
Enabling oral drug delivery to improve patient compliance October 2018 Corporate Presentation Exhibit 99.1

Forward - Looking Statements This presentation contains forward - looking statements about Lipocine Inc. (the “Company”). These forward - looking statements are made pursuant to the safe harbor provisions of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. These forward - looking statement s relate to the Company’s product candidates, the expected timing of the FDA review process related to our resubmitted NDA for TLANDO™, clini cal and regulatory processes and objectives, potential benefits of the Company’s product candidates, intellectual property and relate d m atters, all of which involve known and unknown risks and uncertainties. Actual results may differ materially from the forward - looking statemen ts discussed in this presentation . Accordingly, the Company cautions investors not to place undue reliance on the forward - looking statements contained in, or made in connection with, this presentation . Several factors may affect the initiation and completion of clinical trials, the potential advantages of the Company’s product candidates and the Company’s capital needs. Among other things, the projected commencement and completion of the Company’s clinical trials may be affected by difficulties or delays. We may encounter delays or other issues in the FDA appro val process, including that the FDA may determine there are deficiencies in our resubmitted NDA. We are also subject to risks related to t he possibility of an advisory committee meeting related to TLANDO™. In addition, the Company’s results may be affected by its ability to manage it s financial resources, difficulties or delays in developing manufacturing processes for its product candidates, preclinical and toxicolog y t esting and regulatory developments. Delays in clinical programs, whether caused by competitive developments, adverse events, patient en rol lment rates, regulatory issues or other factors, could adversely affect the Company’s financial position and prospects. Prior clin ica l trial program designs and results are not necessarily predictive of future clinical trial designs or results. If the Company’s product can did ates do not meet safety or efficacy endpoints in clinical evaluations, they will not receive regulatory approval and the Company will not be a ble to market them. The Company may not be able to enter into any strategic partnership agreements. The Company’s commercial success depends on i ts ability to manufacture, market and sell products without infringing the proprietary rights of third parties. Operating expense and ca sh flow projections involve a high degree of uncertainty, including variances in future spending rates due to changes in corporate pr ior ities, the timing and outcomes of clinical trials, competitive developments and the impact on expenditures and available capital from licensing an d strategic collaboration opportunities. If the Company is unable to raise additional capital when required or on acceptable terms, it m ay have to significantly delay, scale back or discontinue one or more of its drug development or discovery research programs. The Compa ny is at an early stage of development and may not ever have any products that generate significant revenue. The forward - looking statements contained in this presentation are further qualified by the detailed discussion of risks and uncertainties set forth in the Company’s a nnu al report on Form 10 - K and other periodic reports filed by the Company with the Securities and Exchange Commission, all of which can be obtai ned on the Company’s website at www.lipocine.com or on the SEC website at www.sec.gov . The forward - looking statements contained in this document represent the Company’s estimates and assumptions only as of the date of this presentation and the Company undertakes no duty or obligation to update or revise publicly any forward - looking statements contained in this presentation as a result of new information, future events or changes in the Company’s expectations. 2

Men's Health Oral Testosterone Replacement Therapy (“TRT”) Oral Androgen Therapy for Fatty Liver Disease (“NAFLD”/ “NASH”) Women's Health Oral Therapy for Prevention of Preterm Birth (“PTB”) Proprietary Drug Delivery Platform Significant Unmet Need In Both Therapeutic Areas 3 Unique Specialty Pharmaceutical Company Advanced Pipeline
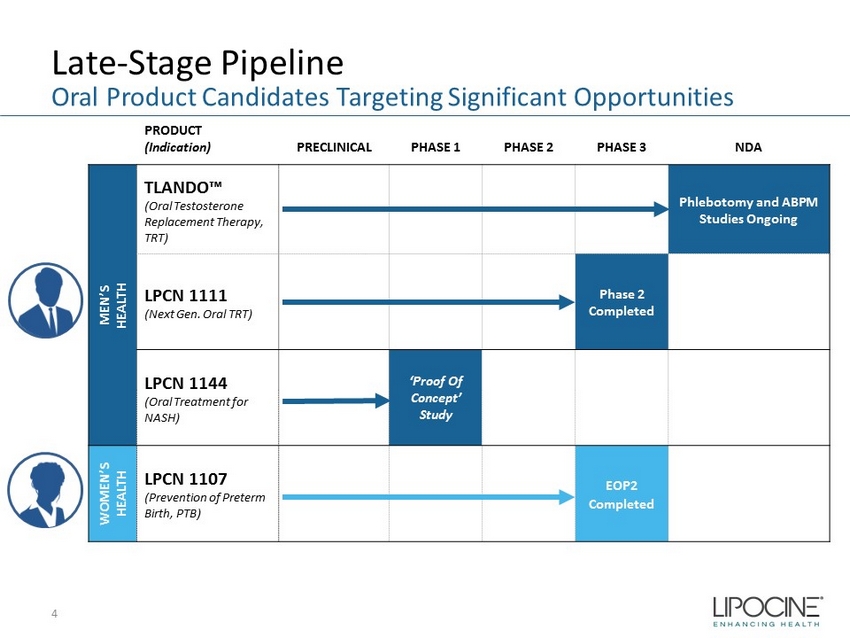
Late - Stage Pipeline 4 Oral Product Candidates Targeting Significant Opportunities PRODUCT (Indication) PRECLINICAL PHASE 1 PHASE 2 PHASE 3 NDA MEN’S HEALTH TLANDO™ (Oral Testosterone Replacement Therapy, TRT) Phlebotomy and ABPM Studies Ongoing LPCN 1111 (Next Gen. Oral TRT) Phase 2 Completed LPCN 1144 (Oral Treatment for NASH) ‘Proof Of Concept’ Study WOMEN’S HEALTH LPCN 1107 (Prevention of Preterm Birth, PTB) EOP2 Completed

5

2018 2017 2016 2014 2015 350 375 400 425 450 475 500 525 550 575 600 625 650 Sep 14 Nov 14 Jan 15 Mar 15 May 15 Jul 15 Sep 15 Nov 15 Jan 16 Mar 16 May 16 Jul 16 Sep 16 Nov 16 Jan 17 Mar 17 May 17 Jul 17 Sept 17 Nov 17 Jan 18 Mar 18 May 18 Jul 18 Monthly TRx (000s) FDA Label Guidance Monthly TRT TRx Trend 6 TRT Market is Growing 2017 Gross Annual Sales - $1.7B Annual estimates of 7.2 million TRx Source: IMS database TRx = Total prescriptions
Issues with Current Non - oral TRT Options • Black Box Warning – Secondary exposure to testosterone – Pulmonary oil micro embolism (POME) and anaphylaxis shock • Inconvenient application or painful injection • Poor persistence reflects need for oral – Average days on therapy is 100 days • More than 50% of patients need dosage adjustment – Burdensome for patients due to multiple doctor visits Potential Barrier To Newly Diagnosed and Existing Patients 7

TLANDO™: Path Forward for Resubmission Confirmed Next Steps in Bring Tlando to Patients Deficiencies and Plan for Resolution Determine extent, if any, of ex vivo conversion of TU to T Obtain definitive evidence pre - approval via ambulatory blood pressure monitoring study to exclude whether TLANDO causes clinically meaningful increase in blood pressure 8 • Definitive Phlebotomy study results expected by end of 4Q 2018 • ABPM Study (N=135, 4 month treatment) initiated based on FDA protocol feedback • ABPM study projected for completion in 1Q 2019 Provide justification for non - applicability of Cmax based secondary endpoints Determine the appropriate stopping criteria that can be reproducibly and accurately identify patients who should discontinue use of TLANDO • Additional analyses of existing data for resubmission • Additional analyses of existing data for resubmission

9

LPCN 1144: Well Positioned for Success Differentiated Mechanism of Action and Well Tolerated Safety Profile ▪ Targeted for NASH Epidemic with No Approved Product – The NASH market could peak at $30 - 40 billion by 2025 1 ▪ Unique Mechanism Targeting Full Spectrum of NASH Pathogenesis + Collateral Health Benefits – Testosterone deficiency induces NAFLD/NASH – Testosterone treatment improves liver functions ▪ Well Tolerated Safety Profile – Prodrug of a bio - identical hormone – Demonstrated with 591 subjects in 12 studies with up to 52 week exposure ▪ Compelling Clinical Biomarker Data – Significant reductions in both the key ALT and TG serum NASH biomarkers – Good potential of histological improvement in NASH and Fibrosis 1. Deutsche Bank industry report, “NASH – the next big global epidemic in 10 years?”, 2014 10
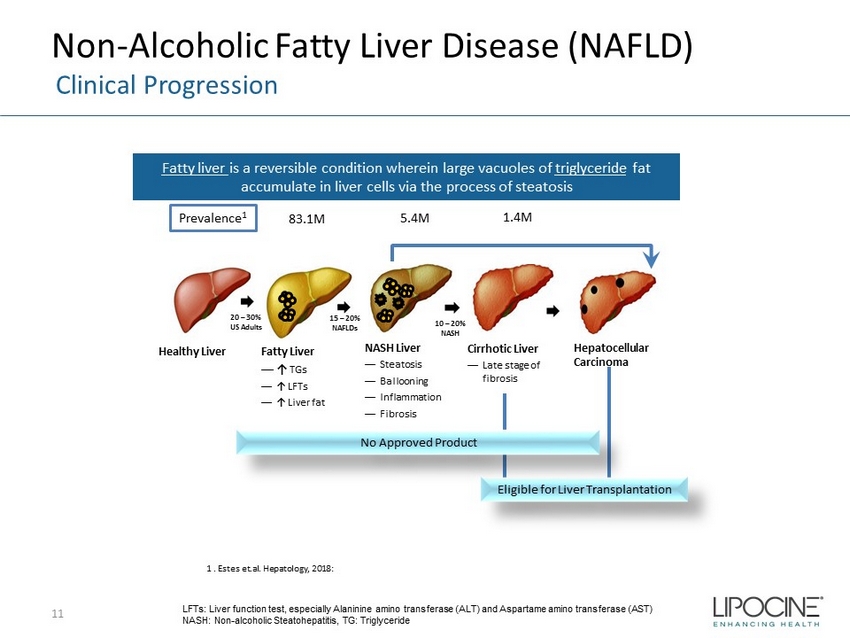
Non - Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Clinical Progression 11 Fatty liver is a reversible condition wherein large vacuoles of triglyceride fat accumulate in liver cells via the process of steatosis LFTs: Liver function test, especially Alaninine amino transferase (ALT) and Aspartame amino transferase (AST) NASH: Non - alcoholic Steatohepatitis, TG: Triglyceride Healthy Liver Fatty Liver — ↑ TGs — ↑ LFTs — ↑ Liver fat NASH Liver — Steatosis — Ballooning — Inflammation — Fibrosis Cirrhotic Liver — Late stage of fibrosis Hepatocellular Carcinoma Eligible for Liver Transplantation 20 – 30% US Adults 15 – 20% NAFLDs 10 – 20% NASH No Approved Product 83.1M 5.4M 1.4M Prevalence 1 1 . Estes et.al. Hepatology, 2018:
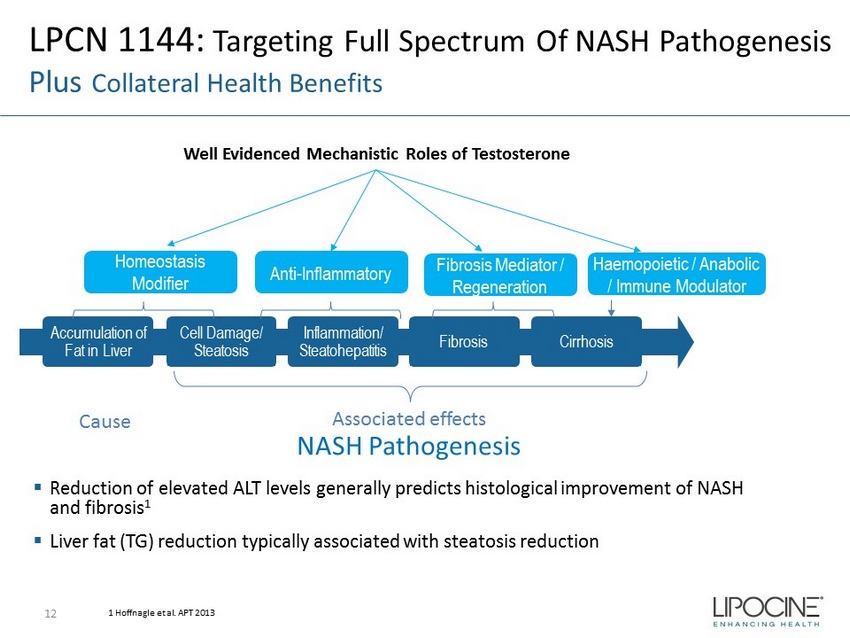
Accumulation of Fat in Liver Cell Damage/ Steatosis Inflammation/ Steatohepatitis Fibrosis Cirrhosis Homeostasis Modifier Anti - Inflammatory Fibrosis Mediator / Regeneration LPCN 1144: Targeting Full Spectrum Of NASH Pathogenesis Plus Collateral Health Benefits ▪ Reduction of elevated ALT levels generally predicts histological improvement of NASH and fibrosis 1 ▪ Liver fat (TG) reduction typically associated with steatosis reduction Haemopoietic / Anabolic / Immune Modulator 1 Hoffnagle et al. APT 2013 Well Evidenced Mechanistic Roles of Testosterone Associated effects Cause NASH Pathogenesis 12
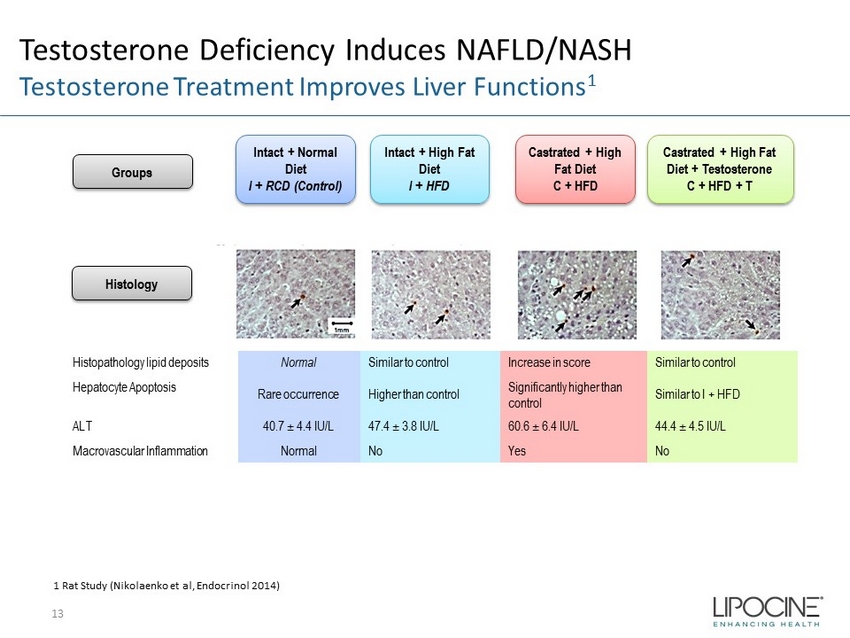
Testosterone Deficiency Induces NAFLD/NASH Testosterone Treatment Improves Liver Functions 1 13 Intact + Normal Diet I + RCD (Control) Intact + High Fat Diet I + HFD Castrated + High Fat Diet C + HFD Castrated + High Fat Diet + Testosterone C + HFD + T 1 Rat Study ( Nikolaenko et al, Endocrinol 2014) Histology Groups Histopathology lipid deposits Normal Similar to control Increase in score Similar to control Hepatocyte Apoptosis Rare occurrence Higher than control Significantly higher than control Similar to I + HFD ALT 40.7 ± 4.4 IU/L 47.4 ± 3.8 IU/L 60.6 ± 6.4 IU/L 44.4 ± 4.5 IU/L Macrovascular Inflammation Normal No Yes No
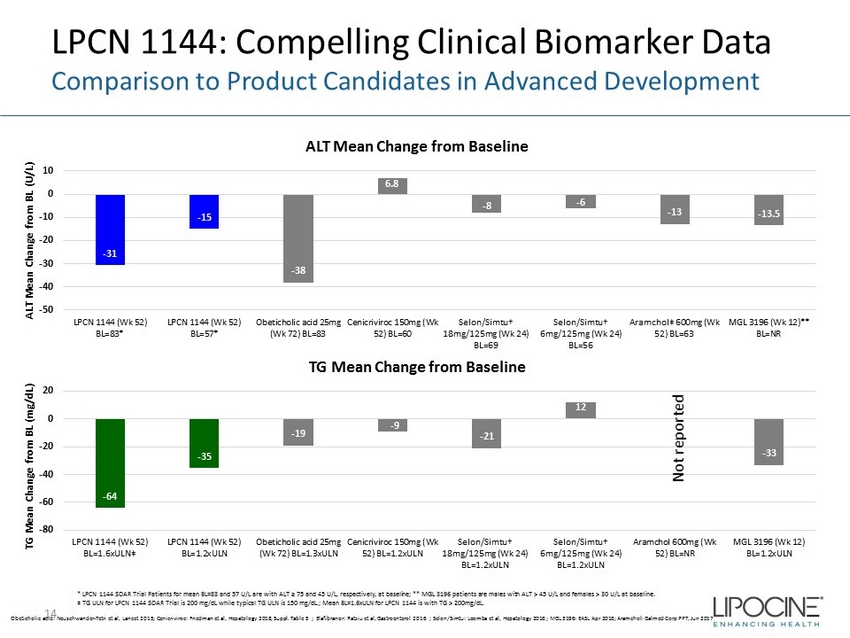
- 64 - 35 - 19 - 9 - 21 12 - 33 -80 -60 -40 -20 0 20 LPCN 1144 (Wk 52) BL=1.6xULN‡ LPCN 1144 (Wk 52) BL=1.2xULN Obeticholic acid 25mg (Wk 72) BL=1.3xULN Cenicriviroc 150mg (Wk 52) BL=1.2xULN Selon/Simtu† 18mg/125mg (Wk 24) BL=1.2xULN Selon/Simtu† 6mg/125mg (Wk 24) BL=1.2xULN Aramchol 600mg (Wk 52) BL=NR MGL 3196 (Wk 12) BL=1.2xULN TG Mean Change from BL (mg/dL) TG Mean Change from Baseline - 31 - 15 - 38 6.8 - 8 - 6 - 13 - 13.5 -50 -40 -30 -20 -10 0 10 LPCN 1144 (Wk 52) BL=83* LPCN 1144 (Wk 52) BL=57* Obeticholic acid 25mg (Wk 72) BL=83 Cenicriviroc 150mg (Wk 52) BL=60 Selon/Simtu† 18mg/125mg (Wk 24) BL=69 Selon/Simtu† 6mg/125mg (Wk 24) BL=56 Aramchol‡ 600mg (Wk 52) BL=63 MGL 3196 (Wk 12)** BL=NR ALT Mean Change from BL (U/L) ALT Mean Change from Baseline LPCN 1144: Compelling Clinical Biomarker Data Comparison to Product Candidates in Advanced Development * LPCN 1144 SOAR Trial Patients for mean BL=83 and 57 U/L are with ALT ≥ 75 and 45 U/L, respectively, at baseline; ** MGL 319 6 p atients are males with ALT > 45 U/L and females > 30 U/L at baseline. ‡ TG ULN for LPCN 1144 SOAR Trial is 200 mg/ dL while typical TG ULN is 150 mg/ dL .; Mean BL=1.6xULN for LPCN 1144 is with TG > 200mg/ dL . Obeticholic acid: Neuschwander - Tetri et al, Lancet 2015; Cenicriviroc : Friedman et al, Hepatology 2018, Suppl. Table 5 ; Elafibranor : Ratziu et al, Gastroenterol 2016 ; Selon / Simtu : Loomba et al, Hepatology 2018 ; MGL 3196: EASL Apr 2018; Aramchol : Galmed Corp PPT, Jun 2017 Not reported 14

15 † Total N is for patients with ALT > 40 U/L at baseline (ALT normal range is ≤ 40 U/L) 43% 48% 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% N = 42* N = 71* LPCN 1144 (Wk 52) Vitamin E (Wk 120) % of ALT Responders at EOS * ALT Responders: Patients with ALT > 40 U/L at baseline, ending with ≤ 40 U/L and more than 30% reduction at end of study post therapy † Total non - alcoholic fatty liver activity score (NAS), comprising the sum of scores for steatosis, inflammation, and ballooning cell injury ‡ Resolution of histological features that fulfil the criteria for diagnosis of NASH 1 Hoffnagle et al. APT 2013 2 Sanyal et al, New Eng J Med, 2010 Comparable LPCN1144 ALT response to Vitamin E in PIVENS Trial 2 † † LPCN 1144: Robust ALT Response Good Potential for Histological Improvement in NASH and Fibrosis 1

LPCN 1144: Oral Testosterone for the Treatment of NASH Summary and Next Steps ▪ Targeted for NASH epidemic with no currently approved product ▪ Unique mechanism targeting full spectrum of NASH pathogenesis + collateral health benefits ▪ Well tolerated safety profile ▪ Compelling clinical biomarker data ▪ Next Steps – In - vivo model Proof - Of - Concept (POC) study in biopsy - confirmed NASH – POC clinical study to assess liver fat changes via MRI - PDFF imaging in confirmed NAFLD/NASH patients 16

17 LPCN 1111 QD TLANDO

LPCN 1111: Next - Generation Oral TRT ▪ Novel prodrug of testosterone for oral delivery ▪ Once - daily potential expected to sustain and improve market share of oral T franchise ▪ Once - daily feasibility established in Phase 2a and 2b clinical trials – Single - daily oral dose provides T levels in eugonadal range ▪ Development status – Phase 2 study completed – FDA Guidance meeting for Phase 3 study design completed 18 Potential Once - Daily Dosing

19

LPCN 1107: Prevention of Preterm Birth (PTB) United States Market Landscape $1B Market Opportunity 3 December 31, 2017 Makena Net Revenue ($M) 4 Makena ® 1 50% Off Guidance 2 30% Compounded 17 - HPC 20% $334 $385 2016 2017 15% 1. Amag estimates Makena market share based on distributor dispensing data and all other market share based on physician market resea rc h data conducted by AMAG. 2. Off guidance represents patients treated outside of guidance of Society for Maternal Fetal Medicine, including patients tr eat ed with unapproved therapies and untreated patients. 3. Based on 140,000 patients, >16 injections/patient and net revenue of ~$425 - $450/injection. 4. AMAG SEC filings 20 2Q ‘18 sales $105 M
LPCN 1107 - Oral HPC ▪ Potential for superior efficacy with Phase 3 target dose ▪ No patient discomfort upon administration ▪ Steady state achieved in 7 days ▪ Orphan drug designation – Major contribution to patient care ▪ Next steps: – Explore partnering opportunities LPCN 1107: First Oral PTB Candidate 21 Addresses Unmet Need
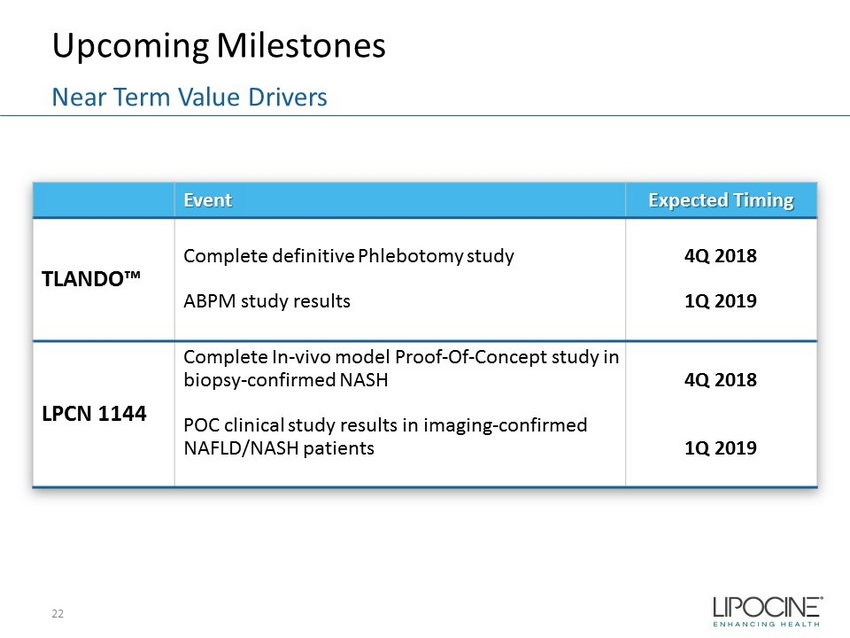
Upcoming Milestones 22 Near Term Value Drivers Event Expected Timing TLANDO™ Complete definitive Phlebotomy study ABPM study results 4Q 2018 1Q 2019 LPCN 1144 Complete In - vivo model Proof - Of - Concept study in biopsy - confirmed NASH POC clinical study results in imaging - confirmed NAFLD/NASH patients 4Q 2018 1Q 2019
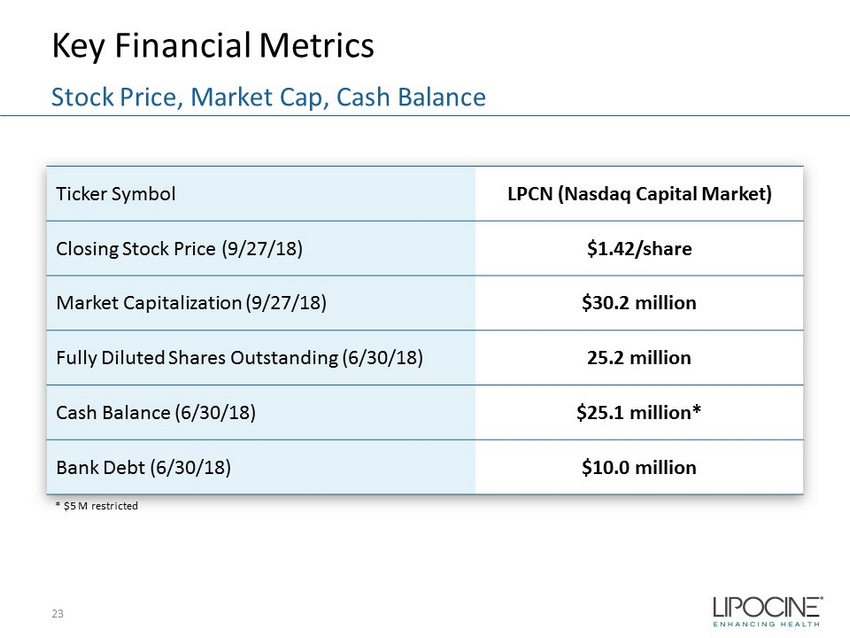
Key Financial Metrics 23 Stock Price, Market Cap, Cash Balance Ticker Symbol LPCN (Nasdaq Capital Market) Closing Stock Price (9/27/18) $1.42/share Market Capitalization (9/27/18) $30.2 million Fully Diluted Shares Outstanding (6/30/18) 25.2 million Cash Balance (6/30/18) $25.1 million* Bank Debt (6/30/18) $10.0 million * $5 M restricted
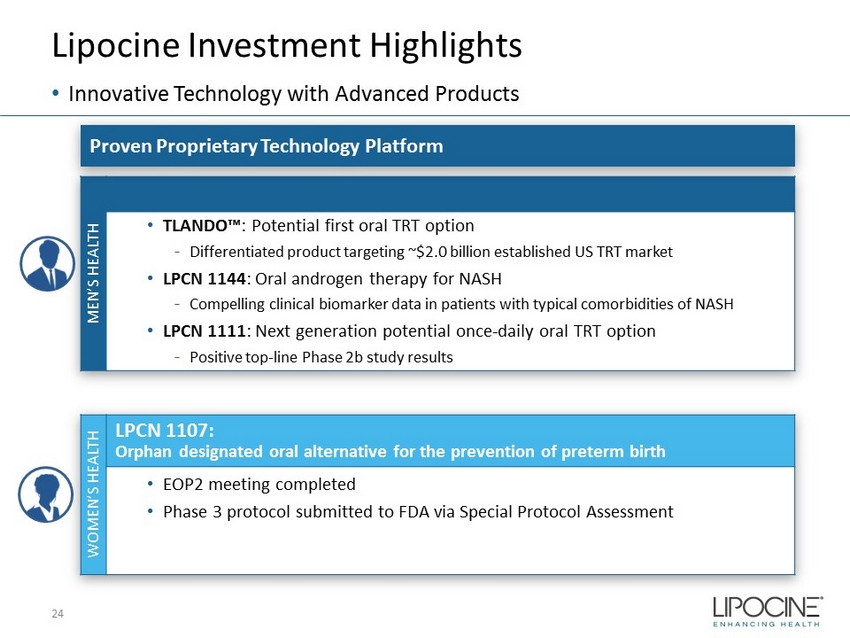
MEN’S HEALTH • TLANDO™ : Potential first oral TRT option - Differentiated product targeting ~$2.0 billion established US TRT market • LPCN 1144 : Oral androgen therapy for NASH - Compelling clinical biomarker data in patients with typical comorbidities of NASH • LPCN 1111 : Next generation potential once - daily oral TRT option - Positive top - line Phase 2b study results WOMEN’S HEALTH LPCN 1107: Orphan designated oral alternative for the prevention of preterm birth • EOP2 meeting completed • Phase 3 protocol submitted to FDA via Special Protocol Assessment Lipocine Investment Highlights 24 • Innovative Technology with Advanced Products Proven Proprietary Technology Platform

25

26
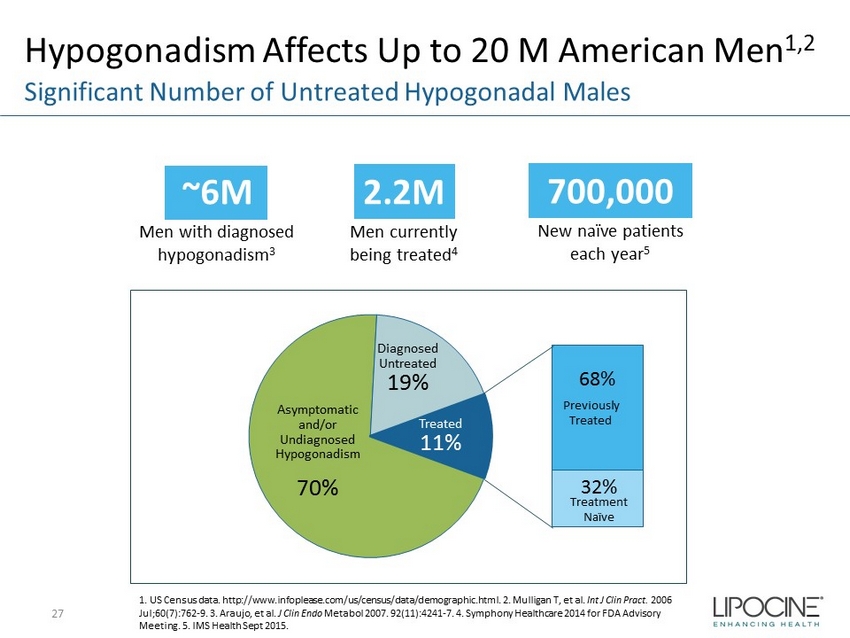
Hypogonadism Affects Up to 20 M American Men 1,2 27 Significant Number of Untreated Hypogonadal Males ~6M Men with diagnosed hypogonadism 3 2.2M Men currently being treated 4 700,000 New naïve patients each year 5 1. US Census data. http://www.infoplease.com/us/census/data/demographic.html. 2. Mulligan T, et al. Int J Clin Pract . 2006 Jul;60(7):762 - 9. 3. Araujo, et al. J Clin Endo Metabol 2007. 92(11):4241 - 7. 4. Symphony Healthcare 2014 for FDA Advisory Meeting. 5. IMS Health Sept 2015. Asymptomatic and/or Undiagnosed Hypogonadism 70% Diagnosed Untreated 19% 68% 32% Treated 11% Previously Treated Treatment Naïve
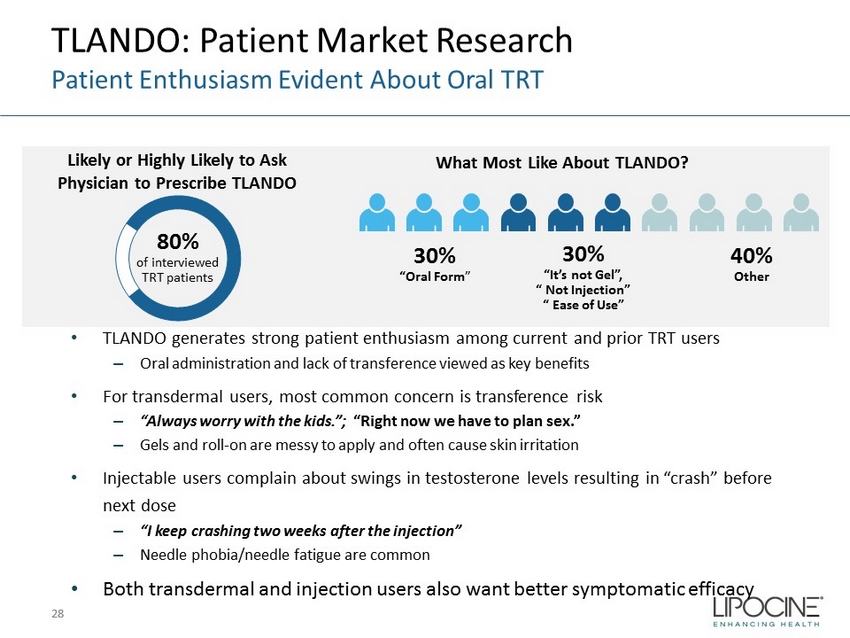
TLANDO: Patient Market Research Patient Enthusiasm Evident About Oral TRT 28 28 80% of interviewed TRT patients 30% 30% “Oral Form ” 30% “It’s not Gel”, “ Not Injection” “ Ease of Use” Likely or Highly Likely to Ask Physician to Prescribe TLANDO What Most Like About TLANDO? Other • TLANDO generates strong patient enthusiasm among current and prior TRT users – Oral administration and lack of transference viewed as key benefits • For transdermal users, most common concern is transference risk – “Always worry with the kids.”; “Right now we have to plan sex.” – Gels and roll - on are messy to apply and often cause skin irritation • Injectable users complain about swings in testosterone levels resulting in “crash” before next dose – “I keep crashing two weeks after the injection” – Needle phobia/needle fatigue are common • Both transdermal and injection users also want better symptomatic efficacy 40% Other
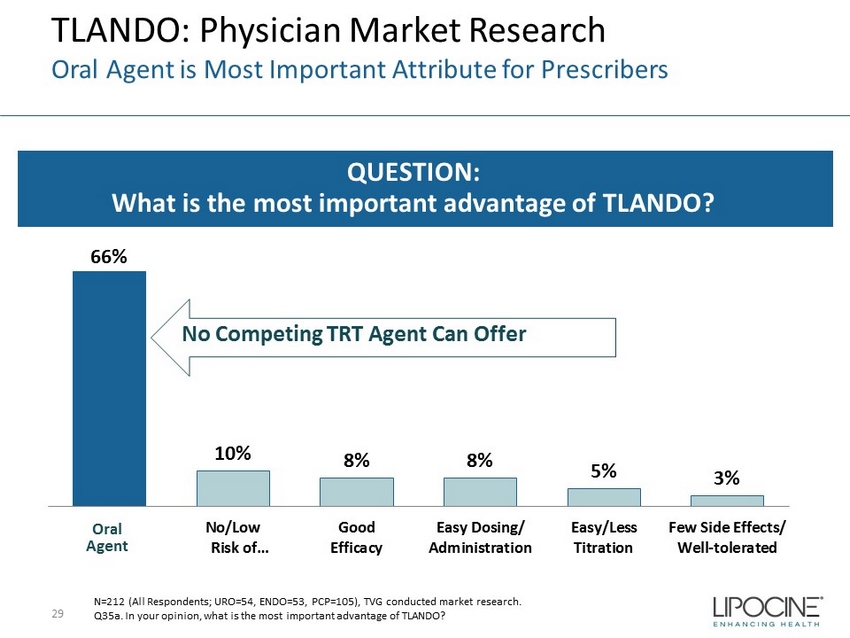
TLANDO: Physician Market Research Oral Agent is Most Important Attribute for Prescribers 29 QUESTION: What is the most important advantage of TLANDO? 66% 10% 8% 8% 5% 3% No/Low Risk of… Good Efficacy Easy Dosing/ Administration Easy/Less Titration Few Side Effects/ Well-tolerated N=212 (All Respondents; URO=54, ENDO=53, PCP=105), TVG conducted market research. Q35a. In your opinion, what is the most important advantage of TLANDO? Oral Agent No Competing TRT Agent Can Offer

-4 -3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 Mean SPB Change (mmHg) 13-001 TLANDO Week 3 (n=193) 13-001 TLANDO Week 7 (n=182) 13-001 TLANDO Week 13 (n=157) 13-001 TLANDO Week 26 (n=144) 13-001 TLANDO Week 39 (n=138) 13-001 TLANDO Week 52 (n=130) 13-001 TLANDO Overall (n=944) TLANDO™ SOAR Study Blood Pressure Data Systolic Clinic BP Measurement - Change From Baseline True mean difference of - 0.62 Meaningful BP change based on Jatenzo BRUDAC briefing document Minimal change in BP from baseline at each visit throughout the SOAR study 30

Oral TU: Dose - Systolic BP Relationship Differences Between Single/Triplicate/ABPM Measurements Brand Mean Single SBP Mean Triplicate SBP Mean ABPM Daytime SBP Study / Dose D SBP from baseline Study / Dose D SBP from baseline Study / Dose D SBP from baseline JATENZO (High Dose) CLAR 09007 Day30 / Pre - titration 316mg BID 3.0 CLAR 15012 Day102 / mean 325mg BID 3.4 CLAR 15012 Day102 / mean 325mg BID 5.05 CLAR 09007 Day90 / mean 292mg BID 3.0 JATENZO (Low Dose) CLAR 12011 Day114 /post titration mean 241mg BID 0.1 CLAR 15012 Visit2 / pre - titration 237mg BID 0.2 TLANDO LPCN 13 - 001 Wk3 / pre - titration 225mg BID - 0.1 TLANDO LPCN 16 - 002 Day24 / Fixed 225mg BID - 0.5 LPCN 16 - 002 Day25 / Fixed 225mg BID 0.2 31
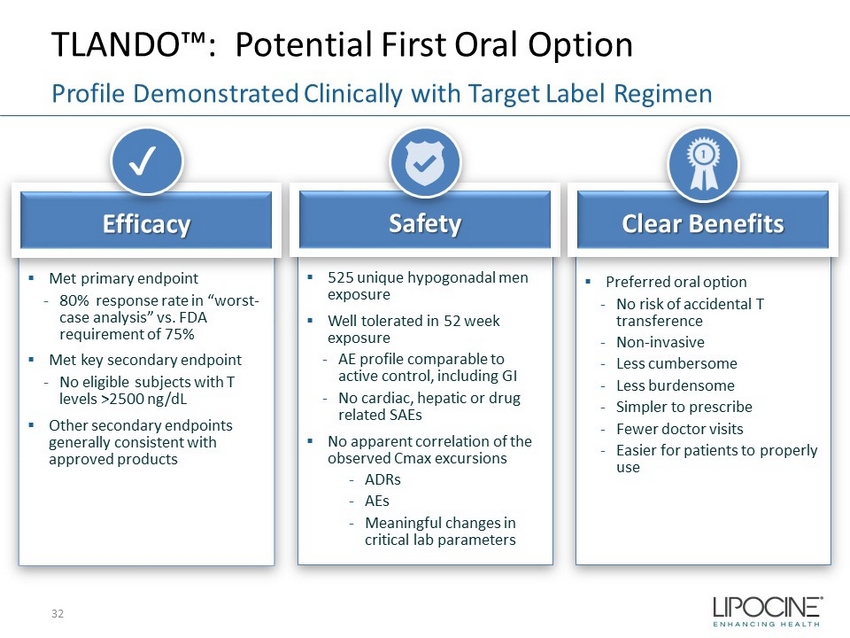
TLANDO™: Potential First Oral Option Profile Demonstrated Clinically with Target Label Regimen ▪ Met primary endpoint - 80% response rate in “worst - case analysis” vs. FDA requirement of 75% ▪ Met key secondary endpoint - No eligible subjects with T levels >2500 ng/ dL ▪ Other secondary endpoints generally consistent with approved products Efficacy ✔ ▪ 525 unique hypogonadal men exposure ▪ Well tolerated in 52 week exposure - AE profile comparable to active control, including GI - No cardiac, hepatic or drug related SAEs ▪ No apparent correlation of the observed Cmax excursions - ADRs - AEs - Meaningful changes in critical lab parameters Safety ▪ Preferred oral option - No risk of accidental T transference - Non - invasive - Less cumbersome - Less burdensome - Simpler to prescribe - Fewer doctor visits - Easier for patients to properly use Clear Benefits 32

33

High PTB Medical Costs • 12% of all US pregnancies 1 (475 - 500K) result in PTB (< 37 weeks) - a leading cause of neonatal mortality and morbidity • First year medical costs for PTB infants are ~ 10x higher than for full term infants 2 • 28% of preterm births are to women with histories of early delivery 34 ≥ $26 Billion Economic Impact 3 1. CDC (2010) 2. J. Maternal - Fetal and Neonatal Medicine, Dec. 2006, 19(12), 773 – 782 3 . Institute of Medicine of the National Academies. Jul.200
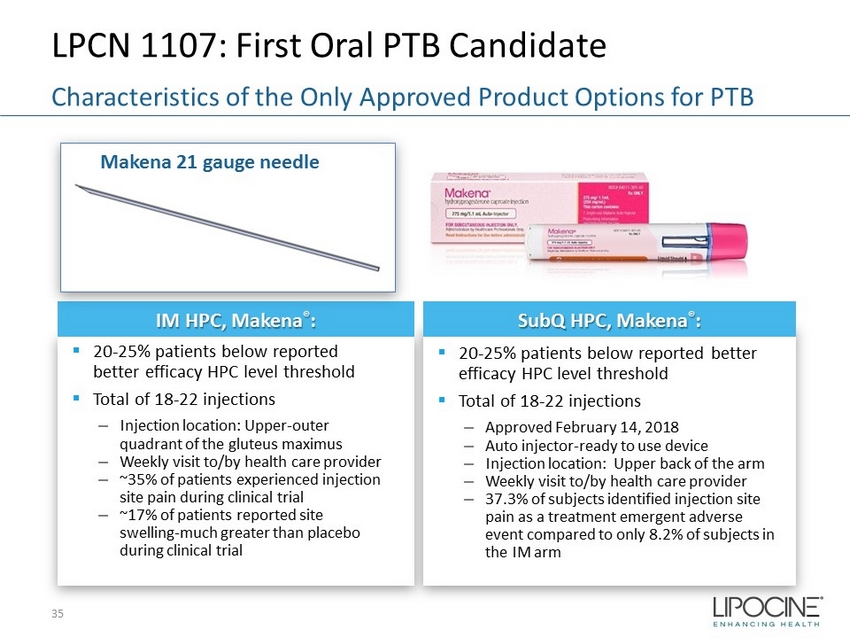
LPCN 1107: First Oral PTB Candidate 35 Characteristics of the Only Approved Product Options for PTB IM HPC, Makena ® : ▪ 20 - 25% patients below reported better efficacy HPC level threshold ▪ Total of 18 - 22 injections – Injection location: Upper - outer quadrant of the gluteus maximus – Weekly visit to/by health care provider – ~35% of patients experienced injection site pain during clinical trial – ~17% of patients reported site swelling - much greater than placebo during clinical trial Makena 21 gauge needle SubQ HPC, Makena ® : ▪ 20 - 25% patients below reported better efficacy HPC level threshold ▪ Total of 18 - 22 injections – Approved February 14, 2018 – Auto injector - ready to use device – Injection location: Upper back of the arm – Weekly visit to/by health care provider – 37.3% of subjects identified injection site pain as a treatment emergent adverse event compared to only 8.2% of subjects in the IM arm
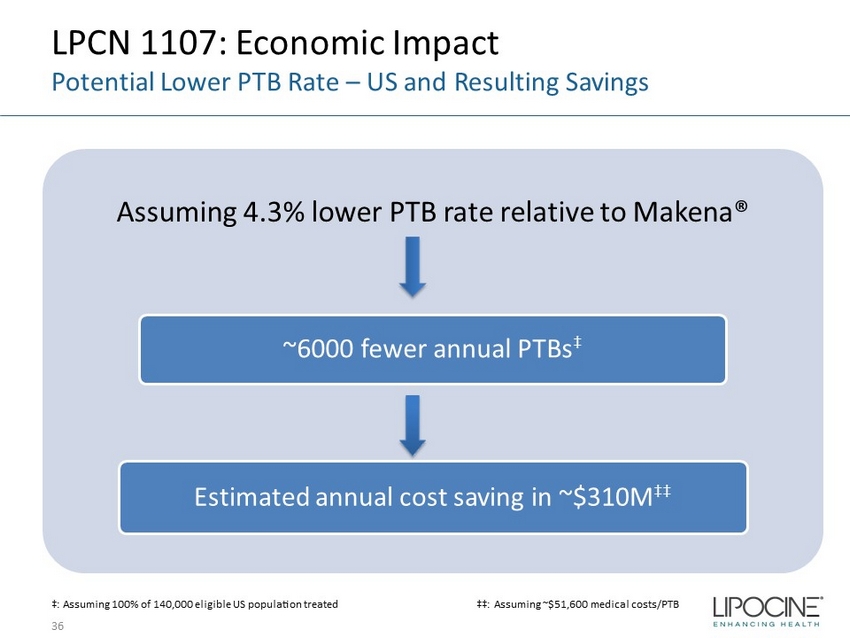
LPCN 1107: Economic Impact Potential Lower PTB Rate – US and Resulting Savings Assuming 4.3% lower PTB rate relative to Makena® ~6000 fewer annual PTBs ‡ Estimated annual cost saving in ~$310M ‡‡ 36 ‡: Assuming 100% of 140,000 eligible US population treated ‡‡: Assuming ~$51,600 medical costs/PTB
LPCN 1107: First Oral PTB Candidate First Oral HPC for Prevention of Recurrent PTB • Preferred route - of - administration is oral Strong Exclusivity Position • Orphan Drug Designation • Technology/IP protection Potential for Superior Efficacy • Fewer PTB babies with significant healthcare cost savings Strong Pharmaco - Economic Justification • Minimize travel related cost/time and healthcare provider cost/time • Premium pricing potential to generic IM injections 37 Commercial Outlook/Drivers
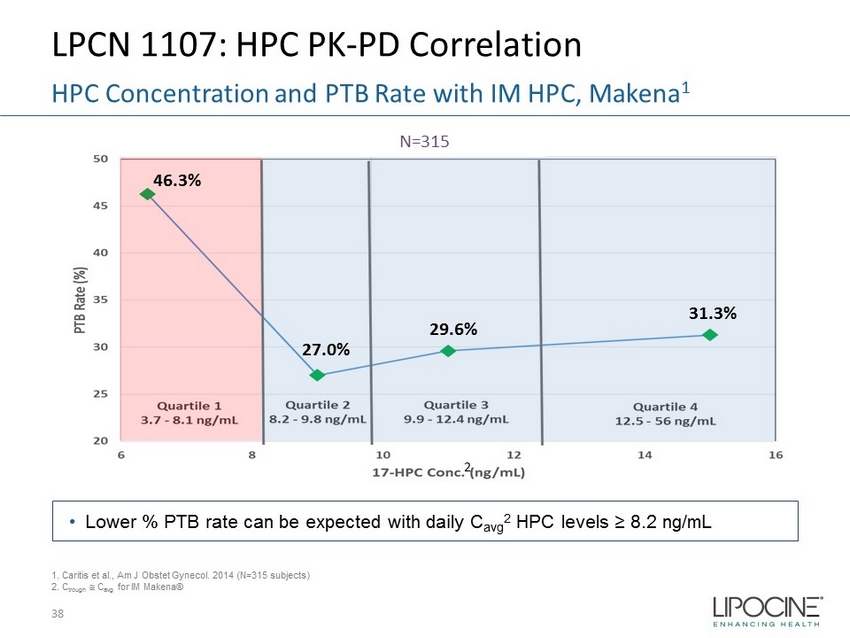
LPCN 1107: HPC PK - PD Correlation 38 HPC Concentration and PTB Rate with IM HPC, Makena 1 N=315 1. Caritis et al., Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2014 (N=315 subjects) 2. C trough C avg for IM Makena® • Lower % PTB rate can be expected with daily C avg 2 HPC levels ≥ 8.2 ng/mL 2 46.3% 27.0% 29.6% 31.3%
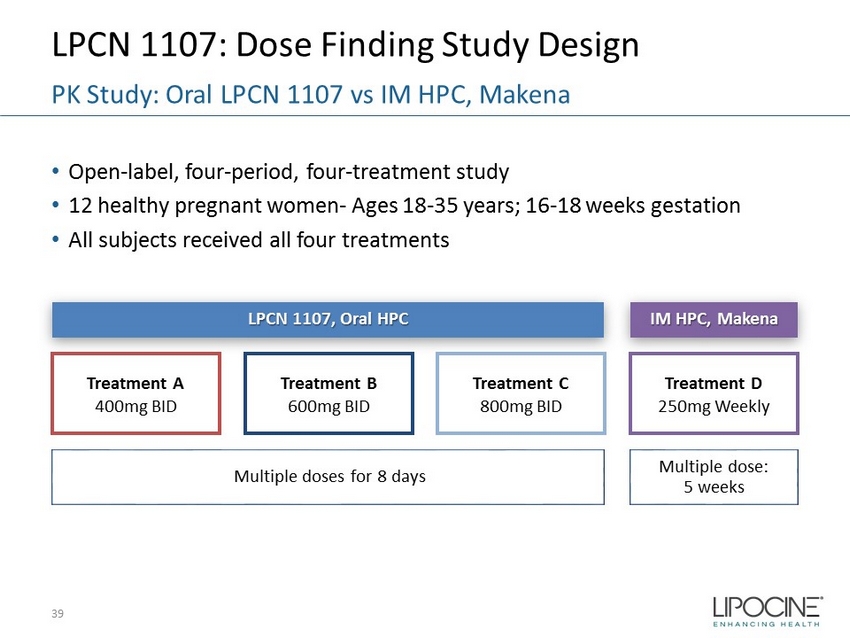
LPCN 1107: Dose Finding Study Design • Open - label, four - period, four - treatment study • 12 healthy pregnant women - Ages 18 - 35 years; 16 - 18 weeks gestation • All subjects received all four treatments 39 PK Study: Oral LPCN 1107 vs IM HPC, Makena Treatment D 250mg Weekly Treatment C 800mg BID Treatment B 600mg BID Treatment A 400mg BID IM HPC, Makena LPCN 1107, Oral HPC Multiple dose: 5 weeks Multiple doses for 8 days
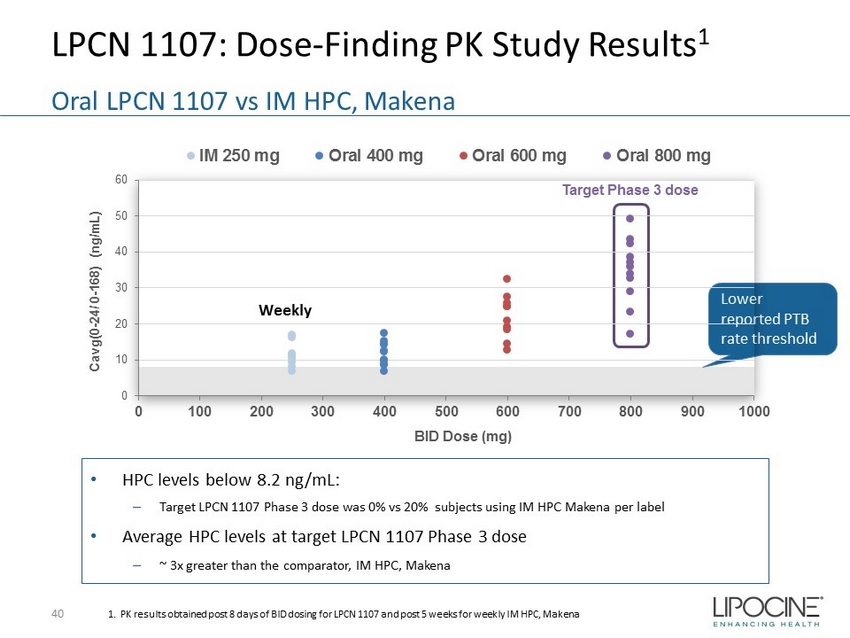
LPCN 1107: Dose - Finding PK Study Results 1 40 Oral LPCN 1107 vs IM HPC, Makena 1. PK results obtained post 8 days of BID dosing for LPCN 1107 and post 5 weeks for weekly IM HPC, Makena Lower reported PTB rate threshold • HPC levels below 8.2 ng/mL: – Target LPCN 1107 Phase 3 dose was 0% vs 20% subjects using IM HPC Makena per label • Average HPC levels at target LPCN 1107 Phase 3 dose – ~ 3x greater than the comparator, IM HPC, Makena Target Phase 3 dose 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000 Cavg(0 - 24/ 0 - 168) (ng/mL) BID Dose (mg) IM 250 mg Oral 400 mg Oral 600 mg Oral 800 mg Weekly
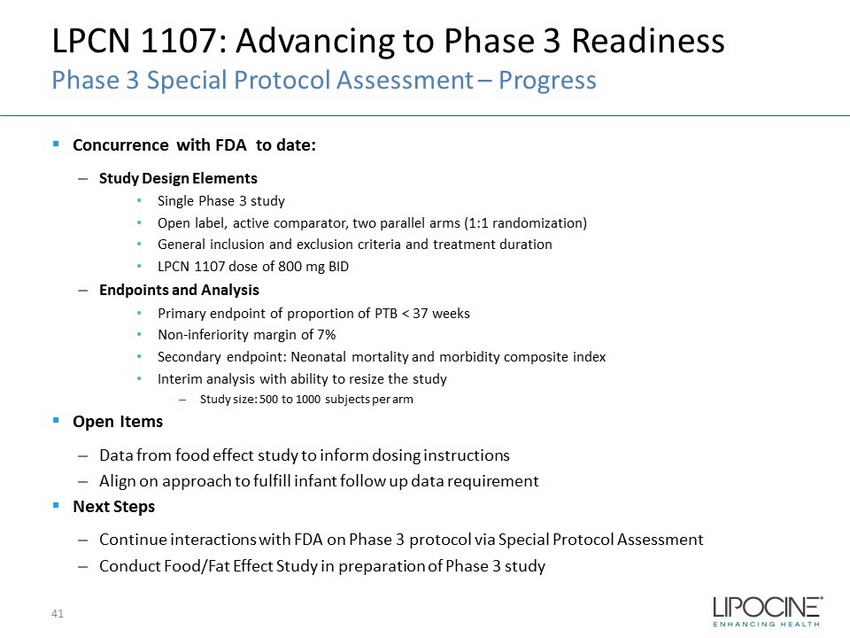
LPCN 1107: Advancing to Phase 3 Readiness Phase 3 Special Protocol Assessment – Progress ▪ Concurrence with FDA to date: – Study Design Elements • Single Phase 3 study • Open label, active comparator, two parallel arms (1:1 randomization) • General inclusion and exclusion criteria and treatment duration • LPCN 1107 dose of 800 mg BID – Endpoints and Analysis • Primary endpoint of proportion of PTB < 37 weeks • Non - inferiority margin of 7% • Secondary endpoint: Neonatal mortality and morbidity composite index • Interim analysis with ability to resize the study – Study size: 500 to 1000 subjects per arm ▪ Open Items – Data from food effect study to inform dosing instructions – Align on approach to fulfill infant follow up data requirement ▪ Next Steps – Continue interactions with FDA on Phase 3 protocol via Special Protocol Assessment – Conduct Food/Fat Effect Study in preparation of Phase 3 study 41

42
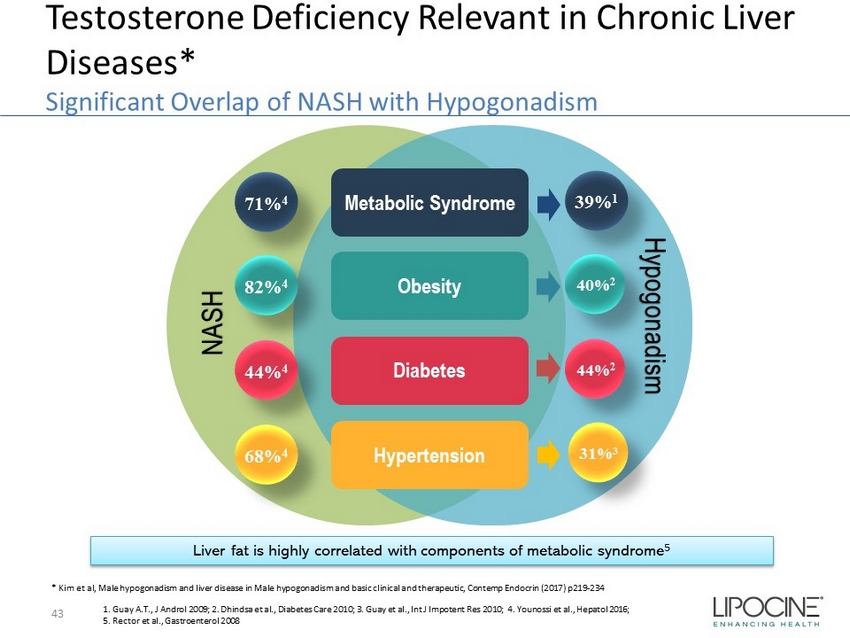
Testosterone Deficiency Relevant in Chronic Liver Diseases* Significant Overlap of NASH with Hypogonadism 43 1. Guay A.T., J Androl 2009; 2. Dhindsa et al., Diabetes Care 2010; 3. Guay et al., Int J Impotent Res 2010; 4. Younossi et al., Hepatol 2016; 5. Rector et al., Gastroenterol 2008 * Kim et al, Male hypogonadism and liver disease in Male hypogonadism and basic clinical and therapeutic, Contemp Endocrin (2017) p219 - 234 Metabolic Syndrome 82% 4 68% 4 44% 4 71% 4 Obesity Diabetes Hypertension 40% 2 31% 3 44% 2 39% 1 Hypogonadism NASH Liver fat is highly correlated with components of metabolic syndrome 5
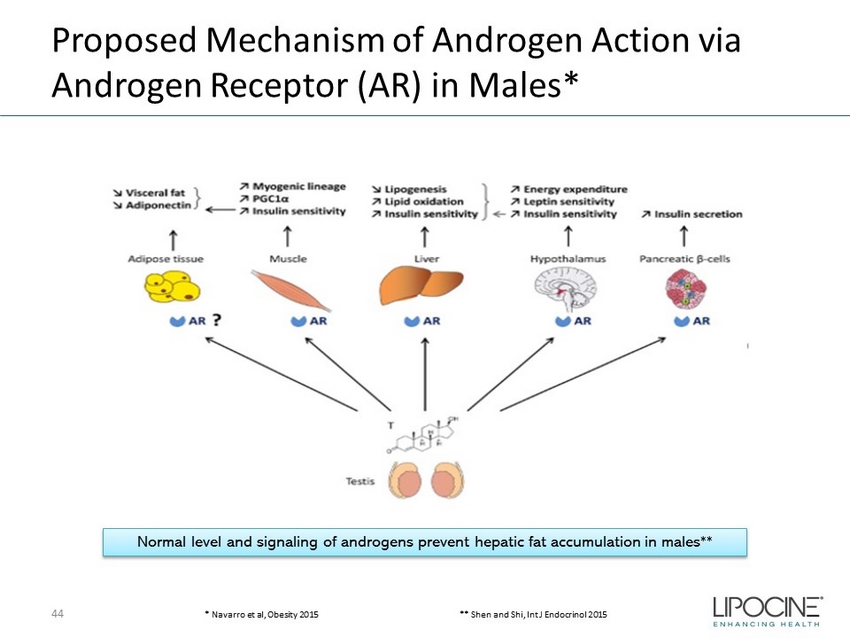
Proposed Mechanism of Androgen Action via Androgen Receptor (AR) in Males* 44 Normal level and signaling of androgens prevent hepatic fat accumulation in males** * Navarro et al, Obesity 2015 ** Shen and Shi, Int J Endocrinol 2015
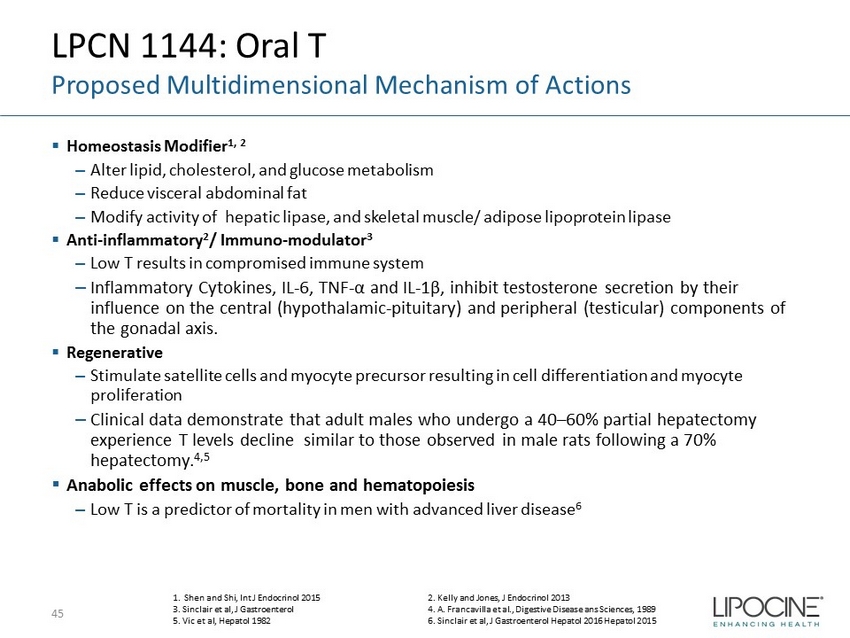
LPCN 1144: Oral T Proposed Multidimensional Mechanism of Actions ▪ Homeostasis Modifier 1, 2 ‒ Alter lipid, cholesterol, and glucose metabolism ‒ Reduce visceral abdominal fat ‒ Modify activity of hepatic lipase, and skeletal muscle/ adipose lipoprotein lipase ▪ Anti - inflammatory 2 / Immuno - modulator 3 ‒ Low T results in compromised immune system ‒ Inflammatory Cytokines, IL - 6, TNF - α and IL - 1β, inhibit testosterone secretion by their influence on the central (hypothalamic - pituitary) and peripheral (testicular) components of the gonadal axis. ▪ Regenerative ‒ Stimulate satellite cells and myocyte precursor resulting in cell differentiation and myocyte proliferation ‒ Clinical data demonstrate that adult males who undergo a 40 – 60% partial hepatectomy experience T levels decline similar to those observed in male rats following a 70% hepatectomy. 4,5 ▪ Anabolic effects on muscle, bone and hematopoiesis ‒ Low T is a predictor of mortality in men with advanced liver disease 6 45 1. Shen and Shi, Int J Endocrinol 2015 2. Kelly and Jones, J Endocrinol 2013 3. Sinclair et al, J Gastroenterol 4. A. Francavilla et al., Digestive Disease ans Sciences, 1989 5. Vic et al, Hepatol 1982 6. Sinclair et al, J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2016 Hepatol 2015

LPCN 1144: General Safety ▪ LPCN 1144 is a prodrug of bioidentical sex hormone – History of safe Ex - US Oral TU use for decades – 8,400 patients / 15,600 patient years of use of over 19 years • Data assures well - characterized safety with respect to prostate, hypertension, polycythemia and liver disease ▪ Extensive clinical safety database with LPCN 1144 – 591 subjects in 12 studies with up to 52 week exposure – Safety profile well - characterized and demonstrated no unexpected risks – Well tolerated with no adverse liver enzyme signals, no deaths or MACE events – No drug related SAEs 46

Comparison* of Advanced Candidates with Biopsy Results Phase 2 end points: ▪ At least 2 point reduction in NAFLD NAS: at least one point reduction either in lobular inflammation or hepatocellular ballooning with no worsening of fibrosis stage 47 Agent Primary target mechanism Reported Trial Results Patient Characteristics Serum TG reduction ALT Reduction Improvement in NASH Improvement in Fibrosis Elafibranor PPAR α δ agonist Homeostasis modifier Anti - inflammatory Fibrosis mediation GOLDEN NAS Score ~4.9 Fib score ~1.7 Robust mild Met NASH resolution Failed to achieve 1 point improvement AramChol SCD1 modulator Anti - steatogenic Anti - oxidant ARREST NAS Score ~5.3 Fib score 2.1 Only diabetics Not reported modest Met NASH resolution Failed to achieve 1 point improvement MGL - 3196 THR - β agonist Homeostasis modifier P2 NAS Score ~4.9 F0 - F1: 57% F2 - F3: 43% Robust modest Met NASH resolution Maybe Positive trend Obeticholic acid FXR agonist Anti - inflammatory antifibrotic Control Bile acid synthesis FLINT NAS Score ~5.3 Fib score ~1.9 mild Robust Improved NAS score >2 1 point improvement Selonsertib ASK1 inhibitor Anti - inflammatory antifibrotic Open label, No placebo NAS Score ~6 71% more than NAS>6 60 - 66% F3 negligible marginal Failed NASH resolution 1 point improvement Cenicriviroc CCR2/5 antagonist Anti - inflammatory antifibrotic CENTAUR NAS Score ~5.3 Fib score ~2.06 negligible negligible Failed NASH resolution Maybe Mixed results * From separate studies not “head to head” Phase 3 approvable regulatory end points: ▪ Complete resolution of NASH with no worsening of fibrosis a nd/or ▪ At least one point improvement in Fibrosis with no worsening of NASH
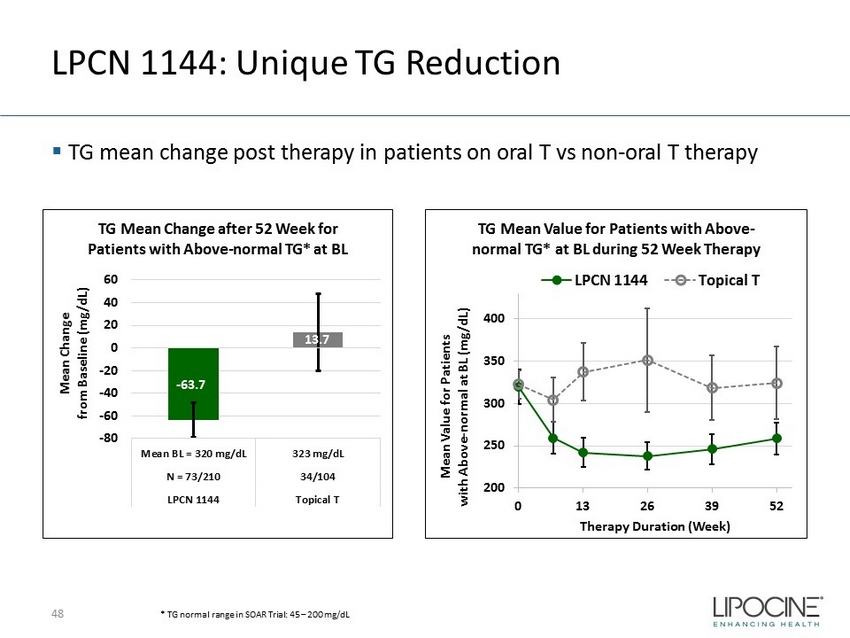
LPCN 1144: Unique TG Reduction ▪ TG mean change post therapy in patients on oral T vs non - oral T therapy 48 - 63.7 13.7 -80 -60 -40 -20 0 20 40 60 Mean BL = 320 mg/dL 323 mg/dL N = 73/210 34/104 LPCN 1144 Topical T Mean Change from Baseline (mg/ dL ) TG Mean Change after 52 Week for Patients with Above - normal TG* at BL 200 250 300 350 400 0 13 26 39 52 Mean Value for Patients with Above - normal at BL (mg/dL) Therapy Duration (Week) TG Mean Value for Patients with Above - normal TG* at BL during 52 Week Therapy LPCN 1144 Topical T * TG normal range in SOAR Trial: 45 – 200 mg/dL
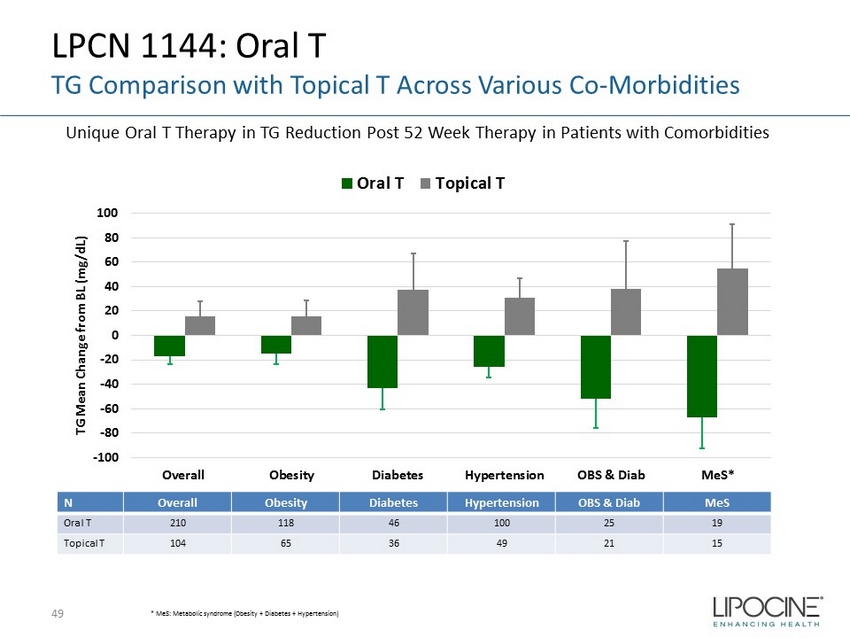
LPCN 1144: Oral T TG Comparison with Topical T Across Various Co - Morbidities 49 -100 -80 -60 -40 -20 0 20 40 60 80 100 Overall Obesity Diabetes Hypertension OBS & Diab MeS* TG Mean Change from BL (mg/dL) Oral T Topical T * MeS : Metabolic syndrome (Obesity + Diabetes + Hypertension) N Overall Obesity Diabetes Hypertension OBS & Diab MeS Oral T 210 118 46 100 25 19 Topical T 104 65 36 49 21 15 Unique Oral T Therapy in TG Reduction Post 52 Week Therapy in Patients with Comorbidities
















































