a change in the total return data made available to us through our vendor provider, our performance graphs going forward will be presented using a comparable index provided by NASDAQ OMX Global Indexes replacing the NASDAQ Global Select Market (NASDAQ US Index) with the NASDAQ US Benchmark Total Return Index and the NASDAQ Electronic Components Stock Index with the ICB: 2733 Electrical Components & Equipment Index.
|
| | | | | | | | |
| Relative Stock Performance |
| Date | | NASDAQ US Benchmark Total Return Index | | ICB: 2733 Electrical Components & Equipment Index | | ATMI | | Russell 2000 |
| 12/31/2008 | | 100.00 | | 100.00 | | 100.00 | | 100.00 |
| 12/31/2009 | | 129.26 | | 140.89 | | 120.67 | | 126.81 |
| 12/31/2010 | | 151.94 | | 186.90 | | 129.23 | | 158.90 |
| 12/31/2011 | | 152.42 | | 159.48 | | 129.81 | | 149.78 |
| 12/31/2012 | | 177.46 | | 184.71 | | 135.32 | | 171.24 |
| 12/31/2013 | | 236.88 | | 261.67 | | 195.79 | | 234.28 |
The cumulative total stockholder return graph and related data provided in Part II Item 5 of this Form 10-K is not “soliciting material,” is not deemed filed with the SEC and is not to be incorporated by reference in any filing by us under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”), or the Exchange Act, whether made before or after the date hereof and irrespective of any general incorporation language in any such filing.
The common stock of ATMI has traded on the NASDAQ Global Select Market under the symbol ATMI since October 13, 1997, and the common stock of our predecessor company traded under that symbol from 1993 until October 12, 1997. This table sets forth, for the periods indicated, the high and low sales price for the common stock as reported on the NASDAQ Global Select Market:
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | | High | | Low |
| Fiscal year ended December 31, 2013 | | | | |
| 1st Quarter | | $ | 23.33 |
| | $ | 19.89 |
|
| 2nd Quarter | | 24.67 |
| | 20.36 |
|
| 3rd Quarter | | 27.53 |
| | 23.55 |
|
| 4th Quarter | | 31.44 |
| | 25.88 |
|
| Fiscal year ended December 31, 2012 | | | | |
| 1st Quarter | | $ | 25.05 |
| | $ | 20.04 |
|
| 2nd Quarter | | 23.83 |
| | 19.30 |
|
| 3rd Quarter | | 21.00 |
| | 18.27 |
|
| 4th Quarter | | 21.00 |
| | 17.59 |
|
As of January 31, 2013, there were approximately 141 holders of record of our common stock.
We have never paid cash dividends on our common stock and have no current plans to do so. The merger agreement with Entegris restricts us from paying any dividends without their consent. Our present policy is to retain earnings, if any, to provide funds for the operation and expansion of our business.
The Transfer Agent and Registrar for ATMI is Continental Stock Transfer & Trust Company.
Purchases of Equity Securities – In August 2010, the Company’s Board of Directors approved a share repurchase program for up to $50.0 million of ATMI common stock. Under the terms of the share repurchase program, repurchases are made from time to time in open market transactions at prevailing market prices or in privately negotiated transactions. Management determines the timing and amount of purchases under the program based upon market conditions or other factors. The program, which has no expiration date, does not require the Company to purchase any specific number or amount of shares and may be suspended or reinstated at any time at the Company’s discretion and without notice.
There were no share repurchases during the three months ended December 31, 2013 of any of our securities registered under Section 12 of the Exchange Act, by or on behalf of us, or any affiliated purchaser. We withheld 2,536 shares through net share settlements during the three months ended December 31, 2013 upon the vesting of restricted stock awards to cover minimum tax withholding obligations. Our merger agreement with Entegris restricts our ability to repurchase shares.
Item 6. Selected Financial Data
These selected consolidated statements of operations for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012, 2011, 2010 and 2009 and the consolidated balance sheet data as of such dates are derived from ATMI’s audited consolidated financial statements. The data below should be read in conjunction with the consolidated financial statements and notes thereto and other financial information included elsewhere in this Form 10-K (in thousands, except per share data).
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 | | 2009 | |
| Consolidated Statements of Operations: | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenues | $ | 360,959 |
| | $ | 365,849 |
| (5) | $ | 351,823 |
| (6) | $ | 336,519 |
| | $ | 230,707 |
| |
| Cost of revenues | 185,013 |
| | 179,258 |
| | 181,101 |
| (7) | 170,740 |
| | 135,653 |
| (14) |
| Gross profit | 175,946 |
| | 186,591 |
| | 170,722 |
| | 165,779 |
| | 95,054 |
| |
| Operating expenses: | | | | | | |
| |
| |
| Research and development | 55,666 |
| (1) | 47,286 |
| | 46,767 |
| | 45,029 |
| | 34,020 |
| (15) |
| Selling, general and administrative | 72,884 |
| (2) | 73,521 |
| | 68,711 |
| (8) | 72,696 |
| | 66,233 |
| (16) |
| Contract termination | — |
| | — |
| | 84,590 |
| (9) | — |
| | — |
| |
| Total operating expenses | 128,550 |
| | 120,807 |
| | 200,068 |
| | 117,725 |
| | 100,253 |
| |
| Operating income (loss) | 47,396 |
| | 65,784 |
| | (29,346 | ) | | 48,054 |
| | (5,199 | ) | |
| Interest income | 944 |
| | 900 |
| | 1,110 |
| | 746 |
| | 1,173 |
| |
| Other income (expense), net | 2,616 |
| (3) | (58 | ) | (6) | (993 | ) | (10) | 3,488 |
| (12) | (2,233 | ) | (17) |
| Income (loss) before income taxes | 50,956 |
| | 66,626 |
| | (29,229 | ) | | 52,288 |
| | (6,259 | ) | |
| Provision (benefit) for income taxes | 12,197 |
| (4) | 18,331 |
| | (18,265 | ) | (11) | 12,665 |
| (13) | (4,475 | ) | |
| Income (loss) from continuing operations | 38,759 |
| | 48,295 |
| | (10,964 | ) | | 39,623 |
| | (1,784 | ) | |
| Loss from discontinued operations, net of taxes | (8,594 | ) | | (5,965 | ) | | (9,055 | ) | | (117 | ) | | (4,876 | ) | |
| Net income (loss) | $ | 30,165 |
| | $ | 42,330 |
| | $ | (20,019 | ) | | $ | 39,506 |
| | $ | (6,660 | ) | |
| Earnings (loss) per common share from continuing operations — diluted | $ | 1.18 |
| | $ | 1.48 |
| | $ | (0.35 | ) | | $ | 1.24 |
| | $ | (0.06 | ) | |
| Weighted average shares outstanding — diluted | 32,751 |
| | 32,664 |
| | 31,703 |
| | 31,895 |
| | 31,398 |
| |
| Consolidated Balance Sheet Data: | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash, cash equivalents, and marketable securities (20) | 131,072 |
| | 166,179 |
| | 109,197 |
| | 147,424 |
| | 107,402 |
| |
| Working capital | 367,631 |
| | 330,646 |
| | 307,352 |
| | 319,742 |
| | 252,644 |
| |
| Total assets | 596,220 |
| | 599,153 |
| | 513,686 |
| | 533,589 |
| | 459,576 |
| (18) |
| Long-term obligations | 11,354 |
| | 12,357 |
| | 6,145 |
| | 20,031 |
| | 18,402 |
| (19) |
| Total stockholders’ equity | 529,160 |
| | 507,276 |
| | 450,331 |
| | 458,425 |
| | 411,490 |
| |
The Company has never declared any cash dividends.
| |
(1) | Includes $11.5 million impairment related to our HPD assets. |
| |
(2) | Includes $2.6 million of net severance costs in order to better streamline business activities with our customers and partners. |
| |
(3) | Includes a $3.3 million gain on sale of marketable securities. |
| |
(4) | Includes $1.8 million of tax benefits (including interest) recognized to reverse previously established reserves for uncertain tax positions due to expiration of statutes of limitation and settlements, $1.1 million of benefits for certain 2012 retroactive provisions of the American Taxpayer Relief Act of 2012, including the US R&D credit; offset by $1.3 million settlement with the South Korea taxing authority. |
| |
(5) | Includes $2.6 million in royalty revenue related to periods prior to and including 2012 associated with IP infringement settlements reached during the year. |
| |
(6) | Revenues were negatively impacted by $6.9 million due to the effects of the SDS Direct transaction which included $5.1 million of revenue reversal for inventory repurchases and an estimated $1.8 million net impact due to excess inventory in the SDS channel, which was partially offset by incremental revenues realized as a result of the transaction. |
| |
(7) | The cost of revenues were favorably impacted by $1.5 million due to the effects of the SDS Direct transaction, representing $1.1 million of cost reversals for inventory repurchased and $0.4 million estimated net effect due to excess inventory in the SDS channel, partially offset by transition service costs and incremental costs on revenues realized following the transaction. |
| |
(8) | Includes a $2.4 million benefit related to state tax credits and distribution expenses of $1.3 million related to the SDS Direct transaction. |
| |
(9) | $84.6 million contract termination charge related to the SDS Direct transaction. |
| |
(10) | Includes $1.3 million foreign exchange loss on Euro exposures partially offset by a $0.9 million investment gain. |
| |
(11) | Includes $31.0 million tax benefit associated with the $84.6 million pre-tax contract termination charge. |
| |
(12) | Includes a $0.5 million gain from the sale of a marketable security and $2.5 million gain on sale of shares of one of our equity-method investees. |
| |
(13) | Includes $1.8 million of tax benefits (including interest) recognized to reverse previously established reserves for uncertain tax positions due to expiration of statutes of limitation and settlements, and a $1.9 million charge related to changes in valuation allowances. |
| |
(14) | Includes $1.1 million charge for incremental excess and obsolete inventory related to product discontinuances and a reserve to cover expected product shelf-life issues; and a $3.1 million impairment charge for long-lived assets written down to their estimated fair values primarily related to the planned idling of manufacturing capacity of our gas products. |
| |
(15) | Includes a $1.6 million impairment charge for long-lived assets written down to their estimated fair values related primarily to idled equipment. |
| |
(16) | Includes a $1.4 million charge to increase our reserves for bad debt to cover exposures related to customer bankruptcy filings and uncertainties of collections; a $2.6 million impairment charge for long-lived assets written down to their estimated fair values primarily related to redundant enterprise management software; and a $0.6 million charge for SG&A severance costs. |
| |
(17) | Includes a $2.5 million impairment charge, primarily related to a write-down associated with an auction-rate security. |
| |
(18) | Balance has been reduced by $0.6 million related to reclassification of unrecognized tax benefits and valuation allowances. |
| |
(19) | Balance has been reduced by $0.6 million related to reclassification of unrecognized tax benefits and valuation allowances. |
| |
(20) | Includes non-current marketable securities of $2.2 million, $12.1 million, $3.3 million, $25.4 million, and $10.6 million at December 31, 2013, 2012, 2011, 2010, and 2009, respectively. |
Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
This discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations should be read together with the consolidated financial statements and the related notes thereto appearing in Item 8 of this Form 10-K.
Company Overview
We believe we are among the leading suppliers of high performance materials, materials packaging and materials delivery systems used worldwide in the manufacture of microelectronics devices. Our products consist of “front-end” semiconductor performance materials, sub-atmospheric pressure gas delivery systems for safe handling and delivery of toxic and hazardous gases to semiconductor process equipment, high-purity materials packaging and dispensing systems that allow for the reliable introduction of low volatility liquids and solids to microelectronics processes. ATMI targets both semiconductor and flat-panel display manufacturers, whose products form the foundation of microelectronics technology rapidly proliferating through the consumer products, information technology, automotive, and communications industries. The market for microelectronics devices is continually changing, which drives demand for new products and technologies at lower cost. ATMI’s customers include many of the leading semiconductor and flat-panel display manufacturers in the world who target leading-edge technologies. ATMI’s objective is to meet the demands of our microelectronics customers with solutions that maximize the efficiency of their manufacturing processes, reduce capital or operating costs, and minimize the time to develop new products and integrate them into their processes.
Use of Estimates
Preparation of our financial statements requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses. Note 1 to the consolidated financial statements in Item 8 of this Form 10-K describes the significant accounting policies used in preparation of the consolidated financial statements. Management believes the most complex and sensitive judgments, because of their significance to the Consolidated Financial Statements, result primarily from the need to make estimates about the effects of matters that are inherently uncertain. The most significant areas involving management judgments and estimates are described below. Actual results in these areas could differ from management’s estimates. These policies are determined by management and have been reviewed by ATMI’s Audit Committee.
Revenue Recognition
We recognize revenue when the following four criteria are met: (1) persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists; (2) delivery has occurred or services have been rendered; (3) the fee is fixed or determinable; and (4) collectability is reasonably assured. Revenues from product sales are generally recognized upon delivery to a common carrier when terms are equivalent to free-on-board (“FOB”) origin and upon receipt by a customer when terms are equivalent to FOB destination. In instances where final acceptance of equipment is specified by the purchase agreement, revenue is deferred until all acceptance criteria have been satisfied, except when reasonable reserves for returns can be effectively established due to substantial successful installation history for homogenous transactions. Should changes in conditions cause management to determine these criteria are not met for certain future transactions, revenue recognized for any reporting period could be adversely affected. We accrue for sales returns, warranty costs, and other allowances based on a current evaluation of our experience based on stated terms of the transactions. Should actual product failure rates or customer return experience differ from our estimates, revisions to the estimated accruals would be required.
Accounts Receivable Allowances
The allowance for doubtful accounts is established to represent our best estimate of the net realizable value of the outstanding accounts receivable balances. We estimate our allowance for doubtful accounts based on past due amounts and historical write-off experience, as well as trends and factors surrounding the credit risk of the markets we operate in and the financial viability of specific customers. In an effort to identify adverse trends, we assess the financial health of the markets we operate in and perform periodic credit evaluations of our customers and ongoing reviews of account balances and aging of receivables. Amounts are considered past due when payment has not been received within the time frame of the credit terms extended. Write-offs are charged directly against the allowance for doubtful accounts and occur only after all collection efforts have been exhausted. Actual write-offs and adjustments could differ from the allowance estimates because of unanticipated changes in the business environment as well as factors and risks surrounding specific customers.
As of December 31, 2013 and 2012 we had $0.9 million of accounts receivable allowances recorded, respectively. Although management believes these reserves are adequate, any adverse changes in market conditions may require us to record additional reserves.
Inventory Valuation Reserves
Inventory valuation reserves are established in order to report inventories at the lower of cost or market value on our consolidated balance sheets. The determination of inventory valuation reserves requires management to make estimates and judgments on the future saleability of inventories. Valuation reserves for excess, obsolete, and slow-moving inventory are estimated by comparing the inventory levels of individual parts to both future sales forecasts or production requirements and historical usage rates in order to identify inventory where the resale value or replacement value is less than inventory cost. Other factors that management considers in determining these reserves include whether individual inventory parts or chemicals meet current specifications and cannot be substituted for or reworked into a part currently being sold or used as a service part, overall market conditions, and other inventory management initiatives.
As of December 31, 2013 and 2012, we had $2.9 million of inventory valuation reserves recorded. Although management believes these reserves are adequate, any adverse changes in market conditions may require us to record additional inventory valuation reserves.
Non-marketable Equity Securities
We selectively invest in non-marketable equity securities of private companies, which range from early-stage companies that are often still defining their strategic direction to more mature companies whose products or technologies may directly support an ATMI product or initiative. Our non-marketable equity investments are recorded using cost basis or the equity method of accounting, depending on the facts and circumstances of each investment. At December 31, 2013, the carrying value of our portfolio of strategic investments in non-marketable equity securities totaled $6.6 million ($6.6 million at December 31, 2012). In certain instances, we loan funds to early-stage investees at market interest rates to enable them to focus on product and technology development. Non-marketable equity and debt securities are included in the consolidated balance sheets under the caption “Other non-current assets.” We receive regular financial information from our equity method investees typically on a one month lag.
Investments in non-marketable equity securities are inherently risky, and some of these companies are likely to fail. Their success (or lack thereof) is dependent on product development, market acceptance, operational efficiency, attracting and retaining talented professionals, and other key business success factors. In addition, depending on their future prospects, they may not be able to raise additional funds when needed or they may receive lower valuations, with less favorable investment terms than in previous financings, and the investments would likely become impaired.
We review our investments quarterly for indicators of impairment; however, for non-marketable equity securities, the impairment analysis may require significant judgment to identify events or circumstances that would likely have a significant adverse effect on the fair value of the investment. The indicators that we use to identify those events or circumstances include (a) the investee’s revenue and earnings trends relative to predefined milestones and overall business prospects, (b) the technological feasibility of the investee’s products and technologies, (c) the general market conditions in the investee’s industry or geographic area, including adverse regulatory or economic changes, (d) factors related to the investee’s ability to remain in business, such as the investee’s liquidity, and the rate at which the investee is using its cash, and (e) the investee’s receipt of additional funding at a lower valuation.
Investments identified as having an indicator of impairment are subject to further analysis to determine if the investment is other-than-temporarily impaired, in which case we write the investment down to its fair value, using the framework required by Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) 820 “Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures.” When an investee is not considered viable from a financial or technological point of view, we write down the entire investment since we consider the estimated fair market value to be nominal. If an investee obtains additional funding at a valuation lower than our carrying amount or requires a new round of equity funding to stay in operation and the new funding does not appear imminent, we presume that the investment is other-than-temporarily impaired, unless specific facts and circumstances indicate otherwise. There were no impairments recognized in our portfolio of non-marketable equity securities in 2013, 2012 or 2011.
Income Taxes
The net deferred tax asset at December 31, 2013 was $11.9 million compared to $16.8 million at December 31, 2012. For our deferred future tax benefits, we believe that our earnings during the periods when the temporary differences become deductible will be sufficient to realize the related future income tax benefits. For those jurisdictions where the expiration date of tax carryforwards or the projected operating results indicate that realization is not likely, a valuation allowance is provided.
In the ordinary course of business there is inherent uncertainty in quantifying our income tax positions. We assess our income tax positions and record tax benefits for all years subject to examination based upon management’s evaluation of the facts, circumstances and information available at the reporting date. For those tax positions where it is more likely than not that a tax benefit will be sustained, we have recorded the largest amount of tax benefit with a greater than 50 percent likelihood of being realized upon ultimate settlement with a taxing authority. For those income tax positions where it is not more likely than not that a tax benefit will be sustained, no tax benefit has been recognized in the financial statements. We adjust these unrecognized tax benefits, including any impact on the related interest and penalties, in light of changing facts and circumstances. A number of years may elapse before a particular matter for which we have established an unrecognized tax benefit is audited and fully resolved. To the extent we prevail in matters for which we have recorded an unrecognized benefit or are required to pay amounts in excess of what we have recorded, our effective tax rate in a given financial statement period could be materially affected. An unfavorable tax settlement might require use of our cash and/or result in an increase in our effective tax rate in the year of resolution. A favorable tax settlement would be recognized as a reduction in our effective tax rate in the year of resolution. For a discussion of current tax matters, refer to Note 9 to the consolidated financial statements in Item 8 of this Form 10-K.
In assessing the need for a valuation allowance, we estimate future taxable income, considering the feasibility of ongoing tax planning strategies and the realizability of tax loss carryforwards. Valuation allowances related to deferred tax assets can be affected by changes to tax laws, changes to statutory tax rates and future taxable income levels. In the event we were to determine that we would not be able to realize all or a portion of our deferred tax assets in the future, we would reduce such amounts through a charge to income in the period in which that determination is made or when tax law changes are enacted. Conversely, if we were to determine that we would be able to realize our deferred tax assets in the future in excess of the net carrying amounts, we would decrease the recorded valuation allowance through an increase to income in the period in which that determination is made. Changes in deferred tax asset valuation allowances recorded in a business combination and income tax uncertainties after the acquisition date generally will affect income tax expense.
Equity-Based Compensation
We account for awards of equity-based compensation under our employee stock plans using the fair value method. Accordingly, we estimate the grant date fair value of our equity-based awards and amortize this fair value to compensation expense over the requisite service period or vesting term.
To estimate the fair value of our stock option awards we currently use the Black-Scholes-Merton options-pricing model. The determination of the fair value of equity-based awards on the date of grant using an options-pricing model is affected by our then current stock price as well as assumptions regarding a number of complex and subjective variables. Management is required to make certain judgments for these variables which include the expected stock price volatility over the term of the awards, the expected term of options based on employee exercise behaviors, and the risk-free interest rate. For awards granted in 2010 and 2011, expected volatility is based on the historical volatility of ATMI common stock for a period shorter than the expected term of the options. We have excluded the historical volatility prior to the public announcement regarding the sale of our non-core businesses in 2004, solely because those businesses that were sold represented a significant portion of ATMI’s consolidated business and were subject to considerable cyclicality associated with the semiconductor equipment industry, which drove increased volatility in ATMI’s stock price, which we did not believe would be representative of future expected volatility. Starting in 2012, awards granted did not have any exclusions related to the determination of expected volatility. The expected term of options granted represents the period of time that options are expected to be outstanding. The risk-free rate is based on the U.S. Treasury yield curve in effect at the time of grant for a period commensurate with the estimated expected term. We recognize expense only for those awards expected to vest. If actual results are not consistent with our assumptions and judgments used in estimating key assumptions, in future periods, the stock option expense that the Company records for future grants may differ significantly from what the Company has recorded in the current period.
To estimate the fair value of our Total Shareholder Return Performance Restricted Stock Units (“TSR PRSUs”), we used a Monte-Carlo simulation of future stock prices for ATMI and the components of the Russell 2000 index. This method uses a risk-neutral framework to model future stock prices. The stock price projections are based upon estimates for the risk-free rate of return, the volatility of our stock and the others included in the Russell 2000 index, and the correlation of each stock within the Russell 2000 index. Management is required to make certain judgments for these estimates.
Equity-based compensation expense is recognized on a ratable basis over the estimated service period of the awards.
Fair Value Measurements
All of our financial assets and liabilities, measured on a recurring basis, are measured at fair value based upon Level 1 or Level 2 inputs, as defined under ASC 820. For Level 1 measurements, we use quoted prices in active markets for identical assets and liabilities. For Level 2 measurements, we use observable inputs other than Level 1 prices, such as quoted prices for similar assets and liabilities; quoted prices in markets with insufficient volume or infrequent transactions (less active markets); or model-derived valuations in which all significant inputs are observable or can be derived principally from or corroborated by observable market data for substantially the full term of the assets or liabilities. For Level 3 measurements, we use unobservable inputs to the valuation methodology that are significant to the measurement of fair value of the assets or liabilities.
We regularly review our financial assets for evidence of impairment and consider the length of the time and the extent to which the market value has been less than cost, as well as, the financial condition and near-term prospects of the issuer, including any specific event that may influence the operations of the issuer.
Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets
The assets and liabilities of acquired businesses are recorded under the purchase method of accounting at their estimated fair values at the dates of acquisition. Goodwill represents costs in excess of fair values assigned to the underlying net assets of acquired businesses.
Goodwill and intangible assets deemed to have indefinite lives are not amortized, but are subject to annual impairment testing by completing an assessment of qualitative factors to determine whether it is more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount as a basis for determining whether it is necessary to perform the two-step goodwill impairment test. We evaluate goodwill for impairment at the reported operating segment level - Micrelectronics and LifeSciences. We first assess qualitative factors to determine whether it is more likely than not that the fair value of the reporting unit is less than its carrying amount. If the qualitative assessment indicates a likelihood that the carrying amount is less than fair value, then the two-step goodwill impairment test is performed. We primarily use the income approach to determine the fair value of our reporting units. We also employ the market approach by the use of revenue and EBITDA multiple comparisons to corroborate the fair value determined using the income approach. Based on our last completed step 1 analysis, the fair value for each of our two reporting units exceeded the carrying value by more than 40 percent. We also note that the price of our common stock has increased approximately 50 percent from December 31, 2011 to December 31, 2013 with a commensurate increase in our market capitalization. At December 31, 2013, the goodwill balance from our continuing operation was $13.7 million and the balance of goodwill in our discontinued operation was $33.7 million.
Other Long-Lived Amortizable Assets
We evaluate the potential impairment of other long-lived assets when appropriate. If the carrying value of assets exceeds the sum of the undiscounted expected future cash flows, the carrying value of the asset is written down to fair value.
Related Party Transactions
The Company’s related parties are primarily unconsolidated equity affiliates. The Company did not engage in any material transactions involving related parties that included terms or other aspects that differ from those which would be negotiated with independent parties.
Results of Continuing Operations
This table shows the effect of pre-tax compensation cost arising from equity-based payment arrangements recognized in income (loss) from continuing operations (in thousands):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, |
| | | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 |
| Cost of revenues | | $ | 161 |
| | $ | 232 |
| | $ | 406 |
|
| Research and development | | 476 |
| | 612 |
| | 794 |
|
| Selling, general, and administrative | | 6,144 |
| | 6,954 |
| | 5,878 |
|
| Total equity-based compensation expense | | $ | 6,781 |
| | $ | 7,798 |
| | $ | 7,078 |
|
Year Ended December 31, 2013 Compared to Year Ended December 31, 2012
Results of Continuing Operations
The following is a summary of selected consolidated earnings information (in thousands of dollars):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, | | |
| | | 2013 | | 2012 | | % Change |
| Revenues | | $ | 360,959 |
| | $ | 365,849 |
| | (1.3 | )% |
| Cost of revenues | | 185,013 |
| | 179,258 |
| | 3.2 | % |
| Gross profit | | 175,946 |
| | 186,591 |
| | (5.7 | )% |
| Gross profit margin | | 48.7 | % | | 51.0 | % | | |
| Operating expenses: | | | | | | |
| Research and development | | 55,666 |
| | 47,286 |
| | 17.7 | % |
| Selling, general and administrative | | 72,884 |
| | 73,521 |
| | (0.9 | )% |
| Total operating expenses | | 128,550 |
| | 120,807 |
| | 6.4 | % |
| Operating income | | 47,396 |
| | 65,784 |
| | (28.0 | )% |
| Interest income | | 944 |
| | 900 |
| | 4.9 | % |
| Other income (expense), net | | 2,616 |
| | (58 | ) | | 4,610.3 | % |
| Income before income taxes | | 50,956 |
| | 66,626 |
| | (23.5 | )% |
| Provision for income taxes | | 12,197 |
| | 18,331 |
| | (33.5 | )% |
| Effective tax rate | | 23.9 | % | | 27.5 | % | | |
| Income from continuing operations | | $ | 38,759 |
| | $ | 48,295 |
| | (19.7 | )% |
| Loss from discontinued operations, net of taxes | | $ | (8,594 | ) | | $ | (5,965 | ) | | (44.1 | )% |
| Net income | | $ | 30,165 |
| | $ | 42,330 |
| | (28.7 | )% |
Analysis of Continuing Operations
Overview
2013 was a year of significant progress and change for ATMI, Inc. as we neared completion of our JangAn manufacturing facility in South Korea, recognized license revenues from our eVOLV process, completed a significant reorganization in our business to better position ourselves with customers and to streamline operations, and embarked on a review of strategic alternatives.
On December 22, 2013, ATMI, Inc. and certain of its subsidiaries and Pall Corporation, entered into a Share and Asset Purchase Agreement pursuant to which, ATMI, Inc agreed to sell to Pall Corporation all assets and liabilities primarily related to the LifeSciences business in exchange for cash proceeds of $185 million, subject to customary working capital adjustments. This transaction closed on February 20, 2014. We estimate the pre-tax gain from this transaction will be approximately $68 million, which will be recognized in the first quarter of 2014. For purposes of this Form 10-K, we have treated the LifeSciences business as a discontinued operation and have excluded the results associated with the discontinued operations from the discussion and analysis below consistent with the treatment of this discontinued operation throughout this Form 10-K.
On February 4, 2014, ATMI and Entegris, Inc. ("Entegris") entered into an Agreement and Plan of Merger pursuant to which, subject to the satisfaction or waiver of certain conditions, ATMI will merge with and into Atomic Merger Corporation, a wholly-owned subsidiary of Entegris ("Merger Sub"). Under the terms of the merger agreement, ATMI shareholders will receive $34.00 in cash, without interest or dividends, for each share of ATMI common stock they hold at the time of closing. We anticipate closing the transaction in the second quarter of 2014.
Revenues for 2013 declined as weakness in our copper materials and NowPak® products were partially offset by volume growth in SDS® and higher license revenues in eVOLV™. Gross Margins also declined approximately 2 percent in full year 2013 compared to full year 2012 due primarily to a combination of lower volume and unfavorable product mix. Also, in the fourth quarter of 2013, we recorded an $11.5 million impairment charge in Research and Development (“R&D”) related to certain of our High Productivity Development assets. Net income from continuing operations declined approximately 20 percent for the full year 2013 compared to the full year 2012.
Results of Continuing Operations
Revenue. Revenues of $361.0 million represent a decline of approximately 1 percent compared to the same period in 2012 as volume weakness in our copper materials and NowPak® product lines was partially offset by SDS volume growth and higher license revenues in eVOLV. Full year 2012 results included a one-time $2.6 million royalty. SDS revenues grew 13 percent compared to the full year 2012. Our copper materials product lines declined 9 percent in 2013 compared to 2012, driven by weak economic conditions, customer material-usage efficiencies, and, the strategic decision to stop selling certain very low margin copper plating electrolytes. Pricing reductions impacted revenues by 2 percent for 2013 compared to 2012. Negative fluctuations in the Japanese Yen decreased revenue approximately 2 percentage points in 2013. Our eVOLV™ product line generated $2.5 million revenue in 2013 an increase of $2.4 million from 2012.
Gross Profit. Gross profit margins were approximately 49 percent in 2013 compared to approximately 51 percent in 2012. Gross profit margins were down primarily due to pricing declines and the $2.6 million one-time royalty recognized in 2012.
Research and Development Expenses. Research and Development expenses ("R&D") increased $8.4 million or approximately 18 percent to $55.7 million in 2013 compared to $47.3 million in 2012. The 2013 results included an $11.5 million impairment charge related to certain of our HPD assets. In the fourth quarter of 2013, we completed negotiations with Intermolecular, Inc. for the use of certain long lived assets, which resulted in the strategic decision to discontinue certain portions of the site, maintenance, and license support for our HPD tools. As a result, we recorded an impairment charge for long-lived assets held and used with a carrying amount of $10.8 million and the related prepaid support fees with a carrying amount of $0.7 million under the caption, research and development expense. These increases were partially offset by $4.1 million in reduced fees associated with our service and usage agreements with Intermolecular, Inc. We also recorded reductions in spending on consumables ($1.4 million), outside services ($0.4 million) and prototypes ($0.6 million), partially offset by the prior year cost reimbursements of $2.9 million related to a collaborative development agreement.
Selling General and Administrative Expenses. Selling, General and Administrative ("SG&A") expenses decreased approximately 1 percent in 2013 to $72.9 million compared to 2012. The decline was driven by lower employee spending of $0.5 million (lower salaries of $0.5 million, lower equity compensation of $0.8 million and reduced benefits costs of $0.4 million, partially offset by increased employee incentives of $1.2 million), lower depreciation of $0.5 million, reduced facilities maintenance of $0.5 million and reduction in various other expenses of $0.5 million, partially offset by higher legal costs of $1.3 million as we evaluated our strategic alternatives and increased severance costs of $1.1 million driven by our 2013 reorganization.
Operating Income. Operating income declined 28 percent to $47.4 million in 2013 driven by lower gross profit and the HPD-related asset impairments.
Interest Income. Interest income was flat in 2013 compared to 2012.
Other Income (expense), net. Other income was $2.6 million in 2013 compared to expense of $0.1 million in 2012. The 2013 income includes a $3.3 million gain from the sale of marketable securities, partially offset by foreign currency losses of $1.0 million. The 2012 results included a loss of $0.5 million on the sale of an auction-rate security and a $0.2 million currency gain.
Loss from Discontinued Operations, net of taxes. The 2013 loss from discontinued operations, net of taxes, was $8.6 million compared to a loss of $6.0 million in 2012. The increase in the loss in 2013 was mostly the result of $2.0 million of reduction in benefits associated with adjustments to the Artelis acquisition earnout liability and $2.0 million of deal costs associated with the sale of the LifeSciences business to Pall Corporation.
Provision for Income Taxes. In 2013, we had an effective income tax rate of 23.9 percent, compared to a 2012 effective income tax rate of 27.5 percent. The 2013 effective income tax rate differs from the Federal statutory rate of 35.0 percent primarily due to lower income tax rates in foreign jurisdictions, state taxes, R&D credits, and a decrease in accrued tax liabilities.
We recorded income tax expense of $0.7 million and an income tax benefit of $0.5 million from discontinued operations for the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
ATMI has not provided for U.S. federal income and foreign withholding taxes on approximately $88.5 million of undistributed earnings from non-U.S. operations as of December 31, 2013, because such earnings are intended to be reinvested indefinitely outside of the United States. These earnings could become subject to additional tax if they are remitted as dividends, loaned to ATMI, or upon sale of subsidiary stock. It is not practicable to estimate the amount or timing of the additional tax, if any, that eventually might be paid on the foreign earnings.
South Korea has granted the Company an income tax exemption that expires in 2014, including the reduction from 100 percent to 50 percent of the exemption in 2013 and 2014. The exemption applies only to income related to one of the Company’s product lines. The effect of the tax exemption was to reduce income tax expense by $0.9 million and $2.3 million for the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012, respectively. In December 2013, the Company was granted a new tax exemption related to the manufacturing of different product lines at its recently-built JangAn facility; the tax exemption is for a seven year period that is expected to start in 2014.
At December 31, 2013, ATMI had $2.3 million of unrecognized tax benefits which, if recognized, would favorably affect the effective income tax rate in future periods. $0.2 million of this amount is included in deferred taxes, and the balance of $2.1 million is included in the caption “Other non-current liabilities” on the consolidated balance sheets, together with $0.3 million of accrued interest (net) on tax reserves and $0 accrued for penalties.
Year Ended December 31, 2012 Compared to Year Ended December 31, 2011
Results of Continuing Operations
The following is a summary of selected consolidated earnings information (in thousands of dollars):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, | | |
| | | 2012 | | 2011 | | % Change |
| Revenues | | $ | 365,849 |
| | $ | 351,823 |
| | 4.0 | % |
| Cost of revenues | | 179,258 |
| | 181,101 |
| | (1.0 | )% |
| Gross profit | | 186,591 |
| | 170,722 |
| | 9.3 | % |
| Gross profit margin | | 51.0 | % | | 48.5 | % | | |
| Operating expenses: | | | | | | |
| Research and development | | 47,286 |
| | 46,767 |
| | 1.1 | % |
| Selling, general and administrative | | 73,521 |
| | 68,711 |
| | 7.0 | % |
| Contract termination | | — |
| | 84,590 |
| | (100.0 | )% |
| Total operating expenses | | 120,807 |
| | 200,068 |
| | (39.6 | )% |
| Operating income (loss) | | 65,784 |
| | (29,346 | ) | | 324.2 | % |
| Interest income | | 900 |
| | 1,110 |
| | (18.9 | )% |
| Other expense, net | | (58 | ) | | (993 | ) | | 94.2 | % |
| Income (loss) before income taxes | | 66,626 |
| | (29,229 | ) | | 327.9 | % |
| Provision (benefit) for income taxes | | 18,331 |
| | (18,265 | ) | | 200.4 | % |
| Effective tax rate | | 27.5 | % | | 62.5 | % | |
|
| Income (loss) from continuing operations | | $ | 48,295 |
| | $ | (10,964 | ) | | 540.5 | % |
| Loss from discontinued operations, net of taxes | | $ | (5,965 | ) | | $ | (9,055 | ) | | 34.1 | % |
| Net income (loss) | | $ | 42,330 |
| | $ | (20,019 | ) | | 311.4 | % |
Analysis of Continuing Operations
Overview
2012 was a year of progress and transition after the October 31, 2011 termination of agreements with Matheson Tri-Gas, Inc. (“Matheson”). Upon termination we assumed responsibility for manufacturing, marketing, selling, and distribution of our SDS® products (the “SDS Direct” transaction). The results from these activities have met or exceeded our expectations, and we have improved interactions with our key customers as a result.
Results of Continuing Operations
Revenues. Revenues increased 4.0 percent to $365.8 million in 2012 compared to 2011 revenues of $351.8 million. The 2011 revenues included a fourth quarter unfavorable impact of $6.9 million associated with the SDS Direct transaction. The growth in 2012 was mostly the result of SDS growth partially mitigated by demand for other products which were down as lower wafer starts were coupled with our customers’ efforts to improve material usage efficiency and to manage inventories in the second half of the year.
Gross Profit. Our consolidated gross profit margin improved by 2.5 percentage points to 51.0 percent in 2012 compared to 48.5 percent in 2011 primarily due to the benefits of the SDS Direct transaction.
Research and Development Expenses. Research and development expenses (“R&D”) increased 1.1 percent in 2012 compared to 2011. Principal components of the higher expenses were increases in outside support services of $1.2 million, consumables of $1.0 million, and depreciation of $0.5 million, partially offset by the successful conclusion of a collaborative development agreement resulting in increased expense reimbursements to us of $2.0 million.
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses. Selling, General and Administrative (“SG&A”) expenses increased by 7.0 percent in 2012 from 2011 due to approximately $4.0 million of costs associated with SDS Direct activities, $1.4 million of severance, a capital based tax credit of $2.4 million recognized in 2011, partially offset by lower recruiting fees of $1.0 million.
Operating Income (Loss). Operating income was $65.8 million in 2012 compared to an operating loss of $29.3 million in 2011. The operating loss in 2011 included an $84.6 million contract termination charge associated with the SDS Direct transaction.
Other expense, net. Other expense, net was $0.1 million in 2012. In 2011, other expense, net was $1.0 million driven by losses from foreign exchange which were partially offset by a $0.7 million gain from a previously reserved investment.
Loss from discontinued operations, net of taxes. The 2012 loss from discontinued operations, net of taxes, was $6.0 million compared to a loss of $9.1 million in 2011. Revenues for 2012 were up approximately 9 percent compared to 2011 with major contributions from higher consumables sales and stronger sales of iCELLisTM systems. Gross margin declined slightly to approximately 34 percent for the year-ended 2012 compared to approximately 35 percent for the same period in 2011. The 2012 loss is a result of the continued R&D and SG&A spending in support of iCELLisTM and XpansionTM bioreactor commercialization efforts partially offset by increased gross profit from revenue growth and a $1.0 million increase in the year-over-year gain due to the change in fair value of the Artelis contingent consideration liability.
Provision (benefit) for Income Taxes. In 2012, we had an effective income tax rate of 27.5 percent, compared to a 2011 effective income tax benefit rate of 62.5 percent. The 2012 effective income tax rate differs from the Federal statutory rate of 35.0 percent primarily due to lower income tax rates in foreign jurisdictions, an increase in certain valuation allowances, and state taxes. If certain 2012 retroactive provisions of The American Taxpayer Relief Act of 2012, including the US R&D credit, had been enacted into law in 2012 instead of 2013, the 2012 effective income tax rate would have been 25.9 percent.
ATMI has not provided for U.S. federal income and foreign withholding taxes on approximately $73.1 million of undistributed earnings from non-U.S. operations as of December 31, 2012, because such earnings are intended to be reinvested indefinitely outside of the United States. These earnings could become subject to additional tax if they are remitted as dividends, loaned to ATMI, or upon sale of subsidiary stock. It is not practicable to estimate the amount or timing of the additional tax, if any, that eventually might be paid on the foreign earnings.
South Korea has granted the Company an income tax exemption that expires in 2014, including the reduction from 100 percent to 50 percent of the exemption in 2013 and 2014. The exemption applies only to income related to one of the Company’s product lines. The effect of the tax exemption was to reduce income tax expense by $2.3 million and $2.8 million for the years ended December 31, 2012 and 2011, respectively.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
We assess liquidity in terms of our ability to generate cash to fund our operating and investing activities. Of particular importance to management are cash flows generated by operating activities, and cash used for capital expenditures, acquisitions, and stock repurchases.
Until required for use in the business, we invest our cash reserves in bank deposits, certificates of deposit, money market securities, government and government-sponsored bond obligations, corporate debt obligations, and other interest bearing marketable debt instruments in accordance with our investment policy. We have contracted with investment advisers to invest our funds consistent with our investment policy. The value of our investments may be adversely affected by increases in interest rates, instability in the global financial markets that reduces the liquidity of securities included in our portfolio, and by other factors which may result in other-than-temporary declines in value of the investments, which could impact our financial position and our overall liquidity. Each of these events may cause us to record charges to reduce the carrying value of our investment portfolio or sell investments for less than our acquisition cost. We attempt to mitigate these risks with the assistance of our investment advisors by investing in high-quality securities and monitoring the overall risk profile of our portfolio. We also maintain a well-diversified portfolio that limits our credit exposure through concentration limits set within our investment policy.
We have financed our operating needs and capital expenditures through cash flows from our operations, and existing cash. We expect to finance current and planned operating requirements principally through cash from operations, as well as existing cash resources. We believe that these funds will be sufficient to meet our operating requirements for the foreseeable future. However, we may, from time to time, seek additional funding through a combination of equity and debt financings or from other sources.
We continue to invest in R&D to provide future sources of revenue through the development of new products, as well as through additional uses for existing products. We consider R&D and the development of new products and technologies an integral part of our growth strategy and a core competency of the Company. Likewise, we continue to make capital expenditures in order to expand and modernize manufacturing and R&D facilities around the globe and to drive efficiencies throughout the organization.
Additionally, management considers, on a continuing basis, potential acquisitions of strategic technologies and businesses complementary to the Company’s current business.
On February 4, 2014, ATMI and Entegris entered into an Agreement and Plan of Merger (the “Merger Agreement”), whereby ATMI would become a wholly-owned subsidiary of Entegris.
Under the terms of the Merger Agreement, ATMI shareholders will receive $34.00 in cash, without interest or dividends, for each share of ATMI common stock they hold at the time of closing. The consummation of the merger is subject to receiving the approval of holders of a majority of the outstanding ATMI common stock entitled to vote on the merger, the expiration or termination of the applicable waiting period under the Hart-Scott-Rodino Antitrust Improvements Act of 1976, as amended, and other customary conditions.
The Merger Agreement includes customary termination provisions for both ATMI and Entegris and provides that, in connection with the termination of the Merger Agreement by Entegris or ATMI, under specified circumstances, ATMI would be required to pay Entegris a termination fee of $30,000,000. In the event the conditions to consummating the merger have been met on the date that the closing of the merger is required to occur but Entegris and Merger Sub fail to consummate the merger, ATMI may terminate the Merger Agreement and, in certain circumstances, Entegris would be required to pay ATMI a termination fee of $100,000,000.
As part of the Merger Agreement, the parties have agreed to certain customary covenants which restrict ATMI pending the closing of the acquisition. Among these obligations, ATMI: (1) must conduct business in the ordinary course consistent with its past practice; (2) may not repatriate any cash, cash equivalents or other assets to the extent that such repatriation would result in a tax liability to ATMI or any of its subsidiaries beyond what has been agreed to with Entegris; (3) may not make or authorize capital expenditures in any calendar year that, individually or in the aggregate, exceed the amounts budgeted in ATMI's current plan by more than 10%; (4) may not establish a record date or declare a dividend; (5) may not amend its Charter or By-laws; (6) may not issue, sell, encumber, repurchase or grant any capital stock or other equity instrument other than amounts agreed to by Entegris; (7) may not acquire, sell, lease (as lessor), license, mortgage, sell and leaseback or otherwise subject to any lien (other than certain permitted liens), or otherwise dispose of any real property or other material properties or assets, other than that which has been agreed to between the parties; (8) may not incur any indebtedness or issue or sell any debt securities or rights to acquire debt securities except as agreed between the parties; (9) may not make any change in financial accounting methods, principles or practices, or elections, except insofar as required by applicable law or generally accepted accounting principles; and (10) may not adopt a plan of complete or partial liquidation, dissolution, merger or conversion or resolution providing for or authorizing such a liquidation, dissolution, merger or conversion.
Refer to Note 17 to the Consolidated Financial Statements in Item 8 of this Form 10-K for further details.
See Part I, Item 1A, “Risk Factors” of this Form 10-K for risk factors that could negatively impact our cash position and ability to fund future operations.
A summary of our cash flows follows (in thousands):
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended December 31, |
| | | 2013 | | 2012 |
| Cash provided by (used for): | | | | |
| Operating activities | | $ | 44,415 |
| | $ | 90,962 |
|
| Investing activities | | (34,802 | ) | | (40,960 | ) |
| Financing activities | | (7,954 | ) | | (836 | ) |
| Effects of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents | | (2,263 | ) | | 2,361 |
|
Operating Activities
In 2013 we generated $44.4 million of cash from operations, which represents a decrease of $46.6 million compared to the $91.0 million of cash generated from operations in 2012. The cash generated from operations was primarily driven by net income and a decline in the use of cash for inventory with more stable inventory levels offset by net income tax payments of $13.1 million and changes in accounts payable mostly due to timing of payments to vendors.
Investing Activities
Net cash used for investing activities was $34.8 million in 2013, a decrease of $6.2 million compared to 2012. Our investing activities primarily relate to purchases, sales and maturities of marketable securities, including $10.9 million of cash generated from the sale of marketable equity securities, and the purchases of property, plant and equipment, including $21.8 million of cash used for the construction of our new South Korean manufacturing facility. The decrease in cash used for investing activities was due to the increase in proceeds from sales or maturities of marketable securities partially offset by increased expenditures related to property, plant and equipment, and spending on cost and equity-basis investments.
Financing Activities
Financing activities resulted in a use of cash of $8.0 million for 2013, which was an increase of $7.1 million versus 2012. The increase was primarily related to purchases of treasury stock, partially offset by an increase in proceeds from the exercise of stock options.
Summary of Contractual Obligations
The following is a summary of consolidated debt, lease, purchase and other obligations at December 31, 2012 (refer to Notes 4, 6, 8, and 13 of the consolidated financial statements in Item 8 of this Form 10-K), in thousands:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Payments Due by Period |
| | Total | | Less Than 1 Year | | 1-3 Years | | 4-5 Years | | Thereafter |
| Contractual Obligations: | | | | | | | | | |
| Capital leases | $ | 149 |
| | $ | 52 |
| | $ | 85 |
| | $ | 12 |
| | $ | — |
|
Operating leases (1) | $ | 11,048 |
| | 3,139 |
| | 4,121 |
| | 934 |
| | 2,854 |
|
| Purchase obligations: | | | | | | | | | |
Inventory (2)(3) | $ | 74,206 |
| | 22,833 |
| | 10,173 |
| | 11,500 |
| | 29,700 |
|
Capital (4) | $ | 1,713 |
| | 1,713 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
Other (5) | $ | 7,389 |
| | 6,111 |
| | 1,278 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Total | $ | 83,308 |
| | 30,657 |
| | 11,451 |
| | 11,500 |
| | 29,700 |
|
Other L/T liabilities (6) | $ | 9,014 |
| | 185 |
| | 8,467 |
| | 316 |
| | 46 |
|
| Total lease, purchase, and other long-term liability obligations | $ | 103,519 |
| | $ | 34,033 |
| | $ | 24,124 |
| | $ | 12,762 |
| | $ | 32,600 |
|
| |
(1) | Includes $3.7 million operating lease commitments from discontinued operations. |
| |
(2) | Includes $65.0 million commitment to purchase raw material from strategic gas suppliers. Purchase commitments beginning in 2019 are variable and dependent on annual sales volumes. |
| |
(3) | Includes $1.2 million inventory commitments from discontinued operations. |
| |
(4) | Includes $0.3 million capital commitments from discontinued operations. |
| |
(5) | Includes $3.9 million commitment to purchase R&D license, maintenance, and royalty fees from Intermolecular, Inc. |
| |
(6) | Includes $3.6 million of asset retirement obligations. |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Payments Due by Period |
| | Total | | Less Than 1 Year | | 1-3 Years | | 4-5 Years | | Thereafter |
| Contractual Obligations: |
| | | | | | | | |
| Total discontinued operations obligations | $ | 5,155 |
| | $ | 1,885 |
| | $ | 428 |
| | $ | 256 |
| | $ | 2,586 |
|
For additional information refer to Note 8 of the consolidated financial statements in Item 8 of this Form 10-K.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
In the fourth quarter of 2013, we amended our existing contracts with Intermolecular, Inc. to significantly reduce our license of HPD technology and R&D support services for 2014. Under the amendment, ATMI will pay a fixed fee for a reduced number of HPD tool site licenses and maintenance support. Volume-based royalties to Intermolecular will resume in 2014. Additionally, we are committed to paying $2.6 million and $1.3 million for R&D licenses in 2014 and 2015, respectively, which is down from $6.9 million in 2013.
In the fourth quarter of 2012, we executed a ten year arrangement to purchase raw material from a global industrial gas supplier. We are committed to making certain upfront payments and to purchasing minimum volumes of gas thereafter. Purchase commitments beginning in year six are dependent on annual sales volumes. We estimate the total value of the contract to be $60.0 million. Under the contract, we have made payments totaling $3.0 million through December 31, 2013, and estimate the remaining contractual obligations under this agreement to approximate $57.0 million.
Operations Outside the United States
For the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011, sales outside the United States, including Asia and Europe, accounted for 83.4 percent, 82.7 percent and 81.2 percent, respectively, of our revenues. Sales to Taiwan for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011 were 27.5 percent, 27.0 percent and 27.7 percent, respectively, of our revenues. Sales to Japan for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011 were 11.4 percent, 13.2 percent and 12.3 percent, respectively, of our revenues. Sales to South Korea for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011 were 20.6 percent, 23.3 percent and 22.4 percent, respectively, of our revenues. Sales to China for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011 were 10.8 percent, 6.7 percent and 6.7 percent, respectively, of our revenues. Management anticipates that sales outside the United States will continue to account for a significant percentage of our total revenues. ATMI has wholly-owned subsidiaries in Taiwan, Singapore, China, Japan, Malaysia and Germany where the Company sells and services its products. ATMI also has a wholly-owned subsidiary in South Korea that manufactures, sells, and distributes materials packaging, materials delivery equipment, and thin-film materials to the semiconductor and flat-panel display markets in South Korea, and NOWPak® to the Taiwan and Japanese markets.
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
Interest Rate Risk
As of December 31, 2013, the Company’s cash and cash equivalents and marketable securities included bank deposits, time deposits, money market securities, corporate debt obligations, and government and government-sponsored bond obligations. As of December 31, 2013, an increase or decrease of 100 basis points in interest rates on securities with maturities greater than one year would not have a material impact on the fair value of the Company’s marketable securities.
Foreign Currency Exchange Risk
Most of the Company’s sales are denominated in U.S. dollars and as a result, the Company has exposure to foreign currency exchange risk with respect to sales made. Approximately 46 percent of the Company’s revenues for the year ended December 31, 2013 were denominated in Japanese Yen (“JPY”), Korean Won (“KRW”), and Euros (“EUR”), but a majority of the product is sourced in U.S. dollars. Management periodically reviews the Company’s exposure to currency fluctuations. In South Korea our price lists are pegged to the U.S. dollar. This exposure may change over time as business practices evolve and could have a material effect on the Company’s financial results in the future. We use forward foreign exchange contracts to hedge specific exposures relating to intercompany payments and anticipated, but not yet committed, sales from our U.S. entity to a Japanese customer denominated in JPY. The terms of the forward foreign exchange contracts are matched to the underlying transaction being hedged, and are typically two years or less.
Because such contracts are directly associated with identified transactions, they are an effective hedge against fluctuations in the value of the foreign currency underlying the transaction. We recognize in earnings (other income (expense), net) changes in the fair value of all derivatives that are designated as economic hedges and recognize in accumulated other comprehensive income any changes in fair value of all derivatives designated as cash flow hedges that are highly effective and meet the other related accounting requirements. Gains and losses associated with contracts designated as cash flow hedges are recognized in earnings when the underlying hedged transaction occurs. Further, we do not enter into derivative instruments for trading or speculative purposes and all of our derivatives were highly effective throughout the periods reported.
At December 31, 2013, we held forward foreign currency exchange contracts, not designated as cash flow hedges, with notional amounts totaling $46.0 million and forward foreign currency exchange contracts designated as cash flow hedges with notional amounts totaling $11.9 million, which are being used to hedge recorded foreign denominated assets, liabilities, and future cash flows which will be settled in either JPY, KRW, EUR, Chinese Yuan Renminbi ("CNY"), or New Taiwan Dollars (“NTD”). Holding other variables constant, if there were a 10 percent decline in foreign exchange rates against the US dollar for the JPY, KRW, EUR, CNY and NTD, the fair market value of the foreign exchange contracts outstanding at December 31, 2013 would decrease by approximately $3.3 million ($1.8 million would be expected to be fully offset by foreign exchange losses on the amount being hedged, and a loss of $1.5 million would be reported in accumulated other comprehensive income, until the forecasted hedged transactions occurred). The effect of an immediate 10 percent change in other foreign exchange rates would not be expected to have a material effect on the Company’s future operating results or cash flows.
In those jurisdictions where we earn revenue and incur expenses in currencies other than the U.S. dollar, the net effect from these currency fluctuations on the Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income would not be expected to be material.
Changes in Market Risk
Although we have seen mixed signs of stability, the global economy continues to deal with the repercussions of the global recession. There can be no assurance that there will not be further deterioration in credit and financial markets and deterioration of confidence in economic conditions. These economic uncertainties affect businesses such as ours in a number of ways, making it more difficult to accurately forecast and plan our future business activities.
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data
The Reports of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm, the consolidated financial statements and the financial statement schedule that are listed in the Index to Consolidated Financial Statements and Financial Statement Schedule are included herein on pages F-1 through F-33.
Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements With Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure
None.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures
Conclusion Regarding the Effectiveness of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Our management, with the participation of our Chief Executive Officer (“CEO”) and Chief Financial Officer (“CFO”), has evaluated the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures (as such term is defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Exchange Act) as of the end of the period covered by this Form 10-K. There are inherent limitations to the effectiveness of any system of disclosure controls and procedures, including the possibility of human error and the circumvention or overriding of the controls and procedures. Accordingly, even effective disclosure controls and procedures can only provide reasonable assurance of achieving their control objectives. Based upon this evaluation, our CEO and CFO concluded that, as of the end of the period covered by this Form 10-K, our disclosure controls and procedures were effective in that they provided reasonable assurance that the information we are required to disclose in the reports we file or submit under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the applicable rules and forms, and that it is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our CEO and CFO, as appropriate, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting. Internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external reporting purposes in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Our management has assessed the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2013. In making its assessment, management has used the criteria set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations (COSO) of the Treadway Commission in Internal Control—Integrated Framework (1992 framework). Our management concluded that based on its assessment, our internal control over financial reporting was effective as of December 31, 2013. The Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2013 has been audited by Ernst & Young LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, as stated in their attestation report on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting, which is included in this annual report.
There has been no change in our internal control over financial reporting during the quarter ended December 31, 2013 that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
Item 9B. Other Information
None.
PART III
Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance
The information required by this Item will be provided in accordance with Instruction G(3) to Form 10-K no later than April 30, 2014.
Item 11. Executive Compensation
The information required by this Item will be provided in accordance with Instruction G(3) to Form 10-K no later than April 30, 2014.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters
The information required by this Item will be provided in accordance with Instruction G(3) to Form 10-K no later than April 30, 2014.
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence
The information required by this Item will be provided in accordance with Instruction G(3) to Form 10-K no later than April 30, 2014.
Item 14. Principal Accountant Fees and Services
The information required by this Item will be provided in accordance with Instruction G(3) to Form 10-K no later than April 30, 2014.
PART IV
Item 15. Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules
The following documents are filed as part of this annual report on Form 10-K:
Reports of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
Consolidated Balance Sheets—December 31, 2013 and 2012
Consolidated Statements of Operations for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011
Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income (Loss) for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011
Consolidated Statements of Stockholders’ Equity for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
| |
| (2) | Financial Statement Schedule: |
Schedule II—Valuation and Qualifying Accounts
The Reports of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm, consolidated financial statements and financial statement schedule listed in the Index to Consolidated Financial Statements and Financial Statement Schedule on page F-1 hereof are filed as part of this report, commencing on page F-2 hereof.
All other financial statement schedules are omitted as the required information is not applicable or the information is shown in the consolidated financial statements or related notes.
The documents set forth below are filed herewith or incorporated herein by reference to the location indicated.
|
| | |
| Exhibit No. | | Description |
| 2.01 | | Agreement and Plan of Merger, dated as of February 4, 2014, by and among ATMI, Inc., Entegris, Inc. and Atomic Merger Corporation (Filed as Exhibit 2.1 to ATMI’s Current Report on Form 8-K on February 4, 2014, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 2.02 | | Share and Asset Purchase Agreement, dated as of December 22, 2013, by and among ATMI, Inc., ATMI Packaging, Inc., Advanced Technology Materials, Inc., ATMI SARL, ATMI Belgium LLC, and Pall Corporation (Filed as Exhibit 2.1 to ATMI’s Current Report on Form 8-K on December 23, 2013, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 3.01 | | Restated Certificate of Incorporation dated as of July 30, 2005 (Filed as Exhibit 3 (i) to ATMI’s Current Report on Form 8-K on August 3, 2005, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 3.02 | | Amended and Restated Bylaws of ATMI, Inc., effective April 1, 2013 (Filed as Exhibit 3.1 to ATMI’s Current Report on Form 8-K on April 3, 2013, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 4.01 | | Specimen of ATMI’s Common Stock Certificate (Filed on September 10, 1997 as Exhibit 4.01 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-4, Registration No. 333-35323). |
| 10.01* | | Employment Agreement between Daniel P. Sharkey and ATMI, Inc. dated December 31, 2004 (Filed as Exhibit 10.1 to ATMI’s Current Report on Form 8-K on January 5, 2005, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 10.02* | | Employment Agreement between Douglas A. Neugold and ATMI, Inc. dated December 31, 2004 (Filed as Exhibit 10.1 to ATMI’s Current Report on Form 8-K/A on January 5, 2005, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 10.03* | | Agreement of Lease between Melvyn J. Powers and Mary P. Powers d/b/a/ M&M Realty and Advanced Technology Materials, Inc., dated December 23, 1994 (Filed as Exhibit 10.04 to ATMI’s 2008 Annual Report on Form 10-K, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 10.04 | | First Amendment to Agreement of Lease dated as of November 22, 2000 by and between Commerce Park Realty, LLC and Advanced Technology Materials, Inc. (Filed as Exhibit 10.05 to ATMI’s 2005 Annual Report on Form 10-K, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 10.05 | | Second Amendment to Agreement of Lease dated as of March 24, 2003 by and between Commerce Park Realty, LLC and Advanced Technology Materials, Inc. (Filed as Exhibit 10.05 to ATMI’s 2005 Annual Report on Form 10-K, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 10.06* | | ATMI, Inc. 1995 Stock Plan (Filed as Exhibit 10.07 to ATMI’s 2008 Annual Report on Form 10-K, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
|
| | |
| 10.07* | | ATMI, Inc. 1997 Stock Plan, dated October 10, 1997 (Filed on April 6, 1998 as Exhibit 99.1 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-8, Registration No. 333-49561). |
| 10.08* | | ATMI, Inc. 1998 Stock Plan, dated May 20, 1998 (Filed on June 9, 1998 as Exhibit 99.1 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-8, Registration No. 333-56349). |
| 10.09 | | Agreement of Lease between Seymour R. Powers, Leon Griss and Ruth Griss and Advanced Technology Materials, Inc., dated November 24, 2000 (Filed as Exhibit 10.10 to ATMI’s 2008 Annual Report on Form 10-K, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 10.10* | | ATMI, Inc. 2000 Stock Plan, dated May 24, 2000 (Filed on September 20, 2000 as Exhibit 99.1 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-8, Registration No. 333-46222). |
| 10.11* | | ATMI, Inc. 2003 Stock Plan (as amended May 21, 2003), (Filed on August 1, 2003 as Exhibit 4.6 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-8, Registration No. 333-107591). |
| 10.12* | | ATMI, Inc. 1998 Employee Stock Purchase Plan, (as amended February 28, 2003), (Filed on August 1, 2003 as Exhibit 4.7 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-8, Registration No. 333-107591). |
| 10.13 | | Alliance Agreement dated as of May 16, 2003 by and between Advanced Technology Materials, Inc. on its own behalf and on behalf of its Affiliates and Enthone, Inc. (Filed as Exhibit 10.15 to ATMI’s 2003 Annual Report on Form 10-K, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). (1) |
| 10.14* | | Non-Employee Directors Deferred Compensation Program of ATMI, Inc. 1998 Stock Plan (Filed as Exhibit 10.19 to ATMI’s 2005 Annual Report on Form 10-K, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 10.15* | | Form of ATMI, Inc. Executive Management Restricted Stock Grant Agreement (Filed as Exhibit 10.20 to ATMI’s 2006 Annual Report on Form 10-K, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 10.16* | | Form of ATMI, Inc. Employee Non-Qualified Stock Option Agreement (Filed as Exhibit 10.21 to ATMI’s 2006 Annual Report on Form 10-K, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 10.17 | | Agreement of Lease between West Real Estate and Management, Inc. and ATMI Packaging, Inc., and ATMI, Inc., dated October 21, 2004 (Filed as Exhibit 10.23 to ATMI’s 2004 Annual Report on Form 10-K, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 10.18* | | Form of ATMI, Inc. Employee Restricted Stock Grant Agreement – Non-Executive Management (Filed as Exhibit 10.23 to ATMI’s 2006 Annual Report on Form 10-K, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 10.19* | | Form of ATMI, Inc. Non-Employee Director Restricted Stock Grant (Filed as Exhibit 10.24 to ATMI’s 2006 Annual Report on Form 10-K, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 10.20 | | First Amendment to Agreement of Lease dated as of March 24, 2003 by and between Seymour R. Powers, Trustee, and Leon Griss and Advanced Technology Materials, Inc. (Filed as Exhibit 10.25 to ATMI’s 2005 Annual Report on Form 10-K, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 10.21* | | Amendment to ATMI’s 1998 Employee Stock Purchase Plan (amended effective February 28, 2003 and January 1, 2007), (Filed as Exhibit 99 to ATMI’s Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2006, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 10.22 | | Second Amendment to Agreement of Lease dated as of January 18, 2007 by and between Seymour R. Powers, Trustee, and Carole Kolsky, Deborah A. Tauber and Stephen L. Griss (as successors to Leon Griss and Ruth Griss) and Advanced Technology Materials, Inc. (Filed as Exhibit 10.27 to ATMI’s 2006 Annual Report on Form 10-K, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 10.23 | | Third Amendment to Agreement of Lease dated as of January 18, 2007 by and between Commerce Park Realty, LLC and Advanced Technology Materials, Inc. (Filed as Exhibit 10.28 to ATMI’s 2006 Annual Report on Form 10-K, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 10.24* | | Form of ATMI, Inc. Non-Employee Directors Non-Qualified Stock Option Agreement (Filed as Exhibit 10.29 to ATMI’s 2006 Annual Report on Form 10-K, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 10.25* | | Employment Agreement between Timothy C. Carlson and ATMI, Inc. dated December 31, 2004 (Filed as Exhibit 10.31 to ATMI’s 2007 Annual Report on Form 10-K, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 10.26* | | Amendment to Employment Agreement between Timothy C. Carlson and ATMI, Inc. dated August 1, 2005 (Filed as Exhibit 10.32 to ATMI’s 2007 Annual Report on Form 10-K, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 10.27* | | Amendment to Employment Agreement between Timothy C. Carlson and ATMI, Inc. dated January 31, 2008, effective as of September 7, 2007 (Filed as Exhibit 10.34 to ATMI’s 2007 Annual Report on Form 10-K, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 10.28* | | Amendment to Employment Agreement between Daniel P. Sharkey and ATMI, Inc. dated January 31, 2008, effective as of September 7, 2007 (Filed as Exhibit 10.35 to ATMI’s 2007 Annual Report on Form 10-K, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 10.29 | | First Amendment to Agreement of Lease between West Real Estate and Management, Inc. and ATMI Packaging, Inc., and ATMI, Inc., dated September 23, 2008 (Filed as Exhibit 10.32 to ATMI’s 2008 Annual Report on Form 10-K, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
|
| | |
| 10.30* | | Amendment to Employment Agreement between Douglas A. Neugold and ATMI, Inc. dated April 14, 2008 (Filed as Exhibit 10.2 to ATMI’s Current Report on Form 8-K, filed on April 16, 2008, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 10.31* | | Amendment to Employment Agreement between Daniel P. Sharkey and ATMI, Inc. dated April 14, 2008 (Filed as Exhibit 10.3 to ATMI’s Current Report on Form 8-K, filed on April 16, 2008, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 10.32* | | Amendment to Employment Agreement between Timothy C. Carlson and ATMI, Inc. dated April 14, 2008 (Filed as Exhibit 10.4 to ATMI’s Current Report on Form 8-K, filed on April 16, 2008, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 10.33* | | First Amendment to Non-Employee Directors Deferred Compensation Program of ATMI, Inc. 1998 Stock Plan (Filed as Exhibit 10.1 to ATMI’s Current Report on Form 8-K, filed on March 6, 2008, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 10.34* | | Amendment to the ATMI, Inc. 1998 Stock Plan (Filed as Exhibit 10.2 to ATMI’s Current Report on Form 8-K, filed on March 6, 2008, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 10.35* | | Amendment to the ATMI, Inc. 2000 Stock Plan (Filed as Exhibit 10.3 to ATMI’s Current Report on Form 8-K, filed on March 6, 2008, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 10.36* | | ATMI, Inc. 2003 Stock Plan (as Amended May 21, 2003 and March 2, 2008) (Filed as Exhibit 10.4 to ATMI’s Current Report on Form 8-K, filed on March 6, 2008, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 10.37* | | ATMI, Inc. Non-Employee Directors Deferred Compensation Program of ATMI, Inc. 2003 Stock Plan (Filed as Exhibit 10.5 to ATMI’s Current Report on Form 8-K, filed on March 6, 2008, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 10.38 | | Third Amendment to Lease dated as of October 30, 2008 by and between Seymour R. Powers, Trustee, and Carole Kolsky, Deborah A. Tauber and Stephen L. Griss (as successors to Leon Griss and Ruth Griss) and Advanced Technology Materials, Inc. (Filed as Exhibit 10.41 to ATMI’s Annual Report on Form 10-K, filed on February 18, 2011, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 10.39 | | Fourth Amendment to Agreement of Lease dated as of October 30, 2008 by and between Commerce Park Realty, LLC and Advanced Technology Materials, Inc. (Filed as Exhibit 10.42 to ATMI’s Annual Report on Form 10-K, filed on February 18, 2011, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 10.40* | | ATMI, Inc. 2010 Stock Plan, dated May 26, 2010 (Filed on June 4, 2010 as Exhibit 4.4 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-8, Registration No. 333-167318). |
| 10.41* | | ATMI, Inc. Non-Employee Directors Deferred Compensation Program of ATMI, Inc. 2010 Stock Plan. (Filed as Exhibit 10.44 to ATMI’s Annual Report on Form 10-K, filed on February 18, 2011, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 10.42 | | Notice of First Renewal Option of Agreement of Lease dated as of October 27, 2010 by and between Seymour R. Powers, Trustee, and Carole Kolsky, Deborah A. Tauber and Stephen L. Griss (as successors to Leon Griss and Ruth Griss) and Advanced Technology Materials, Inc. (Filed as Exhibit 10.45 to ATMI’s Annual Report on Form 10-K, filed on February 18, 2011, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 10.43 | | Notice of First Renewal Option of Agreement of Lease dated as of December 13, 2010 by and between Seymour R. Powers, Trustee, and Carole Kolsky, Deborah A. Tauber and Stephen L. Griss (as successors to Leon Griss and Ruth Griss) and Advanced Technology Materials, Inc. (Filed as Exhibit 10.46 to ATMI’s Annual Report on Form 10-K, filed on February 18, 2011, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 10.44* | | Amended and Restated Employment Agreement dated January 19, 2012 between ATMI, Inc. and Douglas A. Neugold (Filed as Exhibit 10.1 to ATMI’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on January 23, 2012, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 10.45* | | Amended and Restated Employment Agreement dated January 19, 2012 between ATMI, Inc. and Timothy C. Carlson (Filed as Exhibit 10.2 to ATMI’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on January 23, 2012, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 10.46* | | Amended and Restated Employment Agreement dated January 19, 2012 between ATMI, Inc. and Daniel P. Sharkey (Filed as Exhibit 10.3 to ATMI’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on January 23, 2012, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 10.47* | | Form of Total Shareholder Return Performance Restricted Stock Unit Agreement (2012 and 2013 Grants) (Filed as Exhibit 10.5 to ATMI’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on January 23, 2012, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
|
| | |
| 10.48* | | Form of Total Shareholder Return Performance Restricted Stock Unit Agreement (2014 and later Grants) (Filed as Exhibit 10.6 to ATMI’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on January 23, 2012, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 10.49* | | Termination Agreement dated October 31, 2011 between Advanced Technology Materials, Inc. and Matheson Tri-Gas, Inc. (Filed as Exhibit 10.52 to ATMI’s Annual Report on Form 10-K, filed on February 17, 2012, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 10.50 * | | Amendment to ATMI’s 1998 Employee Stock Purchase Plan (amended effective February 28, 2003, January 1, 2007 and September 14, 2012), (Filed as Exhibit 10.1 to ATMI’s Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2012, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 10.51* | | ATMI, Inc. 2003 Stock Plan (as amended May 21, 2003, March 2, 2008 and December 12, 2012) (Filed as Exhibit 10.52 to ATMI's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31,2012, File No. 1-6239). |
| 10.52* | | ATMI, Inc. 2010 Stock Plan, dated May 26, 2010 (as amended December 12, 2012) (Filed as Exhibit 10.53 to ATMI's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2012, File No. 1-6239). |
| 10.53* | | Severance and Release Agreement dated February 12, 2013 between ATMI, Inc. and Tod A. Higinbotham (Filed as Exhibit 99.2 to ATMI’s Current Report on Form 8-K on February 12, 2013, File No. 1-16239, and incorporated herein by reference). |
| 10.54* | | Amendment to Amended and Restated Employment Agreement between ATMI, Inc. and Douglas A. Neugold, dated February 3, 2014. |
| 10.55* | | Amendment to Amended and Restated Employment Agreement between ATMI, Inc. and Timothy C. Carlson, dated February 3, 2014. |
| 10.56* | | Amendment to Amended and Restated Employment Agreement between ATMI, Inc. and Daniel P. Sharkey, dated February 3, 2014. |
| 10.57 |
| Fifth Amendment to Agreement of Lease between West-Bloom Industrial, LLC and ATMI Packaging, Inc., and ATMI, Inc., dated November 19, 2012. |
| 10.58 | | Sixth Amendment to Agreement of Lease between West-Bloom Industrial, LLC and ATMI Packaging, Inc., and ATMI, Inc., dated July 17, 2013. |
| 10.59* | | Amendment to Award Agreements relating to a Change in Control for Executive Team Non-Life Sciences Employee, dated December 4, 2013. |
| 10.60* | | ATMI, Inc. Executive Severance Pay Plan. |
| 10.61* | | Transaction Bonus Agreement, between ATMI, Inc. and Christian F. Kramer, dated January 13, 2014. |
| 21 | | Subsidiaries of ATMI, Inc. |
| 23 | | Consent of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm. |
| 31.1 | | Certification of Chief Executive Officer pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a) and Rule 15d-14(a) of the Securities Exchange Act, as amended. |
| 31.2 | | Certification of Chief Financial Officer pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a) and Rule 15d-14(a) of the Securities Exchange Act, as amended. |
| 32 | | Certification of Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer Pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 is furnished herewith. |
| 101 | | Interactive data files pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T. |
| |
| * | Indicates a management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement. |
| |
(1) | Portions omitted pursuant to a request for confidential treatment. |
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
|
| | |
| | | ATMI, Inc. |
| March 7, 2014 | | |
| | By: | /s/ Douglas A. Neugold |
| | | Douglas A. Neugold |
| | | Chairman, President and Chief Executive Officer |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
|
| | | |
| Signature | | Title | Date |
| | | | |
| /s/ Douglas A. Neugold | | Chairman, President, Chief Executive Officer | March 7, 2014 |
| Douglas A. Neugold | | and Director (principal executive officer) | |
| | | | |
| /s/ Timothy C. Carlson | | Executive Vice President, Chief Financial | March 7, 2014 |
| Timothy C. Carlson | | Officer and Treasurer (principal financial officer) | |
| | | | |
| /s/ David M. Ward | | Vice President, Controller (principal | March 7, 2014 |
| David M. Ward | | accounting officer) | |
| | | | |
| /s/ Mark A. Adley | | | March 7, 2014 |
| Mark A. Adley | | Director | |
| | | | |
| /s/ Eugene G. Banucci, Ph.D. | | | March 7, 2014 |
| Eugene G. Banucci, Ph.D. | | Director | |
| | | | |
| /s/ Stephen H. Mahle | | | March 7, 2014 |
| Stephen H. Mahle | | Director | |
| | | | |
| /s/ C. Douglas Marsh | | | March 7, 2014 |
| C. Douglas Marsh | | Director | |
| | | | |
| /s/ George M. Scalise |
|
| March 7, 2014 |
| George M. Scalise |
| Director |
|
| | | | |
| /s/ Mark B. Segall | | | March 7, 2014 |
| Mark B. Segall | | Director | |
| | | | |
| /s/ Cheryl L. Shavers, Ph.D. | | | March 7, 2014 |
| Cheryl L. Shavers, Ph.D. | | Director | |
ATMI, INC.
INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT
SCHEDULE
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The Board of Directors and Stockholders of ATMI, Inc.
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of ATMI, Inc. as of December 31, 2013 and 2012, and the related consolidated statements of operations, statements of comprehensive income (loss), stockholders’ equity, and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2013. Our audits also included the financial statement schedule listed in the Index at Item 15. These financial statements and schedule are the responsibility of ATMI, Inc.’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements and schedule based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the consolidated financial position of ATMI, Inc. at December 31, 2013 and 2012, and the consolidated results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2013, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles. Also, in our opinion, the related financial statement schedule, when considered in relation to the basic financial statements taken as a whole, presents fairly in all material respects the information set forth therein.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), ATMI, Inc.’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2013, based on criteria established in Internal Control Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (1992 framework) and our report dated March 7, 2014 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
/s/ ERNST & YOUNG LLP
Stamford, Connecticut
March 7, 2014
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The Board of Directors and Stockholders of ATMI, Inc.
We have audited ATMI, Inc.’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2013, based on criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (1992 framework) (the COSO criteria). ATMI, Inc.’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting, and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting included in Item 9A “Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting.” Our responsibility is to express an opinion on ATMI, Inc.’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
In our opinion, ATMI, Inc. maintained in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2013, based on the COSO criteria.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the consolidated balance sheets of ATMI, Inc. as of December 31, 2013 and 2012, and the related consolidated statements of operations, statements of comprehensive income (loss), stockholders’ equity and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2013 of ATMI, Inc. and our report dated March 7, 2014 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
/s/ ERNST & YOUNG LLP
Stamford, Connecticut
March 7, 2014
ATMI, INC.
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(in thousands, except per share data)
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, 2013 | | December 31, 2012 |
| Assets | | | | |
| Current assets: | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 82,646 |
| | $ | 83,709 |
|
| Marketable securities, current portion | | 46,201 |
| | 70,397 |
|
| Accounts receivable, net of allowances of $883 and $881, respectively | | 58,009 |
| | 53,684 |
|
| Inventories, net | | 76,485 |
| | 77,012 |
|
| Income taxes receivable | | 4,778 |
| | — |
|
| Deferred income taxes | | 12,814 |
| | 4,450 |
|
| Prepaid expenses | | 11,232 |
| | 11,838 |
|
| Other current assets | | 10,554 |
| | 8,025 |
|
| Assets held for sale | | 120,618 |
| | 101,051 |
|
| Total current assets | | 423,337 |
| | 410,166 |
|
| Property, plant, and equipment, net | | 120,462 |
| | 111,720 |
|
| Goodwill | | 13,657 |
| | 13,653 |
|
| Other intangibles, net | | 18,386 |
| | 21,178 |
|
| Marketable securities, non-current | | 2,225 |
| | 12,073 |
|
| Deferred income taxes, non-current | | 1,433 |
| | 12,516 |
|
| Other non-current assets | | 16,720 |
| | 17,847 |
|
| Total assets | | $ | 596,220 |
| | $ | 599,153 |
|
| Liabilities and stockholders’ equity | | | | |
| Current liabilities: | | | | |
| Accounts payable | | $ | 27,087 |
| | $ | 35,847 |
|
| Accrued liabilities | | 6,541 |
| | 6,953 |
|
| Accrued salaries and related benefits | | 3,793 |
| | 4,311 |
|
| Income taxes payable | | 1,668 |
| | 16,240 |
|
| Other current liabilities | | 3,509 |
| | 3,792 |
|
| Liabilities held for sale | | 13,108 |
| | 12,377 |
|
| Total current liabilities | | 55,706 |
| | 79,520 |
|
| Deferred income taxes, non-current | | 2,247 |
| | 165 |
|
| Other non-current liabilities | | 9,107 |
| | 12,192 |
|
| Commitments and contingencies (Note 13) | |
|
| |
|
|
| Stockholders’ equity: | | | | |
| Preferred stock, par value $.01 per share: 2,000 shares authorized; none issued | | — |
| | — |
|
| Common stock, par value $.01 per share: 100,000 shares authorized; 42,093 and 41,549 issued and 32,974 and 33,056 outstanding in 2013 and 2012, respectively | | 411 |
| | 405 |
|
| Additional paid-in capital | | 470,886 |
| | 457,669 |
|
| Treasury stock at cost (9,119 and 8,493 shares in 2013 and 2012, respectively) | | (251,577 | ) | | (237,170 | ) |
| Retained earnings | | 300,909 |
| | 270,744 |
|
| Accumulated other comprehensive income | | 8,531 |
| | 15,628 |
|
| Total stockholders’ equity | | 529,160 |
| | 507,276 |
|
| Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity | | $ | 596,220 |
| | $ | 599,153 |
|
ATMI, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
(in thousands, except per share data)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended December 31, |
| | | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 |
| Revenues | | $ | 360,959 |
| | $ | 365,849 |
| | $ | 351,823 |
|
| Cost of revenues | | 185,013 |
| | 179,258 |
| | 181,101 |
|
| Gross profit | | 175,946 |
| | 186,591 |
| | 170,722 |
|
| Operating expenses: | | | | | | |
| Research and development | | 55,666 |
| | 47,286 |
| | 46,767 |
|
| Selling, general and administrative | | 72,884 |
| | 73,521 |
| | 68,711 |
|
| Contract termination | | — |
| | — |
| | 84,590 |
|
| Total operating expenses | | 128,550 |
| | 120,807 |
| | 200,068 |
|
| Operating income (loss) | | 47,396 |
| | 65,784 |
| | (29,346 | ) |
| Interest income | | 944 |
| | 900 |
| | 1,110 |
|
| Impairment of investments | | — |
| | — |
| | (776 | ) |
| Other income (expense), net | | 2,616 |
| | (58 | ) | | (217 | ) |
| Income (loss) before income taxes | | 50,956 |
| | 66,626 |
| | (29,229 | ) |
| Provision (benefit) for income taxes | | 12,197 |
| | 18,331 |
| | (18,265 | ) |
| Income (loss) from continuing operations | | $ | 38,759 |
| | $ | 48,295 |
| | $ | (10,964 | ) |
| Loss from discontinued operations, net of taxes | | $ | (8,594 | ) | | $ | (5,965 | ) | | $ | (9,055 | ) |
| Net income (loss) | | $ | 30,165 |
| | $ | 42,330 |
| | $ | (20,019 | ) |
| Basic earnings (loss) per common share | | | | | | |
| Earnings (loss) per common share from continuing operations | | $ | 1.21 |
|
| $ | 1.51 |
|
| $ | (0.35 | ) |
| Loss per common share from discontinued operations | | $ | (0.27 | ) | | $ | (0.19 | ) |
| $ | (0.29 | ) |
| Weighted average shares outstanding — basic | | 31,911 |
| | 31,931 |
| | 31,703 |
|
| Diluted earnings (loss) per common share | | | | | | |
| Earnings (loss) per common share from continuing operations | | $ | 1.18 |
|
| $ | 1.48 |
|
| $ | (0.35 | ) |
| Loss per common share from discontinued operations | | $ | (0.26 | ) | | $ | (0.18 | ) |
| $ | (0.29 | ) |
| Weighted average shares outstanding — diluted | | 32,751 |
| | 32,664 |
| | 31,703 |
|
See accompanying notes.
ATMI, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (LOSS)
(in thousands, except per share data)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended December 31, |
| | | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 |
| Net income (loss) | | $ | 30,165 |
| | $ | 42,330 |
| | $ | (20,019 | ) |
| Other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax | | | | | | |
| Cumulative translation adjustment | | 1,703 |
| | 5,230 |
| | (3,097 | ) |
| Reclassification adjustment related to marketable securities sold in net unrealized gain position, net of $1,625, $495, and $0 tax provision, respectively. | | (3,489 | ) | | 854 |
| | (1 | ) |
| Change in fair value on available-for-sale securities, net of deferred income tax of $3,215, $326, and $4,351, respectively. | | (5,592 | ) | | 397 |
| | 7,119 |
|
| Reclassification adjustment related to the settlement of derivative financial instruments in a net unrealized gain position, net of $455 tax provision, respectively. | | (799 | ) | | — |
| | — |
|
| Change in fair value of derivative financial instruments, net of deferred income tax of $615 and $636, respectively. | | 1,080 |
| | 1,098 |
| | — |
|
| Comprehensive income (loss) | | $ | 23,068 |
| | $ | 49,909 |
| | $ | (15,998 | ) |
ATMI, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
(in thousands)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Common Stock | | Additional Paid-in Capital | | Treasury Stock | | Retained Earnings | | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income | | Total |
| Balance at December 31, 2010 | | $ | 396 |
| | $ | 435,840 |
| | $ | (230,272 | ) | | $ | 248,433 |
| | $ | 4,028 |
| | $ | 458,425 |
|
| Issuance of 71 shares of common stock pursuant to the exercise of employee stock options | | 1 |
| | 1,265 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 1,266 |
|
| Purchase of 48 treasury shares | | — |
| | — |
| | (901 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | (901 | ) |
| Stock based compensation | | — |
| | 7,539 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 7,539 |
|
| Other | | 2 |
| | (2 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Net loss | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (20,019 | ) | | — |
| | (20,019 | ) |
| Other comprehensive income | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 4,021 |
| | 4,021 |
|
| Total comprehensive loss | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (15,998 | ) |
| Balance at December 31, 2011 | | $ | 399 |
| | $ | 444,642 |
| | $ | (231,173 | ) | | $ | 228,414 |
| | $ | 8,049 |
| | $ | 450,331 |
|
| Issuance of 259 shares of common stock pursuant to the exercise of employee stock options | | 3 |
| | 4,609 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 4,612 |
|
| Purchase of 299 treasury shares | | — |
| | — |
| | (5,997 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | (5,997 | ) |
| Stock based compensation | | — |
| | 8,421 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 8,421 |
|
| Other | | 3 |
| | (3 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Net income | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 42,330 |
| | — |
| | 42,330 |
|
| Other comprehensive income | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 7,579 |
| | 7,579 |
|
| Total comprehensive income | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 49,909 |
|
| Balance at December 31, 2012 | | $ | 405 |
| | $ | 457,669 |
| | $ | (237,170 | ) | | $ | 270,744 |
| | $ | 15,628 |
| | $ | 507,276 |
|
| Issuance of 328 shares of common stock pursuant to the exercise of employee stock options | | 3 |
| | 5,802 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 5,805 |
|
| Purchase of 626 treasury shares | | — |
| | — |
| | (14,407 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | (14,407 | ) |
| Stock based compensation | | — |
| | 7,418 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 7,418 |
|
| Other | | 3 |
| | (3 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Net income | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 30,165 |
| | — |
| | 30,165 |
|
| Other comprehensive loss | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (7,097 | ) | | (7,097 | ) |
| Total comprehensive income | | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 23,068 |
|
| Balance at December 31, 2013 | | $ | 411 |
| | $ | 470,886 |
| | $ | (251,577 | ) | | $ | 300,909 |
| | $ | 8,531 |
| | $ | 529,160 |
|
See accompanying notes.
ATMI, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(in thousands)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended December 31, |
| | | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 |
| Operating activities | | | | | | |
| Net income (loss) | | $ | 30,165 |
| | $ | 42,330 |
| | $ | (20,019 | ) |
| Adjustments to reconcile net income (loss) to cash provided by (used for) operating activities: | | | | | | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | 28,832 |
| | 27,580 |
| | 27,162 |
|
| Deferred income taxes | | 9,900 |
| | 3,049 |
| | (29,443 | ) |
| Stock-based compensation expense | | 7,418 |
| | 8,421 |
| | 7,539 |
|
| Non-cash royalty | | — |
| | (2,600 | ) | | — |
|
| Long-lived asset impairments | | 11,708 |
| | 796 |
| | 594 |
|
| Impairment of investments | | — |
| | — |
| | 776 |
|
| Other | | (2,358 | ) | | (962 | ) | | 604 |
|
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | | | | | | |
| Accounts receivable | | (7,108 | ) | | (9,179 | ) | | 3,986 |
|
| Inventories | | (6,241 | ) | | (14,913 | ) | | (12,390 | ) |
| Other assets | | (1,172 | ) | | 3,988 |
| | (8,233 | ) |
| Accounts payable | | (8,519 | ) | | 17,243 |
| | (161 | ) |
| Accrued expenses, income taxes and other liabilities | | (18,210 | ) | | 15,209 |
| | (1,377 | ) |
| Net cash provided by (used for) operating activities | | 44,415 |
|
| 90,962 |
| | (30,962 | ) |
| Investing activities | | | | | | |
| Capital expenditures | | (43,864 | ) | | (29,333 | ) | | (20,703 | ) |
| Purchases of marketable securities | | (113,973 | ) | | (107,132 | ) | | (86,448 | ) |
| Proceeds from sales or maturities of marketable securities | | 135,458 |
| | 106,535 |
| | 121,755 |
|
| Acquisitions of assets and investments | | (12,480 | ) | | (11,147 | ) | | (6,746 | ) |
| Intangible rights acquired due to contract termination, net | | — |
| | — |
| | (10,410 | ) |
| Other | | 57 |
| | 117 |
| | 81 |
|
| Net cash used for investing activities | | (34,802 | ) |
| (40,960 | ) | | (2,471 | ) |
| Financing activities | | | | | | |
| Purchases of treasury stock | | (14,407 | ) | | (5,997 | ) | | (901 | ) |
| Proceeds from exercise of stock options | | 6,039 |
| | 4,612 |
| | 1,266 |
|
| Other | | 414 |
| | 549 |
| | 14 |
|
| Net cash (used for) provided by financing activities | | (7,954 | ) |
| (836 | ) | | 379 |
|
| Effects of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents | | (2,263 | ) |
| 2,361 |
| | (1,071 | ) |
| Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | | (604 | ) | | 51,527 |
| | (34,125 | ) |
| Cash and cash equivalents, beginning of period | | 86,050 |
| | 34,523 |
| | 68,648 |
|
| Cash and cash equivalents, end of period | | $ | 85,446 |
| | $ | 86,050 |
| | $ | 34,523 |
|
| SUPPLEMENTAL DISCLOSURES OF CASH FLOW INFORMATION: | | | | | | |
| Cash interest paid | | $ | 86 |
| | $ | 145 |
| | $ | 45 |
|
| Cash income taxes paid | | $ | 28,811 |
| | $ | 5,675 |
| | $ | 11,343 |
|
See accompanying notes.
ATMI, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
1. Organization and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Description of Business
ATMI, Inc. (together with its subsidiaries, collectively referred to as the “Company,” “ATMI,” or “we”) believes it is among the leading suppliers of high performance materials, materials packaging and materials delivery systems used worldwide in the manufacture of microelectronics devices. Our products consist of “front-end” semiconductor performance materials, sub-atmospheric pressure gas delivery systems for safe handling and delivery of toxic and hazardous gases to semiconductor process equipment, high-purity materials packaging and dispensing systems that allow for the reliable introduction of low volatility liquids and solids to microelectronics processes. ATMI targets semiconductor and flat-panel display manufacturers, whose products form the foundation of microelectronics technology rapidly proliferating through the consumer products, information technology, automotive, and communications industries. The market for microelectronics devices is continually changing, which drives demand for new products and technologies at lower cost. ATMI’s customers include many of the leading semiconductor manufacturers in the world who target leading edge technologies. ATMI’s objective is to meet the demands of our microelectronics customers with solutions that maximize the efficiency of their manufacturing processes, reduce capital or operating costs, and minimize the time to develop new products and integrate them into their processes.
Consolidation
The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of all subsidiaries where control exists. Equity investments generally consist of 20 percent to 50 percent owned operations which by definition demonstrate significant influence and instances where the Company through voting and similar rights can exercise significant influence. Operations less than 20 percent owned, where the Company does not exercise significant influence, are generally carried at cost. Earnings from equity investments are reported, net of income taxes, within the caption, “Other income (expense), net” on the consolidated statements of operations. Intercompany transactions have been eliminated.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”) requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues, and expenses. While actual results could differ, management believes such estimates to be reasonable.
Revenue Recognition and Accounts Receivable
We recognize revenue when the following four criteria are met: (1) persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists; (2) delivery has occurred or services have been rendered; (3) the fee is fixed or determinable; and (4) collectability is reasonably assured. Revenues from product sales are generally recognized upon delivery to a common carrier when terms are equivalent to free-on-board (“FOB”) origin and upon receipt by a customer when terms are equivalent to FOB destination. In instances where final acceptance of equipment is specified by the purchase agreement, revenue is deferred until all acceptance criteria have been satisfied, except when reasonable reserves for returns can be effectively established due to substantial successful installation history for homogenous transactions. Should changes in conditions cause management to determine these criteria are not met for certain future transactions, revenue recognized for any reporting period could be adversely affected. We accrue for sales returns, warranty costs, and other allowances based on a current evaluation of our experience based on stated terms of the transactions.
Prior to October 31, 2011, we used Matheson as our exclusive contract manufacturer and distribution partner for the manufacture and distribution of our Safe Delivery Source® (“SDS”) products (the “Licensed Products”). Under the terms of the original manufacturing agreement, ATMI retained the right to manufacture 25 percent of all Licensed Products, while Matheson had the right to manufacture 75 percent of all Licensed Products. Upon completion of manufacture, ATMI purchased all Licensed Products produced by Matheson. Under the terms of the distribution agreement, we received payment from Matheson based upon a formula which was dependent on the sale price obtained by Matheson from its customers. ATMI recognized revenue from the sale of Licensed Products to Matheson when Matheson sold the Licensed Products to its customers, because that is when the sales price became fixed and determinable. On October 31, 2011, we terminated the agreements with Matheson for manufacturing, marketing, selling and/or distributing of our SDS products (“SDS Direct transaction”). Matheson provided support services to ATMI during a transition period. Subject to such continuing services, ATMI assumed control of all manufacturing, distribution, logistics and sales services, which Matheson had provided globally prior to execution of the Termination Agreement, other than the distribution of the SDS and VAC product lines in Japan, which services continue to be provided by Matheson’s parent company, Taiyo Nippon Sanso Corporation (“TNSC”). We recognize revenue to TNSC when all the revenue recognition criteria are met, which is upon shipment. In those regions where Matheson was involved in distributing products during the transition period in the first half of 2012, revenues were recognized only after sale of the Licensed Products to the end users.
ATMI, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
During the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011, ATMI recognized $0.2 million, $6.9 million, and $65.8 million of revenues from Matheson, respectively. The decline in revenue from Matheson in 2012 and 2013 is a result of the SDS Direct transaction. During the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011, ATMI recognized revenues from Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Corporation (“TSMC”), of $53.8 million, $48.1 million, and $32.0 million, respectively. During the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011, ATMI recognized revenues from Samsung, a leading global integrated circuit manufacturer of $50.7 million, $57.3 million, and $47.6 million, respectively. During the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011, ATMI recognized revenues from United Microelectronics Corporation (“UMC”), of $37.7 million, $44.7 million, and $48.7 million, respectively.
Billings to customers for shipping and handling are included in revenues. Costs incurred for shipping and handling of products are charged to cost of revenues. Credit is extended to customers based on an evaluation of each customer’s financial condition; generally, collateral is not required. Revenues are presented in the consolidated financial statements net of sales allowances and discounts. Accounts receivable are presented in the consolidated financial statements net of the allowance for doubtful accounts. Taxes collected from customers and remitted to governmental authorities are presented on a net basis; and they are excluded from revenues.
Accounts Receivable Allowances
The allowance for doubtful accounts is established to represent our best estimate of the net realizable value of the outstanding accounts receivable balances. We estimate our allowance for doubtful accounts based on past due amounts and historical write-off experience, as well as trends and factors surrounding the credit risk of the markets we operate in and the financial viability of specific customers. In an effort to identify adverse trends, we assess the financial health of the markets we operate in and perform periodic credit evaluations of our customers and ongoing reviews of account balances and aging of receivables. Amounts are considered past due when payment has not been received within the time frame of the credit terms extended. Write-offs are charged directly against the allowance for doubtful accounts and occur only after all collection efforts have been exhausted.
Concentrations of Credit Risk
Financial instruments that potentially subject the Company to significant concentrations of credit risk consist primarily of cash and cash equivalents, marketable securities, accounts receivable, and currency forward exchange contracts. We invest our cash and cash equivalents and marketable securities in bank deposits, time deposits, money market securities, equity securities, corporate debt obligations, and government and government-sponsored enterprise bond obligations. The Company had amounts due from two customers that accounted for approximately 32 percent of accounts receivable at December 31, 2013 and amounts due from one customer that accounted for approximately 20 percent of accounts receivable at December 31, 2012.
Research and Development
Costs associated with the development of new products and improvements to existing products are charged to expense as incurred.
Cash and Cash Equivalents and Marketable Securities
Highly liquid investments with maturities of three months or less, when acquired, are classified as cash and cash equivalents. Investments in publicly traded securities with maturities greater than three months, when acquired, are classified as marketable securities.
All of the Company’s marketable securities are classified as available-for-sale as of the balance sheet date and are reported at fair value, with unrealized gains and losses included in stockholders’ equity as a component of accumulated other comprehensive income, net of applicable taxes. We regularly review the fair value of marketable security declines below amortized cost to evaluate whether the decline is other-than-temporary. In making this determination, the Company considers all available evidence including, among other things, considering the duration and extent of the decline and the economic factors influencing the market to determine if the fair value will recover to equal or exceed the amortized cost. If we determine that the fair value will not recover, an other-than-temporary impairment is recognized, net of applicable taxes.
In 2012, we sold our only auction-rate security for $4.2 million resulting in a recognized loss of $0.5 million, which is included in the consolidated statements of operations in the caption “Other expense, net.”
Marketable securities that are in a temporarily impaired position, where management has the ability and intent to hold until anticipated recovery or maturity, are classified as either current or non-current based on the remaining contractual maturity of the security. Those securities in a temporarily impaired position with contractual maturities greater than one year are classified as non-current.
ATMI, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
As part of our ongoing cash management optimization efforts during 2013, the Company purchased South Korean time deposits which were classified as marketable securities. At December 31, 2013 and 2012, the Company had $13.3 million and $16.9 million, respectively, of time deposits in South Korea.
As of December 31, 2013, we had $26.5 million of cash and cash equivalents in South Korea, $6.0 million of cash and cash equivalents in Taiwan and $1.9 million in cash and cash equivalents in Japan, which were not available to fund domestic US operations without repatriation. These funds could become subject to additional tax if they are repatriated. It is not practicable to estimate the amount or timing of the additional tax, if any, that eventually might be paid on these foreign funds. We do not anticipate repatriating these funds in the foreseeable future. Refer to Note 17 for a discussion of restrictions related to the merger agreement with Entegris which could limit or restrict our ability to transfer funds from our subsidiaries should the need arise.
Non-marketable Equity and Debt Securities
We selectively invest in non-marketable equity securities of private companies, which range from early-stage companies that are often still defining their strategic direction to more mature companies whose products or technologies may directly support an ATMI product or initiative. Our non-marketable equity investments are recorded using cost basis or the equity method of accounting, depending on the facts and circumstances of each investment. At December 31, 2013, the carrying value of our portfolio of strategic investments in non-marketable equity securities totaled $6.6 million ($6.6 million at December 31, 2012), of which, $4.0 million are accounted for at cost ($4.0 million at December 31, 2012) and $2.6 million are accounted for using the equity method of accounting ($2.6 million at December 31, 2012). In certain instances, we loan funds to early-stage investees at market interest rates to enable them to focus on product and technology development. At December 31, 2013, we had $0.6 million in outstanding loans and accrued interest ($0.2 million at December 31, 2012). Non-marketable equity and debt securities are included in the consolidated balance sheets under the caption “Other non-current assets.” ATMI’s share of the income or losses of all equity-method investees, using the most current financial information available, which is typically one month behind ATMI’s normal closing date, is included in our results of operations from the investment date forward.
Investments in non-marketable equity securities are inherently risky, and some of these companies are likely to fail. Their success (or lack thereof) is dependent on product development, market acceptance, operational efficiency, attracting and retaining talented professionals, and other key business success factors. In addition, depending on their future prospects, they may not be able to raise additional funds when needed or they may receive lower valuations, with less favorable investment terms than in previous financings, and the investments would likely become impaired.
We review our investments quarterly for indicators of impairment; however, for non-marketable equity securities, the impairment analysis may require significant judgment to identify events or circumstances that would likely have a significant adverse effect on the fair value of the investment. The indicators that we use to identify those events or circumstances include (a) the investee’s revenue and earnings trends relative to predefined milestones and overall business prospects, (b) the technological feasibility of the investee’s products and technologies, (c) the general market conditions in the investee’s industry or geographic area, including adverse regulatory or economic changes, (d) factors related to the investee’s ability to remain in business, such as the investee’s liquidity, and the rate at which the investee is using its cash, and (e) the investee’s receipt of additional funding at a lower valuation.
Investments identified as having an indicator of impairment are subject to further analysis to determine if the investment is other-than-temporarily impaired, in which case we write the investment down to its fair value, using the framework required by Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) 820 “Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures.” When an investee is not considered viable from a financial or technological point of view, we write down the entire investment balance to zero since we consider the estimated fair market value to be nominal. If an investee obtains additional funding at a valuation lower than our carrying amount or requires a new round of equity funding to stay in operation and the new funding does not appear imminent, we presume that the investment is other-than-temporarily impaired, unless specific facts and circumstances indicate otherwise. There were no impairments recognized in our portfolio of non-marketable equity securities in 2013, 2012, or 2011.
In July 2005, ATMI made an investment in Anji Microelectronics Co., Ltd. (“Anji”), an entity in the development stage of researching and developing advanced semiconductor materials, with primary operations in Shanghai, China. We have determined that Anji is a variable interest entity. However, we have determined that we are not the primary beneficiary of Anji because we do not have the power, through voting or similar rights, to direct the activities of Anji that most significantly impact the entity’s economic performance, and we are also not expected to absorb significant losses or gains from Anji. ATMI’s carrying value of this cost basis investment is $3.9 million at December 31, 2013. The carrying value of our investment in Anji represents the cash paid, less our share of the cumulative losses during the period we used the equity-method of accounting. At December 31, 2013, our maximum exposure to loss is our carrying value in this investment of $3.9 million.
ATMI, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Inventories
Inventories are stated at the lower of cost or market, using the first-in, first-out (“FIFO”) method. Finished goods and work in process inventories include direct material, direct labor and manufacturing overhead costs. Inventory valuation reserves are established in order to report inventories at the lower of cost or market value on our consolidated balance sheets. The determination of inventory valuation reserves requires management to make estimates and judgments on the future salability of inventories. Valuation reserves for excess, obsolete, and slow-moving inventory are estimated by comparing the inventory levels of individual parts to both future sales forecasts or production requirements and historical usage rates in order to identify inventory where the resale value or replacement value is less than inventory cost. Other factors that management considers in determining these reserves include whether individual inventory parts or chemicals meet current specifications and cannot be substituted for or reworked into a part currently being sold or used as a service part, overall market conditions, and other inventory management initiatives.
As of December 31, 2013 and 2012, we had $2.9 million of inventory valuation reserves recorded.
Property, Plant, and Equipment, net
Property, plant, and equipment are carried at cost, net of accumulated depreciation. Depreciation is calculated on the straight-line method based on the estimated useful lives of the assets, which range from 3 to 35 years (see Note 6). The estimated useful life represents the projected period of time that the asset will be productively employed by the Company and is determined by management based on many factors, including historical experience with similar assets and technological life cycles. Circumstances and events relating to these assets are monitored to ensure that changes in asset lives or impairments are identified and prospective depreciation expense or impairment expense is adjusted accordingly. The depreciation periods used are: buildings, 5 to 35 years; machinery and equipment, 3 to 15 years; software, 5 to 10 years; cylinders and canisters, 7 to 15 years; furniture and fixtures, 5 years; and leasehold improvements, over the lesser of the lease term or estimated useful life. We use accelerated depreciation methods for tax purposes where appropriate.
Asset-Retirement Obligations
An asset-retirement obligation (“ARO”) is recognized in the period in which sufficient information exists to determine the fair value of the liability with a corresponding increase to the carrying amount of the related property, plant, and equipment which is then depreciated over its useful life. The liability is initially measured at fair value and then accretion expense is recorded in each subsequent period. Refer to Note 8 for further discussion on leases.
Income Taxes
Current income taxes are determined based on estimated taxes payable or refundable on tax returns for the current year. Deferred income taxes are determined using enacted tax rates for the effect of temporary differences between the book and tax bases of recorded assets and liabilities. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in income in the period that includes the enactment date. The Company recognizes the benefit of an income tax position only if it is more likely than not (greater than 50 percent) that the tax position will be sustained upon tax examination, based solely on the technical merits of the tax position. Otherwise, no benefit can be recognized. The tax benefits recognized are measured based on the largest benefit that has a greater than 50 percent likelihood of being realized upon ultimate settlement. We adjust these unrecognized tax benefits, including any impact on the related interest and penalties, in light of changing facts and circumstances. A number of years may elapse before a particular matter for which we have established an unrecognized tax benefit is audited and fully resolved. Additionally, the Company accrues interest and related penalties, if applicable, on all tax exposures for which reserves have been established consistent with jurisdictional tax laws, which is included in income tax expense. Refer to Note 9 for more information and disclosures on income taxes.
ATMI, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
The Company measures and reports financial assets and financial liabilities on a fair value basis, consistent with ASC 820 “Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures,” using the following three categories for classification and disclosure purposes:
Level 1 — Quoted prices in active markets for identical assets and liabilities. Level 1 assets and liabilities consist of cash, money market fund deposits, time deposits, certain of our marketable equity instruments, and forward foreign currency exchange contracts that are traded in an active market with sufficient volume and frequency of transactions.
Level 2 — Observable inputs other than Level 1 prices such as quoted prices for similar assets or liabilities; quoted prices in markets with insufficient volume or infrequent transactions (less active markets); or model-derived valuations in which all significant inputs are observable or can be derived principally from or corroborated by observable market data for substantially the full term of the assets or liabilities. Level 2 assets include certain of our marketable debt instruments with quoted market prices that are traded in less active markets or priced using a quoted market price for similar instruments.
Level 3 — Unobservable inputs to the valuation methodology that are significant to the measurement of fair value of assets or liabilities.
Refer to Note 3 for more information regarding the details, methods and assumptions used to estimate the fair value of our other financial instruments.
Foreign Currency Exchange Contracts
We use forward foreign currency exchange contracts to hedge specific or anticipated exposures relating to intercompany payments (primarily U.S. export sales to subsidiaries at pre-established U.S. dollar prices), intercompany loans, future cash flows and other specific and identified exposures. The terms of the forward foreign currency exchange contracts are matched to the underlying transaction being hedged. Because such contracts are directly associated with identified transactions, they are an effective hedge against fluctuations in the value of the foreign currency underlying the transaction.
Changes in the fair value of economic hedges are recognized in earnings as an offset to the change in the fair value of the underlying exposures being hedged. The changes in fair value of derivatives that are designated as cash-flow hedges are deferred in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) and are recognized in earnings when the underlying hedged transaction occurs. Any ineffectiveness is recognized in earnings immediately. We do not enter into derivative instruments for trading or speculative purposes and all of our derivatives were effective throughout the periods reported.
Counterparties to forward foreign currency exchange contracts are major banking institutions with credit ratings of investment grade or better and no collateral is required. There are no significant risk concentrations. We believe the risk of incurring losses on derivative contracts related to credit risk is remote.
Goodwill and Other Indefinite-Lived Intangible Assets
The assets and liabilities of acquired businesses are recorded under the purchase method of accounting at their estimated fair values at the dates of acquisition. Goodwill represents costs in excess of fair values assigned to the underlying net assets of acquired businesses.
Goodwill and intangible assets deemed to have indefinite lives are not amortized, but are subject to annual impairment testing.
For reporting units where the qualitative determination does not indicate that it is more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is more than its carrying value, the prescribed two step test is performed. In order to perform the two-step test we would estimate the fair value of a reporting unit based on the best information available as of October 31, 2013, which primarily incorporates management assumptions about expected future cash flows and contemplates other valuation techniques. No goodwill impairment has been recorded to date.
Other Long-Lived Assets
We evaluate the potential impairment of other long-lived assets when indicators of impairment are present. If the carrying value of assets exceeds the sum of the undiscounted expected future cash flows, the carrying value of the asset is written down to fair value. We amortize acquired patents and other amortizable intangible assets over their estimated useful lives. All amortizable intangible assets are amortized using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets, ranging from 5 to 15 years.
ATMI, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Intercompany Loans
In certain circumstances, the Company maintains intercompany agreements with and among our wholly-owned subsidiaries under which funds are provided to subsidiaries to finance general business activities and are of a long-term investment nature. When settlement of these loans is not planned or anticipated in the foreseeable future, and there is no repayment schedule as part of the agreements, we defer translation gains and losses on these loans in Accumulated other comprehensive income in the period in which they arise.
Translation of Foreign Currencies
We conduct business in many different currencies and, accordingly, are subject to the inherent risks associated with foreign exchange rate movements. The financial position and results of operations of many of our foreign subsidiaries are measured using the local currency as the functional currency. Foreign currency denominated assets and liabilities are translated into U.S. dollars at the exchange rates existing at the respective balance sheet dates, and income and expense items are translated at the average exchange rates during the respective periods. The aggregate effects of translating the balance sheets of these subsidiaries are deferred as a separate component of Stockholders’ equity.
Equity-based Compensation
The Company recognizes compensation expense in its consolidated financial statements for all share-based payments granted based on the fair value on the date of grant. For share-based payments granted with a service period vesting restriction, compensation expense is recognized on a straight-line basis or accelerated attribution method over the awards’ respective vesting period. For share-based payments granted with a performance condition, we accrue compensation expense when we determine it is probable that the awards will be earned. For share-based payments granted with a market condition, expense is recognized using the accelerated attribution method over the awards’ respective vesting period.
Collaborative Arrangements
ATMI entered into a collaborative development agreement (“CDA”) with an advanced memory integrated circuit manufacturer for the purpose of developing molecules, including chemical precursors, and material systems for next generation semiconductor products. ATMI will use its High Productivity Development platform to collaboratively work with this customer on specific statements of work designed to develop next-generation materials. The agreement, which was signed in September 2011 and expired in August 2012, required the customer to make quarterly payments to ATMI over the contract term. The arrangement has been determined to be a reimbursement of research and development costs and was recognized as a reduction of expense under the caption, “Research and development” in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. We recognized $0.9 million and $2.9 million related to the CDA as of December 31, 2011 and December 31, 2012.
Each CDA we execute will be reviewed based on the unique terms and conditions associated with such arrangement to determine, using applicable accounting guidance, the timing of recognition, whether the arrangement is revenue producing or represents a reimbursement of research and development costs, and the appropriate amounts to be recognized. If an arrangement is determined to be revenue producing, we apply applicable accounting standards to ensure proper timing and amounts of revenue recognition. If an arrangement is determined to represent a reimbursement of research and development costs, we apply accounting standards for reimbursements to ensure proper timing, amounts and classification as an offset to research and development expenses.
Severance Expense
During the first quarter of 2013, we initiated actions to better streamline business activities with our customers and partners and reduce our operational infrastructure. As a result, we recognized $2.6 million of severance expense under the caption, Selling, general & administrative in the consolidated statements of operations. All liabilities associated with this action were settled prior to December 31, 2013.
Recently Adopted Accounting Pronouncements
In December 2011, the FASB issued ASU 2011-11-”Balance Sheet (Topic 210): Disclosures about Offsetting Assets and Liabilities” and in January 2013, the FASB issued ASU 2013-01- “Balance Sheet (Topic 210): Clarifying the Scope of Disclosures about Offsetting Assets and Liabilities.” In ASU 2011-11, entities are required to disclose both gross information and net information about both instruments and transactions eligible for offset in the statement of financial position and instruments and transactions subject to an agreement similar to a master netting arrangement. ASU 2013-01 limits the scope of disclosures to derivatives, repurchase agreements and securities lending arrangements. We were required to apply the amendments retrospectively for annual reporting periods beginning on or after January 1, 2013, and interim periods within those annual periods. There was no material impact from the adoption of these Updates.
ATMI, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
In February 2013, the FASB issued ASU 2013-02-”Comprehensive Income (Topic 220): Reporting of Amounts Reclassified out of Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income.” Substantially all of the information that this Update requires was already disclosed in our financial statements under U.S. GAAP, however, this Update requires additional disclosure about amounts reclassified out of accumulated other comprehensive income and their corresponding effect on net income in one place. We were required to apply the amendments prospectively for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2012. There was no material impact from the adoption of this Update. Refer to Note 12 for the disclosures as a result of adoption of this Update.
Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements
In July 2013, the FASB issued ASU 2013-11-“Presentation of an Unrecognized Tax Benefit When a Net Operating Loss Carryforward, a Similar Tax Loss, or a Tax Credit Carryforward Exists.” In this update, entities are required to offset a liability related to an unrecognized tax benefit against a deferred tax asset for a net operating loss carryforward, a similar tax loss or a tax credit carryforward if such settlement is required or expected in the event the uncertain tax position is disallowed. An entity is required to apply the amendments prospectively for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2013, and interim periods within those annual periods. Retrospective application is permitted. We do not anticipate any material impact from this Update.
In January 2013, the FASB issued ASU 2013-05 - “Parent’s Accounting for the Cumulative Translation Adjustment upon Derecognition of Certain Subsidiaries or Groups of Assets within a Foreign Entity or of an Investment in a Foreign Entity. In this update, an entity will apply the guidance in ASC 830 and recognize CTA in earnings when it ceases to have a controlling financial interest in a subsidiary or group of assets within a consolidated foreign entity and the sale or transfer results in the complete or substantially completed liquidation of the foreign entity in which the subsidiary or group of assets resided. However, when an entity sells either a part or all of its investment in a consolidated foreign entity, it would apply the guidance in ASC 810 and recognize CTA in earnings only if the parent no longer has a controlling financial interest in the foreign entity as a result of the sale. An entity is required to apply the amendments prospectively for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2013, and interim periods within those annual periods. Retrospective application is permitted. We do not anticipate any material impact from this Update.
2. Discontinued Operations
On December 22, 2013, ATMI, Inc. and certain of its subsidiaries entered into a Share and Asset Purchase Agreement with Pall Corporation, to sell and transfer all assets and liabilities primarily related to the LifeSciences business, including all equity interests held in ATMI BVBA, a company organized under the laws of Belgium, in exchange for cash proceeds of $185 million, subject to customary working capital adjustments. The Company has accounted for this segment as a discontinued operation. The operating results of this segment, including restated prior periods, are shown as a discontinued operation in the consolidated statements of operations. The assets and liabilities of the discontinued operation have been classified separately on the consolidated balance sheets in the current assets and liabilities, respectively. The consolidated statements of cash flows are presented as a combination of continuing and discontinued operations. We continued to operate the LifeSciences business and generate cash flows through the transaction close on February 20, 2014.
The Company will continue to perform certain services for Pall Corporation for a transition period following the sale of the LifeSciences business as part of an orderly transition. The Company expects the transition period will be no longer than twelve months. The net cash flows expected to be received and paid by the Company related to the transition services during the transition period are not expected to be material.
Revenues and losses from discontinued operations were as follows (in thousands):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended December 31, |
| | | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 |
| Revenues | | $ | 49,358 |
| | $ | 41,584 |
| | $ | 38,264 |
|
| Loss from discontinued operations before income taxes | | (7,845 | ) | | (6,501 | ) | | (9,906 | ) |
| Loss from discontinued operations, net of tax | | $ | (8,594 | ) | | $ | (5,965 | ) | | $ | (9,055 | ) |
ATMI, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
The assets and liabilities of the discontinued operations were as follows (in thousands):
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, 2013 | | December 31, 2012 |
| Assets: | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 2,800 |
| | $ | 2,342 |
|
| Marketable securities | | 3,050 |
| | — |
|
| Accounts receivable, net | | 9,562 |
| | 7,122 |
|
| Inventories, net | | 15,874 |
| | 10,542 |
|
| Other current assets | | 1,924 |
| | 1,423 |
|
| Property, plant and equipment, net | | 14,267 |
| | 13,379 |
|
| Goodwill, net | | 33,735 |
| | 33,178 |
|
| Other intangible assets, net | | 25,248 |
| | 25,752 |
|
| Other non-current assets | | 14,158 |
| | 7,313 |
|
| Total assets | | $ | 120,618 |
| | $ | 101,051 |
|
| Liabilities: | | | | |
| Accounts payable | | $ | 2,946 |
| | $ | 2,726 |
|
| Accrued liabilities | | 2,630 |
| | 1,044 |
|
| Accrued salaries and related benefits | | 2,117 |
| | 1,682 |
|
| Other current liabilities | | 1,240 |
| | 2,307 |
|
| Other non-current liabilities | | 4,175 |
| | 4,618 |
|
| Total liabilities | | 13,108 |
| | 12,377 |
|
3. Fair Value Measurements and Marketable Securities
Assets / Liabilities Measured at Fair Value on a Recurring Basis
This table summarizes the Company’s assets (liabilities) measured at fair value on a recurring basis at December 31, 2013 (in thousands):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | Fair Value Measured Using |
| | | Total | | Quoted Prices in Active Markets for (Level 1) | | Significant Other Observable Inputs (Level 2) | | Significant Unobservable Inputs (Level 3) |
| Cash & cash equivalents | | $ | 82,646 |
| | $ | 82,646 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Available-for-sale marketable securities | | | | | | | | |
| Common stock | | $ | 12,754 |
| | $ | 12,754 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Time deposits | | $ | 13,260 |
| | $ | 13,260 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Corporate debt obligations | | $ | 7,244 |
| | — |
| | $ | 7,244 |
| | — |
|
| Government debt obligations | | $ | 12,943 |
| | — |
| | $ | 12,943 |
| | — |
|
| Government sponsored enterprise debt obligations | | $ | 2,225 |
| | — |
| | $ | 2,225 |
| | — |
|
Foreign currency exchange contract asset (1) | | $ | 30 |
| | $ | 30 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
Foreign currency exchange contract liability (1) | | $ | (409 | ) | | $ | (409 | ) | | — |
| | — |
|
| |
(1) | Refer to Note 5 for additional disclosures on Foreign Currency Exchange Contracts |
In 2013, our valuation methodologies were consistent with previous years, and there were no transfers made among the three levels of the valuation hierarchy.
ATMI, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Assets / Liabilities Measured at Fair Value on a Nonrecurring Basis
During the fourth quarter of 2013, we completed negotiations with Intermolecular, Inc., which resulted in the discontinuation of site, maintenance, and license support for certain long-lived HPD assets. In accordance with the provisions of ASC 360 “Property, Plant and Equipment”, long-lived assets held and used with a carrying amount of $10.8 million and the related prepaid support fees with a carrying amount of $0.7 million were deemed to be impaired and we recorded a charge to reduce the net book value of the assets to zero, which is included in the caption "Research and development" in the consolidated statements of operations.
In 2012, we received $2.6 million of research and development equipment as compensation for a royalty agreement with a third party. The fair value of the equipment was determined using Level 3 inputs, including cash flow analysis and also the use of market comparables for similar equipment. The fair value of the equipment is recorded as revenues in the consolidated statements of operations.
Due to their nature, the carrying value of cash, receivables, and payables approximates fair value.
Marketable securities include at December 31, (in thousands):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Cost | | 2013 Gross Unrealized Gain (Loss) (3) | | Estimated Fair Value | | Cost | | 2012 Gross Unrealized Gain (Loss) (3) | | Estimated Fair Value |
| Securities in unrealized gain position: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Common stock | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 22,376 |
| | $ | 13,049 |
| | $ | 35,425 |
|
| Corporate debt obligations | 3,415 |
| | 6 |
| | 3,421 |
| | 4,211 |
| | 4 |
| | 4,215 |
|
Government debt obligations (1) | 11,393 |
| | 11 |
| | 11,404 |
| | 4,495 |
| | 14 |
| | 4,509 |
|
GSE (2) debt obligations | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 3,501 |
| | — |
| | 3,501 |
|
| U.S. Treasury obligations | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 4,023 |
| | — |
| | 4,023 |
|
| Subtotal | 14,808 |
| | 17 |
| | 14,825 |
| | 38,606 |
| | 13,067 |
| | 51,673 |
|
| Securities in unrealized loss position: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Common stock | 14,870 |
| | (2,116 | ) | | 12,754 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Corporate debt obligations | 3,824 |
| | (1 | ) | | 3,823 |
| | 4,844 |
| | (7 | ) | | 4,837 |
|
| Government debt obligations | 1,039 |
| | — |
| | 1,039 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| GSE debt obligations | 2,226 |
| | (1 | ) | | 2,225 |
| | 8,251 |
| | (1 | ) | | 8,250 |
|
| Subtotal | 21,959 |
| | (2,118 | ) | | 19,841 |
| | 13,095 |
| | (8 | ) | | 13,087 |
|
| Securities at amortized cost: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Time deposits | 13,260 |
| | — |
| | 13,260 |
| | 16,920 |
| | — |
| | 16,920 |
|
| Corporate debt obligations | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 790 |
| | — |
| | 790 |
|
| Government debt obligations | 500 |
| | — |
| | 500 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Subtotal | 13,760 |
| | — |
| | 13,760 |
| | 17,710 |
| | — |
| | 17,710 |
|
| Total marketable securities | $ | 50,527 |
| | $ | (2,101 | ) | | $ | 48,426 |
| | $ | 69,411 |
| | $ | 13,059 |
| | $ | 82,470 |
|
| |
(1) | State and municipal government debt obligations. |
| |
(2) | Government sponsored enterprise. |
| |
(3) | Unrealized gains or losses of less than $500 for each category are reflected as a dash. |
We recorded a $2.0 million gain in earnings as a result of sales of Intermolecular, Inc. common stock during 2013. At December 31, 2013 we own Intermolecular, Inc. common shares with a market value of $12.8 million, including a temporary unrealized loss of $2.1 million due to recent declines in market price of their common stock.
The amortized cost and estimated fair value of available-for-sale securities, by contractual maturity, as of December 31, 2013 are shown below (in thousands); expected maturities may differ from contractual maturities because the issuers of the securities may exercise the right to prepay obligations without prepayment penalties.
ATMI, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
|
| | | | | | | |
| | Cost | | Estimated Fair Value |
| Due in one year or less | $ | 29,779 |
| | $ | 29,789 |
|
| Due between one and three years | 5,878 |
| | 5,883 |
|
| | 35,657 |
| | 35,672 |
|
| Common stock | 14,870 |
| | 12,754 |
|
| | $ | 50,527 |
| | $ | 48,426 |
|
This table shows the Company’s marketable securities that were in an unrealized loss position at December 31, 2013, and also shows the duration of time the security had been in an unrealized loss position (in thousands):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Less Than 12 Months | | 12 Months or Greater | | Total |
| | | Fair Value | | Unrealized Losses | | Fair Value | | Unrealized Losses | | Fair Value | | Unrealized Losses |
| Common stock | | $ | 12,754 |
| | $ | (2,116 | ) | | $ | — |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 12,754 |
| | $ | (2,116 | ) |
| Corporate debt obligations | | — |
| | — |
| | 3,823 |
| | (1 | ) | | 3,823 |
| | (1 | ) |
| Government debt obligations | | 1,039 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 1,039 |
| | — |
|
GSE (1) debt obligations | | 2,225 |
| | (1 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | 2,225 |
| | (1 | ) |
Total (2) | | $ | 16,018 |
| | $ | (2,117 | ) | | $ | 3,823 |
| | $ | (1 | ) | | $ | 19,841 |
| | $ | (2,118 | ) |
| |
(1) | Government sponsored enterprise. |
| |
(2) | As of December 31, 2013, we had 6 securities in an unrealized loss position. We have evaluated the near-term prospects of the investments in relation to the severity and duration of the decline in fair value and based on that evaluation we have concluded that we have the ability and intent to hold these investments until the recovery of fair value. |
4. Inventories
Inventories include at December 31, (in thousands):
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | | 2013 | | 2012 |
| Raw materials | | $ | 25,216 |
| | $ | 23,972 |
|
| Work in process | | 1,615 |
| | 799 |
|
| Finished goods | | 52,592 |
| | 55,127 |
|
| | | 79,423 |
| | 79,898 |
|
| Excess and obsolescence reserve | | (2,938 | ) | | (2,886 | ) |
| Inventories, net | | $ | 76,485 |
| | $ | 77,012 |
|
As of December 31, 2013, the Company had commitments for inventory purchases of $73.0 million.
As December 31, 2013 and 2012, respectively, we had $5.5 million and $5.1 million of finished goods inventory residing at non-ATMI consignment locations.
5. Foreign Currency Exchange Contracts
At December 31, 2013, we held foreign currency exchange contracts, not designated as cash flow hedges, with notional amounts totaling $46.0 million of which $32.5 million will be settled in Euros, $1.2 million will be settled in Taiwan Dollars, $6.6 million will be settled in Korean Won, $1.7 million will be settled in Chinese Yuan Renminbi, and $4.0 million will be settled in Japanese Yen. At December 31, 2013, we held forward foreign currency exchange contracts designated as cash flow hedges with notional amounts totaling $11.9 million, which will be settled in Japanese Yen. The cash flow hedges held at December 31, 2013 mature monthly through the fourth quarter of 2014. At December 31, 2013, the accumulated net unrecognized losses that are expected to be reclassified into earnings during the next twelve months is $1.4 million.
ATMI, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
The Company recorded a net loss of $0.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2013, a net gain of $1.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2012, and a net loss of $2.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2011, under the caption “Other expense, net” in the Consolidated Statements of Operations related to changes in the fair value of the foreign currency exchange contract economic hedges. The Company recorded net gains of $0.3 million and $1.1 million for the twelve months ended December 31, 2013 and December 31, 2012, respectively in other comprehensive income related to the change in the fair value of cash flow hedges. Reclassification of deferred gains in other comprehensive income into earnings was $2.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2013 and reclassification of deferred losses in other comprehensive income into earnings was $0.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2012.
At December 31, 2012, we held foreign currency exchange contracts, not designated as cash flow hedges, with notional amounts totaling $22.6 million, of which $9.0 million were settled in Euros, $4.2 million were settled in Taiwan Dollars, $3.6 million were settled in Japanese Yen, and $5.8 million were settled in Korean Won. At December 31, 2012, we held forward foreign currency exchange contracts designated as cash flow hedges with notional amounts totaling $19.1 million, which were settled in Japanese Yen, and the accumulated net unrecognized losses reclassified into earnings during 2013 was $0.8 million.
6. Property, Plant and Equipment, Net
Property, plant, and equipment, net, consists of the following (in thousands):
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, |
| | | 2013 | | 2012 |
| Land | | $ | 1,203 |
| | $ | 1,149 |
|
| Buildings | | 30,033 |
| | 22,109 |
|
| Machinery and equipment | | 121,610 |
| | 122,043 |
|
| Software | | 26,754 |
| | 25,122 |
|
| Cylinders and canisters | | 64,091 |
| | 57,711 |
|
| Furniture and fixtures | | 2,139 |
| | 1,977 |
|
| Leasehold improvements | | 21,539 |
| | 18,749 |
|
| Construction in progress | | 21,394 |
| | 13,448 |
|
| | | 288,763 |
| | 262,308 |
|
| Accumulated depreciation and amortization | | (168,301 | ) | | (150,588 | ) |
| | | $ | 120,462 |
| | $ | 111,720 |
|
Depreciation and amortization expense for property, plant, and equipment for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011 was 20.4 million, 19.9 million, and 20.1 million, respectively.
Fully depreciated assets, which were no longer in use, of approximately $0.5 million (primarily machinery and equipment and cylinders) and $11.4 million were written off in the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
We recognized disposals and impairment losses from property, plant, and equipment of $11.7 million, $0.9 million, and $0.6 million, in the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011, respectively. Refer to Note 3 for additional information.
As of December 31, 2013, the Company had commitments for capital expenditures of $1.4 million.
This table shows amounts recorded in the consolidated statements of operations related to depreciation expense for property, plant, and equipment (in thousands):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| |
| 2013 |
| 2012 |
| 2011 |
| Cost of revenues |
| $ | 9,286 |
|
| $ | 8,801 |
|
| $ | 8,889 |
|
| Research and development |
| 8,111 |
|
| 7,609 |
|
| 7,211 |
|
| Selling, general, and administrative |
| 3,039 |
|
| 3,446 |
|
| 4,021 |
|
| Total depreciation and amortization |
| $ | 20,436 |
|
| $ | 19,856 |
|
| $ | 20,121 |
|
ATMI, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
7. Goodwill and Other Intangibles
Goodwill and other intangibles balances at December 31, 2013 and 2012 were (in thousands):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Goodwill | | Patents & Trademarks | | Other | | Total Other Intangibles |
| Gross amount as of December 31, 2012 | | $ | 13,653 |
| | $ | 33,404 |
| | $ | 9,784 |
| | $ | 43,188 |
|
| Accumulated amortization | | — |
| | (20,847 | ) | | (1,163 | ) | | (22,010 | ) |
| Balance at December 31, 2012 | | $ | 13,653 |
| | $ | 12,557 |
| | $ | 8,621 |
| | $ | 21,178 |
|
| Gross amount as of December 31, 2013 | | $ | 13,657 |
| | $ | 33,440 |
| | $ | 9,784 |
| | $ | 43,224 |
|
| Accumulated amortization | | — |
| | (22,677 | ) | | (2,161 | ) | | (24,838 | ) |
| Balance at December 31, 2013 | | $ | 13,657 |
| | $ | 10,763 |
| | $ | 7,623 |
| | $ | 18,386 |
|
Changes in carrying amounts of goodwill and other intangibles for the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012, respectively, were (in thousands):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Goodwill | | Patents & Trademarks | | Other | | Total Other Intangibles |
| Balance at December 31, 2011 | | $ | 13,606 |
| | $ | 7,812 |
| | $ | 11,605 |
| | $ | 19,417 |
|
| Acquisitions | | — |
| | 6,268 |
| | — |
| | 6,268 |
|
| Amortization expense | | — |
| | (1,523 | ) | | (967 | ) | | (2,490 | ) |
| Other, including foreign currency translation | | 47 |
| | — |
| | (2,017 | ) | | (2,017 | ) |
| Balance at December 31, 2012 | | $ | 13,653 |
| | $ | 12,557 |
| | $ | 8,621 |
| | $ | 21,178 |
|
| Amortization expense | | — |
| | (1,830 | ) | | (998 | ) | | (2,828 | ) |
| Other, including foreign currency translation | | 4 |
| | 36 |
| | — |
| | 36 |
|
| Balance at December 31, 2013 | | $ | 13,657 |
| | $ | 10,763 |
| | $ | 7,623 |
| | $ | 18,386 |
|
This table shows amounts recorded in the consolidated statements of operations related to amortization expense for intangibles (in thousands):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended December 31, |
| | | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 |
| Research and development | | 399 |
| | 92 |
| | — |
|
| Selling, general, and administrative | | 2,429 |
| | 2,398 |
| | 1,628 |
|
| Total amortization | | $ | 2,828 |
| | $ | 2,490 |
| | $ | 1,628 |
|
The approximate amortization expense expected to be recognized related to intangible assets is (in thousands):
|
| | | |
| Year | Amount |
| 2014 | $ | 2,849 |
|
| 2015 | 2,849 |
|
| 2016 | 2,849 |
|
| 2017 | 2,073 |
|
| 2018 | 1,417 |
|
| Thereafter | 6,349 |
|
| Total | $ | 18,386 |
|
ATMI, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
In October 2012, ATMI acquired commercial and exclusive intellectual property rights related to certain electronic waste recovery technology. ATMI recorded $6.3 million of intangible assets in the acquisition of which $5.5 million was cash consideration and $0.8 million was the non-cash portion. This asset is being amortized over 15 years. The net book value of the intellectual property rights at December 31, 2013 was $5.8 million.
In conjunction with the SDS Direct transaction in 2011, we recognized intangible assets of $11.8 million for the reacquired rights ($8.8 million) and a non-competition agreement ($3.0 million) net of liabilities assumed. The useful lives of the reacquired rights and the non-competition agreement are 10 years and 9 years, respectively. In 2012, $2.0 million of purchase price refinements have reduced the initial values recorded as certain fees have been recovered from the seller, resulting in the final intangible asset cost basis of $9.8 million. The net book value of the intangible assets at December 31, 2013 was $7.6 million.
The license for our distribution rights to Enthone’s copper ECD products, including its ViaForm products, was automatically renewed upon satisfaction of certain conditions in 2013. The net book value of the licensing right at December 31, 2013 was $4.9 million.
8. Leases
The Company leases office, and manufacturing facilities, certain manufacturing equipment, and land under several operating leases expiring between 2014 and 2034. Rental expense was $3.5 million, $3.4 million, and $3.2 million, for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011, respectively.
Below is a schedule of future minimum lease payments for operating leases as of December 31, 2013 (in thousands):
|
| | | |
| | Operating Leases |
| 2014 | $ | 2,760 |
|
| 2015 | 2,124 |
|
| 2016 | 1,570 |
|
| 2017 | 468 |
|
| 2018 | 209 |
|
| Thereafter | 268 |
|
| Total minimum lease payments | $ | 7,399 |
|
We lease two facilities in Danbury, CT. One facility houses our research and development activities and certain of our manufacturing capabilities, and contains approximately 73,000 square feet of space. In December 2010 we exercised a renewal option for the period January 1, 2012 to December 31, 2016. For the period January 1, 2012 to December 31, 2016, the monthly base rent is $47,500. There is one additional five-year renewal period available to ATMI under this lease. We have agreed to certain restoration obligations associated with this facility, which we are accounting for as an asset retirement obligation (“ARO”), associated with the leasehold improvements made to this facility. The discounted fair value of the ARO at December 31, 2013 is $2.8 million.
The other facility in Danbury, CT is our headquarters, and contains approximately 31,000 square feet of space. In October 2010, we exercised a renewal option for the period January 1, 2012 to December 31, 2016. For the period January 1, 2011 to December 31, 2016, the monthly base rent is $17,606. There is one additional five-year renewal period available to ATMI under this lease.
Changes in the carrying amounts of the Company’s AROs at December 31, 2013 are shown below (in thousands):
|
| | | |
| Balance at December 31, 2012 | $ | 3,574 |
|
| Liabilities settled | (8 | ) |
| Liabilities incurred | 28 |
|
| Accretion expense | 54 |
|
| Revisions in estimated cash flows | (33 | ) |
| Balance at December 31, 2013 | $ | 3,615 |
|
The ARO liability is included in the consolidated balance sheets under the caption, “Other non-current liabilities.”
ATMI, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
9. Income Taxes
Pre-tax income (loss) was taxed in these jurisdictions (in thousands):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Year Ended December 31, |
| | | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 |
| Domestic | | $ | 31,561 |
| | $ | 41,970 |
| | $ | (54,333 | ) |
| Foreign | | 19,395 |
| | 24,656 |
| | 25,104 |
|
| Total pre-tax income (loss) | | $ | 50,956 |
| | $ | 66,626 |
| | $ | (29,229 | ) |
Significant components of the provision (benefit) for income taxes for the following years ended are (in thousands):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, |
| | | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 |
| Current: | | | | | | |
| Federal | | $ | (3,817 | ) | | $ | 12,001 |
| | $ | 6,778 |
|
| State | | 271 |
| | 344 |
| | 277 |
|
| Foreign | | 5,082 |
| | 1,638 |
| | 2,632 |
|
| Total current | | 1,536 |
| | 13,983 |
| | 9,687 |
|
| Deferred: | | | | | | |
| Federal | | 10,951 |
| | 3,210 |
| | (26,547 | ) |
| State | | 570 |
| | 436 |
| | (2,070 | ) |
| Foreign | | (860 | ) | | 702 |
| | 665 |
|
| Total deferred | | 10,661 |
| | 4,348 |
| | (27,952 | ) |
| | | $ | 12,197 |
| | $ | 18,331 |
| | $ | (18,265 | ) |
Significant components of the Company’s deferred tax assets and liabilities are (in thousands):
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, |
| | | 2013 | | 2012 |
| Deferred tax assets: | | | | |
| Accrued liabilities | | $ | 3,624 |
| | $ | 4,581 |
|
| Inventory reserves | | 2,166 |
| | 2,227 |
|
| Net operating loss and tax credit carryforwards | | 3,369 |
| | 2,747 |
|
| Equity-based compensation | | 7,929 |
| | 8,613 |
|
| Reacquired rights on contract termination | | 14,112 |
| | 27,013 |
|
| Other, net | | 747 |
| | 96 |
|
| | | 31,947 |
| | 45,277 |
|
| Valuation allowance | | (574 | ) | | (359 | ) |
| | | 31,373 |
| | 44,918 |
|
| Deferred tax liabilities: | | | | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | (16,146 | ) | | (20,525 | ) |
| Unrealized gain on marketable securities | | — |
| | (4,408 | ) |
| Other, net | | (3,309 | ) | | (3,184 | ) |
| | | (19,455 | ) | | (28,117 | ) |
| Net deferred tax assets | | $ | 11,918 |
| | $ | 16,801 |
|
The valuation allowance relates to the realizability of certain U.S. state and foreign net operating losses.
ATMI, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
As of December 31, 2013, the Company had the following deferred tax assets related to net operating loss (“NOLs”) and tax credit carryforwards (in thousands):
|
| | | | | | |
| | | | | Expiration |
| Federal | | | | |
| -Capital Loss | | $ | 472 |
| | 2015-2017 |
| | | $ | 472 |
| | |
| State | | | | |
| -NOLs | | 478 |
| | 2014-2033 |
| -Credits | | 54 |
| | 2024-2028 |
| -Credits | | 216 |
| | None |
| | | $ | 748 |
| | |
| Foreign | | | | |
| -NOLs | | 998 |
| | None |
| -NOLs | | 161 |
| | 2017-2018 |
| -Credits | | 990 |
| | 2017-2018 |
| | | $ | 2,149 |
| | |
| Total | | $ | 3,369 |
| | |
The reconciliation of income tax expense (benefit) from continuing operations computed at the U.S. federal statutory tax rate to the Company’s tax expense (benefit) is (in thousands):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | For the Year Ended December 31, |
| | | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 |
| U.S. statutory rate | | $ | 17,834 |
| | $ | 23,319 |
| | $ | (10,231 | ) |
| State income taxes | | 312 |
| | 507 |
| | (1,165 | ) |
| Foreign income taxes | | (3,193 | ) | | (6,675 | ) | | (6,144 | ) |
| Change in valuation allowance of deferred tax assets | | 235 |
| | 388 |
| | (347 | ) |
| Other, net | | (2,991 | ) | | 792 |
| | (378 | ) |
| | | $ | 12,197 |
| | $ | 18,331 |
| | $ | (18,265 | ) |
We recorded income tax expense of $0.7 million, and income tax benefits of $0.5 million and $0.9 million from discontinued operations for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012, and 2011.
ATMI has not provided for U.S. federal income and foreign withholding taxes on approximately $88.5 million of undistributed earnings from non-U.S. operations as of December 31, 2013, because such earnings are intended to be reinvested indefinitely outside of the United States. These earnings could become subject to additional tax if they are remitted as dividends, loaned to ATMI, or upon sale of subsidiary stock. It is not practicable to estimate the amount or timing of the additional tax, if any, that eventually might be paid on the foreign earnings.
South Korea has granted the Company an income tax exemption that expires in 2014, including the reduction from 100 percent to 50 percent of the exemption in 2013 and 2014. The exemption applies only to income related to one of the Company’s product lines. The effect of the tax exemption was to reduce income tax expense by $0.9 million, $2.3 million, and $2.8 million for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012, and 2011. In December 2013, the Company was granted a new tax exemption related to the manufacturing of different product lines at its recently-built JangAn facility; the tax exemption is for a seven year period that is expected to start in 2014.
ATMI, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
At December 31, 2013, ATMI had $2.3 million of unrecognized tax benefits which, if recognized, would favorably affect the effective income tax rate in future periods. $0.2 million of this amount is included in deferred taxes, and the balance of $2.1 million is included in the caption “Other non-current liabilities” on the consolidated balance sheets, together with $0.3 million of accrued interest (net) on tax reserves and $0 accrued for penalties. At December 31, 2012, the amount of unrecognized tax benefits (out of a total of $30.6 million), which, if recognized, would have favorably affected the effective income tax rate in future periods, was $3.6 million, $0.6 million of accrued interest (net) on tax reserves and $0 accrued for penalties. At December 31, 2011, the amount of unrecognized tax benefits, which, if recognized, would have favorably affected the effective income tax rate in future periods, was $3.7 million, $0.4 million of accrued interest (net) on tax reserves and $0 accrued for penalties.
The reconciliation of the unrecognized tax benefits (exclusive of interest) at the beginning of 2012 through the end of 2013 is (in thousands):
|
| | | |
| Ending Balance - December 31, 2011 | $ | 3,656 |
|
| Increases from prior period positions | 27,015 |
|
| Decreases from prior period positions | (159 | ) |
| Increases from current period positions | 467 |
|
| Decreases related to settlements with taxing authorities | (224 | ) |
| Decreases from lapse of statute of limitations | (127 | ) |
| Ending Balance - December 31, 2012 | $ | 30,628 |
|
| Increases from prior period positions | 359 |
|
| Decreases from prior period positions | (74 | ) |
| Increases from current period positions | 454 |
|
| Decreases related to settlements with taxing authorities | (27,868 | ) |
| Decreases from lapse of statute of limitations | (1,163 | ) |
| Balance at December 31, 2013 | $ | 2,336 |
|
In the next 12 months, the Company does not expect any material decreases to the unrecognized tax benefits for tax positions taken related to previously filed tax returns.
At December 31, 2012, the Company had $27.0 million of unrecognized tax benefits related to the timing of deduction of the reacquired rights due to the Matheson contract termination. This uncertainty was resolved in 2013 as the Internal Revenue Service completed the audit of tax years 2010 and 2011, for which the Company paid $8.2 million (including $0.2 million of interest). Except for interest expense associated with the timing of the payment, since it was an uncertainty related to the timing of the deduction, the reversal of the $27.0 million of unrecognized tax benefits in 2013 had no impact on the income statement or on our effective tax rate. The reversal also resulted in a reclassification between taxes payable and deferred taxes on the balance sheet, to properly reflect in deferred tax assets the future amortization tax effect of the reacquired rights.
10. Defined Contribution Plan
The Company maintains a defined contribution plan (401(k) Plan) covering substantially all of its U.S. employees that is subject to the provisions of the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974. The Company’s matching contributions are discretionary by plan year and were approximately $1.5 million, $1.6 million, and $1.6 million for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011, respectively. The Plan provides for discretionary matching contributions of 100 percent of the first 3 percent of each participant’s eligible compensation plus 50 percent on the next 2 percent of each participant’s eligible compensation, up to statutory limitations. There is no matching contribution above 5 percent of each participant’s eligible compensation.
ATMI, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
11. Stockholders’ Equity
This table shows the effect of pre-tax compensation cost arising from equity-based payment arrangements recognized in income (loss) from continuing operations (in thousands):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | December 31, |
| | | 2013 |
| 2012 |
| 2011 |
| Cost of revenues | | $ | 161 |
|
| $ | 232 |
|
| $ | 406 |
|
| Research and development | | 476 |
|
| 612 |
|
| 794 |
|
| Selling, general, and administrative | | 6,144 |
|
| 6,954 |
|
| 5,878 |
|
| Total equity-based compensation expense | | $ | 6,781 |
|
| $ | 7,798 |
|
| $ | 7,078 |
|
No equity-based compensation cost was capitalized.
Summary of Plans
We currently have two equity-based compensation plans which provide for the granting of up to 4,000,000 shares of common stock pursuant to nonqualified stock options, incentive stock options (“ISOs”), stock appreciation rights, Total Shareholder Return Performance Restricted Stock Units (“TSR PRSU”), and restricted stock awards to employees, directors and consultants of the Company. Stock options typically vest over periods ranging from one to four years with a maximum term of ten years. Restricted stock awards and units typically vest over periods ranging from three to five years. Shares issued as a result of stock option exercises are primarily settled by the issuance of new shares.
This table shows the number of shares approved by shareholders for each plan and the number of shares that remain available for equity awards at December 31, 2013 (in thousands):
|
| | | | | | |
| Stock Plan | | # of Shares Approved | | # of Shares Available |
2010 Stock Plan (1) | | 3,000 |
| | 2,189 |
|
Employee Stock Purchase Plan (2) | | 1,000 |
| | 227 |
|
| Totals | | 4,000 |
| | 2,416 |
|
| |
(1) | Exercise prices for ISOs and non-qualified stock options granted under this plan may not be less than 100 percent of the fair market value for the Company’s common stock on the date of grant. |
| |
(2) | Employees may purchase shares at 95 percent of the closing price on the day previous to the last day of each six-month offering period. This plan is not considered to be compensatory. |
Fair Value
The Company uses the Black-Scholes-Merton options-pricing model to determine the fair value of stock options under ASC 718 “Compensation – Stock Compensation.” Management is required to make certain assumptions with respect to selected model inputs, including anticipated changes in the underlying stock price (i.e., expected volatility) and option exercise activity (i.e., expected term). For awards granted subsequent to January 1, 2006, expected volatility is based on the historical volatility of ATMI common stock for a period shorter than the expected term of the options. For awards granted in 2010 and 2011, expected volatility is based on the historical volatility of ATMI common stock for a period shorter than the expected term of the options. We have excluded the historical volatility prior to the public announcement regarding the sale of our non-core businesses in 2004, solely because those businesses that were sold represented a significant portion of ATMI’s consolidated business and were subject to considerable cyclicality associated with the semiconductor equipment industry, which drove increased volatility in ATMI’s stock price, which we did not believe would be representative of future expected volatility. The expected term of options granted is derived using historical exercise patterns which represent the period of time that options granted are expected to be outstanding. The risk-free rate is based on the U.S. yield curve in effect at the time of grant for a period commensurate with the estimated expected term. In accordance with ASC 718, in the determination of equity-based compensation cost, the Company estimates the total number of instruments that will be forfeited as a result of a failure to provide the requisite service to earn the award.
ATMI, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
To estimate the fair value of our TSR PRSU’s, we use a Monte-Carlo simulation of future stock prices for ATMI and the components of the Russell 2000 index. This method uses a risk-neutral framework to model future stock prices. The stock price projections are based upon estimates for the risk-free rate of return, the volatility of our stock and the others included in the Russell 2000 index, and the correlation of each stock within the Russell 2000 index. Management is required to make certain judgments for these estimates.
The weighted-average fair value of options granted during the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011 was $10.34, $11.66 and $9.66, respectively, based on the Black-Scholes-Merton options-pricing model. These weighted-average assumptions were used for grants in the periods indicated:
|
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 |
| Stock option grants: | | | | | | |
| Risk free interest rate | | 1.59 | % | | 1.52 | % | | 3.15 | % |
| Expected term, in years | | 7.92 |
| | 7.87 |
| | 7.85 |
|
| Expected volatility | | 41.00 | % | | 42.84 | % | | 43.30 | % |
| Dividend yield | | — | % | | — | % | | — | % |
The Company uses historical data to estimate forfeitures of awards from employee terminations in order to estimate compensation cost for awards expected to vest. In addition, we separate employees into groups that have similar characteristics for purposes of making forfeiture estimates.
Stock Option and Restricted Stock Activity
This table shows the option activity under our current and prior plans as of December 31, 2013 and changes during the year then ended (options are expressed in thousands; averages are calculated on a weighted basis; life in years; intrinsic value expressed in thousands):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Number of Options | | Average Exercise Price | | Average Remaining Life | | Aggregate Intrinsic Value |
| Outstanding at December 31, 2012 | | 1,528 |
| | $ | 21.98 |
| | | | |
| Granted | | 180 |
| | $ | 21.92 |
| | | | |
| Exercised | | (391 | ) | | $ | 19.87 |
| | | | |
| Forfeited | | (47 | ) | | $ | 20.65 |
| | | | |
| Expired | | (109 | ) | | 27.48 |
| | | | |
| Outstanding at December 31, 2013 | | 1,161 |
| | $ | 22.22 |
| | 5.4 | | $ | 9,409 |
|
| Exercisable at December 31, 2013 | | 822 |
| | $ | 22.57 |
| | 4.2 | | $ | 6,401 |
|
The aggregate intrinsic value represents the difference between the Company’s closing stock price of $30.21 as of December 31, 2013 and the exercise price of the dilutive options at that date, multiplied by the number of dilutive options outstanding at that date. The total intrinsic value of stock options exercised during the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011 was $2.4 million, $0.6 million, and $0.1 million, respectively. The total fair value of options which vested during the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011 was $1.8 million (184,000 shares), $1.9 million (203,000 shares), and $1.7 million (184,000 shares) respectively.
There was no income tax deficiency recognized in additional paid-in capital from equity-based compensation for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011 respectively. An income tax deficiency was recognized in income tax expense from equity-based compensation totaling $0.2 million, $0.2 million, and $0.9 million for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012, and December 31, 2011, respectively.
ATMI, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
This table shows restricted stock activity as of December 31, 2013 and changes during the year then ended (shares are expressed in thousands; averages are calculated on a weighted basis):
|
| | | | | | | |
| | | Number of Shares | | Average Grant Date Fair Value |
| Nonvested at December 31, 2012 | | 1,073 |
| | $ | 18.75 |
|
| Granted | | 340 |
| | $ | 22.47 |
|
| Vested | | (255 | ) | | $ | 18.00 |
|
| Forfeited | | (152 | ) | | $ | 19.17 |
|
| Nonvested at December 31, 2013 | | 1,006 |
| | $ | 20.14 |
|
The total fair value of restricted stock which vested during the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011 was $4.6 million, $5.7 million and $5.3 million, respectively.
As of December 31, 2013, $2.1 million of unrecognized compensation cost related to non-vested stock options is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of approximately 1.6 years. As of December 31, 2013, $8.9 million of unrecognized compensation cost related to restricted stock is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of approximately 2.2 years. As of December 31, 2013, $0.6 million of unrecognized compensation cost related to TSR PRSU’s is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of approximately 1.2 years.
Earnings Per Share
This table shows the computation of basic and diluted earnings per share (in thousands, except per share data):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 |
| Numerator: | | | | | | |
| Income (loss) from continuing operations | | $ | 38,759 |
| | $ | 48,295 |
| | $ | (10,964 | ) |
| Denominator: | | | | | | |
| Denominator for basic earnings per share | | | | | | |
| - weighted average shares | | 31,911 |
| | 31,931 |
| | 31,703 |
|
| Dilutive effect of employee stock options | | 162 |
| | 168 |
| | — |
|
| Dilutive effect of restricted stock | | 678 |
| | 565 |
| | — |
|
| Denominator for diluted earnings per common share – weighted average shares | | 32,751 |
| | 32,664 |
| | 31,703 |
|
| Earnings (loss) per common share from continuing operations - basic | | 1.21 |
| | 1.51 |
| | (0.35 | ) |
| Earnings (loss) per common share from continuing operations - diluted | | 1.18 |
| | 1.48 |
| | (0.35 | ) |
This table shows the potential common shares excluded from the calculation of weighted-average shares outstanding because their effect was considered to be antidilutive (in thousands):
|
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 |
| Antidilutive shares | | 581 |
| | 1,069 |
| | 2,144 |
|
The Company has never declared or paid cash dividends on its capital stock. Refer to Note 17 for discussion of restrictive covenants related to the Agreement and Plan of Merger with Entegris.
In August 2010, the Company’s Board of Directors approved a share repurchase program for up to $50.0 million of ATMI common stock. The program, which has no expiration date, does not require the Company to purchase any specific number or amount of shares and may be suspended or reinstated at any time at the Company’s discretion and without notice. Under the terms of the share repurchase program, repurchases can be made from time to time in open market transactions at prevailing market prices or in privately negotiated transactions. Management determined the timing and amount of purchases under the repurchase program based upon market conditions or other factors.
ATMI, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Under all the repurchase programs approved by the Company’s Board of Directors, the Company purchased a total of 8,787,077 shares of its common stock at an average price of $27.80 per share. Our merger agreement with Entegris restricts our ability to repurchase shares. Please see Note 17 for further details.
12. Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income
The components of accumulated other comprehensive income are (in thousands):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Currency Translation Adjustments | | Unrealized Gain (Loss) on Available-for- Sale Securities | | Unrealized Gain (Loss) on Derivative Instruments | | Total |
| Balance at December 31, 2010 | | $ | 4,167 |
| | $ | (139 | ) | | — |
| | $ | 4,028 |
|
Reclassification adjustment related to marketable securities in net unrealized gain at prior period end, net of $0 tax provision (1) | | — |
| | (1 | ) | | — |
| | (1 | ) |
| Change in fair value of available-for-sale securities, net of deferred income tax of $4,351 | | — |
| | 7,119 |
| | — |
| | 7,119 |
|
| Cumulative translation adjustment | | (3,097 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | (3,097 | ) |
| Balance at December 31, 2011 | | $ | 1,070 |
| | $ | 6,979 |
| | $ | — |
| | $ | 8,049 |
|
Reclassification adjustment related to marketable securities in net unrealized loss at prior period end, net of $495 tax provision (1) | | — |
| | 854 |
| | — |
| | 854 |
|
| Change in fair value of available-for-sale securities, net of deferred income tax of $326 | | — |
| | 397 |
| | — |
| | 397 |
|
| Change in fair value of derivative financial instruments, net of deferred income tax of $636 | | — |
| | — |
| | 1,098 |
| | 1,098 |
|
| Cumulative translation adjustment | | 5,230 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 5,230 |
|
| Balance at December 31, 2012 | | $ | 6,300 |
| | $ | 8,230 |
| | $ | 1,098 |
| | $ | 15,628 |
|
Reclassification adjustment related to marketable securities in net unrealized gain at prior period end, net of $1,625 tax provision (1) | | — |
| | (3,489 | ) | |
| | (3,489 | ) |
| Change in fair value of available-for-sale securities, net of deferred income tax of $3,215 | | — |
| | (5,592 | ) | |
| | (5,592 | ) |
Reclassification adjustment related to cash flow hedges in net unrealized gain position at prior period end, net of $455 tax provision (1) | |
|
| |
| | (799 | ) | | (799 | ) |
| Change in fair value of derivative financial instruments, net of deferred income tax of $615 | | — |
| |
| | 1,080 |
| | 1,080 |
|
| Cumulative translation adjustment | | 1,703 |
| |
| |
| | 1,703 |
|
| Balance at December 31, 2013 | | $ | 8,003 |
| | $ | (851 | ) | | $ | 1,379 |
| | $ | 8,531 |
|
| |
(1) | Determined based on the average cost method. |
ATMI, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
The reclassifications out of accumulated other comprehensive income are (in thousands): |
| | | | | |
Details about Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income Components | Amount Reclassified from Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income | | Effect on the Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income |
| Realized gains and losses on cash flow hedges | | | |
| Foreign exchange contracts | $ | 1,442 |
| | Revenues |
| | (188 | ) | | Cost of revenues |
| | 1,254 |
| | Total before tax |
| | (455 | ) | | Estimated tax expense |
| | $ | 799 |
| | Net of estimated tax |
| Realized gains and losses on available-for-sale securities | | | |
| Available-for-sale securities | $ | 5,114 |
| | Other income (expense), net |
| | 5,114 |
| | Total before tax |
| | (1,625 | ) | | Estimated tax expense |
| | $ | 3,489 |
| | Net of estimated tax |
| Total reclassifications for the period | $ | 4,288 |
| | Net of estimated tax |
13. Commitments, Contingencies, and Other
ATMI is, from time to time involved in legal actions, governmental audits, and proceedings relating to various matters incidental to its business including contract disputes, intellectual property disputes, product liability claims, employment matters, export and trade matters, and environmental claims. While the outcome of such matters cannot be predicted with certainty, in the opinion of management, after reviewing such matters and consulting with ATMI’s counsel and considering any applicable insurance or indemnifications, any liability which may ultimately be incurred is not expected to materially affect ATMI’s consolidated financial position, cash flows or results of operations.
On or about February 7 and 28, 2014, two putative class action complaints challenging the Merger were filed in the Superior Court of the State of Connecticut, Judicial District of Danbury, captioned Andrew Pace v. ATMI, Inc., et al. and Dolores Carter v. ATMI, Inc., et al., respectively. The complaints were filed on behalf of the public shareholders of ATMI and name as defendants ATMI, the members of its Board of Directors, Entegris and Merger Sub. The complaints generally allege that ATMI’s directors breached their fiduciary duties to ATMI’s shareholders by agreeing to sell ATMI for inadequate and unfair consideration and pursuant to an inadequate and unfair process, and that ATMI, Entegris and Merger Sub aided and abetted those alleged breaches. The complaint in the Carter action also alleges purported disclosure deficiencies in the preliminary proxy statement for the Merger that ATMI filed with the SEC on February 25, 2014. The complaints seek, among other things, to enjoin the Merger. ATMI believes that the claims have no merit and no loss contingency range can be estimated at this time.
In the fourth quarter of 2012, we executed a ten year arrangement to purchase raw material from a global industrial gas supplier. We are committed to making certain upfront payments and to purchasing minimum volumes of gas thereafter. Purchase commitments beginning in year six are dependent on annual sales volumes. We estimate the total value of the contract to be $60.0 million. Under the contract, we have made payments totaling $3.0 million through December 31, 2013, and estimate the remaining contractual obligations under this agreement to approximate $57.0 million.
In the first quarter of 2013, we executed a $16.0 million commitment to purchase raw material from a strategic gas supplier over the next two years. We have purchased approximately $8.0 million in raw material as of December 31, 2013, and have remaining commitments under this agreement of approximately $8.0 million.
In the fourth quarter of 2013, we amended our existing contracts with Intermolecular, Inc. to significantly reduce our license of HPD technology and R&D support services for 2014. Under the amendment, ATMI will pay a fixed fee for a reduced number of HPD tool site licenses and maintenance support. Volume-based royalties to Intermolecular would resume in 2014. Additionally, we are committed to paying $2.6 million and $1.3 million for R&D licenses in 2014 and 2015, respectively, which is down from $6.9 million in 2013.
ATMI is self-insured for U.S. employee medical claims with stop loss risk insurance.
ATMI, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
14. Segments
As a result of the execution of a Share and Asset Purchase Agreement with Pall Corporation, to sell and transfer all assets and liabilities primarily related to the LifeSciences business (refer to Note 2 for additional information) in the fourth quarter of 2013, ATMI’s operations now comprise a single operating segment. The executive team is the chief operating decision maker of ATMI. Discrete financial information is only prepared at the product-line level for revenues and certain direct costs. Functional results are reviewed at the consolidated level.
ATMI sells high-purity materials and materials delivery systems directly to integrated circuit manufacturers and to chemical suppliers for flat-panel display manufacturing. These products consist of ATMI’s patented Safe Delivery Source® (“SDS”) solutions, copper integration and surface preparation products, deposition materials and high-purity liquid materials packaging solutions. The principal drivers for this market are technical performance, yield improvement, time to market, cost, utilization of capital, and risk reduction. The success of an electronic component or device is determined by the increased functionality it can deliver at an acceptable cost.
The All Other category includes corporate expenses, and, revenues and expenses associated with early stage new market opportunities such as our eVOLV™ and BrightBlack® technologies.
Revenues from external customers, by product type, were as follows (in thousands):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Revenue December 31, |
| | | 2013 | | 2012 | | 2011 |
| Implant | | $ | 112,918 |
| | $ | 100,289 |
| | $ | 77,450 |
|
| Display | | 26,206 |
| | 31,902 |
| | 34,663 |
|
| Photo IC | | 24,020 |
| | 24,271 |
| | 27,033 |
|
| Copper Materials | | 174,890 |
| | 191,051 |
| | 193,420 |
|
| Other Microelectronics | | 20,394 |
| | 18,002 |
| | 18,851 |
|
| All Other | | 2,531 |
| | 334 |
| | 406 |
|
| Total Continuing Operations | | $ | 360,959 |
| | $ | 365,849 |
| | $ | 351,823 |
|
15. Geographic Data
The Company’s geographic data for the years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011 are (in thousands):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | U.S. | | Taiwan | | Japan | | South Korea | | China | | Other
Pacific Rim | | Europe and Other | | Total |
| December 31, 2013 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenues | $ | 59,766 |
| | $ | 99,154 |
| | $ | 40,976 |
| | $ | 74,242 |
| | $ | 38,921 |
| | $ | 25,419 |
| | $ | 22,481 |
| | $ | 360,959 |
|
| Long-lived assets | 127,377 |
| | 4,796 |
| | 783 |
| | 33,334 |
| | 2,456 |
| | 266 |
| | 213 |
| | 169,225 |
|
| December 31, 2012 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenues | $ | 63,248 |
| | $ | 98,643 |
| | $ | 48,437 |
| | $ | 85,402 |
| | $ | 24,341 |
| | $ | 22,125 |
| | $ | 23,653 |
| | $ | 365,849 |
|
| Long-lived assets | 136,578 |
| | 6,409 |
| | 2,599 |
| | 18,076 |
| | 343 |
| | 152 |
| | 241 |
| | 164,398 |
|
| December 31, 2011 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenues | $ | 65,990 |
| | $ | 97,289 |
| | $ | 43,292 |
| | $ | 78,777 |
| | $ | 23,651 |
| | $ | 24,215 |
| | $ | 18,609 |
| | $ | 351,823 |
|
| Long-lived assets | 112,579 |
| | 6,037 |
| | 7,872 |
| | 6,440 |
| | 355 |
| | 137 |
| | 277 |
| | 133,697 |
|
Revenues are attributed to countries based on the location of the customer. Long-lived assets are located in the respective geographic regions, as shown above. Other than Taiwan, Japan, China, and South Korea, no one specific country within the Pacific Rim, Europe, South America, and other regions accounted for greater than 10 percent of consolidated revenues and long-lived assets in 2013, 2012 and 2011.
ATMI, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
16. Quarterly Results of Operations (Unaudited)
Summarized quarterly results of operations data is as follows (in thousands, except per share amounts):
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Quarter | |
| | First | | Second | | Third | | Fourth | |
| 2013 | | | | | | | | |
| Revenues | $ | 88,126 |
| | $ | 90,064 |
| | $ | 87,925 |
| | $ | 94,844 |
| |
| Gross profit | 42,598 |
| | 44,169 |
| | 41,795 |
| | 47,384 |
| |
| Operating income | 12,201 |
| (a) | 15,025 |
| | 12,956 |
| (c) | 7,214 |
| (d) |
| Income from continuing operations | $ | 10,210 |
| | $ | 11,669 |
| (b) | $ | 10,492 |
| | $ | 6,388 |
| (e) |
| Loss from discontinued operations, net of taxes | (1,784 | ) | | (2,222 | ) | | (2,044 | ) | | (2,544 | ) | |
| Net income | $ | 8,426 |
| | $ | 9,447 |
| | $ | 8,448 |
| | $ | 3,844 |
| |
| Basic income per common share: |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| Earnings per common share from continuing operations | $ | 0.32 |
| | $ | 0.37 |
| | $ | 0.33 |
| | $ | 0.20 |
| |
| Diluted income per common share: |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| Earnings per common share from continuing operations | $ | 0.31 |
| | $ | 0.36 |
| | $ | 0.32 |
| | $ | 0.19 |
| |
| 2012 | | | | | | | | |
| Revenues | 83,465 |
| | 94,745 |
| | 98,459 |
| (h) | 89,180 |
| |
| Gross profit | 41,250 |
| (f) | 49,235 |
| | 51,503 |
| | 44,603 |
| |
| Operating income | 8,962 |
| | 18,699 |
| (g) | 23,175 |
| | 14,948 |
| |
| Income from continuing operations | $ | 6,357 |
| | $ | 13,172 |
| | $ | 16,857 |
| | $ | 11,909 |
| |
| Income (loss) from discontinued operations, net of taxes | (2,495 | ) | | (1,749 | ) | | (2,432 | ) | | 711 |
| |
| Net income | $ | 3,862 |
| | $ | 11,423 |
| | $ | 14,425 |
| | $ | 12,620 |
| |
| Basic income per common share: |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| Earnings per common share from continuing operations | $ | 0.20 |
| | $ | 0.41 |
| | $ | 0.53 |
| | $ | 0.37 |
| |
| Diluted income per common share: |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| Earnings per common share from continuing operations | $ | 0.19 |
| | $ | 0.40 |
| | $ | 0.52 |
| | $ | 0.36 |
| |
Note: The operating results presented in the table have been restated for prior periods to exclude discontinued operations.
| |
(a) | Includes $1.8 million of severance costs in order to better streamline business activities with our customers and partners. |
| |
(b) | Includes a $1.1 million gain on sale of marketable securities. |
| |
(c) | Includes $0.8 million of severance costs associated with an action to reduce operational infrastructure with the objective of streamlining operations. |
| |
(d) | Includes a $1.2 million gain on sale of marketable securities. |
| |
(e) | Includes $11.5 million impairment charge related to our HPD assets. |
| |
(f) | Includes $1.5 million capitalization of certain logistics and freight costs into inventory. |
| |
(g) | Includes a $0.5 million recognized loss on the sale of an auction rate security. |
| |
(h) | Includes $2.6 million from IP settlement, which represents the settlement of royalties for periods prior to the third quarter of 2013. |
ATMI, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
17. Subsequent Events
On February 20, 2014, we completed the previously announced transaction among ATMI, Inc. and certain of its subsidiaries and Pall Corporation, whereby we sold all assets associated with our LifeSciences business. Cash proceeds from the transaction were $185 million, subject to customary post-closing working capital adjustments. For purposes of this Form 10-K, we have treated the LifeSciences business as a discontinued operation. For additional information refer to Note 2.
On February 4, 2014, ATMI and Entegris entered into an Agreement and Plan of Merger (the “Merger Agreement”), whereby ATMI would become a wholly-owned subsidiary of Entegris.
Under the terms of the Merger Agreement, ATMI shareholders will receive $34.00 in cash, without interest or dividends, for each share of ATMI common stock they hold at the time of closing. The consummation of the merger is subject to receiving the approval of holders of a majority of the outstanding ATMI common stock entitled to vote on the merger, the expiration or termination of the applicable waiting period under the Hart-Scott-Rodino Antitrust Improvements Act of 1976, as amended, and other customary conditions.
The Merger Agreement includes customary termination provisions for both ATMI and Entegris and provides that, in connection with the termination of the Merger Agreement by Entegris or ATMI, under specified circumstances, ATMI would be required to pay Entegris a termination fee of $30,000,000. In the event the conditions to consummating the merger have been met on the date that the closing of the merger is required to occur but Entegris and Merger Sub fail to consummate the merger, ATMI may terminate the Merger Agreement and, under certain circumstances, Entegris would be required to pay ATMI a termination fee of $100,000,000.
As part of the Merger Agreement, the parties have agreed to certain customary covenants which restrict ATMI pending the closing of the acquisition. Among these obligations, ATMI: (1) must conduct business in the ordinary course consistent with its past practice; (2) may not repatriate any cash, cash equivalents or other assets to the extent that such repatriation would result in a tax liability to ATMI or any of its subsidiaries beyond what has been agreed to with Entegris; (3) may not make or authorize capital expenditures in any calendar year that, individually or in the aggregate, exceed the amounts budgeted in ATMI's current plan by more than 10%; (4) may not establish a record date or declare a dividend; (5) may not amend its Charter or By-laws; (6) may not issue, sell, encumber, repurchase or grant any capital stock or other equity instrument other than amounts agreed to by Entegris; (7) may not acquire, sell, lease (as lessor), license, mortgage, sell and leaseback or otherwise subject to any lien (other than certain permitted liens), or otherwise dispose of any real property or other material properties or assets, other than that which has been agreed to between the parties; (8) may not incur any indebtedness or issue or sell any debt securities or rights to acquire debt securities except as agreed between the parties; (9) may not make any change in financial accounting methods, principles or practices, or elections, except insofar as required by applicable law or generally accepted accounting principles; and (10) may not adopt a plan of complete or partial liquidation, dissolution, merger or conversion or resolution providing for or authorizing such a liquidation, dissolution, merger or conversion.
Schedule II—Valuation and Qualifying Accounts
Three Years Ended December 31, 2013
(In thousands)
|
| | | |
| Allowances for Doubtful Accounts and Sales Returns: | |
| | |
| Balance December 31, 2010 | $ | 783 |
|
| Provision charged to income | — |
|
| Doubtful accounts written off (net) | — |
|
| Other adjustments | (2 | ) |
| Balance December 31, 2011 | 781 |
|
| Provision charged to income | 100 |
|
| Doubtful accounts written off (net) | — |
|
| Other adjustments | — |
|
| Balance December 31, 2012 | 881 |
|
| Provision charged to income | 2 |
|
| Doubtful accounts written off (net) | — |
|
| Other adjustments | — |
|
| Balance December 31, 2013 | $ | 883 |
|
|
| | | |
| Allowance for Excess and Obsolete Inventories: | |
| | |
| Balance December 31, 2010 | $ | 1,843 |
|
| Provision charged to income | 555 |
|
| Disposals of inventory written off | (430 | ) |
| Other adjustments | 197 |
|
| Balance December 31, 2011 | 2,165 |
|
| Provision charged to income | 1,560 |
|
| Disposals of inventory written off | (748 | ) |
| Other adjustments | (91 | ) |
| Balance December 31, 2012 | 2,886 |
|
| Provision charged to income | 1,430 |
|
| Disposals of inventory written off | (1,032 | ) |
| Other adjustments | (346 | ) |
| Balance December 31, 2013 | $ | 2,938 |
|
|
| | | |
| Future Income Tax Benefits – Valuation Allowance: | |
| | |
| Balance December 31, 2010 | $ | 1,983 |
|
| Additions charged to income tax expense | 284 |
|
| Reductions credited to income tax expense | (631 | ) |
| Other adjustments | (318 | ) |
| Balance December 31, 2011 | 1,318 |
|
| Additions charged to income tax expense | 388 |
|
| Reductions credited to income tax expense | — |
|
| Other adjustments | (1,347 | ) |
| Balance December 31, 2012 | 359 |
|
| Additions charged to income tax expense | 235 |
|
| Reductions credited to income tax expense | — |
|
| Other adjustments | (20 | ) |
| Balance December 31, 2013 | $ | 574 |
|