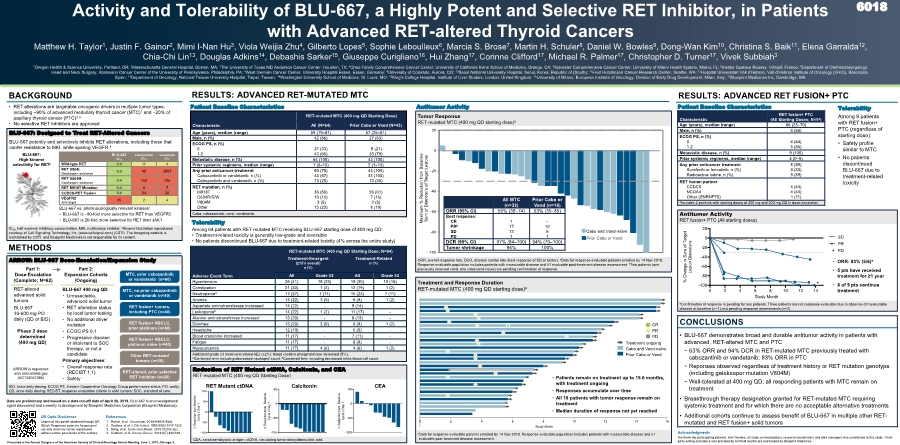
| 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 Study Month aData for response-evaluable patients enrolled by 14 Nov 2018. Response-evaluable population includes patients with measurable disease and ≥1 evaluable post-treatment disease assessment. Treatment and Response Duration RET-mutated MTC (400 mg QD starting dose)a -100 -80 -60 -40 -20 0 20 Maximum % Reduction from Baseline Sum of Diameters of Target Lesions Cabo or Vand-naïve Prior Cabo or Vand Cabo and Vand-naïve ORR, overall response rate, DCR, disease control rate (best response of SD or better). aData for response-evaluable patients enrolled by 14 Nov 2018. Response-evaluable population includes patients with measurable disease and ≥1 evaluable post-treatment disease assessment. bTwo patients (one previously received vand, one cabo/vand-naïve) are pending confirmation of response. CEA, carcinoembryonic antigen; ctDNA, circulating tumor deoxyribonucleic acid. Reduction of RET Mutant ctDNA, Calcitonin, and CEA RET-mutated MTC (400 mg QD Starting Dose) BLU-667 vs. pharmacologically relevant kinases: • BLU-667 is 90-fold more selective for RET than VEGFR2 • BLU-667 is 20-fold more selective for RET than JAK1 Tumor Response RET-mutated MTC (400 mg QD starting dose)a RESULTS: ADVANCED RET-MUTATED MTC METHODS Activity and Tolerability of BLU-667, a Highly Potent and Selective RET Inhibitor, in Patients with Advanced RET-altered Thyroid Cancers Matthew H. Taylor1, Justin F. Gainor2, Mimi I-Nan Hu3, Viola Weijia Zhu4, Gilberto Lopes5, Sophie Leboulleux6, Marcia S. Brose7, Martin H. Schuler8, Daniel W. Bowles9, Dong-Wan Kim10, Christina S. Baik11, Elena Garralda12, Chia-Chi Lin13, Douglas Adkins14, Debashis Sarker15, Giuseppe Curigliano16, Hui Zhang17, Corinne Clifford17, Michael R. Palmer17, Christopher D. Turner17, Vivek Subbiah3 1Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, OR; 2Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA; 3The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX; 4Chao Family Comprehensive Cancer Center, University of California Irvine School of Medicine, Orange, CA; 5Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center, University of Miami Health System, Miami, FL; 6Institut Gustave Roussy, Villejuif, France; 7Department of Otorhinolaryngology: Head and Neck Surgery, Abramson Cancer Center of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA; 8West German Cancer Center, University Hospital Essen, Essen, Germany; 9University of Colorado, Aurora, CO; 10Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea, Republic of (South); 11Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, Seattle, WA; 12Hospital Universitari Vall d’Hebron, Vall d’Hebron Institute of Oncology (VHIO), Barcelona, Spain; 13Department of Oncology, National Taiwan University Hospital, Taipei, Taiwan; 14Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, MO; 15King's College Hospital, Institute of Liver Studies, London, United Kingdom; 16University of Milano, European Institute of Oncology, Division of Early Drug Development, Milan, Italy; 17Blueprint Medicines Inc, Cambridge, MA BACKGROUND • RET alterations are targetable oncogenic drivers in multiple tumor types, including ~90% of advanced medullary thyroid cancer (MTC)1 and 20% of papillary thyroid cancer (PTC)2,3 • No selective RET inhibitors are approved BLU-667: High kinome selectivity for RETa BLU-667: Designed to Treat RET-Altered Cancers • BLU-667 was approximately 90-fold more selective for RET than VEGFR2 • BLU-667 was 20-fold more selective for RET than JAK1 Table presents IC50, half maximal inhibitory concentration Part 1: Dose-Escalation (Complete; N=62) RET-altered advanced solid tumors BLU-667 30-600 mg PO daily (QD or BID) Phase 2 dose determined (400 mg QD) BLU-667 400 mg QD • Unresectable, advanced solid tumor • RET alteration status by local tumor testing • No additional driver mutation • ECOG PS 0-1 • Progressive disease or intolerant to SOC therapy, or not a candidate Primary objectives: • Overall response rate (RECIST 1.1) • Safety Part 2: Expansion Cohorts (Ongoing) RET fusion+ NSCLC, prior platinum (n=80) RET fusion+ NSCLC, platinum naïve (n=40) MTC, prior cabozantinib or vandetanib (n=60) MTC, no prior cabozantinib or vandetanib (n=40) RET fusion+ tumors, including PTC (n=40) RET-altered, prior selective RET inhibitor (n=20) Other RET-mutated tumors (n=20) Antitumor Activity Characteristic RET fusion+ PTC (All Starting Doses; N=9a) Age (years), median (range) 66 (23–70) Male, n (%) 5 (56) ECOG PS, n (%) 0 1-2 4 (44) 5 (56) Metastatic disease, n (%) 9 (100) Prior systemic regimens, median (range) 2 (0–8) Any prior anticancer treatment Sorafenib or lenvatinib, n (%) Radioactive iodine, n (%) 8 (89) 3 (33) 8 (89) RET fusion partner CCDC6 NCOA4 Other (SNRNP70) 4 (44) 4 (44) 1 (11) aIncludes 2 patients with starting doses of 200 mg and 300 mg QD in dose-escalation. CONCLUSIONS • BLU-667 demonstrates broad and durable antitumor activity in patients with advanced, RET-altered MTC and PTC - 63% ORR and 94% DCR in RET-mutated MTC previously treated with cabozantinib or vandetanib; 83% ORR in PTC - Reponses observed regardless of treatment history or RET mutation genotype (including gatekeeper mutation V804M) - Well-tolerated at 400 mg QD; all responding patients with MTC remain on treatment • Breakthrough therapy designation granted for RET-mutated MTC requiring systemic treatment and for which there are no acceptable alternative treatments • Additional cohorts continue to assess benefit of BLU-667 in multiple other RET- mutated and RET fusion+ solid tumors BLU-667 IC50 Cabozantinib IC50 Vandetanib IC50 Wild-type RET 0.4 11 4 RET V804L Gatekeeper resistance 0.3 45 3597 RET V804M Gatekeeper resistance 0.4 162 726 RET M918T Mutation 0.4 8 7 CCDC6-RET Fusion 0.4 34 20 VEGFR2 Anti-target 35 2 4 BLU-667 potently and selectively inhibits RET alterations, including those that confer resistance to MKI, while sparing VEGFR.4 Patient Baseline Characteristics RESULTS: ADVANCED RET FUSION+ PTC Patient Baseline Characteristics Tolerability Among 9 patients with RET fusion+ PTC (regardless of starting dose): • Safety profile similar to MTC • No patients discontinued BLU-667 due to treatment-related toxicity Adverse Event Term RET-mutated MTC (400 mg QD Starting Dose; N=64) Treatment-Emergent (≥15% overall) n (%) Treatment-Related n (%) All Grade ≥3 All Grade ≥3 Hypertension 26 (41) 15 (23) 19 (30) 10 (16) Constipation 21 (33) 1 (2) 12 (19) 1 (2) Neutropeniaa 17 (27) 7 (11) 15 (23) 7 (11) Anemia 14 (22) 3 (5) 6 (9) 1 (2) Aspartate aminotransferase increased 14 (22) - 9 (14) - Leukopeniab 14 (22) 1 (2) 11 (17) - Alanine aminotransferase increased 13 (20) - 8 (13) - Diarrhea 13 (20) 3 (5) 6 (9) 1 (2) Headache 12 (19) - 5 (8) - Blood creatinine increased 11 (17) - 7 (11) - Fatigue 11 (17) - 6 (9) - Hypocalcemia 11 (17) 4 (6) 4 (6) 1 (2) Additional grade ≥3 treatment related AEs (≥2%): blood creatine phosphokinase increased (5%). aCombined term including decreased neutrophil count. bCombined term including decreased white blood cell count. Characteristic RET-mutated MTC (400 mg QD Starting Dose) All (N=64) Prior Cabo or Vand (N=43) Age (years), median (range) 59 (19–81) 57 (25–81) Male, n (%) 42 (66) 27 (63) ECOG PS, n (%) 0 1-2 21 (33) 43 (66) 9 (21) 33 (79) Metastatic disease, n (%) 64 (100) 43 (100) Prior systemic regimens, median (range) 1 (0–10) 2 (1–10) Any prior anticancer treatment Cabozantinib or vandetanib, n (%) Cabozantinib and vandetanib, n (%) 50 (78) 43 (67) 13 (20) 43 (100) 43 (100) 13 (30) RET mutation, n (%) M918T C634R/S/W V804M Other 36 (56) 10 (16) 3 (5) 15 (23) 26 (61) 7 (16) 2 (5) 8 (19) Cabo, cabozantinib; vand, vandetanib. 6018 IC50, half maximal inhibitory concentration, MKI, multikinase inhibitor. aKinome illustration reproduced courtesy of Cell Signaling Technology, Inc. (www.cellsignal.com) (CSTI). The foregoing website is maintained by CSTI, and Blueprint Medicines is not responsible for its content. ARROW: BLU-667 Dose-Escalation/Expansion Study Acknowledgments We thank the participating patients, their families, all study co-investigators, research coordinators and data managers who contributed to this study. Third- party writing assistance was provided by Ashfield Healthcare and funded by Blueprint Medicines. References 1. Romei, et al. Oncotarget, 2018;9:9875-9884. 2. Santoro, et al. J Clin Invest. 1992;89(5):1517-1522. 3. Song, et al. Endocrinol Metab. 2015;30:252-262. 4. Subbiah, et al. Cancer Discov. 2018;8(7):836-849. QR Code Disclaimer Copies of this poster obtained through QR (Quick Response) code are for personal use only and may not be reproduced without written permission of the authors. BID, twice daily dosing; ECOG PS, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status; PO, orally; QD, once daily dosing; RECIST, response evaluation criteria in solid tumors; SOC, standard of care. • ORR: 83% (5/6)a • 5 pts have received treatment for ≥1 year • 8 of 9 pts continue treatment aConfirmation of response is pending for two patients. Three patients are not response evaluable due to absence of measurable disease at baseline (n=1) and pending response assessments (n=2). Antitumor Activity RET fusion+ PTC (All starting doses) Tolerability Among 64 patients with RET-mutated MTC receiving BLU-667 starting dose of 400 mg QD: • Treatment-related toxicity is generally low-grade and reversible • No patients discontinued BLU-667 due to treatment-related toxicity (4% across the entire study) All MTC (n=32) Prior Cabo or Vand (n=16) ORR (95% CI) 56% (38–74) 63% (35–85) Best response: CR PRb SD PD 1 17 13 1 - 10 5 1 DCR (95% CI) 97% (84–100) 94% (70–100) Tumor shrinkage 94% 100% Treatment ongoing Cabo and Vand-naïve Prior Cabo or Vand CR PR PD Presented at the Annual Congress of the American Society of Clinical Oncology Annual Meeting, June 1, 2019, Chicago, IL 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 -100 -80 -60 -40 -20 0 20 Study Month % C h a n g e i n S u m o f T a r g e t L e s i o n D i a m e t e r s * SD PR PD • Patients remain on treatment up to 15.6 months, with treatment ongoing • Responses accumulate over time • All 18 patients with tumor response remain on treatment • Median duration of response not yet reached * Data are preliminary and based on a data cut-off date of April 28, 2019. BLU-667 is an investigational agent discovered and currently in development by Blueprint Medicines Corporation (Blueprint Medicines). ARROW is registered with clinicaltrials.gov (NCT03037385) * RET Mutant ctDNA Calcitonin CEA -100 -50 0 50 100 % R e d u c t i o n f r o m B a s e l i n e C y c l e 2 D a y 1 RET Mutant ctDNA -100 -50 0 50 % R e d u c t i o n f r o m B a s e l i n e C y c l e 2 D a y 1 Calcitonin -100 -50 0 50 % R e d u c t i o n f r o m B a s e l i n e C y c l e 2 D a y 1 CEA |
