Exhibit 99.3
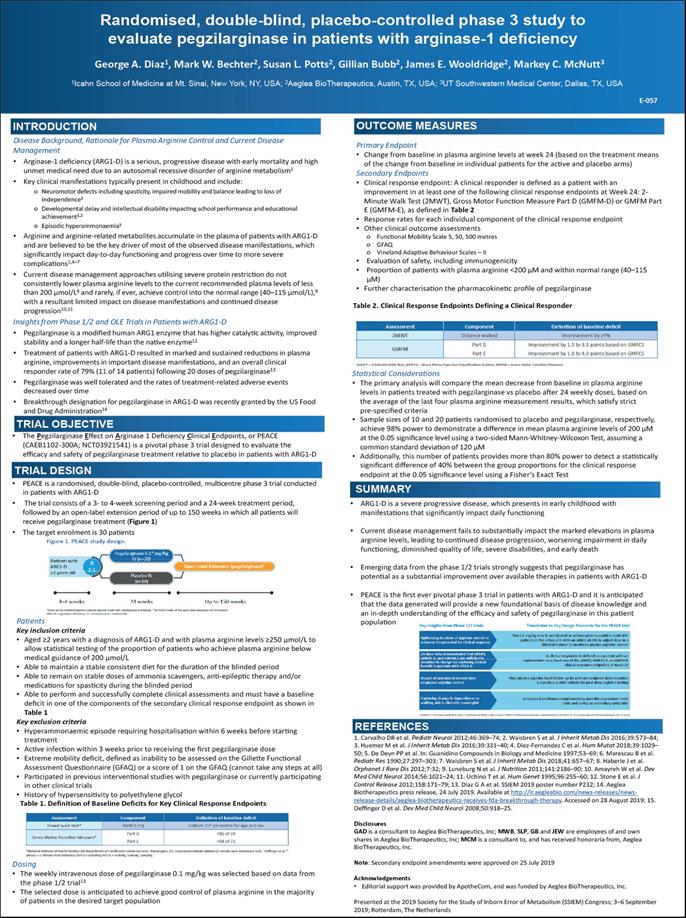
Randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 study to evaluate pegzilarginase in patients with arginase-1 deficiency George A. Diaz1, Mark W. Bechter2, Susan L. Potts2, Gillian Bubb2, James E. Wooldridge2, Markey C. McNutt3 1Icahn School of Medicine at Mt. Sinai, New York, NY, USA; 2Aeglea BioTherapeutics, Austin, TX, USA; 3UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX, USA E-057 INTRODUCTION Disease Background, Rationale for Plasma Arginine Control and Current Disease Management Arginase-1 deficiency (ARG1-D) is a serious, progressive disease with early mortality and high unmet medical need due to an autosomal recessive disorder of arginine metabolism1 Key clinical manifestations typically present in childhood and include: Neuromotor defects including spasticity, impaired mobility and balance leading to loss of independence1 Developmental delay and intellectual disability impacting school performance and educational achievement1,2 Episodic hyperammonaemia3 Arginine and arginine-related metabolites accumulate in the plasma of patients with ARG1-D and are believed to be the key driver of most of the observed disease manifestations, which significantly impact day-to-day functioning and progress over time to more severe complications1,4–7 Current disease management approaches utilising severe protein restriction do not consistently lower plasma arginine levels to the current recommended plasma levels of less than 200 μmol/L8 and rarely, if ever, achieve control into the normal range (40–115 μmol/L),9 with a resultant limited impact on disease manifestations and continued disease progression10,11 Insights from Phase 1/2 and OLE Trials in Patients with ARG1-D Pegzilarginase is a modified human ARG1 enzyme that has higher catalytic activity, improved stability and a longer half-life than the native enzyme12 Treatment of patients with ARG1-D resulted in marked and sustained reductions in plasma arginine, improvements in important disease manifestations, and an overall clinical responder rate of 79% (11 of 14 patients) following 20 doses of pegzilarginase13 Pegzilarginase was well tolerated and the rates of treatment-related adverse events decreased over time Breakthrough designation for pegzilarginase in ARG1-D was recently granted by the US Food and Drug Administration14 Trial objective The Pegzilarginase Effect on Arginase 1 Deficiency Clinical Endpoints, or PEACE(CAEB1102-300A; NCT03921541) is a pivotal phase 3 trial designed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of pegzilarginase treatment relative to placebo in patients with ARG1-d trial design PEACE is a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre phase 3 trial conducted in patients with ARG1-D The trial consists of a 3- to 4-week screening period and a 24-week treatment period, followed by an open-label extension period of up to 150 weeks in which all patients will receive pegzilarginase treatment (Figure 1) t he target enrolment is 30 patients Patients Key inclusion criteria Aged ≥2 years with a diagnosis of ARG1-D and with plasma arginine levels ≥250 μmol/L to allow statistical testing of the proportion of patients who achieve plasma arginine below medical guidance of 200 μmol/L Able to maintain a stable consistent diet for the duration of the blinded period Able to remain on stable doses of ammonia scavengers, anti-epileptic therapy and/or medications for spasticity during the blinded period Able to perform and successfully complete clinical assessments and must have a baseline deficit in one of the components of the secondary clinical response endpoint as shown in Table 1 Key exclusion criteria Hyperammonaemic episode requiring hospitalisation within 6 weeks before starting treatment Active infection within 3 weeks prior to receiving the first pegzilarginase dose Extreme mobility deficit, defined as inability to be assessed on the Gillette Functional Assessment Questionnaire (GFAQ) or a score of 1 on the GFAQ (cannot take any steps at all) Participated in previous interventional studies with pegzilarginase or currently participating in other clinical trials History of hypersensitivity to polyethylene glycol Table 1. Definition of Baseline Deficits for Key Clinical Response Endpoints Dosing The weekly intravenous dose of pegzilarginase 0.1 mg/kg was selected based on data from the phase 1/2 trial13 The selected dose is anticipated to achieve good control of plasma arginine in the majority of patients in the desired target population outcome measures Primary Endpoint Change from baseline in plasma arginine levels at week 24 (based on the treatment means of the change from baseline in individual patients for the active and placebo arms) Secondary Endpoints Clinical response endpoint: A clinical responder is defined as a patient with an improvement in at least one of the following clinical response endpoints at Week 24: 2- Minute Walk Test (2MWT), Gross Motor Function Measure Part D (GMFM-D) or GMFM Part E (GMFM-E), as defined in Table 2 Response rates for each individual component of the clinical response endpoint Other clinical outcome assessments Functional Mobility Scale 5, 50, 500 metres GFAQ Vineland Adaptive Behaviour Scales – II Evaluation of safety, including immunogenicity Proportion of patients with plasma arginine <200 μM and within normal range (40–115 μM) Further characterisation the pharmacokinetic profile of pegzilarginase Table 2. Clinical Response Endpoints Defining a Clinical Responder Statistical Considerations The primary analysis will compare the mean decrease from baseline in plasma arginine levels in patients treated with pegzilarginase vs placebo after 24 weekly doses, based on the average of the last four plasma arginine measurement results, which satisfy strict pre-specified criteria Sample sizes of 10 and 20 patients randomised to placebo and pegzilarginase, respectively, achieve 98% power to demonstrate a difference in mean plasma arginine levels of 200 μM at the 0.05 significance level using a two-sided Mann-Whitney-Wilcoxon Test, assuming a common standard deviation of 120 μM Additionally, this number of patients provides more than 80% power to detect a statistically significant difference of 40% between the group proportions for the clinical response endpoint at the 0.05 significance level using a Fisher’s Exact Test Summary ARG1-D is a severe progressive disease, which presents in early childhood with manifestations that significantly impact daily functioning Current disease management fails to substantially impact the marked elevations in plasma arginine levels, leading to continued disease progression, worsening impairment in daily functioning, diminished quality of life, severe disabilities, and early death Emerging data from the phase 1/2 trials strongly suggests that pegzilarginase has potential as a substantial improvement over available therapies in patients with ARG1-D PEACE is the first ever pivotal phase 3 trial in patients with ARG1-D and it is anticipated that the data generated will provide a new foundational basis of disease knowledge and an in-depth understanding of the efficacy and safety of pegzilarginase in this patient population References 1. Carvalho DR et al. Pediatr Neurol 2012;46:369–74; 2. Waisbren S et al. J Inherit Metab Dis 2016;39:573–84; 3. Huemer M et al. J Inherit Metab Dis 2016;39:331–40; 4. Diez-Fernandez C et al. Hum Mutat 2018;39:1029– 50; 5. De Deyn PP et al. In: Guanidino Compounds in Biology and Medicine 1997;53–69; 6. Marescau B et al. Pediatr Res 1990;27:297–303; 7. Waisbren S et al. J Inherit Metab Dis 2018;41:657–67; 8. Haberle J et al. Orphanet J Rare Dis 2012;7:32; 9. Luneburg N et al. J Nutrition 2011;141:2186–90; 10. Amayreh W et al. Dev Med Child Neurol 2014;56:1021–24; 11. Uchino T et al. Hum Genet 1995;96:255–60; 12. Stone E et al. J Control Release 2012;158:171–79; 13. Diaz G A et al. SSIEM 2019 poster number P232; 14. Aeglea Biotherapeutics press release, 24 July 2019. Available at http://ir.aegleabio.com/news-releases/news- release-details/aeglea-biotherapeutics-receives-fda-breakthrough-therapy. Accessed on 28 August 2019; 15. Oeffinger D et al. Dev Med Child Neurol 2008;50:918–25. Disclosures GAD is a consultant to Aeglea BioTherapeutics, Inc; MWB, SLP, GB and JEW are employees of and own shares in Aeglea BioTherapeutics, Inc; MCM is a consultant to, and has received honoraria from, Aeglea BioTherapeutics, Inc. Note: Secondary endpoint amendments were approved on 25 July 2019 Acknowledgements Editorial support was provided by ApotheCom, and was funded by Aeglea BioTherapeutics, Inc. Presented at the 2019 Society for the Study of Inborn Error of Metabolism (SSIEM) Congress; 3–6 September 2019; Rotterdam, The Netherlands Figure 1. peace study design. Patients with arg1-d ≥2 years old r2:1 pegzilarginase 0.1* mg/kg iv (n=20)open label extension (pegzilarginase) weeks 24 weeks up to 150 weeks *Dose can be modified based on plasma arginine levels with maintenance of blinding .”the first 8 weeks of the open -label extension will be blinded. Arg1-d=arginase-1 deficiency; iv=intravenous; r= randomized. Assessment component definition of baseline deficit Timed walk test* 2mwd(m) bottom 15th percentile for age and sex gross motor function measure* Part d <35 of 39 part e <68 of 72 *national institute of health toolbox (us department of health and human service, washington, dc, usa) motor domain dataset (2-minute walk endurance test); *oeffinger et al.15 2mwd=2-minute walk distance; part d=standing; part e walking, running, jumping. Assessment component definition of baseline deficit 2mwt distance walked improvement by≥9% Gmfm part d improvement by 1.5 to 3.3 points based on gmfcs. Part e improvement by 1.8 to 4.0 points based on gmfcs 2mwr=2-minute walk test; gmfcs= gross motor function classification system; gmfm=gross motors function measure. Key insights from phase ½ trials translation to key design elements for the peace trial Optimizing duration of arginine control to enhance the potential for clinical response the 0.1 mg/kg dose is anticipated to achieve plasma arginine control in patients in the active arm with an added ability to adjust dose in a blinded manner to maximise plasma arginine control 20-dose data demonstrated that 6mwt, gmfm-d, and gmfm-=e are sufficiently sensitive to change for capturing clinical benefit in patients with arg1-d a clinical responder is defined as a patient with an improvement in at least one of the 2mwt, gmfm-d, or gmfm-e clinical response endpoints at week 24 Impact of unplanned missed dose on plasma arginine control final plasma arginine level follow-up for primary endpoint determination is based on a strict criteria for post-dose arginine testing Capturing change in dependence on walking aids is clinically meaningful introduced additional complementary mobility assessment tools (fms and gfaq)as secondary endpoints 2/6mwt=2/6-minute walk test; functional mobility scale; gfaq=Gillette functional assessment questionnaire; gmfm(-m or-d)= gross motor function measure (part e or d).
