Table of Contents
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
(Mark One)
x ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE |
SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the fiscal year endedDecember 31, 2006
OR
¨ TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE |
SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the transition period from to
Commission file number 001-16751
WELLPOINT, INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| Indiana | 35-2145715 | |
| (State or other jurisdiction of | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) | |
| incorporation or organization) | ||
| 120 Monument Circle | ||
| Indianapolis, Indiana | 46204 | |
| (Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip Code) | |
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code:(317) 488-6000
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
Title of each class | Name of each exchange on which registered | |
Common Stock, Par Value $0.01 | New York Stock Exchange |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: NONE
Indicate by check mark if the Registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark if the Registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Exchange Act. Yes ¨ No x
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of Registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, or a non-accelerated filer. See definition of “accelerated filer and large accelerated filer” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
Large accelerated filer x | Accelerated filer ¨ | Non-accelerated filer ¨ |
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes ¨ No x
The aggregate market value of the voting and non-voting common equity held by non-affiliates of the Registrant (assuming solely for the purposes of this calculation that all Directors and executive officers of the Registrant are “affiliates”) as of June 30, 2006 was approximately $45,015,102,335.
As of February 12, 2007, 612,428,063 shares of the Registrant’s Common Stock were outstanding.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Part III of this Annual Report on Form 10-K incorporates by reference information from the Registrant’s Definitive Proxy Statement for the Annual Meeting of Shareholders to be held May 16, 2007.
Table of Contents
Indianapolis, Indiana
Annual Report to Securities and Exchange Commission
December 31, 2006
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1
Table of Contents
This Annual Report on Form 10-K, including the Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations, contains forward-looking statements, within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995, that reflect our views about future events and financial performance. When used in this report, the words “may,” “will,” “should,” “anticipate,” “estimate,” “expect,” “plan,” “believe,” “predict,” “potential,” “intend” and similar expressions are intended to identify forward-looking statements. Forward-looking statements are subject to known and unknown risks and uncertainties that could cause actual results to differ materially from those projected. You are cautioned not to place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements that speak only as of the date hereof. You are also urged to carefully review and consider the various disclosures made by us which attempt to advise interested parties of the factors which affect our business, including “Risk Factors” set forth in Part I Item 1A hereof and our reports filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission from time to time.
References in this Annual Report on Form 10-K to the term “WellPoint” or the “Company” refer to WellPoint, Inc. and its direct and indirect subsidiaries, as the context requires, after the merger of Anthem, Inc. and WellPoint Health Networks Inc. on November 30, 2004. References to the term “WHN” refers to WellPoint Health Networks Inc. prior to the merger. References to the terms “we,” “our,” or “us,” refer to WellPoint.
2
Table of Contents
PART I
General
We are the largest health benefits company in terms of commercial membership in the United States, serving over 34 million medical members as of December 31, 2006. We are an independent licensee of the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association, or BCBSA, an association of independent health benefit plans. We serve our members as the Blue Cross licensee for California and as the Blue Cross and Blue Shield, or BCBS, licensee for: Colorado, Connecticut, Georgia, Indiana, Kentucky, Maine, Missouri (excluding 30 counties in the Kansas City area), Nevada, New Hampshire, New York (as BCBS in 10 New York city metropolitan and surrounding counties, and as Blue Cross or BCBS in selected upstate counties only), Ohio, Virginia (excluding the Northern Virginia suburbs of Washington, D.C.), and Wisconsin. We also serve our members throughout the country as UniCare. We are licensed to conduct insurance operations in all 50 states through our subsidiaries.
We offer a broad spectrum of network-based managed care plans to the large and small employer, individual, Medicaid and senior markets. Our managed care plans include preferred provider organizations, or PPOs, health maintenance organizations, or HMOs, point-of-service plans, or POS plans, traditional indemnity plans and other hybrid plans, including consumer-driven health plans, or CDHPs, hospital only and limited benefit products. In addition, we provide a broad array of managed care services to self-funded customers, including claims processing, underwriting, stop loss insurance, actuarial services, provider network access, medical cost management and other administrative services. We also provide an array of specialty and other products and services including life and disability insurance benefits, pharmacy benefit management, specialty pharmacy, dental, vision, behavioral health benefit services, long-term care insurance and flexible spending accounts.
For our insured products, we charge a premium and assume all or a portion of the health care risk. Under self-funded and partially insured products, we charge a fee for services, and the employer or plan sponsor reimburses us for all or most of the health care costs. Approximately 93% of our 2006 operating revenue was derived from premium income, while approximately 7% was derived from administrative fees and other revenues.
Through December 31, 2006, our customer base primarily included Large Groups with 51 to 4,999 eligible employees (47% of our medical members at December 31, 2006) and Individuals under age 65 and Small Groups of one to 50 eligible employees, also known as ISG (17% of our medical members as of December 31, 2006). Other major customer types included National Accounts (multi-state employer groups with 5,000 or more employees, accounting for 15% of our medical members at December 31, 2006), BlueCard Host (enrollees of non-owned BCBS plans who receive benefits in our BCBS markets, accounting for 12% of our medical members at December 31, 2006), Senior (over age 65 individuals enrolled in Medicare Supplement or Medicare Advantage policies, accounting for 4% of our medical members at December 31, 2006) and State Sponsored Programs (primarily Medicaid and State Children’s Health Insurance Plans, accounting for 5% of our medical members at December 31, 2006).
We market our products through an extensive network of independent agents and brokers (primarily for Individual, Small Group and Senior customers) and through our in-house sales force that are compensated on a commission basis for new sales and retention of existing business (primarily for Large Group customers). National Accounts are generally sold through independent brokers or consultants retained by the customer working with our in-house sales force.
The aging of the population and other demographic characteristics and advances in medical technology continue to contribute to rising health care costs. Our managed care plans and products are designed to encourage
3
Table of Contents
providers and members to participate in quality, cost-effective health benefit plans by using the full range of our innovative medical management services, quality initiatives and financial incentives. Our leading market share and high business retention rates enable us to realize the long-term benefits of investing in preventive and early detection programs. Our ability to provide cost-effective health benefits products and services is enhanced through a disciplined approach to internal cost containment, prudent management of our risk exposure and successful integration of acquired businesses.
Our results of operations depend in large part on accurately predicting health care costs and on our ability to manage future health care costs through underwriting standards, medical management, product design and negotiation of favorable provider contracts.
We believe health care is local, and feel that we have the strong local presence required to understand and meet local customer needs. Our local presence and national expertise have created opportunities for collaborative programs that reward physicians and hospitals for clinical quality and excellence. We feel that our commitment to health improvement and care management provides added value to customers and health care professionals.
Our vision is to transform health care and become the most valued company in our industry. Our mission is to improve the lives of people we serve and the health of our communities. One of the strategies to achieve our vision and fulfill our mission is automation of interactions with customers, brokers, agents, employees and other stakeholders through web-enabled technology and enhancing internal operations. We continue to develop our e-business strategy with the goal of becoming widely regarded as an e-business leader in the health benefits industry. The strategy includes not only sales and distribution of health benefits products on the Internet, but also implementation of advanced capabilities that improve service benefiting customers, agents, brokers, and partners while optimizing administrative costs.
On January 8, 2007, we unveiled a comprehensive plan to help address the growing ranks of the uninsured. Our plan is a blend of public and private initiatives aimed at ensuring universal coverage for children and providing new and more attractive options for the uninsured. This plan is part of our mission to improve the lives of the people we serve and the health of our communities.
We recently announced the launch of360º Health, a program to integrate all care management programs and tools into a centralized, consumer-friendly resource that assists patients in navigating the health care system, using their health benefits and accessing the most comprehensive and appropriate care available. Additionally, we recently began collaboration with 19 other Blue Cross and Blue Shield plans to launch the nation’s largest private database of health care information. Blue Health IntelligenceSM, or BHI, is a unique resource that will improve health care quality by providing the most detailed view available of health care trends, best practices and comparative costs through a claims database of 79 million people. BHI will strengthen the movement toward greater health care transparency and informed decision making by employers and, ultimately, providers and consumers.
WellPoint is a large accelerated filer (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended) and is required, pursuant to Item 101 of Regulation S-K, to provide certain information regarding its website and the availability of certain documents filed with or furnished to the Securities and Exchange Commission, or SEC. Our Internet website iswww.wellpoint.com. We make available free of charge, or through our Internet website, our Annual Report on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, Current Reports on Form 8-K, and amendments to those reports filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 as soon as reasonably practicable after we electronically file such material with or furnish it to the SEC. We also include on our Internet website our Corporate Governance Guidelines, our Standards of Ethical Business Conduct and the charter of each standing committee of our Board of Directors. In addition, we intend to disclose on our Internet website any amendments to, or waivers from, our Standards of Ethical Business Conduct that are required to be publicly disclosed pursuant to rules of the SEC and the New York Stock Exchange, or NYSE. WellPoint, Inc., which name changed from Anthem, Inc. effective November 30, 2004, is an Indiana corporation incorporated on July 17, 2001.
4
Table of Contents
As required by NYSE Rule 303A.12, in 2006 we filed with the NYSE the annual chief executive officer certificate with no qualifications, indicating that the chief executive officer is unaware of any violations of the NYSE corporate governance standards. In addition, we are filing certifications required by Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 as exhibits to this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Recent Transactions
We intend to continue our expansion through organic growth and strategic acquisitions and transactions. Listed below are the more significant transactions that we recently completed:
| • | We maintain a common stock repurchase program as authorized by our Board of Directors. Repurchases are made from time to time at prevailing market prices, subject to certain restrictions on volume, pricing and timing. During the year ended December 31, 2006, we repurchased and retired approximately 60.7 million shares at an average price of $74.91, for an aggregate cost of $4.6 billion. On March 15, May 16, August 17 and December 7, 2006, our Board of Directors authorized increases of $1.0 billion, $1.0 billion, $0.5 billion and $1.0 billion, respectively, in our common stock repurchase program, which increased the total authorized common stock repurchases to $5.5 billion since the current program’s inception in 2005. As of December 31, 2006, $0.9 billion remained authorized by our Board of Directors for future repurchases. Subsequent to December 31, 2006, we repurchased and retired approximately 6.0 million shares for an aggregate cost of approximately $463.5 million, leaving approximately $486.3 million for authorized future repurchases at February 12, 2007. Our stock repurchase program is discretionary as we are under no obligation to repurchase shares. We repurchase shares because we believe it is a prudent use of surplus capital. |
| • | On December 28, 2005 (December 31, 2005 for accounting purposes) we completed our acquisition of WellChoice, Inc., or WellChoice. Under the terms of the merger agreement, the stockholders of WellChoice received consideration of $38.25 in cash and 0.5191 of a share of WellPoint common stock for each share of WellChoice common stock outstanding. In addition, WellChoice stock options and other awards were converted to WellPoint awards in accordance with the merger agreement. The purchase price including cash, fair value of stock and stock awards and estimated transaction costs was approximately $6.5 billion. WellChoice merged with and into WellPoint Holding Corp., a direct and wholly-owned subsidiary of WellPoint, with WellPoint Holding Corp. as the surviving entity in the merger. |
| • | On July 11, 2005, we announced that an agreement was reached with representatives of more than 700,000 physicians nationwide involved in two multi-district class-action lawsuits against us and other health benefits companies. As part of the agreement, we agreed to pay $135.0 million to physicians and to contribute $5.0 million to a not-for-profit foundation whose mission is to promote higher quality health care and to enhance the delivery of care to the disadvantaged and underserved. In addition, up to $58.0 million will be paid in legal fees. As a result of the agreement, we incurred a pre-tax expense of $103.0 million during the year ended December 31, 2005, or $0.10 EPS, which represented the final settlement amount of the agreement that was not previously accrued. Appeals of the settlement initially filed by certain physicians have been resolved. Final cash payments under the agreement totaling $209.5 million, including accrued interest, were made on October 5 and 6, 2006. |
| • | On June 9, 2005, we completed our acquisition of Lumenos, Inc., or Lumenos, for approximately $185.0 million in cash paid to the stockholders of Lumenos. Lumenos is recognized as a pioneer and market leader in consumer-driven health programs. |
| • | On April 25, 2005, our Board of Directors approved a two-for-one split of shares of common stock, which was effected in the form of a 100% common stock dividend. All shareholders of record on May 13, 2005 received one additional share of WellPoint common stock for each share of common stock held on that date. The additional shares of common stock were distributed to shareholders of record in the form of a stock dividend on May 31, 2005. All applicable historical weighted average share and per share amounts and all references to stock compensation data and market prices of our |
5
Table of Contents
common stock for all periods presented in this Annual Report on Form 10-K have been adjusted to reflect this two-for-one stock split. |
| • | On November 30, 2004, Anthem, Inc., or Anthem, and WellPoint Health Networks Inc., or WHN, completed their merger. WHN merged with and into Anthem Holding Corp., a direct and wholly-owned subsidiary of Anthem, with Anthem Holding Corp. as the surviving entity in the merger. In connection with the merger, Anthem amended its articles of incorporation to change its name to WellPoint, Inc., or WellPoint. As a result of the merger, each WHN stockholder received consideration of $23.80 in cash and one share of WellPoint common stock for each share of WHN common stock held. In addition, WHN stock options and other awards were converted to WellPoint awards in accordance with the merger agreement. The purchase price including cash, fair value of stock and stock awards and estimated transaction costs was approximately $15.8 billion. |
Industry Overview
The health benefits industry has experienced significant change in the last decade. The increasing focus on health care costs by employers, the government and consumers has led to the growth of alternatives to traditional indemnity health insurance. HMO, PPO and hybrid plans, such as POS plans and CDHPs, are among the various forms of managed care products that have developed over the past decade. Through these types of products, insurers attempt to contain the cost of health care by negotiating contracts with hospitals, physicians and other providers to deliver health care to members at favorable rates. These products usually feature medical management and other quality and cost optimization measures such as pre-admission review and approval for certain non-emergency services, pre-authorization of outpatient surgical procedures, network credentialing to determine that network doctors and hospitals have the required certifications and expertise, and various levels of care management programs to help members better understand and navigate the medical system. In addition, providers may have incentives to achieve certain quality measures, may share medical cost risk or have other incentives to deliver quality medical services in a cost-effective manner. Also, certain plans offer members incentives for healthy behaviors, smoking cessation and weight management. Members are charged periodic, pre-paid premiums and pay co-payments, coinsurance and deductibles when they receive services. While the distinctions between the various types of plans have lessened over recent years, PPO, POS and CDHP products generally provide reduced benefits for out-of-network services, while traditional HMO products generally provide little to no reimbursement for non-emergency out-of-network utilization. An HMO plan may also require members to select one of the network primary care physicians to coordinate their care and approve any specialist or other services.
Recently, economic factors and greater consumer awareness have resulted in the increasing popularity of products that offer larger, more extensive networks, more member choice related to coverage, physicians and hospitals, and a desire for greater flexibility for customers to assume larger deductibles and co-payments in return for lower premiums. CDHPs, which are relatively high deductible PPO products and which are often paired with some type of member health care expenditure account that can be used at the member’s discretion to help fund member out-of-pocket costs, help to meet this demand. CDHPs also usually incorporate member education, wellness, and care management programs, to help customers make better informed health care decisions. We believe we are well-positioned in each of our regions to respond to these market preferences.
Each of the BCBS companies, of which there were 39 independent primary licensees as of December 31, 2006, works cooperatively in a number of ways that create significant market advantages, especially when competing for very large multi-state employer groups. As a result of this cooperation, each BCBS company is able to take advantage of other BCBS licensees’ substantial provider networks and discounts when any member works or travels outside of the state in which their policy is written. This program is referred to as BlueCard®, and is a source of revenue for providing member services in our states for individuals who are customers of BCBS plans not affiliated with us.
6
Table of Contents
Competition
The managed care industry is highly competitive, both nationally and in our regional markets. Competition continues to be intense due to aggressive marketing, business consolidations, a proliferation of new products and increased quality awareness and price sensitivity among customers.
Health benefits industry participants compete for customers mainly on the following factors:
| • | price; |
| • | quality of service; |
| • | access to provider networks; |
| • | access to care management and wellness programs; |
| • | innovation, breadth and flexibility of products and benefits; |
| • | reputation (including National Committee on Quality Assurance, or NCQA, accreditation status); |
| • | brand recognition; and |
| • | financial stability. |
Over the last few years, a health plan’s ability to interact with employers, members and other third parties (including health care professionals) via the Internet has become a more important competitive factor. During the last several years, we have made significant investments in technology to enhance our electronic interaction with employers, members and third parties.
We believe our exclusive right to market products under the most recognized brand in the industry, BCBS, in our most significant markets provides us with an advantage over our competition. In addition, our provider networks in our regions enable us to achieve cost-efficiencies and service levels enabling us to offer a broad range of health benefits to our customers on a more cost-effective basis than many of our competitors. We strive to distinguish our products through provider access, service, product value and brand recognition.
To build our provider networks, we compete with other health benefits plans for contracts with hospitals, physicians and other providers. We believe that physicians and other providers primarily consider member volume, reimbursement rates, timeliness of reimbursement and administrative service capabilities along with the reduction of non-value added administrative tasks when deciding whether to contract with a health benefits plan.
At the sales and distribution level, we compete for qualified agents and brokers to distribute our products. Strong competition exists among insurance companies and health benefits plans for agents and brokers with demonstrated ability to secure new business and maintain existing accounts. We believe that commission structure, support services, reputation, prior relationships, quality and price of the products are the factors agents and brokers consider in choosing whether to market our products. We believe that we have good relationships with our agents and brokers, and that our products, support services and commission structure compare favorably to our competitors in all of our regions.
Reportable Segments
Through December 31, 2006, we managed our operations through three reportable segments: Health Care, Specialty and Other.
Health Care
Our Health Care segment is an aggregation of various operating segments, principally differentiated by geographic areas within which we offer similar health benefit products and services, including commercial
7
Table of Contents
accounts, Senior, Medicaid and other State Sponsored businesses. These geographic areas include California, Colorado, Connecticut, Georgia, Indiana, Kentucky, Maine, Missouri, Nevada, New Hampshire, New York, Ohio, Virginia, and Wisconsin. In addition, UniCare provides services throughout the country.
Specialty
Our Specialty segment is comprised of businesses providing life and disability insurance benefits, pharmacy benefit management, specialty pharmacy, dental, vision, behavioral health benefit services and long-term care insurance. We ceased underwriting workers compensation business effective December 31, 2005; however, we continue to provide network rental and medical management services to workers compensation carriers.
Other
Our Other segment is comprised of our Medicare processing business, including National Government Services, Inc., which name changed from AdminaStar Federal, Inc. effective November 17, 2006, United Government Services, LLC and Empire Medicare Services, Inc.; Arcus Healthy Living Services, Inc., which works to develop innovative means to promote quality care, well being and education; Arcus Financial Services, Inc., which provides a number of products to WellPoint-owned health plans associated with tax-advantaged accounts such as Health Savings Accounts, Flexible Spending Accounts and Health Reimbursement Accounts; intersegment revenue and expense eliminations; and corporate expenses not allocated to our Health Care or Specialty segments.
For additional information regarding the operating results of our segments, see the Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations and Note 19 to our audited consolidated financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2006 included in this Form 10-K.
We announced a new organizational structure designed to facilitate our 2010 strategic plan. This new structure capitalizes on our unique local presence, and emphasizes company-wide innovation and strong customer focus. As a result of this new organizational structure we are organized around two strategic business units: Commercial and Consumer Business, or CCB, and Specialty, Senior and State-Sponsored Business, or 4SB. In addition, our government services business includes the Federal Employee Program and National Government Services, Inc., which acts as a Medicare contractor in several regions across the nation. We expect to revise our reportable segments in the first quarter of 2007 in accordance with the new organizational structure which reflects how our chief operating decision maker evaluates the performance of our business beginning January 1, 2007.
Products and Services
Health Care
A general description of our health benefit products and services is provided below:
Preferred Provider Organization. PPO products offer the member an option to select any health care provider, with benefits reimbursed by us at a higher level when care is received from a participating network provider. Coverage is subject to co-payments or deductibles and coinsurance, with member cost sharing usually limited by out-of-pocket maximums.
Consumer-Driven Health Plans. CDHPs provide consumers with increased financial responsibility, choice and control regarding how their health care dollars are spent. Generally, CDHPs combine a high-deductible PPO plan with an employer-funded and/or employee-funded personal care account. Some or all of the dollars remaining in the personal care account at year-end can be rolled over to the next year for future health care needs.
8
Table of Contents
Traditional Indemnity. Indemnity products offer the member an option to select any health care provider for covered services. Coverage is subject to deductibles and coinsurance, with member cost sharing usually limited by out-of-pocket maximums.
Health Maintenance Organization. HMO products include comprehensive managed care benefits, generally through a participating network of physicians, hospitals and other providers. A member in one of our HMOs must typically select a primary care physician, or PCP, from our network. PCPs generally are family practitioners, internists or pediatricians who provide necessary preventive and primary medical care, and are generally responsible for coordinating other necessary health care services. We offer HMO plans with varying levels of co-payments, which result in different levels of premium rates.
Point-of-Service. POS products blend the characteristics of HMO and indemnity plans. Members can have comprehensive HMO-style benefits through participating network providers with minimum out-of-pocket expenses (co-payments) and also can go directly, without a referral, to any provider they choose, subject to, among other things, certain deductibles and coinsurance. Member cost sharing is limited by out-of-pocket maximums.
Management Services. In addition to fully insured products, we provide administrative services to large group employers that maintain self-funded health plans. These administrative services include underwriting, actuarial services, medical management, claims processing and administrative services for self-funded employers. Self-funded health plans are also able to use our provider networks and to realize savings through our negotiated provider arrangements, while allowing employers the ability to design certain health benefit plans in accordance with their own requirements and objectives. We also underwrite stop loss insurance for self-funded plans.
Senior Plans. We offer a wide variety of senior plans, products and options such as Medicare supplemental plans, Medicare Advantage and Medicare Part D Prescription Drug Plans, or Medicare Part D. Medicare supplemental plans typically pay the difference between health care costs incurred by a beneficiary and amounts paid by Medicare. Medicare Advantage plans provide Medicare beneficiaries with a managed care alternative to traditional Medicare. Medicare Part D offers a prescription drug plan to Medicare eligible members. We offer Medicare Part D to eligible Medicare beneficiaries in all 50 states. Our Medicare-approved drug discount cards afford Medicare beneficiaries, without facilitated prescription drug coverage, access to our drug discounts. We are also the United States default plan for point of service facilitated, enrollment, as defined by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, or CMS.
BlueCard. BlueCard host members are generally members who reside in or travel to a state in which a WellPoint subsidiary is the Blue Cross and/or Blue Shield licensee and who are covered under an employer sponsored health plan serviced by a non-WellPoint controlled BCBS licensee, who is the “home” plan. We perform certain administrative functions for BlueCard host members, for which we receive administrative fees from the BlueCard members’ home plans. Other administrative functions, including maintenance of enrollment information and customer service, are performed by the home plan.
Medicaid Plans and Other State-Sponsored Programs. We have contracts to serve members enrolled in Medicaid, State Children’s Health Insurance Programs and other publicly funded health care programs for low income and/or high medical risk individuals. We currently provide services in California, Colorado, Connecticut, Indiana, Kansas, Massachusetts, Nevada, New York, New Hampshire, Ohio, Texas, Virginia, West Virginia and Wisconsin.
Specialty
Pharmacy Products. We offer pharmacy services and pharmacy benefit management services to our members. Our pharmacy services incorporate features such as drug formularies (where we develop lists of
9
Table of Contents
preferred, cost effective drugs), a pharmacy network and maintenance of a prescription drug database and mail order capabilities. Pharmacy benefit management services provided by us include management of drug utilization through outpatient prescription drug formularies, retrospective review and drug education for physicians, pharmacists and members. Two of our subsidiaries are also licensed pharmacies and make prescription dispensing services available through mail order for pharmacy benefit management clients. In July 2005, we launched Precision Rx Specialty Solutions, a full service specialty pharmacy designed to help improve quality and cost of care by coordinating a relatively new class of prescription medications commonly referred to as biopharmaceuticals, also known as specialty medications.
In September 2005, we were awarded contracts to offer Medicare Part D to eligible Medicare beneficiaries in all 50 states. We began offering these plans to customers through our health benefit subsidiaries throughout the country and providing administrative services for Medicare Part D offerings through our pharmacy benefits management companies on January 1, 2006.
Life Insurance. We offer an array of competitive group life insurance benefit products to both large and small group customers in conjunction with our health plans. The life products include term life, accidental death and dismemberment.
Disability. We offer short-term and long-term disability programs, usually in conjunction with our health plans.
Behavioral Health. We offer specialized behavioral health plans and benefit management. These plans cover mental health and substance abuse treatment services on both an inpatient and an outpatient basis. We have implemented employee assistance and behavioral managed care programs for a wide variety of businesses throughout the United States. These programs are offered through our subsidiaries and through third party behavioral health networks.
Dental. Our dental plans include networks in certain states in which we operate. Many of the dental benefits are provided to customers enrolled in our health plans and are offered on both an insured and self-funded basis.
Vision Services. Our vision plans include networks within the states we operate. Many of the vision benefits are provided to customers enrolled in our health plans and are offered on both an insured and self-funded basis.
Long-Term Care Insurance. We offer long-term care insurance products to our California members through a subsidiary. The long-term care products include tax-qualified and non-tax qualified versions of a skilled nursing home care plan and comprehensive policies covering skilled, intermediate and custodial long-term care and home health services.
Other
Medicare Fiscal Intermediary Operations. Through contracts held by National Government Services, Inc., United Government Services, LLC, Anthem Health Plans of Maine, Inc., Anthem Health Plans of New Hampshire, Inc., Empire Medicare Services division of EmpireHealthChoice Assurance, Inc. and Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Georgia Inc., we serve as fiscal intermediaries providing administrative services for the Medicare program, which generally provides coverage for persons who are 65 or older and for persons who are disabled or with end-stage renal disease. Part A of the Medicare program provides coverage for services provided by hospitals, skilled nursing facilities and other health care facilities. Part B of the Medicare program provides coverage for services provided by physicians, physical and occupational therapists and other professional providers, as well as certain durable medical equipment and medical supplies. As a fiscal intermediary, we are compensated for our services on a cost reimbursement basis.
10
Table of Contents
Customer Types
Our products are generally developed and marketed with an emphasis on the differing needs of various customer groups. In particular, our product development and marketing efforts take into account the differing characteristics between the various customer groups served by us, including individuals and small employers, large employers, seniors and Medicaid recipients, as well as the unique needs of educational and public entities, federal employee health and benefit programs, national employers and state-run programs servicing low-income, high-risk and under-served markets. Each business unit is responsible for product design, pricing, enrolling, underwriting and servicing customers in specific customer groups. We believe that one of the keys to our success has been the focus on distinct customer groups defined generally by employer size and geographic region, which better enables us to develop benefit plans and services that meet the unique needs of the distinct markets.
In each geographic region, we balance the need to customize products with the efficiencies of product standardization. Overall, we seek to establish pricing and product designs to achieve an appropriate level of profitability for each of our customer categories. As of December 31, 2006, our customer types included the following categories:
| • | Large Group includes employer customers with 51 to 4,999 employees eligible to participate as a member in one of our health plans. In addition, Large Group includes customers with 5,000 or more eligible employees with less than 5% of eligible employees located outside of the headquarter’s state. These groups are generally sold through brokers or consultants working with industry specialists from our in-house sales force. Large Group cases may be experience rated or sold on a self-insured basis. The customer’s buying decision is typically based upon the size and breadth of our networks, customer service, the quality of our medical management services, the administrative cost included in our quoted price, our financial stability, reputation and our ability to effectively service large complex accounts. Large Group also includes members in the Federal Employee Program, or FEP. As a BCBSA licensee, we participate in a nationwide contract with the Federal government whereby we cover Federal employees and their dependents in our multi-state service area. Service area is defined as the geographic area in which we are licensed to sell BCBS products. We participate in the overall financial risk for medical claims on a pooled basis with the other participating BCBS companies, and are reimbursed for our costs plus a fee. Large Group accounted for 47% of our medical members at December 31, 2006. |
| • | Individual (under 65) and small groups are defined as members who purchase health insurance services as individuals or through employers with one to 50 eligible employees. While individual policies are generally sold through independent agents and brokers or our in-house sales force, small groups are sold almost exclusively through independent agents and brokers. Small group cases are sold on a fully-insured basis. Individual business is also sold on a fully-insured basis and is usually medically underwritten at the point of initial issuance. Individual and small group customers are generally more sensitive to product pricing and, to a lesser extent, the configuration of the network, and the efficiency of administration. Account turnover is generally higher with individual and small groups as compared to large groups. Individuals and small groups accounted for 17% of our medical members at December 31, 2006. |
| • | National Accounts are defined as multi-state employer groups primarily headquartered in a WellPoint service area with 5,000 or more eligible employees, with at least 5% or more eligible employees located in a service area outside of the headquarter’s state. Service area is defined as the geographic area in which we are licensed to sell BCBS products. National Accounts are generally sold through independent brokers or consultants retained by the customer working with our in-house sales force. We have a significant advantage when competing for very large National Accounts due to our ability to access the national provider networks of BCBS companies and take advantage of their provider discounts in their local markets. National Accounts represented 15% of our medical members at December 31, 2006. |
| • | BlueCard host customers are defined as enrollees of other BCBS plans, or the “home” plans, who receive health care services in our BCBSA licensed markets. BlueCard host membership accounted for 12% of our medical members at December 31, 2006. |
11
Table of Contents
| • | Senior customers are defined as members age 65 and over with Medicare Supplement or Medicare Advantage policies. Medicare Supplement policies are sold to Medicare recipients as supplements to the benefits they receive from the Medicare program. Rates are filed with and in some cases approved by state insurance departments. The Medicare Advantage program is the managed care alternative to the federally funded Medicare program. Most of the premium is paid directly by the Federal government on behalf of the participant who may also be charged a small premium. Medicare Supplement and Medicare Advantage products are marketed in the same manner. Senior business accounted for 4% of our medical members at December 31, 2006. |
| • | State Sponsored program membership is defined as eligible members with state sponsored managed care alternatives for the Medicaid and State Children’s Health Insurance programs that we manage. Total State Sponsored program business accounted for 5% of our medical members at December 31, 2006. |
We expect to revise our customer type definitions in the first quarter of 2007 in accordance with the new organizational structure which reflects how our chief operating decision maker evaluates the performance of our business beginning January 1, 2007.
In addition to reporting our medical membership by customer type, we report by funding arrangement according to the level of risk that we assume in the product contract. Our two principal funding arrangement categories are fully-insured and self-funded. Fully-insured products are products in which we indemnify our policyholders against costs for health benefits. Self-funded products are offered to customers, generally larger employers, who elect to retain some or all of the financial risk associated with their employees’ health care costs. Some customers choose to purchase stop-loss coverage to limit their retained risk. These customers are reported with our self-funded business.
The following tables set forth our medical membership by customer type and funding arrangement:
| December 31 | ||||
| 2006 | 20051 | |||
| (In thousands) | ||||
Customer Type: | ||||
Large Group | 16,014 | 16,362 | ||
Individual and Small Group (ISG) | 5,654 | 5,645 | ||
National Accounts | 5,044 | 4,776 | ||
BlueCard | 4,279 | 3,915 | ||
Total National | 9,323 | 8,691 | ||
Senior | 1,229 | 1,224 | ||
State Sponsored2 | 1,881 | 1,934 | ||
Total medical membership by customer type | 34,101 | 33,856 | ||
Funding Arrangement: | ||||
Self-Funded | 16,745 | 16,584 | ||
Fully-Insured | 17,356 | 17,272 | ||
Total medical membership by funding arrangement | 34,101 | 33,856 | ||
1 | Medical membership data for 2005 has been reclassified to conform to the current presentation. Our reclassifications for minimum premium amendments to fully-insured contracts resulted in an increase in self-funded membership and a corresponding decrease in fully-insured membership, with no impact on total medical membership. |
2 | During the quarter ended December 31, 2006, our ownership of a joint venture in Puerto Rico changed from a 50 percent ownership of a Medicaid managed care subsidiary to a smaller percentage ownership in the joint venture’s parent company. Accordingly, as of December 31, 2006 and going forward, we no longer include the 222,000 members related to this investment in our reported enrollment. |
12
Table of Contents
For additional information regarding the change in medical membership between years, see the Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations included in this Form 10-K.
Networks and Provider Relations
Our relationships with physicians, hospitals and professionals that provide health care services to our members are guided by regional and national standards for network development, reimbursement and contract methodologies.
We attempt to provide market-based hospital reimbursement along industry standards. We also seek to ensure that physicians in our network are paid in a timely manner at appropriate rates. We use multi-year contracting strategies, including case or fixed rates, to limit our exposure to medical cost inflation and increase cost predictability. In all regions, we seek to maintain broad provider networks to ensure member choice while implementing programs designed to improve the quality of care received by our members.
It is generally our philosophy not to delegate full financial responsibility to our physician providers in the form of capitation-based reimbursement. However, in certain markets we believe capitation can be a useful method to lower costs and reduce underwriting risk, and we therefore have some capitation contracts.
Depending on the consolidation and integration of physician groups and hospitals, reimbursement strategies vary across markets. Fee-for-service is our predominant reimbursement methodology for physicians. We generally use a resource-based relative value system, or RBRVS, fee schedule to determine fee-for-service reimbursement. However, we also use proprietary fee schedules in certain markets. The RBRVS structure was developed and is maintained by CMS, and is used by the Medicare program and other major payers. The RBRVS and proprietary systems are independent of submitted fees and therefore are not as vulnerable to inflation. In addition, we have implemented and continue to expand physician incentive contracting, which recognizes clinical quality and performance as a basis for reimbursement.
Like our physician contracts, our hospital contracts provide for a variety of reimbursement arrangements depending on the network. Our hospital contracts recognize unique hospital attributes, such as academic medical centers or community hospitals, and the volume of care performed for our members. Most hospitals are reimbursed on a fixed amount per day for covered services (per diem) or a case rate basis similar to Medicare (Diagnosis Related Groups). Other hospitals are reimbursed on a discount from approved charge basis for covered services. Hospital outpatient services are reimbursed based on fixed case rates, fee schedules or percent of charges. To improve predictability of expected cost, we frequently use a multi-year contracting approach and have been transitioning to case rate payment methodologies. Many of our hospital contracts have reimbursement linked to improved clinical performance, patient safety and medical error reduction.
Medical Management Programs
Our medical management programs include a broad array of activities that facilitate improvements in the quality of care provided to our members and promote cost effective medical care. These medical management activities and programs are administered and directed by physicians and trained nurses employed by us. One of the goals of our medical management strategies is to ensure that the care delivered to our members is supported by appropriate medical and scientific evidence.
Precertification. A traditional medical management program involves assessment of the appropriateness of certain hospitalizations and other medical services prior to the service being rendered. For example, precertification is used to determine whether a set of hospital and medical services is being appropriately applied to the member’s clinical condition, in accordance with criteria for medical necessity as that term is defined in the member’s benefits contract. Most of our health plans have implemented precertification programs for certain high cost radiology studies, addressing an area of historically significant cost trends.
13
Table of Contents
Concurrent review. Another traditional medical management strategy we use is concurrent review, which is based on nationally recognized criteria developed by third-party medical specialists. With concurrent review, the requirements and intensity of services during a patient’s hospital stay are reviewed, often by an onsite skilled nurse professional in collaboration with the hospital’s medical and nursing staff, in order to coordinate care and determine the most effective transition of care from the hospital setting.
Formulary management. We have developed formularies, which are selections of drugs based on clinical quality and effectiveness. A pharmacy and therapeutics committee of physicians uses scientific and clinical evidence to ensure that our members have access to the appropriate drug therapies.
Medical policy. A medical policy group comprised of physician leaders from various areas of the country, working in cooperation with academic medical centers, practicing community physicians and medical specialty organizations such as the American College of Radiology and national organizations such as the Centers for Disease Control and the American Cancer Society, determines our national policy for the application of new technologies.
Quality programs. We are actively engaged with our hospital networks to enable them to improve medical and surgical care and achieve better outcomes for our members. We endorse, encourage and incent hospitals to support national initiatives to improve clinical care, patient outcomes and reduce medication errors and hospital infections. We have demonstrated our leadership in developing hospital quality programs.
External review procedures. We work with outside experts through a process of external review to provide our members scientifically and clinically, evidenced-based medical care. When we receive member concerns, we have formal appeals procedures that ultimately allow coverage disputes related to medical necessity decisions under the benefits contract to be settled by independent expert physicians.
Service management. In HMO and POS networks, primary care physicians serve as the overall coordinators of members’ health care needs by providing an array of preventive health services and overseeing referrals to specialists for appropriate medical care. In PPO networks, patients have access to network physicians without a primary care physician serving as the coordinator of care.
Care Management Programs
We recently introduced our360º Health suite of integrated care management programs and tools, offered through our wholly-owned subsidiary, Health Management Corporation, or HMC.360º Health offers the following programs, among others, that have been proven to increase quality and reduce medical costs for our members:
Condition Management andMaternity Management programs serve as excellent adjuncts to physician care. A dedicated nurse and added support from our team of dietitians, exercise physiologists, pharmacists, health educators and other health professionals help participants understand their condition, their doctor’s orders and how to become a better self-manager of their condition.
24/7 NurseLine offers access to qualified, registered nurses anytime. This allows our members to make informed decisions about the appropriate level of care and avoid unnecessary worry. This program includes a robust audiotape library, accessible by phone, with more than 400 health topics, as well as on-line health education topics designed to educate members about symptoms and treatment of many common health concerns.
Advanced Care Management reaches out to participants with multiple health care issues who are at risk for frequent and high levels of medical care in order to offer support and assistance in managing their health care needs. Advanced Care Management identifies candidates through claims analysis using predictive modeling techniques, the use of health risk assessment data, utilization management reports and referrals from a physician or one of our other programs, such as the 24/7 NurseLine.
14
Table of Contents
Early Risk Management utilizes integrated information systems and sophisticated data analytics to assist our members to improve their compliance with evidence-based care guidelines, providing Personal Care Notes that alert members to potential gaps in care, enable more prudent health care choices, and assist in the realization of member out-of-pocket cost savings.
Healthy ReturnsSM, HMC’s secure web-based solution, complements other programs by reinforcing telephonic coaching and mail campaigns. The web site engages participants in regularly assessing their health status, gives them feedback about their progress, and tracks important health measures such as blood pressure, weight and blood glucose levels.
Health Care Quality Initiatives
Increasingly, the health care industry is able to define quality health care based on preventive health measurements, outcomes of care and optimal care management for chronic disease. A key to our success has been our ability to work with our network physicians and hospitals to improve the quality and outcomes of the health care services provided to our members. Our ability to promote quality medical care has been recognized by the NCQA, the largest and most respected national accreditation program for managed care health plans.
Several quality health care measures, including the Health Plan Employer Data and Information Set, or HEDIS, have been incorporated into the oversight certification by NCQA. HEDIS measures range from preventive services, such as screening mammography and pediatric immunization, to elements of care, including decreasing the complications of diabetes and improving treatment for patients with heart disease. For the HMO and POS plans, NCQA’s highest accreditation is granted only to those plans that demonstrate levels of service and clinical quality that meet or exceed NCQA’s rigorous requirements for consumer protection and quality improvement. Plans earning this accreditation level must also achieve HEDIS results that are in the highest range of national or regional performance. For the PPO plans, NCQA’s highest accreditation is granted to those plans that have excellent programs for quality improvement and consumer protection and that meet or exceed NCQA’s standards. Overall, our managed care plans have been rated “Excellent”, the highest accreditation, by NCQA.
We have committed to measuring our progress in improving the quality of care that our members receive through the Member Health Index, or MHI. Comprised of 20 clinically relevant measures, the MHI combines prevention, care management, clinical outcome and patient safety metrics.
Our wholly-owned clinical research and health outcomes research subsidiary, HealthCore, has supported biopharmaceutical manufacturers, health professionals, and health plans by enabling more effective medical management and increased physician adherence to evidence based care, and creating new knowledge on the value of clinical therapies, resulting in better care decisions.
Pricing and Underwriting of Our Products
We price our products based on our assessment of current health care claim costs and emerging health care cost trends, combined with charges for administrative expenses, risk and profit. We continually review our product designs and pricing guidelines on a national and regional basis so that our products remain competitive and consistent with our profitability goals and strategies.
In applying our pricing to each employer group and customer, we maintain consistent, competitive, strict underwriting standards. We employ our proprietary accumulated actuarial data in determining underwriting and pricing parameters. Where allowed by law and regulation, we underwrite individual policies based upon the medical history of the individual applying for coverage, small groups based upon case specific underwriting procedures and large groups based on each group’s aggregate claim experience. Also, we employ credit underwriting procedures with respect to our self-funded products.
15
Table of Contents
In most circumstances, our pricing and underwriting decisions follow a prospective rating process in which a fixed premium is determined at the beginning of the contract period. Any deviation, favorable or unfavorable, from the medical costs assumed in determining the premium is our responsibility. Some of our larger groups employ retrospective rating reviews, where positive experience is partially refunded to the group, and negative experience is charged against a rate stabilization fund established from the group’s favorable experience, or charged against future favorable experience.
BCBSA License
We have filed for registration of and maintain several service marks, trademarks and trade names at the federal level and in various states in which we operate. We have the exclusive right to use the BCBS names and marks for our health benefits products in California (Blue Cross only), Colorado, Connecticut, Georgia, Indiana, Kentucky, Maine, Missouri (excluding 30 counties in the Kansas City area), Nevada, New Hampshire, New York (as BCBS in 10 New York City metropolitan and surrounding counties, and as Blue Cross or BCBS in selected upstate counties only), Ohio, Virginia (excluding the Northern Virginia suburbs of Washington, D.C.) and Wisconsin.
Each license requires an annual fee to be paid to the BCBSA. The fee is based upon enrollment and premium. BCBSA is a national trade association of Blue Cross and Blue Shield licensees, the primary function of which is to promote and preserve the integrity of the BCBS names and marks, as well as provide certain coordination among the member companies. Each BCBSA licensee is an independent legal organization and is not responsible for obligations of other BCBSA member organizations. We have no right to market products and services using the BCBS names and marks outside of the states in which we are licensed to sell BCBS products.
We believe that the BCBS names and marks are valuable identifiers of our products and services in the marketplace. The license agreements, which have a perpetual term, contain certain requirements and restrictions regarding our operations and our use of the BCBS names and marks. Upon termination of the license agreements, we would cease to have the right to use the BCBS names and marks in one or more of the states that we are authorized to use the marks and the BCBSA could thereafter issue a license to use the BCBS names and marks in these states to another entity. Events that could cause the termination of a license agreement with the BCBSA include failure to comply with minimum capital requirements imposed by the BCBSA, a change of control or violation of the BCBSA ownership limits on our capital stock, impending financial insolvency, the appointment of a trustee or receiver or the commencement of any action against a licensee seeking its dissolution.
The license agreements with the BCBSA contain certain requirements and restrictions regarding our operations and our use of the BCBS names and marks, including:
| • | minimum capital and liquidity requirements; |
| • | enrollment and customer service performance requirements; |
| • | participation in programs that provide portability of membership between plans; |
| • | disclosure to the BCBSA relating to enrollment and financial conditions; |
| • | disclosures as to the structure of the BCBS system in contracts with third parties and in public statements; |
| • | plan governance requirements; |
| • | a requirement that at least 80% (or, in the case of Blue Cross of California, substantially all) of a licensee’s annual combined net revenue attributable to health benefit plans within its service area must be sold, marketed, administered or underwritten under the BCBS names and marks; |
| • | a requirement that at least 66 2/3% of a licensee’s annual combined national revenue attributable to health benefit plans must be sold, marketed, administered or underwritten under the BCBS names and marks; |
16
Table of Contents
| • | a requirement that neither a plan nor any of its licensed affiliates may permit an entity other than a plan or a licensed affiliate to obtain control of the plan or the licensed affiliate or to acquire a substantial portion of its assets related to licensable services; |
| • | a requirement that limits beneficial ownership of our capital stock to less than 10% for institutional investors and less than 5% for non-institutional investors; |
| • | a requirement that we guarantee certain contractual and financial obligations of our licensed affiliates; and |
| • | a requirement that we indemnify the BCBSA against any claims asserted against it resulting from the contractual and financial obligations of any subsidiary that serves as a fiscal intermediary providing administrative services for Medicare Parts A and B. |
We believe that we and our licensed affiliates are currently in compliance with these standards. The standards under the license agreements may be modified in certain instances by the BCBSA.
Regulation
General
Our operations are subject to comprehensive and detailed state and federal regulation throughout the United States in the jurisdictions in which we do business. Supervisory agencies, including state health, insurance and corporation departments, have broad authority to:
| • | grant, suspend and revoke licenses to transact business; |
| • | regulate many aspects of our products and services; |
| • | monitor our solvency and reserve adequacy; and |
| • | scrutinize our investment activities on the basis of quality, diversification and other quantitative criteria. |
To carry out these tasks, these regulators periodically examine our operations and accounts.
Regulation of Insurance Company and HMO Business Activity
The federal government, as well as the governments of the states in which we conduct our operations, have adopted laws and regulations that govern our business activities in various ways. These laws and regulations, which vary significantly by state, may restrict how we conduct our businesses and may result in additional burdens and costs to us. Areas of governmental regulation include but are not limited to:
| • | licensure; |
| • | premium rates; |
| • | benefits; |
| • | service areas; |
| • | market conduct; |
| • | utilization review activities; |
| • | prompt payment of claims; |
| • | universal health care regulation based on the availability to individuals and small groups of a government sponsored health plan administered by a private contractor and funded by increased premium taxes; |
17
Table of Contents
| • | assessments for state run immunization programs; |
| • | requirements that pharmacy benefit managers pass manufacturers’ rebates to customers; |
| • | member rights and responsibilities; |
| • | sales and marketing activities; |
| • | quality assurance procedures; |
| • | plan design and disclosures, including mandated benefits; |
| • | collection, access or use of protected health information; |
| • | eligibility requirements; |
| • | provider rates of payment; |
| • | surcharges on provider payments; |
| • | provider contract forms; |
| • | provider access standards; |
| • | premium taxes and assessments for the uninsured and or underinsured; |
| • | underwriting, marketing and rating restrictions for small group products; |
| • | member and provider complaints and appeals; |
| • | underwriting and pricing; |
| • | financial arrangements; |
| • | financial condition (including reserves and minimum capital or risk based capital requirements); |
| • | reimbursement or payment levels for government funded business; and |
| • | corporate governance. |
These laws and regulations are subject to amendments and changing interpretations in each jurisdiction.
Our Senior plans, Medicaid plans and other State-Sponsored programs are subject to extensive federal and state laws and regulations.
States generally require health insurers and HMOs to obtain a certificate of authority prior to commencing operations. If we were to establish a health insurance company or an HMO in any state where we do not presently operate, we generally would have to obtain such a certificate. The time necessary to obtain such a certificate varies from state to state. Each health insurer and HMO must file periodic financial and operating reports with the states in which it does business. In addition, health insurers and HMOs are subject to state examination and periodic license renewal. The health benefits business also may be adversely impacted by court and regulatory decisions that expand the interpretations of existing statutes and regulations. It is uncertain whether we can recoup, through higher premiums or other measures, the increased costs of mandated benefits or other increased costs caused by potential legislation, regulation or court rulings.
Medicare Changes
The Medicare Prescription Drug, Improvement and Modernization Act of 2003, or MMA, became law in December 2003. The MMA significantly changed and expanded Medicare. In a pertinent part, the MMA added prescription drug benefits to Medicare for all Medicare eligible individuals starting January 1, 2006. Effective January 1, 2006, we began offering Medicare Part D approved prescription drug plans to Medicare eligible
18
Table of Contents
individuals in all regions of the country. In addition, we are also providing various administrative services for other entities offering prescription drug plans to their employees and retirees through our pharmacy benefit management companies and other affiliated companies.
HIPAA and Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act
The federal Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996, or HIPAA, imposes obligations for issuers of health insurance coverage and health benefit plan sponsors. This law requires guaranteed health care coverage for small employers having two to 50 employees and for individuals who meet certain eligibility requirements. It also requires guaranteed renewability of health care coverage for most employers and individuals. The law limits exclusions based on preexisting conditions for individuals covered under group policies to the extent the individuals had prior creditable coverage.
The Administrative Simplification provisions of HIPAA imposed a number of requirements on covered entities (including insurers, HMOs, group health plans, providers and clearinghouses). These requirements include uniform standards of common electronic health care transactions; privacy and security regulations; and unique identifier rules for employers, health plans and providers. We complied timely with requirements that have gone into effect, and intend to comply with future requirements on or before the compliance dates.
Other federal legislation includes the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act, which generally placed restrictions on the disclosure of non-public information to non-affiliated third parties, and required financial institutions, including insurers, to provide customers with notice regarding how their non-public personal information is used, including an opportunity to “opt out” of certain disclosures. State departments of insurance and certain federal agencies adopted implementing regulations as required by federal law. The Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act also gives banks and other financial institutions the ability to affiliate with insurance companies, which may lead to new competitors in the insurance and health benefits fields.
Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974
The provision of services to certain employee welfare benefit plans is subject to the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974, as amended, or ERISA, a complex set of laws and regulations subject to interpretation and enforcement by the Internal Revenue Service and the Department of Labor. ERISA regulates certain aspects of the relationships between us, the employers who maintain employee welfare benefit plans subject to ERISA and participants in such plans. Some of our administrative services and other activities may also be subject to regulation under ERISA. In addition, certain states require licensure or registration of companies providing third party claims administration services for benefit plans. We provide a variety of products and services to employee welfare benefit plans that are covered by ERISA. Plans subject to ERISA can also be subject to state laws and the question of whether ERISA preempts a state law has been, and will continue to be, interpreted by many courts.
HMO and Insurance Holding Company Laws
We are regulated as an insurance holding company and are subject to the insurance holding company acts of the states in which our subsidiaries are domiciled. These acts contain certain reporting requirements as well as restrictions on transactions between an insurer or HMO and its affiliates. These holding company laws and regulations generally require insurance companies and HMOs within an insurance holding company system to register with the insurance department of each state where they are domiciled and to file with those states’ insurance departments certain reports describing capital structure, ownership, financial condition, certain intercompany transactions and general business operations. In addition, various notice and reporting requirements generally apply to transactions between insurance companies and HMOs and their affiliates within an insurance holding company system, depending on the size and nature of the transactions. Some insurance holding company laws and regulations require prior regulatory approval or, in certain circumstances, prior notice
19
Table of Contents
of certain material intercompany transfers of assets as well as certain transactions between insurance companies, HMOs, their parent holding companies and affiliates. Among other restrictions, state insurance and HMO laws may restrict the ability of our regulated subsidiaries to pay dividends.
Additionally, the holding company acts of the states in which our subsidiaries are domiciled restrict the ability of any person to obtain control of an insurance company or HMO without prior regulatory approval. Under those statutes, without such approval (or an exemption), no person may acquire any voting security of an insurance holding company, which controls an insurance company or HMO, or merge with such a holding company, if as a result of such transaction such person would “control” the insurance holding company. “Control” is generally defined as the direct or indirect power to direct or cause the direction of the management and policies of a person and is presumed to exist if a person directly or indirectly owns or controls 10% or more of the voting securities of another person.
Guaranty Fund Assessments
Under insolvency or guaranty association laws in most states, insurance companies can be assessed for amounts paid by guaranty funds for policyholder losses incurred when an insurance company becomes insolvent. Most state insolvency or guaranty association laws currently provide for assessments based upon the amount of premiums received on insurance underwritten within such state (with a minimum amount payable even if no premium is received). Under many of these guaranty association laws, assessments against insurance companies that issue policies of accident or sickness insurance are made retrospectively. The amount and timing of any future assessments, however, cannot be reasonably estimated and are beyond our control.
While the amount of any assessments applicable to life and health guaranty funds cannot be predicted with certainty, we believe that future guaranty association assessments for insurer insolvencies will not have a material adverse effect on our liquidity and capital resources.
Risk-Based Capital Requirements
The states of domicile of our regulated subsidiaries have statutory risk-based capital, or RBC, requirements for health and other insurance companies based on the RBC Model Act. These RBC requirements are intended to assess the capital adequacy of life and health insurers, taking into account the risk characteristics of an insurer’s investments and products. The RBC Model Act sets forth the formula for calculating the RBC requirements, which are designed to take into account asset risks, insurance risks, interest rate risks and other relevant risks with respect to an individual insurance company’s business. In general, under these laws, an insurance company must submit a report of its RBC level to the insurance department or insurance commissioner of its state of domicile for each calendar year.
The law requires increasing degrees of regulatory oversight and intervention as an insurance company’s RBC declines. The RBC Model Act provides for four different levels of regulatory attention depending on the ratio of a company’s total adjusted capital (defined as the total of its statutory capital, surplus and asset valuation reserve) to its risk-based capital. The level of regulatory oversight ranges from requiring the insurance company to inform and obtain approval from the domiciling insurance commissioner of a comprehensive financial plan for increasing its RBC, to mandatory regulatory intervention requiring an insurance company to be placed under regulatory control in a rehabilitation or liquidation proceeding. As of December 31, 2006, the RBC levels of our insurance subsidiaries exceeded all RBC thresholds.
Employees
At December 31, 2006, we had approximately 42,000 persons employed on a full-time basis. As of December 31, 2006, a small portion of employees were covered by collective bargaining agreements: 144 employees in the Sacramento, California area with the Office and Professional Employees International Union, Local 29; 119 employees in the greater Detroit, Michigan area with the International Brotherhood of Teamsters,
20
Table of Contents
Chauffeurs, Warehousemen and Helpers of America, Local No. 614; 17 employees in the New York city metropolitan area with the Office and Professional Employees International Union, Local 153; and 149 employees in Milwaukee, Wisconsin with the Office and Professional Employees International Union, Local 9. Our employees are an important asset, and we seek to develop them to their full potential. We believe that our relationship with our employees is good.
The following factors, among others, could cause actual results to differ materially from those contained in forward-looking statements made in this Annual Report on Form 10-K and presented elsewhere by management from time to time. Such factors, among others, may have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, and results of operations and you should carefully consider them. It is not possible to predict or identify all such factors. Consequently, you should not consider any such list to be a complete statement of all our potential risks or uncertainties. Because of these and other factors, past performance should not be considered an indication of future performance.
Changes in state and federal regulations, or the application thereof, may adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Our insurance, managed health care and health maintenance organization, or HMO, subsidiaries are subject to extensive regulation and supervision by the insurance, managed health care or HMO regulatory authorities of each state in which they are licensed or authorized to do business, as well as to regulation by federal and local agencies. We cannot assure you that future regulatory action by state insurance or HMO authorities will not have a material adverse effect on the profitability or marketability of our health benefits or managed care products or on our business, financial condition and results of operations. In addition, because of our participation in government-sponsored programs such as Medicare and Medicaid, changes in government regulations or policy with respect to, among other things, reimbursement levels, could also adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations. In addition, we cannot assure you that application of the federal and/or state tax regulatory regime that currently applies to us will not, or future tax regulation by either federal and/or state governmental authorities concerning us could not, have a material adverse effect on our business, operations or financial condition.
State legislatures and Congress continue to focus on health care issues. A number of states, including California, Connecticut, and Pennsylvania, are contemplating significant reform of their health insurance markets. These proposals include provisions affecting both public programs and privately-financed health insurance arrangements. Broadly stated, these proposals attempt to increase the number of insured by raising the eligibility levels for public programs and compelling individuals and employers to purchase health coverage. At the same time, they reform the underwriting and marketing practices of health plans. As these proposals are still being debated in the various legislatures, we cannot assure you that, if enacted into law, these proposals would not have a negative impact on our business, operations or financial condition.
From time to time, Congress has considered various forms of managed care reform legislation which, if adopted, could fundamentally alter the treatment of coverage decisions under ERISA. Additionally, there have been legislative attempts to limit ERISA’s preemptive effect on state laws. If adopted, such limitations could increase our liability exposure and could permit greater state regulation of our operations. Other proposed bills and regulations, including those related to HIPAA standard transactions and code sets, consumer-driven health plans and health savings accounts and insurance market reform, at state and federal levels may impact certain aspects of our business, including premium receipts, provider contracting, claims payments and processing and confidentiality of health information. While we cannot predict if any of these initiatives will ultimately become effective or, if enacted, what their terms will be, their enactment could increase our costs, expose us to expanded liability or require us to revise the ways in which we conduct business. Further, as we continue to implement our e-business initiatives, uncertainty surrounding the regulatory authority and requirements in this area may make it difficult to ensure compliance.
21
Table of Contents
Our inability to contain health care costs, implement increases in premium rates on a timely basis, maintain adequate reserves for policy benefits, maintain our current provider agreements or avoid a downgrade in our ratings may adversely affect our business and profitability.
Our profitability depends in large part on accurately predicting health care costs and on our ability to manage future health care costs through underwriting criteria, medical management, product design and negotiation of favorable provider contracts. The aging of the population and other demographic characteristics and advances in medical technology continue to contribute to rising health care costs. Government-imposed limitations on Medicare and Medicaid reimbursement have also caused the private sector to bear a greater share of increasing health care costs. Changes in health care practices, inflation, new technologies, the cost of prescription drugs, clusters of high cost cases, changes in the regulatory environment and numerous other factors affecting the cost of health care may adversely affect our ability to predict and manage health care costs, as well as our business, financial condition and results of operations. Relatively small differences between predicted and actual health care costs as a percentage of premium revenues can result in significant changes in our results of operations.
In addition to the challenge of managing health care costs, we face pressure to contain premium rates. Our customer contracts may be subject to renegotiation as customers seek to contain their costs. Alternatively, our customers may move to a competitor to obtain more favorable premiums. Fiscal concerns regarding the continued viability of programs such as Medicare and Medicaid may cause decreasing reimbursement rates or a lack of sufficient increase in reimbursement rates for government-sponsored programs in which we participate. A limitation on our ability to increase or maintain our premium or reimbursement levels or a significant loss of membership resulting from our need to increase or maintain premium or reimbursement levels could adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
The reserves that we establish for health insurance policy benefits and other contractual rights and benefits are based upon assumptions concerning a number of factors, including trends in health care costs, expenses, general economic conditions and other factors. Actual experience will likely differ from assumed experience, and to the extent the actual claims experience is less favorable than estimated based on our underlying assumptions, our incurred losses would increase and future earnings could be adversely affected.
In addition, our profitability is dependent upon our ability to contract on favorable terms with hospitals, physicians and other health care providers. The failure to maintain or to secure new cost-effective health care provider contracts may result in a loss in membership or higher medical costs. In addition, our inability to contract with providers, or the inability of providers to provide adequate care, could adversely affect our business.
Claims-paying ability and financial strength ratings by recognized rating organizations are an important factor in establishing the competitive position of insurance companies and health benefits companies. Rating organizations continue to review the financial performance and condition of insurers. Each of the rating agencies reviews its ratings periodically and there can be no assurance that our current ratings will be maintained in the future. We believe our strong ratings are an important factor in marketing our products to customers, since ratings information is broadly disseminated and generally used throughout the industry. If our ratings are downgraded or placed under surveillance or review, with possible negative implications, the downgrade, surveillance or review could adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations. These ratings reflect each rating agency’s opinion of our financial strength, operating performance and ability to meet our obligations to policyholders and creditors, and are not evaluations directed toward the protection of investors in our common stock.
22
Table of Contents
A reduction in the enrollment in our health benefits programs could have an adverse effect on our business and profitability.
A reduction in the number of enrollees in our health benefits programs could adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations. Factors that could contribute to a reduction in enrollment include: failure to obtain new customers or retain existing customers; premium increases and benefit changes; our exit from a specific market; reductions in workforce by existing customers; negative publicity and news coverage; failure to attain or maintain nationally recognized accreditations; and general economic downturn that results in business failures.
There are risks associated with being a contractor with the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services to provide Medicare Part D Prescription Drug benefits.
The Medicare Prescription Drug, Improvement and Modernization Act of 2003, or MMA, became law in December 2003. The MMA significantly changed and expanded Medicare coverage. The MMA added the availability of prescription drug benefits for all Medicare eligible individuals starting January 1, 2006. Effective January 1, 2006, we began offering Medicare approved prescription drug plans to Medicare eligible individuals nationwide. In addition, we are also providing various administrative services for other entities offering prescription drug plans to their employees and retirees through our pharmacy benefit management and other affiliated companies. We are also the United States default plan for point of service facilitated enrollment, as defined by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, or CMS. While we believe we have adequately reviewed our assumptions and estimates regarding this complex and recent program, including those related to collectability of receivables and establishment of liabilities, the actual results may be different than our assumptions and estimates. Risks associated with the Medicare prescription drug plans include potential uncollectability of receivables resulting from processing and/or verifying enrollment (including facilitated enrollment), inadequacy of underwriting assumptions, inability to receive and process information, uncollectability of premiums from members, increased pharmaceutical costs, and the underlying seasonality of this business.
We are subject to funding risks with respect to revenue received from participation in Medicare and Medicaid programs.
We participate as a payer in Medicare Advantage, Medicare Part D and Medicaid programs and receive revenues from the Medicare and Medicaid programs to provide benefits under these programs. Revenues for these programs are dependent upon annual funding from the federal government and/or applicable state governments. Funding for these programs is dependent upon many factors outside of our control including general economic conditions at the federal or applicable state level and general political issues and priorities. An unexpected reduction or inadequate government funding for these programs may adversely affect our revenues and financial results.
The health benefits industry is subject to negative publicity, which can adversely affect our business and profitability.
The health benefits industry is subject to negative publicity. Negative publicity may result in increased regulation and legislative review of industry practices, which may further increase our costs of doing business and adversely affect our profitability by: adversely affecting our ability to market our products and services; requiring us to change our products and services; or increasing the regulatory burdens under which we operate.
In addition, as long as we use the Blue Cross and Blue Shield names and marks in marketing our health benefits products and services, any negative publicity concerning the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association or other Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association licensees may adversely affect us and the sale of our health benefits products and services. Any such negative publicity could adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
23
Table of Contents
We face competition in many of our markets and customers and brokers have flexibility in moving between competitors.
As a health benefits company, we operate in a highly competitive environment and in an industry that is currently subject to significant changes from business consolidations, new strategic alliances, legislative reform, aggressive marketing practices by other health benefits organizations and market pressures brought about by an informed and organized customer base, particularly among large employers. This environment has produced and will likely continue to produce significant pressures on the profitability of health benefits companies.
We are dependent on the services of independent agents and brokers in the marketing of our health care products, particularly with respect to individuals, seniors and small employer group members. Such independent agents and brokers are typically not exclusively dedicated to us and may frequently also market health care products of our competitors. We face intense competition for the services and allegiance of independent agents and brokers. We cannot assure you that we will be able to compete successfully against current and future competitors or that competitive pressures faced by us will not materially and adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
A change in our health care product mix may impact our profitability.
Our health care products that involve greater potential risk generally tend to be more profitable than administrative services products and those health care products where we are able to shift risk to employer groups. Individuals and small employer groups are more likely to purchase our higher-risk health care products because such purchasers are generally unable or unwilling to bear greater liability for health care expenditures. Typically, government-sponsored programs also involve our higher-risk health care products. A shift of enrollees from more profitable products to less profitable products could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
From time to time, we have implemented price increases in certain of our health care businesses. While these price increases may improve profitability, there can be no assurance that this will occur. Subsequent unfavorable changes in the relative profitability between our various products could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
Our pharmacy benefit management companies operate in an industry faced with a number of risks and uncertainties in addition to those we face with our core health care business.
The following are some of the pharmacy benefit industry-related risks that could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations:
| • | the application of federal and state anti-remuneration laws; |
| • | compliance requirements for pharmacy benefit manager fiduciaries under ERISA, including compliance with fiduciary obligations under ERISA in connection with the development and implementation of items such as formularies, preferred drug listings and therapeutic intervention programs, contracting network practices, specialty drug distribution and other transactions and potential liability regarding the use of patient-identifiable medical information; |
| • | a number of federal and state legislative proposals are being considered that could adversely affect a variety of pharmacy benefit industry practices, including without limitation, the receipt of rebates from pharmaceutical manufacturers, the regulation of the development and use of formularies, and legislation imposing additional rights to access to drugs for individuals enrolled in managed care plans; |
| • | the application of federal and state laws and regulations related to the operation of Internet and mail-service pharmacies; |
| • | our inability to contract on favorable terms with pharmaceutical manufacturers. |
24
Table of Contents
The failure to adhere to these or other relevant laws and regulations could expose our pharmacy benefit management business to civil and criminal penalties. There can be no assurance that our business will not be subject to challenge under various laws and regulations or contractual arrangements. Any such noncompliance or challenge may have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
As a holding company, we are dependent on dividends from our subsidiaries. Our regulated subsidiaries are subject to state regulations, including restrictions on the payment of dividends and maintenance of minimum levels of capital.
We are a holding company whose assets include all of the outstanding shares of common stock of our subsidiaries including our intermediate holding companies and regulated insurance and HMO subsidiaries. As a holding company, we depend on dividends from our subsidiaries. Among other restrictions, state insurance and HMO laws may restrict the ability of our regulated subsidiaries to pay dividends. Our ability to repurchase shares or pay dividends in the future to our shareholders and meet our obligations, including paying operating expenses and debt service on our outstanding and future indebtedness, will depend upon the receipt of dividends from our subsidiaries. An inability of our subsidiaries to pay dividends in the future in an amount sufficient for us to meet our financial obligations may materially adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Most of our regulated subsidiaries are subject to RBC standards, imposed by their states of domicile. These laws are based on the RBC Model Act adopted by the National Association of Insurance Commissioners, or NAIC, and require our regulated subsidiaries to report their results of risk-based capital calculations to the departments of insurance and the NAIC. Failure to maintain the minimum RBC standards could subject our regulated subsidiaries to corrective action, including state supervision or liquidation. Our regulated subsidiaries are currently in compliance with the risk-based capital or other similar requirements imposed by their respective states of domicile. As discussed in more detail below, we are a party to license agreements with the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association which contain certain requirements and restrictions regarding our operations, including minimum capital and liquidity requirements, which could restrict the ability of our regulated subsidiaries to pay dividends.
We face risks related to litigation.
We are, or may be in the future, a party to a variety of legal actions that affect any business, such as employment and employment discrimination-related suits, employee benefit claims, breach of contract actions, tort claims and intellectual property-related litigation. In addition, because of the nature of our business, we are subject to a variety of legal actions relating to our business operations, including the design, management and offering of our products and services. These could include: claims relating to the denial of health care benefits; claims relating to the rescission of health insurance policies; medical malpractice actions; allegations of anti-competitive and unfair business activities; provider disputes over compensation and termination of provider contracts; disputes related to self-funded business; disputes over co-payment calculations; disputes related to the pharmacy benefit management business; claims related to the failure to disclose certain business practices; and claims relating to customer audits and contract performance.
Recent court decisions and legislative activity may increase our exposure for any of these types of claims. In some cases, substantial non-economic, treble or punitive damages may be sought. We currently have insurance coverage for some of these potential liabilities. Other potential liabilities may not be covered by insurance, insurers may dispute coverage or the amount of insurance may not be enough to cover the damages awarded. In addition, certain types of damages, such as punitive damages, may not be covered by insurance, and insurance coverage for all or certain forms of liability may become unavailable or prohibitively expensive in the future. Any adverse judgment against us resulting in such damage awards could have an adverse effect on our cash flows, results of operations and financial condition.
25
Table of Contents
In addition, we are also involved in pending and threatened litigation of the character incidental to the business transacted, arising out of our operations and our 2001 demutualization, and are from time to time involved as a party in various governmental investigations, audits, reviews and administrative proceedings. These investigations, audits and reviews include routine and special investigations by various state insurance departments, state attorneys general and the U.S. Attorney General. Such investigations could result in the imposition of civil or criminal fines, penalties and other sanctions. We believe that any liability that may result from any one of these actions, or in the aggregate, is unlikely to have a material adverse effect on our consolidated results of operations or financial position.
For additional information concerning legal actions affecting us, see Part I, Item 3, Legal Proceedings.
We are a party to license agreements with the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association that entitle us to the exclusive and in certain areas non-exclusive use of the Blue Cross and Blue Shield names and marks in our geographic territories. The termination of these license agreements or changes in the terms and conditions of these license agreements could adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
We use the Blue Cross and Blue Shield names and marks as identifiers for our products and services under licenses from the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association. Our license agreements with the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association contain certain requirements and restrictions regarding our operations and our use of the Blue Cross and Blue Shield names and marks, including: minimum capital and liquidity requirements imposed by the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association; enrollment and customer service performance requirements; participation in programs that provide portability of membership between plans; disclosures to the Blue Cross Blue and Shield Association relating to enrollment and financial conditions; disclosures as to the structure of the Blue Cross and Blue Shield system in contracts with third parties and in public statements; plan governance requirements; a requirement that at least 80% (or, in the case of Blue Cross of California, substantially all) of a licensee’s annual combined local net revenue attributable to health benefit plans within its service areas must be sold, marketed, administered or underwritten under the Blue Cross and Blue Shield names and marks; a requirement that at least 66 2/3% of a licensee’s annual combined national net revenue attributable to health benefit plans must be sold, marketed, administered or underwritten under the Blue Cross and Blue Shield names and marks; a requirement that neither a plan nor any of its licensed affiliates may permit an entity other than a plan or a licensed affiliate to obtain control of the plan or the licensed affiliate or to acquire a substantial portion of its assets related to licensable services; a requirement that we guarantee certain contractual and financial obligations of our licensed affiliates; and a requirement that we indemnify the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association against any claims asserted against it resulting from the contractual and financial obligations of any subsidiary that serves as a fiscal intermediary providing administrative services for Medicare Parts A and B. Failure to comply with the foregoing requirements could result in a termination of the license agreements.
The standards under the license agreements may be modified in certain instances by the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association. For example, from time to time there have been proposals considered by the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association to modify the terms of the license agreements to restrict various potential business activities of licensees. These proposals have included, among other things, a limitation on the ability of a licensee to make its provider networks available to insurance carriers or other entities not holding a Blue Cross or Blue Shield license. To the extent that such amendments to the license agreements are adopted in the future, they could have a material adverse effect on our future expansion plans or results of operations.
Upon the occurrence of an event causing termination of the license agreements, we would no longer have the right to use the Blue Cross and Blue Shield names and marks in one or more of our geographic territories. Furthermore, the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association would be free to issue a license to use the Blue Cross and Blue Shield names and marks in these states to another entity. Events that could cause the termination of a license agreement with the Blue Cross Blue and Shield Association include failure to comply with minimum capital requirements imposed by the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association, a change of control or violation of the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association ownership limitations on our capital stock, impending financial insolvency and the appointment of a trustee or receiver or the commencement of any action against a licensee
26
Table of Contents
seeking its dissolution. We believe that the Blue Cross and Blue Shield names and marks are valuable identifiers of our products and services in the marketplace. Accordingly, termination of the license agreements could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Upon termination of a license agreement, the Blue Cross and Blue and Shield Association would impose a “Re-establishment Fee” upon us, which would allow the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association to “re-establish” a Blue Cross and or Blue Shield presence in the vacated service area. Through December 31, 2006 the fee was set at $83.41 per licensed enrollee. As of December 31, 2006, we reported 28.5 million Blue Cross and or Blue Shield enrollees. If the Re-establishment Fee was applied to our total Blue Cross and or Blue Shield enrollees, we would be assessed approximately $2.4 billion by the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association.
Our investment portfolios are subject to varying economic and market conditions, as well as regulation. If we fail to comply with these regulations, we may be required to sell certain investments.
The market values of our investments vary from time to time depending on economic and market conditions. For various reasons, we may sell certain of our investments at prices that are less than the carrying value of the investments. In addition, in periods of declining interest rates, bond calls and mortgage loan prepayments generally increase, resulting in the reinvestment of these funds at the then lower market rates. We cannot assure you that our investment portfolios will produce positive returns in future periods. Our regulated subsidiaries are subject to state laws and regulations that require diversification of our investment portfolios and limit the amount of investments in certain riskier investment categories, such as below-investment-grade fixed maturity securities, mortgage loans, real estate and equity investments, which could generate higher returns on our investments. Failure to comply with these laws and regulations might cause investments exceeding regulatory limitations to be treated as non-admitted assets for purposes of measuring statutory surplus and risk-based capital, and, in some instances, require the sale of those investments.
As a Medicare fiscal intermediary, we are subject to complex regulations. If we fail to comply with these regulations, we may be exposed to criminal sanctions and significant civil penalties.
Like a number of other Blue Cross and Blue Shield companies, we serve as a fiscal intermediary for the Medicare program, which generally provides coverage for persons who are 65 or older and for persons with end-stage renal disease. Part A of the Medicare program provides coverage for services provided by hospitals, skilled nursing facilities and other health care facilities. Part B of the Medicare program provides coverage for services provided by physicians, physical and occupational therapists and other professional providers. Part B also includes coverage for durable medical equipment such as diabetic supplies and wheelchairs. As a fiscal intermediary, we receive reimbursement for certain costs and expenditures, which is subject to adjustment upon audit by CMS. The laws and regulations governing fiscal intermediaries for the Medicare programs are complex, subject to interpretation and can expose a fiscal intermediary to penalties for non-compliance. If we fail to comply with these laws and regulations, we could be subject to criminal fines, civil penalties or other sanctions.
Regional concentrations of our business may subject us to economic downturns in those regions.
Most of our revenues are generated in the states of California, Colorado, Connecticut, Georgia, Indiana, Kentucky, Maine, Missouri, Nevada, New Hampshire, New York, Ohio, Virginia and Wisconsin. Due to this concentration of business in these states, we are exposed to potential losses resulting from the risk of an economic downturn in these states. If economic conditions in these states deteriorate, we may experience a reduction in existing and new business, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
27
Table of Contents
Large-scale medical emergencies may have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Large-scale medical emergencies can take many forms and can cause widespread illness and death. For example, there have been various incidents of suspected bioterrorist activity in the United States. To date, these incidents have resulted in related isolated incidents of illness and death. However, federal and state law enforcement officials have issued warnings about additional potential terrorist activity involving biological and other weapons. In addition, natural disasters such as the hurricanes experienced in the southeastern part of the United States in 2005 and the potential for a wide-spread pandemic of influenza coupled with the lack of availability of appropriate preventative medicines can have a significant impact on the health of the population of wide-spread areas. If the United States were to experience widespread bioterrorist or other attacks, large-scale natural disasters in our concentrated coverage areas or a large-scale pandemic or epidemic, our covered medical expenses could rise and we could experience a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations or, in the event of extreme circumstances, our viability.
We have built a significant portion of our current business through mergers and acquisitions and we expect to pursue acquisitions in the future.
The following are some of the risks associated with acquisitions that could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations:
| • | some of the acquired businesses may not achieve anticipated revenues, earnings or cash flow; |
| • | we may assume liabilities that were not disclosed to us or which were under-estimated; |
| • | we may be unable to integrate acquired businesses successfully and realize anticipated economic, operational and other benefits in a timely manner, which could result in substantial costs and delays or other operational, technical or financial problems; |
| • | acquisitions could disrupt our ongoing business, distract management, divert resources and make it difficult to maintain our current business standards, controls and procedures; |
| • | we may finance future acquisitions by issuing common stock for some or all of the purchase price, which could dilute the ownership interests of our shareholders; |
| • | we may also incur additional debt related to future acquisitions; and |
| • | we would be competing with other firms, some of which may have greater financial and other resources, to acquire attractive companies. |
We have substantial indebtedness outstanding and may incur additional indebtedness in the future. As a holding company, we are not able to repay our indebtedness except through dividends from subsidiaries, some of which are restricted in their ability to pay such dividends under applicable insurance law and undertakings. Such indebtedness could also adversely affect our ability to pursue desirable business opportunities.
As of December 31, 2006, we had indebtedness outstanding of approximately $7.0 billion and had available borrowing capacity under our revolving credit facility of approximately $1.2 billion, which credit facility expires on September 30, 2011. Our debt service obligations require us to use a portion of our cash flow to pay interest and principal on debt instead of for other corporate purposes, including funding future expansion. If our cash flow and capital resources are insufficient to service our debt obligations, we may be forced to seek extraordinary dividends from our subsidiaries, sell assets, seek additional equity or debt capital or restructure our debt. However, these measures might be unsuccessful or inadequate in permitting us to meet scheduled debt service obligations.
As a holding company, we have no operations and are dependent on dividends from our subsidiaries for cash to fund our debt service and other corporate needs. Our subsidiaries are separate legal entities. Furthermore,
28
Table of Contents
our subsidiaries are not obligated to make funds available to us, and creditors of our subsidiaries will have a superior claim to certain of our subsidiaries’ assets. State insurance laws restrict the ability of our regulated subsidiaries to pay dividends, and in some states we have made special undertakings that may limit the ability of our regulated subsidiaries to pay dividends. In addition, our subsidiaries’ ability to make any payments to us will also depend on their earnings, the terms of their indebtedness, business and tax considerations and other legal restrictions. We cannot assure you that our subsidiaries will be able to pay dividends or otherwise contribute or distribute funds to us in an amount sufficient to pay the principal of or interest on the indebtedness owed by us.
We may also incur future debt obligations that might subject us to restrictive covenants that could affect our financial and operational flexibility. Our breach or failure to comply with any of these covenants could result in a default under our credit agreements. If we default under our credit agreements, the lenders could cease to make further extensions of credit or cause all of our outstanding debt obligations under our credit agreements to become immediately due and payable, together with accrued and unpaid interest. If the indebtedness under our notes or our credit agreements is accelerated, we may be unable to repay or finance the amounts due. Indebtedness could also limit our ability to pursue desirable business opportunities, and may affect our ability to maintain an investment grade rating for our indebtedness.
The value of our intangible assets may become impaired.
Due largely to our recent acquisitions, goodwill and other intangible assets represent a substantial portion of our assets. Goodwill and other intangible assets were approximately $22.8 billion as of December 31, 2006, representing approximately 44% of our total assets. If we make additional acquisitions it is likely that we will record additional intangible assets on our balance sheet. In accordance with applicable accounting standards, we periodically evaluate our goodwill and other intangible assets to determine whether all or a portion of their carrying values may no longer be recoverable, in which case a charge to earnings may be necessary. Any future evaluations requiring an impairment of our goodwill and other intangible assets could materially affect our results of operations and shareholders’ equity in the period in which the impairment occurs. A material decrease in shareholders’ equity could, in turn, negatively impact our debt ratings or potentially impact our compliance with existing debt covenants.
We face intense competition to attract and retain employees.
We are dependent on retaining existing employees and attracting and retaining additional qualified employees to meet current and future needs and achieving productivity gains from our investments in technology. We face intense competition for qualified employees, and there can be no assurance that we will be able to attract and retain such employees or that such competition among potential employers will not result in increasing salaries. An inability to retain existing employees or attract additional employees could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
An unauthorized disclosure of sensitive or confidential member information could have an adverse effect on our business, reputation and profitability.
As part of our normal operations, we collect, process and retain sensitive and confidential member information. We are subject to various federal and state laws and rules regarding the use and disclosure of sensitive or confidential member information, including HIPAA and the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act. Despite the security measures we have in place to ensure compliance with applicable laws and rules, our facilities and systems, and those of our third party service providers, may be vulnerable to security breaches, acts of vandalism, computer viruses, misplaced or lost data, programming and/or human errors or other similar events. Any security breach involving the misappropriation, loss or other unauthorized disclosure of sensitive or confidential member information, whether by us or by one of our vendors, could have a material adverse effect on our business, reputation and results of operations.
The failure to effectively maintain and modernize our information systems and e-business organization could adversely affect our business.
Our business depends significantly on effective information systems, and we have many different information systems for our various businesses. Our information systems require an ongoing commitment of
29
Table of Contents
significant resources to maintain and enhance existing systems and develop new systems in order to keep pace with continuing changes in information processing technology, evolving industry and regulatory standards, and changing customer preferences. In addition, we may from time to time obtain significant portions of our systems-related or other services or facilities from independent third parties, which may make our operations vulnerable to such third parties’ failure to perform adequately.
As a result of our merger and acquisition activities, we have acquired additional systems. Our failure to maintain effective and efficient information systems, or our failure to efficiently and effectively consolidate our information systems to eliminate redundant or obsolete applications, could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations. In addition, as we convert or migrate members to our more efficient and effective systems, the risk of disruption in our customer service is increased during the migration or conversion process and such disruption could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Also, our vision for the future includes becoming a premier e-business organization by modernizing interactions with customers, brokers, agents, providers, employees and other stakeholders through web-enabling technology and redesigning internal operations. The goal of our e-business strategy is to become widely regarded as an e-business leader in the health benefits industry. The strategy includes not only sales and distribution of health benefits products on the Internet, but also implementation of advanced self-service capabilities benefiting customers, agents, brokers, providers, partners and employees. We cannot assure you that we will be able to realize successfully our e-business vision or integrate e-business operations with our current method of operations. The failure to maintain successful e-business capabilities could result in competitive and cost disadvantages to us as compared to our competitors.
We are dependent on the success of our relationship with a large vendor for a significant portion of our information system resources and certain other vendors for various other services.
We have an agreement with International Business Machines Corporation, or IBM, pursuant to which we outsourced a portion of our core applications development as well as a component of our data center operations and help desk to IBM. We are dependent upon IBM for these support functions. If our relationship with IBM is terminated for any reason, we may not be able to find an alternative partner in a timely manner or on acceptable financial terms. As a result, we may not be able to meet the demands of our customers and, in turn, our business, financial condition and results of operations may be harmed. The contract with IBM includes several service level agreements, or SLAs, related to issues such as performance and job disruption with significant financial penalties if these SLAs are not met. We also outsource a component of our data center to another vendor, which could assume much of the IBM work and mitigate business disruption should a termination with IBM occur. We may not be adequately indemnified against all possible losses through the terms and conditions of the agreement. In addition, some of our termination rights are contingent upon payment of a fee, which may be significant.
We have also entered into agreements with large vendors pursuant to which we have outsourced certain functions such as data entry related to claims and billing processes and call center operations for member and provider queries as well as certain Medicare Part D sales. If these vendor relationships were terminated for any reason, we may not be able to find alternative partners in a timely manner or on acceptable financial terms. As a result, we may not be able to meet the full demands of our customers and, in turn, our business, financial condition and results of operations may be harmed.
We may experience difficulties integrating the business of WellChoice with our business and may incur substantial costs in connection with the integration, which could cause us to lose many of the anticipated potential benefits of the acquisition.
We acquired WellChoice with the expectation that the acquisition will result in various benefits, including, among others, benefits relating to a stronger and more diverse network of doctors and other health care providers, expanded and enhanced affordable health care services, enhanced revenues, a strengthened market position for us across the United States, cross-selling opportunities, technology, cost savings and operating efficiencies. Achieving the anticipated benefits of the acquisition is subject to a number of uncertainties, including whether
30
Table of Contents
we integrate WellChoice in an efficient and effective manner, and general competitive factors in the marketplace. Failure to achieve these anticipated benefits could result in increased costs, decreases in the amount of expected revenues and diversion of management’s time and energy and could materially impact our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Indiana law, and other applicable laws, and our articles of incorporation and bylaws, may prevent or discourage takeovers and business combinations that our shareholders might consider in their best interest.
Indiana law and our articles of incorporation and bylaws may delay, defer, prevent or render more difficult a takeover attempt that our shareholders might consider in their best interests. For instance, they may prevent our shareholders from receiving the benefit from any premium to the market price of our common stock offered by a bidder in a takeover context. Even in the absence of a takeover attempt, the existence of these provisions may adversely affect the prevailing market price of our common stock if they are viewed as discouraging takeover attempts in the future.
We are regulated as an insurance holding company and subject to the insurance holding company acts of the states in which our insurance company subsidiaries are domiciled, as well as similar provisions included in the health statutes and regulations of certain states where these subsidiaries are regulated as managed care companies or HMOs. The insurance holding company acts and regulations and these similar health provisions restrict the ability of any person to obtain control of an insurance company or HMO without prior regulatory approval. Under those statutes and regulations, without such approval (or an exemption), no person may acquire any voting security of a domestic insurance company or HMO, or an insurance holding company which controls an insurance company or HMO, or merge with such a holding company, if as a result of such transaction such person would “control” the insurance holding company, insurance company or HMO. “Control” is generally defined as the direct or indirect power to direct or cause the direction of the management and policies of a person and is presumed to exist if a person directly or indirectly owns or controls 10% or more of the voting securities of another person.
Further, the Indiana corporation law contains business combination provisions that, in general, prohibit for five years any business combination with a beneficial owner of 10% or more of our common stock unless the holder’s acquisition of the stock was approved in advance by our Board of Directors. The Indiana corporation law also contains control share acquisition provisions that limit the ability of certain shareholders to vote their shares unless their control share acquisition is approved in advance.
Our articles of incorporation restrict the beneficial ownership of our capital stock in excess of specific ownership limits. The ownership limits restrict beneficial ownership of our voting capital stock to less than 10% for institutional investors and less than 5% for non-institutional investors, both as defined in our articles of incorporation. Additionally, no person may beneficially own shares of our common stock representing a 20% or more ownership interest in us. These restrictions are intended to ensure our compliance with the terms of our licenses with the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association. By agreement between us and the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association, these ownership limits may be increased. Our articles of incorporation prohibit ownership of our capital stock beyond these ownership limits without prior approval of a majority of our continuing directors (as defined in our articles of incorporation). In addition, as discussed above in the risk factor describing our license agreements with the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association, such license agreements are subject to termination upon a change of control and re-establishment fees would be imposed upon termination of the license agreements.
Certain other provisions included in our articles of incorporation and bylaws may also have anti-takeover effects and may delay, defer or prevent a takeover attempt that our shareholders might consider in their best interests. In particular, our articles of incorporation and bylaws: permit our Board of Directors to issue one or more series of preferred stock; divide our Board of Directors into three classes serving staggered three-year terms; restrict the maximum number of directors; limit the ability of shareholders to remove directors; impose
31
Table of Contents
restrictions on shareholders’ ability to fill vacancies on our Board of Directors; prohibit shareholders from calling special meetings of shareholders; impose advance notice requirements for shareholder proposals and nominations of directors to be considered at meetings of shareholders; and impose restrictions on shareholders’ ability to amend our articles of incorporation and bylaws.
Certain hedging activities may affect the value of our common stock.
The New York Public Asset Fund (the “Fund”) sold 7,000,000 shares of our common stock in a public offering which closed on September 22, 2006. Concurrently, the Fund sold in a private sale approximately 5,900,000 shares of our common stock to affiliates of J.P. Morgan Securities, Inc. (“JP Morgan”). The Fund used substantially all of the net proceeds from its sale of the shares to purchase two tranches of cash settled, equity-linked notes, each tranche relating to approximately 6,336,550 of our shares, which will mature approximately 6.5 and 12.5 months, respectively, after September 22, 2006. These notes were issued by an affiliate of JPMorgan, and the return on these notes is linked to the future performance of our common stock.
At the time of the offering, we were advised that JPMorgan Chase Bank, National Association (London Branch) (“JPMorgan Chase Bank”) expected to enter into hedging transactions through one or more of its affiliates in connection with the issuance of the equity-linked notes to the Fund. We were further advised that after establishing its initial hedge, JP Morgan Chase Bank and/or its affiliates would modify its hedge position from time to time prior to the maturity or early redemption of the equity-linked notes by entering into or unwinding various derivatives and/or purchasing or selling our common stock. In particular, these hedging transactions are likely to occur shortly before the maturity or early repayment of the equity-linked notes. Holders of the equity-linked notes may demand early redemption at any time prior to their maturity.
The effect, if any, of these transactions on the market price for our common stock will depend on market conditions and cannot be ascertained at this time, but any of these activities could reduce the price of our common stock and/or lead to periods of heightened volatility in the price of our common stock. We do not make any representations or prediction as to the direction or magnitude of any effect that the transactions described above may have on the price of the shares of our common stock. In addition, no representation is made that JPMorgan Chase Bank and/or its affiliates will engage in these transactions or that these transactions, once commenced, will not be discontinued without notice.
We also face other risks that could adversely affect our business, financial condition or results of operations, which include:
| • | any requirement to restate financial results in the event of inappropriate application of accounting principles; |
| • | a significant failure of internal controls over financial reporting; |
| • | failure of our prevention and control systems related to employee compliance with internal polices, including data security; |
| • | provider fraud that is not prevented or detected and impacts our medical costs or those of self-insured customers; |
| • | failure to protect our proprietary information; and |
| • | failure of our corporate governance policies or procedures. |
ITEM 1B. UNRESOLVED SEC STAFF COMMENTS.
None.
We have set forth below a summary of our principal office space (locations greater than 100,000 square feet). We believe that our facilities will be sufficient to meet our needs for the foreseeable future.
32
Table of Contents
Location | Amount (Square Feet) of | Principal Usage | ||
370 Basset Rd., North Haven, CT | 566,000 | Operations | ||
220 Virginia Ave., Indianapolis, IN1 | 557,000 | Operations | ||
21555 Oxnard St., Woodland Hills, CA1 | 421,000 | Operations | ||
11 Corporate Woods, Albany, NY1 | 375,000 | Operations | ||
1831 Chestnut St., St. Louis, MO | 312,000 | Operations | ||
DCS, 2015 Staples Mill Rd., Richmond, VA | 295,000 | Operations | ||
700 Broadway, Denver, CO | 285,000 | Operations | ||
3350 Peachtree Rd., Atlanta, GA1 | 272,000 | Operations | ||
9901 Linn Station Rd., Louisville, KY1 | 255,000 | Operations | ||
DCN, 2015 Staples Mill Rd., Richmond, VA | 249,000 | Operations | ||
13550 Triton Office Park Blvd., Louisville, KY1 | 234,000 | Operations | ||
4241 Irwin Simpson Rd., Mason, OH1 | 224,000 | Operations | ||
15 MetroTech Center, Brooklyn, NY1 | 217,000 | Operations | ||
4361 Irwin Simpson Rd., Mason, OH | 213,000 | Operations | ||
2000 & 2100 Corporate Center Drive, Newbury Park, CA1 | 211,000 | Operations | ||
2 Gannett Dr., South Portland, ME | 208,000 | Operations | ||
400 S. Salina St., Syracuse, NY1 | 203,000 | Operations | ||
120 Monument Circle, Indianapolis, IN1 | 202,000 | Principal executive offices | ||
3000 Goff Falls Rd., Manchester, NH1 | 201,000 | Operations | ||
2221 Edward Holland Drive, Richmond, VA1 | 193,000 | Operations | ||
8115-8125 Knue Road, Indianapolis, IN1 | 184,000 | Operations | ||
6740 N. High St., Worthington, OH | 178,000 | Operations | ||
85 Crystal Run, Middletown, NY1 | 172,000 | Operations | ||
1351 Wm. Howard Taft, Cincinnati, OH | 167,000 | Operations | ||
6737 West Washington St., West Allis, WI1 | 159,000 | Operations | ||
5151-5155 Camino Ruiz, Camarillo, CA1 | 149,000 | Operations | ||
2357 Warm Springs Rd., Columbus, GA | 147,000 | Operations | ||
233 S. Wacker Drive, Chicago, IL1 | 146,000 | Operations | ||
602 S. Jefferson St., Roanoke, VA | 131,000 | Operations | ||
4553 La Tienda Drive, Thousand Oaks, CA1 | 120,000 | Operations | ||
2825 West Perimeter Road, Indianapolis, IN1 | 111,000 | Operations | ||
3 Huntington Quadrangle, Melville, NY1 | 109,000 | Operations | ||
11 West 42nd St., New York, NY1 | 105,000 | Operations |
1 | Leased property |
Our facilities support our various business segments. We believe that our properties are adequate and suitable for our business as presently conducted.
Litigation
Multi-District Litigation Settlement Agreement
In May 2000, a case titledCalifornia Medical Association vs. Blue Cross of California, et al.(the “CMA Litigation”), was filed in U.S. district court in San Francisco against Blue Cross of California (“BCC”), a subsidiary of WellPoint Health Networks Inc. (“WHN”) at the time, and now a Company subsidiary. The lawsuit alleges that BCC violated the Racketeer Influenced and Corrupt Organizations Act (“RICO”).
33
Table of Contents
In August 2000, WHN was added as a defendant to Shane v. Humana, et al., a class-action lawsuit brought on behalf of health care providers nationwide alleging RICO violations (the “Shane Litigation”). Effective upon the November 30, 2004 merger with WHN, WHN became a wholly owned subsidiary of the Company. On September 26, 2002, Anthem was added as a defendant to the Shane Litigation.
In May 2003, in a case titledKenneth Thomas, M.D., et al., v. Blue Cross Blue Shield Association, et al. (the “Thomas Litigation”), several medical providers filed suit in federal district court in Miami, Florida against the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association (“BCBSA”) and Blue Cross and Blue Shield plans across the country, including the Company and WellChoice. The suit alleges that the BCBSA and the Blue Cross and Blue Shield plans violated RICO and challenges many of the same practices as the CMA Litigation and the Shane Litigation.
In October 2000, the federal Judicial Panel on Multidistrict Litigation (“MDL”) issued an order consolidating the CMA Litigation, the Shane Litigation and various other pending managed care class-action lawsuits against the Company and other companies before District Court Judge Federico Moreno in the Southern District of Florida for purposes of pretrial proceedings. A mediator was appointed by Judge Moreno and the parties conducted court-ordered mediation. On December 9, 2004, Judge Moreno issued a new scheduling order extending the expert discovery deadline to February 7, 2005 and setting trial for September 6, 2005.
On July 11, 2005, the Company entered into a settlement agreement (the “Agreement”) with representatives of more than 700,000 physicians nationwide to resolve the CMA Litigation, the Shane Litigation, the Thomas Litigation and certain other similar cases brought by physicians. Under the Agreement, the Company agreed to make cash payments totaling up to $198.0 million, of which $135.0 million is to be paid to physicians and $5.0 million contributed to a not-for-profit foundation whose mission is to promote higher quality health care and to enhance the delivery of care to the disadvantaged members of the public. In addition, up to $58.0 million will be paid in legal fees to be determined by the court. The Company also has agreed to implement and maintain a number of operational changes such as standardizing the definition of medical necessity in physician contracts, creating a formalized Physician Advisory Committee and modifying some of the Company’s claims payment and physician contracting provisions. The Agreement was subject to, and conditioned upon, review and approval by the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of Florida. The court preliminarily approved the settlement in an order filed July 15, 2005. The hearing for final approval was held on December 2, 2005 in Miami, Florida. The Court issued a final order approving the settlement on December 22, 2005, and issued an amended final order approving the settlement on January 4, 2006. As a result of the Agreement, the Company incurred a pre-tax expense of $103.0 million, or $0.10 per diluted share after tax, for the year ended December 31, 2005, which represents the final settlement amount of the Agreement that was not previously accrued. Appeals of the settlement initially filed by certain physicians have been resolved. Final cash payments under the Agreement totaling $209.5 million, including accrued interest, were made on October 5 and 6, 2006.
The WellChoice transaction was closed on December 28, 2005, after the settlement was reached with the plaintiffs in the CMA Litigation, the Shane Litigation and the Thomas Litigation. The former WellChoice company, which was merged with and into a wholly-owned subsidiary of WellPoint, continues to be a defendant in the Thomas Litigation, and is not affected by the settlement between the Company and plaintiffs. The Company believes that any liability that may result from this action is unlikely to have a material adverse effect on its financial position or results of operations.
Other Litigation
Prior to WHN’s acquisition of the group benefit operations (“GBO”) of John Hancock Mutual Life Insurance Company (“John Hancock”), John Hancock entered into a number of reinsurance arrangements, including with respect to personal accident insurance and the occupational accident component of workers’ compensation insurance, a portion of which was originated through a pool managed by Unicover Managers, Inc. Under these arrangements, John Hancock assumed risks as a reinsurer and transferred certain of such risks to other companies. Similar reinsurance arrangements were entered into by John Hancock following WHN’s
34
Table of Contents
acquisition of the GBO of John Hancock. These various arrangements have become the subject of disputes, including a number of legal proceedings to which John Hancock is a party. The Company is currently in arbitration with John Hancock regarding these arrangements. The Company believes that the liability that may result from this matter is unlikely to have a material adverse effect on its consolidated financial position or results of operations.
In various California state courts, the Company is defending a number of individual lawsuits and two purported class actions alleging the wrongful rescission of individual health insurance policies. The suits name the Company as well as BCC and BC Life & Health Insurance Company (“BCL&H”), both Company subsidiaries. The lawsuits generally allege breach of contract, bad faith and unfair business practices in a purported practice of rescinding new individual members following the submission of large claims. In December 2006, the California Medical Association filed a motion to intervene in one of the class actions. The motion has not been heard. In addition, the California Department of Managed Health Care and California Department of Insurance are conducting investigations of the allegations. The parties have agreed to mediate most of these lawsuits and the mediation has resulted in the resolution of some of these lawsuits. BCC and BCL&H recently announced an initiative to revise their rescission policies and practices in California.
In various California state courts, several hospitals have filed suits against BCC and WHN for payment of claims denied where the member was rescinded. These lawsuits are currently in the process of moving into arbitration. In addition, a recent suit brought against BCC, BCL&H and WHN by a non-contracting hospital in a California state court is a purported class action. This suit also seeks to recover for payment of claims denied where the member was rescinded. In December 2006, this purported class of hospitals also filed a motion to intervene in one of the individual class action cases referenced above. The motion has not been heard. The Company denies any wrongdoing. The Company intends to vigorously defend these proceedings; however, their ultimate outcome cannot be presently determined.
Other Contingencies
From time to time, the Company and certain of its subsidiaries are parties to various legal proceedings, many of which involve claims for coverage encountered in the ordinary course of business. The Company, like HMOs and health insurers generally, excludes certain health care services from coverage under its HMO, PPO and other plans. The Company is, in its ordinary course of business, subject to the claims of its enrollees arising out of decisions to restrict or deny reimbursement for certain services. The loss of even one such claim, if it results in a significant punitive damage award, could have a material adverse effect on the Company. In addition, the risk of potential liability under punitive damage theories may increase significantly the difficulty of obtaining reasonable settlements of coverage claims.
In addition to the lawsuits described above, the Company is also involved in other pending and threatened litigation of the character incidental to the business transacted, arising out of its operations and its 2001 demutualization, and is from time to time involved as a party in various governmental investigations, audits, reviews and administrative proceedings. These investigations, audits and reviews include routine and special investigations by state insurance departments, state attorneys general and the U.S. Attorney General. Such investigations could result in the imposition of civil or criminal fines, penalties and other sanctions. The Company believes that any liability that may result from any one of these actions, or in the aggregate, is unlikely to have a material adverse effect on its consolidated financial position or results of operations.
35
Table of Contents
ITEM 4. SUBMISSION OF MATTERS TO A VOTE OF SECURITY HOLDERS.
The Company did not submit any matters to a vote of security holders during the fourth quarter of 2006.
PART II
ITEM 5. MARKET FOR REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES.
Market Prices
The Company’s Common Stock, par value $0.01 per share, is listed on the NYSE under the symbol “WLP”. On February 12, 2007, the closing price on the NYSE was $80.69. As of February 12, 2007, there were 146,423 shareholders of record of the Common Stock. The following table presents high and low sales prices for the Common Stock on the NYSE for the periods indicated.
| High | Low | |||||
2006 | ||||||
First Quarter | $ | 80.37 | $ | 71.62 | ||
Second Quarter | 77.70 | 65.50 | ||||
Third Quarter | 79.93 | 72.12 | ||||
Fourth Quarter | 79.07 | 70.15 | ||||
2005 | ||||||
First Quarter1 | $ | 63.98 | $ | 54.58 | ||
Second Quarter1 | 71.23 | 58.20 | ||||
Third Quarter | 77.40 | 65.06 | ||||
Fourth Quarter | 80.40 | 70.25 | ||||
1 | The market prices for the Company’s stock reflect the two-for-one stock split, which was approved by the Board of Directors on April 25, 2005. |
Dividends
No cash dividends have been paid on our common stock. The declaration and payment of future dividends will be at the discretion of our Board of Directors and must comply with applicable law. Future dividend payments will depend upon our financial condition, results of operations, future liquidity needs, potential acquisitions, regulatory and capital requirements and other factors deemed relevant by our Board of Directors. In addition, we are a holding company whose primary assets are 100% of the capital stock or other equity instrument of Anthem Insurance Companies, Inc., Anthem Southeast, Inc., Anthem Holding Corp., WellPoint Holding Corp., WellPoint Acquisition, LLC, WellPoint Insurance Services, Inc., Lumenos, Inc. and ATH Holding Company, LLC. Our ability to pay dividends to our shareholders, if authorized by our Board of Directors, is significantly dependent upon the receipt of dividends from our insurance subsidiaries. The payment of dividends by our insurance subsidiaries without prior approval of the insurance department of each subsidiary’s domiciliary jurisdiction is limited by formula. Dividends in excess of these amounts are subject to prior approval by the respective insurance departments.
Securities Authorized for Issuance under Equity Compensation Plans
The information required by this Item concerning securities authorized for issuance under the Company’s equity compensation plans is set forth in or incorporated by reference into Part III Item 12 of this Form 10-K.
36
Table of Contents
Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
The following table presents information related to our repurchases of common stock for the periods indicated.
Period | Total Number of Shares Purchased1 | Average Price Paid per Share | Total Number of Shares Purchased as Part of Publicly Announced Programs2 | Approximate Dollar Value of Shares that May Yet Be Purchased Under the Programs | ||||||
(In millions, except share and per share data) | ||||||||||
October 1, 2006 to October 31, 2006 | 2,137,134 | $ | 76.91 | 2,137,017 | $ | 335.6 | ||||
November 1, 2006 to November 30, 2006 | 4,517,109 | 74.33 | 4,515,292 | — | ||||||
December 1, 2006 to December 31, 2006 | 788,315 | 76.61 | 654,000 | 949.8 | ||||||
| 7,442,558 | 75.31 | 7,306,306 | ||||||||
1 | Total number of shares purchased includes 136,252 shares delivered to or withheld by the Company in connection with employee payroll tax withholding upon exercise or vesting of stock awards. Stock grants to employees and directors and stock issued for stock option plans and stock purchase plans in the consolidated statements of shareholders’ equity are shown net of these shares purchased. |
2 | Represents the number of shares repurchased through our repurchase program authorized by our Board of Directors. During the year ended December 31, 2006, the Company repurchased approximately 60.7 million shares at a cost of $4.6 billion under the program. Remaining authorization under the program is $949.8 million as of December 31, 2006. |
Performance Graph
The following Performance Graph and related information compares the cumulative total return to shareholders of our common stock for the period from October 30, 2001, the date of our initial public offering, through December 31, 2006, with the cumulative total return over such period of (i) the Standard & Poor’s 500 Stock Index (the “S&P 500 Index”) and (ii) the Morgan Stanley Healthcare Payor Index (the “MS Healthcare Payor Index”). The graph assumes an investment of $100 on October 30, 2001 in each of our common stock, the S&P 500 Index and the MS Healthcare Payor Index (and the reinvestment of all dividends). The performance shown is not necessarily indicative of future performance.
The comparisons shown in the graph below are based on historical data and the Company cautions that the stock price performance shown in the graph below is not indicative of, and is not intended to forecast, the potential future performance of our common stock. Information used in the graph was obtained from D.F. King & Co., Inc., a source believed to be reliable, but the Company is not responsible for any errors or omissions in such information. The following graph and related information shall not be deemed “soliciting materials” or to be “filed” with the Securities and Exchange Commission, nor shall such information be incorporated by reference into any future filing under the Securities Act of 1933 or the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, except to the extent that we specifically incorporate it by reference into such filing.
37
Table of Contents
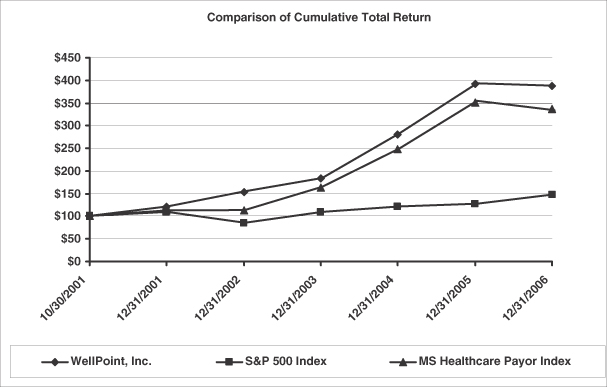
October 30, 2001 | December 31, 2001 | December 31, 2002 | December 31, 2003 | December 31, 2004 | December 31, 2005 | December 31, 2006 | |||||||||||||||
WellPoint, Inc. | $ | 100 | $ | 121 | $ | 154 | $ | 183 | $ | 281 | $ | 390 | $ | 385 | |||||||
S&P 500 Index | $ | 100 | $ | 109 | $ | 85 | $ | 109 | $ | 121 | $ | 127 | $ | 147 | |||||||
MS Healthcare Payor Index | $ | 100 | $ | 112 | $ | 113 | $ | 164 | $ | 248 | $ | 352 | $ | 331 | |||||||
| * | Based upon an initial investment of $100 on October 30, 2001 with dividends reinvested |
38
Table of Contents
ITEM 6. SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA.
The table below provides selected consolidated financial data of WellPoint. The information has been derived from our consolidated financial statements for each of the years in the five year period ended December 31, 2006. You should read this selected consolidated financial data in conjunction with the audited consolidated financial statements and notes and Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations included in this Form 10-K.
| As of and for the Years Ended December 31 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2006 | 20051 | 20041 | 2003 | 20021 | ||||||||||||||||
| (In millions, except where indicated and except per share data) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Income Statement Data | ||||||||||||||||||||
Total operating revenue2,3 | $ | 56,074.6 | $ | 43,918.4 | $ | 20,353.7 | $ | 16,429.9 | $ | 12,963.2 | ||||||||||
Total revenue3 | 56,953.0 | 44,541.3 | 20,707.9 | 16,724.2 | 13,255.0 | |||||||||||||||
Net income | 3,094.9 | 2,463.8 | 960.1 | 774.3 | 549.1 | |||||||||||||||
Per Share Data | ||||||||||||||||||||
Basic net income per share | $ | 4.93 | $ | 4.03 | $ | 3.15 | $ | 2.80 | $ | 2.31 | ||||||||||
Diluted net income per share | 4.82 | 3.94 | 3.05 | 2.73 | 2.26 | |||||||||||||||
Other Data (unaudited) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Benefit expense ratio4 | 81.2 | % | 80.2 | % | 81.8 | % | 80.7 | % | 82.2 | % | ||||||||||
Selling, general and administrative expense ratio4 | 15.7 | % | 16.6 | % | 17.1 | % | 18.9 | % | 19.4 | % | ||||||||||
Income before income taxes as a percentage of total revenue | 8.6 | % | 8.7 | % | 7.0 | % | 7.2 | % | 6.1 | % | ||||||||||
Net income as a percentage of total revenue | 5.4 | % | 5.5 | % | 4.6 | % | 4.6 | % | 4.1 | % | ||||||||||
Medical membership(In thousands) | 34,101 | 33,856 | 27,728 | 11,927 | 11,053 | |||||||||||||||
Balance Sheet Data | ||||||||||||||||||||
Cash and investments3 | $ | 20,812.2 | $ | 20,336.0 | $ | 15,792.2 | $ | 7,478.2 | $ | 6,726.4 | ||||||||||
Total assets3 | 51,759.8 | 51,287.2 | 39,663.3 | 13,408.9 | 12,413.6 | |||||||||||||||
Long-term debt3 | 6,493.2 | 6,324.7 | 4,289.5 | 1,662.8 | 1,659.4 | |||||||||||||||
Total liabilities3 | 27,184.0 | 26,294.1 | 20,204.3 | 7,409.0 | 7,051.3 | |||||||||||||||
Total shareholders’ equity | 24,575.8 | 24,993.1 | 19,459.0 | 5,999.9 | 5,362.3 | |||||||||||||||
1 | The net assets for WellChoice, Inc. and the net assets of and results of operations for Lumenos, Inc., WellPoint Health Networks Inc., and Trigon Healthcare, Inc. are included from their respective acquisition dates of December 28, 2005 (effective December 31, 2005 for accounting purposes), June 9, 2005, November 30, 2004, and July 31, 2002. |
2 | Operating revenue is obtained by adding premiums, administrative fees and other revenue. |
3 | Certain prior year amounts have been reclassified to conform to the current year presentation. |
4 | The benefit expense ratio represents benefit expenses as a percentage of premium revenue. The selling, general and administrative expense ratio represents selling, general and administrative expenses as a percentage of total operating revenue. |
ITEM 7. MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS.
References to the terms “we”, “our”, or “us” used throughout this Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations, or MD&A, refer to WellPoint, Inc. (name changed from Anthem, Inc. effective November 30, 2004), an Indiana holding company, and unless the context otherwise requires, its direct and indirect subsidiaries.
Certain prior year amounts have been reclassified to conform to current year presentation.
39
Table of Contents
The structure of our Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations is as follows:
| I. | Executive Summary |
| II. | Overview |
| III. | Significant Transactions |
| IV. | Membership—December 31, 2006 Compared to December 31, 2005 |
| V. | Cost of Care |
| VI. | Results of Operations—Year Ended December 31, 2006 Compared to the Year Ended December 31, 2005 |
| VII. | Membership—December 31, 2005 Compared to December 31, 2004 |
| VIII. | Results of Operations—Year Ended December 31, 2005 Compared to the Year Ended December 31, 2004 |
| IX. | Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates |
| X. | Liquidity and Capital Resources |
| XI. | Safe Harbor Statement under the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995 |
I. Executive Summary
We are the largest health benefits company in terms of commercial membership in the United States, serving over 34 million medical members as of December 31, 2006. We are an independent licensee of the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association, or BCBSA, an association of independent health benefit plans. We serve our members as the Blue Cross licensee for California and as the Blue Cross and Blue Shield, or BCBS, licensee for: Colorado, Connecticut, Georgia, Indiana, Kentucky, Maine, Missouri (excluding 30 counties in the Kansas City area), Nevada, New Hampshire, New York (as BCBS in 10 New York City metropolitan and surrounding counties, and as Blue Cross or BCBS in selected upstate counties only), Ohio, Virginia (excluding the Northern Virginia suburbs of Washington, D.C.), and Wisconsin. We also serve customers throughout the country as UniCare. We are licensed to conduct insurance operations in all 50 states through our subsidiaries.
No other health benefits company has the leading local market presence in as many geographic areas. This market position offers advantages in attracting physicians and hospitals to our networks at attractive rates and in helping to keep our products affordable.
Operating revenue for the year ended December 31, 2006 was $56.1 billion, an increase of $12.2 billion, or 28%, over the year ended December 31, 2005. Operating revenue increases were primarily driven by the December 28, 2005 acquisition of WellChoice, Inc., or WellChoice, described in “Significant Transactions” below, as well as premium rate increases across all customer types, the addition of the New York state prescription drug contract and Medicare Part D Prescription Drug Plan, or Medicare Part D, enrollment.
We have successfully executed our strategy to deliver on our long-term goal of achieving at least 15% growth in fully diluted earnings per share, or EPS, and exceeded our goal in 2006 as our EPS increased by 22%. We have accomplished this by focusing on profitable enrollment growth with innovative product offerings, pricing with discipline, implementing initiatives to optimize the cost of care, continuing to leverage administrative costs over a larger membership base, further penetrating our specialty businesses and by using our cash flow effectively.
40
Table of Contents
We intend to continue expanding through a combination of organic growth and strategic acquisitions and transactions in both existing and new markets. Our growth strategy is designed to enable us to take advantage of the additional economies of scale provided by increased overall membership as well as providing us access to new and evolving technologies and products. In addition, we believe geographic diversity reduces our exposure to local or regional regulatory, economic and competitive pressures and provides us with increased opportunities for growth. While we have achieved strong growth as a result of strategic mergers and acquisitions, we have also achieved organic growth in our existing markets by providing excellent service, offering competitively priced products and effectively capitalizing on the brand strength of the Blue Cross and Blue Shield names and marks.
Effective January 1, 2006, we began marketing Medicare Part D to eligible Medicare beneficiaries in all 50 states. As of December 31, 2006, we had approximately 1.6 million Medicare Part D members. See also Part I, Item 1A, Risk Factors, for additional information regarding Medicare Part D.
II. Overview
Through December 31, 2006, we managed our operations through three reportable segments: Health Care, Specialty and Other.
Our Health Care segment includes strategic business units delineated primarily by geographic areas within which we offer similar products and services, including commercial accounts, individual, senior and government programs such as the Federal Employee Program, or FEP, and Medicaid. We offer a diversified mix of managed care products, including preferred provider organizations, or PPOs, health maintenance organizations, or HMOs, traditional indemnity benefits and point of service, or POS plans. We also offer a variety of hybrid benefit plans, including consumer-driven health plans, or CDHPs, hospital only and limited benefit products. Additionally, we provide a broad array of managed care services to self-funded customers, including claims processing, underwriting, stop loss insurance, actuarial services, provider network access, medical management, care management and other administrative services.
Our Specialty segment is comprised of businesses providing specialty products and services such as group life and disability insurance benefits, pharmacy benefit management, or PBM, specialty pharmacy, dental, vision, behavioral health benefit services and long-term care insurance. We ceased underwriting workers compensation business effective December 31, 2005; however, we continue to provide network rental and medical management services to workers compensation carriers.
Our Other segment is comprised of our Medicare processing business, including National Government Services, Inc., which name changed from AdminaStar Federal, Inc., effective November 17, 2006, United Government Services, LLC, and Empire Medicare Services, Inc.; Arcus Healthy Living Services, Inc., which works to develop innovative means to promote quality care, well being and education; Arcus Financial Services, Inc., which provides a number of products to WellPoint-owned health plans associated with tax-advantaged accounts such as Health Savings Accounts, Flexible Spending Accounts and Health Reimbursement Accounts; intersegment revenue and expense eliminations; and corporate expenses not allocated to our Health Care or Specialty segments.
We have announced a new organizational structure designed to support our 2010 strategic plan. This new structure capitalizes on our unique local presence and emphasizes company-wide innovation and strong customer focus. As a result of this new organizational structure we are organized around two strategic business units: Commercial and Consumer Business, or CCB, and Specialty, Senior and State-Sponsored Business, or 4SB. In addition, our government services business includes the Federal Employees Program and National Government Services, Inc., which acts as a Medicare contractor in several regions across the nation. We expect to revise our reportable segments in the first quarter of 2007 in accordance with the new organizational structure, which reflects how our chief operating decision maker evaluates the performance of our business beginning January 1, 2007. See Note 19 to our audited consolidated financial statements as of and for the year ended December 31, 2006 included in this Form 10-K.
41
Table of Contents
Our operating revenue consists of premiums, administrative fees and other revenue. Premium revenue comes from fully-insured contracts where we indemnify our policyholders against costs for covered health and life benefits. Administrative fees come from contracts where our customers are self-insured, or where the fee is based on either processing of transactions or a percent of network discount savings realized. Additionally, we earn administrative fee revenues from our Medicare processing business and from other health-related businesses including care management programs. Other revenue is principally generated from member co-payments and deductibles associated with the mail-order sale of drugs by our PBM companies.
Our benefit expense includes costs of care for health services consumed by our members, such as outpatient care, inpatient hospital care, professional services (primarily physician care) and pharmacy benefit costs. All four components are affected both by unit costs and utilization rates. Unit costs include the cost of outpatient medical procedures per visit, inpatient hospital care per admission, physician fees per office visit and prescription drug costs. Utilization rates represent the volume of consumption of health services and typically vary with the age and health status of our members and their social and lifestyle choices, along with clinical protocols and medical practice patterns in each of our markets. A portion of benefit expense recognized in each reporting period consists of actuarial estimates of claims incurred but not yet paid by us. Any changes in these estimates are recorded in the period the need for such an adjustment arises.
Our selling expense consists of external broker commission expenses, and generally varies with premium volume. Our general and administrative expense consists of fixed and variable costs. Examples of fixed costs are depreciation, amortization and certain facilities expenses. Other costs are variable or discretionary in nature. Certain variable costs, such as premium taxes, vary directly with premium volume. Other variable costs, such as salaries and benefits, do not vary directly with changes in premium, but are more aligned with changes in membership. The acquisition or loss of a significant block of business would likely impact staffing levels, and thus salary and benefit expense. Discretionary costs include professional and consulting expenses and advertising. Other factors can impact our administrative cost structure, including systems efficiencies, inflation and changes in productivity.
Our cost of drugs consists of the amounts we pay to pharmaceutical companies for the drugs we sell via mail order through our PBM. This amount excludes the cost of drugs related to affiliated health customers recorded in benefit expense. Our cost of drugs can be influenced by the volume of prescriptions at our PBM, as well as cost changes, driven by prices set by pharmaceutical companies and mix of drugs sold.
Our results of operations depend in large part on our ability to accurately predict and effectively manage health care costs through effective contracting with providers of care to our members and our medical and care management programs. Several economic factors related to health care costs, such as regulatory mandates of coverage and direct-to-consumer advertising by providers and pharmaceutical companies, have a direct impact on the volume of care consumed by our members. The potential effect of escalating health care costs as well as any changes in our ability to negotiate competitive rates with our providers may impose further risks to our ability to profitably underwrite our business, and may have a material impact on our results of operations.
This MD&A should be read in conjunction with our audited consolidated financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2006 included in this Form 10-K.
III. Significant Transactions
Stock Repurchase Program
We maintain a common stock repurchase program as authorized by our Board of Directors. Repurchases may be made from time to time at prevailing market prices, subject to certain restrictions on volume, pricing and timing. During the year ended December 31, 2006, we repurchased and retired approximately 60.7 million shares at an average share price of $74.91, for an aggregate cost of $4.6 billion. On March 15, May 16, August 17 and
42
Table of Contents
December 7, 2006, our Board of Directors authorized increases of $1.0 billion, $1.0 billion, $0.5 billion and $1.0 billion, respectively, in our common stock repurchase program, which increased the total authorized common stock repurchases to $5.5 billion since the current program’s inception in 2005. As of December 31, 2006, $0.9 billion remained authorized for future repurchases. Subsequent to December 31, 2006, we repurchased and retired approximately 6.0 million shares for an aggregate cost of approximately $463.5 million, leaving approximately $486.3 million for authorized future repurchases at February 12, 2007. Our stock repurchase program is discretionary as we are under no obligation to repurchase shares. We repurchase shares because we believe it is a prudent use of surplus capital.
Acquisition of WellChoice, Inc.
On December 28, 2005 (December 31, 2005 for accounting purposes), WellPoint completed its acquisition of WellChoice. The acquisition of WellChoice strengthened our leadership in providing health benefits to National Accounts and provided us with a strategic presence in New York City, the headquarters of more Fortune 500 companies than any other U.S. city. Under the terms of the merger agreement, the stockholders of WellChoice (other than subsidiaries of WellPoint) received consideration of $38.25 in cash and 0.5191 of a share of WellPoint common stock for each share of WellChoice common stock outstanding. In addition, WellChoice stock options and other awards were converted to WellPoint awards in accordance with the merger agreement. The purchase price including cash, fair value of stock and stock awards and estimated transaction costs was approximately $6.5 billion.
Multi-District Litigation Settlement Agreement
On July 11, 2005, we announced that an agreement was reached with representatives of more than 700,000 physicians nationwide involved in two multi-district class-action lawsuits against us and other health benefits companies. As part of the Multi-District Litigation Settlement Agreement, or the Agreement, we agreed to pay $135.0 million to physicians and to contribute $5.0 million to a not-for-profit foundation whose mission is to promote higher quality health care and to enhance the delivery of care to the disadvantaged and underserved. In addition, up to $58.0 million will be paid in legal fees. As a result of the Agreement, we incurred a pre-tax expense of $103.0 million during the year ended December 31, 2005, or $0.10 EPS, which represents the final settlement amount of the Agreement that was not previously accrued. Appeals of the settlement initially filed by certain physicians were resolved and final cash payments under the agreement totaling $209.5 million, including accrued interest, were made on October 5 and 6, 2006.
Acquisition of Lumenos, Inc.
On June 9, 2005, we completed our acquisition of Lumenos, Inc., or Lumenos, for approximately $185.0 million in cash paid to the stockholders of Lumenos. Lumenos is recognized as a pioneer and market leader in consumer-driven health programs.
Two-For-One Stock Split
On April 25, 2005, WellPoint’s Board of Directors approved a two-for-one split of shares of common stock, which was effected in the form of a 100 percent common stock dividend. All shareholders of record on May 13, 2005 received one additional share of WellPoint common stock for each share of common stock held on that date. The additional shares of common stock were distributed to shareholders of record in the form of a stock dividend on May 31, 2005. All historical weighted average share and per share amounts and all references to stock compensation data and market prices of our common stock for all periods presented in this MD&A have been adjusted to reflect this two-for-one stock split.
Merger with WellPoint Health Networks Inc.
On November 30, 2004, Anthem, Inc. and WellPoint Health Networks Inc., or WHN, completed their merger. The merger with WHN helped us to create the nation’s leading health benefits company and the largest
43
Table of Contents
holder of Blue Cross and/or Blue Shield licenses in the country. Additionally, our merger with WHN increased our presence in several new strategic markets, most notably California. Under the terms of the merger agreement, the stockholders of WHN (other than subsidiaries of WHN) received consideration of $23.80 in cash and one share of Anthem, Inc. common stock for each WHN share outstanding. In addition, WHN stock options and other awards were converted to WellPoint, Inc. awards in accordance with the merger agreement. The purchase price including cash, fair value of stock and stock awards and estimated transaction costs was approximately $15.8 billion. Anthem, Inc., the surviving corporate parent, was renamed WellPoint, Inc. concurrent with the merger.
IV. Membership—December 31, 2006 Compared to December 31, 2005
Through December 31, 2006, our medical membership included six different customer types: Large Group, Individual and Small Group, National Accounts, BlueCard, Senior and State Sponsored.
| • | Large Group consists of those employer customers with 51 to 4,999 employees eligible to participate as a member in one of our health plans. In addition, Large Group includes customers with 5,000 or more eligible employees with less than 5% of eligible employees located outside of the headquarter’s state. Large Group also includes members in the Federal Employee Program, or FEP, which provides health insurance coverage to United States government employees and their dependents within our geographic markets through our participation in the national contract between the BCBSA and the U.S. Office of Personnel Management. |
| • | Individual and Small Group, or ISG, consists of individual customers under age 65 as well as those employer customers with one to 50 eligible employees. |
| • | National Accounts customers are multi-state employer groups primarily headquartered in a WellPoint service area with 5,000 or more eligible employees, with at least 5% of eligible employees located outside of the headquarter’s state. Service area is defined as the geographic area in which we are licensed to sell BCBS products. |
| • | BlueCard host members represent enrollees of Blue Cross and/or Blue Shield plans not owned by WellPoint who receive health care services in our BCBSA licensed markets. BlueCard membership consists of estimated host members using the national BlueCard program. Host members are generally members who reside in or travel to a state in which a WellPoint subsidiary is the Blue Cross and/or Blue Shield licensee and who are covered under an employer-sponsored health plan issued by a non-WellPoint controlled BCBSA licensee (i.e., the “home” plan). We perform certain administrative functions for BlueCard members, for which we receive administrative fees from the BlueCard members’ home plans. Other administrative functions, including maintenance of enrollment information and customer service, are performed by the home plan. Host members are computed using, among other things, the average number of BlueCard claims received per member per month. |
| • | Senior members are Medicare-eligible individual members age 65 and over who have enrolled in Medicare Advantage, a managed care alternative for the Medicare program, or who have purchased Medicare Supplement benefit coverage. |
| • | State Sponsored membership represents eligible members with state sponsored managed care alternatives in Medicaid and State Children’s Health Insurance programs. |
We expect to revise our customer type definitions in the first quarter of 2007 in accordance with the new organizational structure, as described above, which reflects how our chief operating decision maker evaluates the performance of our business beginning January 1, 2007.
In addition to reporting our medical membership by customer type, we report by funding arrangement according to the level of risk that we assume in the product contract. Our two funding arrangement categories are fully-insured and self-funded. Fully-insured products are products in which we indemnify our policyholders against costs for health benefits. Self-funded products are offered to customers, generally larger employers, who
44
Table of Contents
elect to retain some or all of the financial risk associated with their employees’ health care costs. Some customers choose to purchase stop-loss coverage to limit their retained risk. These customers are reported with our self-funded business.
The following table presents our medical membership by customer type, funding arrangement and geographical region as of December 31, 2006 and 2005. Also included below are key metrics from our Specialty segment, including prescription volume for our PBM companies and membership by product. The membership data presented is unaudited and in certain instances includes estimates of the number of members represented by each contract at the end of the period.
| December 31 | ||||||||||
| 2006 | 20051 | Change | % Change | |||||||
| (In thousands) | ||||||||||
Medical Membership | ||||||||||
Customer Type | ||||||||||
Large Group | 16,014 | 16,362 | (348 | ) | (2 | )% | ||||
Individual and Small Group | 5,654 | 5,645 | 9 | — | ||||||
National Accounts | 5,044 | 4,776 | 268 | 6 | ||||||
BlueCard | 4,279 | 3,915 | 364 | 9 | ||||||
Total National | 9,323 | 8,691 | 632 | 7 | ||||||
Senior | 1,229 | 1,224 | 5 | — | ||||||
State Sponsored | 1,881 | 1,934 | (53 | ) | (3 | ) | ||||
Total medical membership by customer type | 34,101 | 33,856 | 245 | 1 | ||||||
Funding Arrangement1 | ||||||||||
Self-Funded | 16,745 | 16,584 | 161 | 1 | ||||||
Fully-Insured | 17,356 | 17,272 | 84 | — | ||||||
Total medical membership by funding arrangement | 34,101 | 33,856 | 245 | 1 | ||||||
Regional Membership | ||||||||||
East | 13,879 | 13,800 | 79 | 1 | ||||||
Central | 10,907 | 10,970 | (63 | ) | (1 | ) | ||||
West | 9,315 | 9,086 | 229 | 3 | ||||||
Total medical membership by region | 34,101 | 33,856 | 245 | 1 | ||||||
Specialty Metrics | ||||||||||
PBM prescription volume2 | 392,668 | 344,621 | 48,047 | 14 | ||||||
Behavioral health membership | 16,937 | 15,669 | 1,268 | 8 | ||||||
Life and disability membership | 5,970 | 5,826 | 144 | 2 | ||||||
Dental membership | 5,270 | 5,195 | 75 | 1 | ||||||
Vision membership | 1,536 | 816 | 720 | 88 | ||||||
Medicare Part D membership3 | 1,568 | — | 1,568 | NA | ||||||
1 | Medical membership data for 2005 has been reclassified to conform to the current presentation. Our reclassifications for minimum premium amendments to fully-insured contracts resulted in an increase in self-funded membership and a corresponding decrease in fully-insured membership, with no impact on total medical membership. |
2 | Represents prescription volume for the years ended December 31, 2006 and 2005. |
3 | Effective January 1, 2006, the Company began marketing Medicare Part D to eligible Medicare beneficiaries in all 50 states. Membership includes auto-assigned, stand-alone, Medicare Advantage, group waiver and external PBM members with the prescription drug plans. Certain of our Medicare Part D members are also Senior medical members. |
45
Table of Contents
During the twelve months ended December 31, 2006, total medical membership increased approximately 245,000, or 1%, primarily due to increases in our BlueCard and National Accounts partially offset by the loss of 315,000 Large Group members in the state of Georgia, as well as approximately 95,000 members of another Large Group account, which was previously disclosed. Also, in December 2006, our ownership of a joint venture in Puerto Rico changed from a 50 percent ownership of a Medicaid managed care subsidiary to a smaller percentage in the joint venture’s parent company. Accordingly, we no longer include the 222,000 members related to this investment in our reported enrollment.
Large Group membership decreased 348,000, or 2%, primarily due to the loss of the state of Georgia PPO contract and the other Large Group account previously disclosed, partially offset by new sales.
National Accounts membership increased 268,000, or 6%, primarily due to success in attracting new customers as they recognize the value of the BCBS networks and discounts.
BlueCard membership increased 364,000, or 9%, during the twelve months ended December 31, 2006, due to increased sales by other BCBSA licensees to accounts with members who reside in or travel to our licensed areas.
State Sponsored membership decreased 53,000, or 3%, primarily due to the membership accounting change related to our Puerto Rico joint venture investment discussed above. Partially offsetting this 222,000 member decrease, we added 68,000 new members from the acquisition of QualChoice Select, Inc. and won new business from five awards in 2006 due to our comprehensive array of health management services we make available to the nation’s Medicaid recipients.
Self-funded medical membership increased 161,000, or 1%, primarily due to increases in our National Accounts and BlueCard businesses and shifts in the mix of business from fully-insured to self-funded, partially offset by the loss of the state of Georgia PPO contract and the other Large Group contract noted above, as well as the impact of the Puerto Rico joint venture membership accounting change. Fully-insured membership increased by 84,000 members, primarily due to the August 1, 2006 acquisition of QualChoice Select, Inc.
Our specialty metrics are derived from membership and activity from our specialty products. These products are often ancillary to our health business, and can therefore be impacted by growth in our medical membership.
Prescription volume in our PBM companies increased by 48,047,000, or 14%, during the year ended December 31, 2006, primarily due to growth in both our retail and mail order operations driven by the addition of Medicare Part D.
Behavioral health membership increased 1,268,000, or 8%, during the year ended December 31, 2006, primarily due to a 568,000 membership gain from the acquisition of Behavioral Health Network in New Hampshire in October 2006, as well as 347,000 new members from sales of our behavioral health products.
Vision membership increased 720,000, or 88%, due to the introduction of our Blue View Vision product and the associated conversion of 432,000 members of a competing plan in Virginia to this new product, as well as new sales in several markets.
V. Cost of Care
The following discussion summarizes our aggregate cost of care trends for the full year 2006 for our Large Group and ISG fully-insured businesses only. In order to provide a more meaningful comparison to the current period due to the acquisition of WellChoice, cost of care information as discussed below is presented as if WellPoint and WellChoice were combined for all of 2005. Accordingly, cost of care reported previously for WellPoint is not comparable to the information presented below.
46
Table of Contents
Our cost of care trends are calculated by comparing the year-over-year change in average per member per month claim costs for which we are responsible, which excludes member co-payments and deductibles. While our cost of care trend varies by geographic location, our aggregate cost of care was less than 8% for the full year 2006.
Costs for outpatient and inpatient services are the primary drivers of overall cost trends. Cost trend increases for outpatient services were primarily driven by higher per visit costs as more procedures are being performed during each visit to outpatient providers, particularly emergency room visits, as well as the impact of price increases included within certain provider contracts. However, we are seeing the positive impact of our expanding radiology management programs on our outpatient trends. These programs are designed to ensure appropriate use of radiology services by our members. Inpatient trends have been driven primarily by unit cost, a reflection of negotiated contract increases with hospitals. Utilization (admissions per 1,000 members) remains flat, while average length of hospital stay and hospital days per 1,000 members have both decreased slightly.
Pharmacy benefit cost trend increased primarily due to pharmacy unit cost (cost per prescription) trend. The unit cost trend in 2006 is reflecting a return to normal cost trends compared to 2005 when the unit cost trend was favorably impacted by merger synergies and improved pharmaceutical contracting following the merger with WHN, the non-renewal of pharmacy only business from a large state customer with historically high utilization and cost trends and the impact of lower utilization for the COX 2 Inhibitor therapeutic class of drugs. In addition, the increased use of specialty drugs, also known as biotech drugs, which generally have a higher cost and are being utilized more frequently, has increased the unit cost trend in 2006. These increases in unit costs were partially offset by increases in our generic usage rates and benefit plan design changes.
In response to cost trends, we continue to pursue contracting and plan design changes, promote and implement performance-based contracts that reward clinical outcomes and quality, and expand our radiology management, disease management and advanced care management programs. We recently announced the launch of360º Health, a program to integrate all care management programs and tools into a centralized, consumer-friendly resource that assists patients in navigating the health care system, using their health benefits and accessing the most comprehensive and appropriate care available. In addition, we are expanding our specialty pharmacy programs and continuously evaluate our drug formulary to ensure the most effective pharmaceutical therapies are available for our members.
47
Table of Contents
VI. Results of Operations—Year Ended December 31, 2006 Compared to the Year Ended December 31, 2005
Our consolidated results of operations for the years ended December 31, 2006 and 2005 are discussed in the following section.
| Year Ended December 31 | Comparable Year Ended | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 2006 | 2005 | % Change | $ Change | % Change | ||||||||||||||||||
| (In millions, except per share data) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Premiums | $ | 51,971.9 | $ | 40,680.0 | 28 | % | $ | 46,531.1 | $ | 5,440.8 | 12 | % | ||||||||||
Administrative fees | 3,509.6 | 2,719.2 | 29 | 3,325.0 | 184.6 | 6 | ||||||||||||||||
Other revenue | 593.1 | 519.2 | 14 | 518.2 | 74.9 | 14 | ||||||||||||||||
Total operating revenue | 56,074.6 | 43,918.4 | 28 | 50,374.3 | 5,700.3 | 11 | ||||||||||||||||
Net investment income | 878.7 | 633.1 | 39 | 718.7 | NM | 3 | NM | 3 | ||||||||||||||
Net realized losses on investments | (0.3 | ) | (10.2 | ) | (97 | ) | (5.4 | ) | NM | 3 | NM | 3 | ||||||||||
Total revenues | 56,953.0 | 44,541.3 | 28 | 51,087.6 | NM | 3 | NM | 3 | ||||||||||||||
Benefit expense | 42,218.8 | 32,625.2 | 29 | 37,676.0 | 4,542.8 | 12 | ||||||||||||||||
Selling, general and administrative expense: | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Selling expense | 1,654.5 | 1,474.2 | 12 | 1,549.6 | 104.9 | 7 | ||||||||||||||||
General and administrative expense | 7,163.2 | 5,798.5 | 24 | 6,770.0 | 393.2 | 6 | ||||||||||||||||
Total selling, general and administrative expense | 8,817.7 | 7,272.7 | 21 | 8,319.6 | 498.1 | 6 | ||||||||||||||||
Cost of drugs | 301.2 | 288.0 | 5 | 288.0 | NM | 3 | NM | 3 | ||||||||||||||
Interest expense | 403.5 | 226.2 | 78 | 226.2 | NM | 3 | NM | 3 | ||||||||||||||
Amortization of other intangible assets | 297.4 | 238.9 | 24 | 238.9 | NM | 3 | NM | 3 | ||||||||||||||
Total expenses | 52,038.6 | 40,651.0 | 28 | 46,748.7 | NM | 3 | NM | 3 | ||||||||||||||
Income before income tax expense | 4,914.4 | 3,890.3 | 26 | 4,338.9 | NM | 3 | NM | 3 | ||||||||||||||
Income tax expense | 1,819.5 | 1,426.5 | 28 | 1,604.9 | NM | 3 | NM | 3 | ||||||||||||||
Net income | $ | 3,094.9 | $ | 2,463.8 | 26 | $ | 2,734.0 | NM | 3 | NM | 3 | |||||||||||
Average diluted shares outstanding | 642.1 | 625.8 | 3 | NM | 3 | NM | 3 | NM | 3 | |||||||||||||
Diluted net income per share | $ | 4.82 | $ | 3.94 | 22 | NM | 3 | NM | 3 | NM | 3 | |||||||||||
Benefit expense ratio4 | 81.2 | % | 80.2 | % | 100 | bp5 | 81.0 | % | 20 | bp5 | ||||||||||||
Selling, general and administrative expense ratio6 | 15.7 | % | 16.6 | % | (90 | )bp5 | 16.5 | % | (80 | )bp5 | ||||||||||||
Income before income taxes as a percentage of total revenue | 8.6 | % | 8.7 | % | (10 | )bp5 | NM | 3 | NM | 3 | ||||||||||||
Net income as a percentage of total revenue | 5.4 | % | 5.5 | % | (10 | )bp5 | NM | 3 | NM | 3 | ||||||||||||
Certain of the following definitions are also applicable to all other results of operations tables in this discussion:
1 | See below for discussion of “comparable basis” information. |
2 | For certain line items impacted by our acquisition of WellChoice, comparable basis is not meaningful due to related capitalization and purchase accounting. |
3 | NM = Not meaningful. |
48
Table of Contents
4 | Benefit expense ratio = Benefit expense ÷ Premiums. |
5 | bp = basis point; one hundred basis points = 1%. |
6 | Selling, general and administrative expense ratio = Total selling, general and administrative expense ÷ Total operating revenue. |
We discuss our 2006 and 2005 operations using “comparable basis” information, which is presented to provide a more meaningful prior-year comparison to the current year, due to our December 28, 2005 acquisition of WellChoice. Comparable basis information is not calculated in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles, or GAAP, and is not intended to represent or be indicative of the results of WellPoint had the acquisition been completed as of January 1, 2005. Comparable basis information for the year ended December 31, 2005 was calculated by adding the reclassified historical statements of income for WellPoint and WellChoice and includes no intercompany eliminations or pro forma adjustments.
| Year Ended December 31, 2005 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| WellPoint, Inc. | WellChoice, Inc. | WellPoint, Inc. Comparable Basis | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| As Reported | Reclassifications1 | Reclassified | As Reported | Reclassifications1 | Reclassified | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| (In millions) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Premiums | $ | 41,216.7 | $ | (536.7 | ) | $ | 40,680.0 | $ | 5,862.4 | $ | (11.3 | ) | $ | 5,851.1 | $ | 46,531.1 | ||||||||||||
Administrative fees | 2,729.9 | (10.7 | ) | 2,719.2 | 561.5 | 44.3 | 605.8 | 3,325.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Other revenue (expense) | 566.5 | (47.3 | ) | 519.2 | (1.0 | ) | — | (1.0 | ) | 518.2 | ||||||||||||||||||
Total operating revenue | 44,513.1 | (594.7 | ) | 43,918.4 | 6,422.9 | 33.0 | 6,455.9 | 50,374.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net investment income | 633.1 | — | 633.1 | 85.6 | — | 85.6 | 718.7 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Net realized (losses) gains on investments | (10.2 | ) | — | (10.2 | ) | 4.8 | — | 4.8 | (5.4 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
Total revenues | 45,136.0 | (594.7 | ) | 44,541.3 | 6,513.3 | 33.0 | 6,546.3 | 51,087.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Benefit expense | 33,219.9 | (594.7 | ) | 32,625.2 | 5,078.4 | (27.6 | ) | 5,050.8 | 37,676.0 | |||||||||||||||||||
Selling, general and administrative expense: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Selling expense | 1,474.2 | — | 1,474.2 | — | 75.4 | 75.4 | 1,549.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||
General and administrative expense | 5,798.5 | — | 5,798.5 | 986.3 | (14.8 | ) | 971.5 | 6,770.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Total selling, general and administrative expense | 7,272.7 | — | 7,272.7 | 986.3 | 60.6 | 1,046.9 | 8,319.6 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Cost of drugs | 288.0 | — | 288.0 | — | — | — | 288.0 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Interest expense | 226.2 | — | 226.2 | — | — | — | 226.2 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Amortization of other intangible assets | 238.9 | — | 238.9 | — | — | — | 238.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Total expenses | 41,245.7 | (594.7 | ) | 40,651.0 | 6,064.7 | 33.0 | 6,097.7 | 46,748.7 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Income before income tax expense | 3,890.3 | — | 3,890.3 | 448.6 | — | 448.6 | 4,338.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Income tax expense | 1,426.5 | — | 1,426.5 | 178.4 | — | 178.4 | 1,604.9 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Net income | $ | 2,463.8 | $ | — | $ | 2,463.8 | $ | 270.2 | $ | — | $ | 270.2 | $ | 2,734.0 | ||||||||||||||
Benefit expense ratio2 | 80.6 | % | 80.2 | % | 86.6 | % | 86.3 | % | 81.0 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
Selling, general and administrative expense ratio3 | 16.3 | % | 16.6 | % | 15.4 | % | 16.2 | % | 16.5 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
1 | To reflect the reclassification of certain historical amounts to a consistent presentation format. |
49
Table of Contents
2 | Benefit expense ratio = Benefit expense ÷ Premiums. |
3 | Selling, general and administrative expense ratio = Total selling, general and administrative expense ÷ Total operating revenue. |
| Year Ended December 31, 2005 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| WellPoint, Inc. | WellChoice, Inc. | WellPoint, Inc. Comparable Basis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| As Reported | Reclassifications1 | Reclassified | As Reported | Reclassifications1 | Reclassified | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| (In millions) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Operating Revenue | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Health Care | $ | 42,597.5 | $ | (730.5 | ) | $ | 41,867.0 | $ | — | $ | 6,292.6 | $ | 6,292.6 | $ | 48,159.6 | ||||||||||||
Specialty | 2,863.1 | 203.0 | 3,066.1 | — | 32.1 | 32.1 | 3,098.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Other | (947.5 | ) | (67.2 | ) | (1,014.7 | ) | — | 131.2 | 131.2 | (883.5 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
Commercial Managed Care | — | — | — | 5,530.7 | (5,530.7 | ) | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||
Other Insurance Products and Services | — | — | — | 892.2 | (892.2 | ) | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||
Total operating revenue | $ | 44,513.1 | $ | (594.7 | ) | $ | 43,918.4 | $ | 6,422.9 | $ | 33.0 | $ | 6,455.9 | $ | 50,374.3 | ||||||||||||
Operating Gain (Loss)2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Health Care | $ | 3,459.0 | $ | (41.0 | ) | $ | 3,418.0 | $ | — | $ | 371.6 | $ | 371.6 | $ | 3,789.6 | ||||||||||||
Specialty | 388.1 | 38.3 | 426.4 | — | 0.5 | 0.5 | 426.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Other | (114.6 | ) | 2.7 | (111.9 | ) | — | (13.9 | ) | (13.9 | ) | (125.8 | ) | |||||||||||||||
Commercial Managed Care | — | — | — | 331.5 | (331.5 | ) | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||
Other Insurance Products and Services | — | — | — | 26.7 | (26.7 | ) | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||
1 | To reflect the reclassification of certain historical amounts to a consistent presentation format. |
2 | We use operating gain (loss) to evaluate the performance of our reportable segments, as described in Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No.131,Disclosure about Segments of an Enterprise and Related Information. Operating gain (loss) is defined as operating revenue less benefit expense, selling expense, general and administrative expense and cost of drugs. |
Premiums increased $11.3 billion, or 28%, to $52.0 billion in 2006. On a comparable basis, premiums increased $5.4 billion, or 12%, primarily due to premium rate increases across all customer types, the addition of the New York state prescription drug contract and new enrollment in our Medicare Part D products.
Administrative fees increased $790.4 million, or 29%, to $3.5 billion in 2006. On a comparable basis, administrative fees increased $184.6 million, or 6%, primarily due to self-funded membership growth in National Accounts, including BlueCard, and rate increases in Large Group and National Accounts. Self-funded membership growth was driven by successful efforts to attract large self-funded accounts and was attributable to our network breadth, discounts, service and increased focus on health improvement and wellness, as well as the popularity of the BlueCard program.
Other revenue principally includes amounts from mail-order prescription drug sales by our PBM companies, which provide services to members of our Health Care segment and third party clients. Other revenue increased $73.9 million, or 14%, to $593.1 million in 2006. On a comparable basis, other revenue increased $74.9 million, or 14%, primarily due to revenue generated by growth in mail-order prescription revenue from both our Health Care segment and third parties. Increased mail-order prescription volume resulted from additional utilization of our PBM companies’ mail-order pharmacy option with the introduction of Medicare Part D.
Net investment income increased $245.6 million, or 39%, to $878.7 million in 2006 primarily resulting from invested assets acquired with the acquisition of WellChoice, growth in invested assets from reinvestment of cash generated from operations and higher interest rates. This growth was partially offset by the use of cash for repurchases of our common stock.
50
Table of Contents
A summary of our net realized gains (losses) on investments for the years ended December 31, 2006 and 2005 is as follows:
| Years Ended December 31 | ||||||||||||
| 2006 | 2005 | $ Change | ||||||||||
| (In millions) | ||||||||||||
Net realized losses from the sale of fixed maturity securities | $ | (47.9 | ) | $ | (25.3 | ) | $ | (22.6 | ) | |||
Net realized gains from the sale of equity securities | 98.5 | 22.0 | 76.5 | |||||||||
Other-than-temporary impairments—credit related | (32.5 | ) | (14.8 | ) | (17.7 | ) | ||||||
Other-than-temporary impairments—interest rate related | (23.7 | ) | — | (23.7 | ) | |||||||
Other realized gains | 5.3 | 7.9 | (2.6 | ) | ||||||||
Net realized losses | $ | (0.3 | ) | $ | (10.2 | ) | $ | 9.9 | ||||
Net realized losses in 2006 primarily related to other-than-temporary impairments of investments and the sale of fixed maturity securities at a loss due to the restructuring of the combined portfolio after our acquisition of WellChoice at the end of 2005. Other-than-temporary impairments—credit related were primarily due to the length of time that equity securities’ fair value was below their cost basis. Other-than-temporary impairments—interest related were primarily due to the prevailing interest rate environment and our intent to hold fixed maturity securities until their anticipated recovery. SeeCritical Accounting Policies and Estimates in this MD&A for a discussion of our investment impairment review process. These losses were partially offset by realized gains on the sale of equity securities during 2006.
Net realized losses in 2005 primarily related to net realized losses on sales of fixed maturity securities due to the restructuring of the combined portfolio after our merger with WHN at the end of 2004 and credit-related other-than-temporary impairments of equity and fixed maturity securities. These realized losses were partially offset by net realized gains on sales of equity securities and other invested assets.
Benefit expense increased $9.6 billion, or 29%, to $42.2 billion in 2006. On a comparable basis, benefit expense increased $4.5 billion, or 12%, primarily due to increased cost of care, which was driven by higher costs in outpatient and inpatient services, the addition of the New York State prescription drug contract and benefit expense for our Medicare Part D products.
On a comparable basis, our benefit expense ratio increased 20 basis points to 81.2% in 2006. This increase was primarily related to a change in business mix, primarily driven by the addition of the New York State prescription drug contract, growth in FEP and State Sponsored business, as well as the introduction of Medicare Part D. All of these products have a higher benefit expense ratio than the WellPoint average. These increases were partially offset by disciplined pricing and the non-recurrence of $35.0 million of benefit expense recorded in the second quarter of 2005 related to the multi-district litigation settlement agreement, or MDL settlement agreement, discussed in Significant Transactions within this MD&A.
Selling, general and administrative expense increased $1.5 billion, or 21%, to $8.8 billion in 2006. On a comparable basis, selling, general and administrative expense increased $498.1 million, or 6%. The increase in selling, general and administrative expense was primarily due to increases in volume-sensitive costs such as commissions, premium taxes and other expenses associated with growth in our business, as well as additional share-based compensation expense resulting from our January 1, 2006 adoption of Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 123 (revised 2004),Share-Based Payment,or FAS 123R. See Note 12 to our audited consolidated financial statements as of and for the year ended December 31, 2006 included in this Form 10-K.
On a comparable basis, our selling, general and administrative expense ratio decreased 80 basis points to 15.7% in 2006, primarily due to growth in premium income, continued expense control and further leveraging of general and administrative costs over a larger membership base. In addition, the 2005 selling, general and administrative expense ratio was negatively impacted by $68.0 million, or 10 basis points, related to the MDL settlement agreement.
51
Table of Contents
Cost of drugs increased $13.2 million, or 5%, to $301.2 million in 2006. This increase is primarily attributable to increased mail-order prescription volume by our PBM companies, partially offset by higher utilization of generic prescription drugs.
Interest expense increased $177.3 million, or 78%, to $403.5 million in 2006, primarily due to additional interest expense on the debt incurred in conjunction with the acquisition of WellChoice.
Amortization of other intangible assets increased $58.5 million, or 24%, to $297.4 million in 2006, primarily due to additional amortization expense related to identifiable intangible assets with finite lives resulting from the acquisition of WellChoice.
Income tax expense increased $393.0 million, or 28%, to $1.8 billion in 2006, consistent with the increase in pre-tax income. The effective tax rate in 2006 and 2005 was 37.0% and 36.7%, respectively. The increase in the effective tax rate in 2006 was primarily related to increases in state taxes due to the addition of operations in New York following the acquisition of WellChoice.
Reportable Segments
We use operating gain to evaluate the performance of our reportable segments, as described in Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 131,Disclosure about Segments of an Enterprise and Related Information. Through December 31, 2006, our reportable segments were Health Care, Specialty and Other. Operating gain is calculated as total operating revenue less benefit expense, selling, general and administrative expense and cost of drugs. It does not include net investment income, net realized gains (losses) on investments, interest expense, amortization of other intangible assets or income taxes, as these items are managed in a corporate shared service environment and are not the responsibility of operating segment management. For additional information, see Note 19 to our audited consolidated financial statements included in this Form 10-K. The discussions of segment results for the years ended December 31, 2006 and 2005 presented below are based on operating gain, as described above, and operating margin, which is calculated as operating gain divided by operating revenue. Our definitions of operating gain and operating margin may not be comparable to similarly titled measures reported by other companies.
Health Care
Our Health Care segment’s summarized results of operations for the year ended December 31, 2006 and 2005 are as follows:
| Year Ended December 31 | Comparable Year Ended 2005 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2006 | 2005 | % Change | $ Change | % Change | |||||||||||||||||
| (In millions) | |||||||||||||||||||||
Operating revenue | $ | 53,860.6 | $ | 41,867.0 | 29 | % | $ | 48,159.6 | $ | 5,701.0 | 12 | % | |||||||||
Operating gain | $ | 4,288.3 | $ | 3,418.0 | 25 | % | $ | 3,789.6 | $ | 498.7 | 13 | % | |||||||||
Operating margin | 8.0 | % | 8.2 | % | (20 | )bp | 7.9 | % | 10 | bp | |||||||||||
Operating revenue increased $12.0 billion, or 29%, to $53.9 billion in 2006. On a comparable basis, operating revenue increased $5.7 billion, or 12%, primarily due to premium rate increases across all customer types, the addition of the New York state prescription drug contract and our Medicare Part D products.
Operating gain increased $870.3 million, or 25%, to $4.3 billion in 2006. On a comparable basis, operating gain increased $498.7 million, or 13%, primarily due to disciplined pricing across all lines of business and continued expense control, the non-recurrence of $103.0 million in benefit and general and administrative expense related to the MDL settlement agreement, as well as the addition of the New York state prescription drug
52
Table of Contents
contract and Medicare Part D. These increases were partially offset by the impact of increased share-based compensation expense following the adoption of FAS 123R in 2006.
The operating margin decreased by 20 basis points from 8.2% in 2005 to 8.0% in 2006. On a comparable basis, operating margin increased 10 basis points in 2006. The 2006 operating margin was impacted by 30 basis points related to increased share-based compensation following the adoption of FAS 123R, as well as 20 basis points related to a business mix shift, including the addition of lower margin governmental business. The 2005 operating margin included a 20 basis point impact related to the MDL settlement agreement.
Specialty
Our Specialty segment’s summarized results of operations for the year ended December 31, 2006 and 2005 are as follows:
| Year Ended December 31 | Comparable Year Ended 2005 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2006 | 2005 | % Change | $ Change | % Change | |||||||||||||||||
| (In millions) | |||||||||||||||||||||
Operating revenue | $ | 3,566.2 | $ | 3,066.1 | 16 | % | $ | 3,098.2 | $ | 468.0 | 15 | % | |||||||||
Operating gain | $ | 523.6 | $ | 426.4 | 23 | % | $ | 426.9 | $ | 96.7 | 23 | % | |||||||||
Operating margin | 14.7 | % | 13.9 | % | 80 | bp | 13.8 | % | 90 | bp | |||||||||||
Operating revenue increased $500.1 million, or 16%, to $3.6 billion in 2006. On a comparable basis, operating revenue increased $468.0 million, or 15%, primarily due to increased prescription volume by our PBM companies, including specialty pharmacy, driven by the addition of Medicare Part D, partially offset by the sale of our workers compensation business in Wisconsin in 2005.
Operating gain increased $97.2 million, or 23%, to $523.6 million in 2006. On a comparable basis, operating gain increased $96.7 million, or 23%, primarily due to increased prescription volume by our PBM companies, as well as a change in estimate in noncurrent reserves for future policy benefits following the change of experience factors for waiver of premium reserves based on the recently released group term life mortality study. These increases were partially offset by the sale of our workers compensation business in Wisconsin in 2005.
Operating margin increased 80 basis points from 13.9% in 2005 to 14.7% in 2006. On a comparable basis, operating margin increased 90 basis points in 2006, primarily due to the change in estimate in reserves mentioned in the preceding paragraph, as well as increased prescription volume and higher utilization of generic prescription drugs in our mail-order PBM companies.
Other
Our summarized results of operations for our Other segment for the year ended December 31, 2006 and 2005 are as follows:
| Year Ended December 31 | Comparable Year Ended | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 2006 | 2005 | % Change | $ Change | % Change | ||||||||||||||||||
| (In millions) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Operating revenue from external customers | $ | 454.6 | $ | 333.6 | 36 | % | $ | 464.8 | $ | (10.2 | ) | (2 | )% | |||||||||
Elimination of intersegment revenue | (1,806.8 | ) | (1,348.3 | ) | 34 | % | (1,348.3 | ) | (458.5 | ) | 34 | % | ||||||||||
Total operating revenue | $ | (1,352.2 | ) | $ | (1,014.7 | ) | 33 | % | $ | (883.5 | ) | $ | (468.7 | ) | 53 | % | ||||||
Operating loss | $ | (75.0 | ) | $ | (111.9 | ) | (33 | )% | $ | (125.8 | ) | $ | 50.8 | (40 | )% | |||||||
53
Table of Contents
Operating revenue from external customers increased $121.0 million, or 36%, to $454.6 million in 2006. On a comparable basis, operating revenue from external customers decreased $10.2 million, or 2%. On both a reported and comparable basis, the elimination of intersegment revenue increased $458.5 million, or 34%, in 2006, reflecting additional sales by our PBM companies of Medicare Part D and specialty pharmacy products to our Health Care segment.
Operating loss decreased $36.9 million, or 33%, to $75.0 million in 2006. On a comparable basis, operating loss decreased $50.8 million, or 40%, primarily due to lower expenses related to retention bonuses and other compensation costs associated with the merger between the former Anthem, Inc. and the former WellPoint Health Networks Inc.
VII. Membership—December 31, 2005 Compared to December 31, 2004
The following table presents our medical membership by customer type, funding arrangement and geographical region as of December 31, 2005 and 2004. Also included below are key metrics from our Specialty segment, including prescription volume for our PBM companies and membership by product. The membership data presented is unaudited and in certain instances includes estimates of the number of members represented by each contract at the end of the period.
| WellPoint, Inc. as Reported December 31, 20051 | WellChoice 20052 | WellPoint 20053 | WellPoint, Inc. 2004 | WellPoint Without 2004 | |||||||||||
| Change | % Change | ||||||||||||||
| (In thousands) | |||||||||||||||
Medical Membership | |||||||||||||||
Customer Type | |||||||||||||||
Large Group | 16,362 | 3,085 | 13,277 | 13,073 | 204 | 2 | % | ||||||||
Individual and Small Group (ISG) | 5,645 | 349 | 5,296 | 5,199 | 97 | 2 | |||||||||
National Accounts | 4,776 | 1,235 | 3,541 | 3,212 | 329 | 10 | |||||||||
BlueCard | 3,915 | (93 | ) | 4,008 | 3,463 | 545 | 16 | ||||||||
Total National | 8,691 | 1,142 | 7,549 | 6,675 | 874 | 13 | |||||||||
Senior | 1,224 | 147 | 1,077 | 1,059 | 18 | 2 | |||||||||
State Sponsored | 1,934 | 64 | 1,870 | 1,722 | 148 | 9 | |||||||||
Total medical membership by customer type | 33,856 | 4,787 | 29,069 | 27,728 | 1,341 | 5 | |||||||||
Funding Arrangement | |||||||||||||||
Self-Funded | 16,584 | 1,879 | 14,705 | 13,302 | 1,403 | 11 | |||||||||
Fully-Insured | 17,272 | 2,908 | 14,364 | 14,426 | (62 | ) | — | ||||||||
Total medical membership by funding arrangement | 33,856 | 4,787 | 29,069 | 27,728 | 1,341 | 5 | |||||||||
Regional Membership | |||||||||||||||
East | 13,800 | 5,030 | 8,770 | 8,508 | 262 | 3 | |||||||||
Central | 10,970 | (125 | ) | 11,095 | 10,565 | 530 | 5 | ||||||||
West | 9,086 | (118 | ) | 9,204 | 8,655 | 549 | 6 | ||||||||
Total medical membership by region | 33,856 | 4,787 | 29,069 | 27,728 | 1,341 | 5 | |||||||||
Specialty Metrics | |||||||||||||||
PBM prescription volume4 | 344,621 | — | 344,621 | 336,541 | 8,080 | 2 | |||||||||
Behavioral health membership | 15,669 | — | 15,669 | 11,753 | NM | 5 | NM | 5 | |||||||
Life and disability membership | 5,826 | — | 5,826 | 5,306 | NM | 5 | NM | 5 | |||||||
Dental membership | 5,195 | 265 | 4,930 | 5,048 | NM | 5 | NM | 5 | |||||||
Vision membership | 816 | — | 816 | 773 | 43 | 6 | |||||||||
54
Table of Contents
1 | Amounts reported at December 31, 2005, include membership from the WellChoice acquisition that closed on December 28, 2005 and from the Lumenos acquisition that closed on June 9, 2005. |
2 | Represents membership at December 31, 2005, resulting from the WellChoice acquisition. Medical membership is shown net of overlapping BlueCard host membership. |
3 | WellPoint without WellChoice membership was calculated by subtracting membership resulting from the WellChoice acquisition from WellPoint, Inc.’s reported membership at December 31, 2005. |
4 | Represents annual PBM prescription volume for mail order and retail prescriptions for the full years ended December 31, 2005 and 2004. |
5 | Changes from prior period information are not meaningful due to different counting methodologies used by the former Anthem, Inc. and the former WellPoint Health Networks Inc. |
During the twelve months ended December 31, 2005, total medical membership increased approximately 6,128,000, or 22%, primarily due to our acquisition of WellChoice and organic growth in all customer types. Excluding the impact of the WellChoice acquisition: BlueCard membership increased 545,000, or 16%, representing membership growth in other Blue Cross and Blue Shield licensees with members who reside in or travel to our licensed areas; National Accounts membership increased 329,000, or 10%, primarily due to new sales, as well as in-group increases in membership and members acquired from the acquisition of Lumenos; Large Group membership increased 204,000, or 2% primarily due to our acquisition of Lumenos as well as new sales throughout the year; State Sponsored membership increased 148,000, or 9% due to new sales, primarily in the West region; and ISG membership increased 97,000, or 2%, primarily due to the introduction of new, more affordable product designs and an overall increase in consumer awareness of our wide variety of quality products and services as well as efforts to market products to the uninsured.
Self-funded medical membership increased 3,282,000 or 25%, primarily due to our merger with WellChoice and increases in our BlueCard, National Accounts and Large Group businesses. Fully-insured membership increased by 2,846,000 or 20%, due to our merger with WellChoice. However, on a comparable basis, fully-insured membership decreased by 62,000 primarily due to a Large Group fully-insured account in the East region, which represented approximately 140,000 medical members, converting to self-funded during the third quarter of 2005. This was partially offset by growth in our ISG and State Sponsored businesses, as well as new sales and positive in-group change in Large Group.
Our specialty metrics are derived from membership and activity from our specialty products. These products are often ancillary to our health business, and can therefore be impacted by growth in our medical membership. Prescription volume at our PBM increased 8,080,000 prescriptions, or 2%, in 2005 primarily due to growth in both our mail order and retail operations.
55
Table of Contents
VIII. Results of Operations—Year Ended December 31, 2005 Compared to the Year Ended December 31, 2004
Our consolidated results of operations for the years ended December 31, 2005 and 2004 are discussed in the following section.
Year Ended December 31 | % Change | Comparable Year Ended | $ Change | % Change | ||||||||||||||||||
| 2005 | 20041 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| (In millions, except per share data) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Premiums | $ | 40,680.0 | $ | 18,678.3 | 118 | % | $ | 38,050.3 | $ | 2,629.7 | 7 | % | ||||||||||
Administrative fees | 2,719.2 | 1,457.0 | 87 | 2,493.0 | 226.2 | 9 | ||||||||||||||||
Other revenue | 519.2 | 218.4 | 138 | 489.2 | 30.0 | 6 | ||||||||||||||||
Total operating revenue | 43,918.4 | 20,353.7 | 116 | 41,032.5 | 2,885.9 | 7 | ||||||||||||||||
Net investment income | 633.1 | 311.7 | 103 | 563.1 | NM | 4 | NM | 4 | ||||||||||||||
Net realized (losses) gains on investments | (10.2 | ) | 42.5 | (124 | ) | 75.9 | NM | 4 | NM | 4 | ||||||||||||
Total revenues | 44,541.3 | 20,707.9 | 115 | 41,671.5 | NM | 4 | NM | 4 | ||||||||||||||
Benefit expense | 32,625.2 | 15,280.6 | 114 | 30,731.0 | 1,894.2 | 6 | ||||||||||||||||
Selling, general and administrative expense: | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Selling expense | 1,474.2 | 537.2 | 174 | 1,358.0 | 116.2 | 9 | ||||||||||||||||
General and administrative expense | 5,798.5 | 2,940.5 | 97 | 5,479.3 | 319.2 | 6 | ||||||||||||||||
Total selling, general and administrative expense | 7,272.7 | 3,477.7 | 109 | 6,837.3 | 435.4 | 6 | ||||||||||||||||
Cost of drugs | 288.0 | 95.0 | 203 | 269.8 | 18.2 | 7 | ||||||||||||||||
Interest expense | 226.2 | 142.3 | 59 | 190.4 | NM | 4 | NM | 4 | ||||||||||||||
Amortization of other intangible assets | 238.9 | 61.4 | 289 | 104.5 | NM | 4 | NM | 4 | ||||||||||||||
Merger-related undertakings | — | 61.5 | (100 | ) | 61.5 | NM | 4 | NM | 4 | |||||||||||||
Loss on repurchase of debt securities | — | 146.1 | (100 | ) | 146.1 | NM | 4 | NM | 4 | |||||||||||||
Total expenses | 40,651.0 | 19,264.6 | 111 | 38,340.6 | NM | 4 | NM | 4 | ||||||||||||||
Income before income tax expense | 3,890.3 | 1,443.3 | 170 | 3,330.9 | NM | 4 | NM | 4 | ||||||||||||||
Income tax expense | 1,426.5 | 483.2 | 195 | 1,238.3 | NM | 4 | NM | 4 | ||||||||||||||
Net income | $ | 2,463.8 | $ | 960.1 | 157 | $ | 2,092.6 | NM | 4 | NM | 4 | |||||||||||
Average diluted shares outstanding | 625.8 | 314.6 | 99 | NM | 4 | NM | 4 | NM | 4 | |||||||||||||
Diluted net income per share | $ | 3.94 | $ | 3.05 | 29 | NM | 4 | NM | 4 | NM | 4 | |||||||||||
Benefit expense ratio5 | 80.2 | % | 81.8 | % | (160 | )bp6 | 80.8 | % | (60 | )bp6 | ||||||||||||
Selling, general and administrative expense ratio7 | 16.6 | % | 17.1 | % | (50 | )bp6 | 16.7 | % | (10 | )bp6 | ||||||||||||
Income before income taxes as a percentage of total revenue | 8.7 | % | 7.0 | % | 170 | bp6 | NM | 4 | NM | 4 | ||||||||||||
Net income as a percentage of total revenue | 5.5 | % | 4.6 | % | 90 | bp6 | NM | 4 | NM | 4 | ||||||||||||
Certain of the following definitions are also applicable to all other results of operations tables in this discussion:
1 | Financial results for 2004 include operations of the former WellPoint Health Networks Inc. for the one month period ended December 31, 2004 and the former Anthem, Inc. for the year ended December 31, 2004. |
56
Table of Contents
2 | See below for discussion of “comparable basis” information. |
3 | For certain line items impacted by the merger of Anthem and WHN, comparable basis is not meaningful due to related capitalization and purchase accounting. |
4 | NM = Not meaningful. |
5 | Benefit expense ratio = Benefit expense ÷ Premiums. |
6 | bp = basis point; one hundred basis points = 1%. |
7 | Selling, general and administrative expense ratio = Total selling, general and administrative expense ÷ Total operating revenue. |
We discuss our 2005 and 2004 operations using “comparable basis” information, which is presented to provide a more meaningful 2004 comparison to 2005, due to the merger with WHN. Comparable basis information is not calculated in accordance with GAAP and is not intended to represent or be indicative of the results of WellPoint, Inc. had the merger been completed as of January 1, 2004. Comparable basis information for the year ended December 31, 2004 was calculated by adding the reclassified historical statements of income for the former WHN for the 11 months ended November 30, 2004 to the reported results of WellPoint, Inc. for the year ended December 31, 2004, which includes one month of the former WHN. Comparable basis information contains no intercompany eliminations or pro forma adjustments.
| WellPoint, Inc. as Reported Year Ended December 31, 2004 | WellPoint Health Networks Inc. Eleven Months Ended November 30, 2004 | Reclassification Adjustments1 | WellPoint, Inc. Year Ended | ||||||||||||
| (In millions) | |||||||||||||||
Premiums | $ | 18,678.3 | $ | 19,804.7 | $ | (432.7 | ) | $ | 38,050.3 | ||||||
Administrative fees | 1,457.0 | 1,108.9 | (72.9 | ) | 2,493.0 | ||||||||||
Other revenue | 218.4 | 54.1 | 216.7 | 489.2 | |||||||||||
Total operating revenue | 20,353.7 | 20,967.7 | (288.9 | ) | 41,032.5 | ||||||||||
Net investment income | 311.7 | 276.3 | (24.9 | ) | 563.1 | ||||||||||
Net realized gains on investments | 42.5 | 8.4 | 25.0 | 75.9 | |||||||||||
Total revenues | 20,707.9 | 21,252.4 | (288.8 | ) | 41,671.5 | ||||||||||
Benefit expense | 15,280.6 | 15,925.5 | (475.1 | ) | 30,731.0 | ||||||||||
Selling, general and administrative expense: | |||||||||||||||
Selling expense | 537.2 | 820.8 | — | 1,358.0 | |||||||||||
General and administrative expense | 2,940.5 | 2,493.4 | 45.4 | 5,479.3 | |||||||||||
Total selling, general and administrative expense | 3,477.7 | 3,314.2 | 45.4 | 6,837.3 | |||||||||||
Cost of drugs | 95.0 | 32.6 | 142.2 | 269.8 | |||||||||||
Interest expense | 142.3 | 48.1 | — | 190.4 | |||||||||||
Amortization of other intangible assets | 61.4 | 7.8 | 35.3 | 104.5 | |||||||||||
Other expenses | — | 36.6 | (36.6 | ) | — | ||||||||||
Merger-related undertakings | 61.5 | — | — | 61.5 | |||||||||||
Loss on repurchase of debt securities | 146.1 | — | — | 146.1 | |||||||||||
Total expenses | 19,264.6 | 19,364.8 | (288.8 | ) | 38,340.6 | ||||||||||
Income before income tax expense | 1,443.3 | 1,887.6 | — | 3,330.9 | |||||||||||
Income tax expense | 483.2 | 755.1 | — | 1,238.3 | |||||||||||
Net income | $ | 960.1 | $ | 1,132.5 | $ | — | $ | 2,092.6 | |||||||
Benefit expense ratio2 | 81.8 | % | 80.8 | % | |||||||||||
Selling, general and administrative expense ratio3 | 17.1 | % | 16.7 | % | |||||||||||
1 | Represents the reclassification of certain WHN historical amounts to conform to a consistent presentation with WellPoint. |
2 | Benefit expense ratio = Benefit expense ÷ Premiums. |
3 | Selling, general and administrative expense ratio = Total selling, general and administrative expense ÷ Total operating revenue. |
57
Table of Contents
| WellPoint, Inc. as Reported Year Ended December 31, 2004 | WellPoint Health Networks Inc. Eleven Months Ended November 30, 2004 | Reclassification Adjustments | WellPoint, Inc. Year Ended | |||||||||||||
| (In millions) | ||||||||||||||||
Operating Revenue: | ||||||||||||||||
Health Care | $ | 19,427.7 | $ | 20,014.8 | $ | (460.3 | ) | $ | 38,982.2 | |||||||
Specialty | 1,447.0 | 976.0 | 423.0 | 2,846.0 | ||||||||||||
Other: | ||||||||||||||||
External customers | 208.6 | 37.4 | 69.9 | 315.9 | ||||||||||||
Elimination of intersegment revenue | (729.6 | ) | (60.5 | ) | (321.5 | ) | (1,111.6 | ) | ||||||||
Total Other | (521.0 | ) | (23.1 | ) | (251.6 | ) | (795.7 | ) | ||||||||
Total operating revenue | $ | 20,353.7 | $ | 20,967.7 | $ | (288.9 | ) | $ | 41,032.5 | |||||||
Operating Gain (Loss) | ||||||||||||||||
Health Care | $ | 1,497.4 | $ | 1,507.7 | $ | (9.2 | ) | $ | 2,995.9 | |||||||
Specialty | 105.2 | 226.0 | 6.0 | 337.2 | ||||||||||||
Other | (102.2 | ) | (38.3 | ) | 1.8 | (138.7 | ) | |||||||||
Premiums increased $22.0 billion, or 118%, to $40.7 billion in 2005. On a comparable basis, premium increased $2.6 billion, or 7%, primarily due to premium rate increases in our Large Group, ISG and Senior businesses and membership gains in our ISG, State Sponsored and Senior membership types. Partially offsetting the impact of premium rate increases was the conversion of some Large Group customers from fully-insured contracts to self-funded arrangements and the non-renewal of certain fully-insured accounts.
Administrative fees increased $1.3 billion, or 87%, to $2.7 billion in 2005. On a comparable basis, administrative fees increased $226.2 million, or 9%, primarily due to increased self-funded membership in our National and Large Group businesses. These membership gains are driven by the popularity of the BlueCard program, as well as successful efforts to attract large self-funded accounts and the continuing trend towards self-funded arrangements over fully-insured contracts among our Large Group customers.
Other revenue principally includes amounts from mail-order drug sales by our PBM companies, which provides services to members of our Health Care segment and third party clients. Other revenue increased $300.8 million, or 138%, to $519.2 million in 2005. On a comparable basis, other revenue increased $30.0 million, or 6%, primarily due to additional mail-order prescription revenue and increased prices of prescription drugs sold by our PBM companies. Increased mail-order prescription volume resulted from both membership increases and additional utilization of our PBM’s mail-order pharmacy option.
Net investment income increased $321.4 million, or 103%, to $633.1 million in 2005 primarily resulting from invested assets acquired with the WHN merger (net of cash used in the merger) and from growth in invested assets from reinvestment of cash generated from operations.
A summary of our net realized (losses) gains on investments for the years ended December 31, 2005 and 2004 is as follows:
| Year Ended December 31 | ||||||||||||
| 2005 | 2004 | $ Change | ||||||||||
| (In millions) | ||||||||||||
Net realized (losses) gains from the sale of fixed maturity securities | $ | (25.3 | ) | $ | 40.6 | $ | (65.9 | ) | ||||
Net realized gains from the sale of equity securities | 22.0 | 3.3 | 18.7 | |||||||||
Other-than-temporary impairments—credit related | (14.8 | ) | (0.8 | ) | (14.0 | ) | ||||||
Other realized gains (losses) | 7.9 | (0.6 | ) | 8.5 | ||||||||
Net realized (losses) gains | $ | (10.2 | ) | $ | 42.5 | $ | (52.7 | ) | ||||
58
Table of Contents
In 2005, net realized gains and losses from the sale of fixed maturity and equity securities were primarily due to restructuring of our portfolio as a result of integration activities related to our merger with WHN.
During 2004, we reallocated securities in our fixed maturity portfolio, primarily to optimize future after-tax income by investing in a higher mix of tax-exempt fixed maturity securities. The sale of fixed maturity securities associated with this reallocation resulted in the majority of the net realized gains reported during the year ended December 31, 2004.
Net gains or losses on investments are influenced by market conditions when an investment is sold, and will vary from year to year.
Other-than-temporary impairments in 2005 were approximately equal between equity securities and fixed maturity securities, while in 2004, other-than-temporary impairments were substantially related to equity securities. Other-than-temporary impairments in both 2005 and 2004 are primarily due to the length of time that such securities’ fair value had been less than cost.
Benefit expense increased $17.3 billion, or 114%, to $32.6 billion in 2005. On a comparable basis, benefit expense increased $1.9 billion, or 6%, primarily due to increased cost of care, which was driven primarily by higher costs in outpatient and inpatient services. In addition, our benefit expense included $35.0 million in 2005 related to the MDL settlement agreement discussed in Significant Transactions within this MD&A. On a comparable basis, our benefit expense ratio decreased 60 basis points from 80.8% in 2004 to 80.2% in 2005. The decrease in our benefit expense ratio is driven by moderating cost of care trends coupled with disciplined underwriting practices.
Selling, general and administrative expense increased $3.8 billion, or 109%, to $7.3 billion in 2005. On a comparable basis, selling, general and administrative expense increased $435.4 million, or 6%, primarily due to increases in volume-sensitive costs such as higher commissions, premium taxes and other expenses associated with growth in our business; increased incentive compensation, including merger-related stay bonuses; and costs associated with the transition of information technology infrastructure services to IBM. In addition, we incurred expenses related to the MDL settlement agreement and start-up costs related to Medicare Part D. On a comparable basis, our selling, general and administrative expense ratio decreased 10 basis points to 16.6% in 2005, primarily due to growth in operating revenue and the leveraging of costs over a larger membership base, partially offset by the factors noted above.
Cost of drugs increased $193.0 million, or 203%, to $288.0 million in 2005. On a comparable basis cost of drugs increased $18.2 million, or 7%, primarily due to higher mail-order prescription volume at our PBM companies.
Interest expense increased $83.9 million, or 59%, to $226.2 million in 2005, primarily due to additional interest expense on the debt incurred in conjunction with the WHN merger, partially offset by reduced interest expense from the repurchase of debt securities in December of 2004.
Amortization of other intangible assets increased $177.5 million, or 289%, to $238.9 million in 2005, primarily due to a full year of additional amortization expense related to identifiable intangible assets with finite lives resulting from the WHN merger.
Income tax expense increased $943.3 million, or 195%, to $1,426.5 million in 2005. Included in 2005 was $28.4 million in tax benefits associated with a refund claim recognizing the deductibility of capital losses on the sale of certain subsidiaries that occurred in prior years. Included in 2004 was $44.8 million in tax benefits associated with a change in Indiana laws governing the state’s high-risk health insurance pool.
Our net income as a percentage of total revenue increased 90 basis points, from 4.6% in 2004 to 5.5% in 2005. The increase in this metric reflects a combination of all factors discussed above.
59
Table of Contents
The discussion of segment results for the years ended December 31, 2005 and 2004 presented below are based on operating gain, as described above, and operating margin, which is calculated as operating gain divided by operating revenue. Our definitions of operating gain and operating margin may not be comparable to similarly titled measures reported by other companies.
Health Care
Our Health Care segment’s summarized results of operations for the year ended December 31, 2005 and 2004 are as follows:
Year Ended December 31 | % Change | Comparable Year Ended 2004 | $ Change | % Change | |||||||||||||||||
| 2005 | 2004 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| (In millions) | |||||||||||||||||||||
Operating revenue | $ | 41,867.0 | $ | 19,427.7 | 116 | % | $ | 38,982.2 | $ | 2,884.8 | 7 | % | |||||||||
Operating gain | $ | 3,418.0 | $ | 1,497.4 | 128 | % | $ | 2,995.9 | $ | 422.1 | 14 | % | |||||||||
Operating margin | 8.2 | % | 7.7 | % | 50 | bp | 7.7 | % | 50 | bp | |||||||||||
Operating revenue increased $22.4 billion, or 116%, to $41.9 billion. On a comparable basis, operating revenue increased $2.9 billion, or 7%, primarily due to growth in premium income as a result of premium rate increases in our Large Group and ISG businesses resulting from underwriting discipline. Also contributing to premium revenue growth was higher membership, primarily in our ISG and State Sponsored businesses. Administrative fees also increased primarily due to additional self-funded membership in National Accounts and Large Group businesses.
Operating gain increased $1.9 billion, or 128%, to $3.4 billion. On a comparable basis, operating gain increased $422.1 million, or 14%, primarily due to premium rate increases mentioned above along with membership growth and lower than expected cost of care within our ISG, Senior and Large Group businesses. Partially offsetting this increase was the impact of the $103.0 million pre-tax expense recognized in connection with the MDL settlement agreement in 2005.
Specialty
Our Specialty segment’s summarized results of operations for the years ended December 31, 2005 and 2004 are as follows:
| Year Ended December 31 | % Change | Comparable Year Ended 2004 | $ Change | % Change | |||||||||||||||||
| 2005 | 2004 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| (In millions) | |||||||||||||||||||||
Operating revenue | $ | 3,066.1 | $ | 1,447.0 | 112 | % | $ | 2,846.0 | $ | 220.1 | 8 | % | |||||||||
Operating gain | $ | 426.4 | $ | 105.2 | 305 | % | $ | 337.2 | $ | 89.2 | 26 | % | |||||||||
Operating margin | 13.9 | % | 7.3 | % | 660 | bp | 11.8 | % | 210 | bp | |||||||||||
Operating revenue increased $1.6 billion, or 112%, to $3.1 billion. On a comparable basis, operating revenue increased $220.1 million, or 8%, primarily due to increases in PBM operating revenue driven by improved pharmaceutical contracting and increased script volume, particularly mail-order script volume. This increase was partially offset by decreases in behavioral health revenue due to the standardization in funding arrangements between Health Care and Specialty segments.
Operating gain increased $321.2 million, or 305%, to $426.4 million. On a comparable basis, operating gain increased $89.2 million or 26%, primarily due to an increase in PBM, behavioral health and dental businesses.
60
Table of Contents
On a comparable basis, PBM operating gain increased due to higher script volume and improved pharmaceutical contracting. In addition, operating gain from behavioral health increased as we standardized funding arrangements between the Health Care and Specialty segments. Finally, membership growth, driven primarily by the transition of 1.9 million behavioral health members from an outside vendor, also contributed to the improved results in Specialty segment. These gains are partially offset by decreased rates on workers’ compensation insurance in California driven by unfavorable legislation.
Other
Our summarized results of operations for our Other segment for the years ended December 31, 2005 and 2004 are as follows:
| Year Ended December 31 | % Change | Comparable 2004 | $ Change | % Change | ||||||||||||||||||
| 2005 | 2004 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| (In millions) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Operating revenue from external customers | $ | 333.6 | $ | 208.6 | 60 | % | $ | 315.9 | $ | 17.7 | 6 | % | ||||||||||
Elimination of intersegment revenue | (1,348.3 | ) | (729.6 | ) | 85 | % | (1,111.6 | ) | (236.7 | ) | 21 | % | ||||||||||
Total operating revenue | $ | (1,014.7 | ) | $ | (521.0 | ) | 95 | % | $ | (795.7 | ) | $ | (219.0 | ) | 28 | % | ||||||
Operating loss | $ | (111.9 | ) | $ | (102.2 | ) | 9 | % | $ | (138.7 | ) | $ | 26.8 | (19 | )% | |||||||
Operating revenue from external customers increased $125.0 million, or 60%, to $333.6 million. On a comparable basis, operating revenue from external customers increased $17.7 million, or 6%. The elimination of intersegment revenue increased $618.7 million, or 85%. On a comparable basis, the elimination of intersegment revenue increased $236.7 million, or 21%, reflecting additional sales by our PBM companies to our Health Care segment.
Operating loss increased $9.7 million, or 9%, to $111.9 million. On a comparable basis, operating loss decreased $26.8 million or 19%, primarily due to expenses not allocated to the Health Care or Specialty segments.
IX. Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
We prepare our consolidated financial statements in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles, or GAAP. Application of GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the amounts reported in our consolidated financial statements and accompanying notes and within this MD&A. We consider some of our most important accounting policies that require estimates and management judgment to be those policies with respect to liabilities for medical claims payable, income taxes, goodwill and other intangible assets, investments and retirement benefits, which are discussed below. Our significant accounting policies are summarized in Note 2 to our audited consolidated financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2006 included in this Form 10-K.
Medical Claims Payable
The most judgmental accounting estimate in our consolidated financial statements is our liability for medical claims payable. At December 31, 2006, this liability was $5.3 billion and represented 19% of our total consolidated liabilities. We record this liability and the corresponding benefit expense for incurred but not paid claims including the estimated costs of processing such claims. Incurred but not paid claims include (1) an
61
Table of Contents
estimate for claims that are incurred but not reported, as well as claims reported to us but not yet processed through our systems, which approximated 95%, or $5.1 billion, of our total medical claims liability as of December 31, 2006; and (2) claims reported to us and processed through our systems but not yet paid, which approximated 5%, or $239.3 million, of the total medical claims liability as of December 31, 2006. The level of claims payable processed through our systems but not yet paid may fluctuate from one period end to the next, from 1% to 5% of our total medical claims liability, due to timing of when claim payments are made.
Liabilities for both claims incurred but not reported and reported but not yet processed through our systems are determined in aggregate, employing actuarial methods that are commonly used by health insurance actuaries and meet Actuarial Standards of Practice. Actuarial Standards of Practice require that the claim liabilities be adequate under moderately adverse circumstances. We determine the amount of the liability for incurred but not paid claims by following a detailed actuarial process that entails using both historical claim payment patterns as well as emerging medical cost trends to project our best estimate of claim liabilities. Under this process, historical data of paid claims is formatted into “claim triangles,” which compare claim incurred dates to the dates of claim payments. This information is analyzed to create “completion factors” that represent the average percentage of total incurred claims that have been paid through a given date after being incurred. Completion factors are applied to claims paid through the financial statement date to estimate the ultimate claim expense incurred for the current period. Actuarial estimates of incurred but not paid claim liabilities are then determined by subtracting the actual paid claims from the estimate of the ultimate incurred claims.
For the most recent incurred months (generally the most recent two months), the percentage of claims paid for claims incurred in those months is generally low. This makes the completion factor methodology less reliable for such months. Therefore, incurred claims for recent months are not projected from historical completion and payment patterns; rather they are projected by estimating the claims expense for those months based on recent claims expense levels and health care trend levels, or “trend factors”.
Because the reserve methodology is based upon historical information, it must be adjusted for known or suspected operational and environmental changes. These adjustments are made by our actuaries based on their knowledge and their estimate of emerging impacts to benefit costs and payment speed. Circumstances to be considered in developing our best estimate of reserves include changes in utilization levels, unit costs, mix of business, benefit plan designs, provider reimbursement levels, processing system conversions and changes, claim inventory levels, claim processing patterns, claim submission patterns and operational changes resulting from business combinations. A comparison of prior period liabilities to re-estimated claim liabilities based on subsequent claims development is also considered in making the liability determination. In our comparison of prior year, the methods and assumptions are not changed as reserves are recalculated, rather the availability of additional paid claims information drives our changes in the re-estimate of the unpaid claim liability. To the extent appropriate, changes in such development are recorded as a change to current period benefit expense.
In addition to incurred but not paid claims, the liability for medical claims payable includes reserves for premium deficiencies, if appropriate. Premium deficiencies are recognized when it is probable that expected claims and administrative expenses will exceed future premiums on existing medical insurance contracts without consideration of investment income. Determination of premium deficiencies for longer duration life and disability contracts, which are reported with reserves for future policy benefits, includes consideration of investment income. For purposes of premium deficiencies, contracts are grouped in a manner consistent with our method of acquiring, servicing and measuring the profitability of such contracts.
We regularly review and set assumptions regarding cost trends and utilization when initially establishing claim liabilities. We continually monitor and adjust the claims liability and benefit expense based on subsequent paid claims activity. If it is determined that our assumptions regarding cost trends and utilization are significantly different than actual results, our income statement and financial position could be impacted in future periods. Adjustments of prior year estimates may result in additional benefit expense or a reduction of benefit expense in the period an adjustment is made. Further, due to the considerable variability of health care costs, adjustments to
62
Table of Contents
claim liabilities occur each quarter and are sometimes significant as compared to the net income recorded in that quarter. Prior period development is recognized immediately upon the actuary’s judgment that a portion of the prior period liability is no longer needed or that an additional liability should have been accrued. That determination is made when sufficient information is available to ascertain that the re-estimate of the liability is reasonable.
While there are many factors that are used as a part of the estimation of our medical claims payable liability, the two key assumptions having the most significant impact on our incurred but not paid liability as of December 31, 2006 were the completion and trend factors. As discussed above, these two key assumptions can be influenced by other operational variables including system changes, provider submission patterns and business combinations.
There is variation in the reasonable choice of completion factors by duration for durations of three months through 12 months where the completion factors have the most significant impact. As previously discussed, completion factors tend to be less reliable for the most recent months and therefore are not specifically utilized for months one and two. At December 31, 2006, the variability in months three to five was estimated to be between 20 and 70 basis points, while months six through twelve have much lower variability ranging from 10 to 20 basis points.
Over the period from December 31, 2005 to December 31, 2006, completion factors have increased. With consideration of claim payments through December 31, 2006, the completion factors used to determine the incurred but not paid claim liability estimate for the December 31, 2005 valuation period have developed higher than those used at December 31, 2005, primarily because we are receiving claims information from our providers more timely as a result of increased electronic submissions. In addition, we are paying claims more quickly once they have been received. This resulted in approximately $113.6 million of redundancy in the December 31, 2005 estimate and is included in the statement of income for the year ended December 31, 2006. This continued increase has been taken into consideration when determining the completion factors used in establishing the December 31, 2006 incurred but not paid claim liability by choosing factors that reflect the more recent experience. The difference in completion factor assumptions, assuming moderately adverse experience, results in variability of 2%, or approximately $101.0 million, in the December 31, 2006 incurred but not paid claim liability, depending on the completion factors chosen. It is important to note that the completion factor methodology inherently assumes that historical completion rates will be reflective of the current period. However, it is possible that the actual completion rates for the current period will develop differently from historical patterns and therefore could fall outside the possible variations described herein.
Over the period from December 31, 2004 to December 31, 2005, completion factors increased. With consideration of claims payment through December 31, 2005, the completion factors used to determine the incurred but not paid claim liability estimate for the December 31, 2004 valuation period have developed higher than those used at December 31, 2004, primarily because we are receiving claims information from our providers more timely as a result of increased electronic submissions. This resulted in approximately $194.3 million of redundancy in the December 31, 2004 estimate and included in the statement of income for the year ended December 31, 2005. In 2003, results presented represent the former Anthem, Inc. on a stand alone basis. Due to the acquisition of WHN at the end of 2004, these periods are not on a comparable basis. Therefore, changes in assumptions from 2003 to 2004 are not meaningful in comparing these periods.
The other major assumption used in the establishment of the December 31, 2006 incurred but not paid claim liability was the trend factors used in determining the claims expense per member per month for the most recent two incurral months. At December 31, 2006, there was a 740 basis point differential in the high and low trend factors assuming moderately adverse experience. This range of trend factors would imply variability of 10%, or approximately $504.0 million, in the incurred but not paid claims liability, depending upon the trend factor used. Because historical trend factors are often not representative of current claim trends, the trend experience for the most recent six to nine months, plus knowledge of recent events likely affecting current trends, have been taken
63
Table of Contents
into consideration in establishing the incurred but not paid claim liability at December 31, 2006. As we look at the year-over-year claim trend for the prior period (November and December 2005) compared to the current period (November and December 2006), the trend used in our reserve models have increased moderately due to mix changes resulting from the introduction of Part D drug plans and other product changes. However, claim trends observed as of December 31, 2005 based upon subsequent claim runout were lower than anticipated in the assumptions used to estimate medical claims payable at December 31, 2005. This decline was due to moderating outpatient service trends and declines in pharmacy benefit cost trend. This difference between the trends assumed in establishing the December 31, 2005 medical claims payable, and the trend observed based upon subsequent claims runout through the twelve months ended December 31, 2006, resulted in approximately $504.1 million of redundancy in the December 31, 2005 estimate and included in the statement of income for the year ended December 31, 2006.
Over the period from 2004 to 2005, claim trends declined. Claim trends observed based upon subsequent claim runout were lower than anticipated in the assumptions used to estimate medical claims payable at December 31, 2004. This decline was due to moderating outpatient service trends and declines in pharmacy benefit cost trend. This difference between the trends assumed in establishing the December 31, 2004 medical claims payable, and the trend observed based upon subsequent claims runout, resulted in approximately $450.6 million of redundancy in the December 31, 2004 estimate and included in the statement of income for the year ended December 31, 2005.
As summarized below, Note 10 to our audited consolidated financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2006 included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K provides historical information regarding the accrual and payment of our medical claims liability. Components of the total incurred claims for each year include amounts accrued for current year estimated claims expense as well as adjustments to prior year estimated accruals. In Note 10 to our audited consolidated financial statements, the line labeled “Net incurred medical claims: Prior years (redundancies)” accounts for those adjustments made to prior year estimates. The impact of any reduction of “Net incurred medical claims: Prior years (redundancies)” claims may be offset as we establish the estimate of “Net incurred medical claims: Current year”. Our reserving practice is to consistently recognize the actuarial best estimate of our ultimate liability for our claims. When we recognize a release of the redundancy, we disclose the amount that is not in the ordinary course of business, if material. We believe we have consistently applied our methodology in determining our best estimate for unpaid claims liability at each reporting date.
64
Table of Contents
A reconciliation of the beginning and ending balance for medical claims payable for the years ended December 31, 2006, 2005 and 2004 is as follows:
| Years Ended December 31 | ||||||||||||
| 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | ||||||||||
| (In millions) | ||||||||||||
Gross medical claims payable, beginning of period | $ | 4,853.4 | $ | 4,134.0 | $ | 1,836.0 | ||||||
Ceded medical claims payable, beginning of period | (27.7 | ) | (31.9 | ) | (8.7 | ) | ||||||
Net medical claims payable, beginning of period | 4,825.7 | 4,102.1 | 1,827.3 | |||||||||
Business combinations and purchase adjustments | (6.4 | ) | 784.5 | 2,331.0 | ||||||||
Net incurred medical claims: | ||||||||||||
Current year | 42,613.2 | 32,865.6 | 15,344.9 | |||||||||
Prior years (redundancies) | (617.7 | ) | (644.9 | ) | (171.9 | ) | ||||||
Total net incurred medical claims | 41,995.5 | 32,220.7 | 15,173.0 | |||||||||
Net payments attributable to: | ||||||||||||
Current year medical claims | 37,486.0 | 28,997.1 | 12,453.2 | |||||||||
Prior years medical claims | 4,089.5 | 3,284.5 | 2,776.0 | |||||||||
Total net payments | 41,575.5 | 32,281.6 | 15,229.2 | |||||||||
Net medical claims payable, end of period | 5,239.3 | 4,825.7 | 4,102.1 | |||||||||
Ceded medical claims payable, end of period | 51.0 | 27.7 | 31.9 | |||||||||
Gross medical claims payable, end of period | $ | 5,290.3 | $ | 4,853.4 | $ | 4,134.0 | ||||||
Current year medical claims paid as a percent of current year net incurred medical claims | 88.0 | % | 88.2 | % | 81.2 | % | ||||||
Prior year redundancies in the current period as a percent of prior year net medical claims payable less prior year redundancies in the current period | 14.7 | % | 18.7 | % | 10.4 | % | ||||||
Prior year redundancies in the current period as a percent of prior year net incurred medical claims | 1.9 | % | 4.2 | % | 1.4 | % | ||||||
Amounts incurred related to prior years vary from previously estimated liabilities as the claims are ultimately settled. Liabilities at any period end are continually reviewed and re-estimated as information regarding actual claims payments, or runout, becomes known. This information is compared to the originally established year end liability. Negative amounts reported for incurred related to prior years result from claims being settled for amounts less than originally estimated. The prior year redundancy of $617.7 million shown above for the year ended December 31, 2006 represents an estimate based on paid claim activity from January 1, 2006 to December 31, 2006. Medical claim liabilities are usually described as having a “short tail”, which means that they are generally paid within several months of the member receiving service from the provider. Accordingly, the majority, or approximately 82%, of the $617.7 million redundancy relates to claims incurred in calendar year 2005, with the remaining 18% related to claims incurred in 2004 and prior.
The ratio of current year medical claims paid as a percent of current year net medical claims incurred was 88.0% for 2006, 88.2% for 2005 and 81.2% for 2004. The 2004 ratio was impacted by having only one month of medical claims incurred and paid during 2004 for the former WHN. If the former WHN had not been included during 2004, current year medical claims payments would have been $12,057.7 million, current year net incurred medical claims would have been $13,835.1 million and the adjusted ratio would have been approximately 87.2% for 2004. Comparison of the 2006 ratio of 88.0% and the 2005 ratio of 88.2% reflect a moderate decline due to system conversions and integration activity that impacted the 2006 ratio. Comparison of the 2005 ratio of 88.2% and the adjusted 2004 ratio of 87.2% indicate that we paid claims faster between those periods. The increase was primarily attributable to improved processes and our provider networks submitting claims information to us more timely as a result of increased electronic submissions. The result of these changes is an enhanced ability to adjudicate and pay claims more quickly.
65
Table of Contents
We calculate the percentage of prior year redundancies in the current period as a percent of prior year net incurred claims payable less prior year redundancies in the current period in order to demonstrate the development of the prior year reserves. This metric was 14.7% for 2006, 18.7% for 2005 and 10.4% for 2004. As discussed previously, the 400 basis point decrease in this metric for 2006 was caused by actual completion factors and claim trends differing from the assumptions used to support our best estimate of the incurred but not paid claim liability of the prior period.
We calculate the percentage of prior year redundancies in the current period as a percent of prior year net incurred medical claims to indicate the percentage of redundancy included in the preceding year calculation of current year net incurred medical claims. We believe this calculation indicates the reasonableness of our prior year estimation of incurred medical claims and the consistency of our methodology. This metric was 1.9% for 2006, 4.2% for 2005 and 1.4% for 2004. This ratio is calculated using the redundancy of $617.7 million, shown above, which represents an estimate based on paid claim activity from January 1, 2006 to December 31, 2006. The 2006 ratio is impacted by having no net incurred medical claims for the former WellChoice, Inc. in 2005. If the former Wellchoice, Inc. had been included for the full year 2005, this ratio would have been approximately 1.6%. The 2005 ratio is impacted by having only one month of net incurred medical claims for WHN in 2004. If WHN had been included for the full year 2004, estimated prior year net incurred medical claims would have been $30,819.1 million, and the adjusted ratio would have been approximately 2.1% for the year ended December 31, 2005.
The following table shows the variance between total net incurred medical claims as reported in the above table for each of 2005 and 2004 and the incurred claims for such years had it been determined retrospectively (computed as the difference between “net incurred medical claims—current year” for the year shown and “net incurred medical claims—prior years (redundancies)” for the immediately following year):
| Years Ended December 31 | ||||||||
| 2005 | 2004 | |||||||
| (In millions) | ||||||||
Total net incurred medical claims, as reported | $ | 32,220.7 | $ | 15,173.0 | ||||
Retrospective basis, as described above | 32,247.9 | 14,700.0 | ||||||
Variance | $ | (27.2 | ) | $ | 473.0 | |||
Variance to total net incurred medical claims, as reported | (0.1 | )% | 3.1 | % | ||||
Given that our business is primarily short tailed, the variance to total net incurred medical claims, as reported above, is used to assess the reasonableness of our estimate of ultimate incurred medical claims for a given calendar year with the benefit of one year of experience. We expect that substantially all of the development of the 2006 estimate of medical claims payable will be known during 2007.
The 2005 variance of $(27.2) million and variance to total incurred medical claims, as reported of (0.1)% are impacted by having no WellChoice, Inc. activity in the total incurred as reported during 2005 and full development of activity from the former WellChoice, Inc. in the retrospective basis amount. The adjusted variance would be approximately $(175.2) million and the variance to total incurred would be approximately (0.5)% if the impact of WellChoice is removed.
The 2004 variance of $473.0 million and variance to total incurred medical claims, as reported of 3.1% are impacted by having only one month of total incurred as reported for WHN during 2004 and a full development of WHN activity in the retrospective basis amount. The adjusted variance would be approximately $136.5 million and the variance to total incurred would be approximately 1.0% if the impact of WHN is removed.
These small variances to total net incurred medical claims, adjusted for the impacts of WellChoice, Inc. and WHN, shows that our estimates of this liability have approximated the actual experience for the years depicted.
66
Table of Contents
Income Taxes
We account for income taxes in accordance with Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 109,Accounting for Income Taxes. This standard requires, among other things, the separate recognition of deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities. Such deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities represent the tax effect of temporary differences between financial reporting and tax reporting measured at tax rates enacted at the time the deferred tax asset or liability is recorded. A valuation allowance must be established for deferred tax assets if it is “more likely than not” that all or a portion may be unrealized. Our judgment is required in determining an appropriate valuation allowance.
At each financial reporting date, we assess the adequacy of the valuation allowance by evaluating each of our deferred tax assets based on the following:
| • | the types of temporary differences that created the deferred tax asset; |
| • | the amount of taxes paid in prior periods and available for a carry-back claim; |
| • | the forecasted future taxable income, and therefore, likely future deduction of the deferred tax item; and |
| • | any significant other issues impacting the likely realization of the benefit of the temporary differences. |
During 2006 the valuation allowance increased by $0.5 million. This resulted from realized and unrealized capital losses of subsidiaries, which are not included in our consolidated tax return. During 2004 and 2003, the valuation allowance decreased by $33.8 million and $81.9 million, respectively. The 2004 and 2003 reductions resulted from utilizing alternative minimum tax, or AMT, credits and net operating losses on our federal income tax return for which we had a deferred tax asset with a corresponding valuation allowance. As deferred tax assets related to those deductions are available for use in the tax return, a valuation was no longer required and was reduced. The decrease in the valuation allowance in 2004 was partially offset by an additional $5.6 million related to Indiana state taxes, as discussed below.
During 2004 and 2003, we recorded additional tax liabilities of $44.1 million and $81.9 million, respectively, offsetting the reduction in valuation allowances discussed above. These additional liabilities were recorded for uncertainty on several tax issues, including the lack of clear guidance from the Internal Revenue Service, or IRS, on various tax issues relating to our conversion in 1986 from tax-exempt to tax-paying status.
During the third quarter of 2006, we decreased our state deferred tax liability by $43.0 million, resulting in a tax benefit, net of federal taxes, of $28.0 million, or $0.04 per basic and diluted share, for the year ended December 31, 2006. This resulted from a lower effective tax rate due to changes in our state apportionment factors following the WellChoice acquisition.
During 2005, a refund claim we filed in 2003 was approved by the Congressional Joint Committee on Taxation. The claim related to initially disallowed losses on the sale of certain subsidiaries in the late 1990s. A tax benefit of $28.4 million related to this claim was recorded in the first quarter of 2005. Net income related to this claim was $0.04 per basic and diluted share for the year ended December 31, 2005.
As a result of legislation enacted in Indiana on March 16, 2004, we recorded deferred tax assets and liabilities, with a corresponding net tax benefit in our income statement of $44.8 million, or $0.15 per basic share and $0.14 per diluted share, for the year ended December 31, 2004. The legislation eliminated the creation of tax credits resulting from the payment of future assessments to the Indiana Comprehensive Health Insurance Association, or ICHIA. ICHIA is Indiana’s high-risk health insurance pool. Our historical ICHIA assessment payments far exceeded our Indiana income tax liability. Thus, the recognition of a state deferred tax asset was not warranted, as a future Indiana tax liability was unlikely. Under the new legislation, ICHIA tax credits are limited to any unused ICHIA assessment paid prior to December 31, 2004. FAS 109 requires that deferred assets or liabilities be established in the period a change in law is enacted. These deferred tax assets and liabilities reflect
67
Table of Contents
temporary differences, net operating loss carryforwards and tax credits relating to our Indiana income tax filings. Following guidance in FAS 109, a valuation allowance of $5.6 million was established for the portion of the deferred tax asset, which we believe will likely not be utilized. There is no carryforward limitation on the tax credits and the net operating loss carryforwards do not begin to expire until 2018. We believe we will have sufficient taxable income in future years to offset these carryforwards; therefore, no additional valuation allowance was recorded.
We, like other companies, frequently face challenges from tax authorities regarding the amount of taxes due. These challenges include questions regarding the timing and amount of deductions that we have taken on our tax returns. In evaluating any additional tax liability associated with various positions taken in our tax return filings, we record additional tax liability for potential adverse tax outcomes. Based on our evaluation of our tax positions, we believe we have appropriately accrued for tax exposures. To the extent we prevail in matters we have accrued for, our future effective tax rate would be reduced and net income would increase. If we are required to pay more than accrued, our future effective tax rate would increase and net income would decrease. Our effective tax rate and net income in any given future period could be materially impacted.
In the ordinary course of business, we are regularly audited by federal and state authorities, and from time to time, these audits result in proposed assessments. We believe our tax positions comply with applicable tax law and intend to defend our positions vigorously through the IRS appeals process. We believe we have adequately provided for any reasonable foreseeable outcome related to these matters. Accordingly, although their ultimate resolution may require additional tax payments, we do not anticipate any material impact to earnings from these matters. As of December 31, 2006, the IRS was nearing completion of its examination of our 2003 tax year. The IRS will continue auditing our 2004 tax year and will initiate a review of the 2005 and 2006 tax years during 2007. In addition, the IRS has invited us to join the Compliance Assurance Program, or CAP, for 2007. The objective of CAP is to reduce taxpayer burden and uncertainty while assuring the IRS of the accuracy of tax returns prior to filing, thereby reducing or eliminating the need for post-filing examinations. Various tax examinations and proceedings also continue for certain subsidiaries for tax years prior to being included in our consolidated tax return.
For additional information, see Note 14 to our audited consolidated financial statements as of and for the year ended December 31, 2006 included in this Form 10-K. See alsoNew Accounting Pronouncementsdisclosure included in this Critical Accounting Polices and Estimates section of our MD&A for discussion of new accounting guidance related to uncertain tax positions.
Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets
Our consolidated goodwill at December 31, 2006 was $13.4 billion and other intangible assets were $9.4 billion. The sum of goodwill and intangible assets represents 44% of our total consolidated assets and 93% of our consolidated shareholders’ equity at December 31, 2006.
We follow Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 141,Business Combinations, and Statement of Accounting Standards No. 142,Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets. FAS 141 specifies the types of acquired intangible assets that are required to be recognized and reported separately from goodwill. Under FAS 142, goodwill and other intangible assets (with indefinite lives) are not amortized but are tested for impairment at least annually. We completed our annual impairment tests of existing goodwill and other intangible assets (with indefinite lives) for each of the years ended December 31, 2006, 2005 and 2004 and based upon these tests we have not incurred any impairment losses related to any goodwill and other intangible assets (with indefinite lives).
On December 28, 2005, we purchased 100% of the outstanding common stock of WellChoice, Inc. In accordance with FAS 141, we allocated the purchase price to the fair value of assets acquired, including intangible assets, and liabilities assumed. This allocation process included the review of relevant information
68
Table of Contents
about the assets and liabilities, independent appraisals and other valuations to determine the fair value of assets acquired and liabilities assumed. The allocation resulted in $3.5 billion of non-tax deductible goodwill and $1.7 billion of identifiable intangible assets.
On November 30, 2004, we completed our merger with WHN and purchased 100% of the outstanding common stock of WHN. In accordance with FAS 141, we allocated the purchase price to the fair value of assets acquired, including intangible assets, and liabilities assumed. This allocation process included the review of relevant information about the assets and liabilities, independent appraisals and other valuations to determine the fair value of assets acquired and liabilities assumed. The allocation resulted in $7.6 billion of non-tax deductible goodwill and $7.0 billion of identifiable intangible assets.
While we believe we have appropriately allocated the purchase price of our acquisitions, this allocation requires many assumptions to be made regarding the fair value of assets and liabilities acquired. In addition, the annual impairment testing required under FAS 142 requires us to make assumptions and judgments regarding the estimated fair value of our goodwill and intangibles. Such assumptions include the discount factor used to determine the fair value of a reporting unit, which is ultimately used to identify potential goodwill impairment. Such estimated fair values might produce significantly different results if other reasonable assumptions and estimates were to be used. If we are unable to support a fair value estimate in future annual goodwill impairment tests or if significant impairment indicators are noted relative to other intangible assets subject to amortization, we may be required to record impairment losses against future income.
For additional information, see Note 4 to our audited consolidated financial statements as of and for the year ended December 31, 2006 included in this Form 10-K.
Investments
Current and long term available-for-sale investment securities were $17.5 billion at December 31, 2006 and represented 34% of our total consolidated assets at December 31, 2006. In accordance with Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 115,Accounting for Certain Investments in Debt and Equity Securities,our fixed maturity and equity securities are classified as “available-for-sale” securities and are reported at fair value. We classify our investments in available-for-sale fixed maturity securities as either current or noncurrent assets based on their contractual maturity. Investment income is recorded when earned, and realized gains or losses, determined by specific identification of investments sold, are included in income when the securities are sold.
WellPoint maintains various rabbi trusts to account for the assets and liabilities under certain deferred compensation plans. Under these plans, the participants can defer certain types of compensation and elect to receive a return on the deferred amounts based on the changes in fair value of various investment options, primarily a variety of mutual funds. Rabbi trust assets were previously classified as noncurrent available-for-sale investments. Effective January 1, 2006 and in connection with a restructuring of the plans, WellPoint changed its classification for the majority of such securities from available-for-sale to trading, which are reported in “Other invested assets, current” in the consolidated balance sheet. The change in the fair value of the trading portfolio rabbi trust assets during 2006 resulted in $35.6 million of realized gains, which, together with net investment income from trading portfolio rabbi trust assets of $8.6 million, is classified in general and administrative expense in the consolidated statement of income, consistent with the related increase in compensation expense.
During December 2006, WellPoint initiated a program whereby it generally purchases corporate-owned life insurance policies on participants in the deferred compensation plans. The cash surrender value of the corporate-owned life insurance policies is reported in “Other invested assets, long-term” in the consolidated balance sheets. The change in cash surrender value is reported as an offset to premium expense classified as general and administrative expense.
In addition to available-for-sale investment securities, we held other long-term investments of $628.8 million, or 1% of total consolidated assets, at December 31, 2006. These long-term investments consist primarily
69
Table of Contents
of real estate, cash surrender value of corporate-owned life insurance policies and certain other investments. Due to their less liquid nature, these investments are classified as long-term.
An impairment review of securities to determine if declines in fair value below cost are other-than-temporary is subjective and requires a high degree of judgment. We evaluate our investment securities on a quarterly basis, using both quantitative and qualitative factors, to determine whether a decline in value is other-than-temporary. Such factors considered include the length of time and the extent to which a security’s market value has been less than its cost, financial condition and near term prospects of the issuer, recommendations of investment advisors, and forecasts of economic, market or industry trends. If any declines are determined to be other-than-temporary, we charge the losses to income when that determination is made. We have a committee made up of certain accounting and investment associates and management responsible for managing the impairment review process. The current economic environment and recent volatility of securities markets increase the difficulty of assessing investment impairment and the same influences tend to increase the risk of potential impairment of these assets. We recorded charges for other-than-temporary impairment of securities of $56.2 million, $14.8 million and $0.8 million, respectively, for the years ended December 31, 2006, 2005 and 2004. The $56.2 million impairment for the year ended December 31, 2006 primarily related to our intent to hold fixed maturity securities that were in an unrealized loss position due to the prevailing interest rate environment, as well as other-than-temporary impairments of equity securities that had been in an unrealized loss position for an extended period of time. Impairments recorded in 2005 and 2004 were primarily the result of the continued credit deterioration on specific issuers in the bond and equity markets.
We believe we have adequately reviewed our investment securities for impairment and that our investment securities are carried at fair value. However, over time, the economic and market environment may provide additional insight regarding the fair value of certain securities, which could change our judgment regarding impairment. This could result in realized losses relating to other-than-temporary declines being charged against future income.
A summary of available-for-sale investments with unrealized losses as of December 31, 2006 along with the related fair value, aggregated by the length of time that investments have been in a continuous unrealized loss position, is as follows:
Less than Twelve Months | Twelve Months or More | Total | |||||||||||||||||||
| Fair Value | Gross Unrealized Losses | Fair Value | Gross Unrealized Losses | Fair Value | Gross Unrealized Losses | ||||||||||||||||
| (In millions) | |||||||||||||||||||||
Fixed maturity securities | $ | 3,884.1 | $ | (28.8 | ) | $ | 5,306.4 | $ | (103.3 | ) | $ | 9,190.5 | $ | (132.1 | ) | ||||||
Equity securities | 234.6 | (15.3 | ) | 21.0 | (0.6 | ) | 255.6 | (15.9 | ) | ||||||||||||
Total | $ | 4,118.7 | $ | (44.1 | ) | $ | 5,327.4 | $ | (103.9 | ) | $ | 9,446.1 | $ | (148.0 | ) | ||||||
Our fixed maturity investment portfolio is sensitive to interest rate fluctuations, which impact the fair value of individual securities. Unrealized losses reported above were primarily caused by the effect of a rising interest rate environment on certain securities with stated interest rates currently below market rates. We currently have the ability and intent to hold these securities until their full cost can be recovered. Therefore, we do not believe the unrealized losses represent an other-than-temporary impairment as of December 31, 2006.
During the year ended December 31, 2006, we sold $5.9 billion of fixed maturity and equity securities resulting in gross realized losses of $95.7 million. Subsequent to the acquisition of WellChoice, during 2006, we restructured our investment portfolios to align the merged portfolios with our overall investment guidelines. The majority of the sales of fixed maturity securities resulted in realized losses due to the prevailing interest rate environment. For equity securities, the 2006 sales to restructure the merged portfolios primarily resulted in realized gains. Similarly, subsequent to the merger with WHN, during 2005, we restructured our investment
70
Table of Contents
portfolios to align the merged portfolios with our overall investment guidelines. The majority of the sales of fixed maturity securities resulted in realized losses due to the prevailing interest rate environment. For equity securities, the 2005 sales to restructure the merged portfolios primarily resulted in realized gains.
A primary objective in the management of the fixed maturity and equity portfolios is to maximize total return relative to underlying liabilities and respective liquidity needs. In achieving this goal, assets may be sold to take advantage of market conditions or other investment opportunities as well as tax considerations. Sales will generally produce realized gains and losses.
In the ordinary course of business, we may sell securities at a loss for a number of reasons, including, but not limited to: (i) changes in the investment environment; (ii) expectation that the fair value could deteriorate further; (iii) desire to reduce our exposure to an issuer or an industry; (iv) changes in credit quality; or (v) changes in expected cash flow.
We participate in securities lending programs whereby marketable securities in our investment portfolio are transferred to independent brokers or dealers based on, among other things, their creditworthiness in exchange for collateral initially equal to at least 102% of the value of the securities on loan and is thereafter maintained at a minimum of 100% of the market value of the securities loaned. The market value of the securities on loan to each borrower is monitored daily and the borrower is required to deliver additional collateral if the market value of the collateral falls below 100% of the market value of the securities on loan. The fair value of the collateral amounted to $904.7 million and $1,389.9 million, which represented 103% and 102% of the carrying value at December 31, 2006 and 2005, respectively. Under guidance provided in FAS 140,Accounting for Transfers and Servicing of Financial Assets and Extinguishments of Liabilities, we recognize the collateral as an asset, which is reported as “securities lending collateral” on our balance sheet and we record a corresponding liability for the obligation to return the collateral to the borrower, which is reported as “securities lending payable”. The securities on loan are reported in the applicable investment category on the balance sheet.
Through our investing activities, we are exposed to financial market risks, including those resulting from changes in interest rates and changes in equity market valuations. We manage the market risks through our investment policy, which establishes credit quality limits and limits of investments in individual issuers. Ineffective management of these risks could have an impact on our future earnings and financial position.
We have evaluated the impact on the fixed maturity portfolio’s fair value considering an immediate 100 basis point change in interest rates. A 100 basis point increase in interest rates would result in an approximate $619.0 million decrease in fair value, whereas a 100 basis point decrease in interest rates would result in an approximate $583.0 million increase in fair value. An immediate 10% decrease in each equity investment’s value, arising from market movement, would result in a fair value decrease of $207.1 million. Alternatively, an immediate 10% increase in each equity investment’s value, attributable to the same factor, would result in a fair value increase of $207.1 million.
For additional information, see Part II, Item 7A, Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk, of this Form 10-K, and Note 5 to our audited consolidated financial statements as of and for the year ended December 31, 2006 included in this Form 10-K.
Retirement Benefits
Pension Benefits
We sponsor defined benefit pension plans for our employees, including plans sponsored by the former WellChoice and WHN prior to the related mergers. These plans are accounted for in accordance with FAS 87,Employers’ Accounting for Pensions, which requires that amounts recognized in financial statements be determined on an actuarial basis. As permitted by FAS 87, we calculate the value of plan assets described below. Further, the difference between our expected rate of return and the actual performance of plan assets, as well as certain changes in pension liabilities, are amortized over future periods.
71
Table of Contents
An important factor in determining our pension expense is the assumption for expected long-term return on plan assets. As of our September 30, 2006 measurement date, we selected a long-term rate of return on plan assets of 8.00% for all plans. We use a total portfolio return analysis in the development of our assumption. Factors such as past market performance, the long-term relationship between fixed maturity and equity securities, interest rates, inflation and asset allocations are considered in the assumption. The assumption includes an estimate of the additional return expected from active management of the investment portfolio. Peer data and historical returns are also reviewed for appropriateness of the selected assumption. The expected long-term rate of return is calculated by the geometric averaging method, which calculates an expected multi-period return, reflecting volatility drag on compound returns. We believe our assumption of future returns is reasonable. However, if we lower our expected long-term return on plan assets, future contributions to the pension plan and pension expense would likely increase.
The assumed long-term rate of return on assets is applied to a calculated value of plan assets, which recognizes changes in the fair value of plan assets in a systematic manner over three years, producing the expected return on plan assets that is included in the determination of pension expense. The difference between this expected return and the actual return on plan assets is deferred and amortized over the average remaining service of the workforce as a component of pension expense. The net deferral of past asset gains or losses affects the calculated value of plan assets and, ultimately, future pension expense.
The discount rate reflects the current rate at which the pension liabilities could be effectively settled at the end of the year based on our September 30, 2006 measurement date. The selected discount rate for all plans is 5.90% (compared to a weighted average discount rate of 5.31% for 2006 expense recognition), which was developed using a yield curve approach. Using yields available on high-quality fixed maturity securities with various maturity dates, the yield curve approach provides a “customized” rate, which is meant to match the expected cash flows of our specific benefit plans. The net effect of changes in the discount rate, as well as the net effect of other changes in actuarial assumptions and experience, have been deferred and amortized as a component of pension expense in accordance with FAS 87.
In managing the plan assets, our objective is to be a responsible fiduciary while minimizing financial risk. Plan assets include a diversified mix of investment grade fixed maturity securities and equity securities across a range of sectors and levels of capitalization to maximize the long-term return for a prudent level of risk. In addition to producing a reasonable return, the investment strategy seeks to minimize the volatility in the Company’s expense and cash flow. As of our September 30, 2006 measurement date, we had approximately 67% of plan assets invested in equity securities, 27% in fixed maturity securities and 6% in other assets. No plan assets were invested in WellPoint common stock as of the measurement date.
For the year ended December 31, 2006, there were no contributions required under the Employee Retirement Income Securities Act of 1974, as amended, or ERISA; however we elected to make discretionary contributions totaling $108.6 million during the three months ended September 30, 2006. For the year ending December 31, 2007, we do not expect any required contributions under ERISA; however, we may elect to make discretionary contributions up to the maximum amount deductible for income tax purposes.
At December 31, 2006, our consolidated net prepaid pension asset was $274.1 million. For the years ended December 31, 2006, 2005 and 2004, we recognized consolidated pretax pension expense of $32.6 million, $48.6 million and $40.8 million, respectively.
Effective January 1, 2006, we curtailed the benefits under the WellPoint Cash Balance Pension Plan, or the Plan, which name changed from the Anthem Cash Balance Pension Plan effective January 1, 2006. Most participants will no longer have pay credits added to their accounts, but continue to earn interest on existing account balances. Employees hired on or after January 1, 2006, are not eligible to participate in the Plan. Certain participants will be “grandfathered” into the Plan based on age and years of service in previously merged plans. Grandfathered participants continue to receive pay credits under the Plan formula. We recorded a curtailment
72
Table of Contents
gain of $4.6 million in the first quarter of 2006. We increased our matching contributions to certain defined contribution plans during 2006 at amounts equal to or greater than the curtailment gain amount.
The Empire Blue Cross Blue Shield Cash Balance Pension Plan, or the Empire Plan, was merged into the Plan on December 31, 2006. Effective January 1, 2007, we curtailed the benefits under the Empire Plan. Most participants will no longer have pay credits added to their accounts, but will continue to earn interest on existing account balances. Participants will continue to earn years of service for vesting. Employees hired on or after January 1, 2007 will not be able to participate in the Plan. Certain participants will be “grandfathered” into the Plan based on age and years of service in the Empire Plan. Grandfathered participants will continue to receive pay credits under the Plan formula. There will be no curtailment gain or loss associated with the curtailment of benefits under the Empire Plan.
Other Postretirement Benefits
We provide most associates with certain life, medical, vision and dental benefits upon retirement. We use various actuarial assumptions including a discount rate and the expected trend in health care costs to estimate the costs and benefit obligations for our retiree benefits. We recognized a postretirement benefit liability of $554.4 million at December 31, 2006.
At our September 30, 2006 measurement date, the selected discount rate for all plans was 5.90% (compared to a weighted average discount rate of 5.29% for 2006 expense recognition). We developed this rate using a yield curve approach as described above.
The assumed health care cost trend rates used to measure the expected cost of other benefits at our September 30, 2006 measurement dates was 9.00% for 2007 with a gradual decline to 5.00% by the year 2012. These estimated trend rates are subject to change in the future. The health care cost trend assumption has a significant effect on the amounts reported. For example, an increase in the assumed health care cost trend rate of one percentage point would increase the postretirement benefit obligation as of December 31, 2006 by $44.3 million and would increase service and interest costs by $2.9 million. Conversely, a decrease in the assumed health care cost trend rate of one percentage point would decrease the postretirement benefit obligation by $38.1 million as of December 31, 2006 and would decrease service and interest costs by $2.6 million.
For additional information regarding retirement benefits, see Note 17 to our audited consolidated financial statements as of and for the year ended December 31, 2006 included in this Form 10-K. See alsoNew Accounting Pronouncementsdisclosure included in this Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates section of our MD&A for discussion of new accounting guidance related to retirement benefits.
New Accounting Pronouncements
We maintain a share-based employee compensation plan. Prior to January 1, 2006, we accounted for the plan under the recognition and measurement provisions of Accounting Principles Board Opinion No. 25,Accounting for Stock Issued to Employees (“APB 25”). Effective January 1, 2006, we adopted the fair value recognition provisions of FAS 123R under the modified prospective method of adoption for which compensation expense related to stock options is recognized on a prospective basis. Also in accordance with the prospective method of adoption, prior period results have not been restated. See Note 2, Basis of Presentation and Significant Accounting Policies, and Note 12, Capital Stock, to our audited consolidated financial statements as of and for the year ended December 31, 2006 included in this Form 10-K.
In July 2006, FASB issued FASB Interpretation No. 48,Accounting for Uncertainty in Income Taxes-an interpretation of FASB Statement 109 (“FIN 48”). Among other things, FIN 48 creates a model to address uncertainty in tax positions and clarifies the accounting for income taxes by prescribing a minimum recognition threshold which all income tax positions must achieve before being recognized in the financial statements. In
73
Table of Contents
addition, FIN 48 requires expanded annual disclosures, including a rollforward of the beginning and ending aggregate unrecognized tax benefits as well as specific detail related to tax uncertainties for which it is reasonably possible the amount of unrecognized tax benefit will significantly increase or decrease within twelve months. FIN 48 was effective for us on January 1, 2007. Any differences between the amounts recognized in the statements of financial position prior to the adoption of FIN 48 and the amounts reported after adoption are generally accounted for as a cumulative-effect adjustment recorded to the beginning balance of retained earnings. We do not expect the adoption of FIN 48 to have a material impact on our beginning retained earnings at January 1, 2007. See Note 2 to our audited consolidated financial statements as of and for the year ended December 31, 2006 included in this Form 10-K.
In September 2006, FASB issued Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 158,Employers’ Accounting for Defined Benefit Pension and Other Postretirement Plans – an amendment of FASB Statements No. 87, 88, 106, and 132(R)(“FAS 158”). FAS 158 retains the previous measurement and disclosure requirements of prior accounting guidance. In addition, FAS 158 requires the recognition of the funded status of pension and other postretirement benefit plans on the balance sheet (“recognition provisions”). Furthermore, for fiscal years ending after December 15, 2008, FAS 158 requires fiscal-year-end measurements of plan assets and benefit obligations, eliminating the use of earlier measurement dates which are currently permissible. The recognition provisions of FAS 158 were effective for us on December 31, 2006. The adoption of FAS 158 decreased our accumulated other comprehensive income by $99.5 million at December 31, 2006. See Note 2 to our audited consolidated financial statements as of and for the year ended December 31, 2006 included in this Form 10-K.
There were no other new accounting pronouncements issued during 2006 that had a material impact on our financial position, operating results or disclosures.
X. Liquidity and Capital Resources
Introduction
Our cash receipts result primarily from premiums, administrative fees, investment income, other revenue, proceeds from the sale or maturity of our investment securities, proceeds from borrowings, and proceeds from exercise of stock options and our employee stock purchase plan. Cash disbursements result mainly from claims payments, administrative expenses, taxes, purchases of investment securities, interest expense, payments on long-term borrowings, capital expenditures and repurchases of our common stock. Cash outflows fluctuate with the amount and timing of settlement of these transactions. Any future decline in our profitability would likely have some negative impact on our liquidity.
We manage our cash, investments and capital structure so we are able to meet the short and long-term obligations of our business while maintaining financial flexibility and liquidity. We forecast, analyze and monitor our cash flows to enable investment and financing within the overall constraints of our financial strategy.
A substantial portion of the assets held by our regulated subsidiaries are in the form of cash and cash equivalents and investments. After considering expected cash flows from operating activities, we generally invest cash that exceeds our near term obligations in longer term marketable fixed maturity securities, to improve our overall investment income returns. Our investment strategy is to make investments consistent with insurance statutes and other regulatory requirements, while preserving our asset base. Our investments are generally available-for-sale to meet liquidity and other needs. Excess capital at our subsidiaries is paid annually by subsidiaries in the form of dividends to their respective parent companies for general corporate use, as permitted by applicable regulations.
The availability of financing in the form of debt or equity is influenced by many factors including our profitability, operating cash flows, debt levels, debt ratings, contractual restrictions, regulatory requirements and market conditions. We have access to a $2.5 billion commercial paper program supported by a $2.5 billion senior credit facility, which allows us to maintain further operating and financial flexibility.
74
Table of Contents
Liquidity—Year Ended December 31, 2006 Compared to Year Ended December 31, 2005
During 2006, net cash flow provided by operating activities was $4,044.2 million, compared to $3,135.5 million in 2005, an increase of $908.7 million. This increase resulted from improved premium collections, and higher net income, including the impact of the acquisition of WellChoice, partially offset by higher tax payments.
Net cash flow used in investing activities was $457.3 million in 2006, compared to $5,151.6 million of cash used in 2005. The table below outlines the decrease in cash flow used in investing activities of $4,694.3 million between the two periods:
| Change in Cash Used in Investing Activities | ||||
| (In millions) | ||||
Decrease in net purchases of investments | $ | 1,441.8 | ||
Decrease in securities lending collateral | 1,216.6 | |||
Decrease in net purchases of subsidiaries | 2,471.5 | |||
Increase in net purchases of property and equipment | (35.9 | ) | ||
Increase in other, net | (399.7 | ) | ||
Net decrease in cash used in investing activities | $ | 4,694.3 | ||
The decrease in net purchases of investments resulted from the portfolio restructure in 2005 following the WHN merger, with lower amounts of restructuring in 2006 following the WellChoice acquisition. The decrease in securities lending collateral is consistent with the decrease in amounts outstanding under this program. The offset to the reduction of securities lending collateral is a reduction of securities lending payable, which is reported with cash used in financing activities. The decrease in net purchase of subsidiaries resulted from the WellChoice acquisition in 2005, with no corresponding acquisition during 2006. The increase in other, net includes the purchase of corporate-owned life insurance policies on participants in our deferred compensation plans.
Net cash flow used in financing activities was $3,725.0 million in 2006 compared to cash provided by financing activities of $3,299.1 million in 2005. The table below outlines the increase in cash used in financing activities of $7,024.1 million between the two periods:
| Change in Cash Used in Financing Activities | ||||
| (In millions) | ||||
Decrease in net proceeds from commercial paper borrowings | $ | (1,114.2 | ) | |
Decrease in net proceeds from long-term borrowings | (1,038.8 | ) | ||
Decrease in securities lending payable | (1,216.6 | ) | ||
Increase in bank overdrafts | 293.1 | |||
Increase in repurchases of common stock | (4,216.8 | ) | ||
Increase in proceeds from exercise of employee stock options and employee stock purchase plan | 130.2 | |||
Decrease in proceeds from sale of put options and costs related to issuance of common stock | 2.5 | |||
Increase in excess tax benefits from share-based compensation | 136.5 | |||
Net increase in cash used in financing activities | $ | (7,024.1 | ) | |
The decrease in net proceeds from commercial paper borrowings reflects repayment of commercial paper following our offering of senior unsecured notes in January 2006 as compared to net issuances of commercial paper in 2005 used to partially fund the WellChoice acquisition. The decrease in net proceeds from long-term borrowings was impacted by issuance of the bridge loan of $1,700.0 in 2005, as compared to 2006 activity including our issuance of senior unsecured notes of $2,700.0 in January 2006, repayment of the bridge loan in January 2006 and scheduled debt maturity of $450.0 in July 2006.
75
Table of Contents
On January 10, 2006, we issued $700.0 million of 5.000% notes due 2011; $1,100.0 million of 5.250% notes due 2016; and $900.0 million of 5.850% notes due 2036 under a registration statement filed on December 28, 2005. The proceeds from this debt issuance were used to repay a bridge loan of $1,700.0 million and approximately $1,000.0 million in commercial paper borrowed to partially fund the December 28, 2005 WellChoice acquisition.
Our securities lending payable declined during 2006, reflecting reduced amounts outstanding under the program. The offset to this is included in cash used in investing activities above.
The increase in bank overdrafts reflects an increase in checks issued but outstanding at December 31, 2006 as compared to December 31, 2005.
We increased our common stock repurchases during 2006, completing an additional $4,216.8 million in 2006 as compared to 2005.
Liquidity—Year Ended December 31, 2005 Compared to Year Ended December 31, 2004
During 2005, net cash provided by operating activities was $3,135.5 million, as compared to $1,078.5 million in 2004, an increase of $2,057.0 million. The increase resulted from improved net income, including the impact of our merger with WHN. Net cash provided by operating activities for 2005 included a full year of WHN cash flow activity following the merger.
Net cash used in investing activities was $5,151.6 million in 2005, compared to cash used of $2,131.9 million in 2004, an increase in cash used of $3,019.7 million. The table below outlines the changes in investing cash flow between the two years:
| Change in Cash Used in Investing Activities | ||||
| (In millions) | ||||
Increase in net purchases of investments | $ | (1,749.7 | ) | |
Increase in net purchases of subsidiaries | (349.8 | ) | ||
Increase in net sale of subsidiaries | 92.8 | |||
Decrease in proceeds from settlement of a cash flow hedge | (15.7 | ) | ||
Increase in securities lending collateral | (973.4 | ) | ||
Increase in net purchases of property and equipment | (23.9 | ) | ||
Net increase in cash used in investing activities | $ | (3,019.7 | ) | |
The purchase of investment securities in 2005 increased from 2004 resulting from increased cash flows from operations driven by improved net income, including the impact of our merger with WHN. The increase in 2005 subsidiary purchases resulted primarily from the use of cash for the WellChoice and Lumenos acquisitions, as compared to cash used for the WHN merger in 2004. The increase in 2005 sale of subsidiaries resulted primarily from the receipt of cash for the sale of certain subsidiaries, as compared to no activity in 2004. The increase in securities lending collateral reflects increased amounts under this program. The offset to this is an increase in securities lending payable which is reported with cash provided by financing activities.
76
Table of Contents
Net cash flow provided by financing activities was $3,299.1 million in 2005 compared to cash provided by financing activities of $2,046.1 million in 2004. The table below outlines the increase in cash flow provided by financing activities of $1,253.0 million between the two years:
| Change in Cash Provided by Financing Activities | ||||
| (In millions) | ||||
Increase in proceeds from exercise of employee stock options and employee stock purchase plan | $ | 270.3 | ||
Increase in repurchases of common stock | (251.1 | ) | ||
Increase in net proceeds from commercial paper borrowings | 15.0 | |||
Decrease in repayment of long-term borrowings | 643.4 | |||
Decrease in long-term borrowings | (70.2 | ) | ||
Decrease in proceeds from issuance of common stock under Equity Security Units stock purchase contracts | (230.0 | ) | ||
Increase in securities lending payable | 973.4 | |||
Decrease in bank overdrafts | (103.5 | ) | ||
Other | 5.7 | |||
Net increase in cash provided by financing activities | $ | 1,253.0 | ||
The increase in proceeds from the exercise of employee stock options reflects the significant increase in employees with vested options due to our merger with WHN. The increase in repurchases of common stock reflects the activity in our Board-approved common stock repurchase program. The decrease in repayments of long-term debt resulted primarily from the significant amount of repayments in 2004 as new long-term debt was issued to partially pay off outstanding long-term debt and fund the WHN merger. The decrease in proceeds from the issuance of common stock under Equity Security Units stock purchase contracts reflects the maturity of these instruments in 2004.
The increase in securities lending payable reflects increased amounts outstanding under this program, and is offset in cash used in investing activities. The decrease in bank overdrafts reflects fewer checks issued but outstanding at December 2005 as compared to December 2004.
Financial Condition
We maintained a strong financial condition and liquidity position, with consolidated cash, cash equivalents and investments, including long-term investments, of $20.8 billion at December 31, 2006. Since December 31, 2005, total cash, cash equivalents and investments, including long-term investments, increased by $476.2 million as cash generated from operations was used for the repurchase of our common stock.
Many of our subsidiaries are subject to various government regulations that restrict the timing and amount of dividends and other distributions that may be paid to their respective parent companies. Also, in connection with the WHN merger, the Company and certain of our subsidiaries in California and Georgia executed undertakings with the California Department of Managed Health Care, the California Department of Insurance and the Georgia Department of Insurance which contained various commitments, including the commitment to provide $61.5 million of support for health benefit programs in those states. Additional undertakings include the requirement to maintain certain capital levels at those subsidiaries.
During 2006, we received $2.3 billion of dividends from our subsidiaries. At December 31, 2006, we held at the parent company approximately $1.7 billion of cash, cash equivalents and investments, which is available for general corporate use, including investment in our businesses, acquisitions, share and debt repurchases and interest payments.
77
Table of Contents
Our consolidated debt-to-total capital ratio (calculated as the sum of debt divided by the sum of debt plus shareholders’ equity) was 22.2% as of December 31, 2006 and 21.4% as of December 31, 2005, which increased only slightly considering our $4.6 billion of common stock repurchases during 2006.
Our senior debt is rated “BBB+” by Standard & Poor’s, “A-” by Fitch, Inc., “Baa1” by Moody’s Investor Service, Inc. and “a-” by AM Best Company, Inc. We intend to maintain our senior debt investment grade ratings. A significant downgrade in our debt ratings could adversely affect our borrowing capacity and costs.
Future Sources and Uses of Liquidity
On December 28, 2005, we filed a shelf registration with the Securities and Exchange Commission to register an unlimited amount of any combination of debt or equity securities in one or more offerings. At the time of an offering, specific information regarding terms of the offering and the securities being offered will be provided. Proceeds from any future offerings are expected to be used for general corporate purposes, including the repayment of debt, capitalization of our subsidiaries or the financing of possible acquisitions or business expansion. On January 10, 2006, we issued $700.0 million of 5.000% notes due 2011; $1.1 billion of 5.250% notes due 2016; and $900.0 million of 5.850% notes due 2036 under this registration statement. The proceeds from this debt issuance were used to repay a bridge loan of $1,700.0 million and $1,000.0 million in commercial paper borrowed to partially fund the December 28, 2005 acquisition of WellChoice.
On November 29, 2005, we entered into a senior revolving credit facility, or the facility, with certain lenders for general corporate purposes. We amended the facility on September 21, 2006. The facility, as amended, provides credit up to $2.5 billion (reduced for any commercial paper issuances) and matures on September 30, 2011. The interest rate on this facility is based on either (i) the LIBOR rate plus a predetermined percentage rate based on our credit rating at the date of utilization, or (ii) a base rate as defined in the facility agreement. Our ability to borrow under this facility is subject to compliance with certain covenants. There were no amounts outstanding under this facility as of December 31, 2006 or during the year then ended. At December 31, 2006, we had $1.2 billion available under this facility.
We have Board of Directors’ approval to borrow up to $2.5 billion under our commercial paper program (increased from $2.0 billion on March 15, 2006). Proceeds from any issuance of commercial paper may be used for general corporate purposes, including the repurchase of our debt and common stock. Commercial paper notes are short-term senior unsecured notes, with a maturity not to exceed 270 days from date of issuance. When issued, the notes bear interest at the then current market rates. There were $1.3 billion of borrowings outstanding under this commercial paper program as of December 31, 2006. Commercial paper borrowings outstanding at December 31, 2006 are classified as long-term debt as our practice and intent is to replace short-term commercial paper outstanding at expiration with additional short-term commercial paper for an uninterrupted period extending for more than one year or with borrowings under our senior credit facility.
As discussed in “Financial Condition” above, many of our subsidiaries are subject to various government regulations that restrict the timing and amount of dividends and other distributions that may be paid. Based upon these requirements, we are currently estimating approximately $2.7 billion of dividends to be paid to the parent company during 2007.
During December 2004, WellPoint completed a tender offer to purchase subsidiary surplus notes from the holders, and purchased $258.0 million of 9.125% notes due 2010 and $174.9 million of 9.000% notes due 2027. During December 2006, the subsidiary repurchased these surplus notes from WellPoint.
We maintain a common stock repurchase program as authorized by our Board of Directors. Repurchases may be made from time to time at prevailing market prices, subject to certain restrictions on volume, pricing and timing. We purchased approximately 60.7 million shares during the year ended December 31, 2006 at a cost of $4.6 billion. On March 15, May 16, August 17 and December 7, 2006, our Board of Directors authorized
78
Table of Contents
increases of $1.0 billion, $1.0 billion, $0.5 billion and $1.0 billion, respectively, in our common stock repurchase program, which increased the total authorized common stock repurchases to $5.5 billion since the current program’s inception in 2005. As of December 31, 2006, we had $0.9 billion of authorization remaining under this program. Subsequent to December 31, 2006, we repurchased and retired approximately 6.0 million shares for an aggregate cost of approximately $463.5 million, leaving approximately $486.3 million for authorized future repurchases at February 12, 2007. Our stock repurchase program is discretionary as we are under no obligation to repurchase shares. We repurchase shares because we believe it is a prudent use of surplus capital.
Our current pension funding strategy is to fund an amount at least equal to the minimum required funding as determined under ERISA with consideration of maximum tax deductible amounts. For the year ended December 31, 2006, no contributions to retirement benefit plans under ERISA were required, however, the Company elected to make tax deductible discretionary contributions totaling $108.6 million.
Contractual Obligations and Commitments
Our estimated contractual obligations and commitments as of December 31, 2006 are as follows:
| Payments Due by Period | |||||||||||||||
| Total | Less than 1 Year | 1-3 Years | 3-5 Years | More than 5 Years | |||||||||||
(In millions) | |||||||||||||||
Long-term debt, including capital leases1 | $ | 10,871.9 | $ | 2,130.3 | $ | 908.5 | $ | 1,286.9 | $ | 6,546.2 | |||||
Operating lease commitments | 1,061.4 | 145.7 | 270.5 | 202.2 | 443.0 | ||||||||||
Projected other postretirement benefits | 919.1 | 37.5 | 200.9 | 207.6 | 473.1 | ||||||||||
Purchase obligations: | |||||||||||||||
IBM outsourcing agreements2 | 935.6 | 170.1 | 340.2 | 340.2 | 85.1 | ||||||||||
Other purchase obligations3 | 450.0 | 105.2 | 149.5 | 128.6 | 66.7 | ||||||||||
Other long-term liabilities | 761.7 | — | 302.7 | 301.0 | 158.0 | ||||||||||
Venture capital commitments | 261.5 | 88.0 | 164.4 | 7.8 | 1.3 | ||||||||||
Total contractual obligations and commitments | $ | 15,261.2 | $ | 2,676.8 | $ | 2,336.7 | $ | 2,474.3 | $ | 7,773.4 | |||||
1 | Includes estimated interest expense. |
2 | Relates to agreements with International Business Machines Corporation, or IBM, to provide information technology infrastructure services. See Note 18 to the audited consolidated financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2006 for further information. |
3 | Includes obligations related to IT service agreements and telecommunication contracts. |
In addition to the contractual obligations and commitments discussed above, we have a variety of other contractual agreements related to acquiring materials and services used in our operations. However, we do not believe these other agreements contain material noncancelable commitments.
We believe that funds from future operating cash flows, cash and investments and funds available under our credit agreement or from public or private financing sources will be sufficient for future operations and commitments, and for capital acquisitions and other strategic transactions.
For additional information on our debt and lease commitments, see Notes 7 and 16, respectively, to our audited consolidated financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2006 included in this Form 10-K.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
We have agreed to guarantee up to $37.0 million of debt incurred by an unaffiliated entity to partially finance the purchase of a hospital.
79
Table of Contents
In connection with an investment in a joint venture to develop and operate a well-being center in California, we may be required, based on specific targets, to make additional capital contributions up to $18.0 million. The well-being center was completed and began operations during November 2006.
In connection with the formation in 2000 of a joint venture providing Medicaid services in Puerto Rico, we agreed under certain circumstances to provide additional funding to the joint venture entity. Since the formation of the joint venture in 2000, we have not been required to make any payments under this guarantee. During December 2006, the joint venture was terminated and the guarantee was extinguished.
For additional information on these off-balance sheet arrangements, see Note 18 to our audited consolidated financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2006 included in this Form 10-K.
Risk-Based Capital
Our regulated subsidiaries’ states of domicile have statutory risk-based capital, or RBC, requirements for health and other insurance companies largely based on the NAIC’s RBC Model Act. These RBC requirements are intended to measure capital adequacy, taking into account the risk characteristics of an insurer’s investments and products. The NAIC sets forth the formula for calculating the RBC requirements, which are designed to take into account asset risks, insurance risks, interest rate risks and other relevant risks with respect to an individual insurance company’s business. In general, under this Act, an insurance company must submit a report of its RBC level to the state insurance department or insurance commissioner, as appropriate, at the end of each calendar year. Our risk-based capital as of December 31, 2006, which was the most recent date for which reporting was required, was in excess of all mandatory RBC thresholds. In addition to exceeding the RBC requirements, we are in compliance with the liquidity and capital requirements for a licensee of the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association and with the tangible net worth requirements applicable to certain of our California subsidiaries.
XI. Safe Harbor Statement under the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995
This document contains certain forward-looking information about WellPoint, Inc. (“WellPoint”) that is intended to be covered by the safe harbor for “forward-looking statements” provided by the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. Forward-looking statements are statements that are not historical facts. Words such as “expect(s)”, “feel(s)”, “believe(s)”, “will”, “may”, “anticipate(s)” and similar expressions are intended to identify forward-looking statements. These statements include, but are not limited to, financial projections and estimates and their underlying assumptions; statements regarding plans, objectives and expectations with respect to future operations, products and services; and statements regarding future performance. Such statements are subject to certain risks and uncertainties, many of which are difficult to predict and generally beyond the control of WellPoint, that could cause actual results to differ materially from those expressed in, or implied or projected by, the forward-looking information and statements. These risks and uncertainties include: those discussed and identified in public filings with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) made by WellPoint; trends in health care costs and utilization rates; our ability to secure sufficient premium rate increases; competitor pricing below market trends of increasing costs; increased government regulation of health benefits, managed care and pharmacy benefit management operations; risks and uncertainties regarding the Medicare Part D Prescription Drug benefits program, including potential uncollectability of receivables resulting from processing and/or verifying enrollment (including facilitated enrollment), inadequacy of underwriting assumptions, inability to receive and process information, uncollectability of premium from members, increased pharmaceutical costs, and the underlying seasonality of the business; significant acquisitions or divestitures by major competitors; introduction and utilization of new prescription drugs and technology; a downgrade in our financial strength ratings; litigation and investigations targeted at health benefits companies and our ability to resolve litigation and investigations within estimates; our ability to contract with providers consistent with past practice; other potential uses of cash in the future that present attractive alternatives to share repurchases; our ability to achieve expected synergies and operating efficiencies in the WellChoice, Inc. acquisition within the expected time frames or at all, and to successfully
80
Table of Contents
integrate our operations; our ability to meet expectations regarding repurchases of shares of our common stock; future bio-terrorist activity or other potential public health epidemics; and general economic downturns. Readers are cautioned not to place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements that speak only as of the date hereof. WellPoint does not undertake any obligation to republish revised forward-looking statements to reflect events or circumstances after the date hereof or to reflect the occurrence of unanticipated events. Readers are also urged to carefully review and consider the various disclosures in WellPoint’s various SEC reports.
ITEM 7A. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK.
As a result of our investing and borrowing activities, we are exposed to financial market risks, including those resulting from changes in interest rates and changes in equity market valuations. Potential impacts discussed below are based upon sensitivity analyses performed on WellPoint’s financial position as of December 31, 2006. Actual results could vary from these estimates. Our primary objectives with our investment portfolio are to provide safety and preservation of capital, sufficient liquidity to meet cash flow requirements, the integration of investment strategy with the business operations and an attainment of a competitive after-tax total return.
Investments
Our investment portfolio is exposed to three primary sources of risk: credit quality risk, interest rate risk and market valuation risk.
The primary risks associated with our fixed maturity securities are credit quality risk and interest rate risk. Credit quality risk is defined as the risk of a credit downgrade to an individual fixed maturity security and the potential loss attributable to that downgrade. Credit quality risk is managed through our investment policy, which establishes credit quality limitations on the overall portfolio as well as diversification and percentage limits on securities of individual issuers. The result is a well-diversified portfolio of fixed maturity securities, with an average credit rating of approximately AA. Interest rate risk is defined as the potential for economic losses on fixed maturity securities due to a change in market interest rates. Our fixed maturity portfolio is invested primarily in U.S. government securities, corporate bonds, asset-backed bonds, mortgage-related securities and municipal bonds, all of which represent an exposure to changes in the level of market interest rates. Interest rate risk is managed by maintaining asset duration within a band based upon our liabilities, operating performance and liquidity needs. Additionally, we have the capability of holding any security to maturity, which would allow us to realize full par value.
Our portfolio includes corporate securities (approximately 34% of the total fixed maturity portfolio at December 31, 2006), which are subject to credit/default risk. In a declining economic environment, corporate yields will usually increase prompted by concern over the ability of corporations to make interest payments, thus causing a decrease in the price of corporate securities, and the decline in value of the corporate fixed maturity portfolio. This risk is managed through fundamental credit analysis, diversification of issuers and industries and an average credit rating of the corporate fixed maturity portfolio of approximately A-.
Our equity portfolio is comprised of large capitalization and small capitalization domestic equities, foreign equities and index mutual funds. Our equity portfolio is subject to the volatility inherent in the stock market, driven by concerns over economic conditions, earnings and sales growth, inflation, and consumer confidence. These systematic risks cannot be managed through diversification alone. However, more routine risks, such as stock/industry specific risks, are managed by investing in a diversified equity portfolio.
As of December 31, 2006, approximately 88% of our available-for-sale investments were fixed maturity securities. Market risk is addressed by actively managing the duration, allocation and diversification of our investment portfolio. We have evaluated the impact on the fixed maturity portfolio’s fair value considering an immediate 100 basis point change in interest rates. A 100 basis point increase in interest rates would result in an
81
Table of Contents
approximate $619.0 million decrease in fair value, whereas a 100 basis point decrease in interest rates would result in an approximate $583.0 million increase in fair value. While we classify our fixed maturity securities as “available-for-sale” for accounting purposes, we believe our cash flows and duration of our portfolio should allow us to hold securities to maturity, thereby avoiding the recognition of losses should interest rates rise significantly.
Our available-for-sale equity securities portfolio, as of December 31, 2006, was approximately 12% of our investments. An immediate 10% decrease in each equity investment’s value, arising from market movement, would result in a fair value decrease of $207.1 million. Alternatively, an immediate 10% increase in each equity investment’s value, attributable to the same factor, would result in a fair value increase of $207.1 million.
Long-Term Debt
Our total long-term debt at December 31, 2006 was $7.0 billion, and included $1.3 billion of commercial paper. The carrying value of the commercial paper approximates fair value as the underlying instruments have variable interest rates at market value. The remainder of the debt is subject to interest rate risk as these instruments have fixed interest rates and the fair value is affected by changes in market interest rates.
At December 31, 2006, we had $5.6 billion of senior unsecured notes with fixed interest rates. These notes, at par value, included $200.0 million at 3.50% due 2007, $300.0 million at 3.75% due 2007, $300.0 million at 4.25% due 2009, $700.0 million at 5.000% due 2011, $350.0 million at 6.375% due 2012, $800.0 million at 6.80% due 2012, $500.0 million at 5.00% due 2014, $1,100.0 million at 5.250% due 2016, $500.0 million at 5.95% due 2034 and $900.0 at 5.850% due 2036. These notes had combined carrying and estimated fair value of $5.6 billion and $5.6 billion, respectively, at December 31, 2006.
Our subordinated debt includes surplus notes issued by one of our insurance subsidiaries. Par value of amounts outstanding at December 31, 2006 included $42.0 million of 9.125% surplus notes due 2010 and $25.1 million of 9.000% surplus notes due 2027. Any payment of interest or principal on the surplus notes may be made only with the prior approval of the Indiana Department of Insurance. The combined carrying value of the surplus notes was $66.6 million and $66.5 million at December 31, 2006 and 2005, respectively. The estimated fair value of the surplus notes exceeded the carrying value by $13.6 million and $16.7 million at December 31, 2006 and 2005, respectively.
Should interest rates increase or decrease in the future, the estimated fair value of our fixed rate debt would decrease or increase accordingly.
Derivatives
We use derivative financial instruments, specifically interest rate swap agreements, to hedge exposure in interest rate risk on our borrowings. Our derivative use is generally limited to hedging purposes and we generally do not use derivative instruments for speculative purposes.
During the year ended December 31, 2006, we entered into two fair value hedges with a total notional value of $440.0 million. The first hedge is a $240.0 million notional amount interest rate swap agreement to receive a fixed 6.800% rate and pay a LIBOR-based floating rate and expires on August 1, 2012. The second hedge is a $200.0 million notional amount interest rate swap agreement to receive a fixed 5.000% rate and pay a LIBOR-based floating rate and expires on December 15, 2014.
During the year ended December 31, 2005, we entered into two fair value hedges with a total notional value of $660.0 million. The first hedge is a $360.0 million notional amount interest rate swap agreement to exchange a fixed 6.800% rate for a LIBOR-based floating rate and expires on August 1, 2012. The second hedge is a $300.0 million notional amount interest rate swap agreement to exchange a fixed 5.000% rate for LIBOR-based floating
82
Table of Contents
rate and expires December 15, 2014. During the year ended December 31, 2004, we entered into a $300.0 million notional amount interest rate swap agreement to exchange a fixed 3.750% rate for a LIBOR-based floating rate. This swap agreement expires on December 14, 2007.
During the year ended December 31, 2005, we entered into a floating to fixed rate cash flow hedge with a total notional value of $480.0 million. The purpose of this hedge is to offset the variability of the cash flows due to the rollover of our variable-rate one-month commercial paper issuance. In December 2006, the total notional value was reduced to $240.0 million. This swap agreement expires in December 2007. During the year ended December 31, 2006 and 2005, no gain or loss from hedged ineffectiveness was recorded in earnings and the commercial paper borrowings remain outstanding at December 31, 2006.
Changes in interest rates will affect the estimated fair value of these swap agreements. As of December 31, 2006, we recorded an asset of $17.4 million and a liability of $29.0 million, the estimated fair value of the swaps at that date. We have evaluated the impact on the interest rate swap’s fair value considering an immediate 100 basis point change in interest rates. A 100 basis point increase in interest rates would result in an approximate $59.2 million decrease in fair value, whereas a 100 basis point decrease in interest rates would result in an approximate $59.2 million increase in fair value.
During the year ended December 31, 2005, we entered into forward starting pay fixed swaps with an aggregate notional amount of $875.0 million. The objective of these hedges was to eliminate the variability of cash flows in the interest payments on the debt securities to be issued to partially fund the cash portion of the WellChoice acquisition. These swaps were terminated in January 2006, and we paid a net $24.7 million, the net fair value at the time of termination. In addition, we recorded an unrealized loss of $16.0 million, net of tax, as accumulated other comprehensive income. Following the January 10, 2006 issuance of debt securities in connection with the WellChoice acquisition, the unamortized fair value of the forward starting pay fixed swaps included in accumulated other comprehensive income began amortizing into earnings, as an increase to interest expense, over the life of the hedged debt securities.
During the year ended December 31, 2004, we entered into forward starting pay fixed swaps and treasury lock swaps with an aggregate notional amount of $2.0 billion. The objective of these hedges was to eliminate the variability of cash flows in the interest payments on the debt securities to be issued to partially fund the cash portion of the WHN merger. These swaps were terminated in 2004, and we received a net $15.7 million, the net fair value at the time of termination. In addition, we recorded an unrealized gain of $10.2 million, net of tax, as accumulated other comprehensive income. Following the completion of the WHN merger on November 30, 2004, we issued debt securities, and the unamortized fair value of the forward starting pay fixed swaps included in balances in accumulated other comprehensive income began amortizing into earnings, as a reduction of interest expense, over the life of the debt securities.
The unrecognized loss for all cash flow hedges included in accumulated other comprehensive income at December 31, 2006 was $5.6 million. As of December 31, 2006, the total amount of amortization over the next twelve months for all cash flow hedges will increase interest expense by approximately $0.7 million.
83
Table of Contents
ITEM 8. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA.
WELLPOINT, INC.
CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Years ended December 31, 2006, 2005 and 2004
Contents
| 85 | ||
Audited Consolidated Financial Statements: | ||
| 86 | ||
| 87 | ||
| 88 | ||
| 89 | ||
| 90 | ||
84
Table of Contents
Report of Independent Registered
Public Accounting Firm
Shareholders and Board of Directors
WellPoint, Inc.
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of WellPoint, Inc. (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2006 and 2005, and the related consolidated statements of income, shareholders’ equity, and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2006. Our audits also included the financial statement schedule listed in the Index at Item 15(a). These financial statements and schedule are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements and schedule based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the consolidated financial position of WellPoint, Inc. at December 31, 2006 and 2005, and the consolidated results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2006, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles. Also, in our opinion, the related financial statement schedule, when considered in relation to the basic financial statements taken as a whole, presents fairly in all material respects the information set forth therein.
As discussed in Note 2 to the consolidated financial statements, during 2006, the Company changed its method of accounting for the recognition of share-based compensation expense and the recognition of the funded status of its defined benefit pension and postretirement plans.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the effectiveness of WellPoint, Inc.’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2006, based on criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission and our report dated February 14, 2007 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
/s/ ERNST & YOUNG LLP
Indianapolis, Indiana
February 14, 2007
85
Table of Contents
Consolidated Balance Sheets
| (In millions, except share data) | December 31 | ||||||
| 2006 | 2005 | ||||||
Assets | |||||||
Current assets: | |||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 2,602.1 | $ | 2,740.2 | |||
Investments available-for-sale, at fair value: | |||||||
Fixed maturity securities (amortized cost of $481.5 and $734.8) | 465.4 | 734.6 | |||||
Equity securities (cost of $1,669.7 and $1,388.4) | 1,984.5 | 1,448.2 | |||||
Other invested assets, current | 72.8 | 307.0 | |||||
Accrued investment income | 157.2 | 156.8 | |||||
Premium and self-funded receivables | 2,520.2 | 2,216.4 | |||||
Other receivables | 1,172.7 | 743.7 | |||||
Securities lending collateral | 904.7 | 1,389.9 | |||||
Deferred tax assets, net | 642.6 | 689.0 | |||||
Other current assets | 1,284.5 | 1,022.7 | |||||
Total current assets | 11,806.7 | 11,448.5 | |||||
Long-term investments available-for-sale, at fair value: | |||||||
Fixed maturity securities (amortized cost of $15,004.6 and $14,941.0) | 14,972.4 | 14,825.5 | |||||
Equity securities (cost of $82.7 and $71.3) | 86.2 | 72.7 | |||||
Other invested assets, long-term | 628.8 | 207.8 | |||||
Property and equipment, net | 988.6 | 1,078.6 | |||||
Goodwill | 13,383.5 | 13,469.1 | |||||
Other intangible assets | 9,396.2 | 9,686.4 | |||||
Other noncurrent assets | 497.4 | 498.6 | |||||
Total assets | $ | 51,759.8 | $ | 51,287.2 | |||
Liabilities and shareholders’ equity | |||||||
Liabilities | |||||||
Current liabilities: | |||||||
Policy liabilities: | |||||||
Medical claims payable | $ | 5,290.3 | $ | 4,853.4 | |||
Reserves for future policy benefits | 76.3 | 82.1 | |||||
Other policyholder liabilities | 2,240.6 | 1,752.3 | |||||
Total policy liabilities | 7,607.2 | 6,687.8 | |||||
Unearned income | 987.9 | 1,057.1 | |||||
Accounts payable and accrued expenses | 3,242.2 | 2,860.4 | |||||
Income taxes payable | 538.2 | 833.4 | |||||
Security trades pending payable | 124.8 | 181.8 | |||||
Securities lending payable | 904.7 | 1,389.9 | |||||
Current portion of long-term debt | 521.0 | 481.2 | |||||
Other current liabilities | 1,397.4 | 1,286.8 | |||||
Total current liabilities | 15,323.4 | 14,778.4 | |||||
Long-term debt, less current portion | 6,493.2 | 6,324.7 | |||||
Reserves for future policy benefits, noncurrent | 646.9 | 679.9 | |||||
Deferred tax liability, net | 3,350.2 | 3,267.1 | |||||
Other noncurrent liabilities | 1,370.3 | 1,244.0 | |||||
Total liabilities | 27,184.0 | 26,294.1 | |||||
Commitments and contingencies—Note 18 | |||||||
Shareholders’ equity | |||||||
Preferred stock, without par value, shares authorized—100,000,000; shares issued and outstanding—none | — | — | |||||
Common stock, par value $0.01, shares authorized—900, 000, 000; shares issued and outstanding: 615,500,865 and 660,424,174 | 6.1 | 6.6 | |||||
Additional paid-in capital | 19,863.5 | 20,915.4 | |||||
Retained earnings | 4,656.1 | 4,173.5 | |||||
Unearned share-based compensation | — | (82.1 | ) | ||||
Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) | 50.1 | (20.3 | ) | ||||
Total shareholders’ equity | 24,575.8 | 24,993.1 | |||||
Total liabilities and shareholders’ equity | $ | 51,759.8 | $ | 51,287.2 | |||
See accompanying notes.
86
Table of Contents
Consolidated Statements of Income
| (In millions, except per share data) | Years ended December 31 | ||||||||||
| 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | |||||||||
Revenues | |||||||||||
Premiums | $ | 51,971.9 | $ | 40,680.0 | $ | 18,678.3 | |||||
Administrative fees | 3,509.6 | 2,719.2 | 1,457.0 | ||||||||
Other revenue | 593.1 | 519.2 | 218.4 | ||||||||
Total operating revenue | 56,074.6 | 43,918.4 | 20,353.7 | ||||||||
Net investment income | 878.7 | 633.1 | 311.7 | ||||||||
Net realized (losses) gains on investments | (0.3 | ) | (10.2 | ) | 42.5 | ||||||
Total revenues | 56,953.0 | 44,541.3 | 20,707.9 | ||||||||
Expenses | |||||||||||
Benefit expense | 42,218.8 | 32,625.2 | 15,280.6 | ||||||||
Selling, general and administrative expense: | |||||||||||
Selling expense | 1,654.5 | 1,474.2 | 537.2 | ||||||||
General and administrative expense | 7,163.2 | 5,798.5 | 2,940.5 | ||||||||
Total selling, general and administrative expense | 8,817.7 | 7,272.7 | 3,477.7 | ||||||||
Cost of drugs | 301.2 | 288.0 | 95.0 | ||||||||
Interest expense | 403.5 | 226.2 | 142.3 | ||||||||
Amortization of other intangible assets | 297.4 | 238.9 | 61.4 | ||||||||
Merger-related undertakings | — | — | 61.5 | ||||||||
Loss on repurchase of debt securities | — | — | 146.1 | ||||||||
Total expenses | 52,038.6 | 40,651.0 | 19,264.6 | ||||||||
Income before income tax expense | 4,914.4 | 3,890.3 | 1,443.3 | ||||||||
Income tax expense | 1,819.5 | 1,426.5 | 483.2 | ||||||||
Net income | $ | 3,094.9 | $ | 2,463.8 | $ | 960.1 | |||||
Net income per share | |||||||||||
Basic | $ | 4.93 | $ | 4.03 | $ | 3.15 | |||||
Diluted | $ | 4.82 | $ | 3.94 | $ | 3.05 | |||||
See accompanying notes.
87
Table of Contents
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
| (In millions) | Years ended December 31 | |||||||||||
| 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | ||||||||||
Operating activities | ||||||||||||
Net income | $ | 3,094.9 | $ | 2,463.8 | $ | 960.1 | ||||||
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | ||||||||||||
Net realized losses (gains) on investments | 0.3 | 10.2 | (42.5 | ) | ||||||||
Loss on disposal of assets | 1.7 | 2.7 | 0.8 | |||||||||
Loss on repurchase of debt securities | — | — | 146.1 | |||||||||
Deferred income taxes | 273.7 | (102.6 | ) | (103.4 | ) | |||||||
Amortization, net of accretion | 471.9 | 437.9 | 191.0 | |||||||||
Depreciation expense | 133.0 | 118.7 | 78.1 | |||||||||
Share-based compensation | 246.9 | 81.2 | 10.0 | |||||||||
Excess tax benefits from share-based compensation | (136.5 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
Changes in operating assets and liabilities, net of effect of business combinations: | ||||||||||||
Receivables, net | (649.4 | ) | (230.4 | ) | (2.5 | ) | ||||||
Other invested assets, current | 234.9 | — | — | |||||||||
Other assets | (362.4 | ) | (165.6 | ) | (89.9 | ) | ||||||
Policy liabilities | 874.2 | 46.3 | 26.8 | |||||||||
Unearned income | (69.5 | ) | (38.2 | ) | 34.0 | |||||||
Accounts payable and accrued expenses | (91.7 | ) | 188.6 | (33.1 | ) | |||||||
Other liabilities | 134.2 | (136.7 | ) | 28.5 | ||||||||
Income taxes | (112.0 | ) | 459.6 | (125.5 | ) | |||||||
Net cash provided by operating activities | 4,044.2 | 3,135.5 | 1,078.5 | |||||||||
Investing activities | ||||||||||||
Purchases of fixed maturity securities | (11,198.0 | ) | (17,457.0 | ) | (7,242.7 | ) | ||||||
Proceeds from fixed maturity securities: | ||||||||||||
Sales | 9,630.1 | 14,391.4 | 6,273.5 | |||||||||
Maturities, calls and redemptions | 721.6 | 1,344.5 | 952.5 | |||||||||
Purchase of equity securities | (2,434.5 | ) | (4,530.6 | ) | (6.6 | ) | ||||||
Proceeds from sales of equity securities | 2,950.9 | 4,480.0 | 1.3 | |||||||||
Changes in securities lending collateral | 485.2 | (731.4 | ) | 242.0 | ||||||||
Purchases of subsidiaries, net of cash acquired | (25.4 | ) | (2,589.7 | ) | (2,239.9 | ) | ||||||
Proceeds from sales of subsidiaries, net of cash sold | — | 92.8 | — | |||||||||
Purchases of property and equipment | (193.9 | ) | (161.8 | ) | (136.8 | ) | ||||||
Proceeds from sale of property and equipment | 6.4 | 10.2 | 9.1 | |||||||||
Other, net | (399.7 | ) | — | 15.7 | ||||||||
Net cash used in investing activities | (457.3 | ) | (5,151.6 | ) | (2,131.9 | ) | ||||||
Financing activities | ||||||||||||
Net (repayments of) proceeds from commercial paper borrowings | (306.0 | ) | 808.2 | 793.2 | ||||||||
Proceeds from long-term borrowings | 2,668.2 | 1,700.0 | 1,770.2 | |||||||||
Repayment of long-term borrowings | (2,162.1 | ) | (155.1 | ) | (798.5 | ) | ||||||
Changes in securities lending payable | (485.2 | ) | 731.4 | (242.0 | ) | |||||||
Changes in bank overdrafts | 414.3 | 121.2 | 224.7 | |||||||||
Repurchase and retirement of common stock | (4,550.2 | ) | (333.4 | ) | (82.3 | ) | ||||||
Proceeds from exercise of employee stock options and employee stock purchase plan | 559.5 | 429.3 | 159.0 | |||||||||
Proceeds from sale of put options | — | 1.1 | — | |||||||||
Excess tax benefits from share-based compensation | 136.5 | — | — | |||||||||
Proceeds from issuance of common stock under Equity Security Unit stock purchase contracts | — | — | 230.0 | |||||||||
Costs related to issuance of common stock | — | (3.6 | ) | (8.2 | ) | |||||||
Net cash (used in) provided by financing activities | (3,725.0 | ) | 3,299.1 | 2,046.1 | ||||||||
Change in cash and cash equivalents | (138.1 | ) | 1,283.0 | 992.7 | ||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year | 2,740.2 | 1,457.2 | 464.5 | |||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at end of year | $ | 2,602.1 | $ | 2,740.2 | $ | 1,457.2 | ||||||
See accompanying notes.
88
Table of Contents
Consolidated Statements of Shareholders’ Equity
| (In millions) | Common Stock | Additional | Retained | Unearned Share-Based Compensation | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) | Total Shareholders’ Equity | |||||||||||||||||||||
Number of Shares | Par Value | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
January 1, 2004 | 137.6 | $ | 1.4 | $ | 4,708.7 | $ | 1,154.3 | $ | (3.2 | ) | $ | 138.7 | $ | 5,999.9 | |||||||||||||
Net income | — | — | — | 960.1 | — | — | 960.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Change in net unrealized gains on investments | — | — | — | — | — | (2.5 | ) | (2.5 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
Change in net unrealized gain on cash flow hedges | — | — | — | — | — | 9.7 | 9.7 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Change in additional minimum pension liability | — | — | — | — | — | (0.1 | ) | (0.1 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
Comprehensive income | 967.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock and conversion of stock options in connection with WellPoint Health Networks Inc. merger, net of issue costs and elimination of subsidiary held stock | 154.2 | 1.6 | 12,029.2 | — | (46.9 | ) | — | 11,983.9 | |||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock under Equity Security Units stock purchase contracts | 5.3 | — | 230.0 | — | — | — | 230.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Repurchase and retirement of common stock | (1.0 | ) | — | (34.6 | ) | (47.7 | ) | — | — | (82.3 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock under employee stock plans, net of repurchases under stock-for-stock option exercises, restricted stock amortization and related tax benefits | 6.5 | — | 500.3 | (106.6 | ) | (33.4 | ) | — | 360.3 | ||||||||||||||||||
December 31, 2004 | 302.6 | 3.0 | 17,433.6 | 1,960.1 | (83.5 | ) | 145.8 | 19,459.0 | |||||||||||||||||||
Net income | — | — | — | 2,463.8 | — | — | 2,463.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Change in net unrealized gains on investments | — | — | — | — | — | (157.2 | ) | (157.2 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
Change in net unrealized gains on cash flow hedges | — | — | — | — | — | (9.7 | ) | (9.7 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
Change in additional minimum pension liability | — | — | — | — | — | 0.8 | 0.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Comprehensive income | 2,297.7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock and conversion of stock options in connection with WellChoice, Inc., net, of issue costs and elimination of subsidiary held stock and other purchase accounting adjustments | 42.7 | 0.4 | 2,953.1 | — | — | — | 2,953.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Repurchase and retirement of common stock | (3.9 | ) | — | (146.6 | ) | (186.8 | ) | — | — | (333.4 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock under employee stock plans, net of repurchases under stock-for-stock option exercises, restricted stock amortization and related tax benefits | 12.0 | 0.1 | 675.3 | (60.5 | ) | 1.4 | — | 616.3 | |||||||||||||||||||
Two-for-one stock split | 307.0 | 3.1 | — | (3.1 | ) | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||
December 31, 2005 | 660.4 | 6.6 | 20,915.4 | 4,173.5 | (82.1 | ) | (20.3 | ) | 24,993.1 | ||||||||||||||||||
Net income | — | — | — | 3,094.9 | — | — | 3,094.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Change in net unrealized losses on investments | — | — | — | — | — | 180.2 | 180.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Change in net unrealized losses on cash flow hedges | — | — | — | — | — | (5.6 | ) | (5.6 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
Change in additional minimum pension liability | — | — | — | — | — | (4.7 | ) | (4.7 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
Comprehensive income | 3,264.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Repurchase and retirement of common stock | (60.7 | ) | (0.6 | ) | (1,937.3 | ) | (2,612.3 | ) | — | — | (4,550.2 | ) | |||||||||||||||
Reclassification of unearned share-based compensation in connection with adoption of FAS 123R | — | — | (82.1 | ) | — | 82.1 | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock under employee stock plans, net of related tax benefit | 15.8 | 0.1 | 967.5 | — | — | — | 967.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Adoption of FAS 158, net of tax | — | — | — | — | — | (99.5 | ) | (99.5 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
December 31, 2006 | 615.5 | $ | 6.1 | $ | 19,863.5 | $ | 4,656.1 | $ | — | $ | 50.1 | $ | 24,575.8 | ||||||||||||||
See accompanying notes.
89
Table of Contents
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
December 31, 2006
(In Millions, Except Per Share Data)
1. Organization
WellPoint, Inc. (“WellPoint”), which name changed from Anthem, Inc. (“Anthem”) effective November 30, 2004, is the largest health benefits company in terms of commercial membership in the United States, serving over 34 million medical members as of December 31, 2006. WellPoint and its consolidated subsidiaries (the “Company”) offer a broad spectrum of network-based managed care plans to the large and small employer, individual, Medicaid and senior markets. The Company’s managed care plans include preferred provider organizations (“PPOs”), health maintenance organizations (“HMOs”), point-of-service (“POS”) plans, traditional indemnity plans and other hybrid plans, including consumer-driven health plans (“CDHPs”), hospital only and limited benefit products. In addition, the Company provides a broad array of managed care services to self-funded customers, including claims processing, underwriting, stop loss insurance, actuarial services, provider network access, medical cost management and other administrative services. The Company also provides an array of specialty and other products and services such as life and disability insurance benefits, pharmacy benefit management, specialty pharmacy, dental, vision, behavioral health benefits services, long-term care insurance and flexible spending accounts. The Company has licenses in all 50 states.
The Company is an independent licensee of the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association (“BCBSA”), an association of independent health benefit plans, and serves its members as the Blue Cross licensee for California and as the Blue Cross and Blue Shield licensee for: Colorado, Connecticut, Georgia, Indiana, Kentucky, Maine, Missouri (excluding 30 counties in the Kansas City area), Nevada, New Hampshire, New York (as Blue Cross Blue Shield in 10 New York City metropolitan and surrounding counties and as Blue Cross or Blue Cross Blue Shield in selected upstate counties only), Ohio, Virginia (excluding the Northern Virginia suburbs of Washington, D.C.) and Wisconsin. The Company also serves customers throughout various parts of the country as UniCare.
2. Basis of Presentation and Significant Accounting Policies
Basis of Presentation: The accompanying consolidated financial statements of the Company include the accounts of WellPoint and its subsidiaries and have been prepared in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”). All significant intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
Use of Estimates:The preparation of consolidated financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the amounts reported in the consolidated financial statements and accompanying notes. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Two-for-One Stock Split:On April 25, 2005, WellPoint’s Board of Directors approved a two-for-one split of shares of common stock, which was effected in the form of a 100 percent common stock dividend. All shareholders of record on May 13, 2005 received one additional share of WellPoint common stock for each share of common stock held on that date. The additional shares of common stock were distributed to shareholders of record in the form of a stock dividend on May 31, 2005. All historical weighted average share and per share amounts and all references to share-based compensation data and market prices of WellPoint’s common stock for all periods presented have been adjusted to reflect this two-for-one stock split.
Investments: In accordance with FAS 115,Accounting for Certain Investments in Debt and Equity Securities, fixed maturity and equity securities are classified as “available-for-sale” or “trading” and are reported
90
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
2. Basis of Presentation and Significant Accounting Policies (continued)
at fair value. The Company classifies its investments in available-for-sale fixed maturity securities as either current or noncurrent assets based on their contractual maturities. Certain investments used to satisfy contractual, regulatory or other requirements continue to be classified as long-term, without regard to contractual maturity. The unrealized gains or losses on both current and long-term fixed maturity and equity securities classified as available-for-sale are included in accumulated other comprehensive income as a separate component of shareholders’ equity, unless the decline in value is deemed to be other-than-temporary and the Company does not have the intent and ability to hold such securities until their full cost can be recovered, in which case the securities are written down to fair value and the loss is charged to realized losses in current operations. The Company evaluates its investment securities for other-than-temporary declines based on quantitative and qualitative factors.
In November 2005, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued FASB Staff Position FAS Nos. 115-1 and 124-1,The Meaning of Other-Than-Temporary Impairment and Its Application to Certain Investments(the “FSP”),which was effective for the Company January 1, 2006. The adoption of the FSP did not have a significant impact on the Company’s consolidated financial position or results of operations.
WellPoint maintains various rabbi trusts to account for the assets and liabilities under certain deferred compensation plans. Under these plans, the participants can defer certain types of compensation and elect to receive a return on the deferred amounts based on the changes in fair value of various investment options, primarily a variety of mutual funds. Rabbi trust assets were previously classified as noncurrent available-for-sale investments. Effective January 1, 2006 and in connection with a restructuring of the plans, WellPoint changed its classification for the majority of such securities from available-for-sale to trading, which are reported in other invested assets, current in the consolidated balance sheet. The change in the fair value of the trading portfolio rabbi trust assets during 2006 resulted in $35.6 of realized gains, which, together with net investment income from trading portfolio rabbi trust assets of $8.6, is classified in general and administrative expense in the consolidated statement of income, consistent with the related increase in deferred compensation expense.
During December 2006, WellPoint initiated a program whereby it generally purchases corporate-owned life insurance policies on participants in the deferred compensation plans. The cash surrender value of the corporate-owned life insurance policies is reported in other invested assets, long-term in the consolidated balance sheets. The change in cash surrender value is reported as an offset to the premium expense of the policies, classified as general and administrative expense.
The Company uses the equity method of accounting for investments in companies in which its ownership interest enables the Company to influence the operating or financial decisions of the investee company. The Company’s proportionate share of equity in net income of these unconsolidated affiliates is reported with net investment income.
For asset-backed securities included in fixed maturity securities, the Company recognizes income using an effective yield based on anticipated prepayments and the estimated economic life of the securities. When estimates of prepayments change, the effective yield is recalculated to reflect actual payments to date and anticipated future payments. The net investment in the securities is adjusted to the amount that would have existed had the new effective yield been applied since the acquisition of the securities. Such adjustments are reflected in net investment income.
All securities sold resulting in investment gains and losses are recorded on the trade date. Realized gains and losses are determined on the basis of the cost or amortized cost of the specific securities sold.
91
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
2. Basis of Presentation and Significant Accounting Policies (continued)
The Company participates in securities lending programs whereby marketable securities in its investment portfolio are transferred to independent brokers or dealers based on, among other things, their creditworthiness in exchange for collateral initially equal to at least 102 percent of the value of the securities on loan and is thereafter maintained at a minimum of 100 percent of the market value of the securities loaned. The market value of the securities on loan to each borrower is monitored daily and the borrower is required to deliver additional collateral if the market value of the collateral falls below 100 percent of the market value of the securities on loan. The fair value of the collateral amounted to $904.7 and $1,389.9, which represents 103 percent and 102 percent of the market value of the securities on loan at December 31, 2006 and 2005, respectively. In accordance with FAS 140,Accounting for Transfers and Servicing of Financial Assets and Extinguishments of Liabilities, the Company recognizes the collateral as an asset, which is reported as “securities lending collateral” on its balance sheet and the Company records a corresponding liability for the obligation to return the collateral to the borrower, which is reported as “securities lending payable.” The securities on loan are reported in the applicable investment category on the balance sheet.
Cash Equivalents: All highly liquid investments with maturities of three months or less when purchased are classified as cash equivalents.
Derivative Financial Instruments: In accordance with FAS 133,Accounting for Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities, all investments in derivatives are recorded at fair value. A derivative is typically defined as an instrument whose value is “derived” from an underlying instrument, index or rate, has a notional amount, requires little or no initial investment and can be net settled. The Company typically invests in the following types of derivative financial instruments: interest rate swaps, call options, embedded derivatives and warrants. Derivatives embedded within non-derivative instruments (such as options embedded in convertible fixed maturity securities) are bifurcated from the host instrument when the embedded derivative is not clearly and closely related to the host instrument.
The Company’s derivatives are reported as other current assets or liabilities or other noncurrent assets or liabilities, as appropriate, with the exception of embedded derivative instruments not subject to bifurcation, which are reported together with their host instrument. If certain correlation, hedge effectiveness and risk reduction criteria are met, a derivative may be specifically designated as a hedge of exposure to changes in fair value or cash flow. The accounting for changes in the fair value of a derivative depends on the intended use of the derivative and the nature of any hedge designation thereon.
Any amounts excluded from the assessment of hedge effectiveness, as well as the ineffective portion of the gain or loss, are reported in results of operations immediately. If the derivative is not designated as a hedge, the gain or loss resulting from the change in the fair value of the derivative is recognized in results of operations in the period of change.
The Company’s accounting for changes in the fair value of derivatives is as follows:
Nature of Hedge Designation: | Derivative’s Change in Fair Value Reflected In: | |||
No hedge designation | Realized investment gains or losses | |||
Fair value hedge | Realized investment gains or losses, along with the change in the fair value of the hedged asset or liability | |||
Cash flow hedge | Other comprehensive income, with subsequent reclassification to earnings when the hedged transaction, asset or liability impacts earnings | |||
92
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
2. Basis of Presentation and Significant Accounting Policies (continued)
The Company discontinues hedge accounting prospectively when it is determined that one of the following has occurred: (i) the derivative is no longer highly effective in offsetting changes in the fair value or cash flows of a hedged item; (ii) the derivative expires or is sold, terminated or exercised; (iii) the derivative is undesignated as a hedge instrument because it is unlikely that a forecasted transaction will occur; (iv) a hedged firm commitment no longer meets the definition of a firm commitment; or (v) management determines that the designation of the derivative as a hedge instrument is no longer appropriate.
If hedge accounting is discontinued, the derivative will continue to be carried in the Company’s consolidated balance sheet at its fair value. When hedge accounting is discontinued because the derivative no longer qualifies as an effective fair value hedge, the related hedged asset or liability will no longer be adjusted for fair value changes. When hedge accounting is discontinued because it is probable that a forecasted transaction will not occur, the accumulated unrealized gains and losses included in accumulated other comprehensive income will be recognized immediately in results of operations. When hedge accounting is discontinued because the hedged item no longer meets the definition of a firm commitment, any asset or liability that was recorded pursuant to the firm commitment will be removed from the balance sheet and recognized as a gain or loss in current period results of operations. In all other situations in which hedge accounting is discontinued, changes in the fair value of the derivative are recognized in current period results of operations.
The Company’s use of derivatives is limited by statutes and regulations promulgated by the various regulatory bodies to which it is subject, and by its own derivative policy.
Credit exposure associated with non-performance by the counterparties to derivative instruments is generally limited to the uncollateralized fair value of the asset related to instruments recognized in the consolidated balance sheets. The Company attempts to mitigate the risk of non-performance by selecting counterparties with high credit ratings and monitoring their creditworthiness and by diversifying derivatives among multiple counterparties.
The Company has exposure to economic losses due to interest rate risk arising from changes in the level or volatility of interest rates. The Company attempts to mitigate its exposure to interest rate risk through active portfolio management, which includes rebalancing its existing portfolios of assets and liabilities, as well as changing the characteristics of investments to be purchased or sold in the future. In addition, derivative financial instruments are used to modify the interest rate exposure of certain liabilities or forecasted transactions. These strategies include the use of interest rate swaps and forward contracts. These instruments are generally used to lock interest rates or to hedge (on an economic basis) interest rate risks associated with variable rate debt. The Company has used these types of instruments as designated hedges against specific liabilities.
The contractual or notional amounts for derivatives are used to calculate the exchange of contractual payments under the agreements and are not representative of the potential for gain or loss on these instruments. Interest rates and equity prices affect the fair value of derivatives. The fair values generally represent the estimated amounts that the Company would expect to receive or pay upon termination of the contracts at the reporting date. Dealer quotes are available for substantially all of the Company’s derivatives. For derivative instruments not actively traded, fair values are estimated using values obtained from independent pricing services, costs to settle or quoted market prices of comparable instruments.
Premium and Self-Funded Receivables:Premium and self-funded receivables include the uncollected amounts from insured and self-funded groups, and are reported net of an allowance for doubtful accounts of $120.8 and $96.0 at December 31, 2006 and 2005, respectively. The allowance for doubtful accounts is based on historical collection trends and management’s judgment regarding the ability to collect specific accounts.
93
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
2. Basis of Presentation and Significant Accounting Policies (continued)
Other Receivables: Other receivables include proceeds due from brokers on investment trades, government programs, pharmacy sales, reinsurance, claim recoveries and other miscellaneous amounts due to the Company. These receivables have been reduced by an allowance for uncollectible amounts of $118.0 and $90.9 at December 31, 2006 and 2005, respectively, which is based on historical collection trends and management’s judgment regarding the ability to collect specific accounts.
The Company’s pharmacy benefit managers (“PBM”) contract with pharmaceutical manufacturers, some of whom provide rebates based on use of the manufacturers’ products by the PBM’s affiliated and non-affiliated clients. The Company accrues rebates receivable on a monthly basis based on the terms of the applicable contracts, historical data and current estimates. The PBM bills these rebates to the manufacturers on a quarterly basis. The Company records rebates attributable to affiliated clients as a reduction to benefit expense. Rebates attributable to non-affiliated clients are accrued as rebates receivable and a corresponding payable for the amounts of the rebates to be remitted to non-affiliated clients in accordance with their contracts is also recorded. The Company generally receives rebates between two to five months after billing.
Property and Equipment: Property and equipment is recorded at cost, net of accumulated depreciation. Depreciation is computed principally by the straight-line method over estimated useful lives ranging from 15 to 39 years for buildings and improvements, three to seven years for furniture and equipment, and three to five years for computer software. Leasehold improvements are depreciated over the term of the related lease. Certain costs related to the development or purchase of internal-use software are capitalized and amortized in accordance with AICPA Statement of Position 98-1,Accounting for the Costs of Computer Software Developed or Obtained for Internal Use.
Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets:The Company follows FAS 141,Business Combinations, and FAS 142,Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets. FAS 141 requires business combinations to be accounted for using the purchase method of accounting and it also specifies the types of acquired intangible assets that are required to be recognized and reported separately from goodwill. Under FAS 142, goodwill and other intangible assets with indefinite lives are not amortized but are tested for impairment at least annually. Goodwill represents the excess of cost of acquisition over the fair value of net assets acquired. Other intangible assets represent the values assigned to subscriber bases, provider and hospital networks, Blue Cross and Blue Shield trademarks, licenses, non-compete and other agreements. Goodwill and other intangible assets are allocated to reportable segments based on the fair value of the components of the businesses acquired.
Retirement Benefits: Pension benefits are recorded in accordance with FAS 87,Employers’ Accounting for Pensions.In September 2006, the FASB issued FAS 158,Employers’ Accounting for Defined Benefit Pension and Other Postretirement Plans – an amendment of FASB Statements No. 87, 88, 106, and 132(R). FAS 158 retains the previous measurement and disclosure requirements of FAS 87. In addition, FAS 158 requires the recognition of the funded status of pension and other postretirement benefit plans on the consolidated balance sheet (“recognition provisions”). Furthermore, for fiscal years ending after December 15, 2008, FAS 158 requires fiscal-year-end measurements of plan assets and benefit obligations, eliminating the use of earlier measurement dates currently permissible. Effective with the adoption of the recognition provisions of FAS 158 on December 31, 2006, previously unrecognized actuarial gains or losses and prior service cost were recognized on the balance sheet within accumulated other comprehensive income, net of any resulting deferred tax balances. The adoption of FAS 158 decreased accumulated other comprehensive income by $99.5 at December 31, 2006. Prepaid pension benefits represent prepaid costs related to defined benefit pension plans and are reported with other noncurrent assets. Postretirement benefits represent outstanding obligations for retiree medical, life,
94
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
2. Basis of Presentation and Significant Accounting Policies (continued)
vision and dental benefits. Liabilities for pension and other postretirement benefits are reported with current and noncurrent liabilities based on the amount by which the actuarial present value of benefits payable in the next 12 months included in the benefit obligation exceeds the fair value of plan assets.
Medical Claims Payable: Liabilities for medical claims payable include estimated provisions for incurred but not paid claims on an undiscounted basis, as well as estimated provisions for expenses related to the processing of claims. Incurred but not paid claims include (1) an estimate for claims that are incurred but not reported, as well as claims reported to the Company but not yet processed through its systems; and (2) claims reported to the Company and processed through its systems but not yet paid.
Liabilities for both claims incurred but not reported and reported but not yet processed through the Company’s systems are determined in aggregate employing actuarial methods that are commonly used by health insurance actuaries and meet Actuarial Standards of Practice. Actuarial Standards of Practice require that the claim liabilities be adequate under moderately adverse circumstances. The Company determines the amount of the liability for incurred but not paid claims by following a detailed actuarial process that entails using both historical claim payment patterns as well as emerging medical cost trends to project its best estimate of claim liabilities.
The Company regularly reviews and sets assumptions regarding cost trends and utilization when initially establishing claim liabilities. It continually monitors and adjusts the claims liability and benefit expense based on subsequent paid claims activity. If the Company’s assumptions regarding cost trends and utilization are significantly different than actual results, the Company’s income statement and financial position could be impacted in future periods.
Premium deficiencies are recognized when it is probable that expected claims and administrative expenses will exceed future premiums on existing medical insurance contracts without consideration of investment income. Determination of premium deficiencies for longer duration life and disability contracts includes consideration of investment income. For purposes of premium deficiencies, contracts are deemed to be either short or long duration and are grouped in a manner consistent with the Company’s method of acquiring, servicing and measuring the profitability of such contracts. Once established, premium deficiencies are released commensurate with actual claims experience over the remaining life of the contract.
Reserves for Future Policy Benefits: Reserves for future policy benefits include liabilities for life and long-term disability insurance policy benefits based upon interest, mortality and morbidity assumptions from published actuarial tables, modified based upon the Company’s experience. Future policy benefits also include liabilities for insurance policies for which some of the premiums received in earlier years are intended to pay anticipated benefits to be incurred in future years. Future policy benefits are continually monitored and reviewed, and when reserves are adjusted, differences are reflected in benefit expense.
The current portion of reserves for future policy benefits relates to the portion of such reserves that the Company expects to pay within one year. The Company believes that its liabilities for future policy benefits, along with future premiums received are adequate to satisfy its ultimate benefit liability; however, these estimates are inherently subject to a number of variable circumstances. Consequently, the actual results could differ materially from the amounts recorded in the consolidated financial statements of the Company.
95
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
2. Basis of Presentation and Significant Accounting Policies (continued)
Other Policyholder Liabilities: Other policyholder liabilities include certain case-specific reserves as well as rate stabilization reserves associated with retrospectively rated insurance contracts. Rate stabilization reserves represent accumulated premiums that exceed what customers owe based on actual claim experience and are paid based on contractual requirements.
Revenue Recognition: Gross premiums for fully-insured contracts are recognized as revenue over the period insurance coverage is provided. Premiums applicable to the unexpired contractual coverage periods are reflected in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets as unearned income. Premiums include revenue from retrospectively rated contracts where revenue is based on the estimated ultimate loss experience of the contract. Premium revenue includes an adjustment for retrospectively rated refunds based on an estimate of incurred claims. Premium rates for certain lines of business are subject to approval by the Department of Insurance of each respective state.
Administrative fees include revenue from certain group contracts that provide for the group to be at risk for all, or with supplemental insurance arrangements, a portion of their claims experience. The Company charges these self-funded groups an administrative fee, which is based on the number of members in a group or the group’s claim experience. In addition, administrative fees include amounts received for the administration of Medicare or certain other government programs. Under the Company’s self-funded arrangements, revenue is recognized as administrative services are performed. All benefit payments under these programs are excluded from benefit expense.
Other revenue principally includes amounts from mail-order prescription drug sales, which are recognized as revenue when the Company ships prescription drug orders.
Federal Income Taxes:The Company files a consolidated income tax return. Deferred income tax assets and liabilities are recognized for temporary differences between the financial statement and tax return bases of assets and liabilities based on enacted tax rates and laws. The deferred tax benefits of the deferred tax assets are recognized to the extent realization of such benefits is more likely than not. Deferred income tax expense or benefit generally represents the net change in deferred income tax assets and liabilities during the year. Current income tax expense represents the tax consequences of revenues and expenses currently taxable or deductible on various income tax returns for the year reported.
In July 2006, FASB Interpretation No. 48,Accounting for Uncertainty in Income Taxes—an interpretation of FASB Statement 109 (“FIN 48”) was issued. Among other things, FIN 48 creates a model to address uncertainty in tax positions and clarifies the accounting for income taxes by prescribing a minimum recognition threshold, which all income tax positions must achieve before being recognized in the financial statements. In addition, FIN 48 requires expanded annual disclosures, including a rollforward of the beginning and ending aggregate unrecognized tax benefits as well as specific detail related to tax uncertainties for which it is reasonably possible the amount of unrecognized tax benefit will significantly increase or decrease within twelve months. FIN 48 was effective on January 1, 2007. The cumulative effect of the adoption of FIN 48 is not expected to have a material impact on the Company’s beginning retained earnings at January 1, 2007.
Share-Based Compensation:The Company’s compensation philosophy provides for share-based compensation, including stock options and restricted stock awards, as well as an employee stock purchase plan. Stock options are granted for a fixed number of shares with an exercise price at least equal to the fair value of the shares at the date of the grant. Restricted stock awards are issued at the fair value of the stock on the grant date. The employee stock purchase plan allows for a purchase price per share which is 85% of the lower of the fair
96
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
2. Basis of Presentation and Significant Accounting Policies (continued)
value of a share of common stock on (i) the first trading day of the plan quarter, or (ii) the last trading day of the plan quarter. Through December 31, 2005, the Company historically accounted for share-based compensation using the intrinsic value method under Accounting Principles Board Opinion No. 25,Accounting for Stock Issued to Employees(“APB 25”), and, accordingly, recognized no compensation expense related to stock options and employee stock purchases. For grants of restricted stock, other than those awarded under long-term incentive agreements, unearned compensation equivalent to the fair value of the shares at the date of grant was recorded as a separate component of shareholders’ equity and subsequently amortized to compensation expense over the award’s vesting period. The Company has historically reported pro forma results under the disclosure-only provisions of FAS 123,Accounting for Stock-Based Compensation (“FAS 123”), as amended by FAS 148,Accounting for Stock-Based Compensation—Transition and Disclosure.
On December 16, 2004, FAS 123 (revised 2004),Share-Based Payment(“FAS 123R”), was issued. FAS 123R is a revision of FAS 123, supersedes APB 25 and amends FAS 95,Statement of Cash Flows. Generally, the approach in FAS 123R is similar to the approach described in FAS 123. However, FAS 123R requires all share-based payments to employees, including grants of employee stock options and discounts associated with employee stock purchases, to be recognized as compensation expense in the income statement based on their fair values. Pro forma disclosure of compensation expense is no longer an alternative. Additionally, excess tax benefits, which result from actual tax benefits exceeding deferred tax benefits previously recognized based on grant date fair value, are recognized as additional paid-in-capital and are reclassified from operating cash flows to financing cash flows in the consolidated statement of cash flows.
The Company adopted FAS 123R on January 1, 2006, using the modified prospective transition method. Under the modified prospective transition method, fair value accounting and recognition provisions of FAS 123R are applied to share-based awards granted or modified subsequent to the date of adoption and prior periods presented are not restated. In addition, for awards granted prior to the effective date, the unvested portion of the awards are recognized in periods subsequent to the adoption based on the grant date fair value determined for pro forma disclosure purposes under FAS 123.
The Company’s share-based employee compensation plans and assumptions are described in Note 12. The following table illustrates the effect on net income and earnings per share if the Company had applied the fair value recognition provisions of FAS 123 to share-based employee compensation:
| Years ended December 31 | ||||||||
| 2005 | 2004 | |||||||
Reported net income | $ | 2,463.8 | $ | 960.1 | ||||
Add: Share-based employee compensation expense for restricted stock and stock awards included in reported net income (net of tax) | 52.8 | 6.6 | ||||||
Less: Total share-based employee compensation expense determined under fair value based method for all awards (net of tax) | (175.3 | ) | (89.5 | ) | ||||
Pro forma net income | $ | 2,341.3 | $ | 877.2 | ||||
Basic earnings per share: | ||||||||
As reported | $ | 4.03 | $ | 3.15 | ||||
Pro forma | 3.83 | 2.88 | ||||||
Diluted earnings per share: | ||||||||
As reported | $ | 3.94 | $ | 3.05 | ||||
Pro forma | 3.72 | 2.80 | ||||||
97
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
2. Basis of Presentation and Significant Accounting Policies (continued)
Earnings per Share:Earnings per share amounts, on a basic and diluted basis, have been calculated based upon the weighted-average common shares outstanding for the period.
Basic earnings per share excludes dilution and is computed by dividing income available to common shareholders by the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding for the period. Diluted earnings per share include the dilutive effect of stock options, restricted stock and purchase contracts included in Equity Security Units, using the treasury stock method. The treasury stock method assumes exercise of stock options, vesting of restricted stock and conversion of stock purchase rights under purchase contracts included in Equity Security Units, with the assumed proceeds used to purchase common stock at the average market price for the period. The difference between the number of shares assumed issued and number of shares assumed purchased represents the dilutive shares. The purchase contracts included in Equity Security Units were settled in November 2004, and the common stock issued is included in the basic earnings per share calculation at December 31, 2004 and thereafter.
Advertising costs: The Company uses print, broadcast and other advertising to promote its products. The cost of advertising is expensed as incurred and totaled $223.7, $143.9, and $40.4 for the years ended December 31, 2006, 2005 and 2004, respectively.
Reclassifications: Certain prior year amounts have been reclassified to conform to the current year presentation.
3. Business Combinations
WellChoice, Inc. Acquisition
On December 28, 2005, the Company completed its acquisition of WellChoice, Inc. (“WellChoice”). The acquisition was accounted for using the purchase method of accounting, and was deemed effective December 31, 2005 for accounting purposes. Accordingly, the operating results of WellChoice are included in WellPoint’s consolidated financial statements in periods following December 31, 2005.
Under the merger agreement, WellChoice stockholders received thirty-eight dollars and twenty-five cents ($38.25) in cash and 0.5191 of a share of WellPoint common stock for each share of WellChoice common stock outstanding. The value of the transaction is estimated to be approximately $6,463.9, including cash of $3,126.4, the issuance of 42.4 shares of common stock, valued at $3,180.8, 0.3 shares of WellChoice restricted stock and stock units converted to WellPoint stock, valued at $19.8, WellChoice stock options converted to WellPoint stock options, valued at $113.4, and $23.5 of transaction costs. The fair value of common stock issued was based on $74.97 per share, which represents the average closing price of the Company’s common stock for the five trading days ranging from two days before to two days after September 27, 2005, the date the merger was announced.
In accordance with FAS 141 the purchase price was allocated to the fair value of WellChoice assets acquired and liabilities assumed, including identifiable intangible assets. The excess of purchase price over the fair value of net assets acquired resulted in $3,450.4 of non-tax deductible goodwill which was allocated to the Health Care segment.
98
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
3. Business Combinations (continued)
The fair values of WellChoice assets acquired and liabilities assumed at the date of the acquisition, adjusted for final purchase price allocations, are summarized as follows:
Current assets | $ | 4,284.4 | |
Goodwill | 3,450.4 | ||
Other intangible assets | 1,729.5 | ||
Other noncurrent assets | 186.4 | ||
Total assets acquired | 9,650.7 | ||
Current liabilities | 2,482.9 | ||
Noncurrent liabilities | 703.9 | ||
Total liabilities assumed | 3,186.8 | ||
Net assets acquired | $ | 6,463.9 | |
Of the $1,729.5 of acquired intangible assets, $1,152.8 was assigned to Blue Cross and Blue Shield trademarks, which are not subject to amortization due to their indefinite life. The remaining acquired intangible assets consist of $563.2 of subscriber base with an average life of 15 years and $13.5 of provider contracts with a 20 year life. The values assigned to goodwill and intangible assets with finite and indefinite lives were determined based on independent third-party valuations.
The pro forma effects of this acquisition were not material to the Company’s consolidated results of operations.
Lumenos, Inc. Acquisition
On June 9, 2005, the Company completed its acquisition of Lumenos, Inc. (“Lumenos”), a market leader in consumer-driven health programs. The total consideration for the acquisition was approximately $185.0 in cash paid to the stockholders of Lumenos. The acquisition was accounted for using the purchase method of accounting, and was deemed effective June 1, 2005 for accounting purposes. Accordingly, the results of operations for Lumenos are included in the Company’s consolidated financial statements for periods following June 1, 2005. In accordance with FAS 141, the purchase price was allocated to the fair value of Lumenos assets acquired and liabilities assumed, including identifiable intangible assets, and the excess of purchase price over the fair value of net assets acquired resulted in $119.3 of non-tax deductible goodwill, which was allocated to the Health Care segment. The pro forma effects of this acquisition were not material to the Company’s consolidated results of operations.
Merger with WellPoint Health Networks Inc.
On November 30, 2004, Anthem and WellPoint Health Networks Inc. (“WHN”) completed their merger and Anthem purchased 100% of the outstanding common stock of WHN. WHN merged with and into Anthem Holding Corp., a direct and wholly owned subsidiary of Anthem, with Anthem Holding Corp. as the surviving entity in the merger. In connection with the merger, Anthem amended its articles of incorporation to change its name to WellPoint, Inc. In addition, the ticker symbol for Anthem’s common stock listed on the New York Stock Exchange was changed to “WLP”. WHN’s operating results are included in WellPoint’s consolidated financial statements for the periods following November 30, 2004.
99
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
3. Business Combinations (continued)
As a result of the merger, each WHN stockholder received twenty-three dollars and eighty cents ($23.80) in cash, without interest, and one share of WellPoint common stock for each share of WHN common stock held. The purchase price was $15,773.6 and included cash of $3,718.8, the issuance of approximately 310.6 shares of WellPoint common stock, valued at $11,293.8, WHN stock options converted to WellPoint stock options and other stock awards for approximately 43.7 shares, valued at $563.6, and $197.4 of transaction costs. The fair value of common stock issued was based on $36.35 per share, which represents the average closing price of the Company’s common stock for the five trading days ranging from two days before to two days after October 27, 2003, the date the merger was announced.
In accordance with FAS 141, the purchase price was allocated to the fair value of WHN assets acquired and liabilities assumed, including identifiable intangible assets. The excess of purchase price over the fair value of net assets acquired resulted in $7,626.4 of non-tax deductible goodwill, of which $7,397.6 was allocated to the Health Care segment and $228.8 to the Specialty segment.
The fair values of WHN assets acquired and liabilities assumed at the date of the merger, adjusted for final purchase price allocations, are summarized as follows:
Current assets | $ | 11,381.6 | |
Goodwill | 7,626.4 | ||
Other intangible assets | 7,031.7 | ||
Other noncurrent assets | 1,100.5 | ||
Total assets acquired | 27,140.2 | ||
Current liabilities | 6,969.2 | ||
Noncurrent liabilities | 4,397.4 | ||
Total liabilities assumed | 11,366.6 | ||
Net assets acquired | $ | 15,773.6 | |
Of the $7,031.7 of acquired intangible assets, $4,370.0 was assigned to Blue Cross and Blue Shield and other trademarks, $271.0 was assigned to provider networks, and $258.0 was assigned to a license for a state sponsored program, which are not subject to amortization due to their indefinite life. The remaining acquired intangible assets consist of $2,030.0 of subscriber base with an average life of 20 years and $102.7 of provider contracts with a 23 year life. The values assigned to goodwill and intangible assets with finite and indefinite lives were determined based on independent third-party valuations.
In connection with the WHN merger, the Company executed certain undertakings with the California Department of Managed Health Care, the California Department of Insurance (“California DOI”), and the Georgia Department of Insurance (“Georgia DOI”), which contained various commitments by the Company. Expenses for merger related undertakings of $61.5 were recorded in 2004 for certain obligations under these agreements with the California DOI and the Georgia DOI. Under these obligations, during 2005, WellPoint donated $35.0 to community clinics in California and $15.0 for a program to be conducted through California community colleges to support the training of new nurses in California. Further, Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Georgia, Inc. and Blue Cross and Blue Shield Healthcare Plan of Georgia, Inc., are funding the establishment and administration of a telemedicine network to benefit health care in rural Georgia under the $11.5 commitment established in connection with the WHN merger.
100
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
3. Business Combinations (continued)
The unaudited pro forma information includes the results of operations for WHN for the periods prior to the merger, adjusted for interest expense on long-term debt and reduced investment income related to the cash and investment securities used to fund the acquisition, additional amortization and depreciation associated with the purchase and the related income tax effects. The unaudited pro forma financial information is presented for informational purposes only and may not be indicative of the results of operations had WHN been owned by WellPoint for the full year ended December 31, 2004, nor is it necessarily indicative of future results of operations.
The following summary of unaudited pro forma financial information presents revenues, net income and per share data of WellPoint for the year ended December 31, 2004 as if the WHN merger had occurred on January 1, 2004.
Pro forma revenues | $ | 42,124.0 | |
Pro forma net income | $ | 1,910.3 | |
Pro forma earning per share: | |||
Basic | $ | 3.10 | |
Diluted | $ | 3.00 | |
Pro forma shares outstanding: | |||
Basic | 615.9 | ||
Diluted | 636.8 |
4. Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets
A summary of the change in the carrying amount of goodwill by reportable segment (see Note 19) for 2006 and 2005 is as follows:
| Health Care | Specialty | Total | ||||||||||
Balance as of January 1, 2005 | $ | 9,629.3 | $ | 388.6 | $ | 10,017.9 | ||||||
Goodwill acquired | 3,565.6 | — | 3,565.6 | |||||||||
Purchase price allocation adjustments | 40.5 | (154.9 | ) | (114.4 | ) | |||||||
Balance as of December 31, 2005 | 13,235.4 | 233.7 | 13,469.1 | |||||||||
Goodwill acquired | 31.0 | 3.2 | 34.2 | |||||||||
Purchase price allocation adjustments | (116.2 | ) | (3.6 | ) | (119.8 | ) | ||||||
Balance as of December 31, 2006 | $ | 13,150.2 | $ | 233.3 | $ | 13,383.5 | ||||||
For a period of time after the date of a merger or acquisition, the initial fair values allocated to net assets acquired may be subject to change as these fair value estimates are refined. Changes in these fair value estimates are recorded as adjustments to goodwill. Subsequent to the purchase allocation period, additional changes to fair value of net assets acquired are recorded in current operations, except for certain adjustments related to income taxes and severance, which continue to be adjusted to goodwill.
Goodwill acquired in 2006 included $34.2 related to miscellaneous acquisitions deemed not material to the Company’s consolidated financial statements. Goodwill adjustments in 2006 included a reduction of $54.5 related to the tax benefit on the exercise of stock options issued as part of the WellChoice, WHN and Trigon Healthcare, Inc. (“Trigon”) acquisitions. Goodwill adjustments also include an increase of $86.5 related to employee termination and other exit costs and a reduction of $30.9 for other purchase accounting adjustments related to the WellChoice acquisition. Deferred tax allocation adjustments resulted in a reduction of $120.9 to goodwill in 2006.
101
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
4. Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets (continued)
Goodwill acquired in 2005 included $3,445.2 related to the acquisition of WellChoice, $119.5 related to the acquisition of Lumenos and $0.9 related to other acquisitions. Goodwill adjustments of $75.4 in 2005 relate primarily to adjustments for costs associated with employee terminations and costs for exiting certain activities in connection with the WHN merger. Goodwill adjustments in 2005 also include a reduction of $161.1 related to the tax benefit on the exercise of stock options issued as part of the WHN and Trigon acquisitions and a reduction of $28.7 for other purchase accounting adjustments related to the WHN merger and initial WellChoice-related termination cost accruals.
The following table represents a summary of employee termination and other exit costs recorded in connection with the WHN merger and WellChoice acquisition:
| Employee Termination Costs | Other Exit Activities | Total | ||||||||||
Initial WHN-related accrual at November 30, 2004 | $ | 252.0 | $ | — | $ | 252.0 | ||||||
Purchase accounting adjustments to initial WHN-related accrual | 44.5 | 27.6 | 72.1 | |||||||||
Payments and costs charged against liability | (261.4 | ) | (27.6 | ) | (289.0 | ) | ||||||
Initial WellChoice-related accrual at December 31, 2005 | 3.3 | — | 3.3 | |||||||||
Accrued costs December 31, 2005 | 38.4 | — | 38.4 | |||||||||
Purchase accounting adjustments to initial WellChoice-related accrual | 29.6 | 56.9 | 86.5 | |||||||||
Payments and costs charged against liability | (48.8 | ) | (8.0 | ) | (56.8 | ) | ||||||
Accrued costs December 31, 2006 | $ | 19.2 | $ | 48.9 | $ | 68.1 | ||||||
The components of other intangible assets as of December 31 are as follows:
| 2006 | 2005 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Gross Carrying Amount | Accumulated Amortization | Net Carrying Amount | Gross Carrying Amount | Accumulated Amortization | Net Carrying Amount | |||||||||||||||
Intangible assets with finite lives: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Subscriber base | $ | 3,102.6 | $ | (661.1 | ) | $ | 2,441.5 | $ | 3,103.0 | $ | (381.1 | ) | $ | 2,721.9 | ||||||
Provider and hospital networks | 154.1 | (30.2 | ) | 123.9 | 153.6 | (21.4 | ) | 132.2 | ||||||||||||
Other | 11.5 | (6.4 | ) | 5.1 | 18.9 | (12.3 | ) | 6.6 | ||||||||||||
Total | 3,268.2 | (697.7 | ) | 2,570.5 | 3,275.5 | (414.8 | ) | 2,860.7 | ||||||||||||
Intangible assets with indefinite life: | ||||||||||||||||||||
Blue Cross and Blue Shield trademarks | 6,296.7 | — | 6,296.7 | 6,296.7 | — | 6,296.7 | ||||||||||||||
Provider relationships | 271.0 | — | 271.0 | 271.0 | — | 271.0 | ||||||||||||||
License | 258.0 | — | 258.0 | 258.0 | — | 258.0 | ||||||||||||||
Total | 6,825.7 | — | 6,825.7 | 6,825.7 | — | 6,825.7 | ||||||||||||||
Other intangible assets | $ | 10,093.9 | $ | (697.7 | ) | $ | 9,396.2 | $ | 10,101.2 | $ | (414.8 | ) | $ | 9,686.4 | ||||||
As required by FAS 142, the Company completed its annual impairment tests of existing goodwill and other intangible assets with indefinite lives during the fourth quarters of 2006, 2005 and 2004. These tests involved the use of estimates related to the fair value of the reporting unit to which the goodwill and other intangible assets with indefinite lives are allocated. There were no impairment losses recorded during 2006, 2005 and 2004.
102
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
4. Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets (continued)
As of December 31, 2006, estimated amortization expense for each of the five years ending December 31, is as follows: 2007, $282.5; 2008, $265.2; 2009, $247.2; 2010, $226.7; and 2011, $209.6.
5. Investments
A summary of current and long-term investments, available-for-sale, is as follows:
| Cost or Amortized Cost | Gross Unrealized Gains | Gross Unrealized Losses | |||||||||||||||
| Less than 12 Months | Greater than 12 Months | Estimated Fair Value | |||||||||||||||
December 31, 2006: | |||||||||||||||||
Fixed maturity securities: | |||||||||||||||||
United States Government securities | $ | 1,255.6 | $ | 4.1 | $ | (2.8 | ) | $ | (8.3 | ) | $ | 1,248.6 | |||||
States, municipalities and political | 3,426.9 | 24.5 | (3.6 | ) | (19.6 | ) | 3,428.2 | ||||||||||
Corporate securities | 5,200.1 | 39.9 | (15.2 | ) | (35.5 | ) | 5,189.3 | ||||||||||
Redeemable preferred securities | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||
Options embedded in convertible debt securities | 40.6 | — | — | — | 40.6 | ||||||||||||
Mortgage-backed securities | 5,562.9 | 15.3 | (7.2 | ) | (39.9 | ) | 5,531.1 | ||||||||||
Total fixed maturity securities | 15,486.1 | 83.8 | (28.8 | ) | (103.3 | ) | 15,437.8 | ||||||||||
Equity securities | 1,752.4 | 334.2 | (15.3 | ) | (0.6 | ) | 2,070.7 | ||||||||||
Total investments, available-for-sale | $ | 17,238.5 | $ | 418.0 | $ | (44.1 | ) | $ | (103.9 | ) | $ | 17,508.5 | |||||
December 31, 2005: | |||||||||||||||||
Fixed maturity securities: | |||||||||||||||||
United States Government securities | $ | 1,951.9 | $ | 4.4 | $ | (11.5 | ) | $ | (1.9 | ) | $ | 1,942.9 | |||||
States, municipalities and political | 2,902.4 | 7.2 | (22.1 | ) | (12.7 | ) | 2,874.8 | ||||||||||
Corporate securities | 5,997.5 | 21.3 | (54.9 | ) | (7.2 | ) | 5,956.7 | ||||||||||
Redeemable preferred securities | 14.7 | 0.8 | — | — | 15.5 | ||||||||||||
Options embedded in convertible debt securities | 19.0 | — | — | — | 19.0 | ||||||||||||
Mortgage-backed securities | 4,797.1 | 11.7 | (45.7 | ) | (5.1 | ) | 4,758.0 | ||||||||||
Total fixed maturity securities | 15,682.6 | 45.4 | (134.2 | ) | (26.9 | ) | 15,566.9 | ||||||||||
Equity securities | 1,734.5 | 114.6 | (27.6 | ) | (0.4 | ) | 1,821.1 | ||||||||||
Total investments, available-for-sale | $ | 17,417.1 | $ | 160.0 | $ | (161.8 | ) | $ | (27.3 | ) | $ | 17,388.0 | |||||
The December 31, 2005 summary of available-for-sale investments includes certain rabbi trust assets with a cost or amortized cost of $281.6 and estimated fair value of $307.0. These assets were classified as available-for-sale at December 31, 2005 and classified as trading securities at January 1, 2006 and are reported in other invested assets, current on the balance sheets. In December 2006, the Company invested the majority of its rabbi trust assets in corporate-owned life insurance policies. The cash surrender value of the corporate-owned life insurance policies is reported in other invested assets, long-term on the balance sheet.
103
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
5. Investments (continued)
The following table summarizes for fixed maturity securities and equity securities in an unrealized loss position at December 31, the aggregate fair value and gross unrealized loss by length of time those securities have been continuously in an unrealized loss position.
| 2006 | 2005 | |||||||||||||||||
| Number of Securities | Fair Value | Gross Unrealized Loss | Number of Securities | Fair Value | Gross Unrealized Loss | |||||||||||||
(Securities are whole amounts) | ||||||||||||||||||
Fixed maturity securities: | ||||||||||||||||||
12 months or less | 1,628 | $ | 3,884.1 | $ | (28.8 | ) | 4,057 | $ | 9,164.7 | $ | (134.2 | ) | ||||||
Greater than 12 months | 3,068 | 5,306.4 | (103.3 | ) | 934 | 1,115.1 | (26.9 | ) | ||||||||||
Total fixed maturity securities | 4,696 | 9,190.5 | (132.1 | ) | 4,991 | 10,279.8 | (161.1 | ) | ||||||||||
Equity securities: | ||||||||||||||||||
12 months or less | 1,103 | 234.6 | (15.3 | ) | 1,662 | 403.9 | (27.6 | ) | ||||||||||
Greater than 12 months | 1 | 21.0 | (0.6 | ) | 29 | 4.8 | (0.4 | ) | ||||||||||
Total equity securities | 1,104 | 255.6 | (15.9 | ) | 1,691 | 408.7 | (28.0 | ) | ||||||||||
Total fixed maturity and equity securities | 5,800 | $ | 9,446.1 | $ | (148.0 | ) | 6,682 | $ | 10,688.5 | $ | (189.1 | ) | ||||||
The Company’s fixed maturity investment portfolio is sensitive to interest rate fluctuations, which impact the fair value of individual securities. Accordingly, unrealized losses on fixed maturity securities reported above were generally caused by the effect of a rising interest rate environment on certain securities with stated interest rates currently below market rates. The Company has the ability and intent to hold these fixed maturity securities until their full cost can be recovered. Therefore, the Company does not believe the unrealized losses represent an other-than-temporary impairment as of December 31, 2006.
The amortized cost and fair value of fixed maturity securities at December 31, 2006, by contractual maturity, are shown below. Expected maturities may be less than contractual maturities because the issuers of the securities may have the right to prepay obligations without prepayment penalties.
| Amortized Cost | Estimated Fair Value | |||||
Due in one year or less | $ | 545.3 | $ | 543.6 | ||
Due after one year through five years | 4,547.2 | 4,521.4 | ||||
Due after five years through ten years | 2,769.5 | 2,768.7 | ||||
Due after ten years | 2,061.2 | 2,073.0 | ||||
Mortgage-backed securities | 5,562.9 | 5,531.1 | ||||
Total available-for-sale debt securities | $ | 15,486.1 | $ | 15,437.8 | ||
104
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
5. Investments (continued)
The major categories of net investment income for the years ended December 31 are as follows:
| 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | ||||||||||
Fixed maturity securities | $ | 767.5 | $ | 570.9 | $ | 299.1 | ||||||
Equity securities | 43.8 | 33.9 | 8.1 | |||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | 94.1 | 47.6 | 11.8 | |||||||||
Other invested assets, long-term | 2.3 | 3.4 | 0.8 | |||||||||
Investment income | 907.8 | 655.8 | 319.8 | |||||||||
Investment expense | (29.1 | ) | (22.7 | ) | (8.1 | ) | ||||||
Net investment income | $ | 878.7 | $ | 633.1 | $ | 311.7 | ||||||
Net realized investment gains (losses) and net change in unrealized appreciation (depreciation) in investments for the years ended December 31, were as follows:
| 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | ||||||||||
Net realized investment (losses) gains: | ||||||||||||
Fixed maturity securities: | ||||||||||||
Gross realized gains from sales | $ | 38.3 | $ | 90.9 | $ | 92.0 | ||||||
Gross realized losses from sales | (86.2 | ) | (116.2 | ) | (51.4 | ) | ||||||
Gross realized losses from other-than-temporary impairments | (26.4 | ) | (7.3 | ) | — | |||||||
Net realized (losses) gains on fixed maturity securities | (74.3 | ) | (32.6 | ) | 40.6 | |||||||
Equity securities | ||||||||||||
Gross realized gains from sales | 108.0 | 43.9 | 3.4 | |||||||||
Gross realized losses from sales | (9.5 | ) | (21.9 | ) | (0.1 | ) | ||||||
Gross realized losses from other-than-temporary impairments | (29.8 | ) | (7.5 | ) | (0.8 | ) | ||||||
Net realized gains on equity securities | 68.7 | 14.5 | 2.5 | |||||||||
Other realized investment gains (losses) | 5.3 | 7.9 | (0.6 | ) | ||||||||
Net realized investment (losses) gains | (0.3 | ) | (10.2 | ) | 42.5 | |||||||
Net change in unrealized appreciation (depreciation) in investments: | ||||||||||||
Fixed maturity securities | 67.4 | (244.2 | ) | (61.3 | ) | |||||||
Equity securities | 255.1 | 1.3 | 59.1 | |||||||||
Other invested assets, long-term | (23.4 | ) | — | (1.4 | ) | |||||||
Total net change in unrealized appreciation (depreciation) in investments | 299.1 | (242.9 | ) | (3.6 | ) | |||||||
Deferred income tax (expense) benefit | (118.9 | ) | 85.7 | 1.1 | ||||||||
Net change in unrealized appreciation (depreciation) in investments | 180.2 | (157.2 | ) | (2.5 | ) | |||||||
Net realized gains (losses) and change in unrealized appreciation (depreciation) in investments | $ | 179.9 | $ | (167.4 | ) | $ | 40.0 | |||||
During the year ended December 31, 2006, the Company sold $5,886.3 of fixed maturity and equity securities which resulted in gross realized losses of $95.7. Subsequent to the acquisition of WellChoice, during 2006, the Company restructured its investment portfolios to align the merged portfolios with the Company’s overall investment guidelines. The majority of the sales of fixed maturity securities resulted in realized losses due to the prevailing interest rate environment. For equity securities, the 2006 sales to restructure the merged
105
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
5. Investments (continued)
portfolios primarily resulted in realized gains. Similarly, subsequent to the merger with WHN, during 2005, the Company restructured its investment portfolios to align the merged portfolios with the Company’s overall investment guidelines. The majority of the sales of fixed maturity securities resulted in realized losses due to the prevailing interest rate environment. For equity securities, the 2005 sales to restructure the merged portfolios primarily resulted in realized gains. During 2004, the majority of the sales of fixed maturity securities resulted in realized gains. Impairments recorded in 2006, 2005 and 2004 were primarily the result of the continued credit deterioration on specific issuers in the bond markets and certain equity securities’ fair value remaining below cost for an extended period of time.
A primary objective in the management of the fixed maturity and equity portfolios is to maximize total return relative to underlying liabilities and respective liquidity needs. In achieving this goal, assets may be sold to take advantage of market conditions or other investment opportunities as well as tax considerations. Sales will generally produce realized gains and losses.
In the ordinary course of business, the Company may sell securities at a loss for a number of reasons, including, but not limited to: (i) changes in the investment environment; (ii) expectation that the fair value could deteriorate further; (iii) desire to reduce exposure to an issuer or an industry; (iv) changes in credit quality; or (v) changes in expected cash flow.
Investment securities are exposed to various risks, such as interest rate, market and credit. Due to the level of risk associated with certain investment securities and the level of uncertainty related to changes in the value of investment securities, it is possible that changes in these risk factors in the near term could have an adverse material impact on the Company’s results of operations or shareholders’ equity.
A significant judgment in the valuation of investments is the determination of when an other-than-temporary decline in value has occurred. The Company follows a consistent and systematic process for impairing securities that sustain other-than-temporary declines in value. The Company has established a committee responsible for the impairment review process. The decision to impair a security incorporates both quantitative criteria and qualitative information. The impairment review process considers a number of factors including, but not limited to: (a) the length of time and the extent to which the fair value has been less than book value, (b) the financial condition and near term prospects of the issuer, (c) the intent and ability of the Company to retain its investment for a period of time sufficient to allow for any anticipated recovery in value, (d) whether the debtor is current on interest and principal payments and (e) general market conditions and industry or sector specific factors. For securities that are deemed to be other-than-temporarily impaired, the security is adjusted to fair value and the resulting losses are recognized in realized gains or losses in the consolidated statements of income. The new cost basis of the impaired securities is not increased for future recoveries in fair value.
At December 31, 2006, no investments other than investments in U.S. government agency securities exceeded 10% of shareholders’ equity.
The carrying value of fixed maturity investments that did not produce income during 2006 and 2005 was $6.9 and $4.7 at December 31, 2006 and 2005, respectively.
As of December 31, 2006 the Company had committed approximately $261.5 to future capital calls from various third-party investments in exchange for an ownership interest in the related entity.
106
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
5. Investments (continued)
At December 31, 2006 and 2005, securities with carrying values of approximately $342.3 and $227.9, respectively, were deposited by the Company’s insurance subsidiaries under requirements of regulatory authorities.
During 2006, 2005 and 2004, the Company entered into securities lending programs. Securities on loan under the Company’s securities lending programs are included in the investment captions shown on the accompanying consolidated balance sheets. Under these programs, brokers and dealers who borrow securities are required to deliver substantially the same security to the Company upon completion of the transaction. The fair value of securities on loan as of December 31, 2006 and 2005 was $879.7 and $1,360.1, respectively. Income earned on security lending transactions for the year ended December 31, 2006, 2005 and 2004 was $1.9, $1.6 and $0.1, respectively.
6. Derivative Financial Instruments
A summary of the aggregate contractual or notional amounts and estimated fair values related to derivative financial instruments at December 31 is as follows:
| 2006 | 2005 | |||||||||||||||||||
Contractual/ Notional Amount | Estimated Fair Value | Contractual/ Notional Amount | Estimated Fair Value | |||||||||||||||||
| Asset | (Liability) | Asset | (Liability) | |||||||||||||||||
Swaps | $ | 1,640.0 | $ | 17.4 | $ | (29.0 | ) | $ | 2,315.0 | $ | 5.6 | $ | (44.9 | ) | ||||||
Equity warrants | 0.6 | 4.3 | — | 0.6 | 3.7 | — | ||||||||||||||
Options embedded in convertible debt securities | 149.4 | 40.6 | — | 148.6 | 19.0 | — | ||||||||||||||
Futures | — | 1.9 | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
Total | $ | 1,790.0 | $ | 64.2 | $ | (29.0 | ) | $ | 2,464.2 | $ | 28.3 | $ | (44.9 | ) | ||||||
For the years ended December 31, 2006, 2005 and 2004, the Company recognized realized gains related to derivative financial instruments of $13.3, $1.5 and $0.7, respectively.
Fair Value Hedges
During the year ended December 31, 2006, the Company entered into two fair value hedges with a total notional value of $440.0. The first hedge is a $240.0 notional amount interest rate swap agreement to receive a fixed 6.800% rate and pay a LIBOR-based floating rate and expires on August 1, 2012. The second hedge is a $200.0 notional amount interest rate swap agreement to receive a fixed 5.000% rate and pay a LIBOR-based floating rate and expires on December 15, 2014.
During the year ended December 31, 2005, the Company entered into two fair value hedges with a total notional value of $660.0. The first hedge is a $360.0 notional amount interest rate swap agreement to exchange a fixed 6.800% rate for a LIBOR-based floating rate and expires on August 1, 2012. The second hedge is a $300.0 notional amount interest rate swap agreement to exchange a fixed 5.000% rate for LIBOR-based floating rate and expires December 15, 2014.
During the year ended December 31, 2004, the Company entered into a $300.0 notional amount interest rate swap agreement to exchange a fixed 3.750% rate for a LIBOR-based floating rate. The swap agreement expires December 14, 2007.
107
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
6. Derivative Financial Instruments (continued)
For the years ended December 31, 2006, 2005 and 2004, the Company recognized (expense) income of $(11.1), $0.5 and $0.1, respectively, from these swap agreements, which were recorded as an (increase) reduction of interest expense.
Cash Flow Hedges
During the year ended December 31, 2005, the Company entered into a floating to fixed rate cash flow hedge with a total notional value of $480.0. The purpose of this hedge is to offset the variability of the cash flows due to the rollover of the Company’s variable-rate one-month commercial paper issuance. In December 2006, the total notional value was reduced to $240.0. This swap agreement expires in December 2007. During the years ended December 31, 2006 and 2005, no gain or loss from hedged ineffectiveness was recorded in earnings and the commercial paper borrowings remain outstanding at December 31, 2006.
During the year ended December 31, 2005, the Company entered into forward starting pay fixed swaps with an aggregate notional amount of $875.0. The objective of these hedges was to eliminate the variability of cash flows in the interest payments on the debt securities to be issued to partially fund the cash portion of the WellChoice acquisition. These swaps were terminated in January 2006, and the Company paid a net $24.7, the net fair value at the time of termination. In addition, the Company recorded an unrealized loss of $16.0, net of tax, as accumulated other comprehensive income. Following the January 10, 2006 issuance of debt securities in connection with the WellChoice acquisition, the unamortized fair value of the forward starting pay fixed swaps included in accumulated other comprehensive income began amortizing into earnings, as an increase to interest expense, over the life of the hedged debt securities.
During the year ended December 31, 2004, the Company entered into forward starting pay fixed swaps and treasury lock swaps with an aggregate notional amount of $2,000.0. The objective of these hedges was to eliminate the variability of cash flows in the interest payments on the debt securities to be issued to partially fund the cash portion of the WHN merger. These swaps were terminated in 2004, and the Company received a net $15.7, the net fair value at the time of termination. In addition, the Company recorded an unrealized gain of $10.2, net of tax, as accumulated other comprehensive income. Following the completion of the WHN merger on November 30, 2004, the Company issued debt securities, and the unamortized fair value of the forward starting pay fixed swaps included in accumulated other comprehensive income began amortizing into earnings, as a reduction of interest expense, over the life of the debt securities.
The unrecognized loss for all cash flow hedges included in accumulated other comprehensive income at December 31, 2006 was $5.6. As of December 31, 2006, the total amount of amortization over the next twelve months for all cash flow hedges will increase interest expense by approximately $0.7.
108
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
7. Long-Term Debt
The carrying value of long-term debt at December 31 consists of the following:
| 2006 | 2005 | |||||||
Senior unsecured notes: | ||||||||
6.375%, face amount of $450.0, due 2006 | $ | — | $ | 455.9 | ||||
3.500%, face amount of $200.0, due 2007 | 198.3 | 195.5 | ||||||
3.750%, face amount of $300.0, due 2007 | 294.9 | 292.1 | ||||||
4.250%, face amount of $300.0, due 2009 | 298.4 | 297.8 | ||||||
5.000%, face amount of $700.0, due 2011 | 694.6 | — | ||||||
6.375%, face amount of $350.0, due 2012 | 369.1 | 375.2 | ||||||
6.800%, face amount of $800.0, due 2012 | 793.5 | 786.1 | ||||||
5.000%, face amount of $500.0, due 2014 | 484.3 | 481.2 | ||||||
5.250%, face amount of $1,100.0, due 2016 | 1,088.5 | — | ||||||
5.950%, face amount of $500.0, due 2034 | 494.1 | 493.9 | ||||||
5.850%, face amount of $900.0, due 2036 | 888.4 | — | ||||||
Surplus notes: | ||||||||
9.125%, face amount of $42.0, due 2010 | 41.8 | 41.7 | ||||||
9.000%, face amount of $25.1, due 2027 | 24.8 | 24.8 | ||||||
Variable rate debt: | ||||||||
Commercial paper program | 1,295.3 | 1,601.4 | ||||||
Bridge loan | — | 1,700.0 | ||||||
Capital leases, stated or imputed rates from 1.830% to 27.480% due through 2015 | 48.2 | 60.3 | ||||||
Total debt | 7,014.2 | 6,805.9 | ||||||
Current portion of debt | (521.0 | ) | (481.2 | ) | ||||
Long-term debt, less current portion | $ | 6,493.2 | $ | 6,324.7 | ||||
On June 15, 2006, the Company repaid $450.0 of its 6.375% notes, which matured on that date.
On January 10, 2006, the Company issued $700.0 of 5.000% notes due 2011; $1,100.0 of 5.250% notes due 2016; and $900.0 of 5.850% notes due 2036, under a shelf registration statement filed with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission on December 28, 2005. The proceeds from this debt issuance were used to repay the bridge loan of $1,700.0 (as further described below) and to repay approximately $1,000.0 of commercial paper, which were both obtained to partially fund the December 28, 2005 WellChoice acquisition.
WellPoint had cash requirements of approximately $3,138.0 for the WellChoice acquisition, including both the cash portion of the purchase price and estimated transaction costs. In anticipation of the acquisition, on December 28, 2005, WellPoint entered into a bridge loan agreement under which it could borrow up to $3,000.0. On December 28, 2005, WellPoint borrowed $1,700.0 under this bridge facility to partially fund the WellChoice acquisition. The interest rate on this bridge loan was based on either (i) the LIBOR rate plus a predetermined percentage rate based on the Company’s credit rating at the date of utilization, or (ii) a base rate as defined in the facility agreement. The weighted-average interest rate on the bridge loan at December 31, 2005 was 7.250%. The bridge loan was classified as long-term debt at December 31, 2005 in accordance with FAS 6,Classification of Short-Term Obligations Expected to Be Refinanced (“FAS 6”), as this short-term borrowing was replaced with a long-term borrowing on January 10, 2006.
109
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
7. Long-Term Debt (continued)
On November 29, 2005, the Company entered into a senior credit facility (the “facility”) with certain lenders for general corporate purposes. The Company amended this facility in September 2006. The facility provides credit for up to $2,500.0 (reduced for any commercial paper issuances) and matures on September 30, 2011. The interest rate on this facility is based on either (i) the LIBOR rate plus a predetermined percentage rate based on the Company’s credit rating at the date of utilization, or (ii) a base rate as defined in the facility agreement. The Company’s ability to borrow under the facility is subject to compliance with certain covenants. Commitment fees for the facility were $2.4 in 2006 and there are no conditions that are probable of occurring under which the facility may be withdrawn. There were no amounts outstanding under the senior credit facility as of December 31, 2006 or during the year then ended. At December 31, 2006, the Company had $1,204.7 available under this facility.
Surplus notes are unsecured obligations of Anthem Insurance Companies, Inc. (“Anthem Insurance”), a wholly owned subsidiary, and are subordinate in right of payment to all of Anthem Insurance’s existing and future indebtedness. Any payment of interest or principal on the surplus notes may be made only with the prior approval of the Indiana Department of Insurance (“IDOI”), and only out of capital and surplus funds of Anthem Insurance that the IDOI determines to be available for the payment under Indiana insurance laws. During December 2004, WellPoint completed a tender offer to purchase Anthem Insurance surplus notes from the holders, and purchased $258.0 of 9.125% notes due 2010 and $174.9 of 9.000% notes due 2027. The Company recorded a loss of $146.1 which was recorded as loss on repurchase of debt securities in the statement of income for the year ended December 31, 2004.
The Company has an authorized commercial paper program of up to $2,500.0, the proceeds of which may be used for general corporate purposes. The weighted-average interest rate on commercial paper borrowings at December 31, 2006 and 2005 was 5.42% and 4.40%, respectively. Commercial paper borrowings have been classified as long-term debt at December 31, 2006 and 2005 in accordance with FAS 6, as the Company’s practice and intent is to replace short-term commercial paper outstanding at expiration with additional short-term commercial paper for an uninterrupted period extending for more than one year or with borrowings under the senior credit facility described above.
Interest paid during 2006, 2005 and 2004 was $343.0, $238.7, and $146.7, respectively.
The Company was in compliance with all applicable covenants under its outstanding debt agreements.
Future maturities of debt, including capital leases, are as follows: 2007, $1,816.3; 2008, $9.1; 2009, $308.0; 2010, $45.6; 2011, $698.6; and thereafter, $4,136.6.
8. Fair Value of Financial Instruments
In the normal course of business, WellPoint invests in various financial assets, incurs various financial liabilities and enters into agreements involving derivative securities.
Fair values are disclosed for all financial instruments for which it is practicable to estimate fair value, whether or not such values are recognized in the consolidated balance sheets. Management attempts to obtain quoted market prices for these disclosures. Where quoted market prices are not available, fair values are estimated using present value or other valuation techniques. These techniques are significantly affected by management’s assumptions, including discount rates and estimates of future cash flows. Potential taxes and other transaction costs have not been considered in estimating fair values. The estimates presented herein are not necessarily indicative of the amounts that the Company would realize in a current market exchange.
110
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
8. Fair Value of Financial Instruments (continued)
Non-financial instruments such as real estate, property and equipment, other current assets, deferred income taxes and intangible assets, and certain financial instruments such as policy liabilities are excluded from the fair value disclosures. Therefore, the fair value amounts cannot be aggregated to determine the underlying economic value of the Company.
The carrying amounts reported in the consolidated balance sheets for cash and cash equivalents, accrued investment income, premium and self-funded receivables, other receivables, securities lending collateral, unearned income, accounts payable and accrued expenses, income taxes payable, security trades pending payable and certain other current liabilities approximate fair value because of the short term nature of these items. These assets and liabilities are not listed in the following table.
The following methods and assumptions were used to estimate the fair value of each class of financial instrument:
Current and long-term investments, available-for-sale, at fair value:The carrying amount approximates fair value, based on quoted market prices, where available. For securities not actively traded, fair values were estimated using values obtained from independent pricing services or quoted market prices of comparable instruments.
Other invested assets, current: Other invested assets, current include securities held in rabbi trusts that are classified as trading. The carrying amount approximates fair value, based on quoted market prices, where available. For securities not actively traded, fair values were estimated using values obtained from independent pricing services or quoted market prices of comparable instruments.
Other invested assets, long-term: Other invested assets, long-term include primarily the Company’s investments in limited partnerships, joint ventures and other non-controlled corporations, as well as, beginning in 2006, the cash surrender value of corporate-owned life insurance policies. Investments in limited partnerships, joint ventures and other non-controlled corporations are carried at the Company’s share in the entities’ undistributed earnings, which approximates fair value. The carrying value of corporate-owned life insurance policies are the cash surrender value as reported by the respective insurer.
Long-term debt—notes and capital leases: The fair value of notes is based on quoted market prices for the same or similar debt, or, if no quoted market prices were available, on the current rates estimated to be available to the Company for debt of similar terms and remaining maturities. Capital leases are carried at the unamortized present value of the minimum lease payments, which approximates fair value.
Long-term debt—commercial paper:The carrying amount for commercial paper approximates fair value as the underlying instruments have variable interest rates at market value.
Derivatives—interest rate swaps:The fair value of the interest rate swaps are based on the quoted market prices by the financial institution that is the counterparty to the swap.
Derivatives—equity warrants:The fair value of equity warrants are based on quoted market prices, where available. For warrants not actively traded, fair values were estimated using values obtained from independent pricing services, quoted market prices of comparable instruments, or independent pricing models.
111
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
8. Fair Value of Financial Instruments (continued)
The carrying values and estimated fair values of the Company’s financial instruments at December 31 are as follows:
| 2006 | 2005 | |||||||||||
| Carrying Value | Estimated Fair Value | Carrying Value | Estimated Fair Value | |||||||||
Assets: | ||||||||||||
Investments available-for-sale: | ||||||||||||
Fixed maturity securities | $ | 15,437.8 | $ | 15,437.8 | $ | 15,560.1 | $ | 15,560.1 | ||||
Equity securities | 2,070.7 | 2,070.7 | 1,520.9 | 1,520.9 | ||||||||
Other invested assets, current | 72.8 | 72.8 | 307.0 | 307.0 | ||||||||
Other invested assets, long-term | 628.8 | 628.8 | 207.8 | 207.8 | ||||||||
Interest rate swaps and equity warrants (reported with other noncurrent assets) | 21.7 | 21.7 | 9.3 | 9.3 | ||||||||
Liabilities: | ||||||||||||
Debt: | ||||||||||||
Commercial paper | 1,295.3 | 1,295.3 | 1,601.4 | 1,601.4 | ||||||||
Notes and capital leases | 5,718.9 | 5,752.3 | 5,204.5 | 5,323.1 | ||||||||
Interest rate swaps (reported with other noncurrent liabilities) | 29.0 | 29.0 | 44.9 | 44.9 | ||||||||
9. Property and Equipment
A summary of property and equipment at December 31 is as follows:
| 2006 | 2005 | |||||||
Land and improvements | $ | 60.1 | $ | 60.8 | ||||
Building and components | 469.9 | 451.4 | ||||||
Data processing equipment, furniture and other equipment | 709.4 | 673.1 | ||||||
Computer software, purchased and internally developed | 782.3 | 679.1 | ||||||
Leasehold improvements | 138.7 | 133.4 | ||||||
| 2,160.4 | 1,997.8 | |||||||
Accumulated depreciation and amortization | (1,171.8 | ) | (919.2 | ) | ||||
Property and equipment, net | $ | 988.6 | $ | 1,078.6 | ||||
Property and equipment includes assets purchased under noncancelable capital leases of $54.9 and $54.7 at December 31, 2006 and 2005, respectively. Total accumulated amortization on leased assets at December 31, 2006 and 2005 was $30.1 and $17.0, respectively. Depreciation expense for 2006, 2005 and 2004 was $133.0, $118.7 and $78.1, respectively. Amortization expense on leased assets, computer software and leasehold improvements for 2006, 2005 and 2004 was $137.4, $109.9, and $57.6, respectively, which includes amortization expense on computer software, both purchased and internally developed, for 2006, 2005 and 2004 of $122.9, $101.9 and $49.8, respectively. Capitalized costs related to the internal development of software of $470.5 and $409.9 at December 31, 2006 and 2005, respectively, are reported with computer software.
112
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
10. Medical Claims Payable
A reconciliation of the beginning and ending balances for medical claims payable is as follows:
| Years Ended December 31 | ||||||||||||
| 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | ||||||||||
Gross medical claims payable, beginning of period | $ | 4,853.4 | $ | 4,134.0 | $ | 1,836.0 | ||||||
Ceded medical claims payable, beginning of period | (27.7 | ) | (31.9 | ) | (8.7 | ) | ||||||
Net medical claims payable, beginning of period | 4,825.7 | 4,102.1 | 1,827.3 | |||||||||
Business combinations and purchase adjustments | (6.4 | ) | 784.5 | 2,331.0 | ||||||||
Net incurred medical claims: | ||||||||||||
Current year | 42,613.2 | 32,865.6 | 15,344.9 | |||||||||
Prior years (redundancies) | (617.7 | ) | (644.9 | ) | (171.9 | ) | ||||||
Total net incurred medical claims | 41,995.5 | 32,220.7 | 15,173.0 | |||||||||
Net payments attributable to: | ||||||||||||
Current year medical claims | 37,486.0 | 28,997.1 | 12,453.2 | |||||||||
Prior years medical claims | 4,089.5 | 3,284.5 | 2,776.0 | |||||||||
Total net payments | 41,575.5 | 32,281.6 | 15,229.2 | |||||||||
Net medical claims payable, end of period | 5,239.3 | 4,825.7 | 4,102.1 | |||||||||
Ceded medical claims payable, end of period | 51.0 | 27.7 | 31.9 | |||||||||
Gross medical claims payable, end of period | $ | 5,290.3 | $ | 4,853.4 | $ | 4,134.0 | ||||||
Amounts incurred related to prior years vary from previously estimated liabilities as the claims are ultimately settled. Liabilities at any year end are continually reviewed and re-estimated as information regarding actual claims payments become known. This information is compared to the originally established year end liability. Negative amounts reported for incurred related to prior years result from claims being settled for amounts less than originally estimated. The favorable development in medical claims payable for the years ended December 31, 2006, 2005, and 2004 is primarily attributable to actual claim payment patterns and cost trends differing from those assumed at the time the liability was established.
11. Reinsurance
The Company reinsures certain of its risks with other companies and assumes risk from other companies. The Company remains primarily liable to policyholders under ceded insurance contracts and is contingently liable for amounts recoverable from reinsurers in the event that such reinsurers do not meet their contractual obligations.
The Company evaluates the financial condition of its reinsurers and monitors concentrations of credit risk arising from similar geographic regions, activities, or economic characteristics of the reinsurers to minimize its exposure to significant losses from reinsurer insolvencies.
113
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
11. Reinsurance (continued)
A summary of direct, assumed and ceded premiums written and earned for the years ended December 31, is as follows:
| 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Written | Earned | Written | Earned | Written | Earned | |||||||||||||||||||
Direct | $ | 52,143.2 | $ | 52,061.5 | $ | 40,776.0 | $ | 40,829.4 | $ | 18,792.8 | $ | 18,731.1 | ||||||||||||
Assumed | 63.4 | 63.4 | 22.2 | 41.3 | 5.9 | 5.4 | ||||||||||||||||||
Ceded | (154.3 | ) | (153.0 | ) | (169.4 | ) | (190.7 | ) | (58.7 | ) | (58.2 | ) | ||||||||||||
Net premiums | $ | 52,052.3 | $ | 51,971.9 | $ | 40,628.8 | $ | 40,680.0 | $ | 18,740.0 | $ | 18,678.3 | ||||||||||||
Percentage of amount assumed to net premiums | 0.1 | % | 0.1 | % | — | % | 0.1 | % | — | % | — | % | ||||||||||||
A summary of net premiums written and earned for the Company’s segments for the years ended December 31 is as follows:
| 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Written | Earned | Written | Earned | Written | Earned | |||||||||||||||||||
Reportable segments: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Health Care | $ | 51,093.2 | $ | 51,018.4 | $ | 39,810.4 | $ | 39,803.4 | $ | 18,480.3 | $ | 18,420.2 | ||||||||||||
Specialty | 1,046.2 | 1,040.4 | 853.5 | 911.7 | 269.7 | 268.1 | ||||||||||||||||||
Other | (86.9 | ) | (86.9 | ) | (35.1 | ) | (35.1 | ) | (10.0 | ) | (10.0 | ) | ||||||||||||
Net premiums | $ | 52,052.5 | $ | 51,971.9 | $ | 40,628.8 | $ | 40,680.0 | $ | 18,740.0 | $ | 18,678.3 | ||||||||||||
The effect of reinsurance on benefit expense for the years ended December 31 is as follows:
| 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | ||||||||||
Direct | $ | 42,320.5 | $ | 32,779.7 | $ | 15,312.1 | ||||||
Assumed | 43.1 | 8.5 | 9.6 | |||||||||
Ceded | (144.8 | ) | (163.0 | ) | (41.1 | ) | ||||||
Benefit expense | $ | 42,218.8 | $ | 32,625.2 | $ | 15,280.6 | ||||||
The effect of reinsurance on certain assets and liabilities at December 31 is as follows:
| 2006 | 2005 | |||||||
Policy liabilities, assumed | $ | 106.2 | $ | 169.0 | ||||
Unearned income, assumed | 0.1 | 0.3 | ||||||
Premiums payable, ceded | 35.2 | 25.7 | ||||||
Premiums receivable, assumed | 11.6 | 7.3 | ||||||
12. Capital Stock
Shares Issued for the WellChoice Acquisition
On December 28, 2005, as partial consideration in the WellChoice acquisition, the Company issued 0.5191 of a share of WellPoint common stock for each share of WellChoice common stock outstanding, resulting in
114
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
12. Capital Stock (continued)
additional outstanding shares of approximately 42.7. The $3,200.6 fair value of the common shares issued was determined based on $74.97 per share, which represents the average closing price of the Company’s common stock for the five trading days ranging from two days before to two days after September 27, 2005, the date the acquisition was announced. Transaction costs of $11.6 reduced the aggregate fair value and $3,189.0 was recorded as par value of common stock and additional paid-in capital.
Shares Issued for the WHN Merger
Effective November 30, 2004, as partial consideration in the WHN merger, the Company issued one share of common stock for each WHN share outstanding, resulting in additional outstanding shares of approximately 310.6. The $11,293.8 fair value of the common shares issued was determined based on $36.35 per share, which represents the average closing price of the Company’s common stock for the five trading days ranging from two days before to two days after October 27, 2003, the date the merger was announced. Offering costs of $8.3 reduced the aggregate fair value and $12,030.8 was recorded as par value of common stock and additional paid-in capital.
Stock Incentive Plans
The Company’s 2001 Stock Incentive Plan, as amended and restated on January 1, 2003 (“2001 Stock Plan”) is an omnibus plan, which allowed for the grant of stock options, stock, restricted stock, phantom stock, stock appreciation rights and performance awards to eligible employees and non-employee directors. On March 15, 2006, the Board of Directors adopted the WellPoint 2006 Incentive Compensation Plan (the “2006 Incentive Plan”), which was approved by WellPoint’s shareholders on May 16, 2006. The 2006 Incentive Plan allows the flexibility to grant or award stock options, stock appreciation rights, restricted stock awards, restricted stock units, performance unit awards, performance share awards, cash-based awards and other share-based awards to eligible persons. Following approval of the 2006 Incentive Plan on May 16, 2006, no new awards have been or will be made under the 2001 Stock Plan, but the awards outstanding under the 2001 Stock Plan will remain in effect in accordance with their terms.
The 2006 Incentive Plan allows the Company to grant these share-based incentive awards to employees, non-employee directors and consultants covering a total of up to 20.0 shares of Company common stock, plus (i) 7.0 shares of Company common stock, as previously approved by the Company’s shareholders, but not underlying any outstanding options or other awards under the 2001 Stock Plan, and (ii) any additional shares of Company common stock subject to outstanding options or other awards under the 2001 Stock Plan that expire, are forfeited or otherwise terminate unexercised on or after March 15, 2006, less 0.1 shares of Company common stock granted under the 2001 Stock Plan between March 15, 2006 and May 16, 2006.
In connection with the WellChoice acquisition, the Company assumed the WellChoice, Inc. 2003 Omnibus Incentive Plan, which provided for the granting of stock options to employees and non-employee directors. WellChoice stock options were converted to WellPoint stock options using the option exchange ratio as defined in the merger agreement. The converted stock options were recorded at the acquisition date as additional paid-in capital and valued at $113.4 using a binomial lattice model. The following weighted-average assumptions were used for the conversion: risk-free interest rate of 4.32%; volatility factor of 22.00%; expected dividend yield of 0.00%; and expected option life of three years.
In connection with the WHN merger, the Company assumed the WellPoint Health Networks Inc. 1999 Stock Incentive Plan, the WellPoint Health Networks Inc. 2000 Employee Stock Option Plan, the Cobalt
115
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
12. Capital Stock (continued)
Corporation Equity Incentive Plan, the RightCHOICE Managed Care, Inc. 2001 Stock Incentive Plan, the RightCHOICE Managed Care, Inc. 1994 Equity Incentive Plan and the RightCHOICE Managed Care, Inc. Nonemployee Directors’ Stock Option Plan, which collectively provided for the granting of stock options to employees and non-employee directors. WHN stock options were converted to WellPoint stock options using the option exchange ratio as defined in the merger agreement. The converted stock options were recorded at the acquisition date as additional paid-in capital and valued at $559.9 using a Black-Scholes option-pricing model. The following weighted-average assumptions were used for the conversion: risk-free interest rate of 3.07%; volatility factor of 33.00%; expected dividend yield of 0.00%; and expected option life of three years.
Stock options are granted for a fixed number of shares with an exercise price at least equal to the fair value of the shares at the grant date. The stock options granted in 2006 and 2005 generally vest over three years in equal semi-annual installments and have a term of ten years from the grant date. The stock options granted prior to 2005 generally vest in equal annual installments over three years and expire ten years from the grant date.
Certain option grants contain provisions whereby the employee continues to vest in the award subsequent to termination due to retirement. Prior to the adoption of FAS 123R, the Company’s expense attribution methodology did not consider such vesting provisions and the fair value of the awards was amortized over the stated vesting periods. Effective with the adoption of FAS 123R, the Company changed its attribution method for newly granted awards and now considers all vesting and other provisions, including retirement eligibility, in determining the requisite service period over which the fair value of the awards will be recognized.
Restricted stock awards are issued at the fair value of the stock on the grant date. The restrictions lapse in three equal annual installments. Prior to the adoption of FAS 123R, unearned compensation for grants of restricted stock equivalent to the fair value of the shares at the date of grant was recorded as a separate component of shareholders’ equity and subsequently amortized to compensation expense over the awards’ vesting period. In accordance with FAS 123R, shareholders’ equity is credited commensurate with the recognition of compensation expense. All unamortized unearned compensation at January 1, 2006 was reclassified to additional paid-in capital.
For the years ended December 31, 2006, 2005 and 2004, the Company recognized share-based compensation cost of $246.9, $81.2 and $10.0, respectively, as well as related tax benefits of $89.9, $28.5 and $3.6, respectively. As a result of the adoption of FAS 123R effective January 1, 2006, the Company’s income before income taxes and net income for the year ended December 31, 2006 were $158.2 and $97.9 lower, respectively, than if the Company had continued to account for the share-based compensation programs under APB 25. Accordingly, the reported basic and diluted earnings per share for the year ended December 31, 2006 were $0.16 and $0.15, respectively, lower than had the Company not adopted FAS 123R effective January 1, 2006.
In addition to the higher compensation cost under FAS 123R, the adoption of FAS 123R resulted in a higher number of diluted shares outstanding for purposes of calculating diluted earnings per share due to a change in the calculation of dilutive stock options under the treasury method.
116
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
12. Capital Stock (continued)
A summary of stock option activity for the year ended December 31, 2006 is as follows:
Number of Shares | Weighted-Average Option Price per Share | Weighted-Average Remaining Contractual Life | Aggregate Intrinsic Value | ||||||||
Outstanding at January 1, 2006 | 44.2 | $ | 40.99 | ||||||||
Granted | 6.6 | 76.52 | |||||||||
Exercised | (13.8 | ) | 36.71 | ||||||||
Forfeited or expired | (1.8 | ) | 63.70 | ||||||||
Outstanding at December 31, 2006 | 35.2 | 48.19 | 6.7 | $ | 1,073.8 | ||||||
Exercisable at December 31, 2006 | 25.0 | 41.12 | 6.0 | 940.2 | |||||||
The intrinsic value of options exercised during the years ended December 31, 2006, 2005 and 2004 amounted to $482.1, $490.5 and $363.0, respectively. The Company recognized tax benefits of $168.5, $199.1 and $141.4 in 2006, 2005 and 2004, respectively, from option exercises and disqualifying dispositions. The total fair value of shares vested during the years ended December 31, 2006, 2005 and 2004 was $105.3, $59.5 and $11.6, respectively. During the years ended December 31, 2006, 2005 and 2004 the Company received cash of $505.2, $417.2 and $137.1, respectively, from exercises of stock options.
A summary of the status of nonvested restricted stock activity for the year ended December 31, 2006 is as follows:
| Shares | Weighted-Average Grant Date Fair Value per Share | |||||
Nonvested at January 1, 2006 | 2.6 | $ | 56.85 | |||
Granted | 1.0 | 76.33 | ||||
Vested | (1.3 | ) | 52.19 | |||
Forfeited | (0.3 | ) | 64.58 | |||
Nonvested at December 31, 2006 | 2.0 | 68.74 | ||||
As of December 31, 2006, the total remaining unrecognized compensation cost related to nonvested stock options and restricted stock amounted to $83.4 and $75.4, respectively, which will be amortized over the weighted-average remaining requisite service periods of 10 and 12 months, respectively.
As of December 31, 2006, there were 28.2 shares of common stock available for future grants under the 2006 Incentive Plan.
Employee Stock Purchase Plan
The Company has registered 6.0 shares of common stock for the Employee Stock Purchase Plan (“Stock Purchase Plan”) which is intended to provide a means to encourage and assist employees in acquiring a stock ownership interest in WellPoint. No employee will be permitted to purchase more than $25,000 (actual dollars) worth of stock in any calendar year, based on the fair value of the stock at the beginning of each plan quarter. Employees become participants by electing payroll deductions from 1% to 15% of gross compensation. Payroll
117
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
12. Capital Stock (continued)
deductions are accumulated during each quarter and applied toward the purchase of stock on the last trading day of each quarter. Once purchased, the stock is accumulated in the employee’s investment account. The purchase price per share is 85% of the lower of the fair value of a share of common stock on either the first or last trading day of the quarter. During 2006, 2005 and 2004, 0.9, 1.0 and 0.6 shares of common stock, respectively were purchased under the Stock Purchase Plan, resulting in $11.6, $12.8 and $5.2 of related compensation cost, respectively. As of December 31, 2006, there were approximately 2.5 shares of common stock available for issuance under the Stock Purchase Plan.
Fair Value
As described in Note 2, the Company adopted FAS 123R on January 1, 2006, using the modified prospective transition method. The pro forma information regarding net income and earnings per share presented in Note 2 has been determined as if the Company accounted for its stock-based compensation using the fair value method.
In 2005, the Company began using a binomial lattice valuation model to estimate the fair value of all future stock options granted. The binomial lattice model is deemed to provide a more accurate estimate of the fair values of employee stock options as it incorporates the impact of employee exercise behavior and allows for the input of a range of assumptions. Expected volatility assumptions used in the binomial lattice model are based on an analysis of implied volatilities of publicly traded options on WellPoint stock and historical volatility of WellPoint’s stock price. The risk-free interest rate is derived from the U.S. Treasury strip rates at the time of the grant. The expected term of the options was derived from the outputs of the binomial lattice model, which incorporates post-vesting forfeiture assumptions based on an analysis of historical data. The dividend yield was based on the Company’s estimate of future dividend yields. Similar groups of employees that have dissimilar exercise behavior are considered separately for valuation purposes. The Company utilizes the “multiple-grant” approach, as described in FAS 123R, for recognizing compensation expense associated with each separately vesting portion of the share-based award. Prior to 2005, the Company historically used a Black-Scholes option pricing model to estimate the fair value of stock options with inputs for volatility and expected term of the options primarily based on historical information.
The following weighted-average assumptions were used to estimate the fair values of options granted during the years ended December 31:
| 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | |||||||
Risk-free interest rate | 4.59 | % | 4.09 | % | 3.56 | % | |||
Volatility factor | 26.00 | % | 28.00 | % | 37.00 | % | |||
Dividend yield | — | — | — | ||||||
Weighted-average expected life | 5.1 years | 3.9 years | 4.5 years |
The following weighted-average fair values were determined for the years ending December 31:
| 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | |||||||
Options granted during the year | $ | 24.52 | $ | 19.71 | $ | 16.38 | |||
Restricted stock and stock awards granted during the year | 76.33 | 65.77 | 53.93 | ||||||
Employee stock purchases during the year | 12.32 | 13.27 | 9.18 | ||||||
118
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
12. Capital Stock (continued)
The binomial lattice and Black-Scholes option-pricing models require the input of highly subjective assumptions including the expected stock price volatility. Because the Company’s stock option grants have characteristics significantly different from those of traded options, and because changes in the subjective input assumptions can materially affect the fair value estimate, in management’s opinion, existing models do not necessarily provide a reliable single measure of the fair value of its stock option grants.
Stock Repurchase Program
Under the Board of Directors’ authorization, WellPoint maintains a common stock repurchase program. Repurchases may be made from time to time at prevailing market prices, subject to certain restrictions on volume, pricing and timing. During 2006, the Company repurchased and retired approximately 60.7 shares at an average cost per share of $74.91 for an aggregate cost of $4,550.2. During 2005, WellPoint repurchased and retired approximately 5.1 shares at an average cost per share of $64.92 for an aggregate cost of $333.4. During 2004, the Company repurchased and retired 2.0 shares, at an average per share price of $41.12, for an aggregate cost of $82.3. The excess of cost of the repurchased shares over par value is charged on a pro rata basis to additional paid-in capital and retained earnings. On December 7, 2006, the Board of Directors authorized an increase of $1,000.0 in the Company’s stock repurchase program, increasing the program to $5,500.0 since the current program’s inception in 2005. As of December 31, 2006, the Company had Board of Directors’ authorization to purchase up to an additional $949.8 of common stock. Subsequent to December 31, 2006, we repurchased and retired approximately 6.0 shares for an aggregate cost of approximately $463.5, leaving approximately $486.3 for authorized future repurchases at February 12, 2006. The Company’s stock repurchase program is discretionary as the Company is under no obligation to repurchase shares. Shares are repurchased under the program because the Company believes it is a prudent use of capital.
Equity Security Units
At the time of its initial public offering on November 2, 2001, the Company issued 4.6 Equity Security Units at 6.00%. Each Equity Security Unit contained a purchase contract under which the holder agreed to purchase, for twenty-five dollars, shares of the Company’s common stock on November 15, 2004. In November 2004, the Company received $230.0 for the issuance of approximately 10.6 shares of Anthem common stock pursuant to the purchase contract portion of the Equity Security Units. The number of shares purchased was determined based on the average trading price of the Company’s common stock at the time of settlement.
Put Options
During 2005, WellPoint sold put options to independent third parties that would have required WellPoint to purchase 1.0 shares of its common stock if exercised. All of these put options expired unexercised in 2005 and WellPoint recorded $1.1 as net realized gains on investments.
119
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
13. Earnings per Share
The denominator for basic and diluted earnings per share at December 31 is as follows:
| 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | ||||
Denominator for basic earnings per share—weighted-average shares | 627.9 | 610.9 | 305.2 | |||
Effect of dilutive securities: | ||||||
Employee and director stock options and non vested restricted stock awards | 14.2 | 14.9 | 4.4 | |||
Shares to be contingently issued under long-term incentive plan | — | — | 0.4 | |||
Incremental shares from conversion of Equity Security Unit purchase contracts | — | — | 4.6 | |||
Denominator for diluted earnings per share | 642.1 | 625.8 | 314.6 | |||
During the year ended December 31, 2006, weighted average stock options of 5.3 were excluded from the denominator for diluted earnings per share because the stock options were anti-dilutive. There were no anti-dilutive stock options during the years ended December 31, 2005 and 2004. Shares were issued under the long-term incentive plan in April 2004. The Equity Security Unit purchase contracts were settled on November 15, 2004, and approximately 10.6 shares of the Company’s common stock were issued and included in the basic earnings per share calculation.
120
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
14. Income Taxes
The components of deferred income taxes at December 31 are as follows:
| 2006 | 2005 | |||||||
Deferred tax assets relating to: | ||||||||
Pension and postretirement benefits | $ | 255.2 | $ | 210.7 | ||||
Accrued expenses | 418.5 | 401.0 | ||||||
Alternative minimum tax and other credits | 2.0 | 203.7 | ||||||
Insurance reserves | 192.3 | 188.8 | ||||||
Net operating loss carryforwards | 64.5 | 71.0 | ||||||
Bad debt reserves | 83.8 | 65.6 | ||||||
Depreciation and amortization | 24.7 | 37.9 | ||||||
State income tax | 105.4 | 116.2 | ||||||
Deferred compensation | 169.6 | 177.8 | ||||||
Other | 57.3 | 55.1 | ||||||
Total deferred tax assets | 1,373.3 | 1,527.8 | ||||||
Valuation allowance | (22.8 | ) | (22.3 | ) | ||||
Total deferred tax assets, net of valuation allowance | 1,350.5 | 1,505.5 | ||||||
Deferred tax liabilities relating to: | ||||||||
Unrealized gains (losses) on securities | 103.1 | (16.6 | ) | |||||
Acquisition related: | ||||||||
Goodwill and conversion | 50.4 | 43.3 | ||||||
Trademarks and software development | 2,676.4 | 2,683.5 | ||||||
Subscriber base, provider and hospital networks | 962.0 | 1,067.3 | ||||||
Other | 18.6 | 8.9 | ||||||
Investment basis difference | 51.0 | 147.3 | ||||||
Pension benefits | 120.5 | 81.1 | ||||||
Other | 76.1 | 68.8 | ||||||
Total deferred tax liabilities | 4,058.1 | 4,083.6 | ||||||
Net deferred tax liability | $ | (2,707.6 | ) | $ | (2,578.1 | ) | ||
Deferred tax asset—current | $ | 642.6 | $ | 689.0 | ||||
Deferred tax liability—noncurrent | (3,350.2 | ) | (3,267.1 | ) | ||||
Net deferred tax liability | $ | (2,707.6 | ) | $ | (2,578.1 | ) | ||
The net increase in the valuation allowance for 2006 and 2005 was $0.5 and $0.0, respectively. The increase resulted from realized and unrealized capital losses of subsidiaries not included in the Company’s consolidated tax return. The remaining valuation allowance is primarily attributable to the uncertainty of alternative minimum tax credits and net operating loss carryforwards. As deferred tax assets related to these types of deductions are recognized in the tax return, the valuation allowance is no longer required and is reduced.
121
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
14. Income Taxes (continued)
Significant components of the provision for income taxes for the years ended December 31, consist of the following:
| 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | |||||||||
Current tax expense: | |||||||||||
Federal | $ | 1,397.9 | $ | 1,401.5 | $ | 508.2 | |||||
State and local | 133.9 | 113.7 | 27.2 | ||||||||
Total current tax expense | 1,531.8 | 1,515.2 | 535.4 | ||||||||
Deferred tax expense (benefit) | 287.7 | (88.7 | ) | (52.2 | ) | ||||||
Total income tax expense | $ | 1,819.5 | $ | 1,426.5 | $ | 483.2 | |||||
A reconciliation of income tax expense recorded in the consolidated statements of income and amounts computed at the statutory federal income tax rate for the years ended December 31, is as follows:
| 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Amount | Percent | Amount | Percent | Amount | Percent | ||||||||||||||||
Amount at statutory rate | $ | 1,720.0 | 35.0 | % | $ | 1,361.6 | 35.0 | % | $ | 505.2 | 35.0 | % | |||||||||
State and local income taxes net of federal tax benefit | 84.6 | 1.7 | 61.0 | 1.6 | (35.7 | ) | (2.5 | ) | |||||||||||||
Tax exempt interest and dividends received deduction | (41.5 | ) | (0.8 | ) | (29.0 | ) | (0.7 | ) | (14.7 | ) | (1.0 | ) | |||||||||
Non-deductible acquisition expense | — | — | — | — | 21.5 | 1.5 | |||||||||||||||
Other, net | 56.4 | 1.1 | 32.9 | 0.8 | 6.9 | 0.5 | |||||||||||||||
Total income tax expense | $ | 1,819.5 | 37.0 | % | $ | 1,426.5 | 36.7 | % | $ | 483.2 | 33.5 | % | |||||||||
During the third quarter of 2006, the Company decreased its state deferred tax liability by $43.0, resulting in a tax benefit, net of federal taxes, of $28.0, or $0.04 per basic and diluted shares, for the year ended December 31, 2006. This resulted from a lower effective tax rate due to changes in the Company’s state tax apportionment factors following the WellChoice acquisition.
During the first quarter of 2005, a refund claim filed by the Company in 2003 was approved by the Congressional Joint Committee on Taxation. The claim relates to initially disallowed losses on the sale of certain subsidiaries in the late 1990s. A tax benefit of $28.4 related to this claim was recorded in the first quarter of 2005. Net income per basic and diluted share related to this claim was $0.04 for the year ended December 31, 2005.
As a result of legislation enacted in Indiana on March 16, 2004, the Company recorded deferred tax assets and liabilities, with a corresponding net tax benefit in the income statement of $44.8, or $0.15 per basic share and $0.14 per diluted share, for the year ended December 31, 2004. The legislation eliminated the creation of tax credits resulting from the payment of future assessments to the Indiana Comprehensive Health Insurance Association (“ICHIA”), Indiana’s high-risk health insurance pool. Under the new legislation, ICHIA tax credits are limited to any unused ICHIA assessment paid prior to December 31, 2004. A valuation allowance of $5.6 was established for the portion of the deferred tax asset, which the Company believes will likely not be utilized. There is no carryforward limitation on the tax credits and the net operating loss carryforwards do not begin to expire until 2018.
122
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
14. Income Taxes (continued)
In certain states, the Company pays premium taxes in lieu of state income taxes. Premium taxes are reported with general and administrative expense.
At December 31, 2006, the Company had unused federal tax net operating loss carryforwards of approximately $184.4 to offset future taxable income. The loss carryforwards expire in the years 2007 through 2024. During 2006, 2005 and 2004 federal income taxes paid totaled $1,553.3, $994.0 and $646.3, respectively.
15. Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss)
A reconciliation of the components of accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) at December 31 is as follows:
| 2006 | 2005 | |||||||
Investments: | ||||||||
Gross unrealized gains | $ | 418.0 | $ | 160.0 | ||||
Gross unrealized losses | (148.0 | ) | (189.1 | ) | ||||
Net pretax unrealized gains (losses) | 270.0 | (29.1 | ) | |||||
Deferred tax (liability) asset | (108.2 | ) | 10.7 | |||||
Net unrealized gains (losses) on investments | 161.8 | (18.4 | ) | |||||
Cash flow hedges: | ||||||||
Gross unrealized losses | (8.5 | ) | — | |||||
Deferred tax asset | 2.9 | — | ||||||
Net unrealized loss on cash flow hedges | (5.6 | ) | — | |||||
Additional minimum pension liability: | ||||||||
Gross additional minimum pension liability | — | (2.9 | ) | |||||
Deferred tax asset | — | 1.0 | ||||||
Net additional minimum pension liability | — | (1.9 | ) | |||||
Defined benefit pension plans: | ||||||||
Reclassification of additional minimum pension liability | (10.6 | ) | — | |||||
Deferred net actuarial loss | (98.6 | ) | — | |||||
Deferred net actuarial loss | (109.2 | ) | — | |||||
Deferred prior service costs | (7.0 | ) | — | |||||
Deferred tax asset | 45.2 | — | ||||||
Net unrecognized period benefit costs for defined benefit pension plans | (71.0 | ) | — | |||||
Postretirement benefit plans: | ||||||||
Deferred net actuarial loss | (87.0 | ) | — | |||||
Deferred prior service credits | 29.6 | — | ||||||
Deferred tax asset | 22.3 | — | ||||||
Net unrecognized period benefit costs for postretirement benefit plans | (35.1 | ) | — | |||||
Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) | $ | 50.1 | $ | (20.3 | ) | |||
123
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
15. Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) (continued)
Comprehensive income (loss) reclassification adjustments for the years ended December 31 are as follows:
| 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | ||||||||||
Investments: | ||||||||||||
Net holding gain (loss) on investment securities arising during the period, net of tax expense (benefit) of $118.9, $(89.4), and $14.0, respectively | $ | 180.5 | $ | (163.8 | ) | $ | 26.1 | |||||
Reclassification adjustment for net realized gain on investment securities, net of tax (benefit) expense of $0.0, $(3.6), and $15.4, respectively | (0.3 | ) | 6.6 | (28.6 | ) | |||||||
Total reclassification adjustment on investments | 180.2 | (157.2 | ) | (2.5 | ) | |||||||
Cash flow hedges: | ||||||||||||
Holding (loss) gain, net of tax (benefit) expense of $(2.9), $(5.2) and $5.2, respectively | (5.6 | ) | (9.7 | ) | 9.7 | |||||||
Other: | ||||||||||||
Net change in additional minimum pension liability, net of tax (benefit) expense of $(3.0), $0.4 and $0.0, respectively | (4.7 | ) | 0.8 | (0.1 | ) | |||||||
Net gain (loss) recognized in other comprehensive income, net of tax expense (benefit) of $113.0, $(90.6) and $3.8, respectively | $ | 169.9 | $ | (166.1 | ) | $ | 7.1 | |||||
16. Leases
The Company leases office space and certain computer and related equipment using noncancelable operating leases. At December 31, 2006, future lease payments for operating leases with initial or remaining noncancelable terms of one year or more consisted of the following:
2007 | $ | 145.7 | |
2008 | 140.2 | ||
2009 | 130.3 | ||
2010 | 105.7 | ||
2011 | 96.5 | ||
Thereafter | 443.0 | ||
Total minimum payments required | $ | 1,061.4 | |
The Company has certain lease agreements that contain contingent payment provisions. Under these provisions, the Company pays contingent amounts in addition to base rent, primarily based upon annual changes in the consumer price index. The schedule above contains estimated amounts for potential future increases in lease payments based on the contingent payment provisions.
Lease expense for 2006, 2005 and 2004 was $221.3, $149.3 and $62.8, respectively.
17. Retirement Benefits
The Company, through certain subsidiaries, sponsors various non-contributory employee defined benefit plans.
The WellPoint Cash Balance Pension Plan (the “Plan”), which name changed from the Anthem Cash Balance Pension Plan effective January 1, 2006, is a cash balance pension plan sponsored by Anthem Insurance.
124
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
17. Retirement Benefits (continued)
The Plan covered eligible employees of the Company and certain subsidiaries prior to its merger with WHN. Effective January 1, 2006, the plan sponsor curtailed the benefits under the Plan. As a result, most participants’ accounts no longer accrue pay credits, but do continue to earn interest. Employees hired on or after January 1, 2006 are not eligible to participate in the Plan. Certain participants were “grandfathered” into the Plan based on age and years of service. Grandfathered participants continue to accrue pay credits under the Plan formula. The Company recorded a curtailment gain of $4.6 during the three months ended March 31, 2006.
Prior to June 30, 2006, Anthem Holding Corp. sponsored the WellPoint Health Networks Inc. Pension Accumulation Plan (the “WHN Plan”), a defined benefit pension plan which covered eligible employees of WHN and certain WHN subsidiaries prior to its merger with Anthem. Effective January 1, 2004, the plan sponsor curtailed benefits under the WHN Plan, with the result that most participants’ accounts no longer accrued pay credits, but do continue to earn interest. Employees of WHN hired after December 31, 2003 were not eligible to participate in the WHN Plan, except for certain employees covered by collective bargaining agreements. Certain participants were “grandfathered” into the WHN Plan based on age and years of service. Grandfathered participants continue to accrue pay credits under the WHN Plan formula. Effective June 30, 2006, the WHN Plan was merged into the Plan.
Prior to December 31, 2006, WellPoint Holding Corp. sponsored the Empire Blue Cross Blue Shield Cash Balance Pension Plan (the “Empire Plan”) a cash balance defined benefit plan which covered eligible employees of WellChoice and certain of its subsidiaries prior to WellPoint’s acquisition of WellChoice. The Empire Plan was merged into the Plan on December 31, 2006. Effective January 1, 2007, the plan sponsor curtailed benefits under the Empire Plan. As a result, most participants’ accounts no longer accrue pay credits, but continue to earn interest. Employees hired on or after January 1, 2007 are not eligible to participate in the Plan. Certain participants were “grandfathered” into the Plan based on age and years of service in the former Empire Plan. Grandfathered participants continue to receive pay credits under the Plan formula. There will be no curtailment gain or loss associated with the curtailment of benefits under the Empire Plan.
The UGS Pension Plan is a defined benefit pension plan, which covers eligible employees (including certain employees covered by a collective bargaining agreement) of National Government Services, Inc., which name changed from AdminaStar Federal, Inc. effective November 17, 2006, who were formerly employed by United Government Services, LLC (“UGS”). Effective January 1, 2004, the plan sponsor curtailed benefits under the UGS Pension Plan, resulting in most non-bargained participants’ accounts no longer accruing pay credits but continuing to earn interest. Employees subject to collective bargaining, as well as certain non-bargained employees who were “grandfathered” based on age and years of service, continue to receive pay credits. Non-bargained employees of UGS hired after December 31, 2003 are not eligible to participate in the UGS Pension Plan.
The Employees’ Retirement Plan of Blue Cross of California (the “BCC Plan”) provides retirement benefits to eligible employees of Blue Cross of California who are covered by a collective bargaining agreement. Effective January 1, 2007, the plan sponsor curtailed benefits under the BCC Plan by providing that no Blue Cross of California employees hired after December 31, 2006 are eligible to participate in the BCC Plan. There will be no curtailment gain or loss associated with the curtailment of benefits under the BCC Plan.
All of the plans’ assets consist primarily of common stocks, fixed maturity securities, investment funds and short-term investments. The funding policies for all plans are to contribute amounts at least sufficient to meet the minimum funding requirements set forth in the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974, as amended (“ERISA”), and the Pension Protection Act of 2006 and in accordance with income tax regulations, plus such additional amounts as are necessary to provide assets sufficient to meet the benefits to be paid to plan participants.
125
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
17. Retirement Benefits (continued)
In addition, the Company offers certain employees postretirement benefits including certain life, medical, vision and dental benefits upon retirement. There are several postretirement benefit plans, which differ in amounts of coverage, deductibles, retiree contributions, years of service and retirement age. The Company may fund certain benefit costs through discretionary contributions to a Voluntary Employees’ Beneficiary Association (“VEBA”) trust. Other costs are accrued, with the retiree paying a portion of the costs. Postretirement plan assets held in the VEBA trust consist primarily of bonds and equity securities.
The Company currently uses a September 30 measurement date for determining benefit obligations and fair value of plan assets and will adopt the fiscal-year-end measurement requirements of FAS 158 on December 31, 2008.
The following tables disclose consolidated “pension benefits”, which include the defined benefit pension plans described above, and consolidated “other benefits”, which include other postretirement benefits described above. Weighted average calculations were computed using assumptions at the relevant measurement dates. The effect of acquisitions on the consolidated benefit obligation and plan assets is reflected through the business combination lines of the tables below.
The reconciliation of the benefit obligation is as follows:
| Pension Benefits | Other Benefits | |||||||||||||||
| 2006 | 2005 | 2006 | 2005 | |||||||||||||
Benefit obligation at beginning of year | $ | 1,966.0 | $ | 1,380.3 | $ | 603.2 | $ | 431.6 | ||||||||
Service cost | 60.1 | 59.0 | 12.1 | 8.1 | ||||||||||||
Interest cost | 102.4 | 78.5 | 31.1 | 25.0 | ||||||||||||
Plan amendments | 10.2 | — | (20.2 | ) | — | |||||||||||
Actuarial (gain) loss | (140.3 | ) | 83.5 | (6.3 | ) | 74.2 | ||||||||||
Benefits paid | (183.5 | ) | (110.4 | ) | (35.3 | ) | (27.1 | ) | ||||||||
Business combinations | 1.8 | 475.1 | 19.2 | 91.4 | ||||||||||||
Benefit obligation at end of year | $ | 1,816.7 | $ | 1,966.0 | $ | 603.8 | $ | 603.2 | ||||||||
The changes in the fair value of plan assets are as follows:
| Pension Benefits | Other Benefits | |||||||||||||||
| 2006 | 2005 | 2006 | 2005 | |||||||||||||
Fair value of plan assets at beginning of year | $ | 1,911.9 | $ | 1,347.1 | $ | 41.9 | $ | 40.6 | ||||||||
Actual return on plan assets | 150.4 | 124.9 | (0.7 | ) | 3.7 | |||||||||||
Employer contributions | 108.6 | 117.8 | 33.3 | 24.7 | ||||||||||||
Benefits paid | (183.5 | ) | (110.4 | ) | (35.2 | ) | (27.1 | ) | ||||||||
Business combinations | — | 432.5 | — | — | ||||||||||||
Fair value of plan assets at end of year | $ | 1,987.4 | $ | 1,911.9 | $ | 39.3 | $ | 41.9 | ||||||||
126
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
17. Retirement Benefits (continued)
The reconciliation of the funded status to the net benefit cost recognized is as follows:
| Pension Benefits | Other Benefits | ||||||||||||||
| 2006 | 2005 | 2006 | 2005 | ||||||||||||
Funded status | $ | 170.7 | $ | (54.1 | ) | $ | (564.5 | ) | $ | (561.2 | ) | ||||
Unrecognized net actuarial loss | — | 289.5 | — | 94.0 | |||||||||||
Unrecognized prior service cost | — | (6.4 | ) | — | (12.0 | ) | |||||||||
Net amount recognized at the measurement date | 170.7 | 229.0 | (564.5 | ) | (479.2 | ) | |||||||||
Contributions made after the measurement date | 1.5 | 0.5 | 10.1 | 6.9 | |||||||||||
Net amount recognized at December 31 | $ | 172.2 | $ | 229.5 | $ | (554.4 | ) | $ | (472.3 | ) | |||||
The net amount recognized in the consolidated balance sheets is as follows:
| Pension Benefits | Other Benefits | |||||||||||||||
| 2006 | 2005 | 2006 | 2005 | |||||||||||||
Noncurrent assets | $ | 274.1 | $ | 290.6 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||
Current liabilities | (6.9 | ) | — | (19.1 | ) | — | ||||||||||
Noncurrent liabilities | (95.0 | ) | (64.0 | ) | (535.3 | ) | (472.3 | ) | ||||||||
Accumulated other comprehensive income | — | 2.9 | — | — | ||||||||||||
Net amount recognized at December 31 | $ | 172.2 | $ | 229.5 | $ | (554.4 | ) | $ | (472.3 | ) | ||||||
The amounts included in accumulated other comprehensive income that have not been recognized as components of net period benefit costs are as follows:
| Pension Benefits | Other Benefits | ||||||||||||
| 2006 | 2005 | 2006 | 2005 | ||||||||||
Net actuarial loss | $ | 109.2 | $ | — | $ | 87.0 | $ | — | |||||
Prior service cost (credit) | 7.0 | — | (29.6 | ) | — | ||||||||
Net amount recognized at December 31 | $ | 116.2 | $ | — | $ | 57.4 | $ | — | |||||
The estimated net actuarial loss and prior service cost (credit) for the defined benefit pension plans that will be amortized from accumulated other comprehensive income into net periodic benefit costs over the next fiscal year are $1.2 and $(0.6), respectively. The estimated net loss and prior service cost (credit) for postretirement benefit plans that will be amortized from accumulated other comprehensive income into net periodic benefit costs over the next fiscal year are $4.8 and $(2.9), respectively.
127
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
17. Retirement Benefits (continued)
The incremental effect of applying FAS 158 on individual line items in the consolidated balance sheet at December 31, 2006, including the effect of related deferred taxes, is as follows:
| Before Application of FAS 158 | Adjustments | After Application of FAS 158 | ||||||||
Deferred tax assets, net | $ | 632.7 | $ | 9.9 | $ | 642.6 | ||||
Total current assets | 11,796.8 | 9.9 | 11,806.7 | |||||||
Other noncurrent assets | 596.1 | (98.7 | ) | 497.4 | ||||||
Total assets | 51,848.6 | (88.8 | ) | 51,759.8 | ||||||
Other current liabilities | 1,371.4 | 26.0 | 1,397.4 | |||||||
Total current liabilities | 15,297.4 | 26.0 | 15,323.4 | |||||||
Deferred tax liability, net | 3,403.8 | (53.6 | ) | 3,350.2 | ||||||
Other noncurrent liabilities | 1,332.0 | 38.3 | 1,370.3 | |||||||
Total liabilities | 27,173.3 | 10.7 | 27,184.0 | |||||||
Accumulated other comprehensive income | 149.6 | (99.5 | ) | 50.1 | ||||||
Total shareholders’ equity | 24,675.3 | (99.5 | ) | 24,575.8 | ||||||
The accumulated benefit obligation for the defined benefit pension plans was $1,803.7 and $1,942.1 at December 31, 2006 and 2005, respectively.
As of December 31, 2006, certain pension plans of the Company had accumulated benefit obligations in excess of plan assets. For those same plans, the projected benefit obligation was also in excess of plan assets. Such plans had a combined projected benefit obligation, accumulated benefit obligation and fair value of plan assets of $103.4, $94.5 and $0.0, respectively.
The weighted-average assumptions used in calculating the benefit obligations for all plans are as follows:
| Pension Benefits | Other Benefits | |||||||||||
| 2006 | 2005 | 2006 | 2005 | |||||||||
Discount rate | 5.90 | % | 5.31 | % | 5.90 | % | 5.29 | % | ||||
Rate of compensation increase | 4.50 | % | 4.39 | % | 4.50 | % | 4.42 | % | ||||
Expected rate of return on plan assets | 8.00 | % | 7.80 | % | 7.11 | % | 6.95 | % | ||||
128
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
17. Retirement Benefits (continued)
The components of net periodic benefit cost included in the consolidated statements of income are as follows:
| 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | ||||||||||
Pension Benefits | ||||||||||||
Service cost | $ | 60.1 | $ | 59.0 | $ | 47.2 | ||||||
Interest cost | 102.4 | 78.5 | 54.7 | |||||||||
Expected return on assets | (144.6 | ) | (102.6 | ) | (71.9 | ) | ||||||
Recognized actuarial loss | 17.9 | 17.3 | 14.4 | |||||||||
Amortization of prior service cost | 1.4 | (3.6 | ) | (3.6 | ) | |||||||
Curtailment gain | (4.6 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
Net periodic benefit cost | $ | 32.6 | $ | 48.6 | $ | 40.8 | ||||||
Other Benefits | ||||||||||||
Service cost | $ | 12.1 | $ | 8.1 | $ | 4.3 | ||||||
Interest cost | 31.1 | 25.0 | 15.0 | |||||||||
Expected return on assets | (2.8 | ) | (2.7 | ) | (2.5 | ) | ||||||
Recognized actuarial loss | 4.2 | 0.4 | 0.4 | |||||||||
Amortization of prior service cost | (2.5 | ) | (4.0 | ) | (6.3 | ) | ||||||
Net periodic benefit cost | $ | 42.1 | $ | 26.8 | $ | 10.9 | ||||||
The weighted-average assumptions used in calculating the net periodic benefit cost for all plans are as follows:
| 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | |||||||
Pension Benefits | |||||||||
Discount rate | 5.31 | % | 5.83 | % | 6.25 | % | |||
Rate of compensation increase | 4.39 | % | 4.34 | % | 4.50 | % | |||
Expected rate of return on plan assets | 8.00 | % | 8.16 | % | 8.00 | % | |||
Other Benefits | |||||||||
Discount rate | 5.29 | % | 5.87 | % | 6.25 | % | |||
Rate of compensation increase | 4.42 | % | 4.26 | % | 4.50 | % | |||
Expected rate of return on plan assets | 6.95 | % | 6.05 | % | 6.00 | % | |||
The weighted average assumed health care cost trend rates to be used for next year to measure the expected cost of other benefits is 9.00% with a gradual decline to 5.0% by the year 2012. These estimated trend rates are subject to change in the future. The health care cost trend rate assumption has a significant effect on the amounts reported. For example, an increase in the assumed health care cost trend rate of one percentage point would increase the postretirement benefit obligation as of December 31, 2006 by $44.3 and would increase service and interest costs by $2.9. Conversely, a decrease in the assumed health care cost trend rate of one percentage point would decrease the postretirement benefit obligation by $38.1 as of December 31, 2006 and would decrease service and interest costs by $2.6.
An important factor in determining the Company’s pension expense is the assumption for expected long-term rate of return on plan assets. The Company uses a total portfolio return analysis in the development of its
129
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
17. Retirement Benefits (continued)
assumption. Factors such as past market performance, the long-term relationship between fixed maturity and equity securities, interest rates, inflation and asset allocations are considered in the assumption. The assumption includes an estimate of the additional return expected from active management of the investment portfolio. Peer data and historical returns are also reviewed for appropriateness of the selected assumption. The expected long-term rate of return is calculated by the geometric averaging method, which calculates an expected multi-period return, reflecting volatility drag on compound returns.
In managing the plan assets, the Company’s objective is to be a responsible fiduciary while minimizing financial risk to the Company. In addition to producing a reasonable return, the investment strategy seeks to minimize the volatility in the Company’s expense and cash flow. Over time, the Company has increased the duration and allocation of fixed maturity securities to more closely match the sensitivity of plan assets with the plan obligations.
Plan assets include a diversified mix of investment grade fixed maturity securities and equity securities across a range of sectors and levels of capitalization to maximize the long-term return for a prudent level of risk. As of the measurement date, the Company’s weighted-average targeted asset allocation and actual allocation by asset category are as follows:
Target Allocation for All | Actual Allocation | ||||||||||||||
| Pension Benefit Assets | Other Benefit Assets | ||||||||||||||
| 2006 | 2005 | 2006 | 2005 | ||||||||||||
Equity securities: | |||||||||||||||
Domestic equities | 51 | % | 51 | % | 42 | % | 48 | % | 43 | % | |||||
International equities | 14 | 16 | 14 | 18 | 12 | ||||||||||
Fixed maturity securities | 33 | 27 | 37 | 26 | 42 | ||||||||||
Other | 2 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 3 | ||||||||||
Total | 100 | % | 100 | % | 100 | % | 100 | % | 100 | % | |||||
The Company’s current funding strategy is to fund an amount at least equal to the minimum required funding as determined under ERISA with consideration of maximum tax deductible amounts. The Company may elect to make discretionary contributions up to the maximum amount deductible for income tax purposes. For the year ended December 31, 2006, no contributions were required under ERISA; however, the Company made tax deductible discretionary contributions totaling $108.6 to the defined benefit pension plans. Employer contributions related to other benefits represent payments to retirees for current benefits. Contributions to the VEBA are generally not material. The Company may elect to make discretionary contributions up to the maximum amount deductible for income tax purposes.
130
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
17. Retirement Benefits (continued)
The Company’s estimated future payments for pension benefits and postretirement benefits, which reflect expected future service, as appropriate, are as follows:
| Pension Benefits | Other Benefits | |||||
2007 | $ | 156.3 | $ | 37.5 | ||
2008 | 139.3 | 39.2 | ||||
2009 | 150.9 | 40.9 | ||||
2010 | 202.9 | 42.6 | ||||
2011 | 151.8 | 44.2 | ||||
2012 - 2016 | 845.8 | 231.5 | ||||
In addition to the defined benefit plans, the Company maintains the WellPoint 401(k) Retirement Savings Plan, which name changed from the Anthem 401(k) Long Term Savings Investment Plan effective December 31, 2005, a qualified defined contribution plan covering substantially all employees. Voluntary employee contributions are matched by the Company subject to certain limitations. Contributions made by the Company totaled $85.2, $74.6 and $34.0 during 2006, 2005 and 2004, respectively.
18. Commitments and Contingencies
Multi-District Litigation Settlement Agreement
In May 2000, a case titledCalifornia Medical Association vs. Blue Cross of California, et al. (the “CMA Litigation”), was filed in U.S. district court in San Francisco against Blue Cross of California (“BCC”), a subsidiary of WHN at the time, and now a Company subsidiary. The lawsuit alleges that BCC violated the Racketeer Influenced and Corrupt Organizations Act (“RICO”).
In August 2000, WHN was added as a defendant to Shane v. Humana, et al., a class-action lawsuit brought on behalf of health care providers nationwide alleging RICO violations (the “Shane Litigation”). Effective upon the November 30, 2004 merger with WHN, WHN became a wholly owned subsidiary of the Company. On September 26, 2002, Anthem was added as a defendant to the Shane Litigation.
In May 2003, in a case titledKenneth Thomas, M.D., et al., v. Blue Cross Blue Shield Association, et al., (the “Thomas Litigation”) several medical providers filed suit in federal district court in Miami, Florida against the BCBSA and Blue Cross and Blue Shield plans across the country, including the Company and WellChoice. The suit alleges that the BCBSA and the Blue Cross and Blue Shield plans violated RICO and challenges many of the same practices as the CMA Litigation and the Shane Litigation.
In October 2000, the federal Judicial Panel on Multidistrict Litigation (“MDL”) issued an order consolidating the CMA Litigation, the Shane Litigation and various other pending managed care class-action lawsuits against the Company and other companies before District Court Judge Federico Moreno in the Southern District of Florida for purposes of pretrial proceedings. A mediator was appointed by Judge Moreno and the parties conducted court-ordered mediation. On December 9, 2004, Judge Moreno issued a new scheduling order extending the expert discovery deadline to February 7, 2005 and setting trial for September 6, 2005.
On July 11, 2005, the Company entered into a settlement agreement (the “Agreement”) with representatives of more than 700,000 (actual number) physicians nationwide to resolve the CMA Litigation, the Shane Litigation, the Thomas Litigation and certain other similar cases brought by physicians. Under the Agreement,
131
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
18. Commitments and Contingencies (continued)
the Company agreed to make cash payments totaling up to $198.0, of which $135.0 is to be paid to physicians and $5.0 contributed to a not-for-profit foundation whose mission is to promote higher quality health care and to enhance the delivery of care to the disadvantaged members of the public. In addition, up to $58.0 will be paid in legal fees to be determined by the court. The Company also has agreed to implement and maintain a number of operational changes such as standardizing the definition of medical necessity in physician contracts, creating a formalized Physician Advisory Committee and modifying some of the Company’s claims payment and physician contracting provisions. The Agreement was subject to, and conditioned upon, review and approval by the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of Florida. The court preliminarily approved the settlement in an order filed July 15, 2005. The hearing for final approval was held on December 2, 2005 in Miami, Florida. The Court issued a final order approving the settlement on December 22, 2005, and issued an amended final order approving the settlement on January 4, 2006. As a result of the Agreement, the Company incurred a pre-tax expense of $103.0, or $0.10 per diluted share after tax, for the year ended December 31, 2005, which represents the final settlement amount of the Agreement that was not previously accrued. Appeals of the settlement initially filed by certain physicians have been resolved. Final cash payments under the Agreement totaling $209.5, including accrued interest, were made on October 5 and 6, 2006.
The WellChoice transaction was closed on December 28, 2005, after the settlement was reached with the plaintiffs in the CMA Litigation, the Shane Litigation and the Thomas Litigation. The former WellChoice company, which was merged with and into a wholly-owned subsidiary of WellPoint, continues to be a defendant in the Thomas Litigation, and is not affected by the settlement between the Company and plaintiffs. The Company believes that any liability that may result from this action is unlikely to have a material adverse effect on its financial position or results of operations.
Other Litigation
Prior to WHN’s acquisition of the group benefit operations (“GBO”) of John Hancock Mutual Life Insurance Company (“John Hancock”), John Hancock entered into a number of reinsurance arrangements, including with respect to personal accident insurance and the occupational accident component of workers’ compensation insurance, a portion of which was originated through a pool managed by Unicover Managers, Inc. Under these arrangements, John Hancock assumed risks as a reinsurer and transferred certain of such risks to other companies. Similar reinsurance arrangements were entered into by John Hancock following WHN’s acquisition of the GBO of John Hancock. These various arrangements have become the subject of disputes, including a number of legal proceedings to which John Hancock is a party. The Company is currently in arbitration with John Hancock regarding these arrangements. The Company believes that the liability that may result from this matter is unlikely to have a material adverse effect on its consolidated financial condition or results of operations.
In various California state courts, the Company is defending a number of individual lawsuits and two purported class actions alleging the wrongful rescission of individual insurance policies. The suits name the Company as well as BCC and BC Life & Health Insurance Company (“BCL&H”), both Company subsidiaries. The lawsuits generally allege breach of contract, bad faith and unfair business practices in a purported practice of rescinding new individual members following the submission of large claims. In December 2006, the California Medical Association filed a motion to intervene in one of the class actions. The motion has not been heard. In addition, the California Department of Managed Health Care and California Department of Insurance are conducting investigations of the allegations. The parties have agreed to mediate most of these lawsuits and the mediation has resulted in the resolution of some of these lawsuits. BCC and BCL&H recently announced an initiative to revise their rescission policies and practices in California.
132
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
18. Commitments and Contingencies (continued)
In various California state courts, several hospitals have filed suits against BCC and WHN for payment of claims denied where the member was rescinded. These lawsuits are currently in the process of moving into arbitration. In addition, a recent suit brought against BCC, BCL&H and WHN by a non-contracting hospital in California state court is a purported class action. This suit also seeks to recover for payment of claims denied where the member was rescinded. In December 2006, this purported class of hospitals also filed a motion to intervene in one of the individual class action cases referenced above. The motion has not been heard. The Company denies any wrongdoing. The Company intends to vigorously defend these proceedings; however, their ultimate outcome cannot be presently determined.
Other Contingencies
From time to time, the Company and certain of its subsidiaries are parties to various legal proceedings, many of which involve claims for coverage encountered in the ordinary course of business. The Company, like HMOs and health insurers generally, excludes certain health care services from coverage under its HMO, PPO and other plans. The Company is, in its ordinary course of business, subject to the claims of its enrollees arising out of decisions to restrict or deny reimbursement for certain services. The loss of even one such claim, if it results in a significant punitive damage award, could have a material adverse effect on the Company. In addition, the risk of potential liability under punitive damage theories may increase significantly the difficulty of obtaining reasonable settlements of coverage claims.
In addition to the lawsuits described above, the Company is also involved in other pending and threatened litigation of the character incidental to the business transacted, arising out of its operations and its 2001 demutualization, and is from time to time involved as a party in various governmental investigations, audits, reviews and administrative proceedings. These investigations, audits and reviews include routine and special investigations by state insurance departments, state attorneys general and the U.S. Attorney General. Such investigations could result in the imposition of civil or criminal fines, penalties and other sanctions. The Company believes that any liability that may result from any one of these actions, or in the aggregate, is unlikely to have a material adverse effect on its consolidated financial position or results of operations.
Contractual Obligations and Commitments
The Company entered into certain agreements with International Business Machines Corporation (“IBM”) to provide information technology infrastructure services. These services were previously performed in-house. The Company’s remaining commitment under these contracts at December 31, 2006 is approximately $935.6 over a six year period. The Company has the ability to terminate these agreements upon the occurrence of certain events, subject to certain early termination fees.
On July 15, 2004, the Company agreed to guarantee up to $37.0 of debt incurred by an unaffiliated entity to partially finance the purchase of a hospital. While the maximum amount of the guaranty may be reduced in periods after September 30, 2006 as determined by reference to the leverage ratio (as defined in the guaranty) of the unaffiliated entity, the maximum guaranty remained $37.0 at December 31, 2006. The guaranty also provides for full payment of all obligations under the guaranty to become immediately due and payable under specified circumstances. In connection with the guaranty, the unaffiliated entity agreed to reimburse the Company upon demand for any amounts paid by the Company under the guaranty. The obligations of the unaffiliated entity under the reimbursement agreement are secured by a second lien on certain real estate collateral. In addition, the parent company of the unaffiliated entity has provided a guaranty in favor of the Company guaranteeing the obligations of the unaffiliated entity under the reimbursement agreement.
133
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
18. Commitments and Contingencies (continued)
In connection with an investment in July 2004 in a joint venture to develop and operate a well-being center in California, the Company may be required to make an additional capital contribution of up to $18.0 during the first three years that the well-being center is in operation if cash flows and room nights generated by the Company do not exceed specified targets. Construction of the well-being center was completed during December 2006.
In connection with the formation in 2000 of a joint venture providing Medicaid services in Puerto Rico, the Company agreed under certain circumstances to provide additional funds to the joint-venture entity. Since the formation of the joint venture in 2000, the Company has not been required to make any payments under this guarantee of funding. During December 2006, the joint venture was terminated and the guarantee was extinguished.
Vulnerability from Concentrations
Financial instruments that potentially subject the Company to concentrations of credit risk consist primarily of cash equivalents, investment securities, premium receivables and instruments held through hedging activities. All investment securities are managed by professional investment managers within policies authorized by the Board of Directors. Such policies limit the amounts that may be invested in any one issuer and prescribe certain investee company criteria. Concentrations of credit risk with respect to premium receivables are limited due to the large number of employer groups that constitute the Company’s customer base in the geographic regions in which it conducts business. As of December 31, 2006, there were no significant concentrations of financial instruments in a single investee, industry or geographic location.
19. Segment Information
Through December 31, 2006, the Company had three reportable segments: Health Care, Specialty, and Other.
The Health Care segment is an aggregation of various operating segments, principally differentiated only by geography. These Health Care operating segments have similar economic, product, distribution, customer and regulatory characteristics, and meet the aggregation criteria as defined under paragraph 17 of FAS 131,Disclosures about Segments of an Enterprise and Related Information (“FAS 131”). Operating segments comprising the Health Care segment provide a broad spectrum of network-based health plans and other health care-related products to large and small employers and individuals.
The Specialty segment is maintained as a separate segment providing various products, including pharmacy benefits management, specialty pharmacy, dental, vision, life and disability insurance and behavioral health benefit services.
In addition to intersegment sales and expense eliminations and corporate expenses not allocated to reportable segments, the Other segment includes results from the Company’s government health services and other businesses that do not meet the quantitative thresholds for an operating segment defined under FAS 131.
The Company announced a new organizational structure designed to facilitate the Company’s 2010 strategic plan. This new structure emphasizes unique local presence, company-wide innovation and strong customer focus. As a result of this new organizational structure the Company is organized around two strategic business units: Commercial and Consumer Business, and Specialty, Senior and State-Sponsored Business. In addition, our
134
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
19. Segment Information (continued)
government services business includes the Federal Employee Program and National Government Services, Inc., which acts as a Medicare contractor in several regions across the nation. The Company expects to revise its reportable segments in the first quarter of 2007 in accordance with the new organizational structure, which reflects how the chief operating decision maker evaluates the performance of the business beginning January 1, 2007.
As a result of these organizational changes, during 2006, the Company recorded general and administrative expenses of $50.3, $3.4 and $1.6 for employee termination costs in the Health Care, Specialty and Other segments, respectively. The Company made payments of $3.7 during 2006 related to these termination costs and as of December 31, 2006, a liability of $51.6 remained for future payments of termination costs. The total severance charges of $55.3 related to the reorganization were partially offset by non-cash benefits of $21.6 related to additional share-based award forfeitures.
Through its participation in various federal government programs, the Company generated approximately 16%, 12% and 17% of its total consolidated revenues from agencies of the U.S. government for the years ended December 31, 2006, 2005 and 2004, respectively. These revenues are contained in all three of the Company’s reportable segments.
The Company defines operating revenues to include premium income, administrative fees and other revenues. Operating revenues are derived from premiums and fees received primarily from the sale and administration of health benefit products. Operating expenses are comprised of benefit expense, selling expense, general and administrative expense and cost of drugs. The Company calculates operating gain or loss as operating revenue less operating expenses.
The accounting policies of the segments are consistent with those described in the summary of significant accounting policies in Note 2 except that certain shared administrative expenses for each segment are recognized on a pro rata allocated basis, which in aggregate approximates the consolidated expense. Any difference between the allocated expenses and actual consolidated expense is included in other expenses not allocated to reportable segments. Intersegment sales and expenses are recorded at cost, and eliminated in the consolidated financial statements. The Company evaluates performance of the reportable segments based on operating gain or loss as defined above. The Company evaluates investment income, interest expense, amortization expense and income taxes, and asset and liability details on a consolidated basis as these items are managed in a corporate shared service environment and are not the responsibility of segment operating management.
135
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
19. Segment Information (continued)
Financial data by reportable segment for the years ended December 31 is as follows:
| Health Care | Specialty | Other and Eliminations | Total | |||||||||||
Year ended December 31, 2006 | ||||||||||||||
Operating revenue from external customers | $ | 53,860.6 | $ | 1,759.4 | $ | 454.6 | $ | 56,074.6 | ||||||
Intersegment revenues | — | 1,806.8 | (1,806.8 | ) | — | |||||||||
Operating gain (loss) | 4,288.3 | 523.6 | (75.0 | ) | 4,736.9 | |||||||||
Depreciation and lease amortization expense | — | — | 270.4 | 270.4 | ||||||||||
Year ended December 31, 2005 | ||||||||||||||
Operating revenue from external customers | 41,867.0 | 1,717.8 | 333.6 | 43,918.4 | ||||||||||
Intersegment revenues | — | 1,348.3 | (1,348.3 | ) | — | |||||||||
Operating gain (loss) | 3,418.0 | 426.4 | (111.9 | ) | 3,732.5 | |||||||||
Depreciation and lease amortization expense | 6.0 | 0.4 | 222.2 | 228.6 | ||||||||||
Year ended December 31, 2004 | ||||||||||||||
Operating revenue from external customers | 19,498.5 | 646.6 | 208.6 | 20,353.7 | ||||||||||
Intersegment revenues | (70.8 | ) | 800.4 | (729.6 | ) | — | ||||||||
Operating gain (loss) | 1,497.4 | 105.2 | (102.2 | ) | 1,500.4 | |||||||||
Depreciation and lease amortization expense | 18.6 | 0.6 | 116.5 | 135.7 | ||||||||||
The major product revenues from external customers for each of the reportable segments for the years ended December 31, are as follows:
| 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | |||||||
Health Care | |||||||||
Managed care products | $ | 50,892.3 | $ | 39,565.5 | $ | 18,272.1 | |||
Managed care services | 2,963.3 | 2,301.5 | 1,218.7 | ||||||
Other | 5.0 | — | 7.7 | ||||||
Total Health Care | 53,860.6 | 41,867.0 | 19,498.5 | ||||||
Specialty | |||||||||
Pharmacy products | 610.4 | 594.9 | 233.0 | ||||||
Dental/Vision | 804.7 | 738.1 | 281.4 | ||||||
Other | 344.3 | 384.8 | 132.2 | ||||||
Total Specialty | 1,759.4 | 1,717.8 | 646.6 | ||||||
Other | |||||||||
Medicare services | 450.0 | 325.5 | 206.1 | ||||||
Other | 4.6 | 8.1 | 2.5 | ||||||
Total Other | 454.6 | 333.6 | 208.6 | ||||||
Total revenues from external customers | $ | 56,074.6 | $ | 43,918.4 | $ | 20,353.7 | |||
The classification between managed care products and managed care services for the Health Care segment in the above table primarily distinguishes between the level of risk assumed. Managed care products represent insurance products where the Company bears the insurance risk, whereas managed care services represent product offerings where the Company provides claims adjudication and other administrative services to the customer, but the customer principally bears the insurance risk.
136
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
19. Segment Information (continued)
Asset and equity details by reportable segment have not been disclosed, as they are not reported internally by the Company.
A reconciliation of reportable segment operating revenues to the amounts of total revenues included in the consolidated statements of income for the years ended December 31, is as follows:
| 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | |||||||||
Reportable segments operating revenues | $ | 56,074.6 | $ | 43,918.4 | $ | 20,353.7 | |||||
Net investment income | 878.7 | 633.1 | 311.7 | ||||||||
Net realized (losses) gains on investments | (0.3 | ) | (10.2 | ) | 42.5 | ||||||
Total revenues | $ | 56,953.0 | $ | 44,541.3 | $ | 20,707.9 | |||||
A reconciliation of reportable segment operating gain to income before income taxes included in the consolidated statements of income for the years ended December 31 is as follows:
| 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | ||||||||||
Reportable segments operating gain | $ | 4,736.9 | $ | 3,732.5 | $ | 1,500.4 | ||||||
Net investment income | 878.7 | 633.1 | 311.7 | |||||||||
Net realized (losses) gains on investments | (0.3 | ) | (10.2 | ) | 42.5 | |||||||
Interest expense | (403.5 | ) | (226.2 | ) | (142.3 | ) | ||||||
Amortization of other intangible assets | (297.4 | ) | (238.9 | ) | (61.4 | ) | ||||||
Merger-related undertakings | — | — | (61.5 | ) | ||||||||
Loss on repurchase of debt securities | — | — | (146.1 | ) | ||||||||
Income before income taxes | $ | 4,914.4 | $ | 3,890.3 | $ | 1,443.3 | ||||||
20. Related Party Transactions
WellPoint Foundation, Inc. (the “Foundation”), which name changed from Anthem Foundation, Inc. effective July 1, 2006, is an Indiana non-profit organization exempt from federal taxation under Section 501(c)(3) of the Internal Revenue Code. The Foundation was formed to conduct, support and assist charitable, health-related, educational, and other community-based programs and projects. Effective July 1, 2006, WellPoint Foundation, a Section 501(c)(3) non-profit organization previously formed to improve the health and well-being of individuals in communities served by the former WHN, was merged into the Foundation. The officers and directors of the Foundation are also officers of the Company. These officers and directors receive no compensation from the Foundation for the management services performed for the Foundation but may be reimbursed by the Foundation for any cash expenditures incurred on behalf of the Foundation. The Foundation is not a subsidiary of the Company and the financial results of the Foundation are not consolidated with the Company’s financial statements. The Company contributed $3.0 to the Foundation during 2004 and no contributions were made to the Foundation in 2006 or 2005. The Company has no current legal obligations for future commitments to the Foundation.
21. Statutory Information
WellPoint’s insurance subsidiaries report their accounts in conformity with accounting practices prescribed or permitted by state insurance regulatory authorities (“statutory”), which vary in certain respects from GAAP. Typical differences of GAAP reporting as compared to statutory reporting are the inclusion of unrealized gains or losses relating to fixed maturity securities in shareholders’ equity, recognition of all assets including those that are
137
Table of Contents
WellPoint, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (continued)
21. Statutory Information (continued)
non-admitted for statutory purposes and recognition of all deferred tax assets without regard to statutory limits. The National Association of Insurance Commissioners (“NAIC”) developed a codified version of the statutory accounting principles, designed to foster more consistency among the states for accounting guidelines and reporting.
WellPoint’s insurance subsidiaries are domiciled in various jurisdictions. These subsidiaries prepare statutory financial statements in accordance with accounting practices prescribed or permitted by the respective jurisdictions’ insurance regulators. Prescribed statutory accounting practices are set forth in a variety of publications of the NAIC as well as state laws, regulations and general administrative rules.
WellPoint’s ability to pay dividends and other credit obligations is significantly dependent on receipt of dividends from its subsidiaries. The payment of dividends to WellPoint by its insurance subsidiaries without prior approval of the insurance departments of each subsidiary’s domiciliary jurisdiction is limited by formula. Dividends in excess of these amounts are subject to prior approval by the respective state insurance departments.
WellPoint’s insurance subsidiaries are subject to risk-based capital requirements. Risk-based capital is a method developed by the NAIC to determine the minimum amount of statutory capital appropriate for an insurance company to support its overall business operations in consideration of its size and risk profile. The formula for determining the amount of risk-based capital specifies various factors, weighted based on the perceived degree of risk, which are applied to certain financial balances and financial activity. Below minimum risk-based capital requirements are classified within certain levels, each of which requires specified corrective action. As of December 31, 2006 and 2005, all of WellPoint’s insurance subsidiaries exceeded the minimum risk-based capital requirements.
Statutory-basis capital and surplus for WellPoint’s insurance subsidiaries was $7,981.6 and $7,487.0 at December 31, 2006 and 2005, respectively. Statutory-basis net income of WellPoint’s insurance subsidiaries was $2,931.2, $2,385.1 and $1,545.9 for 2006, 2005 and 2004, respectively. Statutory-basis net income includes WellChoice and WHN statutory results for the full year ended December 31, 2006 and 2005 and WHN statutory results for the full year ended December 31, 2004.
22. Selected Quarterly Financial Data (Unaudited)
Selected quarterly financial data is as follows:
| For the Quarter Ended | ||||||||||||
| March 31 | June 30 | September 30 | December 31 | |||||||||
2006 | ||||||||||||
Total revenues | $ | 13,819.7 | $ | 14,151.9 | $ | 14,425.9 | $ | 14,555.5 | ||||
Income before income taxes | 1,172.7 | 1,203.3 | 1,254.6 | 1,283.8 | ||||||||
Net income | 731.8 | 751.2 | 810.8 | 801.1 | ||||||||
Basic net income per share | 1.12 | 1.20 | 1.31 | 1.30 | ||||||||
Diluted net income per share | 1.09 | 1.17 | 1.29 | 1.28 | ||||||||
2005 | ||||||||||||
Total revenues | $ | 10,943.1 | $ | 11,149.0 | $ | 11,156.9 | $ | 11,292.3 | ||||
Income before income taxes | 928.9 | 896.6 | 1,023.4 | 1,041.4 | ||||||||
Net income | 611.7 | 559.4 | 640.7 | 652.0 | ||||||||
Basic net income per share | 1.01 | 0.92 | 1.05 | 1.06 | ||||||||
Diluted net income per share | 0.98 | 0.90 | 1.02 | 1.04 | ||||||||
138
Table of Contents
ITEM 9. CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE.
There have been no changes in or disagreements with the Company’s independent registered public accounting firm on accounting or financial disclosures.
ITEM 9A. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
The Company carried out an evaluation as of December 31, 2006, under the supervision and with the participation of the Company’s management, including the Company’s Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, of the effectiveness of the design and operation of the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures as defined in Rule 13a-15(e) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. Based upon that evaluation, the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer concluded that the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures are effective in timely alerting them to material information relating to the Company (including its consolidated subsidiaries) required to be disclosed in the Company’s reports under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. In addition based on that evaluation, the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer concluded that the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures were effective in ensuring that information required to be disclosed by the Company in the reports that it files or submits under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 is accumulated and communicated to the Company’s management, including the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosures.
Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Management, under the supervision and with the participation of the principal executive officer and principal financial officer, of WellPoint, Inc. (the “Company”) is responsible for establishing and maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting as such term is defined in Exchange Act Rule 13a-15(f) (“Internal Control”). The Company’s Internal Control is designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of our financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external reporting purposes in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”). The Company’s Internal Control includes those policies and procedures that (i) pertain to the maintenance of records that in reasonable detail accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the Company; (ii) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with GAAP, and that receipts and expenditures of the Company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the Company; and (iii) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of the Company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of inherent limitations in any Internal Control, no matter how well designed, misstatements due to error or fraud may occur and not be detected. Accordingly, even effective Internal Control can provide only reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with GAAP.
Management, under the supervision and with the participation of the principal executive officer and principal financial officer, assessed the effectiveness of the Company’s Internal Control as of December 31, 2006. Management’s assessment was based on criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission.
Based on management’s assessment, management has concluded that the Company’s Internal Control was effective as of December 31, 2006 to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external reporting purposes in accordance with GAAP.
139
Table of Contents
Ernst & Young LLP, our independent registered public accounting firm, has audited the consolidated financial statements of the Company for the year ended December 31, 2006, and has also issued an audit report dated February 14, 2007, on management’s assessment of the Company’s Internal Control, which is included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
/s/ LARRY C. GLASSCOCK | /s/ DAVID C. COLBY | |
Chairman, President and Chief Executive Officer | Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer |
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
There have been no changes in the Company’s Internal Control that occurred during the three months ended December 31, 2006 that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, the Company’s Internal Control. During the year ended December 31, 2006, the Company implemented changes in its general ledger and consolidation systems, as a result of integration activity following the November 30, 2004 merger with WellPoint Health Networks Inc. and the December 28, 2005 acquisition of WellChoice, Inc. The Company believes these changes have not negatively affected its Internal Control.
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
Shareholders and Board of Directors
WellPoint, Inc.
We have audited management’s assessment, included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting, that WellPoint, Inc. maintained effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2006, based on criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (the “COSO criteria”). WellPoint, Inc.’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on management’s assessment and an opinion on the effectiveness of the company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, evaluating management’s assessment, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
140
Table of Contents
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
In our opinion, management’s assessment that WellPoint, Inc. maintained effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2006, is fairly stated, in all material respects, based on the COSO criteria. Also, in our opinion, WellPoint, Inc. maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2006, based on the COSO criteria.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the consolidated balance sheets of WellPoint, Inc. as of December 31, 2006 and 2005, and the related consolidated statements of income, shareholders’ equity, and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2006, and our report dated February 14, 2007 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
/s/ ERNST & YOUNG LLP
Indianapolis, Indiana
February 14, 2007
141
Table of Contents
None.
PART III
ITEM 10. DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE.
The information required by this Item concerning the Executive Officers, the Directors and nominees for Director, Audit Committee members and financial expert of the Company and concerning disclosure of delinquent filers under Section 16(a) of the Exchange Act and concerning the Company’s Standards of Business Conduct is incorporated herein by reference from the Company’s definitive Proxy Statement for its 2007 Annual Meeting of Shareholders, which will be filed with the Commission pursuant to Regulation 14A within 120 days after the end of the Company’s last fiscal year.
ITEM 11. EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION.
The information required by this Item concerning remuneration of the Company’s Executive Officers and Directors, material transactions involving such Executive Officers and Directors and Compensation Committee interlocks, as well as the Compensation Committee Report, are incorporated herein by reference from the Company’s definitive Proxy Statement for its 2007 Annual Meeting of Shareholders, which will be filed with the Commission pursuant to Regulation 14A within 120 days after the end of the Company’s last fiscal year.
ITEM 12. SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS.
The information required by this Item concerning the stock ownership of management and five percent beneficial owners and securities authorized for issuance under equity compensation plans is incorporated herein by reference from the Company’s definitive Proxy Statement for its 2007 Annual Meeting of Shareholders, which will be filed with the Commission pursuant to Regulation 14A within 120 days after the end of the Company’s last fiscal year.
ITEM 13. CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE.
The information required by this Item concerning certain relationships and related person transactions and director independence is incorporated herein by reference from the Company’s definitive Proxy Statement for its 2007 Annual Meeting of Shareholders, which will be filed with the Commission pursuant to Regulation 14A within 120 days after the end of the Company’s last fiscal year.
ITEM 14. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTANT FEES AND SERVICES.
The information required by this Item concerning principal accounting fees and services is incorporated herein by reference from the Company’s definitive Proxy Statement for its 2007 Annual Meeting of Shareholders, which will be filed with the Commission pursuant to Regulation 14A within 120 days after the end of the Company’s last fiscal year.
142
Table of Contents
PART IV
ITEM 15. EXHIBITS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES.
(a) 1. Financial Statements:
The following consolidated financial statements of the Company are set forth in Part II, Item 8.
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2006 and 2005
Consolidated Statements of Income for the years ended December 31, 2006, 2005 and 2004
Consolidated Statements of Shareholders’ Equity for the years ended December 31, 2006, 2005 and 2004
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the years ended December 31, 2006, 2005 and 2004
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
2. Financial Statement Schedule:
The following financial statement schedule of the Company is included in Item 15(c):
Schedule II—Condensed Financial Information of Registrant (Parent Company Only).
All other schedules for which provision is made in the applicable accounting regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission are not required under the related instructions, are inapplicable, or the required information is included in the consolidated financial statements, and therefore have been omitted.
3. Exhibits:
A list of exhibits required to be filed as part of this report is set forth in the Index to Exhibits, which immediately precedes such exhibits, and is incorporated herein by reference.
(b) Exhibits
The response to this portion of Item 15 is submitted as a separate section of this report.
(c) Financial Statement Schedule
Schedule II—Condensed Financial Information of Registrant (Parent Company Only).
143
Table of Contents
Schedule II—Condensed Financial Information of Registrant
WellPoint, Inc. (Parent Company Only)
Balance Sheets
| (In millions, except share data) | December 31 | ||||||
| 2006 | 2005 | ||||||
Assets | |||||||
Current assets: | |||||||
Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 203.1 | $ | 716.1 | |||
Investments available-for-sale, at fair value: | |||||||
Fixed maturity securities (amortized cost of $26.9 and $136.9) | 26.8 | 136.6 | |||||
Equity securities (cost of $299.8 and $8.2) | 323.0 | 9.0 | |||||
Other invested assets, current | 30.3 | — | |||||
Other receivables | 27.4 | 25.4 | |||||
Net due from subsidiaries | 185.8 | 175.9 | |||||
Securities lending collateral | 278.4 | — | |||||
Deferred tax assets, net | 2,583.7 | 2,591.7 | |||||
Other current assets | 103.2 | 4.1 | |||||
Total current assets | 3,761.7 | 3,658.8 | |||||
Long-term investments available for sale, at fair value: | |||||||
Fixed maturity securities (amortized cost of $1,153.6 and $1,611.6) | 1,142.9 | 1,599.2 | |||||
Equity securities (cost of $11.4 and $0.0) | 8.3 | — | |||||
Other invested assets, long-term | 385.0 | — | |||||
Property and equipment | 5.6 | 4.0 | |||||
Investment in subsidiary surplus notes | — | 539.4 | |||||
Investment in subsidiaries | 29,847.4 | 28,335.2 | |||||
Other noncurrent assets | 17.4 | 5.6 | |||||
Total assets | $ | 35,168.3 | $ | 34,142.2 | |||
Liabilities and shareholders’ equity | |||||||
Liabilities | |||||||
Current liabilities: | |||||||
Accounts payable and accrued expenses | $ | 266.8 | $ | 23.2 | |||
Income taxes payable | 513.0 | 618.7 | |||||
Securities lending payable | 278.4 | — | |||||
Current portion of long-term debt | 493.2 | — | |||||
Other current liabilities | 93.9 | 100.5 | |||||
Total current liabilities | 1,645.3 | 742.4 | |||||
Long-term debt | 6,037.1 | 5,848.0 | |||||
Deferred income taxes | 2,468.1 | 2,513.7 | |||||
Other noncurrent liabilities | 442.0 | 45.0 | |||||
Total liabilities | 10,592.5 | 9,149.1 | |||||
Commitments and contingencies—Note 6 | |||||||
Shareholders’ equity | |||||||
Preferred stock, without par value, shares authorized—100,000,000; | — | — | |||||
Common stock, par value $0.01, shares authorized—900,000,000; | 6.1 | 6.6 | |||||
Additional paid-in capital | 19,863.5 | 20,915.4 | |||||
Retained earnings | 4,656.1 | 4,173.5 | |||||
Unearned share-based compensation | — | (82.1 | ) | ||||
Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) | 50.1 | (20.3 | ) | ||||
Total shareholders’ equity | 24,575.8 | 24,993.1 | |||||
Total liabilities and shareholders’ equity | $ | 35,168.3 | $ | 34,142.2 | |||
See accompanying notes.
144
Table of Contents
Schedule II—Condensed Financial Information of Registrant—(continued)
WellPoint, Inc. (Parent Company Only)
Statements of Income
| (In millions) | Years ended December 31 | |||||||||||
| 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | ||||||||||
Revenues | ||||||||||||
Net investment income | $ | 81.6 | $ | 77.6 | $ | 23.8 | ||||||
Net realized (losses) gains on investments | (17.4 | ) | (3.1 | ) | (10.8 | ) | ||||||
Other revenue | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.4 | |||||||||
Total revenues | 64.6 | 74.9 | 13.4 | |||||||||
Expenses | ||||||||||||
General and administrative expense | 208.3 | 95.8 | 32.9 | |||||||||
Interest expense | 327.6 | 185.9 | 92.2 | |||||||||
Merger-related undertakings | — | — | 50.0 | |||||||||
Loss on repurchase of debt securities | — | — | 146.1 | |||||||||
Total expenses | 535.9 | 281.7 | 321.2 | |||||||||
Loss before income tax credits and equity in net income of subsidiaries | (471.3 | ) | (206.8 | ) | (307.8 | ) | ||||||
Income tax credits | (161.8 | ) | (46.4 | ) | (98.1 | ) | ||||||
Equity in net income of subsidiaries | 3,404.4 | 2,624.2 | 1,169.8 | |||||||||
Net income | $ | 3,094.9 | $ | 2,463.8 | $ | 960.1 | ||||||
See accompanying notes.
145
Table of Contents
Schedule II—Condensed Financial Information of Registrant—(continued)
WellPoint, Inc. (Parent Company Only)
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
| (In millions) | Year ended December 31 | |||||||||||
| 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | ||||||||||
Operating activities | ||||||||||||
Net income | $ | 3,094.9 | $ | 2,463.8 | $ | 960.1 | ||||||
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | ||||||||||||
(Undistributed) distributed earnings of subsidiaries | (1,059.1 | ) | 398.9 | (72.1 | ) | |||||||
Net realized losses on investments | 17.4 | 3.1 | 10.8 | |||||||||
Loss on repurchase of debt securities | — | — | 146.1 | |||||||||
Deferred income taxes | (58.6 | ) | 32.0 | 67.8 | ||||||||
Amortization, net of accretion | 6.5 | 10.1 | 10.2 | |||||||||
Depreciation | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 | |||||||||
Share-based compensation | 149.0 | 75.9 | — | |||||||||
Excess tax benefits from share-based compensation | (136.5 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
Changes in operating assets and liabilities, net of effect of business combinations: | ||||||||||||
Receivables, net | (2.0 | ) | (25.1 | ) | — | |||||||
Other invested assets, current | (30.3 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
Other assets | (114.0 | ) | 6.6 | 11.7 | ||||||||
Amounts due (from) to subsidiaries | (3.0 | ) | (94.0 | ) | 122.4 | |||||||
Accounts payable and accrued expenses | 45.7 | 32.0 | 6.3 | |||||||||
Other liabilities | 443.7 | (18.9 | ) | 15.2 | ||||||||
Income taxes | (103.3 | ) | 443.2 | (67.9 | ) | |||||||
Net cash provided by operating activities | 2,250.7 | 3,327.9 | 1,210.9 | |||||||||
Investing activities | ||||||||||||
Purchases of investments | (2,095.1 | ) | (3,538.9 | ) | (1,376.4 | ) | ||||||
Proceeds from sales, maturities and redemptions of investments | 2,346.2 | 1,774.1 | 1,934.6 | |||||||||
Redemption (purchase) of subsidiary surplus notes | 432.9 | — | (582.2 | ) | ||||||||
Capitalization of subsidiaries | (34.8 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
Change in securities lending collateral | (278.4 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
Purchases of subsidiaries, net of cash acquired | — | (3,505.9 | ) | (3,718.9 | ) | |||||||
Other, net | (411.6 | ) | — | 15.7 | ||||||||
Net cash used in investing activities | (40.8 | ) | (5,270.7 | ) | (3,727.2 | ) | ||||||
Financing activities | ||||||||||||
Net (payment) proceeds from commercial paper borrowings | (306.0 | ) | 808.2 | 793.2 | ||||||||
Proceeds from long-term borrowings | 2,668.2 | 1,700.0 | 1,770.1 | |||||||||
Repayment of long-term borrowings | (1,700.0 | ) | (150.0 | ) | (224.3 | ) | ||||||
Changes in securities lending payable | 278.4 | — | — | |||||||||
Change in bank overdrafts | 190.7 | — | — | |||||||||
Repurchase and retirement of common stock | (4,550.2 | ) | (333.4 | ) | (82.2 | ) | ||||||
Proceeds from exercise of employee stock options and employee stock purchase plan | 559.5 | 429.3 | 159.0 | |||||||||
Proceeds from sale of put options | — | 1.1 | — | |||||||||
Excess tax benefits from share-based compensation | 136.5 | — | — | |||||||||
Proceeds from issuance of common stock under Equity Security Unit stock purchase contracts | — | — | 230.0 | |||||||||
Costs related to the issuance of common stock | — | (3.6 | ) | (8.3 | ) | |||||||
Net cash (used in) provided by financing activities | (2,722.9 | ) | 2,451.6 | 2,637.5 | ||||||||
Change in cash and cash equivalents | (513.0 | ) | 508.8 | 121.2 | ||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year | 716.1 | 207.3 | 86.1 | |||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at end of year | $ | 203.1 | $ | 716.1 | $ | 207.3 | ||||||
See accompanying notes.
146
Table of Contents
Schedule II—Condensed Financial Information of Registrant—(continued)
WellPoint, Inc.
(Parent Company Only)
Notes to Condensed Financial Statements
December 31, 2006
(In Millions, Except Per Share Data)
1. Basis of Presentation and Significant Accounting Policies
On November 30, 2004, Anthem, Inc. (“Anthem”) and WellPoint Health Networks Inc. (“WHN”) completed their merger. WHN merged with and into Anthem Holding Corp., a direct and wholly-owned subsidiary of Anthem, with Anthem Holding Corp. as the surviving entity in the merger. In connection with the merger, Anthem amended its articles of incorporation to change its name to WellPoint, Inc. (“WellPoint”). In addition, the ticker symbol for Anthem’s common stock listed on the New York Stock Exchange was changed to “WLP”. WHN’s operating results are included in WellPoint’s consolidated financial statements for the period following November 30, 2004.
In WellPoint’s parent company only financial statements, WellPoint’s investment in subsidiaries is stated at cost plus equity in undistributed earnings of the subsidiaries. WellPoint’s share of net income of its unconsolidated subsidiaries is included in income using the equity method of accounting.
WellPoint’s investment in subsidiary surplus notes is stated at estimated fair value.
Certain amounts presented in the parent company only financial statements are eliminated in the consolidated financial statements of WellPoint.
Certain prior year amounts have been reclassified to conform to the current year presentation.
As discussed in Note 2 to the consolidated financial statements, during 2006, WellPoint adopted FAS 123 (revised 2004),Share-Based Payment, and FAS 158,Employers’ Accounting for Defined Benefit Plans—an amendment of FASB Statements No. 87, 88, 106 and 132(R).
WellPoint’s parent company only financial statements should be read in conjunction with WellPoint’s audited consolidated financial statements and the accompanying notes included in this Form 10-K.
2. Subsidiary Transactions
Dividends
WellPoint received cash dividends from subsidiaries of $2,346.4, $3,023.1 and $1,097.7 during 2006, 2005 and 2004, respectively.
Investment in Subsidiaries
On December 28, 2005, WellPoint completed its acquisition of WellChoice, Inc. (“WellChoice”) and purchased 100% of the outstanding common stock of WellChoice. As a result of the acquisition, each WellChoice stockholder received $38.25 in cash, without interest, and 0.5191 shares of WellPoint common stock for each share of WellChoice common stock held. The purchase price was $6,463.9 and included cash of $3,126.4, the issuance of 42.4 shares of WellPoint common stock, valued at $3,180.8, 0.3 shares of WellChoice restricted stock and stock units converted to WellPoint stock valued at $19.8, WellChoice stock options converted to WellPoint stock options and other stock awards valued at $113.4, and $23.5 of transaction costs. The fair value of common stock issued was based on $74.97 per share, which represents the average closing price of the Company’s common stock for the five trading days ranging from two days before to two days after September 27, 2005, the date the merger was announced.
147
Table of Contents
Schedule II—Condensed Financial Information of Registrant—(continued)
WellPoint, Inc.
(Parent Company Only)
Notes to Condensed Financial Statements (continued)
2. Subsidiary Transactions (continued)
On June 9, 2005, WellPoint completed its acquisition of Lumenos, Inc. (“Lumenos”). The total consideration for the acquisition was approximately $185.0 in cash paid to stockholders of Lumenos.
As described in Note 1, on November 30, 2004, Anthem completed its merger with WHN and purchased 100% of the outstanding common stock of WHN. As a result of the merger, each WHN stockholder received $23.80 in cash, without interest, and one share of WellPoint common stock for each share of WHN common stock held. The purchase price was $15,773.6 and included cash of $3,718.8, the issuance of approximately 310.6 shares of WellPoint common stock, valued at $11,293.8, WHN stock options converted to WellPoint stock options and other stock awards for approximately 43.7 shares valued at $563.6, and $197.4 of transaction costs. The fair value of common stock issued was based on $36.35 per share, which represents the average closing price of the Company’s common stock for the five trading days ranging from two days before to two days after October 27, 2003, the date the merger was announced. In connection with the WHN merger, WellPoint executed certain undertakings with the California Department of Managed Health Care, the California Department of Insurance (“California DOI”), and the Georgia Department of Insurance which contained various commitments by WellPoint. Expenses for merger-related undertakings with the California DOI of $50.0 were recorded by WellPoint in 2004.
Capital contributions to subsidiaries were $167.8, $60.1 and $14.7 during 2006, 2005 and 2004, respectively. The contributions in 2006 included non-cash amounts of $133.0. The 2005 and 2004 contributions were non-cash.
Amounts Due to and From Subsidiaries
During December 2004, WellPoint completed a tender offer to purchase surplus notes of Anthem Insurance Companies, Inc. a direct wholly-owned subsidiary, and purchased $258.0 of 9.125% notes due 2010 and $174.9 of 9.00% notes due 2027. A loss of $146.1 was recorded by WellPoint, representing the amount fair value exceeded par value at the time of purchase. During December 2006, Anthem Insurance Companies, Inc. redeemed the surplus notes at par value, and cash of $432.9 was received by WellPoint.
At December 31, 2006, 2005 and 2004 WellPoint reported $185.8, $175.9 and $34.4 due from subsidiaries, respectively. These amounts consisted principally of administrative expenses and are routinely settled, and as such, are classified as current assets.
148
Table of Contents
Schedule II—Condensed Financial Information of Registrant—(continued)
WellPoint, Inc.
(Parent Company Only)
Notes to Condensed Financial Statements
3. Long-Term Debt
The carrying value of long-term debt at December 31 consists of the following:
| December 31 | |||||||
| 2006 | 2005 | ||||||
Senior unsecured notes: | |||||||
3.500%, face amount of $200.0, due 2007 | $ | 198.3 | $ | 195.5 | |||
3.750%, face amount of $300.0, due 2007 | 294.9 | 292.1 | |||||
4.250%, face amount of $300.0, due 2009 | 298.4 | 297.8 | |||||
5.000%, face amount of $700.0, due 2011 | 694.6 | — | |||||
6.800%, face amount of $800.0, due 2012 | 793.5 | 786.1 | |||||
5.000%, face amount of $500.0, due 2014 | 484.3 | 481.2 | |||||
5.250%, face amount of $1,100.0, due 2016 | 1,088.5 | — | |||||
5.950%, face amount of $500.0, due 2034 | 494.1 | 493.9 | |||||
5.850%, face amount of $900.0, due 2036 | 888.4 | — | |||||
Variable rate debt: | |||||||
Commercial paper program | 1,295.3 | 1,601.4 | |||||
Bridge loan | — | 1,700.0 | |||||
Total debt | 6,530.3 | 5,848.0 | |||||
Current portion of debt | (493.2 | ) | — | ||||
Long-term debt, less current portion | $ | 6,037.1 | $ | 5,848.0 | |||
On January 10, 2006, WellPoint issued $700.0 of 5.000% notes due 2011; $1,100.0 of 5.250% notes due 2016; and $900.0 of 5.850% notes due 2036, under a shelf registration statement filed with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission on December 28, 2005. The proceeds from this debt issuance were used to repay the bridge loan of $1,700.0 (as further described below) and to repay approximately $1,000.0 of commercial paper, which were both obtained to partially fund the December 28, 2005 WellChoice acquisition.
WellPoint had cash requirements of approximately $3,138.0 for the WellChoice acquisition, including both the cash portion of the purchase price and estimated transaction costs. In anticipation of the acquisition, on December 28, 2005, WellPoint entered into a bridge loan agreement under which it could borrow up to $3,000.0. On December 28, 2005, WellPoint borrowed $1,700.0 under this bridge facility to partially fund the WellChoice acquisition. The interest rate on this bridge loan was based on either (i) the LIBOR rate plus a predetermined percentage rate based on the WellPoint’s credit rating at the date of utilization, or (ii) a base rate as defined in the facility agreement. The weighted-average interest rate on the bridge loan at December 31, 2005 was 7.250%. The bridge loan was classified as long-term debt at December 31, 2005 in accordance with FAS 6,Classification of Short-Term Obligations Expected to Be Refinanced (“FAS 6”), as this short-term borrowing was replaced with a long-term borrowing on January 10, 2006.
On November 29, 2005, WellPoint entered into a senior credit facility (the “facility”) with certain lenders for general corporate purposes. WellPoint amended this facility in September 2006. The facility provides credit for up to $2,500.0 (reduced for any commercial paper issuances) and matures on September 30, 2011. The interest rate on this facility is based on either (i) the LIBOR rate plus a predetermined percentage rate based on WellPoint’s credit rating at the date of utilization, or (ii) a base rate as defined in the facility agreement.
149
Table of Contents
Schedule II—Condensed Financial Information of Registrant—(continued)
WellPoint, Inc.
(Parent Company Only)
Notes to Condensed Financial Statements (continued)
3. Long-Term Debt (continued)
WellPoint’s ability to borrow under the facility is subject to compliance with certain covenants. Commitment fees for the facility were $2.4 in 2006 and there are no conditions that are probable of occurring under which the facility may be withdrawn. There were no amounts outstanding under the senior credit facility as of December 31, 2006 or during the year then ended. At December 31, 2006, WellPoint had $1,204.7 available under this facility.
WellPoint has an authorized commercial paper program of up to $2,500.0, the proceeds of which may be used for general corporate purposes. The weighted-average interest rate on commercial paper borrowings at December 31, 2006 and 2005 were 5.42% and 4.40%, respectively. Commercial paper borrowings have been classified as long-term debt at December 31, 2006 and 2005 in accordance with FAS 6, as WellPoint’s practice and intent is to replace short-term commercial paper outstanding at expiration with additional short-term commercial paper for an uninterrupted period extending for more than one year or with borrowings under the senior credit facility described above.
Interest paid during 2006, 2005 and 2004 was $293.0, $181.6 and $86.7, respectively.
WellPoint was in compliance with all applicable covenants under its outstanding debt agreements.
Future maturities of long-term debt are as follows: 2007, $1,788.5; 2008, $0.0; 2009, $298.4; 2010, $0.0; 2011, $694.6; and thereafter, $3,748.8.
4. Derivative Financial Instruments
The information regarding derivative financial instruments contained in Note 6 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements of WellPoint and its subsidiaries is incorporated herein by reference.
5. Capital Stock
The information regarding capital stock contained in Note 12 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements of WellPoint and its subsidiaries is incorporated herein by reference.
6. Commitments and Contingencies
The information regarding commitments and contingencies contained in Note 18 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements of WellPoint and its subsidiaries is incorporated herein by reference.
150
Table of Contents
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
WELLPOINT, INC. | ||
By: | /S/ LARRY C. GLASSCOCK | |
Larry C. Glasscock Chairman, President and Chief Executive Officer | ||
Dated: February 26, 2007
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
Signature | Title | Date | ||
/s/ LARRY C. GLASSCOCK Larry C. Glasscock | Chairman, President and Chief Executive Officer (Principal Executive Officer) | February 26, 2007 | ||
/S/ DAVID C. COLBY David C. Colby | Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial Officer) | February 26, 2007 | ||
/S/ WAYNE S. DEVEYDT Wayne S. DeVeydt | Senior Vice President, Chief of Staff and Chief Accounting Officer (Chief Accounting Officer) | February 26, 2007 | ||
/S/ LENOX D. BAKER, JR., M.D. Lenox D. Baker, Jr., M.D. | Director | February 26, 2007 | ||
/S/ SUSAN B. BAYH Susan B. Bayh | Director | February 26, 2007 | ||
/S/ SHEILA P. BURKE Sheila P. Burke | Director | February 26, 2007 | ||
/S/ WILLIAM H.T. BUSH William H.T. Bush | Director | February 26, 2007 | ||
/S/ JULIE A. HILL Julie A. Hill | Director | February 26, 2007 | ||
/S/ WARREN Y. JOBE Warren Y. Jobe | Director | February 26, 2007 | ||
/S/ VICTOR S. LISS Victor S. Liss | Director | February 26, 2007 | ||
151
Table of Contents
Signature | Title | Date | ||
/S/ WILLIAM G. MAYS William G. Mays | Director | February 26, 2007 | ||
/S/ RAMIRO G. PERU Ramiro G. Peru | Director | February 26, 2007 | ||
/S/ JANE G. PISANO Jane G. Pisano | Director | February 26, 2007 | ||
/S/ SENATOR DONALD W. RIEGLE, JR. Senator Donald W. Riegle, Jr. | Director | February 26, 2007 | ||
/S/ WILLIAM J. RYAN William J. Ryan | Director | February 26, 2007 | ||
/S/ GEORGE A. SCHAEFER, JR. George A. Schaefer, Jr. | Director | February 26, 2007 | ||
/S/ JACKIE M. WARD Jackie M. Ward | Director | February 26, 2007 | ||
/S/ JOHN E. ZUCCOTTI John E. Zuccotti | Director | February 26, 2007 | ||
152
Table of Contents
Exhibit Number | Exhibit | |
| 2.1 | Amended and Restated Agreement and Plan of Merger, effective as of October 26, 2003, among WellPoint, Inc. (the “Company”), Anthem Holding Corp. and WellPoint Health Networks Inc., incorporated by reference to Appendix A to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-4 (Registration No. 333-110830) (exhibits thereto will be furnished supplementally to the Securities and Exchange Commission upon request). | |
| 2.2 | Agreement and Plan of Merger, dated as of May 2, 2005, among the Company, Light Acquisition Corp. and Lumenos, Inc., incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.3 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2005. | |
| 2.3 | Agreement and Plan of Merger, dated as of September 27, 2005, among the Company, WellPoint Holding Corp. and WellChoice, Inc., incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on September 30, 2005. | |
| 3.1 | Articles of Incorporation of the Company, as amended effective November 30, 2004, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on November 30, 2004. | |
| 3.2 | By-Laws of the Company, amended and restated effective November 30, 2004, as further amended November 30, 2005 and October 28, 2006, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.2 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on November 2, 2006. | |
| 4.1 | Articles of Incorporation of the Company, as amended effective November 30, 2004 (Included in Exhibit 3.1). | |
| 4.2 | By-Laws of the Company, amended and restated effective November 30, 2004, as further amended November 30, 2005 and October 28, 2006 (Included in Exhibit 3.2). | |
| 4.3 | Specimen of Certificate of the Company’s common stock, $0.01 par value per share, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-8 (Registration No. 333-120851). | |
| 4.4 | Indenture, dated as of July 31, 2002, between the Company and The Bank of New York, as trustee, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.13 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2002. | |
(a) First Supplemental Indenture, dated as of July 31, 2002, between the Company and The Bank of New York, Trustee, establishing 4.875% Notes due 2005 and 6.800% Notes due 2012, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.14 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2002. | ||
(b) Form of 4.875% Note due 2005 (Included in Exhibit 4.4(a)), incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.14 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2002. | ||
(c) Form of 6.800% Note due 2012 (Included in Exhibit 4.4(a)), incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.14 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2002. | ||
| 4.5 | Senior Note Indenture, dated as of December 31, 2002, between the Company and The Bank of New York, as trustee, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.16 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on August 25, 2004. | |
(a) First Supplemental Indenture, dated as of August 27, 2004, between the Company and The Bank of New York, as trustee, establishing 3.50% Senior Notes due 2007, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.20 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on August 27, 2004. | ||
153
Table of Contents
Exhibit Number | Exhibit | |
(b) Form of 3.50% Senior Note due 2007 (included as Exhibit A in Exhibit 4.5(a)), incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.21 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on August 27, 2004. | ||
| 4.6 | Amended and Restated Indenture, dated as of June 8, 2001, by and between WellPoint Health Networks Inc. (as predecessor by merger to Anthem Holding Corp., “WellPoint Health”) and The Bank of New York, as trustee, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.3 to WellPoint Health’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on June 12, 2001. | |
(a) First Supplemental Indenture, dated as of November 30, 2004, between Anthem Holding Corp. and The Bank of New York, as trustee, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.11(a) to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2004. | ||
(b) Form of Note evidencing WellPoint Health’s 6 3/8% Notes due 2012, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to WellPoint Health’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on January 16, 2002. | ||
| 4.7 | Indenture, dated as of December 9, 2004, between the Company and The Bank of New York Trust Company, N.A., as trustee, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on December 15, 2004. | |
(a) Form of the Company’s 3.750% Notes due 2007 (included in Exhibit 4.7). | ||
(b) Form of the Company’s 4.250% Notes due 2009 (included in Exhibit 4.7). | ||
(c) Form of the Company’s 5.000% Notes due 2014 (included in Exhibit 4.7). | ||
(d) Form of the Company’s 5.950% Notes due 2034 (included in Exhibit 4.7). | ||
| 4.8 | Indenture, dated as of January 10, 2006, between the Company and The Bank of New York Trust Company, N.A., as trustee, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on January 11, 2006. | |
(a) Form of 5.00% Notes due 2011, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.2 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on January 11, 2006. | ||
(b) Form of 5.25% Notes due 2016, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.3 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on January 11, 2006. | ||
(c) Form of 5.85% Notes due 2036, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.4 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on January 11, 2006. | ||
| 4.9 | Upon the request of the Securities and Exchange Commission, the Company will furnish copies of any other instruments defining the rights of holders of long-term debt of the Company or its subsidiaries. | |
| 10.1* | Anthem 2001 Stock Incentive Plan, amended and restated as of January 1, 2003, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1(iii) to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2003. | |
(a) Form of Stock Incentive Plan General Stock Option Grant Agreement as of March 1, 2006, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1(b) to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2006. | ||
(b) Form of Stock Incentive Plan Stock Option Grant Agreement with Larry Glasscock as of March 1, 2006, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1(b) to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2006. | ||
(c) Form of Stock Incentive Plan General Restricted Stock Award Agreement as of March 1, 2006, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1(c) to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2006. | ||
154
Table of Contents
Exhibit Number | Exhibit | ||
(d) Form of Stock Incentive Plan Restricted Stock Award Agreement for Annual Bonus over two times target as of March 1, 2006, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1(d) to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2006. | |||
(e) Form of Stock Incentive Plan Restricted Stock Award Agreement with Larry Glasscock as of March 1, 2006, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1(e) to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2006. | |||
| 10.2 | * | WellPoint 2006 Incentive Compensation Plan, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.58 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on May 18, 2006. | |
(a) Form of Incentive Compensation Plan Nonqualified Stock Option Award Agreement, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.58(a) to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2006. | |||
(b) Form of Incentive Compensation Plan Nonqualified Stock Option Award Agreement for Larry C. Glasscock, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.58 (b) to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2006. | |||
(c) Form of Incentive Compensation Plan Restricted Stock Award Agreement; incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.58 (c) to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2006. | |||
(d) Form of Incentive Compensation Plan Restricted Stock Award Agreement for Annual Bonus over two times target, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.58 (d) to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2006. | |||
(e) Form of Incentive Compensation Plan Restricted Stock Award Agreement with Larry C. Glasscock, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.58(e) to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2006. | |||
(f) Form of Non-Qualified Stock Option Award Agreement, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.58(f) to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on November 2, 2006. | |||
(g) Form of Restricted Stock Award Agreement, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.58(g) to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on November 2, 2006. | |||
(h) First Amendment to the WellPoint 2006 Incentive Compensation Plan, effective as of December 6, 2006. | |||
| 10.3 | * | Anthem Annual Incentive Plan, effective January 1, 2003, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.32 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2003. | |
| 10.4 | * | Anthem Employee Stock Purchase Plan, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 (Registration No. 333-67714). | |
(a) Amendment No. 1 to Anthem Employee Stock Purchase Plan, dated July 2, 2002, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2(i) to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2002. | |||
(b) Amendment No. 2 to Anthem Employee Stock Purchase Plan, dated July 29, 2002, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2(ii) to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2002. | |||
| 10.5 | * | WellPoint, Inc. Comprehensive Non-Qualified Deferred Compensation Plan, effective as of December 31, 2005, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2005. | |
155
Table of Contents
Exhibit Number | Exhibit | ||
| 10.6 | * | WellPoint, Inc. Executive Agreement Plan, amended and restated effective January 1, 2006, with certain other effective dates, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.7 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on November 2, 2006. | |
| 10.7 | * | WellPoint, Inc. Executive Salary Continuation Plan effective January 1, 2006, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.59 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2006. | |
| 10.8 | * | WellPoint Directed Executive Compensation Plan, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.13 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2006. | |
| 10.9 | * | WellPoint, Inc. Board of Directors Compensation Program, approved February 2, 2005, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on February 8, 2005. | |
| 10.10 | * | WellPoint Board of Directors’ Deferred Compensation Plan, as amended and restated effective January 1, 2005, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2005. | |
(a) First Amendment to the WellPoint Board of Directors’ Deferred Compensation Plan, dated as of December 7, 2006. | |||
| 10.11 | * | Anthem Deferred Compensation Plan, amended and restated effective January 1, 1997, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.14(i) to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 (Registration No. 333-67714). | |
(a) First Amendment to Anthem Deferred Compensation Plan, adopted December 16, 1998, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.14(ii) to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 (Registration No. 333-67714). | |||
(b) Second Amendment to Anthem Deferred Compensation Plan, executed March 30, 2000, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.14(iii) to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 (Registration No. 333-67714). | |||
(c) Third Amendment to Anthem Deferred Compensation Plan, effective January 1, 2006, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.8 (c) to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2005. | |||
| 10.12 | * | Anthem Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan, amended and restated effective January 1, 1997, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.16(i) to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 (Registration No. 333-67714). | |
(a) First Amendment to the Anthem Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan, executed on March 30, 2000, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.16(ii) to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 (Registration No. 333-67714). | |||
(b) Second Amendment to the Anthem Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan, executed on September 1, 2000, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.16(iii) to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 (Registration No. 333-67714). | |||
| 10.13 | * | Anthem 2001-2003 Long-Term Incentive Plan, effective January 1, 2001, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.18 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 (Registration No. 333-67714). | |
(a) First Amendment to the Anthem 2001-2003 Long-Term Incentive Plan, dated April 25, 2002, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.18(i) to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2002. | |||
156
Table of Contents
Exhibit Number | Exhibit | ||
| 10.14 | * | WellPoint Health Networks Inc. 1999 Stock Incentive Plan (as amended through December 6, 2000), incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.37 to WellPoint Health’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2000. | |
(a) Form of WellPoint Health Networks Inc. 1999 Stock Incentive Plan Notice of Grant of Stock Option and Stock Option Agreement, revised December 2001, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.01 to WellPoint Health’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2004. | |||
(b) Form of WellPoint Health Networks Inc. 1999 Stock Incentive Plan Notice of Grant of Stock Option and Stock Option Agreement, revised September 2003, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.02 to WellPoint Health’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2004. | |||
(c) Form of WellPoint Health Networks Inc. 1999 Stock Incentive Plan Restricted Share Right Grant Agreement (Non-Officers), as of January 26, 2004, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.05 to WellPoint Health’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2004. | |||
(d) Form of WellPoint Health Networks Inc. 1999 Stock Incentive Plan Restricted Share Right Grant Agreement (Officers), as of January 26, 2004, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.06 to WellPoint Health’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2004. | |||
(e) Form of WellPoint Health Networks Inc. 1999 Stock Incentive Plan Notice of Automatic Grant of Stock Option, Notice of Annual Automatic Grant of Stock Option, Notice of Grant of Stock Option and Automatic Stock Option Agreement for Non-Employee Directors, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.09 to WellPoint Health’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2004. | |||
| 10.15 | * | WellPoint Health Networks Inc. Officer Change-in-Control Plan (As amended and restated through December 4, 2001) (as revised in October 2003), incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.13 to WellPoint Health’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2003. | |
| 10.16 | * | WellPoint Health Networks Inc. Supplemental Executive Retirement Plan (As restated effective December 4, 2001) (As amended October 24, 2003), incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.14 to WellPoint Health’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2003. | |
| 10.17 | * | Form of letter agreement, dated February 2004, between WellPoint Health and executive officers of WellPoint Health, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.83 to WellPoint Health’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2003. | |
| 10.18 | * | Empire HealthChoice, Inc. Executive Savings Plan, as Amended and Restated effective January 1, 1999, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to Empire HealthChoice, Inc.’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 (Registration No. 333-99051). | |
(a) First Amendment, dated December 18, 2002, to the Empire Blue Cross and Blue Shield Executive Savings Plan Trust, as Amended and Restated as of January 1, 1999, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.33 (a) to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2005. | |||
(b) Second Amendment, dated as of December 17, 2003, to the Empire Blue Cross and Blue Shield Executive Savings Plan, as Amended and Restated as of January 1, 1999, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.33(b) to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2005. | |||
157
Table of Contents
Exhibit Number | Exhibit | ||
| 10.19 | * | WellChoice, Inc. Long-Term Incentive Compensation Plan, as amended on March 24, 2004, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.8 to WellChoice, Inc.’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2004. | |
(a) Goals for the 2004-2006 cycle and the 2005-2007 cycle under the WellChoice, Inc. Long-Term Incentive Compensation Plan, as amended on March 24, 2004, incorporated by reference to WellChoice, Inc.’s Definitive Proxy Statement for its 2005 Annual Meeting of Shareholders filed on March 28, 2005 in the Executive Compensation section and the “Long-Term Incentive Plan (Award for 2005-2007 Performance Period)” section of the Compensation Committee Report on Executive Compensation, respectively. | |||
| 10.20 | * | WellChoice Supplemental Plans Trust, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.35 to WellChoice, Inc.’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2004. | |
| 10.21 | * | WellChoice, Inc. 2003 Omnibus Incentive Plan, as amended on September 22, 2004, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.37 to WellChoice, Inc.’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2004. | |
| 10.22 | * | Empire BlueCross BlueShield 2005 Executive Savings Plan (Effective December 27, 2004), incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.38 to WellChoice, Inc.’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2004. | |
| 10.23 | * | Employment Agreement by and between WellPoint, Inc. and Larry C. Glasscock, dated as of December 28, 2005, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.39 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2005. | |
| 10.24 | * | Employment Agreement between WellPoint, Inc. and Angela F. Braly, dated as of February 24, 2007, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on February 26, 2007. | |
| 10.25 | * | Employment Agreement by and between Anthem Insurance Companies, Inc. and Samuel R. Nussbaum, M.D., dated as of January 2, 2001 (with respect to Section 5(c) only), incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 (Registration No. 333-67714). | |
| 10.26 | * | Employment Agreement between the Company and Michael A. Stocker, M.D., dated as of December 28, 2005, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.42 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2005. | |
(a) Amendment One to Employment Agreement between the Company and Michael A. Stocker, M.D., effective November 1, 2006. | |||
| 10.27 | * | Form of Employment Agreement, dated on or about January 1, 2006, between the Company and each of the following: Angela F. Braly; Mark L. Boxer; Randal Brown; Marjorie W. Dorr; Randall Lewis; and, Samuel R. Nussbaum, M.D., incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.43 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2005. | |
| 10.28 | * | Executive Agreement, dated March 8, 2005, between the Company and Wayne DeVeydt, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.44 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2005. | |
| 10.29 | Blue Cross License Agreement by and between Blue Cross Blue Shield Association and the Company, including revisions, if any, adopted by the Member Plans through November 17, 2005 meeting, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.45 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2005. | ||
| 10.30 | Blue Shield License Agreement by and between Blue Cross Blue Shield Association and the Company, including revisions, if any, adopted by the Member Plans through November 17, 2005 meeting, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.46 to the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2005. | ||
158
Table of Contents
Exhibit Number | Exhibit | ||
| 10.31 | Undertakings to California Department of Insurance, dated November 8, 2004, delivered by WellPoint Health, BC Life, Anthem, Inc. and Anthem Holding Corp., incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99.2 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on November 10, 2004. | ||
| 10.32 | Undertakings to California Department of Managed Health Care, dated November 23, 2004, delivered by WellPoint Health, Blue Cross of California, Anthem, Inc. and Anthem Holding Corp., incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99.2 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on November 30, 2004. | ||
| 10.33 | Undertakings to California Department of Managed Health Care, dated November 23, 2004, delivered by WellPoint Health, Golden West, Anthem, Inc. and Anthem Holding Corp, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99.3 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on November 30, 2004. | ||
| 10.34 | Undertakings, dated January 7, 1993, by WellPoint Health, Blue Cross of California and certain subsidiaries to the California Department of Corporations, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.24 to WellPoint Health’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 (Registration No. 33-54898). | ||
| 10.35 | Orders Approving Notice of Material Modification and Undertakings, dated September 7, 1995, by Blue Cross of California, WellPoint Health and WellPoint Health’s subsidiaries to the California Department of Corporations, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.47 to WellPoint Health’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 1995. | ||
| 10.36 | Amended and Restated Undertakings, dated March 5, 1996, by Blue Cross of California, WellPoint Health and certain of its subsidiaries to the California Department of Corporations, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99.1 to WellPoint Health’s Current Report on Form 8-K dated March 5, 1996. | ||
| 10.37 | Indemnification Agreement, dated as of May 17, 1996, by and among WellPoint Health, WellPoint Health Networks Inc., a Delaware corporation, and Western Health Partnerships, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99.9 to WellPoint Health’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed June 3, 1996. | ||
| 10.38 | Undertakings, dated July 31, 1997, by WellPoint Health, Blue Cross of California and WellPoint California Services, Inc. to the California Department of Corporations, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99.12 to WellPoint Health’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on August 5, 1997. | ||
| 10.39 | Settlement Agreement, dated as of July 11, 2005, by and among the Company, the Representative Plaintiffs, the Signatory Medical Societies and Class Counsel, incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.58 to the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2005. | ||
| 10.40 | * | 2006 Annual Salary Information for Chief Executive Officer and Named Executive Officers. | |
| 21 | Subsidiaries of the Company. | ||
| 23 | Consent of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm. | ||
| 31.1 | Certification of Chief Executive Officer pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a) and Rule 15d-14(a) of the Exchange Act Rules, as adopted pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | ||
| 31.2 | Certification of Chief Financial Officer pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a) and Rule 15d-14(a) of the Exchange Act Rules, as adopted pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | ||
| 32.1 | Certification of Chief Executive Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | ||
| 32.2 | Certification of Chief Financial Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | ||
| * | Indicates management contracts or compensatory plans or arrangements. |
159