UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
FORM 10-K/A
| | | | | |
| (Mark One) | |
| ☒ | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
| For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2020 |
| OR |
| ☐ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
| For the transition period from ___ to ___ |
|
Commission File Number: 001-37552 |
WILLSCOT MOBILE MINI HOLDINGS CORP.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter) | | | | | |
| Delaware | 82-3430194 |
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation) | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
4646 E Van Buren St., Suite 400
Phoenix, Arizona 85008
(Address of principal executive offices)
(480) 894-6311
(Registrant’s telephone number, including area code)
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act: | | | | | | | | |
| Title of Each Class | Trading Symbol(s) | Name of Each Exchange on Which Registered |
| Common Stock, par value $0.0001 per share | WSC | The Nasdaq Capital Market |
| Warrants to purchase Common Stock(1) | WSCWW | OTC Markets Group Inc. |
| Warrants to purchase Common Stock(2) | WSCTW | OTC Markets Group Inc. |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None.
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulations S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files). Yes ☒ No ☐
(1) Issued in connection with the initial public offering of Double Eagle Acquisition Corp., the registrant's legal predecessor company, in September 2015, which are exercisable for one-half of one share of the registrant's common stock for an exercise price of $5.75.
(2) Issued in connection with the registrant's acquisition of Modular Space Holding, Inc. in August 2018, which are exercisable for one share of the registrant's common stock at an exercise price of $15.50 per share.
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company, or an emerging growth company. See definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company,” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| | | | | |
Large accelerated filer ☒ | Accelerated filer ☐ |
Non-accelerated filer ☐ | Smaller reporting company ☐ |
| Emerging growth company ☐ |
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has filed a report on and attestation to its management's assessment of the effectiveness of its internal control over financial reporting under Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (15 U.S.C. 7262(b)) by the registered public accounting firm that prepared or issued its audit report. ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes ☐ No ☒
The aggregate market value of the common shares held by non-affiliates of the registrant, computed as of June 30, 2020 (the last business day of the registrant’s most recently completed second quarter), was approximately $715,019,406.
Shares of Common Stock, par value $0.0001 per share, outstanding: 226,826,328 shares at May 5, 2021.
Documents Incorporated by Reference
The information required by Part III of this Report, to the extent not set forth herein, is incorporated herein by reference from the registrant's definitive proxy statement relating to the Annual Meeting of Shareholders to be held in 2021, which definitive proxy statement was filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on April 23, 2021.
EXPLANATORY NOTE
This Amendment No. 1 (“Amendment No. 1”) to the Annual Report on Form 10-K/A amends and restates certain items noted below in the Annual Report on Form 10-K of Willscot Mobile Mini Holdings Corp. (the “Company”) for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2020 originally filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission (the "SEC") on February 26, 2021 (the “Original Filing”).
Restatement Background
We are filing this Amendment No. 1 to restate our financial statements to conform with the SEC staff’s April 12, 2021 Staff Statement on Accounting and Reporting Considerations for Warrants Issued by Special Purpose Acquisition Companies (“SPACs”) (the “SEC Staff Statement”). The SEC Staff Statement addressed certain accounting and reporting considerations related to warrants of a kind similar to those issued by the Company that preclude our warrants from being classified as components of equity for certain reporting periods. Consistent with common market practice, the Company’s financial statements, which had been audited by the Company’s independent registered public accounting firm, previously accounted for these warrants as components of equity. These warrants will now be classified as liabilities.
On April 27, 2021, management of the Company, after consultation with the Audit Committee of the Board of Directors of the Company and Ernst & Young LLP, the Company’s independent registered public accounting firm, concluded that the Company’s consolidated financial statements for the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018 and for each of the interim quarterly periods therein (the “Non-Reliance Period”) which were included in the Company's Original Filing should no longer be relied upon and that the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2020 should be amended to restate the consolidated financial statements contained therein to conform our accounting for certain previously issued warrants with the SEC Staff Statement.
In the SEC Staff Statement, the SEC staff clarified its interpretation of certain generally accepted accounting principles related to certain contractual terms that are commonly included in warrants issued in connection with the initial public offerings of SPACs. This interpretation requires us to conform our accounting to the SEC Staff Statement and classify our warrants as liabilities rather than as being components of equity. As a result of the SEC Staff Statement, the Company has restated its consolidated financial statements herein for the Non-Reliance Period to reflect the warrants as liabilities with the associated gains or losses recognized as a result of the changes in fair values and extinguishment. These non-cash adjustments to the financial statements do not impact the Company’s operational performance indicators, GAAP metrics above Operating Income, non-GAAP metrics, or the Company’s free cash flow.
Internal Control Considerations
In connection with the restatement, management of the Company has reassessed the effectiveness of the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures and internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2020. Management of the Company has concluded that the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures and internal controls over financial reporting were not effective as of December 31, 2020, due to a material weakness in internal control over financial reporting related to the accounting for the Warrants. Management has concluded that controls were ineffective due to required changes in our financial statements for certain previously issued warrants to conform with the SEC Staff Statement. Accordingly, the Company’s control to evaluate the accounting for warrants did not operate effectively to apply the provision of ASC 815-40, as further interpreted by the SEC on April 12, 2021. As of April 30, 2021, the Company has implemented its remediation plan. For a discussion of management’s consideration of our disclosure controls and procedures, internal controls over financial reporting, the material weaknesses identified, and remediation plans, see Part II, Item 9A, “Controls and Procedures” of this Form 10-K/A.
Items Amended
For the reasons discussed above, the Company is filing this Amendment No. 1 in order to amend the following items in our Original Filing to the extent necessary to reflect the adjustments discussed above and make corresponding revisions to our financial data and certain other information included elsewhere in this Amendment No. 1.
•Part I, Item 1A - Risk Factors
•Part II, Item 5 - Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
•Part II, Item 6 - Selected Financial Data
•Part II, Item 7 - Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
•Part II, Item 8 - Financial Statements and Supplementary Data
•Part II, Item 9A - Controls and Procedures
•Part IV, Item 15 - Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules
•Signatures
However, for the convenience of the reader, this Amendment No. 1 sets forth the Original Filing in its entirety, as amended to reflect the restatement.
This Amendment speaks as of the filing date of the Original Filing and does not reflect events occurring after the filing date of the Original Filing.
The Company has not filed, and does not intend to file, amendments to its Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q for any of the quarters for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019. Accordingly, investors should rely only on the financial information and other disclosures regarding the restated periods in this Form 10-K/A or in future filings with the SEC (as applicable), and not on any previously issued or filed reports, earnings releases or similar communications relating to these periods.
In addition, as required by Rule 12b-15 under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”), new certifications by the Company’s principal executive officer and principal financial officer are filed herewith as exhibits to this Amendment No. 1 pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a) of the Exchange Act and Section 1350 of Chapter 63 of Title 18 of the United States Code (18 U.S.C. 1350).
WillScot Mobile Mini Holdings Corp.
Annual Report on Form 10-K/A
Table of Contents
PART I
ITEM 1. Business
Unless the context otherwise requires, “we,” “us,” “our” and the “Company” refers to WillScot Mobile Mini Holdings Corp. ("WillScot Mobile Mini") and its subsidiaries.
Our Company
Headquartered in Phoenix, Arizona, we are a leading business services provider specializing in innovative flexible work space and portable storage solutions. We service diverse end markets across all sectors of the economy from a network of approximately 275 branch locations and additional drop lots throughout the United States (“US”), Canada, Mexico, and the United Kingdom ("UK").
With roots dating back more than 60 years, we lease modular space and portable storage units (our “lease fleet”) to customers in the commercial and industrial, construction, education, energy and natural resources, government, and other end markets. We offer our customers an extensive section of “Ready to Work” solutions. In addition to our "Ready to Work" solutions, we offer value-added products and services, such as the rental of steps, ramps, and furniture packages, damage waivers, and other amenities to improve the overall customer experience. These turnkey solutions offer customers flexible, low-cost, and timely solutions to meet their flexible work space and storage needs on an outsourced basis.
On July 1, 2020, WillScot Corporation ("WillScot") combined with Mobile Mini, Inc. ("Mobile Mini") in a stock-for-stock merger (the "Merger"), and WillScot changed names to WillScot Mobile Mini Holdings Corp. WillScot Mobile Mini is the holding company for the Williams Scotsman and Mobile Mini family of companies. As a result of the Merger, the Company operates in four reportable segments as follows: North America Modular Solutions ("NA Modular"), North America Storage Solutions ("NA Storage"), United Kingdom Storage Solutions ("UK Storage"), and Tank and Pump Solutions ("Tank and Pump"). The NA Modular segment aligns with the WillScot legacy business prior to the Merger, and the NA Storage, UK Storage, and Tank and Pump segments align with the Mobile Mini segments prior to the Merger. Within this Annual Report, we have presented certain financial information on a pro forma basis and supplemental pro forma financial statements within Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations to include Mobile Mini's results as if the Merger and related financing transactions had occurred on January 1, 2019, as we believe this is a better representation of the go-forward combined company and is useful to investors.
Products and Services
Modular Space Solutions
Our modular space units meet a broad range of customer needs. Our modular units are typically made of steel and aluminum frames, as well as traditional building materials, and range from standalone portable units as small as 24 square feet to large complex units that can be coupled together or stacked to create versatile work spaces in excess of 10,000 square feet. In all cases, we deploy modular units to customers rapidly from our extensive branch network using our hybrid in-house and outsourced logistics and service infrastructure. We specialize in turnkey ‘Ready to Work’ solutions, which means our units can arrive fully equipped with air conditioning, heating, and filtration units, electrical and Ethernet ports, plumbing and utility hookups, as well as our proprietary line of furnishings and appliances, which we together refer to as Value-Added Products and Services (“VAPS”). Our units are transported by truck, either towed (if fitted with axles and hitches) or mounted on flat-bed trailers.
Modular space units have attractive economic characteristics, and our ability to lease and maintain our assets’ profitability over economic lives, which often exceed 20 years, is a unique capability and competitive advantage. We utilize standard fleet maintenance procedures across the branch network, monitor fleet condition and allocate capital expenditures centrally, and ensure all units meet consistent quality and condition requirements, regardless of unit age, prior to delivery to a customer. Modular leasing is complemented by new unit sales and sales of rental units. In connection with our leasing and sales activities, we provide services including delivery and installation, maintenance and ad hoc services, and removal services at the end of lease transactions.
Panelized and Stackable Offices. Our FlexTM panelized and stackable offices are the next generation of modular space technology and offer maximum flexibility and design configurations. These units provide a modern, innovative design, smaller footprint, ground level access, and interchangeable panels, including all glass panels that allow customers to configure the space to their precise requirements. These units have the ability to expand upwards (up to three stories) and outwards, providing maximum versatility.
Single-Wide Modular Space Units. Single-wide modular space units include mobile offices and sales offices. These units offer maximum ease of installation and removal and are deployed across the broadest range of applications in our fleet. These units typically have “open interiors,” which can be modified using movable partitions, and include tile floors, air conditioning, heating, and filtration units, partitions and, if requested, toilet facilities.
Section Modulars and Redi-Plex. Section modulars are two or more units combined into one structure. Redi-Plex complexes offer advanced versatility for large, open floor plans or custom layouts with private offices. Redi-Plex is built with clearspan construction, which eliminates interference from support columns and allows for up to sixty feet of open building width and building lengths that increase in twelve-foot increments based on the number of units coupled together. Our proprietary design meets a wide range of national and state building, electrical, mechanical, and plumbing codes, which creates versatility in fleet management. Examples of section modular units include hospital diagnostic annexes, special events headquarters, temporary data centers, and larger general commercial offices.
Classrooms. Classroom units are generally double-wide units adapted specifically for use by school systems or universities. Classroom units usually feature teaching aids, air conditioning, heating, and filtration units, windows and, if requested, toilet facilities.
Ground Level Offices and Container Offices. We also offer steel ground level offices from 10 to 40 feet in length and 8 or 10 feet in width. Many of these units are converted to office use from International Organization for Standardization ("ISO") certified shipping containers. These offices are available in various configurations, including all-office floor plans or office and storage combination units that provide a 10‑ or 15‑foot office with the remaining area available for storage. Ground level offices provide the advantage of ground accessibility for ease of access and high security in an all‑steel design. These office units are equipped with electrical wiring, air conditioning, heating, filtration units, phone jacks, carpet or tile, high security doors, and windows with security bars or shutters. Some of these offices are also equipped with sinks, hot water heaters, cabinets, and toilet facilities.
Other Modular Space. We offer a range of other specialty products that vary across regions and provide flexibility to serve demands for local markets. Examples include workforce accommodation units with dining facilities used to house workers, often in remote locations, blast-resistant units, and toilet facilities to complement office and classroom units.
Portable Storage Solutions
Portable Storage Containers. Our portable storage containers offer an assortment of differentiated features such as patented locking systems, premium and multiple door options, optional climate control, and numerous configuration options. Standard portable storage containers are made from weather‑resistant corrugated steel and are available in lengths ranging from 5 to 48 feet, widths of either 8 feet or 10 feet, and a variety of configuration options. Doors can be placed at the front, front and back, or the sides of containers. Other options include partitions and shelving. Storage containers can be equipped with our patented Tri‑Cam Locking System®, which features a waist‑level opening lever and interlocking bars to provide easy access for the owner without sacrificing security. We also offer ContainerGuardLock®, an optional security device, which features a hidden six‑pin tumbler system and is made from drill‑resistant hardened steel. We believe these steel storage containers are a cost‑effective alternative to mass warehouse storage, with a high level of security to protect our customers' goods.
Steel containers have a long useful life with no technical obsolescence. Our portable storage containers have estimated useful lives of 30 years from the date we build or acquire and remanufacture them, with average residual values in excess of 50%. We maintain our steel containers on a regular basis by removing rust, painting them with rust inhibiting paint, plug‑welding holes, and occasionally replacing the wooden floor or a rusted steel panel. Repainting the outside of storage units is the most common maintenance item. A properly maintained container is essentially in the same condition as when it was initially remanufactured.
The remanufacturing process begins with the purchase of used ISO containers from leasing companies, shipping lines, and brokers. These containers were originally built to ISO standards and are 8 feet wide, up to 9.5 feet high and 20, 40 or 45 feet long. After acquisition, we remanufacture and modify these ISO containers. Remanufacturing typically involves cleaning, removing rust and dents, repairing floors and sidewalls, painting, adding our signs, and further customizing units by adding our proprietary easy opening door system and our patented locking system. Modification typically involves splitting some containers into differing lengths.
VAPS
We offer a thoughtfully curated portfolio of VAPS that make modular space and portable storage units more productive, comfortable, secure, and “Ready to Work” for our customers. We lease furniture, steps, ramps, basic appliances, internet connectivity devices, and other items to our customers for use in connection with our products. We also offer our lease customers a damage waiver program that protects them in case the leased unit is damaged. For customers who do not select the damage waiver program, we bill them for the cost of repairs above and beyond normal wear and tear. Importantly, management believes that our scale, branch network, supply chain, and sales performance management tools give us a significant advantage in delivering “Ready to Work” solutions and growing VAPS revenue relative to our competitors.
Delivery, Installation and Removal
We operate a hybrid in-house and outsourced logistics and service infrastructure that provides delivery, site work, installation, disassembly, unhooking and removal, and other services to our customers for an additional fee as part of our leasing and sales operations. Revenue from delivery, site work, and installation results from the transportation of units to a customer's location, site work required prior to installation, and installation of the units which have been leased or sold. Typically, modular units are placed on temporary foundations constructed by our in‑house service technicians or
subcontractors. These in‑house service technicians or subcontractors also generally install any ancillary products and VAPS. We also derive revenue from disassembling, unhooking, and removing units once a lease expires. We believe that our logistics and service capabilities are unrivaled in the industry, differentiate us from competitors, and enhance our value proposition to our customers.
Tank and Pump Solutions
Our Tank and Pump Solutions business offers a broad range of liquid and solid specialty containment equipment and services complemented by an assortment of pumps, filtration units, and waste hauling services. In addition, ancillary products for rental and for sale are available, such as hoses, pipes, filters, and spill containment. Our principal products and services within our Tank and Pump Solutions business include steel tanks, stainless steel tank trailers, roll‑off boxes, vacuum boxes, dewatering boxes, pumps and filtration equipment, and value‑added services.
Our fleet of steel tanks offers flexible sizes and other options such as weir, gas buster, and open top steel tanks for applications ranging from temporary storage of chemicals, water, and other liquids, thorough mixing, agitation, and circulation of stored liquids with other products, and removal of gas from fluids circulated in the wellbore—such as mud used during drilling operations and settling of solids in liquids prior to filtration or discharge. Our stainless-steel tankers meet Department of Transportation specifications for use in the storage and transportation of chemical, caustics, and other liquids and are offered insulated or non‑insulated with level indication and vapor recovery capability. Roll‑off boxes provide simple, leak‑proof storage and transportation of solid industrial byproducts and are utilized for a variety of containment applications where it is necessary to maintain the homogeneity of the contents. Roll-tarps or rolling metal lids are available to protect the contents from the elements during transport or storage. Vacuum roll‑off boxes are also offered to pair with a vacuum truck for containment, storage, or transportation of pressurized contents. Dewatering boxes are configured to provide for the draining of excess liquid from slurry or sludge which reduces storage, transportation, and disposal costs. Upon completion of dewatering, the container is generally picked up by a roll‑off truck for content disposal. Vacuum dewatering boxes are also offered. In addition, we offer a variety of pumps and filtration equipment that can be used primarily for liquid circulation and filtration in municipal and industrial applications.
Additional services performed by our specialty containment employees include transportation of containers for waste management between multiple locations or in-plant, waste management oversight and service provision by an on-site dedicated team, system design including assessment of pumping, filtration and temporary storage needs, and field services to correctly install and connect customer containment equipment.
Product Leases
We primarily lease our modular and portable storage units to customers, which results in a highly diversified and predictable recurring revenue stream. For the year ended December 31, 2020, over 90% of new lease orders were on our standard lease agreement, pre-negotiated master lease, or national account agreements. The initial lease periods vary, and our leases are customarily renewable on a month-to-month basis after their initial term. For the year ended December 31, 2020, the average effective duration of our consolidated lease portfolio was approximately 32 months. As a result, our lease revenue is highly predictable due to its recurring nature and the underlying stability and diversification of our lease portfolio.
For the year ended December 31, 2020, our average minimum contractual lease term at the time of delivery in our NA Modular segment for modular space units and portable storage units was 11 months and 7 months, respectively. However, given that our customers value flexibility, they consistently extend their leases or renew on a month-to-month basis such that the average effective duration of our NA Modular segment lease portfolio was over 34 months. Customers are responsible for the costs of delivery and set-up, dismantling and pick-up, customer-specified modifications, costs to return custom modifications back to standard configuration at end of lease, and any loss or damage beyond normal wear and tear. Our leases generally require customers to maintain liability and property insurance covering the units during the lease term and to indemnify us from losses caused by the negligence of the customer or their employees.
Rental contracts with customers within our NA Storage and UK Storage segments are generally based on a 28‑day rate and billing cycle. The rental continues until cancelled by the customer or us. On average, steel storage containers on rent in our NA Storage and UK Storage segments for the year ended December 31, 2020 had been in place for over 31 months, and the steel ground level offices on rent for the year ended December 31, 2020 had been in place for approximately 15 months. Rental contracts provide that the customer is responsible for the cost of delivery and pickup and specify that the customer is liable for any damage done to the unit beyond ordinary wear and tear. Customers may purchase a damage waiver to avoid damage liability in certain circumstances, which provides an additional source of recurring revenue. Customer possessions stored within a portable storage unit are the responsibility of that customer.
Rental contracts with Tank and Pump Solutions customers typically offer daily, weekly, or monthly rates. Certain larger customers have multi‑year agreements that limit rate increases during the term of the contract. The rental duration varies widely by application, and the rental continues until the unit is returned in clean condition to us. Rental contracts specify that the customer is responsible for carrying commercial general liability insurance, is liable for any damage to the unit beyond ordinary wear and tear, and for all materials the customer contains in rented equipment. The customer is contractually responsible for the cost of delivery and pickup, as well as thoroughly emptying and cleaning the equipment before return.
Demand for our products varies by end market. Construction customers typically reflect higher demand during months with more temperate weather, while demand from large retailers is stronger from September through December, when
more space is needed to store holiday inventories. Retail customers usually return these rented units in December and early in the following year, but also undertake ongoing rolling store renovations which present consistent recurring demand throughout the year. In our Tank and Pump Solutions business, demand from customers is typically higher in the middle of the year from March to October, driven by the timing of customer maintenance projects.
As of December 31, 2020, we had over 368,000 total units including over 157,000 modular space units, over 197,000 portable storage units, over 12,500 tank and pump units, and other value-added products representing fleet net book value of $2.9 billion. Approximately 109,766 of our modular space units, or 70% and 151,206 of our portable storage units, or 76% were on rent as of December 31, 2020, and tank and pump Original Equipment Cost ("OEC") utilization was 64.8% as of December 31, 2020.
Product Sales
We complement our core leasing business by selling both new and used units, allowing us to leverage our scale, achieve purchasing benefits, and redeploy capital employed in our lease fleet. Generally, we purchase new units from a broad network of third-party manufacturers. We only purchase new modular space units for resale when we have obtained firm purchase orders (which normally are non-cancelable and include up-front deposits) for such units. Buying units directly for resale adds scale to our purchasing, which is beneficial to our overall supplier relationships and purchasing terms. New unit sales are a natural extension of our leasing operations in situations where customers have long-lived or permanent projects, making it more cost-effective to purchase rather than to lease a standard unit, and our customers benefit from our product expertise and delivery and installation capabilities.
In the normal course of managing our business, we also sell idle, used rental units at fair market value and units that are already on rent if the customer expresses interest in owning, rather than continuing to rent, the unit. The sale of units from our rental equipment has historically been both a profitable and cost-effective method to finance the replenishment and upgrade of our lease fleet, as well as to generate free cash flow during periods of lower rental demand and utilization. Our sales business may include modifying or customizing units to meet customer requirements. We also offer delivery, installation, and removal-related services for an additional fee as part of our sales operations.
Customers
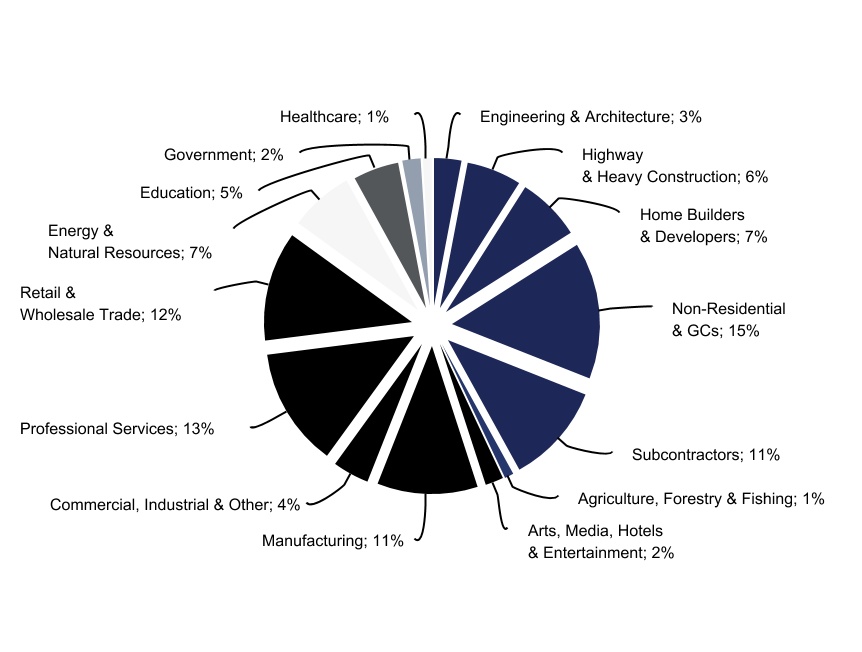
Our customers operate in a diversified set of end markets, including construction, commercial and industrial, retail and wholesale trade, education, energy and natural resources, government, and healthcare. Core to our operating model is the ability to redeploy standardized assets across end markets. We have recently serviced emerging demand in the healthcare and government sectors related to COVID‑19, as well as expanded space requirements related to social distancing. We track several market leading indicators in order to predict demand, including those related to our two largest end markets, the commercial and industrial end market, and the construction end market, which collectively accounted for approximately 43% and 42% of our pro forma revenues, respectively, for the year ended December 31, 2020. In order to optimize the use of fleet assets across our branch network, we centrally manage fleet rebalancing across our end markets. This allows us to serve 15 distinct end markets in which no customer accounted for more than 2% of pro forma revenue for the year ended December 31, 2020.
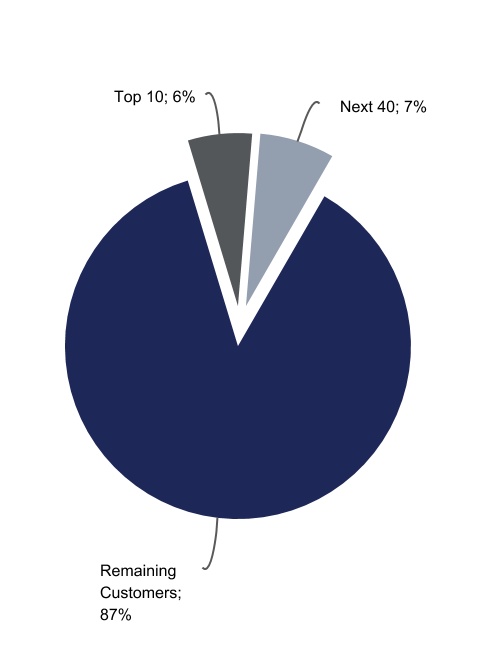
For the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019, and 2018, no one customer accounted for more than 3% of our total pro forma revenues. For the year ended December 31, 2020, no one customer accounted for more than 2% of pro forma revenues, our top 10 customers accounted for approximately 6% of pro forma revenues, and our top 50 customers accounted for less than 13% of revenues on a pro forma basis, reflecting low customer concentration and significant project diversification within our portfolio.
Our logistics and service infrastructure is designed to enable us to meet or exceed our customers’ expectations by reacting quickly, efficiently, and with consistent service levels. As a result, we have established strong relationships with a diverse customer base, ranging from large multinational companies to local sole proprietors. Including customers acquired from Mobile Mini, we served over 85,000 unique customers in 2020. We believe that our customers prefer our modular space and portable storage products over fixed, on-site built space because they are a quick, flexible, cost‑effective, and low-risk solution for temporary or permanent expansion or storage.
Our strategy involves operating standardized rental equipment and "Ready to Work" solutions that can be redeployed across our diversified customer base and branch network in 15 discrete end markets. Key customer end markets include:
Construction and Infrastructure
We provide office and storage space to a broad array of contractors associated with non-residential buildings and non-building infrastructure. Our client portfolio includes many of the largest general contractors and engineering, architecture, procurement, and construction companies in North America, as well as home builders, developers, and subcontractors. Examples include highway, street, bridge, and tunnel contractors; water, sewer, communication, and power line contractors; and special construction trades, including glass, glazing, and demolition. Our construction and infrastructure customer base is characterized by a wide variety of contractors that are associated with original construction as well as capital improvements in the private, institutional, and municipal arenas. Units are used as offices, break rooms, accommodations, security offices, and other applications.
Commercial and Industrial
Customers in this category use our products as their primary office or retail space, to expand their existing commercial workspace, to increase their storage capabilities, or as temporary space for festivals, sporting, and other events. Customers in this category span a variety of industries ranging from commercial offices; chemicals and other manufacturing; agriculture, forestry and fishing; arts, media, hotels, and entertainment; and other industrial end markets.
The commercial and industrial segment also includes customers in retail and wholesale trade. These include department, drug, grocery, and strip mall stores, logistics, warehousing and distribution services, as well as restaurants, service stations, and dry cleaners. Our customers in retail and wholesale trade include big‑box retailers who have storage needs during renovations or other large on-site projects. On a stand‑alone basis, retail and wholesale trade customers comprised approximately 11% of fiscal year 2020 rental revenue; on a pro forma basis, these customers comprised approximately 12% of fiscal year 2020 rental revenue.
Energy and Natural Resources
Our products are leased to companies involved in electricity generation and transmission, utilities, up- mid- and down-stream oil and gas, mining exploration and extraction, and other related sectors. Units are used as temporary offices, break rooms, accommodations, security offices, and other applications.
Education
Rapid shifts in populations within regions, as well as recent needs to expand square footage per student in in-person education settings, often necessitate quick expansion of education facilities, particularly in elementary and secondary schools and universities and colleges. Regional and local governmental budgetary pressures, classroom size reduction legislation, refurbishment of existing facilities, and the expansion of charter schools have made modular classrooms a convenient and cost-effective way to expand capacity in education settings. In addition, our products are used as classrooms when schools are undergoing large scale modernization, which allows continuous operation of a school while modernization progresses.
Government and Institutions
Government customers consist of national, state, provincial, and local public sector organizations. Modular space and portable storage solutions are particularly attractive to focused niches such as healthcare facilities, small municipal buildings, courthouses, military installations, national security buildings, and offices during building modernization, as well as disaster relief.
Competitive Strengths
We believe that the following competitive strengths have been instrumental to our success and position us for future growth:
North American Leader in Turnkey Modular Space and Portable Storage Solutions
The Mobile Mini Merger brought together WillScot’s leading modular space capabilities and Mobile Mini’s leading portable storage solutions to create an industry-leading specialty leasing platform. We benefit from complementary capabilities, a diverse customer base with over 85,000 customers across different end markets, and an unrivaled geographic footprint of approximately 275 branch locations and additional drop lots.
Our broad and complementary network serves the largest North American metropolitan areas with local teams who are experts in their respective markets. Our cost‑effective coverage model serves smaller customers at the local and regional level, while also addressing the needs of larger national customers looking for a full suite of high-quality services that can be provided on a consistent basis throughout North America. Since geographic proximity to customers can be a competitive advantage in the modular space and portable storage industry, we believe that our extensive branch network allows us to better serve existing customers and attract new customers.
We believe our extensive scale results in significant operational benefits, such as optimization of fleet yield and utilization, efficient capital allocation, superior service capabilities, and the ability to offer consistent "Ready to Work" solutions across all of our branch locations.
VAPS
We deliver "Ready to Work" solutions through our growing offering of VAPS, such as the rental of steps, ramps, furniture packages, damage waivers, and other amenities. This thoughtfully curated portfolio of VAPS makes modular space and portable storage units more productive, comfortable, and secure for our customers and allows us to generate higher revenue per transaction and return on capital. These turnkey solutions offer customers flexible, low‑cost, capital efficient, and timely solutions to meet their space needs on an outsourced basis.
VAPS have been a substantial source of revenue growth in our NA Modular segment. We have been able to successfully drive a material increase in customer VAPS spend into our recently acquired businesses, which generates highly tangible revenue synergies. We believe our ability to drive VAPS growth following our historical acquisitions highlights the value proposition our VAPS provide to our customers. We expect to replicate a similar cross‑selling opportunity within Mobile Mini’s ground level offices.
Sophisticated Logistics And Service Capabilities
Building off of the largest branch network in the industry, we operate a sophisticated hybrid in-house and outsourced logistics and service infrastructure that we believe is highly differentiated from our competitors and enhances the value proposition we provide to customers. Precise scheduling of installations and removals, same-day delivery capabilities on certain products, and ability to mobilize large volumes of equipment in any geography serviced by our branch network are all unique capabilities that differentiate WillScot Mobile Mini, particularly among more demanding customer segments. We believe that continuing to further optimize our logistics and service capabilities through the deployment of technology is an opportunity for further cost efficiency and differentiation with our customers.
Investments in Technology Provide a Competitive Advantage Over Our Small and Midsize Competitors
We believe our technology serves as a primary differentiator over small and midsize competitors in local markets and initiatives underway to consolidate our operations onto our state of the art SAP enterprise resource planning platform will result in further efficiencies. Effective use of real‑time information allows us to monitor and optimize the utilization of our fleet, allocate our fleet to the highest demand markets, optimize pricing, and determine the best allocation of our capital to invest in fleet and branches.
We are able to dynamically price and approach customer accounts in a strategic and statistically informed manner. We also believe our ability to leverage this data helps us to increase our market share and effectively manage supply and demand dynamics in our fleet in order to maximize cash flow in all phases of the economic cycle, including identifying opportunities where underutilized lease fleet can be sold to generate cash.
Similarly, technology is continuing to develop related to our fleet to offer an enhanced experience for our customers. Unit tracking, electronic locking/security systems, and other customer‑facing technological benefits differentiate our fleet from competitors who have not invested in these capabilities. We believe we possess superior technology infrastructure relative to our competition and we intend to extend this advantage further by leveraging our infrastructure investments.
Diversified Revenue Base by End Market, Product, Service and Geography
We have established strong relationships with a diverse customer base, ranging from large national accounts to small local businesses. Our customers operate in a diversified set of end markets, including commercial and industrial, construction, education, energy and natural resources, government, and other end markets. For the year ended December 31, 2020, the top 50 combined customers for WillScot Mobile Mini accounted for less than 13% of pro forma revenues. We believe that the diversity of our customer end markets reduces our exposure to changes related to a given customer, shifts within an industry or geographic region, and end market industry seasonality, while also providing significant opportunities to grow our business. Furthermore, the nature of our products is such that their use is generally agnostic to industry. This flexibility insulates utilization from exposure to industry‑specific shocks, provided there are other needs and applications for these products within a reasonable distance. Accordingly, our business has been able to support front‑line workers and other essential businesses during the COVID‑19 crisis by providing temporary testing sites, treatment centers, exam rooms, hospital swing space, temperature screening checkpoints, office space to support social distancing, and storage for related supplies.
The following chart illustrates the breakdown of our customers and revenue by end markets, on a pro forma basis, as of December 31, 2020. In order to optimize the use of fleet assets across our branch network, we centrally manage fleet rebalancing across our end markets. This allows us to serve 15 distinct end markets in which no customer accounted for more than 2% of pro forma revenue for the year ended December 31, 2020.
| | | | | |
| REVENUE MIX BY END MARKET | CUSTOMER CONCENTRATION |
Attractive Cost and Revenue Synergy Opportunities with the Ability to Leverage Best Practices Across Both Companies
We have a strong track record of integrations generating significant synergies with our acquisitions of Modular Space Holdings, Inc. ("ModSpace"), Onsite Space LLC ("Tyson"), and Acton Mobile Holdings LLC ("Acton"), driving $61.0 million in cumulative annual synergies achieved as of December 31, 2020, and an additional $10.2 million in remaining synergies expected to be realized in the future.
We anticipate approximately $50 million of annual cost savings opportunities from the combination with Mobile Mini from purchasing and procurement economies of scale and general and administrative expense savings, particularly with respect to the consolidation of corporate‑related functions and elimination of redundancies. Similar to the ModSpace integration, we expect to incur approximately $75 million of one‑time cash integration, capital investment, restructuring, lease impairment, and other related charges in the first two years post-closing to realize the annual recurring cost savings. These costs will be incurred to integrate and consolidate information technology systems and for other consulting costs, breakage costs for redundant and overlapping leased facilities, fleet relocation costs, severance, and other personnel costs. We anticipate approximately 80% of these cost savings to be realized in our run rate by the end of 2022. However, there is no guarantee that we will achieve these cost savings in the amount or in the time frame that we anticipate. See “Risk Factors—Risks Relating to the Mobile Mini Merger—We may be unable to successfully acquire and integrate new operations, including Mobile Mini and our conversion to its SAP enterprise resource planning system, which could cause our business to suffer."
Our Asset Base Provides Highly Attractive Asset-Level Returns with Long Useful Lives
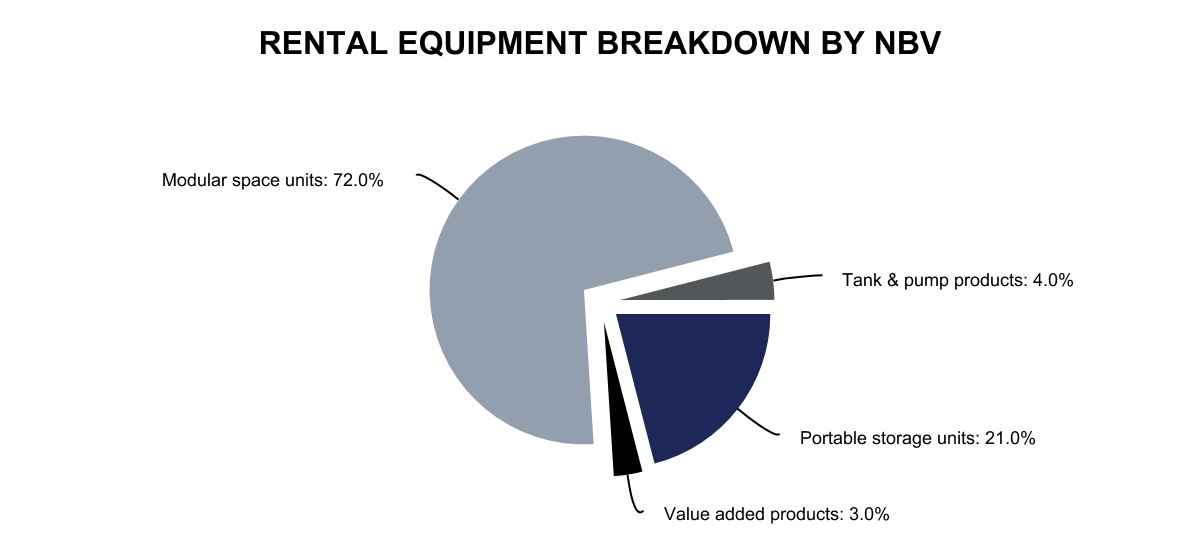
The combination of long, predictable lease durations, long asset lives, and attractive unit economics underpins the compelling cash generation capability in our business model. As such, we have made significant investments in our lease fleet and consolidated several competitors. For the year ended December 31, 2020, our modular space and portable storage lease fleet consisted of over 121 million square feet of relocatable space, comprising over 157,000 units, and over 197,000 storage solutions containers and office units.
We believe we generate an attractive internal rate of return ("IRR") in our modular space portfolio driven by the long economic life of our fleet, exceeding 20 years on average, inclusive of any capital expenditure ("capex") required to maintain the fleet to its value maximizing earning potential. Adding VAPS to our modular units increases the IRR of those units over the 20+ year useful life of the asset. On average, the payback period of a modular unit is only 36 months including VAPS.
Similarly, we believe portable storage containers are able to generate a higher IRR over their 30‑year useful life. These units require even less maintenance capex and have an average payback period of only 30 months. We believe the stability of cash flows combined with strong economic returns make both modular space and portable storage containers highly attractive specialty rental asset classes, and our logistics and service capabilities and investments in technology further enhance the returns we can generate from these assets.
The following chart illustrates the breakdown of the net book value ("NBV") of our rental equipment between the various modular space product types, portable storage and VAPS as of December 31, 2020.
Our Business Generates Predictable Recurring Cash Flow Due to Our Long-Term Leases and Flexible Capex Requirements
Our recurring revenue, combined with our flexible capex requirements, efficient working capital, and tax profile, has allowed us to generate substantial free cash flow, both in periods of growth and economic downturn. The long term nature of our leases, with average lease durations in excess of 32 months as of December 31, 2020, produces strong operating income and predictable cash flow.
We exercise control and discretion over capex, due to the longevity and relative simplicity of our products, the ability to invest only where needed and when needed to meet demand, and the ability to sell excess fleet during lower utilization periods. During periods of economic stress, we have the ability to substantially reduce capex throughout the portfolio in order to maximize cash flow, resulting in a counter‑cyclical free cash flow profile. See discussion of “COVID‑19 impact on business" within our "Recent Developments" section below.
Our Industry
We primarily operate within the modular space, portable storage, and specialty containment markets. Our services also span across a variety of related sectors, including furniture rental, transportation and logistics, facilities rental services, and commercial real estate.
Modular Space Market
The modular space market is fragmented. Modular space units are non-residential structures designed to meet federal, provincial, state, and local building codes and, in most cases, are designed to be relocatable. Modular space units are constructed offsite, utilizing manufacturing techniques to prefabricate single or multi-story whole building solutions in deliverable modular sections. Units are typically constructed of steel, wood and conventional building materials and can be permanent or relocatable.
The modular space market has evolved in recent years as businesses and other potential customers increasingly recognize the value of modular space. The key growth drivers in this market are similar to portable storage and include:
Growing need and demand for space: driven by general economic activity, including gross domestic product growth, industrial production, mining and natural resources activity, non-residential construction, urbanization, public and education spending, and the scale and frequency of special events.
Shift from traditional fixed, on-site built space to modular space solutions: driven by several advantages as compared with fixed, on-site built space, including:
•Quick to install: the pre-fabrication of modular space units allows them to be put in place rapidly, providing potential long-term solutions to needs that may have materialized quickly.
•Flexibility: flexible assembly design allows modular space units to be built to suit a customer’s needs while offering customers the ability to adjust their space as their needs change.
•Cost effectiveness: modular space units provide a cost-effective solution for temporary and permanent space requirements and allow customers to improve returns on capital in their core business.
•Quality: the pre-fabrication of modular space units is based on a repeatable process in a controlled environment, resulting in more consistent quality.
•Mobility: modular space units can easily be disassembled, transported to a new location and re-assembled.
•Environmentally friendly: relocatable buildings promote the reuse of facilities, on an as-needed basis, by the occupants.
Portable Storage Market
The portable storage market, like the modular space market, is highly fragmented and remains primarily local in nature. Portable storage units are typically ground‑level entry, windowless storage containers made of heavy exterior metals for secure storage and water tightness. Portable storage units can be built to specification or can be remanufactured from existing storage products, such as ISO shipping containers. Remanufacturing typically involves cleaning, removing rust and dents, repairing floors and sidewalls, painting, and adding company logos or signs as well as our patented Tri‑Cam Locking System®.
Portable storage units continue to find new applications as business needs change and develop. Demand for portable storage is driven by a number of factors, including:
Versatility: portable storage units can be easily customized to suit customer specifications. While standard applications include locking double‑door systems to facilitate loading. However, custom entrances, such as rolling or sliding doors, can be added for personnel access.
Affordability: portable storage provides customers with a flexible and low‑cost storage alternative to permanent warehouse space and fixed‑site self‑storage.
Safety: units can be easily outfitted with fire and water‑resistant surfaces and materials. ISO containers are often wind and leak‑proof by virtue of their uses in logistics and shipping. Nearly all units are made from steel, which is a low‑cost, durable material.
Security: a variety of enhanced locking mechanisms are available for portable storage units, including our patented Tri‑Cam Locking System® and ContainerGuardLock®. These features offer additional protection for high‑value goods and inventory.
Convenience: portable storage units provide immediate ground‑level access for consumers and can be easily transported in large quantities via truck, rail, or cargo ship.
Aesthetics: portable storage units can be easily painted and decorated with company colors and logos and are less conspicuous than other portable storage alternatives such as van trailers.
Specialty Containment Market
This market is served by our Tank and Pump Solutions business. In the specialty containment sector, we service different markets: the industrial market, comprised mainly of chemical facilities and refineries, also known as the “downstream” market and, to a lesser extent, companies engaged in the exploration and production of oil and natural gas, or the “upstream” market. Additionally, we serve a diversified group of customers engaged in projects in the construction, pipeline, and mining markets. Downstream customers utilize tank and pump equipment and services to manage and remove liquid and solid waste generated by ongoing operating activities as well as turn‑around projects and large‑scale expansion projects. Upstream customers, who we estimate represent approximately 2% of pro forma rental revenues for the year ended December 31, 2020, tend to rent steel tanks to store and transport water and propellant used in well hydraulic fracturing. Other customers utilize a wide variety of our products differentiated by the type of project in which they are engaged.
Other Related Markets
In the normal course of providing our “Ready to Work” solutions, we perform services that are characteristic of activities in other industries. For example, we coordinate a broad network of third-party and in-house transportation and service resources to support the timely movement of our products to, as well as maintenance on, customer sites. Additionally, we design, source, lease, and maintain a broad offering of ancillary products, including furniture, which render our modular units immediately functional in support of our customers’ needs. We have developed networks of third‑party service providers that we coordinate to expand the breadth of capabilities that our customers can source through us. These third‑party‑managed services represent incremental revenue and margin opportunities for us and simplify the number of vendor touchpoints for our customers.
We also provide technical expertise and oversight for customers regarding building design and permitting, site preparation, and expansion or contraction of installed space based on changes in project requirements. Further, we have the capability to compete in adjacent markets, such as commercial and institutional housing, which have received less focus historically in the modular space market. We believe that this broad service capability differentiates us from other rental and business services providers and clearly differentiates us in the marketplace.
Competition
Although our competition varies significantly by local market, the modular space and portable storage industry is highly competitive and fragmented as a whole. We believe that participants in our industry compete on the basis of customer
relationships, product quality and availability, delivery speed, VAPS and service capabilities, pricing, and overall ease of doing business. We typically compete with one or more local providers in all of our markets, as well as with a limited number of national and regional companies.
Our competitors include lessors of storage units, mobile offices, van trailers, and other structures used for portable storage. As a provider of portable storage, we also compete with conventional fixed self-storage facilities. Some of our competitors may have greater market share in certain geographic regions. Significant modular space and portable storage competitors include McGrath RentCorp, PODS, Pac-Van, ATCO Structures & Logistics, BOXX Modular, and 1-800-PACK-RAT in North America, and Wernick Hire and Elliott in the UK. Numerous other regional and local companies compete in individual markets.
Our Tank and Pump Solutions business offers liquid and solid containment products. The liquid and solid containment industry is also highly fragmented, consisting principally of local providers, with a handful of regional and national providers. We compete based on factors including quality and breadth of equipment, technical applications expertise, knowledgeable and experienced sales and service personnel, on‑time delivery and proactive logistics management, geographic areas serviced, rental rates, and customer service. Our competitors include United Rentals, Rain For Rent, Adler Tanks, Sprint/Republic Services, and numerous other smaller competitors.
Strategic Acquisitions
We believe the scalability of our branch network, corporate and shared services infrastructure, technology, and processes allows us to integrate acquisitions efficiently, realize cost savings, cross-sell VAPS, and improve the yield on acquired assets. As such, we manage an active acquisition pipeline and consider acquisitions to be an important component of our growth strategy.
Human Capital Management
As of December 31, 2020, we employed approximately 4,300 people worldwide, the majority of which are full time. Of these employees, approximately 3,800 are employed in North America, approximately 370 are employed in the UK, and approximately 100 are employed in Mexico. We have collective bargaining agreements in portions of our Mexico-based operations representing approximately 2% of our employees. Approximately 86% of employees work in our branch locations, while 14% serve in various corporate functions. We have not experienced a strike or significant work stoppage, and we consider our relations with the labor unions and employees to be good.
Our Chief Human Resources Officer along with other members of our executive leadership team develop and execute our human capital strategy. This includes attracting, acquiring, developing and engaging talent to deliver our strategy, designing employee compensation and benefits programs, and developing and integrating our inclusion and diversity ("I&D") initiatives.
Company Values
We believe that our people are our most valuable asset. Our company values are lived through our employees, acknowledged by our vendors and aligned to the needs of our customers and communities. We are:
Dedicated to Health & Safety: We are subject to certain environmental, health and safety and other laws and regulations in countries, states or provinces, and localities in which we operate. Our health and safety programs are designed around global standards with appropriate variations addressing the multiple jurisdictions and regulations, specific hazards and unique working environments of our operations. We take responsibility for our own well-being and for those around us. Health and safety are first, last and everything in-between.
Committed to Inclusion & Diversity: We are stronger together when we celebrate our differences and strive for inclusiveness. We believe that a rich culture of inclusion and diversity enables us to create, develop and fully leverage the strengths of our workforce to exceed customer expectations and meet our growth objectives. We encourage collaboration and support the diverse voices and thoughts of our employees and communities.
Driven to Excellence: We measure success through our results and achievement of our goals. We continuously improve ourselves and our products and services in pursuit of maximizing shareholder value.
Trustworthy & Reliable: We hold ourselves accountable to do the right thing especially when nobody’s looking.
Devoted to Our Customers: We anticipate the growing needs of our customers and strive to exceed their expectations and make it easy to do business with us.
Community Focused: We actively engage in the communities we serve and deliver sustainable solutions.
Inclusion and Diversity
We encourage and empower the diverse voices and contributions of our stakeholders to drive increased market share and global value. In 2020, we established a role in our human resources department to lead our I&D efforts company-wide. Our developing inclusiveness resource teams are established to support our employees and provide opportunities for exposure, development, and contribution to the organization.
Environmental and Social Responsibility and Safety
We are committed to upholding the highest standards when it comes to our environmental and social responsibilities, as well as the safety of our employees and our business partners, which we believe serves as a competitive advantage. We are a sustainable organization with long-lived, reusable and renewable assets that are constantly redeployed to customers with minimal residual environmental impact.
Our policies and practices are evident of our commitment to environmental responsibility and accountability and respect for human rights and fair labor standards. We have a company-wide focus on safety and have implemented numerous measures to promote workplace safety. Customers are increasingly focused on safety records in their sourcing decisions due to increased regulations to report all incidents that occur at their sites and the costs associated with such incidents. Our consolidated Total Recordable Incident Rate ("TRIR") remains well below 1.0, demonstrating what we believe to be exceptional performance in the area of workplace safety. TRIR is an important safety metric required by the Occupational Safety and Health Administration ("OSHA").
COVID-19 Safety Protocols
Our business, along with the rest of the world, faced unprecedented challenges in 2020 due to the impact of COVID-19. We remained dedicated to protecting the health and safety of our employees, vendors, and customers and adjusted our business to meet various country, state, and local requirements. We are considered an “essential business” and our employees are considered “essential workers”. We have continued to service our customers throughout the pandemic, while implementing robust health and safety protocols to protect our employees and customers, and we believe these robust protocols have differentiated us as a sophisticated partner in the eyes of our more demanding customer segments.
We follow US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and/or applicable country, state and local guidelines at the locations where we operate. To comply with public health guidance and reduce the risk of COVID-19 transmission, employees are required, prior to commencing work at our facilities and offices each day, to check their temperature and complete a daily symptom certification that is documented and reviewed by our COVID-19 team members. We provide masks and hand sanitizer to our employees, as well as require adherence to appropriate social distancing practices and regularly recurring cleaning/sanitization protocols at our locations. COVID-19 testing for employees is covered by insurance and we actively track key COVID-19 metrics. We have also deployed robust remote-work capabilities and technology across the workforce providing employees flexibility to operate when not required to be on-site at a company location.
Health & Wellness
The health and wellness of our employees is an extremely important facet of our workplace environment. We offer several health and wellness incentives to our employees. Our employee assistance program ("EAP") provides a variety of services to employees in need and was especially important during 2020 as COVID-19 impacted our workforce in different ways. We responded to the pandemic by continuing to prioritize employee health and safety as we conducted our business.
Employee Engagement
We believe that engaged employees are vital to continued business success. As such, we provide consistent touchpoints with employees to ensure that we have a strong understanding of employee sentiment. We have creative programming throughout the year designed to provide engagement opportunities for our workforce that unifies us, even as physical distance separates us. These touchpoints became increasingly more important in 2020 due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic.
Talent and Recruitment
We work diligently to attract top talent from a variety of sources to meet the current and future demands of our business. We have a strong employee value proposition that leverages our collaborative working environment, shared commitment to our company values. We strive to balance the recruitment of best-in-class external resources with the development and advancement of our in-house talent to foster a rich diversity of skills and perspectives, which we believe is an important source of competitive advantage.
Community and Partnering
We are proud to make a difference in places that we live and work. We strive to help our communities and hometowns by giving our time and talent to improve our surroundings. Our employees are encouraged to utilize up to 16 hours of paid time off to volunteer in their local communities. We have numerous partnerships with charitable organizations across the country that allow our employees to get involved and give back. Many of our senior leaders serve on boards of non-profit organizations. In 2020, we and our employees generously gave over $420,000 to a variety of causes that improve and advance our local communities.
Total Rewards or Pay Equity
We provide market competitive compensation and benefit packages to our employees. Beyond base compensation, we also offer short and long-term incentive programs, 401(k) with employee matching opportunities, healthcare and insurance benefits, health savings and flexible spending accounts, paid time off, family leave and tuition reimbursement among others (programs may vary by country/region, job level, and time with the organization). We obtain annual employee feedback on the
benefits we offer to ensure that we continue to offer competitive packages that appeal to top talent and allow us to recruit and retain our human capital.
Intellectual Property
We operate primarily under the WillScot and Mobile Mini brands. We protect our products and services through the use of trademarks and patents, none of which are individually material to our business. Our trademarks and patents are registered or pending applications for registrations in the US Patent and Trademark Office and various non‑US jurisdictions. On our Modular fleet, we maintain a patent for the design of our Flex units in the US and other patents in the US and non-US jurisdictions concerning various assembly and panel components. We believe that Flex represents the most innovative and versatile purpose built modular space in the industry, which has helped us expand commercially into new end markets. On our Storage fleet, we have patented our proprietary Tri‑Cam Locking System®, ContainerGuardLock® and other continued improvements in locking technology in the markets in which we operate, as well as in Europe and China. We believe that continued innovation differentiates WillScot Mobile Mini with our customers and represents a source of long-term competitive advantage.
Recent Developments
Mobile Mini Merger
On July 1, 2020, we closed the Merger at which time Mobile Mini became a wholly-owned subsidiary of WillScot. Concurrent with the closing of the Merger, we changed our name to WillScot Mobile Mini Holdings Corp. We believe that the Merger is resulting in strategic and financial benefits by combining the two industry leaders in the complementary modular space and portable storage solutions markets. We are executing the integration of the two companies' operating and financial systems, with a significant portion of these efforts being focused currently on the conversion of the combined company onto a single enterprise resource planning system, which is expected to take place in the first half of 2021.
Reportable Segments
Following the Merger, we modified our management structure and expanded from two reporting segments to four reporting segments: NA Modular, NA Storage, UK Storage, and Tank and Pump. Prior to the Merger, WillScot had two reporting segments, US Modular and Other North America Modular. These two segments were combined to create the new NA Modular segment, which represents the legacy WillScot operations. The other new segments, NA Storage, UK Storage, and Tank and Pump align to the legacy operations and segments reported by Mobile Mini. The new reporting segments are aligned with how we operate and analyze our business results.
Financing Activities
In anticipation of the Merger, on June 15, 2020, WillScot completed a private offering of $650.0 million in aggregate principal amount of 6.125% senior secured notes due 2025 (the “2025 Secured Notes”). The offering proceeds from the 2025 Secured Notes of $650.0 million were used to repay the 7.875% senior secured notes due 2022 (the “2022 Secured Notes”), repay Mobile Mini senior notes and pay certain fees and expenses related to the Merger and financing transactions.
On July 1, 2020, in connection with the completion of the Merger, we entered into a new asset-based credit agreement (the "2020 ABL Facility"), that provides for revolving credit facilities in the aggregate principal amount of up to $2.4 billion. Proceeds from the 2020 ABL Facility of $1.5 billion were used to repay the WillScot 2017 ABL facility, the Mobile Mini line of credit, and fees and expenses related to the Merger and financing transactions. The 2020 ABL Facility matures July 1, 2025.
On August 11, 2020, we redeemed $49.0 million of our 6.875% senior secured notes (the “2023 Secured Notes”) at a redemption price of 103.0% plus accrued and unpaid interest. This repayment was funded by the 2020 ABL facility.
On August 25, 2020, we completed a private offering of $500.0 million in aggregate principal amount of 4.625% senior secured notes due 2028 (the “2028 Secured Notes”). Proceeds from the 2028 Secured Notes were used to repay the $441.0 million remaining outstanding principal of the 2023 Secured Notes at a redemption price of 103.438% plus accrued and unpaid interest.
Sapphire Exchange
On June 30, 2020, as contemplated by the Merger Agreement, Sapphire Holding S.à r.l. (“Sapphire Holdings”), our largest shareholder, which is controlled by TDR Capital LLP (“TDR Capital”), exchanged (the “Sapphire Exchange”) each of its shares of common stock of Williams Scotsman Holdings Corp. ("Holdings"), a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Company, pursuant to an existing exchange agreement between WillScot and Sapphire Holdings, for 1.3261 shares of newly issued WillScot Class A common stock, par value $0.0001 per share (the “Class A Common Stock”). As a result of the Sapphire Exchange, all issued and outstanding shares of WillScot’s Class B common stock, par value $0.0001 per share, were automatically canceled for no consideration and the existing exchange agreement was automatically terminated. As a result of the Sapphire Exchange, Sapphire Holdings received 10,641,182 shares of Class A Common Stock.
Share Conversion
In connection with the Merger, on July 1, 2020, WillScot issued 106,426,722 shares of its Class A Common Stock in exchange for the outstanding shares of common stock of Mobile Mini, par value $0.01 per share, and subsequently filed an amended and restated certificate of incorporation, which reclassified all outstanding shares of the Class A Common Stock and converted such shares into shares of Common Stock, par value of $0.0001 per share, of WillScot Mobile Mini.
COVID‑19 impact on business
Since the outbreak of COVID‑19 was designated as a global pandemic by the World Health Organization (the “WHO”) in March 2020, our operations have generally continued to operate normally, albeit at lower activity levels in the second and third quarters of 2020, and with additional safety protocols in place as we have been considered an essential business in most jurisdictions. However, there have been significant changes to the global economic situation as a consequence of the COVID‑19 pandemic. The global pandemic has resulted in significant global social and business disruption, and in response we have modified the way we communicate and conduct business with our customers, suppliers, and employees.
During the year ended December 31, 2020, financial results for our operations were impacted by the COVID‑19 pandemic as we experienced reduced demand, particularly in the second and third quarters of the year. During this time, a portion of new project deliveries from our customers were either cancelled or delayed as a result of the COVID‑19 pandemic, and it remains unclear as to what extent such disruptions may impact our financial results in the future. On a pro forma basis, our deliveries were down 25% in the second quarter year over year and 13% in the third quarter year over year due to reduced demand primarily attributable to the current global economic situation as a consequence of the COVID‑19 pandemic. However, these impacts moderated in the fourth quarter and demand rebounded with deliveries up 2% year over year in the fourth quarter and up 0.3% sequentially from the third quarter to the fourth quarter of 2020. Furthermore, reduced delivery activity was substantially offset by reduced lease terminations which were approximately 19% below 2019 levels in the second and third quarters which helped stabilize our units on rent. Though recent demand has improved, the reduced delivery demand during the the second and third quarters of 2020 caused us to reduce variable costs and capital spending during those periods. These actions contributed to expanded profitability and cash flow in these periods, and activity levels and costs began to normalize heading into the fourth quarter. Despite this unprecedented demand shock, our long lease durations, our predictable cash inflows, and the fact that the majority of our gross profit in any given period is from units already out on rent, we believe we have visibility into our future cash flows and are able to plan ahead to adjust for varying demand levels.
The following summarizes many of the key actions we have taken in response to the COVID-19 pandemic:
Employee safety and health
We have implemented various employee safety measures to contain the spread of COVID‑19, including domestic and international travel restrictions, the promotion of social distancing and work‑from‑home practices, extensive cleaning protocols, daily symptom assessments, and enhanced use of personal protective equipment such as masks. We continue to closely monitor all guidance provided by applicable government agencies to ensure the safety of our employees, vendors, and customers as our top priority.
Sales and leasing operations
We continue to monitor government restrictions, which vary significantly across our geographic markets. As a result of the shelter‑in‑place orders and increased social distancing measures, some of our markets, such as special events and sports and entertainment, have experienced sustained reductions in demand for new projects. Other sectors, such as health care, have experienced increased demand, while other sectors such as construction have remained active but with varying degrees of project disruption, some of which are quite significant. We are also responding to demand across our end markets from customers in need of additional office space to facilitate social distancing. As we serve many critical sectors of the economy, we will continue to help support customers who remain operational, as well as those who are actively engaged in the COVID-19 response. We believe that our branch locations are considered essential businesses in most jurisdictions and as such have continued to operate normally with the aforementioned safety protocols in place, while our customer service and sales teams are working closely with customers to meet current demand.
Available Information
Our website address is www.willscotmobilemini.com. We make available, free of charge through our website, our Annual Report on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, Current Reports on Form 8-K, and amendments to those reports filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 (the “Exchange Act”) as soon as reasonably practicable after such documents are electronically filed with, or furnished to, the United States Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”). The SEC maintains an internet website at www.sec.gov that contains reports, proxy and information statements and other information regarding WillScot Mobile Mini.
Regulatory and Environmental Compliance
We are subject to certain environmental, transportation, anti-corruption, import control, health and safety, and other laws and regulations in countries, states or provinces, and localities in which we operate. We incur significant costs in our business to comply with these laws and regulations. However, from time to time we may be subject to additional costs and
penalties as a result of non-compliance. The discovery of currently unknown matters or conditions, new laws and regulations, or different enforcement or interpretation of existing laws and regulations could materially harm our business or operations in the future.
We are subject to laws and regulations that govern and impose liability for activities that may have adverse environmental effects, including discharges into air and water and handling and disposal of hazardous substances and waste. As of the date of this filing, no environmental matter has been material to our operations. Based on our management’s assessment, we believe that any environmental matters relating to us of which we are currently aware will not be material to our overall business or financial condition.
The jurisdictions in which we operate are also subject to anti-bribery laws and regulations, such as the US Foreign Corrupt Practices Act of 1977, as amended (the “FCPA”). These regulations prevent companies and their officers, employees, and agents from making payments to officials and public entities of foreign countries to facilitate obtaining new contracts. Violations of these laws and regulations may result in criminal sanctions and significant monetary penalties.
Certain of our units are subject to regulation in certain states under motor vehicle and similar registrations and certificate of title statutes. Management believes that the Company has complied, in all material respects, with all motor vehicle registration and similar certificate of title statutes in states where such statutes clearly apply to modular space units. We have not taken actions under such statutes in states where we have determined that such statutes do not apply to modular space units. However, in certain states, the applicability of such statutes to modular space units is not clear beyond doubt. If additional registration and related requirements are deemed to be necessary in such states or if the laws in such states or other states were to change to require us to comply with such requirements, we could be subject to additional costs, fees, and taxes as well as administrative burdens in order to comply with such statutes and requirements. Management does not believe that the effect of such compliance will be material to our business or financial condition.
ITEM 1A. Risk Factors
Risks Relating to Our Business
We may be unable to successfully acquire and integrate new operations, including Mobile Mini and our conversion to its enterprise resource planning system, which could cause our business to suffer.
We may be unable to successfully make strategic acquisitions or integrate acquired businesses or assets into our operations, including Mobile Mini, for various reasons. We completed the Mobile Mini Merger on July 1, 2020. While the Mobile Mini integration is underway, we may explore other acquisitions in the future that meet our strategic growth plans.
In particular, we are engaged in a conversion of the Company’s legacy enterprise resource planning system ("ERP") to Mobile Mini’s ERP. The ERP is designed to accurately maintain the company’s books and records and provide information important to the operation of the business to the company’s management team. The Company’s ERP conversion will continue to require significant investment of human and financial resources. In implementing the ERP, we may experience significant delays, increased costs and other difficulties. Any significant disruption or deficiency in the design and implementation of the ERP could adversely affect our ability to process orders, deliver units, send invoices and track payments, fulfill contractual obligations or otherwise operate our business. While we have invested significant resources in planning and project management, significant implementation issues may arise which could significantly impact our operations and financial performance.
Additionally, we cannot predict if or when acquisitions will be completed, and we may face significant competition for acquisition targets. Acquisitions involve numerous risks, including the following:
•difficulties in integrating the operations, technologies, products and personnel of the acquired companies;
•diversion of management’s attention from normal daily operations of the business;
•loss of key employees;
•difficulties in entering markets in which we have no or limited prior experience and where our competitors in such markets have stronger market positions;
•difficulties in complying with regulations, such as environmental regulations, and managing risks related to an acquired business;
•an inability to timely obtain financing, including any amendments required to existing financing agreements;
•an inability to implement uniform standards, controls, procedures and policies;
•undiscovered and unknown problems, defects, liabilities or other issues related to any acquisition that become known to us only after the acquisition, particularly relating to rental equipment on lease that are unavailable for inspection during the diligence process; and
•loss of key customers, suppliers or employees.
In connection with acquisitions, we may assume liabilities or acquire damaged assets, some of which may be unknown to us at the time of such acquisitions.
We assess the condition and regulatory certification of an acquired fleet as part of our acquisition due diligence. In some cases, fleet condition or regulatory certification may be difficult to determine due to the fleet being on lease at the time of acquisition and/or inadequate certification records. Fleet acquisitions may therefore result in a rectification cost that we may not have factored into the acquisition price, impacting deployability and ultimate profitability of the fleet we acquired.
We must continue to take actions to realize the combined cost synergies that we forecast for the acquisition. We may incur more costs than we anticipated to achieve the forecast synergies (thus reducing the net benefit of the cost synergies), realize synergies later than we expected or fail altogether to achieve a portion of the cost savings we anticipated. Any of these events could cause reductions in our earnings per share, impact our ability to borrow funds under our credit facility, decrease or delay the accretive effect of the acquisitions that we anticipated and negatively impact our stock price.
Acquisitions are inherently risky, and we cannot provide assurance that the Mobile Mini Merger, or any future acquisitions will be successful or will not materially adversely affect our business, results of operations and financial condition. If we do not manage new markets effectively, some of our new branches and acquisitions may lose money or fail, and we may have to close unprofitable branches. Closing a branch in such circumstances would likely result in additional expenses that would cause our operating results to suffer. To manage growth successfully, we will need to continue to identify additional qualified managers and employees to integrate acquisitions within our established operating, financial and other internal procedures and controls. We will also need to effectively motivate, train and manage our employees. Failure to successfully integrate recent and future acquisitions and new branches into existing operations could materially adversely affect our results of operations and financial condition.
Global or local economic movements could have a material adverse effect on our business.
Our business, which operates in the US, Canada, Mexico and the UK, may be negatively impacted by economic movements or downturns in the local markets in which we operate or global markets generally. These adverse economic conditions may reduce commercial activity, cause disruption and extreme volatility in global financial markets and increase rates of default and bankruptcy. Reduced commercial activity has historically resulted in reduced demand for our products and services. For example, reduced commercial activity in the construction, energy and natural resources sectors in certain markets in which we operate, particularly the US and Canada, has negatively impacted our business in the past. Disruptions in financial markets could negatively impact the ability of our customers to pay their obligations to us in a timely manner and increase our counterparty risk. If economic conditions worsen, we may face reduced demand and an increase, relative to historical levels, in the time it takes to receive customer payments. If we are not able to adjust our business in a timely and effective manner to changing economic conditions, our business, results of operations and financial condition may be materially adversely affected.
Moreover, the level of demand for our products and services is sensitive to the level of demand within various sectors, particularly the commercial and industrial, construction, education, energy and natural resources, and government end markets. Each of these sectors is influenced not only by the state of the general global economy, but also by a number of more specific factors as well. For example, a decline in global or local energy prices may materially adversely affect demand for modular buildings within the energy and resources sector. The levels of activity in these sectors and geographic regions may also be cyclical, and we may not be able to predict the timing, extent or duration of the activity cycles in the markets in which we or our key customers operate. A decline or slowed growth in any of these sectors or geographic regions could result in reduced demand for our products and services, which may materially adversely affect our business, results of operations and financial condition.
Our operations are exposed to operational, economic, political and regulatory risks.
We operate in the US, Canada, Mexico and the UK. For the year ended December 31, 2020, approximately 89.8%, 5.8%, 1.0%, and 3.4% of our revenue was generated in the US, Canada, Mexico and the UK, respectively. For the year ended December 31, 2020, approximately 76.9%, 16.2%, 3.4%, and 3.5% of our revenue was derived from our NA Modular Solutions business, NA Storage Solutions business, UK Storage Solutions business and Tank and Pump Solutions business, respectively.
Our operations in any of these countries could be affected by foreign and domestic economic, political and regulatory risks, including the following:
•regulatory requirements that are subject to change and that could restrict our ability to assemble, lease or sell products;
•inflation, recession, and fluctuations in foreign currency exchange and interest rates;
•trade protection measures, including increased duties and taxes and import or export licensing requirements;
•compliance with applicable antitrust and other regulatory rules and regulations relating to potential acquisitions;
•different local product preferences and product requirements;
•pressures on management time and attention due to the complexities of overseeing multi-national operations;
•challenges in maintaining staffing;
•different labor regulations and the potential impact of collective bargaining;
•potentially adverse consequences from changes in, or interpretations of, tax laws;
•political and economic instability;
•enforcement of remedies in various jurisdictions;
•the risk that the business partners upon whom we depend for technical assistance will not perform as expected;
•compliance with applicable export control laws and economic sanctions laws and regulations;
•price controls and ownership regulations;
•obstacles to the repatriation of earnings and cash;
•differences in business practices that may result in violation of company policies, including, but not limited to, bribery and collusive practices; and
•reduced protection for intellectual property in some countries.
These and other risks may materially adversely affect our business, results of operations and financial condition.
Our operations may be adversely impacted as a result of COVID‑19.
As a result of the ongoing global pandemic, governments around the world have implemented quarantines and significant restrictions on travel as well as work restrictions that prohibit many employees from going to work. As millions of cases of COVID‑19 have been confirmed around the world, we expect COVID‑19 to continue to impact general commercial activity related to our supply chain and customer base, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, or result of operations. To the extent that the COVID‑19 pandemic continues, worsens, or vaccines are delayed, governments may impose additional restrictions or additional governments may impose restrictions. COVID‑19 and those restrictions could result in additional businesses being shut down, additional work restrictions and supply chains being interrupted, slowed, or rendered inoperable. As a result, it may be challenging to obtain and process raw materials to support our business needs, we may need to recognize material charges in future periods for impairments of our rental equipment, property, plant, and equipment and/or intangible assets. Furthermore, our employees, suppliers or customers could become ill, quarantined or otherwise unable to work and/or travel due to health reasons or governmental restrictions. The COVID‑19 global pandemic has affected and may continue to affect our industry and the industries in which our customers operate, and there may be an adverse impact on customer demand for our rentals. We also have been, and will be, adversely impacted by project delays, early returns of equipment on rent with customers and payment delay, or non‑payment, by customers who are significantly impacted by COVID‑19. If our customers’ businesses continue to be affected, they might delay or reduce purchases from or payments to us, which could adversely affect our business, financial condition or results of operations.
In addition, increased volatility and diminished expectations for the global economy, coupled with the prospect of decreased business and consumer confidence and increased unemployment resulting from the COVID‑19 pandemic, may precipitate an economic slowdown and recession. If the economic climate deteriorates, our ability to continue to grow our business organically or through additional acquisitions and integration of acquired businesses, as well as the financial condition of customers, suppliers and lenders, could be adversely affected, resulting in a negative impact on the business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows of our company.
The situation surrounding COVID-19 remains fluid. A delay in wide distribution of a vaccine, or a lack of public acceptance of a vaccine, could lead people to continue to self-isolate and not participate in the economy at pre-pandemic levels for a prolonged period of time. Further, even if a vaccine is widely distributed and accepted, there can be no assurance that the vaccine will ultimately be successful in limiting or stopping the spread of COVID-19. Therefore, it remains difficult to predict the potential impact of the virus on our results of operations and financial position. The potential effects of COVID‑19 also could impact many of our risk factors, as discussed herein, including, but not limited to our exposure to operational, economic, political and regulatory risks; risks related to global or local economic movements; changes in trade policies; and labor disruptions. However, given the evolving health, economic, social, and governmental environments, the potential impact that COVID‑19 could have on our risk factors that are further described herein remains uncertain. Any future pandemics could similarly negatively impact our operations and financial results.
Any failure of our management information systems could disrupt our business operations both in the field and back office, which could result in decreased lease or sale revenue and increase overhead costs.
We rely heavily on information systems across our operations. We also utilize third-party cloud providers to host certain of our applications and to store data. Our ability to effectively manage our business depends significantly on the reliability and capacity of these systems. The failure of our management information systems to perform as anticipated could damage our reputation with our customers, disrupt our business or result in, among other things, decreased lease and sales revenue and increased overhead costs. Any such failure could harm our business, results of operations and financial condition. In addition, the delay or failure to implement information system upgrades and new systems effectively could disrupt our business, distract management’s focus and attention from business operations and growth initiatives and increase our implementation and operating costs, any of which could materially adversely affect our operations and operating results.
We believe we have implemented appropriate measures to mitigate potential risks; however, like other companies, our information technology systems may be vulnerable to a variety of interruptions due to our own error or events beyond our control. The measures that we employ to protect our systems may not detect or prevent cybersecurity breaches, natural disasters, terrorist attacks, telecommunication failures, computer viruses, hackers, phishing attacks, and other security issues. We have previously been the target of an attempted cyber-attack and have from time to time experienced threats to our data
and systems, computer virus attacks and phishing attempts, and we may be subject to breaches of the information systems that we use. We have not experienced a material cybersecurity breach. We have programs in place that are intended to detect, contain and respond to data security incidents and that provide employee awareness training regarding phishing, malware, and other cyber risks to protect against cyber risks and security breaches. However, because the techniques used to obtain unauthorized access, disable or degrade service, or sabotage systems change frequently and may be difficult to detect for long periods of time, we may be unable to anticipate these techniques or implement adequate preventative measures. In addition, because our systems contain information about individuals and other businesses, the failure to maintain the security of the data we hold, whether the result of our own error or the malfeasance or errors of others, could harm our reputation or give rise to legal liabilities leading to lower revenue, increased costs, regulatory sanctions and other potential material adverse effects on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
Effective management of our fleet is vital to our business, and our failure to properly safeguard, design, manufacture, repair and maintain our fleet could harm our business and reduce our operating results and cash flows.
Our modular space and portable storage units have long economic lives and managing our fleet is a critical element to our leasing business. Rental equipment asset management requires designing and building long-lived products that anticipate customer needs and changes in legislation, regulations, building codes and local permitting in the various markets in which we operate. In addition, we must cost-effectively maintain and repair our fleet to maximize the economic life of the products and the proceeds we receive from product sales. As the needs of our customers change, we may incur costs to relocate or retrofit our assets to better meet shifts in demand. If the distribution of our assets is not aligned with regional demand, we may be unable to take advantage of sales and leasing opportunities in certain regions, despite excess inventory in other regions. If we are not able to successfully manage our lease assets, our business, results of operations and financial condition may be materially adversely affected.
If we do not appropriately manage the design, manufacture, repair and maintenance of our product fleet, or if we delay or defer such repair or maintenance or suffer unexpected losses of rental equipment due to theft or obsolescence, we may be required to incur impairment charges for equipment that is beyond economic repair or incur significant capex to acquire new rental equipment to serve demand. These failures may also result in personal injury or property damage claims, including claims based on poor indoor air quality and termination of leases or contracts by customers. Costs of contract performance, potential litigation and profits lost from termination could materially adversely affect our future operating results and cash flows.
Trade policies and changes in trade policies, including the imposition of tariffs, their enforcement and downstream consequences, may materially adversely affect our business, results of operations, and outlook.
Tariffs and/or other developments with respect to trade policies, trade agreements and government regulations may materially, adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations. For example, the US government has imposed tariffs on steel, aluminum and lumber imports from certain countries, which could result in increased costs to us for these materials. Without limitation, (i) tariffs currently in place and (ii) the imposition by the federal government of new tariffs on imports to the US could materially increase (a) the cost of our products that we are offering for sale or lease, (b) the cost of certain products that we source from foreign manufacturers, and (c) the cost of certain raw materials or products that we utilize. We may not be able to pass such increased costs on to our customers, and we may not be able to secure sources of certain products and materials that are not subject to tariffs on a timely basis. Although we actively monitor our procurement policies and practices to avoid undue reliance on foreign-sourced goods subject to tariffs, when practicable, such developments may materially adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
We face significant competition in the modular space, portable storage and tank and pump industries. Such competition may result in pricing pressure or an inability to maintain or grow our market share. If we are unable to compete successfully, we could lose customers and our revenue and profitability could decline.
Although our competition varies significantly by market, the modular space, portable storage, and the tank and pump solutions industries are highly competitive, in general, and the portable storage and tank and pump solutions industries are highly fragmented. We compete on the basis of a number of factors, including customer relationships, product quality and availability, delivery speed, VAPS and service capabilities, pricing, and overall ease of doing business. We may experience pricing pressures in our operations as some of our competitors seek to obtain market share by reducing prices, and we may face reduced demand for our products and services if our competitors are able to provide new or innovative products or services that better appeal to customers. In most of our end markets, we face competition from national, regional and local companies who have an established market position in the specific service area, and we expect to encounter similar competition in any new markets that we may enter. In certain markets, some of our competitors may have greater market share, less debt, greater pricing flexibility, more attractive product or service offerings, better brand recognition or superior marketing and financial resources. Increased competition could result in lower profit margins, substantial pricing pressure and reduced market share. Price competition, together with other forms of competition, may materially adversely affect our business, results of operations and financial condition.
If we do not manage our credit risk effectively, collect on our accounts receivable, or recover our rental equipment from our customers, it could materially adversely affect our business, financial condition and results of operations.
We perform credit evaluation procedures on our customers on each transaction and require security deposits or other forms of security from our customers when we identify a significant credit risk. Failure to manage our credit risk and receive timely payments on our customer accounts receivable may result in the write-off of customer receivables and loss of units if we are unable to recover our rental equipment from our customers’ sites. If we are not able to manage credit risk, or if a large number of customers should have financial difficulties at the same time, our credit and rental equipment losses would increase above historical levels. If this should occur, our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows may be materially adversely affected.
We intend to continue to launch operations into new geographic markets and/or add other business unit operations in existing markets, which may be costly and may not be successful.
WillScot and Mobile Mini have in the past, and we intend in the future, to expand our Modular Space, Storage Solutions and Tank and Pump Solutions operations into new geographic markets in North America. This expansion could require financial resources that would not therefore be available for other aspects of our business. In addition, this expansion could require the time and attention of management, leaving less time to focus on existing business. If we fail to manage the risks inherent in our geographic expansion, we could incur capital and operating costs without any related increase in revenue, which would harm our operating results.
Changes in state building codes could adversely impact our ability to remarket our buildings, which could have a material adverse impact on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Building codes are generally reviewed, debated and, in certain cases, modified on a national level every three years as an ongoing effort to keep the regulations current and improve the life, safety and welfare of the building’s occupants. All aspects of a given code are subject to change, including, but not limited to, such items as structural specifications for earthquake safety, energy efficiency and environmental standards, fire and life safety, transportation, lighting and noise limits. On occasion, state agencies have undertaken studies of indoor air quality and noise levels with a focus on permanent and modular classrooms. This process leads to a systematic change that requires engagement in the process and recognition that past methods will not always be accepted. New modular construction is very similar to conventional construction where newer codes and regulations generally increase cost. New governmental regulations may increase our costs to acquire new rental equipment, as well as increase our costs to refurbish existing equipment.
Compliance with building codes and regulations entails risk as state and local government authorities do not necessarily interpret building codes and regulations in a consistent manner, particularly where applicable regulations may be unclear and subject to interpretation. These regulations often provide broad discretion to governmental authorities that oversee these matters, which can result in unanticipated delays or increases in the cost of compliance in particular markets. The construction and modular industries have developed many “best practices” which are constantly evolving. Some of our peers and competitors may adopt practices that are more or less stringent than ours. When, and if, regulators clarify regulatory standards, the effect of the clarification may be to impose rules on our business and practices retroactively, at which time we may not be in compliance with such regulations and we may be required to incur costly remediation. If we are unable to pass these increased costs on to our customers, our business, financial condition, operating cash flows and results of operations could be negatively impacted.
Our operations face foreign currency exchange rate exposure, which may materially adversely affect our business, results of operations and financial condition.
We hold assets, incur liabilities, earn revenue and pay expenses in certain currencies other than the US Dollar, primarily the Canadian Dollar, the Mexican Peso and the British Pound. Our consolidated financial results are denominated in US Dollars, and therefore, during times of a strengthening US Dollar, our reported revenue in non-US Dollar jurisdictions will be reduced because the local currency will translate into fewer US Dollars. Revenue and expenses are translated into US Dollars at the average exchange rate for the period. In addition, the assets and liabilities of our non-US Dollar subsidiaries are translated into US Dollars at the exchange rates in effect on the balance sheet date. Foreign currency exchange adjustments arising from certain intercompany obligations with and between our domestic companies and our foreign subsidiaries are marked-to-market and recorded as a non-cash loss or gain in each of our financial periods in our consolidated statements of operations. Accordingly, changes in currency exchange rates will cause our foreign currency translation adjustment in the consolidated statements of comprehensive income (loss) to fluctuate. In addition, fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates will impact the amount of US Dollars we receive when we repatriate funds from our non-US Dollar operations.
Fluctuations in interest rates and commodity prices may also materially adversely affect our revenues, results of operations and cash flows.
Although we have converted a portion of our senior secured revolving credit facility borrowings into fixed-rate debt through interest rate swaps, a significant portion of our borrowings under the facility remain variable rate debt. Fluctuations in interest rates may negatively impact the amount of interest payments, as well as our ability to refinance portions of our existing debt in the future at attractive interest rates. In addition, certain of our end markets, as well as portions of our cost structure,
such as transportation costs, are sensitive to changes in commodity prices, which can impact both demand for and profitability of our services. These changes could impact our future earnings and cash flows, assuming other factors are held constant.
Significant increases in raw material and labor costs could increase our operating costs significantly and harm our profitability.
We incur labor costs and purchase raw materials, including steel, lumber, siding and roofing, paint, glass, fuel and other products to perform periodic repairs, modifications and refurbishments to maintain physical conditions of our units and in connection with get-ready, delivery and installation of our units. The volume, timing and mix of such work may vary quarter-to-quarter and year-to-year. Generally, increases in labor and raw material costs will increase the acquisition costs of new units and also increase the repair and maintenance costs of our fleet. We also maintain a truck fleet to deliver units to and return units from our customers, the cost of which is sensitive to maintenance and fuel costs and rental rates on leased equipment. During periods of rising prices for labor or raw materials, and in particular, when the prices increase rapidly or to levels significantly higher than normal, we may incur significant increases in our acquisition costs for new units and higher operating costs that we may not be able to recoup from customers through changes in pricing, which could materially adversely affect our business, results of operations and financial condition. If raw material prices decline significantly, we may have to write down our raw materials inventory values. If this happens, our results of operations and financial condition could decline.
Fluctuations in fuel costs or oil prices, a reduction in fuel supplies, or a sustained decline in oil prices may have a material adverse effect on our business and results of operations.
In connection with our business, to better serve our customers and limit our capex, we often move our fleet from branch to branch. In addition, the majority of our customers arrange for delivery and pickup of our units through us. Accordingly, we could be materially adversely affected by significant increases in fuel prices that result in higher costs to us for transporting equipment. In the event of fuel and trucking cost increases, we may not be able to promptly raise our prices to make up for increased costs. A significant or prolonged price fluctuation or disruption of fuel supplies could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
Additionally, oil prices have been volatile and are subject to fluctuations in response to changes in supply and demand, market uncertainty and a variety of additional factors that are beyond our control. If oil prices remain volatile for an extended period of time or there is a sustained decline in demand for oil, demand for our Tank and Pump Solutions products from refineries and companies engaged in the exploration and production of oil and natural gas could be adversely impacted, which would in turn have an adverse effect on our results of operations and financial condition.
Third parties may fail to manufacture or provide necessary components for our products properly or in a timely manner.
We are often dependent on third parties to manufacture or supply components for our products. We typically do not enter into long-term contracts with third-party suppliers. We may experience supply problems as a result of financial or operating difficulties or the failure or consolidation of our suppliers. We may also experience supply problems as a result of shortages and discontinuations resulting from product obsolescence or other shortages or allocations by suppliers. Unfavorable economic conditions may also adversely affect our suppliers or the terms on which we purchase products. In the future, we may not be able to negotiate arrangements with third parties to secure products that we require in sufficient quantities or on reasonable terms. If we cannot negotiate arrangements with third parties to produce our products or if the third parties fail to produce our products to our specifications or in a timely manner, our business, results of operations and financial condition may be materially adversely affected.
We are subject to risks associated with labor relations, labor costs and labor disruptions.
We are subject to the costs and risks generally associated with labor disputes and organizing activities related to unionized labor. From time to time, strikes, public demonstrations or other coordinated actions and publicity may disrupt our operations. We may incur increased legal costs and indirect labor costs as a result of contractual disputes, negotiations or other labor-related disruptions. We have collective bargaining agreements with employees in portions of our Mexico-based operations, which accounted for approximately 2.0% of our total employees as of December 31, 2020. These operations may be more highly affected by labor force activities than others, and all collective bargaining agreements must be renegotiated annually. Other locations may also face organizing activities or effects. Labor organizing activities could result in additional employees becoming unionized. Furthermore, collective bargaining agreements may limit our ability to reduce the size of work forces during an economic downturn, which could put us at a competitive disadvantage. We believe a unionized workforce outside of Mexico would generally increase our operating costs, divert attention of management from servicing customers and increase the risk of work stoppages, all of which could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations or financial condition.
Failure to retain key personnel could impede our ability to execute our business plan and growth strategy.
Our ability to profitably execute our business plan depends on our ability to attract, develop and retain qualified personnel. Certain of our key executives, managers and employees have knowledge and an understanding of our business and our industry, and/or have developed meaningful customer relationships, that cannot be duplicated readily. Our ability to attract and retain qualified personnel is dependent on, among other things, the availability of qualified personnel and our ability to provide a competitive compensation package, including the implementation of adequate drivers of retention and rewards
based on performance, and work environment. Failure to retain qualified key personnel may materially adversely affect our business, results of operations and financial condition. The departure of any key personnel and our inability to enforce non-competition agreements could have a negative impact on our business.
Moreover, labor shortages, the inability to hire or retain qualified employees and increased labor costs could have a material adverse effect on our ability to control expenses and efficiently conduct our operations. We may not be able to continue to hire and retain the sufficiently skilled labor force necessary to operate efficiently and to support our operating strategies. Labor expenses could also increase as a result of continuing shortages in the supply of personnel.
If we determine that our goodwill, intangible assets, and indefinite-life intangible assets have become impaired, we may incur impairment charges, which may adversely impact our operating results.
We have a substantial amount of goodwill and indefinite-life intangible assets (trade names), which represents the excess of the total purchase price of our acquisitions over the fair value of the assets acquired, and other intangible assets. As of December 31, 2020, we had approximately $1,171.2 million and $495.9 million of goodwill and intangible assets, net, respectively, in our consolidated balance sheets, which represented approximately 21.0% and 9.0% of total assets, respectively, and primarily arose through our acquisition of Mobile Mini.
We test goodwill and indefinite-lived intangible assets for impairment on an annual basis and when events occur or circumstances change that indicate that the fair value of the reporting unit or intangible asset may be below its carrying amount. Fair value determinations require considerable judgment and are sensitive to inherent uncertainties and changes in estimates and assumptions regarding revenue growth rates, EBIT margins, capex, working capital requirements, tax rates, terminal growth rates, discount rates, exchange rates, royalty rates, benefits associated with a taxable transaction and synergistic benefits available to market participants. Impairment may result from, among other things, deterioration in the performance of the business, adverse market conditions, stock price and adverse changes in applicable laws and regulations, including changes that restrict our activities. Declines in market conditions, a trend of weaker than anticipated financial performance for our reporting units or declines in projected revenue, a decline in our share price for a sustained period of time, an increase in the market-based weighted average cost of capital or a decrease in royalty rates, among other factors, are indicators that the carrying value of our goodwill or indefinite-life intangible assets may not be recoverable. These risks may be heightened by the COVID-19 pandemic. In the event impairment is identified, a charge to earnings would be recorded which may materially adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations.
Our ability to use our net operating loss carryforwards and other tax attributes may be limited.
As of December 31, 2020, we had US net operating loss (“NOL”) carryforwards of approximately $1,187.5 million and $700.5 million for US federal income tax and state tax purposes, respectively, available to offset future taxable income, prior to consideration of annual limitations that Section 382 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 may impose. The US NOL carryforwards begin to expire in 2021 for state and 2022 for federal if not utilized. In addition, we had foreign NOLs of $14.1 million as a result of operations in Canada and Mexico. Our Mexico and Canadian NOL carryforwards begin to expire in 2025 and 2038, respectively, if not utilized.
Our US NOL and tax credit carryforwards could expire unused and be unavailable to offset future income tax liabilities. Under Section 382 of the Internal Revenue Code and corresponding provisions of US state law, if a corporation undergoes an “ownership change,” generally defined as a greater than 50% change, by value, in its equity ownership over a three-year period, the corporation’s ability to use its US NOLs and other applicable tax attributes before the ownership change, such as research and development tax credits, to offset its income after the ownership change may be limited. We have completed Section 382 analysis for the Mobile Mini Merger. As a result, if we earn net taxable income, our ability to use our pre-Mobile Mini Merger US NOL carryforwards to offset US federal taxable income may be subject to limitations, which could potentially result in increased future tax liability to us. In addition, at the state level, there may be periods during which the use of US NOLs is suspended or otherwise limited, which could accelerate or permanently increase state taxes owed.
Lastly, we may experience ownership changes in the future as a result of subsequent shifts in our stock ownership, some of which may be outside of our control. If we determine that an ownership change has occurred and our ability to use our historical NOL and tax credit carryforwards is materially limited, it may result in increased future tax obligations and income tax expense.
Some of the tax loss carryforwards could expire, and if we do not have sufficient taxable income in future years to use the tax benefits before they expire, the benefit may be permanently lost. In addition, the taxing authorities could challenge our calculation of the amount of our tax attributes, which could reduce certain of our recognized tax benefits. Further, tax laws in certain jurisdictions may limit the ability to use carryforwards upon a change in control.
We may be unable to recognize deferred tax assets such as those related to our tax loss carryforwards and, as a result, lose future tax savings, which could have a negative impact on our liquidity and financial position.
We recognize deferred tax assets primarily related to deductible temporary differences based on our assessment that the item will be utilized against future taxable income and the benefit will be sustained upon ultimate settlement with the applicable taxing authority. Such deductible temporary differences primarily relate to tax loss carryforwards and business interest expense limitations. Tax loss carryforwards arising in a given tax jurisdiction may be carried forward to offset taxable
income in future years from such tax jurisdiction and reduce or eliminate income taxes otherwise payable on such taxable income, subject to certain limitations. Deferred interest expense exists primarily within our US operating companies, where interest expense was not previously deductible as incurred but may become deductible in the future subject to certain limitations. We may have to write down, through income tax expense, the carrying amount of certain deferred tax assets to the extent we determine it is not probable we will realize such deferred tax assets under US GAAP.
Unanticipated changes in our tax obligations, the adoption of a new tax legislation, or exposure to additional income tax liabilities could affect profitability.
We are subject to income taxes in the US, Canada, Mexico and the UK. Our tax liabilities are affected by the amounts we charged for inventory, services, funding and other transactions on an intercompany basis. We are subject to potential tax examinations in these jurisdictions. Tax authorities may disagree with our intercompany charges, cross-jurisdictional transfer pricing or other tax positions and assess additional taxes. We regularly assess the likely outcomes of these examinations to determine the appropriateness of our tax provision. However, there can be no assurance that we will accurately predict the outcomes of these potential examinations, and the amounts that we ultimately pay upon resolution of examinations could be materially different from the amounts we previously included in our income tax provision and, therefore, could have a material impact on our results of operations and cash flows. In addition, our future effective tax rate could be adversely affected by changes to our operating structure, changes in the mix of earnings in countries with differing statutory tax rates, changes in the valuation allowance of deferred tax assets, changes in tax laws and the discovery of new information in the course of our tax return preparation process. Changes in tax laws or regulations, including changes in the US related to the treatment of accelerated depreciation expense, carry-forwards of net operating losses, and taxation of foreign income and expenses may increase tax uncertainty and adversely affect our results of operations.
We are subject to various laws and regulations, including those governing government contracts, corruption and the environment. Obligations and liabilities under these laws and regulations may materially harm our business.
Government Contract Laws and Regulations
We lease and sell our products to government entities, and this subjects us to statutes and regulations applicable to companies doing business with the government. The laws governing government contracts can differ from the laws governing private contracts. For example, many government contracts contain favorable pricing terms and conditions that are not typically included in private contracts, such as clauses that make certain obligations of government entities subject to budget appropriations. Many government contracts can be terminated or modified, in whole or in part, at any time, without penalty, by the government. In addition, our failure to comply with these laws and regulations might result in administrative penalties or the suspension of our government contracts or debarment and, as a result, the loss of the related revenue which would harm our business, results of operations and financial condition. We are not aware of any action contemplated by any regulatory authority related to any possible non-compliance by or in connection with our operations.
Our operations are subject to an array of governmental regulations in each of the jurisdictions in which we operate. For example, our activities in the US are subject to regulation by several federal and state government agencies, including the Occupational Safety and Health Administration, and by federal and state laws. Our operations and activities in other jurisdictions are subject to similar governmental regulations. Similar to conventionally constructed buildings, the modular business industry is also subject to regulations by multiple governmental agencies in each jurisdiction relating to, among others, environmental, zoning and building standards, and health, safety and transportation matters. These regulations affect our Storage Solutions and Tank and Pump Solutions customers, most of whom use our storage units to store their goods on their own properties for various lengths of time. If local zoning laws or planning permission regulations in one or more of our markets no longer allow our units to be stored on customers' sites, our business in that market will suffer. Noncompliance with applicable regulations, implementation of new regulations or modifications to existing regulations may increase costs of compliance, require a termination of certain activities or otherwise materially adversely affect our business, results of operations and financial condition.
US Government Contract Laws and Regulations
Our government customers include the US government, which means we are subject to various statutes and regulations applicable to doing business with the US government. These types of contracts customarily contain provisions that give the US government substantial rights and remedies, many of which are not typically found in commercial contracts and which are unfavorable to contractors, including provisions that allow the government to unilaterally terminate or modify our federal government contracts, in whole or in part, at the government’s convenience. Under general principles of US government contracting law, if the government terminates a contract for convenience, the terminated company may generally recover only its incurred or committed costs and settlement expenses and profit on work completed prior to the termination. If the government terminates a contract for default, the defaulting company may be liable for any extra costs incurred by the government in procuring undelivered items from another source.
In addition, US government contracts and grants normally contain additional requirements that may increase our costs of doing business, reduce our profits, and expose us to liability for failure to comply with these terms and conditions. These requirements include, for example:
• specialized disclosure and accounting requirements unique to US government contracts;
•financial and compliance audits that may result in potential liability for price adjustments, recoupment of government funds after such funds have been spent, civil and criminal penalties, or administrative sanctions such as suspension or debarment from doing business with the US government;
•public disclosures of certain contract and company information; and
•mandatory socioeconomic compliance requirements, including labor requirements, non-discrimination and affirmative action programs and environmental compliance requirements.
If we fail to comply with these requirements, our contracts may be subject to termination, and we may be subject to financial and/or other liability under our contracts or under the Federal Civil False Claims Act (the "False Claims Act"). The False Claims Act’s “whistleblower” provisions allow private individuals, including present and former employees, to sue on behalf of the US government. The False Claims Act statute provides for treble damages and other penalties, and if our operations are found to be in violation of the False Claims Act, we could face other adverse action, including suspension or prohibition from doing business with the US government. Any penalties, damages, fines, suspension or damages could adversely affect our ability to operate our business and our financial results.
Department of Transportation Regulations
We operate in the US pursuant to operating authority granted by the US Department of Transportation (the “DOT”). Our drivers must comply with the safety and fitness regulations of the DOT, including those relating to drug and alcohol testing and hours of service. Such matters as equipment weight and dimensions are also subject to government regulations. Our safety record could be ranked poorly compared to peer firms. A poor safety ranking may result in the loss of customers or difficulty attracting and retaining qualified drivers which could affect our results of operations. Should additional rules be enacted in the future, compliance with such rules could result in additional costs.
Anti-Corruption Laws and Regulations
We are subject to various anti-corruption laws that prohibit improper payments or offers of payments to foreign governments and their officials by a US person for the purpose of obtaining or retaining business. We operate in countries that may present a more corruptible business environment than the US Such activities create the risk of unauthorized payments or offers of payments by one of our employees or agents that could be in violation of various laws, including the FCPA. We have implemented safeguards and policies to discourage these practices by our employees and agents. However, existing safeguards and any future improvements may prove to be ineffective and employees or agents may engage in conduct for which we might be held responsible.
If employees violate our policies or we fail to maintain adequate record-keeping and internal accounting practices to accurately record our transactions, we may be subject to regulatory sanctions. Violations of the FCPA or other anti-corruption laws may result in severe criminal or civil sanctions and penalties, including suspension or debarment from US government contracting, and we may be subject to other liabilities which could materially adversely affect our business, results of operations and financial condition. We are also subject to similar anti-corruption laws in other jurisdictions.
Environmental Laws and Regulations
We are subject to a variety of national, state, regional and local environmental laws and regulations. Among other things, these laws and regulations impose limitations and prohibitions on the discharge and emission of, and establish standards for the use, disposal and management of, regulated materials and waste and impose liabilities for the costs of investigating and cleaning up, and damages resulting from, present and past spills, disposals or other releases of hazardous substances or materials. In the ordinary course of business, we use and generate substances that are regulated or may be hazardous under environmental laws. We have an inherent risk of liability under environmental laws and regulations, both with respect to ongoing operations and with respect to contamination that may have occurred in the past on our properties or as a result of our operations. For example, we own, transport and rent tanks and boxes in which waste materials are placed by our customers. Although we have a policy which, with certain limited exceptions, requires customers to return tanks and containers clean of any substances, they may fail to comply with these obligations. Additionally, we may provide waste hauling services, which involves environmental risks during transport. While we endeavor to comply with all regulatory requirements, from time to time, our operations or conditions on properties that we have acquired have resulted in liabilities under these environmental laws. We may in the future incur material costs to comply with environmental laws or sustain material liabilities from claims concerning noncompliance or contamination. Under certain environmental laws, we could be held responsible for all of the costs relating to any contamination at, or migration to or from, our or our predecessors' past or present facilities. These laws often impose liability even if the owner, operator or lessor did not know of, or was not responsible for, the release of such hazardous substances. We have no reserves for any such liabilities.
We are also required to obtain environmental permits from governmental authorities for certain of our operations. If we violate or fail to obtain or comply with these laws, regulations, or permits, we could be fined or otherwise sanctioned by regulators. We could also become liable if employees or other parties are improperly exposed to hazardous materials.
In addition, ongoing governmental review of hydraulic fracturing (“fracking”) and its environmental impact could lead to changes to this activity or its substantial curtailment, which could adversely affect our revenue and results of operations. Approximately 2% of our consolidated rental revenue for the year ended December 31, 2020 was related to customers involved in the upstream exploration and production of oil and natural gas. A portion of this revenue involves rentals to customers that use the fracking method to extract natural gas. The US Environmental Protection Agency has issued regulations or guidance regarding certain aspects of the process. Other federal, state and local governments and
governmental agencies also investigate and/or regulate fracking. Additional governmental regulation could result in increased costs of compliance or the curtailment of fracking in the future, which would adversely affect our revenue and results of operations.
We cannot predict what environmental legislation or regulations will be enacted in the future, how existing or future laws or regulations will be administered or interpreted, or what environmental conditions may be found to exist at our facilities or at third party sites for which we may be liable. Enactment of stricter laws or regulations, stricter interpretations of existing laws and regulations or the requirement to undertake the investigation or remediation of currently unknown environmental contamination at sites we own or third-party sites may require us to make additional expenditures, some of which could be material.
Our customer base includes customers operating in a variety of industries which may be subject to changes in their competitive environment as a result of the global, national or local economic climate in which they operate and/or economic or financial disruptions to their industry.
Our customer base includes customers operating in a variety of industries, including commercial and industrial, construction, education, energy and natural resources, government, retail and other end markets. Many of these customers, across this wide range of industries, are facing economic and/or financial pressure from changes to their industry resulting from the global, national and local economic climate in which they operate and industry‑specific economic and financial disruptions, including, in some cases, consolidation and lower sales revenue from physical locations, resulting from the impact of the COVID‑19 pandemic and the related changes in political, social and economic conditions. These and any future changes to any of the industries in which our customers operate could cause them to rent fewer units from us or otherwise be unable to satisfy their obligations to us. In addition, certain of our customers are facing financial pressure and such pressure, from COVID‑19 or other factors, may result in consolidation in some industries and/or an increase in bankruptcy filings by certain customers. Each of these facts and industry impacts, individually or in the aggregate, could have a materially adverse effect on our operating results.
Our operational measures designed to increase revenue while continuing to control operating costs may not generate the expected improvements and efficiencies and may not drive growth or returns.
We continually initiate new operational processes designed to increase revenue while continuing to pursue our strategy of reducing operating costs where available. Additionally, we employ a hybrid sales strategy of using local sales people in addition to a centralized call center team designed to meet customer needs and drive revenue growth. However, no assurance can be given that these strategies will achieve the desired goals and efficiencies in the future. The success of these strategies is somewhat dependent on a number of factors that are beyond our control.
Even if we carry out these processes in the manner we currently expect, we may not achieve the improvements or efficiencies we anticipate, or on the timetable we anticipate. There may be unforeseen productivity, revenue or other consequences resulting from our strategies that will adversely affect us or impact our strategies for asset management. Therefore, there can be no guarantee that our strategies will prove effective in achieving desired profitability, margins, or returns on capital employed. Additionally, these strategies may have adverse consequences if our cost cutting and operational changes are deemed by customers to adversely impact product quality or service levels.
We may not be able to adequately protect our intellectual property and other proprietary rights that are material to our business.
Our ability to compete effectively depends in part upon protection of our rights in trademarks, copyrights and other intellectual property rights we own or license, including patents to the Mobile Mini locking system. Our use of contractual provisions, confidentiality procedures and agreements, and trademark, copyright, unfair competition, trade secret and other laws to protect our intellectual property and other proprietary rights may not be adequate. Litigation may be necessary to enforce our intellectual property rights and protect our proprietary information and patents, or to defend against claims by third parties that our services or our use of intellectual property infringe their intellectual property rights. Any litigation or claims brought by or against us could result in substantial costs and diversion of resources. A successful claim of trademark, copyright or other intellectual property infringement against us could prevent us from providing services, which could harm our business, financial condition or results of operations. In addition, a breakdown in our internal policies and procedures may lead to an unintentional disclosure of our proprietary, confidential or material non‑public information, which could in turn harm our business, financial condition or results of operations.
Our operations could be subject to natural disasters and other business disruptions, which could materially adversely affect our information systems, future revenue, financial condition, cash flows and increase our costs and expenses.
Our operations could be subject to natural disasters and other business disruptions such as pandemics, fires, floods, hurricanes, earthquakes and terrorism, which could adversely affect our information systems, future revenue, financial condition, and cash flows and increase our costs and expenses. See "Our operations may be adversely impacted as a result of COVID-19." In addition, the occurrence and threat of terrorist attacks may directly or indirectly affect economic conditions, which could adversely affect demand for our products and services. In the event of a major natural or man-made disaster, we could experience loss of life of our employees, destruction of facilities or business interruptions, any of which may materially
adversely affect our business. If any of our facilities or a significant amount of our rental equipment were to experience a catastrophic loss, it could disrupt our operations, delay orders, shipments and revenue recognition and result in expenses to repair or replace the damaged rental equipment and facility not covered by asset, liability, business continuity or other insurance contracts. Also, we could face significant increases in premiums or losses of coverage due to the loss experienced during and associated with these and potential future natural or man-made disasters that may materially adversely affect our business. In addition, attacks or armed conflicts that directly impact one or more of our properties could significantly affect our ability to operate those properties and thereby impair our results of operations.
In general, any of these events could cause consumer confidence and spending to decrease or result in increased volatility in the global economy and worldwide financial markets. Any such occurrence could materially adversely affect our business, results of operations and financial condition.
We may incur property, casualty or other losses not covered by our insurance.
We are partly self-insured for a number of different risk categories, such as property, general liability (including product liability), workers' compensation, automobile claims, crime, and cyber liability, with insurance coverage for certain catastrophic risks. The types and amounts of insurance may vary from time to time based on our decisions with respect to risk retention and regulatory requirements. The occurrence of significant claims, a substantial rise in costs to maintain our insurance, or the failure to maintain adequate insurance coverage could have an adverse impact on our financial condition and results of operations.
We may not be able to redeploy our units effectively should a significant number of our leased units be returned during a short period of time, which could adversely affect our financial performance.
While our typical lease terms include contractual provisions requiring customers to retain units on lease for a specified period, our customers generally rent their units for periods longer than the contractual lease terms. As of December 31, 2020, the average lease duration of our lease portfolio was approximately 32 months. If a significant number of leased units are returned in a short period of time, a large supply of units would need to be remarketed. Our failure to effectively remarket a large influx of units returning from leases could materially adversely affect our financial performance.
Failure to close our unit sales transactions as we project could cause our actual revenue or cash flow for a particular fiscal period to differ from expectations.
Sales of new and used modular space and portable storage units to customers represented approximately 6.7% of WillScot Mobile Mini's revenue during the year ended December 31, 2020. Sale transactions are subject to certain factors that are beyond our control, including permit requirements, the timely completion of prerequisite work by others and weather conditions. Accordingly, the actual timing of the completion of these transactions may take longer than we expect. As a result, our actual revenue and cash flow in a particular fiscal period may not consistently correlate to our internal operational plans and budgets. If we are unable to accurately predict the timing of these sales, we may fail to take advantage of business and growth opportunities otherwise available, and our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows may be materially adversely affected.
Certain of our warrants are accounted for as liabilities and the changes in the fair values of the warrants could have a material effect on our financial results.
The Company accounts for (i) the 2015 Private Warrants as liabilities for all periods presented, (ii) the 2015 Public Warrants as liabilities through the first quarter of 2020 and (iii) the 2018 Warrants as liabilities until June 30, 2020, the date all issued and outstanding shares of the Company's Class B Common Stock were cancelled. Prior to the SEC Staff Statement on April 12, 2021, the Company had previously accounted for its Warrants as components of equity, consistent with common market practice. Under liability accounting treatment, the Company is required to measure the fair value of the warrants at the end of each reporting period and recognize changes in the fair value from the prior period in the Company's operating results for the current period. Fluctuations in the fair value of our Warrants are primarily driven by changes in our stock price. As a result of this recurring fair value measurement, our financial statements and results of operations may fluctuate quarterly based on factors which are outside our control. We expect that we will recognize non-cash gains or losses due to the quarterly mark-to-market of our Warrants and that such gains or losses could be material and may not be reflective of the performance of our underlying business operations.
A material weakness in our internal control over financial reporting related to our accounting for warrants was determined to exist. If we are unable to maintain an effective system of internal controls, we may not be able to accurately report our financial results, which could lead to a loss of investor confidence in our financial statements and have an adverse effect on our stock price.
Following the issuance of the SEC Staff Statement on April 12, 2021, management of the Company concluded that the Company’s previously issued consolidated financial statements should be restated to conform our accounting for warrants with the SEC Staff Statement. In connection with the restatement, a material weakness in internal control over financial reporting related to the accounting for the warrants was determined to exist.
The Company’s management has completed the restatement for warrant accounting and has developed and implemented a remediation plan to address the material weakness. However, we cannot assure you that the testing of the
operational effectiveness of the new control will be complete within a specific timeframe. There can be no assurances that the accounting for warrants and other financial instruments will not change in the future and require restatement of previously accepted accounting positions.
Effective internal controls are necessary for us to provide reliable and accurate financial statements and to effectively prevent fraud. We devote significant resources and time to comply with the internal control over financial reporting requirements of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 as amended (the "Sarbanes-Oxley Act"). There is no assurance that material weaknesses or significant deficiencies will not occur or that we will be successful in adequately remediating any such material weaknesses and significant deficiencies. We may in the future discover areas of our internal controls that need improvement. We cannot be certain that we will be successful in maintaining adequate internal control over our financial reporting and financial processes. Furthermore, as we grow our business, including through acquisition, our internal controls will become more complex, and we will require significantly more resources to ensure our internal controls remain effective. Additionally, the existence of any material weakness or significant deficiency would require management to devote significant time and incur significant expense to remediate any such material weaknesses or significant deficiencies, and management may not be able to remediate any such material weaknesses or significant deficiencies in a timely manner. The existence of any material weakness in our internal control over financial reporting could also result in errors in our financial statements that could require us to restate our financial statements, cause us to fail to meet our reporting obligations, subject us to investigations from regulatory authorities or cause stockholders to lose confidence in our reported financial information, all of which could materially and adversely affect us.
Risks Relating to Our Capital Structure
Global capital and credit market conditions could materially and adversely affect our ability to access the capital and credit markets or the ability of key counterparties to perform their obligations to us.
Although we believe the banks participating in our credit facility have adequate capital and resources, we can provide no assurance that all of those banks will continue to operate as a going concern in the future. If any of the banks in our lending group were to fail, it is possible that the borrowing capacity under our facility would be reduced. Practical, legal and tax limitations may also limit our ability to access and service the working capital needs of our businesses. In the event that the availability under our credit facility were reduced significantly, we could be required to obtain capital from alternate sources to finance our capital needs. The options for addressing such capital constraints would include, among others, obtaining commitments from the remaining banks in the lending group or from new banks to fund increased amounts under the terms of our credit facility, and seeking to access the public capital markets. In addition, we may delay certain capex to ensure that we maintain appropriate levels of liquidity. If it became necessary to access additional capital, any such alternatives could have terms less favorable than those terms under our credit facility, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows.
In addition, in the future we may need to raise additional funds to, among other things, refinance existing indebtedness, fund existing operations, improve or expand our operations, respond to competitive pressures or make acquisitions. If adequate funds are not available on acceptable terms, we may be unable to achieve our business or strategic objectives or compete effectively. Our ability to pursue certain future opportunities may depend in part on our ongoing access to debt and equity capital markets. We cannot assure you that any such financing will be available on terms satisfactory to us or at all. If we are unable to obtain financing on acceptable terms, we may have to curtail our growth by, among other things, curtailing the expansion of our fleet of units or our acquisition strategy. Additionally, future credit market conditions could increase the likelihood that one or more of our lenders may be unable to hone their commitments under our credit facility, which could have an adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
Economic disruptions affecting key counterparties could also materially adversely affect our business. We monitor the financial strength of our larger customers, derivative counterparties, lenders, vendors, service providers and insurance carriers on a periodic basis using publicly-available information to evaluate our exposure to those who have or who we believe may likely experience significant threats to their ability to adequately perform their obligations to us. The information available will differ from counterparty to counterparty and may be insufficient for us to adequately interpret or evaluate our exposure and/or determine appropriate or timely responses.
Our leverage may make it difficult for us to service our debt and operate our business.
As of December 31, 2020, we had $2,454.6 million of total indebtedness, excluding deferred financing fees and finance leases, consisting of $1,304.6 million of borrowings under our 2020 ABL Facility, $650.0 million of our 2025 Secured Notes, and $500.0 million of our 2028 Secured Notes. Our leverage could have important consequences, including
•making it more difficult to satisfy our obligations with respect to our various debt and liabilities;
•requiring us to dedicate a substantial portion of our cash flow from operations to debt payments, thus reducing the availability of cash flow to fund internal growth through working capital and capex on our existing fleet or a new fleet and for other general corporate purposes;
•increasing our vulnerability to a downturn in our business or adverse economic or industry conditions;
•placing us at a competitive disadvantage compared to our competitors that have less debt in relation to cash flow and that, therefore, may be able to take advantage of opportunities that our leverage would prevent us from pursuing;
•limiting our flexibility in planning for or reacting to changes in our business and industry;
•restricting us from pursuing strategic acquisitions or exploiting certain business opportunities or causing us to make non-strategic divestitures; and
•limiting our ability to borrow additional funds or raise equity capital in the future and increasing the costs of such additional financings.
Our ability to meet our debt service obligations or to refinance our debt depends on our future operating and financial performance, which will be affected by our ability to successfully implement our business strategy as well as general economic, financial, competitive, regulatory and other factors beyond our control. If our business does not generate sufficient cash flow from operations, or if future borrowings are not available to us in an amount sufficient to enable us to pay our indebtedness or to fund our other liquidity needs, we may need to refinance all or a portion of our indebtedness on or before its maturity, sell assets, reduce or delay capital investments or seek to raise additional capital, any of which could have a material adverse effect on our operations. In addition, we may not be able to affect any of these actions, if necessary, on commercially reasonable terms or at all. Any refinancing of our debt could be at higher interest rates and may require us to comply with more onerous covenants, which could further restrict our business operations. The terms of our existing or future debt instruments may limit or prevent us from taking any of these actions. If we default on the payments required under the terms of certain of our indebtedness, that indebtedness, together with debt incurred pursuant to other debt agreements or instruments that contain cross-default or cross-acceleration provisions, may become payable on demand, and we may not have sufficient funds to repay all of our debts. As a result, our inability to generate sufficient cash flow to satisfy our debt service obligations, or to refinance or restructure our obligations on commercially reasonable terms or at all, would have an adverse effect, which could be material, on our business, financial condition and results of operations, as well as on our ability to satisfy our debt obligations.
Despite our current level of indebtedness, we and our subsidiaries will still be able to incur significant additional amounts of debt, which could further exacerbate the risks associated with our substantial indebtedness.
We and our subsidiaries may be able to incur substantial additional debt in the future. Although the credit agreement that governs our credit facility and the indentures that govern our outstanding notes contain restrictions on the incurrence of additional debt, these restrictions are subject to a number of significant qualifications and exceptions, and under certain circumstances, the amount of debt that we could incur in compliance with these restrictions could be substantial. In addition, the credit agreement that governs our credit facility and the indentures do not prevent us from incurring other obligations that do not constitute indebtedness under those agreements. If we add debt to our and our subsidiaries’ existing debt levels, the risks associated with our substantial indebtedness described above, including our possible inability to service our debt, will increase.
We are subject to and may, in the future become subject to, covenants that limit our operating and financial flexibility and, if we default under our debt covenants, we may not be able to meet our payment obligations.
The credit agreement that governs our credit facility and the indentures that govern our outstanding notes, as well as any instruments that govern any future debt obligations, contain covenants that impose significant restrictions on the way our subsidiaries can operate, including restrictions on the ability to:
• incur or guarantee additional debt and issue certain types of stock;
• create or incur certain liens;
• make certain payments, including dividends or other distributions, with respect to our equity securities;
• prepay or redeem junior debt;
• make certain investments or acquisitions, including participating in joint ventures;
• engage in certain transactions with affiliates;
• create unrestricted subsidiaries;
• create encumbrances or restrictions on the payment of dividends or other distributions, loans or advances to, and on
the transfer of, assets to the issuer or any restricted subsidiary;
• sell assets, consolidate or merge with or into other companies;
• sell or transfer all or substantially all our assets or those of our subsidiaries on a consolidated basis; and
• issue or sell share capital of certain subsidiaries.
Although these limitations are subject to significant exceptions and qualifications, these covenants could limit our ability to finance future operations and capital needs and our ability to pursue acquisitions and other business activities that may be in our interest. Our subsidiaries’ ability to comply with these covenants and restrictions may be affected by events beyond our control. These include prevailing economic, financial and industry conditions. If any of our subsidiaries default on their obligations under our credit facility or our secured notes, then the relevant lenders or holders could elect to declare the debt, together with accrued and unpaid interest and other fees, if any, immediately due and payable and proceed against any
collateral securing that debt. If the debt under our credit facility, the indentures or any other material financing arrangement that we enter into were to be accelerated, our assets may be insufficient to repay in full such indebtedness.
The credit agreement that governs our credit facility also requires our subsidiaries to satisfy specified financial maintenance tests in the event that we do not satisfy certain excess liquidity requirements. Deterioration in our operating results, as well as events beyond our control, including increases in raw materials prices and unfavorable economic conditions, could affect the ability to meet these tests, and we cannot assure that we will meet these tests. If an event of default occurs under our credit facility, the lenders could terminate their commitments and declare all amounts borrowed, together with accrued and unpaid interest and other fees, to be immediately due and payable. Borrowings under other debt instruments that contain cross-acceleration or cross-default provisions also may be accelerated or become payable on demand. In these circumstances, our assets may not be sufficient to repay in full that indebtedness and our other indebtedness then outstanding.
The amount of borrowings permitted at any time under our credit facility is subject to compliance with limits based on a periodic borrowing base valuation of the collateral thereunder. As a result, our access to credit under the credit facility is subject to potential fluctuations depending on the value of the borrowing base of eligible assets as of any measurement date, as well as certain discretionary rights of the agent in respect of the calculation of such borrowing base value. As a result of any change in valuation, the availability under the credit facility may be reduced, or we may be required to make a repayment of the credit facility, which may be significant. The inability to borrow under the credit facility or the use of available cash to repay the credit facility as a result of a valuation change may adversely affect our liquidity, results of operations and financial position.
The uncertainty regarding the potential phase-out of LIBOR may negatively impact our operating results.
LIBOR, the interest rate benchmark used as a reference rate on our variable rate debt, including our credit facility and interest rate swaps, is expected to be phased out after 2021, when private-sector banks are no longer required to report the information used to set the rate. Without this data, LIBOR may no longer be published, or the lack of quality and quantity of data may cause the rate to no longer be representative of the market. At this time, no consensus exists as to what rate or rates will become accepted alternatives to LIBOR, although the US Federal Reserve, in connection with the Alternative Reference Rates Committee ("ARRC"), a steering committee comprised of large US financial institutions, is considering replacing US dollar LIBOR with the Secured Overnight Financing Rate ("SOFR"). SOFR is a more generic measure than LIBOR and considers the cost of borrowing cash overnight, collateralized by US Treasury securities. Given the inherent differences between LIBOR and SOFR or any other alternative benchmark rate that may be established, there are many uncertainties regarding a transition from LIBOR, including but not limited to the need to amend all contracts with LIBOR as the referenced rate and how this will impact our cost of variable rate debt and derivative financial instruments. We will also need to consider new contracts and if they should reference an alternative benchmark rate or include suggested fallback language, as published by the ARRC. The consequences of these developments with respect to LIBOR cannot be entirely predicted and span multiple future periods but could result in an increase in the cost of our variable rate debt or derivative financial instruments which may be detrimental to our financial position or operating results.
Our largest stockholder may have the ability to influence our business and matters requiring approval by our stockholders.
Sapphire Holding, which is controlled by TDR Capital, beneficially owns approximately 26% of the issued and outstanding shares of our Common Stock and warrants giving it the right to buy 2,425,000 additional shares of our Common Stock. Pursuant to a stockholders agreement entered into on July 1, 2020, by and among us and TDR Capital and certain of its affiliates, including Sapphire Holding, TDR Capital has the right to nominate two directors to our Board of Directors, for so long as TDR Capital beneficially owns at least 15% of our Common Stock and one director for so long as TDR Capital beneficially owns at least 5% of our Common Stock. Two directors nominated by Sapphire Holding currently serve on our Board of Directors. Sapphire Holding may have the ability to influence matters requiring approval by our stockholders, including the election and removal of directors, amendments to our certificate of incorporation and bylaws, any proposed merger, consolidation or sale of all or substantially all of our assets and certain other corporate transactions. Sapphire Holding may have interests that are different from those of other stockholders.
In August 2018, Sapphire Holding pledged all of the shares of WillScot’s Class A Common Stock that it owned as security for a margin loan under which Sapphire Holding borrowed $125.0 million (the "Margin Loan"). The Margin Loan was scheduled to mature on August 23, 2020. On August 21, 2020, Sapphire Holdings entered into an amended and restated margin loan agreement which, among other things, extends the maturity date of the Margin Loan to August 29, 2022. As of December 31, 2020, 59,725,558 shares of Common Stock are pledged to secure repayment of amounts outstanding under the Margin Loan. An event of default under the Margin Loan could result in the foreclosure on the pledged securities and another stockholder beneficially owning a significant amount of our Common Stock. There can be no assurance that Sapphire Holdings will be able to extend, repay or refinance the loan on terms acceptable to it or at all.
The historical market price of WillScot Mobile Mini’s Common Stock has been volatile and the market price of our Common Stock may continue to be volatile and the value of your investment may decline.
The historical market price of our Common Stock has been volatile and the market price of our Common Stock may continue to be volatile moving forward. Volatility may cause wide fluctuations in the price of our Common Stock on Nasdaq. The market price of our Common Stock is likely to be affected by:
• changes in general conditions in the economy, geopolitical events or the financial markets;
• variations in our quarterly operating results;
• changes in financial estimates by securities analysts;
• our share repurchase or dividend policies;
• other developments affecting us, our industry, customers or competitors;
• changes in demand for our products or the prices we charge due to changes in economic conditions, competition or other factors;
• general economic conditions in the markets where we operate;
• the cyclical nature of our customers’ businesses and certain end markets that we service;
• rental rate changes in response to competitive factors;
• bankruptcy or insolvency of our customers, thereby reducing demand for our used units;
• seasonal rental patterns;
• acquisitions or divestitures and related costs;
• labor shortages, work stoppages or other labor difficulties;
• possible unrecorded liabilities of acquired companies;
•possible write‑offs or exceptional charges due to changes in applicable accounting standards, goodwill impairment, or divestiture or impairment of assets;
• the operating and stock price performance of companies that investors deem comparable to us;
• the number of shares available for resale in the public markets under applicable securities laws; and
• the composition of our shareholder base.
ITEM 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments
None.
ITEM 2. Properties
Our corporate headquarters are located in Phoenix, Arizona. Prior to the Merger with Mobile Mini, WillScot's corporate headquarters were located in Baltimore, Maryland. Our executive, financial, accounting, legal, administrative, management information systems, and human resources functions operate from these two leased offices.
We operate approximately 275 branch locations and additional drop lots across the US, Canada, Mexico, and the UK. Collectively, we lease approximately 84% of our branch properties and own the remaining balance.
Our management believes that none of our properties, on an individual basis, is material to our operations, and we also believe that satisfactory alternative properties could be found in all of our markets, if ever necessary.
Subject to certain exceptions, substantially all of our owned real and personal property in the US and Canada is encumbered under our credit facility and our secured notes. We do not believe that the encumbrances will materially detract from the value of our properties, or materially interfere with their use in the operation of our business.
ITEM 3. Legal Proceedings
We are involved in various lawsuits, claims, and legal proceedings that arise in the ordinary course of business. These matters involve, among other things, disputes with vendors or customers, personnel and employment matters, and personal injury. We assess these matters on a case-by-case basis as they arise and establish reserves as required.
As of December 31, 2020, there were no material pending legal proceedings in which we or any of our subsidiaries are a party or to which any of our property is subject.
ITEM 4. Mine Safety Disclosures
Not applicable.
PART II
ITEM 5. Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
Common Stock
Our Common Stock is listed on the Nasdaq Capital Market under the symbol “WSC.” Our certificate of incorporation authorizes the issuance of 500,000,000 shares of Common Stock with a par value of $0.0001 per share. The Company had 229,038,158 shares of Common Stock issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2020. The outstanding shares of the Company's Common Stock are duly authorized, validly issued, fully paid and non-assessable.
Preferred Stock
Our certificate of incorporation authorizes the issuance of 1,000,000 shares of Preferred Stock with a par value of $0.0001 per share. As of December 31, 2020, no shares of Preferred Stock were issued and outstanding, and no designation of rights and preferences of preferred stock had been adopted. Our preferred stock is not quoted on any market or system, and there is not currently a market for our preferred stock.
2015 Warrants
The Company issued warrants to purchase Common Stock as components of units sold in its initial public offering (the “2015 Public Warrants”). The Company also issued warrants to purchase its Common Stock in a private placement concurrently with its initial public offering (the “2015 Private Warrants,” and together with the 2015 Public Warrants, the "2015 Warrants"). The 2015 Private Warrants are identical to the 2015 Public Warrants, except that, if held by original investors (or their permitted assignees), the 2015 Private Warrants may be exercised on a cashless basis and are not subject to redemption. Each 2015 Warrant entitles its holder to purchase one half of one share of our Common Stock in accordance with its terms. The 2015 Warrants became exercisable on December 29, 2017 and expire on November 29, 2022.
Pursuant to the warrant agreement, dated as of September 10, 2015 between Double Eagle Acquisition Corp. (defined below) and Continental Stock Transfer & Trust Company (the “2015 Warrant Agreement”), WillScot’s share price performance target was achieved on January 21, 2020 and, on January 24, 2020, WillScot delivered a notice (the "Warrant Redemption Notice") to redeem all of its 2015 Public Warrants that remained unexercised on February 24, 2020. As described in the Redemption Notice and permitted under the 2015 Warrant Agreement, holders of these 2015 Public Warrants who exercised them following the date of the Redemption Notice were required to do so on a cashless basis. From January 1, 2020 through January 24, 2020, 796,610 2015 Public Warrants were exercised for cash, resulting in WillScot receiving cash proceeds of $4.6 million and issuing 398,305 shares of Common Stock. Between January 24, 2020 and February 24, 2020, 5,836,048 2015 Public Warrants were exercised on a cashless basis. An aggregate of 1,097,162 shares of Common Stock was issued in connection with these cashless exercises. Thereafter, the Company completed the redemption of 38,509 remaining 2015 Public Warrants under the Redemption Notice for $0.01 per warrant. As of December 31, 2020, no 2015 Public Warrants were outstanding.
As of December 31, 2020, there were 12,710,000 2015 Private Warrants outstanding. The 2015 Private Warrants have not traded in an established public trading market within the two most recent fiscal years.
2018 Warrants
On August 15, 2018, WillScot issued warrants ("the 2018 Warrants") to the former ModSpace shareholders as part of the acquisition of ModSpace. Our 2018 Warrants are listed on an OTC Markets Group, Inc. Pink Open Market under the symbol "WSCTW." Over-the-counter market quotations reflect inter-dealer prices, without retail mark-up, mark-down or commission, and may not represent actual transactions.
Each 2018 Warrant entitles the holder thereof to purchase one share of WillScot Class A Common Stock at an exercise price of $15.50 per share, subject to potential adjustment. The 2018 Warrants were not exercisable or transferable until February 11, 2019 and expire on November 29, 2022. As of December 31, 2020, 9,730,241 2018 Warrants were outstanding.
Holders
As of December 31, 2020, there were 47 holders of record of our Common Stock, no holders of record of our Preferred Stock, 8 holders of record of our 2015 Warrants, and 37 holders of record of our 2018 Warrants. The number of holders of record does not include a substantially greater number of “street name” holders or beneficial holders whose Common Stock or warrants are held of record by banks, brokers and other financial institutions.
Dividend Policy
To date, we have not declared or paid dividends on our common stock. We have strong recurring cash flows, which gives us flexibility in how we allocate capital, and we review the appropriate mix of growth investments, debt reduction, and returns to shareholders on an ongoing basis. Declaration or payment of dividends, if any, in the future, will be at the discretion of our Board of Directors and will depend on our then current financial condition, results of operations, capital requirements and other factors deemed relevant by the Board of Directors.
Securities Authorized for Issuance under Equity Compensation Plans
On July 2, 2020, we filed a registration statement on Form S-8 registering 6,488,988 shares of Common Stock, relating to awards to be undertaken in the future, with such vesting conditions, as applicable, to be determined in accordance with the WillScot Mobile Mini 2020 Incentive Award Plan (the "2020 Incentive Plan"). The following types of awards can be issued under the 2020 Incentive Plan: non-qualified stock options, incentive stock options, stock appreciation rights, restricted stock awards, restricted stock units, performance compensation awards and stock bonus awards. See Note 18 in Part II, Item 8 herein for additional information.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Plan Category | Number of securities to be issued upon exercise of outstanding options, warrants and rights
| | Weighted-average exercise price of outstanding options, warrants, and rights
| | Number of securities remaining available for issuance under equity compensation plans (excluding securities reflected in column (a))
|
| As of December 31, 2020: | | | | | |
| Equity compensation plans approved by security holders | 2,043,695 | | | $ | 13.83 | | | 4,422,773 | |
| Equity compensation plans not approved by security holders | — | | | $ | — | | | — | |
| Total | 2,043,695 | | | $ | 13.83 | | | 4,422,773 | |
Repurchases
On August 7, 2020, our Board of Directors approved a stock repurchase program that authorizes us to repurchase up to $250 million of our outstanding shares of Common Stock and equivalents. The stock repurchase program does not obligate us to purchase any particular number of shares, and the timing and exact amount of any repurchases will depend on various factors, including market pricing and conditions, business, legal, accounting, and other considerations.
We may repurchase our shares in open market transactions from time to time or through privately negotiated transactions in accordance with federal securities laws, at our discretion. The repurchase program, which has no expiration date, may be increased, suspended, or terminated at any time. The program is expected to be implemented over the course of several years and is conducted subject to the covenants in the agreements governing our indebtedness.
During the year ended December 31, 2020, no shares of Common Stock were repurchased, and the Company repurchased $35.3 million warrants and share equivalents, including withholding taxes on net share settlements of employee stock awards.
2015 Warrants
The following information describes repurchases of the 2015 Warrants during the fourth quarter of the year ended December 31, 2020:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Period | Total Number of 2015 Warrants Purchased | | Average price paid per warrant | | Total number of warrants purchased as part of a publicly announced plan | | Maximum number of warrants that may yet be purchased under the plan |
| October 1, 2020 - October 31, 2020 | — | | | $ | — | | | — | | | 17,561,700 | |
| November 1, 2020 - November 30, 2020 | 1,650,000 | | | $ | 3.52 | | | — | | | 15,841,700 | |
| December 1, 2020 - December 31, 2020 | 3,131,700 | | | $ | 5.03 | | | — | | | 12,710,000 | |
| Total | 4,781,700 | | | | | — | | | 12,710,000 | |
2018 Warrants
The following information describes the repurchases of the 2018 Warrants during the fourth quarter of the year ended December 31, 2020:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Period | Total Number of 2018 Warrants Purchased | | Average price paid per warrant | | Total number of warrants purchased as part of a publicly announced plan | | Maximum number of warrants that may yet be purchased under the plan |
| October 1, 2020 - October 31, 2020 | — | | | $ | — | | | — | | | 9,782,106 | |
| November 1, 2020 - November 30, 2020 | 37,156 | | | $ | 5.57 | | | — | | | 9,744,950 | |
| December 1, 2020 - December 31, 2020 | 14,709 | | | $ | 5.93 | | | — | | | 9,730,241 | |
| Total | 51,865 | | | | | — | | | 9,730,241 | |
Performance Graph
The following stock price performance graph should not be deemed incorporated by reference by any general statement incorporating by reference this Annual Report on Form 10-K into any filing under the Exchange Act or the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, except to the extent that we specifically incorporate this information by reference and shall not otherwise be deemed filed under such acts.
The graph below compares the cumulative total return of our Common Stock from January 1, 2016, through December 31, 2020, with the comparable cumulative return of two indices, the Russell 2000 and the Nasdaq US Benchmark TR Index. The graph plots the growth in value of an initial investment in each of our common shares, the Russell 2000 Index, and the Nasdaq US Benchmark Index over the indicated time periods, and assumes reinvestment of all dividends, if any, paid on the securities. We have not paid any cash dividends and, therefore, the cumulative total return calculation for us is based solely upon share price appreciation and not upon reinvestment of cash dividends. The share price performance shown on the graph is not necessarily indicative of future price performance.
ITEM 6. Selected Financial Data
As discussed in Note 1 to the consolidated financial statements, the financial statements as of December 31, 2020 and 2019 and for each of the three years in the period ending December 31, 2020 have been restated to conform with the SEC Staff Statement related to accounting for warrants.
WillScot was incorporated under the name Double Eagle Acquisition Corporation ("Double Eagle") on June 26, 2015. Prior to November 29, 2017, Double Eagle was a Nasdaq-listed special purpose acquisition company. On November 29, 2017, Double Eagle acquired Williams Scotsman International, Inc. (“WSII”) from Algeco Scotsman Global S.à r.l., which is majority owned by an investment fund managed by TDR Capital (the “Business Combination”). In connection with the Business Combination, Double Eagle domesticated to Delaware and changed its name to WillScot Corporation.
On December 20, 2017, WSII acquired 100% of the issued and outstanding ownership of Acton Mobile Holdings LLC.
On August 15, 2018, WSII acquired ModSpace. Results of operations from ModSpace subsequent to the acquisition are included in our consolidated operating results.
On July 1, 2020, WillScot Corporation merged with Mobile Mini, Inc. Results of operations from Mobile Mini, Inc. subsequent to the Merger are included in our consolidated operating results.
As a result of the Merger, we evaluated our operating structure and, accordingly, our segment structure and determined we operate in four reportable segments as follows: North America Modular Solutions ("NA Modular"), North America Storage Solutions ("NA Storage"), United Kingdom Storage Solutions ("UK Storage") and Tank and Pump Solutions ("Tank and Pump"). The NA Modular segment aligns with the WillScot legacy business prior to the Merger and the NA Storage, UK Storage and Tank and Pump segments align with the Mobile Mini segments prior to the Merger.
In connection with the Merger, we determined our reportable segments as discussed above and retrospectively adjusted prior years' presentation to conform to the current presentation of reportable segments.
The following selected historical financial information should be read together with the consolidated financial statements and accompanying notes and “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.” The selected historical financial information in this section is not intended to replace WillScot Mobile Mini’s consolidated financial statements and the related notes.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Consolidated Results | As of and for the Year Ended December 31, |
| (in thousands) | 2020
(as restated) | | 2019
(as restated) | | 2018
(as restated) |
| Revenues: | | | | | |
| Leasing and services revenue: | | | | | |
| Leasing | $ | 1,001,447 | | | $ | 744,185 | | | $ | 518,235 | |
| Delivery and installation | 274,156 | | | 220,057 | | | 154,557 | |
| Sales revenue: | | | | | |
| New units | 53,093 | | | 59,085 | | | 53,603 | |
| Rental units | 38,949 | | | 40,338 | | | 25,017 | |
| Total revenues | 1,367,645 | | | 1,063,665 | | | 751,412 | |
| Costs: | | | | | |
| Costs of leasing and services: | | | | | |
| Leasing | 227,376 | | | 213,151 | | | 143,120 | |
| Delivery and installation | 220,102 | | | 194,107 | | | 143,950 | |
| Costs of sales: | | | | | |
| New units | 34,841 | | | 42,160 | | | 36,863 | |
| Rental units | 24,772 | | | 26,255 | | | 16,659 | |
| Depreciation of rental equipment | 200,581 | | | 174,679 | | | 121,436 | |
| Gross profit | 659,973 | | | 413,313 | | | 289,384 | |
| | | | | |
| Expenses: | | | | | |
| Selling, general and administrative | 360,626 | | | 271,004 | | | 234,820 | |
| Transaction costs | 64,053 | | | — | | | 20,051 | |
| Other depreciation and amortization | 43,249 | | | 12,395 | | | 13,304 | |
| Impairment losses on long-lived assets | — | | | 2,848 | | | 1,600 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Lease impairment expense and other related charges | 4,876 | | | 8,674 | | | — | |
| Restructuring costs | 6,527 | | | 3,755 | | | 15,468 | |
| Currency (gains) losses, net | (355) | | | (688) | | | 2,454 | |
| Other income, net | (1,718) | | | (2,200) | | | (4,574) | |
| Operating income | 182,715 | | | 117,525 | | | 6,261 | |
| Interest expense | 119,886 | | | 122,504 | | | 98,433 | |
| Fair value (gain) loss on common stock warrant liabilities | (3,461) | | | 109,622 | | | (23,830) | |
| Loss on extinguishment of debt | 42,401 | | | 8,755 | | | — | |
| Income (loss) before tax | 23,889 | | | (123,356) | | | (68,342) | |
| Income tax benefit | (51,451) | | | (2,191) | | | (38,600) | |
| Net income (loss) | 75,340 | | | (121,165) | | | (29,742) | |
| Net income (loss) attributable to non-controlling interest, net of tax | 1,213 | | | (421) | | | (4,532) | |
| Net income (loss) attributable to WillScot Mobile Mini | $ | 74,127 | | | $ | (120,744) | | | $ | (25,210) | |
| | | | | |
| Earnings (loss) per share attributable to WillScot Mobile Mini – basic | $ | 0.44 | | | $ | (1.11) | | | $ | (0.29) | |
| Earnings (loss) per share attributable to WillScot Mobile Mini – diluted | $ | 0.25 | | | $ | (1.11) | | | $ | (0.53) | |
| | | | | |
| Cash Flow Data: | | | | | |
| Net cash from operating activities | $ | 304,812 | | | $ | 172,566 | | | $ | 37,149 | |
| Net cash from investing activities | $ | (125,360) | | | $ | (152,582) | | | $ | (1,217,202) | |
| Net cash from financing activities | $ | (158,958) | | | $ | (26,063) | | | $ | 1,180,037 | |
| | | | | |
| Other Financial Data: | | | | | |
Adjusted EBITDA - NA Modular(a) | $ | 394,805 | | | $ | 356,548 | | | $ | 215,533 | |
Adjusted EBITDA - NA Storage(a) | $ | 99,837 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
Adjusted EBITDA - UK Storage(a) | $ | 17,822 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
Adjusted EBITDA - Tank and Pump(a) | $ | 17,843 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | |
Consolidated Adjusted EBITDA(a) | $ | 530,307 | | | $ | 356,548 | | | $ | 215,533 | |
Free Cash Flow(a) | $ | 162,279 | | | $ | 19,984 | | | $ | (96,907) | |
Adjusted Gross Profit(a) | $ | 860,554 | | | $ | 587,992 | | | $ | 410,820 | |
Net CAPEX(a) | $ | 142,533 | | | $ | 152,582 | | | $ | 134,056 | |
| | | | | |
| Balance Sheet Data (end of year): | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 24,937 | | | $ | 3,045 | | | $ | 8,958 | |
| Rental equipment, net | $ | 2,933,722 | | | $ | 1,944,436 | | | $ | 1,929,290 | |
| Total assets | $ | 5,572,205 | | | $ | 2,897,649 | | | $ | 2,752,485 | |
| Total debt, excluding current portion | $ | 2,453,809 | | | $ | 1,632,589 | | | $ | 1,674,540 | |
| Total shareholders’ equity | $ | 2,063,873 | | | $ | 490,609 | | | $ | 593,665 | |
(a) WillScot Mobile Mini presents Adjusted EBITDA, Free Cash Flow, Adjusted Gross Profit and Net CAPEX, which are measurements not calculated in accordance with GAAP and are defined below in the section "Reconciliation of non-GAAP Financial Measures," because they are key metrics used by management to assess financial performance. Our business is capital intensive, and these additional metrics allow management to further evaluate its operating performance. See below for reconciliations of non-GAAP financial measures.
Quarterly Consolidated Results for the Year Ended December 31, 2020 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands, except for units on rent and monthly rental rate) | Q1 | | Q2 | | Q3 | | Q4 | | Full Year |
| Revenue | $ | 255,821 | | | $ | 256,862 | | | $ | 417,315 | | | $ | 437,647 | | | $ | 1,367,645 | |
| Gross profit | $ | 106,190 | | | $ | 109,964 | | | $ | 209,564 | | | $ | 234,255 | | | $ | 659,973 | |
| Adjusted EBITDA | $ | 89,544 | | | $ | 97,520 | | | $ | 163,559 | | | $ | 179,684 | | | $ | 530,307 | |
| Net CAPEX | $ | 30,540 | | | $ | 36,383 | | | $ | 33,323 | | | $ | 42,287 | | | $ | 142,533 | |
| Modular space units on rent (average during the period) | 87,989 | | | 87,096 | | | 111,227 | | | 111,793 | | | 99,526 | |
| Average modular space utilization rate | 69.2 | % | | 68.5 | % | | 70.6 | % | | 70.9 | % | | 70.2 | % |
| Average modular space monthly rental rate | $ | 653 | | | $ | 669 | | | $ | 640 | | | $ | 670 | | | $ | 658 | |
| Portable storage units on rent (average during the period) | 16,346 | | | 15,869 | | | 143,840 | | | 160,538 | | | 84,148 | |
| Average portable storage utilization rate | 64.1 | % | | 62.5 | % | | 73.2 | % | | 81.2 | % | | 75.9 | % |
| Average portable storage monthly rental rate | $ | 119 | | | $ | 120 | | | $ | 131 | | | $ | 136 | | | $ | 132 | |
| Average tank and pump solutions rental fleet utilization based on original equipment cost | — | % | | — | % | | 58.2 | % | | 65.2 | % | | 61.7 | % |
Quarterly Consolidated Results for the Year Ended December 31, 2019 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands, except for units on rent and monthly rental rate) | Q1 | | Q2 | | Q3 | | Q4 | | Full Year |
| Revenue | $ | 253,685 | | | $ | 263,713 | | | $ | 268,222 | | | $ | 278,045 | | | $ | 1,063,665 | |
| Gross profit | $ | 103,331 | | | $ | 101,484 | | | $ | 99,308 | | | $ | 109,190 | | | $ | 413,313 | |
| Adjusted EBITDA | $ | 83,354 | | | $ | 87,554 | | | $ | 87,424 | | | $ | 98,216 | | | $ | 356,548 | |
| Net CAPEX | $ | 41,814 | | | $ | 43,199 | | | $ | 37,761 | | | $ | 29,808 | | | $ | 152,582 | |
| Modular space units on rent (average during the period) | 93,309 | | | 92,300 | | | 91,233 | | | 90,013 | | | 91,682 | |
| Average modular space utilization rate | 72.4 | % | | 71.9 | % | | 71.2 | % | | 70.7 | % | | 72.0 | % |
| Average modular space monthly rental rate | $ | 575 | | | $ | 611 | | | $ | 630 | | | $ | 641 | | | $ | 614 | |
| Portable storage units on rent (average during the period) | 17,419 | | | 16,544 | | | 16,416 | | | 16,944 | | | 16,878 | |
| Average portable storage utilization rate | 66.1 | % | | 63.3 | % | | 63.0 | % | | 66.1 | % | | 65.8 | % |
| Average portable storage monthly rental rate | $ | 119 | | | $ | 121 | | | $ | 123 | | | $ | 118 | | | $ | 120 | |
Reconciliation of non-GAAP Financial Measures
The following presents definitions and reconciliations to the nearest comparable GAAP measure of certain non-GAAP financial measures used in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Adjusted EBITDA
We define EBITDA as net income (loss) plus interest (income) expense, income tax expense (benefit), depreciation and amortization. Our adjusted EBITDA ("Adjusted EBITDA") reflects the following further adjustments to EBITDA to exclude certain non-cash items and the effect of what we consider transactions or events not related to our core business operations:
•Currency (gains) losses, net: on monetary assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies other than the subsidiaries’ functional currency. Substantially all such currency gains (losses) are unrealized and attributable to financings due to and from affiliated companies.
•Goodwill and other impairment charges related to non-cash costs associated with impairment charges to goodwill, other intangibles, rental fleet and property, plant and equipment.
•Restructuring costs, lease impairment expense, and other related charges associated with restructuring plans designed to streamline operations and reduce costs including employee and lease termination costs.
•Transaction costs including legal and professional fees and other transaction specific related costs.
•Costs to integrate acquired companies, including outside professional fees, non-capitalized costs associated with system integrations, non-lease branch and fleet relocation expenses, employee training costs, and other costs required to realize cost or revenue synergies.
•Non-cash charges for stock compensation plans.
•Gains and losses resulting from changes in fair value and extinguishment of common stock warrant liabilities.
•Other expense includes consulting expenses related to certain one-time projects, financing costs not classified as interest expense, and gains and losses on disposals of property, plant, and equipment.
Adjusted EBITDA has limitations as an analytical tool, and you should not consider the measure in isolation or as a substitute for net income (loss), cash flow from operations or other methods of analyzing WillScot Mobile Mini’s results as reported under US GAAP. Some of these limitations are:
•Adjusted EBITDA does not reflect changes in, or cash requirements for our working capital needs;
•Adjusted EBITDA does not reflect our interest expense, or the cash requirements necessary to service interest or principal payments, on our indebtedness;
•Adjusted EBITDA does not reflect our tax expense or the cash requirements to pay our taxes;
•Adjusted EBITDA does not reflect historical cash expenditures or future requirements for capex or contractual commitments;
•Adjusted EBITDA does not reflect the impact on earnings or changes resulting from matters that we consider not to be indicative of our future operations;
•although depreciation and amortization are non-cash charges, the assets being depreciated and amortized will often have to be replaced in the future and Adjusted EBITDA does not reflect any cash requirements for such replacements; and
•other companies in our industry may calculate Adjusted EBITDA differently, limiting its usefulness as a comparative measure.
Because of these limitations, Adjusted EBITDA should not be considered as discretionary cash available to reinvest in the growth of our business or as measures of cash that will be available to meet our obligations. The following tables provide an unaudited reconciliation of Net income (loss) to Adjusted EBITDA:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2020 | (as restated) |
| (in thousands) | Q1 | | Q2 | | Q3 | | Q4 | | Full Year |
| Net income (loss) | $ | 91,655 | | | $ | (14,130) | | | $ | (6,051) | | | $ | 3,866 | | | $ | 75,340 | |
| Income tax expense (benefit) | 790 | | | (285) | | | (66,675) | | | 14,719 | | | (51,451) | |
| Income (loss) before income tax | 92,445 | | | (14,415) | | | (72,726) | | | 18,585 | | | 23,889 | |
| Loss on extinguishment of debt | — | | | — | | | 42,401 | | | — | | | 42,401 | |
| Interest expense | 28,257 | | | 28,519 | | | 33,034 | | | 30,076 | | | 119,886 | |
| Fair value (gain) loss on common stock warrant liabilities | (95,329) | | | 26,963 | | | 22,303 | | | 42,602 | | | (3,461) | |
| Depreciation and amortization | 49,022 | | | 48,377 | | | 71,704 | | | 74,727 | | | 243,830 | |
| Currency losses (gains), net | 898 | | | (380) | | | (371) | | | (502) | | | (355) | |
| Restructuring costs, lease impairment expense and other related charges | 1,601 | | | 2,143 | | | 4,798 | | | 2,861 | | | 11,403 | |
| Transaction costs | 9,431 | | | 1,619 | | | 52,191 | | | 812 | | | 64,053 | |
| Integration costs | 1,685 | | | 2,153 | | | 7,083 | | | 7,417 | | | 18,338 | |
| Stock compensation expense | 1,787 | | | 2,227 | | | 2,944 | | | 2,921 | | | 9,879 | |
| Other | (253) | | | 314 | | | 198 | | | 185 | | | 444 | |
| Adjusted EBITDA | $ | 89,544 | | | $ | 97,520 | | | $ | 163,559 | | | $ | 179,684 | | | $ | 530,307 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2019 | (as restated) |
| (in thousands) | Q1 | | Q2 | | Q3 | | Q4 | | Full Year |
| Net loss | $ | (27,574) | | | $ | (56,835) | | | $ | (1,197) | | | $ | (35,559) | | | $ | (121,165) | |
| Income tax expense (benefit) | 378 | | | (1,180) | | | (1,220) | | | (169) | | | (2,191) | |
| Loss before income tax | (27,196) | | | (58,015) | | | (2,417) | | | (35,728) | | | (123,356) | |
| Loss on extinguishment of debt | — | | | 7,244 | | | — | | | 1,511 | | | 8,755 | |
| Interest expense | 31,115 | | | 31,668 | | | 30,005 | | | 29,716 | | | 122,504 | |
| Fair value loss on common stock warrant liabilities | 17,545 | | | 45,397 | | | 2,194 | | | 44,486 | | | 109,622 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | 43,887 | | | 46,917 | | | 47,358 | | | 48,912 | | | 187,074 | |
| Currency (gains) losses, net | (316) | | | (354) | | | 234 | | | (252) | | | (688) | |
| Goodwill and other impairment charges | 2,290 | | | 348 | | | — | | | 210 | | | 2,848 | |
| Restructuring costs, lease impairment expense and other related charges | 4,741 | | | 3,152 | | | 1,863 | | | 2,673 | | | 12,429 | |
| Integration costs | 10,138 | | | 8,242 | | | 5,483 | | | 2,744 | | | 26,607 | |
| Stock compensation expense | 1,290 | | | 1,900 | | | 1,812 | | | 1,684 | | | 6,686 | |
| Other | (140) | | | 1,055 | | | 892 | | | 2,260 | | | 4,067 | |
| Adjusted EBITDA | $ | 83,354 | | | $ | 87,554 | | | $ | 87,424 | | | $ | 98,216 | | | $ | 356,548 | |
Net Income Excluding Gain/Loss from Warrants
We define Net Income Excluding Gain/Loss from Warrants as Net Income plus or minus the impact of the change in the fair value of the warrant liability. Management believes that our financial statements that will include the impact of this mark-to-market expense or income may not be necessarily reflective of the actual financial performance of our business.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2020 | (as restated) |
| (in thousands) | Q1 | | Q2 | | Q3 | | Q4 | | Full Year |
| Net income (loss) | $ | 91,655 | | | $ | (14,130) | | | $ | (6,051) | | | $ | 3,866 | | | $ | 75,340 | |
| Fair value (gain) loss on common stock warrant liabilities | (95,329) | | | 26,963 | | | 22,303 | | | 42,602 | | | (3,461) | |
| Net (Loss) Income Excluding Gain/Loss from Warrants | $ | (3,674) | | $ | — | | $ | 12,833 | | $ | — | | $ | 16,252 | | $ | — | | $ | 46,468 | | $ | — | | $ | 71,879 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2019 | (as restated) |
| (in thousands) | Q1 | | Q2 | | Q3 | | Q4 | | Full Year |
| Net loss | $ | (27,574) | | | $ | (56,835) | | | $ | (1,197) | | | $ | (35,559) | | | $ | (121,165) | |
| Fair value loss on common stock warrant liabilities | 17,545 | | | 45,397 | | | 2,194 | | | 44,486 | | | 109,622 | |
| Net (Loss) Income Excluding Gain/Loss from Warrants | $ | (10,029) | | $ | — | | $ | (11,438) | | $ | — | | $ | 997 | | $ | — | | $ | 8,927 | | $ | — | | $ | (11,543) | |
Adjusted Gross Profit and Adjusted Gross Profit Percentage
We define Adjusted Gross Profit as gross profit plus depreciation on rental equipment. Adjusted Gross Profit Percentage is defined as Adjusted Gross Profit divided by revenue. Adjusted Gross Profit and Percentage are not measurements of our financial performance under GAAP and should not be considered as an alternative to gross profit, gross profit percentage, or other performance measures derived in accordance with GAAP. In addition, our measurement of Adjusted Gross Profit and Adjusted Gross Profit Percentage may not be comparable to similarly titled measures of other companies. Management believes that the presentation of Adjusted Gross Profit and Adjusted Gross Profit Percentage provides useful information to investors regarding our results of operations because it assists in analyzing the performance of our business.
The following table provides an unaudited reconciliation of gross profit to Adjusted Gross Profit and Adjusted Gross Profit Percentage on a historical basis:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| (in thousands) | 2020 | | 2019 | | |
| Revenue (A) | $ | 1,367,645 | | | $ | 1,063,665 | | | |
| | | | | |
| Gross profit (B) | $ | 659,973 | | | $ | 413,313 | | | |
| Depreciation of rental equipment | 200,581 | | | 174,679 | | | |
| Adjusted Gross Profit (C) | $ | 860,554 | | | $ | 587,992 | | | |
| | | | | |
| Gross Profit Percentage (B/A) | 48.3 | % | | 38.9 | % | | |
| Adjusted Gross Profit Percentage (C/A) | 62.9 | % | | 55.3 | % | | |
Net CAPEX
We define Net CAPEX as purchases of rental equipment and refurbishments and purchases of property, plant and equipment (collectively, "Total Capital Expenditures"), less proceeds from sale of rental equipment and proceeds from the sale of property, plant and equipment (collectively, "Total Proceeds"), which are all included in cash flows from investing activities. Management believes that the presentation of Net CAPEX provides useful information to investors regarding the net capital invested into our rental fleet and property, plant and equipment each year to assist in analyzing the performance of our business.
The following tables provide unaudited reconciliations of Net CAPEX on a historical quarterly basis:
Quarterly Consolidated Results for the Year Ended December 31, 2020 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands) | Q1 | | Q2 | | Q3 | | Q4 | | Full Year |
| Total Capital Expenditures | $ | 41,166 | | | $ | 41,702 | | | $ | 48,484 | | | $ | 57,485 | | | $ | 188,837 | |
| Total Proceeds | 10,626 | | | 5,319 | | | 15,161 | | | 15,198 | | | 46,304 | |
| Net CAPEX | $ | 30,540 | | | $ | 36,383 | | | $ | 33,323 | | | $ | 42,287 | | | $ | 142,533 | |
Quarterly Consolidated Results for the Year Ended December 31, 2019 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands) | Q1 | | Q2 | | Q3 | | Q4 | | Full Year |
| Total Capital Expenditures | $ | 53,502 | | | $ | 63,485 | | | $ | 50,490 | | | $ | 45,969 | | | $ | 213,446 | |
| Total Proceeds | 11,688 | | | 20,286 | | | 12,729 | | | 16,161 | | | 60,864 | |
| Net CAPEX | $ | 41,814 | | | $ | 43,199 | | | $ | 37,761 | | | $ | 29,808 | | | $ | 152,582 | |
Free Cash Flow
We define Free Cash Flow as net cash provided by operating activities, less purchases of, and proceeds from, rental equipment and property, plant and equipment, which are all included in cash flows from investing activities. Management believes that the presentation of Free Cash Flow provides useful information to investors regarding our results of operations because it provides useful additional information concerning cash flow available to meet future debt service obligations and working capital requirements.
Free Cash Flow for the three months ended June 30, 2020, 2019 and 2018, is derived by subtracting the cash flows from operating activities and the relevant line items within investing activities for the three months ended March 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018, from corresponding items for the six months ended June 30, 2020, 2019 and 2018, respectively. Free Cash Flow for the three months ended September 30, 2020, 2019 and 2018, is derived by subtracting the cash flows from operating activities and the relevant line items within investing activities for the six months ended June 30, 2020, 2019 and 2018, from corresponding items for the nine months ended September 30, 2020, 2019 and 2018, respectively. Free Cash Flow for the three months ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018, is derived by subtracting the cash flows from operating activities and the relevant line items within investing activities for the nine months ended September 30, 2020, 2019 and 2018, from corresponding items for the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018, respectively.
The following tables provide a reconciliation of net cash provided by operating activities to Free Cash Flow:
Quarterly Consolidated Results for the Year Ended December 31, 2020 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands) | Q1 | | Q2 | | Q3 | | Q4 | | Full Year |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | $ | 38,348 | | | $ | 75,379 | | | $ | 61,368 | | | $ | 129,717 | | | $ | 304,812 | |
| Purchase of rental equipment and refurbishments | (39,648) | | | (40,034) | | | (42,591) | | | (50,110) | | | (172,383) | |
| Proceeds from sale of rental equipment | 6,786 | | | 5,316 | | | 13,179 | | | 13,668 | | | 38,949 | |
| Purchase of property, plant and equipment | (1,518) | | | (1,668) | | | (5,893) | | | (7,375) | | | (16,454) | |
| Proceeds from the sale of property, plant and equipment | 3,840 | | | 3 | | | 1,982 | | | 1,530 | | | 7,355 | |
| Free Cash Flow | $ | 7,808 | | | $ | 38,996 | | | $ | 28,045 | | | $ | 87,430 | | | $ | 162,279 | |
Quarterly Consolidated Results for the Year Ended December 31, 2019 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands) | Q1 | | Q2 | | Q3 | | Q4 | | Full Year |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | $ | 15,256 | | | $ | 44,798 | | | $ | 39,022 | | | $ | 73,490 | | | $ | 172,566 | |
| Purchase of rental equipment and refurbishments | (51,873) | | | (61,215) | | | (47,789) | | | (44,229) | | | (205,106) | |
| Proceeds from sale of rental equipment | 11,601 | | | 11,482 | | | 8,421 | | | 10,597 | | | 42,101 | |
| Purchase of property, plant and equipment | (1,629) | | | (2,270) | | | (2,701) | | | (1,740) | | | (8,340) | |
| Proceeds from the sale of property, plant and equipment | 87 | | | 8,804 | | | 4,308 | | | 5,564 | | | 18,763 | |
| Free Cash Flow | $ | (26,558) | | | $ | 1,599 | | | $ | 1,261 | | | $ | 43,682 | | | $ | 19,984 | |
Cautionary Note Regarding Forward Looking Statements
This Annual Report on Form 10-K contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of the US Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995 and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act. The words “estimates,” “expects,” “anticipates,” “believes,” “forecasts,” “plans,” “intends,” “may,” “will,” “should,” “shall,” “outlook,” “guidance” and variations of these words and similar expressions identify forward-looking statements, which are generally not historical in nature and relate to expectations for future financial performance or business strategies or objectives.
Forward-looking statements are subject to a number of risks, uncertainties, assumptions and other important factors, many of which are outside our control, which could cause actual results or outcomes to differ materially from those discussed in the forward-looking statements. Although we believe that these forward-looking statements are based on reasonable assumptions, we can give no assurance that any such forward-looking statement will materialize.
Important factors that may affect actual results or outcomes include, among others:
•our ability to successfully acquire and integrate new operations, including Mobile Mini and our conversion to its enterprise resource planning system, and to realize anticipated synergies from the Merger with Mobile Mini;
•operational, economic, political and regulatory risks;
•the effect of global or local economic conditions in the industries and markets in which the Company operates and any changes therein, including financial market conditions and levels of end market demand;
•the impact of the global pandemic related to COVID-19, including the financial condition of the Company’s customers and suppliers and employee health and safety;
•risks associated with cybersecurity and IT systems disruptions, including our ability to manage the business in the event a disaster shuts down our management information systems;
•effective management of our rental equipment;
•trade policies and changes in trade policies, including the imposition of tariffs, their enforcement and downstream consequences;
•our ability to effectively compete in the modular space, portable storage and tank and pump industries;
•our ability to effectively manage our credit risk, collect on our accounts receivable, and recover our rental equipment;
•our ability to effectively launch operations into new geographic markets and/or add other business unit operations in existing markets;
•the effect of changes in state building codes on our ability to remarket our buildings;
•foreign currency exchange rate exposure;
•fluctuations in interest rates and commodity prices;
•significant increases in raw material and labor costs;
•fluctuations in fuel costs or oil prices, a reduction in fuel supplies, or a sustained decline in oil prices;
•our reliance on third party manufacturers and suppliers;
•risks associated with labor relations, labor costs and labor disruptions;
•failure to retain key personnel;
•impairment of our goodwill, intangible assets and indefinite-life intangible assets;
•our ability to use our net operating loss carryforwards and other tax attributes;
•our ability to recognize deferred tax assets such as those related to our tax loss carryforwards and, as a result, utilize future tax savings;
•unanticipated changes in our tax obligations, the adoption of a new tax legislation, or exposure to additional income tax liabilities;
•various laws and regulations, including those governing government contracts, corruption and the environment;
•changes in the competitive environment of our customer base as a result of the global, national or local economic climate in which they operate and/or economic or financial disruptions to their industry;
•risks associated with operational measures designed to increase revenue while continuing to control operating costs;
•our ability to adequately protect our intellectual property and other proprietary rights that are material to our business;
•natural disasters and other business disruptions such as pandemics, fires, floods, hurricanes, earthquakes and terrorism;
•property, casualty or other losses not covered by our insurance;
•our ability to redeploy our units effectively should a significant number of our leased units be returned during a short period of time;
•our ability to close our unit sales transactions;
•fluctuations in the fair value of common stock warrant liabilities;
•our ability to maintain an effective system of internal controls and accurately report our financial results and remediate material weaknesses;
•public company requirements that may strain our resources and divert management's attention;
•our ability to manage growth and execute our business plan;
•changes in the supply and price of new and used products we lease;
•unanticipated threats including market entry by a new competitor;
•rising costs adversely affecting our profitability; and
•other factors detailed under the section entitled "Risk Factors."
Any forward-looking statement speaks only at the date which it is made, and we undertake no obligation, and disclaim any obligation, to update or revise any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise, except as required by law.
ITEM 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
The following Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations (“MD&A”) is intended to help the reader understand WillScot Mobile Mini Holdings Corp. ("WillScot Mobile Mini"), formerly known as WillScot Corporation ("WillScot"), our operations and our present business environment. MD&A is provided as a supplement to, and should be read in conjunction with, our financial statements and the accompanying notes thereto, contained in Part II, Item 8 of this report. The discussion of results of operations in this MD&A is presented on a historical basis, as of or for the year ended December 31, 2020 or prior periods. As the Merger was completed on July 1, 2020, unless the context otherwise requires, the terms “we”, “us”, “our” “Company” and “WillScot Mobile Mini” means WillScot and its subsidiaries when referring to periods prior to July 1, 2020 (prior to the Merger) and to WillScot Mobile Mini and its subsidiaries when referring to periods on or after July 1, 2020 (after the Merger).
The consolidated financial statements were prepared in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the US (“GAAP”). We use certain non-GAAP financial information that we believe is important for purposes of comparison to prior periods and development of future projections and earnings growth prospects. This information is also used by management to measure the performance of our ongoing operations and analyze our business performance and trends. Reconciliations of non-GAAP measures are provided in the Other Non-GAAP Financial Data and Reconciliations section.
Executive Summary
We are a leading business services provider specializing in innovative flexible work space and portable storage solutions. We service diverse end markets across all sectors of the economy throughout the United States ("US"), Canada, Mexico, and the United Kingdom ("UK"). We are also a leading provider of specialty containment solutions in the US with over 12,500 tank and pump units in our fleet. As of December 31, 2020, our branch network included approximately 275 branch locations and additional drop lots to service our over 85,000 customers. We offer our customers an extensive selection of “Ready to Work” modular space and portable storage solutions with over 157,000 modular space units and over 197,000 portable storage units in our fleet.
We primarily lease, rather than sell, our modular and portable storage units to customers, which results in a highly diversified and predictable recurring revenue stream. Over 90% of new lease orders are on our standard lease agreement, pre-negotiated master lease or national account agreements. The initial lease periods vary, and our leases are customarily renewable on a month-to-month basis after their initial term. Our lease revenue is highly predictable due to its recurring nature and the underlying stability and diversification of our lease portfolio. However, given that our customers value flexibility, they consistently extend their leases or renew on a month-to-month basis such that the average effective duration of our lease portfolio, is 32 months. We complement our core leasing business by selling both new and used units, allowing us to leverage scale, achieve purchasing benefits and redeploy capital employed in our lease fleet.
We remain focused on our core priorities of growing leasing revenues by increasing units on rent, both organically and through our consolidation strategy, delivering “Ready to Work” solutions to our customers with value added products and services ("VAPS"), and on continually improving the overall customer experience.
The year ended December 31, 2020 was another transformational year for WillScot Mobile Mini as we completed the Merger with Mobile Mini on July 1, 2020 at which time Mobile Mini became a wholly-owned subsidiary of WillScot. Concurrent with the closing of the Merger, we changed our name to WillScot Mobile Mini Holdings Corp.
For the year ended December 31, 2020, key drivers of our financial performance included:
•Total revenues increased by $303.9 million, or 28.6%, attributable to the addition of Mobile Mini's revenues to our consolidated results once the Merger closed on July 1, 2020.
•Leasing revenue increased $257.2 million, or 34.6%, delivery and installation revenue increased $54.1 million, or 24.6%, rental unit sales decreased $1.4 million, or 3.5%, and new sales revenue decreased $6.0 million, or 10.2%.
Key leasing revenue drivers include:
–Average modular space units on rent increased 7,844 units, or 8.6%, and average portable storage units on rent increased 67,270 units, or 398.6%. Both increases were primarily driven by the Mobile Mini Merger.
–Average modular space monthly rental rate increased $44, or 7.2%, to $658 driven by a $71, or 11.6% increase in the NA Modular segment, offset partially by the dilutive impact of lower rates due to mix on the Mobile Mini modular space units.
–Average portable storage monthly rental rate increased $12, or 10.0%, to $132 driven primarily by the accretive impact of higher rates from the Mobile Mini portable storage fleet.
–Average utilization for modular space units decreased 180 basis points ("bps") to 70.2% and average utilization for portable storage units increased to 75.9%, or 10.1 percentage points, driven by higher utilization of the Mobile Mini portable storage units.
•NA Modular segment revenue, which represents the activities of WillScot prior to the Merger and represented 76.9% of consolidated revenue for the year ended December 31, 2020, decreased $12.5 million, or 1.2%, to $1,051.2 million driven by decreased sales volumes of $26.6 million, or 26.8%, and a $12.0 million, or 5.5%, reduction in delivery and installation revenues as a result of reductions in demand for new project deliveries. However, these reductions were partially offset by an increase in leasing revenue of $26.1 million, or 3.5%, due to continued growth of pricing and value-added products. NA Modular revenue drivers for the year ended December 31, 2020 include:
–Modular space average monthly rental rate of $685 for the year, increased 11.6% representing a continuation of the long-term price optimization initiative and VAPS penetration opportunities across our portfolio.
–Average modular space units on rent for the year decreased 4,808 units, or 5.2% driven by lower deliveries, including reduced demand for new project deliveries as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020. Average modular space units on rent dropped 0.5% sequentially from Q3 into Q4 to 86,011, which compares to a 1.3% drop from Q3 to Q4 in 2019, as delivery volumes returned to prior year levels and return volumes remained lower than 2019 levels.
–Average modular space monthly utilization decreased 310 basis points to 68.9% for the year ended December 31, 2020, but only dropped 10 basis points sequentially from Q3 into Q4.
•Generated consolidated net income of $75.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2020, represented an increase of $196.5 million, and included a $42.4 million loss on extinguishment of debt related to our recent financing activities and $93.8 million of discrete costs expensed in the period related to transaction and integration activities, partly offset by a $51.5 million non-cash income tax benefit. Net income also included a $3.5 million fair value gain on common stock warrant liabilities in the current period, while there was a $109.6 million fair value loss on common stock warrant liabilities in the prior period. Discrete costs in the period included $64.1 million of Merger transaction costs, $18.3 million of integration costs, and $11.4 million of restructuring costs, lease impairment expense and other related charges. As discussed in Note 14 to the consolidated financial statements, the $51.5 million income tax benefit was primarily driven by the reversal of $54.6 million of the federal valuation allowance and certain state valuation allowances during the year ended December 31, 2020 due to the Merger, which partly offset these other discrete costs.
•Generated Adjusted EBITDA of $530.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2020, representing an increase of $173.8 million, or 48.8%, as compared to 2019. Of this increase, $135.5 million was driven by the addition of Mobile Mini to our consolidated results and the remainder was driven by strong organic growth in our NA Modular segment.
–Adjusted EBITDA in our NA Modular segment, which represents the activities of WillScot prior to the Merger, increased $38.3 million, or 10.7% primarily driven by increases in leasing gross profit driven by increased pricing, including VAPS, and significant cost reductions both from acquisition synergy realization and actions taken to reduce variable costs in a reduced demand environment during the second and third quarters of 2020.
–Consolidated Adjusted EBITDA Margin was 38.8% and increased 530 bps versus prior year driven by a 410 bps increased in the NA Modular segment, as well as the addition of the higher margin Mobile Mini operations.
•Generated Free Cash Flow of $162.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2020, representing an increase of $142.3 million as compared to 2019. Net cash provided by operating activities increased $132.2 million to $304.8 million. Additionally, net cash used in investing activities, excluding cash acquired from the Merger, decreased $10.0 million as a result of reduced capital spending needs across all segments given reduced demand for new project deliveries. Excluding the impact of $64.1 million of Merger transaction costs paid during the year, we generated $226.3 million of free cash flow for year ended December 31, 2020 and have repaid approximately $162.4 million of the 2020 ABL Facility since the Merger that closed on July 1, 2020. This was possible due to our resilient lease revenues and strong margin expansion and capex reductions across the NA Modular, NA Storage, and UK segments, as well as reduced interest costs due to our financing activity during the year. Free cash flow increased sequentially to $87.4 million in the fourth quarter of 2020, including $7.4 million of integration costs, which is the best indicator of our run-rate heading into 2021.
In addition to using GAAP financial measurements, we use Adjusted EBITDA and Free Cash Flow, which are non-GAAP financial measures, to evaluate our operating results. As such, we include in this Annual Report on Form 10-K reconciliations to their most directly comparable GAAP financial measures. These reconciliations and descriptions of why we believe these measures provide useful information to investors as well as a description of the limitations of these measures are included in "Item 6. Selected Financial Data."
Recent Developments
Refer to the Recent Developments section in Part I, Item 1, Business, herein for further information about the Mobile Mini Merger and certain related financing transactions and the impact of COVID-19 on our business.
Business Environment and Outlook
Our customers operate in a diversified set of end markets, including construction, commercial and industrial, retail and wholesale trade, education, energy and natural resources, government and healthcare. We track several market leading indicators in order to predict demand, including those related to our two largest end markets, the commercial and industrial sector and the construction sector, which collectively accounted for approximately 85% of our revenues in the year ended December 31, 2020. Market fundamentals underlying these end markets were impacted in 2020 as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic which resulted in delivery volume declines, primarily in the second and third quarters, in response to shelter-in-place orders and other market restrictions. Gross Domestic Product ("GDP") in the US, where the majority of our revenues are generated, is estimated to have declined by over 2% in 2020, and estimates from Dodge Data & Analytics suggest that non-residential construction square footage starts in the US declined by over 15% as compared to 2019. Based on our analyses of industry forecasts and macroeconomic indications, we expect modest market recovery in 2021 following the declines experienced in 2020, and expect both GDP and non-residential construction square footage starts in the US to grow 2-3% in 2021.
Core to our operating model is the ability to redeploy standardized assets across end markets, and we have recently serviced emerging demand in the healthcare and government sectors related to COVID-19, as well as expanded space requirements related to social distancing. Current improving market conditions, potential market catalysts such as increased infrastructure spending, and idiosyncratic growth levers such as continued penetration of our customer base with our VAPS offering, long-term pricing tailwinds, cross-selling between our Modular and Storage segment customers, and other commercial best practice sharing between our segments provide us confidence in our continued organic growth outlook.
Our Business and Growth Strategies
We will maintain a leading market position and continue pursuing the following strategies, all of which we have demonstrated in our historical results and are contributing to our growth, expanding profitability and free cash flow, and overall growth in return on invested capital:
Optimize Pricing Across Fleet
We continue to advance multiple pricing strategies across our fleet to drive revenue growth. Leveraging our expertise developed in NA Modular, we plan to implement dynamic pricing, customer segmentation, and contract standardization in our other segments. Our long history of success, demonstrated by 13 consecutive quarters of double-digit rate growth as of December 31, 2020 in the U.S. within our NA Modular segment, gives us confidence that we can successfully deploy this strategy. The turnover of our fleet, with average lease durations of nearly three years, creates natural and recurring opportunities to capture incremental price increases. As the market leader in our industry, with an estimated 45% market share in the modular sector and 25% market share in the storage sector, we offer the broadest fleet portfolio, the most differentiated turnkey VAPS, and the most consistent service capabilities across the largest branch network to help our customers be 'Ready to Work'.
Expand Penetration of Value-Added Products and Services
As of December 31, 2020, we estimate that we have over $150 million of annual organic revenue growth opportunity as the average VAPS rate of our units on rent in our NA Modular segment converges over time to the VAPS price and penetration levels achieved on our most recently delivered units, and as we begin to cross-sell this offering into our NA Storage segment ground level office fleet. We believe this growth opportunity could be substantially larger if we successfully penetrate more of our modular space orders, and expand our VAPS offering for portable storage units.
Enhance Cross-Selling Between Segments
The combination of WillScot and Mobile Mini created a leading business services provider specializing in innovative flexible work space and portable storage solutions. At the outset of the merger, we recognized that there was 80% end-market overlap and 40% customer overlap, a clear strategic opportunity for our complementary product lines. By offering a combined product suite, we simplify our customers' procurement needs and enable productivity from start to finish for projects. We believe cross-selling will also increase utilization and yield of our combined fleet. Our sales force is optimally positioned to improve efficiency by leveraging our management information systems and using real-time information to monitor and optimize conversion of customer opportunities across our core segments. In turn, we expect that our broadened and enhanced fleet will attract new customers, increase customer retention, and increase margins and return on invested capital.
Generate Cash Flow Through Operational Efficiencies, Cost Reductions, and Technology
We are implementing many initiatives designed to improve operations and increase profitability. We continually assess our branch operating footprint, vendor base, and operating structure to maximize revenue generation while minimizing costs. The Merger provides us with increased scale, numerous operational best practices from both the legacy WillScot and
legacy Mobile Mini businesses, and a state-of-the-art SAP ERP platform, all of which we believe will significantly improve the operating efficiency of the combined businesses. We have a proven track record of efficiently integrating acquisitions and quickly eliminating operational redundancies while maintaining acquired customer relationships.
Deploy Capital to Strategically Support Organic Growth and Optimize Returns
We maintain a disciplined focus on our return on capital and the Merger allows us to invest opportunistically across multiple attractive asset classes prioritizing our investments to where we see the strongest potential returns. We continually assess both our existing lease fleet and customer demand for opportunities to deploy capital more efficiently. We manage our maintenance capex and growth capex to align with the economic conditions in which we operate. Within our existing lease fleet, we examine the potential cash and earnings generation of an asset sale versus continuing to lease the asset. In addition, we examine the relative benefits of organic expansion opportunities versus expansion through acquisition to obtain a favorable return on capital.
Leverage Scale and Organic Initiatives with Accretive Acquisitions
Our markets for modular space and portable storage solutions are fragmented. We estimate that approximately 55% of the modular market and approximately 75% of the portable storage market in North America are supplied by regional and local competitors. We have the broadest network of operating branches in North America, as well as a scalable corporate center and information technology systems, which position us to continue to acquire and integrate other companies while expanding the products and services available and offered to acquired customers. Furthermore, we have realized over $60 million of cost synergies from acquisitions in the past three years and have identified nearly $60 million of additional cost reductions that we have yet to execute. We expect to pursue acquisitions opportunistically that will provide further scale efficiencies and allow us to improve returns generated by the acquired assets. We continually evaluate our portfolio of businesses to ensure that our operations remain in line with our broader strategic goals.
Use Free Cash Flow to Drive Value Creation
Free cash flow generation has accelerated rapidly in recent years, and we expect this trend to continue as we execute our strategy. While we see numerous organic and inorganic opportunities to re-invest in our core businesses, we believe we can generate surplus free cash flow with which we can both reduce leverage and return capital to shareholders over time. We view this as an additional powerful value creation lever, and we are committed to deploying this capital as productively as possible in the interests of our shareholders.
Components of Our Consolidated Historical Results of Operations
Revenue
Our revenue consists mainly of leasing, services and sales revenue. We derive our leasing and services revenue primarily from the leasing of modular space and portable storage units. Included in leasing revenue are VAPS, such as furniture, steps, ramps, basic appliances, internet connectivity devices, and other items our customers use in connection with our products. Delivery and installation revenue includes fees that we charge for the delivery, site work, installation, disassembly, unhooking and removal, and other services to our customers for an additional fee as part of our leasing and sales operations.
The key drivers of changes in our leasing revenue are:
•the number of units in our lease fleet;
•the average utilization rate of our lease units; and
•the average monthly rental rate per unit, including VAPS.
The average utilization rate of our lease units is the ratio of (i) the average number of units in use during a period (which includes units from the time they are leased to a customer until the time they are returned to us) to (ii) the average total number of units available for lease in our fleet during a period. Our average monthly rental rate per unit for a period is equal to the ratio of (i) our rental income for that period including VAPS but excluding delivery and installation services and other leasing-related revenues, to (ii) the average number of lease units rented to our customers during that period.
The table below sets forth the average number of units on rent in our lease fleet, the average utilization of our lease units, and the average monthly rental rate per unit, including VAPS:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| (in thousands, except unit numbers and rates) | 2020 | | 2019 | | 2018 |
| Modular space units on rent (average during the period) | 99,526 | | | 91,682 | | | 70,257 | |
| Average modular space utilization rate | 70.2 | % | | 72.0 | % | | 71.6 | % |
| Average modular space monthly rental rate | $ | 658 | | | $ | 614 | | | $ | 552 | |
| Portable storage units on rent (average during the period) | 84,148 | | | 16,878 | | | 15,480 | |
| Average portable storage utilization rate | 75.9 | % | | 65.8 | % | | 68.9 | % |
| Average portable storage monthly rental rate | $ | 132 | | | $ | 120 | | | $ | 119 | |
| Average tank and pump solutions rental fleet utilization based on original equipment cost | 61.7 | % | | — | % | | — | % |
In addition to leasing revenue, we also generate revenue from sales of new and used modular space and portable storage units to our customers, as well as delivery, installation, maintenance, removal services and other incidental items related to accommodation services for our customers. Included in our sales revenue are charges for modifying or customizing sales equipment to customers’ specifications.
Gross Profit
We define gross profit as the difference between total revenues and cost of revenues. Cost of revenues associated with our leasing business includes payroll and payroll-related costs for branch operations personnel, material and other costs related to the repair, maintenance, storage and transportation of rental equipment. Cost of revenue also includes depreciation expense associated with our rental equipment. Cost of revenues associated with our new unit sales business includes the cost to purchase, assemble, transport and customize units that are sold. Cost of revenues for our rental unit sales consist primarily of the net book value of the unit at date of sale.
Selling, General and Administrative Expense
Our selling, general and administrative (“SG&A”) expense includes all costs associated with our selling efforts, including marketing costs, marketing salaries and benefits, as well as the salary and commissions of sales personnel. It also includes the leasing of facilities we occupy, professional fees and information systems, our overhead costs, such as salaries of management, administrative and corporate personnel, and integration costs associated with acquisitions and business combinations.
Transaction Costs
Transaction costs include discrete expenses incurred related to the Merger and the 2018 acquisition of ModSpace.
Other Depreciation and Amortization
Other depreciation and amortization includes depreciation of our property, plant and equipment, as well as the amortization of our intangible assets.
Impairment Losses on Long-Lived Assets
We recognize property, plant, and equipment impairment charges when an indicator of impairment is present and the carrying value of assets exceeds the estimated undiscounted cash flows and fair value of the assets.
Lease Impairment Expense and Other Related Charges
Lease impairment expense and other related charges include impairment of right-of-use ("ROU") assets, gain or loss on the exit of a leased property generally associated with lease termination payments and rent expense for locations which have been closed but have not been abandoned or impaired.
Restructuring Costs
Restructuring costs include charges associated with exit or disposal activities that meet the definition of restructuring under Financial Accounting Standards Board ("FASB") ASC Topic 420, Exit or Disposal Cost Obligations (“ASC 420”). Our restructuring plans are generally country or region specific and are typically completed within a one-year period. Prior to the adoption of FASB ASC Topic 842, Leases ("ASC 842") effective January 1, 2019, restructuring costs incurred under these plans included (i) one-time termination benefits related to employee separations, (ii) contract termination costs and, (iii) other related costs associated with exit or disposal activities including, but not limited to, costs for consolidating or closing facilities. After the adoption of ASC 842, restructuring costs include one-time termination benefits related to employee separation costs. The restructuring costs incurred in 2020, 2019 and 2018 primarily relate to the integration of our acquisitions. Costs related to the integration of acquired businesses that do not meet the definition of restructuring under ASC 420, such as employee training costs, duplicate facility costs, and professional services expenses, are included within SG&A expense.
Currency (Gains) Losses, Net
Currency (gains) losses, net include unrealized and realized gains and losses on monetary assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies other than our functional currency at the reporting date.
Other Income, Net
Other income, net primarily consists of the gain (loss) on disposal of non-operational property, plant and equipment, other financing related costs and other non-recurring charges.
Interest Expense
Interest expense consists of the costs of external debt including the Company’s ABL credit facility, 2022 Secured Notes, 2023 Secured Notes, 2025 Secured Notes, 2028 Secured Notes, and the senior unsecured notes due November 15, 2023 (the "Unsecured Notes") and interest on obligations under finance leases.
Fair Value (Gain) Loss on Common Stock Warrant Liabilities
Fair value (gain) loss on common stock warrant liabilities consists of non-cash gains and losses recorded related to changes in the fair value of common stock warrant liabilities as the common stock warrant liabilities are marked-to-market liabilities. It also includes gains and losses recorded related to the settlement of common stock warrant liabilities.
Loss on Extinguishment of Debt
In connection with the Merger and related financing transactions in 2020, using proceeds from the 2025 Secured Notes, we redeemed all of our 2022 Secured Notes. We also completed a private offering of our 2028 Secured Notes in August 2020 and used the offering proceeds to repay our 2023 Secured Notes. As a result of these transactions, we recorded losses on extinguishment of debt.
Income Tax Benefit
We are subject to income taxes in the US, Canada, Mexico and the UK. Our overall effective tax rate is affected by a number of factors, such as the relative amounts of income we earn in differing tax jurisdictions, tax law changes, and certain non-deductible expenses such as compensation disallowance. The rate is also affected by discrete items that may occur in any given year, such as legislative enactments. These discrete items may not be consistent from year to year. Income tax expense (benefit), deferred tax assets and liabilities and liabilities for unrecognized tax benefits reflect our best estimate of current and future taxes to be paid.
Consolidated Results of Operations
Our consolidated statements of net income (loss) for the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019, and 2018 are presented below. The below results only include results from Mobile Mini and ModSpace for the periods subsequent to their acquisition dates and do not include any incremental unrealized cost savings, revenue growth, or pro forma adjustments that management expects to result from the integration of the acquired businesses.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Years Ended December 31, | | 2020 vs. 2019 Change | | 2019 vs 2018 Change |
| 2020 | | 2019 | | 2018 | | |
| in thousands | (as restated) | | (as restated) | | (as restated) | | | | |
| Revenues: | | | | | | | | | |
| Leasing and services revenue: | | | | | | | | | |
| Leasing | $ | 1,001,447 | | | $ | 744,185 | | | $ | 518,235 | | | $ | 257,262 | | | $ | 225,950 | |
| Delivery and installation | 274,156 | | | 220,057 | | | 154,557 | | | 54,099 | | | 65,500 | |
| Sales revenue: | | | | | | | | | |
| New units | 53,093 | | | 59,085 | | | 53,603 | | | (5,992) | | | 5,482 | |
| Rental units | 38,949 | | | 40,338 | | | 25,017 | | | (1,389) | | | 15,321 | |
| Total revenues | 1,367,645 | | | 1,063,665 | | | 751,412 | | | 303,980 | | | 312,253 | |
| Costs: | | | | | | | | | |
| Costs of leasing and services: | | | | | | | | | |
| Leasing | 227,376 | | | 213,151 | | | 143,120 | | | 14,225 | | | 70,031 | |
| Delivery and installation | 220,102 | | | 194,107 | | | 143,950 | | | 25,995 | | | 50,157 | |
| Costs of sales: | | | | | | | | | |
| New units | 34,841 | | | 42,160 | | | 36,863 | | | (7,319) | | | 5,297 | |
| Rental units | 24,772 | | | 26,255 | | | 16,659 | | | (1,483) | | | 9,596 | |
| Depreciation of rental equipment | 200,581 | | | 174,679 | | | 121,436 | | | 25,902 | | | 53,243 | |
| Gross profit | 659,973 | | | 413,313 | | | 289,384 | | | 246,660 | | | 123,929 | |
| Expenses: | | | | | | | | | |
| Selling, general and administrative | 360,626 | | | 271,004 | | | 234,820 | | | 89,622 | | | 36,184 | |
| Transaction costs | 64,053 | | | — | | | 20,051 | | | 64,053 | | | (20,051) | |
| Other depreciation and amortization | 43,249 | | | 12,395 | | | 13,304 | | | 30,854 | | | (909) | |
| Impairment losses on long-lived assets | — | | | 2,848 | | | 1,600 | | | (2,848) | | | 1,248 | |
| Lease impairment expense and other related charges | 4,876 | | | 8,674 | | | — | | | (3,798) | | | 8,674 | |
| Restructuring costs | 6,527 | | | 3,755 | | | 15,468 | | | 2,772 | | | (11,713) | |
| Currency (gains) losses, net | (355) | | | (688) | | | 2,454 | | | 333 | | | (3,142) | |
| Other income, net | (1,718) | | | (2,200) | | | (4,574) | | | 482 | | | 2,374 | |
| Operating income | 182,715 | | | 117,525 | | | 6,261 | | | 65,190 | | | 111,264 | |
| Interest expense | 119,886 | | | 122,504 | | | 98,433 | | | (2,618) | | | 24,071 | |
| Fair value (gain) loss on common stock warrant liabilities | (3,461) | | | 109,622 | | | (23,830) | | | (113,083) | | | 133,452 | |
| Loss on extinguishment of debt | 42,401 | | | 8,755 | | | — | | | 33,646 | | | 8,755 | |
| Income (loss) before tax | 23,889 | | | (123,356) | | | (68,342) | | | 147,245 | | | (55,014) | |
| Income tax benefit | (51,451) | | | (2,191) | | | (38,600) | | | (49,260) | | | 36,409 | |
| Net income (loss) | 75,340 | | | (121,165) | | | (29,742) | | | 196,505 | | | (91,423) | |
| Net income (loss) attributable to non-controlling interest, net of tax | 1,213 | | | (421) | | | (4,532) | | | 1,634 | | | 4,111 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Net income (loss) attributable to WillScot common shareholders | $ | 74,127 | | | $ | (120,744) | | | $ | (25,210) | | | $ | 194,871 | | | $ | (95,534) | |
Comparison of Years Ended December 31, 2020 and 2019
Revenue: Total revenue increased $303.9 million, or 28.6%, to $1,367.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2020 from $1,063.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2019. The increase was driven primarily by the addition of Mobile Mini's revenues to our consolidated results. The Merger closed on July 1, 2020 and drove $316.5 million of the year over year increase. Leasing revenue increased $257.2 million, or 34.6%, as compared to the same period in 2019 driven by an increase of 75,114 average modular space and portable storage units on rent as a result of the Merger, and improved pricing and value-added products in our NA Modular segment. Delivery and installation revenues increased $54.1 million, or 24.6%, due to increased overall activity as a result of the Merger, but was partially offset by lower delivery volumes due to the impact of new project cancellations and delays in the second and third quarter of 2020 as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic. New unit sales decreased $6.0 million, or 10.2%, and rental unit sales decreased $1.4 million, or 3.5%, as a result of lower demand in 2020.
Total average modular space and portable storage units on rent for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 were 183,674 and 108,560, respectively. The increase was due primarily to the units acquired as part of the Merger, partially offset by lower delivery volumes in the NA Modular segment, including reduced demand for new projects as a result of the COVID-19 global pandemic disruption on social and business activities. In total, modular space average units on rent increased 7,844 units, or 8.6%, for the year ended December 31, 2020 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2019. Modular space average monthly rental rates increased 7.2% to $658 for the year ended December 31, 2020. Improved pricing was driven by a continuation of the long-term price optimization and VAPS penetration opportunities across our portfolio, partially offset by the dilutive impact of lower rates on the Mobile Mini modular space units due to product mix. Portable storage average units on rent increased by 67,270 units, or 398.6%, for the year ended December 31, 2020. Average portable storage monthly rental rates of $132 represented an increase of $12, or 10.0%, compared to the year ended December 31, 2019. This increase was driven by the accretive impact of higher rates from the Mobile Mini portable storage fleet. The average modular space unit utilization rate during the year ended December 31, 2020 was 70.2%, as compared to 72.0% during the same period in 2019. This decrease was driven by lower demand as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, partially offset by higher utilization on units acquired as part of the Merger. The average portable storage unit utilization rate during the year ended December 31, 2020 was 75.9%, as compared to 65.8% during the same period in 2019. The increase in average portable storage utilization rate was driven by higher utilization on the acquired Mobile Mini units.
Gross Profit: Our gross profit percentage was 48.3% and 38.9% for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively. Our gross profit percentage, excluding the effects of depreciation ("adjusted gross profit percentage"), was 62.9% and 55.3% for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively.
Gross profit increased $246.7 million, or 59.7%, to $660.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2020 from $413.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2019. The increase in gross profit is a result of a $243.0 million increase in leasing gross profit, increased delivery and installation gross profit of $28.1 million, and increased new and rental unit sale margins of $1.5 million. These increases were primarily a result of increased revenues due to the Merger and to favorable average monthly rental rates in the NA Modular segment on modular space units, as well as modular leasing cost savings due to lower delivery volumes that were achieved as a result of actions we took to scale back variable labor and material costs in response to lower demand for new project deliveries. These increases were offset partially by lower delivery and installation activity volumes in the NA Modular segment in the second and third quarters of 2020 due to reduced delivery demand and by increased depreciation of $25.9 million as a result of fleet acquired in the Merger and capital investments made over the past twelve months in our existing rental equipment.
SG&A Expense: SG&A expense increased $89.6 million, or 33.1%, to $360.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2020, compared to $271.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2019. The primary driver of the increase is related to additional SG&A expense as a result of operating a larger business due to the Merger. SG&A expense for the NA Storage, UK Storage, and Tank and Pump segments totaled $90.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2020.
Transaction Costs: Transaction costs increased $64.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2020. Transaction costs were related to the Merger.
Other Depreciation and Amortization: Other depreciation and amortization increased $30.8 million, or 248.4%, to $43.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2020, compared to $12.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2019. $18.2 million of the increase was driven by increased Other depreciation as a result of the inclusion of Mobile Mini beginning in the third quarter of 2020 and $13.4 million was driven by the amortization of the customer relationship intangible asset acquired in the Merger.
Impairment losses on Long-Lived Assets: Impairment losses on long-lived assets were $2.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 related to the valuation of properties classified as assets held for sale as a result of the ModSpace acquisition. No similar impairments occurred during the year ended December 31, 2020.
Lease Impairment Expense and Other Related Charges: Lease impairment expense and other related charges were $4.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2020 as compared to $8.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2019. The decrease in Lease impairment expense and other related charges of $3.8 million in 2020 is a result of fewer remaining closed locations in 2020 due to successful lease exits related to the ModSpace acquisition.
Restructuring Costs: Restructuring costs were $6.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2020 as compared to $3.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2019. The restructuring charges in the year ended December 31, 2020 were
primarily due to employee terminations costs as a result of the Merger and, to a lesser extent, reductions in force across our branch network in response to COVID-19 economic conditions. The restructuring charges in the year ended December 31, 2019 related primarily to employee termination costs related to the ModSpace and Acton acquisitions and integrations.
Currency (Gains) Losses, net: Currency (gains) losses, net decreased by $0.3 million to a $0.4 million gain for the year ended December 31, 2020 compared to a $0.7 million gain for the year ended December 31, 2019. The decrease in currency (gains) losses, net, are primarily attributable to the impact of foreign currency exchange rate changes on loans and borrowings and intercompany receivables and payables denominated in a currency other than the subsidiaries’ functional currency.
Other Income, Net: Other income, net was $1.7 million and $2.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively. Other income, net of $1.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2020 was primarily related to the reversal of non-operating liabilities of $2.5 million. Other income, net of $2.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 was driven primarily by the receipt of $3.2 million of insurance proceeds related to assets damaged during Hurricane Harvey.
Interest Expense: Interest expense decreased $2.6 million, or 2.1%, to $119.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2020 from $122.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2019. The decrease was driven by lower interest rates on our ABL facilities, the repayment of our 10% Unsecured Notes in 2019 and the lower interest rates on our 2025 Secured Notes and 2028 Secured Notes, partially offset by an $800 million increase in debt outstanding as a result of the Merger.
Fair Value (Gain) Loss on Common Stock Warrant Liabilities: The fair value of common stock warrant liabilities increased $113.1 million, to a $3.5 million gain for the year ended December 31, 2020 from a $109.6 million loss for the year ended December 31, 2019. The increase was primarily attributable to the change in estimated fair value of common stock warrant liabilities.
Loss on Extinguishment of Debt: As a result of the Merger and the related financing transactions, we recorded a loss on extinguishment of debt of $42.4 million in the year ended December 31, 2020. This loss on extinguishment of debt was comprised of the redemption premium and write off of unamortized deferred financing costs associated with the following: (i) $15.2 million due to the redemption of the 2022 Secured Notes, (ii) $22.7 million due to the redemption of the 2023 Secured Notes, and (iii) $4.4 million associated with the 2017 ABL Facility. For the year ended December 31, 2019, we recorded $8.8 million of losses on extinguishment of debt consisting of $1.5 million related to the $30 million redemption of the 2022 Secured Notes at a redemption price of 103% and $7.2 million related to the redemption of the 2023 senior unsecured notes at a redemption price of 102.0%, plus a make-whole premium of 1.1%, for total premiums of 3.1%.
Income Tax Benefit: Income tax benefit increased $49.3 million to a $51.5 million benefit for the year ended December 31, 2020 compared to a $2.2 million benefit for the year ended December 31, 2019. The increase in income tax benefit was driven by a reversal of our valuation allowance of $56.5 million based on our assessment of deferred tax assets, a reduction of reserves for uncertain tax positions of $11.2 million, partially offset by tax expense from pre-tax income and non-deductible expense in the year ended December 31, 2020 as compared to discrete benefits recorded in the year ended December 31, 2019.
Comparison of Years Ended December 31, 2019 and 2018
Revenue: Total revenue increased $312.3 million, or 41.6%, to $1,063.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 from $751.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2018. The increase was primarily the result of a 43.3% increase in leasing and services revenue driven by increased volumes from acquisitions and improved pricing. Improved volumes were driven by units acquired as part of the ModSpace acquisition, as well as, increased modular delivery and installation revenues on the combined rental fleet of 42.4% due to increased transaction volumes and higher revenues per transaction. Average modular space monthly rental rates increased 11.2% for the year ended December 31, 2019, and average modular space units on rent increased 21,425 units, or 30.5%, due to the impact of an additional 8.5 months of contribution from the ModSpace acquisition. Improved pricing was driven by a combination of our price optimization tools and processes, as well as, by continued growth in our “Ready to Work” solutions and increased VAPS penetration across our customer base, offset partially by the average modular space monthly rental rates on acquired units for ModSpace. The increase in leasing and services revenues was further complemented by an increase of $5.5 million, or 10.3%, in new unit sales as compared to 2018. This increase was primarily driven by increased sales as a result of the ModSpace acquisition. Rental unit sales increased $15.3 million, or 61.2%, as compared to 2018.
Total average units on rent for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 were 108,560 and 85,737, respectively. The increase was due to units acquired as part of the ModSpace acquisition, with modular space average units on rent increased by 21,425 units, or 30.5%, for the year ended December 31, 2019. Modular space average monthly rental rates increased 11.2% for the year ended December 31, 2019. Portable storage average units on rent increased by 1,398 units, or 9.0%, for the year ended December 31, 2019. Average portable storage monthly rental rates increased 0.8% for the year ended December 31, 2019. The average modular space unit utilization rate for the year ended December 31, 2019 was 72.0%, as compared to 71.6% in 2018. The increase in average modular space utilization rate was driven by a reduction in the combined modular space unit fleet size across the combined WillScot and ModSpace fleet in 2019. The average portable storage unit utilization rate during the year ended December 31, 2019 was 65.8%, as compared to 68.9% in 2018. The decrease in average portable storage utilization rate was driven by organic declines in the number of portable storage average units on rent in the Modular - US segment.
Gross Profit: Our gross profit percentage was 38.9% and 38.5% for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively. Our gross profit percentage, excluding the effects of depreciation ("adjusted gross profit percentage"), was 55.3% and 54.7% for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively.
Gross profit increased $123.9 million, or 42.8%, to $413.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 from $289.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2018. The increase in gross profit is a result of a $291.5 million increase in modular leasing and services revenue and increased new unit sales gross profit of $0.2 million, offset by increases of $120.2 million in modular leasing and services costs. Increases in modular leasing and services revenues and costs were primarily as a result of increased revenues due to additional units on rent as a result of recent acquisitions as well as increased margins due to favorable average monthly rental rates on modular space units and increased delivery and installation margins driven primarily by higher pricing per transaction. These increases were partially offset by increased depreciation of $53.3 million as a result of additional rental equipment acquired as part of the ModSpace acquisition, as well as continued capital investment in our existing rental equipment.
SG&A Expense: SG&A expense increased $16.1 million, or 6.3%, to $271.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2019, compared to $254.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2018. Employee costs increased $19.5 million driven by the increased size of the workforce, offset partially by employee savings achieved as a result of restructuring activities; and occupancy costs increased $10.3 million largely due to the expansion of our branch network and storage lots, including a portion of the expected cost savings as we have now exited approximately 85% of redundant real estate locations.
Discrete items included in SG&A expense decreased for the year ended December 31, 2019, compared to the year ended December 31, 2018, by $17.7 million as decreases in transaction and integration costs related to the ModSpace and Acton acquisitions and subsequent integrations of $20.1 million and $4.0 million, respectively, were partially offset by increases in stock compensation expense and other acquisition-related activities of $3.3 million and $3.1 million, respectively.
The remaining increases of $4.0 million are primarily related to increased professional fees, insurance, computer, travel, office and other expenses related to operating a larger business as a result of our recent acquisitions and our expanded employee base and branch network.
We estimate incremental cost synergies of approximately $36.0 million related to the ModSpace and Acton acquisitions were realized in 2019, which compares to approximately $6.4 million of synergies realized in 2018 related to the Acton and Onsite Space LLC (d/b/a Tyson Onsite (“Tyson”) acquisitions, bringing cumulative synergies related to the Acton, Tyson, and ModSpace acquisitions from the dates of the acquisitions to December 31, 2019 to approximately $42.4 million. These cost synergies are consistent with our integration plans and we expect to achieve annual recurring cost savings of over $70.0 million once our integration plans are fully executed and in our annual results.
Transaction Costs: Transaction costs decreased $20 million for the year ended December 31, 2019. Transaction costs in 2018 were related to the ModSpace acquisition that closed on August 15, 2018.
Other Depreciation and Amortization: Other depreciation and amortization decreased $0.9 million, or 6.8%, to $12.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2019, compared to $13.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2018. The decrease in other depreciation and amortization was driven primarily by lower depreciation as a result of the decrease in property, plant and equipment. Property, plant and equipment decreased as a result of the transfer of non-producing branches to assets held for sale which are no longer depreciated and the impact of the adoption of ASC 842 which resulted in the reversal of branch assets previously accounted for as failed sale-lease back locations which are compliant sales under ASC 842.
Impairment losses on Long-Lived Assets: Impairment losses on long-lived assets were $2.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 as compared to $1.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2018. In 2019 and 2018, we reclassified certain branch facilities from property, plant and equipment to assets held for sale and recognized an impairment on these assets as the estimated fair value was less than the carrying value of the facilities.
Lease Impairment Expense and Other Related Charges: Lease impairment expense and other related charges was $8.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2019. Effective January 1,2019, in connection with the adoption of ASC 842, we recorded $4.2 million in ROU asset impairments, $2.6 million in rent on closed locations and $1.9 million in lease termination fees.
Restructuring Costs: Restructuring costs were $3.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 as compared to $15.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2018. The 2019 restructuring charges related primarily to employee termination costs as a result of the ModSpace acquisition and integration. The 2018 restructuring charges are comprised of employee termination and lease breakage costs related to the Acton and ModSpace acquisitions and integrations. Prior to the adoption of ASC 842 effective January 1. 2019, the costs associated with leases exited as a result of a restructuring plan were recorded in restructuring expense.
Currency (Gains) Losses, net: Currency (gains) losses, net were a $0.7 million gain for the year ended December 31, 2019 compared to a $2.5 million loss for the year ended December 31, 2018. The decrease in currency losses was primarily attributable to the impact of foreign currency exchange rate changes on loans and borrowings and intercompany receivables and payables denominated in a currency other than the subsidiaries’ functional currency.
Other Income, Net: Other income, net was $2.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 and $4.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2018. The decrease in other income was driven by the receipt of insurance proceeds related to
assets damaged during Hurricane Harvey and other settlements which contributed $5.6 million to other expense, net for the year ended December 31, 2018, offset by the receipt of $2.4 million in insurance proceeds related to assets damaged during hurricanes and the receipt of a $0.9 million settlement during the year ended December 31, 2019.
Interest Expense: Interest expense increased $24.1 million, or 24.5%, to $122.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 from $98.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2018. The increase in interest expense is attributable to the increased financing costs for the full year in 2019, as a result of the ModSpace acquisition which occurred in the third quarter of 2018, offset in part by the one-time bridge financing and upfront commitment fees expensed in 2018 and lower interest costs due to the redemption of our Unsecured Notes in June 2019. In the third quarter of 2018, as part of financing the ModSpace acquisition, we upsized our 2017 ABL Facility to $1.425 billion, issued the 2023 Secured Notes, and issued the Unsecured Notes and incurred bridge financing fees and upfront commitment fees of $20.5 million which were recorded to interest expense.
Fair Value (Gain) Loss on Common Stock Warrant Liabilities: The fair value of common stock warrant liabilities decreased $133.5 million, to a $109.6 million loss for the year ended December 31, 2019 from a $23.8 million gain for the year ended December 31, 2018. The decrease was primarily attributable to the change in estimated fair value of common stock warrant liabilities.
Loss on Extinguishment of Debt: $1.5 million related to the $30 million redemption on December 13, 2019 of the 2022 Secured Notes at a redemption price of 103% and $7.2 million related to the redemption on June 19, 2019 of the 2023 senior unsecured notes. Refer to Part II, Item 8, Note 11 for further information.
Income Tax Benefit: Income tax benefit decreased $36.4 million to $2.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 compared to $38.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2018. The decrease in tax benefit was driven by the lower loss before income tax for the year ended December 31, 2019, approximately $17.0 million less tax benefit, and discrete tax benefits in 2018 related to a reduction in the valuation allowance, tax benefit of $11.9 million, and a tax benefit of $7.0 million related to a change in the Company asserting indefinite re-investment in certain of its foreign businesses.
Business Segments
As a result of the Merger, we evaluated our operating structure and, accordingly, our segment structure and determined we operate in four reportable segments as follows: NA Modular, NA Storage, UK Storage and Tank and Pump. The NA Modular segment represents the activities of WillScot prior to the Merger. The NA Storage, UK Storage and Tank and Pump segments align to the three segments reported by Mobile Mini prior to the Merger.
The following tables and discussion summarize our reportable segment financial information for the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018. Consistent with the presentation of our consolidated financial statements, the below segment results only include results from ModSpace and Mobile Mini for the periods subsequent to the respective acquisition and Merger and do not include any unrealized incremental cost savings, revenue growth or pro forma adjustments that management expects to result from the integration of the acquired and merged businesses.
A Summary Business Segment Supplemental Unaudited Pro Forma Financial Information section has been included in this MD&A in order to provide period over period comparable financial information for the NA Storage, UK Storage and Tank and Pump reporting segments, as these segments were not included in our 2019 reported results.
Business Segment Results
Years Ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, 2020 |
| (in thousands, except for units on rent and rates) | NA Modular | | NA Storage | | UK Storage | | Tank and Pump | | Total |
| Revenue | $ | 1,051,162 | | | $ | 221,829 | | | $ | 46,361 | | | $ | 48,293 | | | $ | 1,367,645 | |
| Gross profit | $ | 451,642 | | | $ | 156,785 | | | $ | 27,642 | | | $ | 23,904 | | | $ | 659,973 | |
| Adjusted EBITDA | $ | 394,805 | | | $ | 99,837 | | | $ | 17,822 | | | $ | 17,843 | | | $ | 530,307 | |
| Capex for rental equipment | $ | 153,327 | | | $ | 14,969 | | | $ | 1,693 | | | $ | 2,394 | | | $ | 172,383 | |
| Average modular space units on rent | 86,874 | | | 8,333 | | | 4,319 | | | — | | | 99,526 | |
| Average modular space utilization rate | 68.9 | % | | 80.6 | % | | 80.8 | % | | — | % | | 70.2 | % |
| Average modular space monthly rental rate | $ | 685 | | | $ | 526 | | | $ | 367 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 658 | |
| Average portable storage units on rent | 15,823 | | | 56,415 | | | 11,910 | | | — | | | 84,148 | |
| Average portable storage utilization rate | 63.5 | % | | 78.2 | % | | 85.9 | % | | — | % | | 75.9 | % |
| Average portable storage monthly rental rate | $ | 122 | | | $ | 147 | | | $ | 76 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 132 | |
| Average tank and pump solutions rental fleet utilization based on original equipment cost | — | % | | — | % | | — | % | | 61.7 | % | | 61.7 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, 2019 |
| (in thousands, except for units on rent and rates) | NA Modular | | NA Storage | | UK Storage | | Tank and Pump | | Total |
| Revenue | $ | 1,063,665 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 1,063,665 | |
| Gross profit | $ | 413,313 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 413,313 | |
| Adjusted EBITDA | $ | 356,548 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 356,548 | |
| Capex for rental equipment | $ | 205,106 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 205,106 | |
| Average modular space units on rent | 91,682 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 91,682 | |
| Average modular space utilization rate | 72.0 | % | | — | % | | — | % | | — | % | | 72.0 | % |
| Average modular space monthly rental rate | $ | 614 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 614 | |
| Average portable storage units on rent | 16,878 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 16,878 | |
| Average portable storage utilization rate | 65.8 | % | | — | % | | — | % | | — | % | | 65.8 | % |
| Average portable storage monthly rental rate | $ | 120 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 120 | |
| Average tank and pump solutions rental fleet utilization based on original equipment cost | — | % | | — | % | | — | % | | — | % | | — | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, 2018 |
| (in thousands, except for units on rent and rates) | NA Modular | | NA Storage | | UK Storage | | Tank and Pump | | Total |
| Revenue | $ | 751,412 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 751,412 | |
| Gross profit | $ | 289,384 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 289,384 | |
| Adjusted EBITDA | $ | 215,533 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 215,533 | |
| Capex for rental equipment | $ | 160,883 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 160,883 | |
| Average modular space units on rent | 70,257 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 70,257 | |
| Average modular space utilization rate | 71.6 | % | | — | % | | — | % | | — | % | | 71.6 | % |
| Average modular space monthly rental rate | $ | 552 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 552 | |
| Average portable storage units on rent | 15,480 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 15,480 | |
| Average portable storage utilization rate | 68.9 | % | | — | % | | — | % | | — | % | | 68.9 | % |
| Average portable storage monthly rental rate | $ | 119 | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | 119 | |
| Average tank and pump solutions rental fleet utilization based on original equipment cost | — | % | | — | % | | — | % | | — | % | | — | % |
NA Modular Segment
Comparison of Years Ended December 31, 2020 and 2019
Revenue: Total revenue decreased $12.5 million, or 1.2%, to $1,051.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2020 from $1,063.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2019. The decrease was primarily driven by declines in new unit sales revenue, which decreased $17.2 million, or 29.1%, compared to 2019, and by declines in rental unit sales revenue, which decreased $9.4 million, or 23.3%. Additionally, delivery and installation revenues declined $12.0 million, or 5.5%, driven by lower delivery volumes related to the impact of new project cancellations and delays as a result of COVID-19 global pandemic disruption on social and business activities. These declines were partially offset by an increase in leasing revenue of $26.1 million, or 3.5%. Average modular space monthly rental rates increased 11.6% for the year ended December 31, 2020 to $685 driven by continuation of the long-term price optimization and VAPS penetration opportunities across our portfolio. Improved pricing was partially offset by lower volumes as average modular space units on rent decreased by 4,808 units, or 5.2% year over year. The decrease was driven primarily by lower delivery volumes, including reduced demand for new projects since mid- March of 2020 as a result of COVID-19.
Gross Profit: Gross profit increased $38.3 million, or 9.3%, to $451.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2020 from $413.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2019. The increase in gross profit was driven by a $44.9 million increase in leasing gross profit driven by improved pricing and VAPS, as well as by lower modular leasing cost due to lower delivery demand in the second and third quarter of 2020 and reduced variable costs. The increase in gross profit from leasing revenues was partially offset by a $7.9 million increase in depreciation of rental equipment primarily as a result of capital investments made over the past twelve months in our existing rental equipment for the year ended December 31, 2020.
Adjusted EBITDA: Adjusted EBITDA increased $38.3 million, or 10.7%, to $394.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2020 from $356.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2019. The increase was driven by higher leasing gross profits discussed above, partially offset by increases in SG&A, excluding discrete and other items, of $6.8 million. SG&A increases were primarily related to increases in occupancy and office costs, insurance costs, and increased bad debt expense, partially offset by decreased travel and entertainment costs due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
Capex for rental equipment: Capex for rental equipment decreased $51.8 million, or 25.3%, to $153.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2020 from $205.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2019. Net CAPEX also decreased $31.3 million, or 20.5%, to $121.3 million. The decreases for both were driven by decreased spend for refurbishments and VAPS due to less constrained fleet and reduced demand as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, and cost improvements experienced over the prior year related to better unit selection and scoping on refurbishments. Decrease to Net CAPEX was also partially driven by lower demand for sales of rental units.
Comparison of Years Ended December 31, 2019 and 2018
Revenue: Total revenue increased $312.3 million, or 41.6%, to $1,063.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 from $751.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2018. The increase was primarily the result of a 43.3% increase in leasing and services revenue driven by increased volumes from acquisitions and improved pricing. Improved volumes were driven by units acquired as part of the ModSpace acquisition, as well as, increased modular delivery and installation revenues on the combined rental fleet of 42.4% due to increased transaction volumes and higher revenues per transaction. Average modular space monthly rental rates increased 11.2% for the year ended December 31, 2019, and average modular space units on rent increased 21,425 units, or 30.5%, due to the impact of an additional 8.5 months of contribution from the ModSpace acquisition. Improved pricing was driven by a combination of our price optimization tools and processes, as well as, by continued growth in our “Ready to Work” solutions and increased VAPS penetration across our customer base, offset partially by the average modular space monthly rental rates on acquired units for ModSpace. The increase in leasing and services revenues was further complemented by an increase of $5.5 million, or 10.3%, in new unit sales as compared to 2018. This increase was primarily driven by increased sales as a result of the ModSpace acquisition. Rental unit sales increased $15.3 million, or 61.2%, as compared to 2018.
Total average units on rent for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 were 108,560 and 85,737, respectively. The increase was due to units acquired as part of the ModSpace acquisition, with modular space average units on rent increased by 21,425 units, or 30.5%, for the year ended December 31, 2019. Modular space average monthly rental rates increased 11.2% for the year ended December 31, 2019. Portable storage average units on rent increased by 1,398 units, or 9.0%, for the year ended December 31, 2019. Average portable storage monthly rental rates increased 0.8% for the year ended December 31, 2019. The average modular space unit utilization rate for the year ended December 31, 2019 was 72.0%, as compared to 71.6% in 2018. The increase in average modular space utilization rate was driven by a reduction in the combined modular space unit fleet size across the combined WillScot and ModSpace fleet in 2019. The average portable storage unit utilization rate during the year ended December 31, 2019 was 65.8%, as compared to 68.9% in 2018. The decrease in average portable storage utilization rate was driven by organic declines in the number of portable storage average units on rent in the Modular - US segment.
Gross Profit: Our gross profit percentage was 38.9% and 38.5% for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively. Our gross profit percentage, excluding the effects of depreciation ("adjusted gross profit percentage"), was 55.3% and 54.7% for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively.
Gross profit increased $123.9 million, or 42.8%, to $413.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 from $289.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2018. The increase in gross profit is a result of a $291.5 million increase in modular leasing and services revenue and increased new unit sales gross profit of $0.2 million, offset by increases of $120.2 million in modular leasing and services costs. Increases in modular leasing and services revenues and costs were primarily as a result of increased revenues due to additional units on rent as a result of recent acquisitions as well as increased margins due to favorable average monthly rental rates on modular space units and increased delivery and installation margins driven primarily by higher pricing per transaction. These increases were partially offset by increased depreciation of $53.3 million as a result of additional rental equipment acquired as part of the ModSpace acquisition, as well as continued capital investment in our existing rental equipment.
Adjusted EBITDA: Adjusted EBITDA increased $141.0 million, or 65.4%, to $356.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 from $215.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2018. The increase was driven by higher revenues and gross profits discussed above excluding depreciation, partially offset by increases in SG&A expense, excluding discrete items, of $33.8 million primarily related to the acquisitions of Acton and ModSpace during the year. Discrete items included in SG&A expense decreased for the year ended December 31, 2019, compared to the year ended December 31, 2018, by $17.7 million as decreases in transaction and integration costs related to the ModSpace and Acton acquisitions and subsequent integrations of $20.1 million and $4.0 million, respectively, were partially offset by increases in stock compensation expense and other acquisition-related activities of $3.3 million and $3.1 million, respectively. The remaining increases of $4.0 million are primarily related to increased professional fees, insurance, computer, travel, office and other expenses related to operating a larger business as a result of our recent acquisitions and our expanded employee base and branch network.
Capex for rental equipment: Capex for rental equipment increased $44.2 million, or 27.5%, to $205.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 from $160.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2018. The increase was driven by increased spend for new units, VAPS, and refurbishments as a result of the increased fleet size due to the Acton, Tyson and ModSpace acquisitions. During the year, our average modular space unit fleet grew over 30% in 2019 as compared to 2018.
Supplemental Pro Forma Information
The following pro forma financial information has been prepared for WillScot Mobile Mini, for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019. These pro forma statements of operations present the historical consolidated statements of operations of WillScot Mobile Mini, giving effect to the following items as if they had occurred on January 1, 2019:
(i) the Merger with Mobile Mini;
(ii) borrowings under the Company’s 2025 Secured Notes and the 2020 ABL Facility;
(iii) extinguishment of the Mobile Mini line of credit and senior notes assumed in the Merger and subsequently repaid;
(iv) repayment of the 2017 ABL Facility and the 2022 Secured Notes repaid contemporaneously with the Merger;
(v) the transaction costs incurred in connection with the Merger; and
(vi) elimination of non-controlling interest in connection with the Sapphire Exchange as contemplated by the Merger.
The adjustments presented on the pro forma financial statements have been identified and presented to provide relevant information necessary for an accurate understanding of the combined company following the transactions and events described above. The pro forma financial information set forth below is based upon available information and assumptions that we believe are reasonable and is for illustrative purposes only. The financial results may have been different if the transactions described above had been completed sooner. You should not rely on the pro forma financial information as being indicative of the historical results that would have been achieved if these transactions and events had been completed as of January 1, 2019. The pro forma combined financial information below should be read in conjunction with the consolidated financial statements and related notes of the Company included elsewhere in this Form 10-K. All pro forma adjustments and their underlying assumptions are described more fully in the notes below.
Accounting Policies
During the preparation of these pro forma combined financial statements, we assessed whether there were any material differences between the Company’s accounting policies and Mobile Mini’s accounting policies. The assessment performed did not identify any material differences and, as such, these pro forma combined financial statements do not adjust for or assume any differences in accounting policies between WillScot and Mobile Mini.
Pro forma Presentation
The following pro forma combined financial information and associated notes are based on the historical financial statements of WillScot and Mobile Mini as described below. In preparing the pro forma combined statements of operations for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, certain historical financial information for Mobile Mini was reclassified to align to the reporting classifications of WillScot.
The pro forma combined statements of operations for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 are based on, derived from, and should be read in conjunction with, WillScot’s historical financial statements. The aforementioned pro forma financial statements are also based on, derived from, and should be read in conjunction with Mobile Mini's historical financial statements.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, 2020 |
| (in thousands) | WillScot Mobile Mini Holdings Corp.
(as restated) | Historical Mobile Mini
(as reclassified) | | Pro Forma Adjustments | | Pro Forma Combined |
| Revenues: | | | | | | | |
| Leasing and services revenue: | | | | | | | |
| Leasing | $ | 1,001,447 | | | $ | 208,374 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 1,209,821 | |
| Delivery and installation | 274,156 | | | 59,999 | | | — | | | 334,155 | |
| Sales revenue: | | | | | | | |
| New units | 53,093 | | | 8,402 | | | — | | | 61,495 | |
| Rental units | 38,949 | | | 7,465 | | | — | | | 46,414 | |
| Total revenues | 1,367,645 | | | 284,240 | | | — | | | 1,651,885 | |
| Costs: | | | | | | | |
| Costs of leasing and services: | | | | | | | |
| Leasing | 227,376 | | | 28,584 | | | — | | | 255,960 | |
| Delivery and installation | 220,102 | | | 42,476 | | | — | | | 262,578 | |
| Costs of sales: | | | | | | | |
| New units | 34,841 | | | 5,457 | | | — | | | 40,298 | |
| Rental units | 24,772 | | | 4,625 | | | — | | | 29,397 | |
| Depreciation of rental equipment (b) | 200,581 | | | 15,360 | | | 2,334 | | | 218,275 | |
| Gross profit | 659,973 | | | 187,738 | | | (2,334) | | | 845,377 | |
| Expenses: | | | | | | | |
| Selling, general and administrative | 360,626 | | | 96,170 | | | — | | | 456,796 | |
| Transaction costs (a) | 64,053 | | | 16,799 | | | (80,852) | | | — | |
| Other depreciation and amortization (c) | 43,249 | | | 19,695 | | | 11,397 | | | 74,341 | |
| | | | | | | |
| Lease impairment expense and other related charges | 4,876 | | | — | | | — | | | 4,876 | |
| Restructuring costs | 6,527 | | | — | | | — | | | 6,527 | |
| Currency losses, net | (355) | | | 39 | | | — | | | (316) | |
| Other income, net | (1,718) | | | 186 | | | — | | | (1,532) | |
| Operating income | 182,715 | | | 54,849 | | | 67,121 | | | 304,685 | |
| Interest expense (d) | 119,886 | | | 16,974 | | | (9,808) | | | 127,052 | |
| Fair value gain on common stock warrant liabilities | (3,461) | | | — | | | — | | | (3,461) | |
| Loss on extinguishment of debt (e) | 42,401 | | | — | | | (19,682) | | | 22,719 | |
| Income before income tax | 23,889 | | | 37,875 | | | 96,611 | | | 158,375 | |
| Income tax (benefit) expense (f) | (51,451) | | | 12,330 | | | 73,670 | | | 34,549 | |
| Net income | 75,340 | | | 25,545 | | | 22,941 | | | 123,826 | |
| Net income attributable to non-controlling interest, net of tax (g) | 1,213 | | | — | | | (1,213) | | | — | |
| Net income attributable to WillScot Mobile Mini | $ | 74,127 | | | $ | 25,545 | | | $ | 24,154 | | | $ | 123,826 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, 2019 |
| (in thousands) | Historical WillScot
(as restated) | | Historical Mobile Mini
(as reclassified) | | Pro Forma Adjustments | | Pro Forma Combined |
| Revenues: | | | | | | | |
| Leasing and services revenue: | | | | | | | |
| Leasing | $ | 744,185 | | | $ | 447,636 | | | $ | — | | | $ | 1,191,821 | |
| Delivery and installation | 220,057 | | | 141,988 | | | — | | | 362,045 | |
| Sales revenue: | | | | | | | |
| New units | 59,085 | | | 16,681 | | | — | | | 75,766 | |
| Rental units | 40,338 | | | 13,713 | | | — | | | 54,051 | |
| Total revenues | 1,063,665 | | | 620,018 | | | — | | | 1,683,683 | |
| Costs: | | | | | | | |
| Costs of leasing and services: | | | | | | | |
| Leasing | 213,151 | | | 67,396 | | | — | | | 280,547 | |
| Delivery and installation | 194,107 | | | 99,634 | | | — | | | 293,741 | |
| Costs of sales: | | | | | | | |
| New units | 42,160 | | | 10,885 | | | — | | | 53,045 | |
| Rental units | 26,255 | | | 9,480 | | | — | | | 35,735 | |
| Depreciation of rental equipment (b) | 174,679 | | | 31,802 | | | 4,667 | | | 211,148 | |
| Gross profit | 413,313 | | | 400,821 | | | (4,667) | | | 809,467 | |
| Expenses: | | | | | | | |
| Selling, general and administrative | 271,004 | | | 208,461 | | | — | | | 479,465 | |
| Other depreciation and amortization (c) | 12,395 | | | 38,781 | | | 22,399 | | | 73,575 | |
| | | | | | | |
| Impairment losses on long-lived assets | 2,848 | | | — | | | — | | | 2,848 | |
| Lease impairment expense and other related charges | 8,674 | | | — | | | — | | | 8,674 | |
| Restructuring costs | 3,755 | | | — | | | — | | | 3,755 | |
| Currency (gains) losses, net | (688) | | | 274 | | | — | | | (414) | |
| Other (income) expense, net | (2,200) | | | 99 | | | — | | | (2,101) | |
| Operating income | 117,525 | | | 153,206 | | | (27,066) | | | 243,665 | |
| Interest expense (d) | 122,504 | | | 41,378 | | | (37,756) | | | 126,126 | |
| Fair value loss on common stock warrant liabilities | 109,622 | | | — | | | — | | | 109,622 | |
| Loss on extinguishment of debt (e) | 8,755 | | | 123 | | | (1,512) | | | 7,366 | |
| (Loss) income before income tax | (123,356) | | | 111,705 | | | 12,202 | | | 551 | |
| Income tax (benefit) expense (f) | (2,191) | | | 27,971 | | | 3,112 | | | 28,892 | |
| Net (loss) income | (121,165) | | | 83,734 | | | 9,090 | | | (28,341) | |
| Net loss attributable to non-controlling interest, net of tax (g) | (421) | | | — | | | 421 | | | — | |
| Net (loss) income attributable to WillScot Mobile Mini | $ | (120,744) | | | $ | 83,734 | | | $ | 8,669 | | | $ | (28,341) | |
Notes to Pro Forma Statements | | | | | |
| (a) | Represents the elimination of discrete transaction costs expensed by WillScot Mobile Mini as part of the Merger. |
| (b) | Represents the adjustment for depreciation of rental fleet relating to the estimated increase in fair value purchase accounting adjustments as a result of the Merger. |
| (c) | Represents the differential in other depreciation and amortization expense related to the estimated fair value purchase accounting adjustments as a result of the Merger. |
| | | | | |
| (d) | Reflects the incremental interest expense related to our debt structure after the Merger as though the following had occurred on January 1, 2019 (i) borrowings under the 2020 ABL Facility, (ii) borrowings under the 2025 Secured Notes, (iii) repayment of the 2017 ABL Facility, (iv) repayment of the 2022 Secured Notes and repayment of the Mobile Mini credit facility and secured notes (the "Mobile Mini debt").
|
| (e) | Represents the elimination of the loss on extinguishment of debt in connection with the repayment of the 2022 Secured Notes and the 2017 ABL Facility in 2020 and partial redemption of the 2022 Secured Notes in 2019. |
| (f) | Reflects the adjustment to recognize the income tax impacts of the unaudited pro forma adjustments for which a tax expense is recognized using a US federal and state statutory tax rate of 25.5%. This rate may vary from the effective tax rates of the historical and combined businesses. In addition, the year ended December 31, 2020 included an adjustment of $56.8 million to eliminate the reversal of valuation allowance as a result of reassessment of the realizability of deferred tax assets as a result of the Merger. |
| (g) | Reflects the pro forma adjustment for the extinguishment of non-controlling interest as a result of the Sapphire Exchange on June 30, 2020. |
The pro forma adjustment to interest expense consists of the following: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| (in thousands) | 2020 | | 2019 |
| ABL Facility interest | $ | (2,561) | | | $ | (16,422) | |
| 2022 Secured Notes interest | (10,631) | | | (23,507) | |
| 2025 Secured Notes interest | 18,247 | | | 39,813 | |
| Mobile Mini debt interest | (15,921) | | | (39,672) | |
| Deferred financing fee amortization | 1,058 | | | 2,032 | |
| Net pro forma adjustment | $ | (9,808) | | | $ | (37,756) | |
Reconciliation of Pro Forma Adjusted EBITDA
The following unaudited table provides a reconciliation of Net income to pro forma unaudited adjusted EBITDA:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| (in thousands) | 2020 | | 2019 |
| (as restated) | | (as restated) |
| Net income (loss) | $ | 123,826 | | | $ | (28,341) | |
| Loss on extinguishment of debt | 22,719 | | | 7,366 | |
| Income tax expense | 34,549 | | | 28,892 | |
| Interest expense | 127,052 | | | 126,126 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | 292,616 | | | 284,723 | |
| Fair value (gain) loss on common stock warrant liabilities | (3,461) | | | 109,622 | |
| Currency gains, net | (316) | | | (414) | |
| Goodwill and other impairment charges | — | | | 2,848 | |
| Restructuring costs, lease impairment expense, other related charges | 11,403 | | | 12,429 | |
| Transaction fees | — | | | 3,129 | |
| Integration costs | 18,338 | | | 26,607 | |
| Stock compensation expense | 15,280 | | | 21,807 | |
| Other | 4,459 | | | 4,647 | |
| Adjusted EBITDA | $ | 646,465 | | | $ | 599,441 | |
Summary Business Segment Supplemental Pro Forma Financial Information
As a result of the Merger and the significant related financing transactions, we believe presenting supplemental pro forma financial information is beneficial to the readers of the financial statements. The following table sets forth key metrics used by management to run the business on a pro forma basis as if the Merger and related financing transactions had occurred on January 1, 2019. Refer to the Supplemental Pro Forma Financial Information section below for the full reconciliation of the statements of operations.
Following the Merger, we modified our management structure and expanded from two reporting segments to four segments: NA Modular, NA Storage, UK Storage and Tank and Pump. Prior to the Merger, WillScot had two reportable segments, US Modular and Other North America Modular. These two segments were combined to create the new NA Modular segment, which represents the legacy WillScot operations. The other new segments, NA Storage, UK Storage, and Tank and Pump align to the legacy operations and segments reported by Mobile Mini. The new reporting segments are aligned with how we operate and analyze our business results.
Pro Forma Comparison of Years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Pro Forma Combined Year Ended December 30, | | 2020 vs. 2019 |
| (in thousands) | 2020 | | 2019 | | $ Change | | % Change |
| (as restated) | | (as restated) | | | | |
| Revenue | $ | 1,651,885 | | | $ | 1,683,683 | | | $ | (31,798) | | | (1.9) | % |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | $ | 456,796 | | | $ | 479,465 | | | $ | (22,669) | | | (5.0) | % |
| Net income | $ | 123,826 | | | $ | (28,341) | | | $ | 152,167 | | | 122.9 | % |
| Adjusted EBITDA | $ | 646,465 | | | $ | 599,441 | | | $ | 47,024 | | | 7.3 | % |
| | | | | | | |
| Other Financial Data: | | | | | | | |
| Adjusted EBITDA - NA Modular | $ | 394,805 | | | $ | 356,548 | | | $ | 38,257 | | | 9.7 | % |
| Adjusted EBITDA - NA Storage | 184,601 | | 169,697 | | | 14,904 | | | 8.1 | % |
| Adjusted EBITDA - UK Storage | 31,080 | | 25,758 | | | 5,322 | | | 17.1 | % |
| Adjusted EBITDA - Tank and Pump | 35,979 | | 47,438 | | | (11,459) | | | (31.8) | % |
Combined Adjusted EBITDA | $ | 646,465 | | | $ | 599,441 | | | $ | 47,024 | | | 7.3 | % |
NA Modular - Quarterly Results
Pro Forma Quarterly Results for the year ended December 31, 2020: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
(in thousands, except for units on rent and
monthly rental rate) | Q1 | | Q2 | | Q3 | | Q4 | | Total |
| Revenue | $ | 255,821 | | | $ | 256,862 | | | $ | 267,867 | | | $ | 270,612 | | | $ | 1,051,162 | |
| Gross profit | $ | 106,190 | | | $ | 109,964 | | | $ | 112,079 | | | $ | 123,409 | | | $ | 451,642 | |
| Adjusted EBITDA | $ | 89,544 | | | $ | 97,520 | | | $ | 100,281 | | | $ | 107,460 | | | $ | 394,805 | |
| Capex for rental equipment | $ | 39,648 | | | $ | 40,034 | | | $ | 34,249 | | | $ | 39,396 | | | $ | 153,327 | |
| Average modular space units on rent | 87,988 | | | 87,096 | | | 86,400 | | | 86,011 | | | 86,874 | |
| Average modular space utilization rate | 69.2 | % | | 68.5 | % | | 68.3 | % | | 68.2 | % | | 68.9 | % |
| Average modular space monthly rental rate | $ | 653 | | | $ | 669 | | | $ | 693 | | | $ | 724 | | | $ | 685 | |
| Average portable storage units on rent | 16,346 | | | 15,869 | | | 15,473 | | | 15,603 | | | 15,823 | |
| Average portable storage utilization rate | 64.1 | % | | 62.5 | % | | 61.3 | % | | 62.6 | % | | 63.5 | % |
| Average portable storage monthly rental rate | $ | 119 | | | $ | 120 | | | $ | 124 | | | $ | 124 | | | $ | 122 | |
Pro Forma Quarterly Results for the year ended December 31, 2019: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
(in thousands, except for units on rent and
monthly rental rate) | Q1 | | Q2 | | Q3 | | Q4 | | Total |
| Revenue | $ | 253,685 | | | $ | 263,713 | | | $ | 268,222 | | | $ | 278,045 | | | $ | 1,063,665 | |
| Gross profit | $ | 103,331 | | | $ | 101,484 | | | $ | 99,308 | | | $ | 109,190 | | | $ | 413,313 | |
| Adjusted EBITDA | $ | 83,354 | | | $ | 87,554 | | | $ | 87,424 | | | $ | 98,216 | | | $ | 356,548 | |
| Capex for rental equipment | $ | 51,873 | | | $ | 61,215 | | | $ | 47,789 | | | $ | 44,229 | | | $ | 205,106 | |
| Average modular space units on rent | 93,309 | | | 92,300 | | | 91,233 | | | 90,013 | | | 91,682 | |
| Average modular space utilization rate | 72.4 | % | | 71.9 | % | | 71.2 | % | | 70.7 | % | | 72.0 | % |
| Average modular space monthly rental rate | $ | 575 | | | $ | 611 | | | $ | 630 | | | $ | 641 | | | $ | 614 | |
| Average portable storage units on rent | 17,419 | | | 16,544 | | | 16,416 | | | 16,944 | | | 16,878 | |
| Average portable storage utilization rate | 66.1 | % | | 63.3 | % | | 63.0 | % | | 66.1 | % | | 65.8 | % |
| Average portable storage monthly rental rate | $ | 119 | | | $ | 121 | | | $ | 123 | | | $ | 118 | | | $ | 120 | |
The NA Modular segment represents the activities of WillScot prior to the Merger. As a result, there are no differences between pro forma results and actual results on a reported basis. Please see comparison of results for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 within "Business Segment Results" above.
NA Storage - Quarterly Results
Pro Forma Quarterly Results for the year ended December 31, 2020: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
(in thousands, except for units on rent and
monthly rental rate) | Q1 | | Q2 | | Q3 | | Q4 | | Total |
| Revenue | $ | 103,495 | | | $ | 92,826 | | | $ | 104,493 | | | $ | 117,336 | | | $ | 418,150 | |
| Gross profit | $ | 71,400 | | | $ | 66,639 | | | $ | 73,384 | | | $ | 83,401 | | | $ | 294,824 | |
| Adjusted EBITDA | $ | 43,994 | | | $ | 40,770 | | | $ | 46,465 | | | $ | 53,372 | | | $ | 184,601 | |
| Capex for rental equipment | $ | 5,200 | | | $ | 7,272 | | | $ | 7,234 | | | $ | 7,735 | | | $ | 27,441 | |
| Average modular space units on rent | 15,509 | | | 15,757 | | | 16,383 | | | 16,948 | | | 16,152 | |
| Average modular space utilization rate | 77.8 | % | | 78.6 | % | | 80.4 | % | | 80.9 | % | | 79.4 | % |
| Average modular space monthly rental rate | $ | 497 | | | $ | 463 | | | $ | 505 | | | $ | 547 | | | $ | 504 | |
| Average portable storage units on rent | 105,441 | | | 101,463 | | | 105,221 | | | 120,439 | | | 108,167 | |
| Average portable storage utilization rate | 73.1 | % | | 70.6 | % | | 73.4 | % | | 83.0 | % | | 75.1 | % |
| Average portable storage monthly rental rate | $ | 146 | | | $ | 143 | | | $ | 145 | | | $ | 150 | | | $ | 146 | |
Pro Forma Quarterly Results for the year ended December 31, 2019: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
(in thousands, except for units on rent and
monthly rental rate) | Q1 | | Q2 | | Q3 | | Q4 | | Total |
| Revenue | $ | 99,565 | | | $ | 98,045 | | | $ | 104,641 | | | $ | 113,262 | | | $ | 415,513 | |
| Gross profit | $ | 68,357 | | | $ | 66,523 | | | $ | 73,302 | | | $ | 80,740 | | | $ | 288,922 | |
| Adjusted EBITDA | $ | 37,957 | | | $ | 37,474 | | | $ | 43,084 | | | $ | 51,182 | | | $ | 169,697 | |
| Capex for rental equipment | $ | 11,841 | | | $ | 16,166 | | | $ | 11,107 | | | $ | 7,200 | | | $ | 46,314 | |
| Average modular space units on rent | 15,974 | | | 15,522 | | | 15,835 | | | 16,192 | | | 15,881 | |
| Average modular space utilization rate | 80.5 | % | | 80.5 | % | | 80.9 | % | | 80.4 | % | | 80.6 | % |
| Average modular space monthly rental rate | $ | 413 | | | $ | 449 | | | $ | 470 | | | $ | 502 | | | $ | 458 | |
| Average portable storage units on rent | 107,658 | | | 105,770 | | | 109,723 | | | 119,642 | | | 110,728 | |
| Average portable storage utilization rate | 76.1 | % | | 74.5 | % | | 76.8 | % | | 82.5 | % | | 77.5 | % |
| Average portable storage monthly rental rate | $ | 144 | | | $ | 143 | | | $ | 145 | | | $ | 151 | | | $ | 146 | |
Pro Forma Comparison of Years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019
NA Storage
Revenue: Total revenue increased $2.7 million, or 0.6%, to $418.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2020 from $415.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2019. Leasing revenues for the year ended December 31, 2020 increased year-over-year by $4.8 million, or 1.6%, resulting from the combination of increased revenues in the first quarter, decreased year-over-year revenue in the second quarter due to the impact of COVID-19, flat year-over-year revenue in the third quarter and increased revenues in the fourth quarter, when compared to the prior-year periods. Modular space average units on rent increased 1.7% compared to 2019 and average modular space monthly rental rates increased 10.0% year-over-year but were offset by a 2.3% decrease in average portable storage units on rent. Delivery and installation revenues decreased $7.3 million year-over year. Beginning late in the first quarter, the COVID-19 pandemic resulted in fewer new units placed on rent as well as a decrease in returned units leading to a year-over-year decrease in our delivery and installation revenues. Sales revenues increased $5.1 million compared to the prior year.
Gross Profit: Gross profit increased $5.9 million, or 2.0%, for the year ended December 31, 2020 to $294.8 million from $288.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2019. This gross profit increase was driven primarily by a $6.8 million, or 2.5%, year-over-year increase within leasing and a $1.3 million increase related to sales, offset by decreased delivery and installation gross profit of $1.5 million. Within leasing activity, reduced expenses of $2.0 million from strong cost management in response to the COVID-19 pandemic combined with the $4.8 million revenue increase resulted in a $6.8 million year-over-year increase in leasing gross profit. Reduced expenses in this area include lower maintenance costs of $2.0 million and reductions in personnel costs. For delivery and installation, gross profit decreased $1.5 million as the effect of reduced revenue was largely mitigated by proactive cost management resulting in a $3.0 million reduction in outside hauling expense combined with reduced salaries for drivers and lower fuel costs. Sales gross profit increased $1.3 million on larger sales volume.
Adjusted EBITDA: Adjusted EBITDA increased $14.9 million, or 8.8%, to $184.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2020 from $169.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 and the margin expanded to 44.1% from 40.8%. The increase in Adjusted EBITDA was driven by a reduction in SG&A expense and the higher gross profit discussed above. Excluding integration and stock-based compensation, SG&A expense decreased due to reduced costs for personnel of approximately $8.0 million and $2.3 million due to curtailed travel, partially offset by increased occupancy and other costs.
Capex for Rental Equipment: Purchases of rental equipment and refurbishments of $27.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2020 were $18.9 million lower than for the year ended December 31, 2019. Rental fleet expenditures were reduced significantly during the year ended December 31, 2020 in response to COVID-19, especially after the first quarter of 2020, and were primarily to meet demand for specific products, largely ground level offices.
UK Storage - Quarterly Results
Pro Forma Quarterly Results for the year ended December 31, 2020: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
(in thousands, except for units on rent and
monthly rental rate) | Q1 | | Q2 | | Q3 | | Q4 | | Total |
| Revenue | $ | 20,197 | | | $ | 17,154 | | | $ | 21,653 | | | $ | 24,708 | | | $ | 83,712 | |
| Gross profit | $ | 11,372 | | | $ | 10,991 | | | $ | 12,671 | | | $ | 14,971 | | | $ | 50,005 | |
| Adjusted EBITDA | $ | 6,405 | | | $ | 6,853 | | | $ | 8,306 | | | $ | 9,516 | | | $ | 31,080 | |
| Capex for rental equipment | $ | 337 | | | $ | 522 | | | $ | 677 | | | $ | 1,016 | | | $ | 2,552 | |
| Average modular space units on rent | 7,850 | | | 7,912 | | | 8,444 | | | 8,834 | | | 8,262 | |
| Average modular space utilization rate | 74.2 | % | | 74.6 | % | | 79.1 | % | | 82.4 | % | | 77.6 | % |
| Average modular space monthly rental rate | $ | 326 | | | $ | 313 | | | $ | 356 | | | $ | 377 | | | $ | 344 | |
| Average portable storage units on rent | 23,328 | | | 22,870 | | | 23,146 | | | 24,496 | | | 23,462 | |
| Average portable storage utilization rate | 83.7 | % | | 82.2 | % | | 83.2 | % | | 88.6 | % | | 84.4 | % |
| Average portable storage monthly rental rate | $ | 73 | | | $ | 70 | | | $ | 75 | | | $ | 78 | | | $ | 74 | |
Pro Forma Quarterly Results for the year ended December 31, 2019: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
(in thousands, except for units on rent and
monthly rental rate) | Q1 | | Q2 | | Q3 | | Q4 | | Total |
| Revenue | $ | 20,959 | | | $ | 20,920 | | | $ | 20,499 | | | $ | 20,179 | | | $ | 82,557 | |
| Gross profit | $ | 11,129 | | | $ | 11,367 | | | $ | 11,106 | | | $ | 11,329 | | | $ | 44,931 | |
| Adjusted EBITDA | $ | 6,070 | | | $ | 6,396 | | | $ | 6,704 | | | $ | 6,588 | | | $ | 25,758 | |
| Capex for rental equipment | $ | 921 | | | $ | 1,190 | | | $ | 1,546 | | | $ | 561 | | | $ | 4,218 | |
| Average modular space units on rent | 8,440 | | | 8,460 | | | 8,360 | | | 8,008 | | | 8,316 | |
| Average modular space utilization rate | 79.0 | % | | 79.0 | % | | 78.0 | % | | 75.4 | % | | 77.8 | % |
| Average modular space monthly rental rate | $ | 319 | | | $ | 327 | | | $ | 320 | | | $ | 336 | | | $ | 326 | |
| Average portable storage units on rent | 23,910 | | | 23,594 | | | 23,927 | | | 24,910 | | | 24,087 | |
| Average portable storage utilization rate | 85.9 | % | | 85.0 | % | | 85.9 | % | | 88.9 | % | | 86.4 | % |
| Average portable storage monthly rental rate | $ | 70 | | | $ | 70 | | | $ | 69 | | | $ | 72 | | | $ | 70 | |
Pro Forma Comparison of Years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019
UK Storage
Revenue: Total revenue increased $1.1 million, or 1.3%, to $83.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2020 from $82.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2019. Currency fluctuations were immaterial for the current period. Leasing revenues increased 4.0% and delivery and installation revenues decreased 9.8%. Within leasing activity, average monthly rental rates for modular space units and portable storage units increased 5.5% and 5.7% year-over-year, respectively. These increases were partially offset by a 0.6% decline in modular space average units on rent and a 2.6% decrease in average portable storage units on rent. The decrease in delivery and installation revenues is due to an overall decrease in newly placed and returned units primarily resulting from a slower economy during the current-year period as a result of COVID-19. Sales revenues increased $0.6 million compared to the prior year.
Gross Profit: Gross profit increased $5.1 million, or 11.4%, to $50.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2020 from $44.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2019. Proactive cost management fully mitigated the lower delivery and installation revenues and included reduced delivery and installation cost of $2.3 million. Gross profit on leasing increased 6.9% year-over-year. Gross profit on sales increased $1.3 million. Depreciation on rental equipment also decreased by $0.2 million.
Adjusted EBITDA: Adjusted EBITDA increased $5.3 million, or 20.5%, to $31.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2020 from $25.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 and the margin expanded to 37.1% from 31.2%. The increase resulted primarily from the favorable gross profit discussed above and decreased SG&A expense related largely to lower travel costs.
Capex for Rental Equipment: Purchases of rental equipment and refurbishments of $2.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2020 were $1.6 million lower than for the year ended December 31, 2019. Rental fleet expenditures were reduced in 2020 in response to COVID-19.
Tank and Pump - Quarterly Results
Pro Forma Quarterly Results for the year ended December 31, 2020: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
(in thousands, except for units on rent and
monthly rental rate) | Q1 | | Q2 | | Q3 | | Q4 | | Total |
| Revenue | $ | 26,884 | | | $ | 23,684 | | | $ | 23,302 | | | $ | 24,991 | | | $ | 98,861 | |
| Gross profit | $ | 13,279 | | | $ | 11,723 | | | $ | 11,430 | | | $ | 12,474 | | | $ | 48,906 | |
| Adjusted EBITDA | $ | 9,477 | | | $ | 8,659 | | | $ | 8,507 | | | $ | 9,336 | | | $ | 35,979 | |
| Capex for rental equipment | $ | 4,514 | | | $ | 941 | | | $ | 431 | | | $ | 1,963 | | | $ | 7,849 | |
| Average tank and pump solutions rental fleet utilization based on original equipment cost | 66.4 | % | | 60.5 | % | | 58.2 | % | | 65.2 | % | | 62.6 | % |
Pro Forma Quarterly Results for the year ended December 31, 2019: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
(in thousands, except for units on rent and
monthly rental rate) | Q1 | | Q2 | | Q3 | | Q4 | | Total |
| Revenue | $ | 30,934 | | | $ | 32,961 | | | $ | 30,185 | | | $ | 27,867 | | | $ | 121,947 | |
| Gross profit | $ | 16,210 | | | $ | 16,643 | | | $ | 15,573 | | | $ | 13,875 | | | $ | 62,301 | |
| Adjusted EBITDA | $ | 12,203 | | | $ | 13,037 | | | $ | 11,885 | | | $ | 10,313 | | | $ | 47,438 | |
| Capex for rental equipment | $ | 10,254 | | | $ | 6,025 | | | $ | 2,197 | | | $ | 1,843 | | | $ | 20,319 | |
| Average tank and pump solutions rental fleet utilization based on original equipment cost | 74.1 | % | | 73.5 | % | | 68.3 | % | | 68.6 | % | | 71.1 | % |
Pro Forma Comparison of Years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019
Tank and Pump
Revenue: Total revenue decreased $23.0 million, or 18.9%, to $98.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2020 from $121.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2019. Industrial softening, which began in the second half of 2019, was exacerbated in 2020 by an oversupply of oil leading to lower oil prices. Further, the effects of COVID-19 have resulted in decreased demand for oil. The business environment during 2020 resulted in reduced demand for our products as utilization based on OEC reduced from 71.1% for the year ended December 31, 2019 to 62.6% for year ended December 31, 2020 and experienced a decrease in average rental rates compared to the prior-year period. However, utilization levels stabilized sequentially during the third quarter of 2020 and increased 700 bps to 65.2% in the fourth quarter as compared to the third quarter. Year-over-year leasing revenue decreased $15.2 million, or 18.7%, while delivery and installation revenue decreased $6.8 million, or 19.3%. Sales revenues decreased $1.0 million compared to the prior-year period.
Gross Profit: Gross profit decreased $13.4 million, or 21.5%, for the year ended December 31, 2020 to $48.9 million from $62.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2019. Gross profit for leasing activity decreased $12.2 million driven by the decreased revenue as discussed above offset by reduced costs of $3.1 million, including decreased repairs and maintenance of $1.2 million and lower re-rent expense due to the lower activity. Gross profit for delivery and installation activity decreased $2.1 million reflecting the lower revenues offset by a $4.7 million decrease in expense, including $1.9 million less expense for outside hauling and a reduction in employee costs for delivery drivers. Depreciation of rental equipment decreased $1.4 million.
Adjusted EBITDA: Adjusted EBITDA decreased $11.4 million, or 24.1%, to $36.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2020 from $47.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 and the margin contracted to 36.4% from 38.9%. The decrease in Adjusted EBITDA was driven by the lower gross profit discussed above, offset by a $3.4 million reduction SG&A expense including $2.0 million in decreased employee costs.
Capex for rental equipment: Purchases of rental equipment and refurbishments were reduced significantly during 2020 due to the unfavorable environment for this segment. For the year ended December 31, 2020, expenditures of $7.8 million were $12.5 million lower than for the year ended December 31, 2019.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Overview
WillScot Mobile Mini is a holding company that derives all of its operating cash flow from its operating subsidiaries. Our principal sources of liquidity include cash generated by operating activities from our subsidiaries, borrowings under the 2020 ABL Facility, and sales of equity and debt securities. We believe that our liquidity sources and operating cash flows are sufficient to address our operating, debt service and capital requirements over the next twelve months.
We have been consistently engaged in the debt and equity capital markets both opportunistically and as necessary to support the growth of our business, desired leverage levels, and other capital allocation priorities. Subsequent to the Merger, we believe we have ample liquidity in the 2020 ABL Facility to support both organic operations and other capital allocation priorities as they arise.
We continue to review available acquisition opportunities with the awareness that any such acquisition may require us to incur additional debt to finance the acquisition and/or to issue shares of our Common Stock or other equity securities as acquisition consideration or as part of an overall financing plan. In addition, we will continue to evaluate options to improve our liquidity, such as the issuance of additional unsecured and secured debt, equity securities and/or equity-linked securities. There can be no assurance as to the timing of any such issuance. If we obtain additional capital by issuing equity, the interests of our existing stockholders will be diluted. If we incur additional indebtedness, that indebtedness may contain significant financial and other covenants that may significantly restrict our operations. We cannot assure you that we could obtain refinancing or additional financing on favorable terms or at all. From time to time, we may also seek to streamline our capital structure and improve our financial position through refinancing or restructuring our existing debt or retiring certain of our securities for cash or other consideration.
In anticipation of the Merger, on June 15, 2020, we completed a private offering of $650.0 million in aggregate principal amount of the 2025 Secured Notes. The proceeds from the 2025 Secured Notes of $650.0 million were used to consummate the Merger and the related financing transactions, which included repayment of the 2022 Secured Notes, repayment of the Mobile Mini senior notes, and payment of certain fees and expenses related to the Merger and the related financing transactions. The 2025 Secured Notes mature on June 15, 2025 and bear interest at a rate of 6.125% per annum. Interest is payable semi-annually on June 15 and December 15 of each year, beginning December 15, 2020.
On July 1, 2020, in connection with the completion of the Merger, Holdings, WSII, and certain of its subsidiaries, entered into the 2020 ABL Facility, which provides for revolving credit facilities in the aggregate principal amount of up to $2.4 billion, consisting of: (i) a senior secured asset-based US dollar revolving credit facility in the aggregate principal amount of $2.0 billion (the “US Facility”), available to WSII and certain of its subsidiaries (collectively, the “US Borrowers”), and (ii) a $400 million senior secured asset-based multicurrency revolving credit facility (the "Multicurrency Facility") together with the US Facility (collectively, the “2020 ABL Facility”), available to be drawn in US Dollars, Canadian Dollars, British Pounds Sterling or Euros by the US Borrowers, and certain of WSII’s wholly-owned subsidiaries organized in Canada and in the UK. Borrowing availability under the 2020 ABL Facility is equal to the lesser of $2.4 billion and the applicable borrowing bases. The borrowing bases are a function of, among other things, the value of the assets in the relevant collateral pool of which our rental equipment represents the largest component. On July 1, 2020, in connection with the completion of the Merger, approximately $1.47 billion of proceeds from the 2020 ABL Facility were used to repay the 2017 ABL Facility, repay Mobile Mini's asset-backed lending facility, and pay fees and expenses related to the Merger and the related financing transactions. On August 11, 2020, we redeemed $49.0 million of our 2023 Secured Notes at a redemption price of 103.0% plus accrued and unpaid interest using proceeds from the 2020 ABL Facility. At December 31, 2020, we had $1.1 billion of available borrowing capacity under the 2020 ABL Facility.
On August 25, 2020, we completed a private offering of $500.0 million in aggregate principal amount of the 2028 Secured Notes. Proceeds from the 2028 Secured notes were used to repay the $441.0 million remaining outstanding principal of the 2023 Secured Notes at a redemption price of 103.438% plus accrued and unpaid interest. The 2028 Secured Notes mature on August 15, 2028 and bear interest at a rate of 4.625% per annum. Interest is payable semi-annually on August 15 and February 15 of each year, beginning February 25, 2021.
COVID-19 Impact on Liquidity
Although there is uncertainty related to the continued impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on future results, we believe our predictable lease revenue streams underpinned by long lease durations, combined with steps we have taken to reduce cost and capital spending, increased our internally generated free cash flow in 2020, and we expect our free cash flow generation to continue to increase. Further, the approximately $1.1 billion of availability under our 2020 ABL Facility as of December 31, 2020, provides additional liquidity in excess of our free cash flow generation. We continue to manage all aspects of our business including, but not limited to, monitoring the financial health of our customers, suppliers and other third-party relationships, actively managing our cost structure, reducing or delaying capital spending and developing new opportunities for growth. We believe that the actions we have taken in recent years to increase our scale and competitive position and strengthen our balance sheet have positioned us well to manage through periods of economic disruption.
Cash Flows
Significant factors driving our liquidity include cash flows generated from operating activities and capex. Our ability to fund our capital needs will be affected by our ongoing ability to generate cash from operations and access to capital markets.
The following summarizes our change in cash and cash equivalents for the periods presented:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| (in thousands) | 2020 | | 2019 | | 2018 |
| Net cash from operating activities | $ | 304,812 | | | $ | 172,566 | | | $ | 37,149 | |
| Net cash from investing activities | (125,360) | | | (152,582) | | | (1,217,202) | |
| Net cash from financing activities | (158,958) | | | (26,063) | | | 1,180,037 | |
| Effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents | 1,398 | | | 166 | | | (211) | |
| Net change in cash and cash equivalents | $ | 21,892 | | | $ | (5,913) | | | $ | (227) | |
Comparison of the Years Ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 and December 31, 2019 and 2018
Cash Flows from operating activities
Cash provided by operating activities for the year ended December 31, 2020 was $304.8 million as compared to $172.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2019, an increase of $132.2 million. The increase in cash provided by operating activities was driven by an increase of $136.7 million of net income, adjusted for non-cash items, primarily due to the impact of the Merger on revenues and gross profit. This was partially offset by a decrease of $4.4 million in the net movements of the operating assets and liabilities which was primarily attributable to a decrease in accounts payable and other accrued liabilities of $20.9 million, an increase in prepaid and other assets of $12.7 million, and a decrease in accrued interest of $7.7 million, compared to the same period in 2019. This was partially offset by a decrease in cash used from accounts receivable of $36.9 million compared to the same period in 2019.
Cash provided by operating activities for the year ended December 31, 2019 was $172.6 million as compared to $37.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2018, an increase of $135.5 million. This increase was primarily due to an increase in net income of $159.1, million, adjusted for non-cash items, in 2019 as compared to 2018, as a result of the impact of the ModSpace acquisition on operations, which is reflected in our results for all of 2019, but is only included for four and a half months in 2018. This increase in net income, adjusted for non-cash items, was partially offset by a decrease of $23.7 million in the net movements of the operating assets and liabilities. The decrease in operating assets and liabilities was attributable to an increase in trade receivables and an increase in cash interest payments during the year ended December 31, 2019, partially offset by an increase in accounts payable and accrued liabilities.
Cash flows from investing activities
Cash used in investing activities for the year ended December 31, 2020 was $125.4 million as compared to $152.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2019, a decrease of $27.2 million. The decrease in cash used in investing activities was driven by a $32.7 million decrease in cash used for purchase of rental equipment and refurbishments. Cash used for purchase of rental equipment and refurbishments decreased compared to 2019 as fleet was less constrained due to reduced utilization and reduced demand for new project deliveries as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic and the current period impact of prior year spend. Additionally, $17.2 million of cash was acquired as part of the Merger. This increase was partially offset by an $11.4 million decrease in proceeds from sale of property, plant and equipment, an increase of $8.2 million on purchases of property, plant and equipment and a $3.2 million decrease in proceeds from the sale of rental equipment. Proceeds from sale of rental equipment decreased compared to the prior year due to lower sales demand.
Cash used in investing activities for the year ended December 31, 2019 was $152.6 million as compared to $1,217.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2018, a decrease of $1,064.6 million. The decrease in cash used in investing activities was driven by a $1,083.1 million decrease in cash used for business acquisitions, an $11.3 million increase in proceeds from the sale of rental equipment, and an $18.1 million increase in proceeds from the sale of property, plant, and equipment. The decrease in cash used in business acquisitions was due to the acquisition of ModSpace during the year ended December 31, 2018, with no business acquisitions during the year ended December 31, 2019. Proceeds from the sale of rental equipment increased due to increased sales volume as a result of the acquisition of ModSpace. Proceeds from the sale of property, plant and equipment increased primarily as a result of the sale of non-operating branch locations during the year ended December 31, 2019, as part of the ongoing integration and consolidation process following the acquisition of ModSpace. The overall decrease in cash used in investing activities for the year ended December 31, 2019 was partially offset by an increase in capex of $44.2 million in 2019, which was primarily driven by increased refurbishments of existing fleet, following our recent acquisitions, and purchases of VAPS to drive revenue growth.
Cash flows from financing activities
Cash used in financing activities for the year ended December 31, 2020 was $159.0 million as compared to $26.1 million cash provided by financing activities for the year ended December 31, 2019, an increase of $132.9 million cash used. The increase in cash used in financing activities was driven by an increase of $62.9 million for payment of financing costs, an increase of $27.4 million for payment of debt extinguishment costs, payment of $21.8 million for the repurchase and cancellation of warrants, payment of $4.2 million for Common Stock issuance costs, an increase of $12.8 million of taxes paid on employee stock awards, and an increase of $8.4 million of principal payments on finance lease obligations. Additionally, there was a net increase of $5.1 million of payments on borrowings, comprised of an increase in repayments of borrowings of $2,239.7 million that was partially offset by an increase receipts from borrowings of $2,234.6 million. The cash used in financing activities was partially offset by an increase in receipts from the issuance of Common Stock from the exercise of options and warrants of $9.7 million.
Cash used in financing activities for the year ended December 31, 2019 was $26.1 million as compared to $1,180.0 million cash provided by financing activities for the year ended December 31, 2018, an increase of $1,206.1 million cash used. The increase in cash used by financing activities is primarily due to a reduction in borrowings, net of repayments of $1,086.0 million, a decrease in receipts from the issuance of Common Stock of $146.3 million primarily related to the financing of the ModSpace acquisition and an increase in debt extinguishment costs of $7.1 million. In connection with the ModSpace acquisition, in 2018 we borrowed an aggregate of $1,097.1 million related to the issuance of the 2023 Secured Notes and the Unsecured Notes, and through the up-sized 2017 ABL Facility. The 2018 stock issuance was used to finance the acquisition of ModSpace. We paid redemption premium costs of $7.1 million in 2019 as a result of the redemption of the Unsecured Notes and the $30.0 million prepayment on the 2022 Secured Notes. The decrease in cash provided by financing activities was
partially offset by a decrease in financing fees payments of $34.0 million due to the significant fees incurred in 2018 as part of the financing activities noted above in connected with the acquisition of ModSpace.
Contractual Obligations
The following table presents information relating to our contractual obligations and commercial commitments as of December 31, 2020: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands) | Total | | Less than 1 year | | Between 1 to 3 years | | Between 3 to 5 years | | More than 5 years |
| Long-term indebtedness, including current portion and interest (a)(b) | $ | 2,915,812 | | | $ | 87,613 | | | $ | 262,839 | | | $ | 1,999,918 | | | $ | 565,442 | |
| Payroll tax withholding (c) | 10,350 | | | 5,175 | | | 5,175 | | | — | | — | | — | |
| Operating lease liabilities | 279,677 | | | 60,120 | | | 92,258 | | | 59,878 | | | 67,421 | |
| Total | $ | 3,205,839 | | | $ | 152,908 | | | $ | 360,272 | | | $ | 2,059,796 | | | $ | 632,863 | |
| | | | | |
| (a) | Long-term indebtedness includes borrowings and interest under the 2020 ABL Facility, the 2025 Secured Notes, the 2028 Secured Notes, and finance leases. |
| (b) | Includes the obligations under our interest rate swap agreement that effectively convert $400 million in aggregate notional amount of variable-rate debt under the Company’s 2020 ABL Facility into fixed-rate debt. The future obligations under the interest rate swaps were calculated using the 1-month LIBOR rate as of December 31, 2020. |
| (c) | Amounts relate to the delay in payment of employer payroll taxes in accordance with the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act of 2020 (the ‘‘CARES Act’’). |
At December 31, 2020, in addition to the above contractual obligations, we had $14.5 million of potential long-term tax liabilities, including interest and penalties, related to uncertain tax positions. Because of the high degree of uncertainty regarding the future cash flows associated with these potential long-term tax liabilities, we are unable to estimate the years in which settlement will occur with the respective taxing authorities.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
We have no off-balance sheet arrangements that have or are reasonably likely to have a current or future material effect on our financial condition, changes in financial condition, revenues or expenses, results of operations, liquidity, capex or capital resources.
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
Our discussion and analysis of our financial condition, results of operations, liquidity and capital resources is based on our consolidated financial statements, which have been prepared in accordance with GAAP. GAAP requires that we make estimates and judgments that affect the reported amount of assets, liabilities, revenue, expenses and the related disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities. We base these estimates on historical experience and on various other assumptions that we consider reasonable under the circumstances and reevaluate our estimates and judgments as appropriate. The actual results experienced by us may differ materially and adversely from our estimates. We believe that the following critical accounting policies involve a higher degree of judgment or complexity in the preparation of financial statements:
Revenue Recognition
A performance obligation is a promise in a contract to transfer a distinct good or service to the customer. A contract’s transaction price is allocated to each distinct performance obligation and recognized as revenue when, or as, the performance obligation is satisfied.
Leasing and Services Revenue
The majority of revenue is generated by rental income subject to the guidance of ASC 840, Leases ("ASC 840") in 2018 and ASC 842 in 2019 and 2020. The remaining revenue is generated by performance obligations in contracts with customers for services or sale of units subject to the guidance in ASC 605, Revenue ("ASC 605"), in 2018 and ASU 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606) ("ASC 606") in 2019 and 2020.
Leasing Revenue
Income from operating leases is recognized on a straight-line basis over the lease term. The Company's lease arrangements can include multiple lease and non-lease components. Examples of lease components include, but are not limited to, the lease of modular space, portable storage units and VAPS. Examples of non-lease components include, but are not limited to, the delivery, installation, maintenance, and removal services commonly provided in a bundled transaction with the lease components. Arrangement consideration is allocated between lease deliverables and non-lease components based on the relative estimated selling (leasing) price of each deliverable. Estimated selling (leasing) price of the lease deliverables is based upon the estimated stand-alone selling price of the related performance obligations using an adjusted market approach.
When leases and services are billed in advance, recognition of revenue is deferred until services are rendered. If equipment is returned prior to the contractually obligated period, the excess, if any, between the amount the customer is contractually required to pay over the cumulative amount of revenue recognized to date is recognized as incremental revenue upon return.
Rental equipment is leased primarily under operating leases and, from time to time, under sales-type lease arrangements. Operating lease minimum contractual terms within the NA Modular segment generally range from 1 month to 60 months and averaged approximately 9 months across this segment's rental fleet for the year ended December 31, 2020.Rental contracts with customers within the NA Storage and UK Storage segments are generally based on a 28-day rate and billing cycle. The rental continues until cancelled by the Company or the customer. There were no material sales-type lease arrangements as of December 31, 2020 or 2019.
The Company may use third parties to satisfy its performance obligations, including both the provision of rental units and other services. To determine whether it is the principal or agent in the arrangement, the Company reviews each third-party relationship on a contract-by-contract basis. The Company is considered an agent when its role is to arrange for another entity to provide the rental units and other services to the customer. In these instances, the Company does not control the rental unit or service before it is provided. The Company is considered the principal when it controls the rental unit or service prior to transferring control to the customer. WillScot Mobile Mini may be a principal in the fulfillment of some rental units and services and an agent for other rental units and services within the same contract. Revenue is recognized on a gross basis when the Company is the principal in the arrangement and on a net basis when it is the agent.
The adoption of ASC 842 at January 1, 2019, did not have a significant impact on the recognition of leasing revenue. Based on the requirements of ASC 842, the Company records changes in estimated collectability, directly against leasing revenue.
Services Revenue
The Company generally has three non-lease service-related performance obligations in its contracts with customers:
•Delivery and installation of the modular or portable storage unit;
•Maintenance and other ad hoc services performed during the lease term; and
•Removal services that occur at the end of the lease term.
Consideration is allocated to each of these performance obligations within the contract based upon their estimated relative standalone selling prices using the estimated cost plus a margin approach. Revenue from these activities is recognized as the services are performed.
Sales Revenue
Sales revenue is generated by the sale of new and rental units. Revenue from the sale of new and rental units is generally recognized at a point in time upon the transfer of control to the customer, which occurs when the unit is delivered and installed in accordance with the contract. Sales transactions constitute a single performance obligation.
Other Matters
The Company's non-lease revenues do not include material amounts of variable consideration, other than the variability noted for services arrangements expected to be performed beyond a twelve-month period.
The Company's payment terms vary by the type and location of its customer and the product or services offered. The time between invoicing and when payment is due is not significant. While the Company may bill certain customers in advance, its contracts do not contain a significant financing component based on the short length of time between upfront billings and the performance of contracted services. For certain products, services, or customer types, the Company requires payment before the products or services are delivered to the customer.
Revenue is recognized net of taxes collected from customers, which are subsequently remitted to governmental authorities.
Goodwill and Goodwill Impairment
For acquired businesses, the Company records assets acquired and liabilities assumed at their estimated fair values on the respective acquisition dates. Based on these values, the excess purchase price over the fair value of the net assets acquired is recorded as goodwill. Generally, reporting units are at the operating segment level or one level below the operating segment (the component level), if discrete financial information is prepared and regularly reviewed by segment management. Goodwill acquired in a business combination is assigned to each of the Company’s reporting units that are expected to benefit from the combination.
The Company performs its annual impairment test of goodwill as of October 1 at the reporting unit level, as well as during any reporting period in which events or changes in circumstances occur that, in management’s judgment, may constitute triggering events under ASC 350-20, Intangibles – Goodwill and Other, Testing Goodwill for Impairment. The Company performs its assessment of goodwill utilizing either a qualitative or quantitative impairment test. The qualitative impairment test assesses company-specific, industry, market and general economic factors to determine whether it is more likely than not that the fair value of the reporting unit is less than its carrying amount. If the Company concludes that it is more likely than not that the fair value of the reporting unit is less than its carrying amount, or elects not to use the qualitative
impairment test, a quantitative impairment test is performed. The quantitative impairment test involves a comparison of the estimated fair value of a reporting unit to its carrying amount. The Company uses an independent valuation specialist for its annual impairment tests to assist in the valuation.
The Company has historically used the quantitative impairment test to evaluate goodwill for impairment. The Company used the qualitative approach for the reporting units acquired in the Merger due to the proximity of the July 1, 2020 acquisition date to the October 1, 2020 measurement date.
Determining the fair value of a reporting unit is judgmental in nature and involves the use of significant estimates and assumptions. These estimates and assumptions include revenue growth rates and operating margins used to calculate projected future cash flows, risk-adjusted discount rates, value of net operating losses, future economic and market conditions and determination of appropriate market comparables. Management bases fair value estimates on assumptions it believes to be reasonable but that are unpredictable and inherently uncertain. Actual future results may differ from these estimates.
If the carrying amount of the reporting unit exceeds the calculated fair value of the reporting unit, an impairment charge would be recognized for the excess, not to exceed the amount of goodwill allocated to that reporting unit.
Intangible Assets Other than Goodwill
Intangible assets that are acquired by the Company and determined to have an indefinite useful life are not amortized but are tested for impairment at least annually. The Company’s indefinite-lived intangible assets consist of the Williams Scotsman trade name and the Mobile Mini trade name. The Company performs its assessment of indefinite-lived intangible assets utilizing either a qualitative or quantitative impairment test. When utilizing a quantitative impairment test, the Company calculates fair value using a relief-from-royalty method. This method is used to estimate the cost savings that accrue to the owner of an intangible asset who would otherwise have to pay royalties or license fees on revenues earned through the use of the asset. If the carrying amount of the indefinite-lived intangible asset exceeds its fair value, an impairment charge would be recorded to the extent the recorded indefinite-lived intangible asset exceeds the fair value.
Other intangible assets that have finite useful lives are measured at cost less accumulated amortization and impairment losses, if any. Amortization is recognized in profit or loss over the estimated useful lives of the intangible asset.
Purchase Accounting
The Company accounts for acquisitions of businesses under the acquisition method. Under the acquisition method of accounting, the Company records assets acquired and liabilities assumed at their estimated fair value on the date of acquisition. Goodwill is measured as the excess of the fair value of the consideration transferred over the fair value of the identifiable net assets. Estimated fair values of acquired assets and liabilities are provisional and could change as additional information is received. When appropriate, our estimates of the fair values of assets and liabilities acquired include assistance from independent third-party valuation firms. Valuations are finalized as soon as practicable, but not later than one year from the acquisition date. Any subsequent changes to purchase price allocations result in a corresponding adjustment to goodwill.
Long-lived assets (principally rental equipment), goodwill and other intangible assets generally represent the largest components of our acquisitions. Rental equipment is valued utilizing a replacement cost approach. Intangible assets are recognized at their estimated fair values as of the date of acquisition and generally consist of customer relationships and trade names. Determination of the estimated fair value of intangible assets requires judgment. The estimated fair value of customer relationships is determined based on estimates and judgments regarding discounted future after-tax earnings and cash flows arising from lease renewals and new lease arrangements expected from customer relationships. The fair value of trade name intangible assets is determined utilizing the relief from royalty method. Under this form of the income approach, a royalty rate based on observed market royalties is applied to projected revenue supporting the trade name and discounted to present value.
Rental Equipment
Rental equipment is comprised of modular space and portable storage units held for rent or on rent to customers, tank and pump solutions products, which consist primarily of liquid and solid containment units, pumps and filtration equipment, and VAPS which are in use or available to be used by customers. Rental equipment is measured at cost less accumulated depreciation and impairment losses. Cost includes expenditures that are directly attributable to the acquisition of the asset. Costs of improvements and betterments to rental equipment are capitalized when such costs extend the useful life of the equipment or increase the rental value of the unit. Costs incurred for equipment to meet a particular customer specification are capitalized and depreciated over the lease term taking in consideration the residual value of the asset. Maintenance and repair costs are expensed as incurred.
Depreciation is generally computed using the straight-line method over estimated useful lives, as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Estimated Useful Life | | Residual Value |
| Modular space units | 10 - 20 years | | 20 - 50% |
| Portable storage units | 30 years | | 55% |
| Tank and pump | 7 - 25 years | | —% |
| VAPS and other related rental equipment | 1 - 8 years | | —% |
Trade Receivables and Allowance for Credit Losses
The Company is exposed to credit losses from trade receivables generated through its leasing and sales business. The Company assesses each customer’s ability to pay for the products it leases or sells by conducting a credit review. The credit review considers expected billing exposure and timing for payment and the customer’s established credit rating. The Company performs its credit review of new customers at inception of the customer relationship and for existing customers when the customer transacts new leases after a defined period of dormancy. The Company also considers contract terms and conditions, country risk and business strategy in the evaluation.
The Company monitors ongoing credit exposure through an active review of customer balances against contract terms and due dates. The Company may employ collection agencies and legal counsel to pursue recovery of defaulted receivables. The allowances for credit losses reflect the estimate of the amount of receivables that the Company will be unable to collect based on historical write-off experience and, as applicable, current conditions and reasonable and supportable forecasts that affect collectability. This estimate could require change based on changing circumstances, including changes in the economy or in the particular circumstances of individual customers. Accordingly, the Company may be required to increase or decrease our allowances.
In accordance with the adoption of Accounting Standards Update ("ASU") 2016-2, Leases (Topic 842) ("ASC 842"), effective January 1, 2019, and the adoption of ASU 2016-13, Financial Instruments - Credit Losses (Topic 326) ("ASC 326"), effective January 1, 2020, specifically identifiable lease revenue receivables and sales receivables not deemed probable of collection are recorded as a reduction of revenue. The remaining provision for credit losses is recorded as selling, general and administrative expense. For the year ended December 31, 2018, the entire provision for credit losses was recorded as a selling, general and administrative expense. The Company reviews the adequacy of the allowance on a quarterly basis.
Stock-Based Compensation
Prior to the Merger, stock awards were granted under the WillScot Corporation 2017 Incentive Award Plan (the "2017 Incentive Plan"), which included Restricted Stock Awards ("RSAs") and Restricted Stock Units ("RSUs"). On June 24, 2020, WillScot's stockholders approved the WillScot Mobile Mini 2020 Incentive Award Plan ("2020 Incentive Plan") to take effect pending completion of the Merger. The plan amended and restated in its entirety the 2017 Incentive Plan. As a result, all historical and future incentive awards to the Company's Board of Directors, executive officers and employees, as determined by the Company's Compensation Committee ("the Comp Committee"), are granted under the 2020 Incentive Plan. The 2020 Incentive Plan is administered by the Comp Committee. Under the 2020 Incentive Plan, the Comp Committee may grant an aggregate of 6,488,988 shares of Common Stock in the form of non-qualified stock options, incentive stock options, stock appreciation rights, RSAs, RSUs, performance compensation awards and stock bonus awards. Stock-based payments, including the grant of stock options, RSAs and RSUs, are subject to service-based vesting requirements, and expense is recognized on a straight-line basis over the vesting period. Forfeitures are accounted for as they occur.
Stock-based compensation expense includes grants of stock options, time-based RSUs ("Time-Based RSUs") and performance-based RSUs ("Performance-Based RSUs", together with Time-Based RSUs, the "RSUs"). The 2020 Incentive Plan continues the former Market-Based RSUs renamed as "Performance-Based RSUs." RSUs are recognized in the financial statements based on their fair value. In addition, stock-based payments to non-executive directors include grants of RSAs. Time-Based RSUs and RSAs are valued based on the intrinsic value of the difference between the exercise price, if any, of the award and the fair market value of WillScot Mobile Mini's Common Stock on the grant date. Performance-Based RSUs are valued based on a Monte Carlo simulation model to reflect the impact of the Performance-Based RSUs market condition. The probability of satisfying a market condition is considered in the estimation of the grant-date fair value for Performance-Based RSUs and the compensation cost is not reversed if the market condition is not achieved, provided the requisite service has been provided.
RSAs cliff vest in a one year period. Time-Based RSUs vest ratably over a period of four years. Performance-Based RSUs cliff vest based on achievement of the relative total stockholder return ("TSR") of the Company's Common Stock as compared to the TSR of the constituents of the Russell 3000 Index at the grant date over the performance period of three years. The target number of RSUs may be adjusted from 0% to 150% based on the TSR attainment levels defined by the Comp Committee. The 100% target payout is tied to performance at the 50% percentile, with a payout curve ranging from 0% (for performance less than the 25% percentile) to 150% (for performance at or above the 75% percentile). Vesting is also subject to continued service requirements through the vesting date.
Stock options vest in tranches over a period of four years and expire ten years from the grant date. The fair value of each stock option award on the grant date is estimated using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model with the following assumptions: expected dividend yield, expected stock price volatility, weighted-average risk-free interest rate and weighted-average expected term of the options. The volatility assumption used in the Black-Scholes option-pricing model was based on a blend of peer group volatility and Company trading history as the Company did not have a sufficient trading history as a stand-alone public company. Future calculations will use the Company trading history. Additionally, due to an insufficient history with respect to stock option activity and post-vesting cancellations, the expected term assumption is based on the simplified method under GAAP, which is based on the vesting period and contractual term for each tranche of awards. The mid-point between the weighted-average vesting term and the expiration date is used as the expected term under this method. The risk-free interest rate used in the Black-Scholes option-pricing model is based on the implied US Treasury bill yield curve
at the date of grant with a remaining term equal to the Company’s expected term assumption. WillScot Mobile Mini has never declared or paid a cash dividend on common shares.
Warrants
The Company accounts for warrants in accordance with applicable accounting guidance provided in ASC 815-40, as either derivative liabilities or as equity instruments depending on the specific terms of the warrant agreements. In periods subsequent to issuance, warrants classified as liabilities are subject to remeasurement at each balance sheet date and transaction date with changes in the estimated fair values of the common stock warrant liabilities and gains and losses on extinguishment of common stock warrant liabilities reported in the consolidated statements of operations.
The Company accounts for its warrants in the following ways: (i) the 2015 Private Warrants as liabilities for all periods presented, (ii) the 2015 Public Warrants as liabilities through their final redemption in February 2020 and (iii) the 2018 Warrants as liabilities until June 30, 2020, the date all issued and outstanding shares of the Company's Class B Common Stock were cancelled.
Prior to their redemption, the Company's 2015 Public Warrants traded in active markets. When classified as liabilities, warrants traded in active markets with sufficient trading volume represent Level 1 financial instruments as they were publicly traded in active markets and thus had observable market prices which were used to estimate the fair value adjustments for the related common stock warrant liabilities. When classified as liabilities, warrants not traded in active markets, or traded with insufficient volume, represent Level 3 financial instruments that are valued using a Black-Scholes option-pricing model to estimate the fair value adjustments for the related common stock warrant liabilities.
Income Taxes
The Company accounts for income taxes under the asset and liability method, which requires the recognition of deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future tax consequences of events that have been included in the financial statements. Under this method, deferred tax assets and liabilities are determined based on the differences between the financial statement and tax basis of assets and liabilities using enacted tax rates in effect for the year in which the differences are expected to reverse. The effect of a change in tax rates on deferred tax assets and liabilities is recognized in income in the period that includes the enactment date.
The Company records deferred tax assets to the extent it believes that it is more likely than not that these assets will be realized. In making such determination, the Company considers all available positive and negative evidence, including scheduled reversals of deferred tax liabilities, projected future taxable income, tax planning strategies and recent results of operations. Valuation allowances are recorded to reduce the deferred tax assets to an amount that will more likely than not be realized.
The Company assesses the likelihood that each of the deferred tax assets will be realized. To the extent management believes realization of any deferred tax assets is not likely, the Company establishes a valuation allowance. When a valuation allowance is established or there is an increase in an allowance in a reporting period, tax expense is generally recorded in the Company’s consolidated statement of operations. Conversely, to the extent circumstances indicate that a valuation allowance is no longer necessary, that portion of the valuation allowance is reversed, which generally reduces the Company’s income tax expense.
Deferred tax liabilities are recognized for the income taxes on the undistributed earnings of wholly-owned foreign subsidiaries unless such earnings are indefinitely reinvested, or will only be repatriated when possible to do so at minimal additional tax cost. Current income tax relating to items recognized directly in equity is recognized in equity and not in profit (loss) for the year.
In accordance with applicable authoritative guidance, the Company accounts for uncertain income tax positions using a benefit recognition model with a two-step approach; a more-likely-than-not recognition criterion; and a measurement approach that measures the position as the largest amount of tax benefit that is greater than 50% likely of being realized upon ultimate settlement. If it is not more-likely-than-not that the benefit of the tax position will be sustained on its technical merits, no benefit is recorded. Uncertain tax positions that relate only to timing of when an item is included on a tax return are considered to have met the recognition threshold. The Company classifies interest on tax deficiencies and income tax penalties within income tax expense.
ITEM 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk
We are exposed to certain market risks from changes in foreign currency exchange rates and interest rates. Changes in these factors cause fluctuations in our earnings and cash flows. We evaluate and manage exposure to these market risks as follows:
Interest Rate Risk
We are primarily exposed to interest rate risk through our ABL Facility, which bears interest at variable rates based on LIBOR. We had $1.3 billion in outstanding principal under the ABL Facility at December 31, 2020.
In order to manage this risk, we maintain an interest rate swap agreement that effectively converts $400.0 million in aggregate notional amount of variable-rate debt under our ABL Facility into fixed-rate debt. The swap agreement provides for us to pay a fixed rate of 3.06% per annum on the outstanding debt in exchange for receiving a variable interest rate based on 1-month LIBOR. The effect is a synthetically fixed rate of 4.94% on the $400.0 million notional amount, when including the current applicable margin.
An increase in interest rates by 100 basis points on our ABL Facility, inclusive of the impact of our interest rate swaps, would increase annual interest expense by approximately $9.0 million based on current outstanding borrowings.
Foreign Currency Risk
We currently generate the majority of our consolidated net revenues in the US, and the reporting currency for our consolidated financial statements is the US dollar. However, we are exposed to currency risk through our operations in Canada, Mexico, and the UK. For the operations outside the US we bill customers primarily in their local currency, which is subject to foreign currency rate changes. As our net revenues and expenses generated outside of the US increase, our results of operations could be adversely impacted by changes in foreign currency exchange rates. Since we recognize foreign revenues in local foreign currencies, if the US dollar strengthens, it could have a negative impact on our foreign revenues upon translation of those results into the US dollar for consolidation into our financial statements.
In addition, we are exposed to gains and losses resulting from fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates on transactions generated by our foreign subsidiaries in currencies other than their local currencies. These gains and losses are primarily driven by intercompany transactions and rental equipment purchases denominated in currencies other than the functional currency of the purchasing entity. These exposures are included in currency (gains) losses, net, on the consolidated statements of operations. To date, we have not entered into any hedging arrangements with respect to foreign currency risk.
Seasonality
Although demand from certain of our customers is seasonal, our operations as a whole are not impacted in any material respect by seasonality.
Impact of Inflation
Inflationary factors such as increases in the cost of our product and overhead costs may adversely affect our operating results if we are unsuccessful in passing such inflationary increases on to our customers in the form of higher prices. We do not believe that inflation has had a material effect on our results of operations.
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary
Data
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Shareholders and the Board of Directors of WillScot Mobile Mini Holdings Corp.
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of WillScot Mobile Mini Holdings Corp. (the Company) as of December 31, 2020 and 2019, the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive income (loss), changes in equity and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2020, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the “consolidated financial statements”). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company at December 31, 2020 and 2019, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2020, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
Restatement of Financial Statements
As discussed in Note 1 to the consolidated financial statements, the financial statements as of December 31, 2020 and 2019 and for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2020 have been restated to correct a misstatement in the classification of the Company's 2015 Warrants and 2018 Warrants.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the Company's internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2020, based on criteria established in Internal Control-Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 framework) and our report dated February 26, 2021, except for the effect of the material weakness described in the second paragraph of that report, as to which the date is May 10, 2021, expressed an adverse opinion thereon.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Critical Audit Matter
The critical audit matter communicated below is a matter arising from the current period audit of the financial statements that was communicated or required to be communicated to the audit committee and that: (1) relates to accounts or disclosures that are material to the financial statements and (2) involved our especially challenging, subjective or complex judgments. The communication of the critical audit matter does not alter in any way our opinion on the consolidated financial statements, taken as a whole, and we are not, by communicating the critical audit matter below, providing a separate opinion on the critical audit matter or on the accounts or disclosures to which it relates.
| | | | | | | | |
| | Valuation of Intangible Assets Acquired through Mobile Mini Merger |
| Description of the Matter | | During 2020, the Company completed its merger with Mobile Mini, Inc. for net consideration of $1.4 billion, as disclosed in Note 2 to the consolidated financial statements. The transaction was accounted for as a business combination. Auditing the Company's accounting for its merger with Mobile Mini was complex and highly judgmental due to the significant estimation uncertainty in management’s determination of the fair value of identified intangible assets of $383 million, which principally consisted of $217 million and $164 million of customer relationship and tradename intangibles, respectively. The significant estimation uncertainty was primarily due to the sensitivity of the respective fair values to changes in the underlying assumptions. The Company used a discounted cash flow model to measure the customer relationship and tradename intangible assets. The significant assumptions used to estimate the value of the intangible assets included discount rates, royalty rates, and assumptions that form the basis of the forecasted results, in particular revenue growth rates, projected EBITDA margins and customer retention assumptions. These significant assumptions are forward looking and could be affected by future economic and market conditions. |
| | |
| How We Addressed the Matter in Our Audit | | We obtained an understanding, evaluated the design and tested the operating effectiveness of the Company's controls over its valuation of acquired intangible assets. Our tests included controls over the estimation process supporting the recognition and measurement of customer-relationship and tradename intangible assets. For example, we tested controls over management’s review of the valuation models and significant assumptions used to estimate the fair value of the customer relationship and tradename intangible assets, including controls over the completeness and accuracy of the data used in the valuation models. |
| | |
| | To test the estimated fair value of the customer relationship and tradename intangible assets, we performed audit procedures that included, among others, evaluating the Company's selection of the valuation methodology, evaluating the methods and significant assumptions described above, and evaluating the completeness and accuracy of the underlying data supporting the significant assumptions and estimates. We involved our valuation specialists to assist with our evaluation of the methodology used by the Company and significant assumptions included in the fair value estimates. For example, our valuation specialists compared management’s assumptions used to develop the discount rates to the weighted average cost of capital of guideline public companies. Additionally, we compared the significant assumptions related to prospective financial information to the historical results of the Mobile Mini business and to guideline companies in the same industry. We also performed a sensitivity analysis of the significant assumptions to evaluate the change in the fair values that would result from changes in assumptions. |
/s/ Ernst & Young LLP
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2017.
Baltimore, Maryland
February 26, 2021, except for the impact of the matter discussed in Note 1 - Restatement of Previously Reported Financial Statements, as to which the date is May 10, 2021
WillScot Mobile Mini Holdings Corp.
Consolidated Balance Sheets
(in thousands, except share data) | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, |
| 2020 | | 2019 |
| (as restated) | | (as restated) |
| Assets | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 24,937 | | | $ | 3,045 | |
| Trade receivables, net of allowance for credit losses at December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019 of $29,258 and $15,828, respectively | 330,942 | | | 247,596 | |
| Inventories | 21,655 | | | 15,387 | |
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 29,954 | | | 14,621 | |
| Assets held for sale | 12,004 | | | 11,939 | |
| Total current assets | 419,492 | | | 292,588 | |
| Rental equipment, net | 2,933,722 | | | 1,944,436 | |
| Property, plant and equipment, net | 303,650 | | | 147,689 | |
| Operating lease assets | 232,094 | | | 146,698 | |
| Goodwill | 1,171,219 | | | 235,177 | |
| Intangible assets, net | 495,947 | | | 126,625 | |
| Other non-current assets | 16,081 | | | 4,436 | |
| Total long-term assets | 5,152,713 | | | 2,605,061 | |
| Total assets | $ | 5,572,205 | | | $ | 2,897,649 | |
| Liabilities and equity | | | |
| Accounts payable | $ | 106,926 | | | $ | 109,926 | |
| Accrued interest and liabilities | 141,672 | | | 98,375 | |
| Deferred revenue and customer deposits | 135,485 | | | 82,978 | |
| Operating lease liabilities - current | 48,063 | | | 29,133 | |
| Current portion of long-term debt | 16,521 | | | 0 | |
| Total current liabilities | 448,667 | | | 320,412 | |
| Long-term debt | 2,453,809 | | | 1,632,589 | |
| Deferred tax liabilities | 307,541 | | | 70,693 | |
| Operating lease liabilities - non-current | 183,761 | | | 118,429 | |
| Common stock warrant liabilities | 77,404 | | | 153,756 | |
| Other non-current liabilities | 37,150 | | | 46,571 | |
| Long-term liabilities | 3,059,665 | | | 2,022,038 | |
| Total liabilities | 3,508,332 | | | 2,342,450 | |
| Commitments and contingencies (see Note 19) | 0 | | 0 |
| Preferred Stock: $0.0001 par, 1,000,000 shares authorized and 0 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2020 and 2019 | 0 | | | 0 | |
| Common Stock: $0.0001 par, 500,000,000 shares authorized and 229,038,158 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2020 | 23 | | | 0 | |
| Class A Common Stock: $0.0001 par, 400,000,000 shares authorized and 108,818,854 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2019 | 0 | | | 11 | |
| Class B Common Stock: $0.0001 par, 100,000,000 shares authorized and 8,024,419 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2019 | 0 | | | 1 | |
| Additional paid-in-capital | 3,852,291 | | | 2,378,733 | |
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss | (37,207) | | | (62,775) | |
| Accumulated deficit | (1,751,234) | | | (1,825,361) | |
| Total shareholders' equity | 2,063,873 | | | 490,609 | |
| Non-controlling interest | 0 | | | 64,590 | |
| Total equity | 2,063,873 | | | 555,199 | |
| Total liabilities and equity | $ | 5,572,205 | | | $ | 2,897,649 | |
See the accompanying notes which are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
WillScot Mobile Mini Holdings Corp.
Consolidated Statements of Operations
(in thousands, except share and per share data) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Years Ended December 31, |
| 2020 | | 2019 | | 2018 |
| (as restated) | | (as restated) | | (as restated) |
| Revenues: | | | | | |
| Leasing and services revenue: | | | | | |
| Leasing | $ | 1,001,447 | | | $ | 744,185 | | | $ | 518,235 | |
| Delivery and installation | 274,156 | | | 220,057 | | | 154,557 | |
| Sales revenue: | | | | | |
| New units | 53,093 | | | 59,085 | | | 53,603 | |
| Rental units | 38,949 | | | 40,338 | | | 25,017 | |
| Total revenues | 1,367,645 | | | 1,063,665 | | | 751,412 | |
| Costs: | | | | | |
| Costs of leasing and services: | | | | | |
| Leasing | 227,376 | | | 213,151 | | | 143,120 | |
| Delivery and installation | 220,102 | | | 194,107 | | | 143,950 | |
| Costs of sales: | | | | | |
| New units | 34,841 | | | 42,160 | | | 36,863 | |
| Rental units | 24,772 | | | 26,255 | | | 16,659 | |
| Depreciation of rental equipment | 200,581 | | | 174,679 | | | 121,436 | |
| Gross profit | 659,973 | | | 413,313 | | | 289,384 | |
| Expenses: | | | | | |
| Selling, general and administrative | 360,626 | | | 271,004 | | | 234,820 | |
| Transaction costs | 64,053 | | | 0 | | | 20,051 | |
| Other depreciation and amortization | 43,249 | | | 12,395 | | | 13,304 | |
| Impairment losses on long-lived assets | 0 | | | 2,848 | | | 1,600 | |
| Lease impairment expense and other related charges | 4,876 | | | 8,674 | | | 0 | |
| Restructuring costs | 6,527 | | | 3,755 | | | 15,468 | |
| Currency (gains) losses, net | (355) | | | (688) | | | 2,454 | |
| Other income, net | (1,718) | | | (2,200) | | | (4,574) | |
| Operating income | 182,715 | | | 117,525 | | | 6,261 | |
| Interest expense | 119,886 | | | 122,504 | | | 98,433 | |
| Fair value (gain) loss on common stock warrant liabilities | (3,461) | | | 109,622 | | | (23,830) | |
| Loss on extinguishment of debt | 42,401 | | | 8,755 | | | 0 | |
| Income (loss) before income tax | 23,889 | | | (123,356) | | | (68,342) | |
| Income tax benefit | (51,451) | | | (2,191) | | | (38,600) | |
| Net income (loss) | 75,340 | | | (121,165) | | | (29,742) | |
| Net income (loss) attributable to non-controlling interest, net of tax | 1,213 | | | (421) | | | (4,532) | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| Net income (loss) attributable to WillScot Mobile Mini common shareholders | $ | 74,127 | | | $ | (120,744) | | | $ | (25,210) | |
| | | | | |
| Earnings (loss) per share attributable to WillScot Mobile Mini common shareholders: | | | | | |
| Basic | $ | 0.44 | | | $ | (1.11) | | | $ | (0.29) | |
| Diluted | $ | 0.25 | | | $ | (1.11) | | | $ | (0.53) | |
| Weighted average shares: | | | | | |
| Basic | 169,230,177 | | 108,683,820 | | 87,209,605 |
| Diluted | 177,268,383 | | 108,683,820 | | 88,950,564 |
See the accompanying notes which are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
WillScot Mobile Mini Holdings Corp.
Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income (Loss)
(in thousands) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Years Ended December 31, |
| 2020 | | 2019 | | 2018 |
| (as restated) | | (as restated) | | (as restated) |
| Net income (loss) | $ | 75,340 | | | $ | (121,165) | | | $ | (29,742) | |
| Other comprehensive income (loss): | | | | | |
| Foreign currency translation adjustment, net of income tax benefit of $685, $0 and $161 for the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018, respectively | 28,404 | | | 10,586 | | | (11,639) | |
| Net loss on derivatives, net of income tax benefit of $(539), $(1,471) and $(1,822) for the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018, respectively | (1,749) | | | (4,809) | | | (5,955) | |
| Total other comprehensive income (loss) | 26,655 | | | 5,777 | | | (17,594) | |
| Comprehensive income (loss) | 101,995 | | | (115,388) | | | (47,336) | |
| Comprehensive (loss) income attributable to non-controlling interest | (672) | | | 105 | | | (6,137) | |
| Total comprehensive income (loss) attributable to WillScot Mobile Mini | $ | 102,667 | | | $ | (115,493) | | | $ | (41,199) | |
See the accompanying notes which are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
WillScot Mobile Mini Holdings Corp.
Consolidated Statements of Changes in Equity (as restated)
(in thousands) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Common Stock (1) | Class B Common Stock | | | | | | |
| Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | Additional Paid-in Capital | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) | Accumulated Deficit | Total Shareholders' Equity | Non-Controlling Interest | Total Equity |
| Balance at December 31, 2017 (as restated) (2) | 84,645 | | $ | 8 | | 8,024 | | $ | 1 | | $ | 2,053,711 | | $ | (49,497) | | $ | (1,687,014) | | $ | 317,209 | | $ | 48,931 | | $ | 366,140 | |
| Net loss | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | (25,210) | | (25,210) | | (4,532) | | (29,742) | |
| Other comprehensive loss | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | (15,989) | | — | | (15,989) | | (1,605) | | (17,594) | |
| Adoption of ASU 2018-02 | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | (2,540) | | 2,540 | | — | | — | | 0 | |
| Stock-based compensation | — | | — | | — | | — | | 3,439 | | — | | — | | 3,439 | | — | | 3,439 | |
| Issuance of Common Stock and contribution of proceeds to WSII | 9,200 | | 1 | | — | | — | | 131,460 | | — | | — | | 131,461 | | 7,574 | | 139,035 | |
| Acquisition of ModSpace and related financing transactions including stock | 6,458 | | 1 | | — | | — | | 82,195 | | — | | — | | 82,196 | | 13,614 | | 95,810 | |
| Common Stock issued in warrant exchange | 8,206 | | 1 | | — | | | 100,557 | | — | | — | | 100,558 | | — | | 100,558 | |
| Issuance of Common Stock from the exercise of options and warrants | — | | — | | — | | — | | 1 | | — | | — | | 1 | | — | | 1 | |
| Balance at December 31, 2018 (as restated) | 108,509 | | $ | 11 | | 8,024 | | $ | 1 | | $ | 2,371,363 | | $ | (68,026) | | $ | (1,709,684) | | $ | 593,665 | | $ | 63,982 | | $ | 657,647 | |
| Net loss | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | (120,744) | | (120,744) | | (421) | | (121,165) | |
| Other comprehensive income | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | 5,251 | | — | | 5,251 | | 526 | | 5,777 | |
| Adoption of ASC 606 | — | | 0 | | — | | 0 | | 0 | | 0 | | 345 | | 345 | | 0 | | 345 | |
| Adoption of ASC 842 | — | | 0 | | — | | 0 | | 0 | | 0 | | 4,722 | | 4,722 | | 503 | | 5,225 | |
| Issuance of Common Stock from the exercise of options and warrants | 81 | | 0 | | — | | — | | 1,338 | | — | | — | | 1,338 | | — | | 1,338 | |
| Stock-based compensation and issuance of Common Stock from vesting | 229 | | 0 | | — | | — | | 6,032 | | — | | — | | 6,032 | | — | | 6,032 | |
| Balance at December 31, 2019 (as restated) | 108,819 | | $ | 11 | | 8,024 | | $ | 1 | | $ | 2,378,733 | | $ | (62,775) | | $ | (1,825,361) | | $ | 490,609 | | $ | 64,590 | | $ | 555,199 | |
| Net income | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | 74,127 | | 74,127 | | 1,213 | | 75,340 | |
| Other comprehensive income | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | 28,540 | | — | | 28,540 | | (1,885) | | 26,655 | |
| Mobile Mini Merger | 106,427 | | 11 | | — | | — | | 1,348,619 | | — | | — | | 1,348,630 | | — | | 1,348,630 | |
| Sapphire Exchange - See Note 12 | 10,641 | | 1 | | (8,024) | | (1) | | 66,890 | | (2,972) | | — | | 63,918 | | (63,918) | | 0 | |
| Issuance of Common Stock from the exercise of options and warrants | 2,836 | | 0 | | — | | — | | 35,727 | | — | | — | | 35,727 | | — | | 35,727 | |
| Repurchase and cancellation of options and warrants | — | | — | | — | | — | | (300) | | — | | — | | (300) | | — | | (300) | |
| Withholding taxes on net share settlement of stock-based compensation and option exercises | — | | — | | — | | — | | (13,473) | | — | | — | | (13,473) | | — | | (13,473) | |
| Stock-based compensation and issuance of Common Stock from vesting | 315 | | — | | — | | — | | 9,879 | | — | | — | | 9,879 | | — | | 9,879 | |
| Reclassification of ModSpace Warrants | — | | — | | — | | — | | 26,216 | | — | | — | | 26,216 | | — | | 26,216 | |
| Balance at December 31, 2020 (as restated) | 229,038 | | $ | 23 | | 0 | | $ | 0 | | $ | 3,852,291 | | $ | (37,207) | | $ | (1,751,234) | | $ | 2,063,873 | | $ | 0 | | $ | 2,063,873 | |
(1) See Note 1 for information regarding the Company's conversion of Class A Common Stock to Common Stock on July 1, 2020 concurrent with the Merger.
(2) Additional Paid-in Capital and Accumulated Deficit opening balances have been reduced by $68,215 and $50,195, respectively, as a result of the restatement described in Note 1.
See the accompanying notes which are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
WillScot Mobile Mini Holdings Corp.
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
(in thousands) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Years Ended December 31, |
| 2020 | | 2019 | | 2018 |
| (as restated) | | (as restated) | | (as restated) |
| Operating activities: | | | | | |
| Net income (loss) | $ | 75,340 | | | $ | (121,165) | | | $ | (29,742) | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net income (loss) to net cash provided by operating activities: | | | | | |
| Depreciation and amortization | 246,948 | | | 189,436 | | | 136,467 | |
| Provision for credit losses | 32,593 | | | 14,496 | | | 7,656 | |
| Impairment losses on long-lived assets | 0 | | | 2,848 | | | 1,600 | |
| Impairment losses on right of use assets | 57 | | | 4,160 | | | — | |
| Gain on sale of rental equipment and other property, plant and equipment | (14,124) | | | (11,660) | | | (12,878) | |
| Amortization of debt discounts and debt issuance costs | 13,085 | | | 11,450 | | | 7,652 | |
| Fair value (gain) loss on common stock warrant liabilities | (3,461) | | | 109,622 | | | (23,830) | |
| Loss on extinguishment of debt | 42,401 | | | 8,755 | | | 0 | |
| Stock-based compensation expense | 9,879 | | | 6,686 | | | 3,439 | |
| Deferred income tax benefit | (55,155) | | | (2,624) | | | (40,192) | |
| Unrealized currency losses (gains), net | 424 | | | (745) | | | 1,982 | |
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities, net of effect of businesses acquired: | | | | | |
| Trade receivables | (26,723) | | | (63,648) | | | (36,452) | |
| Inventories | 2,775 | | | 869 | | | (1,241) | |
| Prepaid and other assets | (4,547) | | | 8,237 | | | 8,416 | |
| Operating lease assets and liabilities | 789 | | | (438) | | | 0 | |
| Accrued interest | (11,877) | | | (4,217) | | | 17,526 | |
| Accounts payable and other accrued liabilities | (16,046) | | | 4,865 | | | (14,462) | |
| Deferred revenue and customer deposits | 12,454 | | | 15,639 | | | 11,208 | |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | 304,812 | | | 172,566 | | | 37,149 | |
| Investing activities: | | | | | |
| Acquisition of a businesses, net of cash acquired | 17,173 | | | 0 | | | (1,083,146) | |
| Proceeds from sale of rental equipment | 38,949 | | | 42,101 | | | 30,761 | |
| Purchase of rental equipment and refurbishments | (172,383) | | | (205,106) | | | (160,883) | |
| Proceeds from the sale of property, plant and equipment | 7,355 | | | 18,763 | | | 688 | |
| Purchase of property, plant and equipment | (16,454) | | | (8,340) | | | (4,622) | |
| Net cash used in investing activities | (125,360) | | | (152,582) | | | (1,217,202) | |
| Financing activities: | | | | | |
| Receipts from issuance of Common Stock from the exercise of options and warrants | 10,616 | | | 921 | | | 147,201 | |
| Repurchase and cancellation of warrants | (21,777) | | | 0 | | | 0 | |
| Payment of Common Stock issuance costs | (4,222) | | | 0 | | | 0 | |
| Receipts from borrowings | 2,786,793 | | | 552,230 | | | 1,212,629 | |
| Payment of financing costs | (65,475) | | | (2,623) | | | (36,579) | |
| Repayment of borrowings | (2,808,370) | | | (568,686) | | | (143,094) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Payment of debt extinguishment premium costs | (34,610) | | | (7,152) | | | 0 | |
| Principal payments on finance lease obligations | (8,440) | | | (99) | | | (120) | |
| Taxes paid on employee stock awards | (13,473) | | | (654) | | | 0 | |
| Net cash (used in) provided by financing activities | (158,958) | | | (26,063) | | | 1,180,037 | |
| Effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents | 1,398 | | | 166 | | | (211) | |
| Net change in cash and cash equivalents | 21,892 | | | (5,913) | | | (227) | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at the beginning of the year | 3,045 | | | 8,958 | | | 9,185 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at the end of the year | $ | 24,937 | | | $ | 3,045 | | | $ | 8,958 | |
| | | | | |
| Supplemental cash flow information: | | | | | |
| Interest paid | $ | 108,740 | | | $ | 115,582 | | | $ | 51,986 | |
| Income taxes paid (refunded), net | $ | 4,234 | | | $ | (1,148) | | | $ | 2,617 | |
| Capital expenditures accrued or payable | $ | 23,553 | | | $ | 23,946 | | | $ | 20,785 | |
| Non-cash acquisition of a business | $ | 0 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 148,108 | |
See the accompanying notes which are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
WillScot Mobile Mini Holdings Corp.
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
NOTE 1 - Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (as restated)
Organization and Nature of Operations
WillScot Mobile Mini Holdings Corp. (“WillScot Mobile Mini” and, together with its subsidiaries, the “Company”) is a leading provider of modular space and portable storage solutions in the United States (“US”), Canada, Mexico and the United Kingdom ("UK"). The Company also maintains a fleet of specialty containment products, including liquid and solid containment solutions. The Company leases, sells, delivers and installs mobile solutions and storage products through an integrated network of branch locations that spans North America and the UK.
WillScot Corporation, a Delaware corporation (“WillScot”) entered into an Agreement and Plan of Merger, dated as of March 1, 2020, as amended on May 28, 2020 (as so amended, the “Merger Agreement”), by and among WillScot, Mobile Mini, Inc. (“Mobile Mini”), and Picasso Merger Sub, Inc., a wholly-owned subsidiary of WillScot (“Merger Sub”). On July 1, 2020, Merger Sub merged with and into Mobile Mini (the “Merger”). At the effective time of the Merger, the separate corporate existence of Merger Sub ceased, and Mobile Mini continued its existence as the surviving corporation in the Merger and a wholly-owned subsidiary of WillScot. As a result of the Merger, each issued and outstanding share of Mobile Mini Common Stock, par value $0.01 per share (other than treasury shares held by Mobile Mini), was converted automatically into the right to receive 2.405 shares of WillScot’s Class A Common Stock, par value $0.0001 per share (the “WillScot Class A Common Stock”), and cash in lieu of any fractional shares. Immediately following the Merger, WillScot changed its name to “WillScot Mobile Mini Holdings Corp.” and filed an amended and restated certificate of incorporation (the “A&R Charter”), which reclassified all outstanding shares of WillScot Class A Common Stock and converted such shares into shares of Common Stock, par value $0.0001 per share, of WillScot Mobile Mini (“WillScot Mobile Mini Common Stock”). The WillScot Class A Common Stock was listed on the Nasdaq Capital Market (Nasdaq: WSC) up until the Merger, and the WillScot Mobile Mini Common Stock has been listed on the Nasdaq Capital Market (Nasdaq: WSC) since the Merger. As used herein, the term “Common Stock” or “the Company’s Common Stock” refers to WillScot Class A Common Stock prior to filing of the A&R Charter on July 1, 2020 and to WillScot Mobile Mini Common Stock as of and following the filing of the A&R Charter July 1, 2020.
As the Merger closed on July 1, 2020 the preparation of financial statements in accordance with US Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (“GAAP”) requires that our consolidated financial statements and most of the disclosures in these Notes be presented on a historical basis. Unless the context otherwise requires, the terms “Company” and “WillScot Mobile Mini” as used in these financial statements mean WillScot and its subsidiaries when referring to periods prior to July 1, 2020 (prior to the Merger) and to WillScot Mobile Mini, when referring to periods on or after July 1, 2020 (after the Merger).
Basis of Presentation
The consolidated financial statements were prepared in conformity with GAAP.
Principles of Consolidation
The consolidated financial statements comprise the financial statements of WillScot Mobile Mini and its subsidiaries that it controls due to ownership of a majority voting interest. Subsidiaries are fully consolidated from the date of acquisition, being the date on which the Company obtains control, and continue to be consolidated until the date when such control ceases. The financial statements of the subsidiaries are prepared for the same reporting period as WillScot Mobile Mini. All intercompany balances and transactions are eliminated.
Restatement of Previously Reported Financial Statements
On April 12, 2021, in the SEC Staff Statement on Accounting and Reporting Considerations for Warrants Issued by Special Purpose Acquisition Companies (“SPACs”) (the “SEC Staff Statement”), the SEC staff clarified its interpretations of certain generally accepted accounting principles related to certain terms that are common in warrants issued in connection with the initial public offerings of SPACs. The SEC Staff addressed certain accounting and reporting considerations related to warrants of a kind similar to those issued by the Company that preclude the warrants from being classified as components of equity.
In April 2021, management of the Company concluded that the Company’s previously issued consolidated financial statements for the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018 and for each of the interim quarterly periods therein (the “Non-Reliance Period”) should no longer be relied upon. As such, the Company is restating its financial statements in this Annual Report on Form 10-K/A to make the necessary accounting adjustments related to the accounting for certain previously issued warrants to conform with the SEC Staff Statement described below. These warrants include (i) warrants to purchase 9,750,000 shares of common stock at a price of $5.75 per half share issued in a private placement concurrently with the initial public offering (the "IPO") in 2015 (the “2015 Private Warrants”), (ii) warrants to purchase 25,000,000 shares of common stock at a price of $5.75 per half share issued as components of units sold in the IPO in 2015 (the "2015 Public Warrants") and (iii) warrants to purchase 9,999,579 shares of common stock at a price of $15.50 per share issued to former shareholders as part
of a 2018 acquisition (the "2018 Warrants" and collectively with the 2015 Private Warrants and the 2015 Public Warrants, the "Warrants"). Since issuance, the Warrants were classified within equity in the Company's financial statements.
As clarified by the SEC staff interpretation of Accounting Standards Codification 815-40, Contracts in an Entity’s Own Equity, ("ASC 815-40"), the Company's warrant instruments are classified as liabilities for certain periods with changes in the estimated fair values of the derivative instruments reported in the statement of operations.
As a result of the above, the Company has restated its consolidated financial statements for the Non-Reliance Period to reflect (i) the 2015 Private Warrants as liabilities for all periods presented, (ii) the 2015 Public Warrants as liabilities through their final redemption in February 2020 and (iii) the 2018 Warrants as liabilities until June 30, 2020, the date all issued and outstanding shares of the Company's Class B Common Stock were cancelled.
The impact of the restatement on the consolidated balance sheets, consolidated statements of operations and consolidated statements of cash flows for the Non-Reliance Period is presented below. The restatement had no impact on net cash flows from operating, investing or financing activities.
The tables below sets forth the consolidated balance sheet amounts originally reported, adjustments, and the restated amounts as of December 31, 2020 and 2019.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2020 |
| (in thousands, except share data) | As Previously Reported | | Restatement Adjustments | | As Restated |
| Total assets | $ | 5,572,205 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 5,572,205 | |
| Liabilities and equity | | | | | |
| Total current liabilities | $ | 448,667 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 448,667 | |
| Long-term debt | 2,453,809 | | | 0 | | | 2,453,809 | |
| Deferred tax liabilities | 307,541 | | | 0 | | | 307,541 | |
| Operating lease liabilities - non-current | 183,761 | | | 0 | | | 183,761 | |
| Common stock warrant liabilities | 0 | | | 77,404 | | | 77,404 | |
| Other non-current liabilities | 37,150 | | | 0 | | | 37,150 | |
| Long-term liabilities | 2,982,261 | | | 77,404 | | | 3,059,665 | |
| Total liabilities | 3,430,928 | | | 77,404 | | | 3,508,332 | |
| Commitments and contingencies | 0 | | 0 | | 0 |
| Preferred Stock: $0.0001 par, 1,000,000 shares authorized and 0 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2020 | 0 | | | 0 | | | 0 | |
| Common Stock: $0.0001 par, 500,000,000 shares authorized and 229,038,158 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2020 | 23 | | | 0 | | | 23 | |
| Additional paid-in-capital | 3,797,168 | | | 55,123 | | | 3,852,291 | |
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss | (37,207) | | | 0 | | | (37,207) | |
| Accumulated deficit | (1,618,707) | | | (132,527) | | | (1,751,234) | |
| Total shareholders' equity | 2,141,277 | | | (77,404) | | | 2,063,873 | |
| Total liabilities and equity | $ | 5,572,205 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 5,572,205 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2019 |
| (in thousands, except share data) | As Previously Reported | | Restatement Adjustments | | As Restated |
| Total assets | $ | 2,897,649 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 2,897,649 | |
| Liabilities and equity | | | | | |
| Total current liabilities | $ | 320,412 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 320,412 | |
| Long-term debt | 1,632,589 | | | 0 | | | 1,632,589 | |
| Deferred tax liabilities | 70,693 | | | 0 | | | 70,693 | |
| Operating lease liabilities - non-current | 118,429 | | | 0 | | | 118,429 | |
| Common stock warrant liabilities | 0 | | | 153,756 | | | 153,756 | |
| Other non-current liabilities | 46,571 | | | 0 | | | 46,571 | |
| Long-term liabilities | 1,868,282 | | | 153,756 | | | 2,022,038 | |
| Total liabilities | 2,188,694 | | | 153,756 | | | 2,342,450 | |
| Commitments and contingencies | 0 | | 0 | | 0 |
| Class A Common Stock: $0.0001 par, 400,000,000 shares authorized and 108,818,854 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2019 | 11 | | | 0 | | | 11 | |
| Class B Common Stock: $0.0001 par, 100,000,000 shares authorized and 8,024,419 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2019 | 1 | | | 0 | | | 1 | |
| Additional paid-in-capital | 2,396,501 | | | (17,768) | | | 2,378,733 | |
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss | (62,775) | | | 0 | | | (62,775) | |
| Accumulated deficit | (1,689,373) | | | (135,988) | | | (1,825,361) | |
| Total shareholders' equity | 644,365 | | | (153,756) | | | 490,609 | |
| Non-controlling interest | 64,590 | | | 0 | | | 64,590 | |
| Total equity | 708,955 | | | (153,756) | | | 555,199 | |
| Total liabilities and equity | $ | 2,897,649 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 2,897,649 | |
The tables below set forth the consolidated statements of operations amounts originally reported, adjustments, and the restated balances for the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, 2020 |
| (in thousands, except share and per share data) | As Previously Reported | | Restatement Adjustments | | As Restated |
| Operating income | $ | 182,715 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 182,715 | |
| Interest expense | 119,886 | | | 0 | | | 119,886 | |
| Fair value gain on common stock warrant liabilities | 0 | | | (3,461) | | | (3,461) | |
| Loss on extinguishment of debt | 42,401 | | | 0 | | | 42,401 | |
| Income before income tax | 20,428 | | | 3,461 | | | 23,889 | |
| Income tax benefit | (51,451) | | | 0 | | | (51,451) | |
| Net income | 71,879 | | | 3,461 | | | 75,340 | |
| Net income attributable to non-controlling interest, net of tax | 1,213 | | | 0 | | | 1,213 | |
| Net income attributable to WillScot Mobile Mini common shareholders | $ | 70,666 | | | $ | 3,461 | | | $ | 74,127 | |
| | | | | |
| Earnings per share attributable to WillScot Mobile Mini common shareholders: | | | | | |
| Basic | $ | 0.42 | | | $ | 0.02 | | | $ | 0.44 | |
| Diluted | $ | 0.41 | | | $ | (0.16) | | | $ | 0.25 | |
| Weighted average shares: | | | | | |
| Basic | 169,230,177 | | 0 | | | 169,230,177 | |
| Diluted | 173,650,251 | | 3,618,132 | | | 177,268,383 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, 2019 |
| (in thousands, except share and per share data) | As Previously Reported | | Restatement Adjustments | | As Restated |
| Operating income | $ | 117,525 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 117,525 | |
| Interest expense | 122,504 | | | 0 | | | 122,504 | |
| Fair value loss on common stock warrant liabilities | 0 | | | 109,622 | | | 109,622 | |
| Loss on extinguishment of debt | 8,755 | | | 0 | | | 8,755 | |
| Loss before income tax | (13,734) | | | (109,622) | | | (123,356) | |
| Income tax benefit | (2,191) | | | 0 | | | (2,191) | |
| Net loss | (11,543) | | | (109,622) | | | (121,165) | |
| Net loss attributable to non-controlling interest, net of tax | (421) | | | 0 | | | (421) | |
| Net loss attributable to WillScot Mobile Mini common shareholders | $ | (11,122) | | | $ | (109,622) | | | $ | (120,744) | |
| | | | | |
| Loss per share attributable to WillScot Mobile Mini common shareholders: | | | | | |
| Basic | $ | (0.10) | | | $ | (1.01) | | | $ | (1.11) | |
| Diluted | $ | (0.10) | | | $ | (1.01) | | | $ | (1.11) | |
| Weighted average shares: | | | | | |
| Basic | 108,683,820 | | 0 | | | 108,683,820 | |
| Diluted | 108,683,820 | | 0 | | | 108,683,820 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, 2018 |
| (in thousands, except share and per share data) | As Previously Reported | | Restatement Adjustments | | As Restated |
| Operating income | $ | 6,261 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 6,261 | |
| Interest expense | 98,433 | | | 0 | | | 98,433 | |
| Fair value gain on common stock warrant liabilities | 0 | | | (23,830) | | | (23,830) | |
| (Loss) income before income tax | (92,172) | | | 23,830 | | | (68,342) | |
| Income tax benefit | (38,600) | | | 0 | | | (38,600) | |
| Net (loss) income | (53,572) | | | 23,830 | | | (29,742) | |
| Net loss attributable to non-controlling interest, net of tax | (4,532) | | | 0 | | | (4,532) | |
| Net (loss) income attributable to WillScot Mobile Mini | (49,040) | | | 23,830 | | | (25,210) | |
| Non-cash deemed dividend related to warrant exchange | (2,135) | | | 2,135 | | | 0 | |
| Net (loss) income attributable to WillScot Mobile Mini common shareholders | $ | (51,175) | | | $ | 25,965 | | | $ | (25,210) | |
| | | | | |
| (Loss) earnings per share attributable to WillScot Mobile Mini common shareholders: | | | | | |
| Basic | $ | (0.59) | | | $ | 0.30 | | | $ | (0.29) | |
| Diluted | $ | (0.59) | | | $ | 0.06 | | | $ | (0.53) | |
| Weighted average shares: | | | | | |
| Basic | 87,209,605 | | 0 | | | 87,209,605 | |
| Diluted | 87,209,605 | | 1,740,959 | | | 88,950,564 | |
The tables below set forth the consolidated statements of cash flow amounts originally reported, adjustments, and the restated balances for the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, 2020 |
| (in thousands) | As Previously Reported | | Restatement Adjustments | | As Restated |
| Net income | $ | 71,879 | | | $ | 3,461 | | | $ | 75,340 | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | 232,933 | | | 0 | | | 232,933 | |
| Fair value gain on common stock warrant liabilities | 0 | | | (3,461) | | | (3,461) | |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | 304,812 | | | 0 | | | 304,812 | |
| Net cash used in investing activities | (125,360) | | | 0 | | | (125,360) | |
| Net cash used in financing activities | (158,958) | | | 0 | | | (158,958) | |
| Effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents | 1,398 | | | 0 | | | 1,398 | |
| Net change in cash and cash equivalents | 21,892 | | | 0 | | 21,892 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at the beginning of the year | 3,045 | | | 0 | | | 3,045 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at the end of the year | $ | 24,937 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 24,937 | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, 2019 |
| (in thousands) | As Previously Reported | | Restatement Adjustments | | As Restated |
| Net loss | $ | (11,543) | | | $ | (109,622) | | | $ | (121,165) | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash provided by operating activities: | 184,109 | | | 0 | | | 184,109 | |
| Fair value loss on common stock warrant liabilities | 0 | | | 109,622 | | | 109,622 | |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | 172,566 | | | 0 | | | 172,566 | |
| Net cash used in investing activities | (152,582) | | | 0 | | | (152,582) | |
| Net cash used in financing activities | (26,063) | | | 0 | | | (26,063) | |
| Effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents | 166 | | | 0 | | | 166 | |
| Net change in cash and cash equivalents | (5,913) | | | 0 | | | (5,913) | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at the beginning of the year | 8,958 | | | 0 | | | 8,958 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at the end of the year | $ | 3,045 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 3,045 | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, 2018 |
| (in thousands) | As Previously Reported | | Restatement Adjustments | | As Restated |
| Net (loss) income | $ | (53,572) | | | $ | 23,830 | | | $ | (29,742) | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net (loss) income to net cash provided by operating activities: | 90,721 | | | 0 | | | 90,721 | |
| Fair value gain on common stock warrant liabilities | 0 | | | (23,830) | | | (23,830) | |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | 37,149 | | | 0 | | | 37,149 | |
| Net cash used in investing activities | (1,217,202) | | | 0 | | | (1,217,202) | |
| Net cash provided by financing activities | 1,180,037 | | | 0 | | | 1,180,037 | |
| Effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents | (211) | | | 0 | | | (211) | |
| Net change in cash and cash equivalents | (227) | | | 0 | | | (227) | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at the beginning of the year | 9,185 | | | 0 | | | 9,185 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at the end of the year | $ | 8,958 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 8,958 | |
| | | | | |
| Supplemental cash flow information: | | | | | |
| Non-cash deemed dividend related to warrant exchange | $ | 2,135 | | | $ | (2,135) | | | $ | 0 | |
The tables below set forth the unaudited condensed consolidated balance sheet and condensed consolidated statement of operations originally reported, adjustments, and the restated balances as of and for the three and nine months ended September 30, 2020 and the condensed consolidated statement of cash flow amounts originally reported, adjustments, and the restated balances for the nine months ended September 30, 2020.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| September 30, 2020 (unaudited) |
| (in thousands, except share data) | As Previously Reported | | Restatement Adjustments | | As Restated |
| Total assets | $ | 5,624,850 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 5,624,850 | |
| Liabilities and equity | | | | | |
| Total current liabilities | $ | 451,202 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 451,202 | |
| Long-term debt | 2,498,207 | | | 0 | | | 2,498,207 | |
| Deferred tax liabilities | 359,593 | | | 0 | | | 359,593 | |
| Deferred revenue and customer deposits | 11,816 | | | 0 | | | 11,816 | |
| Operating lease liabilities - non-current | 187,056 | | | 0 | | | 187,056 | |
| Common stock warrant liabilities | 0 | | | 56,724 | | | 56,724 | |
| Other non-current liabilities | 22,471 | | | 0 | | | 22,471 | |
| Long-term liabilities | 3,079,143 | | | 56,724 | | | 3,135,867 | |
| Total liabilities | 3,530,345 | | | 56,724 | | | 3,587,069 | |
| Commitments and contingencies | 0 | | 0 | | 0 |
| Common Stock: $0.0001 par, 380,000,000 shares authorized and 227,980,928 shares issued and outstanding at September 30, 2020 | 23 | | | 0 | | | 23 | |
| Additional paid-in-capital | 3,825,940 | | | 33,200 | | | 3,859,140 | |
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss | (66,283) | | | 0 | | | (66,283) | |
| Accumulated deficit | (1,665,175) | | | (89,924) | | | (1,755,099) | |
| Total shareholders' equity | 2,094,505 | | | (56,724) | | | 2,037,781 | |
| Total liabilities and equity | $ | 5,624,850 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 5,624,850 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Three Months Ended September 30, 2020 (unaudited) |
| (in thousands, except share and per share data) | As Previously Reported | | Restatement Adjustments | | As Restated |
| Operating income | $ | 25,012 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 25,012 | |
| Interest expense | 33,034 | | | 0 | | | 33,034 | |
| Fair value loss on common stock warrant liabilities | 0 | | | 22,303 | | | 22,303 | |
| Loss on extinguishment of debt | 42,401 | | | 0 | | | 42,401 | |
| Loss before income tax | (50,423) | | | (22,303) | | | (72,726) | |
| Income tax benefit | (66,675) | | | 0 | | | (66,675) | |
| Net income (loss) attributable to WillScot Mobile Mini common shareholders | $ | 16,252 | | | $ | (22,303) | | | $ | (6,051) | |
| | | | | |
| Earnings (loss) per share attributable to WillScot Mobile Mini common shareholders: | | | | | |
| Basic | $ | 0.07 | | | $ | (0.10) | | | $ | (0.03) | |
| Diluted | $ | 0.07 | | | $ | (0.10) | | | $ | (0.03) | |
| Weighted average shares: | | | | | |
| Basic | 226,649,993 | | 0 | | | 226,649,993 |
| Diluted | 231,216,573 | | (4,566,580) | | | 226,649,993 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Nine Months Ended September 30, 2020 (unaudited) |
| (in thousands, except share and per share data) | As Previously Reported | | Restatement Adjustments | | As Restated |
| Operating income | $ | 91,452 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 91,452 | |
| Interest expense | 89,810 | | | 0 | | | 89,810 | |
| Fair value gain on common stock warrant liabilities | 0 | | | (46,063) | | | (46,063) | |
| Loss on extinguishment of debt | 42,401 | | | 0 | | | 42,401 | |
| (Loss) income before income tax | (40,759) | | | 46,063 | | | 5,304 | |
| Income tax benefit | (66,170) | | | 0 | | | (66,170) | |
| Net income | 25,411 | | | 46,063 | | | 71,474 | |
| Net income attributable to non-controlling interest, net of tax | 1,213 | | | 0 | | | 1,213 | |
| Net income attributable to WillScot Mobile Mini common shareholders | $ | 24,198 | | | $ | 46,063 | | | $ | 70,261 | |
| | | | | |
| Earnings per share attributable to WillScot Mobile Mini common shareholders: | | | | | |
| Basic | $ | 0.16 | | | $ | 0.31 | | | $ | 0.47 | |
| Diluted | $ | 0.16 | | | $ | (0.01) | | | $ | 0.15 | |
| Weighted average shares: | | | | | |
| Basic | 149,283,083 | | 0 | | | 149,283,083 |
| Diluted | 152,544,647 | | (111,702) | | | 152,432,945 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Nine Months Ended September 30, 2020 (unaudited) |
| (in thousands) | As Previously Reported | | Restatement Adjustments | | As Restated |
| Net income | $ | 25,411 | | | $ | 46,063 | | | $ | 71,474 | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | 149,684 | | | 0 | | | 149,684 | |
| Fair value gain on common stock warrant liabilities | 0 | | | (46,063) | | | (46,063) | |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | 175,095 | | | 0 | | | 175,095 | |
| Net cash used in investing activities | (83,073) | | | 0 | | | (83,073) | |
| Net cash used in financing activities | (75,612) | | | 0 | | | (75,612) | |
| Effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents | 542 | | | 0 | | | 542 | |
| Net change in cash and cash equivalents | 16,952 | | | 0 | | | 16,952 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at the beginning of the period | 3,045 | | | 0 | | | 3,045 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at the end of the period | $ | 19,997 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 19,997 | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
The tables below set forth the unaudited condensed consolidated balance sheet and condensed consolidated statement of operations originally reported, adjustments, and the restated balances as of and for the three and six months ended June 30, 2020 and the condensed consolidated statement of cash flow amounts originally reported, adjustments, and the restated balances for the six months ended June 30, 2020.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| June 30, 2020 (unaudited) |
| (in thousands, except share data) | As Previously Reported | | Restatement Adjustments | | As Restated |
| Total assets | $ | 3,501,540 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 3,501,540 | |
| Liabilities and equity | | | | | |
| Total current liabilities | $ | 590,925 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 590,925 | |
| Long-term debt | 1,971,010 | | | 0 | | | 1,971,010 | |
| Deferred tax liabilities | 69,044 | | | 0 | | | 69,044 | |
| Deferred revenue and customer deposits | 12,284 | | | 0 | | | 12,284 | |
| Operating lease liabilities - non-current | 117,159 | | | 0 | | | 117,159 | |
| Common stock warrant liabilities | 0 | | | 34,421 | | | 34,421 | |
| Other non-current liabilities | 36,028 | | | 0 | | | 36,028 | |
| Long-term liabilities | 2,205,525 | | | 34,421 | | | 2,239,946 | |
| Total liabilities | 2,796,450 | | | 34,421 | | | 2,830,871 | |
| Commitments and contingencies | 0 | | 0 | | 0 |
Class A common stock: $0.0001 par, 400,000,000 shares authorized and 121,233,232 shares issued and outstanding at June 30, 2020 | 12 | | | 0 | | | 12 | |
| Additional paid-in-capital | 2,471,312 | | | 33,200 | | | 2,504,512 | |
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss | (84,807) | | | 0 | | | (84,807) | |
| Accumulated deficit | (1,681,427) | | | (67,621) | | | (1,749,048) | |
| Total shareholders' equity | 705,090 | | | (34,421) | | | 670,669 | |
| Total liabilities and equity | $ | 3,501,540 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 3,501,540 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Three Months Ended June 30, 2020 (unaudited) |
| (in thousands, except share and per share data) | As Previously Reported | | Restatement Adjustments | | As Restated |
| Operating income | $ | 41,067 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 41,067 | |
| Interest expense | 28,519 | | | 0 | | | 28,519 | |
| Fair value loss on common stock warrant liabilities | 0 | | | 26,963 | | | 26,963 | |
| Income (loss) before income tax | 12,548 | | | (26,963) | | | (14,415) | |
| Income tax benefit | (285) | | | 0 | | | (285) | |
| Net income (loss) | 12,833 | | | (26,963) | | | (14,130) | |
| Net income attributable to non-controlling interest, net of tax | 1,343 | | | 0 | | | 1,343 | |
| Net income (loss) attributable to WillScot Mobile Mini common shareholders | $ | 11,490 | | | $ | (26,963) | | | $ | (15,473) | |
| | | | | |
| Earnings (loss) per share attributable to WillScot Mobile Mini common shareholders: | | | | | |
| Basic | $ | 0.10 | | | $ | (0.24) | | | $ | (0.14) | |
| Diluted | $ | 0.10 | | | $ | (0.24) | | | $ | (0.14) | |
| Weighted average shares: | | | | | |
| Basic | 110,692,426 | | 0 | | | 110,692,426 |
| Diluted | 111,432,963 | | (740,537) | | | 110,692,426 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Six Months Ended June 30, 2020 (unaudited) |
| (in thousands, except share and per share data) | As Previously Reported | | Restatement Adjustments | | As Restated |
| Operating income | $ | 66,440 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 66,440 | |
| Interest expense | 56,776 | | | 0 | | | 56,776 | |
| Fair value gain on common stock warrant liabilities | 0 | | | (68,366) | | | (68,366) | |
| Income before income tax | 9,664 | | | 68,366 | | | 78,030 | |
| Income tax benefit | 505 | | | 0 | | | 505 | |
| Net income | 9,159 | | | 68,366 | | | 77,525 | |
| Net income attributable to non-controlling interest, net of tax | 1,213 | | | 0 | | | 1,213 | |
| Net income attributable to WillScot Mobile Mini common shareholders | $ | 7,946 | | | $ | 68,366 | | | $ | 76,312 | |
| | | | | |
| Earnings per share attributable to WillScot Mobile Mini common shareholders: | | | | | |
| Basic | $ | 0.07 | | | $ | 0.62 | | | $ | 0.69 | |
| Diluted | $ | 0.07 | | | $ | (0.01) | | | $ | 0.06 | |
| Weighted average shares: | | | | | |
| Basic | 110,174,536 | | 0 | | | 110,174,536 |
| Diluted | 112,209,212 | | 126,906 | | | 112,336,118 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Six Months Ended June 30, 2020 (unaudited) |
| (in thousands) | As Previously Reported | | Restatement Adjustments | | As Restated |
| Net income | $ | 9,159 | | | $ | 68,366 | | | $ | 77,525 | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | 104,568 | | | 0 | | | 104,568 | |
| Fair value gain on common stock warrant liabilities | 0 | | | (68,366) | | | (68,366) | |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | 113,727 | | | 0 | | | 113,727 | |
| Net cash used in investing activities | (66,923) | | | 0 | | | (66,923) | |
| Net cash provided by financing activities | 614,693 | | | 0 | | | 614,693 | |
| Effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents | (394) | | | 0 | | | (394) | |
| Net change in cash and cash equivalents | 661,103 | | | 0 | | | 661,103 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at the beginning of the period | 3,045 | | | 0 | | | 3,045 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at the end of the period | $ | 664,148 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 664,148 | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
The tables below set forth the unaudited condensed consolidated balance sheet and condensed consolidated statement of operations originally reported, adjustments, and the restated balances as of and for the three months ended March 31, 2020 and the condensed consolidated statement of cash flow amounts originally reported, adjustments, and the restated balances for the three months ended March 31, 2020.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| March 31, 2020 (unaudited) |
| (in thousands, except share data) | As Previously Reported | | Restatement Adjustments | | As Restated |
| Total assets | $ | 2,857,737 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 2,857,737 | |
| Liabilities and equity | | | | | |
| Total current liabilities | $ | 313,284 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 313,284 | |
| Long-term debt | 1,625,772 | | | 0 | | | 1,625,772 | |
| Deferred tax liabilities | 67,017 | | | 0 | | | 67,017 | |
| Deferred revenue and customer deposits | 12,666 | | | 0 | | | 12,666 | |
| Operating lease liabilities - non-current | 119,322 | | | 0 | | | 119,322 | |
| Common stock warrant liabilities | 0 | | | 34,049 | | | 34,049 | |
| Other non-current liabilities | 38,603 | | | 0 | | | 38,603 | |
| Long-term liabilities | 1,863,380 | | | 34,049 | | | 1,897,429 | |
| Total liabilities | 2,176,664 | | | 34,049 | | | 2,210,713 | |
| Commitments and contingencies | 0 | | 0 | | 0 |
Class A common stock: $0.0001 par, 400,000,000 shares authorized and 110,555,295 shares issued and outstanding at March 31, 2020 | 11 | | | 0 | | | 11 | |
| Class B common stock: $0.0001 par, 100,000,000 shares authorized and 8,024,419 shares issued and outstanding at March 31, 2020 | 1 | | | 0 | | | 1 | |
| Additional paid-in-capital | 2,402,195 | | | 6,610 | | | 2,408,805 | |
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss | (89,974) | | | 0 | | | (89,974) | |
| Accumulated deficit | (1,692,917) | | | (40,659) | | | (1,733,576) | |
| Total shareholders' equity | 619,316 | | | (34,049) | | | 585,267 | |
| Non-controlling interest | 61,757 | | | 0 | | | 61,757 | |
| Total equity | 681,073 | | | (34,049) | | | 647,024 | |
| Total liabilities and equity | $ | 2,857,737 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 2,857,737 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Three Months Ended March 31, 2020 (unaudited) |
| (in thousands, except share and per share data) | As Previously Reported | | Restatement Adjustments | | As Restated |
| Operating income | $ | 25,373 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 25,373 | |
| Interest expense | 28,257 | | | 0 | | | 28,257 | |
| Fair value gain on common stock warrant liabilities | 0 | | | (95,329) | | | (95,329) | |
| (Loss) income before income tax | (2,884) | | | 95,329 | | | 92,445 | |
| Income tax benefit | 790 | | | 0 | | | 790 | |
| Net (loss) income | (3,674) | | | 95,329 | | | 91,655 | |
| Net loss attributable to non-controlling interest, net of tax | (130) | | | 0 | | | (130) | |
| Net (loss) income attributable to WillScot Mobile Mini common shareholders | $ | (3,544) | | | $ | 95,329 | | | $ | 91,785 | |
| | | | | |
| (Loss) earnings per share attributable to WillScot Mobile Mini common shareholders: | | | | | |
| Basic | $ | (0.03) | | | $ | 0.87 | | | $ | 0.84 | |
| Diluted | $ | (0.03) | | | $ | (0.02) | | | $ | (0.05) | |
| Weighted average shares: | | | | | |
| Basic | 109,656,646 | | 0 | | 109,656,646 |
| Diluted | 109,656,646 | | 3,016,351 | | 112,672,997 |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Three Months Ended March 31, 2020 (unaudited) |
| (in thousands) | As Previously Reported | | Restatement Adjustments | | As Restated |
| Net (loss) income | $ | (3,674) | | | $ | 95,329 | | | $ | 91,655 | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net (loss) income to net cash provided by operating activities: | 42,022 | | | 0 | | | 42,022 | |
| Fair value gain on common stock warrant liabilities | 0 | | | (95,329) | | | (95,329) | |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | 38,348 | | | 0 | | | 38,348 | |
| Net cash used in investing activities | (30,540) | | | 0 | | | (30,540) | |
| Net cash used in financing activities | (5,582) | | | 0 | | | (5,582) | |
| Effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents | (629) | | | 0 | | | (629) | |
| Net change in cash and cash equivalents | 1,597 | | | 0 | | | 1,597 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at the beginning of the period | 3,045 | | | 0 | | | 3,045 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at the end of the period | $ | 4,642 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 4,642 | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
Accounting Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the amounts reported in these consolidated financial statements and accompanying notes. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
The Company considers all highly liquid instruments with a maturity of three months or less when purchased to be cash equivalents.
Trade Receivables and Allowance for Credit Losses
The Company is exposed to credit losses from trade receivables generated through its leasing and sales business. The Company assesses each customer’s ability to pay for the products it leases or sells by conducting a credit review. The credit review considers expected billing exposure and timing for payment and the customer’s established credit rating. The Company performs its credit review of new customers at inception of the customer relationship and for existing customers when the customer transacts new leases after a defined period of dormancy. The Company also considers contract terms and conditions, country risk and business strategy in the evaluation.
The Company monitors ongoing credit exposure through an active review of customer balances against contract terms and due dates. The Company may employ collection agencies and legal counsel to pursue recovery of defaulted receivables. The allowances for credit losses reflect the estimate of the amount of receivables that the Company will be unable to collect based on historical write-off experience and, as applicable, current conditions and reasonable and supportable forecasts that affect collectability. This estimate could require change based on changing circumstances, including changes in the economy or in the particular circumstances of individual customers. Accordingly, the Company may be required to increase or decrease our allowances.
In accordance with the adoption of Accounting Standards Update ("ASU") 2016-2, Leases (Topic 842) ("ASC 842"), effective January 1, 2019, and the adoption of ASU 2016-13, Financial Instruments - Credit Losses (Topic 326) ("ASC 326"), effective January 1, 2020, specifically identifiable lease revenue receivables and sales receivables not deemed probable of collection are recorded as a reduction of revenue. The remaining provision for credit losses is recorded as selling, general and administrative expense. For the year ended December 31, 2018, the entire provision for credit losses was recorded as a selling, general and administrative expense. The Company reviews the adequacy of the allowance on a quarterly basis.
Activity in the allowance for credit losses for the years ended December 31 was as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands) | 2020 | | 2019 | | 2018 |
| Balance at beginning of year | $ | 15,828 | | | $ | 9,340 | | | $ | 4,845 | |
Provision for credit losses, net of recoveries(a) | 31,386 | | | 14,496 | | | 7,656 | |
| Write-offs | (18,034) | | | (7,945) | | | (3,089) | |
| Foreign currency translation and other | 78 | | | (63) | | | (72) | |
| Balance at end of period | $ | 29,258 | | | $ | 15,828 | | | $ | 9,340 | |
(a) For the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, the provision for credit losses includes $18.0 million and $10.0 million, respectively, recorded as a reduction to revenue for the provision of specific receivables whose collection is not considered probable.
Concentration of Credit Risk
The Company’s trade accounts receivable subject the Company to potential concentrations of credit risk. The Company performs on-going credit evaluations of its customers. Receivables related to sales are generally secured by the product sold to the customer. The Company generally has the right to repossess its rental units in the event of non-payment of receivables relating to the Company’s leasing operations. The Company’s large number of customers in diverse geographic areas and end markets mitigates the concentration of credit risk. No single customer accounted for more than 1.2% and 1.5% of the Company’s receivables at December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively. The Company’s top five customers accounted for 4.9% and 4.1% of the receivables at December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively.
Inventories
Inventories consist of raw materials, supplies, and finished units. Inventories are measured at the lower of cost or net realizable value based on the weighted-average cost. The cost includes expenditures incurred in acquiring the inventories, production or conversion costs, and other costs incurred in bringing them to their existing location and condition.
Rental Equipment
Rental equipment is comprised of modular space and portable storage units held for rent or on rent to customers, tank and pump solutions products, which consist primarily of liquid and solid containment units, pumps and filtration equipment, and value-added products and services (“VAPS”) which are in use or available to be used by customers. Rental equipment is measured at cost less accumulated depreciation and impairment losses. Cost includes expenditures that are directly attributable to the acquisition of the asset. Costs of improvements and betterments to rental equipment are capitalized when such costs extend the useful life of the equipment or increase the rental value of the unit. Costs incurred for equipment to meet a particular customer specification are capitalized and depreciated over the lease term taking in consideration the residual value of the asset. Maintenance and repair costs are expensed as incurred.
Depreciation is generally computed using the straight-line method over estimated useful lives, as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Estimated Useful Life | | Residual Value |
| Modular space units | 10 - 20 years | | 20 - 50% |
| Portable storage units | 30 years | | 55% |
| Tank and pump equipment | 7 - 25 years | | 0% |
| VAPS and other related rental equipment | 1 - 8 years | | 0% |
Property, Plant and Equipment
Property, plant and equipment is measured at cost less accumulated depreciation and impairment losses.
The Company capitalizes external costs and directly attributable internal costs to acquire or create internal use software incurred subsequent to the completion of the preliminary project stage. Costs associated with post-implementation activities are expensed as incurred. The Company evaluates implementation costs incurred in a cloud computing arrangement that is a service contract as described in Cloud Computing Arrangements below.
Land is not depreciated. Leasehold improvements are amortized over the shorter of 15 years or the lease term. Assets leased under capital leases are depreciated over the shorter of the lease term or their useful life, unless it is reasonably certain that the Company will obtain ownership by the end of the lease term. Maintenance and repair costs are expensed as incurred.
Depreciation is generally computed using the straight-line method over estimated useful lives as follows:
| | | | | |
| Estimated Useful Life |
| Buildings and leasehold improvements | 10 - 40 years (a) |
| Vehicles, machinery, and equipment | 3 - 30 years |
| Furniture and fixtures | 3 - 10 years |
| Software | 3 - 10 years |
(a) Improvements to leased properties are depreciated over the lesser of the estimated useful life of the asset or the remaining term of the respective lease.
Held for Sale
Property, plant and equipment to be sold is classified as held for sale in the period in which: (i) the Company has approved and committed to a plan to sell the asset, (ii) the asset is available for immediate sale in its present condition, (iii) an active program to locate a buyer and other actions required to sell the asset have been initiated, (iv) the sale of the asset is probable, (v) the asset is being actively marketed for sale at a price that is reasonable in relation to its current fair value, and (vi) it is unlikely that significant changes to the plan will be made or that the plan will be withdrawn.
Assets held for sale are initially measured at the lower of the carrying value or the fair value less cost to sell. Losses resulting from this measurement are recognized in the period in which the held for sale criteria are met while gains are not recognized until the date of sale. Once designated as held for sale, the Company stops recording depreciation expense on the asset. The Company assesses the fair value less cost to sell of long-lived assets held for sale at each reporting period until the assets no longer meet this classification.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
When circumstances indicate the carrying amount of long-lived assets in a held-for-use asset group may not be recoverable, the Company evaluates the assets for potential impairment using internal projections of undiscounted cash flows resulting from the use and eventual disposal of the assets. Events or changes in circumstances that may necessitate a recoverability evaluation include, but are not limited to, adverse changes in the regulatory environment or an expectation it is more likely than not that the asset will be disposed of before the end of its previously estimated useful life. If the carrying amount of the assets exceeds the undiscounted cash flows, an impairment expense is recognized for the amount by which the carrying amount of the asset group exceeds its fair value (subject to the carrying amount not being reduced below fair value for any individual long-lived asset that is determinable without undue cost and effort).
Consistent with the provisions of ASC 842, the Company assesses whether any operating lease asset impairment exists in accordance with the measurement guidance in Accounting Standard Codification ("ASC") 360, Property Plant and Equipment.
Cloud Computing Arrangements
In accordance with ASU 2018-15, Goodwill and Other – Internal-Use Software (Subtopic 350-40) (“ASC 350-40"), the Company evaluates implementation costs incurred in a cloud computing arrangement that is a service contract under the internal-use software framework. Costs related to preliminary project activities and post implementation activities are expensed as incurred. Costs incurred in the development stage are generally capitalized as other assets. Amortization expense is calculated on a straight-line basis over the contractual term of the cloud computing arrangement and recorded as selling, general and administrative expense. Capitalized implementation costs for cloud computing arrangements totaled $4.0 million at December 31, 2020. The comparative financial statement information has not been restated and continues to be reported under the accounting standards in effect for those periods. The adoption of the guidance did not have a material impact on the Company's consolidated balance sheet as of January 1, 2020.
Goodwill and Goodwill Impairment
For acquired businesses, the Company records assets acquired and liabilities assumed at their estimated fair values on the respective acquisition dates. Based on these values, the excess purchase price over the fair value of the net assets acquired is recorded as goodwill. Generally, reporting units are at the operating segment level or one level below the operating segment (the component level), if discrete financial information is prepared and regularly reviewed by segment management.
Goodwill acquired in a business combination is assigned to each of the Company’s reporting units that are expected to benefit from the combination.
The Company performs its annual impairment test of goodwill as of October 1 at the reporting unit level, as well as during any reporting period in which events or changes in circumstances occur that, in management’s judgment, may constitute triggering events under ASC 350-20, Intangibles – Goodwill and Other, Testing Goodwill for Impairment. The Company performs its assessment of goodwill utilizing either a qualitative or quantitative impairment test. The qualitative impairment test assesses company-specific, industry, market and general economic factors to determine whether it is more likely than not that the fair value of the reporting unit is less than its carrying amount. If the Company concludes that it is more likely than not that the fair value of the reporting unit is less than its carrying amount, or elects not to use the qualitative impairment test, a quantitative impairment test is performed. The quantitative impairment test involves a comparison of the estimated fair value of a reporting unit to its carrying amount. The Company uses an independent valuation specialist for its annual impairment tests to assist in the valuation.
The Company has historically used the quantitative impairment test to evaluate goodwill for impairment. The Company used the qualitative approach for the reporting units acquired in the Merger due to the proximity of the July 1, 2020 acquisition date to the October 1, 2020 measurement date.
Determining the fair value of a reporting unit is judgmental in nature and involves the use of significant estimates and assumptions. These estimates and assumptions include revenue growth rates and operating margins used to calculate projected future cash flows, risk-adjusted discount rates, value of net operating losses, future economic and market conditions and determination of appropriate market comparables. Management bases fair value estimates on assumptions it believes to be reasonable but that are unpredictable and inherently uncertain. Actual future results may differ from these estimates.
If the carrying amount of the reporting unit exceeds the calculated fair value of the reporting unit, an impairment charge would be recognized for the excess, not to exceed the amount of goodwill allocated to that reporting unit.
Intangible Assets Other than Goodwill
Intangible assets that are acquired by the Company and determined to have an indefinite useful life are not amortized but are tested for impairment at least annually. The Company’s indefinite-lived intangible assets consist of the Williams Scotsman trade name and the Mobile Mini trade name. The Company performs its assessment of indefinite-lived intangible assets utilizing either a qualitative or quantitative impairment test. When utilizing a quantitative impairment test, the Company calculates fair value using a relief-from-royalty method. This method is used to estimate the cost savings that accrue to the owner of an intangible asset who would otherwise have to pay royalties or license fees on revenues earned through the use of the asset. If the carrying amount of the indefinite-lived intangible asset exceeds its fair value, an impairment charge would be recorded to the extent the recorded indefinite-lived intangible asset exceeds the fair value.
Other intangible assets that have finite useful lives are measured at cost less accumulated amortization and impairment losses, if any. Amortization is recognized in profit or loss over the estimated useful lives of the intangible asset.
Purchase Accounting
The Company accounts for acquisitions of businesses under the acquisition method. Under the acquisition method of accounting, the Company records assets acquired and liabilities assumed at their estimated fair value on the date of acquisition. Goodwill is measured as the excess of the fair value of the consideration transferred over the fair value of the identifiable net assets. Estimated fair values of acquired assets and liabilities are provisional and could change as additional information is received. When appropriate, our estimates of the fair values of assets and liabilities acquired include assistance from independent third-party valuation firms. Valuations are finalized as soon as practicable, but not later than one year from the acquisition date. Any subsequent changes to purchase price allocations result in a corresponding adjustment to goodwill.
Long-lived assets (principally rental equipment), goodwill and other intangible assets generally represent the largest components of our acquisitions. Rental equipment is valued utilizing a replacement cost approach. Intangible assets are recognized at their estimated fair values as of the date of acquisition and generally consist of customer relationships and trade names. Determination of the estimated fair value of intangible assets requires judgment. The estimated fair value of customer relationships is determined based on estimates and judgments regarding discounted future after-tax earnings and cash flows arising from lease renewals and new lease arrangements expected from customer relationships. The fair value of trade name intangible assets is determined utilizing the relief from royalty method. Under this form of the income approach, a royalty rate based on observed market royalties is applied to projected revenue supporting the trade name and discounted to present value.
Debt Issuance Costs
Debt issuance costs are recorded as direct deductions to the corresponding debt in long-term debt on the consolidated balance sheets. If no amounts are outstanding under the Company’s credit agreement as of a period end, the related debt issuance costs are recorded in other non-current assets in the consolidated balance sheets. Debt issuance costs are deferred and amortized to interest expense over the term of the respective debt using the effective interest method or straight-line interest method as appropriate.
Retirement Benefit Obligation
The Company provides benefits to certain of its employees under defined contribution benefit plans. The Company’s contributions to these plans are generally based on a percentage of employee compensation or employee contributions. These plans are funded on a current basis. For its US and Canada employees, the Company sponsors defined contribution benefit plans that have discretionary matching contribution and profit-sharing features. For the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018, the Company made matching contributions of $7.1 million, $5.4 million and $3.8 million to these plans, respectively.
Stock-Based Compensation
Prior to the Merger, stock awards were granted under the WillScot Corporation 2017 Incentive Award Plan (the "2017 Incentive Plan"), which included Restricted Stock Awards ("RSAs") and Restricted Stock Units ("RSUs"). On June 24, 2020, WillScot's stockholders approved the WillScot Mobile Mini 2020 Incentive Award Plan ("2020 Incentive Plan") to take effect pending completion of the Merger. The plan amended and restated in its entirety the 2017 Incentive Plan. As a result, all historical and future incentive awards to the Company's Board of Directors, executive officers and employees, as determined by the Company's Compensation Committee ("the Comp Committee"), are granted under the 2020 Incentive Plan. The 2020 Incentive Plan is administered by the Comp Committee. Under the 2020 Incentive Plan, the Comp Committee may grant an aggregate of 6,488,988 shares of Common Stock in the form of non-qualified stock options, incentive stock options, stock appreciation rights, RSAs, RSUs, performance compensation awards and stock bonus awards. Stock-based payments, including the grant of stock options, RSAs and RSUs, are subject to service-based vesting requirements, and expense is recognized on a straight-line basis over the vesting period. Forfeitures are accounted for as they occur.
Stock-based compensation expense includes grants of stock options, time-based RSUs ("Time-Based RSUs") and performance-based RSUs ("Performance-Based RSUs", together with Time-Based RSUs, the "RSUs"). The 2020 Incentive Plan continues the former Market-Based RSUs renamed as "Performance-Based RSUs." RSUs are recognized in the financial statements based on their fair value. In addition, stock-based payments to non-executive directors include grants of RSAs. Time-Based RSUs and RSAs are valued based on the intrinsic value of the difference between the exercise price, if any, of the award and the fair market value of WillScot Mobile Mini's Common Stock on the grant date. Performance-Based RSUs are valued based on a Monte Carlo simulation model to reflect the impact of the Performance-Based RSUs market condition. The probability of satisfying a market condition is considered in the estimation of the grant-date fair value for Performance-Based RSUs and the compensation cost is not reversed if the market condition is not achieved, provided the requisite service has been provided.
RSAs cliff vest in a one year period. Time-Based RSUs vest ratably over a period of four years. Performance-Based RSUs cliff vest based on achievement of the relative total stockholder return ("TSR") of the Company's Common Stock as compared to the TSR of the constituents of the Russell 3000 Index at the grant date over the performance period of three years. The target number of RSUs may be adjusted from 0% to 150% based on the TSR attainment levels defined by the Comp Committee. The 100% target payout is tied to performance at the 50% percentile, with a payout curve ranging from 0% (for performance less than the 25% percentile) to 150% (for performance at or above the 75% percentile). Vesting is also subject to continued service requirements through the vesting date.
Stock options vest in tranches over a period of four years and expire ten years from the grant date. The fair value of each stock option award on the grant date is estimated using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model with the following assumptions: expected dividend yield, expected stock price volatility, weighted-average risk-free interest rate and weighted-average expected term of the options. The volatility assumption used in the Black-Scholes option-pricing model was based on a blend of peer group volatility and Company trading history as the Company did not have a sufficient trading history as a stand-alone public company. Future calculations will use the Company trading history. Additionally, due to an insufficient history with respect to stock option activity and post-vesting cancellations, the expected term assumption is based on the simplified method under GAAP, which is based on the vesting period and contractual term for each tranche of awards. The mid-point between the weighted-average vesting term and the expiration date is used as the expected term under this method. The risk-free interest rate used in the Black-Scholes option-pricing model is based on the implied US Treasury bill yield curve at the date of grant with a remaining term equal to the Company’s expected term assumption. WillScot Mobile Mini has never declared or paid a cash dividend on common shares.
Foreign Currency Translation and Transactions
The Company’s reporting currency is the US Dollar (“USD”). Exchange rate adjustments resulting from foreign currency transactions are recognized in profit or loss, whereas effects resulting from the translation of financial statements are reflected as a component of accumulated other comprehensive loss, which is a component of shareholders’ equity.
The assets and liabilities of subsidiaries whose functional currency is different from the USD are translated into USD at exchange rates at the reporting date and income and expenses are translated using average exchange rates for the respective period.
Exchange rate adjustments resulting from transactions in foreign currencies (currencies other than the Company entities’ functional currencies) are remeasured to the respective functional currencies using exchange rates at the dates of the transactions and are recognized in currency (gains) losses on the consolidated statements of operations.
Foreign exchange gains and losses arising from a receivable or payable to a consolidated Company entity, the settlement of which is neither planned nor anticipated in the foreseeable future, are considered to form part of a net investment in the Company entity and are included within accumulated other comprehensive loss.
Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities
The Company utilizes derivative financial instruments, specifically interest rate swaps, to manage its exposure to fluctuations in interest rates on variable rate debt. The Company does not use derivatives for trading or speculative purposes.
The Company records derivatives on the balance sheet at fair value within prepaid expenses and other current assets and other non-current assets (if in an unrealized gain position) or within accrued liabilities and other non-current liabilities (if in an unrealized loss position). If a derivative is designated as a cash flow hedge and meets the highly effective threshold, the changes in the fair value of derivatives are recorded in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss). Amounts reported in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) related to the cash flow hedges are reclassified to earnings within interest expense when the hedged item impacts earnings. For any derivative instruments not designated as hedging instruments, changes in fair value would be recognized in earnings within interest expense in the period that the change occurs. Cash flows from derivative instruments are presented within net cash provided by operating activities in the consolidated statements of cash flows. The Company assesses, both at the inception of the hedge and on an ongoing quarterly basis, whether the derivatives designated as cash flow hedges are highly effective in offsetting the changes in cash flows of the hedged items.
The use of derivative financial instruments carries certain risks, including the risk that the counterparties to these contractual arrangements are not able to perform under the agreements. To mitigate this risk, the Company enters into derivative financial instruments only with counterparties with high credit ratings and with major financial institutions. The Company does not anticipate that any of the counterparties will fail to meet their obligations.
Revenue Recognition
A performance obligation is a promise in a contract to transfer a distinct good or service to the customer. A contract’s transaction price is allocated to each distinct performance obligation and recognized as revenue when, or as, the performance obligation is satisfied.
Leasing and Services Revenue
The majority of revenue is generated by rental income subject to the guidance of ASC 840, Leases ("ASC 840") in 2018 and ASC 842 in 2019 and 2020. The remaining revenue is generated by performance obligations in contracts with customers for services or sale of units subject to the guidance in ASC 605, Revenue ("ASC 605"), in 2018 and Accounting Standards Update ("ASU") 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606) ("ASC 606") in 2019 and 2020.
Leasing Revenue
Income from operating leases is recognized on a straight-line basis over the lease term. The Company's lease arrangements can include multiple lease and non-lease components. Examples of lease components include, but are not limited to, the lease of modular space, portable storage units and VAPS. Examples of non-lease components include, but are not limited to, the delivery, installation, maintenance, and removal services commonly provided in a bundled transaction with the lease components. Arrangement consideration is allocated between lease deliverables and non-lease components based on the relative estimated selling (leasing) price of each deliverable. Estimated selling (leasing) price of the lease deliverables is based upon the estimated stand-alone selling price of the related performance obligations using an adjusted market approach.
When leases and services are billed in advance, recognition of revenue is deferred until services are rendered. If equipment is returned prior to the contractually obligated period, the excess, if any, between the amount the customer is contractually required to pay over the cumulative amount of revenue recognized to date is recognized as incremental revenue upon return.
Rental equipment is leased primarily under operating leases and, from time to time, under sales-type lease arrangements. Operating lease minimum contractual terms within the NA Modular segment, as defined in Note 20, generally range from 1 month to 60 months and averaged approximately 9 months across this segment's rental fleet for the year ended December 31, 2020. Rental contracts with customers within the NA Storage and UK Storage segments are generally based on a 28-day rate and billing cycle. The rental continues until cancelled by the Company or the customer. There were no material sales-type lease arrangements as of December 31, 2020 or 2019.
The Company may use third parties to satisfy its performance obligations, including both the provision of rental units and other services. To determine whether it is the principal or agent in the arrangement, the Company reviews each third-party relationship on a contract-by-contract basis. The Company is considered an agent when its role is to arrange for another entity to provide the rental units and other services to the customer. In these instances, the Company does not control the rental unit or service before it is provided. The Company is considered the principal when it controls the rental unit or service prior to transferring control to the customer. WillScot Mobile Mini may be a principal in the fulfillment of some rental units and services and an agent for other rental units and services within the same contract. Revenue is recognized on a gross basis when the Company is the principal in the arrangement and on a net basis when it is the agent.
The adoption of ASC 842 at January 1, 2019, did not have a significant impact on the recognition of leasing revenue. Based on the requirements of ASC 842, the Company records changes in estimated collectability, directly against leasing revenue.
Services Revenue
The Company generally has three non-lease service-related performance obligations in its contracts with customers:
•Delivery and installation of the modular or portable storage unit;
•Maintenance and other ad hoc services performed during the lease term; and
•Removal services that occur at the end of the lease term.
Consideration is allocated to each of these performance obligations within the contract based upon their estimated relative standalone selling prices using the estimated cost plus a margin approach. Revenue from these activities is recognized as the services are performed.
Sales Revenue
Sales revenue is generated by the sale of new and rental units. Revenue from the sale of new and rental units is generally recognized at a point in time upon the transfer of control to the customer, which occurs when the unit is delivered and installed in accordance with the contract. Sales transactions constitute a single performance obligation.
Other Matters
The Company's non-lease revenues do not include material amounts of variable consideration, other than the variability noted for services arrangements expected to be performed beyond a twelve-month period.
The Company's payment terms vary by the type and location of its customer and the product or services offered. The time between invoicing and when payment is due is not significant. While the Company may bill certain customers in advance, its contracts do not contain a significant financing component based on the short length of time between upfront billings and the performance of contracted services. For certain products, services, or customer types, the Company requires payment before the products or services are delivered to the customer.
Revenue is recognized net of taxes collected from customers, which are subsequently remitted to governmental authorities.
Leases as Lessee
The Company leases real estate for certain of its branch offices, administrative offices, rental equipment storage properties, vehicles and equipment, and administrative operations. The Company determines if an arrangement is or contains a lease at inception. Leases are classified as either finance or operating at inception of the lease, with classification affecting the pattern of expense recognition in the income statement. Short-term leases, defined as leases with an initial term of 12 months or less, are not recorded on the balance sheet. Lease expense for short-term leases is recognized on a straight-line basis over the lease term.
The Company has leases that contain both lease and non-lease components and has elected, as an accounting policy, to not separate lease components and non-lease components. Operating and finance lease right of use ("ROU") assets and liabilities are recognized at the commencement date based on the present value of lease payments over the lease term. The lease liability is calculated as the present value of the remaining minimum rental payments for existing leases using either the rate implicit in the lease or, if none exists, the Company's incremental borrowing rate, as the discount rate. The Company uses its incremental borrowing rate at commencement date in determining the present value of lease payments for those leases where the implicit rate is not known. The Company's incremental borrowing rate is a hypothetical rate based on its understanding of what would be the Company's secured credit rating. Variable lease payments are expensed in the period in which the obligation for those payments is incurred. Variable lease payments include payments for common area maintenance, real estate taxes, management fees and insurance.
Many of the Company’s real estate lease agreements include options to extend the lease, which are not included in the minimum lease terms unless the Company is reasonably certain it will exercise the option. Many of these leases include one or more options to renew. Additionally, the Company’s leases do not generally include options to terminate the lease prior to the end of the lease term. The Company’s lease agreements do not contain any material residual value guarantees or material restrictive covenants.
Advertising and Promotion
Advertising and promotion costs, which are expensed as incurred, were $7.3 million, $4.0 million and $4.4 million for the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018, respectively.
Shipping Costs
The Company includes third-party costs to deliver rental equipment to customers in costs of leasing and services, and cost of sales.
Income Taxes
The Company accounts for income taxes under the asset and liability method, which requires the recognition of deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future tax consequences of events that have been included in the financial statements. Under this method, deferred tax assets and liabilities are determined based on the differences between the financial statement and tax basis of assets and liabilities using enacted tax rates in effect for the year in which the differences
are expected to reverse. The effect of a change in tax rates on deferred tax assets and liabilities is recognized in income in the period that includes the enactment date.
The Company records deferred tax assets to the extent it believes that it is more likely than not that these assets will be realized. In making such determination, the Company considers all available positive and negative evidence, including scheduled reversals of deferred tax liabilities, projected future taxable income, tax planning strategies and recent results of operations. Valuation allowances are recorded to reduce the deferred tax assets to an amount that will more likely than not be realized.
The Company assesses the likelihood that each of the deferred tax assets will be realized. To the extent management believes realization of any deferred tax assets is not likely, the Company establishes a valuation allowance. When a valuation allowance is established or there is an increase in an allowance in a reporting period, tax expense is generally recorded in the Company’s consolidated statement of operations. Conversely, to the extent circumstances indicate that a valuation allowance is no longer necessary, that portion of the valuation allowance is reversed, which generally reduces the Company’s income tax expense.
Deferred tax liabilities are recognized for the income taxes on the undistributed earnings of wholly-owned foreign subsidiaries unless such earnings are indefinitely reinvested, or will only be repatriated when possible to do so at minimal additional tax cost. Current income tax relating to items recognized directly in equity is recognized in equity and not in profit (loss) for the year.
In accordance with applicable authoritative guidance, the Company accounts for uncertain income tax positions using a benefit recognition model with a two-step approach; a more-likely-than-not recognition criterion; and a measurement approach that measures the position as the largest amount of tax benefit that is greater than 50% likely of being realized upon ultimate settlement. If it is not more-likely-than-not that the benefit of the tax position will be sustained on its technical merits, no benefit is recorded. Uncertain tax positions that relate only to timing of when an item is included on a tax return are considered to have met the recognition threshold. The Company classifies interest on tax deficiencies and income tax penalties within income tax expense.
The Company accounts for any impacts of the Global Intangible Low-Taxed Income ("GILTI") in the period in which they are incurred.
Fair Value Measurements
The Company maximizes the use of observable inputs and minimizes the use of unobservable inputs when measuring fair value. A financial instrument’s categorization within the fair value hierarchy is based upon the lowest level of input that is significant to the fair value measurement. The inputs are prioritized into three levels that may be used to measure fair value. See further discussion of the levels in Note 16.
Warrants
The Company accounts for warrants in accordance with applicable accounting guidance provided in ASC 815-40, as either derivative liabilities or as equity instruments depending on the specific terms of the warrant agreements. In periods subsequent to issuance, warrants classified as liabilities are subject to remeasurement at each balance sheet date and transaction date with changes in the estimated fair values of the common stock warrant liabilities and gains and losses on extinguishment of common stock warrant liabilities reported in the consolidated statements of operations.
The Company accounts for its warrants in the following ways: (i) the 2015 Private Warrants as liabilities for all periods presented, (ii) the 2015 Public Warrants as liabilities through their final redemption in February 2020 and (iii) the 2018 Warrants as liabilities until June 30, 2020, the date all issued and outstanding shares of the Company's Class B Common Stock were cancelled.
Prior to their redemption, the Company's 2015 Public Warrants traded in active markets. When classified as liabilities, warrants traded in active markets with sufficient trading volume represent Level 1 financial instruments as they were publicly traded in active markets and thus had observable market prices which were used to estimate the fair value adjustments for the related common stock warrant liabilities. When classified as liabilities, warrants not traded in active markets, or traded with insufficient volume, represent Level 3 financial instruments that are valued using a Black-Scholes option-pricing model to estimate the fair value adjustments for the related common stock warrant liabilities.
Recently Issued and Adopted Accounting Standards
The Company qualified as an emerging growth company (“EGC”) as defined under the Jumpstart Our Business Startups Act (the “JOBS Act”) until December 31, 2019. Using exemptions provided under the JOBS Act, the Company elected to defer compliance with new or revised financial accounting standards until a company that is not an issuer (as defined under section 2(a) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act) was required to comply with such standards. WillScot ceased to be an EGC as of December 31, 2019, and as such, is required to comply with the standards and compliance dates for large accelerated filers.
Recently Issued Accounting Standards
In December 2019, the Financial Accounting Standards Board ("FASB") issued ASU 2019-12, Income Taxes (Topic 740): Simplifying the Accounting for Income Taxes, which simplifies the accounting for income taxes by removing certain exceptions to the general principles for income taxes. The new standard is effective for fiscal years and interim periods within
those fiscal years, beginning after December 15, 2020. The Company is currently evaluating the potential impact of adoption of the pronouncement on its consolidated financial statements and does not expect the impact to be material.
In March 2020, the FASB issued ASU 2020-04, Reference Rate Reform (Topic 848), which is elective, and provides for optional expedients and exceptions for applying GAAP to contracts, hedging relationships, and other transactions affected by reference rate reform if certain criteria are met. The Company is currently evaluating the impact of reference rate reform and potential impact of adoption of these elective practical expedients on its consolidated financial statements and does not expect the impact to be material.
In August 2020, the FASB issued ASU 2020-06, Debt, Debt with Conversion and Other Options (Subtopic 470-20) and Derivatives and Hedging – Contracts in Entity’s Own Equity (Subtopic 815-40). The new ASU eliminates the beneficial conversion and cash conversion accounting models for convertible instruments. It also amends the accounting for certain contracts in an entity’s own equity that are currently accounted for as derivatives because of specific settlement provisions. In addition, the new guidance modifies how particular convertible instruments and certain contracts that may be settled in cash or shares impact the diluted EPS computation. The amendments in the ASU are effective for public entities for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2021, including interim periods within those fiscal years. The Company is currently evaluating the potential impact of the adoption of the pronouncement on its consolidated financial statements.
Recently Adopted Accounting Standards
From time to time, new accounting pronouncements are issued by the FASB or other standard setting bodies that are adopted by the Company as of the specified effective date.
ASU 2014-09: Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606)
In May 2014, the FASB issued ASC 606. ASC 606, along with its subsequent related updates prescribe a single comprehensive model for entities to use in the accounting for revenue arising from contracts with customers. The core principle contemplated by this new standard was that an entity should recognize revenue to depict the transfer of promised goods or services to customers in an amount reflecting the consideration to which the entity expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services. New disclosures about the nature, amount, timing and uncertainty of revenue and cash flows arising from contracts with customers are also required.
On January 1, 2019, the Company adopted ASC 606 as well as subsequent updates using the modified retrospective transition approach to those contracts that were not completed as of January 1, 2019. The comparative financial statement information has not been restated and continues to be reported under the accounting standards in effect for those periods. The adoption of the guidance did not have a material impact on the Company's consolidated balance sheet as of January 1, 2019. The Company's accounting for modular leasing revenue is primarily outside the scope of ASC 606 and is recorded under ASC 842.
ASU 2016-02, Leases (Topic 842)
In February 2016, the FASB issued ASC 842. This guidance revises existing practice related to accounting for leases under ASC 840, for both lessees and lessors. ASC 842 requires that lessees recognize: a) a lease liability, which is a lessee’s obligation to make lease payments arising from a lease, measured on a discounted basis; and b) a ROU asset, which is an asset that represents the lessee’s right to use, or control the use of, a specified asset for the lease term. ASC 842 also requires that the seller recognize any gain or loss (based on the estimated fair value of the asset at the time of sale) when control of the asset is transferred instead of amortizing it over the lease period for qualifying sale-leaseback transactions.
Effective January 1, 2019, the Company retrospectively adopted ASC 842. In connection with the adoption of ASC 842, the Company reversed the previous accounting for certain failed sale-leaseback transactions, and reduced property, plant and equipment by $31.0 million, reduced outstanding debt by $37.9 million, increased deferred tax liability by $1.8 million and increased January 1, 2019 equity by $5.2 million. The Company recognized lease liabilities and ROU assets of $138.5 million and $141.4 million as of January 1, 2019, primarily related to its real estate and equipment leases. The comparative financial statement information has not been restated and continues to be reported under the accounting standards in effect for those periods.
The adoption of ASC 842 at January 1, 2019, did not have a significant impact on the recognition of leasing revenue. Per the requirements of ASC 842 the Company records changes in estimated collectability, directly against lease revenue. Such amounts were previously classified as selling, general and administrative expenses.
The Company elected the package of practical expedients permitted under the transition guidance within the new standard that allows it to not reassess: (a) whether any expired or existing contracts are or contain leases, (b) the lease classification for any expired or existing leases and (c) initial direct costs for any expired or existing leases. Historical financial information was not updated, and the financial disclosures required under ASC 842 are not provided for periods prior to January 1, 2019.
ASU 2016-13: Financial Instruments - Credit Losses (Topic 326)
In June 2016, the FASB issued ASC 326, which prescribes that financial assets (or a group of financial assets) should be measured at amortized cost basis to be presented at the net amount expected to be collected based on relevant historical information from historical experience, adjusted for current conditions and reasonable and supportable forecasts that affect collectability. Credit losses relating to these financial assets are recorded through an allowance for credit losses. The Company
adopted ASC 326 effective January 1, 2020. The effect of this guidance was immaterial to the Company's consolidated results of operations, financial position and cash flows.
ASU 2018-15, Intangibles – Goodwill and Other – Internal-Use Software (Subtopic 350-40)
In August 2018, the FASB issued ASC 350-40, which provides guidance on accounting for implementation costs incurred in a cloud computing arrangement that is a service contract. The amendments in this update align the requirements for capitalizing implementation costs incurred in a hosting arrangement that is a service contract with the requirements for capitalizing implementation costs incurred to develop or obtain internal-use software and hosting arrangements that include an internal-use software license.
This guidance also requires entities to present the expense related to capitalized implementation costs in the same line item in the statement of operations as the fees associated with the hosting element (service) of the arrangement and classify payments for capitalized implementation costs in the statement of cash flows in the same manner as payments made for fees associated with the hosting element. The entity is also required to present the capitalized implementation costs in the balance sheet in the same line item that a prepayment for the fees of the associated hosting arrangement would be presented. The Company adopted ASC 350-40 on a prospective basis effective January 1, 2020. As a result of the adoption, capitalized implementation costs incurred in cloud computing arrangements were capitalized in other non-current assets in the consolidated balance sheet. The impact of this guidance did not materially impact the consolidated financial statements.
NOTE 2 - Business Combinations and Acquisitions (as restated)
Tyson Acquisition
On January 3, 2018, the Company acquired all of the issued and outstanding membership interests of Onsite Space LLC, d/b/a Tyson Onsite (“Tyson”) for $24.0 million in cash consideration, net of cash acquired.
ModSpace Acquisition
On August 15, 2018, the Company acquired Modular Space Holdings, Inc. ("ModSpace"), a privately-owned national provider of modular and portable storage units.
Purchase Price
The aggregate purchase price for ModSpace was $1.2 billion and consisted of (i) $1.1 billion in cash, (ii) 6,458,229 shares of WillScot's Class A Common Stock (the "Stock Consideration") with a fair market value of $95.8 million, (iii) warrants to purchase an aggregate of 10,000,000 shares of WillScot’s Class A Common Stock at an exercise price of $15.50 per share with a fair market value of $52.3 million, and (iv) a working capital adjustment of $4.7 million.
The acquisition was funded by the net proceeds of WillScot's issuance of 9,200,000 shares of Class A Common Stock, the net proceeds of the issuance of $300.0 million in senior secured notes and $200.0 million in unsecured notes, and borrowings under the ABL Facility.
As of the date of acquisition, the fair market values of the Stock Consideration and 2018 Warrants were $14.83 per share and $5.23 per warrant, respectively, with the warrant values determined using a Black-Scholes option-pricing model. The fair market value of the Class A shares was determined utilizing the $15.78 per share closing price of the Company's shares on August 15, 2018, discounted by 6.0%, to reflect a lack of marketability based on the lock-up restrictions contemplated by the merger agreement.
The estimated fair values of the Stock Consideration and 2018 Warrants are Level 3 fair value measurements, as defined in Note 16. The fair value of each share and warrant was estimated using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model. The following table summarizes the key inputs utilized to determine the fair value of the Stock Consideration and 2018 Warrants included within the purchase price of ModSpace.
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Stock Consideration
fair value inputs | | 2018 Warrants fair value inputs |
| Expected volatility | 28.6 | % | | 35.0 | % |
| Risk-free rate of interest | 2.2 | % | | 2.7 | % |
| Dividend Yield | 0 | % | | 0 | % |
| Expected life (years) | 0.5 | | 4.3 |
0
Pro Forma Information
The unaudited pro forma information below has been prepared using the purchase method of accounting, giving effect to the ModSpace acquisition as if it had been completed on January 1, 2018. The pro forma information is not necessarily indicative of the Company’s results of operations had the acquisition been completed on the above date, nor is it necessarily indicative of the Company’s future results.
The pro forma information does not reflect any cost savings from operating efficiencies or synergies that could result from the acquisition, and also does not reflect additional revenue opportunities following the acquisition.
| | | | | | | | |
| (unaudited, in thousands) | Year Ended December 31, 2018 (as restated)
(a) | |
| WillScot revenues | $ | 751,412 | | |
| ModSpace revenues | 312,609 | | |
| Pro forma revenues | $ | 1,064,021 | | |
| | |
| WillScot loss from operations before income tax | $ | (68,342) | | |
| ModSpace loss from operations before income tax | (7,457) | | |
| Loss from operations before income tax before pro forma adjustments | (75,799) | | |
| Pro forma adjustments to combined loss from operations before income tax: | | |
| Impact of fair value adjustments/useful life changes on depreciation | 10,135 | | |
| Intangible asset amortization | (625) | | (b) |
| Interest expense | (41,178) | | (c) |
| Elimination of ModSpace interest | 20,279 | | (d) |
| Pro forma loss from operations before income tax | (87,188) | | (e) |
| Income tax benefit | (43,462) | | (f) |
| Pro forma net loss | $ | (43,726) | | |
(a) Pro forma results for the year ended December 31, 2018 include ModSpace historical activity. Post-acquisition ModSpace revenues and pre-tax income are reflected in the Company's historical revenue and pre-tax income amounts.
(b) Amortization of the trade names acquired. The ModSpace trade name was assigned a value of $3.0 million and a life of three years.
(c) In connection with the ModSpace acquisition, the Company drew an incremental $419.0 million on the ABL Facility and issued $300.0 million of 2023 Secured Notes and $200.0 million of unsecured notes. An interest rate of 6.54% was used to calculate pro forma interest expense as a result of the ModSpace acquisition, which represents the weighted-average interest rate for the aforementioned borrowings at December 31, 2018. Interest expense includes amortization of related deferred financing fees on debt incurred in conjunction with the ModSpace acquisition.
(d) Interest on ModSpace historical debt was eliminated.
(e) Pro forma loss from operations before income taxes includes $15.5 million of restructuring expense, $30.0 million of integration costs, and $20.1 million of transaction costs incurred by WillScot for the year ended December 31, 2018. Additionally, pro forma pre-tax loss for the year ended December 31, 2018 also includes $20.5 million of interest expense associated with bridge financing fees incurred in connection with the acquisition of ModSpace.
(f) As the combined pro forma company was in a tax loss position in 2018, all pro forma adjustments for US tax effects are at the federal and state US statutory tax rate of 25.8% since the adjustments represent future deductible or taxable temporary differences.
Mobile Mini Merger
On March 1, 2020, the Company, along with its newly formed subsidiary, Merger Sub, entered into the Merger Agreement with Mobile Mini, hereby referred to as the “Merger”. The Merger was completed on July 1, 2020 and Merger Sub merged with and into Mobile Mini and the separate corporate existence of Merger Sub ceased, and Mobile Mini continued its existence as the surviving corporation in the Merger and a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Company. Mobile Mini is a leading provider of portable storage solutions in North America and the UK and a leading provider of specialty containment solutions in the US.
Purchase Price
Upon completion of the Merger, each issued and outstanding share of Mobile Mini Common Stock, par value $0.01 per share, converted to 2.405 shares of WillScot Class A Common Stock, par value $0.0001 per share, and cash in lieu of any fractional shares.
The Company issued 106,426,721 shares of Class A Common Stock to Mobile Mini stockholders as consideration for the Merger. The trading price of the Class A Common Stock was $12.53 per share on the closing date. In addition, Mobile Mini stock options converted into WillScot Mobile Mini stock options.
The purchase price has been determined to be as follows:
| | | | | |
| (in thousands, except share and per share data) | |
| Mobile Mini Common Stock outstanding | 44,252,275 | |
| Share conversion ratio | 2.405 | |
| Common Stock issued | 106,426,721 | |
| Common Stock per share price as of July 1, 2020 | $ | 12.53 | |
| Fair value of shares of WillScot Class A Common Stock issued | $ | 1,333,527 | |
| Cash paid for fractional shares | 30 | |
| Fair value of Mobile Mini Options converted to WillScot Mobile Mini Options | 19,279 | |
| Total purchase price | $ | 1,352,836 | |
The Merger was accounted for using the acquisition method of accounting, and WillScot is considered the accounting acquirer. Under the acquisition method of accounting, the Company is required to assign the purchase price to tangible and identifiable intangible assets acquired and liabilities assumed based on their fair values at the closing date. The excess of the purchase price over those fair values is recorded as goodwill. The Company's acquisition of Mobile Mini represents a non-cash investing outflow activity of $1,352,836 and the related issuance of equity including stock options represents a non-cash financing inflow activity of $1,352,836.
The purchase price for the Merger was assigned to the underlying assets acquired and liabilities assumed based upon their fair values at the date of acquisition, July 1, 2020. The Company recorded the fair values based on independent valuations, discounted cash flow analyses, quoted market prices, contributory asset charges, and estimates made by management. The following table summarizes the July 1, 2020 preliminary fair values of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed. The final assignment of the fair value of the Merger, including the final valuation of acquired rental equipment, intangible assets, and the related deferred tax liabilities and the final assignment of goodwill to reporting units, was not complete as of December 31, 2020, but will be finalized within the allowable one-year measurement period.
Opening Balance Sheet | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands) | Current Balance | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 17,203 | | |
| Trade receivables | 87,492 | | (a) |
| Inventories | 8,987 | | |
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets | 13,264 | | |
| Rental equipment | 1,033,190 | | (b) |
| Property, plant and equipment, net | 161,401 | | (c) |
| Operating lease assets | 92,054 | | |
| Intangible assets | 382,500 | | (b) |
| Goodwill identified | 928,974 | | (d) |
| Other non-current assets | 2,387 | | |
| Total identifiable assets acquired | 2,727,452 | | |
| Accounts payable | (29,797) | | |
| Accrued liabilities and interest | (38,759) | | |
| Deferred revenue and customer deposits | (38,846) | | |
| Operating lease liabilities | (89,968) | | |
| Debt and finance lease liabilities | (897,244) | | |
| Deferred tax liabilities | (278,727) | | (e) |
| Other long-term liabilities | (1,275) | | |
| Total liabilities assumed | (1,374,616) | | |
| Net assets acquired (purchase price) | $ | 1,352,836 | | |
| | | | | |
| (a) | As of the acquisition date, the fair value of accounts receivable was $87.5 million, and the gross contractual amount was $99.8 million. The Company analyzed information available at the time of acquisition in estimating uncollectible receivables and the fair value of remaining receivables. The Company's analysis, as of the acquisition date, included an assessment of the risk of collectability of receivables by analyzing historical payment trends, the status of collection efforts, and any other pertinent customer specific information that existed as of the acquisition date. |
| (b) | The initial fair value assumptions used included preliminary estimates of the replacement cost of rental equipment, discount rates, royalty rates, and customer attrition rates which have been updated in preparing these valuations and the underlying assets have been adjusted from those previously recorded accordingly. Rental equipment and intangible assets were reduced by approximately $109.8 million and $183.1 million from amounts previously reported, respectively. |
| (c) | The initial fair value assumptions have been updated in preparing these valuations and the underlying assets have been adjusted from those previously recorded accordingly. Property, plant and equipment, net increased by approximately $8.2 million. |
| (d) | The goodwill is reflective of Mobile Mini’s going concern value and operational synergies that the Company expects to achieve that would not be available to other market participants. Goodwill from the Mobile Mini acquisition is not deductible for income tax purposes. |
| (e) | The deferred tax liability is reflective of a deferred tax asset valuation reversal, partially offset by a permanent difference for transaction costs. The change from the preliminary balance of deferred tax liabilities to the current balance was driven by the updates to the preliminary estimates of the replacement cost of rental equipment, discount rates, royalty rates, and customer attrition rates discussed in (b) above. Deferred tax liabilities decreased approximately $68 million from amounts previously reported. |
Mobile Mini has generated $316.5 million of revenue and $23.1 million of pre-tax income since the acquisition date, which is included in the consolidated statement of operations for the year ended December 31, 2020.
Pro Forma Information
The below pro forma results give effect to the following as if they occurred on January 1, 2019, (i) the Merger, (ii) borrowings under the Company's 2025 Secured Notes and 2020 ABL Facility (terms as defined in Note 11) used to repay certain debt in connection with the Merger, (iii) extinguishment of the Mobile Mini revolving credit facility and senior notes assumed in the Merger and immediately repaid, (iv) extinguishment of WillScot's 2017 ABL Facility and WillScot's 2022 Secured Notes (both as defined in Note 11) repaid in connection with the Merger and (v) elimination of WillScot's non-controlling interest and WillScot's Class B Common Stock in connection with the Merger. The pro forma information is not necessarily indicative of the Company’s results of operations had the Merger been completed on January 1, 2019, nor is it necessarily indicative of the Company’s future results. The pro forma information does not reflect any cost savings from operating efficiencies, synergies, or revenue opportunities that could result from the Merger.
The tables below present unaudited pro forma combined statements of operations information for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (unaudited, in thousands) | Year Ended December 31, 2020
(as restated) | | Year Ended December 31, 2019
(as restated) | |
| WillScot revenues | $ | 1,367,645 | | | $ | 1,063,665 | | |
| Mobile Mini revenues | 284,240 | | | 620,018 | | |
| Pro forma revenues | $ | 1,651,885 | | | $ | 1,683,683 | | |
| | | | |
| WillScot Mobile Mini pretax income (loss) | $ | 23,889 | | | $ | (123,356) | | (a) |
| Mobile Mini pretax income | 37,875 | | | 111,705 | | |
| Pro forma pretax income | 61,764 | | | (11,651) | | |
| Pro forma adjustments to combined pretax income: | | | | |
| Elimination of Merger transaction costs | 80,852 | | | 0 | | (b) |
| Impact of fair value mark-ups on rental fleet depreciation | (2,334) | | | (4,667) | | (c) |
| Other depreciation expense and intangible asset amortization | (11,397) | | | (22,399) | | (d) |
| Interest expense | (6,113) | | | (1,916) | | (e) |
| Elimination of Mobile Mini interest | 15,921 | | | 39,672 | | (f) |
| Elimination of loss on extinguishment of debt | 19,682 | | | 1,512 | | (g) |
| Pro forma pretax income | 158,375 | | | 551 | | |
| Income tax expense | (34,549) | | | (28,892) | | (h) |
| Pro forma net income | $ | 123,826 | | | $ | (28,341) | | |
| | | | | |
| (a) | Excludes impact of non-controlling interest which was eliminated as part of the Sapphire Exchange. See Note 12. |
| (b) | Eliminates discrete Merger transaction costs incurred as a result of the Mobile Mini Merger. |
| (c) | Depreciation on rental equipment and property, plant and equipment were adjusted for the preliminary determination of the fair value of equipment acquired in the Mobile Mini Merger. |
| (d) | Represents the differential in other depreciation and amortization expense related to the provisional fair value purchase accounting adjustments as a result of the Merger, principally the amortization of the Mobile Mini customer relationship estimated at $263 million over 13 years. |
| (e) | In connection with the Merger, the Company entered into a new ABL Facility and drew $1.47 billion at close with an estimated interest rate of 2.046%, issued the 2025 Secured Notes at 6.125%, repaid the 2022 Secured Notes and repaid the 2017 ABL Facility. Interest and amortization of deferred financing fees for the 2020 ABL Facility and the 2025 Secured Notes has been included offset by the removal of interest and amortization of deferred financing fees attributable to the 2022 Secured Notes and the 2017 ABL Facility. See Note11 for definitions of terms. |
| (f) | Interest and amortization of deferred financing fees on the senior notes and line of credit maintained by Mobile Mini which were assumed at acquisition and repaid immediately using proceeds from the 2020 ABL Facility and 2025 Secured Notes was eliminated. See Note 11 for definition of terms. |
| (g) | Elimination of loss on extinguishment of debt in connection with the redemption premium on the 2022 Secured Notes and unamortized deferred financing costs on the 2022 Secured Notes and 2017 ABL Facility. See Note11 for definitions of terms. |
| (h) | Reflects the recorded income tax provision plus the adjustment to recognize the income tax impacts of the unaudited pro forma adjustments for which a tax expense is recognized using a US federal and state statutory tax rate of 25.5%. This rate may vary from the effective tax rates of the historical and combined businesses. In addition, eliminates the 2020 reversal of $54.6 million of valuation allowance as a result of reassessment of the realizability of deferred tax assets as a result of the Merger. See Note 14. |
Transaction and Integration Costs
The Company incurred $64.1 million in transaction costs related to the Mobile Mini Merger during the year ended December 31, 2020. The Company incurred $20.1 million in transaction costs during the year ended December 31, 2018 related to the ModSpace acquisition.
The Company records integration costs within selling, general and administrative ("SG&A") expense. The Company incurred $16.6 million in integration costs related to the Mobile Mini Merger for the year ended December 31, 2020. The Company incurred $26.6 million in integration costs related to the ModSpace acquisition for the year ended December 31, 2019. The Company incurred $30.0 million in integration costs related to the ModSpace, Acton, and Tyson acquisitions for the year ended December 31, 2018.
NOTE 3 - Revenue
Revenue Disaggregation
Geographic Areas
The Company had total revenue in the following geographic areas for the years ended December 31, as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| (in thousands) | 2020 | | 2019 | | 2018 |
| US | $ | 1,227,465 | | | $ | 966,766 | | | $ | 685,350 | |
| Canada | 79,630 | | | 80,514 | | | 50,144 | |
| Mexico | 14,190 | | | 16,385 | | | 15,918 | |
| UK | 46,360 | | | 0 | | | 0 | |
| Total revenues | $ | 1,367,645 | | | $ | 1,063,665 | | | $ | 751,412 | |
Major Product and Service Lines
Equipment leasing is the Company's core business, which significantly impacts the nature, timing and uncertainty of the Company's revenue and cash flows. This includes rental modular space, portable space and tank and pump units along with VAPS, which include furniture, steps, ramps, basic appliances, internet connectivity devices, and other items used by customers in connection with the Company's products. Leasing is complemented by new unit sales and sales of rental units. In connection with its leasing and sales activities, the Company provides services including delivery and installation, maintenance and ad hoc services and removal services at the end of lease transactions.
The Company’s revenue by major product and service line for the years ended December 31, was as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| (in thousands) | 2020 | | 2019 | | 2018 |
| Modular space leasing revenue | $ | 596,880 | | | $ | 516,299 | | | $ | 360,240 | |
| Portable storage leasing revenue | 125,216 | | | 24,277 | | | 21,682 | |
| Tank and pump leasing revenue | 29,798 | | | 0 | | | 0 | |
VAPS and third party leasing revenues(a) | 202,938 | | | 159,327 | | | 104,870 | |
Other leasing-related revenue(b) | 46,615 | | | 44,282 | | | 31,443 | |
| Leasing revenue | 1,001,447 | | | 744,185 | | | 518,235 | |
| Delivery and installation revenue | 274,156 | | | 220,057 | | | 154,557 | |
| Total leasing and services revenue | 1,275,603 | | | 964,242 | | | 672,792 | |
| New unit sales revenue | 53,093 | | | 59,085 | | | 53,603 | |
| Rental unit sales revenue | 38,949 | | | 40,338 | | | 25,017 | |
| Total revenues | $ | 1,367,645 | | | $ | 1,063,665 | | | $ | 751,412 | |
(a) Includes $18.8 million, $15.9 million, and $10.8 million of VAPS service revenue for the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018, respectively.
(b) Includes primarily damage billings, delinquent payment charges, and other processing fees.
Leasing and Services Revenue
The majority of revenue (72%, 68%, and 68% for the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018, respectively) is generated by lease income subject to the guidance of ASC 840, or ASC 842 for periods after January 1, 2019. The remaining revenue is generated by performance obligations in contracts with customers for services or sale of units subject to the guidance in ASC 605, or ASC 606 for periods after January 1, 2019.
Future committed leasing revenues under non-cancelable operating leases with the Company’s customers at December 31, 2020 for the years ended December 31, 2021 - 2025 and thereafter were as follows:
| | | | | |
| (in thousands) | Operating Leases |
| 2021 | $ | 232,730 | |
| 2022 | 75,664 | |
| 2023 | 29,419 | |
| 2024 | 11,643 | |
| 2025 | 4,284 | |
| Thereafter | 2,738 | |
| Total | $ | 356,478 | |
Receivables, Contract Assets and Liabilities
The Company manages credit risk associated with its accounts receivables at the customer level. Because the same customers generate the revenues that are accounted for under both ASC 606 and ASC 842, the discussions below on credit risk and the Company's allowance for credit losses address the Company's total revenues.
Concentration of credit risk with respect to the Company's receivables is limited because of a large number of geographically diverse customers who operate in a variety of end user markets. The Company's top five customers with the largest open receivables balances represented 4.9% and 4.1% of the total receivables balance as of December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively. The Company manages credit risk through credit approvals, credit limits, and other monitoring procedures.
The Company's allowance for credit losses reflects its estimate of the amount of receivables that it will be unable to collect. The estimated losses are based upon a review of outstanding receivables, the related aging, including specific accounts if deemed necessary, and on our historical collection experience. The estimated losses are calculated using the loss rate method based upon a review of outstanding receivables, related aging, and historical collection experience. The Company's estimates reflect changing circumstances, including changes in the economy or in the particular circumstances of individual customers, and as a result, the Company may be required to increase or decrease its allowance. During the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019, and 2018, the Company recognized bad debt expense of $13.4 million, $4.5 million, and $7.7 million, respectively, within SG&A expense in its consolidated statements of operations, which included changes in its allowances for credit losses. In accordance with the collectability provisions of ASC 842, the Company has recorded $18.0 million and $10.0 million as reductions of revenue in 2020 and 2019, respectively, that would have been recorded as bad debt expense prior to the adoption of ASC 842.
When customers are billed in advance, the Company defers recognition of revenue until the related services are performed, which generally occurs at the end of the contract. During the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, $37.5 million and $14.0 million, respectively, of deferred revenue relating to these services, was recognized as revenue. At December 31, 2020 and 2019, the Company had approximately $74.1 million and $42.6 million, respectively, of deferred revenue related to these services.
The Company does not have material contract assets, and it did not recognize any material impairments of any contract assets.
The Company's uncompleted contracts with customers have unsatisfied (or partially satisfied) performance obligations. For the future services revenues that are expected to be recognized within twelve months, the Company has elected to utilize the optional disclosure exemption made available regarding transaction price allocated to unsatisfied (or partially unsatisfied) performance obligations. The transaction price for performance obligations that will be completed in greater than twelve months is variable based on the costs ultimately incurred to provide those services and therefore the Company is applying the optional exemption to omit disclosure of such amounts.
The primary costs to obtain contracts for new and rental unit sales with the Company's customers are commissions. The Company pays its sales force commissions on the sale of new and rental units. For new and rental unit sales, the period benefited by each commission is less than one year. As a result, the Company has applied the practical expedient for incremental costs of obtaining a sales contract and expenses commissions as incurred.
NOTE 4 - Leases
As of December 31, 2020, the undiscounted future lease payments for operating and finance lease liabilities were as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operating | | Finance |
| 2021 | $ | 60,120 | | | $ | 18,252 | |
| 2022 | 51,184 | | | 17,158 | |
| 2023 | 41,074 | | | 13,707 | |
| 2024 | 33,336 | | | 10,786 | |
| 2025 | 26,542 | | | 10,893 | |
| Thereafter | 67,421 | | | 13,410 | |
| Total lease payments | 279,677 | | | 84,206 | |
| Less: interest | (47,853) | | | (6,332) | |
| Present value of lease liabilities | $ | 231,824 | | | $ | 77,874 | |
As of December 31, 2019, the undiscounted future lease payments for operating and finance lease liabilities were as follows (in thousands):
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operating | | Finance |
| 2020 | $ | 37,648 | | | $ | 0 | |
| 2021 | 33,903 | | | 0 | |
| 2022 | 27,769 | | | 0 | |
| 2023 | 21,926 | | | 0 | |
| 2024 | 16,685 | | | 0 | |
| Thereafter | 47,916 | | | 0 | |
| Total lease payments | 185,847 | | | 0 | |
| Less: interest | (38,285) | | | 0 | |
| Present value of lease liabilities | $ | 147,562 | | | $ | 0 | |
Finance lease liabilities are included within long-term debt and current portion of long-term debt on the consolidated balance sheets.
The Company’s lease activity during the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 was as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
Financial Statement Line (in thousands) | 2020 | | 2019 |
| Finance Lease Expense | | | |
| Amortization of finance lease assets | $ | 9,556 | | | $ | 0 | |
| Interest on obligations under finance leases | 1,081 | | | 0 | |
| Total finance lease expense | $ | 10,637 | | | $ | 0 | |
| | | |
| Operating Lease Expense | | | |
| Fixed lease expense | | | |
| Cost of leasing and services | $ | 5,723 | | | $ | 6,737 | |
| Selling, general and administrative | 43,482 | | | 34,058 | |
| Lease impairment expense and other related charges | 2,800 | | | 2,611 | |
| Short-term lease expense | | | |
| Cost of leasing and services | 25,576 | | | 29,729 | |
| Selling, general and administrative | 2,067 | | | 2,071 | |
| Lease impairment expense and other related charges | 471 | | | 0 | |
| Variable lease expense | | | |
| Cost of leasing and services | 6,981 | | | 3,787 | |
| Selling, general and administrative | 5,436 | | | 4,231 | |
| Lease impairment expense and other related charges | 855 | | | 0 | |
| Total operating lease expense | $ | 93,391 | | | $ | 83,224 | |
The Company initiated certain restructuring plans associated with the 2018 ModSpace acquisition in order to capture operating synergies as a result of integrating ModSpace into WillScot. The restructuring activities primarily included the termination of leases for duplicative branches, equipment, and corporate facilities. As part of these plans, certain of its leased locations were vacated and leases were terminated or impaired.
During the year ended December 31, 2020, the Company recorded $4.9 million in lease impairment expense and other related charges which is comprised of $0.7 million loss on lease exit and impairment charges and $4.2 million in closed location rent expense. During the year ended December 31, 2019, the Company recorded $8.7 million in lease impairment expense and other related charges which is comprised of $4.2 million in ROU asset impairment on leased locations no longer used in operations, $1.9 million loss on lease exit and $2.6 million in closed location rent expense.
Rent expense included in the consolidated statement of operations was $31.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2018.
Supplemental cash flow information related to leases for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 were as follows: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
Supplemental Cash Flow Information (in thousands) | 2020 | | 2019 |
| Cash paid for the amounts included in the measurement of lease liabilities: | | | |
| Operating cash outflows from operating leases | $ | 45,883 | | | $ | 42,111 | |
| Financing cash outflows from finance leases | $ | 9,568 | | | $ | 0 | |
| | | |
| Right of use assets obtained in exchange for lease obligations | $ | 33,576 | | | $ | 43,013 | |
| Assets obtained in exchange for finance leases | $ | 9,089 | | | $ | 0 | |
Weighted-average remaining operating lease terms and the weighted average discount rates as of December 31, 2020 and 2019 were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Lease Terms and Discount Rates | December 31, 2020 | | December 31, 2019 |
| Weighted-average remaining lease term - operating leases | 6.4 years | | 6.5 years |
| Weighted-average discount rate - operating leases | 5.7 | % | | 7.0 | % |
| Weighted-average remaining lease term - finance leases | 4.6 years | | — | |
| Weighted-average discount rate - finance leases | 2.9 | % | | — | |
The Company presents information related to leasing revenues in Note 3.
NOTE 5 - Inventories
Inventories at December 31, consisted of the following: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands) | 2020 | | 2019 |
| Raw materials | $ | 19,560 | | | $ | 15,387 | |
| Finished units | 2,095 | | | 0 | |
| Inventories | $ | 21,655 | | | $ | 15,387 | |
NOTE 6 - Prepaid Expenses and Other Current Assets
Prepaid expenses and other current assets at December 31 consisted of the following: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands) | 2020 | | 2019 |
| Tax receivables | $ | 4,618 | | | $ | 1,211 | |
| Prepaid insurance | 5,859 | | | 2,099 | |
| Other prepaid expenses | 19,477 | | | 11,311 | |
| Total prepaid expenses and other current assets | $ | 29,954 | | | $ | 14,621 | |
NOTE 7 - Rental Equipment, net
Rental equipment, net at December 31 consisted of the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands) | 2020 | | 2019 |
| Modular space units | $ | 2,520,704 | | | $ | 2,372,069 | |
| Portable storage units | 931,363 | | | 83,402 | |
| Tank and pump products | 132,071 | | | 0 | |
| Value added products | 143,652 | | | 121,855 | |
| Total rental equipment | 3,727,790 | | | 2,577,326 | |
| Less: accumulated depreciation | (794,068) | | | (632,890) | |
| Rental equipment, net | $ | 2,933,722 | | | $ | 1,944,436 | |
NOTE 8 – Property, Plant and Equipment, net
Property, plant and equipment, net at December 31 consisted of the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands) | 2020 | | 2019 |
| Land, buildings, and leasehold improvements | $ | 154,210 | | | $ | 139,861 | |
| Vehicles, machinery, and office equipment | 227,009 | | | 62,169 | |
| Software and other | 20,800 | | | 27,342 | |
| Total property, plant and equipment | 402,019 | | | 229,372 | |
| Less: accumulated depreciation | (98,369) | | | (81,683) | |
| Property, plant and equipment, net | $ | 303,650 | | | $ | 147,689 | |
Depreciation expense related to property, plant and equipment was $28.9 million, $11.4 million, and $12.2 million for the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018, respectively.
As of December 31, 2020, the gross cost of property, plant and equipment assets under finance leases was $78.7 million, with related accumulated depreciation of $9.5 million. The depreciation expense for these assets is presented in other depreciation and amortization in the consolidated statement of operations. NaN property, plant and equipment assets under finance leases were recorded as of December 31, 2019.
NOTE 9 - Goodwill and Intangible Assets
Goodwill
Changes in the carrying amount of goodwill were as follows: | | | | | |
| (in thousands) | |
| Balance at December 31, 2018 | $ | 247,017 | |
| Changes to purchase price accounting - Modspace | (13,479) | |
| Effects of movements in foreign exchange rates | 1,639 | |
| Balance at December 31, 2019 | 235,177 | |
| Acquisition of Mobile Mini | 928,974 | |
| Effects of movements in foreign exchange rates | 7,068 | |
| Balance at December 31, 2020 | $ | 1,171,219 | |
As discussed further in Note 2, the Company acquired Mobile Mini on July 1, 2020. Goodwill was preliminarily allocated to the NA Storage, UK Storage and Tank and Pump segments, as defined in Note 20, in the amounts of $726.5 million, $59.2 million and $143.3 million, respectively. The Company expects to finalize the valuation of the acquired net assets of Mobile Mini, including the final assignment of goodwill to reporting units, within the one-year measurement period from the date of acquisition. The Company expects any adjustments to goodwill for financial reporting to be non-deductible for income tax purposes.
The Company conducted its annual impairment test of goodwill as of October 1, 2020 and determined that there was no impairment of goodwill identified as a result of the annual impairment analysis. The Company considered the economic environment resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic as part of its goodwill impairment test. Due to the uncertain and rapidly evolving nature of the conditions surrounding the COVID-19 pandemic, changes in economic outlook may change the Company's long-term projections.
Accumulated goodwill impairment losses were $792.8 million and pertain to the NA Modular segment. There were no goodwill impairments recorded for the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018.
Intangibles
Intangible assets other than goodwill at December 31, consisted of the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2020 |
| (in thousands) | Weighted average remaining life (in years) | | Gross carrying amount | | Accumulated amortization | | Net book value |
| Intangible assets subject to amortization: | | | | | | | |
| Trade name - ModSpace | 0.7 | | $ | 3,000 | | | $ | (2,375) | | | $ | 625 | |
| Mobile Mini customer relationships | 8.0 | | 217,000 | | | (12,053) | | | 204,947 | |
| Technology | 5.5 | | 1,500 | | | (125) | | | 1,375 | |
| Indefinite-lived intangible assets: | | | | | | | |
| Trade name - Mobile Mini | | | 164,000 | | | — | | | 164,000 | |
| Trade name - WillScot | | | 125,000 | | | — | | | 125,000 | |
| Total intangible assets other than goodwill | | | $ | 510,500 | | | $ | (14,553) | | | $ | 495,947 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2019 |
| (in thousands) | Weighted average remaining life (in years) | | Gross carrying amount | | Accumulated amortization | | Net book value |
| Intangible assets subject to amortization: | | | | | | | |
| Trade name - ModSpace | 1.7 | | $ | 3,000 | | | $ | (1,375) | | | $ | 1,625 | |
| Total intangible assets subject to amortization | | | 3,000 | | | (1,375) | | | 1,625 | |
| | | | | | | |
| Indefinite-lived intangible assets: | | | | | | | |
| Trade name - WillScot | | | 125,000 | | | — | | | 125,000 | |
| Total intangible assets other than goodwill | | | $ | 128,000 | | | $ | (1,375) | | | $ | 126,625 | |
As discussed further in Note 2, the Company acquired Mobile Mini on July 1, 2020. The Company preliminarily recorded $164.0 million of indefinite-lived intangible assets and $218.5 million of intangibles subject to amortization, related to Mobile Mini customer relationships and technology, respectively, in the NA Storage, UK Storage, and Tank and Pump segments. The Company expects to finalize the valuation of the acquired net assets of Mobile Mini, including the related intangible assets, within the one-year measurement period from the date of acquisition. The Company expects any adjustments to intangible assets for financial reporting to be non-deductible for income tax purposes.
In the 2018 ModSpace acquisition, the Company allocated $3.0 million to definite-lived intangible assets, related to the ModSpace trade name. At the time of the acquisition, management estimated that the ModSpace trade name had an estimated useful life of three years.
For the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, the aggregate amount recorded to depreciation and amortization expense for intangible assets subject to amortization, was $14.4 million and $1.0 million, respectively.
As of December 31, 2020, the expected future amortization expense for intangible assets is as follows:
| | | | | |
| (in thousands) | Amortization Expense |
| 2021 | $ | 27,167 | |
| 2022 | 26,542 | |
| 2023 | 26,542 | |
| 2024 | 26,542 | |
| 2025 | 26,542 | |
| Thereafter | 73,612 | |
| Total | $ | 206,947 | |
NOTE 10 - Deferred Revenue and Customer Deposits
Deferred revenue and customer deposits at December 31 consisted of the following: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands) | 2020 | | 2019 |
| Current: | | | |
| Deferred revenue | $ | 133,156 | | | $ | 81,303 | |
| Customer deposits | 2,329 | | | 1,675 | |
| Total current deferred revenue and customer deposits | $ | 135,485 | | | $ | 82,978 | |
| | | |
| Long-term: | | | |
| Deferred revenue | $ | 12,060 | | | $ | 12,342 | |
| Total long-term deferred revenue and customer deposits | $ | 12,060 | | | $ | 12,342 | |
Total long-term deferred revenue and customer deposits are included in Other non-current liabilities on the consolidated balance sheets.
NOTE 11 - Debt
The carrying value of debt outstanding at December 31 consisted of the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands, except rates) | Interest rate | | Year of maturity | | 2020 | | 2019 |
| 2022 Secured Notes | 7.875% | | 2022 | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 264,576 | |
| 2023 Secured Notes | 6.875% | | 2023 | | 0 | | | 482,768 | |
| 2025 Secured Notes | 6.125% | | 2025 | | 637,068 | | | 0 | |
ABL Facility(a) | Varies | | 2025 | | 1,263,833 | | | 885,245 | |
| 2028 Secured Notes | 4.625% | | 2028 | | 491,555 | | | 0 | |
| Finance Leases | Varies | | Varies | | 77,874 | | | 0 | |
| Total debt | | | | | 2,470,330 | | | 1,632,589 | |
| Less: current portion of long-term debt | | | | | 16,521 | | | 0 | |
| Total long-term debt | | | | | $ | 2,453,809 | | | $ | 1,632,589 | |
(a) As of December 31, 2020, the Company had 0 outstanding principal borrowings on the Multicurrency Facility and $7.9 million of related debt issuance costs. No related debt issuance costs were recorded as a direct offset against the principal borrowings on the Multicurrency Facility, and the $7.9 million in excess of principal was included in other non-current assets on the consolidated balance sheet. As of December 31, 2019, the Company had 0 outstanding principal borrowings on the 2017 Canadian ABL Facility and $2.1 million of related debt issuance costs. No related debt issuance costs were recorded as a direct offset against the principal of the 2017 Canadian ABL Facility, and the $2.1 million in excess of principal was included in other non-current assets on the consolidated balance sheet.
Maturities of long-term debt, including finance leases, during the years subsequent to December 31, 2020 are as follows: | | | | | |
| (in thousands) | |
| 2021 | $ | 18,252 | |
| 2022 | $ | 17,158 | |
| 2023 | $ | 13,707 | |
| 2024 | $ | 10,786 | |
| 2025 | $ | 1,965,505 | |
| Thereafter | $ | 513,410 | |
The Company has debt issuance costs recorded as offsets against the carrying value of the related debt. These debt costs will be amortized and included as part of interest expense over the remaining contractual terms of those debt instruments for each of the next five years as follows:
| | | | | |
| (in thousands) | Debt issuance cost amortization |
| 2021 | $ | 14,317 | |
| 2022 | $ | 14,540 | |
| 2023 | $ | 14,778 | |
| 2024 | $ | 15,031 | |
| 2025 | $ | 8,050 | |
| Thereafter | $ | 3,365 | |
Asset Backed Lending Facilities
2017 ABL Facility
On November 29, 2017, Williams Scotsman Holdings Corp ("Holdings"), Williams Scotsman International, Inc. ("WSII"), and certain of its subsidiaries entered into an ABL credit agreement (the "2017 ABL Facility"), as amended, that provided a senior secured revolving credit facility that matured on May 29, 2022. The 2017 ABL Facility consisted of (i) a $1.285 billion asset-backed revolving credit facility for WSII and certain of its domestic subsidiaries (the "2017 US ABL Facility"), (ii) a $140.0 million asset-based revolving credit facility (the “2017 Canadian ABL Facility”) for certain Canadian subsidiaries of WSII, and (iii) an accordion feature that permitted the borrowers to increase the lenders’ commitments in an aggregate amount not to exceed $375.0 million, subject to the satisfaction of customary conditions and lender approval, plus any voluntary prepayments that are accompanied by permanent commitment reductions under the 2017 ABL Facility. Borrowing availability under the 2017 ABL Facility was equal to the lesser of $1.425 billion and the applicable borrowing bases. The borrowing bases were a function of, among other things, the value of the assets in the collateral pool.
Borrowings under the 2017 ABL Facility bore interest at an adjusted LIBOR or base rate, in each case plus an applicable margin. The initial applicable margin was 2.50% for LIBOR borrowings and 1.50% for base rate borrowings. Commencing on March 31, 2018, the applicable margins were subject to one step down of 0.25% or one step-up of 0.25%, based on excess availability levels with respect to the 2017 ABL Facility. The 2017 ABL Facility required the payment of an annual commitment fee on the unused available borrowings between 0.375% and 0.5% per annum. At December 31, 2019, the weighted average interest rate for borrowings under the 2017 ABL Facility was 4.51%. The weighted average interest rate on the balance outstanding as of December 31, 2019, as adjusted for the effects of the interest rate swaps was 5.10%. Refer to Note 15 for a more detailed discussion on interest rate management.
At December 31, 2019, under the 2017 ABL Facility, the aggregate Borrowing Base ("Line Cap") was $1.425 billion and the Borrowers had $509.1 million of available borrowing capacity, including $369.3 million under the 2017 US ABL Facility and $139.8 million under the 2017 Canadian ABL Facility. Borrowing capacity under the 2017 US ABL Facility was made available for up to $75 million of letters of credit and up to $75 million of swingline loans, and borrowing capacity under the 2017 Canadian ABL Facility was made available for up to $60.0 million of letters of credit and $50 million of swingline loans. At December 31, 2019, letters of credit and bank guarantees carried fees of 2.875%. The Company had issued $12.7 million of standby letters of credit under the 2017 ABL Facility at December 31, 2019.
The Company had $903.0 million in outstanding principal under the 2017 ABL Facility at December 31, 2019. Debt issuance costs of $17.8 million were included in the carrying value of the 2017 ABL Facility at December 31, 2019.
2020 ABL Facility
On July 1, 2020, in connection with the completion of the Merger, Holdings, WSII, and certain of its subsidiaries, entered into a new asset-based credit agreement that provides for revolving credit facilities in the aggregate principal amount of up to $2.4 billion, consisting of: (i) a senior secured asset-based US dollar revolving credit facility in the aggregate principal amount of $2.0 billion (the "US Facility"), available to WSII and certain of its subsidiaries (collectively, the "US Borrowers"), and (ii) a $400.0 million senior secured asset-based multicurrency revolving credit facility (the "Multicurrency Facility," together with the US Facility, the "2020 ABL Facility"), available to be drawn in US Dollars, Canadian Dollars, British Pounds Sterling or Euros by the US Borrowers, and certain of WSII's wholly-owned subsidiaries organized in Canada and in the UK. On July 1, 2020, in connection with the completion of the Merger, approximately $1.47 billion of proceeds from the 2020 ABL Facility were used to repay the 2017 ABL Facility and the asset-backed lending facility assumed in the transaction with Mobile Mini, as well as, to pay fees and expense related to the Merger and the related financing transactions. In connection with the repayment of the 2017 ABL facility, the Company wrote off $4.4 million of deferred financing costs to loss on extinguishment of debt. The 2020 ABL Facility matures on July 1, 2025.
Borrowings under the 2020 ABL Facility initially bear interest at (i) in the case of US Dollars, at WSII's option, either an adjusted LIBOR rate plus 1.875% or an alternative base rate plus 0.875%, (ii) in the case of Canadian Dollars, at WSII's option, either a Canadian BA rate plus 1.875% or Canadian prime rate plus 0.875%, and (iii) in the case of Euros and British Pounds Sterling, an adjusted LIBOR rate plus 1.875%. The 2020 ABL Facility requires the payment of an annual commitment
fee on the unused available borrowings of 0.225% per annum. At December 31, 2020, the weighted average interest rate for borrowings under the 2020 ABL Facility was 2.05%. The weighted average interest rate on the balance outstanding as of year end, as adjusted for the effects of the interest rate swap agreements was 2.94%. Refer to Note 15 for a more detailed discussion on interest rate management.
Borrowing availability under the US Facility and the Multicurrency Facility is equal to the lesser of (i) the aggregate Revolver Commitments and (ii) the Line Cap. At December 31, 2020, the Line Cap was $2.4 billion and the Borrowers had $1.1 billion of available borrowing capacity under the 2020 ABL Facility, including $681.0 million under the US ABL Facility and $400.0 million under the Multicurrency Facility. Borrowing capacity under the 2020 ABL Facility is made available for up to $205.6 million of letters of credit and up to $170.0 million of swingline loans. At December 31, 2020, letters of credit and bank guarantees carried fees of 2.00%. The Company had issued $14.4 million of standby letters of credit under the 2020 ABL Facility at December 31, 2020.
The Company had $1.3 billion outstanding principal under the 2020 ABL Facility at December 31, 2020. Debt issuance costs of $40.8 million were included in the carrying value of the 2020 ABL Facility at December 31, 2020.
The obligations of the US Borrowers are unconditionally guaranteed by Holdings and each existing and subsequently acquired or organized direct or indirect wholly-owned US organized restricted subsidiary of Holdings, other than excluded subsidiaries (together with Holdings, the "US Guarantors"). The obligations of the Multicurrency Borrowers are unconditionally guaranteed by the US Borrowers and the US Guarantors, and each existing and subsequently acquired or organized direct or indirect wholly-owned Canadian organized restricted subsidiary of Holdings other than certain excluded subsidiaries (together with the US Guarantors, the "ABL Guarantors").
2022 Senior Secured Notes
In 2017, WSII issued $300.0 million aggregate principal amount of 7.875% senior secured notes due December 15, 2022 (the “2022 Secured Notes”) under an indenture dated November 29, 2017. Interest was payable semi-annually on June 15 and December 15 beginning June 15, 2018.
On December 13, 2019, the Company completed a partial redemption of $30.0 million of the 2022 Secured Notes at a redemption price of 103% using proceeds from its 2017 ABL Facility. The Company recorded a loss on extinguishment of debt of $1.5 million, which included $0.9 million of an early redemption premium and $0.6 million related to the write-off of unamortized deferred financing fees.
In connection with the Merger and related financing transactions in the third quarter of 2020, using proceeds from the 2025 Secured Notes discussed below, the Company redeemed all of its 2022 Secured Notes and recorded a loss on extinguishment of debt in the consolidated statements of operations of $15.2 million comprised of a redemption premium of $10.6 million and write off of unamortized deferred financing fees of $4.6 million.
As of December 31, 2019, unamortized debt issuance costs pertaining to the 2022 Secured Notes were $5.4 million.
2023 Senior Secured Notes
In connection with the acquisition of ModSpace in 2018, $300.0 million in aggregate principal amount of its 6.875% senior secured notes due August 15, 2023 (the “2023 Secured Notes”) were issued. Interest was payable semi-annually on February 15 and August 15 of each year, beginning February 15, 2019.
On May 14, 2019, WSII completed a tack-on offering of $190.0 million in aggregate principal amount to the initial 2023 Secured Notes (the "Tack-On Notes"). The Tack-On Notes were issued as additional securities under the 2023 Secured Notes indenture. The Tack-On Notes and the initial 2023 Secured Notes were treated as a single class of debt securities under the 2023 Secured Notes indenture. The Tack-On Notes have identical terms to the initial 2023 Secured Notes, other than with respect to the issue date and issue price. WSII incurred a total of $3.0 million in debt issuance costs in connection with the tack-on offering, which were deferred and were being amortized through the August 15, 2023 maturity date. Subsequent to the Tack-On Notes, WSII had $490.0 million of 6.875% 2023 Secured Notes. On August 11, 2020, WSII redeemed 10% of the outstanding principal amount of the 2023 Secured Notes, $49.0 million, at a redemption price of 103% plus accrued interest and unpaid interest. This repayment was funded by borrowings under the Company's 2020 ABL Facility.
On August 25, 2020, the Company completed a private offering of its 2028 Secured Notes, discussed below, and used the offering proceeds to repay, along with expenses, the $441.0 million outstanding principal amount of its 2023 Secured Notes at a redemption price of 103.438% plus accrued interest and unpaid interest. The Company recorded a loss on extinguishment of debt in the consolidated statements of operations of $22.7 million comprised of a redemption premium of $16.6 million and a write off of unamortized deferred financing fees of $6.1 million.
Unamortized debt issuance costs of $7.2 million were included in the carrying value of the debt as of December 31, 2019.
2025 Senior Secured Notes
In anticipation of the Merger, on June 15, 2020, Picasso Finance Sub, Inc., a newly-formed indirect finance subsidiary (the "Finance Sub") of the Company completed a private offering of $650.0 million in aggregate principal amount of its 6.125% senior secured notes due 2025 (the "2025 Secured Notes"). The 2025 Secured Notes contained provisions requiring repayment, without penalty, in the event the Merger was not consummated. The offering proceeds from the 2025 Secured Notes of $650.0 million and $5.1 million of interest due through August 1, 2020 were deposited into an escrow account, pending the closing of the Merger. In connection with the completion of the Merger, on July 1, 2020, the offering proceeds were released and the proceeds were used to repay the 2022 Secured Notes, repay Mobile Mini senior notes assumed in the acquisition and pay certain fees and expenses related to the Merger and the related financing transactions. In addition, Finance Sub was merged into WSII on July 1, 2020. The Company recorded $14.3 million in deferred financing fees related to the 2025 Secured Notes.
The 2025 Secured Notes mature on June 15, 2025 and bear interest at a rate of 6.125% per annum. Interest is payable semi-annually on June 15 and December 15 of each year, beginning December 15, 2020.
The Company may redeem the 2025 Secured Notes at any time before June 15, 2022 at a redemption price equal to 100% of the principal amount thereof, plus a customary make whole premium for the 2025 Secured Notes being redeemed, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to but not including the redemption date. Before June 15, 2022, the Company may redeem up to 40% of the aggregate principal amount of the 2025 Secured Notes at a price equal to 106.125% of the principal amount of the 2025 Secured Notes being redeemed, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to but not including the redemption date with the net proceeds of certain equity offerings. At any time prior to June 15, 2022, the Company may also redeem up to 10% of the aggregate principal amount of the 2025 Secured Notes at a redemption price equal to 103% of the principal amount of the 2025 Secured Notes being redeemed during each twelve-month period commencing with the issue date, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to but not including the redemption date. If the Company undergoes a change of control or sells certain of its assets, the Company may be required to offer to repurchase the 2025 Secured Notes.
On and after June 15, 2022, the Company may redeem the 2025 Secured Notes, in whole or in part, at the redemption prices expressed as percentages of principal amount set forth below plus accrued and unpaid interest to but not including the applicable redemption date, subject to the holders' right to receive interest due on an interest payment date falling on or prior to the redemption date, if redeemed during the twelve-month period beginning on June 15 of each of the years set forth below.
| | | | | |
| Year | Redemption Price |
| 2022 | 103.063 | % |
| 2023 | 101.531 | % |
| 2024 and thereafter | 100.000 | % |
The 2025 Secured Notes are unconditionally guaranteed by each of WSII's direct and indirect domestic subsidiaries and WSII's parent, Holdings (collectively, "the Note Guarantors"). WillScot Mobile Mini is not a guarantor of the 2025 Secured Notes. The Note Guarantors, as well as certain of the Company’s non-US subsidiaries, are guarantors or borrowers under the 2020 ABL Facility. To the extent lenders under the 2020 ABL Facility release the guarantee of any Note Guarantor, such Note Guarantor will also be released from obligations under the 2025 Secured Notes. These guarantees are secured by a second priority security interest in substantially all of the assets of WSII and the Note Guarantors, subject to customary exclusions. The guarantees of the 2025 Secured Notes by WillScot Equipment II, LLC, a Delaware limited liability company which holds certain of WSII’s assets in the US, will be subordinated to its obligations under the 2020 ABL Facility.
Unamortized deferred financing costs pertaining to the 2025 Secured Notes were $12.9 million as of December 31, 2020.
2028 Senior Secured Notes
On August 25, 2020, the Company completed a private offering of $500.0 million in aggregate principal amount of 4.625% senior secured notes due 2028 (the "2028 Secured Notes").
The 2028 Secured Notes mature on August 15, 2028. They bear interest at a rate of 4.625% per annum. Interest is payable semi-annually on August 15 and February 15 of each year, beginning February 15, 2021.
The Company may redeem the 2028 Secured Notes at any time before August 15, 2023 at a redemption price equal to 100% of the principal amount thereof, plus a customary make whole premium for the 2028 Secured Notes being redeemed, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to but not including the redemption date. Before August 15, 2023, the Company may redeem up to 40% of the aggregate principal amount of the 2028 Secured Notes at a price equal to 104.625% of the principal amount of the 2028 Secured Notes being redeemed, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to but not including the redemption date with the net proceeds of certain equity offerings. At any time prior to August 15, 2023, the Company may also redeem up to 10% of the aggregate principal amount at a redemption price equal to 103% of the principal amount of the 2028 Secured Notes being redeemed during each twelve-month period commencing with the issue date, plus accrued and unpaid interest, if any, to but not including the redemption date. If the Company undergoes a change of control or sells certain of its assets, the Company may be required to offer to repurchase the 2028 Secured Notes.
On and after August 15, 2023, the Company may redeem the 2028 Secured Notes, in whole or in part, at the redemption prices expressed as percentages of principal amount set forth below plus accrued and unpaid interest to but not including the applicable redemption date, subject to the holders' right to receive interest due on an interest payment date falling on or prior to the redemption date, if redeemed during the twelve-month period beginning on August 15 of each of the years set forth below.
| | | | | |
| Year | Redemption Price |
| 2023 | 102.313 | % |
| 2024 | 101.156 | % |
| 2025 and thereafter | 100.000 | % |
The 2028 Secured Notes are unconditionally guaranteed by the Note Guarantors. WillScot Mobile Mini is not a guarantor of the 2028 Secured Notes. The Note Guarantors, as well as certain of the Company’s non-US subsidiaries, are guarantors or borrowers under the 2020 ABL Facility. To the extent lenders under the 2020 ABL Facility release the guarantee of any Note Guarantor, such Note Guarantor will also be released from obligations under the 2025 Secured Notes. These guarantees are secured by a second priority security interest in substantially all of the assets of WSII and the Note Guarantors, subject to customary exclusions. The guarantees of the 2028 Secured Notes by WillScot Equipment II, LLC, a Delaware limited liability company which holds certain of WSII’s assets in the US, will be subordinated to its obligations under the 2020 ABL Facility.
Unamortized deferred financing costs pertaining to the 2028 Secured Notes were $8.4 million as of December 31, 2020.
The Company is in compliance with all debt covenants and restrictions for the aforementioned debt instruments as of December 31, 2020.
2023 Senior Unsecured Notes
The Company had $200.0 million in aggregate principal amount of senior unsecured notes due November 15, 2023. On June 19, 2019 (the "Redemption Date"), WSII used proceeds from its US ABL Facility to redeem all $200.0 million in aggregate outstanding principal amount of the unsecured notes at a redemption price of 102.0%, plus a make-whole premium of 1.126% and any accrued and unpaid interest to, but not including, the Redemption Date. The Company recorded a loss on extinguishment of $7.2 million, which included $6.2 million of make-whole premiums and $1.0 million related to the write-off of unamortized deferred financing fees.
Finance Leases
The Company maintains finance leases primarily related to transportation equipment. At December 31, 2020, obligations under the finance leases for certain real property and transportation related equipment were $77.9 million. The Company had no finance leases at December 31, 2019.
Mobile Mini Debt
Mobile Mini had $250.0 million in aggregate principal amount of 5.875% senior notes outstanding prior to the Merger. Interest was payable semi-annually on January 1 and July 1. In connection with the Merger, these notes were assumed by WillScot Mobile Mini and subsequently redeemed using proceeds from the 2025 Secured Notes discussed above.
Mobile Mini had a $1.0 billion first lien senior secured revolving credit facility. At June 30, 2020, Mobile Mini had $563.2 million of outstanding principal on the credit facility. In connection with the Merger, this line of credit was assumed by WillScot Mobile Mini and subsequently repaid in full using proceeds from the 2020 ABL Facility discussed above.
NOTE 12 - Equity
Preferred Stock
WillScot Mobile Mini's certificate of incorporation authorizes the issuance of 1,000,000 shares of Preferred Stock with a par value of $0.0001 per share. As of December 31, 2020, the Company has 0 shares of Preferred Stock issued and outstanding.
Common Stock
WillScot Mobile Mini's certificate of incorporation authorizes the issuance of 500,000,000 shares of Common Stock with a par value of $0.0001 per share. The Company has 229,038,158 shares of Common Stock issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2020. The outstanding shares of the Company's Common Stock are duly authorized, validly issued, fully paid and non-assessable.
On July 30, 2018, WillScot closed a public offering of 8,000,000 shares of its Class A Common Stock at an offering price of $16.00 per share. On August 10, 2018, the underwriters exercised their right to purchase an additional 1,200,000 shares at the public offering price. The net offering proceeds, including the exercise of the over-allotment option, were $139.0 million, after deducting discount and offering expenses of $8.2 million. The Company used the proceeds to fund the ModSpace acquisition and to pay related fees and expenses.
On August 15, 2018, WillScot issued 6,458,229 unregistered shares of its Class A Common Stock to former ModSpace shareholders as part of the consideration paid for ModSpace. In connection with the private placement, WillScot entered into a registration rights agreement dated July 26, 2018, under which WillScot granted customary registration rights to the holders of the unregistered common shares. Subject to limited exception, the unregistered shares issued to former ModSpace shareholders could not be sold or otherwise transferred prior to February 15, 2019.
On December 11, 2018, pursuant to the terms of the Warrant Exchange discussed in more detail below, the Company issued 8,205,841 registered Class A common shares.
In connection with the stock compensation vesting and stock option exercises described in Note 18, the Company issued 309,857 shares of Common Stock during the year ended December 31, 2019.
On June 30, 2020, as contemplated by the Merger Agreement, Sapphire Holdings exchanged each of its shares of common stock of Holdings for 1.3261 shares of newly issued WillScot Class A Common Stock (the "Sapphire Exchange"). As a result of the Sapphire Exchange, all issued and outstanding shares of WillScot's Class B Common Stock, par value $0.0001 per share, were automatically canceled for no consideration and the existing exchange agreement was automatically terminated. As a result of the Sapphire Exchange, Sapphire Holdings became a wholly-owned subsidiary of WillScot. Sapphire Holdings received 10,641,182 shares of Common Stock of WillScot in the Sapphire Exchange. Prior to the Sapphire Exchange, Sapphire Holdings' ownership of Holdings was recorded as a non-controlling interest in the consolidated financial statements. Subsequent to the Sapphire Exchange, the Company's subsidiaries are each wholly owned and there is no non-controlling interest. As a result of the Sapphire Exchange, non-controlling interest of $63.9 million was reclassified to $66.9 million of additional paid-in-capital and $(3.0) million to accumulated other comprehensive loss, on the consolidated balance sheet.
In connection with the Merger on July 1, 2020, the Company issued 106,426,722 shares of Class A Common Stock in exchange for Mobile Mini Common Stock outstanding and subsequently filed an amended and restated certificate of incorporation, which reclassified all outstanding shares of the Class A Common Stock and converted such shares into shares of Common Stock, par value of $0.0001 per share, of WillScot Mobile Mini.
In connection with the Sapphire Exchange described above, stock compensation vesting and stock option exercises described in Note 18, and the warrant exercises described below, the Company issued 13,792,582 shares of Common Stock during the year ended December 31, 2020.
Stock Repurchase Program
On August 7, 2020, the Company's Board of Directors approved a stock repurchase program that authorizes the Company to repurchase up to $250 million of its outstanding shares of Common Stock and equivalents. The stock repurchase program does not obligate the Company to purchase any particular number of shares, and the timing and exact amount of any repurchases will depend on various factors, including market pricing, business, legal, accounting, and other considerations.
The Company may repurchase its shares in open market transactions from time to time or through privately negotiated transactions in accordance with federal securities laws, at the Company's discretion. The repurchase program, which has no expiration date, may be increased, suspended, or terminated at any time. The program is expected to be implemented over the course of several years and will be conducted subject to the covenants in the agreements governing our indebtedness.
During the year ended December 31, 2020, 0 shares of Common Stock were repurchased, and the Company repurchased $35.3 million warrants and share equivalents, including withholding taxes on net share settlements of employee stock awards.
Accumulated Other Comprehensive Loss
The changes in accumulated other comprehensive loss ("AOCI"), net of tax, for the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018, were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands) | Foreign Currency Translation | | Unrealized losses on hedging activities | | Total |
| Balance at December 31, 2017 | $ | (49,497) | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | (49,497) | |
| Other comprehensive loss before reclassifications | (11,639) | | | (6,240) | | | (17,879) | |
Reclassifications from AOCI to income(a) | 0 | | | 285 | | | 285 | |
Reclassifications from AOCI to retained earnings(b) | (2,540) | | | 0 | | | (2,540) | |
| Less other comprehensive income attributable to non-controlling interest | 1,068 | | | 537 | | | 1,605 | |
| Balance at December 31, 2018 | (62,608) | | | (5,418) | | | (68,026) | |
| Other comprehensive income (loss) before reclassifications | 10,586 | | | (7,930) | | | 2,656 | |
Reclassifications from AOCI to income(a) | 0 | | | 3,121 | | | 3,121 | |
| Less other comprehensive income (loss) attributable to non-controlling interest | (960) | | | 434 | | | (526) | |
| Balance at December 31, 2019 | (52,982) | | | (9,793) | | | (62,775) | |
| Other comprehensive income (loss) before reclassifications | 28,404 | | | (11,874) | | | 16,530 | |
Reclassifications from AOCI to income(a) | 0 | | | 10,125 | | | 10,125 | |
| Less other comprehensive income attributable to non-controlling interest | 1,183 | | | 702 | | | 1,885 | |
| Impact of elimination of non-controlling interest on accumulated other comprehensive income | (1,299) | | | (1,673) | | | (2,972) | |
| Balance at December 31, 2020 | $ | (24,694) | | | $ | (12,513) | | | $ | (37,207) | |
(a) For the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018, $10.1 million, $3.3 million and $0.4 million, respectively, was reclassified from AOCI into the consolidated statement of operations within interest expense related to the interest rate swaps discussed in Note 14. For the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018, the Company recorded a tax benefit of $2.4 million, $0.8 million and $0.1 million associated with this reclassification, respectively.
(b) In the first quarter of 2018, the Company elected to early adopt ASU 2018-02, Income Statement-Reporting Comprehensive Income (Topic 220) - Reclassification of Certain Tax Effects from Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income, which resulted in a discrete reclassification of $2.5 million from accumulated other comprehensive loss to accumulated deficit effective January 1, 2018.
NOTE 13 - Warrants (as restated)
Warrants
2015 Public Warrants
WillScot was incorporated under the name Double Eagle Acquisition Corporation ("DEAC") on June 26, 2015. On November 29, 2017, DEAC acquired Williams Scotsman International, Inc. (“WSII”) from Algeco Scotsman Global S.à r.l., which is majority owned by an investment fund managed by TDR Capital (the “Business Combination”). In connection with the Business Combination, DEAC domesticated to Delaware and changed its name to WillScot Corporation.
As part of its initial public offering, DEAC issued 2015 Public Warrants. Each 2015 Public Warrant entitled the holder to purchase one-half of one share of WillScot Class A Common Stock at a price of $5.75 per half share (or $11.50 per whole share), subject to adjustment. The Company was able to redeem the 2015 Public Warrants for $0.01 per warrant if the closing price of WillScot’s Class A shares equaled or exceeded $18.00 per share for any 20 trading days within a 30-trading day period ending on the third trading day prior to the date the Company sent a notice of redemption to the warrant holders, providing for a 30-day notice period.
2015 Public Warrant Exchange
On November 8, 2018, WillScot commenced an offer to exchange the 2015 Public Warrants for shares of its Class A Common Stock in a cashless transaction (the “Warrant Exchange”). In the tender offer, each warrant holder had the opportunity to receive 0.18182 registered share of Class A Common Stock in exchange for each warrant tendered by the holder and exchanged pursuant to the offer. In connection, with the Warrant Exchange 45,131,827 of the outstanding 69,499,694 warrants were tendered and accepted for exchange and 8,205,841 shares of Class A Common Stock were issued. The Company capitalized $1.8 million of offering expenses within additional paid-in capital in December 2018 in connection with the Warrant Exchange.
During the year ended December 31, 2019, 135,000 of the 2015 Public Warrants were exercised, resulting in the issuance of 67,500 shares of Class A Common Stock and $0.8 million in proceeds.
2015 Public Warrant Redemption
The Company's share price performance target was achieved on January 21, 2020 and, on January 24, 2020, the Company delivered a notice (the "Redemption Notice") to redeem all of its 2015 Public Warrants that remained unexercised on February 24, 2020. As further described in the Redemption Notice and permitted under the warrant agreement, holders of these warrants who exercised them following the date of the Redemption Notice were required to do so on a cashless basis. From January 1, 2020 through January 24, 2020, 796,610 warrants were exercised for cash, resulting in the Company receiving cash proceeds of $4.6 million and the Company issuing 398,305 shares of the Company's Class A Common Stock. After January 24, 2020 through February 24, 2020, 5,836,048 warrants were exercised on a cashless basis. An aggregate of 1,097,162 shares of the Company's Class A Common Stock was issued in connection with these cashless exercises. Thereafter, the Company completed the redemption of 38,509 remaining warrants under the Redemption Notice for $0.01 per warrant. At December 31, 2020, 0 2015 Public Warrants were outstanding.
2015 Private Warrants
DEAC also issued the 2015 Private Warrants to purchase its Common Stock in a private placement concurrently with its initial public offering. The 2015 Private Warrants were purchased at a price of $0.50 per unit for an aggregate purchase price of $9.75 million. The 2015 Private Warrants are identical to the 2015 Public Warrants, except that, if held by certain original investors (or their permitted assignees), the 2015 Private Warrants may be exercised on a cashless basis and are not subject to redemption.
During the year ended December 31, 2020, 4,781,700 2015 Private Warrants were repurchased for $21.6 million and cancelled. Additionally, 70,000 2015 Private Warrants were exercised, resulting in the Company receiving cash proceeds of $0.4 million and issuing 35,000 shares of Common Stock.
At December 31, 2020, 12,710,000 2015 Private Warrants were outstanding.
2018 Warrants
In connection with the ModSpace acquisition in 2018, WillScot issued the 2018 Warrants to purchase approximately 10.0 million WillScot Class A common shares to former shareholders of ModSpace. Each 2018 Warrant entitles the holder thereof to purchase 1 share of WillScot Class A Common Stock at an exercise price of $15.50 per share, subject to potential adjustment. Subject to limited exception, the 2018 Warrants were not exercisable or transferable until February 11, 2019. The 2018 Warrants expire on November 29, 2022. Under a registration rights agreement dated July 26, 2018, WillScot agreed to file a registration statement by the six-month anniversary of the issuance date. The registration statement became effective February 12, 2019.
During the year ended December 31, 2019, the Company repurchased and terminated 22,063 of the 2018 Warrants for less than $0.1 million.
During the year ended December 31, 2020, 195,410 2018 warrants were exercised, on a cashless basis, and 38,802 shares of the Company's Common Stock were issued. Also during the year ended December 31, 2020, the Company repurchased and subsequently cancelled 51,865 2018 warrants for approximately $0.3 million. At December 31, 2020, 9,730,241 2018 Warrants were outstanding.
The Company accounts for its warrants in the following ways: (i) the 2015 Private Warrants as liabilities for all periods presented, (ii) the 2015 Public Warrants as liabilities through their final redemption in February 2020 and (iii) the 2018 Warrants as liabilities until June 30, 2020, the date all issued and outstanding shares of the Company's Class B Common Stock were cancelled.
The Company determined the following fair values for the outstanding warrants recorded as liabilities at December 31:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands) | 2020
(as restated) | | 2019
(as restated) |
| 2015 Public Warrants | $ | 0 | | | $ | 22,682 | |
| 2015 Private Warrants | 77,404 | | | 72,705 | |
| 2018 Warrants | 0 | | | 58,369 | |
| Total | $ | 77,404 | | | $ | 153,756 | |
NOTE 14 – Income Taxes (as restated)
The components of income tax (benefit) expense for the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018 are comprised of the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands) | 2020 | | 2019 | | 2018 |
| US Federal and State | | | | | |
| Current | $ | 1,601 | | | $ | 827 | | | $ | 668 | |
| Deferred | (58,026) | | | 1,904 | | | (36,149) | |
| Outside of US | | | | | |
| Current | 2,104 | | | (395) | | | 924 | |
| Deferred | 2,870 | | | (4,527) | | | (4,043) | |
| Total income tax benefit | $ | (51,451) | | | $ | (2,191) | | | $ | (38,600) | |
Income tax results differed from the amount computed by applying the US statutory income tax rate of 21% to the income (loss) before income taxes for the following reasons for the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands) | 2020 | | 2019 | | 2018 |
| (as restated) | | (as restated) | | (as restated) |
| Income (loss) before income tax | | | | | |
| US | $ | 6,597 | | | $ | (119,099) | | | $ | (56,994) | |
| Non-US | 17,292 | | | (4,257) | | | (11,348) | |
| Total income (loss) before income tax | $ | 23,889 | | | $ | (123,356) | | | $ | (68,342) | |
| | | | | |
| US Federal statutory income tax expense (benefit) | $ | 5,017 | | | $ | (25,905) | | | $ | (14,352) | |
| Effect of tax rates in foreign jurisdictions | 128 | | | (207) | | | (626) | |
| State income tax expense (benefit), net of federal benefit | 3,962 | | | 1,829 | | | (2,478) | |
| Unremitted foreign earnings | 0 | | | 0 | | | (6,793) | |
| Valuation allowances | (56,479) | | | 961 | | | (11,871) | |
| Non-deductible items | 187 | | | (233) | | | 0 | |
| Non-deductible executive compensation | 1,449 | | | 490 | | | 0 | |
| Non-deductible transaction costs | 4,425 | | | (12) | | | 1,134 | |
| Non-deductible (non-taxable) remeasurement of common stock warrant liabilities | (727) | | | 23,021 | | | (5,004) | |
| Uncertain tax positions | (11,166) | | | 0 | | | 0 | |
| Tax law changes (excluding valuation allowance) (a) | 2,523 | | | (2,785) | | | 64 | |
| Other | (770) | | | 650 | | | 1,326 | |
| Reported income tax benefit | $ | (51,451) | | | $ | (2,191) | | | $ | (38,600) | |
| Effective income tax rate | (215.38) | % | | 1.78 | % | | 56.48 | % |
| | | | | |
| (a) | Tax law changes include the following amounts: 2020 and 2019 primarily represents changes in tax law in non-US jurisdictions and 2018 primarily represents US tax reform items. |
Deferred Income Taxes
Deferred income taxes reflect the net tax effects of temporary differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities and their tax bases, as well as from net operating loss and carryforwards. Significant components of the Company’s deferred tax assets and liabilities are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands) | 2020 | | 2019 |
| Deferred tax assets | | | |
| Deferred interest expense | $ | 128,346 | | | $ | 138,206 | |
| Employee benefit plans | 3,532 | | | 1,916 | |
| Accrued liabilities | 10,692 | | | 8,494 | |
| Deferred revenue | 32,412 | | | 20,951 | |
| Operating lease liability | 58,044 | | | 37,438 | |
| Other | 13,628 | | | 7,817 | |
| Tax loss carryforwards | 295,326 | | | 231,503 | |
| Deferred tax assets, gross | 541,980 | | | 446,325 | |
| Valuation allowance | (25,158) | | | (80,241) | |
| Net deferred income tax asset | $ | 516,822 | | | $ | 366,084 | |
| | | |
| Deferred tax liabilities | | | |
| Rental equipment and other property, plant and equipment | $ | (648,966) | | | $ | (375,682) | |
| Intangible assets | (117,403) | | | (23,690) | |
| ROU asset | (57,820) | | | (37,218) | |
| Deferred tax liability | (824,189) | | | (436,590) | |
| Net deferred income tax liability | $ | (307,367) | | | $ | (70,506) | |
In general, FASB ASC Section 740, “Income Taxes” (“ASC 740”) requires us to evaluate the realizability of our deferred tax assets and reduce the deferred tax assets by valuation allowances to the extent we determine some or all of our deferred tax assets are not more likely than not realizable. To determine the realizability, ASC 740 requires consideration of sources of available taxable income of the proper character and within the time period before which our deferred tax assets, if any, expire due to the passage of time.
The Company's valuation allowance decreased by $55.1 million from 2019. An increase of $1.5 million was recorded in purchase accounting for the Merger in relation to state net operating losses deemed not more likely than not to be realized and a decrease in the change in estimate about the realizability of deferred tax assets for a total amount of $56.6 million was recorded as a tax benefit.
Prior to the Merger, the Company's sources of taxable income were insufficient to realize a significant portion of WillScot's historical deferred tax assets. As a result, at December 31, 2019, the Company maintained valuation allowances of approximately $80.2 million to cover deferred tax assets that were not realizable. The significant WillScot historical deferred tax assets covered by valuation allowances were net operating losses and deferred interest expense. On July 1, 2020, with the Merger, estimates for future taxable income increased significantly; accordingly, the Company concluded that a substantial portion of WillScot's historical deferred tax assets that were previously covered by valuation allowances became more likely than not realizable. As a result, the Company reversed $54.6 million of valuation allowances as a discrete benefit in the third quarter of 2020 relating to the Merger. The significant deferred tax assets of the Company are comprised of net operating losses and deferred interest expense. A small percentage of the net operating losses are subject to an annual limitation based on tax law for which a valuation allowance continues to be maintained.
Tax loss carryforwards at December 31, 2020 are outlined in the table below and include US Federal, US State and non-US (Mexico, Canada and UK). The availability of these tax losses to offset future income varies by jurisdiction. Furthermore, the ability to utilize the tax losses may be subject to additional limitations upon the occurrence of certain events, such as a change in the ownership of the Company. The Company anticipates that our remaining available net operating losses will be consumed prior to their expiration.
The Company’s tax loss carryforwards are as follows at December 31, 2020:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands) | Loss
Carryforward | | Expiration |
| Jurisdiction: | | | |
| US - Federal | $ | 1,187,500 | | | 2022 – 2037, Indefinite |
| US - State | 700,500 | | | 2021 –2040, Indefinite |
| Foreign - Mexico & Canada | 14,100 | | | 2025 – 2038 |
| Total | $ | 1,902,100 | | | |
As of December 31, 2020, the total amount of the basis difference in investments outside the US, which are indefinitely reinvested and for which deferred taxes have not been provided, is approximately $327.3 million. The tax, if any, associated with the recovery of the basis difference is dependent on the manner in which it is recovered and is not readily determinable.
Unrecognized Tax Positions
The Company is subject to taxation in US, Canada, Mexico, UK, and state jurisdictions. The Company’s tax returns are subject to examination by the applicable tax authorities prior to the expiration of statute of limitations for assessing additional taxes, which generally ranges from two to five years after the end of the applicable tax year. Therefore, as of December 31, 2020, tax years for 2014 through 2020 generally remain subject to examination by the tax authorities. In addition, in certain taxing jurisdictions, in the case of carryover tax attributes to years open for assessment, such attributes may be subject to reduction by taxing authorities.
A reconciliation of the beginning and ending amount of unrecognized tax benefits is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands) | 2020 | | 2019 | | 2018 |
| Unrecognized tax benefits – January 1, | $ | 63,747 | | | $ | 64,444 | | | $ | 72,660 | |
| Increases based on tax positions related to current period | 1,211 | | | 0 | | | 1,545 | |
| Increases based on tax positions related to prior period | 0 | | | 268 | | | 0 | |
| Decreases based on tax positions related to prior period | 0 | | | (287) | | | (9,016) | |
| Decrease from expiration of statute of limitations | (10,464) | | | (678) | | | (745) | |
| Unrecognized tax benefits – December 31, | $ | 54,494 | | | $ | 63,747 | | | $ | 64,444 | |
At December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018, respectively, there were $53.2 million, $59.3 million and $60.0 million of unrecognized tax benefits that, if recognized, would affect the annual effective tax rate.
The Company classifies interest on tax deficiencies and income tax penalties within income tax expense. During the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018, the Company recognized approximately $(0.9) million, $0.8 million, and $1.0 million in interest and penalties, respectively. The Company had approximately $1.5 million and $2.4 million for the payment of interest and penalties accrued at December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively.
Future tax settlements or statute of limitation expirations could result in a change to the Company’s uncertain tax positions. The Company believes that it is reasonably possible that approximately $11.3 million of unrecognized tax benefits, as of December 31, 2020, could decrease in the next twelve months as a result of statute of limitation expirations, audit settlements or resolution of tax uncertainties.
NOTE 15 - Derivatives
On November 6, 2018, the Company entered into an interest rate swap agreement (the “Swap Agreement”) with a financial counterparty that effectively converts $400.0 million in aggregate notional amount of variable-rate debt under the Company’s ABL Facility into fixed-rate debt. The Swap Agreement will terminate on May 29, 2022. Under the terms of the Swap Agreement, the Company receives a floating rate equal to one-month LIBOR and makes payments based on a fixed rate of 3.06% on the notional amount. The receive rate under the terms of the Swap Agreement was 0.15% and 1.74% at December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively.
The Swap Agreement was designated and qualified as a hedge of the Company’s exposure to changes in interest payment cash flows created by fluctuations in variable interest rates on the ABL Facility.
The location and the fair value of derivative instruments designated as hedges in the consolidated balance sheets as of December 31 was as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands) | Balance Sheet Location | 2020 | | 2019 |
| Cash Flow Hedges: | | | | |
| Interest rate swap | Accrued liabilities | $ | 11,619 | | | $ | 5,348 | |
| Interest rate swap | Other non-current liabilities | $ | 5,308 | | | $ | 8,943 | |
The fair value of the interest rate swap is based on dealer quotes of market forward rates, a Level 2 input on the fair value hierarchy, and reflects the amount that the Company would receive or pay as of December 31, 2020 for contracts involving the same attributes and maturity dates.
The following table discloses the impact of the interest rate swap, excluding the impact of income taxes, on other comprehensive income (“OCI”), AOCI and the Company’s statement of operations for the years ended December 31:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands) | 2020 | | 2019 | | 2018 |
| Loss recognized in OCI | $ | (2,288) | | | $ | (6,280) | | | $ | (7,777) | |
| Location of loss recognized in income | Interest expense | | Interest expense | | Interest expense |
| Loss reclassified from AOCI into income (effective portion) | $ | (10,125) | | | $ | (3,254) | | | $ | (373) | |
NOTE 16 - Fair Value Measures (as restated)
The fair value of financial assets and liabilities are included at the amount at which the instrument could be exchanged in a current transaction between willing parties, other than in a forced or liquidation sale.
The Company utilizes the suggested accounting guidance for the three levels of inputs that may be used to measure fair value:
| | | | | |
| Level 1 - | Observable inputs such as quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities; |
| Level 2 - | Observable inputs, other than Level 1 inputs in active markets, that are observable either directly or indirectly; and |
| Level 3 - | Unobservable inputs for which there is little or no market data, which require the reporting entity to develop its own assumptions |
The Company has assessed that the fair value of cash and short-term deposits, trade receivables, trade payables, capital lease and other financing obligations, and other current liabilities approximate their carrying amounts.
The following table shows the carrying amounts and fair values of financial liabilities which are disclosed, but not measured, at fair value, including their levels in the fair value hierarchy:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 |
| (as restated) | (as restated) |
| Carrying Amount | Fair Value | Carrying Amount | Fair Value |
| (in thousands) | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 |
US ABL Facilities(a) | $ | 1,263,833 | | $ | 0 | | $ | 1,304,612 | | $ | 0 | | $ | 885,245 | | $ | 0 | | $ | 903,000 | | $ | 0 | |
Multicurrency Facility(a) | 0 | | $ | 0 | | 0 | | 0 | | 0 | | 0 | | 0 | | 0 | |
2022 Secured Notes(a) | 0 | | 0 | | 0 | | 0 | | 264,576 | | 0 | | 282,250 | | 0 | |
2023 Secured Notes(a) | 0 | | 0 | | 0 | | 0 | | 482,768 | | 0 | | 517,334 | | 0 | |
2025 Secured Notes(a) | 637,068 | | 0 | | 694,876 | | 0 | | 0 | | 0 | | 0 | | 0 | |
2028 Secured Notes(a) | 491,555 | | 0 | | 518,820 | | 0 | | 0 | | 0 | | 0 | | 0 | |
| Total | $ | 2,392,456 | | $ | 0 | | $ | 2,518,308 | | $ | 0 | | $ | 1,632,589 | | $ | 0 | | $ | 1,702,584 | | $ | 0 | |
(a) The carrying values of the US ABL Facilities, the Multicurrency Facility, the 2025 Secured Notes, and the 2028 Secured Notes included $40.8 million, $0, $12.9 million, and $8.4 million of unamortized debt issuance costs as of December 31, 2020, which were presented as a direct reduction of the corresponding liability. The carrying values of the US ABL Facility, the Canadian ABL Facility, the 2022 Secured Notes, and the 2023 Secured Notes included $17.8 million, $0, $5.4 million, and $7.2 million of unamortized debt issuance costs at December 31, 2019, which were presented as a direct reduction of the corresponding liability.
The carrying value of the ABL Facility, excluding debt issuance costs, approximates fair value as the interest rates are variable and reflective of market rates. The fair value of the 2022 Secured Notes, the 2023 Secured Notes, the 2025 Secured Notes, and the 2028 Secured Notes is based on their last trading price at the end of each period obtained from a third party.
The location and the fair value of derivative assets and liabilities designated as hedges in the consolidated balance sheet are disclosed in Note 15.
As part of the Merger, on July 2, 2020, the Company converted Mobile Mini's outstanding fully vested stock options to 7,361,516 WillScot Mobile Mini stock options using a conversion ratio of 2.405 as set by the Merger Agreement. The fair value of these options was valued at $19.3 million and is part of the purchase consideration. The value of the Mobile Mini stock options converted to WillScot Mobile Mini stock options in connection with the Merger, was determined utilizing the Black-Scholes option-pricing model and is affected by several variables, the most significant of which are the expected life of the equity award, the exercise price of the stock option as compared to the fair market value of the Common Stock on the Merger date, and the estimated volatility of the Common Stock over the term of the equity award. Estimated volatility is based on the historical volatility of the Company's Common Stock. The risk-free interest rate is based on the US Treasury yield curve in effect at the time of the Merger. The key inputs utilized to determine the fair value of the stock options converted included within the purchase price were expected volatility of 51.92%, risk free rate of interest 0.17%, dividend yield of 0 and expected life of 2 years.
Prior to their redemption, the Company’s 2015 Public Warrants traded in active markets. When classified as liabilities, warrants traded in active markets with sufficient trading volume represent Level 1 financial instruments as they were publicly traded in active markets and thus had observable market prices which were used to estimate the fair value adjustments for the related common stock warrant liabilities. When classified as liabilities, warrants not traded in active markets, or traded with insufficient volume, represent Level 3 financial instruments that are valued using a Black-Scholes option-pricing model to estimate the fair value adjustments for the related common stock warrant liabilities.
The following table shows the carrying amounts and fair values of financial liabilities for which are measured at fair value:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2020 | December 31, 2019 |
| (as restated) | (as restated) |
| Carrying Amount | Fair Value | Carrying Amount | Fair Value |
| (in thousands) | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 |
| 2015 Public Warrants | 0 | | 0 | | 0 | | 0 | | 22,682 | | 22,682 | | 0 | 0 | |
| 2015 Private Warrants | 77,404 | | 0 | | 0 | | 77,404 | | 72,705 | | 0 | | 0 | | 72,705 | |
| 2018 Warrants | 0 | | 0 | | 0 | | 0 | 58,369 | | 0 | | 0 | | 58,369 | |
| Total | $ | 77,404 | | $ | 0 | | $ | 0 | | $ | 77,404 | | $ | 153,756 | | $ | 22,682 | | $ | 0 | | $ | 131,074 | |
Level 3 Disclosures
The Company utilizes a Black Scholes option-pricing model to value the 2015 Private Warrants and 2018 Warrants at each reporting period and transaction date, with changes in fair value recognized in the statements of operations. The estimated fair value of the common stock warrant liability is determined using Level 3 inputs. Inherent in the pricing model are assumptions related to expected share-price volatility, expected life, risk-free interest rate and dividend yield. The Company estimates the volatility of its ordinary shares based on historical volatility that matches the expected remaining life of the warrants. The risk-free interest rate is based on the US Treasury zero-coupon yield curve on the grant date for a maturity similar to the expected remaining life of the warrants. The expected life of the warrants is assumed to be equivalent to their remaining contractual term. The dividend rate is based on the historical rate, which the Company anticipates to remain at zero.
The following table provides quantitative information regarding Level 3 fair value measurements:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2020 | | December 31, 2019 |
| 2015 Private Warrants | | 2015 Private Warrants | 2018 Warrants |
| (as restated) | | (as restated) | (as restated) |
| Stock Price | 23.17 | | | 18.49 | | 18.49 | |
| Strike Price | 11.50 | | | 11.50 | | 15.50 | |
| Expected Life | 1.91 | | 2.91 | 2.91 |
| Volatility | 41.2 | % | | 33.3 | % | 33.3 | % |
| Risk Free rate | 0.13 | % | | 1.61 | % | 1.61 | % |
| Dividend yield | 0 | | | 0 | | 0 | |
| Fair value of warrants | $ | 12.17 | | | $ | 8.29 | | $ | 5.85 | |
The following table presents changes in Level 3 liabilities measured at fair value for the year ended December 31, 2020:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands) | 2015 Private Warrants | | 2018 Warrants |
| (as restated) | | (as restated) |
| Balance- beginning of year | $ | 72,705 | | | $ | 58,369 | |
| Exercise or conversion | (359) | | | (416) | |
| Repurchase | (24,970) | | | 0 | |
| Measurement adjustment | 30,028 | | | (31,737) | |
| Reclassification to equity at June 30, 2020 | 0 | | | (26,216) | |
| Balance- end of year | $ | 77,404 | | | $ | 0 | |
The 2018 Warrants were reclassified to equity at June 30, 2020, the date all issued and outstanding shares of the Company's Class B Common Stock were cancelled. Therefore, the 2018 Warrants were not recorded at fair value at December 31, 2020.
The following table presents changes in Level 3 liabilities measured at fair value for the year ended December 31, 2019:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands) | 2015 Private Warrants | | 2018 Warrants |
| (as restated) | | (as restated) |
| Balance- beginning of year | $ | 21,532 | | | $ | 14,600 | |
| Transferred to public holders | (1,889) | | | 0 | |
| Measurement adjustment | 53,062 | | | 43,878 | |
| Repurchases | 0 | | | (109) | |
| Balance- end of year | $ | 72,705 | | | $ | 58,369 | |
NOTE 17 - Restructuring
Restructuring costs include charges associated with exit or disposal activities that meet the definition of restructuring under FASB ASC Topic 420, Exit or Disposal Cost Obligations (“ASC 420”). The Company's restructuring plans are generally country or region specific and are typically completed within a one-year period. Restructuring costs incurred under these plans include (i) one-time termination benefits related to employee separations, (ii) contract termination costs, and (iii) other related costs associated with exit or disposal activities including, but not limited to, costs for consolidating or closing facilities. Lease exit costs related to the termination of leases for duplicative branches and corporate facilities are now recorded in operating lease liabilities and are not part of the restructuring liabilities. Costs related to the integration of acquired businesses that do not meet the definition of restructuring under ASC 420, such as employee training costs, duplicate facility costs, and professional services expenses, are included within SG&A expense.
The Company incurred costs associated with restructuring plans designed to streamline operations and reduce costs of $6.5 million, $3.8 million, and $15.5 million net of reversals, during the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018, respectively. The following is a summary of the activity in the Company’s restructuring accruals for years ended December 31:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands) | Year Ended December 31, |
| 2020 | 2019 | 2018 |
| Employee Costs | Facility Exit Costs | Total | Employee Costs | Facility Exit Costs | Total | Employee Costs | Facility Exit Costs | Total |
| Beginning balance | $ | 447 | | $ | 0 | | $ | 447 | | $ | 4,544 | | $ | 972 | | $ | 5,516 | | $ | 227 | | $ | 0 | | $ | 227 | |
Reclassification of liability to operating lease asset at the adoption of ASC 842(a) | 0 | | 0 | | 0 | | 0 | | (972) | | (972) | | 0 | | 0 | | 0 | |
| Charges | 6,510 | | 17 | | 6,527 | | 1,955 | | 1,800 | | 3,755 | | 10,182 | | 5,286 | | 15,468 | |
| Cash payments | (5,356) | | 0 | | (5,356) | | (5,694) | | 0 | | (5,694) | | (5,806) | | (4,314) | | (10,120) | |
| Foreign currency translation | 30 | | 0 | | 30 | | (136) | | 0 | | (136) | | (59) | | 0 | | (59) | |
| Non-cash movements | 119 | | (17) | | 102 | | (222) | | (1,800) | | (2,022) | | 0 | | 0 | | 0 | |
| Ending balance | $ | 1,750 | | $ | 0 | | $ | 1,750 | | $ | 447 | | $ | 0 | | $ | 447 | | $ | 4,544 | | $ | 972 | | $ | 5,516 | |
(a) As a result of the adoption of ASC 842, the January 1, 2019 restructuring liability attributable to “cease-use” locations was reclassified to operating lease assets and 2019 costs related to the termination of leases for duplicative branches and corporate facilities are now recorded in lease impairment charges and other related costs.
The restructuring charges for the year ended December 31, 2020 are primarily driven by termination costs as a result of the elimination of positions due to the Merger and reductions in force as a result of COVID-19.
The Company initiated certain restructuring plans associated with the ModSpace acquisition in order to capture operating synergies as a result of integrating ModSpace into WillScot. The restructuring activities primarily include the termination of employees in connection with the consolidation of overlapping facilities and functions within our existing business.
The restructuring charges for the year ended December 31, 2018 primarily relate to employee termination costs and lease exist costs in connection with the integration of Acton, Tyson, and ModSpace acquisitions in order to capture operating synergies as a result of integrating these businesses into WillScot. The restructuring activities include the termination of leases for 26 duplicative branch and corporate facilities and the termination of employees in connection with the consolidation of these overlapping facilities and functions within our existing business.
Segments (as defined in Note 20)
The $6.5 million of restructuring charges for the year ended December 31, 2020 included: $2.1 million of charges pertaining to the NA Modular segment; $4.0 million of charges related to the NA Storage segment; and $0.4 million of charges related to the UK Storage segment.
The $3.8 million of restructuring charges for the year ended December 31, 2019 included charges pertaining to the NA Modular segment.
The $15.5 million of restructuring charges for the year ended December 31, 2018 included charges pertaining to the NA Modular segment.
NOTE 18 - Stock-Based Compensation
Restricted Stock Awards
The following table summarizes the Company's RSA activity during the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Number of Shares | | Weighted-Average Grant Date Fair Value |
| Balance, December 31, 2017 | 0 | | | $ | 0 | |
| Granted | 72,053 | | | $ | 15.57 | |
| Balance, December 31, 2018 | 72,053 | | | $ | 15.57 | |
| Granted | 52,755 | | | $ | 14.69 | |
| Vested | (72,053) | | | $ | 15.57 | |
| Balance, December 31, 2019 | 52,755 | | | $ | 14.69 | |
| Granted | 65,959 | | | $ | 11.75 | |
| Vested | (61,266) | | | $ | 14.28 | |
| Balance, December 31, 2020 | 57,448 | | | $ | 11.75 | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
Compensation expense for RSAs recognized in SG&A expense in the consolidated statements of operations was $0.9 million, $1.0 million, and $0.5 million for the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019, and 2018, respectively. At December 31, 2020, there was $0.2 million of unrecognized compensation cost related to RSAs that was expected to be recognized over the remaining weighted average vesting period of 0.4 years.
Time-Based RSUs
The following table summarizes the Company's Time-Based RSU activity during the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Number of Shares | | Weighted-Average Grant Date Fair Value |
| Balance, December 31, 2017 | 0 | | | $ | 0 | |
| Granted | 921,730 | | | $ | 13.60 | |
| Forfeited | (68,997) | | | $ | 13.60 | |
| Balance, December 31, 2018 | 852,733 | | | $ | 13.60 | |
| Granted | 478,400 | | | $ | 11.69 | |
| Forfeited | (52,648) | | | $ | 12.78 | |
| Vested | (213,180) | | | $ | 12.78 | |
| Balance, December 31, 2019 | 1,065,305 | | | $ | 12.78 | |
| Granted | 632,864 | | | $ | 14.37 | |
| Forfeited | (33,558) | | | $ | 13.28 | |
| Vested | (538,845) | | | $ | 13.24 | |
| Balance, December 31, 2020 | 1,125,766 | | | $ | 13.44 | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
Compensation expense for Time-Based RSUs recognized in SG&A expense in the consolidated statements of operations was $5.6 million, $3.9 million, and $2.3 million for the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019, and 2018, respectively. At December 31, 2020, unrecognized compensation cost related to Time-Based RSUs totaled $13.3 million and was expected to be recognized over the remaining weighted average vesting period of 2.7 years.
Performance-Based RSUs
The following table summarizes the Company's Performance-Based RSU award activity during the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Number of Shares | | Weighted-Average Grant Date Fair Value |
| Balance, December 31, 2018 | 0 | | | $ | 0 | |
| Granted | 302,182 | | | $ | 13.22 | |
| Forfeited | (13,901) | | | $ | 13.22 | |
| Balance, December 31, 2019 | 288,281 | | | $ | 13.22 | |
| Granted | 325,256 | | | $ | 16.35 | |
| Forfeited | (12,700) | | | $ | 14.70 | |
| Vested | (7,449) | | | $ | 16.82 | |
| Balance, December 31, 2020 | 593,388 | | | $ | 14.88 | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
Compensation expense for Performance-Based RSUs recognized in SG&A expense in the consolidated statements of operations was $2.5 million and $1.0 million for the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019, respectively. For the year ended December 31, 2018, 0 compensation expense was recognized for Performance-Based RSUs. At December 31, 2020, unrecognized compensation cost related to Performance-Based RSUs totaled $5.4 million and was expected to be recognized over the remaining vesting period of 1.8 years.
Performance-Based RSUs vest based on the Company’s TSR Percentile Ranking as compared against the TSR for the companies comprising the Russell 3000 Group, measured as of the end of the Performance Period, based on the performance goals set forth in the award agreement.
Stock Options
The following table summarizes the Company's stock option activity during the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| WillScot Options | | Weighted-Average Exercise Price per Share | | Converted
Mobile Mini Options | | Weighted-Average Exercise Price per Share |
| Outstanding options, December 31, 2017 | 0 | | | $ | 0 | | | 0 | | | $ | 0 | |
| Granted | 589,257 | | | $ | 13.60 | | | 0 | | | $ | 0 | |
| Outstanding options, December 31, 2018 | 589,257 | | | $ | 13.60 | | | 0 | | | $ | 0 | |
| Forfeited | (41,302) | | | $ | 13.60 | | | 0 | | | $ | 0 | |
| Exercised | (13,767) | | | $ | 13.60 | | | 0 | | | $ | 0 | |
| Outstanding options, December 31, 2019 | 534,188 | | | $ | 13.60 | | | 0 | | | $ | 0 | |
| Converted at Merger | 0 | | | $ | 0 | | | 7,361,516 | | | $ | 13.52 | |
| Exercised | 0 | | | $ | 0 | | | (428,653) | | | $ | 13.07 | |
| Cancelled in settlement, net of taxes | 0 | | | $ | 0 | | | (4,901,408) | | | $ | 13.04 | |
| Outstanding options, December 31, 2020 | 534,188 | | | $ | 13.60 | | | 2,031,455 | | | $ | 14.78 | |
| | | | | | | |
| Fully vested and exercisable options, December 31, 2018 | 0 | | | $ | 0 | | | 0 | | | $ | 0 | |
| Vested during 2019 | 133,547 | | | $ | 13.60 | | | 0 | | | $ | 0 | |
| Fully vested and exercisable options, December 31, 2019 | 133,547 | | | $ | 13.60 | | | 0 | | | $ | 0 | |
| Vested during 2020 | 133,547 | | | $ | 13.60 | | | 2,031,455 | | | $ | 14.78 | |
| Fully vested and exercisable options, December 31, 2020 | 267,094 | | | $ | 13.60 | | | 2,031,455 | | | $ | 14.78 | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
Under our stock option plans, the Company may issue shares on a net basis at the request of the option holder. This occurs by netting the option costs in shares from the shares exercised.
NaN options were granted in the years ended December 31, 2020 or 2019. In the year ended December 31, 2018, the per share weighted-average fair value of all options granted was $5.51.
At December 31, 2020, the intrinsic value of stock options outstanding and stock options fully vested and currently exercisable was $22.2 million and $19.6 million, respectively. At December 31, 2020, the weighted-average remaining contractual term of options outstanding was 7.2 years for WillScot options and 5.3 years for converted Mobile Mini options.
The total intrinsic value of stock options exercised during the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 were $30.7 million and less than $0.1 million, respectively. No options were exercised during the year ended December 31, 2018.
The total fair value of stock options vested during the years ended December 31, 2020 and 2019 was $31.8 million and $1.8 million, respectively. NaN stock options vested during the year ended December 31, 2018.
WillScot Options
Compensation expense for stock option awards, recognized in SG&A expense in the consolidated statements of operations was $0.7 million, $0.8 million, and $0.6 million for the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019, and 2018, respectively. At December 31, 2020, unrecognized compensation cost related to stock option awards totaled $0.9 million and is expected to be recognized over the remaining vesting period of 1.2 years.
Conversion of Mobile Mini Options at the Merger
As part of the Merger, on July 2, 2020 the Company converted Mobile Mini's outstanding fully vested stock options to 7,361,516 WillScot Mobile Mini stock options using a conversion ratio of 2.405 as set by the Merger Agreement. The fair value of these options was valued at $19.3 million and is part of the purchase consideration.
The value of stock options converted was determined utilizing the Black-Scholes option-pricing model, and is affected by several variables, the most significant of which are the life of the equity award, the exercise price of the stock option as compared to the fair market value of the Common Stock on the Merger date, and the estimated volatility of the Common Stock over the term of the equity award. Estimated volatility is based on the historical volatility of the Company’s Common Stock. The risk-free interest rate is based on the US Treasury yield curve in effect at the time of the Merger.
NOTE 19 - Commitments and Contingencies
Commitments
At December 31, 2020 and 2019, commitments for the acquisition of rental equipment and property, plant and equipment were $5.0 million and $4.5 million, respectively.
Contingencies - Legal Claims
The Company is involved in various lawsuits or claims in the ordinary course of business. Management believes that there is no pending claim or lawsuit which, if adversely determined, would have a material effect on the Company’s financial condition, results of operations or cash flows.
NOTE 20 - Segment Reporting (as restated)
As a result of the Merger, the Company has evaluated its operating structure and, accordingly, its segment structure and has determined it operates in 4 reportable segments as follows: North America Modular Solutions ("NA Modular"), North America Storage Solutions ("NA Storage"), United Kingdom Storage Solutions ("UK Storage") and Tank and Pump Solutions ("Tank and Pump"). The NA Modular segment aligns with the WillScot legacy business prior to the Merger and the NA Storage, UK Storage and Tank and Pump segments align with the Mobile Mini segments prior to the Merger. Total assets for each reportable segment are not available because the Company utilizes a centralized approach to working capital management. Transactions between reportable segments are not significant.
In connection with the Merger, the Company determined its reportable segments as discussed above and retrospectively adjusted prior year's presentation to conform to the current presentation of reportable segments.
The Company defines EBITDA as net income (loss) plus interest (income) expense, income tax (benefit) expense, depreciation and amortization. The Company reflects the further adjustments to EBITDA (“Adjusted EBITDA”) to exclude certain non-cash items and the effect of what the Company considers transactions or events not related to its core business operations. The Chief Operating Decision Maker ("CODM") evaluates business segment performance utilizing Adjusted EBITDA as shown in the reconciliation of the Company’s consolidated net income (loss) to Adjusted EBITDA below. Management believes that evaluating segment performance excluding such items is meaningful because it provides insight with respect to the intrinsic operating results of the Company.
The Company also regularly evaluates gross profit by segment to assist in the assessment of its operational performance. The Company considers Adjusted EBITDA to be the more important metric because it more fully captures the business performance of the segments, inclusive of indirect costs.
Reportable Segments
The following tables set forth certain information regarding each of the Company’s reportable segments for the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019, and 2018, respectively. Consistent with the financial statements, the segment results only include results from Mobile Mini's operations after July 1, 2020, the Merger date. Please refer to the Management Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations included in this document, for pro forma results inclusive of Mobile Mini's financial results for periods prior to the Merger date.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, 2020 |
| (in thousands) | NA Modular | | NA Storage | | UK Storage | | Tank and Pump | | Unallocated Costs | | Total |
| Revenues: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Leasing and services revenue: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Leasing | $ | 770,330 | | | $ | 166,128 | | | $ | 32,633 | | | $ | 32,356 | | | | | $ | 1,001,447 | |
| Delivery and installation | 208,079 | | | 42,655 | | | 9,409 | | | 14,013 | | | | | 274,156 | |
| Sales revenue: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| New units | 41,858 | | | 6,976 | | | 3,124 | | | 1,135 | | | | | 53,093 | |
| Rental units | 30,895 | | | 6,070 | | | 1,195 | | | 789 | | | | | 38,949 | |
| Total revenues | 1,051,162 | | | 221,829 | | | 46,361 | | | 48,293 | | | | | 1,367,645 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Costs: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cost of leasing and services: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Leasing | 194,442 | | | 19,925 | | | 7,391 | | | 5,618 | | | | | 227,376 | |
| Delivery and installation | 175,705 | | | 27,029 | | | 6,353 | | | 11,015 | | | | | 220,102 | |
| Cost of sales: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| New units | 27,555 | | | 4,244 | | | 2,301 | | | 741 | | | | | 34,841 | |
| Rental units | 19,213 | | | 4,261 | | | 1,026 | | | 272 | | | | | 24,772 | |
| Depreciation of rental equipment | 182,605 | | | 9,585 | | | 1,648 | | | 6,743 | | | | | 200,581 | |
| Gross profit | $ | 451,642 | | | $ | 156,785 | | | $ | 27,642 | | | $ | 23,904 | | | | | $ | 659,973 | |
| Other selected data: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Adjusted EBITDA | $ | 394,805 | | | $ | 99,837 | | | $ | 17,822 | | | $ | 17,843 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 530,307 | |
| Selling, general and administrative expense (a) | $ | 242,010 | | | $ | 66,533 | | | $ | 11,468 | | | $ | 12,804 | | | $ | 91,864 | | | $ | 424,679 | |
| Purchases of rental equipment and refurbishments | $ | 153,327 | | | $ | 14,969 | | | $ | 1,693 | | | $ | 2,394 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 172,383 | |
(a) Includes both SG&A expense and Transaction costs from the consolidated statement of operations. | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, 2019 |
| (in thousands) | NA Modular | | NA Storage | | UK Storage | | Tank and Pump | | Unallocated Costs | | Total |
| Revenues: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Leasing and services revenue: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Leasing | $ | 744,185 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 0 | | | | | $ | 744,185 | |
| Delivery and installation | 220,057 | | | 0 | | | 0 | | | 0 | | | | | 220,057 | |
| Sales revenue: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| New units | 59,085 | | | 0 | | | 0 | | | 0 | | | | | 59,085 | |
| Rental units | 40,338 | | | 0 | | | 0 | | | 0 | | | | | 40,338 | |
| Total Revenues | 1,063,665 | | | 0 | | | 0 | | | 0 | | | | | 1,063,665 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Costs: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cost of leasing and services: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Leasing | 213,151 | | | 0 | | | 0 | | | 0 | | | | | 213,151 | |
| Delivery and installation | 194,107 | | | 0 | | | 0 | | | 0 | | | | | 194,107 | |
| Cost of sales: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| New units | 42,160 | | | 0 | | | 0 | | | 0 | | | | | 42,160 | |
| Rental units | 26,255 | | | 0 | | | 0 | | | 0 | | | | | 26,255 | |
| Depreciation of rental equipment | 174,679 | | | 0 | | | 0 | | | 0 | | | | | 174,679 | |
| Gross profit | $ | 413,313 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 0 | | | | | $ | 413,313 | |
| Other selected data: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Adjusted EBITDA | $ | 356,548 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 356,548 | |
| Selling, general and administrative expense | $ | 235,228 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 35,776 | | | $ | 271,004 | |
| Purchases of rental equipment and refurbishments | $ | 205,106 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 205,106 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, 2018 |
| (in thousands) | NA Modular | | NA Storage | | UK Storage | | Tank and Pump | | Unallocated Costs | | Total |
| Revenues: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Leasing and services revenue: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Leasing | $ | 518,235 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 0 | | | | | $ | 518,235 | |
| Delivery and installation | 154,557 | | | 0 | | | 0 | | | 0 | | | | | 154,557 | |
| Sales revenue: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| New units | 53,603 | | | 0 | | | 0 | | | 0 | | | | | 53,603 | |
| Rental units | 25,017 | | | 0 | | | 0 | | | 0 | | | | | 25,017 | |
| Total revenues | 751,412 | | | 0 | | | 0 | | | 0 | | | | | 751,412 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Costs: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cost of leasing and services: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Leasing | 143,120 | | | 0 | | | 0 | | | 0 | | | | | 143,120 | |
| Delivery and installation | 143,950 | | | 0 | | | 0 | | | 0 | | | | | 143,950 | |
| Cost of sales: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| New units | 36,863 | | | 0 | | | 0 | | | 0 | | | | | 36,863 | |
| Rental units | 16,659 | | | 0 | | | 0 | | | 0 | | | | | 16,659 | |
| Depreciation of rental equipment | 121,436 | | | 0 | | | 0 | | | 0 | | | | | 121,436 | |
| Gross profit | $ | 289,384 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 0 | | | | | $ | 289,384 | |
| Other selected data: | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Adjusted EBITDA | $ | 215,533 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 215,533 | |
| Selling, general and administrative expense (a) | $ | 200,895 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 53,976 | | | $ | 254,871 | |
| Purchase of rental equipment and refurbishments | $ | 160,883 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 160,883 | |
(a) Includes both SG&A expense and Transaction costs from the consolidated statement of operations.
The following tables present a reconciliation of the Company’s net income (loss) to Adjusted EBITDA for the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019, and 2018, respectively: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, |
| (in thousands) | 2020 | | 2019 | | 2018 |
| (as restated) | | (as restated) | | (as restated) |
| Net income (loss) attributable to WillScot Mobile Mini | $ | 74,127 | | | $ | (120,744) | | | $ | (25,210) | |
| Net income (loss) attributable to non-controlling interest, net of tax | 1,213 | | | (421) | | | (4,532) | |
| Loss on extinguishment of debt | 42,401 | | | 8,755 | | | 0 | |
| Income tax benefit | (51,451) | | | (2,191) | | | (38,600) | |
| Interest expense | 119,886 | | | 122,504 | | | 98,433 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | 243,830 | | | 187,074 | | | 134,740 | |
| Fair value (gain) loss on common stock warrant liabilities | (3,461) | | | 109,622 | | | (23,830) | |
| Currency (gains) losses, net | (355) | | | (688) | | | 2,454 | |
| Goodwill and other impairment charges | 0 | | | 2,848 | | | 1,600 | |
| Restructuring costs, lease impairment expense and other related charges | 11,403 | | | 12,429 | | | 15,468 | |
| Transaction costs | 64,053 | | | 0 | | | 20,051 | |
| Integration costs | 18,338 | | | 26,607 | | | 30,006 | |
| Stock compensation expense | 9,879 | | | 6,686 | | | 3,439 | |
| Other | 444 | | | 4,067 | | | 1,514 | |
| Adjusted EBITDA | $ | 530,307 | | | $ | 356,548 | | | $ | 215,533 | |
Assets
As discussed further in Note 2, the Company acquired Mobile Mini on July 1, 2020. The Company expects to finalize the valuation of the acquired net assets of Mobile Mini, including the final assignment of goodwill to reporting units, within the one-year measurement period from the date of acquisition.
Assets related to the Company’s reportable segments include the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands) | NA Modular | | NA Storage | | UK Storage | | Tank and Pump | | Total |
| As of December 31, 2020: | | | | | | | | | |
| Goodwill | $ | 235,828 | | | $ | 726,529 | | | $ | 65,600 | | | $ | 143,262 | | | $ | 1,171,219 | |
| Intangible assets, net | $ | 125,625 | | | $ | 329,437 | | | $ | 11,177 | | | $ | 29,708 | | | $ | 495,947 | |
| Rental equipment, net | $ | 1,888,287 | | | $ | 772,356 | | | $ | 147,720 | | | $ | 125,359 | | | $ | 2,933,722 | |
| As of December 31, 2019: | | | | | | | | | |
| Goodwill | $ | 235,177 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 235,177 | |
| Intangible assets, net | $ | 126,625 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 126,625 | |
| Rental equipment, net | $ | 1,944,436 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 0 | | | $ | 1,944,436 | |
NOTE 21 - Related Parties
Related party balances included in the Company’s consolidated balance sheets at December 31, consisted of the following: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands) | Financial statement line Item | 2020 | | 2019 |
| Receivables due from affiliates | Trade receivables, net of allowances for credit losses | $ | 30 | | | $ | 26 | |
| Amounts due to affiliates | Accrued liabilities | (461) | | | (236) | |
| Total related party liabilities, net | | $ | (431) | | | $ | (210) | |
Related party transactions included in the Company’s consolidated statements of operations for the years ended December 31, consisted of the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands) | Financial statement line item | 2020 | | 2019 | | 2018 |
| Leasing revenue from related parties | Leasing revenue | $ | 1,066 | | | $ | 316 | | | $ | 720 | |
| Rental unit sales to related parties | Rental unit sales | 380 | | | 0 | | | 1,548 | |
| Consulting expense to related party (a) | Selling, general & administrative expense | (5,194) | | | (1,029) | | | (3,070) | |
| Total related party expense, net | | $ | (3,748) | | | $ | (713) | | | $ | (802) | |
(a) Two of the Company's directors also serve on the Board of Directors of a consulting firm from which the Company incurs professional fees.
On June 30, 2020, the Company completed the Sapphire Exchange, whereby Sapphire Holdings, an affiliate of TDR, exchanged shares of Class B Common Stock for 10,641,182 shares of Class A Common Stock. As a result of the Sapphire Exchange, all issued and outstanding shares of WillScot’s Class B Common Stock were automatically canceled for no consideration and the existing exchange agreement was automatically terminated.
On August 22, 2018, WillScot’s majority stockholder, Sapphire Holdings, entered into a margin loan (the "Margin Loan") under which all of its WillScot Class A Common Stock was pledged to secure $125.0 million of borrowings under the loan agreement. WillScot is not a party to the loan agreement and has no obligations thereunder, but WillScot delivered an issuer agreement to the lenders under which WillScot has agreed to certain customary obligations relating to the shares pledged by Sapphire Holdings and, subject to applicable law and stock exchange rules, not to take any actions that are intended to materially hinder or delay the exercise of any remedies with respect to the pledged shares. In connection with the Margin Loan, on August 24, 2018, WSII entered into a two-year supply agreement with Target Logistics Management LLC, an affiliate controlled by Sapphire Holdings, under which, subject to limited exceptions, WSII acquired the exclusive right to supply modular units, portable storage units, and other ancillary products ordered by the affiliate in the US.
On August 21, 2020, Sapphire Holdings entered into an amended and restated margin loan agreement which, among other things, extends the maturity date of the Margin Loan to August 29, 2022. As of December 31, 2020, 59,725,558 shares of WillScot Mobile Mini Common Stock, representing approximately 26.1% of WillScot Mobile Mini’s issued and outstanding Common Stock, and 4,850,000 warrants exercisable for one half share of Common Stock were pledged by Sapphire Holdings under the Margin Loan. The two-year supply agreement with Target Logistics Management LLC was not renewed.
The Company purchased rental equipment from related party affiliates of $3.1 million, $4.7 million, and $4.3 million for the years ended December 31, 2020, 2019, and 2018, respectively.
NOTE 22 - Quarterly Financial Data (as restated)
The following tables present certain unaudited consolidated quarterly financial information for each of the eight quarters ended December 31, 2020.
In line with our filings with the SEC, prior to June 30, 2020, WillScot Mobile Mini refers to historical WillScot Corp. filed numbers. Post July 1, 2020, WillScot Mobile Mini refers to the combined company.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands, except share and per share data) | Quarter Ended (unaudited and as restated) |
| 2020 | March 31 | | June 30 | | September 30 | | December 31 |
| Leasing and services revenue | $ | 239,422 | | | $ | 241,783 | | | $ | 384,776 | | | $ | 409,622 | |
| Total revenue | $ | 255,821 | | | $ | 256,862 | | | $ | 417,315 | | | $ | 437,647 | |
| Gross profit | $ | 106,190 | | | $ | 109,964 | | | $ | 209,564 | | | $ | 234,255 | |
| Operating income | $ | 25,373 | | | $ | 41,067 | | | $ | 25,012 | | | $ | 91,263 | |
| Net (loss) income | $ | 91,655 | | | $ | (14,130) | | | $ | (6,051) | | | $ | 3,866 | |
| Net (loss) income attributable to WillScot Mobile Mini | $ | 91,785 | | | $ | (15,473) | | | $ | (6,051) | | | $ | 3,866 | |
| | | | | | | |
| (Loss) earnings per share - basic | $ | 0.84 | | | $ | (0.14) | | | $ | (0.03) | | | $ | 0.02 | |
| (Loss) earnings per share - diluted | $ | (0.05) | | | $ | (0.14) | | | $ | (0.03) | | | $ | 0.02 | |
| Weighted average shares - basic | 109,656,646 | | | 110,692,426 | | | 226,649,993 | | | 228,637,826 | |
| Weighted average shares - diluted | 112,672,997 | | | 110,692,426 | | | 226,649,993 | | | 233,625,946 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands, except share and per share data) | Quarter Ended (unaudited and as restated) |
| 2019 | March 31 | | June 30 | | September 30 | | December 31 |
| Leasing and services revenue | $ | 227,292 | | | $ | 241,784 | | | $ | 249,411 | | | $ | 245,755 | |
| Total revenue | $ | 253,685 | | | $ | 263,713 | | | $ | 268,222 | | | $ | 278,045 | |
| Gross profit | $ | 103,331 | | | $ | 101,484 | | | $ | 99,307 | | | $ | 109,191 | |
| Operating income | $ | 21,464 | | | $ | 26,294 | | | $ | 29,781 | | | $ | 39,986 | |
Net loss(1) | $ | (27,574) | | | $ | (56,836) | | | $ | (1,197) | | | $ | (35,558) | |
Net loss attributable to WillScot Mobile Mini(1) | $ | (26,816) | | | $ | (56,004) | | | $ | (1,492) | | | $ | (36,432) | |
| | | | | | | |
Loss per share - basic(1) | $ | (0.25) | | | $ | (0.52) | | | $ | (0.01) | | | $ | (0.33) | |
Loss per share - diluted(1) | $ | (0.25) | | | $ | (0.52) | | | $ | (0.02) | | | $ | (0.33) | |
Weighted average shares - basic(1) | 108,523,269 | | | 108,693,924 | | | 108,720,857 | | | 108,793,847 | |
Weighted average shares - diluted(1) | 108,523,269 | | | 108,693,924 | | | 109,508,360 | | | 108,793,847 | |
(1) Due to the impact of the restatement described in Note 1, amounts presented herein do not agree to amounts included within previously filed Form 10-Q’s. For the quarters ended March 31, June 30, September 30, and December 31, 2019: Net loss and Net loss attributable to WillScot Mobile Mini has been adjusted by ($17,545), ($45,398), ($2,193), and ($44,486), respectively; loss per share – basic has been adjusted by ($0.16), ($0.42), ($0.02), and ($0.40), respectively; loss per share – diluted has been adjusted by ($0.16), ($0.42), ($0.03), and ($0.40), respectively; and weighted average shares – dilutive has been adjusted by 0, 0, (2,535,605) and (5,286,212), respectively.
NOTE 23 - Earnings (Loss) Per Share (as restated)
Basic earnings (loss) per share (“EPS”) is calculated by dividing net income (loss) attributable to WillScot Mobile Mini by the weighted average number of shares of Common Stock outstanding during the period. The shares of Common Stock issued as a result of the vesting of RSUs and RSAs as well as the exercise of stock options or redemption of warrants are included in EPS based on the weighted average number of days in which they were outstanding during the period.
In 2018, 12,425,000 of WillScot's Class A common shares which had previously been held in escrow and excluded from the weighted average common shares calculation were released from escrow as follows: 6,212,500 of the escrowed
shares were released to shareholders on January 19, 2018, and the remaining escrowed shares were released to shareholders on August 21, 2018.
Prior to June 30, 2020, the Company had shares of Class B Common Stock which had no rights to dividends or distributions made by the Company and, in turn, were excluded from the EPS calculation. On June 30, 2020, the Sapphire Exchange was completed, and all shares of Class B Common Stock were cancelled, and Sapphire Holdings received 10,641,182 shares of Common Stock.
Diluted EPS is computed similarly to basic EPS, except that it includes the potential dilution that could occur if dilutive securities were exercised. Effects of potentially dilutive securities are presented only in periods in which they are dilutive. When liability-classified warrants are in the money and the impact of their inclusion on diluted EPS is dilutive, diluted EPS also assumes share settlement of such instruments through an adjustment to net income available to common stockholders for the fair value (gain) loss on warrant liabilities and inclusion of the number of dilutive shares in the denominator.
The following table reconciles net income (loss) attributable to WillScot Mobile Mini common shareholders and the weighted average shares outstanding for the basic calculation to net income (loss) attributable to WillScot Mobile Mini common shareholders and the weighted average shares outstanding for the diluted calculation for the years ended December 31, 2020 2019 and 2018:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (in thousands) | 2020
(as restated) | 2019
(as restated) | 2018
(as restated) |
| Numerator: | | | |
| Net income attributable to common shareholders - basic | $ | 74,127 | | $ | (120,744) | | $ | (25,210) | |
| Fair value (gain) loss on common stock warrant liabilities | (30,524) | | 0 | | (21,960) | |
| Net income attributable to common shareholders - dilutive | $ | 43,603 | | $ | (120,744) | | $ | (47,170) | |
| | | |
| Denominator: | | | |
| Weighted average Common Shares outstanding - basic | 169,230 | | 108,684 | | 87,210 | |
| Dilutive effect of outstanding securities: | | | |
| Warrants | 752 | | 0 | | 1,741 | |
| RSAs | 39 | | 0 | | 0 | |
| Time-Based RSUs | 778 | | 0 | | 0 | |
| Performance-Based and Market-Based RSUs | 544 | | 0 | | 0 | |
| Stock Options | 634 | | 0 | | 0 | |
| Class B common shares | 5,291 | | 0 | | 0 | |
| Weighted average Common Shares outstanding - dilutive | 177,268 | | 108,684 | | 88,951 | |
For the year ended December 31, 2020, Warrants representing 2,365,806 shares of Common Stock were excluded from the computation of diluted EPS because their effect would have been anti-dilutive.
For the year ended December 31, 2019, Class B Common Shares, Time-Based RSUs, Market-Based RSUs, RSAs, and Warrants representing 10,641,182, 323,422, 273,943, 12,213, and 2,320,423 shares of Common Stock, respectively, were excluded from the computation of diluted EPS because their effect would have been anti-dilutive.
For the year ended December 31, 2018, Class B Common Shares, Time-Based RSUs, RSAs, and Warrants representing 10,641,182, 756,055, 78,094, and 4,308,198 shares of Common Stock, respectively, were excluded from the computation of diluted EPS because their effect would have been anti-dilutive.
ITEM 9. Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure
None.
ITEM 9A. Controls and Procedures
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
The Company’s management, with the participation of the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, evaluated the effectiveness of the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures as of the end of the period covered by this report. That evaluation included consideration of the views expressed in the SEC Staff Statement in which the SEC staff clarified its interpretations of certain generally accepted accounting principles related to warrants issued by SPACs. Prior to the SEC Staff Statement, we believed that our warrant accounting was consistent with generally accepted accounting principles. This position was consistent with market practice, informed by third-party advisors with whom we consult from time to time on complex technical accounting matters, and was contained and fully disclosed in our audited financial statements, SEC filings and investor communications. However, based on the clarifications expressed in the SEC Staff Statement which resulted in the restatement discussed further in Note 1 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company’s management and the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer concluded that the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures were not effective as of December 31, 2020 due to a material weakness in internal control over financial reporting related to the accounting for warrants. As a result, a material weakness was determined to exist as described in Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting at December 31, 2020.
Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
As required by SEC rules and regulations, our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting (“ICFR”), as such term is defined in Exchange Act Rule 13a-15(f). Our ICFR is designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of our consolidated financial statements for external reporting purposes in accordance with GAAP. Our ICFR includes policies and procedures that: (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the Company’s assets, (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with GAAP, and that receipts and expenditures are being made only in accordance with the authorization of management and directors of the Company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of the Company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
ICFR, no matter how well designed, has inherent limitations and may not prevent or detect misstatements in our consolidated financial statements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Under the supervision of the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, management assessed the effectiveness of the Company's ICFR as of December 31, 2020 using the criteria set forth in Internal Control - Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 Framework). Based on that assessment, on February 26, 2021, we filed the Original Filing, at which time the Company's management determined that, as of December 31, 2020, the Company's ICFR was effective based on those criteria.
In connection with the restatement as discussed in Note 1 to the consolidated financial statements, management has reassessed the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2020. Management now concludes that our internal control over financial reporting was not effective as of December 31, 2020 and identified a material weakness in our controls over the accounting for Warrants. The Company’s control to evaluate the accounting for warrants did not effectively apply the provisions of ASC 815-40 as further interpreted by the SEC on April 12, 2021, and the Company’s controls were not appropriately designed to reassess the classification of the warrants at each reporting date thereafter. A material weakness is a deficiency, or combination of deficiencies, in internal controls over financial reporting, such that there is a reasonable possibility that the material misstatement of the Company’s annual or interim financial statements will not be prevented or detected on a timely basis.
Subsequent to the SEC Staff Statement, we implemented a remediation plan that addressed the material weakness in internal control over financial reporting, which related to the accounting for our warrants. In connection with the warrant restatement on Form 10-K/A, the Company has conformed its accounting for its warrants to the SEC Statement. The Company has also designed and implemented a new control to reassess the classification of liability- or equity-classified warrants to conform the accounting for warrants consistent with the SEC Staff Statement, which will be executed at each reporting date by individuals with sufficient experience and training. The Company’s remediation plan has been implemented and as of April 30, 2021, we believe we have remediated this material weakness and will test the operational effectiveness of the control during 2021.
The effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2020 has been audited by Ernst & Young LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, as stated in their report appearing below.
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
As discussed in Note 2 to the consolidated financial statements included in this Amendment No. 1, the Company completed the Merger with Mobile Mini on July 1, 2020. As permitted by interpretive guidance for newly acquired businesses issued by the SEC Staff, management has excluded the ICFR of Mobile Mini from the evaluation of the Company's effectiveness of its ICFR as of December 31, 2020. Total assets and revenues of Mobile Mini that were excluded from management’s assessment constitute 26% of the Company’s consolidated total assets as of December 31, 2020 and 23% of consolidated total revenues for the year ended December 31, 2020. The Company is engaged in the process of integrating policies, processes, people, technology and operations for the post-acquisition combined company, and it will continue to evaluate the impact of any related changes to ICFR.
In connection with the above described restatement, the Company has designed and implemented a new control to reassess the classification of liability- or equity-classified warrants consistent with the SEC Staff Statement, which control will be executed at each reporting date. This new control is being executed by individuals with sufficient experience and training.
Other than the items discussed above, there were no changes in our ICFR that occurred during the year ended December 31, 2020 that materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our ICFR.
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Shareholders and the Board of Directors of WillScot Mobile Mini Holdings Corp.
Opinion on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
We have audited WillScot Mobile Mini Holdings Corp.’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2020, based on criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 framework) (the COSO criteria). In our opinion, because of the effect of the material weakness described below on the achievement of the objectives of the control criteria, WillScot Mobile Mini Holdings Corp. (the Company) has not maintained effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2020, based on the COSO criteria.
In our report dated February 26, 2021, we expressed an unqualified opinion that the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2020, based on the COSO criteria. Management has subsequently identified a deficiency in controls related to the accounting for warrants, and has further concluded that such deficiency represented a material weakness as of December 31, 2020. As a result, management has revised its assessment, as presented in the accompanying Management's Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting; to conclude that the Company’s internal control over financial reporting was not effective as of December 31, 2020. Accordingly, our present opinion on the effectiveness of December 31, 2020’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2020, as expressed herein, is different from that expressed in our previous report.
A material weakness is a deficiency, or combination of deficiencies, in internal control over financial reporting, such that there is a reasonable possibility that a material misstatement of the company's annual or interim financial statements will not be prevented or detected on a timely basis. The following material weakness has been identified and included in management's assessment. Management has identified a material weakness in controls as of December 31, 2020 related to the Company’s accounting for warrants.
As indicated in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting, management’s assessment of and conclusion on the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting did not include the internal controls of Mobile Mini, Inc., which is included in the 2020 consolidated financial statements of WillScot Mobile Mini Holdings Corp. and constituted 26% of the Company's consolidated total assets as of December 31, 2020 and 23% of consolidated total revenues for the year ended December 31, 2020. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting of WillScot Mobile Mini Holdings Corp. also did not include an evaluation of the internal control over financial reporting of Mobile Mini, Inc.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the 2020 consolidated financial statements of the Company. This material weakness was considered in determining the nature, timing and extent of audit tests applied in our audit of the 2020 consolidated financial statements, and this report does not affect our report dated February 26, 2021, except for the effects of the restatement described in Note 1, as to which the date is May 10, 2021, which expressed an unqualified opinion on those financial statements.
Basis for Opinion
The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects.
Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and
expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
/s/ Ernst & Young LLP
Baltimore, Maryland
February 26, 2021, except for the effect of the material weakness described in the second paragraph above, as to which the date is May 10, 2021
ITEM 9B. Other Information
Transition of President and Chief Operating Officer
On February 25, 2021, the Company announced that Kelly Williams, its President and Chief Operating Officer, will leave the Company on July 31, 2021. The Company and Mr. Williams entered into a transition, separation and release agreement on February 25, 2021 (the "Williams Separation Agreement") relating to his transition and ultimate departure from the Company pursuant to which, among other things, in connection with his termination (i) Mr. Williams will receive a lump-sum cash payment, (ii) Mr. Williams' time-based equity will vest, and (iii) Mr. Williams' performance-based equity will vest or not vest depending upon performance targets. Mr. Williams will support the Company in all matters relating to the orderly transition of his duties and responsibilities and will be available to consult with the Company after his termination date.
The foregoing summary does not purport to be complete and is qualified in its entirety by reference to the full text of the William Separation Agreement, which is filed as Exhibit 10.16 to this Annual Report on Form 10-K and incorporated herein by reference.
Adoption of Second Amended and Restated Bylaws
On February 24, 2021, the Board of Directors unanimously approved and adopted the Second Amended and Restated Bylaws of the Company (the "Second A&R Bylaws"). The bylaws of the Company were amended and restated to remove the requirement that the Company "shall" have a President and Chief Operating Officer, providing instead that the Company "may" appoint either of these roles.
The foregoing description of the Second A&R Bylaws is not complete and is subject to, and qualified in its entirety by reference to the full text of the Second A&R Bylaws, which are filed as Exhibit 3.2 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K and incorporated herein by reference.
Annual Executive Compensation Review
Pursuant to their Employment Agreements, the Compensation Committee of the Board has performed an annual review of executive compensation and made adjustments to the compensation of Mr. Soultz and Mr. Boswell. Mr. Soutlz’ base salary was increased from $850,000 to $900,000, his annual target bonus was moved from 125% of base salary to 150% and his annual long-term incentive grant will be increased from $2,600,000 to $3,500,000. Mr. Boswell’s base salary was increased from $525,000 to $600,000, his annual target bonus was moved from 75% of base salary to 125% and his annual long-term incentive grant will be increased from $1,050,000 to $1,400,000. No amendments or modifications were made to their Employment Agreements.
PART III
ITEM 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance
The information to be included under the captions “Proposal 1 – Election of Directors,” “Codes of Business Conduct and Ethics,” and “Audit Committee,” if applicable, in the Company’s definitive proxy statement for the 2021 annual meeting of stockholders, filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on April 23, 2021, is hereby incorporated by reference in answer to this item.
ITEM 11. Executive Compensation
The information to be included under the captions “Executive Compensation,” “Compensation Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation,” and “Compensation Committee Report,” if applicable, in the Company’s definitive proxy statement for the 2021 annual meeting of stockholders, filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on April 23, 2021, is hereby incorporated by reference in answer to this item.
ITEM 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters
The information to be included under the captions “Equity Compensation Plan Information” and “Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management,” if applicable, in the Company’s definitive proxy statement for the 2021 annual meeting of stockholders, filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on April 23, 2021, is hereby incorporated by reference in answer to this item.
ITEM 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence
The information to be included under the captions “Certain Relationships and Related Party Transactions” and “Director Independence,” if applicable, in the Company’s definitive proxy statement for the 2021 annual meeting of stockholders, filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on April 23, 2021, is hereby incorporated by reference in answer to this item.
ITEM 14. Principal Accounting Fees and Services
The information to be included under the caption “Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm Fee Information,” if applicable, in the Company’s definitive proxy statement for the 2021 annual meeting of stockholders, filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on April 23, 2021, is hereby incorporated by reference in answer to this item.
PART IV
ITEM 15. Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules
The following documents are filed as part of this report:
Consolidated Financial Statements | | | | | |
| Page Number |
| Reports of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm | |
| Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2020 and December 31, 2019 | |
| Consolidated Statements of Operations for the Years Ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018 | |
| Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income (Loss) for the Years Ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018 | |
| Consolidated Statements of Changes in Equity for the Years Ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018 | |
| Consolidated Statements of Cash Flow for the Years Ended December 31, 2020, 2019 and 2018 | |
| Notes to the Audited Consolidated Financial Statements | |
Financial Statement Schedule
All schedules have been omitted because the information required to be set forth therein is not applicable or is shown in the financial statements or notes thereto.
Exhibits
The exhibits listed in the accompanying Exhibit Index are filed or incorporated by reference as part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Exhibit Index | | | | | | | | |
| Exhibit No. | | Exhibit Description |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | Supplemental Indenture, dated July 1, 2020, to the Indenture dated June 15, 2020, by and among Williams Scotsman International, Inc. (“WSII”) (as successor to Picasso Finance Sub, Inc.), the guarantors party thereto and Deutsche Bank Trust Company Americas, as trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to WillScot Corporation’s Current Report on Form 8-K, filed July 1, 2020). |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | Private Placement Warrant Purchase Agreement dated September 10, 2015 among Double Eagle Acquisition Corp., Double Eagle Acquisition LLC, Harry E. Sloan, Dennis A. Miller, James M. McNamara, Fredric D. Rosen, the Sara L. Rosen Trust, the Samuel N. Rosen 2015 Trust and the Fredric D. Rosen IRA, (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 of WillScot Corporation’s Current Report on Form 8-K, filed September 16, 2015). |
| | |
| | |
| | ABL Credit Agreement, dated July 1, 2020, by and among Williams Scotsman Holdings Corp., WSII, the guarantors party thereto, the lenders party thereto, and Bank of America, N.A., as administrative agent and collateral agent (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 of the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K, filed July 1, 2020). |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| | |
*Schedules have been omitted pursuant to Item 601(a)(5) of Regulation S-K. The Company hereby undertakes to furnish copies of any of the omitted schedules upon request by the Securities and Exchange Commission.
Signatures
Pursuant to the requirements of the Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized. | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | WillScot Mobile Mini Holdings Corp. |
| | |
| | By: | /s/ CHRISTOPHER J. MINER |
| Date: | May 10, 2021 | | Christopher J. Miner |
| | | Executive Vice President & Chief Legal Officer |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated. | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Signature | | Title | | Date |
| | | | |
| /s/ BRADLEY L. SOULTZ | | Chief Executive Officer and Director (Principal Executive Officer) | | May 10, 2021 |
| Bradley L. Soultz | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ TIMOTHY D. BOSWELL | | Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial Officer) | | May 10, 2021 |
| Timothy D. Boswell | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ SALLY J. SHANKS | | Chief Accounting Officer (Principal Accounting Officer) | | May 10, 2021 |
| Sally J. Shanks | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ ERIK OLSSON | | Chairman of the Board | | May 10, 2021 |
| Erik Olsson | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ MARK S. BARTLETT | | Director | | May 10, 2021 |
| Mark S. Bartlett | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ SARA R. DIAL | | Director | | May 10, 2021 |
| Sara R. Dial | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ JEFFREY S. GOBLE | | Director | | May 10, 2021 |
| Jeffrey S. Goble | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ GERARD E. HOLTHAUS | | Director | | May 10, 2021 |
| Gerard E. Holthaus | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ GARY LINDSAY | | Director | | May 10, 2021 |
| Gary Lindsay | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ KIMBERLY J. MCWATERS | | Director | | May 10, 2021 |
| Kimberly J. McWaters | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ STEPHEN ROBERTSON | | Director | | May 10, 2021 |
| Stephen Robertson | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ JEFF SAGANSKY | | Director | | May 10, 2021 |
| Jeff Sagansky | | | | |
| | | | |
| /s/ MICHAEL W. UPCHURCH | | Director | | May 10, 2021 |
| Michael W. Upchurch | | | | |