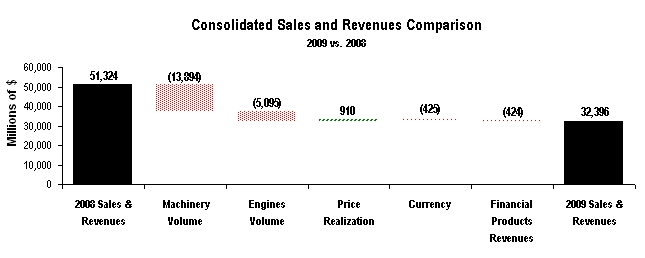
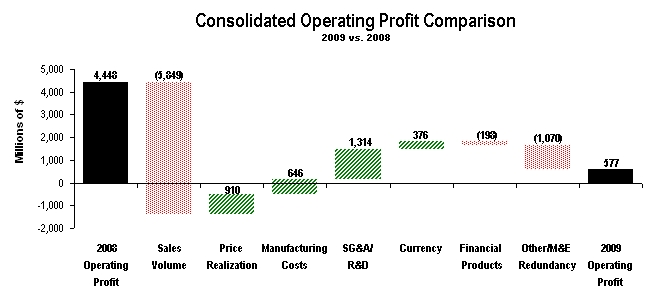
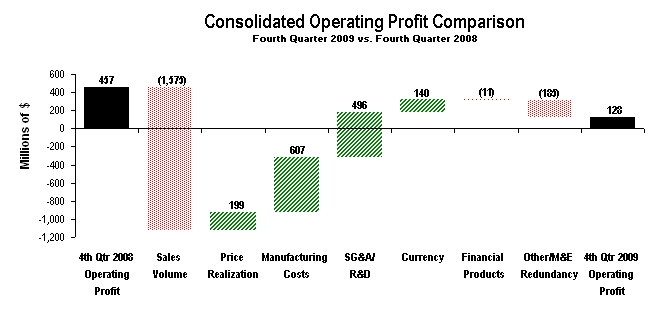
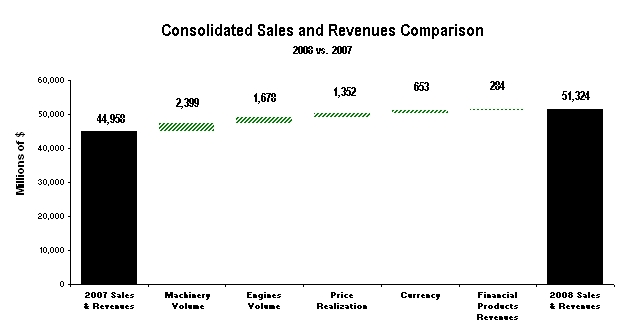
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect reported amounts. The more significant estimates include: residual values for leased assets, fair values for goodwill impairment tests, impairment of available-for-sale securities, warranty liability, stock-based compensation, reserves for product liability and insurance losses, postretirement benefits, post-sale discounts, credit losses and income taxes. We have incorporated many years of data into the determination of each of these estimates and we have not historically experienced significant adjustments. These assumptions are reviewed at least annually with the Audit Committee of the Board of Directors. Following are the methods and assumptions used in determining our estimates and an indication of the risks inherent in each.
Residual values for leased assets — The residual values for Cat Financial's leased assets, which are based upon the estimated wholesale market value of leased equipment at the time of the expiration of the lease, are based on a careful analysis of historical wholesale market sales prices, projected forward on a level trend line without consideration for inflation or possible future pricing action. At the inception of the lease, residual values are derived from consideration of the following critical factors: market size and demand, any known significant market/product trends, total expected hours of usage, machine configuration, application, location, model changes, quantities and past re-marketing experience, third-party residual guarantees and contractual customer purchase options. During the term of the leases, residual amounts are monitored. If estimated market values reflect a non-temporary impairment due to economic factors, obsolescence or other adverse circumstances, the residuals are adjusted to the lower estimated values by a charge to earnings. For equipment on operating leases, the charge is recognized through depreciation expense. For finance leases, it is recognized through a reduction of finance revenue.
Fair values for goodwill impairment tests — We test goodwill for impairment annually, at the reporting unit level, and whenever events or circumstances make it likely that an impairment may have occurred, such as a significant adverse change in the business climate or a decision to sell all or a portion of a reporting unit. We perform our annual goodwill impairment test as of October 1 and monitor for interim triggering events on an ongoing basis.
Goodwill is reviewed for impairment utilizing a two-step process. The first step requires us to compare the fair value of each reporting unit to the respective carrying value, which includes goodwill. If the fair value of the reporting unit exceeds its carrying value, the goodwill is not considered impaired. If the carrying value is greater than the fair value, there is an indication that an impairment may exist and the second step is required. In step two, the implied fair value of the goodwill is calculated as the excess of the fair value of a reporting unit over the fair values assigned to its assets and liabilities. If the implied fair value of goodwill is less than the carrying value of the reporting unit's goodwill, the difference is recognized as an impairment loss.
The impairment test process requires valuation of the respective reporting unit, which we primarily determine using an income approach based on a discounted five year forecasted cash flow with a year-five residual value. The residual value is computed using the constant growth method, which values the forecasted cash flows in perpetuity. The income approach is supported by a reconciliation of our calculated fair value for Caterpillar to the company's market capitalization. The assumptions about future cash flows and growth rates are based on each reporting unit's long-term forecast and are subject to review and approval by senior management. The discount rate is based on our weighted average cost of capital, which we believe approximates the rate from a market participant's perspective. The estimated fair value could be impacted by changes in market conditions, interest rates, growth rates, tax rates, costs, pricing and capital expenditures.
The 2009 annual impairment test, completed in the fourth quarter, indicated the fair value of each of our reporting units was above its respective carrying value, including goodwill, with the exception of our Forest Products reporting unit. Because the carrying value of Forest Products exceeded its fair value, step two in the impairment test process was required. We allocated the fair value to the unit's assets and liabilities and determined the implied fair value of the goodwill was insignificant. Accordingly, we recognized a $22 million non-cash goodwill impairment charge for Forest Products' entire goodwill amount. The primary factor contributing to the impairment was the historic decline in demand for purpose built forest product machines caused by the significant reduction in U.S. housing construction, lower prices for pulp, paper and wood product commodities, and reduced capital availability in the forest products industry. The fair values for all other reporting units were well above their respective carrying values at the measurement date. Additionally, Caterpillar's market capitalization has remained significantly above the net book value of the company.
A prolonged economic downturn resulting in lower long-term growth rates and reduced long-term profitability may reduce the fair value of our reporting units. Industry specific events or circumstances that have a negative impact to the valuation assumptions may also reduce the fair value of our reporting units. Should such events occur and it becomes more likely than not that a reporting unit's fair value has fallen below its carrying value, we will perform an interim goodwill impairment test(s), in addition to the annual impairment test. Future impairment tests may result in a goodwill impairment, depending on the outcome of both step one and step two of the impairment review process. A goodwill impairment would be reported as a non-cash charge to earnings.