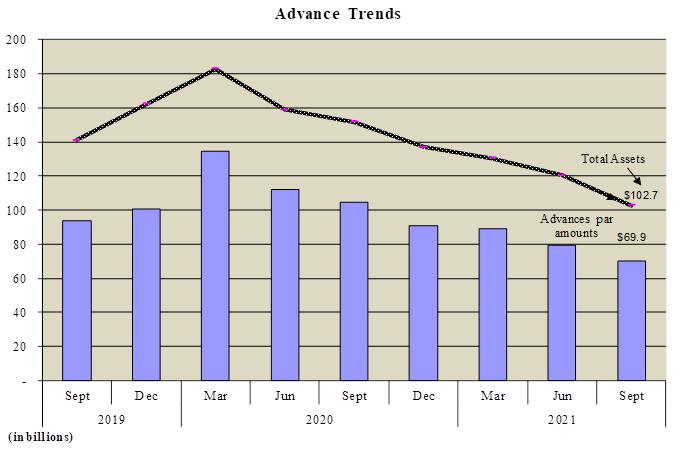
Advances — Par balances decreased at September 30, 2021 to $69.9 billion, compared to $90.7 billion at December 31, 2020. Short-term fixed-rate advances decreased by 15.6% to $10.9 billion at September 30, 2021, down from $12.9 billion at December 31, 2020. ARC advances, which are adjustable-rate borrowings, decreased by 53.8% to $7.9 billion at September 30, 2021, compared to $17.1 billion at December 31, 2020. Given that advances are always well collateralized, a provision for credit loss was not necessary. We have no history of credit losses on advances.
Long-term investment debt securities — Long-term investment debt securities are designated as available-for-sale (AFS) or held-to-maturity (HTM). Our investment profile consists almost exclusively of GSE and Agency issued (GSE-issued) securities.
In the AFS portfolio, long-term investments of floating-rate GSE-issued mortgage-backed securities were carried on the balance sheet at fair values of $634.4 million and $281.3 million at September 30, 2021 and December 31, 2020, respectively. Fixed-rate long-term investments in the AFS portfolio, comprising of fixed-rate GSE-issued mortgage-backed securities, were carried on the balance sheet at fair values of $3.9 billion and $3.2 billion at September 30, 2021 and December 31, 2020, respectively.
In the AFS portfolio, long-term investments of floating rate State and local housing finance agency obligations were carried on the balance sheet at fair value of $901.2 million at September 30, 2021 that were transferred from the HTM portfolio in the second quarter of 2021.
In the HTM portfolio, long-term investments were predominantly GSE-issued fixed- and floating-rate mortgage-backed securities and a small portfolio of housing finance agency bonds. Securities in the HTM portfolio are recorded at amortized cost, adjusted for credit and non-credit losses from the application of pre-ASU 2016-13 credit loss standards (formerly referred to as OTTI), and, beginning January 1, 2020, adjusted for allowances for credit losses under the new framework. Fixed- and floating-rate mortgage-backed securities in the HTM portfolio were $9.7 billion and $11.8 billion at September 30, 2021 and December 31, 2020, respectively. No allowance for credit losses were deemed necessary for GSE-issued investments. Allowance for credit losses was $0.2 million and $0.3 million on private-label MBS at September 30, 2021 and December 31, 2020, respectively.
In the HTM portfolio, State and local housing finance agency obligations were $188.2 million at September 30, 2021 and $1.1 billion at December 31, 2020. Allowance for credit losses on State and local housing finance agency obligations in HTM portfolio was $0.1 million and $0.7 million at September 30, 2021 and December 31, 2020, respectively.
Equity Investments — We own a grantor trust that invests in highly-liquid registered mutual funds. Funds are classified as Equity Investments and were carried on the balance sheet at fair values of $91.8 million and $80.4 million at September 30, 2021 and December 31, 2020, respectively.
Mortgage loans held-for-portfolio — Mortgage loans were investments in Mortgage Partnership Finance loans (MPF or MPF Program) and Mortgage Asset Program (MAP®) loans. As of March 2021, the new MAP mortgage loan program became our only mortgage loan purchase program as we ceased to acquire mortgage loans through MPF.
Unpaid principal balance of MPF loans stood at $2.3 billion at September 30, 2021, a decrease of $0.6 billion from the balance at December 31, 2020. Unpaid principal balance of MAP loans stood at $108.2 million at September 30, 2021.
Historically, credit performance has been strong in the MPF portfolio and delinquency low. Residential collateral values have remained stable in the New York and New Jersey sectors, the primary geographic concentration for our MPF portfolio, and historical loss experience remains very low. Serious delinquencies (typically 90 days or more) at September 30, 2021 were lower than December 31, 2020. Allowance for credit losses decreased to $3.0 million at September 30, 2021, compared to $7.1 million at December 31, 2020.
Capital ratios — Our capital position remains strong. At September 30, 2021, actual risk-based capital was $6.4 billion, compared to required risk-based capital of $822.8 million. To support $102.7 billion of total assets at September 30, 2021, the minimum required total capital was $4.1 billion or 4.0% of assets. Our actual regulatory risk-based capital was $6.4 billion, exceeding required total capital by $2.3 billion. These ratios have remained consistently above the required regulatory ratios through all periods in this report.