UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
| |
| x | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended October 31, 2012
OR
| |
o | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from to
Commission File Number: 000-54283
PATHEON INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
|
| | |
| Canada | | Not Applicable |
(State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
| | |
c/o Patheon Pharmaceuticals Services Inc. 4721 Emperor Boulevard, Suite 200 Durham, NC | | 27703 |
| (Address of principal executive offices) | | (Zip Code) |
(919) 226-3200
(Registrant's telephone number, including area code)
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act: None.
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act:
Restricted Voting Shares
(Title of Class)
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes o No x
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes o No x
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes x No o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes x No o
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (§ 229.405 of this chapter) is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant's knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of "large accelerated filer," "accelerated filer" and "smaller reporting company" in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one):
|
| | | | |
| Large accelerated filer | o | | Accelerated filer | x |
| | | | | |
| Non-accelerated filer | o (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) | | Smaller reporting company | o |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes o No x
The aggregate market value of restricted voting shares held by non-affiliates of the registrant as of April 30, 2012, the last business day of the registrant's most recently completed second fiscal quarter, was $97,987,272 (based on the last reported closing sale price on the Toronto Stock Exchange on that date of $2.22 per share, as converted from C$2.19 using the closing rate of exchange from Reuters).
As of December 14, 2012, the registrant had 129,297,892 restricted voting shares outstanding.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Portions of the definitive Proxy Statement and Information Circular to be delivered to shareholders in connection with the Annual Meeting of Shareholders to be held March 28, 2013 are incorporated by reference into Part III.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
|
| | |
| | PART I | |
| Item 1. | Business | |
| Item 1A. | Risk Factors | |
| Item 1B. | Unresolved Staff Comments | |
| Item 2. | Properties | |
| Item 3. | Legal Proceedings | |
| Item 4. | Mine Safety Disclosures | |
| | PART II | |
| Item 5. | Market for Registrant's Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity
Securities | |
| Item 6. | Selected Financial Data | |
| Item 7. | 'Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations | |
| Item 7A. | Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk | |
| Item 8. | Financial Statements and Supplementary Data | |
| Item 9. | Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure | |
| Item 9A. | Controls and Procedures | |
| Item 9B. | Other Information | |
| | PART III | |
| Item 10. | Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance | |
| Item 11. | Executive Compensation | |
| Item 12. | Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters | |
| Item 13. | Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence | |
| Item 14. | Principal Accountant Fees and Services | |
| | PART IV | |
| Item 15. | Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules | |
| | SIGNATURES | |
| | INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS | |
| | EXHIBIT INDEX | |
CAUTIONARY NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This annual report on Form 10-K contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the "Securities Act"), and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the "Exchange Act"), which reflect our expectations regarding our future growth, results of operations, performance (both operational and financial) and business prospects and opportunities. All statements, other than statements of historical fact, are forward-looking statements. Wherever possible, words such as "plans," "expects," or "does not expect," "forecasts," "anticipates" or "does not anticipate," "believes," "intends" and similar expressions or statements that certain actions, events or results "may," "could," "should," "would," "might" or "will" be taken, occur or be achieved have been used to identify these forward-looking statements. Although the forward-looking statements contained in this annual report on Form 10-K reflect our current assumptions based upon information currently available to us and based upon what we believe to be reasonable assumptions, we cannot be certain that actual results will be consistent with these forward-looking statements. Our current material assumptions include assumptions related to customer volumes, regulatory compliance, foreign exchange rates, employee severance costs associated with termination and projected integration savings related to the Banner Acquisition (as defined below). Forward-looking statements necessarily involve significant known and unknown risks, assumptions and uncertainties that may cause our actual results, performance, prospects and opportunities in future periods to differ materially from those expressed or implied by such forward-looking statements. These risks and uncertainties include, among other things, risks related to international operations and foreign currency fluctuations; customer demand for our services; regulatory matters affecting manufacturing and pharmaceutical development services; impacts of acquisitions, divestitures and restructurings, including our ability to achieve our intended objectives with respect to such transactions and integrate businesses that we may acquire; implementation of our new corporate strategy; our ability to effectively transfer business between facilities; the global economic environment; our exposure to complex production issues; our substantial financial leverage; interest rate risks; potential environmental, health and safety liabilities; credit and customer concentration; competition; rapid technological change; product liability claims; intellectual property; the existence of a significant shareholder; supply arrangements; pension plans; derivative financial instruments; and our dependence upon key management, scientific and technical personnel. These and other risks are described in greater detail in "Item 1A. Risk Factors" of this annual report on Form 10-K. Although we have attempted to identify important risks and factors that could cause actual actions, events or results to differ materially from those described in forward-looking statements, there may be other factors and risks that cause actions, events or results not to be as anticipated, estimated or intended. There can be no assurance that forward-looking statements will prove to be accurate, as actual results and future events could differ materially from those anticipated in such statements. These forward-looking statements are made as of the date of this annual report on Form 10-K, and except as required by law, we assume no obligation to update or revise them to reflect new events or circumstances.
General
All references to "$" or "dollars" in this annual report are to U.S. dollars unless otherwise indicated. References in this Form 10-K to "Patheon," "we," "us," "our" and "our company" refer to Patheon Inc. and its consolidated subsidiaries.
PART I
Item 1. Business.
Overview
We are a leading provider of commercial manufacturing outsourcing services ("CMO") and outsourced pharmaceutical development services ("PDS") to the global pharmaceutical industry. We believe we are the world's third-largest CMO provider and the world's largest PDS provider based on calendar year 2011 revenues provided by PharmSource, a provider of pharmaceutical outsourcing business information. We offer a wide range of services throughout the lifecycle of a pharmaceutical molecule, from early development, through late development to commercial manufacturing, including lifecycle management services. During the fiscal year ended October 31, 2012 ("fiscal 2012"), we provided services to approximately 312 customers throughout the world, including 19 of the world's 20 largest pharmaceutical companies, eight of the world's 10 largest biotechnology companies and eight of the world's 10 largest specialty pharmaceutical companies. In fiscal 2012, we manufactured 12 of the top 100 selling drug compounds in the world based on revenues for the products reported by Evaluate Pharma, a provider of pharmaceutical industry data, and our products were distributed in approximately 60 countries. We are also currently developing 12 of the top 100 development stage drugs in the world on behalf of our customers based on potential revenues for the products reported by Evaluate Pharma.
Our CMO business focuses primarily on prescription products in a wide variety of solid and sterile dosage forms. We have also developed a range of specialized capabilities in high potency, controlled substances and modified release products.
Our PDS business provides a broad range of development services, including finished dosage formulation across approximately 40 dosage forms, early development services, analytical services, formulation expertise and life cycle management. We have established our position as a market leader by leveraging our scale, global reach, specialized capabilities, broad service offerings, scientific expertise and track record of product quality and regulatory compliance to provide cost-effective solutions to our customers.
Company History
The heritage of our company dates back to 1974, when we established Custom Pharmaceuticals Ltd., a contract manufacturing business, in Fort Erie, Canada. Since that time, we have expanded operations through acquisition of contract manufacturing facilities in Canada, Europe, Puerto Rico and the United States, entered into the PDS business and recently acquired additional capabilities with respect to proprietary soft-gel formulations. In addition, we continue to assess our footprint and as market conditions warrant consolidate or dispose of facilities.
In 2006 and 2007, we conducted a review of strategic and financial alternatives that resulted in a $150,000,000 investment in us by JLL Partners Inc., a New York private equity firm ("JLL Partners"), and a refinancing of our North American indebtedness. As a result of this investment, JLL Patheon Holdings, LLC ("JLL Patheon Holdings"), an affiliate of JLL Partners, received two series of preferred stock, one of which it converted into 38,018,538 voting shares in 2009, and the other of which entitles it to elect up to three members of our Board of Directors (our "Board").
JLL Patheon Holdings also made an unsolicited offer to acquire any or all of the outstanding restricted voting shares of Patheon ("JLL Offer") that it did not already own in 2009, which resulted in JLL Patheon Holdings and its affiliates ("JLL") acquiring an additional 33,854,708 restricted voting shares. The restricted voting shares that JLL purchased pursuant to the JLL Offer represented approximately 38% of the outstanding restricted voting shares of Patheon not already owned by JLL. As of October��31, 2012, JLL owned an aggregate of 72,358,181 restricted voting shares, representing approximately 56% of Patheon's total restricted voting shares outstanding.
On December 14, 2012, we completed our acquisition of all of the issued and outstanding shares of capital stock of Sobel USA Inc., a Delaware corporation, and Banner Pharmacaps Europe B.V., a private limited company organized under the laws of The Netherlands (collectively "Banner") for an aggregate purchase price of approximately $269.0 million, subject to post-closing working capital adjustments (the "Banner Acquisition"). Banner is the world's second largest pharmaceutical business focused on delivering proprietary softgel formulations, with four manufacturing facilities, significant proprietary technologies and products, and leading positions in some of the industry's fastest-growing product categories. Banner is headquartered in High Point, N.C., with additional research labs and manufacturing facilities in the Netherlands, Canada and Mexico.
Our Segments
We are organized into two operating segments: CMO and PDS. In addition, we categorize certain selling, general and administrative costs and certain foreign exchange gains and losses under a separate segment reporting line item referred to as "corporate costs." In fiscal 2012, our CMO and PDS segments accounted for 81.5% and 18.5% of our total revenues, respectively. Financial information about our CMO and PDS segments and information regarding net sales and long-lived assets attributable to operations in Canada, the United States, Europe and other countries is contained in "Note 15—Segmented Information" of our consolidated financial statements included in this Form 10-K. Additional financial information about our CMO and PDS segments is contained in "Item 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations." For a discussion of risks attendant to our foreign operations, please see "Item 1A. Risk Factors—Risks Related to our Business and Industry."
The illustration below sets forth the various stages of the drug development and manufacturing process; shaded processes are services that we provide.
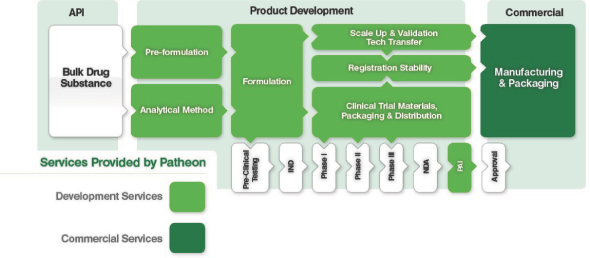 Note: API: Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient
Note: API: Active Pharmaceutical IngredientPAI: Pre-Approval Inspection(s)
Commercial Manufacturing
We believe we are the world's third-largest CMO provider with an approximate 5% global market share in 2011 based on calendar year 2011 market size provided by PharmSource and publicly available information. We operate nine facilities located throughout North America and Europe. We manufacture various sterile dosage forms, as well as solid, conventional and specialized dosage forms. Our sterile dosage forms include aseptically (sterile) filled and terminally sterilized liquids and vials, bottles and pre-filled syringes and sterile lyophilized (freeze-dried) products in vials. Conventional dosage forms include both coated and uncoated compressed tablets and hard shell gelatin capsules. Currently, our capacity utilization is higher for our facilities for sterile dosage forms than for conventional dosage forms. We further differentiate ourselves by offering specialized capabilities relating to high potency, controlled substance and modified release products. In fiscal 2012, our CMO segment generated 81.5% of our total revenues.
Set forth below are our various dosage forms.
| |
| • | Immediate Release Tablets |
| |
| • | Powders/Granules/Coated Beads |
| |
| • | Fast Dispersible Tablets |
| |
| • | Controlled-Release Tablets |
| |
| • | Liquid Small Volume Parenteral (SVP) |
| |
| • | Liquid Large Volume Parenteral (LVP) |
| |
| • | Highly Regulated Products |
| |
| • | Patheon Certified Consultants |
In fiscal 2012, we had a diverse CMO customer base with large, mid-size and emerging pharmaceutical companies comprising 49%, 25% and 10% of our fiscal 2012 CMO revenues, respectively, with the remainder being derived from our early stage, generic and other pharmaceutical customers.
Pharmaceutical Development Services
We believe we are the world's largest PDS provider with an approximate 10% global market share in 2011 based on calendar year 2011 market size provided by PharmSource and publicly available information, offering a broad range of development services across approximately 40 different dosage forms. We operate eight development centers located throughout North America and Europe. Our PDS offerings support customers across various stages of the drug development process, including (i) early development; (ii) pre-formulation, formulation and development of dosage forms; (iii) manufacturing of development stage products during the regulatory drug approval process, including manufacturing of pilot batches; (iv) scale-up and technology transfer services designed to validate commercial-scale drug manufacturing processes; and (v) development of analytical methods and delivery of analytical services. In fiscal 2012, our PDS offerings were provided to a diverse customer base with large, mid-size and emerging pharmaceutical companies comprising 38%, 25% and 34% of our fiscal 2012 PDS revenues, respectively, with the remaining 3% being derived from our early stage pharmaceutical, generic and other customers.
During fiscal 2012, we worked on approximately 432 projects for our customers, including 12 drug candidates at the new drug application ("NDA") stage. Among the projects we worked on during fiscal 2012, 171 projects were at Phase I, 82 projects were at Phase II, 116 projects were at Phase III, and 63 projects were at the pre-clinical or post-approval stage. During the year ended October 31, 2011 ("fiscal 2011") and fiscal 2012, we developed 9 products for customers that received new market approval. Since the beginning of fiscal 2001, our PDS business has developed, on behalf of our customers, 38 new molecular entities ("NME") that have been approved for marketing by regulatory authorities, as well as numerous new formulations of existing NMEs. Any patent and drug approvals that we obtain, or help to obtain, belong to our customers, and we do not receive royalties or earn revenues from products or NMEs that we develop, or help to develop, other than for the development services we provide. Our development group, comprised of approximately 550 scientists and technicians, including approximately 80 holding doctoral degrees, has extensive development experience across a wide variety of pharmaceutical dosage forms. Our PDS business serves as a pipeline for future commercial manufacturing opportunities. Since most of these products are at the beginning of their patent life, these products typically present long-term manufacturing opportunities. During fiscal 2012 and fiscal 2011, we were awarded CMO contracts for 17 new products that had been developed by our PDS business. In fiscal 2012, our PDS segment generated 18.5% of our total revenues.
Performance Enhancement Initiatives
We are committed to providing quality products and services to our customers.
Our new corporate strategy includes accelerating and revising the Patheon Advantage™ program, which combines "lean" manufacturing practices with "six sigma" manufacturing to streamline operations, remove production bottlenecks, increase capacity utilization and improve performance throughout the network; assessing strategic options for the Swindon commercial operation; continuing the evolution of our existing commercial sites into centers of excellence focusing on specific technologies or production types; and focusing improvements in other areas of the business including working capital, pricing, and selling, general and administrative costs.
In addition, we have developed an information technology master plan that sets the overall direction for systems and services for our business. It centers on the development of strategic information technology assets that we believe will drive competitive advantages for our business and includes both the addition of new information technology assets and the enhancement of existing information technology assets.
Customers
In fiscal 2012, we provided services to approximately 300 customers throughout the world, including 19 of the world's 20 largest pharmaceutical companies, eight of the world's 10 largest biotechnology companies and eight of the world's 10 largest specialty pharmaceutical companies. We are also currently developing on behalf of our customers 12 of the 100 top development stage drugs in the world, based on potential revenues for the products reported by EvaluatePharma®. During fiscal 2012, Merck & Co., Inc. accounted for approximately 11.0% of our consolidated revenues. In fiscal 2012, our top 20 customers in our CMO segment accounted for approximately 80% of our CMO revenues.
We have entered into several master service agreements with customers that contemplate long-term multi-product and multi-site commercial manufacturing and/or PDS, including a seven-year manufacturing agreement that led to construction of a
new manufacturing facility within one of our existing sites with significant financing from the customer, a five-year master supply agreement with a global pharmaceutical company to provide development and manufacturing services and "carve-out" arrangements at certain of our facilities under which sizeable parts of our current production have been transferred to us from facilities owned by our customers that were slated for closure or downsizing. These arrangements are part of a trend towards developing broader and longer-term relationships with our customers. We have developed master service agreement templates for both our development and commercial services to allow for the addition of new projects and products without having to renegotiate terms and conditions.
Our CMO customers typically provide a yearly forecast of anticipated product demand. Customers also deliver firm purchase orders, typically three months prior to scheduled production, after which time they may adjust contract quantities or delivery dates within certain limits, provided that we are reimbursed for any expenses incurred in connection with such adjustments. Upon delivery to us of a customer purchase order confirming the quantity and delivery date, the order is scheduled for production. Our CMO customer contracts, typically with multi-year terms, formalize the standard business arrangements outlined above, including production based on the delivery of firm purchase orders. In addition, the contracts typically provide for 12 to 18 months' advance notice for the transfer or discontinuance of any product. The customer assumes liability for all material commitments made in accordance with purchase orders. We maintain the right to pass on price increases to the customer over and above some predetermined minimum percentage. The actual revenues generated by our major customer agreements are based on volumes that are determined by market demands for the customer's product from time to time.
Our PDS business provides services on a fee-for-service basis. We typically respond to a customer request and prepare a quotation which, if accepted, typically forms the basis of the contract with the customer. Our PDS contracts typically require us to perform development services within a designated scope. Frequently, the continuation of our work on a particular project will depend on various factors such as research results and the customer's needs.
Sales and Marketing
Our global sales and marketing group is responsible for generating new business for our CMO and PDS businesses. Our sales team is broken into two distinct groups-territory-based sales executives and key account executives with direct support from the project managers generating additional sales from existing project with existing clients. Each of our territory-based sales teams is responsible for identifying new customers and generating sales from these customers within its territory that are not named as a key account. Our North America territory-based sales team is comprised of 15 members and covers the United States and Canada. We also have a territory-based sales team covering Europe and Japan, which is comprised of 10 members. In addition, we have 11 global key account executives who act as our primary interface with our most significant accounts; currently, approximately 35 of our customers have key account status. Despite the functional and geographical delineation of our sales teams, each sales team or executive seeks to generate sales in both our CMO and PDS segments across our entire network. Determination of which site, or sites, will perform specific services is dictated by the nature of the customer's product, our capabilities and customer preferences.
The projects of our existing customers are managed by site-based project managers and business managers, who also play an integral role in the sales process by ensuring that the existing projects meet our customers' expectations and understanding our customers' projects and evolving needs. These activities can assist the site-based teams in obtaining additional work on existing projects and identifying new projects with existing customers.
Our sales team is supported by global marketing, sales operations and business intelligence groups located at our U.S. headquarters in Research Triangle Park, North Carolina, and regional support resources in Europe and Japan.
Supply Arrangements
For our commercial manufacturing operations, we are required to source various active pharmaceutical ingredients ("APIs"), excipients, raw materials and packaging components from third-party suppliers and/or our actual customers. Our customers specify these components, raw materials and packaging materials in line with their product registration files, and in some cases, they specify the actual supplier from whom we must purchase these inputs. In most cases, our customers manage the sourcing and physical delivery of the API to us at no cost. We generally source and procure all other input materials from established local or regional suppliers specializing in serving the pharmaceutical sector. With the exception of certain patented APIs and excipients, most inputs are available from multiple sources.
Supply arrangements are an inherent part of our ability to produce products for our customers in a timely manner and thus create a degree of dependence that could negatively impact revenues if such supply is interrupted. Such interruptions can be either localized to a specific supplier issue or as a result of wider supply interruptions due to natural disasters or international disruptions caused by geopolitical issues or other events. See "Item 1A. Risk Factors—Risks Related to Our Business and Industry." We work closely with suppliers at both a local and corporate level to establish clear supply agreements that set forth
the supply relationship expectations and the legal terms and conditions of the agreements, including potential liabilities for supply interruption situations. These agreements are critical to our ability to manage and mitigate risk across our supply chain.
Competition
We operate in a market that is highly competitive. We compete to provide CMO and PDS to pharmaceutical companies around the world.
Our competition in the CMO market includes full-service pharmaceutical outsourcing companies; contract manufacturers focusing on a limited number of dosage forms; contract manufacturers providing multiple dosage forms; and large pharmaceutical companies offering third-party manufacturing services to fill their excess capacity. In addition, in Europe, there are a large number of privately owned, dedicated outsourcing companies that serve only their local or national markets. Also, large pharmaceutical companies have been seeking to divest portions of their manufacturing capacity, and any such divested businesses may compete with us in the future. We compete primarily on the basis of the security of supply (quality, regulatory compliance and financial stability), service (on-time delivery and manufacturing flexibility) and cost-effective manufacturing (prices and a commitment to continuous improvement).
Our competition in the PDS market includes a large number of laboratories that offer only a limited range of developmental services, generally at a small scale; providers focused on specific technologies and/or dosage forms; and a few fully integrated companies that can provide the full complement of services necessary to develop, scale-up and manufacture a wide range of dosage forms. We also compete in the PDS market with major pharmaceutical and chemical companies, specialized contract research organizations, research and development firms, universities and other research institutions. We may also compete with the internal operations of pharmaceutical companies that choose to source PDS internally. We compete primarily on the basis of scientific expertise, knowledge and experience in dosage form development, availability of a broad range of equipment, on-time delivery of clinical materials, compliance with current good manufacturing practices ("cGMPs"), regulatory compliance, cost effective services and financial stability.
Some of our competitors may have substantially greater financial, marketing, technical or other resources than we do. Additional competition may emerge and may, among other things, result in a decrease in the fees paid for our services.
One of the many factors affecting competition is the current excess capacity within the pharmaceutical industry of facilities capable of manufacturing drugs in solid dosage forms. Thus, customers currently have a wide range of supply alternatives for these dosage forms. Another factor causing increased competition is that a number of companies in Asia, particularly India, have been entering the CMO and PDS sectors over the past few years, have begun obtaining approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (the "FDA") for certain of their plants and have acquired additional plants in Europe and North America. One or more of these companies may become a significant competitor to us.
Employees
As of November 30, 2012, we had approximately 4,700 employees. National works councils are active at all of our facilities in the United Kingdom, France and Italy consistent with local labor laws. There is no union representation at any of our North American sites. Our management believes that we generally have a good relationship with our employees around the world and the works councils that represent a portion of our European employee base.
Intellectual Property
We rely on a combination of trademark, patent, trade secret and other intellectual property laws of the United States and other countries. We have applied in the United States and in certain foreign countries for registration of a limited number of trademarks and patents, some of which have been registered or issued. Also, many of the formulations used by us in manufacturing products to customer specifications are subject to patents or other intellectual property rights owned by or licensed to the relevant customer. Further, we rely on non-disclosure agreements and other contractual provisions to protect our intellectual property rights and typically enter into mutual confidentiality agreements with customers that own or are licensed users of patented formulations.
We have developed and continue to develop knowledge and expertise ("know-how") and trade secrets in the provision of services in both our PDS and CMO businesses, and we have acquired know how and trade secrets related to soft-gel and other technologies in connection with the Banner Acquisition. Our know-how and trade secrets may not be patentable, but they are valuable in that they enhance our ability to provide high-quality services to our customers.
To the extent that we determine that certain aspects of the services we provide are innovative and patentable, we have filed and pursued, and plan to continue to file and pursue, patent applications to protect such inventions, as well as applications for registration of other intellectual property rights, as appropriate. However, we do not consider any particular patent, trademark, license, franchise or concession to be material to our CMO or PDS segments.
Regulatory Matters
We are required to comply with the regulatory requirements of various local, state, provincial, national and international regulatory bodies having jurisdiction in the countries or localities where we manufacture products or where our customers' products are distributed. In particular, we are subject to laws and regulations concerning research and development, testing, manufacturing processes, equipment and facilities, including compliance with cGMPs, labeling and distribution, import and export, and product registration and listing. As a result, most of our facilities are subject to regulation by the FDA, as well as regulatory bodies of other jurisdictions, such as the European Medicines Agency of the European Union ("EMA") and/or the National Health Surveillance Agency in Brazil ("Anvisa"), depending on the countries in which our customers market and sell the products we manufacture and/or package on their behalf. We are also required to comply with environmental, health and safety laws and regulations, as discussed in "Environmental Matters" below. These regulatory requirements impact many aspects of our operations, including manufacturing, developing, labeling, packaging, storage, distribution, import and export and record keeping related to customers' products. Noncompliance with any applicable regulatory requirements can result in government refusal to approve (i) facilities for testing or manufacturing products or (ii) products for commercialization. The FDA and other regulatory agencies can delay, limit or deny approval for many reasons, including:
| |
| • | Changes to the regulatory approval process, including new data requirements, for product candidates in those jurisdictions, including the United States, in which we or our customers may be seeking approval; |
| |
| • | A product candidate may not be deemed to be safe or effective; |
| |
| • | The ability of the regulatory agency to provide timely responses as a result of its resource constraints; and |
| |
| • | The manufacturing processes or facilities may not meet the applicable requirements. |
In addition, if new legislation or regulations are enacted or existing legislation or regulations are amended or are interpreted or enforced differently, we may be required to obtain additional approvals or operate according to different manufacturing or operating standards or pay additional product or establishment user fees. This may require a change in our research and development and manufacturing techniques or additional capital investments in our facilities.
Our pharmaceutical development and manufacturing projects generally involve products that must undergo pre-clinical and clinical evaluations relating to product safety and efficacy before they are approved as commercial therapeutic products. The regulatory authorities having jurisdiction in the countries in which our customers intend to market their products may delay or put on hold clinical trials, delay approval of a product or determine that the product is not approvable. The FDA or other regulatory agencies can delay approval of a drug if our manufacturing facility is not able to demonstrate compliance with cGMPs, pass other aspects of pre-approval inspections (i.e., compliance with filed submissions) or properly scale up to produce commercial supplies. The FDA and comparable government authorities having jurisdiction in the countries in which our customers intend to market their products have the authority to withdraw product approval or suspend manufacture if there are significant problems with raw materials or supplies, quality control and assurance or the product is deemed adulterated or misbranded.
Some of our manufactured products are listed as controlled substances. Controlled substances are those products that present a risk of substance abuse. In the United States, these types of products are classified by the U.S. Drug Enforcement Agency (the "DEA") as Schedule II, III and IV substances under the Controlled Substances Act of 1970. The DEA classifies substances as Schedule I, II, III, IV or V substances, with Schedule I substances considered to present the highest risk of substance abuse and Schedule V substances the lowest risk. Scheduled substances are subject to DEA regulations relating to manufacturing, storage, distribution, import and export and physician prescription procedures. For example, scheduled drugs are subject to distribution limits and a higher level of recordkeeping requirements. Furthermore, the total amount of controlled substances for manufacture or commercial distribution is limited by the DEA and allocated through quotas. Our quotas or our customers' quotas, if any, may not be sufficient to meet commercial demand or to economically produce the product.
Entities must be registered annually with the DEA to manufacture, distribute, dispense, import, export and conduct research using controlled substances. State controlled substance laws also require registration for similar activities. In addition, the DEA requires entities handling controlled substances to maintain records, file reports, follow specific labeling and packaging requirements and provide appropriate security measures to control against diversion of controlled substances. If we fail to follow these requirements, we may be subject to significant civil and/or criminal penalties and possibly a revocation of one of our DEA registrations.
Products containing controlled substances may generate significant public health and safety issues, and in such instances, federal or state authorities can withdraw or limit the marketing rights or regulatory approvals for these products. For some scheduled substances, the FDA may require us or our customers to develop product attributes or a risk evaluation and mitigation strategy to reduce the inappropriate use of the products, including the manner in which they are marketed and sold, so as to reduce the risk of diversion or abuse of the product. Developing such a program may be time-consuming and could delay approval of product candidates containing controlled substances. Such a program or delays of any approval from the FDA could adversely affect our business, results of operations and financial condition.
Audits are an important means by which prospective and existing customers gain confidence that our operations are conducted in accordance with applicable regulatory requirements. In fiscal 2012, our facilities and development centers were audited by 222 separate customer audit teams, representing both prospective and existing customers. These audits contribute to our ongoing improvement of our manufacturing and development practices. In addition to customer audits, we, like all commercial drug manufacturers, are subject to audits by various regulatory authorities. In fiscal 2012, regulatory authorities conducted 21 such audits, which involved multiple products, at our sites in North America and Europe. Responses to audit observations were submitted to address observations noted. We have yet to receive feedback from most of the inspections conducted in the third and fourth quarters of fiscal 2012. It is not unusual for regulatory agencies or customers to request further clarification and/or follow-up on the responses we provide.
Environmental Matters
Our operations are subject to a variety of environmental, health and safety laws and regulations in each of the jurisdictions in which we operate. These laws and regulations govern, among other things, air emissions, wastewater discharges, the handling and disposal of hazardous substances and wastes, soil and groundwater contamination and employee health and safety. We are also subject to laws and regulations governing the destruction and disposal of raw materials and non-compliant products, the handling of regulated material that is included in our offerings and the disposal of our offerings at the end of their useful life. These laws and regulations have increasingly become more stringent, and we may incur additional expenses to ensure compliance with existing or new requirements in the future. Any failure by us to comply with environmental, health and safety requirements could result in the limitation or suspension of our operations. We also could incur monetary fines, civil or criminal sanctions, third-party claims or cleanup or other costs as a result of violations of or liabilities under such requirements. In addition, compliance with environmental, health and safety requirements could restrict our ability to expand our facilities or require us to acquire costly pollution control equipment, incur other significant expenses or modify our manufacturing processes.
Our manufacturing facilities, in varying degrees, use, store and dispose of hazardous substances in connection with their processes. At some of our facilities, these substances are stored in underground storage tanks or used in refrigeration systems. Some of our facilities, including those in Puerto Rico, have been utilized over a period of years as manufacturing facilities, with operations that may have included on-site landfill or other waste disposal activities and have certain known or potential conditions that may require remediation in the future, and several of these have undergone remediation activities in the past by former owners or operators. Some of our facilities are located near third-party industrial sites and may be impacted by contamination migrating from such sites. A number of our facilities use groundwater from onsite wells for process and potable water, and if these onsite sources became contaminated or otherwise unavailable for future use, we could incur expenses for obtaining water from alternative sources. In addition, our operations have grown through acquisitions, and it is possible that facilities that we have acquired may expose us to environmental liabilities associated with historical site conditions that have not yet been discovered. Some environmental laws impose liability for contamination on current and former owners and operators of affected sites, regardless of fault. If remediation costs or potential claims for personal injury or property or natural resource damages resulting from contamination arise, they may be material and may not be recoverable under any contractual indemnity or otherwise from prior owners or operators or any insurance policy. Additionally, we may not be able to successfully enforce any such indemnity or insurance policy in the future. In the event that new or previously unknown contamination is discovered or new cleanup obligations are otherwise imposed at any of our currently or previously owned or operated facilities, we may be required to take additional, unplanned remedial measures and record charges for which no reserves have been recorded.
Seasonality
Revenues from some of our CMO and PDS operations have traditionally been lower in our first fiscal quarter, being the three months ending January 31. We attribute this trend to several factors, including (i) the reassessment by many customers of their need for additional product in the last quarter of the calendar year in order to use existing inventories of products; (ii) the lower production of seasonal cough and cold remedies in the first fiscal quarter; (iii) limited project activity towards the end of the calendar year by many small pharmaceutical and biotechnology customers involved in PDS projects in order to reassess
progress on their projects and manage cash resources; and (iv) the Patheon-wide facility shutdown during a portion of the traditional holiday period in December and January.
Research and Development
We have not spent any material amount in the last three fiscal years on company-sponsored research and development activities.
Available Information
We maintain a website with the address www.patheon.com. We are not including the information contained on our website as part of, or incorporating it by reference into, this annual report on Form 10-K. We make available, free of charge, on or through our website our annual reports on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K and all amendments to those reports as soon as practicable after such material is electronically filed with or furnished to the Securities and Exchange Commission ("SEC").
Risks Related to Our Business and Industry
We are dependent on our customers' spending on and demand for our manufacturing and development services. A reduction in spending or demand could have a material adverse effect on our business.
The amount of customer spending on pharmaceutical development and manufacturing, particularly the amount our customers choose to spend on outsourcing these services, has a large impact on our sales and profitability. Consolidation in the pharmaceutical industry may impact such spending as customers integrate acquired operations, including research and development departments and manufacturing operations.
Many of our customers finance their research and development spending from private and public sources. We have experienced slowdowns in our customers' spending on pharmaceutical development and related services, which we believe have been primarily due to the lack or decreased availability of capital for specialty and emerging pharmaceutical companies and the consolidation within the pharmaceutical industry, which resulted in the postponement of certain projects. Any reduction in customer and potential customer spending on pharmaceutical development and related services may have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
Furthermore, demand for our CMO segment is driven, in part, by products we bring to market for our PDS customers. Due to the long lead times associated with obtaining regulatory approvals for many of these products, particularly dosage forms, and the competitive advantage that can come from gaining early approval, it is important that we maintain a sufficiently large portfolio of pharmaceutical products and such products are brought to market on a timely basis. If we experience a reduction in research and development by our customers, the decrease in activity in our PDS segment could also negatively affect activity levels in our CMO business. Any decline in demand for our services may have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
The consumers of the products we manufacture for our customers may significantly influence our business, results of operations and financial condition.
We are dependent on demand for the products we manufacture for our customers and have no control or influence over the market demand for our customers' products. Demand for our customers' products can be adversely affected by, among other things, delays in health regulatory approval, the loss of patent and other intellectual property rights protection, the emergence of competing products, including generic drugs, the degree to which private and government drug plans subsidize payment for a particular product and changes in the marketing strategies for such products.
If the products we manufacture for our customers do not gain market acceptance, our revenues and profitability will be adversely affected. The degree of market acceptance of our customers' products will depend on a number of factors, including:
| |
| • | the ability of our customers to publicly establish and demonstrate the efficacy and safety of such products, including compared to competing products; |
| |
| • | the costs to potential consumers of using such products; and |
| |
| • | marketing and distribution support for such products. |
If production volumes of key products that we manufacture for our customers and related revenues are not maintained, it may have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition. Additionally, any changes in product mix due to market acceptance of our customers' products may adversely affect our margins.
Our services and offerings are highly complex, and if we are unable to provide quality and timely offerings to our customers, our business could suffer.
The services we offer are highly exacting and complex, due in part to strict regulatory requirements. As a result of the Banner Acquisition, we have entered into new lines of business, and there may be factors that affect these lines of business with which we are not as familiar compared to our existing business lines. Moreover, it is possible that the integration process with Banner could result in the distraction of our management, the disruption of our ongoing business or inconsistencies in our products, services, standards, controls, procedures and policies. A failure of our quality control systems in our new and existing business units and facilities could cause problems to arise in connection with facility operations or during preparation or provision of products, in both cases, for a variety of reasons, including equipment malfunction, failure to follow specific protocols and procedures, problems with raw materials or environmental factors. Such problems could affect production of a particular batch or series of batches, requiring the destruction of products, or could halt facility production altogether. In addition, our failure to meet required quality standards may result in our failure to timely deliver products to our customers, which in turn could damage our reputation for quality and service. Any such incident could, among other things, lead to increased costs, lost revenue, reimbursement to customers for lost APIs, damage to and possibly termination of existing customer relationships, time and expense spent investigating the cause and, depending on the cause, similar losses with respect to other batches or products. If problems are not discovered before the product is released to the market, we may be subject to regulatory actions, including product recalls, product seizures, injunctions to halt manufacture and distribution, restrictions on our operations, civil sanctions, including monetary sanctions, and criminal actions. In addition, such issues could subject us to litigation, the cost of which could be significant.
Our PDS projects are typically for a shorter term than our CMO projects, and any failure by us to maintain a high volume of PDS projects, including due to lower than expected success rates of the products for which we provide services, could adversely affect our business, results of operations and financial condition.
Unlike our CMO segment, where our contracts are typically multi-year in duration, our PDS segment contracts are generally shorter in term and typically require us to provide development services within a designated scope. Since our PDS business focuses on products that are still in the developmental stages, the viability of many of our PDS projects is not certain. As a result, many of these projects fail to progress to the subsequent development phase. Even if a customer wishes to proceed with a project, the product we are developing on its behalf may fail to receive necessary regulatory approval, or other factors, such as the development of a competing product, may hinder the development of the product.
If we are unable to continue to obtain new projects from existing and new customers, our PDS segment could be adversely affected. Furthermore, although our PDS business acts as a pipeline for our CMO segment, we cannot predict the turnover rate of our PDS projects or how successful we will be in winning new projects that lead to a viable product. As such, an increase in the turnover rate of our PDS projects may negatively affect our CMO segment at a later time. In addition, the discontinuation of a project as a result of our failure to satisfy a customer's requirements may also affect our ability to obtain future projects from the customer involved or from new customers.
Continued volatility and disruption to the global capital and credit markets and the global economy have adversely affected, and may continue to adversely affect, our business and results of operations and have adversely affected, and may continue to adversely affect, our customers and suppliers.
In recent years, the global capital and credit markets and the global economy have experienced a period of significant uncertainty, characterized by the bankruptcy, failure, collapse or sale of various financial institutions and a considerable level of intervention from governments around the world. These conditions have adversely affected the demand for our products and services, which has negatively affected our business and results of operations. In addition, interest rate fluctuations, financial market volatility or credit market disruptions may limit our access to capital, and may also negatively affect our customers' and our suppliers' ability to obtain credit to finance their businesses on acceptable terms or at all. As a result, customers' need for and ability to purchase our products or services may decrease. For example, certain of our customers have decreased their research and development spending due to their lack of access to capital. In addition, lack of access to capital may cause our suppliers to increase their prices, reduce their output or change their terms of sale. If our customers' or suppliers' operating and financial performance deteriorates, or if they are unable to make scheduled payments or obtain credit, our customers may not be able to pay, or may delay payment of, accounts receivable owed to us, and our suppliers may restrict credit or impose different payment terms. Any inability of our customers to pay us for our products and services or any demands by suppliers for different payment terms may adversely affect our earnings and cash flow.
As the contraction of the global capital and credit markets has spread throughout the broader economy, the United States and other major markets around the world have experienced very weak or negative economic growth, a major contributor of which has been continued high unemployment. These recessionary conditions have impacted, and will continue to impact, consumer demand for the products we manufacture for our customers.
Our operations outside the United States and Canada are subject to a number of economic, political and regulatory risks.
We are an international company incorporated and listed in Canada with facilities and offices in eight countries. Although we have had significant international operations for a number of years, the Banner Acquisition has increased our geographic presence in Latin America, including significant manufacturing operations in Mexico with exports to 17 countries in Central America, the Caribbean and South America. In fiscal 2012, we provided services to customers in approximately 60 countries, and nearly half of our revenues were attributable to customers outside the United States and Canada. Our operations outside the United States and Canada could be substantially affected by foreign economic, political and regulatory risks. These risks include:
| |
| • | fluctuations in currency exchange rates; |
| |
| • | the difficulty of enforcing agreements and collecting receivables through some foreign legal systems; |
| |
| • | customers in some foreign countries potentially having longer payment cycles; |
| |
| • | changes in local tax laws, tax rates in some countries that may exceed those of Canada or the United States and lower earnings due to withholding requirements or the imposition of tariffs, exchange controls or other restrictions; |
| |
| • | seasonal reductions in business activity; |
| |
| • | the credit risk of local customers and distributors; |
| |
| • | general economic and political conditions; |
| |
| • | unexpected changes in legal, regulatory or tax requirements; |
| |
| • | relationships with labor unions and works councils; |
| |
| • | the difficulties associated with managing a large global organization; |
| |
| • | the risk that certain governments may adopt regulations or take other actions that would have a direct or indirect adverse impact on our business and market opportunities, including nationalization of private enterprise; |
| |
| • | non-compliance with applicable currency exchange control regulations, transfer pricing regulations or other similar regulations; |
| |
| • | violations of the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act by acts of agents and other intermediaries whom we have limited or no ability to control; and |
| |
| • | violations of regulations enforced by the U.S. Department of The Treasury's Office of Foreign Asset Control ("OFAC"). |
In addition to the foregoing, in July 2010, Sobel USA Inc.'s Mexican subsidiary submitted a voluntary disclosure regarding potential violations of Cuban Asset Control Regulations to OFAC. The subject transactions involved shipments to Cuba of Mexican-origin medicine and agricultural products by this subsidiary. Sobel USA Inc. and its Mexican subsidiary obtained a letter of no enforcement by OFAC and were granted a license by OFAC to engage in transactions with Cuba through January 31, 2013. Although OFAC granted Sobel USA Inc.'s Mexican subsidiary a license to engage in these transactions, our inability to renew this license or the imposition of more restrictive regulations resulting from geopolitical tensions with Cuba may impede our ability to conduct business in Cuba in the future. If any of these economic or political risks materialize and we have failed to anticipate and effectively manage them, we may experience adverse effects on our business and results of operations. If we do not remain in compliance with current regulatory requirements or fail to comply with future regulatory requirements, then such non-compliance may subject us to liability and have a material adverse effect on our business and results of operations.
Fluctuations in exchange rates could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations and financial performance.
Our most significant transaction exposures arise in our Canadian operations. In addition, approximately 90% of the revenues of the Canadian operations and approximately 10% of its operating expenses are transacted in U.S. dollars. As a result, we may experience transaction exposures because of volatility in the exchange rate between the Canadian and U.S. dollar. Based on our current U.S. denominated net inflows, as of October 31, 2012, fluctuations of +/-10% would, everything else being equal, have an annual effect on loss from continuing operations before taxes of approximately +/- $17.8 million, prior to hedging activities.
The objective of our foreign exchange risk management activities is to minimize transaction exposures and the resulting volatility of our earnings. To mitigate exchange-rate risk, we utilize foreign exchange forward contracts and collars in certain circumstances to lock in exchange rates with the objective that the gain or loss on the forward contracts and collars will approximately offset the loss or gain that results from the transaction or transactions being hedged. As of October 31, 2012, we had entered into foreign exchange forward contracts and collars to cover approximately 80% of our Canadian-U.S. dollar cash flow exposures for fiscal 2012.
Translation gains and losses related to certain foreign currency denominated intercompany loans are included as part of
the net investment in certain foreign subsidiaries and are included in accumulated other comprehensive income in shareholders' equity. We do not currently hedge translation exposures.
While we attempt to mitigate our foreign exchange risk by engaging in foreign currency hedging activities using derivative financial instruments, we may not be successful. We may not be able to engage in hedging transactions in the future, and if we do, we may not be able to eliminate foreign currency risk, and foreign currency fluctuations may have a material adverse effect on our results of operations and financial performance.
We are, or may be, party to certain derivative financial instruments, and our results of operations may be negatively affected in the event of non-performance by the counterparties to such instruments.
From time to time, we enter into interest rate swaps and foreign exchange forward contracts and collars to limit our exposure to changes in variable interest rates and foreign exchange rates. Such instruments may result in economic losses if exchange rates decline to a point lower than our fixed rate commitments. When we enter into such swaps and contracts, we are exposed to credit-related losses, which could impact our results of operations and financial condition in the event of non-performance by the counterparties to such instruments. For more information about our foreign currency risks, please see "Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk."
Because a significant portion of our revenues comes from a limited number of customers, any decrease in sales to these customers could harm our business, results of operations and financial condition.
In fiscal 2012, our top 20 customers in our CMO segment accounted for approximately 80% of our CMO revenues. In addition we had one customer in our CMO segment that accounted for approximately 13% of our CMO revenues and two customers in our CMO segment that each accounted for approximately 10% of our CMO revenues. This customer concentration increases credit risk and other risks associated with particular customers and particular products, including risks related to market demand for customer products and regulatory and other operating risks. Disruptions in the production of major products could damage our customer relationships and adversely impact our results of operations in the future. Revenues from customers that have accounted for significant sales in the past, either individually or as a group, may not reach or exceed historical levels in any future period. The loss or a significant reduction of business from any of our major customers may have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
The success of the Banner Acquisition will depend on, among other things, our ability to realize the revenue enhancements we anticipate and to combine the businesses in a manner that does not materially disrupt Banner's existing customer relationships of Banner or result in decreased revenues resulting from any loss of customers and that permits growth opportunities to occur. If we are not able to successfully achieve these objectives, the anticipated benefits of the Banner Acquisition may not be realized fully or at all or may take longer to realize than expected.
We operate in highly competitive markets, and continue to expand into new markets including through the Banner Acquisition, and competition may adversely affect our business.
We operate in a market that is highly competitive. We compete to provide CMO and PDS to pharmaceutical companies around the world.
Our competition in the CMO market includes full-service pharmaceutical outsourcing companies; contract manufacturers focusing on a limited number of dosage forms; contract manufacturers providing multiple dosage forms; and large pharmaceutical companies offering third-party manufacturing services to fill their excess capacity. In addition, in Europe, there are a large number of privately owned, dedicated outsourcing companies that serve only their local or national markets. Also, large pharmaceutical companies have been seeking to divest portions of their manufacturing capacity, and any such divested businesses may compete with us in the future. We compete primarily on the basis of the security of supply (quality, regulatory compliance and financial stability), service (on-time delivery and manufacturing flexibility) and cost-effective manufacturing (prices and a commitment to continuous improvement).
Our competition in the PDS market includes a large number of laboratories that offer only a limited range of developmental services, generally at a small scale; providers focused on specific technologies and/or dosage forms; and a few fully integrated companies that can provide the full complement of services necessary to develop, scale-up and manufacture a wide range of dosage forms. We also compete in the PDS market with major pharmaceutical and chemical companies, specialized contract research organizations, research and development firms, universities and other research institutions. We may also compete with the internal operations of pharmaceutical companies that choose to source PDS services internally. We compete primarily on the basis of scientific expertise, knowledge and experience in dosage form development, availability of a broad range of equipment, on-time delivery of clinical materials, compliance with cGMPs, regulatory compliance, cost effective services and financial stability.
Some of our competitors may have substantially greater financial, marketing, technical or other resources than we do. Additional competition may emerge and may, among other things, result in a decrease in the fees paid for our services, which would affect our results of operations and financial condition.
One of the many factors affecting competition is the current excess capacity within the pharmaceutical industry of facilities capable of manufacturing drugs in solid and semi-solid dosage forms. Thus, customers currently have a wide range of supply alternatives for these dosage forms. Another factor causing increased competition is that a number of companies in Asia, particularly India, that have been entering the CMO and PDS sectors over the past few years, have begun obtaining approval from the FDA for certain of their plants and have acquired additional plants in Europe and North America. One or more of these companies may become a significant competitor to us. Competition may mean lower prices and reduced demand for CMO and PDS, which could have an adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
We may not be able to successfully offer new services.
In order to successfully compete, we will need to offer and develop new services. The related development costs may require a substantial investment, and we may not have the financial resources to fund such initiatives.
In addition, the success of enhanced or new services will depend on several factors, including our ability to:
| |
| • | properly anticipate and satisfy customer needs, including increasing demand for lower cost services; |
| |
| • | enhance, innovate, develop and manufacture new offerings in an economical and timely manner; |
| |
| • | differentiate our offerings from competitors' offerings; |
| |
| • | meet quality requirements and other regulatory requirements of government agencies; |
| |
| • | obtain valid and enforceable intellectual property rights; and |
| |
| • | avoid infringing the proprietary rights of third parties. |
Even if we were to succeed in creating enhanced or new services, those services may not produce revenues in excess of the costs of development and capital investment and may be quickly rendered obsolete by changing customer preferences or by technologies or features offered by our competitors. In addition, innovations may not be accepted quickly in the marketplace because of, among other things, entrenched patterns of clinical practice, the need for regulatory clearance and uncertainty over third-party reimbursement. Moreover, the Banner Acquisition could compound the challenges of integrating complementary products, services and technologies in the future. The integration of Banner could divert a significant amount of management resources, resulting in less employee time and resources available to focus on developing and offering new services, and we may be unable to commit the resources necessary to develop and offer new services.
We rely on our customers to supply many of the necessary ingredients for our products, and for other ingredients, we rely on other third parties. Our inability to obtain the necessary materials or ingredients for the products we manufacture on behalf of our customers may adversely impact our business, results of operations and financial condition.
Our operations require various APIs, components, compounds and raw materials supplied primarily by third parties, including our customers. Our customers specify the components, raw materials and packaging materials required for their products and, in some cases, specify the suppliers from which we must purchase these inputs. In most cases, the customers supply the APIs to us at no cost pursuant to our standard services agreements.
We generally source our components, compounds and raw materials locally, and most of the materials required by us for our CMO business are readily available from multiple sources.
In some cases, we manage the supply chain for our customers, including the sourcing of certain ingredients and packaging material from third-party suppliers. In certain instances, such ingredients or packaging material can only be supplied by a limited number of suppliers or in limited quantities. If our customers or third-party suppliers do not supply API or other raw materials on a timely basis, we may be unable to manufacture products for our customers. Although no one product or customer is material to our operations, a sustained disruption in the supply chain involving multiple customers or vendors at one time could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations.
Furthermore, customers or third-party suppliers may fail to provide us with raw materials and other components that meet the qualifications and standards required by us or our customers. If third-party suppliers are not able to provide us with products that meet our or our customers' specifications on a timely basis, we may be unable to manufacture products, or products may be available only at a higher cost or after a long delay, which could prevent us from delivering products to our customers within required timeframes. Any such delay in delivering our products may create liability for us to our customers for breach of contract or cause us to experience order cancellations and loss of customers. In the event that we produce products with inferior quality components and raw materials, we may become subject to product liability or warranty claims
caused by defective raw materials or components from a third-party supplier or from a customer, or our customer may be required to recall its products from the market.
It is also possible that any of our supplier relationships could be interrupted due to natural disasters, international supply disruptions caused by geopolitical issues or other events or could be terminated in the future. Any sustained interruption in our receipt of adequate supplies could have an adverse effect on our business and financial results. In addition, while we have supply chain processes intended to reduce volatility in component and material pricing, we may not be able to successfully manage price fluctuations. Price fluctuations or shortages may have an adverse effect on our results of operations and financial condition.
Technological change may cause our offerings to become obsolete over time. If customers decrease their purchases of our offerings, our business, results of operations and financial condition may be adversely affected.
The healthcare industry is characterized by rapid technological change. Demand for our services may change in ways that we may not anticipate because of evolving industry standards or as a result of evolving customer needs that are increasingly sophisticated and varied or because of the introduction by competitors of new services and technologies. Any such decreased demand may adversely affect our business, results of operations and financial condition.
We are dependent on key management, scientific and technical personnel.
We are dependent upon the continued support and involvement of our key management, scientific and technical personnel, the majority of whom have employment agreements with us that impose noncompetition and nonsolicitation restrictions following cessation of employment. Because our ability to manage our business activities and, hence, our success depend in large part on the collective efforts of such personnel, our inability to continue to attract and retain such personnel could have a material adverse effect on our business. Moreover, retaining key personnel from Banner who will be instrumental in integrating our businesses will be important to our ability to successfully achieve our business objectives in the future.
In addition, we are not retaining certain members of Banner senior management, which will require existing members of our senior management to assume control or managerial responsibilities of our new businesses. If such personnel are unable to adequately assume such responsibilities or if we are not able to maintain existing relationships between Banner and its customers, business partners or regulators as a result of such personnel changes, it could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition or results of operations.
Certain of our pension plans are underfunded, and additional cash contributions may be required, which may reduce the cash available for our business.
Certain of our employees in Canada, France and the United Kingdom are participants in defined benefit pension plans that we sponsor. In addition, Banner employees in the Netherlands and Mexico are also covered by a defined benefit pension plan. As of October 31, 2012, the unfunded pension liability on our pension plans was approximately $22.3 million in the aggregate. The amount of future contributions to our defined benefit plans will depend upon asset returns and a number of other factors and, as a result, the amounts we will be required to contribute to such plans in the future may vary. Such cash contributions to the plans will reduce the cash available for our business.
In relation to our U.K. pension plan, the trustees are authorized to accelerate the required payment of future contribution obligations if they have received actuarial advice that the plan is incapable of paying all the benefits that have or will become due for payment as they become due. If the trustees of our U.K. pension plan were to be so advised and took such a step, our U.K. subsidiary would be required to meet the full balance of the cost of securing the benefits provided by the plan through the purchase of annuities from an insurance company, to the extent that it was able to do so. The cost would be likely to exceed the amount of any deficit under the plan while the plan was ongoing.
Any failure of our information systems, such as from data corruption, cyber-based attacks or network security breaches, could adversely affect our business and results of operations.
We rely on information systems in our business to obtain, rapidly process, analyze and manage data to:
| |
| • | facilitate the manufacture and distribution of thousands of inventory items to and from our facilities; |
| |
| • | receive, process and ship orders on a timely basis; |
| |
| • | manage the accurate billing of, and collections from, our customers; |
| |
| • | manage the accurate accounting for, and payment to, our vendors; and |
| |
| • | schedule and operate our global network of manufacturing and development facilities. |
Security breaches of this infrastructure can create system disruptions, shutdowns or unauthorized disclosure of confidential information. If we are unable to prevent such breaches, our operations could be disrupted, or we may suffer financial damage or loss because of lost or misappropriated information. We cannot be certain that advances in criminal capabilities, new discoveries in the field of cryptography or other developments will not compromise or breach the technology protecting the networks that access our products and services. If these systems are interrupted, damaged by unforeseen events or fail for any extended period of time, including due to the actions of third parties, then we may not be able to effectively manage our business, and our results of operations could be adversely affected.
From time to time, we may seek to restructure our operations and may divest non-strategic businesses or assets, which may require us to incur restructuring charges, and we may not be able to achieve the cost savings that we expect from any such restructuring efforts or divestitures.
To improve our profitability, we restructured our Canadian manufacturing operations during fiscal 2008. We also are in the process of restructuring our Puerto Rican operations as part of our efforts to eliminate operating losses and develop a long-term plan for our business. As part of our restructuring efforts, we incurred $6.1 million in repositioning expenses, of which $1.7 million related to the shutdown of the Caguas facility, with the remainder related to the plan of termination we announced on May 9, 2012 ("Plan of Termination"). We expect to adopt additional restructuring plans in order to improve our operational efficiency.
We may not be able to achieve the level of benefits that we expect to realize from these or any future restructuring activities, within expected timeframes, or at all. Furthermore, upon the closure of any facilities in connection with our restructuring efforts, we may not be able to divest such facilities at a fair price or in a timely manner. In addition, as part of any plant closures and the transfer of production to another facility, we are required to obtain the consents of our customers and the relevant regulatory agencies, which we may not be able to obtain. Changes in the amount, timing and character of charges related to our current and future restructurings and the failure to complete or a substantial delay in completing our current and any future restructuring plan could have a material adverse effect on our business.
We may also seek to sell some of our assets in connection with the divestiture of a non-strategic business or as part of internal restructuring efforts. In May 2012, we announced that over the following 24 to 36 months, we would be adjusting the scale and scope of business conducted at our Swindon, U.K., facility, including winding down or transferring non-cephalosporin commercial production to other facilities and, as possible an commercially appropriate, directing pharmaceutical development services projects that require commercialization activities to other facilities within our network. In connection with this action, we recorded an impairment charge of $57.9 million in fiscal 2012. To the extent that we are not successful in completing such divestitures or restructuring efforts, we may have to expend substantial amounts of cash, incur debt and continue to absorb loss-making or under-performing divisions. Any divestitures that we are unable to complete may involve a number of risks, including diversion of management's attention, a negative impact on our customer relationships, costs associated with retaining the targeted divestiture, closing and disposing of the impacted business or transferring business to other facilities. Furthermore, our ability to initiate and complete such transactions may be hindered by our Investor Agreement (the "Investor Agreement") with JLL Patheon Holdings. For example, under the terms of the Investor Agreement, we need majority independent director approval to engage in certain types of transactions.
We may in the future engage in acquisitions and joint ventures. We may not be able to complete such transactions, and such transactions, if executed, pose significant risks.
Our future success may depend on our ability to acquire other businesses or technologies or enter into joint ventures that could complement, enhance or expand our current business or offerings and services or that might otherwise offer us growth opportunities. We may face competition from other companies in pursuing acquisitions and joint ventures. Our ability to enter into such transactions may also be limited by applicable antitrust laws and other regulations in the United States, Canada and foreign jurisdictions in which we do business. We may not be able to complete such transactions for reasons including, but not limited to, a failure to secure financing. We anticipate financing future acquisitions through cash provided by operating activities, borrowings under our Credit Facility (as defined below) and/or other debt or equity financing, including takedowns on our shelf registration statement, which the SEC declared effective on October 17, 2012. All of these could reduce our cash available for other purposes or, in the case of an offering of restricted voting shares or other equity under our shelf registration statement, substantially dilute your investment in us. For example, we incurred additional indebtedness to fund the Banner Acquisition, and this additional debt consumed a significant portion of our ability to borrow and may limit our ability to pursue other acquisitions or growth strategies.
Any transactions that we are able to identify and complete may involve a number of risks, including:
| |
| • | the diversion of management's attention to negotiate the transaction and then integrate the acquired businesses or |
joint ventures;
| |
| • | the possible adverse effects on our operating results during the negotiation and integration process; |
| |
| • | significant costs, charges or writedowns; |
| |
| • | the potential loss of customers or employees of the acquired business; and |
| |
| • | our potential inability to achieve our intended objectives for the transaction. |
In addition, we may be unable to maintain uniform standards, controls, procedures and policies with respect to the acquired business, and this may lead to operational inefficiencies. To the extent that we are successful in making acquisitions, we may have to expend substantial amounts of cash, incur debt and assume loss-making divisions.
JLL has significant influence over our business and affairs, and its interests may differ from ours and those of our other shareholders.
As of October 31, 2012, JLL owned an aggregate of 72,358,181 restricted voting shares, representing approximately 56% of our total restricted voting shares outstanding. On December 3, 2012, we mailed our shareholders of record as of November 27, 2012 offering materials related to a $30 million offering of transferable subscription rights (the "Rights Offering"). In connection with the Rights Offering, JLL committed to exercise its basic subscription privilege in full, as well as any available over-subscription privilege up to the full amount of the Rights Offering. On December 13, 2012, a JLL-affiliated entity exercised its subscription rights in full, including its over-subscription privilege, up to the full amount of the Rights Offering. Any excess subscription payments will be returned, without interest or penalty, as soon as practicable after the expiry date of the Rights Offering. JLL Patheon Holdings also owns an aggregate of 150,000 special voting Class I, Preferred Shares, Series D ("Series D Preferred Shares"), pursuant to which it is entitled to elect up to three of our directors based on the number of restricted voting shares that it holds.
In addition, in connection with the investment by JLL Patheon Holdings in our shares, on April 27, 2007, we entered into the Investor Agreement.
Under the Investor Agreement, we currently are required to seek the approval of JLL Patheon Holdings before we undertake certain actions, including share issuances, the payment of dividends, share repurchases, any merger, consolidation or sale of all or substantially all of our assets or a similar business combination transaction and the incurrence of certain indebtedness in excess of $20.0 million.
JLL exercises significant influence over us as a result of its majority shareholder position, voting rights, Board appointment rights and its rights under the Investor Agreement. As a result, JLL has significant influence over our decisions to enter into corporate transactions and has the ability to prevent any transaction that requires shareholder approval. This concentration of ownership and JLL's rights may prevent a change of control of us that might be considered to be in the interests of shareholders or other stakeholders. In addition, if we are unable to obtain requisite approvals from JLL, we may be prevented from executing critical elements of our business strategy.
Our stock price is volatile and could experience substantial declines.
The market price of our restricted voting shares has historically experienced, and may continue to experience, substantial volatility. Such volatility has resulted or may result from fluctuations in our quarterly operating results or anticipated future results, changes in general conditions in the economy or the financial markets, both of which we have experienced in recent years due to the effects of the global financial crisis, and other developments affecting us or our competitors. Some of these factors are beyond our control, such as changes in revenue and earnings estimates by analysts, market conditions within our industry, disclosures by product development partners and actions by regulatory authorities with respect to potential drug candidates and changes in pharmaceutical and biotechnology industries and the government sponsored clinical research sector. In addition, in recent years, the stock market has experienced significant price and volume fluctuations. The stock market, and in particular the market for pharmaceutical and biotechnology company stocks, has also experienced significant decreases in value in the past. This volatility and valuation decline have affected the market prices of securities issued by many companies, often for reasons unrelated to their operating performance, and might adversely affect the price of our restricted voting shares.
In addition, to provide flexibility with respect to any future capital raising alternatives, we filed a universal shelf registration statement with the SEC in October 2012 to register various securities, including restricted voting shares, warrants, subscription rights, subscription receipts and units. The securities under this registration statement may be offered from time to time, separately or together, directly by us or through underwriters, at amounts, prices, interest rates and other terms to be determined at the time of any offering, up to a total dollar amount of $100.0 million, including $30.0 million under the Rights Offering. To the extent that we raise additional capital by issuing equity securities under our shelf registration statement, our shareholders may experience dilution. Any dilution or potential dilution may cause our shareholders to sell their shares, which
would contribute to a downward movement in the trading price of our restricted voting shares.
Our shareholders might have difficulty enforcing U.S. judgments against us, enforcing U.S. judgments in a Canadian court or bringing an original action in Canada to enforce liabilities based upon U.S. federal securities laws.
We are a corporation organized under the Canada Business Corporations Act, and some of our directors and officers reside principally outside of the United States. As a result, it may not be possible for our shareholders to enforce judgments obtained in U.S. courts against us or them within the United States because a substantial portion of our assets and the assets of these persons are located outside the United States. In addition, a Canadian court may not agree to recognize and enforce a judgment of a U.S. court. Accordingly, even if a shareholder obtains a favorable judgment in a U.S. court, he, she or it may be required to re-litigate the claim in other jurisdictions. In addition, it is possible that a Canadian court would not take jurisdiction over a matter involving a claim based on foreign laws, such as the federal securities laws of the United States.
Failure to implement our corporate strategy or realize the expected benefits from this strategy could adversely affect our business and results of operations.
In September 2011, our Board reviewed and approved our current corporate strategy which is focused on improving the performance of our core operations. Our corporate strategy includes, among other things, assessing our global footprint, accelerating our operational excellence programs for our CMO and PDS segments, and continuing the evolution of our existing commercial sites into centers of excellence that focus on specific technologies or production types.
We have incurred and will likely continue to incur expenses in connection with the design, review and implementation of our corporate strategy, and these expenses may exceed our estimates, may be significant and could materially adversely impact our financial performance.
We have based the design of our corporate strategy on certain assumptions regarding our business, markets, cost structures and customers. If our assumptions are incorrect, we may be unable to fully implement our new corporate strategy and, even if fully implemented, our corporate strategy may not yield the benefits that we expect. For example, our corporate strategy may involve the acquisition or disposition of assets, which we may not be able to consummate in a timely manner, on terms acceptable to us or at all, or which may not achieve the benefits or cost savings we anticipate. If we do not effectively manage our corporate strategy or successfully integrate or realize the anticipated benefits of the Banner Acquisition, instead of resulting in growth for and enhanced value to our company, our strategy may cause us to experience operational issues and expose us to operational and regulatory risk, each of which could have material adverse effects on our reputation, business, financial condition and results of operations.
Risks Relating to Regulatory and Legal Matters
Failure to comply with existing and future regulatory requirements could adversely affect our business, results of operations and financial condition.
Our industry is highly regulated. We are required to comply with the regulatory requirements of various local, state, provincial, national and international regulatory bodies having jurisdiction in the countries or localities in which we manufacture products or in which our customers' products are distributed, and the Banner Acquisition has increased the number of jurisdictions where we may be subject to new and existing regulatory requirements. In particular, we are subject to laws and regulations concerning research and development, testing, manufacturing processes, equipment and facilities, including compliance with cGMPs, labeling and distribution, import and export, and product registration and listing, among other things. As a result, most of our facilities are subject to regulation by the FDA, as well as regulatory bodies of other jurisdictions such as the EMEA and/or the NHSA, depending on the countries in which our customers market and sell the products we manufacture and/or package on their behalf. The Banner Acquisition may expose us to more complex and new regulatory and administrative requirements and legal risks, any of which may require expertise in which we have little or no experience. It is possible that compliance with new regulatory requirements could impose significant compliance costs on us. Such costs could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations
These regulatory requirements impact many aspects of our operations, including manufacturing, developing, labeling, packaging, storage, distribution, import and export and record keeping related to customers' products. Noncompliance with any applicable regulatory requirements can result in government refusal to approve (i) facilities for testing or manufacturing products or (ii) products for commercialization. The FDA and other regulatory agencies can delay, limit or deny approval for many reasons, including:
| |
| • | changes to the regulatory approval process, including new data requirements for product candidates in those jurisdictions, including the United States, in which we or our customers may be seeking approval; |
| |
| • | that a product candidate may not be deemed to be safe or effective; |
| |
| • | the ability of the regulatory agency to provide timely responses as a result of its resource constraints; and |
| |
| • | that the manufacturing processes or facilities may not meet the applicable requirements. |
Any delay in, or failure to receive, approval for any of our or our customers' product candidates or the failure to maintain regulatory approval for our or our customers' products could negatively impact our revenue growth and profitability.
In addition, if new legislation or regulations are enacted or existing legislation or regulations are amended or are interpreted or enforced differently, we may be required to obtain additional approvals, operate according to different manufacturing or operating standards or pay additional product or establishment user fees. This may require a change in our research and development and manufacturing techniques or additional capital investments in our facilities. Any related costs may be significant. If we fail to comply with applicable regulatory requirements in the future, including those that apply to any newly acquired businesses, then we may be subject to warning letters and/or civil or criminal penalties and fines, suspension or withdrawal of regulatory approvals, product recalls, seizure of products, restrictions on the import and export of our products, debarment, exclusion, disgorgement of profits, operating restrictions and criminal prosecution and the loss of contracts, including government contracts, and resulting revenue losses. Inspections by regulatory authorities that identify any deficiencies could result in remedial actions, production stoppages or facility closure, which would disrupt the manufacturing process and supply of product to our customers. In addition, such failure to comply could expose us to contractual and product liability claims, including claims by customers for reimbursement for lost or damaged APIs or recall or other corrective actions, the cost of which could be significant.
Our pharmaceutical development and manufacturing projects including any newly acquired development and manufacturing projects, generally involve products that must undergo pre-clinical and clinical evaluations relating to product safety and efficacy before they are approved as commercial therapeutic products. The regulatory authorities having jurisdiction in the countries in which our customers intend to market their products may delay or put on hold clinical trials or delay approval of a product or determine that the product is not approvable. The FDA or other regulatory agencies can delay approval of a drug if our manufacturing facility, including any newly acquired facility, is not able to demonstrate compliance with cGMPs, pass other aspects of pre-approval inspections or properly scale up to produce commercial supplies. The FDA and comparable government authorities having jurisdiction in the countries in which our customers intend to market their products have the authority to withdraw product approval or suspend manufacture if there are significant problems with raw materials or supplies, quality control and assurance or the product we manufacture is adulterated or misbranded. If our pharmaceutical development projects and their related revenues are not maintained, it could materially adversely affect our results of operations and financial condition.
We are subject to regulatory requirements for controlled substances, which may adversely affect our business or subject us to liabilities if we fail to comply.
Some of our manufactured products, including products currently manufactured by Banner, are listed as controlled substances. Controlled substances are those products that present a risk of substance abuse. In the United States, these types of products are classified by the by the DEA as Schedule II, III, and IV substances under the Controlled Substances Act of 1970. The DEA classifies substances as Schedule I, II, III, IV or V substances, with Schedule I substances considered to present the highest risk of substance abuse and Schedule V substances the lowest risk. Scheduled substances are subject to DEA regulations relating to manufacturing, storage, distribution, import and export and physician prescription procedures. For example, scheduled drugs are subject to distribution limits and a higher level of recordkeeping requirements. Furthermore, the total amount of controlled substances for manufacture or commercial distribution is limited by the DEA and allocated through quotas, and we or our customers' quotas, if any, may not be sufficient to meet commercial demand or to economically produce the product.
Entities must be registered annually with the DEA to manufacture, distribute, dispense, import, export and conduct research using controlled substances. State controlled substance laws also require registration for similar activities. In addition, the DEA requires entities handling controlled substances to maintain records, file reports, follow specific labeling and packaging requirements and provide appropriate security measures to control against diversion of controlled substances. In addition, certain of the non-U.S. jurisdictions in which our customers market their products have similar restrictions with respect to controlled substances. If we fail to follow these requirements, we may be subject to significant civil and/or criminal penalties and possibly a revocation of a DEA registration.
Products containing controlled substances may generate significant public health and safety issues, and in such instances, federal or state authorities can withdraw or limit the marketing rights or regulatory approvals for these products. For some scheduled substances, the FDA may require us or our customers to develop product attributes or a risk evaluation and mitigation strategy to reduce the inappropriate use of the products, including the manner in which they are marketed and sold, so as to reduce the risk of diversion or abuse of the product. Developing such a program may be time-consuming and could
delay approval of any product candidates. Such a program or delays of any approval from the FDA could adversely affect our business, results of operations and financial condition.
Decisions of the governmental agencies that regulate us and our customers may affect the demand for our products and significantly influence our business, results of operations and financial condition.
We are dependent on the ability of our customers to obtain regulatory approval and successfully market and obtain third-party coverage and reimbursement for their products and have no control or influence over the regulatory approval process. Delays in obtaining regulatory approval may have a material impact on our operations since our pharmaceutical development and manufacturing projects often involve products that must undergo safety and clinical evaluations before they are approved as commercial therapeutic products. In recent years, our revenues have been negatively impacted due to delays in the regulatory approval of certain of our customers' products.
By way of example, on February 7, 2010, a unit of Johnson & Johnson ("J&J") announced that it received a complete response letter from the FDA regarding an NDA for Ceftobiprole that requested additional information and recommended additional clinical studies before approval. The company originally submitted the application in May 2007, and Ceftobiprole has been approved in Canada and in Switzerland. On June 24, 2010, the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (the "CHMP"), after re-examination, confirmed refusal of Janssen-Cilag International N.V.'s marketing authorization for Ceftobiprole. On September 9, 2010, Basilea Pharmaceutica Ltd. announced that Janssen-Cilag AG, a J&J company, will be discontinuing sale of Ceftobiprole (Zevtera™) for the treatment of complicated skin and soft tissue infections in Switzerland. Janssen-Cilag AG, the holder of the Marketing Authorization in Switzerland, has requested Swissmedic to withdraw the marketing authorization of Zevtera™ and discontinued sale of Zevtera™ as of September 17, 2010. This action was taken based on the unfavorable assessments of the marketing authorization applications for Ceftobiprole in the United States and the European Union. In the first quarter of fiscal 2011, we amended our manufacturing and supply agreement with J&J for Ceftobripole to terminate the agreement two and a half years earlier than was originally planned, which will negatively impact our future revenue streams from J&J for this product.
Since we develop and manufacture products that require regulatory approval, failure to gain all such regulatory approvals in a timely manner may adversely reduce our production levels, which would adversely affect our business, results of operations and financial condition. In the event that regulatory authorities fail to approve the products that we develop and/or manufacture, we may not receive payment from our customers under our contracts.
We are subject to environmental, health and safety laws and regulations, which could subject us to liabilities, increase our costs or restrict our operations in the future.
Our operations, including the operations of Banner, are subject to a variety of environmental, health and safety laws and regulations in each of the jurisdictions in which we operate. These laws and regulations govern, among other things, air emissions, wastewater discharges, the handling and disposal of hazardous substances and wastes, soil and groundwater contamination and employee health and safety. We are also subject to laws and regulations governing the destruction and disposal of raw materials and non-compliant products, the handling of regulated material that is included in our offerings and the disposal of our offerings at the end of their useful life. These laws and regulations have increasingly become more stringent, and we may incur additional expenses to ensure compliance with existing or new requirements in the future. Any failure by us to comply with environmental, health and safety requirements could result in the limitation or suspension of our operations. We also could incur monetary fines, civil or criminal sanctions, third-party claims or cleanup or other costs as a result of violations of or liabilities under such requirements. Although we maintain insurance coverage for environmental liabilities in the aggregate amount of $10 million, the costs of environmental remediation and other liabilities may exceed the amount of such coverage or may not be covered by such insurance. In addition, compliance with environmental, health and safety requirements could restrict our ability to expand our facilities or require us to acquire costly pollution control equipment, incur other significant expenses or modify our manufacturing processes.
Our manufacturing facilities, in varying degrees, use, store and dispose of hazardous substances in connection with their processes. At some of our facilities, these substances are stored in underground storage tanks or used in refrigeration systems. Some of our facilities, including those in Puerto Rico, have been utilized over a period of years as manufacturing facilities, with operations that may have included on-site landfill or other waste disposal activities and have certain known or potential conditions that may require remediation in the future, and several of these have undergone remediation activities in the past by former owners or operators. Some of our facilities are located near third-party industrial sites and may be impacted by contamination migrating from such sites. A number of our facilities use groundwater from onsite wells for process and potable water, and if these onsite sources became contaminated or otherwise unavailable for future use, we could incur expenses for obtaining water from alternative sources. In addition, our operations have grown through acquisitions, and it is possible that facilities that we have acquired may expose us to environmental liabilities associated with historical site conditions that have
not yet been discovered. Some environmental laws impose liability for contamination on current and former owners and operators of affected sites, regardless of fault. If remediation costs or potential claims for personal injury or property or natural resource damages resulting from contamination arise, they may be material and may not be recoverable under any contractual indemnity or otherwise from prior owners or operators or any insurance policy. Additionally, we may not be able to successfully enforce any such indemnity or insurance policy in the future. In the event that new or previously unknown contamination is discovered or new cleanup obligations are otherwise imposed at any of our currently or previously owned or operated facilities, we may be required to take additional, unplanned remedial measures and record charges for which no reserves have been recorded.
We are subject to product and other liability risks that could adversely affect our results of operations and financial condition.
We may be named as a defendant in product liability lawsuits, which may allege that products or services we, or any newly acquired businesses, have provided have resulted or could result in an unsafe condition or injury to consumers. We may also be exposed to other liability lawsuits, such as other tort, regulatory or intellectual property claims. Such lawsuits could be costly to defend and could result in reduced sales, significant liabilities and diversion of management's time, attention and resources. Even claims without merit could subject us to adverse publicity and require us to incur significant legal fees.
Historically, we have sought to manage this risk through the combination of product liability insurance and contractual indemnities and liability limitations in our agreements with customers and vendors. We currently maintain insurance coverage for product and other liability claims in the aggregate amount of $85.0 million. If our existing liability insurance is inadequate or we are not able to maintain such insurance, there may be claims asserted against us that are not covered by such insurance. A partially or completely uninsured claim, if successful and of sufficient magnitude, could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations and financial condition.
We and our customers depend on trademarks, patents, trade secrets, copyrights and other forms of intellectual property protections, but these protections may not be adequate.
We rely on a combination of trademark, patent, trade secret and other intellectual property laws in Canada, the United States and other foreign countries. We have applied in Canada, the United States and in certain countries for registration of a limited number of patents and trademarks, some of which have been registered or issued. Our applications may not be approved by the applicable governmental authorities, and third parties may seek to oppose or otherwise challenge our registrations or applications. We also rely on unregistered proprietary rights, including know-how and trade secrets related to our PDS and CMO services. Although we require our employees to enter into confidentiality agreements prohibiting them from disclosing our proprietary information or technology, these agreements may not provide meaningful protection for our trade secrets and proprietary know-how. Further, third parties who are not party to confidentiality agreements may obtain access to our trade secrets or know-how, and others may independently develop similar or equivalent trade secrets or know-how. If our proprietary information is divulged to third parties, including our competitors, or our intellectual property rights are otherwise misappropriated or infringed, our competitive position could be harmed.
If we are unable to protect the confidentiality of our customers' proprietary information, we may be subject to claims.
Many of the formulations used by us in manufacturing or developing products to customer specifications are subject to trade secret protection, patents or other protections owned or licensed by the relevant customer. We take significant efforts to protect our customer's proprietary and confidential information, including requiring our employees to enter into agreements protecting such information. If, however, any of our employees breaches the non-disclosure provisions in such agreements, or if our customers make claims that their proprietary information has been disclosed, then our business may be materially adversely impacted.
Our services and our customers' products may infringe on or misappropriate the intellectual property rights of third parties.
While we believe that our services do not infringe upon in any material respect or misappropriate the proprietary rights of other parties and/or that meritorious defenses would exist with respect to any assertions to the contrary, our services may be found to infringe on the proprietary rights of others. Any claims that our services infringe third parties' rights, including claims arising from our contracts with our customers, regardless of their merit or resolution, could be costly and may divert the efforts and attention of our management and technical personnel. We may not prevail in such proceedings given the complex technical issues and inherent uncertainties in intellectual property litigation. If such proceedings result in an adverse outcome, we could be required, among other things, to pay substantial damages, license such technology and/or cease the manufacture, use or sale of the infringing processes or offerings, any of which could adversely affect our business.
Tax legislation initiatives or challenges to our tax positions could adversely affect our results of operations and financial condition.
We are a multinational corporation with global operations. As such, we are subject to the tax laws and regulations of Canadian federal, provincial and local governments, the United States and many international jurisdictions. From time to time, various legislative initiatives may be proposed that could adversely affect our effective tax rate or tax payments. In addition, tax laws and regulations are extremely complex and subject to varying interpretations. If our tax positions are challenged by relevant tax authorities, we may not be successful in defending such a challenge and may experience an adverse impact on our results of operations and financial condition.
Changes in healthcare reimbursement in Canada, the United States or internationally could adversely affect customers' demand for our services and our results of operations.
The healthcare industry has changed significantly over time, and we expect the industry to continue to evolve. Some of these changes, such as healthcare reform, adverse changes in government funding of healthcare products and services, legislation or regulations governing the privacy of patient information, or the delivery or pricing of pharmaceuticals and healthcare services or mandated benefits, may cause healthcare industry participants to reduce the amount of our services and products they purchase or the price they are willing to pay for our services and products. For example, the recent passage of healthcare reform legislation in the United States changes laws and regulations governing healthcare service providers and specifically includes certain cost containment measures that may adversely impact some or all of our customers and thus may have an adverse impact on our business. Changes in the healthcare industry's pricing, selling, inventory, distribution or supply policies or practices could also significantly reduce our revenue and profitability. In particular, volatility in individual product demand may result from changes in public or private payer reimbursement or coverage.
Risks Relating to Our Debt
Our substantial level of indebtedness could adversely affect our financial health.
Our total interest-bearing debt as of December 17, 2012 was $595.0 million. As of December 17, 2012, we had approximately $65.0 million available for additional borrowings under our $85.0 million secured revolving credit facility (the "Secured Revolving Facility") and our secured term loan in the amount of $575.0 million (the "Secured Term Loan," and together with the Secured Revolving Facility, the "Credit Facility").
Our substantial financial leverage poses risks to us. Debt service requirements in future periods may be higher than in prior years as a result of a number of factors, including increased borrowing and increases in floating interest rates. In addition, we may incur substantial fees from time to time in connection with debt amendments or refinancing. If our cash flow is not sufficient to service our debt and adequately fund our business, we may be required to seek further additional financing or refinancing or dispose of assets. We may not be able to effect any of these alternatives on satisfactory terms or at all. In addition, our financial leverage could adversely affect our ability to raise additional capital to fund our operations, could impair our ability to respond to operational challenges, changing business and economic conditions and new business opportunities and may make us vulnerable in the event of a downturn in our business.
If we fail to satisfy our obligations under our indebtedness or fail to comply with the financial and other restrictive covenants contained in the agreements governing such indebtedness, such failure could result in an event of default in respect of any or all such indebtedness. An event of default under one or more of our material debt instruments could result in all of our indebtedness becoming immediately due and payable and could permit (i) the Credit Facility lenders and (ii) our other secured lenders to foreclose on our assets securing such indebtedness.
We may not be able to generate sufficient cash to service all of our indebtedness and may be forced to take other actions to satisfy our obligations under our indebtedness, which may not be successful.
Our ability to make scheduled payments or to refinance our debt obligations depends on our financial and operating performance, which is subject to prevailing economic and competitive conditions and to certain financial, business and other factors beyond our control. We may not be able to maintain a sufficient level of cash flow from operating activities to permit us to pay the principal and interest on our Credit Facility and our other indebtedness.
If our cash flows and capital resources are insufficient to fund our debt service obligations, we may be forced to reduce or delay capital expenditures, sell assets, seek additional capital or seek to restructure or refinance our indebtedness, including our Credit Facility. These alternative measures may not be successful and may not permit us to meet our scheduled debt service obligations. In the absence of such cash flows and resources, we could face substantial liquidity problems and might be required to sell material assets or operations to attempt to meet our debt service and other obligations. The instruments governing our indebtedness restrict our ability to conduct asset sales and/or use the proceeds from asset sales. We may not be
able to consummate those asset sales to raise capital or sell assets at prices and on terms that we believe are fair and any proceeds that we receive may not be adequate to meet all debt service obligations then due. If we cannot meet our debt service obligations, the holders of our debt may accelerate our debt and, to the extent such debt is secured, foreclose on our assets. In such an event, we may not have sufficient assets to repay all of our debt.
Our debt agreements contain restrictions that limit our flexibility in operating our business and our ability to raise additional funds.
The agreements that govern the terms of our debt contain, and the agreements that govern our future debt may contain, covenants that restrict our ability and the ability of our subsidiaries to, among other things:
| |
| • | incur additional indebtedness; |
| |
| • | issue additional equity; |
| |
| • | pay dividends on or make distributions in respect of capital stock or make certain other restricted payments or investments; |
| |
| • | enter into agreements that restrict distributions from subsidiaries or restrict our ability to incur liens on certain of our assets; |
| |
| • | make capital expenditures; |
| |
| • | sell or otherwise dispose of assets, including capital stock of subsidiaries; |
| |
| • | enter into transactions with affiliates; |
| |
| • | create or incur liens; and |
A breach of the covenants or restrictions under our indebtedness could result in an event of default, which may allow our lenders to accelerate the related debt and may result in the acceleration of any other debt to which a cross-acceleration or cross-default provision applies. In the event our lenders accelerate the repayment of our indebtedness, we may not have sufficient assets to repay such indebtedness or be able to borrow sufficient funds to refinance it. Even if we are able to obtain new financing, it may not be on commercially reasonable terms or on terms acceptable to us. As a result of these restrictions, we may be:
| |
| • | limited in how we conduct our business and execute our business strategy; |
| |
| • | unable to raise additional debt or equity financing to operate during general economic or business downturns; |
| |
| • | unable to compete effectively or to take advantage of new business opportunities; or |
These restrictions may affect our ability to grow in accordance with our plans.
Despite our substantial level of indebtedness, we may still be able to incur significant additional amounts of debt, which could further exacerbate the risks associated with our substantial debt.
We and our subsidiaries may be able to incur significant additional amounts of debt, including additional secured indebtedness, in the future. The terms of the Credit Facility restrict, but do not completely prohibit, us from doing so. In addition, our Credit Facility allows us to issue additional senior secured notes and other indebtedness and liabilities under certain circumstances. If new debt or other liabilities are added to our current debt levels, then the related risks that we and our subsidiaries now face could intensify.
Risks Relating to the Banner Acquisition
We may not be able to successfully integrate or realize the anticipated benefits of the Banner Acquisition and may not be able to maintain or achieve profitability of the acquired businesses or overall.
We have devoted, and will continue to devote, significant management attention and resources to integrating the business practices and operations of Banner. While we believe that we have sufficient resources to integrate Banner successfully, such integration involves a number of significant risks, including diversion of management's attention and resources. We may encounter difficulties in the integration process, including the following:
| |
| • | the inability successfully to integrate our businesses in a manner that permits us to achieve the operating synergies anticipated to result from the acquisition, either due to integration challenges, personnel shortages or otherwise, any of |
which would result in the anticipated benefits of the acquisition not being realized partly or wholly in the time frame currently anticipated or at all;
| |
| • | lost sales as a result of customers of either of the two companies deciding not to continue business relationships with us; |
| |
| • | the complexities associated with managing new businesses with which we have no prior experience; |
| |
| • | the complexities associated with managing operations out of several different locations, including geographic locations where we have no prior experience, and integrating personnel from multiple companies, while at the same time attempting to provide consistent, high quality products and services under a unified culture; |
| |
| • | the additional complexities of integrating companies with different histories, regulatory restrictions, sales forces, marketing strategies, product markets and customer bases; |
| |
| • | the failure to retain key employees, some of whom could be critical to integrating the companies; |
| |
| • | potential unknown liabilities and unforeseen increased expenses or regulatory conditions associated with the acquisition; and |
| |
| • | performance shortfalls as a result of the diversion of management's attention caused by integrating the companies' operations. |
The anticipated benefits of the Banner Acquisition may not be realized, and significant time and cost beyond that anticipated may be required in connection with the integration of Banner and the continuing operation of the Banner businesses. If we are unable to integrate and manage Banner successfully, or to achieve a substantial portion of the anticipated benefits of the acquisition within the time frame anticipated by management and within budget, it could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition or results of operations.
The integration of Banner may cost more than we anticipate.
We have incurred significant transaction and closing costs associated with the Banner Acquisition, and we have incurred and expect to continue to incur significant integration-related expenses associated with combining the businesses, including expenses relating to personnel training, IT and general system integration, human resources attention to personnel integration matters, marketing and sales force integration, personnel redundancies, the commencement of new regulatory practices with which we have no prior experience, and other operational expenses incurred during the integration process. It is possible that we will incur significant additional unforeseen costs in connection with the Banner Acquisition or integration that will negatively impact our earnings.
If third parties bring claims against us or if Sobel Best N.V. or VION Holdings N.V. breached any representations, warranties or covenants set forth in the purchase agreement, we may not be adequately indemnified for any losses arising therefrom.
Banner may have unknown liabilities, including, but not limited to, product liability, workers' compensation liability, tax liability and liability for improper business or regulatory practices. Although the purchase agreement provides that Sobel Best N.V. or VION Holdings N.V. will indemnify us for losses arising from a breach of the representations, warranties and covenants by Sobel Best N.V. or VION Holdings N.V. set forth in the purchase agreement, such indemnification is limited, in general terms, to an aggregate amount of $25 million and claims may be asserted against Sobel Best N.V. or VION Holdings N.V. only if a claim exceeds $25,000 and the aggregate amount of all claims exceeds $2 million. In addition, with some exceptions, the survival period for claims under the purchase agreement is limited to the 18 month period following the closing of the acquisition. We will be prevented from seeking indemnification for most claims above the aggregate threshold or arising after the applicable survival period for indemnification claims. Moreover, we could experience difficulty enforcing indemnification obligations or we could incur material liabilities for the past activities of Banner. Such liabilities and related legal or other costs could materially harm our business or results of operations.
The Banner Acquisition makes evaluating our operating results difficult and our historical financial information may not accurately indicate how we will perform in the future.
The Banner Acquisition may make it more difficult for us to evaluate and predict our future operating performance. Our
historical results of operations do not give effect to the Banner Acquisition; accordingly, such historical financial information does not necessarily reflect what the financial position, operating results and cash flows of us or Banner will be in the future on a consolidated basis.
Item 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments.
Not applicable.
Item 2. Properties.
We have a network of nine manufacturing facilities, and eight development centers located in North America and Europe. The following table provides additional information about our principal manufacturing facilities and development centers:
|
| | | | | | | | |
| Facility sites | Country | | Segment | | Square Feet | | Owned/Leased |
Burlington(1) | Canada | | CMO | | 45,496 |
| | Leased |
| Mississauga | Canada | | CMO/PDS | | 285,570 |
| | Owned |
| Whitby | Canada | | CMO/PDS | | 233,664 |
| | Owned |
| Cincinnati | United States | | CMO/PDS | | 495,700 |
| | Owned |
| Caguas | Puerto Rico | | CMO | | 209,336 |
| | Owned |
| Manatí | Puerto Rico | | CMO | | 546,872 |
| | Owned |
| Ferentino | Italy | | CMO/PDS | | 290,473 |
| | Owned |
| Monza | Italy | | CMO | | 463,229 |
| | Owned |
Milton Park(2) | United Kingdom | | PDS | | 13,500 |
| | Leased |
| Swindon | United Kingdom | | CMO/PDS | | 355,511 |
| | Owned |
| Bourgoin-Jallieu | France | | CMO/PDS | | 355,228 |
| | Owned |
San Francisco(3) | United States | | PDS | | 5,063 |
| | Leased |
_________________________
| |
| (1) | Our Burlington facility is subject to a lease from Klaus Stephan Reeckmann until 2014, with an annual minimum rent of $269,872, based on an average foreign exchange rate of Canadian dollars ("CAD") to USD for fiscal 2012 of 0.9955. As of September, 2012 we now sublease the majority of this space to Bellwyck Packaging Solutions to whom we sold our global secondary clinical packaging and clinical distribution services business. |
| |
| (2) | Our Milton Park facility is subject to a lease from Lansdown Estates Group Limited until 2020, with an annual minimum rent of $222,166, based on an average foreign exchange rate of British pound sterling to USD for fiscal 2012 of 1.5789. |
| |
| (3) | Our San Francisco facility is subject to a lease from ARE-East Jamie Court, LLC until 2014, with an annual minimum rent of $252,648. |
In connection with the Banner Acquisition, we acquired four additional manufacturing facilities, which are located in High Point, North Carolina, Alberta, Canada, Mexico City, Mexico and Tilburg, The Netherlands. We own each of these manufacturing facilities, and they have approximately 243,000, 63,000, 27,000 and 97,000 square feet, respectively.
We also lease facilities in Research Triangle Park, North Carolina (U.S. headquarters) and Tokyo, Japan (sales office) and, in connection with the Banner Acquisition, we assumed leases related to facilities in High Point, North Carolina and Mexico City, Mexico. Certain of these facilities are pledged as collateral for our $280.0 million, 8.625% senior secured notes, due April 15, 2017 (the "Notes") and our Credit Facility. See "Item 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis-Liquidity and Capital Resources-Financing Arrangements." We believe that our facilities are adequate for our operations and that suitable additional space will be available when needed.
Item 3. Legal Proceedings.
Neither we, nor any of our subsidiaries, are involved in any material pending legal proceeding. Additionally, no such proceedings are known to be contemplated by governmental authorities.
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures
Not applicable.
PART II
Item 5. Market for Registrant's Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity
Securities.
Market Information
Our restricted voting shares are traded on the TSX under the trading symbol "PTI." There is no established public trading market for our shares in the United States. The following table sets forth the reported high and low trading prices (in Canadian dollars) of our restricted voting shares on the TSX for the following periods:
Toronto Stock Exchange
(Canadian $s)
|
| | | | | |
| | High | | Low |
| Fiscal year ending October 31, 2012: | | | |
| Quarter ended January 31, 2012 | 1.42 |
| | 1.08 |
|
| Quarter ended April 30, 2012 | 2.30 |
| | 1.30 |
|
| Quarter ended July 31, 2012 | 2.98 |
| | 1.75 |
|
| Quarter ended October 31, 2012 | 3.90 |
| | 2.41 |
|
| Fiscal year ending October 31, 2011: | | | |
| Quarter ended January 31, 2011 | 2.45 |
| | 2.03 |
|
| Quarter ended April 30, 2011 | 2.81 |
| | 2.23 |
|
| Quarter ended July 31, 2011 | 2.34 |
| | 1.74 |
|
| Quarter ended October 31, 2011 | 2.05 |
| | 1.30 |
|
Holders
As of December 13, 2012, there were approximately 533 holders of record of our restricted voting shares. This number does not include beneficial owners for whom shares are held by nominees in street name.
Dividends
We did not pay dividends on our restricted voting shares during fiscal 2012, fiscal 2011 or our fiscal year ended October 31, 2010 ("fiscal 2010"). We currently do not intend to pay cash dividends on our restricted voting shares for the foreseeable future, as we plan to reinvest our cash to enhance our growth.
Our debt agreements include covenants that limit our ability to pay dividends. See "Note 7—Long-Term Debt" to our consolidated financial statements included in this Form 10-K. The Investor Agreement also prevents us from declaring or paying any dividends without the approval of JLL Patheon Holdings for so long as JLL Patheon Holdings holds at least 13,306,488 restricted voting shares.
Exchange Controls
There is no law or governmental decree or regulation in Canada that restricts the export or import of capital or affects the remittance of dividends, interest or other payments to non-resident holders of our restricted voting shares, other than withholding tax requirements. See "—Certain Canadian Federal Income Tax Considerations."
There is no limitation imposed by Canadian law or by our articles of amalgamation on the right of a non-resident to hold or vote restricted voting shares, other than as provided by the "Investment Canada Act," the "North American Free Trade Agreement Implementation Act (Canada)," the "World Trade Organization Agreement Implementation Act" and the CBCA, which permits our shareholders, by special resolution, to amend our articles of amalgamation to constrain the issue or transfer of any class or series of our securities to persons who are not residents of Canada in certain limited circumstances.
The Investment Canada Act requires notification and, in certain cases, advance review and approval by the Government of Canada of the acquisition by a "non-Canadian" of "control" of a "Canadian business," all as defined in the Investment Canada Act. Generally, the threshold for review will be higher in monetary terms for a member of the World Trade Organization or North American Free Trade Agreement.
Certain Canadian Federal Income Tax Considerations
The following is a summary of the principal Canadian federal income tax considerations generally applicable to holders of our restricted voting shares who, at all relevant times, for purposes of the Income Tax Act (Canada) (the "Tax Act") and the Canada-United States Tax Convention (1980) (the "Canada-U.S. Tax Treaty") (i) are the beneficial owners of such restricted voting shares; (ii) are "qualifying persons" entitled to benefits under the Canada-U.S. Tax Treaty; (iii) are resident in the United States and are neither resident nor deemed to be resident in Canada; (iv) deal at arm's length with, and are not affiliated with, us; (v) hold their restricted voting shares as capital property; (vi) do not use or hold, and are not deemed to use or hold their restricted voting shares in connection with carrying on business in Canada; and (vii) do not hold or use restricted voting shares in connection with a permanent establishment or fixed base in Canada (each, a "U.S. Resident Holder"). Special rules, which are not discussed in this summary, may apply to a U.S. Resident Holder that is an insurer that carries on an insurance business in Canada and elsewhere.
Our restricted voting shares will generally be considered capital property to a U.S. Resident Holder unless either (i) the U.S. Resident Holder holds our restricted voting shares in the course of carrying on a business of buying and selling securities, or (ii) the U.S. Resident Holder has acquired our restricted voting shares in a transaction or transactions considered to be an adventure or concern in the nature of trade.
Limited liability companies ("LLCs") that are not taxed as corporations pursuant to the provisions of the Code generally do not qualify as resident in the United States and are not "qualified persons" for purposes of the Canada-U.S. Tax Treaty. Under the Canada-U.S. Tax Treaty, a resident of the United States who is a member of such an LLC and is otherwise a "qualified person" eligible for benefits under the Canada-U.S. Tax Treaty may be entitled to claim benefits under the Canada-U.S. Tax Treaty in respect of income, profits or gains derived through the LLC. A U.S. Resident Holder who is a member of an LLC should consult with his, her or its own tax advisors with respect to eligibility for benefits in respect of any income, profits or gains derived through such LLC.
The Canada-U.S. Tax Treaty includes limitation on benefits rules that restrict the ability of certain persons who are resident in the United States to claim any or all benefits under the Canada-U.S. Tax Treaty. A U.S. Resident Holder should consult his, her or its own tax advisors with respect to his, her or its eligibility for benefits under the Canada-U.S. Tax Treaty, having regard to these rules.
This summary is based on the current provisions of the Canada-U.S. Tax Treaty and the Tax Act, the regulations thereunder (the "Regulations") and counsel's understanding of the current published administrative policies and assessing practices of the Canada Revenue Agency (the "CRA") made publicly available prior to the date of this annual report on Form 10-K.
This summary also takes into account all specific proposals to amend the Tax Act and the Regulations publicly announced by or on behalf of the Minister of Finance (Canada) prior to the date hereof (the "Tax Proposals"), and assumes that all such Tax Proposals will be enacted in the form proposed. There is no assurance that the Tax Proposals will be enacted in their current form, or at all. This summary does not otherwise take into account or anticipate any changes in the law, whether by legislative, governmental or judicial action, or in the CRA's administrative policies or assessing practices.
This summary does not address the tax laws of any province or territory of, or any jurisdiction outside, Canada, which might materially differ from the Canadian federal considerations.
This summary is of a general nature only and not intended to be, nor should it be construed to be, legal or tax advice to any particular U.S. Resident Holder, and no representations concerning the tax consequences to any particular U.S. Resident Holder are made. U.S. Resident Holders should consult their own tax advisers regarding the income tax consequences, arising from and relating to the acquisition, ownership and disposition of our restricted voting shares with respect to their own particular circumstances.
Currency Conversion
For purposes of the Tax Act, all amounts relating to the acquisition, holding or disposition of our restricted voting shares, including interest, dividends, adjusted cost base and proceeds of disposition, must be converted into Canadian dollars based on the relevant exchange rate applicable on the effective date (as determined in accordance with the Tax Act) of the related acquisition, disposition or recognition of income.
Disposition of Restricted Voting Shares
A U.S. Resident Holder will not be subject to tax under the Tax Act in respect of any capital gain (or entitled to deduct any capital loss) realized on a disposition of restricted voting shares unless our restricted voting shares constitute "taxable
Canadian property" (as defined in the Tax Act) of the U.S. Resident Holder at the time of disposition and the U.S. Resident Holder is not entitled to relief under the Canada-U.S. Tax Treaty.
Generally, restricted voting shares will not be taxable Canadian property of a U.S. Resident Holder at a particular time provided the restricted voting shares are listed on a designated stock exchange (which currently includes the TSX) unless at any time during the 60-month period preceding the disposition (i) the U.S. Resident Holder, persons with whom the U.S. Resident Holder does not deal at arm's length, and the U.S. Resident Holder together with all such persons owned 25% or more of the shares of any class or series of Patheon, and (ii) 50% or more of the fair market value of the restricted voting shares was derived directly or indirectly from one or any combination of real or immovable property situated in Canada, "Canadian resource properties", "timber resource properties" (each defined in the Tax Act), and options in respect of, or interests in, or for civil law rights in, any such properties. Notwithstanding the foregoing, a restricted voting share may also be deemed to be taxable Canadian property of a U.S. Resident Holder in certain circumstances specified in the Tax Act.
A U.S. Resident Holder whose restricted voting shares are, or may be considered to be, taxable Canadian property should consult with his, her or its own tax advisors for advice having regard to such holder's particular circumstances.
Dividends
Dividends on restricted voting shares paid or credited, or deemed to be paid or credited, to a U.S. Resident Holder will be subject to a non-resident withholding tax under the Tax Act at a rate of 25%, subject to reduction under the provisions of an applicable tax treaty or convention. Pursuant to the Canada-U.S. Tax Treaty, the rate of withholding tax on dividends paid or credited to a U.S. Resident Holder that is the beneficial owner of such dividends generally is reduced to 15% or, if the U.S. Resident Holder is a corporation that is the beneficial owner of at least 10% of our voting stock, to 5%.
The Canada-U.S. Tax Treaty generally exempts from Canadian withholding tax dividends paid or credited to (i) a qualifying religious, scientific, literary, educational or charitable organization or (ii) a qualifying trust, company, organization or arrangement constituted and operated exclusively to administer or provide a pension, retirement or employee benefit fund or plan, if such organization or qualifying trust, company or arrangement is a resident of the United States and is exempt from income tax under the laws of the United States.
HOLDERS OF RESTRICTED VOTING SHARES ARE URGED TO CONSULT THEIR OWN TAX ADVISORS TO DETERMINE THE PARTICULAR TAX CONSEQUENCES TO THEM, INCLUDING THE APPLICATION AND EFFECT OF ANY STATE, LOCAL OR FOREIGN INCOME AND OTHER TAX LAWS, OF THE ACQUISITION, OWNERSHIP AND DISPOSITION OF RESTRICTED VOTING SHARES.
Stock Performance Graph
The information in this "Item 5. Market for Registrant's Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity—Stock Performance Graph" is not deemed to be "soliciting material" or to be "filed" with the SEC or subject to Regulation 14A or 14C under the Exchange Act or to the liabilities of Section 18 of the Exchange Act, and will not be deemed to be incorporated by reference into any filing under the Securities Act or the Exchange Act, except to the extent we specifically incorporate it by reference into such filing.
The following graph compares our cumulative total shareholder return from October 31, 2007, with those of the TSX Index and the S&P/TSX Pharmaceutical Index. The measurement points utilized in the graph consist of the last trading day in each fiscal year. The historical stock performance presented below is not intended to and may not be indicative of future stock performance.
Comparison of 5-Year Cumulative Total Return*
Among Patheon Inc., the TSX Index and the S&P/TSX Pharmaceutical Index
* Assumes (1) $100 invested on October 31, 2007 in Patheon's restricted voting shares, the TSX Index and the S&P/TSX Pharmaceutical Index and (2) the immediate reinvestment of all dividends.
Item 6. Selected Financial Data.
The selected financial data set forth below as of and for the years ended October 31, 2012, 2011, 2010, 2009 and 2008 were prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States ("U.S. GAAP"), were derived from our consolidated financial statements, and should be read in conjunction with "Item 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations" and our consolidated financial statements and related notes thereto included in this annual report on Form 10-K.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years ended October 31, |
| | 2008(1) |
| | 2009(2) |
| | 2010(3) |
| | 2011(4) |
| | 2012(5) |
|
| | (Dollar information in millions of USD, except per share information) |
| | $ | | $ | | $ | | $ | | $ |
| Statement of (loss) income data: | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenues | 717.3 |
| | 655.1 |
| | 671.2 |
| | 700.0 |
| | 749.1 |
|
| Income (loss) before discontinued operations | 4.9 |
| | 1.1 |
| | (2.9 | ) | | (15.8 | ) | | (106.4 | ) |
| Adjusted EBITDA | 89.0 |
| | 74.0 |
| | 80.9 |
| | 66.4 |
| | 71.1 |
|
| Basic income (loss) per share from continuing operations | 0.09 |
| | (0.10 | ) | | (0.02 | ) | | (0.12 | ) | | (0.83 | ) |
| Diluted income (loss) per share from continuing operations | 0.01 |
| | (0.10 | ) | | (0.02 | ) | | (0.12 | ) | | (0.83 | ) |
| Weighted-average number of shares outstanding during period—basic (in thousands) | 90,737 |
| | 100,964 |
| | 129,168 |
| | 129,168 |
| | 129,169 |
|
| Weighted-average number of shares outstanding during period—diluted (in thousands) | 123,634 |
| | 100,964 |
| | 129,168 |
| | 129,168 |
| | 129,169 |
|
| Balance sheet data (at period end): | | | | | | | | | |
| Total assets | 703.5 |
| | 794.2 |
| | 813.2 |
| | 824.6 |
| | 742.9 |
|
| Long-term debt | 203.2 |
| | 223.5 |
| | 281.1 |
| | 280.1 |
| | 310.7 |
|
| Deferred revenues | 22.5 |
| | 41.7 |
| | 45.9 |
| | 36.5 |
| | 42.8 |
|
| Other long-term liabilities | 30.6 |
| | 49.5 |
| | 45.1 |
| | 53.7 |
| | 47.8 |
|
| Total shareholders' equity | 222.2 |
| | 244.6 |
| | 249.1 |
| | 237.7 |
| | 124.3 |
|
____________________________
| |
| (1) | Income before discontinued operations included $19.9 million in repositioning expenses. Due to our agreement with JLL Patheon Holdings pursuant to which JLL Patheon Holdings agreed to waive the mandatory redemption requirement in respect of the Series C Preferred Shares that it held in fiscal 2008, the Company reclassified the Series C Preferred Shares to permanent equity from temporary equity on our balance sheet. |
| |
| (2) | Income before discontinued operations included $2.1 million in repositioning expenses and $8.0 million in costs associated with the special committee of independent directors that we formed during fiscal 2009 (the "Special Committee") and JLL Patheon Holdings' December 8, 2009 unsolicited offer to acquire any or all of our outstanding restricted voting shares that it did not already own at a price of $2.00 per share in cash. |
| |
| (3) | Loss before discontinued operations included $6.8 million in repositioning expenses, $12.2 million in refinancing costs, $3.6 million in non-cash impairment charges, a non-cash tax benefit of $21.0 from the release of the valuation allowance on net deferred tax assets in our Canadian operations and $3.0 million in costs associated with the Special Committee and the JLL Offer. The long-term debt increased from fiscal 2009 due to the issuance of the Notes for an aggregate principal amount of $280.0 million, the proceeds from which were used to repay all of the outstanding indebtedness under our then-existing senior secured term loan and our $75.0 million asset-based revolving credit facility ("ABL"), to repay certain other indebtedness and to pay related fees and expenses. We used the remaining proceeds for general corporate purposes. See "Item 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Liquidity and Capital Resources—Summary of Cash Flows—Cash Provided by Financing Activities"). |
| |
| (4) | Loss before discontinued operations included $12.8 million in consulting and professional fees primarily related to our strategic initiatives and our SEC registration and $7.0 million in repositioning expenses, partially offset by proceeds from an insurance settlement of $4.9 million. |
| |
| (5) | Loss before discontinued operations included $57.9 in asset impairments related to our Swindon facility, the recording of a valuation allowance against our Canadian deferred tax assets of $36.6 million, $13.4 million in consulting and professional fees primarily related to our strategic initiatives, $6.1 million in repositioning expenses and $3.2 million in acquisition-related costs. |
References to "Adjusted EBITDA" are to income (loss) before discontinued operations before repositioning expenses, interest expense, foreign exchange losses reclassified from other comprehensive income (loss), refinancing expenses, acquisition-related costs, gains and losses on sale of capital assets, gain on extinguishment of debt, income taxes, asset impairment charges, depreciation and amortization and other income and expenses.
Since Adjusted EBITDA is a non-GAAP measure that does not have a standardized meaning, it may not be comparable to similar measures presented by other issuers. Readers are cautioned that Adjusted EBITDA should not be construed as an alternative to net income (loss) determined in accordance with U.S. GAAP as an indicator of performance. Adjusted EBITDA is used by management as an internal measure of profitability. We have included Adjusted EBITDA because we believe that this measure is used by certain investors to assess our financial performance before non-cash charges and certain costs that we do not believe are reflective of our underlying business.
A reconciliation of Adjusted EBITDA to income (loss) before discontinued operations is set forth below:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years ended October 31, |
| | 2008 | | 2009 | | 2010 | | 2011 | | 2012 |
| | (in millions of USD) |
| | $ | | $ | | $ | | $ | | $ |
| Net loss for the period | (14.6 | ) | | (6.7 | ) | | (4.6 | ) | | (16.4 | ) | | (106.7 | ) |
| Loss from discontinued operations | (19.5 | ) | | (7.8 | ) | | (1.7 | ) | | (0.6 | ) | | (0.3 | ) |
| Income (loss) before discontinued operations | 4.9 |
| | 1.1 |
| | (2.9 | ) | | (15.8 | ) | | (106.4 | ) |
| Add (deduct): | | | | | | | | | |
| Provision for (benefit from) income taxes | 2.2 |
| | 12.6 |
| | (13.8 | ) | | 1.1 |
| | 43.4 |
|
| (Gain) loss on sale of capital assets | (0.7 | ) | | — |
| | 0.2 |
| | 0.2 |
| | 0.4 |
|
| Acquisition-related costs | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 3.2 |
|
| Refinancing expenses | — |
| | — |
| | 12.2 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Interest expense, net | 17.2 |
| | 15.4 |
| | 19.6 |
| | 25.6 |
| | 26.5 |
|
| Repositioning expenses | 19.9 |
| | 2.1 |
| | 6.8 |
| | 7.0 |
| | 6.1 |
|
| Depreciation and amortization | 45.0 |
| | 42.4 |
| | 55.6 |
| | 53.2 |
| | 40.8 |
|
| Asset impairment charge | 0.4 |
| | — |
| | 3.6 |
| | — |
| | 57.9 |
|
| Other | 0.1 |
| | 0.4 |
| | (0.4 | ) | | (4.9 | ) | | (0.8 | ) |
| Adjusted EBITDA | 89.0 |
| | 74.0 |
| | 80.9 |
| | 66.4 |
| | 71.1 |
|
Item 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
The following discussion is designed to provide a better understanding of our consolidated financial statements, including a brief discussion of our business and products, key factors that impact our performance and a summary of our operating results. You should read the following discussion and analysis of financial condition and results of operations together with our consolidated financial statements and the related notes included in this Form 10-K, which have been prepared in accordance with U.S. GAAP. In addition to historical information, the following discussion contains forward-looking statements that involve risks, uncertainties and assumptions. Our actual results could differ materially from those anticipated by the forward-looking statements due to important factors including, but not limited to, those set forth under "Item 1A. Risk Factors" of this Form 10-K.
Executive Overview
Our Company
We are a leading provider of contract manufacturing and development services to the global pharmaceutical industry, offering a wide range of services from developing drug candidates at the pre-formulation stage through the launch, commercialization and production of approved drugs. We have established our position as a market leader by leveraging our scale, global reach, specialized capabilities, broad service offerings, scientific expertise and track record of product quality and regulatory compliance to provide cost-effective solutions to our customers.
We have two reportable segments, CMO and PDS. Our CMO business manufactures prescription products in sterile dosage forms as well as solid and liquid conventional dosage forms, and we differentiate ourselves by offering specialized manufacturing capabilities relating to high potency, controlled substance and sustained release products. Our PDS business provides a broad range of development services, including a wide variety of solid and sterile dosage forms. Additionally, our PDS business serves as a pipeline for future commercial manufacturing opportunities.
Selected Fiscal 2012 Financial Results
The following is a summary of certain key financial results for fiscal 2012 (a more detailed discussion is contained in "-Results of Operations" below):
| |
| • | Revenues for fiscal 2012 increased $49.1 million, or 7.0%, to $749.1 million, from $700.0 million for fiscal 2011. |
| |
| • | Gross profit for fiscal 2012 increased $27.5 million, or 20.9%, to $159.3 million from $131.8 million for fiscal 2011. |
| |
| • | Loss before discontinued operations for fiscal 2012 was $106.4 million, compared to $15.8 million for fiscal 2011. |
| |
| • | Adjusted EBITDA for fiscal 2012 increased $4.7 million to $71.1 million, from $66.4 million for fiscal 2011. |
Strategic Transformation
During fiscal 2012, we continued to advance our strategic transformation plan. The following are certain key activities related to the plan that we undertook beginning in fiscal 2012.
| |
| • | On August 31, 2012, we sold our global secondary clinical packaging and clinical distribution services business to Bellwyck Packaging Solutions, a private company with 20 years experience providing clinical trial and contract services for secondary packaging. |
| |
| • | During the second quarter of 2012, we decided to make certain adjustments over the next 24 to 36 months to the scale and scope of business conducted at our Swindon facility, including winding down or transferring non-cephalosporin commercial production to other facilities and, to the extent possible and commercially appropriate, directing PDS projects that require commercialization activities to other facilities. We are working with each of our affected commercial customers to develop plans to maintain supply chain continuity to the extent possible and commercially appropriate. In connection with these adjustments, we recorded a $57.9 million impairment charge for the impairment of long-term assets at our Swindon facility during the second quarter of fiscal 2012. The impairment charge will not result in any current or future cash expenditures. |
| |
| • | On May 9, 2012, we announced the Plan of Termination to reduce our workforce by approximately 91 employees across our global PDS and CMO segments. In connection with the Plan of Termination, we recorded approximately $4.4 million of estimated expenses associated with employee termination benefits during fiscal 2012. We anticipate that we may further adjust the size of the workforce at our Swindon or other facilities as we continue our transformation process. |
| |
| • | On January 19, 2012, we and PROCAPS S.A. announced an agreement with respect to the marketing of a line of certain prescription pharmaceutical soft-gel development and manufacturing services. |
Changes in Our Management and Board
The following is a summary of certain key changes in our management and Board since the beginning of fiscal 2012:
| |
| • | On November 1, 2012, Michael Lehmann joined our company as President of Global PDS. |
| |
| • | On September 12, 2012, Harry Gill was appointed to the position of Senior Vice President, Quality and Continuous Improvement. |
| |
| • | On August 13, 2012, Mark J. Kontny, Ph.D., President, Global PDS and Chief Scientific Officer, left our company. We incurred a severance charge of approximately $0.4 million in the fourth quarter of fiscal 2012 related to the termination of Dr. Kontny's employment. |
| |
| • | On February 15, 2012, we appointed Stuart Grant as our Executive Vice President, Chief Financial Officer. |
| |
| • | On February 13, 2012, Ramsey Frank resigned as Chairman of the Board and a director of our company. The Board appointed Paul S. Levy, Managing Director, JLL Partners, as our new Chairman and appointed Nicholas O'Leary, Senior Associate, JLL Partners, to our Board, filling the vacant seat left by the departure of Mr. Frank. The Board also appointed Michel Lagarde, an existing member of the Board, as Chair of our Corporate Governance Committee and Daniel Agroskin, Managing Director at JLL Partners, and also an existing member of the Board, to our Corporate Governance Committee, filling the positions vacated by Mr. Frank. |
| |
| • | On December 15, 2011, our Board appointed Michel Lagarde, Principal, JLL Partners, as a director of our company. Mr. Lagarde replaced Thomas S. Taylor, Managing Director, JLL Partners, who left our Board effective December 15, 2011. Mr. Lagarde replaced Mr. Taylor as the Chairman of our Compensation and Human Resources Committee (the "CHR Committee") and is a member of our Audit and Corporate Governance Committees. |
| |
| • | On November 1, 2011, Eric W. Evans, our then Chief Financial Officer, resigned. We incurred a severance charge of approximately $0.4 million in the first quarter of fiscal 2012 related to the termination of Mr. Evans's employment. |
Banner Acquisition and Related Debt and Equity Financings
On December 14, 2012, we completed the Banner Acquisition, whereby we acquired Banner for an aggregate purchase price of approximately $269.0 million, subject to post-closing working capital adjustments. Banner is the world's second largest pharmaceutical business focused on delivering proprietary softgel formulations, with four manufacturing facilities, significant proprietary technologies and products, and leading positions in some of the industry's fastest-growing product categories. Banner is headquartered in High Point, N.C., with additional research labs and manufacturing facilities in the Netherlands, Canada and Mexico.
In connection with the closing of the Banner Acquisition, we entered into the Credit Facility, which is comprised of (i) the Secured Term Loan of $575.0 million and (ii) the Secured Revolving Facility of up to $85.0 million (the "Refinancing"). Up to $30.0 million of the Secured Revolving Facility is available for letters of credit. The Secured Term Loan matures on December 14, 2018, and the Secured Revolving Facility matures on December 14, 2017. We have used or expect to use the Credit Facility to finance the purchase of Banner, repurchase our Notes, repay any borrowings outstanding under our ABL, pay fees and expenses associated with the transactions, and for general corporate purposes.
As part of the Refinancing, on November 26, 2012, we commenced a cash tender offer for our outstanding Notes. Pursuant to the tender offer, as of 12:00 midnight, New York City time, on December 13, 2012, $279.4 million principal amount of our Notes had been tendered and not validly withdrawn, representing approximately 99.80% of the aggregate outstanding principal amount of the Notes. On December 14, 2012, we paid an aggregate of approximately $307.2 million in order to purchase the Notes tendered prior to December 14, 2012. In addition, we deposited with the trustee in respect of the Notes sufficient funds to redeem the remaining outstanding Notes on January 23, 2013 including accrued and unpaid interest. As a result, we have been released from its obligations under the Notes and the indenture governing the Notes pursuant to the satisfaction and discharge provisions of such indenture.
As part of the Rights Offering, we mailed to our shareholders of record as of November 27, 2012 offering materials related to a $30.0 million offering of transferable subscription rights, with each right entitling the holder to subscribe for one whole restricted voting share at a price of, at such holder's choice, either US$3.19 per whole share or CAD$3.19 per whole share. Unless extended, the Rights Offering will remain open until December 28, 2012. Pursuant to JLL Partners Fund V, L.P.'s ("JLL Partners Fund V"), a related party, commitment letter to provide $30.0 million of equity (less amounts invested by other shareholders) to us dated October 28, 2012, JLL Partners Fund V caused one of its affiliated entities to participate in the Rights Offering. Any excess subscription payments will be returned, without interest or penalty, as soon as practicable after the expiry date of the Rights Offering.
Opportunities and Trends
Our target markets include the highly fragmented global market for the manufacture of finished pharmaceutical dosage forms and for PDS. According to PharmSource, a provider of pharmaceutical outsourcing business information, the CMO market totaled $13.7 billion in 2011, and could experience marginal growth of 5% to 7% annually during 2012 to 2016. PharmSource also estimates that the outsourced PDS market (which tends to be more volatile) totaled approximately $1.4 billion in 2011, with growth projections in the 2012 to 2016 period approaching 8 to 10% annually.
Pharmaceutical outsourcing service providers have faced challenges in recent years due to the uncertain economic environment. In the research and development area, emerging pharmaceutical companies have faced funding uncertainties due to limited access to capital, and many larger companies have decreased or delayed product development spending due to uncertainties surrounding industry consolidation, overall market weakness and the regulatory approval environment.
Puerto Rico Operations
We closed our Carolina facility in Puerto Rico effective January 31, 2009. In the second half of fiscal 2010, we performed an impairment analysis based on recent offers, which resulted in the complete write down as the fair value less the cost to sell was nil. We completed the sale of this property on February 17, 2012 for a nominal amount. The results of the Carolina operations have been reported in discontinued operations in fiscal 2012, 2011 and 2010.
In December 2009, we announced our plan to consolidate our Puerto Rico operations into our manufacturing site located in Manati and ultimately close or sell our plant in Caguas. As a result of additional time required to transition manufacturing operations from Caguas to Manati due to longer than expected customer regulatory time lines and increased product demand, the transition will continue beyond the end of calendar year 2012. We now estimate the total project repositioning expenses to be $13.7 million, of which $12.5 million has been incurred as of October 31, 2012. The consolidation also resulted in
accelerated depreciation of Caguas assets of approximately $12.0 million. Because the business in the Caguas facility is being transferred within the existing site network, its results of operations are included in continuing operations.
Selected Financial Information
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | Years ended October 31, |
| (in millions of USD, except per share information) | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| | $ | | $ | | $ |
| Revenues | 749.1 |
| | 700.0 |
| | 671.2 |
|
| Adjusted EBITDA | 71.1 |
| | 66.4 |
| | 80.9 |
|
| Net loss attributable to restricted voting shareholders | (106.7 | ) | | (16.4 | ) | | (4.6 | ) |
| Basic and diluted loss per share | (0.83 | ) | | (0.13 | ) | | (0.04 | ) |
| Total assets | 742.9 |
| | 824.6 |
| | 813.2 |
|
| Total long-term liabilities | 410.4 |
| | 389.4 |
| | 374.8 |
|
Reconciliations of Adjusted EBITDA to loss before discontinued operations are included in "Item 6—Selected Financial Data" and "Note 15—Segmented Information" to our consolidated financial statements included in this Form 10-K.
Results of Operations
The results of the Carolina operations have been segregated and reported as discontinued operations in fiscal 2012, 2011 and 2010.
Fiscal 2012 Compared to Fiscal 2011
Consolidated Statements of Operations
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years ended October 31, |
| (in millions of USD, except per share information) | 2012 | | 2011 | | Change | | Change |
| | $ | | $ | | $ | | % |
| Revenues | 749.1 |
| | 700.0 |
| | 49.1 |
| | 7.0 |
|
| Cost of goods sold | 589.8 |
| | 568.2 |
| | 21.6 |
| | 3.8 |
|
| Gross profit | 159.3 |
| | 131.8 |
| | 27.5 |
| | 20.9 |
|
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | 128.6 |
| | 120.2 |
| | 8.4 |
| | 7.0 |
|
| Repositioning expenses | 6.1 |
| | 7.0 |
| | (0.9 | ) | | (12.9 | ) |
| Acquisition-related costs | 3.2 |
| | — |
| | 3.2 |
| |
|
|
| Impairment charge | 57.9 |
| | — |
| | 57.9 |
| |
|
|
| Loss on sale of capital assets | 0.4 |
| | 0.2 |
| | 0.2 |
| | 100.0 |
|
| Operating (loss) income | (36.9 | ) | | 4.4 |
| | (41.3 | ) | | (938.6 | ) |
| Interest expense, net | 26.5 |
| | 25.6 |
| | 0.9 |
| | 3.5 |
|
| Foreign exchange loss (gain) | 0.5 |
| | (1.6 | ) | | 2.1 |
| | (131.3 | ) |
| Other income, net | (0.9 | ) | | (4.9 | ) | | 4.0 |
| | (81.6 | ) |
| Loss from continuing operations before income taxes | (63.0 | ) | | (14.7 | ) | | (48.3 | ) | | 328.6 |
|
| Current | 9.2 |
| | 1.6 |
| | 7.6 |
| | 475.0 |
|
| Deferred | 34.2 |
| | (0.5 | ) | | 34.7 |
| |
|
| Provision for income taxes | 43.4 |
| | 1.1 |
| | 42.3 |
| |
|
| Loss before discontinued operations | (106.4 | ) | | (15.8 | ) | | (90.6 | ) | | 573.4 |
|
| Loss from discontinued operations | (0.3 | ) | | (0.6 | ) | | 0.3 |
| | (50.0 | ) |
| Net loss for the period | (106.7 | ) | | (16.4 | ) | | (90.3 | ) | | 550.6 |
|
| Net loss attributable to restricted voting shareholders | (106.7 | ) | | (16.4 | ) | | (90.3 | ) | | 550.6 |
|
| Basic and diluted loss per share | | | | | | | |
| From continuing operations | $ | (0.824 | ) | | $ | (0.122 | ) | | | | |
| From discontinued operations | $ | (0.002 | ) | | $ | (0.005 | ) | | | | |
| | $ | (0.826 | ) | | $ | (0.127 | ) | | | | |
| Weighted-average number of shares outstanding during period—basic and diluted (in thousands) | 129,169 |
| | 129,168 |
| | | | |
Operating Income Summary
Revenues for fiscal 2012 increased $49.1 million, or 7.0%, to $749.1 million, from $700.0 million for fiscal 2011. Excluding currency fluctuations, revenues for fiscal 2012 would have been approximately 10.1% higher than in fiscal 2011. CMO revenues for fiscal 2012 increased $38.1 million, or 6.7%, to $610.7 million, from $572.6 million for fiscal 2011. The increase was primarily due to stronger results from our North American and Italian operations, partially offset by the $50.3 million impact from the reservation fee and accelerated deferred revenue recorded in fiscal 2011. PDS revenues for fiscal 2012 increased $11.0 million, or 8.6%, to $138.4 million, from $127.4 million for fiscal 2011, primarily driven by stronger results in our Cincinnati, Toronto and Swindon operations.
Gross profit for fiscal 2012 increased $27.5 million, or 20.9%, to $159.3 million, from $131.8 million for fiscal 2011. The increase in gross profit was primarily due to higher volumes and a margin improvement from 18.9% in fiscal 2011 to 21.3% in fiscal 2012. Gross profit in fiscal 2012 would have increased by $77.8 million, or 94.9%, excluding the benefit from the fiscal 2011 reservation fee and accelerated deferred revenue. The increase in gross margin was due to improvements related to our transformation initiatives (6.1%) and decrease in depreciation expenses (1.6%), which more than offset the unfavorable mix associated with replacing the reservation fee and deferred revenues with ongoing production at lower margins.
Selling, general and administrative expenses for fiscal 2012 increased $8.4 million, or 7.0%, to $128.6 million, from $120.2 million for fiscal 2011. The increase was primarily due to $5.2 million in higher performance based compensation expense and $2.9 million of higher consulting fees primarily related to our strategic and operational review and transformation. Foreign exchange had a favorable impact of $2.5 million on selling, general and administrative expenses versus fiscal 2011.
Acquisition-related costs for fiscal 2012 were $3.2 million. These expenses are associated with the Banner Acquisition. In connection with closing the acquisition on December 14, 2012, we incurred, and expect to incur, additional acquisition-related costs, including investment banker and legal fees. These costs will be recognized as operating expenses as incurred. In
addition, we expect to incur integration costs during the fiscal year ending October 31, 2013 related to system and customer conversions, employee-related severance costs and other integration-related costs.
Impairment charges for fiscal 2012 were $57.9 million relating to the winding down or transferring PDS and non-cephalosporin commercial production from our Swindon, U.K. facility to other facilities.
Operating (loss) income for fiscal 2012 decreased $41.3 million, to a loss of $36.9 million (-5.0% of revenues), from income of $4.4 million (0.7% of revenues) for fiscal 2011 as a result of the factors discussed above.
Foreign Exchange Losses
Foreign exchange loss for fiscal 2012 was $0.5 million, compared to a gain of $1.6 million for fiscal 2011. The foreign exchange loss for fiscal 2012 was primarily due to hedging losses, partially offset by operating exposures. The foreign exchange gain for fiscal 2011 was primarily due to hedging gains, partially offset by operating exposures. The hedging contracts resulted in losses of $0.4 million for fiscal 2012 compared to gains of $1.6 million for fiscal 2011.
Loss from Continuing Operations Before Income Taxes
We reported a loss from continuing operations before income taxes of $63.0 million for fiscal 2012, compared to a loss of $14.7 million for fiscal 2011. The operating items discussed above were the primary drivers of the year over year variance.
Income Taxes
The provision for income taxes was $43.4 million for fiscal 2012, compared to $1.1 million for fiscal 2011. The increase in the provision for income taxes was primarily driven by the recording of a valuation allowance against our Canadian deferred tax assets, lower income, the mix of income and loss from our operating units and pre-tax losses in some entities for which no tax benefits were recognized.
Loss before Discontinued Operations and Loss Per Share from Continuing Operations
We recorded a loss before discontinued operations for fiscal 2012 of $106.4 million, compared to $15.8 million for fiscal 2011. The loss per share from continuing operations for fiscal 2012 was 82.4¢ compared to 12.2¢ for fiscal 2011.
Loss and Loss Per Share from Discontinued Operations
Discontinued operations for fiscal 2012 and 2011 include the results of the Carolina, Puerto Rico operations. Financial details of the operating activities of the Carolina operations are disclosed in "Note 3—Discontinued Operations, Plant Consolidations, Sales and Asset Impairments." The loss from discontinued operations for fiscal 2012 was $0.3 million, or 0.2¢ per share, compared to a loss of $0.6 million, or 0.5¢ per share, for fiscal 2011. These costs relate to the final wind down of the Carolina facility.
Net Loss, Loss Attributable to Restricted Voting Shareholders and Loss Per Share
Net loss attributable to restricted voting shares for fiscal 2012 was $106.7 million, or 82.6¢ per share, compared to $16.4 million, or 12.7¢ per share, for fiscal 2011.
The computation of net loss per share did not include 12,479,678 and 12,628,458 outstanding options in fiscal 2012 and 2011, respectively, because such options were anti-dilutive in nature.
Revenues and Adjusted EBITDA by Business Segment
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years ended October 31, |
| (in millions of USD) | 2012 | | 2011 | | Change | | Change |
| | $ | | $ | | $ | | % |
| Revenues | | | | | | | |
| Commercial Manufacturing | | | | | | | |
| North America | 346.7 |
| | 274.5 |
| | 72.2 |
| | 26.3 |
|
| Europe | 264.0 |
| | 298.1 |
| | (34.1 | ) | | (11.4 | ) |
| Total Commercial Manufacturing | 610.7 |
| | 572.6 |
| | 38.1 |
| | 6.7 |
|
| Pharmaceutical Development Services | 138.4 |
| | 127.4 |
| | 11.0 |
| | 8.6 |
|
| Total Revenues | 749.1 |
| | 700.0 |
| | 49.1 |
| | 7.0 |
|
| Adjusted EBITDA | | | | | | | |
| Commercial Manufacturing | | | | | | | |
| North America | 53.4 |
| | 18.4 |
| | 35.0 |
| | 190.2 |
|
| Europe | 31.1 |
| | 60.8 |
| | (29.7 | ) | | (48.8 | ) |
| Total Commercial Manufacturing | 84.5 |
| | 79.2 |
| | 5.3 |
| | 6.7 |
|
| Pharmaceutical Development Services | 28.5 |
| | 24.1 |
| | 4.4 |
| | 18.3 |
|
| Corporate Costs | (41.9 | ) | | (36.9 | ) | | (5.0 | ) | | 13.6 |
|
| Total Adjusted EBITDA | 71.1 |
| | 66.4 |
| | 4.7 |
| | 7.1 |
|
Commercial Manufacturing
Total CMO revenues for fiscal 2012 increased $38.1 million, or 6.7%, to $610.7 million, from $572.6 million for fiscal 2011, primarily due to stronger results from our North American and Italian operations, offset by weakness in Swindon and Bourgoin. Had local currency exchange rates remained constant to the rates of fiscal 2011, CMO revenues for fiscal 2012 would have been approximately 10.1% higher than fiscal 2011. Excluding the $50.3 million impact from the reservation fee and accelerated deferred revenue recorded in the first half of fiscal 2011, total CMO revenues for fiscal 2012 would have increased $88.4 million, or 17.0% from fiscal 2011.
North American CMO revenues for fiscal 2012 increased $72.2 million, or 26.3%, to $346.7 million, from $274.5 million for fiscal 2011. The increase was due to an increase in customer demand across most North American sites with minimal foreign exchange impact versus fiscal 2011.
European CMO revenues for fiscal 2012 decreased $34.1 million, or 11.4%, to $264.0 million, from $298.1 million for fiscal 2011. Had European currency exchange rates remained constant to the rates of fiscal 2011, European CMO revenues for fiscal 2012 would have been approximately 5.0% lower than fiscal 2011. This reduction was primarily due to the non-recurrence of the $50.3 million in reservation fee and accelerated deferred revenue recorded in the first half of fiscal 2011, partially offset by stronger results from our Italian operations.
Total CMO Adjusted EBITDA for fiscal 2012 increased $5.3 million, or 6.7%, to $84.5 million, from $79.2 million for fiscal 2011. This represents an Adjusted EBITDA margin of 13.9% for fiscal 2012 compared to 13.9% for fiscal 2011. Had local currency exchange rates and foreign exchange gains and losses remained constant to those of fiscal 2011, CMO Adjusted EBITDA for fiscal 2012 would have been approximately $5.2 million higher than reported. The increase was driven by improved margins across our sites as a result of our transformation initiatives and higher volumes, partially offset by unfavorable mix from replacing the reservation fee and accelerated deferred revenue with other production and $7.9 million in consulting fees related to our strategic initiatives.
North American Adjusted EBITDA for fiscal 2012 increased $35.0 million, to $53.4 million, from $18.4 million for fiscal 2011. The increase was primarily driven by higher volumes, margin improvements resulting from the transformation initiatives, partially offset by $2.0 million in consulting fees related to our strategic initiatives. North American CMO recorded $2.6 million in estimated repositioning expenses relating to the Plan of Termination and Puerto Rican operations in fiscal 2012 that were not included in Adjusted EBITDA.
European Adjusted EBITDA for fiscal 2012 decreased $29.7 million, or 48.8%, to $31.1 million, from $60.8 million for fiscal 2011. The decrease was primarily driven by the lower revenue resulting from the non-recurrence of the $50.3 million in reservation fee and accelerated deferred revenue recorded in the first half of fiscal 2011 and $5.9 million in consulting fees related to our strategic initiatives, partially offset by improving margins in fiscal 2012 as a result of our strategic initiatives.
European CMO recorded $1.6 million in estimated repositioning expenses relating to the Plan of Termination, and $55.1 million for an asset impairment charge in fiscal 2012 that were not included in Adjusted EBITDA.
Pharmaceutical Development Services
Total PDS revenues for fiscal 2012 increased by $11.0 million, or 8.6%, to $138.4 million, from $127.4 million for fiscal 2011. Had the local currency rates remained constant to fiscal 2011, PDS revenues for fiscal 2012 would have been 10.0% higher than fiscal 2011. Higher development activities from new contracts across most sites contributed to the improved performance.
Total PDS Adjusted EBITDA for fiscal 2012 increased by $4.4 million, or 18.3%, to $28.5 million, from $24.1 million for fiscal 2011. Had local currency exchange rates and foreign exchange gains and losses remained constant to those of fiscal 2011, PDS Adjusted EBITDA for fiscal 2012 would have been approximately $1.0 million higher than reported. Improved revenues contributed to the higher Adjusted EBITDA, partially offset by $2.3 million in consulting fees related to our strategic initiatives. PDS recorded $1.9 million in estimated repositioning expenses relating to the Plan of Termination and $2.8 million in an asset impairment charge in fiscal 2012 that were not included in Adjusted EBITDA.
Corporate Costs
Corporate costs for fiscal 2012 increased $5.0 million, or 13.6%, to $41.9 million, from $36.9 million for fiscal 2011 primarily due to higher performance based compensation, marketing expenses of $1.7 million, and travel and entertainment of $0.7 million, partially offset by $2.1 million in reduced foreign exchange losses versus fiscal 2011.
Fiscal 2011 Compared to Fiscal 2010
Consolidated Statements of Operations
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years ended October 31 |
| (in millions of USD, except per share information) | 2011 | | 2010 | | $ | | % |
| | $ | | $ | | Change | | Change |
| Revenues | 700.0 |
| | 671.2 |
| | 28.8 |
| | 4.3 |
|
| Cost of goods sold | 568.2 |
| | 536.8 |
| | 31.4 |
| | 5.8 |
|
| Gross profit | 131.8 |
| | 134.4 |
| | (2.6 | ) | | (1.9 | ) |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | 120.2 |
| | 110.6 |
| | 9.6 |
| | 8.7 |
|
| Repositioning expenses | 7.0 |
| | 6.8 |
| | 0.2 |
| | 2.9 |
|
| Impairment charge | — |
| | 3.6 |
| | (3.6 | ) | | — |
|
| Loss on sale of capital assets | 0.2 |
| | 0.2 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Operating income | 4.4 |
| | 13.2 |
| | (8.8 | ) | | (66.7 | ) |
| Interest expense, net | 25.6 |
| | 19.6 |
| | 6.0 |
| | 30.6 |
|
| Foreign exchange gain | (1.6 | ) | | (1.5 | ) | | (0.1 | ) | | 6.7 |
|
| Refinancing expenses | — |
| | 12.2 |
| | (12.2 | ) | | — |
|
| Other income, net | (4.9 | ) | | (0.4 | ) | | (4.5 | ) | | 1,125.0 |
|
| Loss from continuing operations before income taxes | (14.7 | ) | | (16.7 | ) | | 2.0 |
| | (12.0 | ) |
| Current | 1.6 |
| | 6.7 |
| | (5.1 | ) | | (76.1 | ) |
| Deferred | (0.5 | ) | | (20.5 | ) | | 20.0 |
| | (97.6 | ) |
| Provision for (benefit from) income taxes | 1.1 |
| | (13.8 | ) | | 14.9 |
| | (108.0 | ) |
| Loss before discontinued operations | (15.8 | ) | | (2.9 | ) | | (12.9 | ) | | 444.8 |
|
| Loss from discontinued operations | (0.6 | ) | | (1.7 | ) | | 1.1 |
| | (64.7 | ) |
| Net loss for the period | (16.4 | ) | | (4.6 | ) | | (11.8 | ) | | 256.5 |
|
| Net loss attributable to restricted voting shareholders | (16.4 | ) | | (4.6 | ) | | (11.8 | ) | | 256.5 |
|
| Basic and diluted loss per share | | | | | | | |
| From continuing operations | $ | (0.122 | ) | | $ | (0.023 | ) | | | | |
| From discontinued operations | $ | (0.005 | ) | | $ | (0.013 | ) | | | | |
| | $ | (0.127 | ) | | $ | (0.036 | ) | | | | |
| Weighted-average number of shares outstanding during period—basic and diluted (in thousands) | 129,168 |
| | 129,168 |
| | | | |
Operating Income Summary
Revenues for fiscal 2011 increased $28.8 million, or 4.3%, to $700.0 million, from $671.2 million for fiscal 2010. Excluding currency fluctuations, revenues for fiscal 2011 would have been approximately 3.0% higher than fiscal 2010. CMO revenues for fiscal 2011 increased $27.3 million, or 5.0%, to $572.6 million, from $545.3 million for fiscal 2010. PDS revenues for fiscal 2011 increased $1.5 million, or 1.2%, to $127.4 million, from $125.9 million for fiscal 2010.
Gross profit for fiscal 2011 decreased $2.6 million, or 1.9%, to $131.8 million, from $134.4 million for fiscal 2010. The decrease in gross profit was due to a decrease in gross profit margin to 18.9% for fiscal 2011 from 20.1% for fiscal 2010, partially offset by higher revenues. The decrease in gross profit margin was due to unfavorable foreign exchange impact on cost of goods sold related to the weakening of the U.S. dollar (-1.1%), higher labor costs (-0.7%), increase in supplies and maintenance (-0.7%), increase in inventory write-offs (-0.5%), partially offset by favorable mix resulting from the reservation fee and higher deferred revenue amortization related to the amended manufacturing and supply agreement in the United Kingdom.
Selling, general and administrative ("SG&A") expenses for fiscal 2011 increased $9.6 million, or 8.7%, to $120.2 million, from $110.6 million for fiscal 2010. The increase was primarily due to higher consulting and professional fees of $12.8 million, higher costs related to our former CEO's severance of $1.1 million and higher stock-based compensation of $1.4 million, partially offset by elimination of costs associated with the Special Committee of $3.0 million for fiscal 2010, and lower depreciation of $3.0 million. The impact of unfavorable foreign exchange rates on SG&A expense in fiscal 2011 was approximately $3.4 million versus fiscal 2010.
Repositioning expenses for fiscal 2011 increased $0.2 million, or 2.9%, to $7.0 million, from $6.8 million for fiscal 2010. The increase was due to increased expenses in connection with the Zug and Swindon facilities, partially offset by lower expenses in connection with the Caguas closure and consolidation in Puerto Rico during fiscal 2011 compared to fiscal 2010, as the prior period included the initial project accruals.
Impairment charges of $3.6 million were recorded in fiscal 2010 in connection with the consolidation of our Puerto Rico operations into our manufacturing site located in Manati. This charge wrote down the carrying value of the Caguas facility's long-lived assets to their anticipated fair value upon closure of the facility.
Operating income for fiscal 2011 decreased $8.8 million, or 66.7%, to $4.4 million (0.7% of revenues), from $13.2 million (2.0% of revenues) for fiscal 2010 as a result of the factors discussed above.
Interest Expense
Interest expense for fiscal 2011 increased $6.0 million, or 30.6%, to $25.6 million, from $19.6 million for fiscal 2010. The increase in interest expense primarily reflects the higher interest rates on the Notes versus the rates of our previous debt, as well as overall higher debt levels.
Refinancing Expenses
During fiscal 2010, we incurred expenses of $12.2 million in connection with our refinancing activities, which included fees paid to advisors and other related costs.
Other Income, Net
Other income for fiscal 2011 was $4.9 million, compared to $0.4 million for fiscal 2010. The increase of other income was primarily due to the settlement of the insurance claim associated with water damage at our Swindon, U.K. facility, of which $4.9 million was recorded in other income.
Loss from Continuing Operations Before Income Taxes
We reported a loss from continuing operations before income taxes of $14.7 million for fiscal 2011, compared to a loss of $16.7 million for fiscal 2010. The $12.2 million of refinancing expenses during fiscal 2010, along with the other operating items discussed above, were the primary drivers of the year over year variance.
Income Taxes
Income taxes were an expense of $1.1 million for fiscal 2011, compared to a benefit of $13.8 million for fiscal 2010. The increase in tax expense for the period was primarily due to the benefit in fiscal 2010 of releasing $21.0 million of the valuation
allowance pertaining to deferred tax assets in our Canadian operations, partially offset by the mix of earnings in various tax jurisdictions and higher investment tax credits earned in 2011.
Loss before Discontinued Operations and Loss Per Share from Continuing Operations
We recorded a loss before discontinued operations for fiscal 2011 of $15.8 million, compared to a loss before discontinued operations of $2.9 million for fiscal 2010. The loss per share from continuing operations for fiscal 2011 was 12.2¢ compared to a loss per share of 2.3¢ for fiscal 2010.
Loss and Loss Per Share from Discontinued Operations
Discontinued operations for fiscal 2011 and 2010 include the results of the Carolina, Puerto Rico operations. Financial details of the operating activities of the Carolina operations are disclosed in "Note 3—Discontinued Operations, Plant Consolidations, Sales and Asset Impairments." The loss from discontinued operations for fiscal 2011 was $0.6 million, or 0.5¢ per share, compared to a loss of $1.7 million, or 1.3¢ per share, for fiscal 2010. On-going costs of discontinued operations relate to maintaining the Carolina building for sale.
Net Loss, Loss Attributable to Restricted Voting Shareholders and Loss Per Share
Net loss attributable to restricted voting shares for fiscal 2011 increased $11.8 million, to $16.4 million, or 12.7¢ per share, from $4.6 million, or 3.6¢ per share, for fiscal 2010. Because we reported a loss for fiscal 2011 and 2010, there is no impact of dilution.
Revenues and Adjusted EBITDA by Business Segment
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years ended October 31, |
| (in millions of USD) | 2011 | | 2010 | | Change | | Change |
| | $ | | $ | | $ | | % |
| Revenues | | | | | | | |
| Commercial Manufacturing | | | | | | | |
| North America | 274.5 |
| | 251.6 |
| | 22.9 |
| | 9.1 |
|
| Europe | 298.1 |
| | 293.7 |
| | 4.4 |
| | 1.5 |
|
| Total Commercial Manufacturing | 572.6 |
| | 545.3 |
| | 27.3 |
| | 5.0 |
|
| Pharmaceutical Development Services | 127.4 |
| | 125.9 |
| | 1.5 |
| | 1.2 |
|
| Total Revenues | 700.0 |
| | 671.2 |
| | 28.8 |
| | 4.3 |
|
| Adjusted EBITDA | | | | | | | |
| Commercial Manufacturing | | | | | | | |
| North America | 18.4 |
| | 20.6 |
| | (2.2 | ) | | (10.7 | ) |
| Europe | 60.8 |
| | 51.7 |
| | 9.1 |
| | 17.6 |
|
| Total Commercial Manufacturing | 79.2 |
| | 72.3 |
| | 6.9 |
| | 9.5 |
|
| Pharmaceutical Development Services | 24.1 |
| | 36.0 |
| | (11.9 | ) | | (33.1 | ) |
| Corporate Costs | (36.9 | ) | | (27.4 | ) | | (9.5 | ) | | 34.7 |
|
| Total Adjusted EBITDA | 66.4 |
| | 80.9 |
| | (14.5 | ) | | (17.9 | ) |
Commercial Manufacturing
Total CMO revenues for fiscal 2011 increased $27.3 million, or 5.0%, to $572.6 million, from $545.3 million for fiscal 2010. Had local currency exchange rates remained constant to the rates of fiscal 2010, CMO revenues for fiscal 2011 would have been approximately 3.6% higher than fiscal 2010.
North American CMO revenues for fiscal 2011 increased $22.9 million, or 9.1%, to $274.5 million, from $251.6 million for fiscal 2010. Had Canadian dollar exchange rates remained constant to the rates of fiscal 2010, North American CMO revenues for fiscal 2011 would have been approximately 8.7% higher than fiscal 2010. The increase was primarily due to increased worldwide demand for a customer's product manufactured in our Puerto Rico facility, higher volumes in Toronto and new product launch volumes in Cincinnati.
European CMO revenues for fiscal 2011 increased $4.4 million, or 1.5%, to $298.1 million, from $293.7 million for fiscal 2010. The increase was primarily due to higher revenues in the United Kingdom from the reservation fee related to the
amended manufacturing and supply agreement and accelerated deferred revenue versus take-or-pay revenue in fiscal 2010, and higher volumes in Ferentino, partially offset by lower revenues across other sites. Had European currencies remained constant to the rates of fiscal 2010, European CMO revenues for fiscal 2011 would have been approximately 0.6% lower than fiscal 2010.
Total CMO Adjusted EBITDA for fiscal 2011 increased $6.9 million, or 9.5%, to $79.2 million, from $72.3 million for fiscal 2010. This represents an Adjusted EBITDA margin of 13.9% for fiscal 2011 compared to 13.3% for fiscal 2010. Had local currencies remained constant to fiscal 2010 rates, and after eliminating the impact of all foreign exchange gains and losses, CMO Adjusted EBITDA for fiscal 2011 would have been approximately $2.3 million higher than in fiscal 2010.
North American Adjusted EBITDA for fiscal 2011 decreased $2.2 million, or 10.7%, to $18.4 million, from $20.6 million for fiscal 2010. The decrease was primarily driven by $5.0 million in consulting fees related to recent strategic initiatives, fiscal 2010 recognition of accelerated deferred revenue of $4.2 million in Cincinnati and foreign exchange losses of $2.4 million as a result of the weakening of the U.S. dollar against the Canadian dollar. These were partially offset by a $6.7 million Adjusted EBITDA improvement in Puerto Rico, and better operating results in our Canadian operations. North American CMO had $4.0 million in repositioning costs relating to the Puerto Rican operations in fiscal 2011 that was not included in Adjusted EBITDA.
European Adjusted EBITDA for fiscal 2011 increased $9.1 million, or 17.6%, to $60.8 million, from $51.7 million for fiscal 2010. This increase was primarily due to the recognition of the reservation fee related to the amended manufacturing and supply agreement in the United Kingdom and associated deferred revenue amortization, partially offset by lower operating results across other European sites. European CMO has $4.9 million in insurance proceeds relating to the U.K. operations that was recorded in other income and $2.9 million in repositioning costs for the Zug and U.K. operations, both of which were not included in Adjusted EBITDA.
Pharmaceutical Development Services
Total PDS revenues for fiscal 2011 increased by $1.5 million, or 1.2%, to $127.4 million, from $125.9 million for fiscal 2010. Had the local currency rates remained constant to fiscal 2010, PDS revenues for fiscal 2011 would have increased approximately 0.2% from fiscal 2010.
Total PDS Adjusted EBITDA for fiscal 2011 decreased by $11.9 million, or 33.1%, to $24.1 million, from $36.0 million for fiscal 2010. Had local currencies remained constant to the rates of fiscal 2010 and after eliminating the impact of all foreign exchange gains and losses, PDS Adjusted EBITDA for fiscal 2011 would have been approximately $2.2 million higher than reported. Lower than expected sales at certain sites resulting from project cancellations related to customer regulatory approvals, clinical trial outcome issues, and industry consolidation contributed to the reduction in Adjusted EBITDA.
Corporate Costs
Corporate costs for fiscal 2011 increased $9.5 million, or 34.7%, to $36.9 million, from $27.4 million for fiscal 2010. The increase was primarily due to unfavorable foreign exchange of $3.4 million, $4.4 million of higher advisor fees due to registration with the SEC and corporate strategy initiatives, expenses related to the change in our CEO of $3.3 million and higher compensation expenses. These were partially offset by the non-recurrence of $3.0 million in Special Committee costs incurred in fiscal 2010.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Overview
Our cash and cash equivalents totaled $39.4 million at October 31, 2012 and $33.4 million at October 31, 2011. Our total debt was $310.7 million at October 31, 2012 and $281.2 million at October 31, 2011.
Our primary source of liquidity is cash flow from operations. We have also used availability under the ABL, the Secured Revolving Facility and other credit lines for additional cash needs. Our principal uses of cash are for capital expenditures, debt servicing requirements, working capital, employee benefit obligations, and expenditures for consultants to assist in implementing our strategic initiatives.
From time to time, we evaluate strategic opportunities, including potential acquisitions, divestitures or investments in complementary businesses, and we anticipate continuing to make such evaluations. We may also access capital markets through the issuance of debt or equity in connection with the acquisition of complementary businesses or other significant assets or for other strategic opportunities.
Summary of Cash Flows
The following table summarizes our cash flows for the periods indicated:
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | Years ended October 31, |
| (in millions of USD) | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| | $ | | $ | | $ |
| Cash provided by operating activities of continuing operations | 33.4 |
| | 23.9 |
| | 50.7 |
|
| Cash used in operating activities of discontinued operations | (0.4 | ) | | (1.0 | ) | | (0.7 | ) |
| Cash provided by operating activities | 33.0 |
| | 22.9 |
| | 50.0 |
|
| Cash used in investing activities of continuing operations | (52.0 | ) | | (47.4 | ) | | (50.0 | ) |
| Cash provided by investing activities of discontinued operations | 0.1 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Cash provided by financing activities | 26.3 |
| | 2.7 |
| | 31.6 |
|
| Other | (1.4 | ) | | 1.7 |
| | (0.4 | ) |
| Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents during the period | 6.0 |
| | (20.1 | ) | | 31.2 |
|
Cash Provided by Operating Activities
Cash provided by operating activities from continuing operations for fiscal 2012 increased $9.5 million, to $33.4 million, from $23.9 million for fiscal 2011. In fiscal 2012, improved operating performance was partially offset by consulting and repositioning expense payments. Fiscal 2011 cash from operations was primarily driven by the receipt of $29.3 million for the reservation fee and $14.0 million from the insurance claim settlement in Swindon, partially offset by the voluntary pension contribution in the United Kingdom of $4.9 million and reduced operating performance.
Cash provided by operating activities from continuing operations for fiscal 2011 decreased $26.8 million, or 52.9%, to $23.9 million, from $50.7 million for fiscal 2010. Fiscal 2010 cash contributions included take-or-pay receipts in our Swindon operations of $53.1 million versus $29.3 million received from the reservation fee related to the amended manufacturing and supply agreement in the United Kingdom in fiscal 2011. Fiscal 2011 also included previously disclosed voluntary pension contributions in the United Kingdom of $4.9 million, and lower cash from operations, partially offset by $14.0 million from the insurance claim settlement.
Cash provided by operating activities from continuing operations for fiscal 2010 was primarily due to higher deferred revenue (mainly an early payment for a take or pay amount) and better working capital usage, which was partially offset by refinancing costs, higher interest payments and lower cash flows from the commercial operations excluding the deferred revenue amounts.
Cash used in operating activities from discontinued operations for fiscal 2012 decreased $0.6 million, or 60.0%, to $0.4 million, from $1.0 million for fiscal 2011.
Cash used in operating activities from discontinued operations for fiscal 2011 increased $0.3 million, or 42.9%, to $1.0 million, from $0.7 million for fiscal 2010.
Cash used in operating activities from discontinued operations for fiscal 2010 was primarily utility costs, insurance and maintenance for our Carolina facility while it was in the process of being sold.
Cash Used in Investing Activities
The following table summarizes the cash used in investing activities for the periods indicated:
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | Years ended October 31, |
| (in millions of USD) | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| | $ | | $ | | $ |
| Total additions to capital assets | (53.4 | ) | | (47.8 | ) | | (48.7 | ) |
| Proceeds on sale of capital assets | 0.4 |
| | 0.4 |
| | — |
|
| Proceeds on sale of business, net | 1.0 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Net increase in investments | — |
| | — |
| | (1.1 | ) |
| Investment in intangibles | — |
| | — |
| | (0.2 | ) |
| Cash used in investing activities of continuing operations | (52.0 | ) | | (47.4 | ) | | (50.0 | ) |
| Cash provided by investing activities of discontinued operations | 0.1 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Cash used in investing activities | (51.9 | ) | | (47.4 | ) | | (50.0 | ) |
Cash used in investing activities from continuing operations for fiscal 2012 increased $5.6 million, or 11.9%, to $52.0 million, from $47.4 million for fiscal 2011 due to increased capital spend related to customer projects and capacity enhancements.
Cash used in investing activities from continuing operations for fiscal 2011 decreased $2.6 million, or 5.2%, to $47.4 million, from $50.0 million for fiscal 2010. The decrease was primarily due to lower capital expenditures in fiscal 2011 and the non-recurrence of cash contributions in two Italian companies (BSP Pharmaceuticals) in fiscal 2010.
Cash used in investing activities from continuing operations for fiscal 2010 increased $0.5 million, or 1.0%, to $50.0 million, from fiscal 2009.
Our principal ongoing investment activities are capital programs at our sites. The majority of our capital allocation is normally invested in projects that will support growth in capacity and revenues.
During fiscal 2012, our major capital projects (in millions of U.S. dollars) were:
|
| | | |
| • Expansion in Manati, Puerto Rico primarily funded by the customer for increased capacity | $ | 14.8 |
|
| • Capacity enhancement at Toronto site | $ | 6.2 |
|
| • Addition of prefilled syringes line at Monza site | $ | 6.2 |
|
| • Capacity enhancement at Whitby site | $ | 3.0 |
|
| • Expansion of the new PDS unit at the Bourgoin, France site | $ | 1.1 |
|
| • PDS Software enhancements | $ | 1.1 |
|
During fiscal 2011, our major capital projects (in millions of U.S. dollars) were:
|
| | | |
| • Facility infrastructure at Cincinnati to support introduction of new product, primarily funded by a customer | $ | 10.5 |
|
| • Consolidation of Caguas facility in Puerto Rico | $ | 2.3 |
|
| • Addition of PDS capabilities at the Bourgoin site | $ | 2.0 |
|
| • High potency packaging in Toronto | $ | 1.4 |
|
| • Equipment for customer product in Bourgoin | $ | 2.0 |
|
During fiscal 2010, our major capital projects (in millions of U.S. dollars) were:
|
| | | |
| • Facility infrastructure at Cincinnati to support introduction of new product, primarily funded by a customer | $ | 9.8 |
|
| • Consolidation of Caguas facility in Puerto Rico | $ | 4.9 |
|
| • Addition of PDS capabilities at the Bourgoin site | $ | 4.5 |
|
Capital commitments to complete authorized capital projects were $16.9 million at the end of fiscal 2012. Based on current internal projections, we expect to make (or have made) these expenditures during the year ending October 31, 2013 ("fiscal 2013"), and we expect to finance (or have financed) them with cash flows from operations, existing cash reserves, borrowings and customer funding.
Based on current management assessments, total capital expenditures (including expenditures to complete projects authorized at the end of fiscal 2012) for fiscal 2013 are expected to be near the amount of total capital expenditures (excluding Banner-related expenditures) for fiscal 2012, which were approximately $53.4 million. We expect to finance (or have financed) our capital expenditures with cash flows from operations, existing cash reserves, borrowings and customer funding. The major capital projects for fiscal 2013 consist of:
| |
| • | Addition of prefilled syringes line at Monza site; |
| |
| • | New Lyo and Sterile expansion for increased capacity in Ferentino; |
| |
| • | Upgrade manufacturing equipment at Toronto site; and |
| |
| • | PDS Software enhancements. |
Our principal ongoing investment activities are sustaining and project-related capital programs at our network of sites. The majority of our capital allocation is normally invested in project-related programs, which are defined as outlays that will generate growth in capacity and revenues, while sustaining expenditures relate to the preservation of existing assets and capacity.
On December 14, 2012, we completed the Banner Acquisition, whereby we acquired Banner for an aggregate purchase price of approximately $269.0 million, subject to post-closing working capital adjustments. The funds for the acquisition were provided by the Credit Facility, the Rights Offering and cash on hand.
Cash Provided by Financing Activities
The following table summarizes the cash provided by financing activities for the periods indicated:
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | Years ended October 31, |
| (in millions of USD) | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| | $ | | $ | | $ |
| (Decrease) increase in short-term borrowings | (3.8 | ) | | 4.2 |
| | (10.7 | ) |
| Increase in long-term debt | 40.9 |
| | 13.5 |
| | 300.2 |
|
| Increase in deferred financing costs | — |
| | — |
| | (7.3 | ) |
| Repayment of long-term debt | (11.1 | ) | | (15.0 | ) | | (250.6 | ) |
| Proceeds on issuance of restricted voting shares | 0.3 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Cash provided by financing activities of continuing operations | 26.3 |
| | 2.7 |
| | 31.6 |
|
| Cash provided by financing activities | 26.3 |
| | 2.7 |
| | 31.6 |
|
Cash provided by financing activities for fiscal 2012 increased by $23.6 million, to $26.3 million, from $2.7 million for fiscal 2011, due to higher aggregate borrowings primarily from our ABL during fiscal 2012.
Cash provided by financing activities for fiscal 2011 decreased $28.9 million, or 91.5%, to $2.7 million, from $31.6 million for fiscal 2010, primarily due to the refinancing in the second quarter of fiscal 2010.
In April 2010, we issued the Notes for an aggregate principal amount of $280.0 million in a private placement. We used the net proceeds of the offering to repay all of the outstanding indebtedness under our then-existing senior secured term loan and $75.0 million ABL, to repay certain other indebtedness and to pay related fees and expenses. We used the remaining proceeds for general corporate purposes.
We also amended and restated our then-existing $75.0 million ABL in connection with the offering to, among other things, extend the maturity date of this facility to 2014.
During fiscal 2010, the cash inflows were primarily due to the refinancing in the second quarter.
Financing Arrangements
Historical Credit Arrangements
$280.0 Million Senior Secured Notes and $75.0 Million Amended ABL
In April 2010, we issued the Notes for an aggregate principal amount of $280.0 million. We used the net proceeds of the offering to repay all of the outstanding indebtedness under our then-existing senior secured term loan and $75.0 million ABL,
to repay certain other indebtedness and to pay related fees and expenses. We used the remaining proceeds for general corporate purposes.
We also amended and restated our then-existing $75.0 million ABL in connection with the Notes offering to, among other things, extend the maturity date of this facility to April 23, 2014.
The Notes and the ABL were secured by substantially all of our assets and were guaranteed by, and secured by substantially all of the assets of, our subsidiaries in the United States (including Puerto Rico), Canada, the United Kingdom (except Patheon UK Pension Trustees Limited) and the Netherlands. The Notes and the ABL were guaranteed on a limited basis by, and secured by certain assets of, our subsidiaries in France, Italy and Switzerland.
The agreements covering the Notes and ABL contain usual and customary covenants and events of default provisions.
The indenture that governed the Notes and the credit agreement that governed the ABL, contained covenants that restricted our ability and the ability of our subsidiaries to, among other things:
| |
| • | incur additional indebtedness; |
| |
| • | issue additional equity; |
| |
| • | pay dividends on or make distributions in respect of capital stock or make certain other restricted payments or investments; |
| |
| • | enter into agreements that restrict distributions from subsidiaries or restrict our ability to incur liens on certain of our assets; |
| |
| • | make capital expenditures; |
| |
| • | sell or otherwise dispose of assets, including capital stock of subsidiaries; |
| |
| • | enter into transactions with affiliates; |
| |
| • | create or incur liens; and |
Effective December 14, 2012, we terminated all commitments and repaid all amounts owed under the ABL and we were released from our obligations under the Notes and the indenture governing the Notes pursuant to the satisfaction and discharge provisions of such indenture.
$660 Million Credit Facility
On December 14, 2012, in connection with the Banner Acquisition, we entered into a credit agreement that provides for the Secured Term Loan in the amount of $575.0 million and the Secured Revolving Facility of up to $85.0 million (the "Credit Agreement"). Up to $30.0 million of the Secured Revolving Facility is available for letters of credit. The Secured Term Loan matures on December 14, 2018, and the Secured Revolving Facility matures on December 14, 2017. The Secured Term Loan bears interest at a rate per annum equal to, at our option, LIBOR plus 6.00%, with a LIBOR "floor" of 1.25%, or an alternate base rate plus 5.00%, with an alternate base rate "floor" of 2.25%. Borrowings under the Secured Revolving Facility bear interest at a rate per annum equal to, at our option, an adjusted eurodollar rate for the applicable currency plus 5.50% or, if available, an alternate base rate for the applicable currency plus 4.50%. We will also pay a commitment fee of 0.50% per annum on the unused portion of the Secured Revolving Facility with a step down to 0.375% when the first lien leverage ratio is less than or equal to 3.00 to 1.00.
We are required to make the following mandatory prepayments in respect of the Secured Term Loan: (i) 50% of our excess cash flow with step downs to 25% and 0% when we maintain specified first lien leverage ratio levels, (ii) 100% of the net cash proceeds of certain asset sales (including insurance and condemnation proceeds), subject to thresholds, reinvestment rights and certain other exceptions, and (iii) 100% of the net cash proceeds of issuances of debt obligations, subject to certain exceptions and thresholds. In the event the Secured Term Loan is prepaid, refinanced, substituted or replaced (including by way of amendment) in whole or in part prior to December 14, 2013 concurrently with the incurrence of indebtedness similar to the Secured Term Loan with a lower all-in yield than that of the Secured Term Loan, any amounts so prepaid, refinanced, substituted or replaced will be subject to a prepayment fee of 1.00%.
The Credit Agreement provides for (i) certain representations, warranties and affirmative covenants, (ii) certain negative covenants, including a requirement to maintain certain first lien leverage ratio levels and limitations on incurring
indebtedness, liens, fundamental changes, asset sales, investments, dividends and repayment of certain indebtedness, and transactions with affiliates, in each case with baskets, thresholds and exceptions and (iii) certain events of default, including for non-payment of principal and interest, breach of affirmative or negative covenants, certain cross defaults, change in control, bankruptcy events, certain ERISA events, certain unsatisfied judgments and actual or asserted invalidity of guarantees or security documents.
The Credit Facility is guaranteed by certain of our wholly-owned subsidiaries and secured by a first priority pledge on substantially all of our assets and the subsidiary guarantors, in each case subject to certain exceptions.
Financing Ratios
Total interest-bearing debt at October 31, 2012, was $310.7 million and our consolidated ratio of interest-bearing debt to shareholders' equity was 250%.
Total interest-bearing debt at October 31, 2011, was $281.2 million and our consolidated ratio of interest-bearing debt to shareholders' equity was 118%.
The following table summarizes the fixed and variable percentages of debt outstanding at the end of fiscal 2012 and 2011, after taking into account the impact of interest rate swap contracts that we had entered into, and the applicable interest rates at each quarter in fiscal 2011.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | % of Debt Outstanding | Interest Rates at End of Each Quarter in 2012 |
| | 10/31/2012 | | 10/31/2011 | | Q4 12 | | Q3 12 | | Q2 12 | | Q1 12 |
| | % | | % | | % | | % | | % | | % |
| Fixed rate | 90 |
| | 99 |
| | | | | | | | |
| Variable rate based on: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| U.S. Prime (3 months) | 7.0 |
| | — |
| | 3.25 | | 3.25 | | 3.25 | | 3.25 |
| U.K. Libor (3 months) | 3.0 |
| | — |
| | 0.53 | | 0.74 | | 1.01 | | 1.08 |
| Euribor (3 months) | — |
| | 1.0 |
| | | | | | | | |
Effects of Inflation
We do not believe that inflation has had a significant impact on our revenues or results of operations since inception. We expect our operating expenses will change in the future in line with periodic inflationary changes in price levels. Because we intend to retain and continue to use our property and equipment, we believe that the incremental inflation related to the replacement costs of such items will not materially affect our operations. However, the rate of inflation affects our expenses, such as those for employee compensation, which could increase our level of expenses and the rate at which we use our resources. While our management generally believes that we will be able to offset the effect of price-level changes by adjusting our service prices and implementing operating efficiencies, any material unfavorable changes in price levels could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
We do not use off-balance sheet entities to structure any of our financial arrangements. We do not have any interests in unconsolidated special-purpose or structured finance entities.
Tabular Disclosure of Contractual Obligations
Contractual repayments of long-term debt, commitments under operating leases, commitments under capital leases and purchase obligations as of October 31, 2012 were as follows:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Payments Due by Period |
| (in millions of USD) | Total | | Year 1 | | 2-3 Years | | 4-5 Years | | After 5 Years |
| | $ | | $ | | $ | | $ | | $ |
| Long-term debt | 310.7 |
| | — |
| | 30.7 |
| | 280.0 |
| | — |
|
| Interest on long-term debt | 110.4 |
| | 25.7 |
| | 48.4 |
| | 36.3 |
| | — |
|
| Operating leases | 15.7 |
| | 5.7 |
| | 6.3 |
| | 2.2 |
| | 1.5 |
|
Purchase obligations(1) | 16.9 |
| | 16.9 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
Total contractual obligations(2) | 453.7 |
| | 48.3 |
| | 85.4 |
| | 318.5 |
| | 1.5 |
|
_________________________
| |
| (1) | Purchase obligations relate to capital commitments to complete authorized capital projects. |
| |
| (2) | Not included in the table are other long-term liabilities of unfunded termination indemnities in the amount of $5.7 million, employee future benefits in the amount of $30.1 million and other long-term liabilities in the amount of $12.0 million. These other long-term liabilities either have no fixed payment dates or are not settled in cash. See "Note 8—Other Long-Term Liabilities" and "Note 9—Employee Future Benefits" to our consolidated financial statements included in this Form 10-K. |
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
See "Note 2— Summary of Significant Accounting Policies" to our consolidated financial statements included in this Form 10-K for a description of recent accounting pronouncements, including the expected dates of adoption and estimated effects, if any, on our consolidated financial statements.
Critical Accounting Estimates
The preparation of our consolidated financial statements requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses. These estimates and assumptions are based upon management's historical experience and are believed by management to be reasonable under the circumstances. Such estimates and assumptions are evaluated on an ongoing basis and form the basis for making judgments about the carrying values of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. Actual results could differ significantly from these estimates.
Our critical accounting estimates are those we believe are both most important to the portrayal of our financial condition and results and require our most difficult, subjective or complex judgments, often because we must make estimates about the effect of matters that are inherently uncertain. Judgments and uncertainties affecting the application of those policies may result in materially different amounts being reported under different conditions or using different assumptions. We believe the following estimates are the most critical in understanding the judgments that are involved in preparing our consolidated financial statements.
Impairment of Long-lived Depreciable Assets
We test for impairment annually and whenever events or circumstances make it more likely than not that the fair value of our capital assets and identifiable intangible assets ("long-lived depreciable assets") has fallen below its carrying amount. If such indicators are present, we assess the recoverability of the assets or group of assets by determining whether the carrying value of such assets can be recovered through undiscounted future cash flows. In addition, the useful life over which cash flows will occur, their amount and the asset's residual value, if any, are considered in the impairment calculation. In turn, measurement of an impairment loss requires a determination of fair value, which is based on the best information available. We derive the required undiscounted cash flow estimates from our historical experience and internal business plans. To determine fair value, we use quoted market prices when available, or our internal cash flow estimates discounted at an appropriate interest rate and independent appraisals, as appropriate. If the sum of undiscounted future cash flows is less than the carrying amount, the excess of the carrying amount over the estimated fair value, based on discounted future cash flows, is recorded as a charge to earnings.
During the second quarter of fiscal 2012, we decided to make certain adjustments over the next 24 to 36 months to the scale and scope of business conducted at our Swindon facility, including winding down or transferring non-cephalosporin commercial production to other facilities and, to the extent possible and commercially appropriate, directing PDS projects that require commercialization activities to other facilities. We are working with each of our affected commercial customers to develop plans to maintain supply chain continuity to the extent possible and commercially appropriate. In connection with these adjustments, we recorded a $57.9 million impairment charge for the impairment of long-term assets at our Swindon facility during the second quarter of fiscal 2012. The impairment charge will not result in any current or future cash expenditures.
During fiscal 2010, we recorded an impairment charge of $3.6 million in connection with the consolidation of our Puerto Rico operations into our manufacturing site located in Manatí. We recorded this charge to write down the carrying value of our Caguas facility's long-lived assets to their anticipated fair value upon closure of the facility. We also recorded an impairment charge of $0.8 million in discontinued operations to write down the remaining carrying value of the Carolina operations long-lived assets.
Reserve for Doubtful Accounts
We establish an appropriate provision for non-collectible or doubtful accounts. We consider several factors in estimating the allowance for uncollectible accounts receivable, including the age of the receivable, economic conditions that may have an impact on a specific group of customers or a specific customer and disputed services. Our risk management process includes standards and policies relating to customer credit limits, credit terms and customer deposits. Customer deposits relate primarily to our PDS business.
At October 31, 2012 and 2011, we had a reserve for doubtful accounts of $0.8 million and $0.4 million, respectively. These are specific reserves, not general reserves, and are based on factors discussed above.
Inventories
Inventories consisting of raw materials, packaging components, spare parts and work-in-process are valued at the lower of cost and net realizable value. These adjustments are customer specific estimates of net realizable value that we may ultimately realize upon the disposition of the inventories. We perform an assessment of excess, obsolete and problem products on an on-going basis.
We procure inventory based on specific customer orders and forecasts. Customers have limited rights of modification (for example, cancellations) with respect to these orders. Customer modifications to orders affecting inventory previously procured by us and purchases of inventory beyond customer needs may result in excess and obsolete inventory for the related customers. Although we may be able to use some excess components and raw materials for other products manufactured, a portion of the cost of this excess inventory may not be returned to the vendors or recovered from customers. Write-offs or write-downs of inventory could relate to:
| |
| • | declines in the market value of inventory; |
| |
| • | changes in customer demand for inventory, such as cancellation of orders; and |
| |
| • | our purchases of inventory beyond customer needs that result in excess quantities on hand that we may not be able to return to the vendor, use to fulfill orders from other customers or charge back to the customer. |
Adjustments above are recorded as an increase to cost of goods sold.
Payments received from customers for excess and obsolete inventories that have not been shipped to customers or otherwise disposed of are netted against inventory reserves.
Our practice is to dispose of excess and obsolete inventory as soon as practicable after such inventory has been identified as having no value to us.
Employee Future Benefits
As of October 31, 2012, we provided defined benefit pension plans to certain employees in our Canadian, U.K. and French operations and post-employment health and dental coverage to certain of our Canadian employees.
The determination of the obligation and expense for defined benefit pensions and other post-employment benefits is dependent on certain assumptions used by actuaries in calculating such amounts. The assumptions used in determining the accrued benefit obligation and the benefit expense as of and for the year ended October 31, 2012 were as follows:
|
| | | | | |
| | Defined Benefit Pension Plans % | | Other Benefit Plans % |
| Accrued benefit obligation | | | |
| Discount rate | 4.7 | % | | 5.2 | % |
| Rate of compensation increase | 3.5 | % | | — | % |
| Benefit costs recognized | | | |
| Discount rate | 4.9 | % | | 5.2 | % |
| Expected long-term rate of return on plan assets | 5.9 | % | | — | % |
| Rate of compensation increase | 3.5 | % | | — | % |
A 4% to 9% annual rate of increase in the per capita cost of covered health care and dental benefits was assumed for fiscal 2012, with the assumption that the rate will decrease gradually over the next five years to 6% and to remain at that level
thereafter. The following table outlines the effects of a one-percentage-point increase and decrease in the assumed health care and dental benefit trend rates.
|
| | | | | |
| (in millions of USD) | Benefit Obligation | | Benefit Expense |
| | $ | | $ |
| Impact of: | | | |
| 1% increase | 1.1 |
| | 0.1 |
|
| 1% decrease | (0.9 | ) | | (0.1 | ) |
Stock-Based Compensation
We use the fair value method of accounting for stock-based compensation. We use the Black-Scholes option-pricing model to estimate the fair value of the options granted. The determination of the fair value of stock-based awards on the date of grant using an option-pricing model is affected by our stock price as well as assumptions regarding a number of complex and subjective variables. These variables include our expected dividends, the risk-free interest rate, the expected life of the award and the expected stock price volatility over the term of the award. The principal assumptions we used in applying the Black-Scholes model are outlined below.
|
| | |
| | Fiscal 2012 |
| Expected dividend yield | None |
| Risk-free interest rate | 1.3 | % |
| Expected life | 5.5 years |
|
| Volatility | 58 | % |
We do not intend to pay dividends on our restricted voting shares in the foreseeable future and, accordingly, we use a dividend rate of zero in the option-pricing model. The Government of Canada five-year bond rate is used for the risk-free interest rate. The estimated life of the options is five years based on weighted-average life of these options, vesting period and management's estimate based on stock volatility. Expected volatility is a measure of the amount by which our restricted voting shares price has fluctuated or is expected to fluctuate during a period. We considered the historic volatility of our share price in estimating our expected volatility of 58%.
If factors change and we employ different assumptions for estimating stock-based compensation expense in future periods or if we decide to use a different valuation model, the stock-based compensation expense we recognize in future periods may differ significantly from what we have previously recorded and could materially affect our operating income, net income and earnings per share. These differences may result in a lack of consistency in future periods and materially affect the fair value estimate of our stock-based awards. They may also result in a lack of comparability with other companies that use different models, methods and assumptions.
Income Taxes
We follow the liability method of income tax allocation. Under this method, deferred tax assets and liabilities are determined based on differences between the financial reporting and tax bases of assets and liabilities and are measured using the enacted tax rates and laws that will be in effect when the differences are expected to reverse.
Preparation of our consolidated financial statements requires an estimate of income taxes in each of the jurisdictions in which we operate. The process involves an estimate of our current tax expense and an assessment of temporary differences resulting from differing treatment of items such as depreciation and amortization for tax and accounting purposes. These differences result in deferred tax assets and liabilities and are reflected in our consolidated balance sheet.
We evaluate our ability to realize deferred tax assets on a quarterly basis. A valuation allowance is provided if, based upon the weight of available evidence, it is more likely than not that a portion of the deferred tax assets will not be realized.
The factors used to assess the likelihood of realization of these assets include our calculation of cumulative pre-tax book income or loss, turn-around of temporary timing differences, available tax planning strategies that could be implemented to realize the deferred tax assets, and forecasted pre-tax book income and taxable income by specific tax jurisdiction. Actual results may vary from these forecasts and result in a change in our ability to realize benefits of these tax assets in the future. If
we are unable to meet our projected forecasts or implement certain tax planning strategies in jurisdictions for which there is currently no valuation allowance, we may be required to record additional valuation allowances.
During fiscal 2012, we determined that a valuation allowances on our net Canadian, French, U.K. and U.S. deferred tax assets was required due to cumulative losses in these jurisdictions. As a result, we recorded valuation allowances against our deferred assets in the United Kingdom, France, the United States and Canada in fiscal 2012 of $62.3 million. Of the $62.3 million, $5.7 million represents the valuation allowance against deferred assets in other comprehensive income.
Deferred tax assets of $4.3 million and $47.2 million have been recorded at October 31, 2012 and 2011, respectively. These assets consist primarily of deferred revenue, accounting provisions related to employee benefits not currently deductible for tax purposes, research and development investment tax credits, the tax benefit of net operating loss carryforwards, unclaimed research and development expenditures, and deferred financing and share issue costs.
The deferred tax assets recorded at October 31, 2012 and 2011 are net of a valuation allowance of $72.0 million and $9.0 million, respectively.
Deferred tax liabilities of $23.0 million and $27.9 million have been recorded at October 31, 2012 and 2011, respectively. These liabilities have arisen primarily on tax depreciation in excess of book depreciation.
Our tax filings are subject to audit by taxation authorities. Although our management believes that it has adequately provided for income taxes based on the information available, the outcome of audits cannot be known with certainty and the potential impact on our consolidated financial statements is not determinable.
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
Foreign Currency Risk
Our business is conducted in several currencies: Canadian dollars and U.S. dollars for our Canadian operations; U.S. dollars for our U.S. operations; and Euros, U. S. dollars and British Sterling for our European operations. We are subject to foreign currency transaction risk because a significant portion of our revenues and operating expenses from our operations in certain countries are denominated in different currencies. Our material foreign currency transaction risk arises from our Canadian operations. Our Canadian operations negotiate sales contracts for payment in both U.S. and Canadian dollars, and materials and equipment are purchased in both U.S. and Canadian dollars. The majority of the non-material costs (including payroll, facilities' costs and costs of locally sourced supplies and inventory) of our Canadian operations are denominated in Canadian dollars. In fiscal 2012, approximately 90% of the revenues and 10% of the operating expenses of our Canadian operations were transacted in U.S. dollars. As a result, if we do not effectively hedge such foreign currency exposure, our results of operations will be adversely affected by an increase in the value of the Canadian dollar relative to such foreign currency. In addition, we may experience hedging and transactional gains or losses because of volatility in the exchange rate between the Canadian dollar and the U.S. dollar. Based on our current U.S. denominated net inflows, for each 10% change in the Canadian-U.S. dollar exchange rate, the impact on annual pre-tax income, excluding any hedging activities, would be approximately $17.8 million.
To mitigate exchange-rate risk, we utilize foreign exchange forward contracts and collars in certain circumstances to lock in exchange rates with the objective that the gain or loss on the forward contracts and collars will approximately offset the loss or gain that results from the transaction or transactions being hedged. As of October 31, 2012, we had entered into 103 foreign exchange forward contracts and collars covering approximately 80% of our Canadian-U.S. dollar cash flow exposures for fiscal 2012. For additional information please see "Note 12—Financial Instruments, Fair Value and Risk Management" to our consolidated financial statements included in this Form 10-K. We do not hedge any of our other foreign exchange exposures. Our foreign exchange forward contracts and collars mature at various dates through July 2014 and have an aggregate fair value of $137.7 million. As of October 31, 2012, an adverse exchange rate movement of 10% against our foreign exchange forward contracts and collars would result in a pre-tax loss of approximately $13.8 million.
Interest Rate Risk
As of October 31, 2012, our long-term debt consisted of the Notes, which had an aggregate principal amount of $280.0 million and bore interest at a fixed rate, and the $75.0 million ABL, which bore interest at a variable rate. As of October 31, 2012, $30.7 million was outstanding under the ABL. Assuming a fully drawn ABL and a 100 basis point increase in applicable interest rates, our interest expense, net, would have increased by $0.75 million on an annual basis.
On December 14, 2012, we entered into the Credit Facility, comprised of (i) the $575.0 million Secured Term Loan and (ii) the $85.0 million Secured Revolving Facility. The Secured Term Loan and the Secured Revolving Facility each bear
interest at a variable rate. Assuming a fully drawn Secured Revolving Facility and a 100 basis point increase in applicable interest rates, our interest expense, net, would (if not hedged) increase by approximately $6.6 million on an annual basis.
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.
Our consolidated financial statements appear at the end of this annual report on Form 10-K. See "Index to Consolidated Financial Statements."
Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure.
There have been no changes in or corresponding disagreements with our independent accountant during the last two fiscal years.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures
Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Our management, with the participation of our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, has evaluated the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures (as such term is defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Exchange Act) as of the end of the period covered by this annual report on Form 10-K. Based on such evaluation, our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer concluded that, as of the end of the period covered by this annual report on Form 10-K, our disclosure controls and procedures are effective in that they provide reasonable assurances that the information we are required to disclose in the reports we file or submit under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods required by the SEC's rules and forms and that such information is accumulated and communicated to management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, as appropriate, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
There were no changes in our internal control over financial reporting, as such term is defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) under the Exchange Act, during the fourth quarter of fiscal 2012 that materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
In the course of our ongoing preparations for making management's report on internal control over financial reporting as required by Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, from time to time we have identified areas in need of improvement and have taken remedial actions to strengthen the affected controls as appropriate. We make these and other changes to enhance the effectiveness of our internal controls over financial reporting, which do not have a material effect on our overall internal control.
We will continue to evaluate the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures and internal control over financial reporting on an ongoing basis and will take action as appropriate.
Management's Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting, as such term is defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f). Our internal control system was designed to provide reasonable assurance to our management and Board regarding the preparation and fair presentation of published financial statements.
Our internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that:
|
| |
| (i) | pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of our assets; |
|
| |
| (ii) | provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that our receipts and expenditures are being made only in accordance with authorizations of our management and Board; and |
|
| |
| (iii) | provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of our assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements. |
All internal control systems, no matter how well designed, have inherent limitations. Therefore, even those systems determined to be effective can provide only reasonable assurance with respect to financial statement preparation and presentation.
In making the assessment of internal control over financial reporting, our management used the criteria issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission ("COSO") in Internal Control-Integrated Framework. Based on that assessment and those criteria, management has concluded that our internal control over financial reporting was effective as of October 31, 2012.
The effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of October 31, 2012 has not been audited by Ernst & Young LLP, our independent registered public accounting firm. For so long as we qualify as an "emerging growth company" under the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act, our independent registered public accounting firm will not be required to attest to the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting.
Item 9B. Other Information
Discretionary Bonus Payments
As previously disclosed, in December 2011 our CHR Committee adopted the 2012 Patheon Global Bonus Plan (the "2012 Bonus Plan") to reward eligible participants (including our executive officers) for their collective and individual contributions to our success during fiscal 2012. Under our 2012 Bonus Plan, if our company did not meet threshold performance levels for each of Adjusted Corporate EBITDA, Net Free Cash Flow and Revenue (each as defined pursuant to the 2012 Bonus Plan), there would be no payout to our executive officers under the 2012 Bonus Plan. Although our company exceeded its targets for Adjusted Corporate EBITDA and Revenue under the 2012 Bonus Plan, it did not achieve the threshold performance level for Net Free Cash Flow. Accordingly, our executive officers were not eligible for bonus payouts under the 2012 Bonus Plan.
Although our company did not achieve the threshold level of Net Free Cash Flow performance, on December 13, 2012, our CHR Committee decided to award discretionary cash bonuses to, among others, our chief executive officer, our chief financial officer, and our certain of our other named executive officers as disclosed in the Proxy Statement and Information Circular for our 2012 Annual and Special Meeting of Shareholders. Our CHR Committee determined that awarding discretionary cash bonuses to these individuals was consistent with our pay-for-performance philosophy because, among other things, we exceeded our Adjusted EBITDA and Revenue targets under the 2012 Bonus Plan, we exceeded our operational excellence goals, and each of these individuals has made significant contributions to our company's success. The bonuses awarded to these individuals were as follows:
|
| | | | |
| Name | Title | Bonus |
| James C. Mullen | Chief Executive Officer | $ | 1,000,000 |
|
| Stuart Grant | Executive Vice President, Chief Financial Officer | $ | 200,000 |
|
| Geoffrey M. Glass | President, Proprietary Products | $ | 170,000 |
|
| Paul M. Garofolo | Executive Vice President, Global PDS Operations | $ | 190,000 |
|
Adoption of the 2013 Patheon Global Bonus Plan
On December 13, 2012, our CHR Committee adopted the 2013 Patheon Global Bonus Plan (the "2013 Bonus Plan") to reward eligible participants (including our executive officers) for their collective and individual contributions to our success. The 2013 Bonus Plan is effective fiscal years beginning on or after November 1, 2012.
Under the 2013 Bonus Plan, participants become eligible for bonus payouts based on (i) the achievement of corporate and, if applicable, regional or site objectives and (ii) their individual performance ratings. The corporate objectives consist of Corporate Adjusted EBITDA, Corporate Net Free Cash Flow and Corporate Revenue, each as defined pursuant to the 2013 Bonus Plan. Our executive officers' bonus eligibility is determined based solely on the achievement of the predetermined corporate objectives and their individual performance ratings. Our CHR Committee approves the corporate, regional and site
performance objectives, each of which has three possible levels of achievement (minimum, target and maximum) that correspond to three levels of payouts (50%, 100% and 150%, except for Corporate Revenue, which has payout levels of 50%, 100% and 200%).
Each participant's target award is equal to a percentage of his or her earned base pay (less certain benefit amounts) or a specified dollar value as (i) contained in the terms of his or her written employment agreement, (ii) approved by our human resources department for the participant's specific position or employment grade level, or (iii) approved by our CHR Committee for the participant. Provided that all necessary conditions for payout have been met, each participant's payout will equal the product of the participant's target award multiplied by the total achievement of the participant's designated weighted objectives multiplied by a factor ranging from 0 to 1.75 based on his or her individual performance rating; provided, however, that the maximum possible payout to any eligible participant is 200% of target. For our executive officers, each corporate objective (Corporate Adjusted EBITDA, Corporate Net Free Cash Flow and Corporate Revenue) is assigned equal weight for purposes of determining the executive officer's payout, and the payout with respect to achievement of any one corporate objective is not conditioned on the achievement of any other corporate objective.
The foregoing summary is qualified in its entirety by reference to the 2013 Bonus Plan, a copy of which is filed as Exhibit 10.25 to this annual report on Form 10-K and is incorporated herein by reference.
PART III
Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance.
Directors and Executive Officers
Information regarding our directors and executive officers may be found under the captions "Business of the Meeting—Election of Directors" and "Executive Officers" in the Proxy Statement and Information Circular for our 2013 Annual Meeting of Shareholders (our "2013 Proxy Statement"). Such information is incorporated herein by reference.
Compliance With Section 16(a) of the Exchange Act
Information regarding compliance with Section 16(a) of the Exchange Act by our directors, officers and beneficial owners of more than 10% of our restricted voting shares may be found under the caption "Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance" in our 2013 Proxy Statement. Such information is incorporated herein by reference.
Code of Ethics
We have adopted a code of business conduct and ethics that applies to our directors, officers (including our principal executive officer, principal financial officer, principal accounting officer or controller, or persons performing similar functions) and other employees. A copy of our code of business conduct and ethics is available on our website at www.patheon.com under "Investor Relations—Corporate Governance." We intend to post on our website and (if required) file on Form 8-K all disclosures that are required by applicable law or the rules of the SEC concerning any amendment to, or waiver from, our code of business conduct and ethics.
Director Nominees
Information regarding procedures for recommending nominees to our Board may be found under the caption "Corporate Governance—The Board of Directors—Board Committees—Corporate Governance Committee" in our 2013 Proxy Statement. Such information is incorporated herein by reference.
Audit Committee
Information regarding our audit committee may be found under the caption "Corporate Governance—The Board of Directors—Board Committees—Audit Committee" in our 2013 Proxy Statement. Such information is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 11. Executive Compensation.
Information with respect to this item may be found under the caption "Executive Compensation" in our 2013 Proxy Statement. Such information is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters.
Information with respect to this item may be found under the captions "Principal Shareholders and Share Ownership by Management" and "Executive Compensation—Equity Compensation Plan Information" in our 2013 Proxy Statement. Such information is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence.
Information with respect to this item may be found under the captions "Executive Compensation—Compensation Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation" and "Corporate Governance" in our 2013 Proxy Statement. Such information is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 14. Principal Accountant Fees and Services.
Information with respect to this item may be found under the caption "Business of the Meeting—Appointment of Auditors—Independent Auditor Fee Information" in our 2013 Proxy Statement. Such information is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 15. Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules.
(a)(1) Financial Statements
Our consolidated financial statements appear at the end of this annual report on Form 10-K. See "Index to Consolidated Financial Statements."
(a)(2) Financial Statement Schedules
Schedules have been omitted because they are not applicable or the required information is shown in our consolidated financial statements or the related notes thereto. See "Index to Consolidated Financial Statements."
(a)(3) Exhibits
The list of exhibits filed as part of this annual report on Form 10-K is set forth on the Exhibit Index immediately preceding the exhibits hereto and is incorporated herein by reference.
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
|
| | | |
| | | | |
| | PATHEON INC. |
| | | |
| | By: | | /s/ Stuart Grant |
| | Stuart Grant |
| | Executive Vice President, Chief Financial Officer |
| | December 18, 2012 |
We, the undersigned officers and directors of Patheon Inc., hereby severally constitute and appoint James C. Mullen and Stuart Grant, and each of them singly, our true and lawful attorneys, with full power to them and each of them singly, to sign for us in our names in the capacities indicated below, all amendments to this report, and generally to do all things in our names and on our behalf in such capacities to enable Patheon Inc. to comply with the provisions of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, and all requirements of the Securities and Exchange Commission.
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
|
| | |
| Name | Title | Date |
| /s/ James C. Mullen | Chief Executive Officer (Principal Executive Officer) | December 18, 2012 |
| | | |
| /s/ Stuart Grant | Executive Vice President, Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial Officer) | December 18, 2012 |
| | | |
| /s/ Dean F. Wilson | Vice President, Corporate Controller (Principal Accounting Officer) | December 18, 2012 |
| | | |
| /s/ Paul S. Levy | Director | December 18, 2012 |
| | | |
| /s/ Michel Lagarde | Director | December 18, 2012 |
| | | |
| /s/ Nicholas O'Leary | Director | December 18, 2012 |
| | | |
| /s/ Daniel Agroskin | Director | December 18, 2012 |
| | | |
| /s/ Joaquín B. Viso | Director | December 18, 2012 |
| | | |
| /s/ Derek J. Watchorn | Director | December 18, 2012 |
| | | |
| /s/ Brian G. Shaw | Director | December 18, 2012 |
| | | |
| /s/ David E. Sutin | Director | December 18, 2012 |
INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
|
| |
| | Page |
| REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM | F-1 |
| | |
| AUDITED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS: | |
| | |
| Consolidated Balance Sheets | F-2 |
| | |
| Consolidated Statements of Operations | F-3 |
| | |
| 'Consolidated Statements of Changes in Shareholders' Equity | F-4 |
| | |
| Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows | F-5 |
| | |
| Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements | F-6 |
| | |
| | |
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Board of Directors and Shareholders of Patheon Inc.
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Patheon Inc. as of October 31, 2012 and 2011, and the related consolidated statements of operations, changes in shareholders' equity, and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended October 31, 2012. These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audits
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. We were not engaged to perform an audit of the Company's internal control over financial reporting. Our audits included consideration of internal control over financial reporting as a basis for designing audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company's internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion. An audit also includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, and evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion
In our opinion, the financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the consolidated financial position of Patheon Inc. at October 31, 2012 and 2011, and the consolidated results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended October 31, 2012 in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles
As discussed in Note 2 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company changed its comprehensive basis of accounting from Canadian generally accepted accounting principles to U.S. generally accepted accounting principles effective November 1, 2011 and all material amounts and disclosures have been retroactively adjusted for the periods presented.
/s/ Ernst & Young LLP
Raleigh, North Carolina
December 18, 2012
Patheon Inc.
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
|
| | | | | |
| | As of October 31, |
| (in millions of U.S. dollars ) | 2012 | | 2011 |
| | $ | | $ |
| Assets | | | |
| Current | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | 39.4 |
| | 33.4 |
|
| Accounts receivable, net | 161.7 |
| | 158.0 |
|
| Inventories | 82.3 |
| | 81.8 |
|
| Income taxes receivable | 0.4 |
| | 3.1 |
|
| Prepaid expenses and other | 11.9 |
| | 10.7 |
|
| Deferred tax assets—short term | 4.3 |
| | 8.1 |
|
| Total current assets | 300.0 |
| | 295.1 |
|
| Capital assets | 416.4 |
| | 474.2 |
|
| Deferred financing costs | 4.9 |
| | 6.2 |
|
| Deferred tax assets | — |
| | 39.1 |
|
| Goodwill | 3.5 |
| | 3.5 |
|
| Investments | 6.3 |
| | 5.3 |
|
| Long-term assets held for sale | — |
| | 0.2 |
|
| Other long-term assets | 11.8 |
| | 1.0 |
|
| Total assets | 742.9 |
| | 824.6 |
|
| Liabilities and shareholders' equity | | | |
| Current | | | |
| Short-term borrowings | 2.4 |
| | 6.1 |
|
| Accounts payable and accrued liabilities | 186.2 |
| | 181.5 |
|
| Income taxes payable | 5.7 |
| | — |
|
| Deferred revenues—short term | 13.9 |
| | 8.8 |
|
| Current portion of long-term debt | — |
| | 1.1 |
|
| Total current liabilities | 208.2 |
| | 197.5 |
|
| Long-term debt | 310.7 |
| | 280.1 |
|
| Deferred revenues | 28.9 |
| | 27.7 |
|
| Deferred tax liabilities | 23.0 |
| | 27.9 |
|
| Other long-term liabilities | 47.8 |
| | 53.7 |
|
| Total liabilities | 618.6 |
| | 586.9 |
|
| Shareholders' equity | | | |
| Restricted voting shares | 572.5 |
| | 571.9 |
|
| Contributed surplus | 16.5 |
| | 13.5 |
|
| Accumulated deficit | (478.6 | ) | | (371.9 | ) |
| Accumulated other comprehensive income | 13.9 |
| | 24.2 |
|
| Total shareholders' equity | 124.3 |
| | 237.7 |
|
| Total liabilities and shareholders' equity | 742.9 |
| | 824.6 |
|
see accompanying notes
Patheon Inc.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years ended October 31, |
| (in millions of U.S. dollars, except loss per share) | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| | $ | | $ | | $ |
| Revenues | 749.1 |
| | 700.0 |
| | 671.2 |
|
| Cost of goods sold | 589.8 |
| | 568.2 |
| | 536.8 |
|
| Gross profit | 159.3 |
| | 131.8 |
| | 134.4 |
|
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | 128.6 |
| | 120.2 |
| | 110.6 |
|
| Repositioning expenses | 6.1 |
| | 7.0 |
| | 6.8 |
|
| Acquisition-related costs | 3.2 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Impairment charge | 57.9 |
| | — |
| | 3.6 |
|
| Loss on sale of capital assets | 0.4 |
| | 0.2 |
| | 0.2 |
|
| Operating (loss) income | (36.9 | ) | | 4.4 |
| | 13.2 |
|
| Interest expense, net | 26.5 |
| | 25.6 |
| | 19.6 |
|
| Foreign exchange loss (gain) | 0.5 |
| | (1.6 | ) | | (1.5 | ) |
| Refinancing expenses | — |
| | — |
| | 12.2 |
|
| Other income, net | (0.9 | ) | | (4.9 | ) | | (0.4 | ) |
| Loss from continuing operations before income taxes | (63.0 | ) | | (14.7 | ) | | (16.7 | ) |
| Current | 9.2 |
| | 1.6 |
| | 6.7 |
|
| Deferred | 34.2 |
| | (0.5 | ) | | (20.5 | ) |
| Provision for (benefit from) income taxes | 43.4 |
| | 1.1 |
| | (13.8 | ) |
| Loss before discontinued operations | (106.4 | ) | | (15.8 | ) | | (2.9 | ) |
| Loss from discontinued operations | (0.3 | ) | | (0.6 | ) | | (1.7 | ) |
| Net loss for the period | (106.7 | ) | | (16.4 | ) | | (4.6 | ) |
| Net loss attributable to restricted voting shareholders | (106.7 | ) | | (16.4 | ) | | (4.6 | ) |
| Basic and diluted loss per share | | | | | |
| From continuing operations | $ | (0.824 | ) | | $ | (0.122 | ) | | $ | (0.023 | ) |
| From discontinued operations | $ | (0.002 | ) | | $ | (0.005 | ) | | $ | (0.013 | ) |
| | $ | (0.826 | ) | | $ | (0.127 | ) | | $ | (0.036 | ) |
| Weighted-average number of shares outstanding during period—basic and diluted (in thousands) | 129,169 |
| | 129,168 |
| | 129,168 |
|
see accompanying notes
Patheon Inc.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN SHAREHOLDERS' EQUITY
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (in millions of U.S. dollars) | Convertible Preferred Shares | | Restricted Voting Shares | | Contributed Surplus | | Accumulated Deficit | | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income | | 'Total Shareholders' Equity |
| Balance at October 31, 2009 | $ | — |
| | $ | 571.9 |
| | $ | 7.7 |
| | $ | (350.9 | ) | | $ | 15.9 |
| | $ | 244.6 |
|
| Stock-based compensation | — |
| | — |
| | 2.3 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 2.3 |
|
| Comprehensive income (loss): | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net loss attributable to restricted voting shareholders | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (4.6 | ) | | — |
| | (4.6 | ) |
| Change in foreign currency translation on investments in subsidiaries, net of hedging activities | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 1.6 |
| | 1.6 |
|
| Change in value of derivatives designated as foreign currency cash flow hedges | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 9.0 |
| | 9.0 |
|
| Losses on foreign currency hedges reclassified to consolidated statement of operations | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (6.2 | ) | | (6.2 | ) |
| Net change in minimum pension liability | | | | | | | | | 2.4 |
| | 2.4 |
|
| Subtotal | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (4.6 | ) | | 6.8 |
| | 2.2 |
|
| Balance at October 31, 2010 | — |
| | 571.9 |
| | 10.0 |
| | (355.5 | ) | | 22.7 |
| | 249.1 |
|
| Stock-based compensation | — |
| | — |
| | 3.5 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 3.5 |
|
| Comprehensive income (loss): | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net loss attributable to restricted voting shareholders | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (16.4 | ) | | — |
| | (16.4 | ) |
| Change in foreign currency translation on investments in subsidiaries, net of hedging activities | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 5.3 |
| | 5.3 |
|
| Change in value of derivatives designated as foreign currency cash flow hedges | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 1.7 |
| | 1.7 |
|
| Losses on foreign currency hedges reclassified to consolidated statement of operations | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (3.0 | ) | | (3.0 | ) |
| Net change in minimum pension liability | | | | | | | | | (2.5 | ) | | (2.5 | ) |
| Subtotal | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (16.4 | ) | | 1.5 |
| | (14.9 | ) |
| Balance at October 31, 2011 | — |
| | 571.9 |
| | 13.5 |
| | (371.9 | ) | | 24.2 |
| | 237.7 |
|
| Stock options exercised | — |
| | 0.5 |
| | (0.1 | ) | | — |
| | — |
| | 0.4 |
|
| Stock-based compensation | — |
| | — |
| | 3.1 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 3.1 |
|
| Foreign currency translation adjustments | — |
| | 0.1 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 0.1 |
|
| Comprehensive income (loss): | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net loss attributable to restricted voting shareholders | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (106.7 | ) | | — |
| | (106.7 | ) |
| Change in foreign currency translation on investments in subsidiaries, net of hedging activities | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (11.9 | ) | | (11.9 | ) |
| Change in value of derivatives designated as foreign currency cash flow hedges | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 1.3 |
| | 1.3 |
|
| Gains on foreign currency hedges reclassified to consolidated statement of operations | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 0.5 |
| | 0.5 |
|
| Net change in minimum pension liability | | | | | | | | | (0.2 | ) | | (0.2 | ) |
| Subtotal | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | (106.7 | ) | | (10.3 | ) | | (117.0 | ) |
| Balance at October 31, 2012 | $ | — |
| | $ | 572.5 |
| | $ | 16.5 |
| | $ | (478.6 | ) | | $ | 13.9 |
| | $ | 124.3 |
|
see accompanying notes
Patheon Inc.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | Years ended October 31, |
| (in millions of U.S. dollars) | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| | $ | | $ | | $ |
| Operating activities | | | | | |
| Loss before discontinued operations | (106.4 | ) | | (15.8 | ) | | (2.9 | ) |
| Add (deduct) charges to operations not requiring a current cash payment | | | | | |
| Depreciation and amortization | 40.8 |
| | 53.2 |
| | 55.6 |
|
| Impairment charge | 57.9 |
| | — |
| | 3.6 |
|
| Other non-cash interest | 1.2 |
| | 1.1 |
| | 2.5 |
|
| Change in other long-term assets and liabilities | (2.2 | ) | | (4.0 | ) | | 2.2 |
|
| Deferred income taxes | 34.2 |
| | (0.6 | ) | | (19.7 | ) |
| Amortization of deferred revenues | (13.1 | ) | | (45.0 | ) | | (37.4 | ) |
| Loss on sale of capital assets | 0.4 |
| | 0.2 |
| | 0.2 |
|
| Stock-based compensation expense | 3.1 |
| | 3.5 |
| | 2.3 |
|
| Other | (0.9 | ) | | (0.1 | ) | | (0.5 | ) |
| | 15.0 |
| | (7.5 | ) | | 5.9 |
|
| Net change in non-cash working capital balances related to continuing operations | (6.8 | ) | | 1.0 |
| | (2.6 | ) |
| Increase in deferred revenues | 25.2 |
| | 30.4 |
| | 47.4 |
|
| Cash provided by operating activities of continuing operations | 33.4 |
| | 23.9 |
| | 50.7 |
|
| Cash used in operating activities of discontinued operations | (0.4 | ) | | (1.0 | ) | | (0.7 | ) |
| Cash provided by operating activities | 33.0 |
| | 22.9 |
| | 50.0 |
|
| Investing activities | | | | | |
| Additions to capital assets | (53.4 | ) | | (47.8 | ) | | (48.7 | ) |
| Proceeds on sale of capital assets | 0.4 |
| | 0.4 |
| | — |
|
| Proceeds on sale of business, net | 1.0 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Net increase in investments | — |
| | — |
| | (1.1 | ) |
| Investment in intangibles | — |
| | — |
| | (0.2 | ) |
| Cash used in investing activities of continuing operations | (52.0 | ) | | (47.4 | ) | | (50.0 | ) |
| Cash provided by investing activities of discontinued operations | 0.1 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Cash used in investing activities | (51.9 | ) | | (47.4 | ) | | (50.0 | ) |
| Financing activities | | | | | |
| (Decrease) increase in short-term borrowings | (3.8 | ) | | 4.2 |
| | (10.7 | ) |
| Increase in debt | 40.9 |
| | 13.5 |
| | 300.2 |
|
| Increase in deferred financing costs | — |
| | — |
| | (7.3 | ) |
| Repayment of debt | (11.1 | ) | | (15.0 | ) | | (250.6 | ) |
| Proceeds on issuance of restricted voting shares | 0.3 |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Cash provided by financing activities of continuing operations | 26.3 |
| | 2.7 |
| | 31.6 |
|
| Cash provided by financing activities | 26.3 |
| | 2.7 |
| | 31.6 |
|
| Effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents | (1.4 | ) | | 1.7 |
| | (0.4 | ) |
| Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents during the period | 6.0 |
| | (20.1 | ) | | 31.2 |
|
| Cash and cash equivalents, beginning of period | 33.4 |
| | 53.5 |
| | 22.3 |
|
| Cash and cash equivalents, end of period | 39.4 |
| | 33.4 |
| | 53.5 |
|
| Supplemental cash flow information | | | | | |
| Interest paid | 25.4 |
| | 25.0 |
| | 21.1 |
|
| Income taxes paid (received), net | 2.2 |
| | (1.3 | ) | | 9.1 |
|
see accompanying notes
Patheon Inc.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
October 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010
(Dollar information in tabular form is expressed in millions of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise indicated)
1. NATURE OF BUSINESS
Nature of business
Patheon Inc. ("Patheon" or the "Company") is a Canadian public company, which trades under the symbol PTI on The Toronto Stock Exchange ("TSX"). The Company is an independent provider of drug development and manufacturing services to global pharmaceutical, biotechnology and specialty pharmaceutical companies.
Patheon's commercial manufacturing activities relate primarily to various sterile dosage forms, as well as solid, conventional and specialized dosage forms. The Company's sterile dosage forms include aseptically (sterile) filled and terminally sterilized liquids and vials, bottles and pre-filled syringes and sterile lyophilized (freeze-dried) products in vials. Conventional dosage forms include both coated and uncoated compressed tablets and hard shell gelatin capsules. The Company manufactures to customer specifications a wide variety of products in many packaging formats. The Company can be responsible for each aspect of the manufacturing and packaging process, from sourcing raw materials and packaging components to delivering the finished product in consumer-ready form to the customer's distribution facilities.
Patheon's pharmaceutical development services ("PDS") include dosage form development, analytical methods development, pilot batch manufacture of new products for the regulatory drug approval process and the provision of scale-up services designed to demonstrate that a drug can be manufactured in commercial volumes.
2. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Principles of consolidation and basis of presentation
The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company and its wholly-owned subsidiaries. All intercompany transactions have been eliminated.
The preparation of the consolidated financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States ("U.S. GAAP") requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect: the reported amounts of assets and liabilities; the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the consolidated financial statements; and the reported amounts of revenue and expenses in the reporting period. Management believes that the estimates and assumptions used in preparing its consolidated financial statements are reasonable and prudent; however, actual results could differ from those estimates.
Certain prior year amounts in the Audited Consolidated Financial Statements have been reclassified to conform to the current year's presentation.
Changes in accounting policy
The Company historically prepared its consolidated financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in Canada. Effective November 1, 2011, the Company adopted U.S. GAAP as the reporting standard for its consolidated financial statements. These consolidated financial statements, including related notes, have therefore been prepared in accordance with U.S. GAAP. All comparative financial information contained herein has been recast to reflect the Company's results as if the Company had historically reported in accordance with U.S. GAAP. These audited consolidated financial statements reflect all adjustments which are, in the opinion of management, necessary for a fair presentation of the periods presented.
Effective February 1, 2012, the Company adopted ASU 2011-04, "Fair Value Measurement (Topic 820): Amendments to Achieve Common Fair Value Measurement and Disclosure Requirements in U.S. GAAP and IFRSs." This ASU modifies the existing standards to include disclosure of all transfers between Level 1 and Level 2 asset and liability fair value categories. In addition, the ASU provides guidance on measuring the fair value of financial instruments managed within a portfolio and the application of premiums and discounts on fair value measurements. The ASU requires additional disclosure for Level 3 measurements regarding the sensitivity of fair value to changes in unobservable inputs and any interrelationships between those inputs. The adoption of this guidance had no material impact to the Company's financial statements.
Foreign exchange translation
Patheon Inc.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
October 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010
(Dollar information in tabular form is expressed in millions of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise indicated)
The Company's assets and liabilities that are not denominated in U.S. dollars are translated into U.S. dollars as follows: non-monetary assets are translated using the exchange rate in effect at year end, non-monetary assets and liabilities are translated at the exchange rates in effect at the time of acquisition or issue, and revenues and expenses are translated at the average rate during each month. Translation gains and losses related to the carrying value of the Company's foreign operations are included in accumulated other comprehensive income in shareholders' equity. Foreign exchange gains and losses on transactions occurring in a currency different than the entity's functional currency are reflected in income (loss).
Revenue recognition
The Company recognizes revenue for its commercial manufacturing and pharmaceutical development services when services are completed in accordance with specific agreements with its customers and when all costs connected with providing these services have been incurred, the price is fixed or determinable and collectability is reasonably assured. Customer deposits on pharmaceutical development services in progress are included in accounts payable and accrued liabilities.
The Company does not receive any fees on signing of contracts. In the case of pharmaceutical development services, revenue is recognized on the achievement of specific milestones in accordance with the respective development service contracts. In the case of commercial manufacturing services, revenue is recognized when services are complete and the product has met rigorous quality assurance testing.
Deferred revenues
The costs of certain capital assets are reimbursed to the Company by the pharmaceutical companies that are to benefit from the improvements in connection with the manufacturing and packaging agreements in force. These reimbursements are recorded as deferred revenues and are recognized as income over the remaining minimum term of the agreements. In certain instances the Company receives prepayment for future services and these amounts are amortized over the future required service periods.
Financial assets and liabilities
All financial instruments, including derivatives, are included in the consolidated balance sheets and are measured at fair value except for loans and receivables and other financial liabilities, which are measured at amortized cost. Held-for-trading financial instruments are recorded at cost as they are initiated and are subsequently measured at fair value and all revaluation gains and losses are included in net income (loss) in the period in which they arise. Available-for-sale financial instruments are also recorded at cost and are subsequently measured at fair value with all revaluation gains and losses included in other comprehensive income. All financial instrument transactions are recorded on the settlement date. Please refer to Note 12—Financial Instruments, Fair Value and Risk Management.
The Company expenses as incurred all transaction costs, including fees paid to advisors and other related costs. Financing costs, including underwriting and arrangement fees paid to lenders are deferred and carried as an asset on the balance sheet and amortized into interest expense using the effective interest rate method.
Derivatives and hedge accounting
The Company enters into foreign exchange forward contracts and collars to reduce its exposure to foreign currency denominated cash flows and changes in the fair value of foreign denominated assets and liabilities. Please refer to Note 12—Financial Instruments, Fair Value and Risk Management.
All derivative instruments are recorded on the consolidated balance sheets at fair value unless exempted from derivative treatment as a normal purchase and sale. All changes in their fair value are recorded in income (loss) unless cash flow hedge accounting is used, in which case the changes in the fair value associated with the effective portions of the hedge are recorded in other comprehensive income.
Cash and cash equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents include cash in interest-bearing accounts and term deposits with remaining maturities of less than three months at the date the term deposit was acquired.
Patheon Inc.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
October 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010
(Dollar information in tabular form is expressed in millions of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise indicated)
Inventories
Inventories consisting of raw materials, packaging components, spare parts and work-in-process are valued at the lower of cost and net realizable value. Cost approximates average cost, and includes cost of purchased materials, costs of conversion, namely labor and overhead, and other costs, such as freight in, necessary to bringing the inventories to their present location and condition.
Capital assets
Capital assets are carried at cost less accumulated depreciation. The cost of assets disposed of and the related accumulated depreciation are removed from the accounts and any resulting gain or loss is reflected in earnings.
Depreciation is provided on the straight-line basis based on estimated useful lives as follows:
|
| |
| Buildings | 30 – 50 years |
| Building equipment | 15 years |
| Machinery and equipment | 5 – 15 years |
| Office equipment | 3 – 10 years |
| Computer software | 2 – 10 years |
| Furniture and fixtures | 7 – 10 years |
Repairs and maintenance costs are charged to operations as incurred.
Impairment of long-lived depreciable assets
The Company reviews whether there are any indicators of impairment of its capital assets and identifiable intangible assets ("long-lived depreciable assets"). If such indicators are present, the Company assesses the recoverability of the assets or group of assets by determining whether the carrying value of such assets can be recovered through undiscounted future cash flows. If the sum of undiscounted future cash flows is less than the carrying amount, the excess of the carrying amount over the estimated fair value, based on discounted future cash flows, is recorded as a charge to earnings.
Goodwill
Goodwill represents the excess of the purchase price of the Company's interest in subsidiary companies over the fair value of the underlying net identifiable assets arising on acquisitions. Goodwill is not subject to amortization but is subject to an annual review for impairment, or more frequently if events or changes in circumstances indicate that goodwill is impaired. Goodwill impairment has been based on a quantitative assessment of the fair value of an individual reporting unit to the underlying carrying value of the reporting unit's net assets including goodwill. When the carrying amount of the reporting unit exceeds its fair value, the fair value of the reporting unit's goodwill, determined in the same manner as in a business combination, is compared with its carrying amount to measure the amount of the impairment loss, if any.
Employee benefit plans
The Company provides a number of benefit plans to its employees including:
(a) defined benefit pension plans; (b) post-employment benefit plans; (c) defined contribution plans; and (d) unfunded termination indemnities.
The cost of defined benefit pension plans and other post-employment benefits, which include health care and dental benefits, related to employees' current service is charged to earnings annually. The cost is computed on an actuarial basis using the projected benefit method pro-rated based on service and management's best estimates of various actuarial factors, including salary escalation, other cost escalation and retirement ages of employees.
The valuation of defined benefit pension plan assets is at current market value, based on an actuarial valuation, for purposes of calculating the expected return on plan assets. Past service costs resulting from plan amendments are deferred and amortized on a straight-line basis over the remaining service life of employees active at the time of amendment.
Actuarial gains and losses arise from the difference between the actual long-term rate of return on plan assets for a period and the expected long-term rate of return on plan assets for that period, or from changes in actuarial assumptions used to determine the accrued benefit obligation. The excess of the net accumulated actuarial gain or loss over 10% of the greater of the
Patheon Inc.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
October 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010
(Dollar information in tabular form is expressed in millions of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise indicated)
benefit obligations and the fair value of plan assets is amortized over the average remaining service period of active employees. The average remaining service period of the active employees covered by the pension plans and the other retirement benefit plans at the measurement date of October 31, 2012 is 18 years (2011—18 years). When the restructuring of a benefit plan gives rise to both a curtailment and a settlement of obligations, the curtailment is accounted for prior to the settlement.
The cost of defined contribution plans is charged to earnings as funds are contributed by the Company.
Unfunded termination indemnities for the employees of the Company's subsidiary in Italy are accrued based on Italian severance pay statutes. The liability recorded on the consolidated balance sheets is the amount to which the employees would be entitled if the employees' employment with the Company ceased.
Income taxes
The Company follows the liability method of income tax allocation. Under this method, deferred tax assets and liabilities are determined based on differences between the financial reporting and tax bases of assets and liabilities and are measured using the substantively enacted tax rates and laws that will be in effect when the differences are expected to reverse.
The Company evaluates its ability to realize deferred tax assets on a quarterly basis. The factors used to assess the likelihood of realization of these assets include the Company's calculation of cumulative pre-tax book income or loss, turn-around of temporary timing differences, available tax planning strategies that could be implemented to realize the deferred tax assets, and forecasted pre-tax book income and taxable income by specific tax jurisdiction. Actual results may vary from these forecasts and result in a change in the ability of the Company to realize benefits of these tax assets in the future. If the Company is unable to meet its projected forecasts or implement certain tax planning strategies in jurisdictions for which there is currently no valuation allowance, the recording of a valuation allowance may be required.
Stock options
The fair value of stock options granted, modified or settled is recognized on a straight-line basis over the applicable stock option vesting period as stock-based compensation expense in the consolidated statements of operations and contributed surplus in the consolidated balance sheets. On the exercise of stock options, consideration received and the accumulated contributed surplus amount is credited to share capital. The company estimates forfeitures based on a weighted-average of historical forfeitures.
For the purposes of calculating the stock-based compensation expense, the fair value of stock options is estimated at the date of the grant using the Black-Scholes option pricing model and the cost is amortized over the vesting period. This model requires the input of a number of assumptions including dividend yields, expected stock price volatility, expected time until exercise and risk-free interest rates. Although the assumptions used reflect management's best estimates, they involve assumptions based on market conditions generally outside of the control of the Company.
Loss per share
The calculation of loss per share—from continuing and discontinued operations equals reported net loss attributable to restricted voting shareholders—from continuing and discontinued operations divided by the weighted-average number of restricted voting shares outstanding during the year. Diluted income per share would reflect the assumed conversion of all dilutive securities using the treasury stock method.
Under the treasury stock method:
| |
| • | the exercise of options is assumed to be at the beginning of the period (or at the time of issuance, if later); |
| |
| • | options for which the closing fair market value exceeds the option price are the only ones that are assumed to be dilutive; |
| |
| • | the proceeds from the exercise of options, plus future period compensation expense on options granted on or after November 1, 2003, are assumed to be used to purchase restricted voting shares at the average price during the period; |
| |
| • | the number of restricted voting shares assumed to be dilutive, plus the weighted-average number of restricted voting shares outstanding during the year, is used in the denominator of the diluted earnings per share computation; and |
Patheon Inc.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
October 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010
(Dollar information in tabular form is expressed in millions of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise indicated)
| |
| • | the convertible preferred shares are assumed to have been converted at the beginning of the year (or at time of issuance, if later), and the resulting restricted voting shares are included in the denominator. |
Since the Company was in a loss position for the year ended October 31, 2012 ("fiscal 2012"), the year ended October 31, 2011 ("fiscal 2011") and the year ended October 31, 2010 ("fiscal 2010"), there is no dilutive effect. The Company did not include in the calculation of loss per share 12,479,678, 12,628,458, and 8,327,357 outstanding options in fiscal 2012, 2011 and 2010, respectively, because they were anti-dilutive in nature.
Government financing
The Company makes periodic applications for financial assistance under available government assistance programs in the various jurisdictions in which it operates. Grants relating to capital expenditures are reflected as a reduction of the cost of the related assets. Grants and tax credits relating to current operating expenditures are generally recorded as a reduction of expenses at the time the eligible expenses are incurred. In the case of certain foreign subsidiaries, the Company receives investment incentive allowances, which are accounted for as a reduction of income tax expense.
Recently issued accounting pronouncements
In April 2012, the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act (the "JOBS Act") was enacted. Section 107 of the JOBS Act provides that an "emerging growth company" can utilize the extended transition period that is typically available only for private companies for implementing new or revised accounting standards. In other words, as an "emerging growth company," the Company can delay the adoption of certain new or revised accounting standards until such time as those standards apply to private companies. The Company has elected not to avail itself of this exemption and, therefore, will be implementing new or revised accounting standards at the same time as other public companies that are not "emerging growth companies."
In June 2011, the Financial Accounting Standards Board ("FASB") issued ASU 2011-05, "Comprehensive Income (Topic 220): Presentation of Comprehensive Income in U.S. GAAP" ("ASU 2011-05"). ASU 2011-05 requires that comprehensive income and the related components of net income and of other comprehensive income be presented either in a single continuous statement of comprehensive income or in two separate but consecutive statements. ASU 2011-05 also requires reclassification adjustments from other comprehensive income to net income be presented on the face of the financial statements. The amendments are effective for annual reporting periods beginning on or after December 15, 2011, and interim periods within those annual periods. However, in December 2011, the FASB issued ASU 2011-12, "Comprehensive Income (Topic 220): Deferral of the Effective Date for Amendments to the Presentation of Reclassifications of Items Out of Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income in ASU 2011-05" to defer the requirement to present reclassification adjustments from other comprehensive income on the face of the financial statements and allow entities to continue to report reclassifications out of accumulated other comprehensive income consistent with the requirements in effect before ASU 2011-05. Other than a change in presentation, the Company does not expect the adoption of this guidance will have a material impact on the Company's consolidated financial statements.
In December 2011, the FASB issued ASU 2011-11, "Balance Sheet (Topic 210): Disclosures about Offsetting Assets and Liabilities," which requires enhanced disclosures about financial instruments and derivative instruments that are either (1) offset in accordance with either Section 210-20-45 or 815-10-45 or (2) subject to an enforceable master netting arrangement or similar agreement, irrespective of whether they are offset in accordance with either Section 210-20-45 or Section 815-10-45. The amendments are effective for annual reporting periods beginning on or after January 1, 2013, and interim periods within those annual periods. The amendments should be applied retrospectively for all prior periods presented. The Company does not expect adoption of this guidance will have a material impact on its consolidated financial statements.
In September 2011, the FASB issued ASU 2011-08, "Intangibles—Goodwill and Other (Topic 350): Testing Goodwill for Impairment," which amends U.S. GAAP ASC 350, "Intangible Assets—Goodwill and Other." Under this new ASU, an entity may elect the option to assess qualitative factors to determine whether it is necessary to perform the first step in the two-step impairment testing process. This guidance is effective for annual and interim goodwill impairment tests performed for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2011, with early adoption permitted. The Company does not expect adoption of this guidance will have a material impact on its consolidated financial statements.
3. DISCONTINUED OPERATIONS, PLANT CONSOLIDATIONS, SALES AND ASSET IMPAIRMENTS
Puerto Rico
Patheon Inc.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
October 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010
(Dollar information in tabular form is expressed in millions of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise indicated)
The Company announced on December 10, 2009 its plan to consolidate its Puerto Rico operations into its manufacturing site located in Manati and ultimately close or sell its plant in Caguas. As a result of additional time required to transition manufacturing operations from Caguas to Manati due to longer than expected customer regulatory time lines and increased product demand, the transition will continue beyond the end of calendar year 2012. The Company now estimates the total project repositioning expenses to be $13.7 million, of which an additional $1.7 million was recorded in fiscal 2012. The consolidation resulted in additional accelerated depreciation of Caguas assets of approximately $12.0 million through the middle of fiscal 2013. Because the business in the Caguas facility is being transferred within the existing site network, its results of operations are included in continuing operations in the consolidated financial statements.
The results of discontinued operations for the Company's Carolina facility (which the Company closed effective January 31, 2009) for fiscal 2012, 2011 and 2010 are as follows:
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | Years ended October 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| | $ | | $ | | $ |
| Revenues | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Cost of goods sold | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Gross loss | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | 0.4 |
| | 0.6 |
| | 0.9 |
|
| Gain on sale of capital assets | (0.1 | ) | | — |
| | — |
|
| Operating loss | (0.3 | ) | | (0.6 | ) | | (0.9 | ) |
| Asset impairment charge | — |
| | — |
| | 0.8 |
|
| Loss before income taxes | (0.3 | ) | | (0.6 | ) | | (1.7 | ) |
| Net loss for the period | (0.3 | ) | | (0.6 | ) | | (1.7 | ) |
On February 17, 2012, the Company finalized the sale of the Carolina, Puerto Rico facility for a nominal amount. For fiscal 2010, the Company recorded impairment charges of $0.8 million, to write down the carrying value of the Carolina operations long-lived assets to their fair value less cost to sell.
United Kingdom
In the second quarter of fiscal 2012, the Company determined to make certain adjustments over the next 24 to 36 months to the scale and scope of business conducted at its Swindon, U.K., facility. These adjustments include winding down or transferring non-cephalosporin commercial production to other facilities and, to the extent possible and commercially appropriate, directing PDS projects that require commercialization activities to other facilities. The Company will work with each of its affected commercial customers to develop plans to maintain supply chain continuity to the extent possible and commercially appropriate.
In connection with the change in the scale and scope of business to be conducted at its Swindon facility, the Company conducted an impairment analysis on long-term assets at the facility and concluded that a non-cash impairment charge of $57.9 million was required in the second quarter of fiscal 2012 to bring the assets down to their fair value of $9.5 million. The impairment charges reduced assets in the commercial manufacturing outsourcing services ("CMO") segment by $55.1 million and PDS assets by $2.8 million.
The impairment analysis included fair value (Level 3) measurements resulting from future cash flows from operations, as well as market value approach of land and buildings, internal transfer of assets, and expected salvage value on equipment. Cash inflows were based on current customer expectations and future contract expiry dates. Cash outflows were based on expenses needed to run the facility in each period including on-going maintenance and capital expenditures. The Company determined that, in light of certain restrictive covenants that require the use of the Swindon facility as a business industrial site, the best use of the asset is to continue using it in the pharmaceutical business. The corporate weighted-average cost of capital was used for discounting future cash flows.
Patheon Inc.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
October 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010
(Dollar information in tabular form is expressed in millions of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise indicated)
Canada
On August 31, 2012, the Company completed the sale of Burlington Clinical Services ("BCS"), its global secondary clinical packaging and clinical distribution services business, to Bellwyck Packaging Solutions, a private company with 20 years experience providing clinical trial and contract services for secondary packaging. The total consideration for the sale of this business is approximately $2.70 million, of which $1.35 million was paid in cash at closing (subject to the retention of certain amounts in escrow) and $1.35 million will be paid in 24 months from the closing date if certain revenue targets are met by the new owner. The Company recognized a $0.4 million loss on the sale of the business which is recorded in the consolidated statement of operations as "Loss on sale of capital assets."
4. SUPPLEMENTAL BALANCE SHEET INFORMATION
Inventories
|
| | | | | |
| | As of October 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 |
| | $ | | $ |
| Raw materials, packaging components and spare parts | 47.9 |
| | 53.0 |
|
| Work-in-process | 34.4 |
| | 28.8 |
|
| Balance, end of the year | 82.3 |
| | 81.8 |
|
Below is a roll-forward of the Company's inventory provisions for fiscal 2012 and 2011:
|
| | | | | |
| | As of October 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 |
| | $ | | $ |
| Balance, beginning of the year | (12.6 | ) | | (7.8 | ) |
| Additions | (6.5 | ) | | (7.6 | ) |
| Write-offs | 5.1 |
| | 2.8 |
|
| Balance, end of the year | (14.0 | ) | | (12.6 | ) |
Accounts payable and accrued liabilities
The following is the breakdown of accounts payable and accrued liabilities:
|
| | | | | |
| | As of October 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 |
| | $ | | $ |
| Trade payables | 101.2 |
| | 102.5 |
|
| Interest payable | 1.0 |
| | 1.0 |
|
| Accrued salaries and related expenses | 51.4 |
| | 44.0 |
|
| Customer deposits | 16.4 |
| | 17.9 |
|
| Other accruals | 16.2 |
| | 16.1 |
|
| Balance, end of the year | 186.2 |
| | 181.5 |
|
Other long-term assets
Included in other long-term assets for fiscal 2012 is $11.1 million of VAT receivable related to the Company's Italian operations, the majority of which was recorded in accounts receivable in fiscal 2011.
Deferred revenues
The following table summarizes the deferred revenue activity for each of fiscal 2012, 2011 and 2010:
Patheon Inc.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
October 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010
(Dollar information in tabular form is expressed in millions of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise indicated)
|
| | | |
| Balance at October 31, 2009 | $ | 41.7 |
|
| Cash received from customers | 47.4 |
|
| Cash repaid to customers | (1.5 | ) |
| Amortization of deferred revenues | (37.4 | ) |
| Foreign exchange | (0.2 | ) |
Other (1) | (4.1 | ) |
| Balance at October 31, 2010 | $ | 45.9 |
|
| Cash received from customers | 30.4 |
|
| Cash repaid to customers | (3.1 | ) |
| Amortization of deferred revenues | (45.0 | ) |
| Foreign exchange | 0.2 |
|
Other (1) | 8.1 |
|
| Balance at October 31, 2011 | $ | 36.5 |
|
| Cash received from customers | 25.2 |
|
| Cash repaid to customers | (5.7 | ) |
| Amortization of deferred revenues | (13.1 | ) |
| Foreign exchange | (0.1 | ) |
| Balance at October 31, 2012 | $ | 42.8 |
|
(1) Other changes to deferred revenues primarily consist of movement between deferred revenue and other long-term liabilities associated with the amendments and eventual cancellation of a manufacturing agreement.
5. CAPITAL ASSETS
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | As of October 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 |
| | Cost | | Accumulated Depreciation | | Net Book Value | | Cost | | Accumulated Depreciation | | Net Book Value |
| | $ | | $ | | $ | | $ | | $ | | $ |
| Land | 30.7 |
| | — |
| | 30.7 |
| | 30.9 |
| | — |
| | 30.9 |
|
| Buildings | 298.0 |
| | 94.3 |
| | 203.7 |
| | 309.9 |
| | 86.7 |
| | 223.2 |
|
| Machinery and equipment | 420.5 |
| | 283.6 |
| | 136.9 |
| | 450.5 |
| | 269.8 |
| | 180.7 |
|
| Office equipment (including software) | 45.4 |
| | 36.0 |
| | 9.4 |
| | 43.6 |
| | 39.3 |
| | 4.3 |
|
| Furniture and fixtures | 15.5 |
| | 13.3 |
| | 2.2 |
| | 17.5 |
| | 12.9 |
| | 4.6 |
|
| Construction in progress | 33.5 |
| | — |
| | 33.5 |
| | 30.5 |
| | — |
| | 30.5 |
|
| Balance, end of the year | 843.6 |
| | 427.2 |
| | 416.4 |
| | 882.9 |
| | 408.7 |
| | 474.2 |
|
The amount of open purchase commitments related to authorized capital projects at October 31, 2012 and 2011 was approximately $16.9 million and $5.9 million, respectively. The expenditures related to the fiscal 2012 open purchase commitments are expected to be incurred during the year ending October 31, 2013 ("fiscal 2013").
Included in capital assets are assets under capital leases with a cost of $7.5 million and $7.5 million at October 31, 2012 and 2011, respectively. The amount of accumulated depreciation for assets under capital leases is $7.5 million and $7.5 million at October 31, 2012 and 2011, respectively.
6. SHORT-TERM BORROWINGS
Patheon Inc.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
October 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010
(Dollar information in tabular form is expressed in millions of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise indicated)
|
| | | | | |
| | As of October 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 |
| | $ | | $ |
| Italian short-term operating credit facilities (October 2011—€17.0 million), bearing interest at 3-month Euribor plus spreads between 0.5% and 1.25%. | — |
| | 4.2 |
|
| Short-term insurance premium financing | 2.4 |
| | 1.9 |
|
| Balance, end of the period | 2.4 |
| | 6.1 |
|
7. LONG-TERM DEBT
Long-term debt in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets at October 31, 2012 and 2011 consists of the following:
|
| | | | | |
| | As of October 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 |
| | $ | | $ |
| 8.625% senior secured notes due April 15, 2017 | 280.0 |
| | 280.0 |
|
| U.S. obligations under capital leases bearing interest at fixed rate of 5.6%, maturing November 2011. | — |
| | 0.1 |
|
| $75 million senior secured revolving loan facility maturing April 23, 2014, bearing interest ranging from 4.03% to 5.75% based upon floating LIBOR, US, or CAD prime, or federal funds effective rates, plus applicable margins. | 30.7 |
| | — |
|
| Italian unsecured government loan, bearing interest at 0.9% per annum, maturing in 2012. | — |
| | 1.1 |
|
| Total long-term debt outstanding | 310.7 |
| | 281.2 |
|
| Less current portion | — |
| | (1.1 | ) |
| Balance, end of the period | 310.7 |
| | 280.1 |
|
In April 2010, the Company issued $280.0 million in aggregate principal amount of 8.625% senior secured notes due April 15, 2017 (the "Notes") in a private placement. The net proceeds from the Notes were used to repay all of the outstanding indebtedness under the Company's then-existing senior secured term loan and $75.0 million asset-based revolving credit facility ("ABL"), repay certain other indebtedness and to pay related fees and expenses. The remaining proceeds were used for general corporate purposes.
The Company also amended and restated its then-existing $75.0 million ABL. Under the amended terms of the ABL, the maturity date was extended from 2012 to 2014.
Interest on the Notes accrues at the rate of 8.625% per annum and is payable semi-annually in arrears on April 15 and October 15, commencing on October 15, 2010 to the holders of Notes of record on the immediately preceding April 1 and October 1, respectively. Interest on the Notes accrues from the most recent date to which interest has been paid or, if no interest has been paid, from and including the issue date. Interest on the Notes is computed on the basis of a 360-day year comprised of twelve 30-day months.
At any time prior to April 15, 2013, the Company may redeem all or a part of the Notes, at a redemption price equal to the greater of (i) 101% of the principal amount of the Notes redeemed and (ii) the sum of the 2013 redemption price set forth in the table below and all interest payments on the Notes redeemed that would be required from the date of redemption (the "Redemption Date") through April 15, 2013, discounted back to the Redemption date, subject to the rights of holders on the relevant record date to receive interest due on the relevant interest payment date.
In addition, until April 15, 2013, the Company may redeem up to 35.0% of the aggregate principal amount of the Notes at a redemption price equal to 108.625% of the aggregate principal amount thereof, plus accrued and unpaid interest thereon, if any, to the applicable redemption date, subject to the right of holders on the relevant record date to receive interest due on the relevant interest payment date, with the net cash proceeds of one or more equity offerings. At least 65.0% of the sum of the aggregate principal amount of the Notes originally issued under the indenture and any additional notes issued under the indenture after the original issue date must remain outstanding immediately after each redemption, and each redemption must occur within 90 days after the related equity offering.
Additionally, at any time prior to April 15, 2013, the Company may redeem a portion of the Notes, at a redemption price equal to 103.000% of the principal amount thereof, plus accrued and unpaid interest thereon, if any, to the applicable date of
Patheon Inc.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
October 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010
(Dollar information in tabular form is expressed in millions of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise indicated)
redemption, subject to the rights of holders on the relevant record date to receive interest due on the relevant interest payment date; provided that in no event may the Company redeem more than 10.0% of the original aggregate principal amount of the Notes and any additional notes during any twelve-month period.
On and after April 15, 2013, the Company may redeem the Notes, in whole or in part, at the redemption prices (expressed as percentages of the principal amount of the Notes to be redeemed) set forth below, plus accrued and unpaid interest thereon, if any, to the applicable redemption date, subject to the rights of holders on the relevant record date to receive interest due on the relevant interest payment date, if redeemed during the twelve-month period beginning on April 15 of each of the years indicated below:
|
| | | |
| Year | | % |
| 2013 | | 106.469 | % |
| 2014 | | 104.313 | % |
| 2015 | | 102.156 | % |
| 2016 and thereafter | | 100.000 | % |
The agreements that govern the terms of the Company's debt, including the indenture that governs the Notes and the credit agreement that governs the ABL, contain covenants that restrict the Company's ability and the ability of its subsidiaries to, among other things:
| |
| • | incur additional indebtedness; |
| |
| • | issue additional equity; |
| |
| • | pay dividends on or make distributions in respect of capital stock or make certain other restricted payments or investments; |
| |
| • | enter into agreements that restrict distributions from subsidiaries or restrict its ability to incur liens on certain of its assets; |
| |
| • | make capital expenditures; |
| |
| • | sell or otherwise dispose of assets, including capital stock of subsidiaries; |
| |
| • | enter into transactions with affiliates; |
| |
| • | create or incur liens; and |
Provided that the Company is not in default under the ABL or the indenture governing the Notes and is able to demonstrate a certain Fixed Charge Coverage Ratio (as defined in the indenture governing the Notes), and will have a required minimum amount of remaining borrowing availability under the ABL after giving effect thereto, the Company is permitted to pay limited amounts of dividends or other distributions with respect to its restricted voting shares (as more particularly described in the ABL and the indenture governing the Notes, up to the lesser of (i) $15.0 million plus 50.0% of Excess Cash Flow (as defined in the ABL), plus net proceeds of additional permitted equity offerings under the ABL, and (ii) 50.0% of Consolidated Net Income (as defined in the indenture governing the Notes) plus net proceeds from additional permitted equity offerings or sales of restricted investments under the Notes).
In addition, under the ABL, if an event of default occurs or the Company's borrowing availability falls below the greater of $10.0 million or 13.3% of total commitments under the ABL for any two consecutive days (which is defined under the ABL as an "Availability Trigger Event"), the Company will be required to satisfy and maintain a ratio of Consolidated EBITDA to Consolidated Fixed Charges (each as defined in the ABL) of not less than 1.10 to 1.00 until the first day thereafter on which, as applicable, either the event of default has been cured or its borrowing availability has exceeded the greater of $10.0 million or 13.3% of its total commitments for 30 consecutive days. The Company's ability to meet the required ratio can be affected by events beyond the Company's control, and the Company may not be able to meet this ratio. A breach of any of these covenants could result in a default under the ABL.
The Notes and the ABL are secured by substantially all of the Company's assets and are guaranteed by, and secured by substantially all of the assets of, the Company's subsidiaries in the United States (including Puerto Rico), Canada, the United
Patheon Inc.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
October 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010
(Dollar information in tabular form is expressed in millions of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise indicated)
Kingdom (except Patheon UK Pension Trustees Limited) and the Netherlands. The Notes and the ABL are guaranteed on a limited basis by, and secured by certain assets of, the Company's subsidiaries in France, Italy and Switzerland.
The Notes indenture contains language consistent with the ABL, which contains usual and customary covenants and events of default provisions.
Estimated minimum annual repayments of long-term debt based on current exchange rates for the next five years are:
|
| | |
| | $ |
| 2013 | — |
|
| 2014 | 30.7 |
|
| 2015 | — |
|
| 2016 | — |
|
| 2017 | 280.0 |
|
| Thereafter | — |
|
| Total payments | 310.7 |
|
There are no capital leases included in the within the above future repayments of long-term debt.
In the second quarter of fiscal 2011, the Company and a major customer agreed to terminate a supply contract. As part of the agreement, the customer agreed to relieve the Company of the obligation to pay the final amount for equipment under a capital lease maturing in fiscal 2012. This debt obligation was reclassified and amortized through deferred revenues.
8. OTHER LONG-TERM LIABILITIES
|
| | | | | |
| | As of October 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 |
| | $ | | $ |
| Defined benefit pension plans | 22.3 |
| | 30.7 |
|
| Other post-employment benefits | 7.8 |
| | 6.9 |
|
| Unfunded termination indemnities (2012—€4.4 million; 2011—€4.5 million) | 5.7 |
| | 6.2 |
|
| Other long-term liabilities | 12.0 |
| | 9.9 |
|
| | 47.8 |
| | 53.7 |
|
The unfunded termination indemnities relate to the employees of the Company's Italian subsidiary. In accordance with Italian severance pay statutes, an employee benefit is accrued for service to date and is payable when the employee's employment with the Company ceases. The termination indemnity liability is calculated in accordance with local civil and labor laws based on each employee's length of service, employment category and remuneration. The termination liability is adjusted annually by a cost-of-living index provided by the Italian government. Although there is no vesting period, the Italian government has established private accounts for these benefits and has required the Company to contribute $3.0 million in fiscal 2012 and $3.4 million in fiscal 2011 to these accounts, with additional contributions in the future. The liability recorded in the consolidated balance sheets is the amount to which the employees would be entitled if their employment with the Company ceased. The related expenses for fiscal 2012, 2011 and 2010 amounted to $3.0 million, $3.1 million and $2.5 million, respectively.
Other long-term liabilities at October 31, 2012, include $5.2 million of customer funded capital liabilities, $1.0 million of post employment benefits, $2.2 million for a deferred compensation plan and $0.8 million of deferred rent liability. Other long-term liabilities at October 31, 2011, include $4.0 million of customer funded capital liabilities, $0.9 million of post employment benefits, $1.9 million for a deferred compensation plan and $1.1 million of deferred rent liability.
9. EMPLOYEE FUTURE BENEFITS
Background
Patheon Inc.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
October 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010
(Dollar information in tabular form is expressed in millions of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise indicated)
The Company has a number of defined benefit pension plans. In addition, it has other benefit plans that provide post-retirement healthcare and dental benefits. The Company measured the accrued benefit obligation and the fair value of plan assets for accounting purposes as of October 31, 2012 for the defined benefit pension and other benefit plans.
Information about the Company's defined benefit pension and other benefit plans, in aggregate, is as follows:
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | Defined
Benefit
Pension
Plans
2012 | | Other
Benefit
Plans
2012 | | Defined
Benefit
Pension
Plans
2011 | | Other
Benefit
Plans
2011 |
| | $ | | $ | | $ | | $ |
| Change in benefit obligation | | | | | | | |
| Benefit obligation, beginning of the year | 111.0 | | 6.9 | | 94.8 | | 6.4 |
| Current service cost | 2.0 | | 0.1 | | 4.0 | | 0.1 |
| Prior year service costs | 1.2 | | — | | — | | — |
| Interest cost | 5.1 | | 0.4 | | 5.3 | | 0.4 |
| Member contributions during the year | 0.3 | | — | | 1.1 | | — |
| Effect of curtailments | (7.9) | | — | | — | | — |
| Benefits paid | (3.3) | | (0.2) | | (2.4) | | (0.2) |
| Actuarial loss (gain) | 4.3 | | 0.6 | | 7.6 | | 0.1 |
| Currency translation | (0.3) | | — | | 0.6 | | 0.1 |
| Benefit obligation, end of the year | 112.4 | | 7.8 | | 111.0 | | 6.9 |
| Change in plan assets | | | | | | | |
| Market value of plan assets, beginning of year | 80.3 | | — | | 70.2 | | — |
| Actual return on plan assets | 6.9 | | — | | — | | — |
| Member contributions during the year | 0.3 | | — | | 1.1 | | — |
| Employer contributions | 5.6 | | 0.2 | | 10.8 | | 0.2 |
| Benefits paid | (3.3) | | (0.2) | | (2.4) | | (0.2) |
| Currency translation | 0.3 | | — | | 0.6 | | — |
| Market value of plan assets, end of the year | 90.1 | | — | | 80.3 | | — |
| | | | | | | | |
| Unfunded status of plans at October 31, | (22.3) | | (7.8) | | (30.7) | | (6.9 | ) |
As of October 31, 2012 and 2011, other long-term liabilities included an accrued benefit liability of $30.1 million and $37.6 million, respectively, for the defined benefit pension plan and the other benefit plan. A total of $29.4 million and $34.7 million of net actuarial losses are included in other comprehensive income for fiscal 2012 and 2011, respectively, and have not yet been recognized as a component of net periodic pension costs. For all of the Company's plans, the accrued benefit obligations are in excess of plan assets as of October 31, 2012 and 2011. Please refer to Note 8—Other Long-Term Liabilities.
Pension plan assumptions
The following weighted-average assumptions were used to determine the projected benefit obligation of the Company's defined benefit and other post retirement plans at the end of the respective fiscal year:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Defined Benefit Plans | | Other Benefit Plans |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2012 | | 2011 |
| Discount rate | 4.7 | % | | 4.9 | % | | 5.2 | % | | 5.2 | % |
| Rate of future compensation increases | 3.5 | % | | 3.7 | % | | — | % | | — | % |
The following weighted-average assumptions were used to determine the net periodic benefit cost of the Company's defined benefit and other post retirement plans during the respective fiscal year:
Patheon Inc.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
October 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010
(Dollar information in tabular form is expressed in millions of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise indicated)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Defined Benefit Plans | | Other Benefit Plans |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 | | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| Discount rate | 4.9 | % | | 5.2 | % | | 5.8 | % | | 5.2 | % | | 5.2 | % | | 5.3 | % |
| Expected long-term return on plan assets | 5.9 | % | | 6.9 | % | | 6.9 | % | | — | % | | — | % | | — | % |
| Rate of future compensation increases | 3.5 | % | | 3.9 | % | | 4.1 | % | | — | % | | — | % | | — | % |
The 4.7% weighted-average discount rate used to determine the projected benefit obligation of the Company's plans at the end of fiscal 2012 was derived by reference to appropriate benchmark yields on high quality corporate bonds, with terms which approximate the duration of the benefit payments and the relevant benchmark bond indices considering the individual plan's characteristics, to select a rate at which the Company believes the pension benefits could have been effectively settled.
The Company selects an expected long-term rate of return on its pension plan assets and, in doing so, considers a number of factors including, without limitation, recent and historical performance of plan assets, asset allocation and other third-party studies and surveys. The Company considered the pension plan portfolios' asset allocations over a variety of time periods and compared them with third-party studies and reviewed the performance of the capital markets in recent years and other factors and advice from various third parties, such as the pension plans' advisors, investment managers and actuaries. While the Company considered both the recent performance and the historical performance of pension plan assets, the Company's assumptions are based primarily on its estimates of long-term, prospective rates of return. Using the aforementioned methodologies, the Company selected the 5.9% long-term rate of return on plan assets assumption used for the pension plans during fiscal 2012. Differences between actual and expected asset returns are recognized in the net periodic benefit cost over the remaining service period of the active participating employees.
The rate of future compensation increases is an assumption used by the actuarial consultants for pension accounting and is determined based on the Company's current expectation for such increases.
A 4% to 9% annual rate of increase in the per capita cost of covered health care and dental benefits was assumed for fiscal 2012, with the assumption that the rate will decrease gradually over the next five years to 6% and will remain at that level thereafter. The following table outlines the effects of a one-percentage-point increase and decrease in the assumed health care and dental benefit trend rates.
|
| | | | | |
| (in millions of USD) | Benefit Obligation | | Benefit Expense |
| | $ | | $ |
| Impact of: | | | |
| 1% increase | 1.1 |
| | 0.1 |
|
| 1% decrease | (0.9 | ) | | (0.1 | ) |
The cost components of the Company's defined benefit pension plan and other benefit plans in aggregate are as follows:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Years ended October 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| | Defined Benefit Pension Plans | | Other Benefit Plans | | Defined Benefit Pension Plans | | Other Benefit Plans | | Defined Benefit Pension Plans | | Other Benefit Plans |
| | $ | | $ | | $ | | $ | | $ | | $ |
| Service cost | 2.0 |
| | 0.1 |
| | 4.0 |
| | 0.1 |
| | 3.1 |
| | 0.1 |
|
| Interest cost | 5.1 |
| | 0.4 |
| | 5.3 |
| | 0.4 |
| | 4.5 |
| | 0.3 |
|
| Expected return on plan assets | (5.1 | ) | | — |
| | (5.0 | ) | | — |
| | (3.9 | ) | | — |
|
| Amortization of actuarial loss | 1.1 |
| | — |
| | 0.5 |
| | — |
| | 0.8 |
| | — |
|
| Amortization of prior service costs | 0.3 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Net periodic benefit costs | 3.4 |
| | 0.5 |
| | 4.8 |
| | 0.5 |
| | 4.5 |
| | 0.4 |
|
Based on current information available from actuarial estimates, the Company anticipates that contributions required under its defined benefit pension plans and other benefit plans for fiscal 2013 will be approximately $5.5 million, compared to contributions of $5.8 million and $11.0 million that were made in fiscal 2012 and 2011, respectively. Included in the fiscal 2011
Patheon Inc.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
October 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010
(Dollar information in tabular form is expressed in millions of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise indicated)
contributions is a voluntary catch-up contribution of $4.9 million for the benefit plans in the United Kingdom, which was made during the third quarter of fiscal 2011. Required contributions to defined benefit pension plans in future years will be dependent upon a number of variables, including the long-term rate of return on plan assets. The amounts that the Company will be required to contribute to such plans in the future may vary.
The Company also provides retirement benefits for the majority of its employees at its Canadian, U.S., U.K. and Puerto Rican sites under defined contribution pension plans. The total expense for the plans amounted to $4.5 million, $2.8 million and $2.8 million for fiscal 2012, 2011 and 2010, respectively.
The Company amended its U.K. Pension Plan to freeze the accrual of additional benefits related to future service and allow the employees to enter into a defined contribution plan effective February 1, 2012. All current and future U.K. employees will be eligible to participate in the defined contribution plan. Any pension benefits accrued in the U.K. Pension Plan will be retained in that plan until retirement unless the plan participant chooses to transfer the benefits to another arrangement. The curtailment impact reduced the projected benefit obligation by $7.9 million. This resulting gain was applied against the accumulated unrecognized net actuarial losses in other comprehensive (loss) income.
Total cash payments for employee future benefits totaled $10.3 million, $14.6 million and $7.5 million for fiscal 2012, 2011 and 2010, consisting of cash contributed by the Company to its defined benefit pension plans of $5.6 million, $10.8 million and $4.6 million, cash payments directly to beneficiaries for its other benefit plans of $0.2 million, $0.2 million and $0.1 million and cash contributed to its defined contribution plans of $4.5 million, $2.8 million and $2.8 million, respectively.
Pension plan assets
The Pension Committee for the Company's defined benefit plans (the "Pension Committee") has adopted (and revises from time to time) an investment policy for the Canadian and U.K. defined benefit plans with the objective of meeting or exceeding, over time, the expected long-term rate of return on plan assets assumption, weighed against a reasonable risk level. In connection with this objective, the Pension Committee retains professional investment managers that invest plan assets in the following asset classes: equity and fixed income securities and cash and other investments, which may include hedge funds and private equity and global balanced strategies.
The Company's defined benefit plans currently have the following targets for these asset classes, which are intended to be flexible guidelines for allocating the plans' assets among various classes of assets, and are reviewed periodically and considered for readjustment when an asset class weighting is outside of its target (recognizing that these are flexible targets that may vary from time to time) with the objective of achieving the expected long-term rate of return on plan assets assumption, weighed against a reasonable risk level, as follows:
|
| | | |
| | Defined Benefit Plans Canada | Defined Benefit Plans U.K. |
| Asset Category: | | |
| Domestic equity securities | 25-55% | 38 | % |
| Foreign equity securities | 5-30% | 37 | % |
| Debt securities | 30-70% | 25 | % |
| Other | 0-20% | — | % |
The fair value hierarchy must have the following levels: (a) quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical assets or liabilities (Level 1); (b) inputs other than quoted prices included in Level 1 that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly (i.e., as prices) or indirectly (i.e., derived from prices) (Level 2); and (c) inputs for the asset or liability that are not based on observable market data (unobservable inputs) (Level 3).
The fair values of the defined benefit plans' assets at October 31, 2012, by asset categories were as follows:
Patheon Inc.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
October 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010
(Dollar information in tabular form is expressed in millions of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise indicated)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Defined Benefit Plans | Total | | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 |
| | $ | | $ | | $ | | $ |
| Asset Category: | | | | | | | |
| Equity securities | 33.5 |
| | — |
| | 33.5 |
| | — |
|
| Debt securities | 24.0 |
| | — |
| | 24.0 |
| | — |
|
| Cash and other investments | 32.6 |
| | — |
| | 32.6 |
| | — |
|
| Total pension plan assets at fair value | 90.1 |
| | — |
| | 90.1 |
| | — |
|
The fair values of the defined benefit plans' assets at October 31, 2011, by asset categories were as follows:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Defined Benefit Plans | Total | | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 |
| | $ | | $ | | $ | | $ |
| Asset Category: | | | | | | | |
| Equity securities | 44.4 |
| | — |
| | 44.4 |
| | — |
|
| Debt securities | 13.9 |
| | — |
| | 13.9 |
| | — |
|
| Cash and other investments | 22.0 |
| | — |
| | 22.0 |
| | — |
|
| Total pension plan assets at fair value | 80.3 |
| | — |
| | 80.3 |
| | — |
|
Within the equity securities asset class, the investment policy adopted by the Pension Committee provides for investments in a broad range of publicly-traded securities ranging from domestic and international stocks and small to large capitalization stocks. Within the debt securities asset class, the investment policy provides for investments in a broad range of publicly-traded debt securities, including domestic and international treasury issues, and corporate debt securities. In the cash and other investments asset class, investments may be in cash and cash equivalents and other investments, which may include hedge funds and private equity not covered in the classes listed above, provided that such investments are approved by the Pension Committee prior to their selection.
The Pension Committee's investment policy does not allow the use of derivatives for speculative purposes, but such policy does allow its investment managers to use derivatives for the purpose of reducing risk exposures or to replicate exposures of a particular asset class.
Estimated future benefit payments
The following benefit payments, which reflect expected future service, as appropriate, are expected to be paid out of the Company's defined benefit plans and other post-retirement benefit plans:
|
| | | | | |
| | Total Defined Benefit Plan Payments | | Total Other Benefit Plan Payments |
| | $ | | $ |
| 2012 | 2.7 |
| | 0.2 |
|
| 2013 | 2.6 |
| | 0.2 |
|
| 2014 | 3.0 |
| | 0.3 |
|
| 2015 | 3.3 |
| | 0.3 |
|
| 2016 | 3.2 |
| | 0.3 |
|
| 2017 through 2021 | 16.5 |
| | 2.1 |
|
| | 31.3 |
| | 3.4 |
|
The Company expects to incur approximately $1.3 million of amortization from actuarial losses as part of its pension costs in fiscal 2013.
10. SHAREHOLDERS' EQUITY
Share capital
Share capital consists of the following:
Patheon Inc.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
October 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010
(Dollar information in tabular form is expressed in millions of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise indicated)
|
| | | | | |
| | As of October 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 |
| | $ | | $ |
| Authorized | | | |
| Unlimited Class I preferred shares—Issuable from time to time in one or more series, each series comprising the number of shares and having the designation, rights, privileges, restrictions and conditions determined by the Company's Board of Directors. | — |
| | — |
|
| Unlimited restricted voting shares. | — |
| | — |
|
| Issued and outstanding | | | |
| Restricted voting shares of 129,297,892; (2011—129,167,926) | 572.5 |
| | 571.9 |
|
Restricted voting shares
The Company's articles were amended on April 26, 2007 to re-designate the common shares as restricted voting shares. This occurred in connection with the issuance of the Series D special voting preferred shares. The holders of the Series D special voting preferred shares have the right to elect three of nine members of the Board of Directors. The holders of Patheon's restricted voting shares have the right to elect the remaining members of the Board of Directors. Under the rules of the TSX, voting equity securities are not to be designated, or called, common shares unless they have a right to vote in all circumstances that is not less, on a per share basis, than the voting rights of each other class of voting securities. Accordingly, the Company amended its articles to re-designate the common shares as restricted voting shares. This re-designation involved only a change in the name of the securities; the number of shares outstanding and the terms and conditions of the outstanding shares were not affected by the change.
As of October 31, 2012, JLL Patheon Holdings and its affiliates ("JLL") owned an aggregate of 72,358,181 Patheon restricted voting shares, representing approximately 56% of Patheon's total restricted voting shares outstanding.
Incentive stock option plan
The Company has an incentive stock option plan in which directors, officers and key employees of the Company and its consolidated subsidiaries, as well as other persons engaged to provide ongoing management or consulting services to Patheon, are eligible to participate. On March 10, 2011, the Company's shareholders approved an amendment to the stock option plan, which, among other things, provides that the maximum number of shares that may be issued under the plan is 15,500,151, which currently represents 12% of the issued and outstanding restricted voting shares. The plan previously provided that the maximum number of shares that may be issued under the plan was 7.5% of the sum, at any point in time, of the issued and outstanding restricted voting shares of the Company and the aggregate number of restricted voting shares issuable upon exercise of the conversion rights attached to the issued and outstanding Class I Preferred Shares, Series C of the Company. As of October 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010, the total number of restricted voting shares issuable under the plan was 15,500,151 shares, 15,500,151 shares and 9,687,594 shares, respectively, of which there were stock options outstanding to purchase 12,479,678 shares, 12,628,458 shares and 8,327,357 shares, respectively, under the plan. Before the March 2011 amendments, the plan provided that the exercise prices of options were determined at the time of grant and could not be less than the weighted-average market price of the Company's restricted voting shares on the TSX during the two trading days immediately preceding the grant date. Following the March 2011 amendments, the exercise prices of the options may not be less than the closing price of the restricted voting shares on the TSX (or on such other stock exchange in Canada or the United States on which restricted voting shares may be then listed and posted) on the grant date. Options generally expire in no more than 10 years after the grant date and are subject to early expiry in the event of death, resignation, dismissal or retirement of an optionee. Options have vesting periods of either three years or five years, with either one-third or one-fifth vesting on each anniversary of the grant date, respectively.
On June 18, 2012 the Company granted 1,291,750 options to its executive committee members (other than its CEO) that vest upon the earlier of (i) the achievement of an adjusted EBITDA target or (ii) five years after the date of grant.
A summary of the plan and changes during each of fiscal 2012, 2011 and 2010 are as follows:
Patheon Inc.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
October 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010
(Dollar information in tabular form is expressed in millions of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise indicated)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| (Dollar amounts in Canadian dollars) | Shares Number | | Weighted- Average Exercise Price | | Shares Number | | Weighted- Average Exercise Price | | Shares Number | | Weighted- Average Exercise Price |
| | | | $ | | | | $ | | | | $ |
| Outstanding, beginning of the year | 12,628,458 |
| | 2.88 |
| | 8,327,357 |
| | 3.26 |
| | 4,699,348 |
| | 5.12 |
|
| Granted | 2,968,502 |
| | 2.08 |
| | 5,862,000 |
| | 2.50 |
| | 4,741,000 |
| | 2.59 |
|
| Exercised | (129,966 | ) | | 2.59 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Forfeited | (2,987,316 | ) | | 3.37 |
| | (1,560,899 | ) | | 3.34 |
| | (1,112,991 | ) | | 8.23 |
|
| Outstanding, end of the year | 12,479,678 |
| | 2.54 |
| | 12,628,458 |
| | 2.88 |
| | 8,327,357 |
| | 3.26 |
|
| Exercisable, end of the year | 3,717,875 |
| | 2.91 |
| | 3,893,124 |
| | 3.65 |
| | 2,542,246 |
| | 4.52 |
|
The following table summarizes changes in the number and weighted-average grant date fair value of non-vested stock option awards during fiscal 2012: |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Dollar amounts in Canadian dollars) | | | | | | | | | Non-Vested Stock Option Awards | | Weighted- Average Grant Date Fair Value |
| | | | | | | | | | | | $ |
| Balance at beginning of the year | | | | | | | | | 8,735,333 |
| | 1.33 |
|
| Granted | | | | | | | | | 2,968,502 |
| | 1.08 |
|
| Vested | | | | | | | | | (1,929,733 | ) | | 1.34 |
|
| Forfeited | | | | | | | | | (1,012,300 | ) | | 1.34 |
|
| Balance at end of the year |
| | | |
| | | | 8,761,802 |
| | 1.24 |
|
The following table summarizes information about options outstanding at October 31, 2012:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Dollar amounts in Canadian dollars) | Options Outstanding | | Options Exercisable |
| Range of Exercise Prices | Number Outstanding | | Weighted- Average Remaining Contractual Life | | Weighted- Average Exercise Price | | Number Exercisable | | Weighted- Average Exercise Price |
| | | | | | $ | | | | $ |
| $1.54 - 2.07 | 3,076,002 |
| | 9.48 | | 1.95 |
| | 77,000 |
| | 1.54 |
|
| $2.08 - 2.61 | 3,357,233 |
| | 6.97 | | 2.52 |
| | 1,769,433 |
| | 2.56 |
|
| $2.62 - 2.88 | 5,000,000 |
| | 8.36 | | 2.62 |
| | 1,000,000 |
| | 2.62 |
|
| $2.89 - 13.21 | 1,046,443 |
| | 3.74 | | 3.93 |
| | 871,442 |
| | 4.05 |
|
| Total | 12,479,678 |
| | | | | | 3,717,875 |
| | |
The Company issued 129,966 restricted voting shares with an intrinsic value of approximately $0.2 million under the stock option plan during fiscal 2012. The Company did not issue any restricted voting shares under the stock option plan during fiscal 2011 and 2010.
For purposes of calculating the stock-based compensation expense in connection with the Company's incentive stock option plan, the fair value of stock options is estimated at the date of the grant using the Black-Scholes option pricing model and the cost is amortized over the vesting period.
The weighted-average fair value of stock options granted during fiscal 2012, 2011 and 2010 was $1.08, $1.30 and $1.39, respectively. The fair value of stock options for purposes of determining stock-based compensation was estimated on the date of grant using the following assumptions:
Patheon Inc.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
October 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010
(Dollar information in tabular form is expressed in millions of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise indicated)
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| Risk free interest rate | 1.3 | % | | 2.5 | % | | 2.7 | % |
| Expected volatility | 58 | % | | 59 | % | | 60 | % |
| Expected weighted-average life of options | 5.5 years |
| | 5 years |
| | 5 years |
|
| Expected dividend yield | 0 | % | | 0 | % | | 0 | % |
The Company recorded stock-based compensation expense in fiscal 2012, 2011 and 2010 of $3.1 million, $3.5 million and $2.3 million, respectively.
The total fair value of shares that vested during fiscal 2012, 2011 and 2010 was $2.6 million, $2.0 million and $1.3 million, respectively. As of October 31, 2012, the total unrecognized compensation cost related to the nonvested stock options was $5.5 million, which is expected to be recognized through fiscal 2017, with a weighted-average remaining vesting period of 2.42 years.
11. OTHER INFORMATION
Foreign exchange
During fiscal 2012, the Company recorded a foreign exchange loss on cash flow hedges and transactions related to operating exposures of $0.5 million. During fiscal 2011 and 2010, the Company recorded a foreign exchange gain on cash flow hedges and transactions related to operating exposures of $1.6 million and $1.5 million, respectively.
Net change in non-cash working capital balances related to continuing operations
The net changes in non-cash working capital balances related to continuing operations are as follows:
|
| | | | | |
| | 2012 | | 2011 |
| | $ | | $ |
| Accounts receivable | (17.8 | ) | | (17.4 | ) |
| Inventories | (2.7 | ) | | (8.5 | ) |
| Income taxes receivable | 2.2 |
| | 2.6 |
|
| Prepaid expenses and other | 0.7 |
| | (2.1 | ) |
| Accounts payable and accrued liabilities | 5.3 |
| | 26.7 |
|
| Income taxes payable | 5.5 |
| | (0.3 | ) |
| | (6.8 | ) | | 1.0 |
|
Related party transactions
Revenues for contract manufacturing from a company controlled by Joaquin B. Viso (the "Viso Affiliate"), a director and significant shareholder of the Company, were less than $0.3 million, $0.1 million and $0.1 million for fiscal 2012, 2011 and 2010, respectively. These transactions were conducted in the normal course of business and are recorded at the exchanged amounts. Accounts receivable at October 31, 2012 and 2011 were nil, respectively, resulting from these transactions. In addition, Patheon manufactures a product for a third party for which the product's intellectual property is owned by the Viso Affiliate. The manufacturing agreement was originally contracted between the third party and the Viso Affiliate, but has been administered directly between Patheon and the third party on normal commercial terms since 2003.
As of October 31, 2012 and 2011, the Company had an investment of $4.0 million and $3.3 million, respectively, representing an 18% interest in two Italian companies (collectively referred to as "BSP Pharmaceuticals") whose largest investor was an officer of the Company until December 31, 2009. These companies specialize in the manufacture of cytotoxic pharmaceutical products. As a result of the shareholders' agreement with the other investors in BSP Pharmaceuticals that provides the Company with significant influence over BSP Pharmaceuticals' operations, the Company accounts for its investment in BSP Pharmaceuticals using the equity method. Accordingly, for fiscal 2012, 2011 and 2010, the Company recorded investment income of $1.0 million, less than $0.1 million and $0.4 million, respectively.
Patheon Inc.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
October 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010
(Dollar information in tabular form is expressed in millions of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise indicated)
In connection with its investment in BSP Pharmaceuticals, the Company has a management services agreement with BSP Pharmaceuticals that provides on-going sales and marketing services, and provided engineering and operational services during the construction of the BSP facility which was completed in 2008. There were no management fees recorded under this agreement for fiscal 2012, 2011 and 2010. Accounts receivable at October 31, 2011 include a balance of $1.2 million, with no balance at October 31, 2012, respectively, in connection with the management services agreement. These services were conducted in the normal course of business and are recorded at the exchanged amounts.
In connection with certain of BSP Pharmaceuticals' bank financing, the Company had made commitments that it would not dispose of its interest in BSP Pharmaceuticals prior to January 1, 2011, and if needed, irrevocably inject equity (pro-rata) in order to ensure BSP complies with certain specific bank covenants.
On August 27, 2009, in response to the Company's legal action, JLL Patheon Holdings commenced a legal action against each of the then current and former members of the Special Committee in respect of such members' conduct in connection with the JLL Offer and other related matters. On November 30, 2009, the Special Committee of the Company's Board of Directors and JLL Patheon Holdings announced that they entered into a settlement agreement in respect of the pending legal actions between the parties, which was confirmed by the courts on December 4, 2009. As part of this settlement the Company paid JLL Patheon Holdings $1.5 million and Joaquin B. Viso $0.4 million.
12. FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS, FAIR VALUE AND RISK MANAGEMENT
Categories of financial assets and liabilities
The carrying values of the Company's financial instruments, including those held for sale on the consolidated balance sheets are classified into the following categories:
|
| | | | | |
| As of October 31, | 2012 | | 2011 |
| | $ | | $ |
Held-for-trading1 | 39.4 |
| | 33.4 |
|
Loans and receivables2 | 161.7 |
| | 158.0 |
|
Other financial liabilities3 | 499.3 |
| | 463.0 |
|
Derivatives designated as effective hedges4—gain (loss) | 1.4 |
| | (0.5 | ) |
Other derivatives5 | 0.3 |
| | — |
|
_____________________________
| |
| (1) | Includes cash and cash equivalents in bank accounts bearing interest rates up to 1%. |
| |
| (2) | Includes accounts receivable, net of an allowance for doubtful accounts of $0.8 million and $0.4 million at October 31, 2012 and 2011, respectively. |
| |
| (3) | Includes bank indebtedness, accounts payable, accrued liabilities and long-term debt. |
| |
| (4) | Includes the Company's forward contracts and collars in 2012 and 2011. |
| |
| (5) | Includes the contingent consideration receivable related to the Burlington sale. |
The Company has determined the estimated fair values of its financial instruments based on appropriate valuation methodologies; however, considerable judgment is required to develop these estimates. The fair values of the Company's financial instruments are not materially different from their carrying values.
As of October 31, 2012 and 2011, the carrying amount of the financial assets that the Company has pledged as collateral for its long-term debt facilities was $131.2 million and $106.7 million, respectively. Please refer to Note 7—Long Term Debt.
Fair value measurements
The Company classifies and discloses its fair value measurements using a fair value hierarchy that reflects the significance of the inputs used in making the measurements. The fair value hierarchy has the following levels: (a) quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical assets or liabilities (Level 1); (b) inputs other than quoted prices included in Level 1 that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly (i.e., as prices) or indirectly (i.e., derived from prices) (Level 2); and (c) inputs for the asset or liability that are not based on observable market data (unobservable inputs) (Level 3).
Patheon Inc.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
October 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010
(Dollar information in tabular form is expressed in millions of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise indicated)
The fair value is principally applied to financial assets and liabilities such as derivative instruments consisting of foreign exchange forward contracts and collars. The following table provides a summary of the financial assets and liabilities that are measured at fair value as of October 31, 2012 and 2011:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Fair value measurement at October 31, 2012 using: | | Fair value measurement at October 31, 2011 using: |
| Assets measured at fair value | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 | | Total | | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 | | Total |
| | $ | | $ | | $ | | $ | | $ | | $ | | $ | | $ |
| Derivatives designated as hedging instruments: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Foreign exchange forward contracts | — |
| | 2.1 |
| | — |
| | 2.1 |
| | — |
| | 1.2 |
| | — |
| | 1.2 |
|
| Total assets | — |
| | 2.1 |
| | — |
| | 2.1 |
| | — |
| | 1.2 |
| | — |
| | 1.2 |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Contingent consideration receivable | — |
| | — |
| | 0.3 |
| | 0.3 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
| Total assets | — |
| | — |
| | 0.3 |
| | 0.3 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Fair value measurement at October 31, 2012 using: | | Fair value measurement at October 31, 2011 using: |
| Liabilities measured at fair value | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 | | Total | | Level 1 | | Level 2 | | Level 3 | | Total |
| | $ | | $ | | $ | | $ | | $ | | $ | | $ | | $ |
| Derivatives designated as hedging instruments: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Foreign exchange collars | — |
| | 0.7 |
| | — |
| | 0.7 |
| | — |
| | 1.7 |
| | — |
| | 1.7 |
|
| | — |
| | 0.7 |
| | — |
| | 0.7 |
| | — |
| | 1.7 |
| | — |
| | 1.7 |
|
The following table presents the fair value of the Company's derivative financial instruments as well as their classification on the consolidated balance sheets as of October 31, 2012 and 2011:
|
| | | | | | | | | |
| | Asset Derivatives as of October 31, 2012 | | Asset Derivatives as of October 31, 2011 |
| Fair values of derivative instruments | Balance Sheet Location | | Fair Value | | Balance Sheet Location | | Fair Value |
| | | | $ | | | | $ |
| Derivatives designated as hedging instruments: | | | | | | | |
| Foreign exchange forward contracts | Prepaid expenses and other | | 1.8 |
| | Prepaid expenses and other | | 0.2 |
|
| Foreign exchange forward contracts | Other long-term assets | | 0.3 |
| | Other long-term assets | | 1.0 |
|
| Total designated derivatives | | | 2.1 |
| | | | 1.2 |
|
| | | | | | | | |
| Contingent consideration receivable | Other long-term assets | | 0.3 |
| | Other long-term assets | | — |
|
| Total non-designated derivatives | | | 0.3 |
| | | | — |
|
|
| | | | | | | | | |
| | Liability Derivatives as of October 31, 2012 | | Liability Derivatives as of October 31, 2011 |
| | Balance Sheet Location | | Fair Value | | Balance Sheet Location | | Fair Value |
| | | | $ | | | | $ |
| Derivatives designated as hedging instruments: | | | | | | | |
| Foreign exchange collars | Accounts payable and accrued liabilities | | 0.3 |
| | Accounts payable and accrued liabilities | | 1.4 |
|
| Foreign exchange collars | Other long-term liabilities | | 0.4 |
| | Other long-term liabilities | | 0.3 |
|
| Total designated derivatives | | | 0.7 |
| | | | 1.7 |
|
Patheon Inc.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
October 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010
(Dollar information in tabular form is expressed in millions of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise indicated)
On August 31, 2012, the Company completed the sale of its global secondary clinical packaging and clinical distribution services business to Bellwyck Packaging Solutions. The total consideration for the sale of this business is approximately $2.70 million, of which $1.35 million was paid in cash at closing (subject to the retention of certain amounts in escrow) and $1.35 million will be paid in 24 months from the closing date if certain revenue targets are met by the new owner.
The $1.35 million that will be paid 24 months following closing is treated as a contingent consideration receivable for accounting purposes. The contingent consideration receivable was valued at $0.3 million on the closing date at fair value based upon the present value of the agreed-upon revenue targets. The fair value of the contingent consideration receivable will be marked to market on a quarterly basis with an adjustment to the related receivable and the gain/loss on sale of assets.
The following table presents a roll-forward of the Company's only Level 3 financial instrument as of October 31, 2012:
|
| | | | | |
| (in millions of USD) | Contingent Consideration | | Total |
| | $ | | $ |
| Opening balance | — |
| | — |
|
| Purchases | — |
| | — |
|
| Issues | — |
| | — |
|
| Total gains (losses) | | | |
| In net loss | 0.3 |
| | 0.3 |
|
| In other comprehensive income | — |
| | — |
|
| Settlements | — |
| | — |
|
| Transfers out of Level 3 | — |
| | — |
|
| Closing balance (October 31, 2012) | 0.3 |
| | 0.3 |
|
Foreign exchange forward contracts, interest rate swaps and other hedging arrangements
The Company utilizes financial instruments to manage the risk associated with fluctuations in foreign exchange and interest rates. The Company formally documents all relationships between hedging instruments and hedged items, as well as its risk management objective and strategy for undertaking various hedge transactions.
As of October 31, 2012, the Company's Canadian operations had entered into foreign exchange forward contracts to sell an aggregate amount of $69.4 million. These contracts hedge the Canadian operations' expected exposure to U.S. dollar denominated cash flows and mature at the latest on April 2, 2014, at an average exchange rate of $1.0373 Canadian. The mark-to-market value of these financial instruments as of October 31, 2012 was an unrealized gain of $2.2 million, which has been recorded in accumulated other comprehensive income in shareholders' equity, net of associated income tax.
As of October 31, 2012, the Company's Canadian operations had entered into foreign exchange forward contracts to sell an aggregate amount of €6.0 million. These contracts hedge the Canadian operations' expected exposure to Euro denominated receivables and mature at the latest on October 8, 2013, at an average exchange rate of $1.3000 Canadian. The mark-to-market value of these financial instruments as of October 31, 2012 was an unrealized loss of $0.1 million, which has been recorded in accumulated other comprehensive income in shareholders' equity, net of associated income tax.
As of October 31, 2011, the Company's Canadian operations had entered into foreign exchange collars to sell an aggregate amount of US$60.4 million. These contracts hedge the Canadian operations' expected exposure to U.S. dollar denominated cash flows and mature at the latest on July 2, 2014, at an average exchange rate of $0.9927 Canadian. The mark-to-market value of these financial instruments as of October 31, 2012 was an unrealized loss of $0.7 million, which has been recorded in accumulated other comprehensive income in shareholders' equity, net of associated income tax.
Prior to the refinancing in fiscal 2010, the Company had entered into interest rate swap contracts to convert all of the interest costs on its senior secured term loan from a floating to a fixed rate of interest until June 30, 2010, when it canceled the swaps and paid $1.8 million in hedging losses related to these financial instruments. These losses were recorded as part of the refinancing costs the Company incurred in fiscal 2010.
Risks arising from financial instruments and risk management
Patheon Inc.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
October 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010
(Dollar information in tabular form is expressed in millions of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise indicated)
The Company's activities expose it to a variety of financial risks: market risk (including foreign exchange and interest rate), credit risk and liquidity risk. The Company's overall risk management program focuses on the unpredictability of financial markets and seeks to minimize potential adverse effects on the Company's financial performance. The Company uses derivative financial instruments to hedge certain risk exposures. The Company does not purchase any derivative financial instruments for speculative purposes.
Risk management is the responsibility of the Company's corporate finance team. The corporate finance team works with the Company's operational personnel to identify, evaluate and, where appropriate, hedge financial risks. The Company's corporate finance team also monitors material risks and discusses them with the Audit Committee of the Board of Directors.
Foreign exchange risk
As of October 31, 2012, the Company operated in Canada, the United States, Puerto Rico, Italy, France, the United Kingdom and Japan. Foreign exchange risk arises because the value of the local currency receivable or payable for transactions denominated in foreign currencies may vary due to changes in exchange rates ("transaction exposures") and because the non-U.S. dollar denominated financial statements of the Company may vary on consolidation into the reporting currency of U.S. dollars ("translation exposures").
The Company's most significant transaction exposures arise in its Canadian operations. Prior to the refinancing in the second quarter of fiscal 2010, the balance sheet of the Company's Canadian division included U.S. dollar denominated debt which was designated as a hedge against the Company's investments in subsidiaries in the United States and Puerto Rico. The foreign exchange gains and losses related to the effective portion of this hedge were recorded in other comprehensive income. In the third quarter of fiscal 2010, the Company changed the functional currency of its corporate division in Canada to U.S. dollars, thereby eliminating the need for the Company to designate this U.S. dollar denominated debt as a hedge. In addition, approximately 90% of the revenues of the Canadian operations and approximately 10% of its operating expenses are transacted in U.S. dollars. As a result, the Company may experience transaction exposures because of volatility in the exchange rate between the Canadian and U.S. dollar. Based on the Company's current U.S. denominated net inflows, as of October 31, 2012, fluctuations of +/-10% would, everything else being equal, have an effect on loss from continuing operations before taxes of approximately +/- $17.8 million, prior to hedging activities.
The objective of the Company's foreign exchange risk management activities is to minimize transaction exposures and the resulting volatility of the Company's earnings. The Company manages this risk by entering into foreign exchange forward contracts. As of October 31, 2012, the Company has entered into forward foreign exchange contracts to cover approximately 80% of its Canadian-U.S. dollar cash flow exposures for fiscal 2013. The Company does not currently hedge any translation exposures.
Translation gains and losses related to certain foreign currency denominated intercompany loans are included as part of the net investment in certain foreign subsidiaries, and are included in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) in shareholders' equity.
Credit risk
Credit risk arises from cash and cash equivalents held with banks and financial institutions, derivative financial instruments (foreign exchange forward contracts and interest rate swaps with positive fair values), and credit exposure to customers, including outstanding accounts receivable. The maximum exposure to credit risk is equal to the carrying value of the financial assets.
The objective of managing counterparty credit risk is to prevent losses in financial assets. The Company assesses the credit quality of the counterparties, taking into account their financial position, past experience and other factors. Management also monitors the utilization of credit limits regularly. In cases where the credit quality of a customer does not meet the Company's requirements, a cash deposit is received before any services are provided. As of October 31, 2012 and 2011, the Company held deposits of $16.4 million and $17.9 million, respectively.
The carrying amount of accounts receivable are reduced through the use of an allowance account and the amount of the loss is recognized in the consolidated statements of operations within operating expenses. When a receivable balance is considered uncollectible, it is written off against the allowance for accounts receivable. Subsequent recoveries of amounts previously written off are credited against operating expenses in the consolidated statements of operations.
Patheon Inc.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
October 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010
(Dollar information in tabular form is expressed in millions of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise indicated)
Liquidity risk
Liquidity risk arises through excess of financial obligations over available financial assets due at any point in time. The Company's objective in managing liquidity risk is to maintain sufficient readily available reserves in order to meet its liquidity requirements at all times. The Company mitigates liquidity risk by maintaining cash and cash equivalents on hand and through the availability of funding from credit facilities. As of October 31, 2012, the Company was holding cash and cash equivalents of $39.4 million and had undrawn lines of credit available to it of $64.4 million.
The contractual maturities of the Company's financial liabilities are presented in Note 7—Long-Term Debt and reflect the impact of the refinancing in second quarter of fiscal 2010.
13. OTHER COMPREHENSIVE (LOSS) INCOME
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | Years ended October 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| | $ | | $ | | $ |
| Net loss attributable to restricted voting shareholders | (106.7 | ) | | (16.4 | ) | | (4.6 | ) |
| Other comprehensive income, net of income taxes | | | | | |
Change in foreign currency translation on investments in subsidiaries, net of hedging activities1 | (11.9 | ) | | 5.3 |
| | 1.6 |
|
Change in value of derivatives designated as foreign currency and interest rate cash flow hedges2 | 1.3 |
| | 1.7 |
| | 9.0 |
|
(Losses) gains on foreign currency and interest rate cash flow hedges reclassified to consolidated statement of operations3 | 0.5 |
| | (3.0 | ) | | (6.2 | ) |
| Net change in minimum pension liability | (0.2 | ) | | (2.5 | ) | | 2.4 |
|
| Comprehensive (loss) income attributable to restricted voting shareholders | (117.0 | ) | | (14.9 | ) | | 2.2 |
|
_______________________
The amounts disclosed in other comprehensive income have been recorded net of income taxes as follows:
| |
1 | Net of an income tax benefit of $0.5 million (2012), a benefit of $0.4 million (2011), and an expense of $0.1 million (2010). The cumulative translation adjustment as of October 31, 2012 was $38.0 million versus $49.9 million as of October 31, 2011. |
| |
2 | Net of an income tax benefit of $0.1 million (2012), an expense of $0.5 million (2011), and an expense of $1.9 million (2010). |
| |
3 | Net of an income tax benefit of $1.1 million (2011), and a benefit of $0.8 million (2010). |
14. INCOME TAXES
The following is a reconciliation of the expected income tax (benefit) expense obtained by applying a single statutory tax rate of 25.25% (which is a mixture of federal and provincial rates) of Patheon Inc., to the loss from continuing operations before income taxes.
Patheon Inc.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
October 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010
(Dollar information in tabular form is expressed in millions of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise indicated)
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | As of October 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| | $ | | $ | | $ |
| Expected income tax expense (benefit) using statutory tax rates | (15.9 | ) | | (3.9 | ) | | (4.8 | ) |
| Change in valuation allowance | 56.6 |
| | 4.0 |
| | (19.2 | ) |
| Permanent differences and other: | | | | | |
| Foreign | 3.4 |
| | 2.3 |
| | 2.5 |
|
| Domestic | (2.2 | ) | | (5.6 | ) | | (0.7 | ) |
| Foreign rate differentials | 1.5 |
| | 2.5 |
| | 8.4 |
|
| Other | — |
| | 1.8 |
| | — |
|
| Provision for income taxes | 43.4 |
| | 1.1 |
| | (13.8 | ) |
| Effective tax rate | (68.9 | )% | | (7.5 | )% | | 82.7 | % |
Permanent foreign differences reconciling expected income tax expense using statutory tax rates to the provision for income taxes were primarily meals and entertainment costs, employee costs, and salary and benefits that are not deductible in Italy, France, Canada and the United States. Other permanent domestic differences were primarily due to recording research and development investment tax credits and the book versus tax treatment of foreign exchange gains in Canada resulting from the change in functional currency of the Company's corporate division in Canada to U.S. dollars (as previously disclosed).
The tax effects of significant items comprising the Company's net deferred income tax liabilities are as follows:
|
| | | | | |
| | 2012 | | 2011 |
| | $ | | $ |
| Net operating loss carryforward | 18.0 |
| | 15.4 |
|
| Accounting provisions not currently deductible for tax purposes | 4.2 |
| | 11.8 |
|
| Unrealized foreign exchange losses on debt | 0.1 |
| | 0.6 |
|
| Share issue costs | — |
| | 0.3 |
|
| Deferred financing costs | — |
| | 0.3 |
|
| Deferred revenue | 10.6 |
| | 8.2 |
|
| Unclaimed R&D expenditures | 12.3 |
| | 10.0 |
|
| Investment tax credits | 19.6 |
| | 17.9 |
|
| Other | 24.0 |
| | 10.2 |
|
| Book depreciation in excess of tax depreciation | (35.5 | ) | | (46.4 | ) |
| Valuation allowance | (72.0 | ) | | (9.0 | ) |
| | (18.7 | ) | | 19.3 |
|
The short-term and long-term deferred income tax assets and liabilities after netting are as follows:
|
| | | | | |
| | 2012 | | 2011 |
| | $ | | $ |
| Short-term deferred income tax assets | 4.3 |
| | 8.1 |
|
| Long-term deferred income tax assets | — |
| | 39.1 |
|
| Long-term deferred income tax liabilities | (23.0 | ) | | (27.9 | ) |
| | (18.7 | ) | | 19.3 |
|
The Company has tax-effected net operating losses, consisting of federal, state and foreign, of $18.0 million; $11.0 million of the losses have an indefinite life and $7.0 million have expiry dates ranging from October 31, 2015 to October 31, 2031. The Company has tax credits of $28.1 million with expiry dates beginning October 31, 2017.
The Company has not recorded deferred tax liabilities on the unremitted earnings of foreign subsidiaries as the Company currently intends to reinvest these earnings in its foreign operations indefinitely. Under Canadian tax laws, the Company's
Patheon Inc.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
October 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010
(Dollar information in tabular form is expressed in millions of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise indicated)
unremitted earnings from its foreign subsidiaries are exempt from income tax but may be subject to withholding tax at the source upon distribution. Determination of this withholding tax liability is not practicable.
At the end of each quarter of fiscal 2012 the Company assessed its need for valuation allowances against its deferred tax assets in certain jurisdictions. The Company determined that the future realization of its deferred tax assets was uncertain and therefore, recorded a valuation allowance on its Canadian and various foreign deferred tax assets. As a result of this determination, the Company recorded a valuation reserve of $56.6 million through the provision for income taxes in its consolidated statement of operations for fiscal 2012.
During fiscal 2011, the Company adopted uncertain tax provisions standard ASC 740, applied retroactively to November 1, 2007. As a result of the implementation of this standard, the Company recognized no material adjustment in the liability for unrecognized income tax benefits or effect on accumulated deficit. As of October 31, 2012 and 2011, unrecognized tax benefits were $0.8 million and $0.8 million, respectively. At October 31, 2012 and 2011, unrecognized tax benefits of $0.0 million and $0.8 million, respectively, related to permanent income tax differences, will have a favorable effect on the Company's effective tax rate if recognized; the remaining balance would result in a reclassification on the balance sheet.
The Company classifies interest recognized under ASC 740 as a component of interest expense in the consolidated statements of operations. Penalties, if incurred, are recorded as other operating expenses in the consolidated statements of operations. The Company recorded no material amount of interest expense under ASC 740 for fiscal 2012 and 2011.
For Canadian purposes, the Company is generally no longer subject to examinations for the fiscal years ended October 31, 2006 and prior. The Company is currently under examination by the Canada Revenue Agency for the fiscal years ended October 31, 2007 through October 31, 2008. During fiscal 2011, the Canada Revenue Agency concluded examination of the Company's transfer pricing position for the years ended October 31, 2005 through 2008 resulting in no adjustment to Canadian taxable income.
During fiscal 2011, the U.S. Internal Revenue Service concluded an examination of the Company's October 31, 2007 and 2008 consolidated U.S. federal income tax returns. The Company acquiesced to the conclusions reached in the examination. The results of the examination have been reviewed and accepted by the Joint Committee on Taxation. During fiscal 2012, the U.S. Internal Revenue Service conducted a desk review of the U.S. federal income tax return for the Company's October 31, 2010 tax year as a result of a net operating loss carry-back. There were no adjustments proposed and the case is currently under review by the Joint Committee on Taxation.
During fiscal 2011, the French tax authority concluded an examination of the Company's income tax returns for the years ended October 31, 2007 and 2008. The Company appealed the assessment related to transfer pricing, but the French authorities maintained the assessment and the Company has indicated it intends to further appeal and believes the result will be a nil or immaterial assessment. The Company anticipates no material change to unrecognized tax benefits resulting from this examination.
During fiscal 2011, the Hungarian tax authority initiated an examination for the years ended December 31, 2005 through August 12, 2010 as part of the liquidation process. The examination resulted in a nil assessment.
Statutes related to foreign and state jurisdictions are open from October 31, 2004 to October 31, 2012. Certain carry forward tax attributes generated in prior years remain subject to examination and adjustment.
During the next 12 months, the Company expects no material change in the total amount of unrecognized tax benefits. A reconciliation of the beginning and ending amounts of the tax reserves is as follows:
Patheon Inc.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
October 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010
(Dollar information in tabular form is expressed in millions of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise indicated)
|
| | | |
| Balance at October 31, 2009 | $ | 2.7 |
|
| Decrease related to settlements with taxing authorities and changes in law | (1.3 | ) |
| Balance at October 31, 2010 | $ | 1.4 |
|
| Decrease related to positions taken in the current year | (0.8 | ) |
| Increase based on tax positions taken in current year | 0.2 |
|
| Balance at October 31, 2011 | $ | 0.8 |
|
| Decrease related to positions taken in the current year | $ | — |
|
| Increase based on tax positions taken in current year | $ | — |
|
| Balance at October 31, 2012 | $ | 0.8 |
|
Below is a breakout of the Company's (loss) income from continuing operations before income taxes and applicable provision for (benefit from) income taxes:
|
| | | | | | | | |
| Years ended October 31, |
| 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| Loss from continuing operations before income taxes | $ | | $ | | $ |
| Domestic | (14.3 | ) | | (12.5 | ) | | (15.7 | ) |
| Foreign | (48.7 | ) | | (2.2 | ) | | (1.0 | ) |
| | (63.0 | ) | | (14.7 | ) | | (16.7 | ) |
|
| | | | | | | | |
| Years ended October 31, |
| 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| Provision for (benefit from) income taxes | $ | | $ | | $ |
| Domestic | 31.6 |
| | (5.1 | ) | | (15.1 | ) |
| Foreign | 11.8 |
| | 6.2 |
| | 1.3 |
|
| | 43.4 |
| | 1.1 |
| | (13.8 | ) |
15. SEGMENTED INFORMATION
The Company is organized and managed in two business segments: CMO and PDS. These segments are organized around the service activities provided to the Company's customers.
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | As of and for the year ended October 31, 2012 |
| | Commercial | | PDS | | Corp. & Other | | Total |
| | $ | | $ | | $ | | $ |
| Revenues | 610.7 |
| | 138.4 |
| | — |
| | 749.1 |
|
| Adjusted EBITDA | 84.5 |
| | 28.5 |
| | (41.9 | ) | | 71.1 |
|
| Total assets | 617.4 |
| | 69.7 |
| | 55.8 |
| | 742.9 |
|
| Depreciation | 35.0 |
| | 4.9 |
| | 0.9 |
| | 40.8 |
|
| Impairment | 55.1 |
| | 2.8 |
| | — |
| | 57.9 |
|
| Goodwill | 3.5 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 3.5 |
|
| Capital expenditures | 47.3 |
| | 4.7 |
| | 1.4 |
| | 53.4 |
|
Patheon Inc.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
October 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010
(Dollar information in tabular form is expressed in millions of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise indicated)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | As of and for the year ended October 31, 2011 |
| | Commercial | | PDS | | Corp. & Other | | Total |
| | $ | | $ | | $ | | $ |
| Revenues | 572.6 |
| | 127.4 |
| | — |
| | 700.0 |
|
| Adjusted EBITDA | 79.2 |
| | 24.1 |
| | (36.9 | ) | | 66.4 |
|
| Total assets | 673.0 |
| | 84.5 |
| | 67.1 |
| | 824.6 |
|
| Depreciation | 46.4 |
| | 5.8 |
| | 1.0 |
| | 53.2 |
|
| Goodwill | 3.5 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 3.5 |
|
| Capital expenditures | 38.4 |
| | 8.8 |
| | 0.6 |
| | 47.8 |
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | As of and for the year ended October 31, 2010 |
| | Commercial | | PDS | | Corp. & Other | | Total |
| | $ | | $ | | $ | | $ |
| Revenues | 545.3 |
| | 125.9 |
| | — |
| | 671.2 |
|
| Adjusted EBITDA | 72.3 |
| | 36.0 |
| | (27.4 | ) | | 80.9 |
|
| Total assets | 639.5 |
| | 82.1 |
| | 91.6 |
| | 813.2 |
|
| Depreciation | 49.1 |
| | 5.9 |
| | 0.6 |
| | 55.6 |
|
| Impairment | 3.6 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 3.6 |
|
| Goodwill | 3.4 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 3.4 |
|
| Capital expenditures | 38.8 |
| | 8.7 | | 1.2 | | 48.7 |
|
Cash and cash equivalents as well as deferred tax assets are considered to be part of "Corp. & Other" in the breakout of total assets shown above. In fiscal 2012 and 2010 the Company, following an impairment analysis, recorded impairment charges of $57.9 million and $3.6 million related to its Swindon and Caguas facilities, respectively.
The Company evaluates the performance of its segments based on segment Adjusted EBITDA, which is defined as income (loss) before discontinued operations before repositioning expenses, interest expense, foreign exchange losses reclassified from other comprehensive income (loss), refinancing expenses, acquisition-related costs, gains and losses on sale of capital assets, gain on extinguishment of debt, income taxes, asset impairment charges, depreciation and amortization and other income and expenses. The Company's presentation of Adjusted EBITDA may not be comparable to similarly-titled measures used by other companies.
Below is a reconciliation of Adjusted EBITDA to its closest U.S. GAAP measure.
Patheon Inc.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
October 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010
(Dollar information in tabular form is expressed in millions of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise indicated)
|
| | | | | | | | |
| | Years ended October 31, |
| | 2012 | | 2011 | | 2010 |
| | $ | | $ | | $ |
| Adjusted EBITDA: | | | | | |
| Total Adjusted EBITDA per above | 71.1 |
| | 66.4 |
| | 80.9 |
|
| Depreciation and amortization | (40.8 | ) | | (53.2 | ) | | (55.6 | ) |
| Repositioning expenses | (6.1 | ) | | (7.0 | ) | | (6.8 | ) |
| Acquisition-related costs | (3.2 | ) | | — |
| | — |
|
| Interest expense, net | (26.5 | ) | | (25.6 | ) | | (19.6 | ) |
| Impairment charge | (57.9 | ) | | — |
| | (3.6 | ) |
| (Loss) gain on sale of capital assets | (0.4 | ) | | (0.2 | ) | | (0.2 | ) |
| Refinancing expenses | — |
| | — |
| | (12.2 | ) |
| (Provision for) benefit from income taxes | (43.4 | ) | | (1.1 | ) | | 13.8 |
|
| Other | 0.8 |
| | 4.9 |
| | 0.4 |
|
| (Loss) income before discontinued operations | (106.4 | ) | | (15.8 | ) | | (2.9 | ) |
As illustrated in the table below, revenues are attributed to countries based on the location of the customer's billing address, capital assets are attributed to the country in which they are located and goodwill is attributed to the country in which the entity to which the goodwill pertains is located:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | As of and for the year ended October 31, 2012 |
| | Canada | | U.S.* | | Europe | | Other | | Total |
| | $ | | $ | | $ | | $ | | $ |
| Revenues | 13.7 |
| | 434.2 |
| | 259.4 |
| | 41.8 |
| | 749.1 |
|
| Capital assets | 115.7 |
| | 144.8 |
| | 154.4 |
| | 1.5 |
| | 416.4 |
|
| Impairment | — |
| | — |
| | 57.9 |
| | — |
| | 57.9 |
|
| Goodwill | 3.5 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 3.5 |
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | As of and for the year ended October 31, 2011 |
| | Canada | | U.S.* | | Europe | | Other | | Total |
| | $ | | $ | | $ | | $ | | $ |
| Revenues | 12.0 |
| | 348.9 |
| | 302.4 |
| | 36.7 |
| | 700.0 |
|
| Capital assets | 115.6 |
| | 133.6 |
| | 223.3 |
| | 1.7 |
| | 474.2 |
|
| Goodwill | 3.5 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 3.5 |
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | As of and for the year ended October 31, 2010 |
| | Canada | | US* | | Europe | | Other | | Total |
| | $ | | $ | | $ | | $ | | $ |
| Revenues | 16.2 |
| | 319.7 |
| | 310.7 |
| | 24.6 |
| | 671.2 |
|
| Capital assets | 116.4 |
| | 129.4 |
| | 229.9 |
| | 1.7 |
| | 477.4 |
|
| Impairment | — |
| | 3.6 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 3.6 |
|
| Goodwill | 3.4 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 3.4 |
|
_________________________________
* Includes Puerto Rico
During fiscal 2012, the Company had one customer that accounted for approximately 11% of total revenues. In fiscal 2011 and 2010, the Company did not have any one customer that accounted for more than 10% of total revenues.
Patheon Inc.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
October 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010
(Dollar information in tabular form is expressed in millions of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise indicated)
16. COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
Operating leases
The Company has entered into long-term rental agreements expiring at various dates until 2020. The future rental payments for the next five years and thereafter are estimated as follows:
|
| | |
| | $ |
| 2013 | 5.7 |
|
| 2014 | 3.8 |
|
| 2015 | 2.5 |
|
| 2016 | 1.3 |
|
| 2017 | 0.9 |
|
| Thereafter | 1.5 |
|
| Total payments | 15.7 |
|
The Company's total rental expenses related to its operating leases for fiscal 2012, 2011 and 2010 were $7.5 million, $7.2 million and $6.0 million, respectively.
Contingencies
In the fourth quarter of fiscal 2011, a customer gave notice of its intent to seek indemnification against the Company pursuant to a manufacturing service agreement ("MSA") for all costs associated with a recall of an allegedly defective product. The Company recorded an expense of $1.7 million, net of expected insurance proceeds, to cover recall costs and costs to replace returned products. During the first quarter of fiscal 2012, the customer gave further notice of its intent to seek indemnification pursuant to the MSA for all actual and potential third-party claims that have been or may be filed against it in connection with the recall and the alleged product defects, as well as all costs and expenses of the defense and settlement of such claims. During the second quarter of fiscal 2012, the Company accrued an additional $2.4 million, for additional returned products from the customer. A putative class action and three single plaintiff actions are pending in the United States against the customer in connection with the allegedly defective products, and the Company has also been named in the putative class actions. As these cases are at an early stage, the Company is unable to estimate the number of potential claimants or the amount of potential damages for which the Company may be directly or indirectly liable in the above actions.
Other
The Company may be subject to lawsuits, investigations and other claims, including environmental, labor, product, customer disputes and other matters in the normal course of operations and otherwise. The Company believes that adequate provisions have been recorded in the accounts where required. Although it is not possible to estimate the extent of potential costs, if any, the Company believes that the ultimate resolution of such contingencies will not have a material adverse impact on the results of operations, financial position or liquidity.
The Company's tax filings are subject to audit by taxation authorities. Although the Company believes that it has adequately provided for income taxes based on the information available, the outcome of audits cannot be known with certainty and the potential impact on the financial statements is not determinable.
17. REPOSITIONING EXPENSES
On May 9, 2012, the Company announced a plan of termination (the "Plan of Termination") to reduce the Company's workforce by approximately 91 employees across the Company's global PDS and CMO segments. In connection with the Plan of Termination, the Company recorded approximately $4.4 million of estimated expenses associated with employee termination benefits during fiscal 2012. The Company anticipates that it may further adjust the size of the workforce at the Swindon or other facilities as it continues its transformation process.
During fiscal 2012, the Company incurred $6.1 million in repositioning expenses, of which $1.7 million related to the shutdown of the Caguas facility, with the remainder related to the Plan of Termination.
Patheon Inc.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
October 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010
(Dollar information in tabular form is expressed in millions of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise indicated)
During fiscal 2011, the Company incurred $7.0 million in repositioning expenses, of which $4.0 million related to the shutdown of the Caguas facility. The remaining $3.0 million related to the Company's 2011 strategic initiatives in Zug and Swindon.
During fiscal 2010, the Company incurred $6.8 million in repositioning expenses associated with the shutdown of its Caguas facility.
The following is a summary of the Company's repositioning expenses and related liabilities as of and for fiscal
2012, 2011 and 2010:
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| As of and for the year ended October 31, 2012 | Commercial | | PDS | | Corporate | | Total |
| | $ | | $ | | $ | | $ |
| Total repositioning liabilities at October 31, 2011 | | | | | | | 6.7 |
|
| Employee-related expenses | 2.8 |
| | 1.8 |
| | — |
| | 4.6 |
|
| Consulting, professional and project costs | 1.4 |
| | 0.1 |
| | — |
| | 1.5 |
|
| Total expenses | 4.2 |
| | 1.9 |
| | — |
| | 6.1 |
|
| Repositioning expenses paid | | | | | | | (7.3 | ) |
| Total repositioning liabilities at October 31, 2012 | | | | | | | 5.5 |
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| As of and for the year ended October 31, 2011 | Commercial | | PDS | | Corporate | | Total |
| | $ | | $ | | $ | | $ |
| Total repositioning liabilities at October 31, 2010 | | | | | | | 3.2 |
|
| Employee-related expenses | 3.3 |
| | — |
| | 1.0 |
| | 4.3 |
|
| Consulting, professional and project costs | 2.7 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 2.7 |
|
| Total expenses | 6.0 |
| | — |
| | 1.0 |
| | 7.0 |
|
| Repositioning expenses paid | | | | | | | (3.5 | ) |
| Total repositioning liabilities at October 31, 2011 | | | | | | | 6.7 |
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| As of and for the year ended October 31, 2010 | Commercial | | PDS | | Corporate | | Total |
| | $ | | $ | | $ | | $ |
| Total repositioning liabilities at October 31, 2009 | | | | | | | 2.9 |
|
| Employee-related expenses | 3.7 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 3.7 |
|
| Consulting, professional and project management costs | 3.1 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 3.1 |
|
| Total expenses | 6.8 |
| | — |
| | — |
| | 6.8 |
|
| Repositioning expenses paid | | | | | | | (6.4 | ) |
| Foreign exchange | | | | | | | (0.1 | ) |
| Total repositioning liabilities at October 31, 2010 | | | | | | | 3.2 |
|
18. REFINANCING EXPENSES
During fiscal 2010, the Company incurred expenses of $12.2 million in connection with its refinancing activities. These transaction costs relate to expenses associated with obtaining debt financing, including fees paid to advisors and other related costs. Included in the refinancing expenses are $1.8 million in costs related to the previous senior secured term loan that were written off and $1.8 million in losses for the interest rate swaps on the previous debt that were cancelled on June 30, 2010. Financing costs of $7.6 million, including fees paid to lenders, were capitalized and netted against the carrying value of the related debt and amortized to interest expense over the life of the Notes and credit agreement. Please refer to Note 7—Long-Term Debt.
19. QUARTERLY RESULTS OF OPERATIONS - UNAUDITED
The following is a summary of the Company's unaudited quarterly results of operations:
Patheon Inc.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
October 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010
(Dollar information in tabular form is expressed in millions of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise indicated)
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended October 31, 2012 |
| | 1st Quarter(1) | | 2nd Quarter(2) | | 3rd Quarter(3) | | 4th Quarter(4) |
| | (Dollar information in millions of USD, except per share
information) |
| | $ | | $ | | $ | | $ |
| Revenues | 153.9 |
| | 181.5 |
| | 203.7 |
| | 210.0 |
|
| Gross profit | 14.4 |
| | 34.0 |
| | 55.5 |
| | 55.4 |
|
| (Loss) income before discontinued operations | (19.3 | ) | | (79.6 | ) | | 15.5 |
| | (23.0 | ) |
| Loss from discontinued operations | (0.1 | ) | | (0.1 | ) | | — |
| | (0.1 | ) |
| Net (loss) income attributable to restricted voting shareholders | (19.4 | ) | | (79.7 | ) | | 15.5 |
| | (23.1 | ) |
| | | | | | | | |
| Basic and diluted (loss) income per share: | | | | | | | |
| From continuing operations | (0.149 | ) | | (0.616 | ) | | 0.120 |
| | (0.180 | ) |
| From discontinued operations | (0.001 | ) | | (0.001 | ) | | — |
| | — |
|
| | (0.150 | ) | | (0.617 | ) | | 0.120 |
| | (0.180 | ) |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended October 31, 2011 |
| | 1st Quarter(5) | | 2nd Quarter(6) | | 3rd Quarter(7) | | 4th Quarter(8) |
| | (Dollar information in millions of USD, except per share
information) |
| | $ | | $ | | $ | | $ |
| Revenues | 175.7 |
| | 170.0 |
| | 172.7 |
| | 181.6 |
|
| Gross profit | 42.2 |
| | 30.4 |
| | 25.8 |
| | 33.5 |
|
| Income (loss) before discontinued operations | 3.7 |
| | (10.3 | ) | | 0.6 |
| | (9.8 | ) |
| Loss from discontinued operations | (0.2 | ) | | (0.1 | ) | | (0.2 | ) | | (0.1 | ) |
| Net income (loss) attributable to restricted voting shareholders | 3.5 |
| | (10.4 | ) | | 0.4 |
| | (9.9 | ) |
| | | | | | | | |
| Basic and diluted income (loss) per share: | | | | | | | |
| From continuing operations | 0.029 |
| | (0.080 | ) | | 0.005 |
| | (0.075 | ) |
| From discontinued operations | (0.002 | ) | | (0.001 | ) | | (0.002 | ) | | (0.001 | ) |
| | 0.027 |
| | (0.081 | ) | | 0.003 |
| | (0.076 | ) |
| |
| (1) | Loss before discontinued operations included $6.4 million of consulting fees related to strategic initiatives. |
| |
| (2) | Loss before discontinued operations included a $57.9 million impairment charge, $4.4 million of repositioning expenses related to the Plan of Termination and $6.0 million in consulting fees related to strategic initiatives. |
| |
| (3) | Income before discontinued operations included $1.0 million of consulting fees related to strategic initiatives. |
| |
| (4) | Loss before discontinued operations included $36.6 million from recording of a valuation allowance against the Company's Canadian deferred tax assets and $3.2 million of acquisition-related costs. |
| |
| (5) | Revenues included the impact of approximately $32.9 million in reservation fees and deferred revenue amortization from the amended manufacturing and supply agreement in the United Kingdom. |
| |
| (6) | Revenues included the impact of approximately $17.5 million in reservation fees and deferred revenue amortization from the amended manufacturing and supply agreement in the United Kingdom. |
| |
| (7) | Income before discontinued operations included an insurance settlement of $6.0 million in other income and $2.5 million of consulting fees related to strategic initiatives. |
| |
| (8) | Loss before discontinued operations included $6.5 million of consulting fees related to strategic initiatives. |
20. SUBSEQUENT EVENTS
Patheon Inc.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
October 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010
(Dollar information in tabular form is expressed in millions of U.S. dollars, unless otherwise indicated)
Pursuant to a stock purchase agreement entered into on October 28, 2012, on December 14, 2012, the Company completed the acquisition of all of the issued and outstanding shares of capital stock of Sobel USA Inc., a Delaware corporation, and Banner Pharmacaps Europe B.V., a private limited company organized under the laws of The Netherlands (collectively "Banner") from Sobel Best N.V. and VION Holding, N.V., each corporations organized under the laws of The Netherlands, for an aggregate purchase price of approximately $269.0 million, subject to post-closing working capital adjustments (the "Banner Acquisition"). Banner is a pharmaceutical business focused on delivering proprietary softgel formulations, with four manufacturing facilities and a number of proprietary technologies and products.
Pursuant to a debt financing commitment letter entered into on October 28, 2012 and in connection with the closing of the Banner Acquisition, on December 14, 2012, the Company entered into a new senior secured credit facility, comprised of (i) a secured term loan in the amount of $575.0 million (the "Secured Term Loan") and (ii) a secured revolving credit facility of up to $85.0 million (the "Secured Revolving Facility" and, together with the Secured Term Loan, the "Credit Facility"). Up to $30.0 million of the Secured Revolving Facility is available for letters of credit. The Secured Term Loan matures on December 14, 2018, and the Secured Revolving Facility matures on December 14, 2017. The Secured Term Loan bears interest at a rate per annum equal to, at the option of the Company, LIBOR plus 6.00%, with a LIBOR "floor" of 1.25%, or an alternate base rate plus 5.00%, with an alternate base rate "floor" of 2.25%. Borrowings under the Secured Revolving Facility bear interest at a rate per annum equal to, at the option of the Company, an adjusted eurodollar rate for the applicable currency plus 5.50% or, if available, an alternate base rate for the applicable currency plus 4.50%. The Company will also pay a commitment fee of 0.50% per annum on the unused portion of the Secured Revolving Facility with a step down to 0.375% when its first lien leverage ratio is less than or equal to 3.00 to 1.00.
As part of the Refinancing, effective December 14, 2012, the Company terminated all commitments and repaid all amounts owed under the ABL. In addition, on November 26, 2012, the Company commenced a cash tender offer for its outstanding Notes. Pursuant to the Company's previously announced cash tender offer, as of 12:00 midnight, New York City time, on December 13, 2012, $279.4 million principal amount of the Notes had been tendered and not validly withdrawn, representing approximately 99.80% of the aggregate outstanding principal amount of the Notes. On December 14, 2012, the Company paid an aggregate of approximately $307.2 million in order to purchase the Notes tendered prior to December 14, 2012. In addition, the Company deposited with the trustee in respect of the Notes sufficient funds to redeem the remaining outstanding Notes on January 23, 2013 and pay accrued and unpaid interest thereon. As a result, the Company has been released from its obligations under the Notes and the indenture governing the Notes pursuant to the satisfaction and discharge provisions of such indenture.
On December 3, 2012, the Company mailed the holders of record of its restricted voting shares as of November 27, 2012 offering materials related to a $30.0 million offering of transferable subscription rights, with each right entitling the holder to subscribe for one whole restricted voting share at a price of, at such holder's choice, either US$3.19 per whole share or CAD$3.19 per whole share (the "Rights Offering"). Unless extended, the Rights Offering will remain open until December 28, 2012. Pursuant to JLL Partners Fund V, L.P.'s ("JLL Partners Fund V"), a JLL-affiliated entity, commitment letter to provide $30.0 million of equity (less amounts invested by other shareholders) to the Company dated October 28, 2012, JLL Partners Fund V caused one of its affiliated entities to participate in the Rights Offering. Any excess subscription payments will be returned, without interest or penalty, as soon as practicable after the expiry date of the Rights Offering.
EXHIBIT INDEX
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Incorporated By Reference | |
Exhibit Number | Description | Form | Filing Date | Number | Filed Herewith |
| 2.1+ | Stock Purchase Agreement among Patheon Inc. ("Patheon"), Sobel Best N.V. and VION Holding N.V. and Patheon Inc. dated October 28, 2012.+
| 8-K | 10/29/2012 | 2.1 | |
| 3.1 | Articles of Amalgamation of Patheon. | 10/A | 4/13/2011 | 3.1 | |
| 3.2 | Amendment, dated April 26, 2007, to Articles of Amalgamation of Patheon. | 10/A | 4/13/2011 | 3.2 | |
| 3.3 | By-Laws of Patheon dated March 27, 2008. | 10 | 2/25/2011 | 3.3 | |
| 4.1 | 'Form of Patheon's Share Certificate. | 10 | 2/25/2011 | 4.1 | |
| 4.2 | Indenture dated April 23, 2010 among Patheon, certain subsidiaries of Patheon as Guarantors, U.S. Bank National Association and Deutsche Bank Trust Company Americas, with respect to the 8.625% Senior Secured Notes due 2017. | 10 | 2/25/2011 | 4.2 | |
| 4.3 | Form of 8.625% Senior Secured Notes due 2017 (included in Exhibit 4.2). | 10 | 2/25/2011 | 4.3 | |
| 10.1 | Amended and Restated Revolving Credit Agreement dated April 23, 2010 among Patheon, certain subsidiaries of Patheon as Guarantors, the lenders party thereto, JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as U.S. Administrative Agent, JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as Canadian Administrative Agent, and Toronto Branch and J.P. Morgan Europe Limited, as European Administrative Agent. | 10 | 2/25/2011 | 10.1 | |
| 10.2 | Credit Agreement dated December 14, 2012 among Patheon, Patheon Pharmaceuticals Inc., Patheon UK Limited and Patheon Puerto Rico, Inc., the lenders from time to time party thereto, Morgan Stanley Senior Funding, Inc., as the administrative agent and swing line lender, Morgan Stanley Bank, N.A., as the letter of credit issuer, and the other parties thereto.
| 8-K | 12/17/2012 | 10.1 | |
| 10.3 | Purchase Agreement dated March 1, 2007 between Patheon and JLL Partners Fund V, L.P. | 10 | 2/25/2011 | 10.2 | |
| 10.4 | Investor Agreement dated April 27, 2007 between Patheon and JLL Patheon Holdings, LLC. | 10 | 2/25/2011 | 10.3 | |
| 10.5 | Redemption Waiver Agreement dated September 4, 2008 between Patheon and JLL Patheon Holdings, LLC. | 10 | 2/25/2011 | 10.4 | |
| 10.6 | Settlement Agreement dated November 29, 2009 between Patheon and JLL Patheon Holdings, LLC. | 10 | 2/25/2011 | 10.5 | |
| 10.7 | Commitment Letter among Patheon, Morgan Stanley Senior Funding, Inc., UBS Loan Finance LLC, UBS Securities LLC, Credit Suisse AG, Credit Suisse Securities (USA) LLC and KeyBank National Association dated October 28, 2012. | 8-K | 10/29/2012 | 10.1 | |
| 10.8 | Equity Commitment Letter between Patheon and JLL Partners V, L.P. dated October 28, 2012. | 8-K | 10/29/2012 | 10.2 | |
| 10.9 | Lease Agreement dated January 15, 1996 between Lansdown Estates Group Limited and Oxford Asymmetry Limited, assigned to Patheon U.K. Limited on May 3, 2006 in respect of the Milton Park Facility. | 10 | 2/25/2011 | 10.6 | |
| 10.10 | Licence to Assign Lease Agreement in respect of the Milton Park Facility dated April 28, 2006 among MEPC Milton Park No. 1 Limited and MEPC Milton Park No. 2 Limited, EVOTEC (UK) Limited and Patheon UK Limited. | 10 | 2/25/2011 | 10.7 | |
| 10.11 | Contract for the Sale of Leasehold Land in respect of the Milton Park Facility dated May 3, 2006 between EVOTEC (UK) Limited and Patheon UK Limited. | 10 | 2/25/2011 | 10.8 | |
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
| 10.12 | Assignment of Leasehold Property in respect of the Milton Park Facility dated May 3, 2006 between EVOTEC (UK) Limited and Patheon UK Limited. | 10 | 2/25/2011 | 10.9 | |
| 10.13 | Lease Agreement dated December 1, 1993 between Custom Pharmaceuticals and Promix Laboratories, Divisions of Patheon, and The Cadillac Fairview Corporation Limited in respect of the Burlington Facility. | 10 | 2/25/2011 | 10.10 | |
| 10.14 | Lease Renewal Agreement dated April 10, 2004 between Patheon and Klaus Stephan Reeckmann in respect of the Burlington Facility. | 10 | 2/25/2011 | 10.11 | |
| 10.15 | 2011 Amended and Restated Incentive Stock Option Plan.* | 10-Q | 9/9/2011 | 10.2 | |
| 10.16 | Form of Stock Option Agreement under the Incentive Stock Option Plan for certain awards granted on or before March 17, 2010. * | 10 | 2/25/2011 | 10.13 | |
| 10.17 | Form of Stock Option Agreement under the Incentive Stock Option Plan for certain awards granted on or after March 17, 2010. * | 10 | 2/25/2011 | 10.14 | |
| 10.18 | Amended and Restated Restricted Share Unit Plan of Patheon dated September 4, 2008 (the "Restricted Share Unit Plan").* | 10 | 2/25/2011 | 10.15 | |
| 10.19 | "Performance Share Unit Plan of Patheon dated December 13, 2007 (the "Performance Share Unit Plan").* | 10 | 2/25/2011 | 10.16 | | |
| 10.20 | Form of Performance Share Unit Grant Agreement under the Performance Share Unit Plan.* | 10 | 2/25/2011 | 10.17 | | |
| 10.21 | Directors Deferred Share Unit Plan of Patheon dated February 22, 2008, as amended March 27, 2008.* | 10 | 2/25/2011 | 10.18 | | |
| 10.22 | Description of Compensation for Non-Employee Directors of Patheon.* | 10 | 2/25/2011 | 10.19 | | |
| 10.23 | Deferred Compensation Plan of Patheon dated January 1, 2003, as amended December 18, 2008.* | 10 | 2/25/2011 | 10.20 | | |
| 10.24 | The Patheon Global Bonus Plan effective December 15, 2011.*
| 10-Q | 6/13/2012 | 10.1 | | |
| 10.25 | The Patheon Global Bonus Plan effective December 13, 2012.*
| | | | X | |
| 10.26 | Employment Agreement between Patheon Pharmaceuticals Services Inc. and James C. Mullen effective February 7, 2011.* | 10 | 2/25/2011 | 10.21 | | |
| 10.27 | Amended and Restated Employment Agreement dated April 25, 2011 between Patheon Pharmaceuticals Services Inc. and James C. Mullen effective February 7, 2011.* | 10-Q | 6/10/2011 | 10.2 | | |
| 10.28 | Employment Agreement between Patheon Pharmaceuticals Services Inc. and Eric W. Evans effective May 27, 2008.* | 10 | 2/25/2011 | 10.26 | | |
| 10.29 | Severance and General Release Agreement between Patheon Pharmaceuticals Services Inc. and Eric Evans dated November 1, 2011.* | 10-K | 12/19/2011 | 10.31 | | |
| 10.30 | Employment Agreement between Patheon Pharmaceuticals Services Inc. and Harry R. Gill, III dated May 10, 2010.*
| | | | X | |
| 10.31 | Amendment, dated September 11, 2012, to Employment Agreement between Patheon Pharmaceuticals Services Inc. and Harry R. Gill, III dated May 10, 2010.*
| | | | X | |
| 10.32 | Summary of Key Terms of the Employment Arrangement between Patheon Pharmaceuticals Services Inc. and Mark J. Kontny dated March 17, 2010.* | 10 | 2/25/2011 | 10.28 | | |
| 10.33 | Employment Agreement between Patheon Pharmaceuticals Services Inc. and Paul M. Garofolo dated May 12, 2008.* | 10 | 2/25/2011 | 10.33 | | |
| 10.34 | First Amendment, dated November 23, 2008, to Employment Agreement between Patheon Pharmaceuticals Services Inc. and Paul M. Garofolo dated May 12, 2008.* | 10 | 2/25/2011 | 10.34 | | |
| 10.35 | Second Amendment, dated August 1, 2011, to Employment Agreement between Patheon Pharmaceuticals Services Inc. and Paul M. Garofolo dated May 12, 2008.* | 10-K | 12/19/2011 | 10.40 | | |
| 10.36 | Employment Agreement between Patheon Pharmaceuticals Services Inc. and Geoffrey M. Glass dated March 17, 2009.* | 10 | 2/25/2011 | 10.35 | | |
| 10.37 | Addendum, effective October 1, 2009, to Employment Agreement between Patheon Pharmaceuticals Services Inc. and Geoffrey M. Glass dated March 17, 2009.* | 10 | 2/25/2011 | 10.36 | | |
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
| 10.38 | Employment Agreement between Patheon Pharmaceuticals Services Inc. and Stuart Grant effective January 27, 2012.* | 10-Q | 6/13/2012 | 10.2 | | |
| 10.39 | Employment Agreement between Patheon Pharmaceuticals Services Inc. and Michael E. Lytton effective May 9, 2011.*
| 10-Q | 9/9/2011 | 10.3 | | |
| 10.40 | Employment Agreement between Patheon Italia S.p.A. and Antonella Mancuso dated September 3, 2001.*
| 10 | 2/25/2011 | 10.41 | | |
| 10.41 | Amendment, dated January 26, 2012, to Employment Agreement between Patheon Italia S.p.A. and Antonella Mancuso dated September 3, 2001.* | 10-Q | 3/9/2012 | 10.3 | | |
| 10.42 | Employment Agreement between Rebecca Holland New and Patheon Pharmaceuticals Services Inc. dated August 15, 2011.*
| 10-K | 12/19/2011 | 10.49 | | |
| 10.43 | Form of Indemnification Agreement entered into between Patheon and each of Paul S. Levy and Derek J. Watchorn.* | 10 | 2/25/2011 | 10.42 | | |
| 21.1 | Subsidiaries of Patheon.
| | | | X | |
| 23.1 | Consent of Ernst & Young LLP.
| | | | X | |
| 31.1 | Certification by Chief Executive Officer pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as adopted pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002.
| | | | X | |
| 31.2 | Certification by Chief Financial Officer pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as adopted pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002.
| | | | X | |
| 32.1 | Certification by Chief Executive Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002.
| | | | X | |
| 32.2 | Certification by Chief Financial Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002.
| | | | X | |
| 101** | The following materials from Patheon's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended October 31, 2012, formatted in XBRL (Extensible Business Reporting Language): (i) the Consolidated Balance Sheets, (ii) the Consolidated Statements of Operations, (iii) the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows, (iv) the Consolidated Statements of Changes in Shareholders' Equity and (iv) the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. | | | | | | | | X | |
__________________
+ Pursuant to Regulation S-K, Item 601(b)(2), certain schedules (or similar attachments) to this exhibit have not been filed herewith. A list of omitted schedules (or similar attachments) is included in the agreement. The Company agrees to furnish supplementally a copy of any such schedule (or similar attachment) to the Securities and Exchange Commission upon request; provided, however, that the Company may request confidential treatment of omitted items.
* Represents a management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement.
** Pursuant to Rule 406T of Regulation S-T, the Interactive Data Files in Exhibit 101 hereto are deemed not filed or part of a registration statement or prospectus for purposes of Sections 11 or 12 of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, are deemed not filed for purposes of Section 18 of the Securities and Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, and otherwise are not subject to liability under those sections.
 Note: API: Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient
Note: API: Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient