
Corporate Overview November 2022 Nasdaq: ANAB

2 This presentation and any accompanying oral presentation contain “forward‐looking” statements within the meaning of the "safe harbor" provisions of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995, including, but not limited to: the timing of the release of data from our clinical trials, including imsidolimab’s Phase 3 trial in GPP and rosnilimab’s Phase 2 trial in alopecia areata; timing of an IND filing for ANB032; timing of initiation of ANB032’s Phase 2 trial; timing of an IND filing for ANB033; the predicted mechanisms of action of our drug candidates; expectations regarding the commercial potential and anticipated peak annual global sales of JEMPERLI, the timing and potential amount of milestones and royalty payments to be received under the GSK partnership and benefits expected from the agreements with Sagard and DRI Healthcare Trust; and our projected 2022 operating expenditure. Statements including words such as “plan,” “continue,” “expect,” or “ongoing” and statements in the future tense are forward‐ looking statements. These forward‐looking statements involve risks and uncertainties, as well as assumptions, which, if they do not fully materialize or prove incorrect, could cause our results to differ materially from those expressed or implied by such forward‐ looking statements. Forward‐looking statements are subject to risks and uncertainties that may cause the company’s actual activities or results to differ significantly from those expressed in any forward‐looking statement, including risks and uncertainties related to the company’s ability to advance its product candidates, obtain regulatory approval of and ultimately commercialize its product candidates, the timing and results of preclinical and clinical trials, the company’s ability to fund development activities and achieve development goals, the company’s ability to protect intellectual property and other risks and uncertainties described under the heading “Risk Factors” in documents the company files from time to time with the Securities and Exchange Commission. These forward‐looking statements speak only as of the date of this presentation, and the company undertakes no obligation to revise or update any forward‐looking statements to reflect events or circumstances after the date hereof. Certain information contained in this presentation may be derived from information provided by industry sources. The Company believes such information is accurate and that the sources from which it has been obtained are reliable. However, the Company cannot guarantee the accuracy of, and has not independently verified, such information. The trademarks included herein are the property of the owners thereof and are used for reference purposes only. Such use should not be construed as an endorsement of such products. Safe Harbor Statement
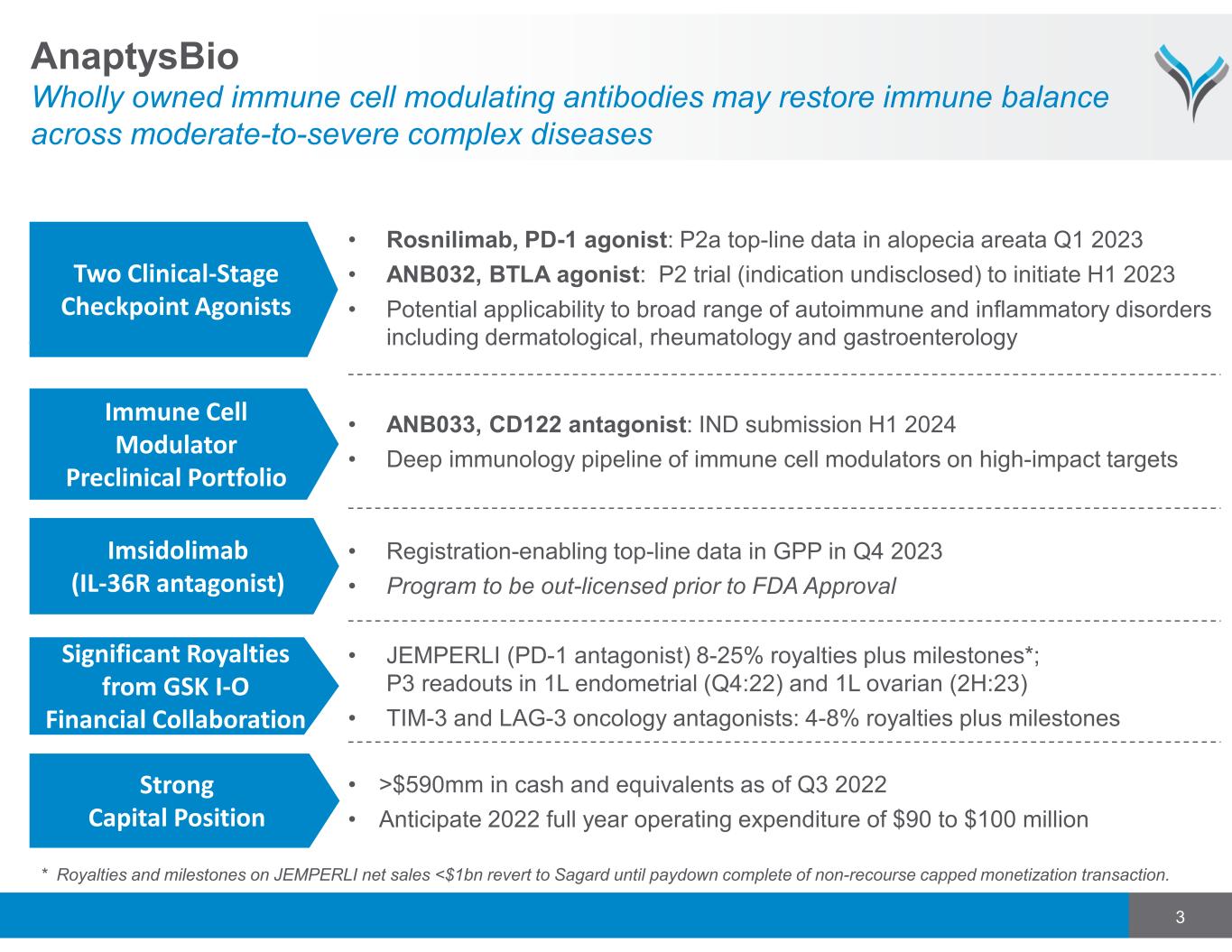
3 AnaptysBio Wholly owned immune cell modulating antibodies may restore immune balance across moderate-to-severe complex diseases Significant Royalties from GSK I-O Financial Collaboration • JEMPERLI (PD-1 antagonist) 8-25% royalties plus milestones*; P3 readouts in 1L endometrial (Q4:22) and 1L ovarian (2H:23) • TIM-3 and LAG-3 oncology antagonists: 4-8% royalties plus milestones Strong Capital Position • >$590mm in cash and equivalents as of Q3 2022 • Anticipate 2022 full year operating expenditure of $90 to $100 million Immune Cell Modulator Preclinical Portfolio • ANB033, CD122 antagonist: IND submission H1 2024 • Deep immunology pipeline of immune cell modulators on high-impact targets Two Clinical-Stage Checkpoint Agonists • Rosnilimab, PD-1 agonist: P2a top-line data in alopecia areata Q1 2023 • ANB032, BTLA agonist: P2 trial (indication undisclosed) to initiate H1 2023 • Potential applicability to broad range of autoimmune and inflammatory disorders including dermatological, rheumatology and gastroenterology • Registration-enabling top-line data in GPP in Q4 2023 • Program to be out-licensed prior to FDA Approval Imsidolimab (IL-36R antagonist) * Royalties and milestones on JEMPERLI net sales <$1bn revert to Sagard until paydown complete of non-recourse capped monetization transaction.
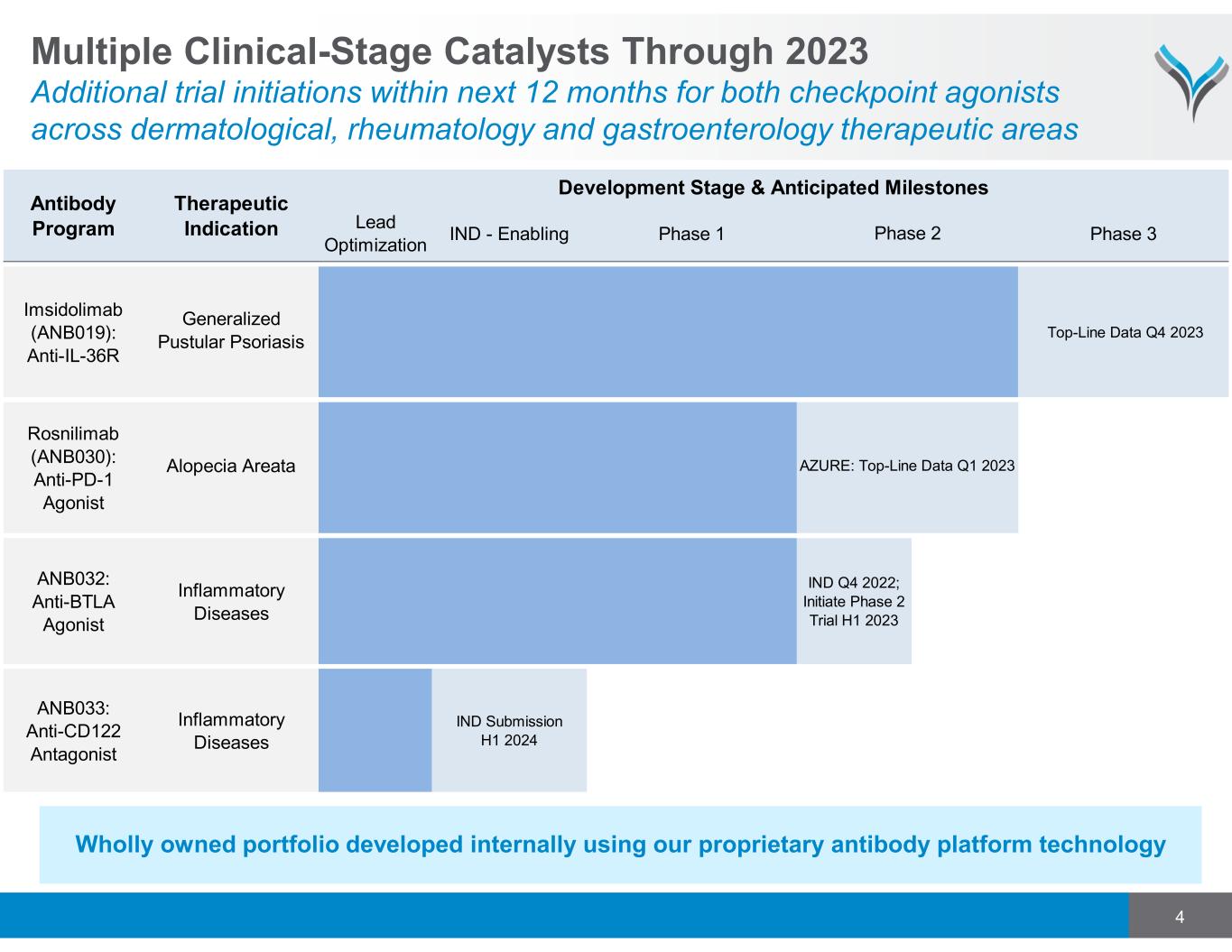
4 Wholly owned portfolio developed internally using our proprietary antibody platform technology Multiple Clinical-Stage Catalysts Through 2023 Additional trial initiations within next 12 months for both checkpoint agonists across dermatological, rheumatology and gastroenterology therapeutic areas Lead Optimization IND - Enabling Phase 1 Phase 3 Generalized Pustular Psoriasis Alopecia Areata ANB032: Anti-BTLA Agonist Inflammatory Diseases IND Q4 2022; Initiate Phase 2 Trial H1 2023 ANB033: Anti-CD122 Antagonist Inflammatory Diseases IND Submission H1 2024 Rosnilimab (ANB030): Anti-PD-1 Agonist AZURE: Top-Line Data Q1 2023 Antibody Program Therapeutic Indication Development Stage & Anticipated Milestones Phase 2 Imsidolimab (ANB019): Anti-IL-36R Top-Line Data Q4 2023

Advantages of Immune Cell Modulation in Treatment of Inflammatory Diseases
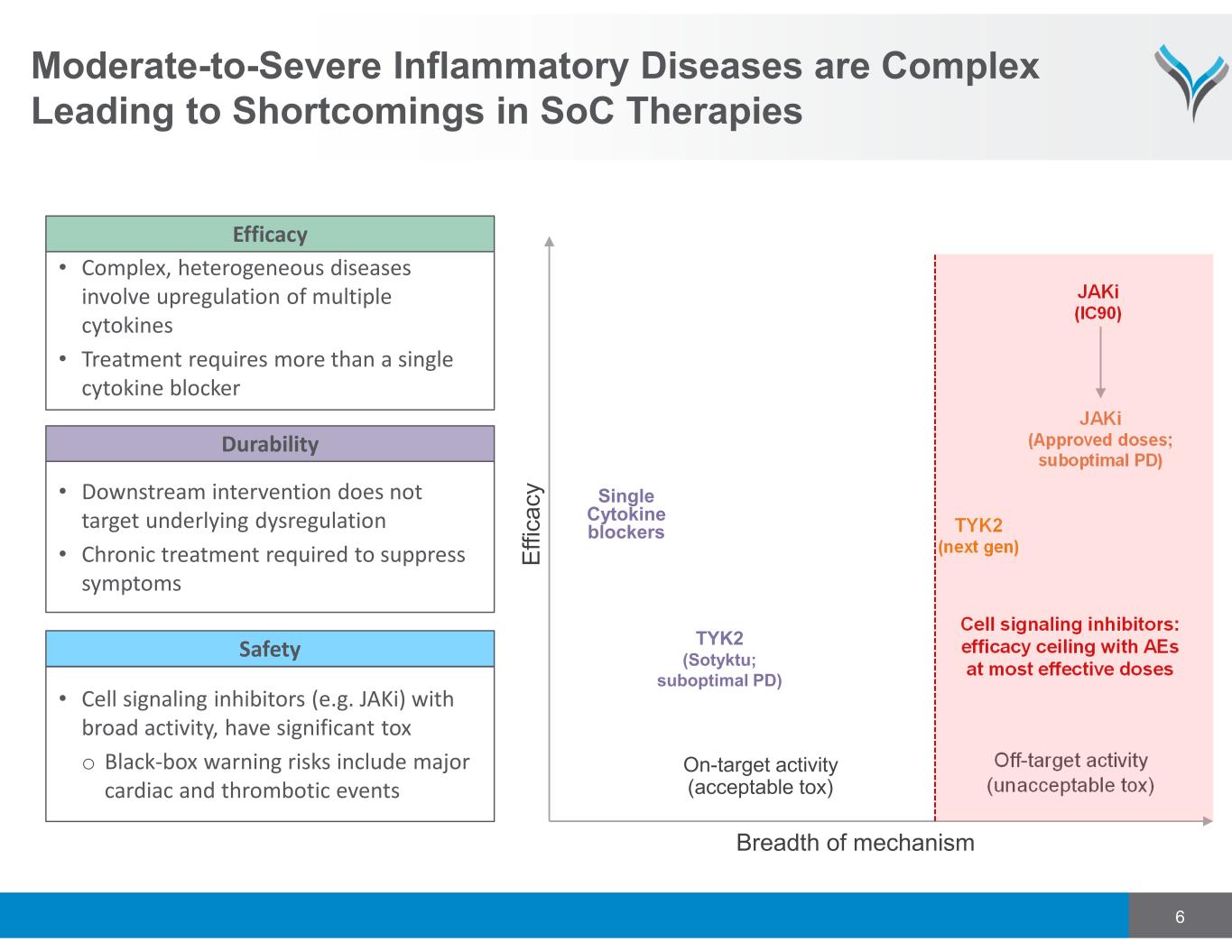
6 Moderate-to-Severe Inflammatory Diseases are Complex Leading to Shortcomings in SoC Therapies Breadth of mechanism JAKi (IC90) JAKi (Approved doses; suboptimal PD) Cell signaling inhibitors: efficacy ceiling with AEs at most effective doses TYK2 (next gen) • Complex, heterogeneous diseases involve upregulation of multiple cytokines • Treatment requires more than a single cytokine blocker Efficacy • Downstream intervention does not target underlying dysregulation • Chronic treatment required to suppress symptoms Durability • Cell signaling inhibitors (e.g. JAKi) with broad activity, have significant tox o Black‐box warning risks include major cardiac and thrombotic events Safety Single Cytokine blockers TYK2 (Sotyktu; suboptimal PD) E ff ic a c y On-target activity (acceptable tox) Off-target activity (unacceptable tox)
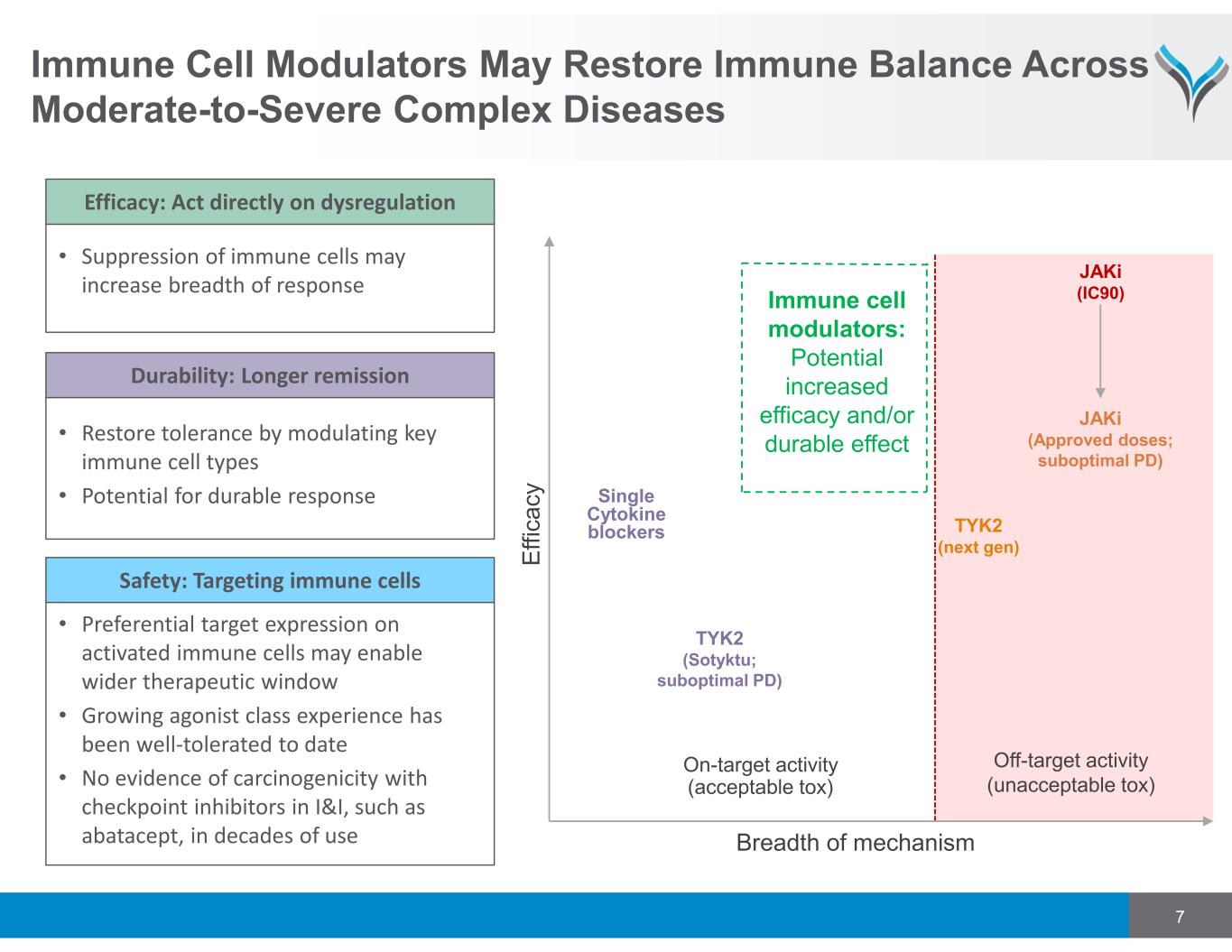
7 Immune Cell Modulators May Restore Immune Balance Across Moderate-to-Severe Complex Diseases JAKi (IC90) JAKi (Approved doses; suboptimal PD) Immune cell modulators: Potential increased efficacy and/or durable effect E ff ic a c y Single Cytokine blockers TYK2 (Sotyktu; suboptimal PD) Breadth of mechanism On-target activity (acceptable tox) Off-target activity (unacceptable tox) TYK2 (next gen) • Suppression of immune cells may increase breadth of response Efficacy: Act directly on dysregulation • Restore tolerance by modulating key immune cell types • Potential for durable response Durability: Longer remission • Preferential target expression on activated immune cells may enable wider therapeutic window • Growing agonist class experience has been well‐tolerated to date • No evidence of carcinogenicity with checkpoint inhibitors in I&I, such as abatacept, in decades of use Safety: Targeting immune cells
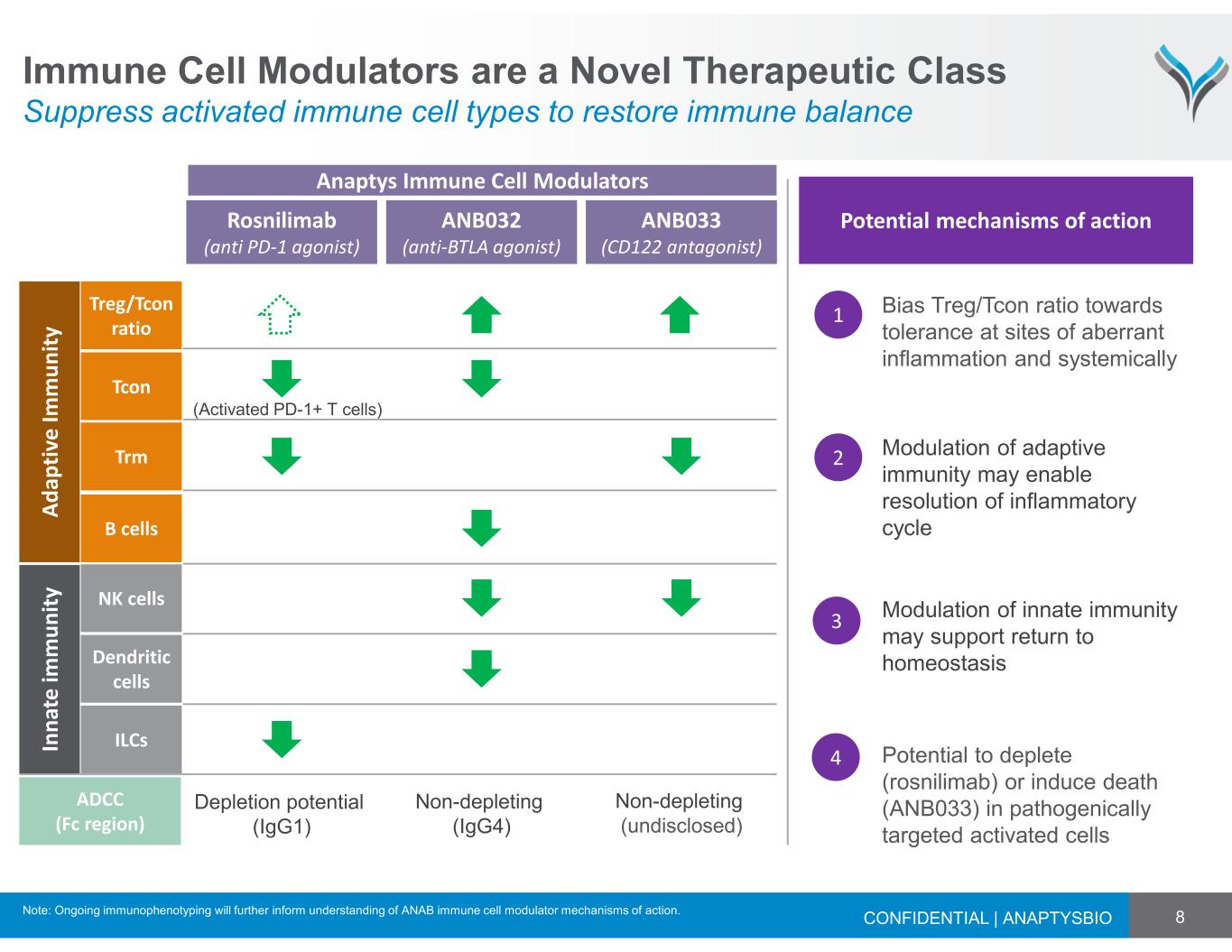
8 Immune Cell Modulators are a Novel Therapeutic Class Suppress activated immune cell types to restore immune balance CONFIDENTIAL | ANAPTYSBIO ANB033 (CD122 antagonist) ANB032 (anti-BTLA agonist) Rosnilimab (anti PD-1 agonist) A d a p ti v e I m m u n it y B cells Trm Tcon Treg/Tcon ratio In n a te i m m u n it y NK cells ILCs Dendritic cells Potential mechanisms of action 1 Bias Treg/Tcon ratio towards tolerance at sites of aberrant inflammation and systemically Potential to deplete (rosnilimab) or induce death (ANB033) in pathogenically targeted activated cells 4 ADCC (Fc region) Depletion potential (IgG1) Non-depleting (IgG4) Non-depleting (undisclosed) Modulation of innate immunity may support return to homeostasis 3 2 Modulation of adaptive immunity may enable resolution of inflammatory cycle (Activated PD-1+ T cells) Anaptys Immune Cell Modulators Note: Ongoing immunophenotyping will further inform understanding of ANAB immune cell modulator mechanisms of action.

Checkpoint Agonists: Rosnilimab (Anti-PD-1 agonist mAb) ANB032 (Anti-BTLA agonist mAb) Autoimmune and Inflammatory Diseases
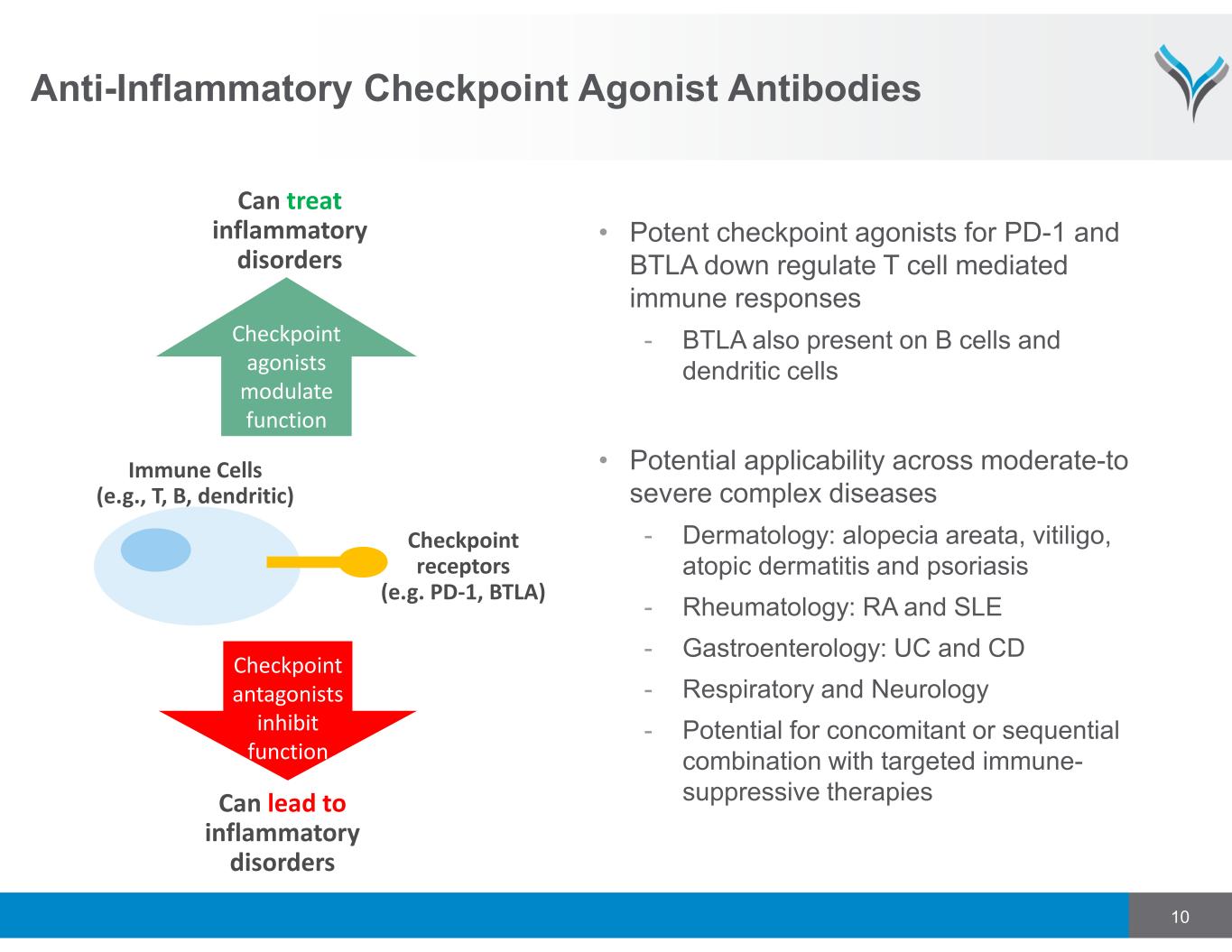
10 Anti-Inflammatory Checkpoint Agonist Antibodies • Potent checkpoint agonists for PD-1 and BTLA down regulate T cell mediated immune responses - BTLA also present on B cells and dendritic cells • Potential applicability across moderate-to severe complex diseases - Dermatology: alopecia areata, vitiligo, atopic dermatitis and psoriasis - Rheumatology: RA and SLE - Gastroenterology: UC and CD - Respiratory and Neurology - Potential for concomitant or sequential combination with targeted immune- suppressive therapies Immune Cells (e.g., T, B, dendritic) Checkpoint receptors (e.g. PD-1, BTLA) Can lead to inflammatory disorders Checkpoint antagonists inhibit function Checkpoint agonists modulate function Can treat inflammatory disorders
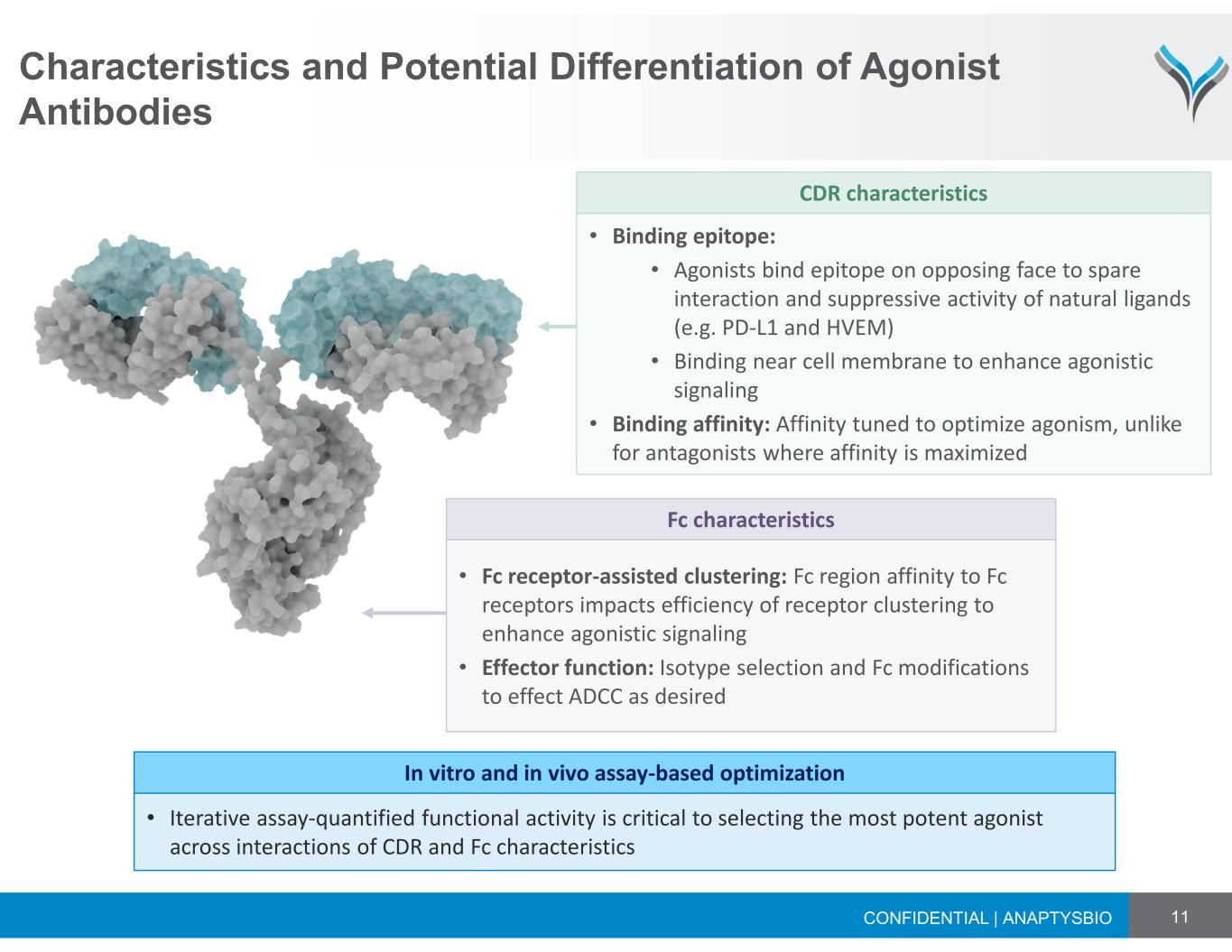
11 Characteristics and Potential Differentiation of Agonist Antibodies CONFIDENTIAL | ANAPTYSBIO • Iterative assay‐quantified functional activity is critical to selecting the most potent agonist across interactions of CDR and Fc characteristics In vitro and in vivo assay-based optimization • Binding epitope: • Agonists bind epitope on opposing face to spare interaction and suppressive activity of natural ligands (e.g. PD‐L1 and HVEM) • Binding near cell membrane to enhance agonistic signaling • Binding affinity: Affinity tuned to optimize agonism, unlike for antagonists where affinity is maximized CDR characteristics • Fc receptor-assisted clustering: Fc region affinity to Fc receptors impacts efficiency of receptor clustering to enhance agonistic signaling • Effector function: Isotype selection and Fc modifications to effect ADCC as desired Fc characteristics
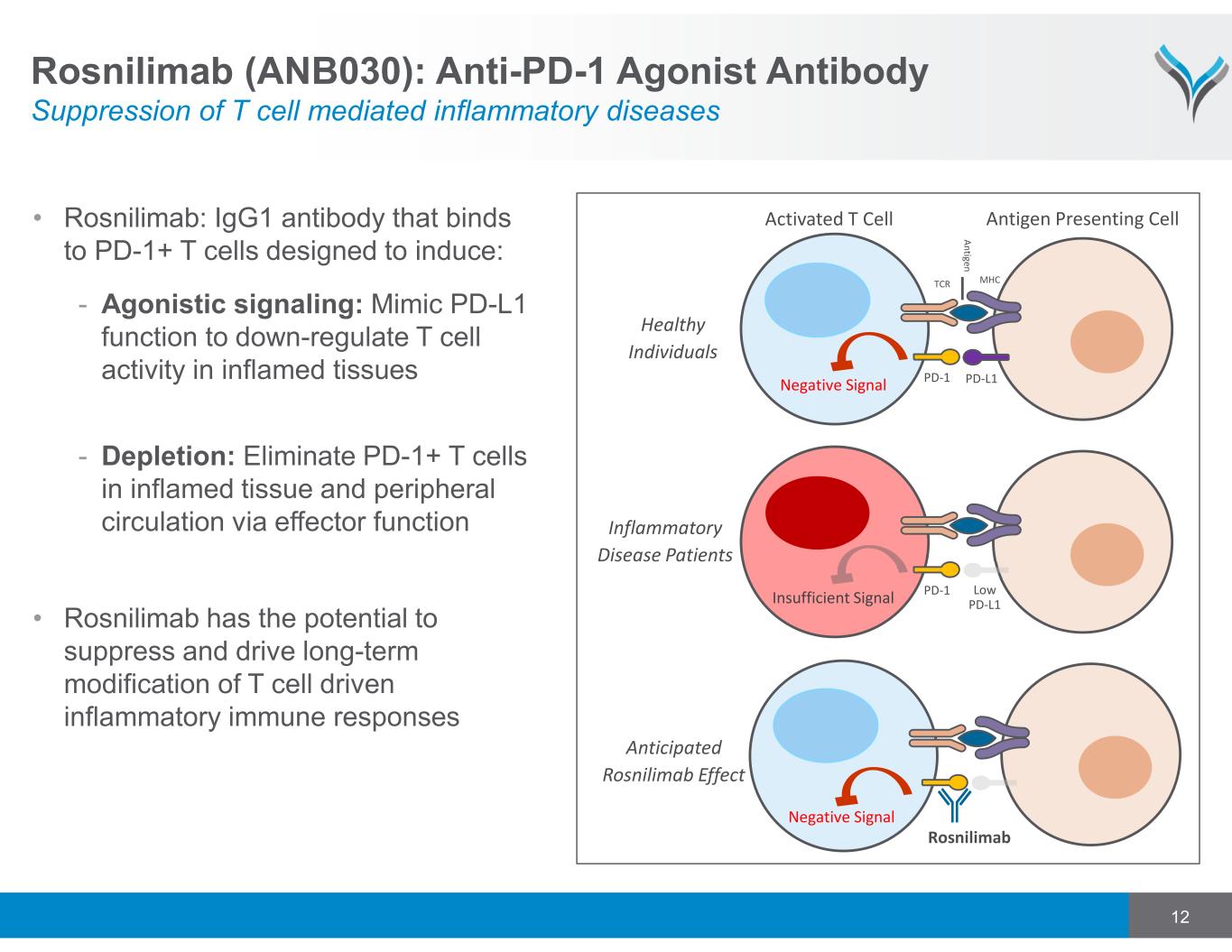
12 • Rosnilimab: IgG1 antibody that binds to PD-1+ T cells designed to induce: - Agonistic signaling: Mimic PD-L1 function to down-regulate T cell activity in inflamed tissues - Depletion: Eliminate PD-1+ T cells in inflamed tissue and peripheral circulation via effector function • Rosnilimab has the potential to suppress and drive long-term modification of T cell driven inflammatory immune responses Negative Signal Anticipated Rosnilimab Effect Activated T Cell MHC A n tig e n TCR PD‐L1PD‐1 Negative Signal Antigen Presenting Cell Healthy Individuals Low PD‐L1 PD‐1 Insufficient Signal Inflammatory Disease Patients Rosnilimab Rosnilimab (ANB030): Anti-PD-1 Agonist Antibody Suppression of T cell mediated inflammatory diseases
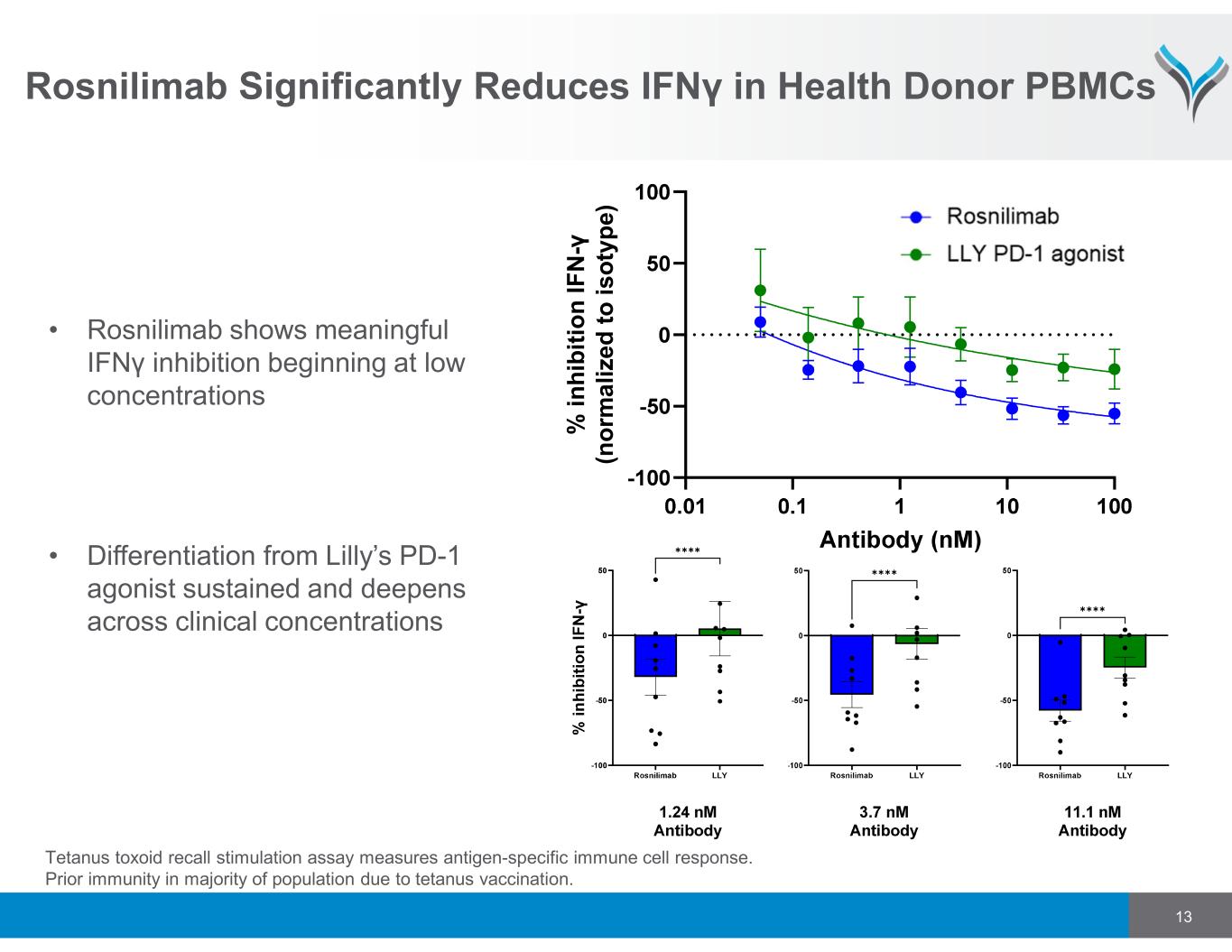
Rosnilimab Significantly Reduces IFNγ in Health Donor PBMCs ✱✱✱✱ ✱✱✱✱ ✱✱✱✱ % i n h ib it io n I F N -γ (n o rm a li z e d t o i s o ty p e ) • Rosnilimab shows meaningful IFNγ inhibition beginning at low concentrations • Differentiation from Lilly’s PD-1 agonist sustained and deepens across clinical concentrations 13 Tetanus toxoid recall stimulation assay measures antigen-specific immune cell response. Prior immunity in majority of population due to tetanus vaccination.
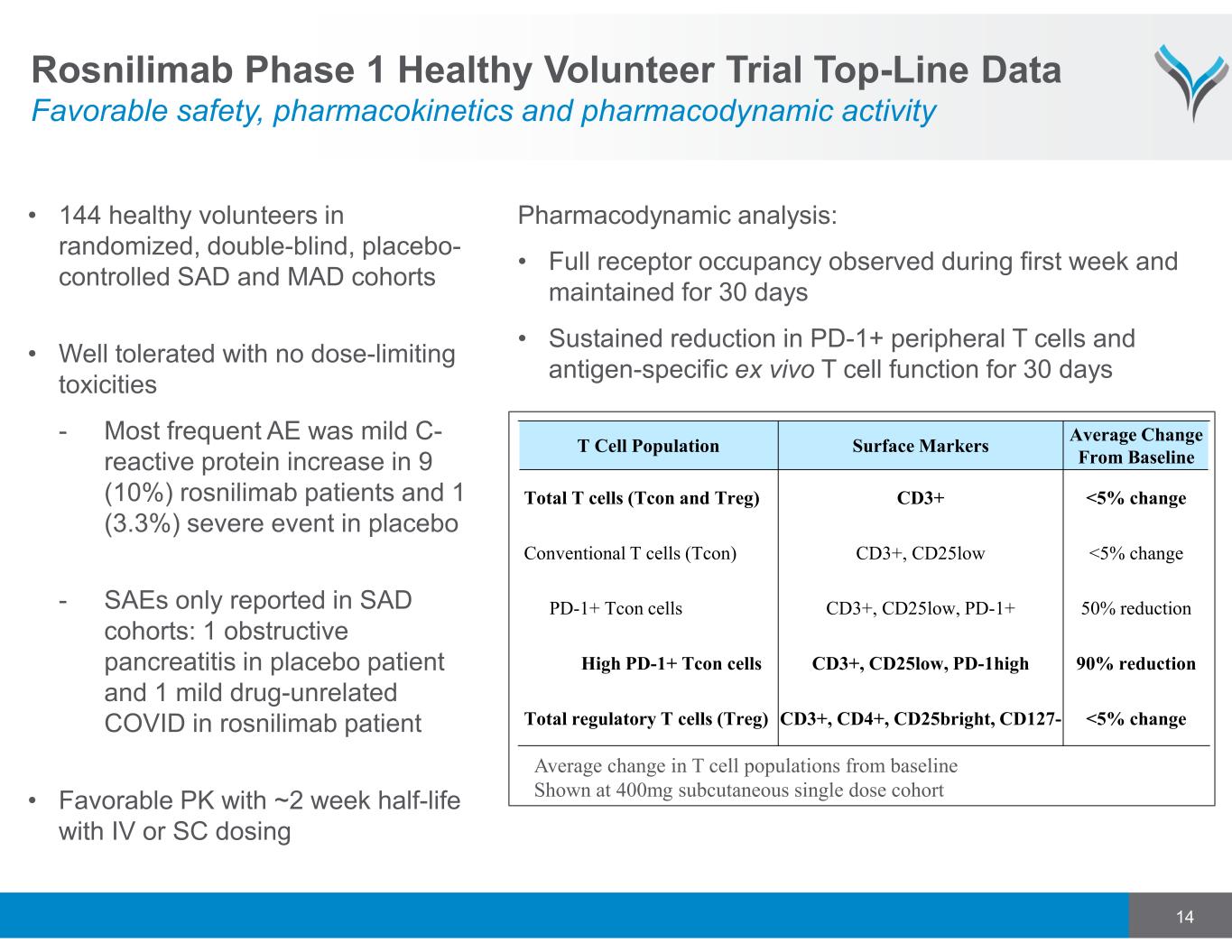
14 T Cell Population Surface Markers Average Change From Baseline Total T cells (Tcon and Treg) CD3+ <5% change Conventional T cells (Tcon) CD3+, CD25low <5% change PD-1+ Tcon cells CD3+, CD25low, PD-1+ 50% reduction High PD-1+ Tcon cells CD3+, CD25low, PD-1high 90% reduction Total regulatory T cells (Treg) CD3+, CD4+, CD25bright, CD127- <5% change Average change in T cell populations from baseline Shown at 400mg subcutaneous single dose cohort Pharmacodynamic analysis: • Full receptor occupancy observed during first week and maintained for 30 days • Sustained reduction in PD-1+ peripheral T cells and antigen-specific ex vivo T cell function for 30 days Rosnilimab Phase 1 Healthy Volunteer Trial Top-Line Data Favorable safety, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamic activity • 144 healthy volunteers in randomized, double-blind, placebo- controlled SAD and MAD cohorts • Well tolerated with no dose-limiting toxicities - Most frequent AE was mild C- reactive protein increase in 9 (10%) rosnilimab patients and 1 (3.3%) severe event in placebo - SAEs only reported in SAD cohorts: 1 obstructive pancreatitis in placebo patient and 1 mild drug-unrelated COVID in rosnilimab patient • Favorable PK with ~2 week half-life with IV or SC dosing
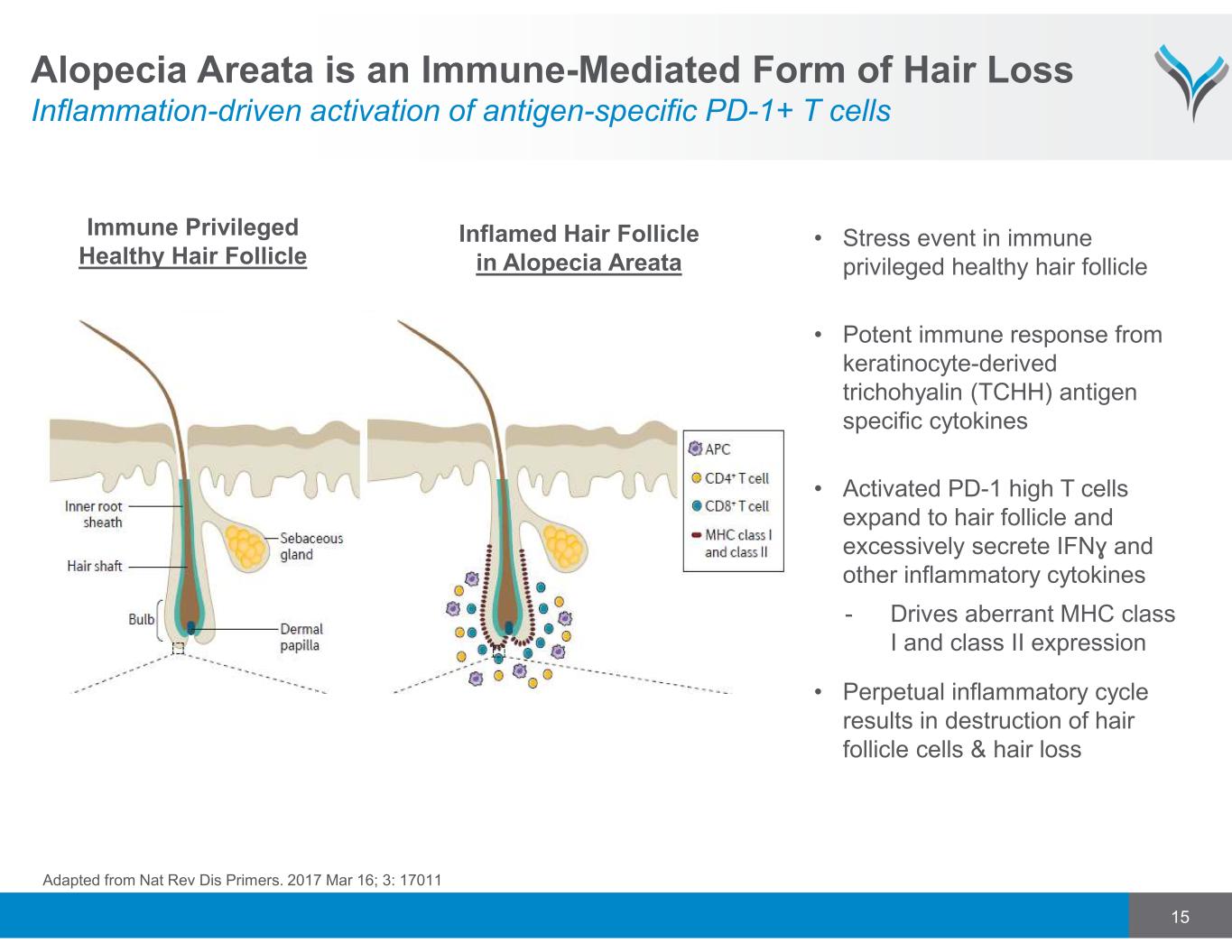
15 Alopecia Areata is an Immune-Mediated Form of Hair Loss Inflammation-driven activation of antigen-specific PD-1+ T cells • Stress event in immune privileged healthy hair follicle • Potent immune response from keratinocyte-derived trichohyalin (TCHH) antigen specific cytokines • Activated PD-1 high T cells expand to hair follicle and excessively secrete IFNɣ and other inflammatory cytokines - Drives aberrant MHC class I and class II expression • Perpetual inflammatory cycle results in destruction of hair follicle cells & hair loss Immune Privileged Healthy Hair Follicle Adapted from Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017 Mar 16; 3: 17011 Inflamed Hair Follicle in Alopecia Areata
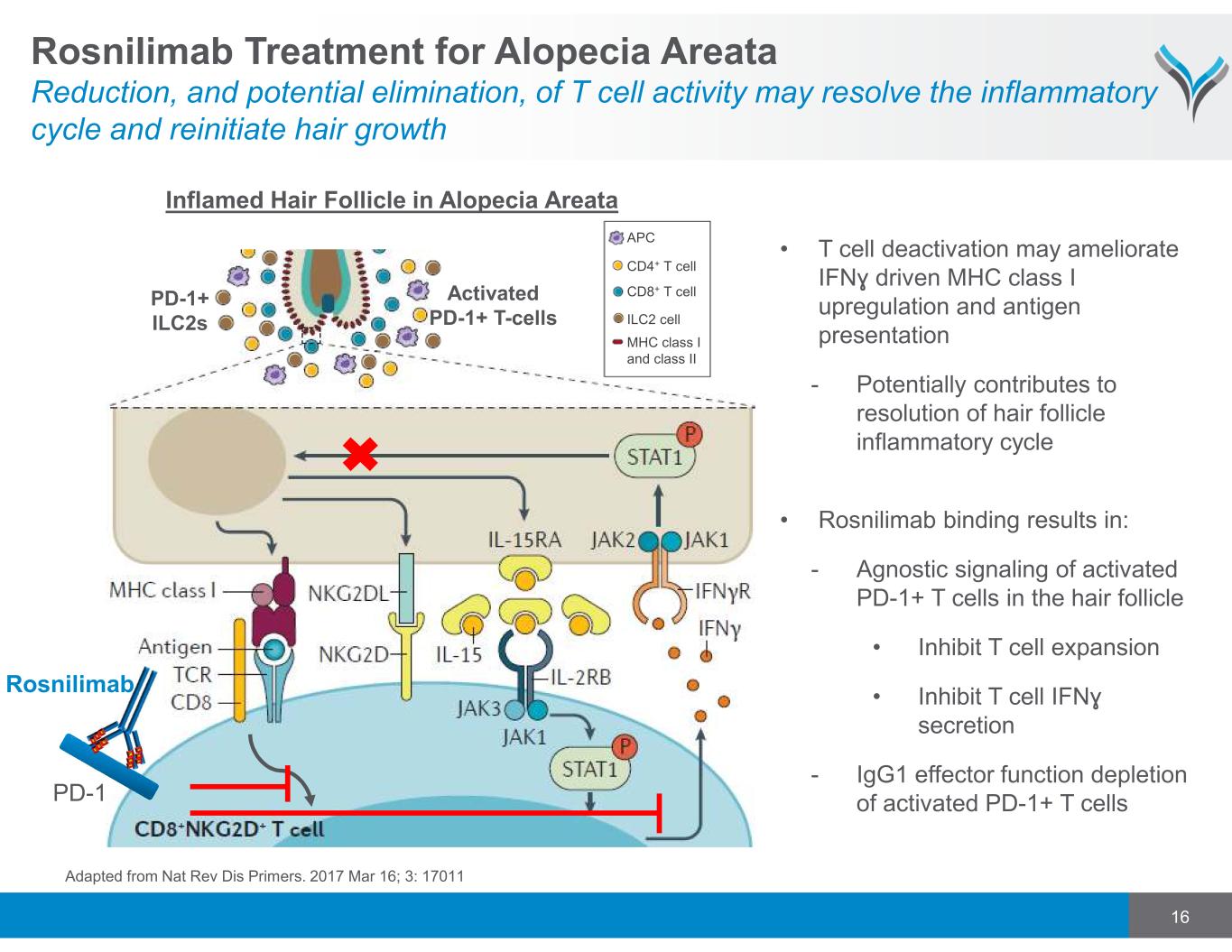
16 • T cell deactivation may ameliorate IFNɣ driven MHC class I upregulation and antigen presentation - Potentially contributes to resolution of hair follicle inflammatory cycle • Rosnilimab binding results in: - Agnostic signaling of activated PD-1+ T cells in the hair follicle • Inhibit T cell expansion • Inhibit T cell IFNɣ secretion - IgG1 effector function depletion of activated PD-1+ T cells Inflamed Hair Follicle in Alopecia Areata Activated PD-1+ T-cells PD-1 Rosnilimab Adapted from Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017 Mar 16; 3: 17011 Rosnilimab Treatment for Alopecia Areata Reduction, and potential elimination, of T cell activity may resolve the inflammatory cycle and reinitiate hair growth PD-1+ ILC2s APC CD4+ T cell CD8+ T cell ILC2 cell MHC class I and class II
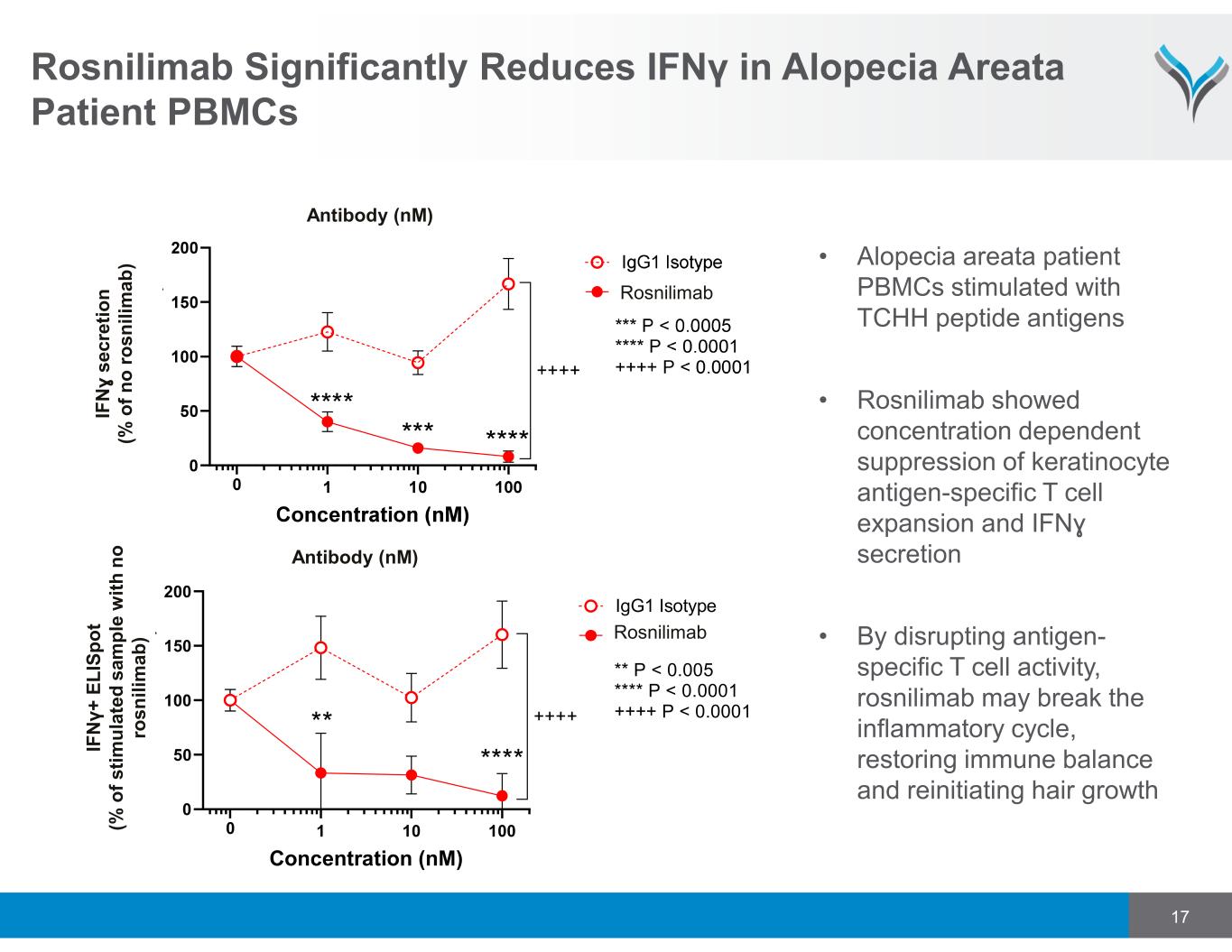
17 Rosnilimab Significantly Reduces IFNγ in Alopecia Areata Patient PBMCs IF N ɣ s e c re ti o n (% o f n o r o s n il im a b ) Antibody (nM) Antibody (nM) Rosnilimab • Alopecia areata patient PBMCs stimulated with TCHH peptide antigens • Rosnilimab showed concentration dependent suppression of keratinocyte antigen-specific T cell expansion and IFNɣ secretion • By disrupting antigen- specific T cell activity, rosnilimab may break the inflammatory cycle, restoring immune balance and reinitiating hair growth 1 10 100 0 50 100 150 200 Concentration (nM) IgG1 Isotype ANB030 0 ** **** ++++ ** P < 0.005 **** P < 0.0001 ++++ P < 0.0001 IF N γ + E L IS p o t (% o f s ti m u la te d s a m p le w it h n o ro s n il im a b ) Rosnilimab
18 Rosnilimab May Show Differentiated Efficacy and Safety for the Treatment of Alopecia Areata “Proof-of-mechanism” P2a trial may inform development in additional diseases Market Dynamics Favorable Clinical Trial Attributes • Up to ~1.5 million U.S. patients - >40% of patients estimated to have ≥50% loss of scalp hair • Chronic condition with substantial quality of life impact: depression, anxiety, other inflammatory conditions • JAKi leave significant unmet need for patients with moderate-to-severe disease - Significant safety concerns: thrombosis and cardiac events - Durability of effect requires chronic (daily and continuous) treatment • Antigen-specific T-cell driven disease • Low and consistent placebo response rates for regulatory endpoint(s) • Do not require concurrent alopecia areata treatment(s) Source: NAAF, National Alopecia Areata Foundation, Benigno M. Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology 2020
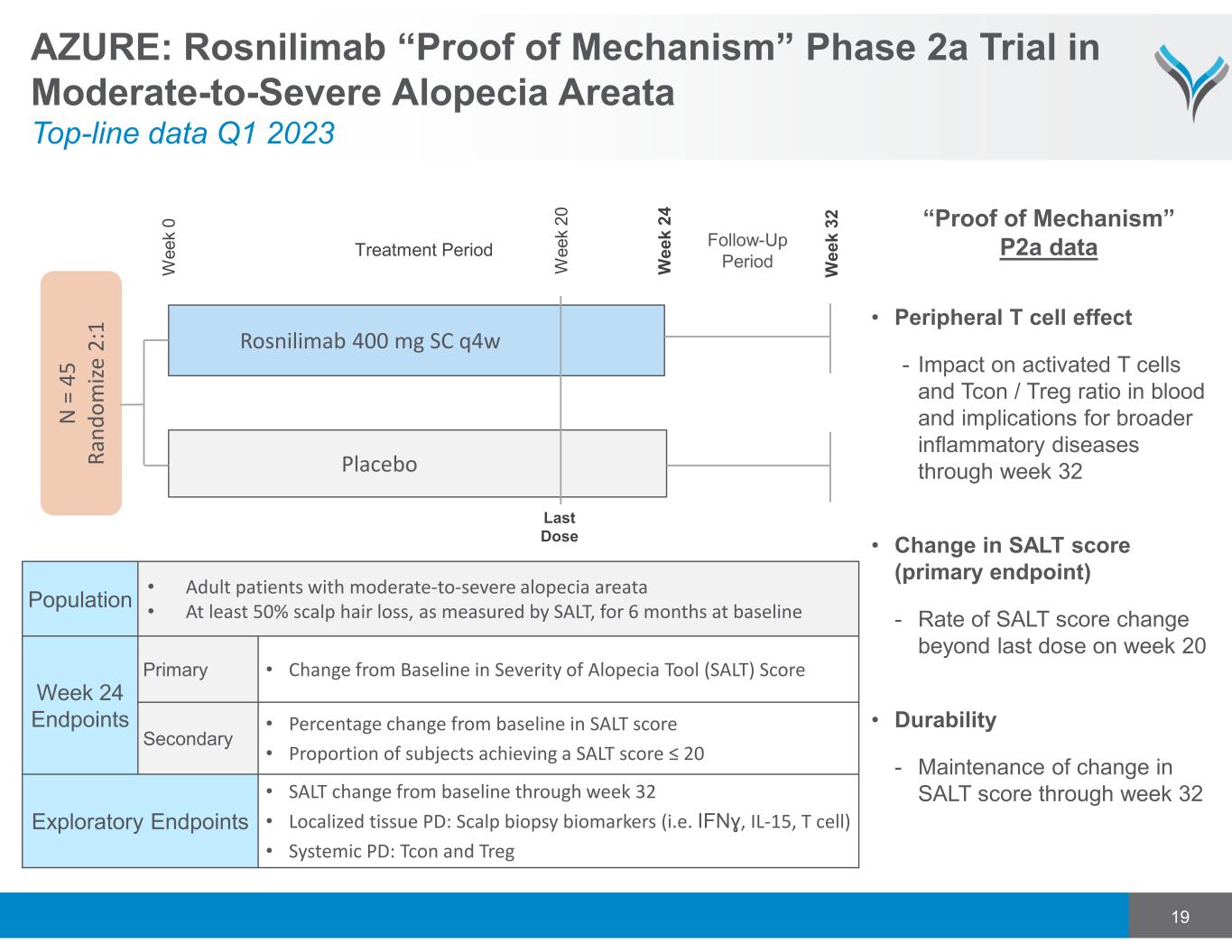
19 AZURE: Rosnilimab “Proof of Mechanism” Phase 2a Trial in Moderate-to-Severe Alopecia Areata Top-line data Q1 2023 Rosnilimab 400 mg SC q4w N = 4 5 R a n d o m iz e 2 :1 Placebo Treatment Period Follow-Up Period W e e k 0 W e e k 2 4 W e e k 3 2 Population • Adult patients with moderate‐to‐severe alopecia areata • At least 50% scalp hair loss, as measured by SALT, for 6 months at baseline Week 24 Endpoints Primary • Change from Baseline in Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) Score Secondary • Percentage change from baseline in SALT score • Proportion of subjects achieving a SALT score ≤ 20 Exploratory Endpoints • SALT change from baseline through week 32 • Localized tissue PD: Scalp biopsy biomarkers (i.e. IFNɣ, IL‐15, T cell) • Systemic PD: Tcon and Treg W e e k 2 0 Last Dose • Peripheral T cell effect - Impact on activated T cells and Tcon / Treg ratio in blood and implications for broader inflammatory diseases through week 32 • Change in SALT score (primary endpoint) - Rate of SALT score change beyond last dose on week 20 • Durability - Maintenance of change in SALT score through week 32 “Proof of Mechanism” P2a data
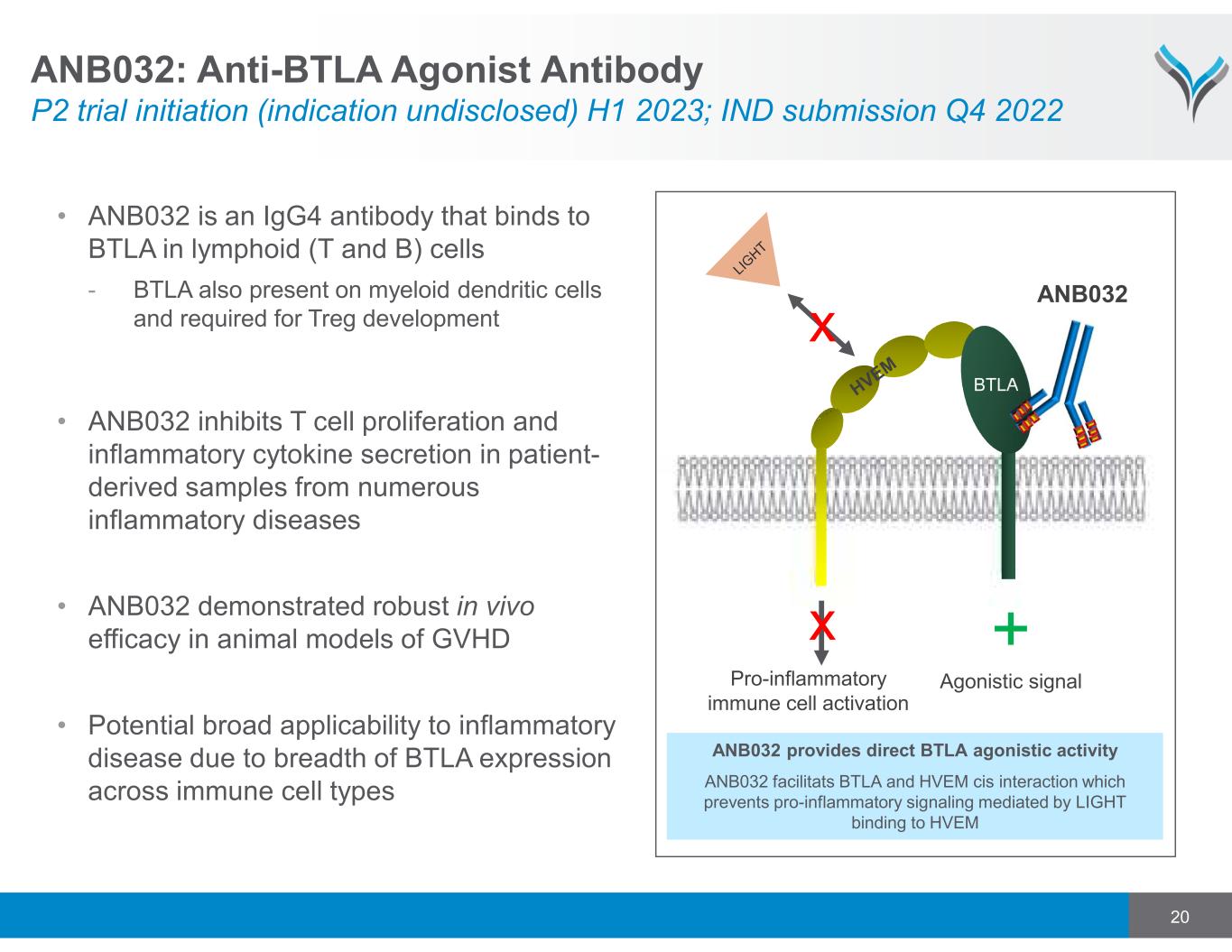
20 • ANB032 is an IgG4 antibody that binds to BTLA in lymphoid (T and B) cells - BTLA also present on myeloid dendritic cells and required for Treg development • ANB032 inhibits T cell proliferation and inflammatory cytokine secretion in patient- derived samples from numerous inflammatory diseases • ANB032 demonstrated robust in vivo efficacy in animal models of GVHD • Potential broad applicability to inflammatory disease due to breadth of BTLA expression across immune cell types Pro-inflammatory immune cell activation x BTLA x ANB032 ANB032 provides direct BTLA agonistic activity ANB032 facilitats BTLA and HVEM cis interaction which prevents pro-inflammatory signaling mediated by LIGHT binding to HVEM + Agonistic signal ANB032: Anti-BTLA Agonist Antibody P2 trial initiation (indication undisclosed) H1 2023; IND submission Q4 2022
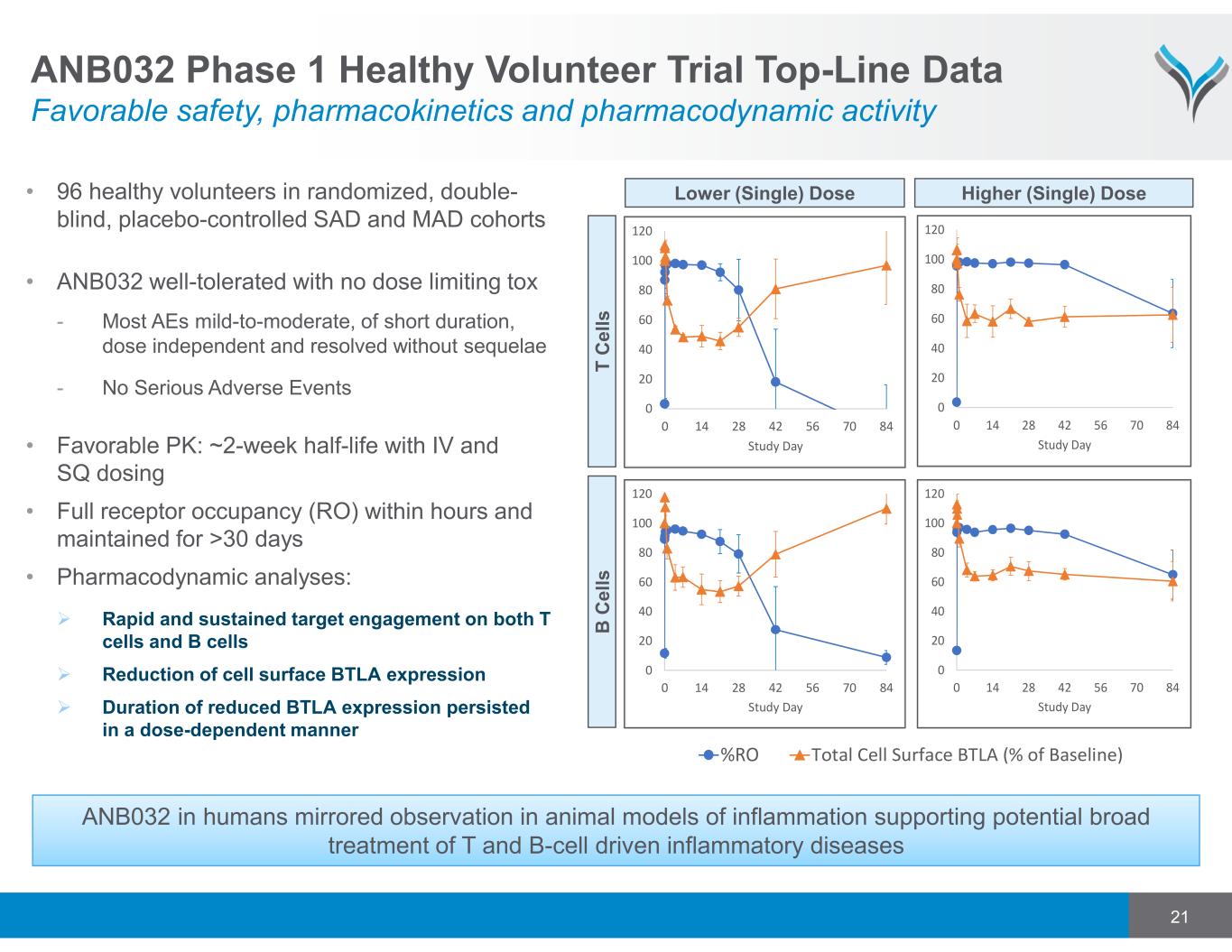
21 • 96 healthy volunteers in randomized, double- blind, placebo-controlled SAD and MAD cohorts • ANB032 well-tolerated with no dose limiting tox - Most AEs mild-to-moderate, of short duration, dose independent and resolved without sequelae - No Serious Adverse Events • Favorable PK: ~2-week half-life with IV and SQ dosing • Full receptor occupancy (RO) within hours and maintained for >30 days • Pharmacodynamic analyses: Rapid and sustained target engagement on both T cells and B cells Reduction of cell surface BTLA expression Duration of reduced BTLA expression persisted in a dose-dependent manner ANB032 Phase 1 Healthy Volunteer Trial Top-Line Data Favorable safety, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamic activity ANB032 in humans mirrored observation in animal models of inflammation supporting potential broad treatment of T and B-cell driven inflammatory diseases T C e ll s B C e ll s Lower (Single) Dose Higher (Single) Dose 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 0 14 28 42 56 70 84 Study Day 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 0 14 28 42 56 70 84 Study Day 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 0 14 28 42 56 70 84 Study Day 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 0 14 28 42 56 70 84 Study Day Total Cell Surface BTLA (% of Baseline)%RO

ANB033 (Anti-CD122 antagonist mAb) Autoimmune and Inflammatory Diseases

Confidential 23 CD122 is a shared beta subunit of the receptors for IL-15 and IL-2 • IL-15 mediates survival of TRM cells • Both IL-15 and IL-2 mediate: - Proliferation of T cells - Inflammatory cytokine secretion (IFNγ) during T cell activation • High affinity antagonist antibody induces death in TRM cells by preferentially inhibiting the lower affinity dimeric receptor complex - Spares Tregs which express higher affinity IL-2 trimeric receptor complex • Targeted elimination of TRM cells may potentially drive durable responses ANB033 MoA: Induce death of TRM cells to achieve and maintain remission Tregs TRM cells CD122 CD122 ANB033: Anti-CD122 Antagonist mAb Targets Pathogenic Tissue Resident Memory T cells (TRM) IND filing targeted H1 2024 ANB033
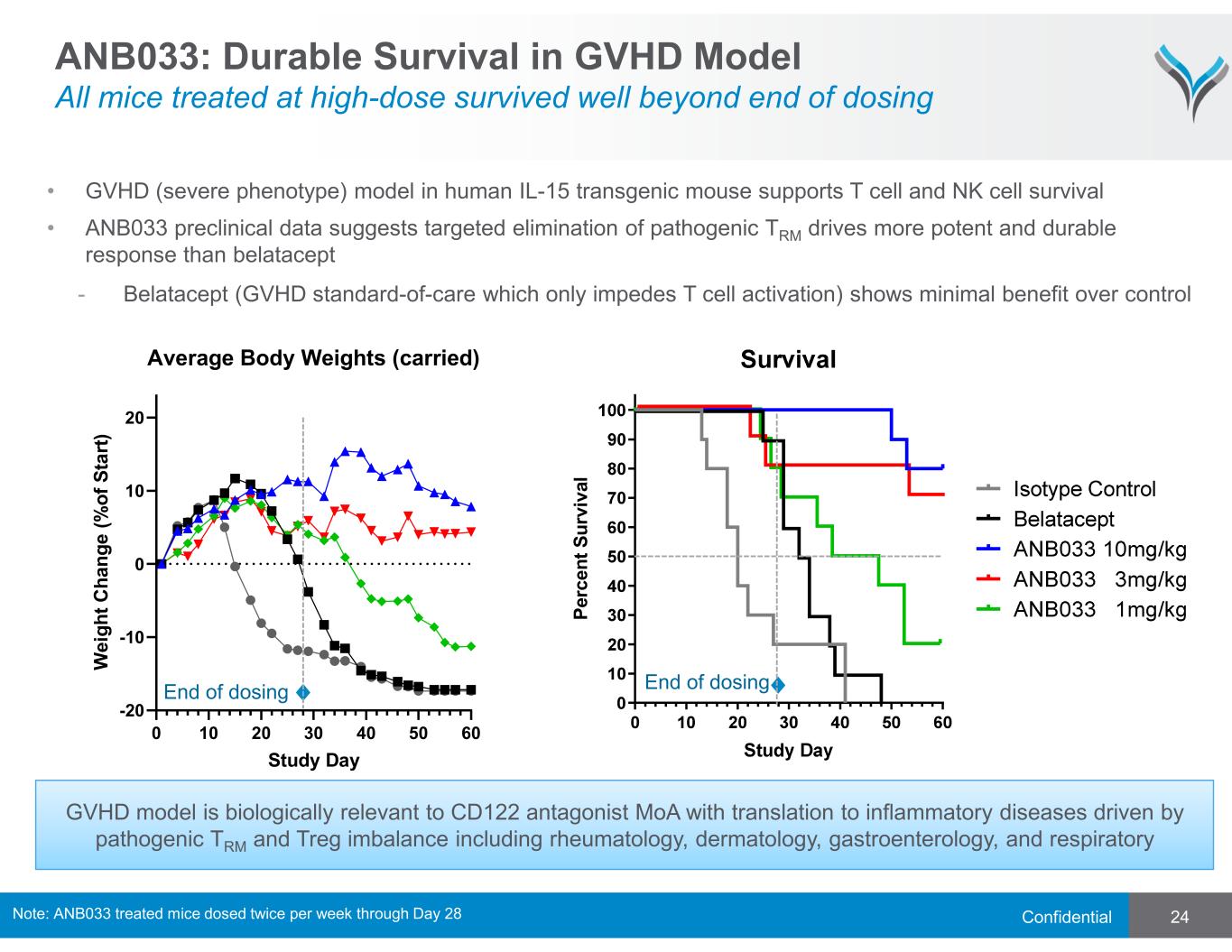
Confidential 24 ANB033: Durable Survival in GVHD Model All mice treated at high-dose survived well beyond end of dosing P e rc e n t S u rv iv a l End of dosing GVHD model is biologically relevant to CD122 antagonist MoA with translation to inflammatory diseases driven by pathogenic TRM and Treg imbalance including rheumatology, dermatology, gastroenterology, and respiratory 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 -20 -10 0 10 20 Average Body Weights (carried) Study Day W e ig h t C h a n g e ( % o f S ta rt ) • GVHD (severe phenotype) model in human IL-15 transgenic mouse supports T cell and NK cell survival • ANB033 preclinical data suggests targeted elimination of pathogenic TRM drives more potent and durable response than belatacept - Belatacept (GVHD standard-of-care which only impedes T cell activation) shows minimal benefit over control End of dosing Note: ANB033 treated mice dosed twice per week through Day 28

Imsidolimab (Anti-IL-36r antagonist mAb) Generalized Pustular Psoriasis (GPP)

26 • GPP is a systemic, life-threatening inflammatory disease characterized by widespread pustules - Associated with unregulated IL-36 signaling - Patients have a high fever and elevated levels of serum CRP and inflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-8) - Severe GPP patients can die from cardio-pulmonary failure, exhaustion, toxicity and infection • GPP ICD-10 diagnostic code analysis by IQVIA assessed US prevalence during 2017-2019 timeframe - ~37,000 unique patients diagnosed at least once - ~15,000 unique patients diagnosed two or more times • FDA has granted Orphan Drug Designation to imsidolimab for the treatment of GPP • Worldwide registry (RADIANCE) of GPP patients ongoing – Increase understanding of patient journey and support enrollment of Phase 3 trial Generalized Pustular Psoriasis (GPP) Systemic inflammatory disease where IL-36 pathway plays key role in pathology
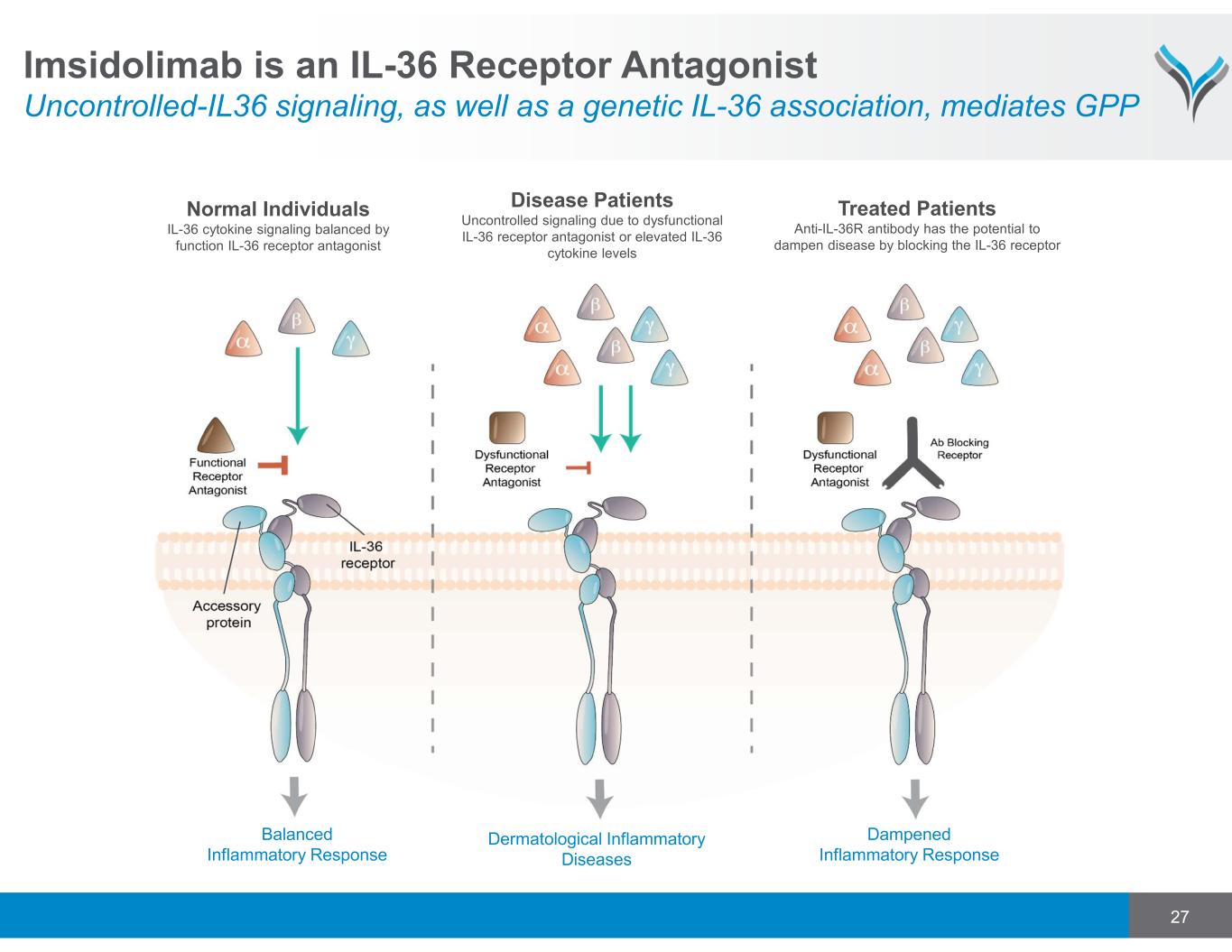
Normal Individuals IL-36 cytokine signaling balanced by function IL-36 receptor antagonist Disease Patients Uncontrolled signaling due to dysfunctional IL-36 receptor antagonist or elevated IL-36 cytokine levels Treated Patients Anti-IL-36R antibody has the potential to dampen disease by blocking the IL-36 receptor 27 Dampened Inflammatory Response Dermatological Inflammatory Diseases Balanced Inflammatory Response Imsidolimab is an IL-36 Receptor Antagonist Uncontrolled-IL36 signaling, as well as a genetic IL-36 association, mediates GPP
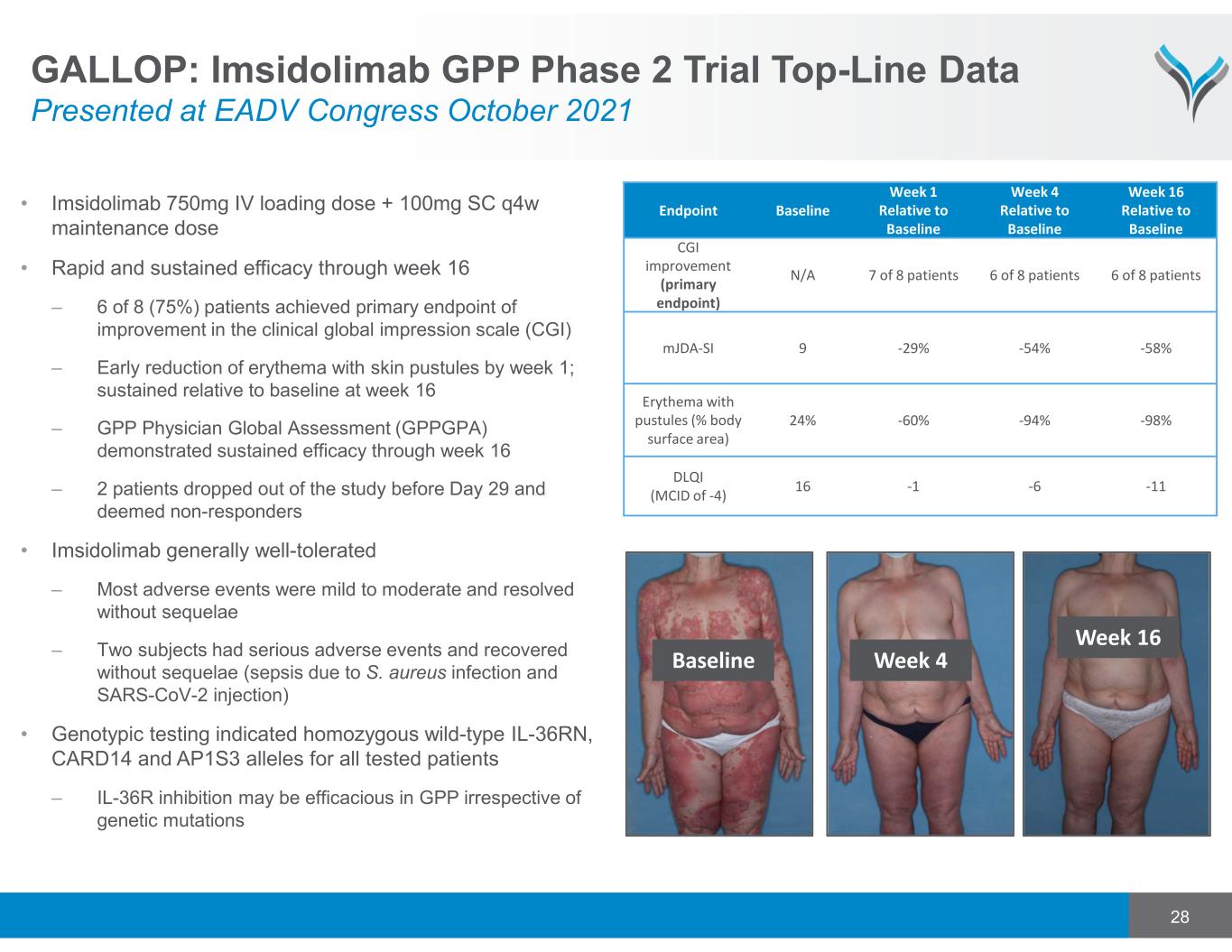
28 • Imsidolimab 750mg IV loading dose + 100mg SC q4w maintenance dose • Rapid and sustained efficacy through week 16 – 6 of 8 (75%) patients achieved primary endpoint of improvement in the clinical global impression scale (CGI) – Early reduction of erythema with skin pustules by week 1; sustained relative to baseline at week 16 – GPP Physician Global Assessment (GPPGPA) demonstrated sustained efficacy through week 16 – 2 patients dropped out of the study before Day 29 and deemed non-responders • Imsidolimab generally well-tolerated – Most adverse events were mild to moderate and resolved without sequelae – Two subjects had serious adverse events and recovered without sequelae (sepsis due to S. aureus infection and SARS-CoV-2 injection) • Genotypic testing indicated homozygous wild-type IL-36RN, CARD14 and AP1S3 alleles for all tested patients – IL-36R inhibition may be efficacious in GPP irrespective of genetic mutations Endpoint Baseline Week 1 Relative to Baseline Week 4 Relative to Baseline Week 16 Relative to Baseline CGI improvement (primary endpoint) N/A 7 of 8 patients 6 of 8 patients 6 of 8 patients mJDA‐SI 9 ‐29% ‐54% ‐58% Erythema with pustules (% body surface area) 24% ‐60% ‐94% ‐98% DLQI (MCID of ‐4) 16 ‐1 ‐6 ‐11 Baseline Week 4 Week 16 GALLOP: Imsidolimab GPP Phase 2 Trial Top-Line Data Presented at EADV Congress October 2021
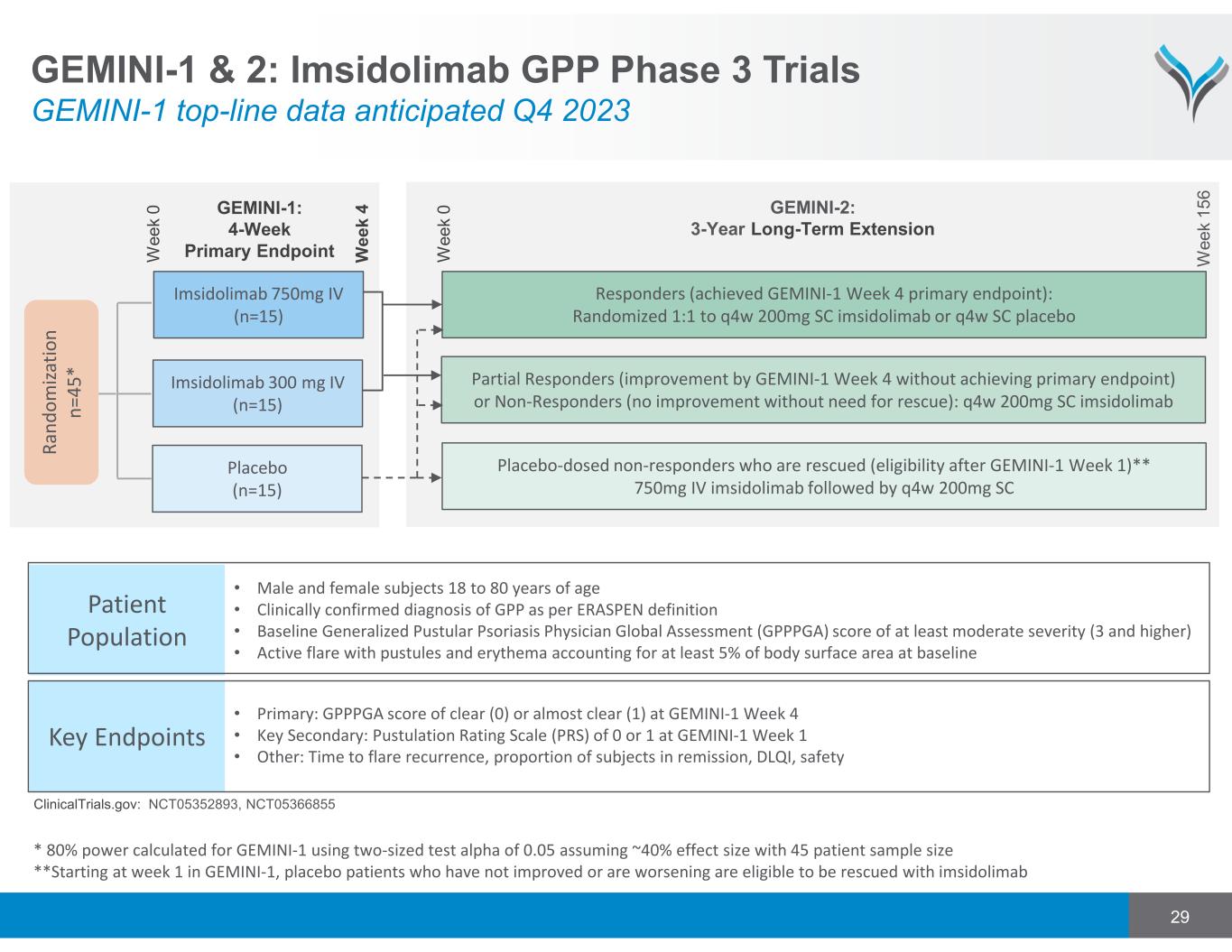
29 Patient Population R a n d o m iz a ti o n n = 4 5 * W e e k 0 Key Endpoints • Male and female subjects 18 to 80 years of age • Clinically confirmed diagnosis of GPP as per ERASPEN definition • Baseline Generalized Pustular Psoriasis Physician Global Assessment (GPPPGA) score of at least moderate severity (3 and higher) • Active flare with pustules and erythema accounting for at least 5% of body surface area at baseline • Primary: GPPPGA score of clear (0) or almost clear (1) at GEMINI‐1 Week 4 • Key Secondary: Pustulation Rating Scale (PRS) of 0 or 1 at GEMINI‐1 Week 1 • Other: Time to flare recurrence, proportion of subjects in remission, DLQI, safety Placebo (n=15) Responders (achieved GEMINI‐1 Week 4 primary endpoint): Randomized 1:1 to q4w 200mg SC imsidolimab or q4w SC placebo W e e k 1 5 6 GEMINI-1: 4-Week Primary Endpoint W e e k 4 Partial Responders (improvement by GEMINI‐1 Week 4 without achieving primary endpoint) or Non‐Responders (no improvement without need for rescue): q4w 200mg SC imsidolimab Placebo‐dosed non‐responders who are rescued (eligibility after GEMINI‐1 Week 1)** 750mg IV imsidolimab followed by q4w 200mg SC GEMINI-2: 3-Year Long-Term Extension * 80% power calculated for GEMINI‐1 using two‐sized test alpha of 0.05 assuming ~40% effect size with 45 patient sample size **Starting at week 1 in GEMINI‐1, placebo patients who have not improved or are worsening are eligible to be rescued with imsidolimab W e e k 0 Imsidolimab 300 mg IV (n=15) Imsidolimab 750mg IV (n=15) GEMINI-1 & 2: Imsidolimab GPP Phase 3 Trials GEMINI-1 top-line data anticipated Q4 2023 ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT05352893, NCT05366855

GSK Immuno-Oncology Financial Collaboration JEMPERLITM (dostarlimab, anti-PD-1 Antagonist) Cobolimab (GSK4069889, anti-TIM-3 Antagonist) GSK4074386 (TSR-033, anti-LAG-3 Antagonist)

31 JEMPERLI (anti‐PD‐1 antagonist) GSK anticipates ~$1.2‐2.4B peak annual sales for JEPMPERLI in currently approved indications and anticipated 1L endometrial/ovarian approvals* • JEMPERLI 12‐25% royalties on annual net sales ≥ $1B • JEMPERLI $75mm commercial milestone on annual net sales ≥ $1B In 2H21, ANAB received $250mm upfront in exchange for only the above receivables until Sagard is paid back one of the following capped returns: : • $312.5MM (125% of upfront) by end 2026 or • $337.5MM (135% of upfront) by end 2027 or • $412.5MM (165% of upfront) anytime after 2027 Sagard: JEMPERLI Capped Non‐Recourse Monetization Cobolimab (anti‐TIM‐3 antagonist) GSK4074386 (anti‐LAG‐3 antagonist) • Both programs being developed in combination with JEMPERLI • 4‐8% royalties on annual net sales on each program • $10mm clinical development, $90mm regulatory and $165mm commercial milestones on each program * In June 2021, GSK estimated potential peak annual global JEMPERLI sales on a non‐risk adjusted basis of £1‐£2 billion Note: Sale of ZEJULA (niraparib) royalty interest in September 2022 to wholly‐owned subsidiary of DRI Healthcare Trust for $35mm upfront + $10mm potential milestone upon FDA approval of ZEJULA for the treatment of endometrial cancer, for which the drug is currently in a fully‐enrolled ongoing RUBY Phase 3 study of dostarlimab + niraparib, to the extent that such approval occurs on or before 12/31/25. Significant Residual Royalties from GSK Immuno-Oncology Financial Collaboration Receivables Excluded from Sagard Monetization • JEMPERLI 8% royalties on annual net sales <$1B • JEMPERLI $15mm regulatory and $90MM commercial milestone on annual net sales <$1B
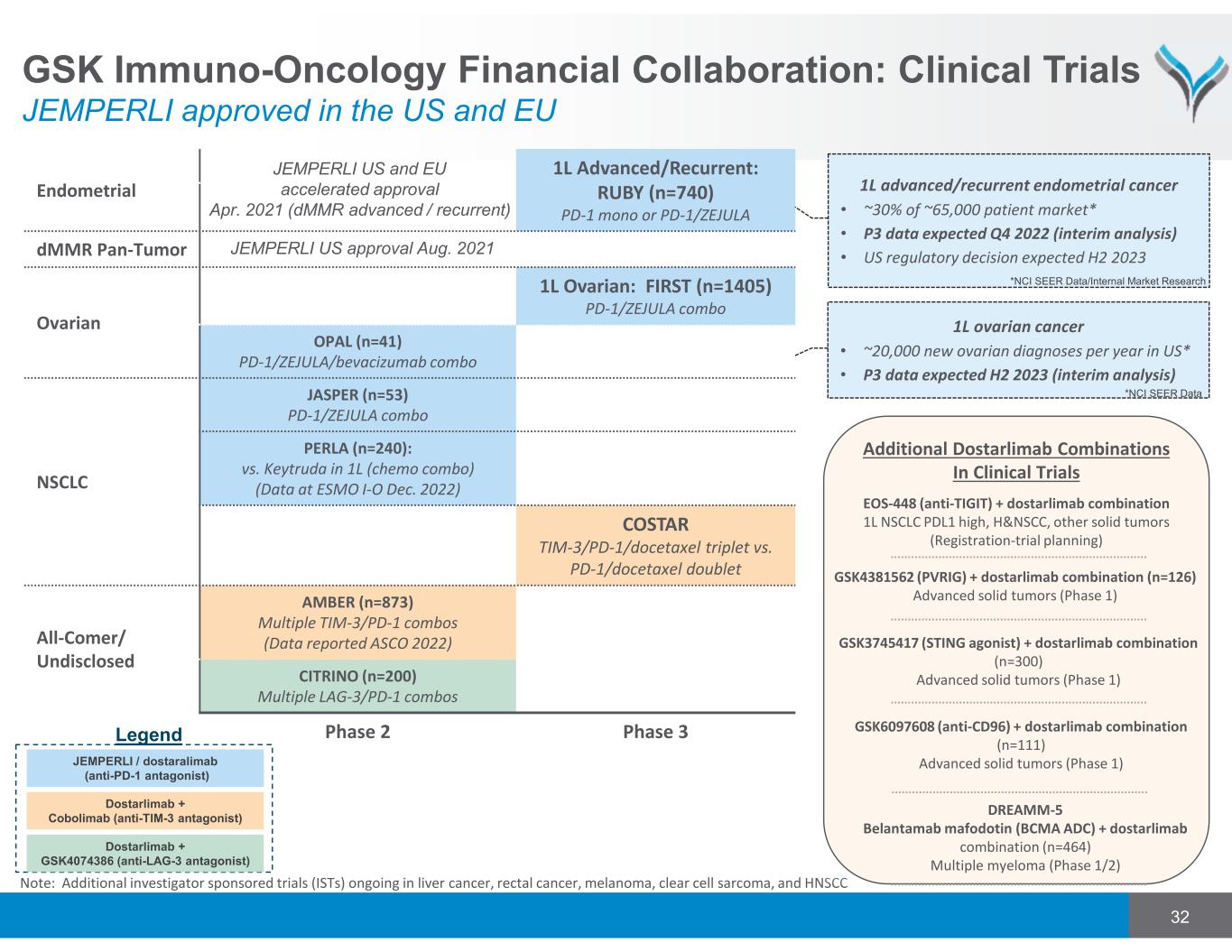
Endometrial 1L Advanced/Recurrent: RUBY (n=740) PD-1 mono or PD-1/ZEJULA dMMR Pan-Tumor Ovarian 1L Ovarian: FIRST (n=1405) PD-1/ZEJULA combo OPAL (n=41) PD-1/ZEJULA/bevacizumab combo NSCLC JASPER (n=53) PD-1/ZEJULA combo PERLA (n=240): vs. Keytruda in 1L (chemo combo) (Data at ESMO I-O Dec. 2022) COSTAR TIM-3/PD-1/docetaxel triplet vs. PD-1/docetaxel doublet All-Comer/ Undisclosed AMBER (n=873) Multiple TIM-3/PD-1 combos (Data reported ASCO 2022) CITRINO (n=200) Multiple LAG-3/PD-1 combos Phase 2 Phase 3 JEMPERLI US and EU accelerated approval Apr. 2021 (dMMR advanced / recurrent) JEMPERLI US approval Aug. 2021 1L ovarian cancer • ~20,000 new ovarian diagnoses per year in US* • P3 data expected H2 2023 (interim analysis) 1L advanced/recurrent endometrial cancer • ~30% of ~65,000 patient market* • P3 data expected Q4 2022 (interim analysis) • US regulatory decision expected H2 2023 *NCI SEER Data/Internal Market Research JEMPERLI / dostaralimab (anti-PD-1 antagonist) Dostarlimab + GSK4074386 (anti-LAG-3 antagonist) Dostarlimab + Cobolimab (anti-TIM-3 antagonist) Legend 32 Note: Additional investigator sponsored trials (ISTs) ongoing in liver cancer, rectal cancer, melanoma, clear cell sarcoma, and HNSCC *NCI SEER Data Additional Dostarlimab Combinations In Clinical Trials DREAMM-5 Belantamab mafodotin (BCMA ADC) + dostarlimab combination (n=464) Multiple myeloma (Phase 1/2) GSK6097608 (anti-CD96) + dostarlimab combination (n=111) Advanced solid tumors (Phase 1) GSK3745417 (STING agonist) + dostarlimab combination (n=300) Advanced solid tumors (Phase 1) EOS-448 (anti-TIGIT) + dostarlimab combination 1L NSCLC PDL1 high, H&NSCC, other solid tumors (Registration‐trial planning) GSK4381562 (PVRIG) + dostarlimab combination (n=126) Advanced solid tumors (Phase 1) GSK Immuno-Oncology Financial Collaboration: Clinical Trials JEMPERLI approved in the US and EU

































