UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM N-CSR
CERTIFIED SHAREHOLDER REPORT OF REGISTERED
MANAGEMENT INVESTMENT COMPANIES
Investment Company Act file number 811-21193
First American Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II, Inc.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in charter)
800 Nicollet Mall, Minneapolis, MN | | 55402 |
(Address of principal executive offices) | | (Zip code) |
Charles D. Gariboldi, Jr., 800 Nicollet Mall, Minneapolis, MN 55402
(Name and address of agent for service)
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code: 800-677-3863
Date of fiscal year end: | August 31 |
| |
Date of reporting period: | August 31, 2008 |
Form N-CSR is to be used by management investment companies to file reports with the Commission not later than 10 days after the transmission to stockholders of any report that is required to be transmitted to stockholders under Rule 30e-1 under the Investment Company Act of 1940 (17 CFR 270.30e-1). The Commission may use the information provided on Form N-CSR in its regulatory, disclosure review, inspection, and policymaking roles.
A registrant is required to disclose the information specified by Form N-CSR, and the Commission will make this information public. A registrant is not required to respond to the collection of information contained in Form N-CSR unless the Form displays a currently valid Office of Management and Budget (“OMB”) control number. Please direct comments concerning the accuracy of the information collection burden estimate and any suggestions for reducing the burden to Secretary, Securities and Exchange Commission, 450 Fifth Street, NW, Washington, DC 20549-0609. The OMB has reviewed this collection of information under the clearance requirements of 44 U.S.C. Section 3507.
Item 1. Report to Shareholders
Annual Report
August 31, 2008

MXN
Minnesota Municipal
Income Fund II
Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II
Primary Investments
First American Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II (the "fund") invests primarily in a wide range of Minnesota municipal securities that, at the time of purchase, are rated investment-grade or are unrated and deemed to be of comparable quality by FAF Advisors, Inc. ("FAF Advisors"). The fund may invest up to 20% of its total assets in municipal securities that, at the time of purchase, are rated lower than investment-grade (securities commonly referred to as "high yield" securities or "junk bonds") or are unrated and deemed to be of comparable quality by FAF Advisors. The fund's investments may include municipal derivative securities, such as inverse floating-rate and inverse interest-only municipal securities, which may be more volatile than traditional municipal securities in certain market conditions. The fund's investments also may include repurchase agreements, futures contracts, options on futures contracts, options, and in terest-rate swaps, caps, and floors.
Fund Objective
The fund is a nondiversified, closed-end management investment company. The investment objective of the fund is to provide current income exempt from both regular federal income tax and regular Minnesota personal income tax. The fund's income may be subject to federal and/or Minnesota alternative minimum tax. Distributions of capital gains will be taxable to shareholders. Investors should consult their tax advisors. As with other investment companies, there can be no assurance the fund will achieve its objective.
Table of Contents
| | 1 | | | Explanation of Financial Statements | |
|
| | 2 | | | Fund Overview | |
|
| | 7 | | | Financial Statements | |
|
| | 10 | | | Notes to Financial Statements | |
|
| | 18 | | | Schedule of Investments | |
|
| | 21 | | | Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm | |
|
| | 22 | | | Notice to Shareholders | |
|
NOT FDIC INSURED NO BANK GUARANTEE MAY LOSE VALUE
Explanation of FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
As a shareholder in the fund, you receive shareholder reports semiannually. We strive to present this financial information in an easy-to-understand format; however, for many investors, the information contained in this shareholder report may seem very technical. So, we would like to take this opportunity to explain several sections of the shareholder report.
The Statement of Assets and Liabilities lists the assets and liabilities of the fund on the last day of the reporting period and presents the fund's net asset value ("NAV") and market price per share. The NAV is calculated by dividing the fund's net assets (assets minus liabilities) by the number of shares outstanding. The market price is the closing price on the exchange on which the fund's shares trade. This price, which may be higher or lower than the fund's NAV, is the price an investor pays or receives when shares of the fund are purchased or sold. The investments, as presented in the Schedule of Investments, comprise substantially all of the fund's assets. Other assets include cash and receivables for items such as income earned by the fund but not yet received. Liabilities include payables for items such as fund expenses incurred but not yet pa id.
The Statement of Operations details the dividends and interest income earned from investments as well as the expenses incurred by the fund during the reporting period. Fund expenses may be reduced through fee waivers or reimbursements. This statement reflects total expenses before any waivers or reimbursements, the amount of waivers and reimbursements (if any), and the net expenses. This statement also shows the net realized and unrealized gains and losses from investments owned during the period. The Notes to Financial Statements provide additional details on investment income and expenses of the fund.
The Statement of Changes in Net Assets describes how the fund's net assets were affected by its operating results and distributions to shareholders during the reporting period. This statement is important to investors because it shows exactly what caused the fund's net asset size to change during the period.
The Statement of Cash Flows is required when a fund has a substantial amount of illiquid investments, a substantial amount of the fund's securities are internally valued, or the fund carries some amount of debt. When presented, this statement explains the change in cash during the reporting period. It reconciles net cash provided by and used for operating activities to the net increase or decrease in net assets from operations and classifies cash receipts and payments as resulting from operating, investing, and financing activities.
The Notes to Financial Statements disclose the organizational background of the fund, its significant accounting policies, federal tax information, fees and compensation paid to affiliates, and significant risks and contingencies. Included within the notes to financial statements is the Financial Highlights. This table provides a per-share breakdown of the components that affected the fund's NAV for the current and past reporting periods. It also shows total return, expense ratios, net investment income ratios, and portfolio turnover rates. The net investment income ratios summarize the income earned less expenses, divided by the average net assets. The expense ratios represent the percentage of average net assets that were used to cover operating expenses during the period. The portfolio turnover rate represents the percentage of the fund's holdings that have changed over the course of the period, and gives an idea of how long the fund holds onto a particular security. A 100% turnover rate implies that an amount equal to the value of the entire portfolio is turned over in a year through the purchase or sale of securities.
The Schedule of Investments details all of the securities held in the fund and their related dollar values on the last day of the reporting period. Securities are usually presented by type (bonds, common stock, etc.) and by industry classification (healthcare, education, etc.). This information is useful for analyzing how your fund's assets are invested and seeing where your portfolio manager believes the best opportunities exist to meet your objectives. Holdings are subject to change without notice and do not constitute a recommendation of any individual security. The Notes to Financial Statements provide additional details on how the securities are valued.
We hope this guide to your shareholder report will help you get the most out of this important resource.
Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II 2008 Annual Report
1
Fund OVERVIEW
Average Annual Total Returns
Based on net asset value ("NAV") for the period ended August 31, 2008
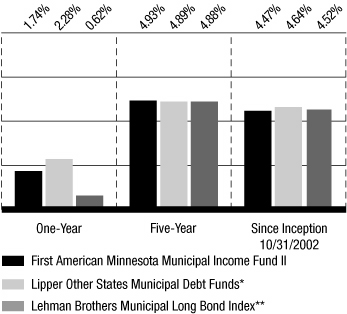
*The Lipper Other States Municipal Debt Funds category median is calculated using the returns of all closed-end exchange traded funds in this category for each period disclosed. Lipper returns assume reinvestment of dividends. Previously, the fund had used the Lipper Minnesota Municipal Debt Funds category, which is no longer in existence.
**The Lehman Brothers Municipal Long Bond Index is comprised of municipal bonds with more than 22 years to maturity and an average credit quality of AA. The index is unmanaged and does not include any fees or expenses in its total return figures.
The average annual total returns for the fund are based on the change in its NAV and assume reinvestment of distributions at NAV. NAV-based performance is used to measure investment management results.
• Average annual total returns based on the change in market price for the one-year, five-year, and since-inception periods ended August 31, 2008, were 3.64%, 4.65%, and 2.79%, respectively.
• Market price returns assume that all distributions have been reinvested at actual prices pursuant to the fund's dividend reinvestment plan. Market price returns reflect any broker commissions or sales charges on dividends reinvested at market price.
• Please remember, you could lose money with this investment. Neither safety of principal nor stability of income is guaranteed. Past performance does not guarantee future results. The investment return and principal value of an investment will fluctuate so that fund shares, when sold, may be worth more or less than their original cost. Closed-end funds, such as this fund, often trade at discounts to NAV. Therefore, you may be unable to realize the full NAV of your shares when you sell.
Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II 2008 Annual Report
2
Fund Management
Douglas J. White, CFA
is primarily responsible for the management of the fund. He has 25 years of financial experience.
Christopher L. Drahn
assists with the management of the fund. He has 28 years of financial experience.
First American Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II posted a total return of 1.74% based on NAV for the fiscal year ended August 31, 2008. The fund's market price return was 3.64% during the year. The fund's competitive group, the Lipper Other States Municipal Debt Funds, produced a median return of 2.28% during the year. The Lehman Brothers Municipal Long Bond Index, the benchmark comparison for the fund, which reflects no fees or expenses, returned 0.62%.
The municipal market endured one of its more tumultuous years ever as fallout from the housing debacle rocked market participants. Deterioration within their relatively new mortgage-backed book of business ultimately led to downgrades for several of the major monoline municipal bond insurers. The impaired credit quality and loss of confidence in many of the insurers affected much of the municipal market (use of insurance had become so pervasive that in recent years close to 50% of all new issuance came to market with an insurance wrap). The market was buffeted by irregular bouts of volatility and selling pressure as a number of accounts unwound positions. For example, tax-exempt money funds were forced to exit insured holdings en masse due to minimum ratings and liquidity requirements. To reduce debt, many municipal market investors were pressured to sell longer-maturity bonds when the floating-rate component of their borrowing programs was no longer money-fund eligible (the municipal market had in recent years developed its own form of "carry" trade, in which investors borrow in the short-term money markets and invest in longer maturities, trying to take advantage of the relative steepness of the municipal yield curve in comparison to other fixed-income markets).
Credit spreads (i.e., the differences in yield between higher- and lower-quality debt) were the first to widen as the market anticipated that lower-quality debt would struggle in a slowing economy. Ultimately, however, the insurer debacle cut an even wider swath through the market. Many insured bonds now trade solely based on the creditworthiness of underlying obligors with little or no value attributed to the insurance wrap. Not surprisingly, in this environment natural stand alone (i.e., without an insurance wrap) AAA and AA rated bonds were generally the best performers for the year.
Portfolio Allocation
As a percentage of total investments on August 31, 2008
| Healthcare Revenue | | | 24 | % | |
| Prerefunded Issues* | | | 16 | % | |
| Housing Revenue | | | 16 | % | |
| Lease Revenue | | | 12 | % | |
| General Obligations | | | 10 | % | |
| Utility Revenue | | | 5 | % | |
| Education Revenue | | | 5 | % | |
| Transportation Revenue | | | 5 | % | |
| Economic Development Revenue | | | 3 | % | |
| Authority Revenue | | | 2 | % | |
| Recreation Authority Revenue | | | 1 | % | |
| Tax Revenue | | | 1 | % | |
| | | | 100 | % | |
*Within the Schedule of Investments, prerefunded issues are classified under their applicable industries.
Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II 2008 Annual Report
3
Fund OVERVIEW
The municipal yield curve steepened over the past 12 months as yields on shorter maturities fell while longer maturity yields rose slightly. In terms of total return, intermediate maturities generally produced the best returns and longer-maturity bonds were the weakest-performing part of the curve. Although the overall municipal market started to regain its bearings near the end of the fiscal year, high-grade bonds still finished at yields of more than 90% (and in some cases more than 100%) of comparable-maturity Treasuries, which typically indicates that the high-grade bonds represent good value relative to Treasuries.
Better-quality bonds provided the best returns during the period. The fund's holdings of AAA- and A-rated bonds outperformed other positions as credit concerns emanating from the subprime loan market caused lower-rated and nonrated bonds to underperform higher-quality issues. While we do not believe the fundamental credit quality of most lower-rated holdings has been impaired, they nonetheless were a drag on performance.
The portfolio's short-intermediate holdings helped performance. As yields on these positions fell over the period, their prices rose more than the prices of shorter and longer maturities.
Prerefunded, lease-revenue, and general obligation sectors were the fund's better performing sectors. Senior care facilities, electric utility, and housing revenue positions lagged and had a negative impact on performance.
Bond Credit Quality Breakdown*
As a percentage of long-term investments on August 31, 2008
| AAA | | | 15 | % | |
| AA | | | 19 | % | |
| A | | | 26 | % | |
| BBB | | | 18 | % | |
| BB | | | 2 | % | |
| Nonrated | | | 20 | % | |
| | | | 100 | % | |
*Individual security ratings are based on information from Moody's Investors Service, Standard & Poor's, and/or Fitch. If there are multiple ratings for a security the lowest rating is used, unless ratings are provided by all three agencies, in which case the middle rating is used.
Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II 2008 Annual Report
4
The volatility in the municipal market during the period was in some respects historic, continuing the trend that began in late summer 2007. For example, municipal bonds continued their underperformance of comparable-maturity U.S. Treasuries to the point where, during the spring of 2008, municipal yields were the highest ever, relative to Treasuries. The volatility was primarily technical in nature, related to increased supply of municipals on the secondary market and the turbulence in the subprime market; it did not reflect broad credit quality deterioration in the municipal bond market. However, a slowing economy or recession resulting from the problems in the housing and financial markets could negatively impact the tax revenues of municipal issuers. A prolonged slowdown would in turn negatively impact some of these issuers' credit quality and poss ibly their ability to make timely interest and principal payments on their bonds. Our research staff is committed to monitoring the credit quality of the portfolio's holdings and we continue to actively manage the portfolio's risk.
We once again wish to express our appreciation for your ongoing investment in the fund. If you have any questions or need assistance with your investments, please call us at 800.677.FUND.
Sincerely,
Douglas J. White, CFA
Head of Tax Exempt Fixed Income
FAF Advisors, Inc.
Christopher L. Drahn
Senior Fixed-Income Portfolio Manager
FAF Advisors, Inc.
Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II 2008 Annual Report
5
Preferred Shares
The preferred shares issued by the fund pay dividends at a specified rate and have preference over common shares in the payments of dividends and the liquidation of assets. Rates paid on preferred shares are reset every seven days and are based on short-term tax-exempt interest rates. Preferred shareholders accept these short-term rates in exchange for low credit risk (preferred shares are rated AAA by Moody's and S&P) and high liquidity (preferred shares trade at par and are remarketed every seven days). The proceeds from the sale of preferred shares are invested at intermediate- and long-term tax-exempt rates. Because these intermediate- and long-term rates are normally higher than the short-term rates paid on preferred shares, common shareholders benefit by receiving higher dividends and/or an increase to the dividend reserve. However, the risk of having preferred shares is that if short-term rates rise higher than interm ediate- and long-term rates, creating an inverted yield curve, common shareholders may receive a lower rate of return than if their fund did not have any preferred shares outstanding. This type of economic environment is unusual and historically has been short term in nature. Investors should also be aware that the issuance of preferred shares results in the leveraging of common shares, which increases the volatility of both the NAV of the fund and the market value of common shares.
Normally, the dividend rates on the preferred shares are set at the market clearing rate determined through an auction process that brings together bidders who wish to buy preferred shares and holders of preferred shares who wish to sell. Since February 15, 2008, however, sell orders have exceeded bids and the regularly scheduled auctions for the fund's preferred shares have failed. When an auction fails, the fund is required to pay the maximum applicable rate on the preferred shares to holders of such shares for successive dividend periods until such time as the shares are successfully auctioned. The maximum applicable rate on the preferred shares is 110% of the higher of (1) the applicable AA Composite Commercial Paper Rate or (2) 90% of the Taxable Equivalent of the Short-Term Municipal Bond Rate.
During any dividend period, the maximum applicable rate could be higher than the dividend rate that would have been set had the auction been successful. In addition, as occurred for a period of time after the fund's fiscal year end, the maximum applicable rate could be higher than the fund's investment yield. Higher maximum applicable rates increase the fund's cost of leverage and reduce the fund's common share earnings.
Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II 2008 Annual Report
6
FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Statement of Assets and Liabilities August 31, 2008
| Assets: | |
| Unaffiliated investments, at value (cost: $33,378,092) (note 2) | | $ | 32,865,525 | | |
| Receivable for accrued interest | | | 458,064 | | |
| Prepaid expenses and other assets | | | 9,681 | | |
| Total assets | | | 33,333,270 | | |
| Liabilities: | |
| Payable for preferred share distributions (note 3) | | | 6,620 | | |
| Payable for investment advisory fees (note 5) | | | 9,830 | | |
| Payable for administrative fees (note 5) | | | 5,617 | | |
| Payable for professional fees | | | 15,082 | | |
| Payable for transfer agent fees | | | 2,561 | | |
| Payable for other expenses | | | 2,574 | | |
| Total liabilities | | | 42,284 | | |
| Preferred shares, at liquidation value | | | 13,000,000 | | |
| Net assets applicable to outstanding common shares | | $ | 20,290,986 | | |
| Net assets applicable to outstanding common shares consist of: | |
| Common shares and additional paid-in capital | | $ | 20,798,974 | | |
| Undistributed net investment income | | | 87,440 | | |
| Accumulated net realized loss on investments and futures contracts | | | (82,861 | ) | |
| Net unrealized depreciation of investments | | | (512,567 | ) | |
| Net assets applicable to outstanding common shares | | $ | 20,290,986 | | |
| Net asset value and market price of common shares: | |
| Net assets applicable to outstanding common shares | | $ | 20,290,986 | | |
| Common shares outstanding (authorized 200 million shares of $0.01 par value) | | | 1,472,506 | | |
| Net asset value per share | | $ | 13.78 | | |
| Market price per share | | $ | 13.00 | | |
| Liquidation preference of preferred shares (note 3): | |
| Net assets applicable to preferred shares | | $ | 13,000,000 | | |
| Preferred shares outstanding (authorized one million shares) | | | 520 | | |
| Liquidation preference per share | | $ | 25,000 | | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the financial statements.
Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II 2008 Annual Report
7
FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Statement of Operations For the Year Ended August 31, 2008
| Investment Income: | |
| Interest from unaffiliated investments | | $ | 1,729,715 | | |
| Dividends from unaffiliated money market fund | | | 7,355 | | |
| Total investment income | | | 1,737,070 | | |
| Expenses (note 5): | |
| Investment advisory fees | | | 135,363 | | |
| Administrative fees | | | 67,698 | | |
| Auction agent fees | | | 34,133 | | |
| Custodian fees | | | 1,735 | | |
| Professional fees | | | 49,185 | | |
| Postage and printing fees | | | 22,738 | | |
| Transfer agent fees | | | 19,022 | | |
| Listing fees | | | 4,599 | | |
| Directors' fees | | | 26,512 | | |
| Insurance fees | | | 11,965 | | |
| Pricing fees | | | 9,354 | | |
| Other expenses | | | 30,121 | | |
| Total expenses | | | 412,425 | | |
| Less: Wavier of advisory fees (note 5) | | | (16,891 | ) | |
| Less: Fee reimbursements (note 5) | | | (31 | ) | |
| Less: Indirect payments from custodian (note 5) | | | (3 | ) | |
| Total net expenses | | | 395,500 | | |
| Net investment income | | | 1,341,570 | | |
| Net realized and unrealized gains (losses) on investments and futures contracts (notes 2 and 4): | |
| Net realized gain (loss) on: | |
| Investments | | | 18,065 | | |
| Futures contracts | | | (11,099 | ) | |
| Net change in unrealized appreciation or depreciation of investments | | | (550,570 | ) | |
| Net loss on investments and futures contracts | | | (543,604 | ) | |
| Distributions to preferred shareholders (note 2): | |
| From net investment income | | | (366,396 | ) | |
| From net realized gain on investments | | | (72,361 | ) | |
| Total distributions | | | (438,757 | ) | |
| Net increase in net assets applicable to common shares resulting from operations | | $ | 359,209 | | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the financial statements.
Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II 2008 Annual Report
8
FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Statements of Changes in Net Assets
| | | Year Ended
8/31/08 | | Year Ended
8/31/07 | |
| Operations: | |
| Net investment income | | $ | 1,341,570 | | | $ | 1,364,828 | | |
| Net realized gain (loss) on: | |
| Investments | | | 18,065 | | | | 110,393 | | |
| Futures contracts | | | (11,099 | ) | | | (36,867 | ) | |
| Net change in unrealized appreciation or depreciation of: | |
| Investments | | | (550,570 | ) | | | (1,277,844 | ) | |
| Futures contracts | | | — | | | | 44,459 | | |
| Distributions to preferred shareholders (note 2): | |
| From net investment income | | | (366,396 | ) | | | (444,604 | ) | |
| From net realized gain on investments | | | (72,361 | ) | | | (7,039 | ) | |
| Net increase (decrease) in net assets applicable to common shares resulting from operations | | | 359,209 | | | | (246,674 | ) | |
| Distributions to common shareholders (note 2): | |
| From net investment income | | | (949,766 | ) | | | (918,843 | ) | |
| From net realized gain on investments | | | (116,711 | ) | | | (16,463 | ) | |
| Total distributions | | | (1,066,477 | ) | | | (935,306 | ) | |
| Total decrease in net assets applicable to common shares | | | (707,268 | ) | | | (1,181,980 | ) | |
| Net assets applicable to common shares at beginning of year | | | 20,998,254 | | | | 22,180,234 | | |
| Net assets applicable to common shares at end of year | | $ | 20,290,986 | | | $ | 20,998,254 | | |
| Undistributed net investment income | | $ | 87,440 | | | $ | 66,794 | | |
Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II 2008 Annual Report
9
Notes to FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(1) Organization
Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II, Inc. (the "fund") is registered under the Investment Company Act of 1940 (as amended) as a non-diversified, closed-end management investment company. The fund invests primarily in Minnesota municipal securities that, at the time of purchase, are rated investment grade or are unrated and deemed to be of comparable quality by FAF Advisors, Inc. ("FAF Advisors"). The fund may invest up to 20% of its total assets in municipal securities that, at the time of purchase, are rated lower than investment grade or are unrated and deemed to be of comparable quality by FAF Advisors. The fund's investments may include municipal derivative securities, such as inverse floating rate and inverse interest-only municipal securities, which may be more volatile than traditional municipal securities in certain market conditions. The fund's investments also may include repurchase agreements, futures contracts, options on futures contracts, options, and interest rate swaps, caps, and floors. Fund shares are listed on the American Stock Exchange under the symbol MXN.
The fund concentrates its investments in Minnesota and therefore, may have more credit risk related to the economic conditions of Minnesota than a portfolio with a broader geographical diversification.
(2) Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Security Valuations
Debt obligations exceeding 60 days to maturity are valued by an independent pricing service that has been approved by the fund's board of directors. The pricing service may employ methodologies that utilize actual market transactions, broker-dealer supplied valuations, or other formula-driven valuation techniques. These techniques generally consider such factors as yields or prices of bonds of comparable quality, type of issue, coupon, maturity, ratings, and general market conditions. Securities for which prices are not available from an independent pricing service but where an active market exists are valued using market quotations obtained from one or more dealers that make markets in the securities or from a widely-used quotation system. Debt obligations with 60 days or less remaining until maturity may be valued at their amortized cost, which approximates market value. Investments in open-end mutual funds are valued at their respective net asset values on the valuation date.
The following investment vehicles, when held by the fund, are priced as follows: Exchange listed futures and options on futures are priced at their last sale price on the exchange on which they are principally traded, as determined by FAF Advisors, on the day the valuation is made. If there were no sales on that day, futures and options on futures will be valued at the last reported bid price. Options on securities, indices, and currencies traded on Nasdaq or listed on a stock exchange, whether domestic or foreign, are valued at the last sale price on Nasdaq or on any exchange on the day the valuation is made. If there were no sales on that day, the options will be valued at the last sale price on the previous valuation date. Last sale prices are obtained from an independent pricing service. Forward contracts (other than currency forward contracts), swaps, and over-the-counter options on securities, indices, and currencies are v alued at the quotations received from an independent pricing service, if available.
When market quotations are not readily available, securities are valued at fair value as determined in good faith by procedures established and approved by the fund's board of directors. Some of the factors which may be considered in determining fair value are fundamental analytical data relating to the investment; the nature and duration of any restrictions on disposition; trading in similar securities of the same issuer or comparable companies; information from broker-dealers; and an evaluation of the forces that influence the market in which the securities are purchased or sold. If events occur that materially affect the value of securities between the close of trading in those
Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II 2008 Annual Report
10
securities and the close of regular trading on the New York Stock Exchange, the securities will be valued at fair value.
As of August 31, 2008, the fund held no fair valued securities.
Security Transactions and Investment Income
For financial statement purposes, the fund records security transactions on the trade date of the security purchase or sale. Dividend income is recorded on the ex-dividend date. Interest income, including accretion of bond discounts and amortization of bond premiums, is recorded on an accrual basis. Security gains and losses are determined on the basis of identified cost, which is the same basis used for federal income tax purposes.
Inverse Floaters
As part of its investment strategy, the fund may invest in certain securities for which the potential income return is inversely related to changes in a floating interest rate ("inverse floaters"). In general, income on inverse floaters will decrease when short-term interest rates increase and increase when short-term interest rates decrease. Inverse floaters may be characterized as derivative securities and may subject the fund to the risks of reduced or eliminated interest payments and losses of invested principal. In addition, inverse floaters have the effect of providing investment leverage and, as a result, the market values of such securities will generally be more volatile than those of fixed-rate, tax-exempt securities. To the extent the fund invests in inverse floaters, the net asset value of the fund's shares may be more volat ile than if the fund did not invest in such securities. As of and for the year ended August 31, 2008, the fund had no outstanding investments in inverse floaters.
Repurchase Agreements
For repurchase agreements entered into with certain broker-dealers, the fund, along with other affiliated registered investment companies, may transfer uninvested cash balances into a joint trading account, the daily aggregate balance of which is invested in repurchase agreements secured by U.S. government or agency obligations. Securities pledged as collateral for all individual and joint repurchase agreements are held by the fund's custodian bank until maturity of the repurchase agreement. All agreements require that the daily market value of the collateral be in excess of the repurchase amount, including accrued interest, to protect the fund in the event of a default. As of August 31, 2008, the fund had no outstanding repurchase agreements.
Futures Transactions
In order to protect against changes in interest rates, the fund may buy and sell interest rate futures contracts. Upon entering into a futures contract, the fund is required to deposit cash or pledge U.S. government securities in an amount equal to 5% of the purchase price indicated in the futures contract (initial margin). Subsequent payments, which are dependent on the daily fluctuations in the value of the underlying security or securities, are made or received by the fund each day (daily variation margin) and recorded as unrealized gains (losses) until the contract is closed. When the contract is closed, the fund records a realized gain (loss) equal to the difference between the proceeds from (or cost of) the closing transaction and the fund's basis in the contract.
Risks of entering into futures contracts, in general, include the possibility that there will not be a perfect price correlation between the futures contracts and the underlying securities. Second, it is possible that a lack of liquidity for futures contracts could exist in the secondary market, resulting in an inability to close a futures position prior to its maturity date. Third, the purchase of a futures
Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II 2008 Annual Report
11
Notes to FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
contract involves the risk that the fund could lose more than the original margin deposit required to initiate a futures transaction. These contracts involve market risk in excess of the amount reflected in the fund's statement of assets and liabilities. Unrealized gains (losses) on outstanding positions in futures contracts held at the close of the period will be recognized as capital gains (losses) for federal income tax purposes. As of August 31, 2008, the fund had no outstanding futures contracts.
Securities Purchased on a When-Issued Basis
Delivery and payment for securities that have been purchased by the fund on a when-issued or forward-commitment basis can take place a month or more after the transaction date. Such securities do not earn interest, are subject to market fluctuation, and may increase or decrease in value prior to their delivery. The fund segregates assets with a market value equal to or greater than the amount of its purchase commitments. The purchase of securities on a when-issued or forward-commitment basis may increase the volatility of the fund's net asset value if the fund makes such purchases while remaining substantially fully invested. As of August 31, 2008, the fund had no outstanding when-issued or forward-commitment securities.
In connection with the ability to purchase securities on a when-issued basis, the fund may also enter into dollar rolls in which the fund sells securities purchased on a forward-commitment basis and simultaneously contracts with a counterparty to repurchase similar (same type, coupon, and maturity), but not identical securities on a specified future date. As an inducement for the fund to "rollover" its purchase commitments, the fund receives negotiated amounts in the form of reductions of the purchase price of the commitment. Dollar rolls are considered a form of leverage. As of and for the year ended August 31, 2008, the fund had no dollar roll transactions.
Taxes
Federal
The fund intends to continue to qualify as a regulated investment company as provided in Subchapter M of the Internal Revenue Code, as amended, and to distribute all taxable income, if any, to its shareholders. Accordingly, no provision for federal income taxes is required.
Financial Accounting Standards Board ("FASB") Interpretation No. 48, "Accounting for Uncertainty in Income Taxes" ("FIN 48") provides guidance for how uncertain tax positions should be recognized, measured, presented, and disclosed in the financial statements. FIN 48 requires the evaluation of tax positions taken or expected to be taken in the course of preparing the fund's tax returns to determine whether the tax positions are "more-likely-than-not" of being sustained by the applicable tax authority. Tax positions not deemed to meet a "more-likely-than-not" threshold would be recorded as a tax benefit or expense in the current year. As of August 31, 2008, the fund did not have any tax positions that did not meet the "more-likely-than-not" threshold of being sustained by the applicable taxing authority. Generally, tax authorities can examine all the tax returns filed for the last three years.
Net investment income and net realized gains and losses may differ for financial statement and tax purposes because of temporary or permanent book/tax differences. These differences are primarily due to deferred straddle losses. To the extent these differences are permanent, reclassifications are made to the appropriate capital accounts in the fiscal period that the differences arise.
| On the Statement of Assets and Liabilities, the following reclassifications were made: | |
|
Undistributed
Net Investment
Income | | Accumulated
Net Realized
Gain (Loss) | |
| $ | (4,762 | ) | | $ | 4,762 | | |
Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II 2008 Annual Report
12
The character of distributions made during the fiscal period from net investment income or net realized gains may differ from its ultimate characterization for federal income tax purposes. In addition, due to the timing of dividend distributions, the fiscal period in which amounts are distributed may differ from the fiscal period that the income or realized gains or losses were recorded by the fund.
The character of common and preferred share distributions paid during the fiscal years ended August 31, 2008 and August 31, 2007, were as follows:
| | | 8/31/08 | | 8/31/07 | |
| Distributions paid from: | |
| Tax exempt income | | $ | 1,311,021 | | | $ | 1,359,239 | | |
| Ordinary income | | | 15,062 | | | | 2,017 | | |
| Long-term capital gains | | | 179,566 | | | | 23,502 | | |
| | | $ | 1,505,649 | | | $ | 1,384,758 | | |
At August 31, 2008, the components of accumulated earnings (deficit) on a tax basis were as follows:
| Undistributed ordinary income | | $ | 2,962 | | |
| Undistributed tax-exempt income | | | 92,852 | | |
| Accumulated capital and post October loss | | | (73,952 | ) | |
| Unrealized appreciation (depreciation) | | | (521,476 | ) | |
| Accumulated earnings (deficit) | | $ | (499,614 | ) | |
The fund incurred losses of $73,952 for tax purposes for the period from November 1, 2007 to August 31, 2008. As permitted by tax regulations, the fund intends to elect to defer and treat the losses as arising in the fiscal year ending August 31, 2009.
State
Minnesota taxable net income is generally based on federal taxable income. The portion of tax-exempt dividends paid by the fund that is derived from interest on Minnesota municipal bonds will be excluded from Minnesota taxable net income of individuals, estates, and trusts, provided that the portion of the tax-exempt dividends paid from these obligations represents 95% or more of the exempt-interest dividends paid by the fund. The remaining portion of these dividends, and dividends that are not exempt-interest dividends or capital gains distributions, will be included in the Minnesota taxable net income of individuals, estates, and trusts, except for dividends directly attributable to interest on obligations of the U.S. government, its territories and possessions.
In 1995, Minnesota enacted a statement of intent that interest on obligations of Minnesota governmental units and Indian tribes be included in the net income of individuals, estates and trusts for Minnesota income tax purposes if a court determines that Minnesota's exemption of such interest and its taxation of interest on obligations of governmental issuers in other states unlawfully discriminates against interstate commerce. See Minn. Stat. § 289A.50, subd. 10. This provision applies to taxable years that begin during or after the calendar year in which any such determination becomes final.
Distributions to Shareholders
Distributions from net investment income are made monthly for common shareholders and weekly for preferred shareholders. Common share distributions are recorded as of the close of business on the ex-dividend date and preferred share dividends are accrued daily. Net realized gains distributions, if any, will be made at least annually. Distributions are payable in cash or, for
Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II 2008 Annual Report
13
Notes to FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
common shareholders pursuant to the fund's dividend reinvestment plan, reinvested in additional common shares of the fund. Under the dividend reinvestment plan, common shares will be purchased in the open market.
Deferred Compensation Plan
Under a Deferred Compensation Plan (the "Plan"), non-interested directors of the First American Family of Funds may participate and elect to defer receipt of part or all of their annual compensation. Deferred amounts are treated as though equivalent dollar amounts had been invested in shares of open-end First American Funds, preselected by each Director. All amounts in the Plan are 100% vested and accounts under the Plan are obligations of the fund. Deferred amounts remain in the fund until distributed in accordance with the Plan.
Use of Estimates in the Preparation of Financial Statements
The preparation of financial statements, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles, requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amount of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the results of operations during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from these estimates.
(3) Auction Preferred Shares
As of August 31, 2008, the fund had 520 auction preferred shares ("AP shares") with a liquidation preference of $25,000 per share. The dividend rate on the AP shares is adjusted every seven days (on Fridays), as determined through an auction process conducted by Bank of New York (the "Auction Agent").
Normally, the dividend rates on the AP shares are set at the market clearing rate determined through an auction process that brings together bidders who wish to buy AP shares and holders of AP shares who wish to sell. Since February 15, 2008, however, sell orders have exceeded bids and the regularly scheduled auctions for the fund's AP shares have failed. When an auction fails, the fund is required to pay the maximum applicable rate on the AP shares to holders of such shares for successive dividend periods until such time as the shares are successfully remarketed. The maximum applicable rate on the AP shares is 110% of the higher of (1) the applicable AA Composite Commercial Paper Rate or (2) 90% of the Taxable Equivalent of the Short-Term Municipal Bond Rate.
During any dividend period, the maximum applicable rate may be higher than the dividend rate that would have been set had the auction been successful. This would increase the fund's cost of leverage and reduce the fund's common share earnings. On August 31, 2008, the maximum applicable rate was 2.66%.
In the event of a failed auction, holders of AP shares will continue to receive dividends at the maximum applicable rate, but generally will not be able to sell their shares until the next successful auction. There is no way to predict when future auctions might succeed in attracting sufficient buyers for the shares offered.
(4) Investment Security Transactions
Cost of purchases and proceeds from sales of securities, other than temporary investments in short-term securities, for the year ended August 31, 2008, aggregated $7,416,018 and $7,593,108, respectively.
Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II 2008 Annual Report
14
(5) Expenses
Investment Advisory Fees
Pursuant to an investment advisory agreement (the "Agreement"), FAF Advisors, a subsidiary of U.S. Bank National Association ("U.S. Bank"), manages the fund's assets and furnishes related office facilities, equipment, research, and personnel. The Agreement as amended June 19, 2008 provides FAF Advisors with a monthly investment advisory fee in an amount equal to an annualized rate of 0.35% of the fund's average weekly net assets including preferred shares. For its fee, FAF Advisors provides investment advice and, in general, conducts the management and investment activities of the fund.
The fund may invest in related money market funds that are series of First American Funds, Inc., subject to certain limitations. In order to avoid the payment of duplicative investment advisory fees to FAF Advisors, which acts as the investment advisor to both the fund and the related money market funds, FAF Advisors will reimburse the fund an amount equal to the investment advisory fee received from the related money market funds that is attributable to the assets of the fund. These reimbursements, if any, are disclosed as "Fee reimbursements" in the Statement of Operations.
Administrative Fees
FAF Advisors serves as the fund's administrator pursuant to an administration agreement between FAF Advisors and the fund. Under this agreement, FAF Advisors receives a monthly administrative fee in an amount equal to an annualized rate of 0.20% of the fund's average weekly net assets including preferred shares. For its fee, FAF Advisors provides numerous services to the fund including, but not limited to, handling the general business affairs, financial and regulatory reporting, and various other services.
Auction Agent Fees
The fund has entered into an auction agency agreement with the Auction Agent. The auction agency agreement provides the Auction Agent with a monthly fee in an amount equal to an annual rate of 0.25% of the fund's average amount of preferred shares outstanding. For its fee, the Auction Agent will act as agent of the fund in conducting the auction of preferred shares at which the applicable dividend rate is determined for each seven-day dividend period.
Custodian Fees
U.S. Bank serves as the fund's custodian pursuant to a custodian agreement with the fund. The custodian fee charged to the fund is equal to an annual rate of 0.005% of average weekly net assets, including preferred shares. These fees are computed weekly and paid monthly.
Under this agreement, interest earned on uninvested cash balances is used to reduce a portion of the fund's custodian expenses. These credits, if any, are disclosed as "Indirect payments from custodian" in the Statement of Operations. Conversely, the custodian charges a fee for any cash overdrafts incurred, which will increase the fund's custodian expenses. For the year ended August 31, 2008, custodian fees were increased by $42 as a result of overdrafts and reduced by $3 as a result of interest earned.
Other Fees and Expenses
In addition to the investment advisory, administrative, auction agent, and custodian fees, the fund is responsible for paying most other operating expenses, including: legal, auditing, and accounting services, postage and printing of shareholder reports, transfer agent fees and expenses, listing fees, outside directors' fees and expenses, insurance, pricing, interest, taxes, and other miscellaneous expenses. For the year ended August 31, 2008, legal fees and expenses of $5,533 were paid to a law firm of which an Assistant Secretary of the fund is a partner.
Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II 2008 Annual Report
15
Notes to FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Expenses that are directly related to the fund are charged directly to the fund. Other operating expenses of the First American Family of Funds are allocated to the fund on several bases, including evenly across all funds, allocated based on relative net assets of all funds within the First American Family of Funds, or a combination of both methods.
(6) Indemnifications
The fund enters into contracts that contain a variety of indemnifications. The fund's maximum exposure under these arrangements is unknown. However, the fund has not had prior claims or losses pursuant to these contracts and expects the risk of loss to be remote.
(7) New Accounting Pronouncements
In September 2006, the FASB issued Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 157, "Fair Value Measurements" ("FAS 157"). FAS 157 clarifies the definition of fair value for financial reporting, establishes a framework for measuring fair value, and requires additional disclosure about the use of fair value measurements. FAS 157 is effective for financial statements issued for fiscal years beginning after November 15, 2007 and interim periods within those fiscal years. As of August 31, 2008, the fund does not believe the adoption of FAS 157 will materially impact the amounts reported in the financial statements; however, additional disclosures will be required about the inputs used to develop the measurements of fair value and the effect of certain measurements reported in the Statement of Operations for a fiscal period.
In March 2008, the FASB issued Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 161, Disclosures about Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities ("FAS 161"). FAS 161 is effective for fiscal years and interim periods beginning after November 15, 2008. FAS 161 may require enhanced disclosures about the fund's derivative and hedging activities. Management is currently evaluating the impact the adoption of FAS 161 will have on the fund's financial statement disclosures.
Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II 2008 Annual Report
16
Notes to FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(8) Financial Highlights
Per-share data for an outstanding common share throughout each period and selected information for each period are as follows:
| | | Year Ended August 31, | | Seven-Month
Fiscal
Period Ended | | Year Ended January 31, | |
| | | 2008 | | 2007 | | 2006 | | 8/31/05 | | 2005 | | 2004 | |
| Per-Share Data | |
| Net asset value, common shares, beginning of period | | $ | 14.26 | | | $ | 15.06 | | | $ | 15.41 | | | $ | 15.19 | | | $ | 14.70 | | | $ | 14.56 | | |
| Operations: | |
| Net investment income | | | 0.91 | | | | 0.93 | | | | 0.93 | | | | 0.53 | | | | 0.94 | | | | 0.82 | | |
Net realized and unrealized gains
(losses) on investments and futures contracts | | | (0.37 | ) | | | (0.79 | ) | | | (0.29 | ) | | | 0.25 | | | | 0.47 | | | | 0.39 | | |
| Distributions to preferred shareholders: | |
| From net investment income | | | (0.25 | ) | | | (0.30 | ) | | | (0.25 | ) | | | (0.10 | ) | | | (0.09 | ) | | | (0.07 | ) | |
| From net realized gain on investments | | | (0.05 | ) | | | (0.01 | ) | | | (0.01 | ) | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | |
| Total from operations | | | 0.24 | | | | (0.17 | ) | | | 0.38 | | | | 0.68 | | | | 1.32 | | | | 1.14 | | |
| Distributions to common shareholders: | |
| From net investment income | | | (0.64 | ) | | | (0.62 | ) | | | (0.69 | ) | | | (0.46 | ) | | | (0.79 | ) | | | (0.80 | ) | |
| From net realized gain on investments | | | (0.08 | ) | | | (0.01 | ) | | | (0.04 | ) | | | — | | | | (0.04 | ) | | | (0.03 | ) | |
| Total distributions to common shareholders | | | (0.72 | ) | | | (0.63 | ) | | | (0.73 | ) | | | (0.46 | ) | | | (0.83 | ) | | | (0.83 | ) | |
Offering costs and underwriting discounts
associated with the issuance of preferred
shares and common shares | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | (0.17 | ) | |
| Net asset value, common shares, end of period | | $ | 13.78 | | | $ | 14.26 | | | $ | 15.06 | | | $ | 15.41 | | | $ | 15.19 | | | $ | 14.70 | | |
| Market value, common shares, end of period | | $ | 13.00 | | | $ | 13.25 | | | $ | 14.24 | | | $ | 15.06 | | | $ | 14.39 | | | $ | 14.60 | | |
| Selected Information | |
| Total return, common shares, net asset value (a) | | | 1.74 | % | | | (1.22 | )% | | | 2.65 | % | | | 4.57 | % (e) | | | 9.36 | % | | | 6.86 | % | |
| Total return, common shares, market value (b) | | | 3.64 | % | | | (2.73 | )% | | | (0.35 | )% | | | 8.00 | % (e) | | | 4.66 | % | | | 4.36 | % | |
Net assets applicable to common shares at end of
period (in millions) | | $ | 20 | | | $ | 21 | | | $ | 22 | | | $ | 23 | | | $ | 22 | | | $ | 22 | | |
Ratio of expenses to average weekly net assets
applicable to common shares before fee waivers (c) | | | 1.98 | % | | | 1.85 | % | | | 1.70 | % | | | 1.67 | % (f) | | | 1.61 | % | | | 1.99 | % | |
Ratio of expenses to average weekly net assets
applicable to common shares after fee waivers (c) | | | 1.90 | % | | | 1.77 | % | | | 1.62 | % | | | 1.59 | % (f) | | | 1.53 | % | | | 1.91 | % | |
Ratio of net investment income to average weekly net assets
applicable to common shares before fee waivers (c) | | | 6.46 | % | | | 6.12 | % | | | 6.13 | % | | | 5.95 | % (f) | | | 6.31 | % | | | 5.87 | % | |
Ratio of net investment income to average weekly net assets
applicable to common shares after fee waivers (c) | | | 6.54 | % | | | 6.20 | % | | | 6.21 | % | | | 6.03 | % (f) | | | 6.39 | % | | | 5.95 | % | |
| Portfolio turnover rate | | | 22 | % | | | 24 | % | | | 18 | % | | | 7 | % | | | 13 | % | | | 22 | % | |
Net assets applicable to preferred shares,
end of period (in millions) | | $ | 13 | | | $ | 13 | | | $ | 13 | | | $ | 13 | | | $ | 13 | | | $ | 13 | | |
| Asset coverage per preferred share (in thousands) (d) | | $ | 64 | | | $ | 65 | | | $ | 68 | | | $ | 69 | | | $ | 68 | | | $ | 67 | | |
Liquidation preference and market value per
preferred share (in thousands) | | $ | 25 | | | $ | 25 | | | $ | 25 | | | $ | 25 | | | $ | 25 | | | $ | 25 | | |
(a) Assumes reinvestment of distributions at net asset value.
(b) Assumes reinvestment of distributions at actual prices pursuant to the fund's dividend reinvestment plan.
(c) Ratios do not reflect the effect of dividend payments to preferred shareholders; income ratios reflect income earned on assets attributable to preferred shares, where applicable.
(d) Represents net assets applicable to common shares plus preferred shares at liquidation value divided by preferred shares outstanding.
(e) Total return has not been annualized.
(f) Annualized.
Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II 2008 Annual Report
17
Schedule of INVESTMENTS
Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II (MXN) August 31, 2008
| DESCRIPTION | | PAR | | VALUE I | |
| (Percentages of each investment category relate to total net assets applicable to outstanding common shares) | |
| Municipal Long-Term Investments — 161.2% | |
| Economic Development Revenue — 1.9% | |
| Agriculture and Economic Development Board, Small Business Program A — Lot 1 (AMT), 5.55%, 8/1/16 | | $ | 400,000 | | | $ | 392,804 | | |
| Education Revenue — 10.1% | |
| Higher Education Facilities, Augsburg College, Series 6, 5.00%, 5/1/28 | | | 200,000 | | | | 183,996 | | |
| Higher Education Facilities, College of Art & Design, 5.00%, 5/1/26 | | | 400,000 | | | | 372,412 | | |
| Higher Education Facilities, St. Catherine's College, 5.38%, 10/1/32 | | | 1,000,000 | | | | 955,130 | | |
| Higher Education Facilities, St. John's University, Series 5 (Prerefunded 10/1/11 @ 100), 5.25%, 10/1/26 A | | | 350,000 | | | | 379,085 | | |
| St. Paul Housing & Redevelopment Authority, Community Peace Academy Project, Series A, 5.00%, 12/1/36 | | | 200,000 | | | | 164,730 | | |
| | | | 2,055,353 | | |
| General Obligations — 16.4% | |
| City of Duluth, Series A, 5.00%, 2/1/34 | | | 700,000 | | | | 708,365 | | |
| Crow Wing County Jail, Series B (MBIA), 5.00%, 2/1/21 | | | 550,000 | | | | 573,799 | | |
| Duluth Independent School District Number 709, Series A (FSA) (MSDCEP), 4.25%, 2/1/23 | | | 500,000 | | | | 494,670 | | |
| Metropolitan Council Minneapolis-St Paul Metropolitan Area, Series C, 5.00%, 3/1/20 | | | 1,000,000 | | | | 1,068,480 | | |
| Puerto Rico Commonwealth, Series A, 5.00%, 7/1/28 | | | 500,000 | | | | 490,105 | | |
| | | | 3,335,419 | | |
| Healthcare Revenue — 54.4% | |
Agricultural and Development Board, Fairview Health Care System,
6.38%, 11/15/29 | | | 25,000 | | | | 25,771 | | |
| 6.38%, 11/15/29 (Prerefunded 11/15/10 @ 101) A | | | 675,000 | | | | 740,590 | | |
| Bemidji Health Care Facilities, North Country Health Services (RAAI), 5.00%, 9/1/31 | | | 1,000,000 | | | | 945,150 | | |
| Columbia Heights Multifamily & Health Care Facilities Revenue, Crest View Project, 5.70%, 7/1/42 | | | 350,000 | | | | 308,392 | | |
Cuyuna Range Hospital District,
5.00%, 6/1/29 | | | 350,000 | | | | 306,477 | | |
| 5.50%, 6/1/35 | | | 400,000 | | | | 364,096 | | |
Duluth Health Care Facility, Benedictine Health System-St. Mary's Hospital
(Prerefunded 2/15/14 @ 100), 5.25%, 2/15/33 A | | | 1,000,000 | | | | 1,107,660 | | |
Glencoe Health Care Facilities, Glencoe Regional Health Services
(Prerefunded 4/1/11 @ 101), 7.50%, 4/1/31 A | | | 400,000 | | | | 451,092 | | |
| Golden Valley Health Care Facilities, Covenant Retirement Communities, 5.50%, 12/1/25 | | | 600,000 | | | | 581,874 | | |
| Illinois Finance Authority Revenue, Franciscan Communities, 5.50%, 5/15/37 | | | 250,000 | | | | 206,748 | | |
| Inver Grove Heights Nursing, Presbyterian Homes, 5.50%, 10/1/33 | | | 250,000 | | | | 233,268 | | |
| Marshall Health Care Facility, Weiner Medical Center Project, 5.35%, 11/1/17 | | | 350,000 | | | | 356,741 | | |
| Minneapolis & St. Paul Housing & Redevelopment Authority, Healthpartners Project, 5.88%, 12/1/29 | | | 750,000 | | | | 743,452 | | |
Minneapolis Health Care Facilities System, Allina Health Systems
(Prerefunded 11/15/12 @ 100), 5.75%, 11/15/32 A | | | 300,000 | | | | 334,065 | | |
| Monticello, Big Lake Community Hospital District, Series C, 6.20%, 12/1/22 | | | 400,000 | | | | 395,928 | | |
| Moorhead Economic Development Authority, Housing Development Eventide Project, Series A, 5.15%, 6/1/29 | | | 300,000 | | | | 256,305 | | |
| New Hope Housing and Health Care Facility, Masonic Home North Ridge, 5.75%, 3/1/15 | | | 400,000 | | | | 394,992 | | |
| Shakopee Health Care Facility, St. Francis Regional Medical Center, 5.10%, 9/1/25 | | | 500,000 | | | | 470,560 | | |
St. Louis Park Health Care Facilities, Park Nicollet Health Systems, Series B (Prerefunded 7/1/14 @ 100),
5.50%, 7/1/25 A | | | 250,000 | | | | 281,382 | | |
| 5.25%, 7/1/30 A | | | 250,000 | | | | 278,073 | | |
| St. Paul Housing & Redevelopment Authority Hospital Revenue, HealthEast Project, 6.00%, 11/15/30 | | | 200,000 | | | | 196,846 | | |
| St. Paul Housing & Redevelopment Authority, Nursing Home Episcopal, 5.63%, 10/1/33 | | | 500,000 | | | | 428,195 | | |
St. Paul Housing & Redevelopment Authority, Regions Hospital
5.25%, 5/15/18 | | | 500,000 | | | | 498,830 | | |
| 5.30%, 5/15/28 | | | 170,000 | | | | 159,812 | | |
St. Paul Housing & Redevelopment Authority, Rossy and Richard Shaller, Sholom East Project,
Series A, 5.25%, 10/1/42 | | | 250,000 | | | | 202,445 | | |
| St. Paul Port Authority, HealthEast Midway Campus, 5.75%, 5/1/25 | | | 600,000 | | | | 573,624 | | |
| Winona Health Care Facilities, Winona Health Obligated Group, Series A, 6.00%, 7/1/34 | | | 200,000 | | | | 200,176 | | |
| | | | 11,042,544 | | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the financial statements.
Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II 2008 Annual Report
18
Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II (MXN)
| DESCRIPTION | | PAR | | VALUE I | |
| Housing Revenue — 27.8% | |
| Cottage Grove Senior Housing Revenue, Cottage Grove Project, 5.00%, 12/1/31 | | $ | 175,000 | | | $ | 147,406 | | |
| Eden Prairie Multifamily Housing, Preserve Place (GNMA), 5.60%, 7/20/28 | | | 500,000 | | | | 510,800 | | |
| Minneapolis Housing Revenue, Keeler Apartments Project, Series A, 5.00%, 10/1/37 | | | 300,000 | | | | 238,254 | | |
| Minneapolis Multifamily Housing, Seward Towers Project (GNMA), 5.00%, 5/20/36 | | | 1,190,000 | | | | 1,120,242 | | |
Minneapolis St. Paul Housing, Finance Board Single Family Mortgage Revenue,
Mortgage-Backed City Living (AMT) (FHLMC) (FNMA) (GNMA), 5.00%, 11/1/38 | | | 197,103 | | | | 167,949 | | |
| Minnesota State Housing Finance Agency, Residential Housing, Series D (AMT), 4.70%, 7/1/27 | | | 1,000,000 | | | | 871,750 | | |
| Moorhead Senior Housing Revenue, Sheyenne Crossing Project, 5.65%, 4/1/41 | | | 330,000 | | | | 284,685 | | |
| Prior Lake Senior Housing Revenue, Shepard's Path Senior Housing, Series B, 5.70%, 8/1/36 | | | 200,000 | | | | 184,066 | | |
Southeast State Multi-County Housing and Redevelopment Authority, Goodhue County Apartments
(Prerefunded 1/1/10 @ 100), 6.75%, 1/1/31 A | | | 320,000 | | | | 338,394 | | |
| St. Paul Multifamily Housing, Selby Grotto Housing Project (AMT) (FHA) (GNMA), 5.50%, 9/20/44 | | | 655,000 | | | | 654,974 | | |
| Washington County Housing and Redevelopment Authority, Woodland Park Apartments, 4.70%, 10/1/26 | | | 1,000,000 | | | | 949,210 | | |
| Worthington Housing Authority, Meadows Worthington Project, Series A, 5.38%, 5/1/37 | | | 200,000 | | | | 165,858 | | |
| | | | 5,633,588 | | |
| Industrial Development Revenue — 2.5% | |
| Duluth Seaway Port Authority, Cargill Project, 4.20%, 5/1/13 | | | 500,000 | | | | 509,755 | | |
| Leasing Revenue — 24.3% | |
Andover Economic Development Authority Public Facility Lease Revenue, Andover Community Center
(Crossover Refunded 2/1/14 @ 100)
5.13%, 2/1/24 ^ | | | 205,000 | | | | 222,265 | | |
| 5.13%, 2/1/24 ^ | | | 295,000 | | | | 319,845 | | |
Hopkins Housing and Redevelopment Authority, Public Facility Lease Revenue, Public Works and Fire Station,
Series A (MBIA) (Prerefunded 2/1/13 @ 100), 5.00%, 2/1/23 A | | | 1,000,000 | | | | 1,091,320 | | |
| Otter Tail County Housing and Redevelopment Authority, Building Lease Revenue, Series A, 5.00%, 2/1/19 | | | 525,000 | | | | 550,168 | | |
| Puerto Rico Public Buildings Authority, Series M (COMGTY), 6.25%, 7/1/31 | | | 200,000 | | | | 219,908 | | |
| Ramsey County Public Improvement, Series A, 4.75%, 1/1/24 | | | 1,000,000 | | | | 1,003,610 | | |
| St. Paul Housing & Redevelopment Authority, Jimmy Lee Recreation Center, 5.00%, 12/1/32 | | | 100,000 | | | | 99,714 | | |
| St. Paul Port Authority Office Building Facility, Robert Street, 5.25%, 12/1/27 | | | 1,000,000 | | | | 1,024,790 | | |
| Washington County Housing and Redevelopment Authority, Lower St. Croix Valley Fire Protection, 5.13%, 2/1/24 | | | 400,000 | | | | 400,376 | | |
| | | | 4,931,996 | | |
| Recreation Authority Revenue — 2.0% | |
| Moorhead Golf Course, Series B, 5.88%, 12/1/21 | | | 400,000 | | | | 400,012 | | |
| Tax Revenue — 4.0% | |
| Minneapolis Development Revenue, Limited Tax Supported Common Bond, Series 2-A (AMT), 5.13%, 6/1/22 | | | 500,000 | | | | 476,465 | | |
Minneapolis Tax Increment Revenue, St. Anthony Falls Project,
5.65%, 2/1/27 | | | 150,000 | | | | 137,769 | | |
| 5.75%, 2/1/27 | | | 200,000 | | | | 185,836 | | |
| | | | 800,070 | | |
| Transportation Revenue — 9.3% | |
Minneapolis & St Paul Metropolitan Airports Commission, Series A,
5.00%, 1/1/19 (AMBAC) | | | 750,000 | | | | 774,420 | | |
| 5.00%, 1/1/19 (MBIA) | | | 750,000 | | | | 784,815 | | |
| 5.25%, 1/1/32 (FGIC) (Prerefunded 1/1/11 @ 100) A | | | 300,000 | | | | 320,454 | | |
| | | | 1,879,689 | | |
| Utility Revenue — 8.5% | |
Chaska Electric, Series A
5.00%, 10/1/30 | | | 500,000 | | | | 493,395 | | |
| 6.10%, 10/1/30 | | | 10,000 | | | | 10,425 | | |
Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II 2008 Annual Report
19
Schedule of INVESTMENTS
Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II (MXN)
| DESCRIPTION | | PAR/
SHARES | | VALUE I | |
Northern Municipal Power Agency, Series A (AGTY),
5.00%, 1/1/18 | | $ | 400,000 | | | $ | 429,604 | | |
| 5.00%, 1/1/20 | | | 250,000 | | | | 262,937 | | |
| Puerto Rico Electric Power Authority, Series VV (MBIA), 5.25%, 7/1/29 | | | 500,000 | | | | 523,995 | | |
| | | | 1,720,356 | | |
Total Municipal Long-Term Investments
(Cost: $33,214,153) | | | 32,701,586 | | |
| Short-Term Investment — 0.8% | |
Federated Minnesota Municipal Cash Trust
(Cost: $163,939) | | | 163,939 | | | | 163,939 | | |
Total Investments p — 162.0%
(Cost: $33,378,092) | | | 32,865,525 | | |
| Preferred Shares at Liquidation Value — (64.1)% | | | (13,000,000 | ) | |
| Other Assets and Liabilities, Net — 2.1% | | | 425,461 | | |
| Total Net Assets — 100.0% | | $ | 20,290,986 | | |
Notes to Schedule of Investments:
I Securities are valued in accordance with procedures described in note 2 in Notes to Financial Statements
A Prerefunded issues are typically backed by U.S. government obligations, which secure the timely payment of principal and interest. These bonds mature at the call date and price indicated.
^ Crossover Refunded securities are typically backed by the credit of the refunding issuer, which secures the timely payment of principal and interest. These bonds mature at the call date and price indicated.
p On August 31, 2008, the cost of investments for federal income tax purposes was $33,387,001. The aggregate gross unrealized appreciation and depreciation of investments, based on this cost, were as follows:
| Gross unrealized appreciation | | $ | 669,429 | | |
| Gross unrealized depreciation | | | (1,190,905 | ) | |
| Net unrealized depreciation | | $ | (521,476 | ) | |
AGTY – Assured Guaranty
AMBAC – American Municipal Bond Assurance Corporation
AMT – Alternative Minimum Tax. As of August 31, 2008, the aggregate market value of securities subject to the Alternative Minimum Tax is $2,563,942 which represents 12.6% of total net assets applicable to common shares.
COMGTY – Commonwealth Guaranty
FGIC – Financial Guaranty Insurance Corporation
FHA – Federal Housing Administration
FHLMC – Federal Home Loan Mortgage Corporation
FNMA – Federal National Mortgage Association
FSA – Financial Security Assurance
GNMA – Government National Mortgage Association
MBIA – Municipal Bond Insurance Association
MSDCEP – Minnesota School District Credit Enhancement Program
RAAI – Radian Asset Assurance Inc.
The accompanying notes are an integral part of the financial statements.
Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II 2008 Annual Report
20
Report of Independent Registered PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
The Board of Directors and Shareholders
First American Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II, Inc.
We have audited the accompanying statement of assets and liabilities of First American Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II, Inc. (the "Fund"), including the schedule of investments, as of August 31, 2008, and the related statements of operations and changes in net assets and the financial highlights for the periods indicated therein. These financial statements and financial highlights are the responsibility of the Fund's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements and financial highlights based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements and financial highlights are free of material misstatement. We were not engaged to perform an audit of the Fund's internal control over financial reporting. Our audits included consideration of internal control over financial reporting as a basis for designing audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Fund's internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion. An audit also includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements and financial highlights, assessing the accounting principles used and sig nificant estimates made by management, and evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. Our procedures included confirmation of securities owned as of August 31, 2008, by correspondence with the custodian. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the financial statements and financial highlights referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of First American Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II, Inc., at August 31, 2008, the results of its operations, the changes in its net assets, and the financial highlights for the periods indicated therein, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
Minneapolis, Minnesota
October 23, 2008
Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II 2008 Annual Report
21
Notice to SHAREHOLDERS (unaudited)
TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF THE DIVIDEND REINVESTMENT PLAN
As a shareholder, you will be automatically enrolled in the fund's Dividend Reinvestment Plan (the plan). It's a convenient and economical way to buy additional shares of the fund by automatically reinvesting dividends and capital gains. The plan is administered by Computershare Trust Company, N.A. ("Computershare"), the plan administrator.
Shareholders may elect not to participate in the plan and to receive all dividends in cash by sending written instructions to Computershare at the address set forth below or by calling Computershare at 800.426.5523. Participation in the plan may be terminated or resumed at any time without penalty by contacting Computershare before the dividend record date; otherwise, the termination or resumption will be effective with respect to any subsequently declared dividend or other distribution.
Eligibility/Participation
In the event you opt out of the plan, you may resume participation in the plan at any time. Reinvestment of distributions will begin with the next distribution paid, provided your request is received before the record date for that distribution.
If your shares are in certificate form, you may re-join the plan directly and have your distributions reinvested in additional shares of the fund. To re-enroll in this plan, call Computershare at 800.426.5523. If your shares are registered in your brokerage firm's name or another name, ask the holder of your shares how you may resume participation.
If you are a beneficial owner and wish to join the plan, you must contact your bank, broker or other nominee to arrange participation in the plan on your behalf.
Alternatively, if you are a beneficial owner of our common stock, you may simply request that the number of shares of our common stock you wish to enroll in the plan be re-registered by the bank, broker or other nominee in your own name as record stockholder. You can then directly participate in the plan as described above. You should contact your bank, broker or nominee for information on how to re-register your shares.
Plan Administration
Whenever the fund declares a dividend or other capital gain distribution payable in cash, non-participants in the plan will receive cash and participants in the plan will receive the equivalent in common shares. Computershare will buy shares of the fund on the American Stock Exchange or elsewhere on the open market (open-market purchases), beginning on the payment date.
The fund will not issue any new shares in connection with the plan. All reinvestments will be at a weighted average price per share of all shares purchased in an open-market to fill the combined purchase order. Each participant will pay a pro rata share of brokerage commissions incurred in connection with the open-market purchases. The number of shares allocated to you is determined by dividing the amount of the dividend or distribution by the applicable price per share.
There is no direct charge for reinvestment of dividends and capital gains, since Computershare fees are paid for by the fund. However, each participant pays a pro rata portion of the brokerage commissions. Brokerage charges are expected to be lower than those for individual transactions because shares are purchased for all participants in blocks. As long as you continue to participate in the plan, distributions paid on the shares in your account will be reinvested.
Computershare maintains accounts for plan participants holding shares in certificate form and will furnish written confirmation of all transactions, including information you need for tax records.
Reinvested shares in your account will be held by Computershare in noncertificated form in your name.
Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II 2008 Annual Report
22
Tax Information
Distributions invested in additional shares of the fund are subject to income tax, to the same extent as if received in cash. Shareholders, as required by the Internal Revenue Service, will receive a Form 1099-DIV regarding the federal tax status of the prior year's distributions.
Plan Withdrawal
If you hold your shares in certificate form, you may terminate your participation in the plan at any time by giving written notice to Computershare or by calling Computershare at 800.426.5523. If your shares are registered in your brokerage firm's name, you may terminate your participation via verbal or written instructions to your investment professional. Written instructions should include your name and address as they appear on the certificate or account.
If notice is received before the record date, all future distributions will be paid directly to the shareholder of record.
If your shares are issued in certificate form and you discontinue your participation in the Plan, you (or your nominee) will receive an additional certificate for all full shares and a check for any fractional shares in your account.
Plan Amendment/Termination
The fund reserves the right to amend or terminate the plan. The fund will give you at least 30 days advance written notice if it makes a material amendment to or terminates the Plan.
Any questions about the Plan should be directed to your investment professional or to Computershare Trust Company, N.A., P.O. Box 43078, Providence, RI, 02940-3078, 800.426.5523.
TAX INFORMATION
The following per-share information describes the federal tax treatment of distributions made during the fiscal year. Exempt-interest dividends are exempt from federal income tax and should not be included in your gross income, but need to be reported on your income tax return for information purposes. Please consult a tax advisor on how to report these distributions at the state and local levels.
Common Share Income Distributions (the fund designates income from tax-exempt securities as 98.86%)
Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II 2008 Annual Report
23
Notice to SHAREHOLDERS (unaudited)
| Payable Date | | Amount | |
| September 26, 2007 | | $ | 0.05000 | | |
| October 24, 2007 | | | 0.05000 | | |
| November 28, 2007 | | | 0.05000 | | |
| December 26, 2007 | | | 0.05000 | | |
| January 10, 2008 | | | 0.05323 | | |
| February 20, 2008 | | | 0.05500 | | |
| March 26, 2008 | | | 0.05500 | | |
| April 23, 2008 | | | 0.05500 | | |
| May 21, 2008 | | | 0.05500 | | |
| June 25, 2008 | | | 0.05750 | | |
| July 23, 2008 | | | 0.05750 | | |
| August 27, 2008 | | | 0.06000 | | |
| Total | | $ | 0.64823 | | |
Common Share Long-Term Gain Distributions
(the fund designates the following amounts as long-term capital gains)
| Payable Date | | Amount | |
| January 10, 2008 | | $ | 0.07603 | | |
Preferred Share Income Distributions
(the fund designates income from tax-exempt securities, 98.86% qualifying as exempt-interest dividends)
| Payable Date | | Amount | |
| Total class "F" | | $ | 704.61 | | |
Preferred Share Long-Term Gain Distributions
(the fund designates the following amounts as long-term capital gains)
| Payable Date | | Amount | |
| December 26, 2007 | | $ | 139.16 | | |
Shareholder Notification of Federal Tax Status:
The fund designates 0.00% of the ordinary income distributions during the fiscal period ended August 31, 2008 as dividends qualifying for the dividends received deduction available to corporate shareholders.
In addition, the fund designates 0.00% of the ordinary income distributions from net investment income during the fiscal period ended August 31, 2008 as qualifying dividend income available to individual shareholders under the Jobs and Growth Tax Relief Reconciliation Act of 2003.
Additional Information Applicable to Foreign Shareholders Only:
The percentage of taxable ordinary income distributions that are designated as interest-related dividends under Internal Revenue Code Section 871(k)(1)(C) for the fund was 1.48%.
The percentage of taxable ordinary income distributions that are designated as short-term capital gain distributions under Internal Revenue Code Section 871(k)(2)(C) for the fund was 31.00%.
HOW TO OBTAIN A COPY OF THE FUND'S PROXY VOTING POLICIES AND PROXY VOTING RECORD
| A description of the policies and procedures that the fund uses to determine how to vote proxies relating to portfolio securities, as well as information regarding how the fund voted proxies relating to portfolio securities is available at www.firstamericanfunds.com and on the U.S. Securities and | |
|
Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II 2008 Annual Report
24
| Exchange Commission's website at www.sec.gov. A description of the funds' policies and procedures is also available without charge, upon request, by calling 800.677.FUND. | |
|
FORM N-Q HOLDINGS INFORMATION
The fund is required to file its complete schedule of portfolio holdings for the first and third quarters of each fiscal year with the Securities and Exchange Commission on Form N-Q. The fund's Forms N-Q are available (1) without charge upon request by calling 800.677.FUND and (2) on the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission's website at www.sec.gov. In addition, you may review and copy the fund's Forms N-Q at the Commission's Public Reference Room in Washington, D.C. You may obtain information on the operation of the Public Reference Room by calling 1-800-SEC-0330.
QUARTERLY PORTFOLIO HOLDINGS
The fund will make portfolio holdings information publicly available by posting the information at www.firstamericanfunds.com on a quarterly basis. The fund will attempt to post such information within 10 business days of the quarter-end.
APPROVAL OF THE FUND'S INVESTMENT ADVISORY AGREEMENT
The Board of Directors of the Fund (the "Board"), which is comprised entirely of independent directors, oversees the management of the Fund and, as required by law, determines annually whether to renew the Fund's advisory agreement with FAF Advisors, Inc. ("FAF Advisors").
At a meeting on May 5-7, 2008, the Board considered information relating to the Fund's investment advisory agreement with FAF Advisors (the "Agreement"). In advance of the meeting, the Board received materials relating to the Agreement, and had the opportunity to ask questions and request further information in connection with its consideration. At a subsequent meeting on June 17-19, 2008, the Board concluded its consideration of and approved the Agreement through June 30, 2009.
In considering the Agreement, the Board, advised by independent legal counsel, reviewed and analyzed the factors it deemed relevant, including: (1) the nature, quality, and extent of FAF Advisors' services to the Fund, (2) the investment performance of the Fund, (3) the profitability of FAF Advisors related to the Fund, including an analysis of FAF Advisors' cost of providing services and comparative expense information, and (4) other benefits that accrue to FAF Advisors through its relationship with the Fund. When reviewing and approving investment company advisory contracts, boards of directors generally also consider the extent to which economies of scale will be realized as the investment company grows and whether fee levels reflect these economies of scale for the benefit of shareholders. The Board noted, however, that because the Fund is a closed-end fund its size would increase only as a result of any appreciation of its portfolio holdings. The Board therefore determined that a consideration of economies of scale was not relevant to its evaluation of the Agreement. In its deliberations, the Board did not identify any single factor which alone was responsible for the Board's decision to approve the Agreement.
Before approving the Agreement, the Board met in executive session with its independent counsel on numerous occasions to consider the materials provided by FAF Advisors and the terms of the Agreement. Based on its evaluation of all material factors, the Board concluded that the Agreement is fair and in the best interests of the Fund's shareholders. In reaching its conclusions, the Board considered the following:
Nature, Quality, and Extent of Investment Advisory Services
The Board examined the nature, quality, and extent of the services provided by FAF Advisors to the Fund. The Board reviewed FAF Advisors' key personnel who provide investment advisory services to
Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II 2008 Annual Report
25
Notice to SHAREHOLDERS (unaudited)
the Fund as well as the fact that, under the Agreement, FAF Advisors has the authority and responsibility to make and execute investment decisions for the Fund within the framework of the Fund's investment policies and restrictions, subject to review by the Board. The Board further considered that FAF Advisors' duties with respect to the Fund include: (i) investment research and security selection, (ii) adherence to (and monitoring compliance with) the Fund's investment policies and restrictions and the Investment Company Act of 1940, and (iii) monitoring the performance of the various organizations providing services to the Fund, including the Fund's sub-administrator, transfer agent, auction agent and custodian. Finally, the Board considered FAF Advisors' representation that the services provided by FAF Advisors under the Agreement are the type of services customarily provided by investment advisors in the fund industry. The B oard also considered compliance reports about FAF Advisors from the Fund's Chief Compliance Officer.
Based on the foregoing, the Board concluded that the Fund is likely to benefit from the nature, quality and extent of the services provided by FAF Advisors under the Agreement.
Investment Performance of the Fund
The Board considered the performance of the Fund, including how the Fund performed versus the median performance of a group of comparable funds selected by an independent data service (the "performance universe") and how the Fund performed versus its benchmark index. All periods considered by the Board ended January 31, 2008.
The Board noted that the Fund underperformed its performance universe and its benchmark for all periods. The Board noted, however, that the Fund's performance has begun to improve. For the one- and three-month periods ended April 30, 2008, the Fund significantly outperformed its performance universe, although it still slightly underperformed its performance universe for the six-month period ended April 30, 2008. The Board also noted FAF Advisors' assertion that the latter half of 2007 witnessed the most volatile and worst performing municipal bond market in over a decade. In light of these and other factors, the Board concluded it would be in the interest of the Fund and its shareholders to renew the Agreement.
Costs of Services and Profits Realized by FAF Advisors
The Board reviewed FAF Advisors' costs in serving as the Fund's investment manager, including the costs associated with the personnel and systems necessary to manage the Fund. The Board also considered the profitability of FAF Advisors and its affiliates resulting from their relationship with the Fund. The Board reviewed fee and expense information for the Fund as compared to that of other funds and accounts managed by FAF Advisors and of comparable funds managed by other advisers. The Board found that while the management fees for FAF Advisors' institutional separate accounts are lower than the Fund's management fees, the Fund receives additional services from FAF Advisors that separate accounts do not receive.
Using information provided by an independent data service, the Board also evaluated the Fund's advisory fee compared to the median advisory fee for other funds similar in size, character and investment strategy, and the Fund's total expense ratio after waivers compared to the median total expense ratio of comparable funds. The Board noted that the Fund's advisory fee was lower than the peer group median advisory fee, and that the Fund's total expense ratio was equal to the peer group median total expense ratio. The Board concluded that the Fund's advisory fee and total expense ratio are reasonable in light of the services provided.
Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II 2008 Annual Report
26
Other Benefits to FAF Advisors
In evaluating the benefits that accrue to FAF Advisors through its relationship with the Fund, the Board noted that FAF Advisors and certain of its affiliates serve the Fund in various capacities, including as advisor, administrator and custodian, and receive compensation from the Fund in connection with providing services to the Fund. The Board considered that each service provided to the Fund by FAF Advisors or one of its affiliates is pursuant to a written agreement, which the Board evaluates periodically as required by law.
After full consideration of these factors, the Board concluded that approval of the Agreement was in the interest of the Fund and its shareholders.
Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II 2008 Annual Report
27
Notice to SHAREHOLDERS (unaudited)
Directors and Officers of the Fund
Independent Directors
Name, Address, and
Year of Birth | | Position(s)
Held with
Fund | | Term of Office and
Length of Time Served | | Principal Occupation(s)
During Past 5 Years | | Number of Portfolios
in Fund Complex
Overseen by Director | | Other
Directorships
Held by
Director† | |
Benjamin R. Field III
P.O. Box 1329
Minneapolis, MN 55440-1329
(1938) | | Director | | Directors serve for a one-year term that expires at the next annual meeting of shareholders. Director of MXN since September 2003 | | Retired; Senior Financial Advisor, Bemis Company, Inc. from May 2002 through February 2004 | | First American Funds Complex: twelve registered investment companies, including sixty-two portfolios | | None | |
|
Roger A. Gibson
P.O. Box 1329
Minneapolis, MN 55440-1329
(1946) | | Director | | Directors serve for a one-year term that expires at the next annual meeting of shareholders. Director of MXN since inception | | Director, Charterhouse Group Inc., a private equity firm, since October 2005; Vice President and Chief Operating Officer, Cargo–United Airlines, from July 2001 through retirement in June 2004 | | First American Funds Complex: twelve registered investment companies, including sixty-two portfolios | | None | |
|
Victoria J. Herget
P.O. Box 1329
Minneapolis, MN 55440-1329
(1951) | | Director | | Directors serve for a one-year term that expires at the next annual meeting of shareholders. Director of MXN since September 2003 | | Investment consultant and non-profit board member | | First American Funds Complex: twelve registered investment companies, including sixty-two portfolios | | None | |
|
John P. Kayser
P.O. Box 1329
Minneapolis, MN 55440-1329
(1949) | | Director | | Directors serve for a one-year term that expires at the next annual meeting of shareholders. Director of MXN since October 2006 | | Retired; Principal from 1983 to 2004, William Blair & Company LLC | | First American Funds Complex; twelve registered investment companies, including sixty-two portfolios | | None | |
|
Leonard W. Kedrowski
P.O. Box 1329
Minneapolis, MN 55440-1329
(1941) | | Director | | Directors serve for a one-year term that expires at the next annual meeting of shareholders. Director of MXN since inception | | Owner and President, Executive and Management Consulting, Inc., a management consulting firm; Board member, GC McGuiggan Corporation (dba Smyth Companies), a label printer; former Chief Executive Officer, Creative Promotions International, LLC, a promotional award programs and products company, through October 2003 | | First American Funds Complex: twelve registered investment companies, including sixty-two portfolios | | None | |
|
Richard K. Riederer
P.O. Box 1329
Minneapolis, MN 55440-1329
(1944) | | Director | | Directors serve for a one-year term that expires at the next annual meeting of shareholders. Director of MXN since inception | | Owner & Chief Executive Officer, RKR Consultants, Inc. and non-profit board member since 2005 | | First American Funds Complex: twelve registered investment companies, including sixty-two portfolios | | Cleveland Cliffs Inc. (a producer of iron ore pellets) | |
|
Joseph D. Strauss
P.O. Box 1329
Minneapolis, MN 55440-1329
(1940) | | Director | | Directors serve for a one-year term that expires at the next annual meeting of shareholders. Director of MXN since inception | | Attorney At Law, Owner and President, Strauss Management Company, a Minnesota holding company for various organizational management business ventures; Owner, Chairman, and Chief Executive Officer, Community Resource Partnerships, Inc., a strategic planning, operations management, government relations, transportation planning, and public relations organization; Owner, Chairman and Chief Executive Officer, ExcensusTM, LLC, a demographic planning and application development firm | | First American Funds Complex: twelve registered investment companies, including sixty-two portfolios | | None | |
|
Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II 2008 Annual Report
28
Independent Directors—concluded
Name, Address, and
Year of Birth | | Position(s)
Held with
Fund | | Term of Office and
Length of Time Served | | Principal Occupation(s)
During Past 5 Years | | Number of Portfolios
in Fund Complex
Overseen by Director | | Other
Directorships
Held by
Director† | |
Virginia L. Stringer
P.O. Box 1329
Minneapolis, MN 55440-1329
(1944) | | Chair; Director | | Directors serve for a one-year term that expires at the next annual meeting of shareholders. Chair of MXN's board since 1998. Director of MXN since August 1998 | | Governance Consultant and non-profit board member; former Owner and President, Strategic Management Resources, Inc., a management consulting firm; Executive Consultant to State Farm Insurance Company through 2003 | | First American Funds Complex: twelve registered investment companies, including sixty-two portfolios | | None | |
|
James M. Wade
P.O. Box 1329
Minneapolis, MN 55440-1329
(1943) | | Director | | Directors serve for a one-year term that expires at the next annual meeting of shareholders. Director of MXN since August 2001 | | Owner and President, Jim Wade Homes, a homebuilding company | | First American Funds Complex: twelve registered investment companies, including sixty-two portfolios | | None | |
|
| †Includes only directorships in a company with a class of securities registered pursuant to Section 12 of the Securities Exchange Act or subject to the requirements of Section 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act, or any company registered as an investment company under the Investment Company Act. | |
|
Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II 2008 Annual Report
29
Notice to SHAREHOLDERS (unaudited)
Officers
Name, Address, and
Year of Birth | | Position(s)
Held with
Fund | | Term of Office and Length of Time Served | | Principal Occupation(s) During Past 5 Years | |
Thomas S. Schreier, Jr.
FAF Advisors, Inc.
800 Nicollet Mall
Minneapolis, MN 55402
(1962)* | | President | | Re-elected by the Board annually; President of MXN since inception | | Chief Executive Officer of FAF Advisors, Inc.; Chief Investment Officer of FAF Advisors, Inc., since September 2007 | |
|
Jeffery M. Wilson
FAF Advisors, Inc.
800 Nicollet Mall
Minneapolis, MN 55402
(1956)* | | Vice
President– Administration | | Re-elected by the Board annually; Vice President – Administration of MXN since inception | | Senior Vice President of FAF Advisors, Inc. | |
|
Charles D. Gariboldi, Jr.
FAF Advisors, Inc.
800 Nicollet Mall
Minneapolis, MN 55402
(1959)* | | Treasurer | | Re-elected by the Board annually; Treasurer of MXN since December 2004 | | Mutual Funds Treasurer, FAF Advisors, Inc., since October 2004; prior thereto, Vice President of Investment Accounting and Fund Treasurer for Thrivent Financial for Lutherans | |
|
Jill M. Stevenson
FAF Advisors, Inc.
800 Nicollet Mall
Minneapolis, MN 55402
(1965)* | | Assistant Treasurer | | Re-elected by the Board annually; Assistant Treasurer of MXN since September 2005 | | Mutual Funds Assistant Treasurer, FAF Advisors, Inc., since September 2005; prior thereto, Director, Senior Project Manager, FAF Advisors, Inc. | |
|
David H. Lui
FAF Advisors, Inc.
800 Nicollet Mall
Minneapolis, MN 55402
(1960)* | | Chief Compliance Officer | | Re-elected by the Board annually; Chief Compliance Officer of MXN since February 2005 | | Chief Compliance Officer, First American Funds and FAF Advisors, Inc., since March 2005; prior thereto, Chief Compliance Officer, Franklin Advisers, Inc. and Chief Compliance Counsel, Franklin Templeton Investments from March 2004 to March 2005; prior thereto, Vice President, Charles Schwab & Co., Inc. | |
|
Mark D. Corns
FAF Advisors, Inc.
800 Nicollet Mall
Minneapolis, MN 55402
(1963)* | | Anti-Money Laundering Officer | | Re-elected by the Board annually; Anti-Money Laundering Officer of MXN since September 2008 | | Director of Compliance, FAF Advisors, Inc., since June 2006; Compliance Manager, FAF Advisors, Inc. from January 2005 to June 2006; prior thereto, Compliance Manager, OppenheimerFunds, Inc. | |
|
Kathleen L. Prudhomme
FAF Advisors, Inc.
800 Nicollet Mall
Minneapolis, MN 55402
(1953)* | | Secretary | | Re-elected by the Board annually; Secretary of MXN since December 2004; prior thereto, Assistant Secretary of MXN since inception | | Deputy General Counsel, FAF Advisors, Inc., since November 2004; prior thereto, Partner, Dorsey & Whitney LLP, a Minneapolis-based law firm | |
|
James D. Alt
Dorsey & Whitney LLP
50 South Sixth Street Suite 1500
Minneapolis, MN 55402
(1951) | | Assistant Secretary | | Re-elected by the Board annually; Assistant Secretary of MXN since December 2004; prior thereto, Secretary of MXN since inception | | Partner, Dorsey & Whitney LLP, a Minneapolis-based law firm | |
|
Richard J. Ertel
FAF Advisors, Inc.
800 Nicollet Mall
Minneapolis, MN 55402
(1967)* | | Assistant Secretary | | Re-elected by the Board annually; Assistant Secretary of MXN since June 2006 and from June 2003 through August 2004 | | Counsel, FAF Advisors, Inc., since May 2006; prior thereto, Counsel, Ameriprise Financial Services, Inc. from September 2004 to May 2006; prior thereto, Counsel, FAF Advisors, Inc. | |
|
*Messrs. Schreier, Wilson, Gariboldi, Lui, Corns, and Ertel, Ms. Stevenson and Ms. Prudhomme are each officers and/or employees of FAF Advisors, Inc., which serves as investment advisor for the fund.
Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II 2008 Annual Report
30
(This page intentionally left blank.)
(This page intentionally left blank.)
BOARD OF DIRECTORS
Virginia Stringer
Chairperson of Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II
Governance Consultant; former Owner and President of Strategic Management
Resources, Inc.
Benjamin Field III
Director of Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II
Retired; former Senior Financial Advisor, Senior Vice President, Chief Financial Officer, and Treasurer of Bemis Company, Inc.
Roger Gibson
Director of Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II
Director of Charterhouse Group, Inc.
Victoria Herget
Director of Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II
Investment Consultant; former Managing Director of Zurich Scudder Investments
John Kayser
Director of Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II
Retired; former Principal, Chief Financial Officer, and Chief Administrative Officer of William Blair & Company, LLC
Leonard Kedrowski
Director of Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II
Owner and President of Executive and Management Consulting, Inc.
Richard Riederer
Director of Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II
Owner and Chief Executive Officer of RKR Consultants, Inc.
Joseph Strauss
Director of Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II
Owner and President of Strauss Management Company
James Wade
Director of Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II
Owner and President of Jim Wade Homes
Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II's Board of Directors is comprised entirely of independent directors.
P.O. Box 1330
Minneapolis, MN 55440-1330
Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II
2008 Annual Report
FAF Advisors, Inc., is a wholly owned subsidiary of U.S. Bank National Association, which is a wholly owned subsidiary of U.S. Bancorp.

This document is printed on paper containing 10% postconsumer waste.
10/2008 0268-08 MXN-AR
Item 2—Code of Ethics
The registrant has adopted a code of ethics that applies to its principal executive officer and principal financial officer. During the period covered by this report, there were no amendments to the provisions of the registrant’s code of ethics that apply to the registrant’s principal executive officer and principal financial officer and that relate to any element of the code of ethics definition enumerated in this Item. During the period covered by this report, the registrant did not grant any waivers, including implicit waivers, from any provision of its code of ethics. The registrant undertakes to provide to any person without charge, upon request, a copy of its code of ethics by calling 1-800-677-3863.
Item 3—Audit Committee Financial Expert
The registrant’s Board of Directors has determined that Leonard W. Kedrowski, Benjamin R. Field III, John P. Kayser, and Richard K. Riederer, members of the registrant’s Audit Committee, are each an “audit committee financial expert” and are “independent,” as these terms are defined in this Item.
Item 4—Principal Accountant Fees and Services
(a) Audit Fees - Ernst & Young LLP (“E&Y”) billed the registrant audit fees totaling $19,754 in the fiscal year ended August 31, 2008 and $23,038 in the fiscal year ended August 31, 2007, including fees associated with the annual audit, SEC Rule 17f-2 security count filings and filings of the registrant’s Form N-CSR.
(b) Audit-Related Fees – E&Y billed the registrant audit-related fees totaling $1,862 in the fiscal year ended August 31, 2008 and $1,896 in the fiscal year ended August 31, 2007, including fees associated with the semi-annual review of fund disclosures.
(c) Tax Fees - E&Y billed the registrant fees of $10,463 in the fiscal year ended August 31, 2008 and $3,770 in the fiscal year ended August 31, 2007 for tax services, including tax compliance, tax advice and tax planning. Tax compliance, tax advice and tax planning services primarily related to preparation of original and amended tax returns, timely RIC qualification reviews, and tax distribution analysis and planning.
(d) All Other Fees - There were no fees billed by E&Y for other services to the registrant during the fiscal years ended August 31, 2008 and August 31, 2007.
(e)(1) The audit committee’s pre-approval policies and procedures pursuant to paragraph (c)(7) of Rule 2-01 of Regulation S-X are set forth below:
Audit Committee policy regarding pre-approval of services provided by the Independent Auditor
The Audit Committee of the First American Funds (“Committee”) has responsibility for ensuring that all services performed by the independent audit firm for the funds do not impair the firm’s independence. This review is intended to provide reasonable oversight without removing management from its responsibility for day-to-day operations. In this regard, the Committee should:
· Understand the nature of the professional services expected to be provided and their impact on auditor independence and audit quality
· Examine and evaluate the safeguards put into place by the Company and the auditor to safeguard independence
· Meet quarterly with the partner of the independent audit firm
· Consider approving categories of service that are not deemed to impair independence for a one-year period
It is important that a qualitative rather than a mere quantitative evaluation be performed by the Committee in discharging its responsibilities.
Policy for Audit and Non-Audit Services Provided to the Funds
On an annual basis, the Committee will review and consider whether to pre-approve the financial plan for audit fees as well as categories of audit-related and non-audit services that may be performed by the funds’ independent audit firm
directly for the funds. At least annually the Committee will receive a report from the independent audit firm of all audit and non-audit services, which were approved during the year.
The engagement of the independent audit firm for any non-audit service requires the written pre-approval of the Treasurer of the funds and all non-audit services performed by the independent audit firm will be disclosed in the required SEC periodic filings.
In connection with the Committee review and pre-approval responsibilities, the review by the Committee will consist of the following:
Audit Services
The categories of audit services and related fees to be reviewed and considered for pre-approval annually by the Committee or its delegate include the following:
· Annual Fund financial statement audits
· Seed audits (related to new product filings, as required)
· SEC and regulatory filings and consents
Audit-related Services
In addition, the following categories of audit-related services are deemed to be consistent with the role of the independent audit firm and, as such, will be considered for pre-approval by the Committee or its delegate, on an annual basis.
· Accounting consultations
· Fund merger support services
· Other accounting related matters
· Agreed Upon Procedure Reports
· Attestation Reports
· Other Internal Control Reports
Notwithstanding any annual pre-approval of these categories of services, individual projects with an estimated fee in excess of $25,000 are subject to pre-approval by the Committee Chair or its delegate on a case-by-case basis. Individual projects with an estimated fee in excess of $50,000 are subject to pre-approval by the Committee or its delegate on a case-by-case basis.
Tax Services
The following categories of tax services are deemed to be consistent with the role of the independent audit firm and, as such, will be considered for pre-approval by the Committee or its delegate, on an annual basis.
· Tax compliance services related to the filing or amendment of the following:
· Federal, state and local income tax compliance, and
· Sales and use tax compliance
· Timely RIC qualification reviews
· Tax distribution analysis and planning
· Tax authority examination services
· Tax appeals support services
· Accounting methods studies
· Fund merger support services
· Tax consulting services and related projects
Notwithstanding any annual pre-approval of these categories of services, individual projects with an estimated fee in excess of $25,000 are subject to pre-approval by the Committee Chair or its delegate on a case-by-case basis. Individual projects with an estimated fee in excess of $50,000 are subject to pre-approval by the Committee or its delegate on a case-by-case basis.
Other Non-audit Services
The SEC auditor independence rules adopted in response to the Sarbanes-Oxley Act specifically allow certain non-audit services. Because of the nature of these services, none of these services may be commenced by the independent audit firm without the prior approval of the Committee. The Committee may delegate this responsibility to one or more of the Committee members, with the decisions presented to the full Committee at the next scheduled meeting.
Proscribed Services
In accordance with SEC rules on independence, the independent audit firm is prohibited from performing services in the following categories of non-audit services:
· Management functions
· Accounting and bookkeeping services
· Internal audit services
· Financial information systems design and implementation
· Valuation services supporting the financial statements
· Actuarial services supporting the financial statements
· Executive recruitment
· Expert services (e.g., litigation support)
· Investment banking
Policy for Pre-approval of Non-Audit Services Provided to Other Entities within the Investment Company Complex
The Committee is also responsible for pre-approving certain non-audit services provided to FAF Advisors, Inc., U.S. Bank N.A., Quasar Distributors, U.S. Bancorp Fund Services, LLC and any other entity under common control with FAF Advisors, Inc., that provides ongoing services to the funds. The only non-audit services provided to these entities which require pre-approval are those services that relate directly to the operations and financial reporting of the funds.
Although the Committee is not required to pre-approve all services provided to FAF Advisors, Inc. and other affiliated service providers, the Committee will annually receive a report from the independent audit firm on the aggregate fees for all services provided to U.S. Bancorp and affiliates.
(e)(2) All of the services described in paragraphs (b) through (d) of this Item 4 were pre-approved by the audit committee.
(f) All services performed on the engagement to audit the registrant’s financial statements for the most recent fiscal year end were performed by the principal accountant’s full-time, permanent employees.
(g) The aggregate non-audit fees billed by E&Y to the registrant, the registrant’s investment adviser, and any entity controlling, controlled by, or under common control with the adviser that provides ongoing services to the registrant, totaled $162,488 in the fiscal year ended August 31, 2008 and $43,615 in the fiscal year ended August 31, 2007.
(h) The registrant’s audit committee has determined that the provision of non-audit services to the registrant’s investment adviser, and any entity controlling, controlled by, or under common control with the investment adviser that provides ongoing services to the registrant, that were not pre-approved is compatible with maintaining E&Y’s independence.
Item 5—Audit Committee of Listed Registrants
(a) The registrant has a separately designated standing audit committee established in accordance with Section 3(a)(58)(A) of the Exchange Act. The members of such audit committee are Leonard W. Kedrowski, Benjamin R. Field III, John P. Kayser, and Richard K. Riederer. Virginia L. Stringer, Chair of the Board of Directors, serves ex officio as a non-voting member of such committee.
(b) Not applicable.
Item 6—Schedule of Investments
The schedule is included as part of the report to shareholders filed under Item 1 of this Form.
Item 7—Disclosure of Proxy Voting Policies and Procedures for Closed-End Management Investment Companies
The registrant has delegated the voting of proxies relating to its voting securities to its investment advisor, FAF Advisors, Inc. (“FAF Advisors”). The proxy voting policies and procedures of FAF Advisors are as follows:
General Principles
FAF Advisors, Inc. is the investment manager for the First American family of mutual funds and for other separately managed accounts. As such, FAF Advisors has been delegated the authority to vote proxies with respect to the investments held in client accounts, unless the client has specifically retained such authority in writing. It is FAF Advisors’ duty to vote proxies in the best interests of clients. In voting proxies, FAF Advisors also seeks to maximize total investment return for clients.
In the event of a sub-adviser, FAF Advisors may delegate proxy voting to the sub-adviser. Where such delegation exists, the sub-advisor will be responsible for developing and enforcing proxy voting policies. FAF Advisors will review these policies annually.
FAF Advisors’ Investment Policy Committee (“IPC”), comprised of the firm’s most senior investment professionals, is charged with oversight of the proxy voting policies and procedures. The IPC is responsible for (1) approving the proxy voting policies and procedures, and (2) oversight of the activities of FAF Advisors’ Proxy Voting Administration Committee (“PVAC”).
The PVAC is responsible for providing an administrative framework to facilitate and monitor FAF Advisors’ exercise of its fiduciary duty to vote client proxies and fulfill the obligations of reporting and recordkeeping under the federal securities laws.
Policies
The IPC, after reviewing and concluding that such policies are reasonably designed to vote proxies in the best interests of clients, has approved and adopted the proxy voting policies of Institutional Shareholder Services, Inc. (“ISS”), a leading national provider of proxy voting administrative and research services. As a result, such policies set forth FAF Advisors’ positions on recurring proxy issues and criteria for addressing non-recurring issues. These policies are reviewed periodically and therefore are subject to change. Even though it has adopted ISS’ policies, FAF Advisors maintains the fiduciary responsibility for all proxy voting decisions.
Procedures
A. Supervision of Proxy Voting Service
The PVAC shall supervise the relationship with FAF Advisors’ proxy voting service, ISS. ISS apprises FAF Advisors of shareholder meeting dates, forward proxy voting materials, provides research on proxy proposals and voting recommendations
and casts the actual proxy votes. ISS also serves as FAF Advisors’ proxy voting record keeper and generates reports on how proxies were voted.
B. Conflicts of Interest
As an affiliate of U.S. Bancorp, a large, multi-service financial institution, FAF Advisors recognizes that there are numerous situations wherein it may have a perceived or real conflict of interest in voting the proxies of issuers or proxy proponents (e.g., a special interest group) who are clients or potential clients of some part of the U.S. Bancorp enterprise. Directors and officers of such companies may have personal or familial relationships with the U.S. Bancorp enterprise and its employees that could give rise to conflicts of interest.
FAF Advisors will vote proxies in the best interest of its clients regardless of such real or perceived conflicts of interest. By adopting ISS’ policies, FAF Advisors believes the risk related to conflicts will be minimized.
To further minimize this risk, the IPC will review ISS’ conflict avoidance policy annually to insure it adequately addresses both the actual and perceived conflicts of interest the proxy voting service may face.
In the event the PVAC determines that ISS faces a material conflict of interest with respect to a specific vote, the PVAC shall direct ISS how to vote. The PVAC shall receive voting direction from the Head of Equity Research who will seek voting direction from appropriate investment personnel. Before doing so, however, the PVAC will confirm that FAF Advisors faces no material conflicts of the nature discussed above.
If the PVAC concludes a material conflict does exist, it will recommend a course of action designed to address the conflict to the IPC. Such actions could include, but are not limited to:
1. Obtaining instructions from the affected clients on how to vote the proxy;
2. Disclosing the conflict to the affected clients and seeking their consent to permit FAF Advisors to vote the proxy;
3. Voting in proportion to the other shareholders;
4. Recusing an IPC member from all discussion or consideration of the matter, if the material conflict is due to such person’s actual or potential conflict of interest; or
5. Following the recommendation of a different independent third party.
In addition to all of the above, members of the IPC and the PVAC must notify FAF Advisors’ Chief Compliance Officer of any direct, indirect or perceived improper influence made by any employee, officer or director within the U.S. Bancorp enterprise or First American Fund complex with regard to how FAF Advisors should vote proxies. The Chief Compliance Officer will investigate the allegations and will report the findings to the FAF Advisors Chief Executive Officer and the General Counsel. If it is determined that improper influence was attempted, appropriate action shall be taken. Such appropriate action may include disciplinary action, notification of the appropriate senior managers within the U.S. Bancorp enterprise, or notification of the appropriate regulatory authorities. In all cases, the IPC shall not consider any improper influence in determining how to vote proxies and will vote in the best interests of clients.
C. Proxy Vote Override
From time to time, a portfolio manager may initiate action to override the policy for a particular vote. Such override shall be reviewed by Legal for material conflicts. If Legal determines no material conflicts exist, the approval of one investment professional on the IPC or the Head of Equity Research shall authorize the override.
D. Review and Reports
The PVAC shall maintain a review schedule. The schedule shall include reviews for the policy, the proxy voting record, account maintenance, and other reviews as deemed prudent by the PVAC. The PVAC shall review the schedule no less than annually.
The PVAC will report all identified conflicts and how they were addressed to the IPC. These reports will include all funds, including those that are sub-advised.
With respect to the review of votes cast on behalf of investments by the First American family of mutual funds, such review will also be reported to the independent Board of Directors of the First American Funds at each of their regularly scheduled meetings.
E. Vote Disclosure to Shareholders
FAF Advisors shall disclose its proxy voting record on the First American Funds’ website at www.firstamericanfunds.com and on the SEC’s website at www.sec.gov. Additionally, shareholders can receive, on request, the voting records for the First American Fund mutual funds by calling a toll free number (1-800-677-3863).
FAF Advisors’ separately managed account clients can contact their relationship manager for more information on FAF Advisors’ policies and the proxy voting record for their account.
The information that will be available includes, name of issuer; ticker/CUSIP; shareholder meeting date; description of item and FAF Advisors’ vote.
ISS Proxy Voting Guidelines Summary
The following is a concise summary of ISS’s proxy voting policy guidelines.
1. Auditors
Auditor Ratification
Vote FOR proposals to ratify auditors, unless any of the following apply:
· An auditor has a financial interest in or association with the company, and is therefore not independent;
· There is reason to believe that the independent auditor has rendered an opinion which is neither accurate nor indicative of the company’s financial position;
· Poor accounting practices are identified that rise to a serious level of concern, such as: fraud; misapplication of GAAP; and material weaknesses identified in Section 404 disclosures; or
· Fees for non-audit services (“other” fees) are excessive.
Vote CASE-BY-CASE on shareholder proposals asking for audit firm rotation, taking into account:
· The tenure of the audit firm;
· The length of rotation specified in the proposal;
· Any significant audit-related issues at the company;
· The number of audit committee meetings held each year;
· The number of financial experts serving on the committee; and
· Whether the company has a periodic renewal process where the auditor is evaluated for both audit quality and competitive price.
2. Board of Directors
Voting on Director Nominees in Uncontested Elections
Vote AGAINST or WITHHOLD from individual directors who:
· Attend less than 75 percent of the board and committee meetings without a valid excuse;
· Sit on more than six public company boards;
· Are CEOs of public companies who sit on the boards of more than two public companies besides their own—withhold only at their outside boards.
Vote AGAINST or WITHHOLD from all nominees of the board of directors, (except from new nominees, who should be considered on a CASE-BY-CASE basis) if:
· The company’s proxy indicates that not all directors attended 75 percent of the aggregate of their board and committee meetings, but fails to provide the required disclosure of the names of the directors involved. If this information cannot be obtained, vote against/withhold from all incumbent directors;
· The company’s poison pill has a dead-hand or modified dead-hand feature. Vote against/withhold every year until this feature is removed;
· The board adopts or renews a poison pill without shareholder approval, does not commit to putting it to shareholder vote within 12 months of adoption (or in the case of an newly public company, does not commit to put the pill to a shareholder vote within 12 months following the IPO), or reneges on a commitment to put the pill to a vote, and has not yet received a withhold/against recommendation for this issue;
· The board failed to act on a shareholder proposal that received approval by a majority of the shares outstanding the previous year (a management proposal with other than a FOR recommendation by management will not be considered as sufficient action taken);
· The board failed to act on a shareholder proposal that received approval of the majority of shares cast for the previous two consecutive years (a management proposal with other than a FOR recommendation by management will not be considered as sufficient action taken);
· The board failed to act on takeover offers where the majority of the shareholders tendered their shares;
· At the previous board election, any director received more than 50 percent withhold/against votes of the shares cast and the company has failed to address the underlying issue(s) that caused the high withhold/against vote;
· The company is a Russell 3000 company that underperformed its industry group (GICS group) under ISS’ “Performance Test for Directors” policy;
· The board is classified, and a continuing director responsible for a problematic governance issue at the board/committee level that would warrant a withhold/against vote recommendation is not up for election—any or all appropriate nominees (except new) may be held accountable.
Vote AGAINST or WITHHOLD from inside directors and affiliated outside directors when:
· The inside or affiliated outside director serves on any of the three key committees: audit, compensation, or nominating;
· The company lacks an audit, compensation, or nominating committee so that the full board functions as that committee;
· The company lacks a formal nominating committee, even if board attests that the independent directors fulfill the functions of such a committee;
· The full board is less than majority independent.
Vote AGAINST or WITHHOLD from the members of the audit committee if:
· The non-audit fees paid to the auditor are excessive (see discussion under “Auditor Ratification”);
· Poor accounting practices are identified which rise to a level of serious concern, such as: fraud; misapplication of GAAP; and material weaknesses identified in Section 404 disclosures; or
· There is persuasive evidence that the audit committee entered into an inappropriate indemnification agreement with its auditor that limits the ability of the company, or its shareholders, to pursue legitimate legal recourse against the audit firm.
Vote AGAINST or WITHHOLD from the members of the compensation committee if:
· There is a negative correlation between the chief executive’s pay and company performance;
· The company reprices underwater options for stock, cash or other consideration without prior shareholder approval, even if allowed in their equity plan;
· The company fails to submit one-time transfers of stock options to a shareholder vote;
· The company fails to fulfill the terms of a burn-rate commitment made to shareholders;
· The company has backdated options (see “Options Backdating” policy);
· The company has poor compensation practices (see “Poor Pay Practices” policy). Poor pay practices may warrant withholding votes from the CEO and potentially the entire board as well.
Vote AGAINST or WITHHOLD from directors, individually or the entire board, for egregious actions or failure to replace management as appropriate.
Classification/Declassification of the Board
Vote AGAINST proposals to classify the board. Vote FOR proposals to repeal classified boards and to elect all directors annually.
Cumulative Voting
Generally vote AGAINST proposals to eliminate cumulative voting. Generally vote FOR proposals to restore or provide for cumulative voting unless:
· The company has proxy access or a similar structure to allow shareholders to nominate directors to the company’s ballot; and
· The company has adopted a majority vote standard, with a carve-out for plurality voting in situations where there are more nominees than seats, and a director resignation policy to address failed elections.
Vote FOR proposals for cumulative voting at controlled companies (insider voting power > 50 percent).
Independent Chair (Separate Chair/CEO)
Generally vote FOR shareholder proposals requiring that the chairman’s position be filled by an independent director, unless there are compelling reasons to recommend against the proposal, such as a counterbalancing governance structure. This should include all the following:
· Designated lead director, elected by and from the independent board members with clearly delineated and comprehensive duties. (The role may alternatively reside with a presiding director, vice chairman, or rotating lead director; however the director must serve a minimum of one year in order to qualify as a lead director.) The duties should include, but are not limited to, the following:
· presides at all meetings of the board at which the chairman is not present, including executive sessions of the independent directors;
· serves as liaison between the chairman and the independent directors;
· approves information sent to the board;
· approves meeting agendas for the board;
· approves meeting schedules to assure that there is sufficient time for discussion of all agenda items;
· has the authority to call meetings of the independent directors;
· if requested by major shareholders, ensures that he is available for consultation and direct communication;
· The company publicly discloses a comparison of the duties of its independent lead director and its chairman;
· The company publicly discloses a sufficient explanation of why it chooses not to give the position of chairman to the independent lead director, and instead combine the chairman and CEO positions;
· Two-thirds independent board;
· All independent key committees;
· Established governance guidelines;
· The company should not have underperformed both its peers and index on the basis of both one-year and three-year total shareholder returns*, unless there has been a change in the chairman/CEO position within that time; and
· The company does not have any problematic governance issues.
Vote FOR the proposal if the company does not provide disclosure with respect to any or all of the bullet points above. If disclosure is provided, evaluate on a CASE-BY-CASE basis.
* The industry peer group used for this evaluation is the average of the 12 companies in the same six-digit GICS group that are closest in revenue to the company. To fail, the company must underperform its index and industry group on all four measures (one- and three-year on industry peers and index).
Majority Vote Shareholder Proposals
Generally vote FOR precatory and binding resolutions requesting that the board change the company’s bylaws to stipulate that directors need to be elected with an affirmative majority of votes cast, provided it does not conflict with the state law where the company is incorporated. Binding resolutions need to allow for a carve-out for a plurality vote standard when there are more nominees than board seats. Companies are strongly encouraged to also adopt a post-election policy (also known as a director resignation policy) that will provide guidelines so that the company will promptly address the situation of a holdover director.
Open Access
Vote shareholder proposals asking for open or proxy access on a CASE-BY-CASE basis, taking into account:
· The ownership threshold proposed in the resolution;
· The proponent’s rationale for the proposal at the targeted company in terms of board and director conduct.
3. Proxy Contests
Voting for Director Nominees in Contested Elections
Vote CASE-BY-CASE on the election of directors in contested elections, considering the following factors:
· Long-term financial performance of the target company relative to its industry;
· Management’s track record;
· Background to the proxy contest;
· Qualifications of director nominees (both slates);
· Strategic plan of dissident slate and quality of critique against management;
· Likelihood that the proposed goals and objectives can be achieved (both slates);
· Stock ownership positions.
Reimbursing Proxy Solicitation Expenses
Vote CASE-BY-CASE on proposals to reimburse proxy solicitation expenses. When voting in conjunction with support of a dissident slate, vote FOR the reimbursement of all appropriate proxy solicitation expenses associated with the election.
Generally vote FOR shareholder proposals calling for the reimbursement of reasonable costs incurred in connection with nominating one or more candidates in a contested election where the following apply:
· The election of fewer than 50 percent of the directors to be elected is contested in the election;
· One or more of the dissident’s candidates is elected;
· Shareholders are not permitted to cumulate their votes for directors; and
· The election occurred, and the expenses were incurred, after the adoption of this bylaw.
4. Takeover Defenses
Poison Pills
Vote FOR shareholder proposals requesting that the company submit its poison pill to a shareholder vote or redeem it UNLESS the company has: (1) A shareholder approved poison pill in place; or (2) The company has adopted a policy concerning the adoption of a pill in the future specifying that the board will only adopt a shareholder rights plan if either:
· Shareholders have approved the adoption of the plan; or
· The board, in its exercise of its fiduciary responsibilities, determines that it is in the best interest of shareholders under the circumstances to adopt a pill without the delay that would result from seeking stockholder approval (i.e., the “fiduciary out” provision). A poison pill adopted under this fiduciary out will be put to a shareholder ratification vote within 12 months of adoption or expire. If the pill is not approved by a majority of the votes cast on this issue, the plan will immediately terminate.
Vote FOR shareholder proposals calling for poison pills to be put to a vote within a year after adoption. If the company has no non-shareholder approved poison pill in place and has adopted a policy with the provisions outlined above, vote AGAINST the proposal. If these conditions are not met, vote FOR the proposal, but with the caveat that a vote within 12 months would be considered sufficient.
Vote CASE-by-CASE on management proposals on poison pill ratification, focusing on the features of the shareholder rights plan. Rights plans should contain the following attributes:
· No lower than a 20 percent trigger, flip-in or flip-over;
· A term of no more than three years;
· No dead-hand, slow-hand, no-hand, or similar feature that limits the ability of a future board to redeem the pill;
· Shareholder redemption feature (qualifying offer clause); if the board refuses to redeem the pill 90 days after a qualifying offer is announced, 10 percent of the shares may call a special meeting, or seek a written consent to vote on rescinding the pill.
Shareholder Ability to Call Special Meetings
Vote AGAINST proposals to restrict or prohibit shareholder ability to call special meetings. Vote FOR proposals that remove restrictions on the right of shareholders to act independently of management.
Supermajority Vote Requirements
Vote AGAINST proposals to require a supermajority shareholder vote. Vote FOR proposals to lower supermajority vote requirements.
5. Mergers and Corporate Restructurings
For mergers and acquisitions, review and evaluate the merits and drawbacks of the proposed transaction, balancing various and sometimes countervailing factors including:
· Valuation - Is the value to be received by the target shareholders (or paid by the acquirer) reasonable? While the fairness opinion may provide an initial starting point for assessing valuation reasonableness, emphasis is placed on the offer premium, market reaction and strategic rationale.
· Market reaction - How has the market responded to the proposed deal? A negative market reaction should cause closer scrutiny of a deal.
· Strategic rationale - Does the deal make sense strategically? From where is the value derived? Cost and revenue synergies should not be overly aggressive or optimistic, but reasonably achievable. Management should also have a favorable track record of successful integration of historical acquisitions.
· Negotiations and process - Were the terms of the transaction negotiated at arm’s-length? Was the process fair and equitable? A fair process helps to ensure the best price for shareholders. Significant negotiation “wins” can also signify the deal makers’ competency. The comprehensiveness of the sales process (e.g., full auction, partial auction, no auction) can also affect shareholder value.
· Conflicts of interest - Are insiders benefiting from the transaction disproportionately and inappropriately as compared to non-insider shareholders? As the result of potential conflicts, the directors and officers of the company may be more likely to vote to approve a merger than if they did not hold these interests. Consider whether these interests may have influenced these directors and officers to support or recommend the merger. The aggregate CIC figure may be a misleading indicator of the true value transfer from shareholders to insiders. Where such figure appears to be excessive, analyze the underlying assumptions to determine whether a potential conflict exists.
· Governance - Will the combined company have a better or worse governance profile than the current governance profiles of the respective parties to the transaction? If the governance profile is to change for the worse, the burden is on the company to prove that other issues (such as valuation) outweigh any deterioration in governance.
6. State of Incorporation
Reincorporation Proposals
Vote CASE-BY-CASE on proposals to change a company’s state of incorporation, taking into consideration both financial and corporate governance concerns, including:
· The reasons for reincorporating;
· A comparison of the governance provisions;
· Comparative economic benefits; and
· A comparison of the jurisdictional laws.
7. Capital Structure
Common Stock Authorization
Vote CASE-BY-CASE on proposals to increase the number of shares of common stock authorized for issuance using a model developed by ISS. Vote FOR proposals to approve increases beyond the allowable increase when a company’s shares are in danger of being delisted or if a company’s ability to continue to operate as a going concern is uncertain.
In addition, for capital requests less than or equal to 300 percent of the current authorized shares that marginally fail the calculated allowable cap (i.e., exceed the allowable cap by no more than 5 percent), on a CASE-BY-CASE basis, vote FOR the increase based on the company’s performance and whether the company’s ongoing use of shares has shown prudence. Factors should include, at a minimum, the following:
· Rationale;
· Good performance with respect to peers and index on a five-year total shareholder return basis;
· Absence of non-shareholder approved poison pill;
· Reasonable equity compensation burn rate;
· No non-shareholder approved pay plans; and
· Absence of egregious equity compensation practices.
Dual-Class Stock
Vote AGAINST proposals to create a new class of common stock with superior voting rights. Vote AGAINST proposals at companies with dual-class capital structures to increase the number of authorized shares of the class of stock that has superior voting rights.
Vote FOR proposals to create a new class of nonvoting or sub-voting common stock if:
· It is intended for financing purposes with minimal or no dilution to current shareholders;
· It is not designed to preserve the voting power of an insider or significant shareholder.
Issue Stock for Use with Rights Plan
Vote AGAINST proposals that increase authorized common stock for the explicit purpose of implementing a non-shareholder approved shareholder rights plan (poison pill).
Preferred Stock
Vote AGAINST proposals authorizing the creation of new classes of preferred stock with unspecified voting, conversion, dividend distribution, and other rights (“blank check” preferred stock), and AGAINST proposals to increase the number of blank check preferred stock authorized for issuance when no shares have been issued or reserved for a specific purpose. Vote FOR proposals to create “declawed” blank check preferred stock (stock that cannot be used as a takeover defense), and FOR proposals to authorize preferred stock in cases where the company specifies the voting, dividend, conversion, and other rights of such stock and the terms of the preferred stock appear reasonable. Vote CASE-BY-CASE on proposals to increase the number of blank check preferred shares after analyzing the number of preferred shares available for issue given a company’s industry and performance in terms of shareholder returns.
8. Executive and Director Compensation
Equity Compensation Plans
Vote CASE-BY-CASE on equity-based compensation plans. Vote AGAINST the equity plan if any of the following factors apply:
· The total cost of the company’s equity plans is unreasonable;
· The plan expressly permits the repricing of stock options without prior shareholder approval;
· There is a disconnect between CEO pay and the company’s performance;
· The company’s three year burn rate exceeds the greater of 2% and the mean plus one standard deviation of its industry group; or
· The plan is a vehicle for poor pay practices.
Poor Pay Practices
Vote AGAINST or WITHHOLD from compensation committee members, the CEO, and potentially the entire board, if the company has poor compensation practices. Vote AGAINST equity plans if the plan is a vehicle for poor compensation practices.
The following practices, while not exhaustive, are examples of poor compensation practices:
· Egregious employment contracts (e.g., multi-year guarantees for salary increases, bonuses, and equity compensation);
· Excessive perks (overly generous cost and/or reimbursement of taxes for personal use of corporate aircraft, personal security systems maintenance and/or installation, car allowances, and/or other excessive arrangements relative to base salary);
· Abnormally large bonus payouts without justifiable performance linkage or proper disclosure (e.g., performance metrics that are changed, canceled, or replaced during the performance period without adequate explanation of the action and the link to performance);
· Egregious pension/SERP (supplemental executive retirement plan) payouts (inclusion of additional years of service not worked that result in significant payouts, or inclusion of performance-based equity awards in the pension calculation;
· New CEO with overly generous new hire package (e.g., excessive “make whole” provisions);
· Excessive severance and/or change-in-control provisions: Inclusion of excessive change-in-control or severance payments, especially those with a multiple in excess of 3X cash pay;
· Severance paid for a “performance termination,” (i.e., due to the executive’s failure to perform job functions at the appropriate level);
· Change-in-control payouts without loss of job or substantial diminution of job duties (single-triggered);
· Perquisites for former executives such as car allowances, personal use of corporate aircraft, or other inappropriate arrangements;
· Poor disclosure practices, (unclear explanation of how the CEO is involved in the pay setting process, retrospective performance targets and methodology not discussed, or methodology for benchmarking practices and/or peer group not disclosed and explained);
· Internal pay disparity (e.g., excessive differential between CEO total pay and that of next highest-paid named executive officer);
· Other excessive compensation payouts or poor pay practices at the company.
Director Compensation
Vote CASE-BY-CASE on compensation plans for non-employee directors, based on the cost of the plans against the company’s allowable cap.
On occasion, director stock plans that set aside a relatively small number of shares when combined with employee or executive stock compensation plans will exceed the allowable cap. Vote for the plan if ALL of the following qualitative factors in the board’s compensation are met and disclosed in the proxy statement:
· Director stock ownership guidelines with a minimum of three times the annual cash retainer.
· Vesting schedule or mandatory holding/deferral period:
· A minimum vesting of three years for stock options or restricted stock; or
· Deferred stock payable at the end of a three-year deferral period.
· Mix between cash and equity:
· A balanced mix of cash and equity, for example 40 percent cash/60 percent equity or 50 percent cash/50 percent equity; or
· If the mix is heavier on the equity component, the vesting schedule or deferral period should be more stringent, with the lesser of five years or the term of directorship.
· No retirement/benefits and perquisites provided to non-employee directors; and
· Detailed disclosure provided on cash and equity compensation delivered to each non-employee director for the most recent fiscal year in a table. The column headers for the table may include the following: name of each non-employee director, annual retainer, board meeting fees, committee retainer, committee-meeting fees, and equity grants.
Employee Stock Purchase Plans—Qualified Plans
Vote CASE-BY-CASE on qualified employee stock purchase plans. Vote FOR employee stock purchase plans where all of the following apply:
· Purchase price is at least 85 percent of fair market value;
· Offering period is 27 months or less; and
· The number of shares allocated to the plan is 10 percent or less of the outstanding shares.
Vote AGAINST qualified employee stock purchase plans where any of the following apply:
· Purchase price is less than 85 percent of fair market value; or
· Offering period is greater than 27 months; or
· The number of shares allocated to the plan is more than 10 percent of the outstanding shares.
Employee Stock Purchase Plans—Non-Qualified Plans
Vote CASE-by-CASE on nonqualified employee stock purchase plans. Vote FOR nonqualified employee stock purchase plans with all the following features:
· Broad-based participation (i.e., all employees of the company with the exclusion of individuals with 5 percent or more of beneficial ownership of the company);
· Limits on employee contribution, which may be a fixed dollar amount or expressed as a percent of base salary;
· Company matching contribution up to 25 percent of employee’s contribution, which is effectively a discount of 20 percent from market value;
· No discount on the stock price on the date of purchase since there is a company matching contribution.
Vote AGAINST nonqualified employee stock purchase plans when any of the plan features do not meet the above criteria. If the company matching contribution exceeds 25 percent of employee’s contribution, evaluate the cost of the plan against its allowable cap.
Options Backdating
In cases where a company has practiced options backdating, vote AGAINST or WITHHOLD on a CASE-BY-CASE basis from the members of the compensation committee, depending on the severity of the practices and the subsequent corrective actions on the part of the board. Vote AGAINST or WITHHOLD from the compensation committee members who oversaw the questionable options practices or from current compensation committee members who fail to respond to the issue proactively, depending on several factors, including, but not limited to:
· Reason and motive for the options backdating issue (inadvertent vs. deliberate grant date changes);
· Length of time of options backdating;
· Size of restatement due to options backdating;
· Corrective actions taken by the board or compensation committee, such as canceling or repricing backdated options, or recoupment of option gains on backdated grants;
· Adoption of a grant policy that prohibits backdating, and creation of a fixed grant schedule or window period for equity grants going forward.
Option Exchange Programs/Repricing Options
Vote CASE-by-CASE on management proposals seeking approval to exchange/reprice options, considering:
· Historic trading patterns—the stock price should not be so volatile that the options are likely to be back “in-the-money” over the near term;
· Rationale for the re-pricing—was the stock price decline beyond management’s control?
· Is this a value-for-value exchange?
· Are surrendered stock options added back to the plan reserve?
· Option vesting—does the new option vest immediately or is there a black-out period?
· Term of the option—the term should remain the same as that of the replaced option;
· Exercise price—should be set at fair market or a premium to market;
· Participants—executive officers and directors should be excluded.
If the surrendered options are added back to the equity plans for re-issuance, then also take into consideration the company’s three-year average burn rate. In addition to the above considerations, evaluate the intent, rationale, and timing of the repricing proposal. The proposal should clearly articulate why the board is choosing to conduct an exchange program at this point in time. Repricing underwater options after a recent precipitous drop in the company’s stock price demonstrates poor timing. Repricing after a recent decline in stock price triggers additional scrutiny and a potential AGAINST vote on the proposal. At a minimum, the decline should not have happened within the past year. Also, consider the terms of the surrendered options, such as the grant date, exercise price and vesting schedule. Grant dates of surrendered options should be far enough back (two to three years) so as not to suggest that repricings are being done to take advantage of short-term downward price movements. Similarly, the exercise price of surrendered options should be above the 52-week high for the stock price.
Vote FOR shareholder proposals to put option repricings to a shareholder vote.
Stock Plans in Lieu of Cash
Vote CASE-by-CASE on plans that provide participants with the option of taking all or a portion of their cash compensation in the form of stock, and on plans that do not provide a dollar-for-dollar cash for stock exchange. In cases where the exchange is not dollar-for-dollar, the request for new or additional shares for such equity program will be considered using the binomial option pricing model. In an effort to capture the total cost of total compensation, ISS will not make any adjustments to carve out the in-lieu-of cash compensation. Vote FOR non-employee director-only equity plans that provide a dollar-for-dollar cash-for-stock exchange.
Transfer Programs of Stock Options
Vote AGAINST or WITHHOLD from compensation committee members if they fail to submit one-time transfers to shareholders for approval.
Vote CASE-BY-CASE on one-time transfers. Vote FOR if:
· Executive officers and non-employee directors are excluded from participating;
· Stock options are purchased by third-party financial institutions at a discount to their fair value using option pricing models such as Black-Scholes or a Binomial Option Valuation or other appropriate financial models;
· There is a two-year minimum holding period for sale proceeds (cash or stock) for all participants.
Additionally, management should provide a clear explanation of why options are being transferred and whether the events leading up to the decline in stock price were beyond management’s control. A review of the company’s historic stock price volatility should indicate if the options are likely to be back “in-the-money” over the near term.
Vote AGAINST equity plan proposals if the details of ongoing Transfer of Stock Options programs are not provided to shareholders. Since TSOs will be one of the award types under a stock plan, the ongoing TSO program, structure and mechanics must be disclosed to shareholders. The specific criteria to be considered in evaluating these proposals include, but not limited, to the following:
· Eligibility;
· Vesting;
· Bid-price;
· Term of options;
· Transfer value to third-party financial institution, employees and the company.
Amendments to existing plans that allow for introduction of transferability of stock options should make clear that only options granted post-amendment shall be transferable.
Shareholder Proposals on Compensation
Advisory Vote on Executive Compensation (Say-on-Pay)
Generally, vote FOR shareholder proposals that call for non-binding shareholder ratification of the compensation of the named executive officers and the accompanying narrative disclosure of material factors provided to understand the Summary Compensation Table.
Compensation Consultants—Disclosure of Board or Company’s Utilization
Generally vote FOR shareholder proposals seeking disclosure regarding the company, board, or compensation committee’s use of compensation consultants, such as company name, business relationship(s) and fees paid.
Disclosure/Setting Levels or Types of Compensation for Executives and Directors
Generally, vote FOR shareholder proposals seeking additional disclosure of executive and director pay information, provided the information requested is relevant to shareholders’ needs, would not put the company at a competitive disadvantage relative to its industry, and is not unduly burdensome to the company. Vote AGAINST shareholder proposals seeking to set absolute levels on compensation or otherwise dictate the amount or form of compensation. Vote AGAINST shareholder proposals requiring director fees be paid in stock only. Vote CASE-BY-CASE on all other shareholder proposals regarding executive and director pay, taking into account company performance, pay level versus peers, pay level versus industry, and long-term corporate outlook.
Pay for Superior Performance
Generally vote FOR shareholder proposals based on a case-by-case analysis that requests the board establish a pay-for-superior performance standard in the company’s compensation plan for senior executives. The proposal should have the following principles:
· Sets compensation targets for the plan’s annual and long-term incentive pay components at or below the peer group median;
· Delivers a majority of the plan’s target long-term compensation through performance-vested, not simply time-vested, equity awards;
· Provides the strategic rationale and relative weightings of the financial and non-financial performance metrics or criteria used in the annual and performance-vested long-term incentive components of the plan;
· Establishes performance targets for each plan financial metric relative to the performance of the company’s peer companies;
· Limits payment under the annual and performance-vested long-term incentive components of the plan to when the company’s performance on its selected financial performance metrics exceeds peer group median performance.
Consider the following factors in evaluating this proposal:
· What aspects of the company’s annual and long-term equity incentive programs are performance-driven?
· If the annual and long-term equity incentive programs are performance driven, are the performance criteria and hurdle rates disclosed to shareholders or are they benchmarked against a disclosed peer group?
· Can shareholders assess the correlation between pay and performance based on the current disclosure?
· What type of industry and stage of business cycle does the company belong to?
Performance-Based Awards
Vote CASE-BY-CASE on shareholder proposal requesting that a significant amount of future long-term incentive compensation awarded to senior executives shall be performance-based and requesting that the board adopt and disclose challenging performance metrics to shareholders, based on the following analytical steps:
· First, vote FOR shareholder proposals advocating the use of performance-based equity awards, such as performance contingent options or restricted stock, indexed options or premium-priced options, unless the proposal is overly restrictive or if the company has demonstrated that it is using a “substantial” portion of performance-based awards for its top executives. Standard stock options and performance-accelerated awards do not meet the criteria to be considered as performance-based awards. Further, premium-priced options should have a premium of at least 25 percent and higher to be considered performance-based awards.
· Second, assess the rigor of the company’s performance-based equity program. If the bar set for the performance-based program is too low based on the company’s historical or peer group comparison, generally vote FOR the proposal. Furthermore, if target performance results in an above target payout, vote FOR the shareholder proposal due to program’s poor design. If the company does not disclose the performance metric of the performance-based equity program, vote FOR the shareholder proposal regardless of the outcome of the first step to the test.
In general, vote FOR the shareholder proposal if the company does not meet both of these two requirements.
Pre-Arranged Trading Plans (10b5-1 Plans)
Generally vote FOR shareholder proposals calling for certain principles regarding the use of prearranged trading plans (10b5-1 plans) for executives. These principles include:
· Adoption, amendment, or termination of a 10b5-1 plan must be disclosed within two business days in a Form 8-K;
· Amendment or early termination of a 10b5-1 plan is allowed only under extraordinary circumstances, as determined by the board;
· Ninety days must elapse between adoption or amendment of a 10b5-1 plan and initial trading under the plan;
· Reports on Form 4 must identify transactions made pursuant to a 10b5-1 plan;
· An executive may not trade in company stock outside the 10b5-1 Plan.
· Trades under a 10b5-1 plan must be handled by a broker who does not handle other securities transactions for the executive.
Recoup Bonuses
Vote on a CASE-BY-CASE on proposals to recoup unearned incentive bonuses or other incentive payments made to senior executives if it is later determined that fraud, misconduct, or negligence significantly contributed to a restatement of financial results that led to the awarding of unearned incentive compensation, taking into consideration:
· If the company has adopted a formal recoupment bonus policy; or
· If the company has chronic restatement history or material financial problems.
Severance Agreements for Executives/Golden Parachutes
Vote FOR shareholder proposals requiring that golden parachutes or executive severance agreements be submitted for shareholder ratification, unless the proposal requires shareholder approval prior to entering into employment contracts. Vote on a CASE-BY-CASE basis on proposals to ratify or cancel golden parachutes. An acceptable parachute should include, but is not limited to, the following:
· The triggering mechanism should be beyond the control of management;
· The amount should not exceed three times base amount (defined as the average annual taxable W-2 compensation during the five years prior to the change of control);
· Change-in-control payments should be double-triggered, i.e., (1) after a change in control has taken place, and (2) termination of the executive as a result of the change in control. Change in control is defined as a change in the company ownership structure.
Supplemental Executive Retirement Plans (SERPs)
Generally vote FOR shareholder proposals requesting to put extraordinary benefits contained in SERP agreements to a shareholder vote unless the company’s executive pension plans do not contain excessive benefits beyond what is offered under employee-wide plans. Generally vote FOR shareholder proposals requesting to limit the executive benefits provided under the company’s supplemental executive retirement plan (SERP) by limiting covered compensation to a senior executive’s annual salary and excluding of all incentive or bonus pay from the plan’s definition of covered compensation used to establish such benefits.
9. Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Issues
Consumer Lending
Vote CASE-BY CASE on requests for reports on the company’s lending guidelines and procedures, including the establishment of a board committee for oversight, taking into account:
· Whether the company has adequately disclosed mechanisms to prevent abusive lending practices;
· Whether the company has adequately disclosed the financial risks of the lending products in question;
· Whether the company has been subject to violations of lending laws or serious lending controversies;
· Peer companies’ policies to prevent abusive lending practices.
Pharmaceutical Pricing
Generally vote AGAINST proposals requesting that companies implement specific price restraints on pharmaceutical products unless the company fails to adhere to legislative guidelines or industry norms in its product pricing.
Vote CASE-BY-CASE on proposals requesting that the company evaluate their product pricing considering:
· The existing level of disclosure on pricing policies;
· Deviation from established industry pricing norms;
· The company’s existing initiatives to provide its products to needy consumers;
· Whether the proposal focuses on specific products or geographic regions.
Product Safety and Toxic Materials
Generally vote FOR proposals requesting the company to report on its policies, initiatives/procedures, and oversight mechanisms related to toxic materials and/or product safety in its supply chain, unless:
· The company already discloses similar information through existing reports or policies such as a supplier code of conduct and/or a sustainability report;
· The company has formally committed to the implementation of a toxic materials and/or product safety and supply chain reporting and monitoring program based on industry norms or similar standards within a specified time frame; and
· The company has not been recently involved in relevant significant controversies or violations.
Vote CASE-BY-CASE on resolutions requesting that companies develop a feasibility assessment to phase-out of certain toxic chemicals and/or evaluate and disclose the financial and legal risks associated with utilizing certain chemicals, considering:
· Current regulations in the markets in which the company operates;
· Recent significant controversy, litigation, or fines stemming from toxic chemicals or ingredients at the company; and
· The current level of disclosure on this topic.
Climate Change
In general, vote FOR resolutions requesting that a company disclose information on the impact of climate change on the company’s operations unless:
· The company already provides current, publicly available information on the perceived impact that climate change may have on the company as well as associated policies and procedures to address such risks and/or opportunities;
· The company’s level of disclosure is comparable to or better than information provided by industry peers; and
· There are no significant fines, penalties, or litigation associated with the company’s environmental performance.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Generally vote FOR proposals requesting a report on greenhouse gas emissions from company operations and/or products unless this information is already publicly disclosed or such factors are not integral to the company’s line of business. Generally vote AGAINST proposals that call for reduction in greenhouse gas emissions by specified amounts or within a restrictive time frame unless the company lags industry standards and has been the subject of recent, significant fines, or litigation resulting from greenhouse gas emissions.
Political Contributions and Trade Associations Spending
Generally vote AGAINST proposals asking the company to affirm political nonpartisanship in the workplace so long as:
· The company is in compliance with laws governing corporate political activities; and
· The company has procedures in place to ensure that employee contributions to company-sponsored political action committees (PACs) are strictly voluntary and not coercive.
Vote AGAINST proposals to publish in newspapers and public media the company’s political contributions as such publications could present significant cost to the company without providing commensurate value to shareholders. Vote CASE-BY-CASE on proposals to improve the disclosure of a company’s political contributions and trade association spending, considering:
· Recent significant controversy or litigation related to the company’s political contributions or governmental affairs; and
· The public availability of a company policy on political contributions and trade association spending including information on the types of organizations supported, the business rationale for supporting these organizations, and the oversight and compliance procedures related to such expenditures.
Vote AGAINST proposals barring the company from making political contributions. Businesses are affected by legislation at the federal, state, and local level and barring contributions can put the company at a competitive disadvantage. Vote AGAINST proposals asking for a list of company executives, directors, consultants, legal counsels, lobbyists, or investment bankers that
have prior government service and whether such service had a bearing on the business of the company. Such a list would be burdensome to prepare without providing any meaningful information to shareholders.
Sustainability Reporting
Generally vote FOR proposals requesting the company to report on policies and initiatives related to social, economic, and environmental sustainability, unless:
· The company already discloses similar information through existing reports or policies such as an environment, health, and safety (EHS) report; a comprehensive code of corporate conduct; and/or a diversity report; or
· The company has formally committed to the implementation of a reporting program based on Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) guidelines or a similar standard within a specified time frame.
Item 8—Portfolio Managers of Closed-End Management Investment Companies
(a)(1) | | Douglas J. White, CFA, is primarily responsible for the day-to-day management of the registrant’s portfolio. Christopher L. Drahn assists with the management of the registrant’s portfolio. |
| | |
| | Mr. White, Head of Tax Exempt Fixed Income, began working in the financial industry in 1983 and joined FAF Advisors, Inc. (the “Advisor”) in 1987. |
| | |
| | Mr. Drahn, Senior Fixed-Income Portfolio Manager, began working in the financial industry when he joined the Advisor in 1980. |
| | |
(a)(2) | | The following table shows, as of the fiscal-year ended August 31, 2008, the number of other accounts each portfolio manager managed within each of the following categories and the total assets in the accounts managed within each category. The table also shows the number of accounts and the total assets in the accounts, if any, with respect to which the advisory fee is based on the performance of the account. |
Portfolio Manager | | Type of Account Managed | | Total
Number of
Accounts | | Total Assets
of All
Accounts | | Accounts
Subject to
Performance-
Based Fee | | Total Assets
Subject to
Performance-
Based Fee | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Christopher L. Drahn | | Registered Investment Company | | 15 | | $ | 2.4 billion | | 0 | | $ | 0 | |
| | Other Pooled Investment Vehicles | | 0 | | $ | 0 | | 0 | | $ | 0 | |
| | Other Accounts | | 5 | | $ | 208.0 million | | 0 | | $ | 0 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Douglas J. White | | Registered Investment Company | | 9 | | $ | 2.3 billion | | 0 | | $ | 0 | |
| | Other Pooled Investment Vehicles | | 0 | | $ | 0 | | 0 | | $ | 0 | |
| | Other Accounts | | 6 | | $ | 123.0 million | | 0 | | $ | 0 | |
| | The registrant’s portfolio managers often manage multiple accounts. The Advisor has adopted policies and procedures regarding brokerage and trade allocation and allocation of investment opportunities that it believes are reasonably designed to address potential conflicts of interest associated with managing multiple accounts for multiple clients. |
| | |
(a)(3) | | Portfolio manager compensation consists primarily of base pay, an annual cash incentive and long term incentive payments. |
| | |
| | Base pay is determined based upon an analysis of the portfolio manager’s general performance, experience, and market levels of base pay for such position. |
| | |
| | Portfolio managers are paid an annual incentive based upon investment performance, generally over the past one- and three-year periods unless the portfolio manager’s tenure is shorter. The maximum potential annual cash incentive is equal to a multiple of base pay, determined based upon the particular portfolio manager’s performance and experience, and market levels of base pay for such position. |
| | |
| | The portion of the maximum potential annual cash incentive that is paid out is based upon performance relative to the portfolio’s Lipper industry peer group (Other States Municipal Debt Funds Category). Generally, the threshold for payment of an annual cash incentive is median performance versus the peer group and the maximum annual cash incentive is attained at top quartile performance versus the peer group. |
| | Investment performance is measured on a pre-tax basis, gross of fees for registrant results and for the Lipper industry peer group. |
| | |
| | Long term incentive payments are paid to portfolio managers on an annual basis based upon general performance and expected contributions to the success of the Advisor. Long-term incentive payments are comprised of two components: (i) performance equity units of the Advisor and (ii) U.S. Bancorp options and restricted stock. |
| | |
| | There are generally no differences between the methods used to determine compensation with respect to the registrant and the other accounts managed by the registrant’s portfolio managers. |
| | |
(a)(4) | | The following table shows the dollar range of equity securities in the registrant beneficially owned by the portfolio manager as of the fiscal-year ended August 31, 2008. |
Portfolio Manager | | Dollar Range of Equity
Securities Beneficially
Owned in the Registrant |
| | |
Christopher L. Drahn | | $0 |
| | |
Douglas J. White | | $0 |
Item 9—Purchases of Equity Securities by Closed-End Management Investment Company and Affiliated Purchasers
Neither the registrant nor any “affiliated purchaser,” as defined in Rule 10b-18(a)(3) under the Exchange Act (17 CFR 240.10b-18(a)(3)), purchased any shares or other units of any class of the registrant’s equity securities that is registered pursuant to Section 12 of the Exchange Act (15 U.S.C. 781).
Item 10—Submission of Matters to a Vote of Security Holders
There have been no material changes to the procedures by which shareholders may recommend nominees to the registrant’s board of directors, where those changes were implemented after the registrant last provided disclosure in response to the requirements of Item 7(d)(2)(ii)(G) of Schedule 14A, or this item.
Item 11—Controls and Procedures
(a) | | The registrant’s principal executive officer and principal financial officer have evaluated the effectiveness of the registrant’s disclosure controls and procedures within 90 days of the date of this filing and have concluded that the registrant’s disclosure controls and procedures were effective, as of that date, in ensuring that information required to be disclosed by the registrant in this Form N-CSR was recorded, processed, summarized and reported timely. |
| | |
(b) | | There were no changes in the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the second fiscal quarter of the period covered by this report that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting. |
Item 12—Exhibits
(a)(1) | | Not applicable. Registrant’s code of ethics is provided to any person upon request without charge. |
| | |
(a)(2) | | Certifications of the principal executive officer and principal financial officer of the registrant as required by Rule 30a-2(a) under the Investment Company Act are filed as exhibits hereto. |
| | |
(a)(3) | | Not applicable. |
| | |
(b) | | Certifications of the principal executive officer and principal financial officer of the registrant as required by Rule 30a-2(b) under the Investment Company Act are filed as exhibits hereto. |
Signatures
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 and the Investment Company Act of 1940, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
First American Minnesota Municipal Income Fund II, Inc.
By: | | |
| /s/ Thomas S. Schreier, Jr. | |
| Thomas S. Schreier, Jr. | |
| President | |
Date: November 7, 2008
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 and the Investment Company Act of 1940, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
By: | | |
| /s/ Thomas S. Schreier, Jr. | |
| Thomas S. Schreier, Jr. | |
| President | |
Date: November 7, 2008
By: | | |
| /s/ Charles D. Gariboldi, Jr. | |
| Charles D. Gariboldi, Jr. | |
| Treasurer | |
Date: November 7, 2008