General Macro-Economic Risk Factors
The global macro-economic environment has a significant impact on our financial plans and ability to implement our business strategy. The macro-economic environment can be significantly impacted by the actions of both the government sector (including central banks) and the private sector. The macro-economic environment may also be affected by natural andman-made catastrophes.
Our business strategy and associated financial plans are developed by considering forecasts of economic growth, both globally and in the specific countries we operate. Actual economic growth can be significantly impacted by the macro-economic environment and can deviate significantly from forecast, thus impacting our financial results and the ability to implement our business strategy.
Changes in the macro-economic environment can also have a significant impact on financial markets, including movements in interest rates, spreads on fixed income assets and returns on public equity and ALDA assets. Our financial plan, including income projections, capital projections, and valuation of liabilities are based on certain assumptions with respect to future movements in interest rates and spreads on fixed income assets, and expected future returns from our public equity and ALDA investments. Actual experience is highly variable and can deviate significantly from our assumptions, thus impacting our financial results. In addition, actual experience that is significantly different from our assumptions and/or changes in the macro-economic environment may result in changes to the assumptions themselves which would also impact our financial results.
Specific changes in the macro-economic environment can have very different impacts across different parts of the business. For example, a rise in interest rates is generally beneficial to us in the long term but can adversely affect valuations of some ALDA assets, especially those that have returns dependent on contractual cash flows, such as real estate.
The spending and savings patterns of our customers could be significantly influenced by the macro-economic environment and could have an impact on the products and services we offer to our customers.
Customer behaviour and emergence of claims on our liabilities can be significantly impacted by the macro-economic environment. For example, a prolonged period of economic weakness could impact the health and well-being of our customers and that could result in increased claims for certain insurance risks.
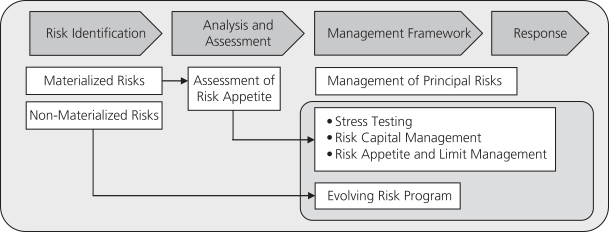
The following sections describe the risk management strategies for each of our five principal risk categories: strategic risk, market risk, credit risk, product risk and operational risk.
Strategic Risk
Strategic risk is the risk of loss resulting from the inability to adequately plan or implement an appropriate business strategy, or to adapt to change in the external business, political or regulatory environment.
Risk Management Strategy
The CEO and Executive Leadership Team establish and oversee execution of business strategies and have accountability to identify and manage the risks embedded in these strategies. They are supported by a number of processes:
| ∎ | | Strategic business, risk and capital planning that is reviewed with the Board of Directors, Executive Leadership Team, and the ERC; |
| ∎ | | Performance and risk reviews of all key businesses with the CEO and annual reviews with the Board of Directors; |
| ∎ | | Risk-based capital attribution and allocation designed to encourage a consistent decision-making framework across the organization; and |
| ∎ | | Review and approval of significant acquisitions and divestitures by the CEO and, where appropriate, the Board of Directors. |
The CEO and Executive Leadership Team are ultimately responsible for our reputation; however, our employees and representatives are responsible for conducting their business activities in a manner that upholds our reputation. This responsibility is executed through an enterprise-wide reputation risk policy that specifies the oversight responsibilities of the Board of Directors and the responsibilities of executive management, communication to and education of all directors, officers, employees and representatives, including our Code of Business Conduct and Ethics, and application of guiding principles in conducting all our business activities.
Environmental, Social and Governance Risks
Environmental, social and governance (“ESG”) risks may impact our investments, underwriting, or operations, and may create a risk of loss of financial, operational, legal, or brand value to Manulife.
In 2018, we established the Manulife Executive Sustainability Council (“the Council”) to anticipate, manage and oversee relevant environmental and social risks. The Council is comprised of asub-group of Manulife’s Executive Leadership Team and has a mandate to integrate environmental and social sustainability into culture, strategy, and decision-making. The Board’s Corporate Governance and Nominating Committee oversees the integration of sustainability into the core business and performance on ESG metrics.
Our enterprise-level approach to ESG risk management is captured in the Environmental Risk Policy that reflects the Company’s commitment to conducting all business activities in a manner that recognizes the need to preserve the natural environment. Business and functional units are responsible for procedures, protocols and due diligence standards to identify, monitor and manage ESG risks.
We report on ESG performance in our annual sustainability reports and other sources such as the Carbon Disclosure Project. Manulife also supports the Financial Stability Board’s Taskforce on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (“TCFD”), and Manulife Asset
40 Manulife Financial Corporation | 2018 Annual Report | Management’s Discussion and Analysis