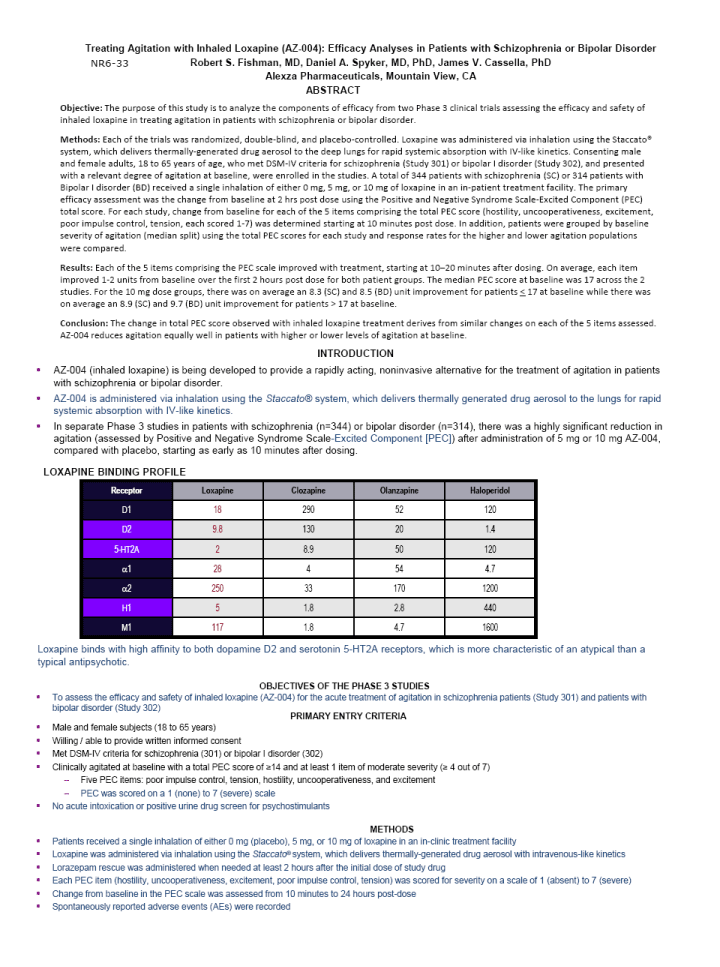
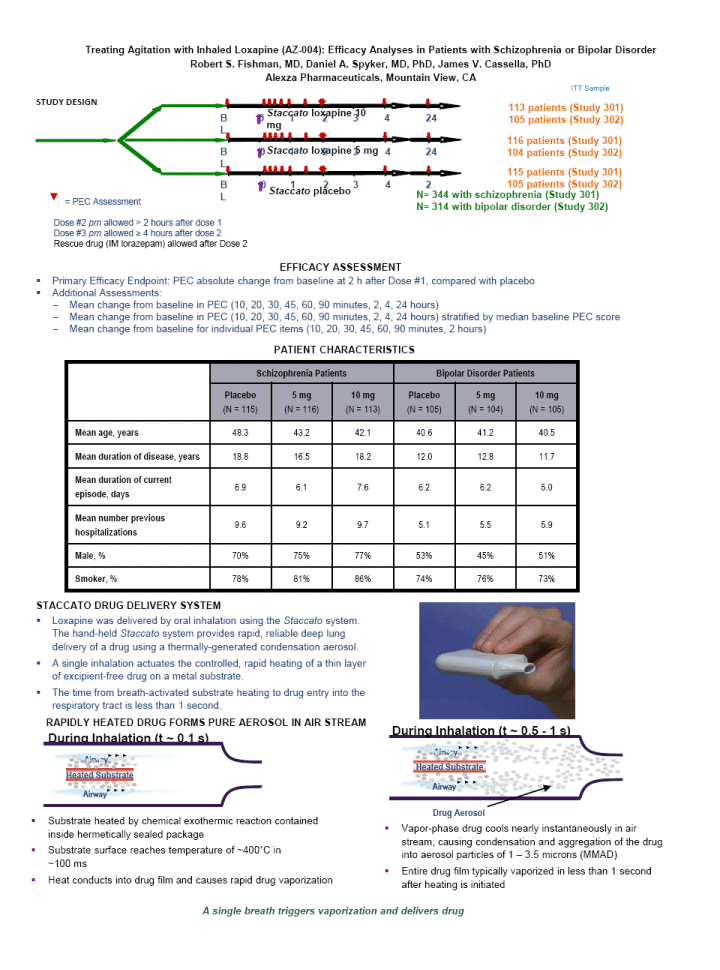
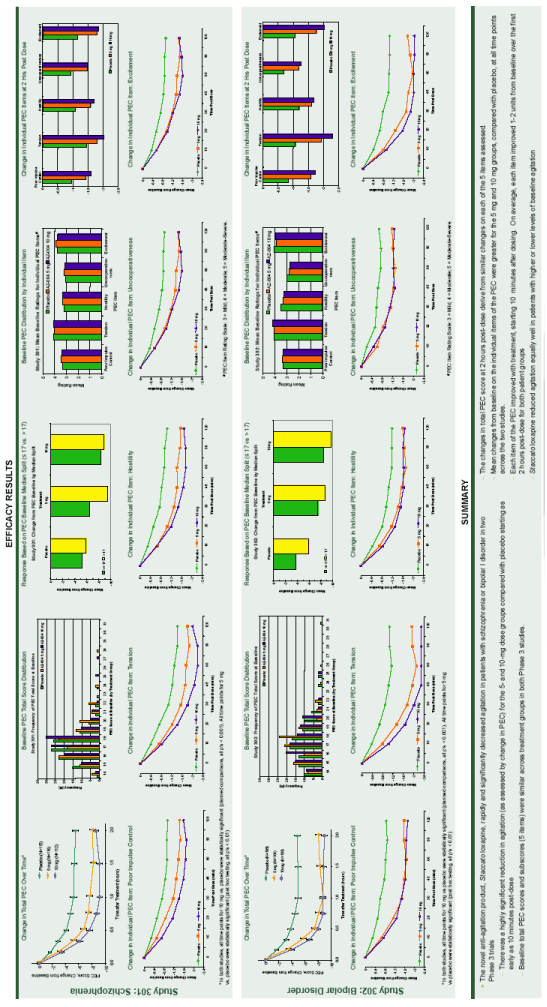
| Treating Agitation with Inhaled Loxapine (AZ-004): Efficacy Analyses in Patients with Schizophrenia or Bipolar Disorder Robert S. Fishman, MD, Daniel A. Spyker, MD, PhD, James V. Cassella, PhD Alexza Pharmaceuticals, Mountain View, CA ABSTRACT Objective: The purpose of this study is to analyze the components of efficacy from two Phase 3 clinical trials assessing the efficacy and safety of inhaled loxapine in treating agitation in patients with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder. Methods: Each of the trials was randomized, double-blind, and placebo-controlled. Loxapine was administered via inhalation using the Staccato(r) system, which delivers thermally-generated drug aerosol to the deep lungs for rapid systemic absorption with IV-like kinetics. Consenting male and female adults, 18 to 65 years of age, who met DSM-IV criteria for schizophrenia (Study 301) or bipolar I disorder (Study 302), and presented with a relevant degree of agitation at baseline, were enrolled in the studies. A total of 344 patients with schizophrenia (SC) or 314 patients with Bipolar I disorder (BD) received a single inhalation of either 0 mg, 5 mg, or 10 mg of loxapine in an in-patient treatment facility. The primary efficacy assessment was the change from baseline at 2 hrs post dose using the Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale-Excited Component (PEC) total score. For each study, change from baseline for each of the 5 items comprising the total PEC score (hostility, uncooperativeness, excitement, poor impulse control, tension, each scored 1-7) was determined starting at 10 minutes post dose. In addition, patients were grouped by baseline severity of agitation (median split) using the total PEC scores for each study and response rates for the higher and lower agitation populations were compared. Results: Each of the 5 items comprising the PEC scale improved with treatment, starting at 10-20 minutes after dosing. On average, each item improved 1-2 units from baseline over the first 2 hours post dose for both patient groups. The median PEC score at baseline was 17 across the 2 studies. For the 10 mg dose groups, there was on average an 8.3 (SC) and 8.5 (BD) unit improvement for patients < 17 at baseline while there was on average an 8.9 (SC) and 9.7 (BD) unit improvement for patients > 17 at baseline. Conclusion: The change in total PEC score observed with inhaled loxapine treatment derives from similar changes on each of the 5 items assessed. AZ-004 reduces agitation equally well in patients with higher or lower levels of agitation at baseline. INTRODUCTION AZ-004 (inhaled loxapine) is being developed to provide a rapidly acting, noninvasive alternative for the treatment of agitation in patients with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder. AZ-004 is administered via inhalation using the Staccato(r) system, which delivers thermally generated drug aerosol to the lungs for rapid systemic absorption with IV-like kinetics. In separate Phase 3 studies in patients with schizophrenia (n=344) or bipolar disorder (n=314), there was a highly significant reduction in agitation (assessed by Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale-Excited Component [PEC]) after administration of 5 mg or 10 mg AZ-004, compared with placebo, starting as early as 10 minutes after dosing. LOXAPINE BINDING PROFILE Receptor Loxapine Clozapine Olanzapine Haloperidol D1 18 290 52 120 D2 9.8 130 20 1.4 5-HT2A 2 8.9 50 120 ?1 28 4 54 4.7 ?2 250 33 170 1200 H1 5 1.8 2.8 440 M1 117 1.8 4.7 1600 Loxapine binds with high affinity to both dopamine D2 and serotonin 5-HT2A receptors, which is more characteristic of an atypical than a typical antipsychotic. OBJECTIVES OF THE PHASE 3 STUDIES To assess the efficacy and safety of inhaled loxapine (AZ-004) for the acute treatment of agitation in schizophrenia patients (Study 301) and patients with bipolar disorder (Study 302) PRIMARY ENTRY CRITERIA Male and female subjects (18 to 65 years) Willing / able to provide written informed consent Met DSM-IV criteria for schizophrenia (301) or bipolar I disorder (302) Clinically agitated at baseline with a total PEC score of ^14 and at least 1 item of moderate severity (^ 4 out of 7) Five PEC items: poor impulse control, tension, hostility, uncooperativeness, and excitement PEC was scored on a 1 (none) to 7 (severe) scale No acute intoxication or positive urine drug screen for psychostimulants METHODS Patients received a single inhalation of either 0 mg (placebo), 5 mg, or 10 mg of loxapine in an in-clinic treatment facility Loxapine was administered via inhalation using the Staccato(r) system, which delivers thermally-generated drug aerosol with intravenous-like kinetics Lorazepam rescue was administered when needed at least 2 hours after the initial dose of study drug Each PEC item (hostility, uncooperativeness, excitement, poor impulse control, tension) was scored for severity on a scale of 1 (absent) to 7 (severe) Change from baseline in the PEC scale was assessed from 10 minutes to 24 hours post-dose Spontaneously reported adverse events (AEs) were recorded NR6-33 |