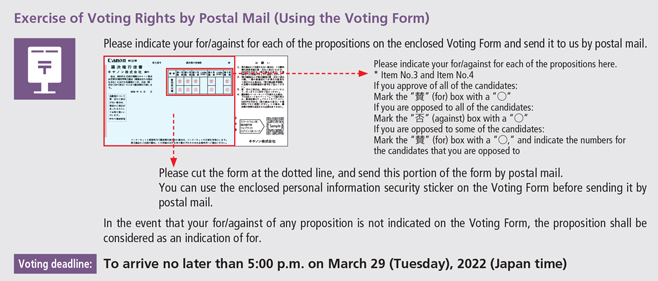
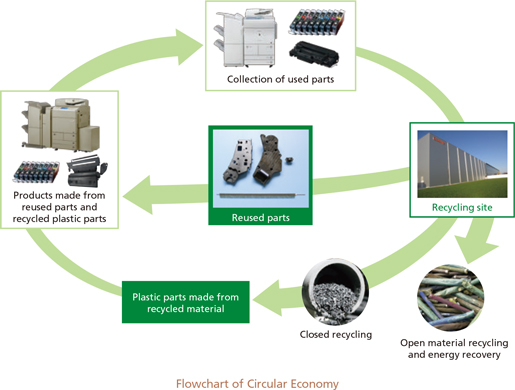
<Notes to Basic Significant Matters Regarding Preparation of Consolidated Financial Statements>
Significant Accounting Policies
| 1. | Principles of Consolidation and Investments Accounted for by the Equity Method |
The number of consolidated subsidiaries was 329, and the number of affiliated companies accounted for by the equity method was 10 as of December 31, 2021.
2. Basis of Presenting Consolidated Financial Statements
The consolidated financial statements of Canon Inc. (“Canon”) are prepared in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (“US GAAP”) pursuant to the provision of paragraph 1, Article 120-3 of the Company Accounting Regulations. However, certain disclosures required under US GAAP are omitted pursuant to the provision of the latter part of paragraph 1, Article 120, as applied mutatis mutandis pursuant to paragraph 3, Article 120-3.
3. Cash Equivalents
All highly liquid investments acquired with original maturities of three months or less from the date of purchase are considered to be cash equivalents.
4. Foreign Currency Translation
Assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies are translated at the rate of exchange in effect at the balance sheet date. Exchange differences are charged or credited to income. Assets and liabilities of subsidiaries located outside Japan are translated into Japanese yen at the rates of exchange in effect at the balance sheet date and income and expense items are translated at the average exchange rates prevailing during the year. The resulting translation adjustments are reported in other comprehensive income (loss).
5. Inventories
Inventories are stated at the lower of cost or net realizable value. Cost is determined by the average method for domestic inventories and principally the first-in, first-out method for overseas inventories.
6. Investments
In accordance with the Financial Accounting Standards Board Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) 321 “Investments”, equity investments that are not consolidated or accounted for under the equity method are measured at fair value and changes are recognized in net income. Realized gains and losses are determined based on the average cost method. Held-to-maturity debt securities are recorded at amortized cost.
7. Property, Plant and Equipment of Depreciation Methods
Property, plant and equipment are depreciated principally by the declining-balance method.
8. Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets
In accordance with ASC 350 “Intangibles – Goodwill and Other”, goodwill and other intangible assets with indefinite useful lives are not amortized, but are instead tested for impairment at least annually, or more frequently if indicators of potential impairment exist. Intangible assets with finite useful lives are amortized over the respective estimated useful lives. Software, patents and developed technology, and customer relationships are amortized using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives, which range primarily from 3 years to 8 years for software, 5 years to 21 years for patents and developed technology and 7 years to 15 years for customer relationships.
9. Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
In accordance with ASC 360 “Property, Plant, and Equipment”, long-lived assets, such as property, plant and equipment, and acquired intangibles subject to amortization, are reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable. If the carrying amount of the asset exceeds its estimated sum of undiscounted future cash flows, an impairment charge is recognized in the amount by which the carrying amount of the asset exceeds the fair value of the asset.
10. Basis of Recording Allowances
(Allowance for credit losses)
In accordance with ASC 326 “Financial Instruments – Credit Losses”, an allowance for credit losses is provided based on a current expected credit loss model.
(Accrued pension and severance cost)
In accordance with ASC 715 “Compensation – Retirement Benefits”, pension and severance cost are accrued based on the projected benefit obligations and the fair value of plan assets at the balance sheet date. Unrecognized actuarial loss is recognized by amortizing a portion in excess of a corridor (i.e., 10% of the greater of the projected benefit obligations or the fair value of plan assets) using the straight-line method over the average remaining service period of employees. Unrecognized prior service cost or credit is amortized using the straight-line method over the average remaining service period of employees.
11. Accounting of Taxes Collected from Customers
Taxes collected from customers and remitted to governmental authorities are excluded from revenues, cost and expenses in the consolidated statements of income.
12. Stock-Based Compensation
Canon measures stock-based compensation cost at the grant date, based on the fair value of the award, and recognizes the cost on a straight-line basis over the requisite service period.
13. Net Income Attributable to Canon Inc. Shareholders Per Share
Basic net income attributable to Canon Inc. shareholders per share is computed by dividing net income attributable to common shareholders by the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding during each year. Diluted net income attributable to Canon Inc. shareholders per share includes the effect from potential issuance of common stock based on the assumption that all stock options were exercised.