Peace of Meat is a Business-To-Business, or B2B, ingredient producer and will be subject to regulation by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, or FDA, to the extent its products are introduced to the United States for use by a manufacturer to produce cultured meat or other food in the United States, and analogous foreign regulatory bodies elsewhere. In the United States, the FDA and the U.S. Department of Agriculture, or USDA, Food Safety and Inspection Service, or FSIS, share an ingredient approval process. The FDA determines the safety of substances and prescribes safe conditions of use. The USDA-FSIS determines the efficacy and suitability of food ingredients in meat, poultry, and egg products. Thus, the USDA’s efficacy and suitability requirements will also apply to the extent the ingredients are destined for use in USDA-regulated meat and poultry products.
For the reasons discussed below, we ourselves do not expect to be directly regulated by the FDA for United States compliance purposes but will apply FDA’s food contact substance standards or analogous foreign regulations when developing our three-dimensional bioprinter. Specifically, we intend to license our production technology, as well as provide associated products and services to food processing and food retail companies through a B2B model. From a regulatory perspective, in the United States, we expect companies manufacturing finished cultured meat products to be subject to regulation by various government agencies, including the FDA, the USDA, the U.S. Federal Trade Commission, or FTC, Occupational Safety and Health Administration and the Environmental Protection Agency, as well as the requirements of various state and local agencies and laws, such as the California Safe Drinking Water and Toxic Enforcement Act of 1986. We likewise expect these products to be regulated by equivalent agencies outside the United States by various international regulatory bodies.
As the manufacturer of technology used to produce cultured meat, and consistent with the Federal Food, Drug and Cosmetic Act, Federal Meat Inspection Act, and Poultry Products Inspection Act, we believe we will not be directly regulated by the FDA or USDA. Rather, we believe the regulatory obligation falls on our customers — cultured meat producers — to ensure that all food produced using our technology is wholesome and not adulterated. Consistent with food industry norms, we expect that our customers will therefore request assurances from us that our products are suitable for their intended use from an FDA regulatory perspective. Therefore, we plan to apply FDA food safety standards when developing our three-dimensional bioprinter as a means of assuring our customers that our bioprinter is safe for its intended use and will not result in the production of adulterated food. In particular, we plan to apply applicable food contact substance requirements, such as those of the FDA, when developing its three-dimensional bioprinter as a means of assuring customers using the Company's technology that our bioprinter is safe for its intended use and will not result in the production of adulterated food. If we are unable to provide regulatory compliance assurance to our customers, we expect that our ability to license our production technology would be adversely impacted.
We have broad discretion as to the use of the net proceeds from this offering and may not use such proceeds effectively.
We currently intend to use the net proceeds from this offering to develop commercial technologies to manufacture alternative foods, including potential acquisitions of other companies whose technologies are complementary or synergistic to our own, such as our purchase of Peace of Meat, as described herein in “Business”, and for general corporate purposes, including working capital requirements. For more information, see “Use of Proceeds.” However, our management will have broad discretion in the application of the net proceeds. Our shareholders may not agree with the manner in which our management chooses to allocate the net proceeds from this offering. The failure by our management to apply these funds effectively could have an adverse impact on our business, financial condition and results of operation. Pending their use, we may invest the net proceeds from this offering in a manner that does not produce income.
If equity research analysts do not publish research or reports about our business or if they issue inaccurate or unfavorable commentary or downgrade the ADSs, the price of the ADSs and trading volume could decline.
The trading market for the ADSs depends in part on the research and reports that industry or securities analysts publish about us or our business. If one or more of the analysts who cover us ceases coverage of our company or fails to publish reports on us regularly, we could lose visibility in the financial markets, which in turn could cause the price of the ADSs or their trading volume to decline. Moreover, if any of the analysts who cover us downgrade the ADSs or issue an adverse or misleading opinion regarding us, our business model or our stock performance, or if our operating results fail to meet the expectations of the investor community, the price of the ADSs could decline.
This offering may cause the trading price of our ADSs to decrease.
The price per ADS, together with the number of ADSs we propose to issue and ultimately will issue if this offering is completed, may result in an immediate decrease in the market price of our ADSs. This decrease may continue after the completion of this offering.
We have never paid dividends on our share capital and we do not intend to pay dividends for the foreseeable future.
We have never declared or paid any dividends on our share capital and do not intend to pay any dividends in the foreseeable future. We anticipate that we will retain all of our future earnings for use in the development and growth of our business and for general corporate purposes. Accordingly, any gains from an investment in the ADSs will depend on price appreciation of the ADSs, which may never occur. In addition, Israeli law limits our ability to declare and pay dividends, and may subject our dividends to certain Israeli withholding taxes.
ADS holders may not receive the same distributions or dividends as those we make to the holders of our Ordinary Shares, and, in some limited circumstances, they may not receive dividends or other distributions on our Ordinary Shares and may not receive any value for them, if it is illegal or impractical to make them available.
The depositary for the ADSs has agreed to pay to ADS holders the cash dividends or other distributions it or the custodian receives on Ordinary Shares or other deposited securities underlying the ADSs, after deducting its fees and expenses. ADS holders will receive these distributions in proportion to the number of Ordinary Shares their ADSs represent. However, the depositary is not responsible if it decides that it is unlawful or impractical to make a distribution available to any holders of ADSs. For example, it would be unlawful to make a distribution to a holder of ADSs if it consists of securities that require registration under the Securities Act, but that are not properly registered or distributed under an applicable exemption from registration. In addition, conversion into U.S. dollars from foreign currency that was part of a dividend made in respect of deposited ordinary shares may require the approval or license of, or a filing with, any government or agency thereof, which may be unobtainable. In these cases, the depositary may determine not to distribute such property and hold it as “deposited securities” or may seek to affect a substitute dividend or distribution, including net cash proceeds from the sale of the dividends that the depositary deems an equitable and practicable substitute. We have no obligation to register under U.S. securities laws any ADSs, ordinary shares, rights or other securities received through such distributions. We also have no obligation to take any other action to permit the distribution of ADSs, ordinary shares, rights or anything else to holders of ADSs. In addition, the depositary may deduct from such dividends or distributions its fees and may withhold an amount on account of taxes or other governmental charges to the extent the depositary believes it is required to make such withholding. These restrictions may cause a material decline in the value of the ADSs.
ADS holders do not have the same rights as holders of our Ordinary Shares.
ADS holders do not have the same rights as holders of our Ordinary Shares. For example, ADS holders may not attend shareholders’ meetings or directly exercise the voting rights attaching to the ordinary shares underlying their ADSs. ADS holders may vote only by instructing the depositary to vote on their behalf. If we request the depositary to solicit voting instructions from ADS holders (which we are not required to do), the depositary will notify ADS holders of a shareholders’ meeting and send or make voting materials available to them. Those materials will describe the matters to be voted on and explain how ADS holders may instruct the depositary how to vote. For instructions to be valid, they must reach the depositary by a date set by the depositary. The depositary will try, as far as practical, subject to the laws of Israel and the provisions of our articles of association or similar documents, to vote or to have its agents vote the deposited ordinary shares as instructed by ADS holders. If we do not request the depositary to solicit voting instructions from ADS holders, they can still send voting instructions, and, in that case, the depositary may try to vote as they instruct, but it is not required to do so. Except by instructing the depositary as described above, ADS holders won’t be able to exercise voting rights unless they surrender their ADSs and withdraw the ordinary shares. However, they may not know about the meeting enough in advance to withdraw the ordinary shares. We cannot assure ADS holders that they will receive the voting materials in time to ensure that they can instruct the depositary to vote their ordinary shares. In addition, the depositary and its agents are not responsible for failing to carry out voting instructions or for the manner of carrying out voting instructions. This means that ADS holders may not be able to exercise voting rights and there may be nothing they can do if their ordinary shares are not voted as they requested. In addition, ADS holders have no right to call a shareholders’ meeting.
ADS holders may be subject to limitations on transfer of their ADSs.
ADSs will be transferable on the books of the depositary. However, the depositary may close its transfer books at any time or from time to time when it deems expedient in connection with the performance of its duties. In addition, the depositary may refuse to deliver, transfer or register transfers of ADSs generally when our books or the books of the depositary are closed, or at any time if we or the depositary deem it advisable to do so because of any requirement of law or of any government or governmental body, under any provision of the deposit agreement, or for any other reason in accordance with the terms of the deposit agreement.
As a foreign private issuer whose ADSs are listed on Nasdaq, we follow certain home country corporate governance practices instead of certain Nasdaq requirements. We are not subject to U.S. proxy rules and are exempt from certain Exchange Act reporting requirements. If we were to lose our foreign private issuer status, our costs to modify our practices and maintain compliance under U.S. securities laws and Nasdaq rules would be significantly higher.
We are a foreign private issuer and are not subject to the same requirements that are imposed upon U.S. domestic issuers by the SEC. We are permitted to follow certain home country corporate governance practices instead of certain requirements of the rules of Nasdaq. As permitted under the Companies Law, pursuant to our articles of association, for as so long as we qualify to use the forms of a foreign private issuer, the quorum for an ordinary meeting of shareholders shall be the presence of at least two shareholders present in person, by proxy or by a voting instrument, who hold at least 25% of the voting power of our shares (and in an adjourned meeting, with some exceptions, a minimum of one shareholder) instead of 33 1⁄3% of our issued share capital as otherwise required under the Nasdaq corporate governance rules. We may also adopt and approve material changes to equity incentive plans in accordance with the Companies Law, which does not impose a requirement of shareholder approval for such actions. In addition, we follow Israeli corporate governance practice instead of the Nasdaq requirements to obtain shareholder approval for certain dilutive events (such as issuances that will result in a change of control, certain transactions other than a public offering involving issuances of a 20% or greater interest in us and certain acquisitions of the stock or assets of another company). Additionally, while the Nasdaq rules require that “independent directors,” as defined in the Nasdaq rules, must have regularly scheduled meetings at which only “independent directors” are present, Israeli law does not require, nor do our independent directors necessarily conduct, regularly scheduled meetings at which only they are present. Accordingly, our shareholders may be afforded less protection than what is provided under the Nasdaq corporate governance rules to investors in U.S. domestic issuers. See “Corporate Governance.”
Additionally, we are exempt from the rules and regulations under the Exchange Act related to the furnishing and content of proxy statements, and our officers, directors, and principal shareholders are exempt from the reporting and short-swing profit recovery provisions contained in Section 16 of the Exchange Act. Furthermore, although under regulations promulgated under the Companies Law, as an Israeli public company listed on Nasdaq, we are required to disclose the compensation of our five most highly compensated officers on an individual basis, this disclosure may not be as extensive as that required of U.S. domestic reporting companies. In addition, we are not required under the Exchange Act to file current reports and quarterly reports, including financial statements, with the SEC as frequently or as promptly as U.S. domestic reporting companies whose securities are registered under the Exchange Act. Moreover, we are not required to comply with Regulation FD, which restricts the selective disclosure of material information. These exemptions and leniencies reduce the frequency and scope of information and protections available to ADS holders in comparison to those applicable to U.S. domestic reporting companies.
If we cease to qualify as a foreign private issuer, we would be required to comply fully with the reporting requirements of the Exchange Act applicable to U.S. domestic issuers. We would lose our foreign private issuer status if a majority of our shares are owned by U.S. residents and a majority of our directors or executive officers are U.S. citizens or residents or we fail to meet additional requirements necessary to avoid loss of foreign private issuer status. If we are not a foreign private issuer, we will be required to file periodic reports and registration statements on U.S. domestic issuer forms with the SEC, which are more detailed and extensive than the forms available to a foreign private issuer. We may also be required to modify certain of our policies to comply with accepted governance practices associated with U.S. domestic issuers and we would lose our ability to rely upon exemptions from certain corporate governance requirements on U.S. stock exchanges that are available to foreign private issuers. Such modifications and subsequent compliance would cause us to incur significant legal, accounting and other expenses that we would not incur as a foreign private issuer.
If we are a “passive foreign investment company” for U.S. federal income tax purposes, there may be adverse U.S. federal income tax consequences to U.S. investors
Based on our income and assets, we believe that we should be treated as a PFIC for the preceding taxable year. However, the determination of our PFIC status is made annually based on the factual tests described below. Consequently, while we may be a PFIC in future years, we cannot estimate with certainty at this stage whether or not we are likely to be treated as a PFIC in the current taxable year or any future taxable years. Generally, if, for any taxable year, at least 75 percent of our gross income is “passive income” or at least 50 percent of our gross assets during the taxable year (based on the average of the fair market values of the assets determined at the end of each quarterly period) are assets that produce or are held for the production of passive income, we will be characterized as a PFIC for U.S. federal income tax purposes. Passive income for this purpose generally includes, among other things, dividends, interest, rents, royalties, gains from commodities and securities transactions, and gains from assets that produce passive income. However, rents and royalties received from unrelated parties in connection with the active conduct of a trade or business should not be considered passive income for purposes of the PFIC test. For example, if we were to be characterized as a PFIC for U.S. federal income tax purposes in any taxable year during which a U.S. Holder (as defined in “Taxation — Material United States federal income tax considerations”) holds ordinary shares or ADSs, such U.S. Holder could be subject to additional taxes and interest charges upon certain distributions by us and any gain recognized on a sale, exchange or other disposition of our shares, whether or not we continue to be characterized as a PFIC. Certain adverse consequences of PFIC status can be mitigated if a U.S. Holder makes a “mark to market” election or an election to treat us as a qualified electing fund, or QEF. Upon request, we expect to provide the information necessary for U.S. Holders to make “qualified electing fund elections” if we are classified as a PFIC. See “Taxation—Passive foreign investment company considerations.”
Whether we are a PFIC for any taxable year will depend on the composition of our income and the composition and value of our assets from time to time. Each U.S. Holder is strongly urged to consult its tax advisor regarding these issues and any available elections to mitigate such tax consequences.
If we are a controlled foreign corporation, there could be adverse U.S. federal income tax consequences to certain U.S. Holders.
Each “Ten Percent Shareholder” (as defined below) in a non-U.S. corporation that is classified as a “controlled foreign corporation,” or a CFC, for U.S. federal income tax purposes generally is required to include in income for U.S. federal tax purposes such Ten Percent Shareholder’s pro rata share of the CFC’s “Subpart F income,” “tested income” and investment of earnings in U.S. property, even if the CFC has made no distributions to its shareholders. Subpart F income generally includes dividends, interest, rents, royalties, gains from the sale of securities and income from certain transactions with related parties. In addition, a Ten Percent Shareholder that realizes gain from the sale or exchange of shares in a CFC may be required to classify a portion of such gain as dividend income rather than capital gain. A non-U.S. corporation generally will be classified as a CFC for U.S. federal income tax purposes if Ten Percent Shareholders own, directly or indirectly, more than 50% of either the total combined voting power of all classes of stock of such corporation entitled to vote or of the total value of the stock of such corporation. A “Ten Percent Shareholder” is a United States person (as defined by the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, or the Code) who owns or is considered to own 10% or more of the value or total combined voting power of all classes of stock entitled to vote of such corporation.
The determination of CFC status is complex and includes complex attribution rules. A non-corporate Ten Percent Shareholder with respect to a CFC generally will not be allowed certain tax deductions or foreign tax credits generally available to a corporate Ten Percent Shareholder. Failure to comply with CFC reporting obligations may subject a Ten Percent Shareholder to significant monetary penalties. We cannot provide any assurances that we will furnish to any Ten Percent Shareholder information that may be necessary to comply with the reporting and tax paying obligations applicable under the CFC rules of the Code. U.S. Holders should consult their own tax advisors with respect to the potential adverse U.S. tax consequences of becoming a Ten Percent Shareholder in a CFC.
CAUTIONARY NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This prospectus contains statements that are forward-looking statements about our expectations, beliefs or intentions regarding, among other things, our product development efforts, business, financial condition, results of operations, strategies, plans and prospects. Forward-looking statements can be identified based on our use of forward-looking words such as “believe,” “expect,” “intend,” “plan,” “may,” “should,” “anticipate,” “could,” “might,” “seek,” “target,” “will,” “project,” “forecast,” “continue” or their negatives or variations of these words or other comparable words, or by the fact that these statements do not relate strictly to historical matters. Forward-looking statements relate to anticipated or expected events, activities, trends or results as of the date they are made. Because forward-looking statements relate to matters that have not yet occurred, these statements are inherently subject to risks and uncertainties that could cause our actual results to differ materially from any future results expressed or implied by the forward-looking statements. Many factors could cause our actual activities or results to differ materially from the activities and results anticipated in forward-looking statements, including, but not limited to, any of the following:
| • | our estimates regarding our expenses, future revenue, capital requirements and needs for additional financing; |
| • | our expectations regarding the success of our cultured meat manufacturing technologies we are developing, which will require significant additional work before we can potentially launch commercial sales; |
| • | our research and development activities associated with technologies for cultured meat manufacturing, including three-dimensional meat production, which involves a lengthy and complex process; |
| • | our expectations regarding the timing for the potential commercial launch of our cultured meat technologies; |
| • | our ability to successfully manage our planned growth, including with respect to our recent acquisition of Peace of Meat, and any future acquisitions, joint ventures, collaborations or similar transactions; |
| • | the potential business or economic disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic; |
| • | the competitiveness of the market for our cultured meat technologies; |
| • | our ability to enforce our intellectual property rights and to operate our business without infringing, misappropriating, or otherwise violating the intellectual property rights and proprietary technology of third parties; |
| • | our ability to predict and timely respond to preferences for alternative proteins and cultured meats and new trends; |
| • | our ability to predict and timely respond to preferences for alternative proteins and cultured meats and new trends; and |
| • | other risks and uncertainties, including those listed under the heading “Risk Factors” in this prospectus and our Annual Report on Form 20-F for the year ended December 31, 2021, filed with the SEC on March 24, 2022. |
We believe that our forward-looking statements are reasonable; however, these statements are only current predictions and are subject to known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors (including those identified above) that may cause our or our industry’s actual results, levels of activity, performance or achievements to be materially different from those anticipated by the forward-looking statements. We describe and/or refer to many of these risks in greater detail under the heading “Risk Factors” in this prospectus. Given these uncertainties, you should not rely upon forward-looking statements as guarantees of future outcomes.
All forward-looking statements contained herein and in any of the foregoing documents speak only as of the date hereof or of such documents, respectively, and are expressly qualified in their entirety by the cautionary statements contained within the “Risk Factors” section of those documents. We do not undertake to update or revise forward-looking statements to reflect events or circumstances that arise after the date on which such statements are made or to reflect the occurrence of unanticipated events, except as required by law.
We estimate that the net proceeds from this offering will be approximately $ million (approximately $ million if the underwriters exercise their over-allotment option in full), assuming the sale of ADSs and no sale of any Pre-Funded Warrants, based upon an assumed public offering price of $ per ADS, the last reported sale price of our ADSs on Nasdaq on , 2022, after deducting the estimated underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us.
A $0.10 increase (decrease) in the assumed public offering price would increase (decrease) the net proceeds we receive from this offering by $ , assuming that the number of shares offered, as set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, remains the same, and after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses. Each increase (decrease) of 100,000 in the number of shares we are offering would increase (decrease) the net proceeds to us from this offering by approximately $ , assuming no change in the assumed public offering price per ADS.
We currently intend to use the net proceeds from this offering for general corporate purposes, which may include operating expenses, working capital, future acquisitions or share repurchases, general capital expenditures and satisfaction of debt obligations. We have not determined the amount of net proceeds to be used specifically for such purposes. As a result, our management will retain broad discretion in the allocation and use of the net proceeds of this offering, and investors will be relying on the judgment of our management with regard to the use of these net proceeds. The precise amount use and timing of the application of such proceeds will depend upon our funding requirements and the availability and cost of other capital. We have no current agreements, commitments or understandings for any material acquisitions or licenses of any products, businesses or technologies that are definitive or probable to close. Pending application of the net proceeds for the purposes as described above, we expect to invest the net proceeds in short-term, interest-bearing securities, investment grade securities, certificates of deposit or direct or guaranteed obligations of the U.S. government.
We have never declared or paid any cash dividends on our ADSs and do not anticipate paying any cash dividends in the foreseeable future. Any future determination to pay dividends will be at the discretion of our board of directors and will depend on our financial condition, operating results, capital requirements and other factors that our board of directors considers to be relevant.
The following table sets forth our capitalization as of September 30, 2022:
| | • | on an actual basis; and
|
| | • | on an as adjusted basis, to give effect to the assumed issuance and sale in this offering of ADSs representing Ordinary Shares at the assumed public offering price of $ per ADS, the last reported sales price of our ADSs on Nasdaq on , 2022, and assuming no sale of any Pre-Funded Warrants, after deducting the estimated underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us. |
The information set forth in the following table should be read in conjunction with, and is qualified in its entirety by, reference to our audited and unaudited financial statements and the notes thereto included elsewhere in this prospectus.
| | | As of September 30, 2022 | |
| | | Actual | | | As adjusted | |
| | | (U.S. Dollars, in thousands) | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | | 11,203 | | | | | |
| Shareholders’ equity: | | | | | | | | |
| Equity: | | | | | | | | |
Ordinary Shares, no per share: 1,000,000,000 ordinary shares authorized (actual and as adjusted); 135,767,137 Ordinary Shares issued and outstanding (actual); Ordinary Shares outstanding (as adjusted) | | | | | | | | |
| Share capital and premium on shares | | | (72,231 | ) | | | | |
| Capital reserves | | | (3,581 | ) | | | | |
| Currency translation differences reserve | | | 2,771 | | | | | |
| Accumulated deficit | | | 48,602 | | | | | |
| Total shareholders’ capital equity | | | (24,439 | ) | | | | |
| | | Each $0.10 increase (decrease) in the assumed public offering price of $ per share, which is the last reported sale price of our ADSs on Nasdaq on , 2022, would increase (decrease) cash and cash equivalents and short term bank deposits by $ , and our total shareholders’ equity on an as adjusted basis by approximately $ , assuming the number of shares offered, as set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, remains the same, and after deducting the estimated underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us. |
| | | Each ,000 increase (decrease) in the number of ADSs offered in this offering would increase or decrease cash and cash equivalents and short term bank deposits by approximately $ , and our total shareholders’ equity on an as adjusted basis by approximately $ , assuming that the price per ADS for the offering remains at $ , which is the last reported sales price of our ADSs on Nasdaq on , 2022, and after deducting the estimated underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us. |
The outstanding share information in the table above is based on Ordinary Shares representable by 13,576,714 ADSs outstanding as of September 30, 2022 and excludes:
The outstanding share information in the table above is based on ordinary shares representable by 13,576,714 ADSs outstanding as of September 30, 2022 and excludes:
| | • | 1,156,835 ADSs issuable upon the exercise of options and restricted share units to purchase ADSs outstanding as of November 22, 2022, at a weighted average exercise price of $7.46 per ADS; |
| | • | a total of 1,021,537 of our ADSs reserved for future issuance under our 2022 Share Incentive Plan, as of November 22, 2022; |
| | • | 704,454 ADSs issuable upon exercise of options and restricted share units outstanding as of November 22, 2022, at an exercise price to be determined at the time of exercise using a pre-determined formula; |
| | • | 4,486,562 ADSs issuable upon the exercise of investor warrants to purchase ADSs outstanding as of November 22, 2022, at a weighted average exercise price of $7.00 per ADS, which warrants are expected to remain outstanding at the consummation of this offering; |
| | • | 140,747 ADSs issuable upon exercise of milestone-based rights to investors that had been granted and remained outstanding as of November 22, 2022, with no exercise price; |
| | • | no sale of Pre-Funded Warrants in this offering; |
| | • | no exercise by the underwriters of their over-allotment option; and |
| | • | no exercise of Underwriter Warrants. |
If you invest in our Securities in this offering, your ownership interest will be immediately diluted to the extent of the difference between the public offering price per ADS and/or Pre-Funded Warrant and the as adjusted net tangible book value per ADS after this offering.
Our net tangible book value as of September 30, 2022, was approximately $12.7 million, or approximately $0.94 per ADS. Our net tangible book value per ADS represents the amount of our total tangible assets less total liabilities divided by the total number of our Ordinary Shares outstanding as of September 30, 2022, and multiplying such amount by 10 (one ADS represents 10 Ordinary Shares).
After giving effect to the issuance and sale of the ADSs offered by us in this offering at an assumed public offering price of $ per ADS, the last reported sale price of our ADSs on Nasdaq on , 2022, and assuming no exercise of the underwriters’ option to purchase additional ADSs (and no sale of any Pre-Funded Warrants in this offering), and after deducting the estimated underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us, our as adjusted net tangible book value on September 30, 2022, would have been approximately $ million, or $ per ADS. This represents an immediate dilution in the as adjusted net tangible book value of $ per ADS to investors purchasing our ADSs in this offering.
The following table illustrates this calculation on a per share basis:
| Assumed offering price per ADS | | | | | | $ | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Net tangible book value per ADS as of September 30, 2022 | | $ | | | | | | |
| Increase in net tangible book value per ADS attributable to the offering | | $ | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| As-adjusted net tangible book value per ADS after giving effect to the offering | | | | | | $ | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Dilution in net tangible book value per ADS to new investors | | | | | | $ | | |
The outstanding share information in the table above is based on ordinary shares representable by 13,576,714 ADSs outstanding as of September 30, 2022 and excludes:
| | • | 1,156,835 ADSs issuable upon the exercise of options and restricted share units to purchase ADSs outstanding as of November 22, 2022, at a weighted average exercise price of $7.46 per ADS; |
| | | a total of 1,021,537 of our ADSs reserved for future issuance under our 2022 Share Incentive Plan, as of November 22, 2022; |
| | | 704,454 ADSs issuable upon exercise of options and restricted share units outstanding as of November 22, 2022, at an exercise price to be determined at the time of exercise using a pre-determined formula; |
| | | 4,486,562 ADSs issuable upon the exercise of investor warrants to purchase ADSs outstanding as of November 22, 2022, at a weighted average exercise price of $7.00 per ADS, which warrants are expected to remain outstanding at the consummation of this offering; |
| | | 140,747 ADSs issuable upon exercise of milestone-based rights to investors that had been granted and remained outstanding as of November 22, 2022, with no exercise price; |
| |
| no sale of Pre-Funded Warrants in this offering; |
| | | no exercise by the underwriters of their over-allotment option; and |
| |
| no exercise of Underwriter Warrants. |
The above illustration of dilution per share to investors participating in this offering assumes no exercise of outstanding options to purchase our Ordinary Shares or outstanding warrants to purchase our ADSs or Ordinary Shares. To the extent outstanding options or warrants are exercised, you may incur further dilution.
A $0.10 increase (decrease) in the assumed public offering price of $ per ADS, which is the last reported sale price of our ADSs on Nasdaq on , 2022, would increase (decrease) our net tangible book value per ADS after this offering by $ and the dilution per ADS to new investors by $ , assuming the number of ADSs offered by us, as set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, remains the same, after deducting the estimated underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us. We may also increase or decrease the number of ADSs we are offering.
An increase (decrease) of 100,000 ADS offered by us, would increase (decrease) our net tangible book value after this offering by approximately $ and would decrease (increase) the net tangible book value per ADS after this offering by $ per ADS and would increase (decrease) the dilution per ADS to new investors by $ , after deducting estimated placement agent fees and estimated offering expenses payable by us. The information discussed above is illustrative only and will adjust based on the actual public offering price and other terms of the offering determined at pricing.
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
You should read the following discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations together with our consolidated financial statements and the related notes included elsewhere in this prospectus. The following discussion is based on our financial information prepared in accordance with IFRS as issued by IASB, which may differ in material respects from generally accepted accounting principles in other jurisdictions, including U.S. generally accepted accounting principles, or GAAP. Some of the information contained in this discussion and analysis, particularly with respect to our plans and strategy for our business and related financing, includes forward-looking statements that involve risks and uncertainties. You should read “Risk Factors” above for a discussion of important factors that could cause actual results to differ materially from the results described in or implied by the forward-looking statements contained in the following discussion and analysis. For a discussion of our results of operations for the year ended December 31, 2020, including a comparison between 2020 and 2019, refer to “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Results of Operations—Year Ended December 31, 2020 Compared to Year Ended December 31, 2019” in our annual report on Form 20-F filed on April 21, 2021.
Operating Results
Revenues
To date, we have not generated any revenue since we commenced our cultured meat operations. We do not expect to receive any revenue unless and until we complete development of and successfully commence out-licensing our technologies, or until we receive revenue from a collaboration or other partnership such as a co-development agreement, or the acquisition of a company that generates revenues. There can be no assurance that we will be successful in developing or ultimately commercializing our technologies, in establishing revenue-generating collaborations or acquiring revenue-generating companies.
Research and Development Expenses
Research and development activities are our primary focus. We do not believe that it is possible at this time to accurately project total expenses required for us to reach the point at which we will be ready to out-license our technologies. Development timelines, the probability of success and development costs can differ materially from expectations. In addition, we cannot forecast whether and when collaboration arrangements will be entered into, if at all, and to what degree such arrangements would affect our development plans and capital requirements. We expect our research and development expenses to increase over the next several years as our development program progresses. We would also expect to incur increased research and development expenses if we were to identify and develop additional technologies.
Research and development expenses include the following:
| • | employee-related expenses, such as salaries and share-based compensation; |
| • | expenses relating to outsourced and contracted services, such as external laboratories and consulting, research and advisory services; |
| • | supply and development costs; |
| • | expenses, such as materials, incurred in operating our laboratories and equipment; and |
| • | costs associated with regulatory compliance. |
We recognize research and development expenses as we incur them.
Marketing expenses consist primarily of professional services, personnel costs, including share-based compensation related to employees, and business development, public relations and investor relations services.
General and Administrative Expenses
General and administrative expenses consist primarily of personnel costs, including share-based compensation related to directors and employees, corporate costs (such as insurance), facility costs, patent application and maintenance expenses, and professional service costs, including legal, accounting, audit, finance and human resource services, and other consulting fees.
Based on the reverse acquisition method, the assets and liabilities of MeaTech (the acquirer for accounting purposes) were recognized in our financial statements at their book value at the date of closing of the merger in January 2020. The acquisition consideration, in the amount of $11.4 million, was set based on the closing price of Ophectra's shares on the TASE on the date of closing of the merger, while any surplus proceeds of the acquisition over the fair value of Ophectra’s net assets (excluding its net assets that were transferred to a settlement in connection with the merger with Ophectra) were recognized in profit or loss as public listing expenses in the amount of $10.2 million, that did not affect cash flow.
Finance Expenses (income), Net
Finance expenses (income), net, consisted primarily of a change in the fair value of financial instruments mandatorily measured at fair value through profit or loss, and exchange rate fluctuations.
We have yet to generate taxable income. As of September 30, 2022, our operating tax loss carryforwards were approximately $24.3 million.
Our results of operations have varied in the past and can be expected to vary in the future due to numerous factors. We believe that period-to-period comparisons of our operating results are not necessarily meaningful and should not be relied upon as indications of future performance.
Below is a summary of our results of operations for the periods indicated (in thousands):
Year Ended December 31, 2021 Compared to Year Ended December 31, 2020
| | | Year Ended December 31, | |
| | | 2021 | | | 2020 | |
| USD in thousands | | | | | | |
| Operating expenses: | | | | | | |
| Research and development expenses | | $ | 7,594 | | | $ | 2,491 | |
| Marketing expenses | | | 1,628 | | | | 506 | |
| General and administrative expenses | | | 8,010 | | | | 5,380 | |
| Public listing expenses | | | - | | | | 10,164 | |
| Loss from operations | | $ | 17,232 | | | $ | 18,541 | |
| Finance income | | | 509 | | | | 110 | |
| Finance expense | | | 1,299 | | | | 93 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Finance expense (income), net | | | 790 | | | | (17 | ) |
| Net loss | | $ | 18,022 | | | $ | 18,524 | |
Research and development expenses
Research and development expenses increased by approximately $5.1 million, or 205%, to approximately $7.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2021, compared to $2.5 million for year ended December 31, 2020. The increase resulted mainly from payroll expenses, materials and professional services expenditures related to our cultured meat research and development operations. The increase reflects Steakholder Food’s growing investment in research and development as we achieve our milestones and expand our cultured meat technology capabilities.
Marketing expenses totaled $2.0 million in the six months ending June 30, 2022 compared to $0.6 million in the same period in 2021. The 224% increase is mainly due to our increased salary expenses and growing investment in our U.S. and global marketing activities.
General and administrative expenses
General and administrative expenses increased by approximately $2.7 million, or 49%, to approximately $8.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2021, compared to approximately $5.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2020. The increase resulted mainly from personnel costs, corporate expenses, professional services (such as legal and audit fees) and operating expenditures.
Net loss totaled $9.2 million in the six months ending June 30, 2022 compared to $7.8 million in the same period in 2021. The 18% increase in the operating loss reflects our growing investment in research and development as well as marketing activities.
Six months Ended June 30, 2022 Compared to Six months Ended June 30, 2021
| | | Six months Ended June 30, | |
| | | 2022 | | | 2021 | |
| USD in thousands | | | | | | |
| Operating expenses: | | | | | | |
| Research and development expenses | | $ | 4,427 | | | $ | 2,910 | |
| Marketing expenses | | | 1,959 | | | | 605 | |
| General and administrative expenses | | | 3,687 | | | | 4,159 | |
| Loss from operations | | $ | 10,073 | | | $ | 7,647 | |
| Finance income | | | (1,062) | | | | (401 | |
| Finance expense | | | 145 | | | | 493 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Finance expense (income), net | | | (917) | | | | 92 | |
| Net loss | | $ | 9,156 | | | $ | 7,766 | |
Research and development expenses
Research and development expenses totaled $4.4 million in the six months ending June 30, 2022 compared to $2.9 million in the same period in 2021. The 52% increase reflects our growing investment in research and development as we achieve our milestones and expand our cultured meat technology capabilities.
Marketing expenses totaled $2.0 million in the six months ending June 30, 2022 compared to $0.6 million in the same period in 2021. The 224% increase is mainly due to our increased salary expenses and growing investment in our U.S. and global marketing activities.
General and administrative expenses
General and administrative expenses totaled $3.7 million in the six months ending June 30, 2022 compared to $4.2 million in the same period in 2021. The 11% increase was primarily due to increased salary expenses and increased payments for legal and professional services
Net loss totaled $9.2 million in the six months ending June 30, 2022 compared to $7.8 million in the same period in 2021. The 18% increase in the operating loss reflects our growing investment in research and development as well as marketing activities.
Nine months Ended September 30, 2022 Compared to Nine months Ended September 30, 2021
| | | Nine months Ended September 30, | |
| | | 2022 | | | 2021 | |
| | | | | | |
| Operating expenses: | | | | | | |
| Research and development expenses | | $ | 7,219 | | | $ | 4,928 | |
| Marketing expenses | | | 2,426 | | | | 872 | |
| General and administrative expenses | | | 4,982 | | | | 5,961 | |
| Loss from operations | | $ | 14,627 | | | $ | 11,761 | |
| Finance income | | | (3,258 | ) | | | (457 | ) |
| Finance expense | | | 262 | | | | 434 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Finance expense (income), net | | | (2,996 | ) | | | (23 | ) |
| Net loss | | $ | 11,632 | | | $ | 11,738 | |
Research and development expenses
Research and development expenses in the nine months ending September 30, 2022 totaled $7.2 million compared to $4.9 million in the same period in 2021. The 46% increase reflects our growing investment in research and development as we continue to achieve our milestones and expand our cultivated meat technology capabilities.
Marketing expenses in the nine months ending September 30, 2022 totaled $2.4 million compared to $0.8 million in the same period in 2021, reflecting increased salary expenses and growing investment in our U.S. and global marketing activities.
General and administrative expenses
General and administrative expenses in the nine months ending September 30, 2022 totaled $5.0 million compared to $6.0 million in the same period in 2021. The 16% decrease was primarily due to lower insurance and share-based payment expenses in the current quarter.
Net loss in the nine months ending September 30, 2022 totaled $11.6 million compared to $11.7 million in the same period in 2021. The minor change reflects continued investment in research and development as well as marketing activities, as indicated above offset by finance income.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Since the commencement of our cultured meat operations, we have not generated any revenue and have incurred operating losses and negative cash flows from our operations. We have funded our operations primarily through the sale of equity securities. From the inception of Steakholder Foods through September 30, 2022, we raised an aggregate of $48.1 million in five rounds of private placements of our securities and our initial public offering of securities on Nasdaq, or IPO, and $6.1 million in proceeds from option exercises. As of December 31, 2021 and September 30, 2022, we had $19.2 million and $11.2 in cash and cash equivalents respectively.
The table below shows a summary of our cash flows for the periods indicated:
Year Ended December 31, 2021 Compared to Year Ended December 31, 2020
| | | Year Ended December 31, | |
| | | 2021 | | | 2020 | |
| | | | | | |
| Net cash used in operating activities | | $ | (13,960 | ) | | $ | (3,832 | ) |
| Net cash used in investing activities | | | (9,340 | ) | | | (1,875 | ) |
| Net cash provided by financing activities | | | 29,023 | | | | 17,345 | |
| Net increase in cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 5,723 | | | $ | 11,638 | |
Net cash used in operating activities
Net cash used in operating activities increased by $10.1 million, or 264%, to approximately $14.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2021 compared to approximately $3.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2020. This increase was due to the increase in net loss.
Net cash used in investing activities
Net cash used in investing activities increased by $7.5 million, or 398%, to approximately $9.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2021 compared to $1.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2020. This increase was driven mainly by our investment in Peace of Meat and our acquisition of laboratory equipment and other fixed assets.
Net cash provided by financing activities
Net cash provided by financing activities increased by $11.7 million, or 67%, to approximately $29.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2021 compared to $17.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2020. This increase was driven mainly from our IPO and issuance of shares and warrants, and receipt of proceeds from the exercise of share options.
Six months Ended June 30, 2022 Compared to Six months Ended June 30, 2021
| | | Six months Ended June 30, | |
| | | 2022 | | | 2021 | |
| USD in thousands | | | | | | |
| Net cash used in operating activities | | $ | (7,448 | ) | | $ | (5,048 | ) |
| Net cash used in investing activities | | | (2,476 | ) | | | (6,381 | ) |
| Net cash provided by financing activities | | | (314) | | | | 29,059 | |
| Net increase in cash and cash equivalents | | $ | (10,238) | | | $ | 17,630 | |
Net cash used in operating activities
Net cash flow used in operating activities totaled $7.4 million in the six months ending June 30, 2022, compared to $5.0 million in the same period in 2021, reflecting a 48% increase, due mainly to the increased expenditures of our growing activities, including the addition of Peace of Meat as a subsidiary as of March 2021.
Net cash used in investing activities
Net cash flow used in investment activities totaled $2.5 million in the six months ending June 30, 2022 compared to $6.3 million in the same period in 2021, reflecting a 61% decrease due mainly to the non-recurring acquisition of Peace of Meat in 2021.
Net cash provided by financing activities
Net cash flow from financing activities was $0.3 million in the six months ending June 30, 2022 compared to $29.1 million in the same period in 2021, during which our IPO took place.
Nine months Ended September 30, 2022 Compared to Nine months Ended September 30, 2021
| | | Nine months Ended September 30, | |
| | | 2022 | | | 2021 | |
| USD in thousands | | | | | | |
| Net cash used in operating activities | | $ | (9,845 | ) | | $ | (9,612 | ) |
| Net cash used in investing activities | | | (2,711 | ) | | | (7,402 | ) |
| Net cash provided by financing activities | | | 5,330 | | | | 28,965 | |
| Net increase in cash and cash equivalents | | $ | (7,226 | ) | | $ | 11,951 | |
Net cash used in operating activities
Net cash flow used in operating activities totaled $9.8 million in the nine months ending September 30, 2022, compared to $9.6 million in the same period in 2021, reflecting a 2% increase. The changes were due mainly to increased expenditures as indicated above, including the addition of Peace of Meat as of March 2021, offset by lower General and Administrative expenses.
Net cash used in investing activities
Net cash flow used in investment activities totaled $2.7 million in the nine months ending September 30, 2022 compared to $7.4 million in the same period in 2021, reflecting a 62% decrease due mainly to the acquisition of Peace of Meat during that period.
Net cash provided by financing activities
Net cash flow from financing activities was $5.3 million in the nine months ending September 30, 2022 (primarily resulting from a registered direct offering in June 2022) compared to $29.0 million in the same period in 2021 (during which we completed our IPO).
We have incurred losses and cash flow deficits from operations since the inception of Steakholder Foods, resulting in an accumulated deficit as of December 31, 2021 and September 30, 2022, of approximately $37 million and $48.6 respectively. We anticipate that we will continue to incur net losses for the foreseeable future. We believe that our existing cash and cash equivalents will be sufficient to fund our projected cash needs through the end of first quarter of 2023. We do not currently have any specific commitments or plans for acquisitions; to the extent we do engage in acquisitions, we will do so after ensuring that we will have sufficient funds available to meet our capital requirements, and such acquisitions are likely to affect our projected cash needs. To meet future capital needs, we would need to raise additional capital through equity or debt financing or other strategic transactions. However, any such financing may not be on favorable terms or even available to us. Our failure to obtain sufficient funds on commercially acceptable terms when needed would have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition. Our forecast of the period of time through which our financial resources will be adequate to support our operations is a forward-looking statement that involves risks and uncertainties, and the actual amount of our expenses could vary materially and adversely as a result of a number of factors. We have based our estimates on assumptions that may prove to be wrong, and our expenses could prove to be significantly higher than we currently anticipate.
Our future capital requirements will depend on many factors, including, but not limited to:
| • | the progress and costs of our research and development activities; |
| • | the costs of development and expansion of our operational infrastructure; |
| • | the costs and timing of developing technologies sufficient to allow food production equipment manufacturers and food manufacturers to product products compliant with applicable regulations; |
| • | our ability, or that of our collaborators, to achieve development milestones and other events or developments under potential future licensing agreements; |
| • | the amount of revenues and contributions we receive under future licensing, collaboration, development and commercialization arrangements with respect to our technologies; |
| • | the costs of filing, prosecuting, enforcing and defending patent claims and other intellectual property rights; |
| • | the costs of contracting with third parties to provide sales and marketing capabilities for us or establishing such capabilities ourselves, once our technologies are developed and ready for commercialization; |
| • | the costs of acquiring or undertaking development and commercialization efforts for any future products or technology; |
| • | the magnitude of our general and administrative expenses; and |
| • | any additional costs that we may incur under future in- and out-licensing arrangements relating to our technologies and futures products. |
Until we can generate significant recurring revenues, we expect to satisfy our future cash needs through capital raising or by out-licensing and/or co-developing applications of one or more of our product candidates. We cannot be certain that additional funding will be available to us on acceptable terms, if at all. If funds are not available on favorable terms, or at all, we may be required to delay, reduce the scope of or eliminate research or development efforts or plans for commercialization with respect to our technologies and make necessary change to our operations to reduce the level of our expenditures in line with available resources.
We are a development-stage technology company and it is not possible for us to predict with any degree of accuracy the outcome of our research and development efforts. As such, it is not possible for us to predict with any degree of accuracy any significant trends, uncertainties, demands, commitments or events that are reasonably likely to have a material effect on our net loss, liquidity or capital resources, or that would cause financial information to not necessarily be indicative of future operating results or financial condition. However, to the extent possible, certain trends, uncertainties, demands, commitments and events are described herein.
Since inception, we have incurred significant losses and negative cash flows from operations and have an accumulated deficit of $48.6 million as of September 30, 2022. We have financed our operations mainly through fundraising from various investors.
Our management expects that we will continue to generate losses and negative cash flows from operations for the foreseeable future, including as a result of material expenses such as leasing expenses. Based on the projected cash flows and cash balances as of September 30, 2022, our management is of the opinion that our existing cash will be sufficient to fund operations until the end of first quarter of 2023 . As a result, there is substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern.
Management’s plans include continuing to secure sufficient financing through the sale of additional equity securities or capital inflows from strategic partnerships. Additional funds may not be available when we need them on terms that are acceptable to us, or at all. If we are unsuccessful in securing sufficient financing, we may need to cease operations.
Our financial statements include no adjustments for measurement or presentation of assets and liabilities, which may be required should we fail to operate as a going concern.
Critical Accounting Policies
We describe our significant accounting policies and estimates in Note 3 to our annual financial statements included elsewhere in this prospectus. We believe that these accounting policies and estimates are critical in order to fully understand and evaluate our financial condition and results of operations.
We prepare our financial statements in accordance with IFRS as issued by the IASB.
In preparing these financial statements, management has made judgments, estimates and assumptions that affect the application of our accounting policies and the reported amounts recognized in the financial statements. On a periodic basis, we evaluate our estimates, including those related to share-based compensation and derivatives. We base our estimates on historical experience, authoritative pronouncements and various other assumptions that we believe to be reasonable under the circumstances. Actual results may differ from these estimates.
Recently-Issued Accounting Pronouncements
Certain recently-issued accounting pronouncements are discussed in Note 3, Summary of Significant Accounting Policies, to the consolidated financial statements included in elsewhere in this registration statement, regarding the impact of the IFRS standards as issued by the IASB that we will adopt in future periods in our consolidated financial statements.
Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
Liquidity Risk
Liquidity risk is the risk that we will encounter difficulty in meeting the obligations associated with our financial liabilities that are settled in cash. Cash flow forecasting is performed in our operating entities and aggregated at a consolidated level. We monitor forecasts of our liquidity requirements to ensure we have sufficient cash to meet operational needs. We may be reliant on our ability to raise additional investment capital from the issuance of both debt and equity securities to fund our business operating plans and future obligations.
Credit risk is the risk of financial loss to us if a debtor or counterparty to a financial instrument fails to meet its contractual obligations, and arises mainly from our receivables.
As part of an agreement with Therapin Ltd. from May 2020, we agreed to convert an NIS 7.25 million investment in Therapin made by Ophectra and assumed by us at the merger, into an interest-free loan, to be repaid by the latter at a rate of NIS 0.48 million per annum for ten years (NIS 4.8 million in total) plus NIS 2.45 million to be paid upon an exit event, including a public offering, or repayment of 14.74% of any distributable surplus or dividend distributed by Therapin, up to the amount of the outstanding balance, as detailed in our separation agreement with Therapin. As part of the agreement, Therapin gave us an option to convert the cash payment to equity of Therapin. Therapin has not provided any guarantees in connection with its repayment of our loan.
We restrict exposure to credit risk in the course of our operations by investing only in bank deposits.
As we have not invested in securities riskier than short-term bank deposits, we do not believe that changes in equity prices pose a material risk to our holdings. However, decreases in the market price of our Ordinary Shares or ADSs could make it more difficult for us to raise additional funds in the future or require us to raise funds at terms unfavorable to us.
Foreign Currency Exchange Risk
Currency fluctuations could affect us primarily through increased or decreased foreign currency-denominated expenses. Currency fluctuations had a material effect on our results of operations during the year ended December 31, 2021, although not in the year ended December 31, 2020.
Critical Accounting Estimates
Critical accounting estimates are those estimates made in accordance with IFRS that involve a significant level of estimation uncertainty and have had or are reasonably likely to have a material impact on the financial condition or results of operations of the registrant. For further information, see Note 2E to our annual consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this prospectus.
This summary below highlights information contained elsewhere, or incorporated by reference, in this prospectus. This summary does not contain all of the information you should consider before investing in our securities. Before you decide to invest in our securities, you should read this summary together with the more detailed information appearing in this prospectus, including “Summary Financial Data,” “Risk Factors,” “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations,” and our consolidated financial statements and the related notes included at the end of this prospectus, before making an investment in our Securities.
Our Company
We are an international deep-tech food company that initiated activities in 2019 and are listed on the Nasdaq Capital Market under the ticker “STKH”. We maintain facilities in Rehovot, Israel and Antwerp, Belgium and recently commenced activities in the United States. We believe that cultivated meat technologies hold significant potential to improve meat production, develop a sustainable livestock system, simplify the meat supply chain, and offer consumers a range of new product offerings.
We aim to provide an alternative to industrialized animal farming that reduces carbon footprint, minimizes water and land usage, and prevents the slaughtering of animals. By adopting a modular factory design, we expect to be able to offer a sustainable solution for producing a variety of beef, chicken, pork and seafood products, both as raw materials and whole cuts.
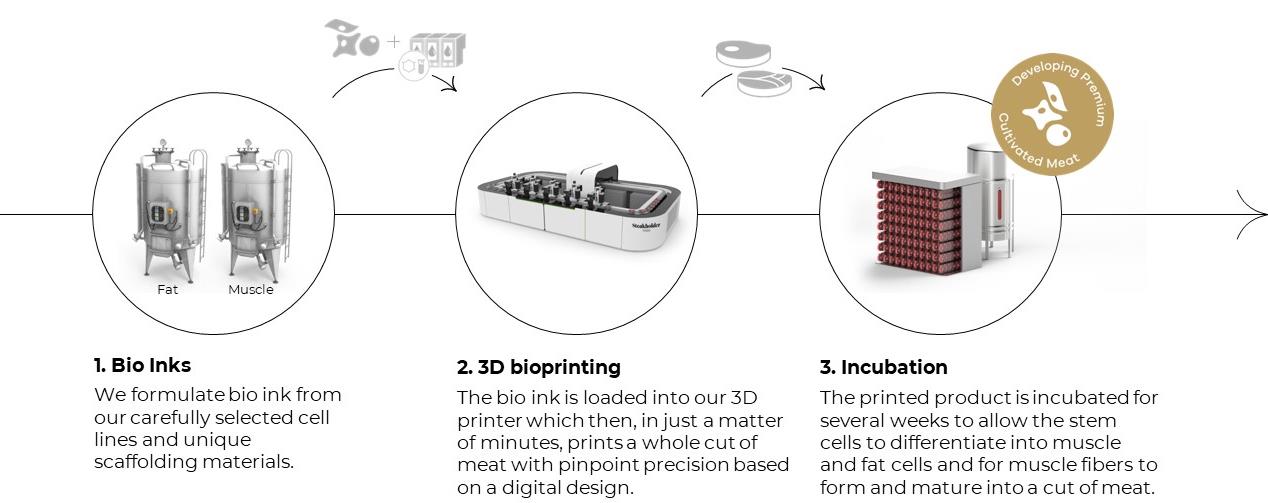
We are developing cultivated meat technologies, including three-dimensional printing technology, together with biotechnology processes and customizable manufacturing processes in order to manufacture cultivated meat that does not require animal slaughter. We are developing a novel, proprietary three-dimensional bioprinter to deposit layers of differentiated stem cells, scaffolding, and cell nutrients in a three-dimensional form of structured cultivated meat. We believe that the cultivated meat production processes we are developing, which are designed to offer our eventual customers an alternative to industrial slaughter, have the potential to improve the quality of the environment, shorten global food supply chains, and reduce the likelihood of health hazards such as zoonotic diseases transferred from animals to humans (including viruses, such as virulent avian influenza and COVID-19, and drug-resistant bacterial pathogens, such as some strains of salmonella).
In December 2021, we announced that we had successfully three-dimensionally printed a 3.67 oz cultivated steak, primarily composed of cultivated fat and muscle tissues. While cultivated meat companies have made some progress developing unstructured, or even undifferentiated, alternative meat products, such as minced meat and sausage, to the best of our knowledge, the industry has struggled in developing high-margin, high-value structured and cultivated meat products such as steak. Unlike minced meat, a cultivated meat steak product has to grow in fibers and contain connective tissues and fat. To be adopted by diners, we believe that cultivated steaks will need to be meticulously engineered to look and smell like conventional meat, both before and after cooking, and to taste and feel like meat to the diner. We believe that we are the first company to be developing both a proprietary bioprinter and the related processes for growing cultivated meat to focus on what we believe is a high value sector of the alternative protein market.
In May 2022, we joined the UN Global Compact initiative, committing to ten universally accepted principles in the areas of human rights, labor, environment, and anti-corruption and to act in support of the issues embodied in the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals.
We are led by our Chief Executive Officer, Arik Kaufman, who has founded various Nasdaq- and Tel Aviv Stock Exchange, or TASE, -traded foodtech companies, and currently serves as director of Wilk Technologies Ltd. He is also a founding partner of BlueOcean Sustainability Fund, LLC, or BlueSoundWaves, led by Ashton Kutcher Guy Oseary and Effie Epstein, which has partnered with Steakholder to assist in attempting to accelerate the Company’s growth. Mr. Kaufman holds extensive personal experience in the fields of food-tech and bio-tech law, and has led and managed numerous complex commercial negotiations, as part of local and international fundraising, M&A transactions and licensing agreements. We have carefully selected personnel for the rest of our executive management team who possess substantial industry experience and share our core values, from fields as diverse as tissue engineering, industrial stem cell growth, and printer and print materials development.
Cultivated Meat Industry and Market Opportunity
Protein is a necessary staple for healthy nutrition. The growth in recent years of both the human population and global wealth is driving a decades-long trend of accelerating demand for meat. The demand for protein products has consistently risen in recent decades and is expected to continue to do so. The rising growth of demand for farm animals for the food industry has created significant environmental, health, financial and ethical challenges.
According to Statista, the value of the global meat sector was estimated at $838 billion in 2020, and was forecast to increase to $1.157 billion by 2025. According to market research firm Fortune Business Insights, the global meat substitute market was estimated at $5.4 billion in 2021 and is expected to grow to $10.8 billion by 2028. According to Facts and Factors Market Research, the cultivated meat category alone is expected to reach $248 million by 2026, with an annual growth rate of approximately 16%. With regard to the longer term, Barclays predicted in November 2021 that by 2040, 20% of the demand for meat globally will be provided by cultivated meat – a $450 billion market opportunity.
The meat industry is showing strong interest in the alternative protein space, both in plant-based and cell-based proteins. There are several drivers underlying the strong engagement with alternative proteins. We believe consumers are looking for less harmful protein sources, with approaches such as flexitarianism already an established middle path between vegetarian diets and those heavy in animal proteins, such as the paleo diet. Many meat processors have experienced the worst of the COVID-19 pandemic outbreaks and are seeking to minimize human involvement in the manufacturing process. To that end, retailers such as Costco and Walmart are increasingly opening their own meat processing facilities on which they can rely exclusively without the involvement of third party manufacturers.
Limitations of Conventional Meat Production
In addition to questions about whether conventional meat production can adequately provide for the growing global population, conventional meat production raises serious environmental issues. According to the United Nations, 8% of the world's freshwater is used for raising livestock for meat and leather. At least 18% of the greenhouse gases entering the atmosphere are from the livestock industry. 26% of the planet's ice-free land is used for livestock grazing and 33% of croplands are used for animal feed. With regard to treatment of animals in conventional meat production, more than 70 billion animals are slaughtered annually with steady increases to be expected in line with increased demand for meat.
Another common consumer concern with industrial-scale animal rearing is the reliance on the intensive use of antibiotics. Antibiotics are used in livestock, especially pigs and poultry, to manage animal health, and to treat or prophylactically prevent diseases such as avian flu and swine flu. Their effects on human health have not been fully resolved, with concerns including the potential growth of antibiotic-resistant diseases in meat for human consumption.
Existing Alternative Proteins and their Limitations
Negative consumer sentiment towards the perceived ethical, health and environmental effects of the global meat industry help explain the strong focus that has developed on creating methods of protein production that are more sustainable, nutritious and conscious of animal welfare. Recent years have seen a combination of increasing consumer awareness and advanced technological development that has led to substantially increased demand for proteins that do not involve animal slaughter besides traditional plant-based proteins, such as soy, peas and chickpeas. Some of the alternative proteins being developed for human consumption for this purpose include:
Mycoproteins: Some of the most commercially successful novel alternative protein products are currently mycoproteins, which are derived from fungi. They are high in protein and fiber, low in saturated fat, and contain no cholesterol. However, they have been associated with allergic and gastrointestinal reactions. They are fermented to become a dough, which can develop a texture similar to that of meat.
Jackfruit: Jackfruit is a tropical fruit native to India, which is high in protein. Its texture is somewhat similar to shredded meat, although its taste is similar to other fruits, such as apples and mangoes. Thus, while it is a good source of protein, it is not generally viewed as an alternative to meat for consumers used to animal proteins due to the difference in taste from traditional meat products.
Insects: Insects are an environmentally-friendly source of protein that requires significantly less land and water, and emits significantly less greenhouse gases than large mammals raised for slaughter. In addition, they can be fed food unsuitable for livestock that would otherwise be wasted. While crickets are the most common source of edible insects, research is currently taking place on new insect species of value for food production, as well as methods to produce them economically at scale. Insects can be consumed in their natural state; however many cultures consider insect consumption to be taboo and many people are disgusted by the idea. As a result, research is taking place into developing insect-based products in different forms not easily discernable as insect-based, including flour.
The Cultivated Meat Solution
We believe that cultivated meat grown through cellular agriculture, which aims to produce cultivated animal proteins without the need for large-scale slaughter, has the potential to satisfy consumer desire for meat while also avoiding the negative impacts of conventional meat production. Cellular agriculture is an efficient, closely-controlled indoor agricultural process that utilizes advanced technologies with conceptual similarities to hydroponics, which are used for growing meat cells rather than fruit. Cultivated meat is grown in cell culture rather than inside animals and applies tissue engineering practices for fat and muscle production for the purpose of human consumption. Instead of animal slaughter, stem cells are isolated from animal tissue, such as from an umbilical cord (following birth), an adipose or a muscle tissue, and then cultivated in vitro to form muscle fibers and fat cells. While also known as “cultured meat”, “clean meat”, “in vitro meat” or “lab-grown meat”, the term “cultivated meat” has gained the most traction as of late and is the term believed to best appeal to consumers.
Cultivated meat production is an advanced technology that operates as part of the wider field of cellular agriculture, which entails growing animal cells in bioreactors and is an emerging solution to the growing demand for alternative proteins. We are aware of a few dozen companies and institutions actively working to develop technologies and other products to meet this demand, some of whom are focused on producing red and white meats, while others are focused on fish and crustaceans. Some of these companies are working on culturing various types of cells, such as chicken, pork, kangaroo and foie gras. We believe this push of scaling-up cellular agriculture has the potential to offer a solution to the scale and environmental challenges confronting conventional meat production. Other alternative protein companies are already selling plant-based meat substitutes, but to our knowledge, these companies are not focused on the production of real meat products produced with animal cells without pea or soy ingredients.
We are engaged with experimentation to develop optimal and cost-effective cell culture media. In so doing, we are also exploring a range of types of and sources for growth factors suited to cell culture. These sources are expected to be sustainable and ethical, providing a route to enabling efficient and cost-effective processes. While many challenges remain, surveys are consistently showing consumer openness toward, and enthusiasm for, cultivated meat. According to “Consumer Acceptance of Cultured Meat: An Updated Review (2018–2020)” published by researchers at the University of Bath, “the evidence suggests that, while most people see more societal benefits than personal benefits of eating cultivated meat, there is a large potential market for cultivated meat products in many countries around the world. Cultivated meat is generally seen as more acceptable than other food technologies, and more appealing than other alternative proteins like insects. Although it is not as broadly appealing as plant-based proteins, evidence suggests it may be more uniquely positioned to appeal to meat-lovers who are resistant to other alternative proteins, and it is more appealing to certain demographic groups".
We believe that cultivated meat could have several potential advantages over conventionally-harvested meat:
| | • | Environmental: At least 18% of the greenhouse gases entering the atmosphere today are from the livestock industry. Research shows that the expected environmental footprint of cultivated meat includes approximately 78% to 96% fewer greenhouse gas emissions, 99% less land use, 82% to 96% less water use and 7% to 45% less energy use than conventionally-produced beef, lamb, pork and poultry. This suggests that the environmental consequences of switching from large-scale, factory farming to lab-grown cultivated meat could have a long-term positive impact on the environment. |
| • | Cost: While the precise economic value of harvested cells has yet to be determined, the potential to harvest large numbers of cells from a small number of live donor animals gives rise to the possibility of considerably higher returns than traditional agriculture, with production cycles potentially measured in months rather than years. By comparison, raising a cow for slaughter generally takes an average of 18 months, over which period 15,400 liters of water and 7 kilograms of feed will be consumed for every kilogram of beef produced. |
| • | Animal Suffering: More and more people are grappling with the ethical question of whether humanity should continue to slaughter animals for food. There is a growing trend of opposition to the way animals are raised for slaughter, often in small, confined spaces with unnatural feeding patterns. In many cases, such animals suffer terribly throughout their lives. This consideration is likely a factor in many consumers choosing to incorporate more flexitarian, vegetarian and vegan approaches to their diets in recent years. |
| • | Controlled Growing Environment: Another potential benefit of cultivated meat is that its growth environment is designed to be less susceptible to biological risk and disease, through standardized, tailored production methods consistent with good manufacturing practices that are controls to contribute to improved nutrition, health and wellbeing. |
| • | Alternate Use of Natural Resources: Eight percent of the world’s freshwater supply and one third of croplands are currently used to provide for livestock. The development of cultivated meat is expected to free up many of these natural resources, especially in developing economies where they are most needed. |
| • | Food Waste: The conventional meat industry’s largest waste management problem relates to the disposal of partially-used carcasses, which are usually buried, incinerated, rendered or composted, with attendant problems such as land, water or air pollution. Cultivated meat offers a potential solution for this problem, with only the desired cuts of meat being produced for consumption and only minimal waste product generated with no leftover carcass. |
Our vision is to be a global leader in the production of meat through advanced biotechnology and engineering solutions for a more sustainable world. We are committed to making the right choice of meat for end consumers simple by developing high-quality meat that is slaughter-free, delicious, nutritious, and safer than farm-raised meat, We accomplish this by adopting a factory design intended to offer a sustainable solution for producing a variety of beef, chicken, sea-food and pork products, whether as raw materials or final consumer products.
Our technologies and processes have the potential to be sustainable. We are developing a meat production process that is designed to provide sustainability in an industry that, due to inefficiencies inherent in conventional meat farming, is not otherwise expected to be able to meet the growing demand for protein caused by rising population numbers and global affluence. These include the large amounts of land and water use that are needed for raising livestock, which causes precious natural resources to be squandered and the release of methane and other greenhouse gases by livestock.
We are designing our cellular agriculture and bioprinting processes to be modular so that customers can initiate their cultivated meat activities at scales suitable for their specific needs and to grow their activities as their needs evolve. Whether a customer wishes to manufacture a hybrid product that includes cultivated and plant-based ingredients, cultivated fat as a raw material, or even 3D-printed steak, each facility can be adapted to scale-out product capabilities and production volumes.
We are developing a fully automated, clean and proprietary process for cultivated meat manufacturing in a controlled, sterile environment, which is expected to significantly increase food safety. Our production facilities will not house a single animal and will contain robust integrated monitoring systems and minimal human interaction, which will greatly reduce the risk of pathogen contamination of the type claimed to have caused the COVID-19 pandemic and numerous other human health crises.
We have carefully selected personnel for our management team who possess substantial industry experience, from diverse fields including the food industry, bioprinting, tissue engineering, industrial stem cell growth, software engineering, electronic and mechanic engineering and print materials development. We believe that this blend of talent and experience in managers who share our core values gives us the requisite insights and capabilities to execute our plan to develop technologies designed to meet demand in a scalable, profitable and sustainable way.
To achieve our mission, we intend to:
| • | Perfect the development of our cultivated meat manufacturing technology and processes. We intend to continue developing and refining our processes, procedures and equipment until we are in a position to commercialize our technologies, whether by manufacturing final products for consumers (B2C and B2B2C models) or ingredients for industrial use, as well as in outlicensing (B2B models). We are continuing to tackle the technological challenges involved in scaling up both our biological and printing processes to industrial-scale levels. |
| • | Commercialize our technologies for use in consumer and business markets. We intend to provide ingredients to business customers for use in consumer products in order to help meet the growing demand for sustainable, slaughter-free cultivated meat products. For example, manufacturers of meat alternatives, such as vegetarian sausages, may choose to include our cultivated fat biomass in their products in order to deliver the signature meaty flavors, aromas and textures of the meat that is otherwise provided by the conventional meat of species such as chicken, beef and pork. We believe that this combination has the potential to unlock a new level of meat experience.
In addition, we intend to license our production technology as well as provide associated products, such as cell lines, printheads, bioreactors and incubators, and services, such as technology implementation, training, and engineering support, whether directly or through contractors, to food processing and food retail companies. We intend to charge our customers a production license fee, based upon the amount of meat printed. We expect that each production facility will periodically require us to provide them with our proprietary materials, such as fresh sets of starter cells, for a fee. In addition, other materials used in the production process, such as cell-culture media and additives in our bio-inks may be sourced from third parties. Whether these materials are customized for the specifics of our production processes, “white-labelled” generic materials or proprietary materials that we have developed, we may charge a fee for restocking such materials; however, we have not yet reached the stage where it would be possible to estimate to what extent this would contribute to any future revenue stream. Finally, we intend to provide paid product implementation and guidance services to our customers looking to establish cultivated meat manufacturing facilities. We expect that each facility licensing our technologies will need to deal with novel challenges and, as a result, will require the assistance of our expert knowledge in order to set up and implement our licensed technologies. |
In addition, we envisage demand for our ingredients in industrial applications other than human consumption, including cosmetics, which involve the extensive use of fat, and pet food. However, our current focus remains the development of cultivated meat and its ingredients for human consumption.
| • | Develop additional alternative proteins to meet growing industry demand. There are substantial technological challenges inherent in expanding our offering beyond our current cultivated beef, pork and avian technologies to additional alternative proteins and cell lines. However, we believe that our experience, know-how and intellectual property portfolio form an excellent basis from which to surmount such challenges. Our first step in this direction was the 2021 acquisition of Peace of Meat BV, or Peace of Meat, with the aim of developing avian fat for the alternative meat industry by applying proprietary technology to mimic the cellular composition of conventional poultry. In addition, in 2022 we commenced a collaboration with Singaporean cultivated seafood developer, Umami Meats, for the joint development of structured seafood products. |
| • | Acquire synergistic and complementary technologies and assets. We intend to optimize our processes and diversify our product range to expand the cultivated meat technologies upon which marketable products can be based. We intend to accomplish this through a combination of internal development, acquisitions and collaborations, with a view to complementing our own processes and diversifying our product range along the cultivated meat production value chain in order to introduce cultivated products to the global market as quickly as possible. See also “- Additional Technologies” below. |
The Commercialization Roadmap
The following table sets forth a road map for the expected commercialization of substitutes for conventionally-farmed meat, which include:
| • | Fully-plant-based meat-like offerings that are already commercially available but lack the organoleptic properties of meat, primarily flavor, aroma, texture and color; |
| • | Hybrid meat products of the type that we are developing, which combines real cultivated fat with plant-based protein to offer meatier products with enhanced organoleptic properties; |
| • | Unstructured meat products, such as hamburgers and minced meat; and |
| • | Fully-cultivated structured meat products, such as 3D-printed steaks. |
We are focusing on developing cultivated fat, primarily for the purpose of commercializing hybrid meat products in the short term, and developing the technologies needed for both unstructured and 3D-printed, structured, cultivated meat products.
In September 2022, we announced the development of Omakase Beef Morsels, a richly-marbled, structured meat product developed using our proprietary 3D-printing process. Inspired by the marbling standard of Wagyu beef, we believe that Omakase Beef Morsels are an innovative culinary achievement elegantly designed as a meat lover's delicacy for premium dining experiences.
The product is made up of multiple layers of muscle and fat tissue, which have been differentiated from bovine stem cells, and showcases the control, flexibility and consistency inherent in our bioprinting technology. Each layer is printed separately using two different bio-inks – one for muscle and one for fat. The layers can be printed in a variety of muscle/fat sequences to obtain differing results of juiciness and marbling of the cut.
Omakase Beef Morsels (Photo credit: Shlomo Arbiv)
Meat and Poultry Ingredients for Hybrid and Unstructured Cultivated Products
Both we and our Belgian subsidiary, Peace of Meat, continue to develop novel, proprietary, stem-cell-based technologies to produce fat, muscle and connective tissue biomass from multiple species, such as chicken, beef and pork without harming any animals. We are leveraging this technology, including through novel hybrid food products, to expedite market entry while we develop an industrial process for cultivating and producing real meat, including through the use of three-dimensional bioprinting technology. The first expected application of the technology is in hybrid food products, which combines plant-based protein with cultivated animal fat biomass and is designed to provide meat analogues with qualities of “meatiness”, such as taste and texture, closer to that of conventional meat products than are currently available in the market today. To this end, we have conducted a number of taste tests where we demonstrated the potential that our cultivated fat biomass has to enhance the taste of plant-based protein products. We believe that a product comprised of as little as 10-25% of our cultivated fat biomass combined with plant-based protein has the potential to enhance meatiness. Our cultivated fat biomass is designed to be free of antibiotics and can be tailored to provide personalized nutritional profiles.
Our fat biomass production technology relies on the use of cells derived from proprietary cell lines. These cells grow naturally in suspension and in high densities. They also proliferate continuously, are relatively large and tend to easily accumulate lipid. This quality of the cells makes them an excellent candidate for producing cultivated fat, so we have used them to build a robust cell line that is free of genetic modifications, which we are now attempting to upscale towards industrial production volumes. Our most advanced cell line is being built with non-GMO or GMO pluripotent stem cells that can differentiate into muscle cells and fat cells and form connective tissue, which need fewer high-cost media components, such as growth factors, for their development. As a result, these cells may have higher growth potential with lower costs than alternative technologies. We have likewise developed the process for isolating, growing and differentiating bovine stem cells into muscle fibers, fat biomass and connective tissue.
In July 2021, Peace of Meat cultivated just over 700 grams of pure chicken fat biomass in a single production run. We believe that producing this quantity of pure cultivated material in one run is a breakthrough toward potentially manufacturing cultivated chicken fat at an industrial scale.
Single production run of chicken fat biomass.
Some of the steps which we are taking in order to keep the growth media cost low include:
| • | Replacing expensive, animal-derived components in cell growth media with chemical replacements, including through in-house production; |
| • | Cell line optimizations, such as through high-throughput analyses of evolved isolates; |
| • | Bioprocess optimization and media recycling; |
| • | Upscaled growth factor production, such as through hollow fiber bioreactors; and |
| • | Long-term market optimization as a result of expected increased demand. |
Structured Fully-Cultivated Meat
In addition to meat ingredients for use in hybrid meats and unstructured, cultivated meat, we are developing the technology and processes to produce cultivated meat steak at an industrial scale. We are working to achieve this by creating an end-to-end technology that combines cellular agriculture with bioprinting to produce complex meat structures. We are developing cellular agriculture technology, such as cell lines, and approaches to working with growth media to support the growth of cells such as fat and muscle cells in a scalable process, and have demonstrated an ability to differentiate stem cells into fat and muscle cells. The media will be composed of food-grade ingredients and we expect their growth factors to be similar to those produced naturally in the bodies of cattle, albeit free of fetal bovine serum, traditionally a significant component of cellular growth media that is harvested from animals. We are engaged with experimentation to develop optimal and cost-effective antibiotic-free cell culture media, and are exploring a range of types of, and sources for, growth factors suited to cell culture. These sources are expected to be sustainable and ethical, providing a route to enabling effective and cost-effective processes. The processes we are developing are designed to allow cells of interest, following humane tissue extraction from the umbilical cord or biopsy, to be isolated, replicated, grown and maintained in vitro under controlled, laboratory conditions.
We are developing proprietary bioprinting and tissue engineering technologies to enable the design and bioprinting of three-dimensional tissues. Our goal is for the meat produced using these technologies to have an authentic texture, flavor, appearance and aroma without being limited to the precise combinations of existing meat tissue, so that fat content of the meat, for example, can be adjusted to amounts other than those occurring naturally in animals in order to meet varied consumer preferences for fattier or leaner cuts of meat. We believe that the novel processes that we are developing have the potential to eventually be competitive with conventional manufacturing technologies for premium products as large-scale production of meat tissues will create new lines of meat without any unnecessary animal use.
In the course of developing our technologies, we intend to develop a large-scale technology demonstration model. We have set forth below an illustration of the process that we are developing that we believe will, upon completion, allow us and our customers to develop and manufacture cultivated steaks at industrial scale.
We are working on slaughter-free meat development processes, including cell proliferation and differentiation and experiments with stem cell growth media to grow high-density stem cells based solely on compounds produced in laboratory processes.
In these experiments, we have developed stem cells able to differentiate into fat or muscle cells which allows for the maturation of fat tissue and muscle fibers following an isolation process of specific stem cells from sources, such as bovine umbilical cords or muscle tissue. These cells are nourished with nutritional compounds that we develop as a growth medium to direct their differentiation into fat tissue or muscle tissue as needed.
In February 2022, we announced the successful development of a novel technology process in which muscle cells are fused into significant muscle fibers that better resemble those in whole cuts of meat. Bovine stem cells were isolated, proliferated in the lab and differentiated into matured muscle cells with improved muscle fiber density, thickness and length.
Cell source for cultivated meat products
The process of industrial scale meat printing necessitates the isolation and development of cells able to produce both animal muscle and fat tissues. Our proprietary cell lines are isolated from various sources that harbor these properties. For example, adult stem cells are isolated from various adult tissues, such as fat and muscle tissues, and stem cells are isolated from the umbilical cord immediately following birth. Each of these cells has advantages and disadvantages and their adaptation to our robust meat production process is currently being evaluated.
We are using software-controlled bioreactors to foster cell proliferation. The initial growth phase leverages exponential growth of stem cells to achieve sufficient cell volumes for food production. These stem cells undergo differentiation into multiple cell types, such as muscle and fat, as well as cell maturation.
We are in the process of developing cell-culturing processes and protocols for use in bioreactor systems. Such bioreactor systems will enable monitoring and control of growth parameters, as well as testing and development of efficient and economical cell-growth processes in industrial breeding containers. Separate from the bioreactor development process, we have commenced development of a cell-suspension growth process. This growth process is different from cell growth on laboratory plates. We expect that the newly-developed processes may allow cell growth on a scale needed for industrial-scale meat development. We have already developed a cell-suspension growth process using chicken, porcine and beef cells in the course of developing both structured and unstructured products.
Structured, three-dimensional printed products require the use of bio-inks, which are printable biological materials produced from the biomass produced in our bioreactors, as well as scaffolding materials. Bioinks produced differ in their differentiation potential into muscle, fat and connective tissue. In this step, our bio-inks are printed in thin layers in the desired combination, which provides creative control over the steak design, in a process that maintains the ongoing viability of the bio-ink cells. Since the printed layers are composed of viable cells, they are then able to coalesce and mature in an incubator with the help of bonding agents that serve as a scaffold that forms three-dimensional tissues. We are in the process of optimizing the characteristics of our proprietary bio-inks, including composition, motility, viscosity, temperature, structural stability, density and jettability, or the ability to be dispersed by a printer, as well as the factors helping the cells to connect in three-dimensional tissues.
Bioprinting is a process of fashioning a specific type or types of native or manipulated cells configured to form the edible tissue analog by depositing scaffolding material mixed with cells and other bio-inks. This is done through the use of an inkjet-style printer with drop-on-demand capabilities where inks are printed precisely into a three-dimensional design.
The image below depicts a potential laboratory model that we could use for the development and production of cultivated meat steaks.
After the completion of the bioprinting process, the tissue is transferred into a special incubator, where, in addition to providing nutrients and other chemical and biological agents, the system may physically manipulate the tissue. This “training” process increases the muscle cells differentiation, a process in which a cell changes its function and phenotype, and produces a stronger, more fibrous tissue.
To date, we have printed several cell types, which coalesced into fat and muscle tissue grown in our laboratory. In December 2021, we announced that we had successfully three-dimensionally printed a 3.67 ounce cultivated steak that was primarily composed of cultivated fat and muscle tissues without using soy or pea protein. The cells used to make the steak were produced with an advanced proprietary process that started by isolating bovine stem cells from tissue samples and multiplying them. Upon reaching sufficient cellular mass, stem cells were formulated into bio-inks compatible with our proprietary 3D bioprinter. The bio-inks were printed from a digital design file of a steak structure. The printed product was placed in an incubator to mature, allowing the stem cells to differentiate into fat and muscle cells and develop into fat and muscle tissue to form our steak.
In May 2022, we announced the development of a novel, multi-nozzle 3D bioprinting system for industrial scale production of complex cultivated meat products without impacting cell viability. We plan to offer the technology to third parties via our wholly-owned private subsidiary, Steakholder Innovation Ltd. as a potential additional revenue stream and to accelerate commercialization.
Cultivated Steak Scaffolding
Growing three-dimensional meat presents a unique challenge. Typically, animal cells must remain within 200 microns of a nutrient supply in order to survive. This is little more than the width of a human hair and is known as the diffusion limit. It is the reason that cells grow along the surface of a petri dish rather than forming vertical piles.
In the next step of the process that we are developing, we intend to build a scaffold to support the growth of three-dimensional meat. A “scaffold”, or “biocompatible scaffolding”, refers to an engineered platform having a predetermined three-dimensional structure that mimics the environment of the natural extracellular material, or ECM. The ECM is a three-dimensional network of large molecules that provide structural and biochemical support to surrounding cells. Collagen is the most abundant component in the ECM that supports the development and growth of complex tissues, and specifically, also muscle tissues. Engineering of bovine muscle tissues in vitro while avoiding the use of animal derived collagen requires the development of plant based scaffolds that would imitate the properties of the ECM. Plants are an obvious candidate for scaffolding as they are sustainable, cost worthy and could be processed to have similar properties of collagen fibers. We are developing technology to allow for the formation of a composite scaffold.
We are focused on developing a process that will allow our food technology customers to operate a high-throughput manufacturing process for high-quality, healthy meat. Our cellular agriculture and bioprinting processes are being designed to be modular, meaning that they can work using different factory sizes. We believe we could license our technology to customers with industrial plants close to urban areas seeking to provide “just in time”, logistically-efficient, local and premium cellular agriculture. In addition, we believe a licensee of our technology could build a plant in a locality that does not have the resources needed for industrial animal husbandry, which would allow places like the United Arab Emirates, Hong Kong or Singapore to potentially become more agriculturally independent by increasing food security. As costs continue to decrease, we believe licensees of our technology could also build production facilities in localities where there is high agricultural seasonality or desertification risk.
Illustration of a contemplated cultivated meat manufacturing plant.
We are developing processes intended to achieve high-volume manufacturing capabilities in line with the needs of today’s value-added food processors and other meat and food industry players. To this end, we are working on processes to scale up production, beginning with different cell types, including induced pluripotent stem cells and embryonic stem cells. We expect high-volume stem cell production to feed into differentiation bioreactors that are dedicated to producing fat and muscle cells. These cells are the key input for our downstream productization stages.
The processes we are developing are advanced biotechnological processes that are intended to produce cultivated meat in a clean environment with minimal environmental impact. We envision that factories utilizing our technologies will exist in greater harmony with their environment than typical current factories by supporting sustainability, utilizing renewable energy sources and recycling or treating their own waste.
We may incorporate novel bioreactor technologies that benefit cellular agriculture and the development of low-cost cell culture media not based on fetal bovine serum.
We also plan to add cell line types to expand the development of cultivated meat to other types of animals, as well as achieving market penetration in the shortest timeframe possible, which would allow us to realize the great potential in the market. We are developing cultivated meat, both unstructured hybrid products and structured, three-dimensional printed products, with an initial emphasis on bovine and porcine cells, and our subsidiary, Peace of Meat, is developing cultivated avian fat, initially for use in hybrid products. We estimate that the first hybrid products based on Peace of Meat technology may enter the market as early as 2025. Beyond hybrid products, cultivated fat is expected to be a component in other fat-based products, whether edible or otherwise, and an integrated component in Steakholder’s printing technology. We are working to create synergy and added value to the cultivated meat market, while also sustaining animal welfare and meeting the growing global demand for meat.
United States
In March 2022, we announced that we intended to open a U.S. office. We expect the new space will include activities in research and development, investor relations and business development. In September 2022, we commenced development of a bovine cell line in the United States. by isolating cells sourced from cattle raised on a farm approved by the United States Department of Agriculture, or USDA.
In February 2021, we finalized our acquisition of Peace of Meat, a Belgian producer of cultivated avian products, for up to $19.9 million in cash and equity, depending on milestone achievements. We intend to leverage Peace of Meat’s cultivated avian technologies to diversify our own bovine-oriented technologies and expedite our entry into the market for plant-based meat alternatives and cultivated products. Peace of Meat was established in Belgium in 2019 and is developing cultivated avian fat directly from animal cells without the need to grow or kill animals. In 2020, Peace of Meat was awarded a subsidy of approximately $1.33 million from the Flemish government, of which $0.5 million has been received, and has received approximately $1 million in private investments. We bought Peace of Meat for approximately $20 million in a cash- and equity-based milestone deal. We believe that the innovative technology of Peace of Meat has the potential to support an industrial process for the production of cultivated avian fat. Peace of Meat has entered into a number of scientific and commercial collaborations, is in the process of positioning itself as a future B2B provider with the potential to cover the entire value chain, has accelerated research and production processes in the industry and has conducted taste tests for hybrid products that it has developed. It intends to open a pilot plant in Belgium.
In April 2021, we commenced food technology development activities through our European subsidiary, MeaTech Europe BV, with an initial focus on hybrid foods using Peace of Meat’s cultivated fat. Hybrid foods are products composed of both plant and cultivated meat ingredients that have the potential to offer a meatier experience than purely plant-based meat alternatives.
In March 2022, we announced that Peace of Meat intends to build an R&D facility and pilot plant in Belgium. The new facility is designed to expand and accelerate our cultivated avian technology and R&D capabilities and help propel our market entry.
In May 2022, Peace of Meat signed a strategic agreement with 3FBIO Ltd., trading as ENOUGH, a leader in the field of mycoprotein, a fungi-based fermented food ingredient, which is expected to help accelerate commercialization of our culture avian fat product. This innovative initiative is expected to create advanced hybrid alternative meat products that better resemble the flavor, aroma, texture, and even nutritional value of conventional meat.
Asia
In November 2022, we received a registered trademark for our name in Japan, which we view as an important next step in our plans to penetrate the Japanese market and other markets in Asia. This follows on our collaboration with Umami Meats, a Singapore-based cultivated seafood company, for the joint development of 3D-printed cultivated structured seafood.
We are working to develop and establish sales and distribution capabilities. In the event that we complete the development of our technologies and secure adequate funding, we intend to consider commercialization collaborations where appropriate.
Apart from end consumers in B2C and B2B2C models of branded products, we believe that our ideal business customers will be value-added food processors and retailers that wish to benefit from cultivated meat manufacturing capabilities. We intend to provide our corporate customers with a solution to these needs in the form of highly-automated, cleaner and ‘just-in-time’ manufacturing of cultivated meat products using a repeatable, consistent manufacturing process. Our goal is for our customers to be able to streamline their meat supply chain, introduce greater manufacturing flexibility and locate their cultivated meat production facilities closer to the point of retail or consumption.
We intend to provide our business licensees with assistance in constructing facilities to employ our proprietary technology and processes. We expect that we will need to collaborate with third parties to obtain and make available to our customers the expertise necessary to provide this assistance. In addition, we intend to procure the equipment our licensees need to deploy our proprietary technology and processes from third-party providers. Some equipment, such as piping, clean rooms and packing and freezing equipment are standard industry equipment and can be sourced on open markets. Other equipment, such as bioreactors and our proprietary bioprinters, will need to be produced by contract manufacturers.
We have sought and continue to seek patent protection as well as other intellectual property rights for our products, processes and technologies in the United States and internationally. Our policy is to pursue, maintain, expand, protect and defend our patent rights and trade secrets, which we believe enable us to deliver long-term protection for the proprietary technologies, inventions and improvements that are commercially important to the development of our business.
During the course of 2022, we received notices of grant or allowance for patent applications in the USA, Canada, Australia and New Zealand relating to our development of systems and methods to apply external forces to muscle tissue that result in the development of high-quality complex structured meat.
We have a growing portfolio of 15 provisional and non-provisional patent applications pending with the USPTO, WIPO (filed through the Paris Convention Treaty, or PCT, and in various countries worldwide. A provisional patent application is a preliminary application, and establishes a priority date for the patenting process of inventions disclosed therein.
Our existing patent portfolio can currently be divided into three main areas:
Mechanical: covering printer components and peripherals used in the fabrication of the tissue cultures with two applications filed
at the national stage of prosecution. The first; directed to print heads operable in a bioprinting systems for the fabrication of edible biostructures using drop-on-demand, the print heads specifically designed to accommodate bio fluids of suspended systems without causing demixing, while still delivering bio fluids with high accuracy and precision.
Following a favorable patentability opinion, the Application was filed in the USPTO and is currently undergoing accelerated examination having received a grant for a petition to make special under the Patent Prosecution Highway (PPH) program. The second application currently undergoing examination in 7 countries, is directed to systems and methods of physically manipulating a resilient container (bladder) of bioprinted tissue culture having non-random three dimensional cell structure over 4 dimensions, namely elongation, compression, torsion and shear, to modulate the tissue and achieve the desired texture for each meat type. The Application was already granted in United States, Australia, and New Zealand, and was given a notice of allowance in Canada.
Current development work in the mechanical area will most likely result in the development of additional intellectual property, although at this point it remains to be seen whether it would be registerable.
Biological: covering initial materials used in the process with several provisional, and PCT applications filed and currently pending.
These include an application directed to methods for harvesting ICM from bovine blastocysts; methods and compositions for the xeno-free propagation of bESC on bovine umbilical stem cells (bUCSC), derived from a bovine umbilical cord; the use of plant-based lecithins and/or their components in a composition as a differentiation drivers for use in selectively promoting adipocytes differentiation; and methods and compositions for accelerated myotube formation.
Applications: covering the final consumable formed using mechanical and biological inputs, with a couple of applications currently pending.
These include a provisional application for a beef-emulating consumable formed of stacked 3D-pronted layers of muscle and fat tissues; and an application for a method and composition for achieving the flaky characteristics associated with fish.
In addition to patent applications, we maintain trade secrets covering know-how and proprietary information relating to our core technologies and make practicable efforts to protect our confidential trade secrets. To this end, we require our employees engaged in the development of intellectual property to enter into confidentiality agreements prohibiting the disclosure of confidential information and further, require disclosure and assignment of any inventions and associated intellectual property rights that are important to our business. Additionally, we require all entering employees to represent they are not bringing in, or are using any third party’s Trade Secrets. We have also registered our new name and logo as registered trademarks in various countries, and maintain ongoing rights to our domain name. Steakholder Foods® was registered in Japan and is currently undergoing examination in several other countries, including US.
While our policy is to obtain patents by application, license or otherwise, to maintain trade secrets and to seek to operate without infringing on the intellectual property rights of third parties, technologies related to our business have been rapidly developing in recent years. Additionally, patent applications that we may file or license from third parties may not result in the issuance of patents, and our current or future issued patents may be challenged, invalidated or circumvented. Therefore, we cannot predict the extent of claims that may be allowed or enforced against our patents, nor be certain of the priority of inventions covered by pending third-party patent applications. If third parties prepare and file patent applications that also claim technology or therapeutics to which we have rights, we may have to engage in proceedings to determine priority of invention, which could result in substantial costs to us, even if the eventual outcome is favorable. Moreover, because of the extensive time required for clinical development and regulatory review of products we may develop, it is possible that the patent or patents on which we rely to protect such products could expire or be close to expiration by the commencement of commercialization, thereby reducing the value of such patent. Loss or invalidation of certain of our patents, or a finding of unenforceability or limited scope of certain of our intellectual property, could also have a material adverse effect on us. See “Risk Factors — Risks Related to our Intellectual Property and Potential Litigation.”.
We expect that demand for our cultivated meat manufacturing plants will be driven by consumer demand for alternative proteins and, more specifically, consumer acceptance of cultivated meat as the alternative protein of choice. We believe that we will compete with other cultivated meat manufacturers, alternative protein manufacturers and the conventional meat industry as a whole. We expect to directly compete with companies licensing know-how or otherwise enabling the establishment of cultivated meat manufacturing plants. We are aware of certain companies that have announced plans to provide their cultivated meat technology on a B2B basis; however, we are not currently aware of a potential competitor focusing on complex, industrial-scale, bioprinted, high-value real meats, such as steak.
Companies such as Upside Foods, Inc. and Mosa Meat BV are focused on producing red meats, while BluNalu, Inc. is focusing on fish and Shiok Meats Pte. Ltd. is focusing on crustaceans. There are different companies working on culturing varying cell types, such as chicken, pork, kangaroo and foie gras. This push on scaling-up cellular agriculture can serve as a solution to the scale and environmental challenges confronting traditional meat production. Other alternative protein competitors such as Beyond Meat, Inc. and Impossible Foods, Inc. are already selling plant-based meat substitutes, but to the best of our knowledge, these companies are not focused on the production of real meat products produced with animal cells.
Companies Developing Vegetable and Insect Protein Alternatives
There are numerous companies focused on developing meat substitutes. In order for a product to achieve commercial acceptance as an alternative to meat, it must have an appearance, taste, smell and nutritional values that are similar enough to the type of meat that it seeks to replace or with which it seeks to compete. These meat substitute companies generally employ proprietary formulae for manufacturing that are based wholly on ingredients of plant origin. In addition, we are aware of several companies developing insect-protein production capabilities, employing among other insects, flies, larvae and grasshoppers.
Companies Developing Cultivated Meat
The cellular agriculture meat sector is in early stages of development. The sector is currently primarily comprised of companies developing a full technology stack from developing cell lines to scaling up cellular cultivation, developing media and researching the food technology aspects of the final product. Market dynamics have led to a large number of companies operating in this manner. We are aware of approximately one company that operates in the cell-based field that is developing cellular agriculture for ground-meat alternatives and appears to be progressing with its technological development. This company has indicated readiness to bring cell-based meat products to market as early as the fourth quarter of 2022 or 2023. We do not believe that any companies in this space have already developed the capability to produce industrial quantities at prices low enough to compete on a dollar-per-pound basis against conventionally-harvested meat.
A number of larger companies have begun engaging in this sector. For example, companies such as Merck & Co., Inc. and Lonza Group AG are currently investing in capabilities to accommodate the market’s desire for change in the cell culture media market. Additionally, a number of bioreactor companies are rumored to be interested in the cellular agriculture market opportunity. Over time, we expect that larger players will continue to increase their exposure to cellular meat production either by selling to, or collaborating with, the many start-ups in the space.
Currently, cellular agriculture companies are for the most part paving their own path, with a goal of producing meat cells suitable as a replacement for ground meat. The ground meat type of cellular product may also be suitable as an ingredient in a hybrid plant-based food product. The cell-types relevant to this effort are primarily muscle and fat cells. What exactly these cell-based companies will offer is likely to be affected by consumer expectations and underlying cost structures. We believe that these companies may have to mix their cellular meat product with plant-based ingredients in the interests of cost or appearance.
Companies Developing Structured Cultivated Meat Products
To our knowledge, there is currently no other company focused on the scaling up of three-dimensional bioprinting. However, there are companies attempting to produce steaks by means of other approaches, such as growing bovine cells, including fat, muscle and connective tissue on a pre-prepared scaffold, in order to create a contiguous piece of meat, which has so far yielded steaks.
Regulators around the world are in the process of developing a regulatory approval process for cultivated meat. Cultivated meat is not yet generally commercially available, but technologies like ours are anticipated to facilitate the imminent scaling up of cultivated meat production. In general, cultivated meat production is expected to be subject to extensive regulatory laws and regulations in the United States and in other jurisdictions such as Canada, Japan, the European Union and the United Kingdom. In the United States, existing food safety requirements are expected to apply. Additional details are being developed at the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, or FDA, and the U.S. Department of Agriculture, or USDA, pursuant to a Memorandum of Understanding, or MOU, published by the FDA and USDA on March 7, 2019 entitled the “Formal Agreement to Regulate Cell-Cultured Food Products from Cell Lines of Livestock and Poultry.” For example, the FDA anticipates publishing Draft Guidance on premarket safety oversight by December 31, 2022, and in September 2021, the USDA published an Advance Notice of Proposed Rulemaking (ANPR), indicating that the USDA will be developing new labeling requirements for foods under its jurisdiction produced through cell culture technology.
Under the MOU, which is expected to affect our customers producing cultivated meat, the two agencies will operate under a joint regulatory framework wherein the FDA will oversee cell collection, cell banks and cell growth and differentiation. A transition from FDA to USDA oversight will then occur during the cell harvest stage, at which point the USDA will oversee the production and labeling of cultivated meat. The USDA will be advancing new labeling requirements. To the best of our knowledge, the regulatory approval details under development, including the Draft Guidance on FDA premarket oversight, are not expected to apply to our business directly, but they are instructive as to the regulatory requirements that our cultivated meat production customers are expected to face and their expectations of us, in the form of customer assurances, regarding our products.
At this time, our business is limited to developing cultivated meat production technology, such as bioprinters, that will be marketed to cultivated meat producers, and that of Peace of Meat, which is limited to developing cultivated meat ingredients, such as cultivated avian fat. In the United States, and consistent with the Federal Food, Drug and Cosmetic Act, or the FDCA, the Federal Meat Inspection Act, and the Poultry Products Inspection Act, food ingredient manufacturers, like Peace of Meat, must comply with the FDA’s food production requirements under the FDCA, as amended by the Food Safety Modernization Act, to ensure that the food is safe, and the USDA's requirements that the ingredients, when used in USDA-regulated meat and poultry products, are effective and suitable for their intended use.
In addition, production equipment manufacturers must ensure that their products do not contribute to the production of adulterated food. The regulatory obligation falls on the food manufacturer to ensure that all food produced, including cultivated meat, is wholesome and not adulterated. Therefore, when sourcing food processing equipment, such as the three-dimensional bioprinter that we are developing, our customers will request assurances that the bioprinter is safe for its intended use and will not result in the production of adulterated food. We intend to monitor developments at the FDA and USDA in connection with the MOU to determine whether any specific requirements or recommendations are published with specific regard to cultivated meat equipment manufacturers.
In the United States, we expect companies manufacturing cultivated meat products to be subject to regulation by various government agencies, including the FDA, USDA, and the FTC. Equivalent foreign regulatory authorities include the Canadian Food Inspection Agency, the Japanese Food Safety Commission, the European Food Safety Authority and authorities of the EU member states, the State Food and Drug Administration of China and the Singapore Food Agency, or SFA. These agencies, among other things, prescribe the requirements and establish the standards for food quality and safety, and regulate various food technologies, including alternative meat product composition, ingredients, manufacturing, labeling and other marketing and advertising to consumers.
In June 2022, Singapore was the first country to approve cultivated meat for sale. The SFA has published comprehensive guidance explaining all of the requirements necessary for the safety assessment of novel foods, covering all of the specifications required for the approval of cultivated meat in Singapore.
In November 2022, the FDA announced that it completed its first pre-market consultation of human food made from cultured animal cells. Through a process with a U.S.-based cultivated meat technology company, which involved evaluating the company’s production process and the cultured cell material made by the production process, including the establishment of cell lines and cell banks, manufacturing controls, and all components and inputs, the FDA determined that it had no further questions about the company’s safety conclusion. As this was the first instance of the FDA giving the greenlight to a cultivated meat product, the FDA further announced that the world is experiencing a food revolution and the FDA is committed to supporting innovation in the food supply.
We expect that federal, state and foreign regulators will have the authority to inspect our customers’ facilities to evaluate compliance with applicable food safety requirements. Federal, state and foreign regulatory authorities also require that certain nutrition and product information appear on the product labels of our customers’ food products and, more generally, that such labels, marketing and advertising be truthful, non-misleading and not deceptive to consumers.
As the cell-based agriculture industry is young and its regulatory framework is emerging and evolving, legislation and regulation may evolve to raise barriers to our go-to-market strategies.
In addition to federal regulatory requirements in the United States, certain states impose their own manufacturing and labeling requirements. For example, states typically require facility registration with the relevant state food safety agency, and those facilities are subject to state inspections as well as federal inspections. Further, states can impose state-specific labeling requirements. In the United States, the USDA will be developing new labeling requirements for foods under its jurisdiction produced through cell culture technology as noted in an Advance Notice of Proposed Rulemaking (ANPR) published in September 2021.
We are subject to labor and employment laws, laws governing advertising, privacy laws, safety regulations and other laws, including consumer protection regulations that regulate retailers or govern the promotion and sale of merchandise. Our operations are subject to various laws and regulations relating to environmental protection and worker health and safety matters. We monitor changes in these laws and believe that we are in material compliance with applicable laws.
Environmental, Health and Safety Matters
We, our agents and our service providers, including our manufacturers, may be subject to various environmental, health and safety laws and regulations, including those governing air emissions, water and wastewater discharges, noise emissions, the use, management and disposal of hazardous, radioactive and biological materials and wastes and the cleanup of contaminated sites. We believe that our business, operations and facilities, including, to our knowledge, those of our agents and service providers, are being operated in compliance in all material respects with applicable environmental and health and safety laws and regulations. Based on information currently available to us, we do not expect environmental costs and contingencies to have a material adverse effect on us. However, significant expenditures could be required in the future if we, our agents or our service providers are required to comply with new or more stringent environmental or health and safety laws, regulations or requirements.
Except as stated above, we are not aware of any environmental risks related to our operations, and therefore, we do not believe that environmental regulations will have a significant effect on us. However, in the future, we may be required to meet environmental protection standards or regulations which could have a material impact on our activities, activities, profitability and ability to remain competitive.
Our subsidiaries and the countries of their incorporation are as follows:
| Name | | Jurisdiction of
Incorporation | | | Parent | | % Ownership (direct or otherwise) | |
| Steakholder Foods USA, Inc. | | | Delaware, U.S. | | | Steakholder Foods Ltd. | | | 100 | % |
| Steakholder Innovation Ltd. | | | Israel | | | Steakholder Foods Ltd. | | | 100 | % |
| Steakholder Foods Europe BV | | | Belgium | | | Steakholder Foods Ltd. | | | 100 | % |
| Peace of Meat BV | | | Belgium | | | Steakholder Foods Europe BV | | | 100 | % |
Property and Infrastructure
Our principal executive offices and laboratory are located at 5 David Fikes St., Rehovot, Israel. The laboratory and office space total approximately 18,300 square feet. The lease for this facility will expire in January 2026, although we have an option to renew it for four years, and the annual rent (including parking fees) is approximately $0.7 million, linked to the Israeli CPI.
As of October 31, 2022, we had 48 employees based at our office and laboratory in Rehovot, Israel and 32 employees based at our office in Antwerp, Belgium.
Local labor laws govern the length of the workday and workweek, minimum wages for employees, procedures for hiring and dismissing employees, determination of severance pay, annual leave, sick days, advance notice of termination, Social Security payments or regional equivalents, and other conditions of employment, including equal opportunity and anti-discrimination laws. None of our employees is party to any collective bargaining agreements. We generally provide our employees with benefits and working conditions beyond the required minimums. We believe we have a good relationship with our employees, and have never experienced any employment-related work stoppages.
Legal Proceedings
From time to time, we may be party to litigation or other legal proceedings that we consider to be a part of the ordinary course of our business. We are not currently involved in any legal proceedings that could reasonably be expected to have a material adverse effect on our business, prospects, financial condition or results of operations.
The following table sets forth the name, age and position of each of our executive officers and directors as of the date of this prospectus. Unless otherwise stated, the address of our executive officers and directors is Steakholder Foods Ltd., 5 David Fikes St., Rehovot 7638205, Israel.
| Name | | Age | | Position |
| Executive Officers: | | | | |
| Arik Kaufman | | 42 | | Chief Executive Officer |
| Guy Hefer | | 41 | | Chief Financial Officer |
| Dan Kozlovski | | 38 | | Chief Technologies Officer |
| Non-Employee Directors: | | | | |
| Yaron Kaiser | | 44 | | Chairman of the Board of Directors |
| David Gerbi(1)(2)(3) | | 43 | | Director |
| Eli Arad(1)(2)(3) | | 49 | | Director |
| Sari Singer(1)(2)(3) | | 42 | | Director |
(1) Member of the audit committee
(2) Member of the compensation committee
(3) Independent director as defined under Nasdaq Marketplace Rule 5605(a)(2) and SEC Rule 10A-3(b)(1).
Arik Kaufman, Chief Executive Officer
Arik Kaufman has served as our Chief Executive Officer since January 2022. He has founded various Nasdaq- and TASE-traded foodtech companies, and currently serves as director of Wilk Technologies Ltd. He is also a founding partner of the BlueSoundWaves collective, led by Ashton Kutcher Guy Oseary and Effie Epstein, which recently partnered with Steakholder Foods to assist in attempting to accelerate the Company’s growth. Mr. Kaufman holds extensive personal experience in the fields of food-tech and bio-tech law, and has led and managed numerous complex commercial negotiations, as part of local and international fundraising, M&A transactions and licensing agreements. He holds a B.A. degree in Law from Reichman University (formerly the Interdisciplinary Center Hertzliya).
Guy Hefer, Chief Financial Officer
Guy Hefer has served as our Chief Financial Officer since October 2020. He has over ten years of experience in investment banking and corporate finance roles. Between 2019 and 2020, he was the chief financial officer of Prytek Holdings Pte Ltd., a private holding group investing in technology companies globally. Prior to that, Mr. Hefer was an investment banker at Leumi Partners Ltd. between 2018 and 2019 and GCA Altium Israel Ltd. between 2017 and 2018 in Israel and at Barclays investment banking division between 2011 and 2016 in the UK and in Israel. Prior to that Guy worked at Fahn Kanne Grant Thornton Israel, an accounting firm in Israel between 2009 and 2011. Mr. Hefer holds a B.A. degree in Accounting and Economics from the Tel Aviv University, Israel.
Dan Kozlovski, Chief Technologies Officer
Dan Kozlovski has served as our Chief Technologies Officer since February 2022, having previously served as our Vice President of Research & Development from August 2020 after joining us in December 2019. He specializes in R&D and product development, with expertise in three-dimensional computer-aided design. Mr. Kozlovski has more than ten years of experience working in high-technology companies in the printing market. Previously, he served as Future Platform R&D Mechanical Engineer at HP Indigo Division from June 2018 to December 2019. Mr. Kozlovski has also worked as Mechanical Team Leader at Nano Dimension Ltd. from August 2015 to June 2018. Mr. Kozlovski holds a B.Sc. degree in Mechanical Engineering from Ben Gurion University of the Negev and an Executive MBA in Technology, Innovation & Entrepreneurship Management from Tel Aviv University.
Yaron Kaiser, Chairman of the Board of Directors
Yaron Kaiser has founded various Nasdaq- or TASE-traded foodtech companies, and has served as Chairperson of Wilk Technologies Ltd. since January 2021. Mr. Kaiser is a founding partner of the BlueSoundWaves collective since 2021, and practices law in the fields of securities, commercial and corporate law, representing numerous public companies on fundraising, IPOs, M&A, the Israel Securities Authority and corporate governance, most recently at JST & Co., Law Office, between 2010 and May 2021, and since then as a founding partner of Kaufman Kaiser Raz, Law Firm. He holds an LL.B. degree from the College of Management Academic Studies, Israel.
Eli Arad has served as a director since February 2018. Mr. Arad has been chief executive officer of the real-estate and life science investment company Merchavia Holdings and Investments Ltd (TASE:MRHL) since 2011. Mr. Arad has served as a director of Cleveland Diagnostics, Inc., a clinical-stage biotechnology company developing technology to improve cancer diagnostics since 2016, E.N. Shoham Business Ltd. (TASE:SHOM) since 2019, and a number of privately-held companies (Veoli Ltd., Train Pain Ltd., EFA Ltd., Nervio Ltd. and Cardiosert Ltd.). He has had leadership roles in many biomedical startup companies, and has extensive experience in all areas of financial management. Mr. Arad is a certified practicing accountant who holds a diploma in Accounting from Ramat Gan College and an Executive B.A. (Hons.) in Business Administration from the Ruppin Academic Center.
David Gerbi has served as a director since August 2019. Mr. Gerbi is managing partner of accounting firm Gerbi & Co., and serves as Chief Financial Officer of Israir Group Ltd. (TASE:ISRG) since 2017, Erech Finance Cahalacha Ltd. (TASE:EFNC) since 2019, Nur Ink Innovations Ltd. (TASE:NURI) since June 2021 and Bee-io Honey Ltd. (TASE:BHNY) since November 2021. Mr. Gerbi holds a B.A. in Business Administration and Accounting from the Israeli College of Management Academic Studies and an M.B.A. in Finance from Tel Aviv University.
Sari Singer has served as a director since March 2021. Ms. Singer has served as General Counsel and Executive Vice President at NewMed Energy LP (formerly Delek Drilling LP), the oil and gas arm of the Delek Group in Israel, and a partner in the Leviathan offshore gas field, as well as other petroleum assets offshore Israel and Cyprus, since 2012, where she has led significant strategic processes, including restructurings and complex financing rounds totaling some $7 billion in various transactions in the international and domestic markets. Ms. Singer holds an LL.B. (cum laude) from Tel Aviv University and has been a member of the Israel Bar since 2007.
There are no family relationships among any of our directors or officers.
Compensation of Executive Officers and Directors
Aggregate Compensation of Office Holders
The aggregate compensation we paid to our executive officers and directors for the year ended December 31, 2021, was approximately $1.2 million. This amount includes approximately $0.2 million paid, set aside or accrued to provide pension, severance, retirement or similar benefits or expenses, but does not include share-based compensation expenses, or business travel, professional and business association dues and expenses reimbursed to office holders, and other benefits commonly reimbursed or paid by companies in our industry. As of the date of this prospectus, options to purchase 2,472,540 Ordinary Shares granted to our officers and directors were outstanding under our share option plans at a weighted average exercise price of $0.62 per share, in addition to 157,790 restricted share units with no exercise price.
Individual Compensation of Office Holders
The table and summary below outlines the compensation granted to our then-Chief Executive Officer and Chief Technology Officer, the then-Chairman of our board of directors, our then-Deputy Chief Executive Officer, our Chief Financial Officer and our then-Vice President of Research and Development (now Chief Technologies Officer), with respect to the year ended December 31, 2021. For purposes of the table and the summary below, “compensation” includes base salary, bonuses, equity-based compensation, retirement or termination payments, benefits and perquisites such as car, phone and social benefits and any undertaking to provide such compensation.
| Name and Principal Position | | Salary(1) | | | Bonus(2) | | | Equity-Based
Compensation(3) | | | Other Compensation(4) | | | Total | |
| | | (USD in thousands) | |
| Mr. Steven H. Lavin | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Chairman of the Board of Directors(5) | | $ | 180 | | | $ | - | | | $ | 281 | | | | - | | | $ | 461 | |
| Mr. Sharon Fima | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Chief Executive Officer & Chief Technology Officer(6) | | | 240 | | | | - | | | | 83 | | | | - | | | | 323 | |
Mr. Omri Schanin (7) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Deputy Chief Executive Officer | | | 190 | | | | 46 | | | | 121 | | | | - | | | | 357 | |
| Mr. Guy Hefer | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Chief Financial Officer | | | 193 | | | | 39 | | | | 116 | | | | - | | | | 348 | |
| Mr. Dan Kozlovski | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Vice-President, Research & Development (later Chief Technologies Officer) | | $ | 170 | | | $ | 48 | | | $ | 24 | | | | - | | | $ | 242 | |
| (1) | Salary includes the officer’s gross salary plus payment by us of social benefits on behalf of the officer. Such benefits may include payments, contributions and/or allocations for savings funds (e.g., Managers’ Life Insurance Policy), pension, severance, risk insurance (e.g., life, or work disability insurance), payments for social security and tax gross-up payments, vacation, medical insurance and benefits, convalescence or recreation pay and other benefits and perquisites consistent with our policies. |
| (2) | Represents annual bonuses paid with respect to 2021. |
| (3) | Represents the equity-based compensation expenses recorded in our consolidated financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2021, based on the options’ fair value on the grant date, calculated in accordance with applicable accounting guidance for equity-based compensation. For a discussion of the assumptions used in reaching this valuation, see Note 10(B) to our annual consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this prospectus. |
| (4) | Represents benefits and perquisites such as car, phone and social benefits. |
| (5) | Mr. Levin resigned his position as Chairman on January 24, 2022. |
| (6) | Mr. Fima resigned as Chief Executive Officer & Chief Technology Officer on January 24, 2022. |
| (7) | Mr. Schanin resigned as Deputy Chief Executive Officer as of April 27, 2022. |
Employment Agreements and Director Fees
We have entered into written employment agreements with each of our executive officers, which provide for notice periods of varying duration for termination of the agreement by us or by the relevant executive officer, during which time the executive officer will continue to receive base salary and benefits. These agreements also contain customary provisions regarding noncompetition, confidentiality of information and assignment of inventions. However, the enforceability of the noncompetition provisions may be limited under applicable law. See “Risk Factors — Risks relating to our operations — Under applicable employment laws, we may not be able to enforce covenants not to compete” for a further description of the enforceability of non-competition clauses.
The material employment terms for Mr. Kaufman, our Chief Executive Officer, are as follows: (1) a gross annual salary of NIS 564,000 ($176,000); (2) reimbursement of annual travel expenses of up to NIS 60,000 ($19,000); (3) options to purchase 500,000 Ordinary Shares (currently equivalent to 50,000 ADSs), vesting over three years from the date of his appointment as Chief Executive Officer, pursuant to which 1/12 will vest every quarter until fully vested, expiring one year following Mr. Kaufman’s cessation of service in all then-applicable capacities, but in any case after four years, with an exercise price of $0.519 per ordinary share (currently equivalent to $5.19 per ADS) and subject to acceleration upon termination pursuant to our sale or change in control; (4) an annual performance bonus in the aggregate amount of NIS 282,000 ($87,000), subject to his meeting certain performance milestones as determined by our board of directors on an annual basis; (5) termination of the employment relationship upon provision of six months’ advance notice by either party; (6) severance pay equal to 25% of the gross annual salary upon termination of Mr. Kaufman’s employment by us, not for cause, following three to twelve months of service, or 50% following twelve or more months of service (or 50% of these amounts upon Mr. Kaufman’s resignation); and (7) social benefits that we pay on behalf of officers, such as payments, contributions and/or allocations for savings funds (e.g., Managers’ Life Insurance Policy), pension, severance, risk insurance (e.g., life, or work disability insurance), payments for social security and tax gross-up payments, vacation, medical insurance and benefits, convalescence or recreation pay and other benefits and perquisites consistent with our policies, such as inclusion in our directors’ and officers’ liability insurance policy, and provision of indemnification, exculpation and exemption undertakings to the fullest extent permitted by the Companies Law.
The material terms for Mr. Kaiser, the Chairman of our board of directors, are as follows: (1) an annual fee of $150,000, to be paid in four equal quarterly installments in USD or in NIS at the then-current exchange rate, which will automatically increase by an amount equal to seven percent at the end of each year of service; (2) reimbursement of annual travel expenses of up to $18,000; (3) options to purchase 350,000 Ordinary Shares (currently equivalent to 35,000 ADSs), vesting over three years from the date of his appointment as Chairman, pursuant to which 1/12 will vest every quarter until fully vested, expiring one year following Mr. Kaiser’s cessation of service in all then-applicable capacities, but in any case after four years, with an exercise price of $0.519 per ordinary share (currently equivalent to $5.19 per ADS) and subject to acceleration upon termination pursuant to our sale or change in control; (4) an annual bonus equal to 50% of the bonus awarded to the Chief Executive Officer in the applicable year; (5) severance pay equal to 12.5% of Mr. Kaiser’s annual fee upon the involuntary termination of his directorship, not for cause, following three to twelve months of service, or 25% following twelve or more months of service (or 50% of these amounts upon Mr. Kaiser’s resignation); and (6) other benefits and perquisites consistent with our policies, such as inclusion in our directors’ and officers’ liability insurance policy, and provision of indemnification, exculpation and exemption undertakings to the fullest extent permitted by the Companies Law.
In addition, we pay fees to our non-executive directors in return for their service on our board of directors, in accordance with our compensation policy.
Our other employees are employed under the terms prescribed in their respective employment contracts. The employees are entitled to the social benefits prescribed by law and as otherwise provided in their agreements. These agreements each contain provisions standard for a company in our industry regarding non-competition, confidentiality of information and assignment of inventions. Under currently applicable labor laws, we may not be able to enforce covenants not to compete and therefore may be unable to prevent our competitors from benefiting from the expertise of some of our former employees. See “Risk Factors—Risks Related to Our Operations” for a further description of the enforceability of non-competition clauses.
Executive officers are also employed on the terms and conditions prescribed in employment agreements. These agreements provide for notice periods of varying duration for termination of the agreement by us or by the relevant executive officer, during which time the executive officer will continue to receive base salary and benefits. See “Risk Factors—Risks Related to Our Operations—If we are unable to attract and retain qualified employees, our ability to implement our business plan may be adversely affected.”
Option and RSU Allocation Plan
In June 2018, the board of directors of Ophectra adopted our Option and RSU Allocation Plan, as amended, or the share option plan, to issue options to purchase our Ordinary Shares and restricted stock units to our directors, officers, employees and consultants, and those of our affiliated companies (as such term is defined under share option plan), or the Grantees. The share option plan is administered by our board of directors or a committee that was designated by the board of directors for such purpose, or the Administrator.
Under the share option plan, we may grant options to purchase Ordinary Shares and/or RSUs, or options, under four tracks: (i) Approved 102 capital gains options through a trustee, which was approved by the Israeli Tax Authority in accordance with Section 102(a) of the Israeli Income Tax Ordinance (New Version), 1961, or ITO, and granted under the tax track set forth in Section 102(b)(2) of the ITO. The holding period under this tax track is 24 months from the date of issuance of options to the trustee or such period as may be determined in any amendment of Section 102 of the ITO, or any applicable tax ruling or guidelines; (ii) Approved 102 earned income options through a trustee, granted under the tax track set forth is Section 102(b)(1) of the ITO. The holding period under this tax track is 12 months from the date of issuance of options to the trustee or such period as may be determined in any amendment of Section 102 of the ITO; (iii) Unapproved 102 options (the options will not be issued through a trustee and will not be subject to a holding period); and (iv) 3(i) options (the options will not be subject to a holding period). These options shall be subject to taxation pursuant to Section 3(i) of the ITO, or Section 3(i).
Options pursuant to the first three tax tracks (under Section 102 of the ITO) can be granted to our employees and directors and the grant of options under Section 3(i) can be granted to our consultants and controlling shareholders (a controlling shareholder is defined under the Section 102 of the ITO is a person who holds, directly or indirectly, alone or together with a “relative,” (i) the right to at least 10% of the company’s issued capital or 10% of the voting power; (ii) the right to hold at least 10% of the company’s issued capital or 10% of the voting power, or the right to purchase such rights; (iii) the right to receive at least 10% of the company’s profits; or (iv) the right to appoint a company’s director). Grantees who are not Israeli residents may be granted options that are subject to the applicable tax laws in their respective jurisdictions.
We determine, in our sole discretion, under which of the first three tax tracks above the options are granted and we notify the Grantee in a grant letter, as to the elected tax track. As mentioned above, consultants and controlling shareholders can only be granted Section 3(i) options.
The number of Ordinary Shares authorized to be issued under the share option plan will be proportionately adjusted for any increase or decrease in the number of Ordinary Shares issued as a result of a distribution of bonus shares, change in our capitalization (split, combination, reclassification of the shares or other capital change), or issuance of rights to purchase Ordinary Shares or payment of a dividend. We will not issue fractions of Ordinary Shares and the number of Ordinary Shares shall be rounded up to the closest number of ordinary shares.
In the event of a (i) merger or consolidation in which we (in this context, specifically Steakholder Foods Ltd.) are not the surviving entity or pursuant to which the other company becomes our parent company or that pursuant to which we are the surviving company but another entity holds 50% or more of our voting rights, (ii) an acquisition of all or substantially all of our Ordinary Shares, (iii) the sale of all or substantially all of our assets, or (iv) any other event with a similar impact, we may exchange all of our outstanding options granted under the share option plan that remain unexercised prior to any such transaction for options to purchase shares of the successor corporation (or those of an affiliated company) following the consummation of such transaction.
The exercise price of an option granted under the share option plan will be specified in the grant letter every Grantee received from us in which the Grantee notifies of the decision to grant him/her options under the share option plan, and will be denominated in our functional currency at the time of grant or the currency in which the Grantee is paid, at our discretion.
The Administrator may, in its absolute discretion, accelerate the time at which options granted under the share option plan or any portion of which will vest.
Unless otherwise determined by the Administrator, in the event that the Grantee’s employment was terminated, not for Cause (as defined in the share option plan), the Grantee may exercise that portion of the options that had vested as of the date of such termination until the end of the specified term in the grant letter or the share option plan. The portion of the options that had not vested at such date, will be forfeited and can be re-granted to other Grantees, in accordance with the terms of the share option plan.
At the discretion of our board of directors, and subject to receipt of taxation authority approvals, we may allow Grantees to exercise their options on a cashless basis.
2022 Share Incentive Plan
The 2022 Share Incentive Plan, or the 2022 Plan, provides for the grant of equity-based incentive awards to our employees, directors, office holders, service providers and consultants in order to incentivize them to increase their efforts on behalf of the Company and to promote the success of the Company’s business.
Shares Available for Grants. The maximum number Shares (which means ordinary shares, of no par value, (including ordinary shares resulting or issued as a result of share split, reverse share split, bonus shares, combination or other recapitalization events, and including in the form of ADSs), or shares of such other class of shares as shall be designated by the board of directors of the Company in respect of the relevant award) available for issuance under the 2022 Plan is equal to the sum of (i) 8,500,000 Shares, (ii) 1,127,850 Shares, which represents the number of Shares available for issuance under the Option and RSU Allocation Plan, or the Prior Plan, on the effective date of the 2022 Plan, and (iii) an annual increase on the first day of each year beginning in 2023 and on January 1st of each calendar year thereafter and ending on January 1, 2032, equal to the lesser of (A) 5% of the outstanding ordinary shares of the Company on the last day of the immediately preceding calendar year, on a fully diluted basis; and (B) such amount as determined by our board of directors if so determined prior to January 1 of a calendar year. Shares issued under the 2022 Plan may be, in whole or in part, authorized but unissued Shares, (and, subject to obtaining a ruling as it applies to 102 awards) treasury shares (dormant shares) or otherwise Shares that shall have been or may be repurchased by the Company (to the extent permitted pursuant to the Companies Law).
Any Shares (a) underlying an award granted under the 2022 Plan or an award granted under the Prior Plan (in an amount not to exceed 8,498,490 Shares under the Prior Plan) that has expired, or was cancelled, terminated, forfeited, or settled in cash in lieu of issuance of Shares, for any reason, without resulting in the issuance of Shares; (b) if permitted by the Company, subject to an award that are tendered to pay the exercise price of an award; or withholding tax obligations with respect to an award; or if permitted by the Company, subject to an award that are not delivered to a Grantee because such Shares are withheld to pay the exercise price of such award; or withholding tax obligations with respect to such award may again be available for issuance under the 2022 Plan and for issuance upon exercise or (if applicable) vesting thereof for the purposes of the 2022 Plan, unless determined otherwise by the Board. Our board of directors may also reduce the number of ordinary shares reserved and available for issuance under the 2022 Plan in its discretion.
The maximum aggregate number of Shares that may be issued pursuant to the exercise of incentive stock options granted under the 2022 Plan, or the ISO Limit, shall be the sum of (a) the aggregate number of Shares set forth in clauses (a) and (b) in the above paragraph; and (b) any Shares underlying awards granted under the Prior Plan that are returned to the 2022 Plan (not to exceed 8,498,490 Shares). To the extent permitted under Section 422 of the United States Internal Revenue Code of 1986, and any applicable regulations promulgated thereunder, all as amended (the “Code”), any Shares covered by an award that has expired, or was cancelled, terminated, forfeited, or settled in cash without the issuance of Shares shall not count against the ISO Limit. Shares that actually have been issued under the 2022 Plan shall not become available for future issuance hereunder pursuant to incentive stock options.
Administration. Our board of directors, or a duly authorized committee of our board of directors, or the Administrator, or the Administrator, will administer the 2022 Plan. Under the 2022 Plan, the Administrator has the authority, subject to applicable law, to interpret the terms of the 2022 Plan and any award agreements or awards granted thereunder, designate recipients of awards, determine and amend the terms of awards, including the exercise price of an option award, the fair market value of an ordinary share, the time and vesting schedule applicable to an award or the method of payment for an award, accelerate or amend the vesting schedule applicable to an award, prescribe the forms of agreement for use under the 2022 Plan and take all other actions and make all other determinations necessary for the administration of the 2022 Plan.
The Administrator also has the authority to approve the conversion, substitution, cancellation or suspension under and in accordance with the 2022 Plan of any or all option awards or ordinary shares, and the authority to modify option awards to eligible individuals who are foreign nationals or are individuals who are employed outside Israel to recognize differences in local law, tax policy or custom, in order to effectuate the purposes of the 2022 Plan but without amending the 2022 Plan; provided, that if the Administrator takes such action with respect to an award held by a U.S. service provider, it shall do so in accordance with the requirements of Section 409A of the Code, if applicable.
The Administrator also has the authority to amend and rescind rules and regulations relating to the 2022 Plan or terminate the 2022 Plan at any time before the date of expiration of its ten year term.
Eligibility. The 2022 Plan provides for granting awards under various tax regimes, including, without limitation, in compliance with Section 102 of the Israeli Income Tax Ordinance (New Version) 5271-1961, and the regulations and rules promulgated thereunder, all as amended from time to time (the “Ordinance”), and Section 3(i) of the Ordinance and in compliance with Section 422 of the Code and Section 409A of the Code as they relate to U.S. service providers when granted Nonqualified Stock Options, and to U.S. service providers who are Employees when granted Incentive Stock Options.
Grants. All awards granted pursuant to the 2022 Plan will be evidenced by an award agreement, in a form approved, from time to time, by the Administrator in its sole discretion. The award agreement will set forth the terms and conditions of the award, including the type of award, number of shares subject to such award, vesting schedule and conditions (including performance goals or measures) and the exercise price, if applicable. Certain awards under the 2022 Plan may constitute or provide for a deferral of compensation, subject to Section 409A of the Code, which may impose additional requirements on the terms and conditions of such awards.
Unless otherwise determined by the Administrator and stated in the award agreement, and subject to the conditions of the 2022 Plan, awards vest and become exercisable under the following schedule: 25% of the shares covered by the award on the first anniversary of the vesting commencement date determined by the Administrator (and in the absence of such determination, the date on which such award was granted) and 6.25% of the Shares covered by the award at the end of each subsequent three-month period thereafter over the course of the following three years; provided that the grantee remains continuously as an employee or provides services to the company throughout such vesting dates.
Each award will expire ten years from the date of the grant thereof, unless such shorter term of expiration is otherwise designated by the Administrator.
Awards. The 2022 Plan provides for the grant of stock options (including incentive stock options and nonqualified stock options), ordinary shares, restricted shares, RSUs, stock appreciation rights and other share-based awards.
Options granted under the 2022 Plan to the Company employees who are U.S. residents may qualify as “incentive stock options” within the meaning of Section 422 of the Code, or may be non-qualified stock options. The exercise price of an option may not be less than the par value of the Shares (if the Shares bear a par value) for which such option is exercisable. The exercise price of an Incentive Stock Option may not be less than 100% of the fair market value of the underlying share on the date immediately preceding the day of the grant or such other amount as may be required pursuant to the Code, and in the case of Incentive Stock Options granted to ten percent stockholders, not less than 110%.
Nonqualified stock options may not be granted to a U.S. service provider unless (i) the Shares underlying such options constitute “service recipient stock” under Section 409A of the Code and such options meet the other requirements to be exempt from Section 409A of the Code or (ii) such options comply with the requirements of Section 409A of the Code. A nonqualified stock option may be granted with an exercise price lower than the minimum exercise price set forth above if (i) such option is granted pursuant to an assumption or substitution for another option in accordance with and pursuant to Section 409A of the Code or (ii) the Administrator expressly determined that the option will have a lower exercise price and the Option complies with Section 409A of the Code or meets another exemption under Section 409A of the Code.
Incentive stock options may be granted only to U.S. service providers who are employees of the Company. However, if for any reason an option (or portion thereof) does not qualify as an incentive stock option, then, to the extent of such non-qualification, such option (or portion thereof) shall be treated as a nonqualified stock option granted under the 2022 Plan.
An RSU may be awarded to any service provider, including under Section 102 of the Ordinance. Subject to Applicable Law, RSUs may be granted in consideration of a reduction in the recipient’s other compensation. No payment of exercise price shall be required as consideration for RSUs, unless included in the award agreement or as required by applicable law. The grantee shall not possess or own any ownership rights in the Shares underlying the RSUs. Settlement of vested RSUs shall be made in the form of Shares. Distribution to a grantee of an amount (or amounts) from settlement of vested RSUs can be deferred to a date after vesting as determined by the Administrator; provided, that no such deferral shall be made with respect to RSUs held by a U.S. service provider if such deferral would cause such RSUs to fail to qualify for an exemption under Section 409A of the Code and become subject to the requirements of Section 409A of the Code, unless expressly determined by the Administrator, or would violate the requirements of Section 409A. In no event shall any dividends or dividend equivalent rights be paid before the vesting of the portion of the RSUs to which such dividends or dividend equivalent rights relate, unless otherwise provided for in an award agreement or determined by the Committee. Any RSUs granted under the 2022 Plan that are not exempt from the requirements of Section 409A of the Code shall contain such restrictions or other provisions so that such RSUs will comply with the requirements of Section 409A of the Code.
Exercise. An award under the 2022 Plan may be exercised by providing the Company with a written or electronic notice of exercise and full payment of the exercise price for such shares underlying the award, if applicable, in such form and method as may be determined by the Administrator and permitted by applicable law. An award may not be exercised for a fraction of a share. With regard to tax withholding, exercise price and purchase price obligations arising in connection with awards under the 2022 Plan, the Administrator may, in its discretion, accept cash, provide for net withholding of shares in a cashless exercise mechanism or direct a securities broker to sell shares and deliver all or a part of the proceeds to the Company or the trustee. The exercise period of an award will be determined by the Administrator and stated in the award agreement, but will in no event be longer than ten (10) years from the date of grant of the award. Notwithstanding anything to the contrary, the Administrator may extend the periods for which awards held by any grantee may continue to vest and/or be exercisable; it being clarified that such awards may lose their entitlement to certain tax benefits under applicable law; if done so with respect to a U.S service provider, the Administrator shall act in accordance with Section 409A of the Code, as applicable.
Transferability. Other than by will, the laws of descent and distribution or as otherwise provided under the 2022 Plan, neither the options nor any right in connection with such options are assignable or transferable.
Termination of Employment. In the event of termination of a grantee’s employment or service with the Company or any of its affiliates, all vested and exercisable awards held by such grantee as of the date of termination may be exercised within three months after such date of termination, unless otherwise determined by the Administrator, but in no event later than the date of expiration of the award as set forth in the award agreement. After such three-month period, all such unexercised awards will terminate and the shares covered by such awards shall again be available for issuance under the 2022 Plan.
In the event of termination of a grantee’s employment or service with the Company or any of its affiliates due to such grantee’s death or permanent disability, or in the event of the grantee’s death within the three month period (or such longer period as determined by the Administrator) following his or her termination of service, all vested and exercisable awards held by such grantee as of the date of termination may be exercised by the grantee or the grantee’s legal guardian, estate or by a person who acquired the right to exercise the award by bequest or inheritance, as applicable, within one year after such date of termination, unless otherwise provided by the Administrator, but in no event later than the date of expiration of the award as set forth in the award agreement. Any awards which are unvested as of the date of such termination or which are vested but not then exercised within the one year period following such date, will terminate and the shares covered by such awards shall again be available for issuance under the 2022 Plan.
Notwithstanding any of the foregoing, if a grantee’s employment or services with the Company or any of its affiliates is terminated for “cause” (as defined in the 2022 Plan), all outstanding awards held by such grantee (whether vested or unvested) will terminate on the date of such termination and the shares covered by such awards shall again be available for issuance under the 2022 Plan.
Any Option that is intended to be an incentive stock option and is exercised later than three (3) months after the grantee ceases to be employed by the Company (or any parent or subsidiary), except in the case of death or “Disability” (as defined in Section 22(e)(3) of the Code), will be deemed a nonqualified stock option. If the grantee ceases to be employed by the Company (or any parent or subsidiary) due to disability, any option that is intended to be an incentive stock option and is exercised later than twelve (12) months after such termination date will be deemed a nonqualified stock option.
Voting Rights. Except with respect to restricted share awards, grantees will not have the rights as a shareholder of the Company with respect to any shares covered by an award until the award has vested and/or the grantee has exercised such award, paid any exercise price for such award and becomes the record holder of the shares. With respect to restricted share awards, grantees will possess all incidents of ownership of the restricted shares, including the right to vote and receive dividends on such shares.
Dividends. Grantees holding restricted share awards will be entitled to receive dividends and other distributions with respect to the shares underlying the restricted share award. Any stock split, stock dividend, combination of shares or similar transaction will be subject to the restrictions of the original restricted share award. Grantees holding RSUs will not be eligible to receive dividend but may be eligible to receive dividend equivalents.
Transactions. In the event of a share split, reverse share split, share dividend, recapitalization, combination or reclassification of the Company’s shares, the Administrator in its sole discretion may, and where required by applicable law shall, without the need for a consent of any holder, make an appropriate adjustment in order to adjust (i) the number and class of shares reserved and available for the outstanding awards, (ii) the number and class of shares covered by outstanding awards, (iii) the exercise price per share covered by any award, (iv) the terms and conditions concerning vesting and exercisability and the term and duration of the outstanding awards, (v) the type or class of security, asset or right underlying the award (which need not be only that of the Company, and may be that of the surviving corporation or any affiliate thereof or such other entity party to any of the above transactions), and (vi) any other terms of the award that in the opinion of the Administrator should be adjusted; provided that any fractional shares resulting from such adjustment shall be rounded to the nearest whole share unless otherwise determined by the Administrator. In the event of a distribution of a cash dividend to all shareholders, the Administrator may determine, without the consent of any holder of an award, that the exercise price of an outstanding and unexercised award shall be reduced by an amount equal to the per share gross dividend amount distributed by the Company, subject to applicable law.
In the event of a merger or consolidation of the Company or a sale of all, or substantially all, of the Company’s shares or assets or other transaction having a similar effect on the Company, or change in the composition of the board of directors, or liquidation or dissolution, or such other transaction or circumstances that our board of directors determines to be a relevant transaction, then without the consent of the grantee, (i) unless otherwise determined by the Administrator, any outstanding award will be assumed or substituted by such successor corporation, or (ii) regardless of whether or not the successor corporation assumes or substitutes the award (a) provide the grantee with the option to exercise the award as to all or part of the shares, and may provide for an acceleration of vesting of unvested awards, (b) cancel the award and pay in cash, shares of the Company, the acquirer or other corporation which is a party to such transaction or other property as determined by the Administrator as fair in the circumstances, or (c) provide that the terms of any award shall be otherwise amended, modified or terminated, as determined by the Administrator to be fair in the circumstances. Changes with respect to awards held by U.S. service providers shall be made in accordance with the requirements of Section 409A of the Code or Section 424 of the Code, as applicable and to the extent necessary to avoid adverse tax consequences under Section 409A of the Code, a transaction or other event will not be deemed a Merger/Sale for purposes of awards granted to U.S. service providers unless the transaction or other event qualifies as a change in control event within the meaning of Section 409A of the Code.
Corporate Governance Practices
As a foreign private issuer, we are permitted to follow certain Israeli corporate governance practices instead of the Nasdaq Capital Market corporate governance rules, or the Nasdaq Marketplace Rules, provided that we disclose which requirements we are not following and the equivalent Israeli requirements. Pursuant to the “foreign private issuer exemption”:
| • | Quorum. As permitted under the Companies Law, pursuant to our articles of association, the quorum required for an ordinary meeting of shareholders consists of at least two shareholders present in person or by proxy who hold or represent between them at least 25% of the voting power of our shares (and, with respect to an adjourned meeting, generally one or more shareholders who hold or represent any number of shares), instead of 33 1∕3% of the issued share capital provided under Nasdaq Marketplace Rule 5260(c). |
| • | Shareholder Approval. Although the Nasdaq Marketplace Rules generally require shareholder approval of equity compensation plans and material amendments thereto, we follow Israeli practice, which is to have such plans and amendments approved only by the board of directors, unless such arrangements are for the compensation of chief executive officer or directors, in which case they also require the approval of the compensation committee and the shareholders. In addition, rather than follow the Nasdaq Marketplace Rule requiring shareholder approval for the issuance of securities in certain circumstances, we follow Israeli law, under which a private placement of securities requires approval by our board of directors and shareholders if it will cause a person to become a controlling shareholder (generally presumed at 25% ownership) or if: (a) the securities issued amount to 20% or more of our outstanding voting rights before the issuance; (b) some or all of the consideration is other than cash or listed securities or the transaction is not on market terms; and (c) transaction will increase the relative holdings of a shareholder that holds 5% or more of our outstanding share capital or voting rights or will cause any person to become, as a result of the issuance, a holder of more than 5% of our outstanding share capital or voting rights. |
| • | Executive Sessions. While the Nasdaq Marketplace Rules require that “independent directors,” as defined in the Nasdaq Marketplace Rules, must have regularly scheduled meetings at which only “independent directors” are present. Israeli law does not require, nor do our independent directors necessarily conduct, regularly scheduled meetings at which only they are present. |
In all other respects, we intend to comply with the rules generally applicable to U.S. domestic companies listed on the Nasdaq Capital Market. We may in the future decide to use the foreign private issuer exemption with respect to some or all of the other Nasdaq Capital Market corporate governance rules. Accordingly, our shareholders may not be afforded the same protections as provided under Nasdaq Marketplace Rules.
Our board of directors consists of four directors, three of whom are deemed independent directors under the corporate governance standards of the Nasdaq Marketplace Rules and the independence requirements of Rule 10A-3 of the Exchange Act, as well as the standards of the Companies Law.
Under our articles of association, our board of directors must consist of no less than three and no more than seven directors (including the external directors, if any), divided into three classes with staggered three-year terms. Each class of directors consists, as nearly as possible, of one-third of the total number of directors constituting the entire board of directors. At each annual general meeting of our shareholders, the election or re-election of directors following the expiration of the term of office of the directors of that class of directors will be for a term of office that expires on the third annual general meeting following such election or re-election. Therefore, beginning with the annual general meeting of 2022, each year the term of office of only one class of directors will expire.
Our directors are divided among the three classes as follows:
| | • | the Class I directors are Messrs. Eli Arad and David Gerbi and their respective terms will expire at the Company’s annual general meeting of shareholders to be held in 2023; |
| | • | the Class II director is Ms. Sari Singer and her term will expire at the Company’s annual general meeting of shareholders to be held in 2024; and |
| | • | the Class III director is Mr. Yaron Kaiser his term will expire at the Company’s annual general meeting of shareholders to be held in 2025. |
Pursuant to our articles of association, the vote general required to appoint a director is a simple majority vote of holders of our voting shares participating and voting at the relevant meeting, provided that (i) in the event of a contested election, the method of calculation of the votes and the manner in which the resolutions will be presented to our shareholders at the general meeting shall be determined by our board of directors in its discretion, and (ii) in the event that our board of directors does not or is unable to make a determination on such matter, then the directors will be elected by a plurality of the voting power represented at the general meeting in person or by proxy and voting on the election of directors.
Each director will hold office until the annual general meeting of our shareholders for the year in which such director’s term expires, unless the tenure of such director expires earlier pursuant to the Companies Law or unless such director is removed from office. Under our articles of association, the approval of the holders of at least 65% of the total voting power of our shareholders is generally required to remove any of our directors from office.
In addition, our articles of association allow our board of directors to appoint new directors to fill vacancies which can occur for any reason or as additional directors, provided that the number of board members shall not exceed the maximum number of directors mentioned above. A director so appointed will hold office until the next annual general meeting of our shareholders for the election of the class of directors in respect of which the vacancy was created, or in the case of a vacancy due to the number of directors being less than the maximum number of directors stated in our articles of association, until the next annual general meeting of our shareholders for the election of the class of directors to which such director was assigned by our board of directors. Our board of directors may continue to operate for as long as the number of directors is no less than the minimum number of directors mentioned above.
In addition, under the Companies Law, our board of directors must determine the minimum number of directors who are required to have financial and accounting expertise. Under applicable regulations, a director with financial and accounting expertise is a director who, by reason of his or her education, professional experience and skill, has a high level of proficiency in and understanding of business accounting matters and financial statements. He or she must be able to thoroughly comprehend the financial statements of the company and initiate discussion regarding the manner in which financial information is presented. In determining the number of directors required to have such expertise, the board of directors must consider, among other things, the type and size of the company and the scope and complexity of its operations. Our board of directors has determined that we require at least one director with the requisite financial and accounting expertise and that Eli Arad and David Gerbi have such expertise.
The Companies Law requires a public Israeli company to have at least two external directors who meet certain independence criteria to ensure that they are unaffiliated with the company and its controlling shareholder. An external director must have either financial and accounting expertise or professional qualifications, as defined in the regulations promulgated under the Companies Law, and at least one of the external directors is required to have financial and accounting expertise. An external director is entitled to reimbursement of expenses and compensation as provided in the regulations promulgated under the Companies Law, but is otherwise prohibited from receiving any other compensation from the company, directly or indirectly, during his or her term and for two years thereafter.
Pursuant to regulations promulgated under the Companies Law, as a company with shares traded on Nasdaq, we have elected no to comply with the requirements to appoint external directors and related rules concerning the composition of the audit committee and compensation committee of the board of directors. We are still subject to the gender diversity rule under the Companies Law, which requires that if, at the time a director is to be elected or appointed, all members of the board of directors are of the same gender, the director to be appointed must be of the other gender. The conditions to the exemptions from the Companies Law requirements are that: (i) the company does not have a “controlling shareholder,” as such term is defined under the Companies Law, (ii) its shares are traded on certain U.S. stock exchanges, including Nasdaq, and (iii) it comply with the director independence requirements and the audit committee and compensation committee composition requirements under U.S. laws, including the rules of the applicable exchange, that are applicable to U.S. domestic issuers.
Committees of the Board of Directors
Our board of directors has established the following committees. Each committee operates in accordance with a written charter that sets forth the committee’s structure, operations, membership requirements, responsibilities and authority to engage advisors.
Under the Companies Law, the Exchange Act and Nasdaq Marketplace Rules, we are required to maintain an audit committee.
The responsibilities of an audit committee under the Companies Law include identifying and addressing flaws in the business management of the company, reviewing and approving related party transactions, establishing whistleblower procedures, overseeing the company’s internal audit system and the performance of its internal auditor, and assessing the scope of the work and recommending the fees of the company’s independent accounting firm. In addition, the audit committee is required to determine whether certain related party actions and transactions are “material” or “extraordinary” for the purpose of the requisite approval procedures under the Companies Law and to establish procedures for considering proposed transactions with a controlling shareholder.
In accordance with U.S. law and Nasdaq Marketplace Rules, our audit committee is also responsible for the appointment, compensation and oversight of the work of our independent auditors and for assisting our board of directors in monitoring our financial statements, the effectiveness of our internal controls and our compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
Under the Companies Law, the audit committee must consist of at least three directors who meet certain independence criteria. Under the Nasdaq Marketplace Rules, we are required to maintain an audit committee consisting of at least three independent directors, all of whom are financially literate and one of whom has accounting or related financial management expertise. Each of the members of the audit committee is required to be “independent” as such term is defined in Rule 10A-3(b)(1) under the Exchange Act.
Our audit committee currently consists of Eli Arad, Sari Singer and David Gerbi. All members are independent directors as defined in the Companies Law, SEC rules and Nasdaq listing requirements. Our board of directors has determined that all members of our audit committee meet the requirements for financial literacy under the applicable rules and regulations of the SEC and Nasdaq Marketplace Rules. Our board of directors has determined that Eli Arad and David Gerbi are audit committee financial experts as defined by the SEC rules and have the requisite financial experience as defined by the Nasdaq Marketplace Rules.
Under both the Companies Law and Nasdaq Marketplace Rules, we are required to establish a compensation committee.
The responsibilities of a compensation committee under the Companies Law include recommending to the board of directors, for ultimate shareholder approval by a special majority, a policy governing the compensation of directors and officers based on specified criteria, reviewing modifications to and implementing such compensation policy from time to time, and approving the actual compensation terms of directors and officers prior to approval by the board of directors.
The Companies Law stipulates that the compensation committee must consist of at least three directors who meet certain independence criteria. Under Nasdaq Marketplace Rules, we are required to maintain a compensation committee consisting of at least two independent directors; each of the members of the compensation committee is required to be independent under Nasdaq Marketplace Rules relating to compensation committee members, which are different from the general test for independence of board and committee members.
Our compensation committee currently consists of Eli Arad, Sari Singer and David Gerbi. All members are independent directors as defined in the Companies Law, SEC rules and regulations, and Nasdaq Marketplace Rules.
We do not have a standing nominating committee. In accordance with Rule 5605(e)(2) of the Nasdaq Rules, a majority of the independent directors may recommend a director nominee for selection by the board of directors. Our board of directors believes that the independent directors can satisfactorily carry out the responsibility of properly selecting or approving director nominees without the formation of a standing nominating committee. As we do not have a standing nominating committee, we will not have a nominating committee charter in place.
Our board of directors will consider candidates for nomination who have a high level of personal and professional integrity, strong ethics and values and the ability to make mature business judgments. In general, in identifying and evaluating nominees for director, our board of directors will also consider experience in corporate management such as serving as an officer or former officer of a publicly held company, experience as a board member of another publicly held company, professional and academic experience relevant to our business, leadership skills, experience in finance and accounting or executive compensation practices, whether candidate has the time required for preparation, participation and attendance at board meetings and committee meetings, if applicable, independence and the ability to represent the best interests of our stockholders.
Under the Companies Law, the board of directors is required to appoint an internal auditor recommended by the audit committee. The role of the internal auditor is to examine, among other things, whether the company’s actions comply with applicable law and proper business procedures. The internal auditor may not be an interested party, a director or an officer of the company, or a relative of any of the foregoing, nor may the internal auditor be our independent accountant or a representative thereof. Our current internal auditor is Mr. Daniel Spira, CPA, who is a member of the board of directors of the Institute of Internal Auditors in Israel and Chairman of its Auditing and Knesset Relations Committee.
Fiduciary Duties and Approval of Related Party Transactions
Fiduciary duties of directors and officers
Israeli law imposes a duty of care and a duty of loyalty on all office holders. An office holder is defined in the Companies Law as a general manager, chief business manager, deputy general manager, vice general manager, any other person assuming the responsibilities of any of these positions regardless of such person’s title, a director, and any other manager directly subordinate to the general manager. The duty of care requires a director or officer to act with the level of care with which a reasonable director or officer in the same position would have acted under the same circumstances. The duty of care includes, among other things, a duty to use reasonable means, under the circumstances, to obtain information on the advisability of a given action brought for the office holder’s approval or performed by virtue of the office holder’s position and other important information pertaining to such action. The duty of loyalty requires the director or officer to act in good faith and in the best interests of the company, and includes, among other things, the duty to:
| | • | refrain from any act involving a conflict of interest between the performance of the office holder’s duties in the company and the office holder’s other duties or personal affairs;
|
| | • | refrain from any activity that is competitive with the business of the company;
|
| | • | refrain from exploiting any business opportunity of the company for the purpose of gaining a personal advantage for the office holder or others; and
|
| | • | disclose to the company any information or documents relating to the company’s affairs which the office holder received as a result of the office holder’s position. |
Disclosure of Personal Interests of an Office Holder and Approval of Certain Transactions
Under the Companies Law, a company may approve an act specified above which would otherwise constitute a breach of the office holder’s fiduciary duty, provided that the office holder acted in good faith, the act or its approval does not harm the company, and the office holder discloses to the company his or her personal interest in the transaction (including any significant fact or document) a sufficient time before the approval of such act. Any such approval is subject to the terms of the Companies Law, setting forth, among other things, the appropriate bodies of the company required to provide such approval, and the methods of obtaining such approval.
The Companies Law requires that an office holder promptly disclose to the company any direct or indirect personal interest that he or she may have and all related material information or documents known to him or her relating to any existing or proposed transaction by the company. An interested office holder’s disclosure must be made promptly and, in any event, no later than the first meeting of the board of directors at which the transaction is considered. A personal interest includes an interest of any person in an act or transaction of a company, including a personal interest of one’s relative or of a corporate body in which such person or a relative of such person is a 5% or greater shareholder, director, or general manager or in which such person has the right to appoint at least one director or the general manager, but excluding a personal interest stemming solely from one’s ownership of shares in the company. A personal interest includes the personal interest of a person for whom the office holder holds a voting proxy or the personal interest of the office holder with respect to the officer holder’s vote on behalf of a person for whom he or she holds a proxy even if such shareholder has no personal interest in the matter.
If it is determined that an office holder has a personal interest in a non-extraordinary transaction (meaning any transaction that is in the ordinary course of business, on market terms or that is not likely to have a material impact on the company’s profitability, assets or liabilities), approval by the board of directors is required for the transaction unless the company’s articles of association provide for a different method of approval. Any such transaction that is adverse to the company’s interests may not be approved by the board of directors.
Approval first by the company’s audit committee and subsequently by the board of directors is required for an extraordinary transaction (meaning any transaction that is not in the ordinary course of business, not on market terms or that is likely to have a material impact on the company’s profitability, assets or liabilities) in which an office holder has a personal interest.
Under the Companies Law, unless the articles of association of a company provide otherwise, a transaction with an office holder or with a third party in which the office holder has a personal interest, which is not an extraordinary transaction, requires approval by the board of directors or a committee authorized by the board of directors. If the transaction considered is an extraordinary transaction with an office holder or third party in which the office holder has a personal interest, then audit committee approval is required prior to approval by the board of directors. Under specific circumstances, shareholder approval may also be required. For the approval of compensation arrangements with directors and executive officers, see “Compensation—Compensation of Directors and Executive Officers.”
Any persons who have a personal interest in the approval of a transaction that is brought before a meeting of the board of directors or the audit committee may generally not be present at the meeting or vote on the matter. However, if the chairman of the board of directors or the chairman of the audit committee, as applicable, has determined that the presence of an office holder with a personal interest is required, such office holder may be present at the meeting for the purpose of presenting the matter. Notwithstanding the foregoing, a director who has a personal interest may be present at the meeting of the board of directors or the audit committee (as applicable) and vote on the matter if a majority of the members of the board of directors or the audit committee (as applicable) have a personal interest in the approval of such transaction. If a majority of the directors at a board of directors meeting have a personal interest in the transaction, such transaction also generally requires approval of the shareholders of the company.
Disclosure of Personal Interests of a Controlling Shareholder and Approval of Transactions
Pursuant to the Companies Law, certain disclosure requirements also apply to a controlling shareholder of a public company, in which a controlling shareholder has a personal interest. For these purposes, a controlling shareholder is any shareholder that has the ability to direct the company’s actions, including any shareholder holding 25% or more of the voting rights if no other shareholder owns more than 50% of the voting rights in the company. Two or more shareholders with a personal interest in the approval of the same transaction are deemed to be one shareholder. Extraordinary transactions with a controlling shareholder or in which a controlling shareholder has a personal interest, including a private placement in which a controlling shareholder has a personal interest, and the terms of engagement of the company, directly or indirectly, with a controlling shareholder or a controlling shareholder’s relative (including through a corporation controlled by a controlling shareholder), regarding the company’s receipt of services from the controlling shareholder, and if such controlling shareholder is also an office holder or employee of the company, regarding his or her terms of employment, require the approval of each of (i) the audit committee (or the compensation committee with respect to the terms of the engagement as an office holder or employee, including insurance, indemnification and compensation), (ii) the board of directors and (iii) the shareholders, in that order. In addition, the shareholder approval must fulfill one of the following requirements:
| • | a majority of the shares held by shareholders who are not controlling shareholders and have no personal interest in the transaction and are voting at the meeting must be voted in favor of approving the transaction, excluding abstentions; or |
| • | the shares voted by shareholders who are non-controlling shareholders and who have no personal interest in the transaction who vote against the transaction represent no more than 2% of the voting rights in the company. |
Such majority determined in accordance with the majority requirement described above is hereinafter referred to as the Compensation Special Majority Requirement.
Any such transaction for which the term is more than three years must be approved in the same manner every three years, unless with respect to certain transactions as permitted by the Companies Law, the audit committee has determined that a longer term is reasonable under the circumstances. In addition, transactions with a controlling shareholder or a controlling shareholder’s relative who serves as an executive officer in a company, directly or indirectly (including through a corporation under his control), involving the receipt of services by a company or their compensation can have a term of five years from the company’s initial public offering under certain circumstances.
The Companies Law requires that every shareholder that participates, in person or by proxy, in a vote regarding a transaction with a controlling shareholder, must indicate in advance or in the ballot whether or not that shareholder has a personal interest in the vote in question. Failure to so indicate generally results in the invalidation of that shareholder’s vote for purposes of the Compensation Special Majority Requirement.
Disclosure of Compensation of Executive Officers
For so long as we qualify as a foreign private issuer, we are not required to comply with the proxy rules applicable to U.S. domestic filers, including the requirement applicable to emerging growth companies to disclose the compensation of our chief executive officer and other two most highly compensated executive officers on an individual, rather than an aggregate, basis. Nevertheless, regulations promulgated under the Companies Law require us to disclose in the proxy statement for the annual general meeting of our shareholders (or to include a reference therein to other previously furnished public disclosure) the annual compensation of our five most highly compensated executive officers on an individual, rather than an aggregate, basis. This disclosure will not be as extensive as that required of a U.S. domestic issuer.
Compensation of Directors and Executive Officers
Directors. Under the Companies Law, the compensation of our directors requires the approval of our compensation committee, the subsequent approval of the board of directors and, unless exempted under regulations promulgated under the Companies Law, the approval of the shareholders at a general meeting. If the compensation of our directors is inconsistent with our compensation policy, then, provided that those provisions that must be included in the compensation policy according to the Companies Law have been considered by the compensation committee and board of directors, and provided that shareholder approval is obtained by the Compensation Special Majority Requirement.
Executive Officers (other than the Chief Executive Officer). The Companies Law requires the approval of the compensation of a public company’s executive officers (other than the chief executive officer and who does not also serve as a director) in the following order: (i) the compensation committee, (ii) the company’s board of directors and (iii) if such compensation arrangement is inconsistent with the company’s compensation policy, the company’s shareholders (approved by the Compensation Special Majority Requirement). However, if the shareholders of the company do not approve a compensation arrangement with a non-director executive officer that is inconsistent with the company’s compensation policy, the compensation committee and board of directors may override the shareholders’ decision if each of the compensation committee and the board of directors provide detailed reasons for their decision.
An amendment to an existing compensation arrangement with a non-director executive officer requires only the approval of the compensation committee, if the compensation committee determines that the amendment is immaterial. However, if such non-director executive officer is subordinate to the chief executive officer, an immaterial amendment to an existing compensation arrangement shall not require the approval of the compensation committee if (i) such amendment is approved by the chief executive officer, (ii) the company’s compensation policy allows for such immaterial amendments to be approved by the chief executive officer and (iii) the engagement terms are consistent with the company’s compensation policy.
Chief Executive Officer. The Companies Law requires the approval of the compensation of a public company’s chief executive officer in the following order: (i) the company’s compensation committee, (ii) the company’s board of directors and (iii) the company’s shareholders (approved by the Compensation Special Majority Requirement). However, if the shareholders of the company do not approve the compensation arrangement with the chief executive officer who is not a director, the compensation committee and board of directors may override the shareholders’ decision if each of the compensation committee and the board of directors provide a detailed report for their decision. The approval of each of the compensation committee and the board of directors should be in accordance with the company’s compensation policy; however, in special circumstances, they may approve compensation terms of a chief executive officer that are inconsistent with such policy provided that they have considered those provisions that must be included in the compensation policy according to the Companies Law and that shareholder approval was obtained (by the Compensation Special Majority Requirement ). In the case of a new chief executive officer, the compensation committee may waive the shareholder approval requirement with regards to the approval of the engagement terms of a candidate for the chief executive officer position, if the compensation committee determines that the compensation arrangement is consistent with the company’s compensation policy, and that the chief executive officer did not have on the date of his appointment or during the two-year period preceding his appointment, an “affiliation” (including an employment relationship, a business or professional relationship or control) with the company or a controlling shareholder of the company or a relative thereof and that subjecting the approval of the engagement to a shareholder vote would impede the company’s ability to employ the chief executive officer candidate. However, if the chief executive officer candidate will serve as a member of the board of directors, such candidate’s compensation terms as chief executive officer must be approved in accordance with the rules applicable to approval of compensation of directors
Under the Companies Law, we are required to approve, at least once every three years, a compensation policy with respect to our directors and officers. Following the recommendation of our compensation committee, the compensation policy must be approved by our board of directors and our shareholders. The shareholder approval must be by a simple majority of all votes cast, provided that (i) such majority includes a simple majority of the votes cast by non-controlling shareholders having no personal interest in the matter or (ii) the total number of votes of shareholders mentioned in clause (i) above who voted against such transaction does not exceed 2% of the total voting rights in the company.
Under special circumstances, the board of directors may approve the compensation policy despite the objection of the shareholders on the condition that the compensation committee and then the board of directors decide, on the basis of detailed grounds, and after discussing again with the compensation policy, that approval of the compensation policy, despite the objection of shareholders, is for the benefit of the company.
Directors’ Service Contracts
There are no arrangements or understandings between us and any of our subsidiaries, on the one hand, and any of our directors, on the other hand, providing for benefits upon termination of their employment or service as directors of our company or any of our subsidiaries.
Under the Companies Law, a shareholder has a duty to refrain from abusing its power in the company and to act in good faith and in a customary manner in exercising its rights and performing its obligations to the company and other shareholders, including, among other things, when voting at meetings of shareholders on the following matters:
| • | an amendment to the articles of association; |
| • | an increase in the company’s authorized share capital; |
| • | the approval of related party transactions and acts of office holders that require shareholder approval. |
A shareholder also has a general duty to refrain from discriminating against other shareholders.
The remedies generally available upon a breach of contract also apply to a breach of the shareholder duties mentioned above, and in the event of discrimination against other shareholders, additional remedies may be available to the injured shareholder.
In addition, any controlling shareholder, any shareholder that knows that its vote can determine the outcome of a shareholder vote and any shareholder that, under a company’s articles of association, has the power to appoint or prevent the appointment of an office holder, or any other power with respect to a company, is under a duty to act with fairness towards the company. The Companies Law does not describe the substance of this duty except to state that the remedies generally available upon a breach of contract also apply in the event of a breach of the duty to act with fairness, taking the shareholder’s position in the company into account.
Exculpation, Insurance and Indemnification of Directors and Officers
Under the Companies Law, a company may not exculpate an office holder from liability for a breach of the duty of loyalty. An Israeli company may exculpate an office holder in advance from liability to the company, in whole or in part, for damages caused to the company as a result of a breach of duty of care but only if a provision authorizing such exculpation is included in its articles of association. Our articles of association include such a provision. An Israeli company may not exculpate in advance a director from liability arising from a breach of his or her duty of care in connection with a prohibited dividend or distribution to shareholders.
As permitted under the Companies Law, our articles of association provide that we may indemnify an office holder in respect of the following liabilities, payments and expenses incurred for acts performed by him or her as an office holder, either in advance of an event or following an event:
| • | financial liability that was imposed upon him in favor of another person pursuant to a judgment, including a compromise judgment or an arbitrator’s award approved by a court; |
| • | reasonable litigation expenses, including attorneys’ fees paid by an officeholder following an investigation or proceeding conducted against him by an authority authorized to conduct such investigation or proceeding, and which ended without the filing of an indictment against him and without any financial obligation being imposed on him as an alternative to a criminal proceeding, or which ended without the filing of an indictment against him but with the imposition of a financial obligation as an alternative to a criminal proceeding for an offense which does not require proof of mens rea or in connection with a financial sanction; |
| • | reasonable litigation expenses, including attorneys’ fees paid by the officeholder or which he was required to pay by a court, in a proceeding filed against him by the Company or on its behalf or by another person, or in criminal charges from which he was acquitted, or in criminal charges in which he was convicted of an offense which does not require proof of mens rea; |
| • | certain compensation payments made to an injured party imposed on an office holder by an administrative proceeding, pursuant to certain provisions of the Israeli Securities Law; |
| • | expenses incurred by an officeholder in connection with an administrative proceeding conducted in such officer holder’s regard, including reasonable litigation expenses, and including attorneys’ fees; and |
| • | any other liability or expense in respect of which it is permitted or shall be permitted by Law to indemnify an officeholder. |
As permitted under the Companies Law, our articles of association provide that we may insure an office holder against the following liabilities incurred for acts performed by him or her as an office holder:
| • | Breach of the duty of care to the Company or to a third party, including a breach arising out of the negligent conduct of the office holder; |
| • | Breach of the duty of care to the Company, provided that the office holder acted in good faith and had reasonable grounds to believe that the act would not prejudice the company ; |
| • | financial liability imposed upon an office holder in favor of a third party; |
| • | financial liability imposed on the office holder in favor of a third-party harmed by a breach in an administrative proceeding, pursuant to certain provisions of the Israeli Securities Law; |
| • | expenses incurred or to be incurred by an office holder in connection with an administrative proceeding, instituted against him or her, pursuant to certain provisions of the Israeli Securities Law, including reasonable litigation expenses, and including attorneys’ fees; and |
| • | any other event in respect of which it is permitted and/or shall be permitted by Law to insure the liability of an officeholder. |
Under the Companies Law, a company may not indemnify, exculpate or insure an office holder against any of the following:
| • | a breach of the duty of loyalty, except for indemnification and insurance for a breach of the duty of loyalty to the company to the extent that the office holder acted in good faith and had a reasonable basis to believe that the act would not prejudice the company; |
| • | a breach of duty of care committed intentionally or recklessly, excluding a breach arising out of the negligent conduct of the office holder; |
| • | an act or omission committed with intent to derive illegal personal benefit; or |
| • | a fine, monetary sanction or forfeit levied against the office holder. |
Under the Companies Law, exculpation, indemnification and insurance of office holders must be approved by the compensation committee and the board of directors and, with respect to directors, the chief executive officer or controlling shareholders, their relatives and third parties in which controlling shareholders have a personal interest, also by the shareholders. However, under regulations promulgated under the Companies Law, the insurance of office holders shall not require shareholder approval and may be approved by only the compensation committee if the engagement terms are determined in accordance with the company’s compensation policy, which was approved by the shareholders by the same special majority required to approve a compensation policy, provided that the insurance policy is on market terms and the insurance policy is not likely to materially impact the company’s profitability, assets, or obligations.
Our articles of association permit us to exculpate, indemnify and insure our office holders to the fullest extent permitted or to be permitted by law. Our office holders are currently covered by a directors’ and officers’ liability insurance policy. As of the date of this prospectus, no claims for directors’ and officers’ liability insurance have been filed under this policy and we are not aware of any pending or threatened litigation or proceeding involving any of our office holders, including our directors, in which indemnification is sought.
The following table sets forth information with respect to the beneficial ownership of our Ordinary Shares as of November 22, 2022 and after this offering by:
| | ● | each person or entity known by us to own beneficially 5% or more of our outstanding Ordinary Shares; |
| | ● | each of our directors and executive officers individually; and |
| | ● | all of our executive officers and directors as a group. |
The beneficial ownership of our Ordinary Shares is determined in accordance with the rules of the SEC. Under these rules, a person is deemed to be a beneficial owner of a security if that person has or shares voting power, which includes the power to vote or to direct the voting of the security, or investment power, which includes the power to dispose of or to direct the disposition of the security. For purposes of the table below, we deem Ordinary Shares issuable pursuant to options that are currently exercisable or exercisable within 60 days of the date of this registration statement to be outstanding and to be beneficially owned by the person holding the options or warrants for the purposes of computing the percentage ownership of that person, but we do not treat them as outstanding for the purpose of computing the percentage ownership of any other person. The percentage of ordinary shares beneficially owned after the offering is based on Ordinary Shares to be outstanding immediately after the offering, which includes our Ordinary Shares being offered for sale in this offering. The percentage of Ordinary Shares beneficially owned prior to the offering is based on 140,384,407 Ordinary Shares outstanding as of November 22, 2022.
The percentages of Ordinary Shares beneficially owned after the offering assume that the underwriters will not exercise their over-allotment option to purchase additional Ordinary Shares in the offering. Except where otherwise indicated, we believe, based on information furnished to us by such owners, that the beneficial owners of the Ordinary Shares listed below have sole investment and voting power with respect to such shares.
None of our shareholders has different voting rights from other shareholders. We are not aware of any arrangement that may, at a subsequent date, result in a change of control of our company. As of the date of this prospectus, there was one holder of record of our Ordinary Shares in the United States.
Unless otherwise noted below, each shareholder’s address is c/o Steakholder Foods Ltd., 5 David Fikes St., Rehovot 7638205, Israel.
| | | Shares Beneficially Owned Prior to Offering | | | Shares Beneficially Owned After Offering | |
| Name of Beneficial Owner | | Number | | | Percentage | | | Number | | | Percentage | |
| 5% or greater shareholders | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Shimon Cohen(1) | | | 12,175,320 | | | | 8.7 | % | | |
|
|
|
|
| |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Directors and executive officers | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Arik Kaufman(2) | | | 408,270 | | | | * | | | | | | | | | |
Guy Hefer(3) | | | 270,830 | | | | * | | | | | | | | | |
Dan Kozlovski(4) | | | 133,340 | | | | * | | | | | | | | | |
Yaron Kaiser(5) | | | 1,522,780 | | | | 1.1 | % | | | | | | | | |
David Gerbi(6) | | | 145,660 | | | | * | | | | | | | | | |
Eli Arad(7) | | | 145,660 | | | | * | | | | | | | | | |
Sari Singer(8) | | | 152,100 | | | | * | | | | | | | | | |
| All directors and executive officers as a group (7 persons) | | | 2,778,640 | | | | 2.0 | % | | | | | | | | |
* Less than one percent (1%).
| | (1) | This information is based solely on a Schedule 13D filed with the SEC on September 22, 2022, pursuant to which Shimon Cohen reported that he is the direct and beneficial owner of 12,175,320 Ordinary Shares, which represents (i) 305,616 ADSs held by Mr. Cohen in his individual capacity and (ii) 437,245 ADSs, 222,068 ADSs and 252,603 ADSs held indirectly by Mr. Cohen through S.C. Ma’agarei Enosh Ltd., Reshet Bitachon Ltd. and Ma’agarim Proyektim Ltd., respectively, each of which Mr. Cohen is the sole owner, manager and shareholder. The address for Shimon Cohen is 20 Derech HaShalom, Tel Aviv, 61250 Israel. |
| | (2) | Consists of 283,270 Ordinary Shares and options to purchase 125,000 Ordinary Shares exercisable within 60 days of the date of this prospectus, with an exercise price of $0.519. These options expire on March 16, 2026. |
| | (3) | Consists of options to purchase 145,830 Ordinary Shares exercisable within 60 days of the date of this prospectus, with an exercise price of NIS 3.49 ($1.00), expiring on March 24, 2025., and options to purchase 125,000 Ordinary Shares exercisable within 60 days of the date of this prospectus, with an exercise price of $0.716, expiring on July 20, 2025. |
| | (4) | Consists of options to purchase 133,340 Ordinary Shares exercisable within 60 days of the date of this prospectus, with an exercise price of NIS 1.90 ($0.55). These options expire on August 5, 2024. |
| | (5) | Consists of 1,435,280 Ordinary Shares based on information provided to us by Mr. Kaiser, and options to purchase 87,500 Ordinary Shares exercisable within 60 days of the date of this prospectus, with an exercise price of $0.519. These options expire on March 16, 2026. |
| | (6) | Consists of 42,450 Ordinary Shares and RSUs vesting into 5,010 Ordinary Shares within 60 days of the date of this prospectus. |
| | (7) | Consists of 42,450 Ordinary Shares and RSUs vesting into 5,010 Ordinary Shares within 60 days of the date of this prospectus. |
| | (8) | Consists of 44,910 Ordinary Shares and RSUs vesting into 8,990 Ordinary Shares within 60 days of the date of this prospectus. |
CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
Our board of directors, acting through our audit committee, is responsible for the review, approval, or ratification of related party transactions between us and related persons. Under Israeli law, related party transactions are subject to special approval requirements, see “Management — Fiduciary duties and approval of specified related party transactions and compensation under Israeli law.”
Employment Agreements and Director Fees
We have entered into written employment agreements with each of our executive officers, which provide for notice periods of varying duration for termination of the agreement by us or by the relevant executive officer, during which time the executive officer will continue to receive base salary and benefits. These agreements also contain customary provisions regarding noncompetition, confidentiality of information and assignment of inventions. However, the enforceability of the noncompetition provisions may be limited under applicable law. See “Risk factors - Risks relating to our operations - Under applicable employment laws, we may not be able to enforce covenants not to compete” for a further description of the enforceability of non-competition clauses. For further information, see “Management - Employment and Consulting Agreements.”
Directors and Officers Insurance Policy and Indemnification and Exculpation Agreements
In accordance with our articles of association, we have obtained Directors and Officers insurance for our executive officers and directors, and provide indemnification, exculpation and exemption undertakings to each of our directors and officers to the fullest extent permitted by the Companies Law.
Private Issuances of Securities
In January 2020, following the closing of the merger between MeaTech and Ophectra, we issued former shareholders of MeaTech warrants to receive Ordinary Shares, including to the following related parties: (1) warrants to receive 1,036,098 Ordinary Shares each to Sharon Fima, then our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Technical Officer, and Omri Schanin, our Depuy Chief Executive Officer; and (2) warrants to receive 1,291,158 Ordinary Shares to Liran Damati, then a substantial shareholder. The warrants have no exercise price and vest upon the achievement of certain milestones (for further details, see “Item 4.—Information on the Company—History and Development of the Company”).
In May 2020, pursuant to approvals of our audit committee, board of directors and a general meeting of our shareholders: (1) we issued 1,043,846 Ordinary Shares and options to purchase 6,030,286 Ordinary Shares at an exercise price of NIS 3.36 (approximately $1.03) per share in return for a private investment of $750,000 by EL Capital Investments LLC, a company controlled by Mr. Steven Lavin, who was concurrently appointed to our board of directors as its chairman; and (2) we issued options to purchase 1,967,327 Ordinary Shares at an exercise price of NIS 2.49 (approximately $0.76) per share and options to purchase 1,967,328 Ordinary Shares at an exercise price of NIS 3.486 (approximately $1.07) to Silver Road Capital Ltd., the majority of whose shares were owned by directors at the time, Mr. Steven Lavin and Mr. Daniel Ayalon.
Engagement with BlueSoundWaves
On October 6, 2021, we entered into a services and collaboration agreement, or the Services and Collaboration Agreement, with BlueOcean Sustainability Fund, LLC, or BlueSoundWaves, pursuant to which BlueSoundWaves provides us with marketing and promotional services, strategic consulting advice, and partner and investor engagement services in the United States. As consideration for such services, BlueSoundWaves received (i) an option to purchase 6,215,770 Ordinary Shares, currently equal to 621,577 ADSs, and (ii) 1,243,150 of our ordinary restricted shares, currently equal to 124,315 ADSs.
BlueOcean Sustainability Management Fund LP, a Cayman partnership, and the managing partner of BlueSoundWaves holds all of the outstanding share capital of BlueOcean Kayomot Ltd., an Israeli company. Messrs. Kaufman and Kaiser are directors of BlueOcean Kayomot Ltd. and founding partners of BlueSoundWaves. Mr. Kaufman also serves as the chief executive officer of BlueOcean Kayomot Ltd.
DESCRIPTION OF SHARE CAPITAL
The following description of our share capital and provisions of our articles of association, are summaries and do not purport to be complete.
Upon the closing of this offering, our authorized share capital will consist of 1,000,000,000 Ordinary Shares, no par value, of which shares will be issued and outstanding (including those represented by ADSs) assuming that the underwriters do not exercise their over-allotment option to purchase additional ADSs).
All of our outstanding Ordinary Shares are validly issued, fully paid and non-assessable. Our Ordinary Shares are not redeemable and do not have any preemptive rights.
As of November 22, 2022, an additional 1,156,835 of our ADSs were issuable upon the exercise of options and restricted share units to purchase ADSs outstanding as of such date, at a weighted average exercise price of $7.46 per ADS;
As of November 22, 2022, an additional 704,454 of our ADSs were issuable upon exercise of options and restricted share units outstanding as of such date at an exercise price to be determined at the time of exercise using a pre-determined formula;
As of November 22, 2022, an additional 4,486,562 of our ADSs were issuable upon the exercise of investor warrants to purchase ADSs outstanding as of such date at a weighted average exercise price of $7.00 per ADS, which warrants are expected to remain outstanding at the consummation of this offering.
We may also issue and redeem redeemable securities on such terms and in such manner as our board of directors shall determine.
Registration number and purposes of the company
Our registration number with the Israeli Registrar of Companies is 520041955. Our purpose as set forth in our articles of association is to engage in any lawful activity.
Our fully paid Ordinary Shares are issued in registered form and may be freely transferred under our articles of association, unless the transfer is restricted or prohibited by another instrument, applicable law or the rules of a stock exchange on which the ordinary shares are listed for trade. The ownership or voting of our Ordinary Shares by non-residents of Israel is not restricted in any way by our articles of association or the laws of the State of Israel, except for ownership by nationals of some countries that are, or have been, in a state of war with Israel.
Under our articles of association, our board of directors must consist of not less than three (3) but no more than seven (7) directors. Pursuant to our articles of association, each of our directors is appointed by a simple majority vote of holders of our Ordinary Shares, participating and voting at an annual general meeting of our shareholders provided that (i) in the event of a contested election the method of calculation of the votes and the manner in which the resolutions will be presented to our shareholders at the general meeting shall be determined by our board of directors in its discretion, and (ii) in the event that our board of directors does not or is unable to make a determination on such matter, then the directors will be elected by a plurality of the voting power represented at the general meeting in person or by proxy and voting on the election of directors. In addition, our directors are divided into three classes, one class being elected each year at the annual general meeting of our shareholders, and serve on our board of directors until the third annual general meeting following such election or re-election or until they are removed by a vote of 65% of the total voting power of our shareholders at a general meeting of our shareholders or upon the occurrence of certain events in accordance with the Companies Law and our articles of association. In addition, our articles of association provide that vacancies on our board of directors may be filled by a vote of a simple majority of the directors then in office. A director so appointed will hold office until the next annual general meeting of our shareholders for the election of the class of directors in respect of which the vacancy was created, or in the case of a vacancy due to the number of directors being less than the maximum number of directors stated in our articles of association, until the next annual general meeting of our shareholders for the election of the class of directors to which such director was assigned by our board of directors.
Dividend and Liquidation Rights
We may declare a dividend to be paid to the holders of our Ordinary Shares in proportion to their respective shareholdings. Under the Companies Law, dividend distributions are determined by the board of directors and do not require the approval of the shareholders of a company unless the Company’s articles of association provide otherwise. Our articles of association do not require shareholder approval of a dividend distribution and provide that dividend distributions may be determined by our board of directors.
Pursuant to the Companies Law, the distribution amount is limited to the greater of retained earnings or earnings generated over the previous two years, according to our then last reviewed or audited financial statements (less the amount of previously distributed dividends, if not reduced from the earnings), provided that the end of the period to which the financial statements relate is not more than six months prior to the date of the distribution. If we do not meet such criteria, then we may distribute dividends only with court approval. In each case, we are only permitted to distribute a dividend if our board of directors and, if applicable, the court determines that there is no reasonable concern that payment of the dividend will prevent us from satisfying our existing and foreseeable obligations as they become due.
In the event of our liquidation, after satisfaction of liabilities to creditors, our assets will be distributed to the holders of our Ordinary Shares in proportion to their shareholdings. This right, as well as the right to receive dividends, may be affected by the grant of preferential dividend or distribution rights to the holders of a class of shares with preferential rights that may be authorized in the future.
Under Israeli law, we are required to hold an annual general meeting of our shareholders once every calendar year and no later than 15 months after the date of the previous annual general meeting. All meetings other than the annual general meeting of shareholders are referred to in our articles of association as special general meetings. Our board of directors may call special general meetings of our shareholders whenever it sees fit, at such time and place, within or outside of Israel, as it may determine. In addition, the Companies Law provides that our board of directors is required to convene a special general meeting of our shareholders upon the written request of (1) any two or more of our directors, (2) one-quarter or more of the serving members of our board of directors or (3) one or more shareholders holding, in the aggregate, either (a) 5% or more of our outstanding issued shares and 1% or more of our outstanding voting power or (b) 5% or more of our outstanding voting power.
Under Israeli law, one or more shareholders holding at least 1% of the voting rights at the general meeting of the shareholders may request that the board of directors include a matter in the agenda of a general meeting of the shareholders to be convened in the future, provided that it is appropriate to discuss such a matter at the general meeting. Our articles of association contain procedural guidelines and disclosure items with respect to the submission of shareholder proposals for general meetings.
Subject to the provisions of the Companies Law and the regulations promulgated thereunder, shareholders entitled to participate and vote at general meetings of shareholders are the shareholders of record on a date to be decided by the board of directors, which, as a company listed on an exchange outside Israel, may be between four and 40 days prior to the date of the meeting. Furthermore, the Companies Law requires that resolutions regarding the following matters must be passed at a general meeting of shareholders:
| • | amendments to our articles of association; |
| • | appointment, terms of service or and termination of service of our auditors; |
| • | appointment of directors, including external directors (if applicable); |
| • | approval of certain related party transactions; |
| • | increases or reductions of our authorized share capital; |
| • | the exercise of our board of directors’ powers by a general meeting, if our board of directors is unable to exercise its powers and the exercise of any of its powers is required for our proper management. |
The Companies Law requires that a notice of any annual general meeting or special general meeting be provided to shareholders at least 21 days prior to the meeting and if the agenda of the meeting includes, among other things, the appointment or removal of directors, the approval of transactions with office holders or interested or related parties, or an approval of a merger, notice must be provided at least 35 days prior to the meeting. Under the Companies Law and our articles of association, shareholders are not permitted to take action by way of written consent in lieu of a meeting.
All ordinary shares have identical voting and other rights in all respects.
Pursuant to our articles of association, holders of our Ordinary Shares have one vote for each ordinary share held on all matters submitted to a vote before the shareholders at a general meeting of shareholders. The quorum required for our general meetings of shareholders consists of at least two shareholders present in person or by proxy in accordance with the Companies Law who hold or represent at least 331⁄3% of the total outstanding voting power of our shares, except that if (i) any such general meeting was initiated by and convened pursuant to a resolution adopted by the board of directors and (ii) at the time of such general meeting we qualify as to use the forms and rules of a “foreign private issuer,” the requisite quorum will consist of two or more shareholders present in person or by proxy who hold or represent at least 25% of the total outstanding voting power of our shares. The requisite quorum shall be present within half an hour of the time fixed for the commencement of the general meeting. A general meeting adjourned for lack of a quorum shall be adjourned either to the same day in the next week, at the same time and place, to such day and at such time and place as indicated in the notice to such meeting, or to such day and at such time and place as the chairperson of the meeting shall determine. At the reconvened meeting, any number of shareholders present in person or by proxy shall constitute a quorum, unless a meeting was called pursuant to a request by our shareholders, in which case the quorum required is one or more shareholders, present in person or by proxy and holding the number of shares required to call the meeting as described above.
Our articles of association provide that all resolutions of our shareholders require a simple majority vote, unless otherwise required by the Companies Law or by our articles of association. Under the Companies Law, certain actions require the approval of a special majority, including: (i) an extraordinary transaction with a controlling shareholder or in which the controlling shareholder has a personal interest, (ii) the terms of employment or other engagement of a controlling shareholder of the company or a controlling shareholder’s relative (even if such terms are not extraordinary) and (iii) certain compensation-related matters. Under our articles of association, the alteration of the rights, privileges, preferences or obligations of any class of our shares (to the extent there are classes other than ordinary shares) requires the approval of a simple majority of the class so affected (or such other percentage of the relevant class that may be set forth in the governing documents relevant to such class), in addition to a majority of all classes of shares voting together as a single class at a shareholder meeting. Under our articles of association, the approval of the holders of at least 65% of the total voting power of our shareholders is generally required to remove any of our directors from office.
Access to corporate records
Under the Companies Law, all shareholders generally have the right to review minutes of our general meetings, our shareholder register (including with respect to material shareholders), our articles of association, our financial statements, other documents as provided in the Companies Law, and any document we are required by law to file publicly with the Israeli Registrar of Companies or the Israel Securities Authority. Any shareholder who specifies the purpose of its request may request to review any document in our possession that relates to any action or transaction with a related party which requires shareholder approval under the Companies Law. We may deny a request to review a document if we determine that the request was not made in good faith, that the document contains a trade secret or a patent or that the document’s disclosure may otherwise impair our interests.
Acquisitions under Israeli Law
Full tender offer. A person wishing to acquire shares of a public Israeli company who would, as a result, hold over 90% of the target company’s voting rights or the target company’s issued and outstanding share capital (or of a class thereof), is required by the Companies Law to make a tender offer to all of the company’s shareholders for the purchase of all of the issued and outstanding shares of the company (or the applicable class). If (a) the shareholders who do not accept the offer hold less than 5% of the issued and outstanding share capital of the company (or the applicable class) and the shareholders who accept the offer constitute a majority of the offerees that do not have a personal interest in the acceptance of the tender offer or (b) the shareholders who did not accept the tender offer hold less than 2% of the issued and outstanding share capital of the company (or of the applicable class), all of the shares that the acquirer offered to purchase will be transferred to the acquirer by operation of law. A shareholder who had its shares so transferred may petition an Israeli court within six months from the date of acceptance of the full tender offer, regardless of whether such shareholder agreed to the offer, to determine whether the tender offer was for less than fair value and whether the fair value should be paid as determined by the court. However, an offeror may provide in the offer that a shareholder who accepted the offer will not be entitled to petition the court for appraisal rights as described in the preceding sentence, as long as the offeror and the company disclosed the information required by law in connection with the full tender offer. If the full tender offer was not accepted in accordance with any of the above alternatives, the acquirer may not acquire shares of the company that will increase its holdings to more than 90% of the company’s voting rights or the company’s issued and outstanding share capital (or of the applicable class) from shareholders who accepted the tender offer. Shares purchased in contradiction to the full tender offer rules under the Companies Law will have no rights and will become dormant shares.
Special tender offer. The Companies Law provides that an acquisition of shares of an Israeli public company must be made by means of a special tender offer if as a result of the acquisition the purchaser would become a holder of 25% or more of the voting rights in the company. This requirement does not apply if there is already another holder of 25% or more of the voting rights in the company. Similarly, the Companies Law provides that an acquisition of shares of an Israeli public company must be made by means of a special tender offer if as a result of the acquisition the purchaser would become a holder of more than 45% of the voting rights in the company, if there is no other shareholder of the company who holds more than 45% of the voting rights in the company. These requirements do not apply if (i) the acquisition occurs in the context of a private placement by the company that received shareholders’ approval as a private placement whose purpose is to give the purchaser 25% or more of the voting rights in the company, if there is no person who holds 25% or more of the voting rights in the company or as a private placement whose purpose is to give the purchaser 45% of the voting rights in the company, if there is no person who holds 45% of the voting rights in the company, (ii) the acquisition was from a shareholder holding 25% or more of the voting rights in the company and resulted in the purchaser becoming a holder of 25% or more of the voting rights in the company, or (iii) the acquisition was from a shareholder holding more than 45% of the voting rights in the company and resulted in the purchaser becoming a holder of more than 45% of the voting rights in the company. A special tender offer must be extended to all shareholders of a company. A special tender offer may be consummated only if (i) at least 5% of the voting power attached to the company’s outstanding shares will be acquired by the offeror and (ii) the number of shares tendered in the offer exceeds the number of shares whose holders objected to the offer (excluding the purchaser, its controlling shareholders, holders of 25% or more of the voting rights in the company and any person having a personal interest in the acceptance of the tender offer, or anyone on their behalf, including any such person’s relatives and entities under their control).
In the event that a special tender offer is made, a company’s board of directors is required to express its opinion on the advisability of the offer, or shall abstain from expressing any opinion if it is unable to do so, provided that it gives the reasons for its abstention. The board of directors shall also disclose any personal interest that any of the directors has with respect to the special tender offer or in connection therewith. An office holder in a target company who, in his or her capacity as an office holder, performs an action the purpose of which is to cause the failure of an existing or foreseeable special tender offer or is to impair the chances of its acceptance, is liable to the potential purchaser and shareholders for damages, unless such office holder acted in good faith and had reasonable grounds to believe he or she was acting for the benefit of the company. However, office holders of the target company may negotiate with the potential purchaser in order to improve the terms of the special tender offer, and may further negotiate with third parties in order to obtain a competing offer.
If a special tender offer is accepted, then shareholders who did not respond to or that had objected the offer may accept the offer within four days of the last day set for the acceptance of the offer and they will be considered to have accepted the offer from the first day it was made.
In the event that a special tender offer is accepted, then the purchaser or any person or entity controlling it or under common control with the purchaser or such controlling person or entity at the time of the offer may not make a subsequent tender offer for the purchase of shares of the target company and may not enter into a merger with the target company for a period of one year from the date of the offer, unless the purchaser or such person or entity undertook to effect such an offer or merger in the initial special tender offer. Shares purchased in contradiction to the special tender offer rules under the Companies Law will have no rights and will become dormant shares.
Merger. The Companies Law permits merger transactions if approved by each party’s board of directors and, unless certain conditions described under the Companies Law are met, a simple majority of the outstanding shares of each party to the merger that are represented and voting on the merger. The board of directors of a merging company is required pursuant to the Companies Law to discuss and determine whether in its opinion there exists a reasonable concern that as a result of a proposed merger, the surviving company will not be able to satisfy its obligations towards its creditors, such determination taking into account the financial status of the merging companies. If the board of directors determines that such a concern exists, it may not approve a proposed merger. Following the approval of the board of directors of each of the merging companies, the boards of directors must jointly prepare a merger proposal for submission to the Israeli Registrar of Companies.
For purposes of the shareholder vote of a merging company whose shares are held by the other merging company, or by a person or entity holding 25% or more of the voting rights at the general meeting of shareholders of the other merging company, or by a person or entity holding the right to appoint 25% or more of the directors of the other merging company, unless a court rules otherwise, the merger will not be deemed approved if a majority of the shares voted on the matter at the general meeting of shareholders (excluding abstentions) that are held by shareholders other than the other party to the merger, or by any person or entity who holds 25% or more of the voting rights of the other party or the right to appoint 25% or more of the directors of the other party, or any one on their behalf including their relatives or corporations controlled by any of them, vote against the merger. In addition, if the non-surviving entity of the merger has more than one class of shares, the merger must be approved by each class of shareholders. If the transaction would have been approved but for the separate approval of each class or the exclusion of the votes of certain shareholders as provided above, a court may still approve the merger upon the request of holders of at least 25% of the voting rights of a company, if the court holds that the merger is fair and reasonable, taking into account the valuation of the merging companies and the consideration offered to the shareholders. If a merger is with a company’s controlling shareholder or if the controlling shareholder has a personal interest in the merger, then the merger is instead subject to the same special majority approval that governs all extraordinary transactions with controlling shareholders.
Under the Companies Law, each merging company must deliver to its secured creditors the merger proposal and inform its unsecured creditors of the merger proposal and its content. Upon the request of a creditor of either party to the proposed merger, the court may delay or prevent the merger if it concludes that there exists a reasonable concern that, as a result of the merger, the surviving company will be unable to satisfy the obligations of the merging company, and may further give instructions to secure the rights of creditors.
In addition, a merger may not be completed unless at least 50 days have passed from the date that a proposal for approval of the merger is filed with the Israeli Registrar of Companies and 30 days from the date that shareholder approval of both merging companies is obtained.
The Companies Law allows us to create and issue shares having rights different from those attached to our Ordinary Shares, including shares providing certain preferred rights with respect to voting, distributions or other matters and shares having preemptive rights. No preferred shares will be authorized under our articles of association. In the future, if we do authorize, create and issue a specific class of preferred shares, such class of shares, depending on the specific rights that may be attached to it, may have the ability to frustrate or prevent a takeover or otherwise prevent our shareholders from realizing a potential premium over the market value of their Ordinary Shares. The authorization and designation of a class of preferred shares will require an amendment to our articles of association, which requires the prior approval of the holders of a majority of the voting power attached to our issued and outstanding shares at a general meeting of shareholders. The convening of the meeting, the shareholders entitled to participate and the vote required to be obtained at such a meeting will be subject to the requirements set forth in the Companies Law and our articles of association.
In addition, we have a classified board structure whereby our directors are divided into three classes with staggered three-year terms. At each annual general meeting of the Company’s shareholders, the election or re-election of directors (other than external directors, if any) following the expiration of the term of office of the directors of that class of directors will be for a term of office that expires on the third annual general meeting following such election or re-election, such that from the annual general meeting of 2023 and thereafter, each year the term of office of only one class of directors will expire. We believe this mechanism effectively limits the ability of any investor or potential investor or group of investors or potential investors to gain control of our board of directors.
Our directors are divided among the three classes as follows:
| | • | the Class I directors are Messrs. Eli Arad and David Gerbi and their respective terms will expire at the Company’s annual general meeting of shareholders to be held in 2023; |
| | • | the Class II director is Ms. Sari Singer and her term will expire at the Company’s annual general meeting of shareholders to be held in 2024; and |
| | • | the Class III director is Mr. Yaron Kaiser his term will expire at the Company’s annual general meeting of shareholders to be held in 2025. |
Approval of Business Combination Transactions
According to our articles of association, unless otherwise approved by our board of directors in advance, the Company cannot enter into a business combination (as defined in the articles of association) with any shareholder or any of its affiliates and/or investors for a period of three years following (i) with respect to any shareholder holding twenty percent (20%) or more of the voting power of the Company’s share capital and (ii) with respect to all shareholders, each time as such shareholder and/or any of its affiliates and/or investors become(s) (other than due to a buyback, redemption or cancellation of shares by the Company) the holder(s) (beneficially or of record) of 20% or more of the issued and outstanding voting power of the Company’s share capital.
Our articles of association provide that unless the Company consents in writing to the selection of an alternative forum, the federal district courts of the United States shall be the exclusive forum for the resolution of any complaint asserting a cause of action arising under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended; and, for the avoidance of any doubt, such provision does not apply to any claim asserting a cause of action arising under the Exchange Act. Our articles of association also provide that unless the Company consents in writing to the selection of an alternative forum, the competent courts in Tel Aviv, Israel shall be the exclusive forum for any derivative action or proceeding brought on behalf of the Company, any action asserting a breach of a fiduciary duty owed by any of the Company’s directors, officers or other employees to the Company or shareholders of the Company or any action asserting a claim arising pursuant to any provision of the Companies Law or the Israeli Securities Law, and the regulations promulgated thereunder.
Amendment of Articles of association
Any amendment of our articles of associations requires, in addition to the approval of the shareholders of the Company, the approval of our board of directors with the affirmative vote of a majority of the then serving directors.
Pursuant to the Companies Law and our articles of association, our board of directors may exercise all powers and take all actions that are not required under law or under our articles of association to be exercised or taken by our shareholders, including the power to borrow money for company purposes.
Our articles of association enable us to increase or reduce our share capital. Any such changes are subject to Israeli law and must be approved by a resolution duly passed by our shareholders at a general meeting of shareholders. In addition, transactions that have the effect of reducing capital, such as the declaration and payment of dividends in the absence of sufficient retained earnings or profits, require the approval of both our board of directors and an Israeli court.
Transfer Agent and Registrar
The transfer agent and registrar for our ordinary shares is Computershare Inc.
DESCRIPTION OF THE OFFERED SECURITIES
American Depositary Shares
The Bank of New York Mellon, as depositary, registers and delivers the ADSs. Each ADS represents ten Ordinary Shares (or a right to receive ten Ordinary Shares). Each ADS also represents any other securities, cash or other property which may be held by the depositary. The depositary’s office at which the ADSs are administered and its principal executive office are located at 240 Greenwich Street, New York, New York 10286.
You may hold ADSs either (A) directly (i) by having an American Depositary Receipt, or ADR, which is a certificate evidencing a specific number of ADSs, registered in your name or (ii) by having uncertificated ADSs registered in your name or (B) indirectly by holding a security entitlement in ADSs through your broker or other financial institution that is a direct or indirect participant in The Depository Trust Company, or DTC. If you hold ADSs directly, you are a registered ADS holder, also referred to as an ADS holder. This description assumes you are an ADS holder. If you hold the ADSs indirectly, you must rely on the procedures of your broker or other financial institution to assert the rights of ADS holders described in this section. You should consult with your broker or financial institution to find out what those procedures are.
Registered holders of uncertificated ADSs will receive statements from the depositary confirming their holdings.
ADS holders are not treated as shareholders and do not have shareholder rights. Israeli law governs shareholder rights. The depositary is the holder of the Ordinary Shares underlying the ADSs. Registered holders of ADSs have ADS holder rights. A deposit agreement among us, the depositary, ADS holders and all other persons indirectly or beneficially holding ADSs sets out ADS holder rights as well as the rights and obligations of the depositary. New York law governs the deposit agreement and the ADSs.
The following is a summary of the material provisions of the deposit agreement. For more complete information, you should read the entire deposit agreement and the form of ADR. For directions on how to obtain copies of those documents see “Where You Can Find More Information.”
Dividends and Other Distributions
How will you receive dividends and other distributions on the shares?
The depositary has agreed to pay or distribute to ADS holders the cash dividends or other distributions it or the custodian receives on Ordinary Shares or other deposited securities, upon payment or deduction of its fees and expenses. You will receive these distributions in proportion to the number of Ordinary Shares your ADSs represent.
Cash. The depositary will convert any cash dividend or other cash distribution we pay on the Ordinary Shares into U.S. dollars, if it can do so on a reasonable basis and can transfer the U.S. dollars to the United States. If that is not possible or if any government approval is needed and cannot be obtained, the deposit agreement allows the depositary to distribute the foreign currency only to those ADS holders to whom it is possible to do so. It will hold the foreign currency it cannot convert for the account of the ADS holders who have not been paid. It will not invest the foreign currency and it will not be liable for any interest.
Before making a distribution, any withholding taxes or other governmental charges that must be paid will be deducted. The depositary will distribute only whole U.S. dollars and cents and will round fractional cents to the nearest whole cent. If the exchange rates fluctuate during a time when the depositary cannot convert the foreign currency, you may lose some or all of the value of the distribution.
Shares. The depositary may distribute additional ADSs representing any Ordinary Shares we distribute as a dividend or free distribution. The depositary will only distribute whole ADSs. It will sell Ordinary Shares which would require it to deliver a fraction of an ADS (or ADSs representing those Ordinary Shares) and distribute the net proceeds in the same way as it does with cash. If the depositary does not distribute additional ADSs, the outstanding ADSs will also represent the new shares. The depositary may sell a portion of the distributed Ordinary Shares (or ADSs representing those Ordinary Shares) sufficient to pay its fees and expenses in connection with that distribution.
Rights to purchase additional shares. If we offer holders of our securities any rights to subscribe for additional Ordinary Shares or any other rights, the depositary may (i) exercise those rights on behalf of ADS holders, (ii) distribute those rights to ADS holders or (iii) sell those rights and distribute the net proceeds to ADS holders, in each case after deduction or upon payment of its fees and expenses. To the extent the depositary does not do any of those things, it will allow the rights to lapse. In that case, you will receive no value for them. The depositary will exercise or distribute rights only if we ask it to and provide satisfactory assurances to the depositary that it is legal to do so. If the depositary exercises rights, it will purchase the securities to which the rights relate and distribute those securities or, in the case of Ordinary Shares, new ADSs representing the new Ordinary Shares, to subscribing ADS holders, but only if ADS holders have paid the exercise price to the depositary. U.S. securities laws may restrict the ability of the depositary to distribute rights or ADSs or other securities issued on exercise of rights to all or certain ADS holders, and the securities distributed may be subject to restrictions on transfer.
Other Distributions. The depositary will send to ADS holders anything else we distribute on deposited securities by any means it thinks is legal, fair and practical. If it cannot make the distribution in that way, the depositary will have a choice. It may decide to sell what we distributed and distribute the net proceeds, in the same way as it does with cash. Or, it may decide to hold what we distributed, in which case ADSs will also represent the newly distributed property. However, the depositary is not required to distribute any securities (other than ADSs) to ADS holders unless it receives satisfactory evidence from us that it is legal to make that distribution. The depositary may sell a portion of the distributed securities or property sufficient to pay its fees and expenses in connection with that distribution. U.S. securities laws may restrict the ability of the depositary to distribute securities to all or certain ADS holders, and the securities distributed may be subject to restrictions on transfer.
The depositary is not responsible if it decides that it is unlawful or impractical to make a distribution available to any ADS holders. We have no obligation to register ADSs, Ordinary Shares, rights or other securities under the Securities Act. We also have no obligation to take any other action to permit the distribution of ADSs, shares, rights or anything else to ADS holders. This means that you may not receive the distributions we make on our Ordinary Shares or any value for them if it is illegal or impractical for us to make them available to you.
Deposit, Withdrawal and Cancellation
How are ADSs issued?
The depositary will deliver ADSs if you or your broker deposits Ordinary Shares or evidence of rights to receive Ordinary Shares with the custodian. Upon payment of its fees and expenses and of any taxes or charges, such as stamp taxes or stock transfer taxes or fees, the depositary will register the appropriate number of ADSs in the names you request and will deliver the ADSs to or upon the order of the person or persons that made the deposit.
How can ADS holders withdraw the deposited securities?
You may surrender your ADSs to the depositary for the purpose of withdrawal. Upon payment of its fees and expenses and of any taxes or charges, such as stamp taxes or stock transfer taxes or fees, the depositary will deliver the Ordinary Shares and any other deposited securities underlying the ADSs to the ADS holder or a person the ADS holder designates at the office of the custodian. Or, at your request, risk and expense, the depositary will deliver the deposited securities at its office, if feasible. However, the depositary is not required to accept surrender of ADSs to the extent it would require delivery of a fraction of a deposited share or other securities. The depositary may charge you a fee and its expenses for instructing the custodian regarding delivery of deposited securities.
How do ADS holders interchange between certificated ADSs and uncertificated ADSs?
You may surrender your ADR to the depositary for the purpose of exchanging your ADR for uncertificated ADSs. The depositary will cancel that ADR and will send to the ADS holder a statement confirming that the ADS holder is the registered holder of uncertificated ADSs. Alternatively, upon receipt by the depositary of a proper instruction from a registered holder of uncertificated ADSs requesting the exchange of uncertificated ADSs for certificated ADSs, the depositary will execute and deliver to the ADS holder an ADR evidencing those ADSs.
Voting Rights
How do you vote?
ADS holders may instruct the depositary how to vote the number of deposited Ordinary Shares their ADSs represent. If we request the depositary to solicit your voting instructions (and we are not required to do so), the depositary will notify you of a shareholders’ meeting and send or make voting materials available to you. Those materials will describe the matters to be voted on and explain how ADS holders may instruct the depositary how to vote. For instructions to be valid, they must reach the depositary by a date set by the depositary. The depositary will try, as far as practical, subject to the laws of Israel and the provisions of our articles of association or similar documents, to vote or to have its agents vote the Ordinary Shares or other deposited securities as instructed by ADS holders. If we do not request the depositary to solicit your voting instructions, you can still send voting instructions, and, in that case, the depositary may try to vote as you instruct, but it is not required to do so.
Except by instructing the depositary as described above, you won’t be able to exercise voting rights unless you surrender your ADSs and withdraw the Ordinary Shares. However, you may not know about the meeting enough in advance to withdraw the Ordinary Shares. In any event, the depositary will not exercise any discretion in voting deposited securities and it will only vote or attempt to vote as instructed.
We cannot assure you that you will receive the voting materials in time to ensure that you can instruct the depositary to vote the Ordinary Shares represented by your ADSs. In addition, the depositary and its agents are not responsible for failing to carry out voting instructions or for the manner of carrying out voting instructions. This means that you may not be able to exercise your right to vote and there may be nothing you can do if the Ordinary Shares represented by your ADSs are not voted as you requested.
In order to give you a reasonable opportunity to instruct the depositary as to the exercise of voting rights relating to deposited securities, if we request the depositary to act, we agree to give the depositary notice of any such meeting and details concerning the matters to be voted upon at least 30 days in advance of the meeting date.
| Persons depositing or withdrawing ordinary shares or ADS holders must pay | | For |
| $5.00 (or less) per 100 ADSs (or portion of 100 ADSs) | | Issuance of ADSs, including issuances resulting from a distribution of ordinary shares or rights or other property cancellation of ADSs for the purpose of withdrawal, including if the deposit agreement terminates |
| | | |
| $.05 (or less) per ADS | | Any cash distribution to ADS holders |
| | | |
| A fee equivalent to the fee that would be payable if securities distributed to you had been ordinary shares and the ordinary shares had been deposited for issuance of ADSs | | Distribution of securities distributed to holders of deposited securities (including rights) that are distributed by the depositary to ADS holders |
| | | |
| $.05 (or less) per ADS per calendar year | | Depositary services |
| Persons depositing or withdrawing ordinary shares or ADS holders must pay | | For |
| Registration or transfer fees | | Transfer and registration of ordinary shares on our share register to or from the name of the depositary or its agent when you deposit or withdraw ordinary shares |
| | | |
| Expenses of the depositary | | Cable (including SWIFT), telex and facsimile transmissions (when expressly provided in the deposit agreement) Converting foreign currency to U.S. dollars |
| | | |
| Taxes and other governmental charges the depositary or the custodian has to pay on any ADSs or ordinary shares underlying ADSs, such as stock transfer taxes, stamp duty or withholding taxes | | As necessary |
| | | |
| Any charges incurred by the depositary or its agents for servicing the deposited securities | | As necessary |
The depositary collects its fees for delivery and surrender of ADSs directly from investors depositing Ordinary Shares or surrendering ADSs for the purpose of withdrawal or from intermediaries acting for them. The depositary collects fees for making distributions to investors by deducting those fees from the amounts distributed or by selling a portion of distributable property to pay the fees. The depositary may collect its annual fee for depositary services by deduction from cash distributions or by directly billing investors or by charging the book-entry system accounts of participants acting for them. The depositary may collect any of its fees by deduction from any cash distribution payable (or by selling a portion of securities or other property distributable) to ADS holders that are obligated to pay those fees. The depositary may generally refuse to provide fee-attracting services until its fees for those services are paid.
From time to time, the depositary may make payments to us to reimburse us for costs and expenses generally arising out of establishment and maintenance of the ADS program, waive fees and expenses for services provided to us by the depositary or share revenue from the fees collected from ADS holders. In performing its duties under the deposit agreement, the depositary may use brokers, dealers, foreign currency dealers or other service providers that are owned by or affiliated with the depositary and that may earn or share fees, spreads or commissions.
The depositary may convert foreign currency itself or through any of its affiliates or the custodian or we may convert foreign currency and pay U.S. dollars to the depositary. Where the depositary converts foreign currency itself or through any of its affiliates, the depositary acts as principal for its own account and not as agent, advisor, broker or fiduciary on behalf of any other person and earns revenue, including, without limitation, fees and transaction spreads that it will retain for its own account. The revenue is based on, among other things, the difference between the exchange rate assigned to the currency conversion made under the deposit agreement and the rate that the depositary or its affiliate receives when buying or selling foreign currency for its own account. The depositary makes no representation that the exchange rate used or obtained by it or its affiliates in any currency conversion under the deposit agreement will be the most favorable rate that could be obtained at the time or that the method by which that rate will be determined will be most favorable to ADS holders, subject to its obligations to act without negligence or bad faith. The methodology used to determine exchange rates used in currency conversions made by the depositary is available upon request. Where the custodian converts foreign currency, the custodian has no obligation to obtain the most favorable rate that could be obtained at the time or to ensure that the method by which that rate will be determined will be the most favorable to ADS holders, and the depositary makes no representation that the rate is the most favorable rate and will not be liable for any direct or indirect losses associated with the rate. In certain instances, the depositary may receive dividends or other distributions from us in U.S. dollars that represent the proceeds of a conversion of foreign currency or translation from foreign currency at a rate that was obtained or determined by us and, in such cases, the depositary will not engage in, or be responsible for, any foreign currency transactions and neither it nor we make any representation that the rate obtained or determined by us is the most favorable rate and neither it nor we will be liable for any direct or indirect losses associated with the rate
You will be responsible for any taxes or other governmental charges payable on your ADSs or on the deposited securities represented by any of your ADSs. The depositary may refuse to register any transfer of your ADSs or allow you to withdraw the deposited securities represented by your ADSs until those taxes or other charges are paid. It may apply payments owed to you or sell deposited securities represented by your ADSs to pay any taxes owed and you will remain liable for any deficiency. If the depositary sells deposited securities, it will, if appropriate, reduce the number of ADSs to reflect the sale and pay to ADS holders any proceeds, or send to ADS holders any property, remaining after it has paid the taxes
Tender and Exchange Offers; Redemption, Replacement or Cancellation of Deposited Securities
The depositary will not tender deposited securities in any voluntary tender or exchange offer unless instructed to do by an ADS holder surrendering ADSs and subject to any conditions or procedures the depositary may establish.
If deposited securities are redeemed for cash in a transaction that is mandatory for the depositary as a holder of deposited securities, the depositary will call for surrender of a corresponding number of ADSs and distribute the net redemption money to the holders of called ADSs upon surrender of those ADSs.
If there is any change in the deposited securities such as a subdivision, combination or other reclassification, or any merger, consolidation, recapitalization or reorganization affecting the issuer of deposited securities in which the depositary receives new securities in exchange for or in lieu of the old deposited securities, the depositary will hold those replacement securities as deposited securities under the deposit agreement. However, if the depositary decides it would not be lawful and practical to hold the replacement securities because those securities could not be distributed to ADS holders or for any other reason, the depositary may instead sell the replacement securities and distribute the net proceeds upon surrender of the ADSs.
If there is a replacement of the deposited securities and the depositary will continue to hold the replacement securities, the depositary may distribute new ADSs representing the new deposited securities or ask you to surrender your outstanding ADSs in exchange for new ADSs identifying the new deposited securities.
If there are no deposited securities underlying ADSs, including if the deposited securities are cancelled, or if the deposited securities underlying ADSs have become apparently worthless, the depositary may call for surrender or of those ADSs or cancel those ADSs upon notice to the ADS holders.
Amendment and Termination
How may the deposit agreement be amended?
We may agree with the depositary to amend the deposit agreement and the ADRs without your consent for any reason. If an amendment adds or increases fees or charges, except for taxes and other governmental charges or expenses of the depositary for registration fees, facsimile costs, delivery charges or similar items, or prejudices a substantial right of ADS holders, it will not become effective for outstanding ADSs until 30 days after the depositary notifies ADS holders of the amendment. At the time an amendment becomes effective, you are considered, by continuing to hold your ADSs, to agree to the amendment and to be bound by the ADRs and the deposit agreement as amended.
How may the deposit agreement be terminated?
The depositary will initiate termination of the deposit agreement if we instruct it to do so. The depositary may initiate termination of the deposit agreement if:
| • | 60 days have passed since the depositary told us it wants to resign but a successor depositary has not been appointed and accepted its appointment; |
| • | we delist the ADSs from an exchange in the United States on which they were listed and do not list them on another exchange in the United States or list our Ordinary Shares on an exchange outside the United States and make arrangements for trading of ADSs on the U.S. over the counter market within a reasonable time; |
| • | the depositary has reason to believe the ADSs have become, or will become, ineligible for registration on Form F-6 under the Securities Act; |
| • | we appear to be insolvent or enter insolvency proceedings; |
| • | all or substantially all the value of the deposited securities has been distributed either in cash or in the form of securities; |
| • | there are no deposited securities underlying the ADSs or the underlying deposited securities have become apparently worthless; or |
| • | there has been a replacement of deposited securities. |
If the deposit agreement will terminate, the depositary will notify ADS holders at least 90 days before the termination date. At any time after the termination date, the depositary may sell the deposited securities. After that, the depositary will hold the money it received on the sale, as well as any other cash it is holding under the deposit agreement, unsegregated and without liability for interest, for the pro rata benefit of the ADS holders that have not surrendered their ADSs. Normally, the depositary will sell as soon as practicable after the termination date.
After the termination date and before the depositary sells, ADS holders can still surrender their ADSs and receive delivery of deposited securities, except that the depositary may refuse to accept a surrender for the purpose of withdrawing deposited securities or reverse previously accepted surrenders of that kind if it would interfere with the selling process. The depositary may refuse to accept a surrender for the purpose of withdrawing sale proceeds until all the deposited securities have been sold. The depositary will continue to collect distributions on deposited securities, but, after the termination date, the depositary is not required to register any transfer of ADSs or distribute any dividends or other distributions on deposited securities to the ADSs holder (until they surrender their ADSs) or give any notices or perform any other duties under the deposit agreement except as described in this paragraph.
Limitations on Obligations and Liability
Limits on our obligations and the obligations of the depositary; Limits on liability to holders of ADSs
The deposit agreement expressly limits our obligations and the obligations of the depositary. It also limits our liability and the liability of the depositary. We and the depositary:
| • | are only obligated to take the actions specifically set forth in the deposit agreement without negligence or bad faith, and the depositary will not be a fiduciary or have any fiduciary duty to holders of ADSs; |
| • | are not liable if we are or it is prevented or delayed by law or circumstances beyond our or its control from performing our or its obligations under the deposit agreement; |
| • | are not liable if we exercise or it exercises discretion permitted under the deposit agreement; |
| • | are not liable for the inability of any holder of ADSs to benefit from any distribution on deposited securities that is not made available to holders of ADSs under the terms of the deposit agreement, or for any special, consequential or punitive damages for any breach of the terms of the deposit agreement; |
| • | have no obligation to become involved in a lawsuit or other proceeding related to the ADSs or the deposit agreement on your behalf or on behalf of any other person; |
| • | are not liable for the acts or omissions of any securities depository, clearing agency or settlement system; |
| • | may rely upon any documents we believe or it believes in good faith to be genuine and to have been signed or presented by the proper person; and |
| • | the depositary has no duty to make any determination or provide any information as to our tax status, or any liability for any tax consequences that may be incurred by ADS holders as a result of owning or holding ADSs or be liable for the inability or failure of an ADS holder to obtain the benefit of a foreign tax credit reduced rate of withholding or refund of amounts withheld in respect of tax or any other tax benefit. |
In the deposit agreement, we and the depositary agree to indemnify each other under certain circumstances.
Requirements for Depositary Actions
Before the depositary will deliver or register a transfer of ADSs, make a distribution on ADSs, or permit withdrawal of shares, the depositary may require:
| • | payment of stock transfer or other taxes or other governmental charges and transfer or registration fees charged by third parties for the transfer of any Ordinary Shares or other deposited securities; |
| • | satisfactory proof of the identity and genuineness of any signature or other information it deems necessary; and |
| • | compliance with regulations it may establish, from time to time, consistent with the deposit agreement, including presentation of transfer documents. |
The depositary may refuse to deliver ADSs or register transfers of ADSs when the transfer books of the depositary or our transfer books are closed or at any time if the depositary or we think it advisable to do so.
Your Right to Receive the Ordinary Shares Underlying your ADSs
ADS holders have the right to cancel their ADSs and withdraw the underlying Ordinary Shares at any time except:
| • | when temporary delays arise because: (i) the depositary has closed its transfer books or we have closed our transfer books; (ii) the transfer of Ordinary Shares is blocked to permit voting at a shareholders’ meeting; or (iii) we are paying a dividend on our shares; |
| • | when you owe money to pay fees, taxes and similar charges; or |
| • | when it is necessary to prohibit withdrawals in order to comply with any laws or governmental regulations that apply to ADSs or to the withdrawal of Ordinary Shares or other deposited securities. |
This right of withdrawal may not be limited by any other provision of the deposit agreement.
Direct Registration System
In the deposit agreement, all parties to the deposit agreement acknowledge that the Direct Registration System, or DRS, and Profile Modification System, or Profile, will apply to the ADSs. DRS is a system administered by DTC that facilitates interchange between registered holding of uncertificated ADSs and holding of security entitlements in ADSs through DTC and a DTC participant. Profile is a feature of DRS that allows a DTC participant, claiming to act on behalf of a registered holder of uncertificated ADSs, to direct the depositary to register a transfer of those ADSs to DTC or its nominee and to deliver those ADSs to the DTC account of that DTC participant without receipt by the depositary of prior authorization from the ADS holder to register that transfer.
In connection with and in accordance with the arrangements and procedures relating to DRS/Profile, the parties to the deposit agreement understand that the depositary will not determine whether the DTC participant that is claiming to be acting on behalf of an ADS holder in requesting registration of transfer and delivery as described in the paragraph above has the actual authority to act on behalf of the ADS holder (notwithstanding any requirements under the Uniform Commercial Code). In the deposit agreement, the parties agree that the depositary’s reliance on and compliance with instructions received by the depositary through the DRS/Profile system and in accordance with the deposit agreement will not constitute negligence or bad faith on the part of the depositary.
Shareholder Communications; Inspection of Register of Holders of ADSs
The depositary will make available for your inspection at its office all communications that it receives from us as a holder of deposited securities that we make generally available to holders of deposited securities. The depositary will send you copies of those communications or otherwise make those communications available to you if we ask it to. You have a right to inspect the register of holders of ADSs, but not for the purpose of contacting those holders about a matter unrelated to our business or the ADSs.
The deposit agreement provides that, to the extent permitted by law, ADS holders waive the right to a jury trial of any claim they may have against us or the depositary arising out of or relating to our shares, the ADSs or the deposit agreement, including any claim under the U.S. federal securities laws. If we or the depositary opposed a jury trial demand based on the waiver, the court would determine whether the waiver was enforceable in the facts and circumstances of that case in accordance with applicable case law.
You will not by agreeing to the terms of the deposit agreement, be deemed to have waived our or the depositary’s compliance with U.S. federal securities laws or the rules and regulations promulgated thereunder.
Pre-Funded Warrants
The following summary of certain terms and provisions of Pre-Funded Warrants that are being offered hereby is not complete and is subject to, and qualified in its entirety by, the provisions of the Pre-Funded Warrants, the form of which is filed as an exhibit to the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part. Prospective investors should carefully review the terms and provisions of the form of Pre-Funded Warrant for a complete description of the terms and conditions of the Pre-Funded Warrants.
Duration and Exercise Price. Each Pre-Funded Warrant offered hereby will have an initial exercise price per share equal to $0.001. The Pre-Funded Warrants will be immediately exercisable and may be exercised at any time until the Pre-Funded Warrants are exercised in full. The exercise price and number of ADSs issuable upon exercise is subject to appropriate adjustment in the event of share dividends, share splits, reorganisations or similar events affecting our Ordinary Shares and the exercise price.
Exercisability. The Pre-Funded Warrants will be exercisable, at the option of each holder, in whole or in part, by delivering to us a duly executed exercise notice accompanied by payment in full for the number of ADSs purchased upon such exercise (except in the case of a cashless exercise as discussed below). A holder (together with its affiliates) may not exercise any portion of the Pre-Funded Warrant to the extent that the holder would own more than 9.99% of the outstanding Ordinary Shares immediately after exercise. No fractional shares of ADSs will be issued in connection with the exercise of a pre-funded warrant. In lieu of fractional ADSs, we will either pay the holder an amount in cash equal to the fractional amount multiplied by the exercise price or round up to the next whole ADS.
Cashless Exercise. If, at the time a holder exercises its Pre-Funded Warrants, a registration statement registering the issuance of the ADS underlying the Pre-Funded Warrants under the Securities Act is not then effective or available and an exemption from registration under the Securities Act is not available for the issuance of such shares, then in lieu of making the cash payment otherwise contemplated to be made to us upon such exercise in payment of the aggregate exercise price, the holder may elect instead to receive upon such exercise (either in whole or in part) the net number of Pre-Funded Warrants determined according to a formula set forth in the Pre-Funded Warrants.
Transferability. Subject to applicable laws, a Pre-Funded Warrant may be transferred at the option of the holder upon surrender of the Pre-Funded Warrant to us together with the appropriate instruments of transfer.
Exchange Listing. We do not intend to list the Pre-Funded Warrants on Nasdaq or any other national securities exchange or nationally recognized trading system. The ADSs issuable upon exercise of the Pre-Funded Warrants are currently listed on Nasdaq.
Right as a Shareholder. Except as otherwise provided in the Pre-Funded Warrants or by virtue of such holder’s ownership of ADSs, the holders of the Pre-Funded Warrants do not have the rights or privileges of holders of our Ordinary Shares, including any voting rights, until they exercise their Pre-Funded Warrants.
Fundamental Transaction. In the event of a fundamental transaction, as described in the Pre-Funded Warrants and generally including any reorganisation, recapitalisation or reclassification of our ADSs, the sale, transfer or other disposition of all or substantially all of our properties or assets, our consolidation or merger with or into another person, the acquisition of more than 50% of our outstanding ADSs, or any person or group becoming the beneficial owner of 50% of the voting power represented by our outstanding ADSs, the holders of the Pre-Funded Warrants will be entitled to receive upon exercise of the Pre-Funded Warrants the kind and amount of securities, cash or other property that the holders would have received had they exercised the Pre-Funded Warrants immediately prior to such fundamental transaction. In addition, upon a fundamental transaction, the holder will have the right to require us to repurchase its Pre-Funded Warrants at their fair value using the Black Scholes option pricing formula; provided, however, that we will pay such holder using the same type or form of consideration (and in the same proportion) that is being offered and paid to the holders of our common stock in connection with the fundamental transaction, whether that consideration be in the form of cash, stock or any combination thereof, or whether the holders of our ADSs are given the choice to receive from among alternative forms of consideration in connection with the fundamental transaction.
Warrants
The following summary of certain terms and provisions of Warrants that are being offered hereby is not complete and is subject to, and qualified in its entirety by, the provisions of the Warrants, the form of which is filed as an exhibit to the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part. Prospective investors should carefully review the terms and provisions of the form of Warrant for a complete description of the terms and conditions of the Warrants.
Duration and Exercise Price. Each Warrant offered hereby will have an initial exercise price per share equal to $ . The Warrants will be immediately exercisable and will have a term of five (5) years. The exercise price and number of ADSs issuable upon exercise is subject to appropriate adjustment in the event of share dividends, share splits, reorganisations or similar events affecting our Ordinary Shares and the exercise price.
Exercisability. The Warrants will be exercisable, at the option of each holder, in whole or in part, by delivering to us a duly executed exercise notice accompanied by payment in full for the number of ADSs purchased upon such exercise (except in the case of a cashless exercise as discussed below). A holder (together with its affiliates) may not exercise any portion of the Warrant to the extent that the holder would own more than 9.99% of the outstanding Ordinary Shares immediately after exercise. No fractional shares of ADSs will be issued in connection with the exercise of a Warrant. In lieu of fractional ADSs, we will either pay the holder an amount in cash equal to the fractional amount multiplied by the exercise price or round up to the next whole ADS.
Cashless Exercise. If, at the time a holder exercises its Warrants, a registration statement registering the issuance of the ADS underlying the Warrants under the Securities Act is not then effective or available and an exemption from registration under the Securities Act is not available for the issuance of such shares, then in lieu of making the cash payment otherwise contemplated to be made to us upon such exercise in payment of the aggregate exercise price, the holder may elect instead to receive upon such exercise (either in whole or in part) the net number of Warrants determined according to a formula set forth in the Warrants.
Transferability. Subject to applicable laws, a Warrant may be transferred at the option of the holder upon surrender of the Warrant to us together with the appropriate instruments of transfer.
Exchange Listing. We do not intend to list the Warrants on Nasdaq or any other national securities exchange or nationally recognized trading system. The ADSs issuable upon exercise of the Warrants are currently listed on Nasdaq.
Right as a Shareholder. Except as otherwise provided in the Warrants or by virtue of such holder’s ownership of ADSs, the holders of the Warrants do not have the rights or privileges of holders of our Ordinary Shares, including any voting rights, until they exercise their Warrants.
Fundamental Transaction. In the event of a fundamental transaction, as described in the Warrants and generally including any reorganisation, recapitalisation or reclassification of our ADSs, the sale, transfer or other disposition of all or substantially all of our properties or assets, our consolidation or merger with or into another person, the acquisition of more than 50% of our outstanding ADSs, or any person or group becoming the beneficial owner of 50% of the voting power represented by our outstanding ADSs, the holders of the Warrants will be entitled to receive upon exercise of the Warrants the kind and amount of securities, cash or other property that the holders would have received had they exercised the Warrants immediately prior to such fundamental transaction. In addition, upon a fundamental transaction, the holder will have the right to require us to repurchase its Warrants at their fair value using the Black Scholes option pricing formula; provided, however, that we will pay such holder using the same type or form of consideration (and in the same proportion) that is being offered and paid to the holders of our common stock in connection with the fundamental transaction, whether that consideration be in the form of cash, stock or any combination thereof, or whether the holders of our ADSs are given the choice to receive from among alternative forms of consideration in connection with the fundamental transaction.
SHARES ELIGIBLE FOR FUTURE SALE
ADSs representing our Ordinary Shares trade on the Nasdaq Capital Market. However, a liquid trading market for the ADSs may not be sustained after this offering. Sales of substantial amounts of the ADSs following this offering, or the perception that these sales could occur, could adversely affect prevailing market prices of the ADSs and could impair our future ability to obtain capital, especially through an offering of equity securities. Assuming no exercise of options outstanding following the offering, or exercise of the Pre-Funded Warrants, we will have an aggregate of ADSs outstanding upon completion of this offering. Of these shares, the ADSs underlying the Pre-Funded Warrants sold in this offering will be freely tradable without restriction or further registration under the Securities Act, assuming we maintain the effectiveness of the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part, unless purchased by “affiliates” (as that term is defined under Rule 144 of the Securities Act), who may sell only the volume of shares described below and whose sales would be subject to additional restrictions described below.
The remaining ADSs will be held by our existing shareholders. Because substantially all of these ADSs have been held for more than six months, they also will be freely tradable without restriction or further registration, except that shares held by affiliates must be sold only subject to the fulfillment of certain conditions, including manner of sale provisions, notice requirements, and a volume limitation that limits the number of shares that may be sold thereby, within any three-month period, and except for the lock-up restrictions described below.
In general, under Rule 144 under the Securities Act as in effect on the date hereof, a person who holds restricted ordinary shares or ADSs (assuming there are any restricted shares) and is not one of our affiliates at any time during the three months preceding a sale, and who has beneficially owned these restricted shares for at least six months, would be entitled to sell an unlimited number of our Ordinary Shares or ADSs, provided current public information about us is available. In addition, under Rule 144, a person who holds restricted shares in us and is not one of our affiliates at any time during the three months preceding a sale, and who has beneficially owned these restricted shares for at least one year, is entitled to sell an unlimited number of shares immediately upon the closing of this offering without regard to whether current public information about us is available. Our affiliates who have beneficially owned our Ordinary Shares or ADSs for at least six months are entitled to sell within any three month period a number of shares that does not exceed the greater of:
| | • | 1% of the number of Ordinary Shares or ADSs then outstanding; or |
| | • | the average weekly trading volume of our or ADSs on Nasdaq during the four calendar weeks preceding the filing of a notice on Form 144 with respect to the sale; provided that current public information about us is available and the affiliate complies with the manner of sale requirements imposed by Rule 144. |
Affiliates are also subject to additional restrictions on the manner of sales under Rule 144 and notice filing requirements.
Regulation S under the Securities Act provides that securities owned by any person may be sold without registration in the United States, provided that the sale is effected in an offshore transaction and no directed selling efforts are made in the United States (as these terms are defined in Regulation S), subject to certain other conditions. In general, this means that our Ordinary Shares may be sold in some manner outside the United States without requiring registration in the United States.
TAXATION AND GOVERNMENT PROGRAMS
The following is a general summary of certain material Israeli and U.S. federal income tax considerations. The discussion is not intended to be, nor should it be construed as, legal or tax advice to any particular shareholder or prospective shareholder. The discussion is based on laws and relevant interpretations thereof in effect as of the date hereof, all of which are subject to change or different interpretations, possibly with retroactive effect.
Israeli tax considerations and government program
The following is a summary of the current tax regime in the State of Israel, which applies to us and to persons who hold our Ordinary Shares or ADSs.
This summary does not discuss all the aspects of Israeli tax law that may be relevant to a particular investor in light of his or her personal investment circumstances or to some types of investors subject to special treatment under Israeli law. Examples of this kind of investor include traders in securities or persons who do not hold our Ordinary Shares or ADSs as a capital asset. Some parts of this discussion are based on a new tax legislation which has not been subject to judicial or administrative interpretation. The discussion should not be construed as legal or professional tax advice and does not cover all possible tax considerations.
HOLDERS AND POTENTIAL INVESTORS ARE URGED TO CONSULT THEIR OWN TAX ADVISORS AS TO THE ISRAELI OR OTHER TAX CONSEQUENCES OF THE PURCHASE, OWNERSHIP AND DISPOSITION OF OUR ORDINARY SHARES OR ADSs, INCLUDING, IN PARTICULAR, THE EFFECT OF ANY FOREIGN, STATE OR LOCAL TAXES.
General corporate tax structure in Israel
Israeli resident companies are generally subject to corporate tax on both ordinary income and capital gains, currently at the rate of 23% of a company’s taxable income. Capital gains derived by an Israeli resident company are subject to tax at the prevailing corporate tax rate. Under Israeli tax law, a corporation will be considered as an “Israeli resident” if it meets one of the following: (a) it was incorporated in Israel; or (b) the control and management of its business are operated from Israel.
Taxation of our shareholders
Capital gains
Capital gains tax is imposed on the disposal of capital assets by an Israeli resident, and on the disposal of capital assets by a non-resident of Israel if those assets (i) are located in Israel, (ii) are shares or a right to shares in an Israeli resident corporation, (iii) represent, directly or indirectly, rights to assets located in Israel, unless a tax treaty between Israel and the seller’s country of residence provides otherwise, or (iv) a right in a foreign resident corporation, which in its essence is the owner of a direct or indirect right to property located in Israel (with respect to the portion of the gain attributed to the property located in Israel). The Israeli tax Ordiance (“ITO”) distinguishes between “Real Gain” and “Inflationary Surplus.” Real Gain is the excess of the total capital gain over Inflationary Surplus. The Inflationary Surplus is a portion of the total capital gain which is equivalent to the increase of the relevant asset’s price that is attributable to the increase in the Israeli consumer price index or, in certain circumstances, a foreign currency exchange rate, between the date of purchase and the date of sale. Inflationary Surplus is not subject to tax in Israel under certain conditions.
Real Gain accrued by individuals on the sale of our ordinary shares or ADSs generally will be taxed at the rate of 25%. However, if the individual shareholder is a “Substantial Shareholder” (i.e., a person who holds, directly or indirectly, alone or together with another person who collaborates with such person on a permanent basis, 10% or more of one of the company’s means of control) at the time of sale or at any time during the preceding 12-month period , such gain will be taxed at the rate of 30%. In addition, capital gains generated by an individual claiming deduction of financing expenses in respect of such gain will be taxed at the rate of up to 30%. In addition, capital gains generated by an individual claiming deduction of interest and linkage differences expenses in respect of such gain will be taxed at the rate of 30%. Real Capital Gain derived by corporations will be generally subject to a corporate tax rate of 23% (in 2022).
Individual (that the income in his hands from the sale of the securities is in the form of income from a “business”) and corporate shareholders dealing in securities in Israel are taxed at the tax rates applicable to business income in 2022, a tax rate of 23% for corporations and a marginal tax rate of up to 47% for individuals. In addition, a 3% excess tax is levied on individuals whose total taxable income in Israel in 2022 exceeds NIS 663,240 (approximately $192,000). To the extent that the securities registered according to the shelf offer report are deleted from trading on the stock exchange, the tax rate to be deducted at source at the time of sale (after deletion) will be at a rate of thirty percent (30%), As long as no approval has been issued by the assessing officer instructing the rate of tax deduction at another source, including exemption from withholding tax.
Notwithstanding the foregoing, capital gain derived from the sale of our Ordinary Shares or ADSs by a shareholder who is a non-resident of Israel may be exempt from Israeli taxation, provided that the following conditions, among others, are met: (i) the Ordinary Shares or ADSs were purchased upon or after the listing of the securities on the stock exchange, (ii) the seller does not have a permanent establishment in Israel to which the derived capital gain is attributable, (iii) if the seller is a corporation, no more than 25% of its means of control are held, directly and indirectly, by shareholders who are Israeli residents, and (iv) if the seller is a corporation, there are no Israeli residents that are directly or indirectly entitled to 25% or more of the revenues or profits of the corporation. In addition, the sale of Ordinary Shares or ADSs may be exempt from Israeli capital gains tax under the provisions of an applicable tax treaty. For example, the United States-Israel Tax Treaty, or the Treaty, generally exempts U.S. residents from Israeli capital gains tax in connection with such sale, provided (i) the U.S. treaty resident did not own, directly or indirectly, 10% or more of the Israeli resident company’s voting power at any time within the 12-month period preceding such sale; (ii) the seller, if an individual, is present in Israel for less than 183 days during the taxable year; and (iii) the capital gain from the sale was not derived through a permanent establishment of the U.S. resident in Israel. However, under the United States-Israel Tax Treaty, a Treaty U.S. Resident may be permitted to claim a credit for the Israeli tax against the U.S. federal income tax imposed with respect to the sale, exchange or disposition of the shares, subject to the limitations under U.S. laws applicable to foreign tax credits. The United States-Israel Tax Treaty does not provide such credit against any U.S. state or local taxes.
Upon the sale of securities, the purchaser, the Israeli stockbroker or the Israeli financial institution through which the shares are held is obligated, subject to the above exemptions, to withhold tax from the real gain at the rate of 25% or 23% in respect of an individual or corporation, respectively.
Upon the sale of securities traded on a stock exchange, a detailed return, including a computation of the tax due, must be filed and an advance payment must be made on January 31 and July 31 of every tax year, in respect of sales of securities made within the previous six months by Israeli residents for whom tax has not already been deducted. However, if all tax due was withheld at source according to applicable provisions of the ITO and the regulations promulgated thereunder, there is no need to file a return and no advance payment must be paid. Capital gains are also reportable on the annual income tax return.
Regardless of whether non-Israeli shareholders may be liable for Israeli capital gains tax on the sale of our Ordinary Shares or ADSs, the payment of the consideration for such sale may be subject to withholding of Israeli tax at source and holders of our Ordinary Shares may be required to demonstrate that they are exempt from tax on their capital gains in order to avoid withholding at source at the time of sale. Specifically, the Israel Tax Authority may require shareholders who are not liable for Israeli capital gains tax on such a sale to sign declarations in forms specified by the Israel Tax Authority, provide documentation (including, for example, a certificate of residency) or obtain a specific exemption from the Israel Tax Authority confirming their status as non-Israeli residents (and, in the absence of such declarations or exemptions, the Israel Tax Authority may require the purchaser of the shares to withhold tax at source).
Dividends
A shareholder who is an Israeli resident individual generally will be subject to income tax at a rate of 25% on dividends we pay. However, a 30% tax rate will apply if the dividend recipient is a Substantial Shareholder, as defined above, at the time of distribution or at any time during the preceding 12 month period. If the recipient of the dividend is an Israeli resident corporation, such dividend generally will not be included in the company’s taxable income, provided that the source of the dividend is income that was derived or accrued within Israel.
Dividends distributed by an Israeli resident company to a non-resident of Israel (either individual or corporation) are generally subject to tax at the rate of 25% (30% if the dividend recipient is a Substantial Shareholder at the time of distribution or at any time during the preceding 12-month period). These rates may be reduced under the provisions of an applicable tax treaty. Under the Treaty, the following tax rates will apply in respect of dividends distributed by an Israeli resident company to a U.S. resident: (i) if, during that portion of the taxable year which precedes the payment of the dividend and during the whole of its prior taxable year (if any), the U.S. resident is a corporation that holds at least 10% of the outstanding voting shares of the Israeli corporation and not more than 25% of the gross income of the Israeli corporation for such prior taxable year (if any) consists of certain types of interest or dividends, the tax rate is 12.5%; (ii) if both the conditions mentioned in section (i) above are met and the dividend is paid from an Israeli resident company’s income that was entitled to a reduced tax rate appli
cable to a Benefited, Approved or Privileged Enterprise under the Encouragement Law the tax rate is 15%; and (iii) in all other cases, the tax rate is 25%. The reduced rates under the Treaty will not apply if the dividend income is attributable to a permanent establishment of the U.S. treaty resident in Israel. We are obligated to withhold tax upon the distribution of dividends.
A non-Israeli resident who receives dividends from which tax was withheld is generally exempt from the obligation to file tax returns in Israel with respect to such income, provided that (i) such income was not generated from business conducted in Israel by the taxpayer, (ii) the taxpayer has no other taxable sources of income in Israel with respect to which a tax return is required to be filed, and (iii) the taxpayer is not obligated to pay excess tax (as further explained below).
Subject to the provisions of an applicable tax treaty, individuals who are subject to income tax in Israel (whether any such individual is an Israeli resident or non-Israeli resident) are also subject to an additional tax at a rate of 3% on annual income (including, but not limited to, income derived from dividends, interest and capital gains) exceeding NIS 663,240 (approximately $192,000) for 2022, which amount is linked to the annual change in the Israeli CPI.
Foreign exchange regulations
Non-residents of Israel who hold our Ordinary Shares or ADSs are able to receive any dividends, and any amounts payable upon the dissolution, liquidation and winding up of our affairs, in non-Israeli currency at the prevailing rate of exchange. However, Israeli income tax is generally required to have been paid or withheld on these amounts. In addition, the statutory framework for the potential imposition of currency exchange control has not been eliminated, and these controls may be restored at any time by administrative action.
Estate and gift tax
Israeli law presently does not impose estate or gift taxes.
Certain Material United States Federal Income Tax Considerations
The following discussion describes certain material United States federal income tax considerations relating to the acquisition, ownership, and disposition of shares, ADSs, warrants, pre-funded warrants, which we collectively refer to as Securities, and the ADSs issued or issuable upon the exercise of the warrants and pre-funded warrants by a U.S. Holder (as defined below) that acquires our Securities in this offering and holds them as a capital asset. This discussion is based on the tax laws of the United States, including the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, Treasury regulations promulgated or proposed thereunder, and administrative and judicial interpretations thereof, all as in effect on the date hereof. These tax laws are subject to change, possibly with retroactive effect, and subject to differing interpretations that could affect the tax consequences described herein. In addition, this section is based in part upon the representations of the depositary and the assumption that each obligation in the deposit agreement and any related agreements will be performed in accordance with its terms. This discussion does not address the tax consequences to a U.S. Holder under the laws of any state, local or foreign taxing jurisdiction.
For purposes of this discussion, a “U.S. Holder” is a beneficial owner of our securities that, for United States federal income tax purposes, is:
| | • | an individual who is a citizen or resident of the United States; |
| | • | a domestic corporation (or other entity taxable as a corporation); |
| | • | an estate the income of which is subject to United States federal income taxation regardless of its source; or |
| | • | a trust if (1) a court within the United States is able to exercise primary supervision over the trust’s administration and one or more United States persons have the authority to control all substantial decisions of the trust or (2) a valid election under the Treasury regulations is in effect for the trust to be treated as a United States person. |
A “Non-U.S. Holder” is a beneficial owner of our Securities that is neither a U.S. Holder nor a partnership (or other entity or arrangement treated as a partnership for United States federal income tax purposes).
This discussion does not address all aspects of United States federal income taxation that may be applicable to U.S. Holders in light of their particular circumstances or status (including, for example, banks and other financial institutions, insurance companies, broker and dealers in securities or currencies, traders that have elected to mark securities to market, regulated investment companies, real estate investment trusts, partnerships or other pass-through entities, corporations that accumulate earnings to avoid U.S. federal income tax, tax-exempt organizations, pension plans, persons that hold our shares as part of a straddle, hedge or other integrated investment, persons subject to alternative minimum tax or whose “functional currency” is not the U.S. dollar, and persons that actually or constructively own ten percent or more (by vote or value) of our shares).
If a partnership (including any entity or arrangement treated as a partnership for United States federal income tax purposes) holds our securities, the tax treatment of a person treated as a partner in the partnership for United States federal income tax purposes generally will depend on the status of the partner and the activities of the partnership. Partnerships (and other entities or arrangements so treated for United States federal income tax purposes) and their partners should consult their own tax advisors.
In general, and taking into account the earlier assumptions, for United States federal income and Israeli tax purposes, a holder that holds ADRs evidencing ADSs will be treated as the owner of the shares represented by those ADRs. Exchanges of shares for ADRs, and ADRs for shares, generally will not be subject to United States federal income or to Israeli tax.
This discussion addresses only U.S. Holders and does not discuss any tax considerations other than United States federal income tax considerations. Prospective investors are urged to consult their own tax advisors regarding the United States federal, state, and local, and foreign tax consequences of the purchase, ownership, and disposition of our securities.
Tax Treatment of Pre-Funded Warrants
Although it is not entirely free from doubt, we believe a pre-funded warrant should be treated as an ADS for U.S. federal income tax purposes and a holder of pre-funded warrants should generally be taxed in the same manner as a holder of our ADSs, as described below (except as otherwise noted below). However, our characterization is not binding on the U.S. Internal Revenue Services, or IRS, and the IRS may treat the pre-funded warrants as warrants to acquire our ADSs. If so, the tax consequences, including the amount and character of your gain, with respect to an investment in our pre-funded warrants could change. Accordingly, each holder should consult his, her or its own tax advisor regarding the risks associated with the acquisition of pre-funded warrants pursuant to this offering (including potential alternative characterizations). The balance of this discussion generally assumes that the characterization described above is respected for U.S. federal income tax purposes unless otherwise noted.
Dividends
We do not expect to make any distribution with respect to our securities. However, if we make any such distribution, under the United States federal income tax laws, and subject to the PFIC rules discussed below, the gross amount of any dividend we pay out of our current or accumulated earnings and profits (as determined for United States federal income tax purposes) will be includible in income for a U.S. Holder and subject to United States federal income taxation. Dividends paid to a noncorporate U.S. Holder that constitute qualified dividend income will be taxable at a preferential tax rate applicable to long-term capital gains of, currently, 20 percent, provided that the U.S. Holder holds the securities for more than 60 days during the 121-day period beginning 60 days before the ex-dividend date and meets other holding period requirements. If we are treated as a PFIC, dividends paid to a U.S. Holder will not be treated as qualified dividend income. If we are not treated as a PFIC, dividends we pay with respect to the securities generally will be qualified dividend income, provided that the holding period requirements are satisfied by the U.S. Holder.
A U.S. Holder must include any Israeli tax withheld from the dividend payment in the gross amount of the dividend even though the holder does not in fact receive it. The dividend is taxable to the holder when the holder, in the case of shares, or the Depositary, in the case of ADSs, receives the dividend, actually or constructively. Because we are not a United States corporation, the dividend will not be eligible for the dividends-received deduction generally allowed to United States corporations in respect of dividends received from other United States corporations. The amount of the dividend distribution includible in a U.S. Holder’s income will be the U.S. dollar value of the NIS payments made, determined at the spot NIS/U.S. dollar rate on the date the dividend distribution is includible in income, regardless of whether the payment is in fact converted into U.S. dollars. Generally, any gain or loss resulting from currency exchange fluctuations during the period from the date the dividend payment is included in income to the date the payment is converted into U.S. dollars will be treated as ordinary income or loss and will not be eligible for the special tax rate applicable to qualified dividend income. The gain or loss generally will be income or loss from sources within the United States for foreign tax credit limitation purposes.
Dividends paid with respect to our securities will be treated as foreign source income, which may be relevant in calculating the holder’s foreign tax credit limitation. The limitation on foreign taxes eligible for credit is calculated separately with respect to specific classes of income. For this purpose, dividends that we distribute generally should constitute “passive category income,” or, in the case of certain U.S. Holders, “general category income.” A foreign tax credit for foreign taxes imposed on distributions may be denied if holders do not satisfy certain minimum holding period requirements. The rules relating to the determination of the foreign tax credit are complex, and you should consult your tax advisor to determine whether and to what extent you will be entitled to this credit.
To the extent a distribution with respect to our securities exceeds our current or accumulated earnings and profits, as determined under United States federal income tax principles, the distribution will be treated, first, as a tax-free return of the U.S. Holder’s investment, up to the holder’s adjusted tax basis in its securities, and, thereafter, as capital gain, which is subject to the tax treatment described below in “—Gain on sale, exchange or other taxable disposition.”
Subject to certain limitations, the Israeli tax withheld in accordance with the Treaty and paid over to Israel will be creditable or deductible against a U.S. Holder’s United States federal income tax liability.
Subject to the discussion below under “Information reporting and backup withholding,” if you are a Non-U.S. Holder, you generally will not be subject to United States federal income (or withholding) tax on dividends received by you on your securities, unless you conduct a trade or business in the United States and such income is effectively connected with that trade or business (or, if required by an applicable income tax treaty, the dividends are attributable to a permanent establishment or fixed base that such holder maintains in the United States).
Gain on sale, exchange or other taxable disposition
Subject to the PFIC rules described below under “—Passive foreign investment company considerations,” a U.S. Holder that sells, exchanges or otherwise disposes securities in a taxable disposition generally will recognize capital gain or loss for United States federal income tax purposes equal to the difference between the U.S. dollar value of the amount realized and the holder’s tax basis, determined in U.S. dollars, in the securities. Gain or loss recognized on such a sale, exchange or other disposition of securities generally will be long-term capital gain if the U.S. Holder’s holding period in the securities exceeds one year. Long-term capital gains of non-corporate U.S. Holders are generally taxed at preferential rates. The gain or loss generally will be income or loss from sources within the United States for foreign tax credit limitation purposes. A U.S. Holder’s ability to deduct capital losses is subject to limitations.
Subject to the discussion below under “Information reporting and backup withholding,” if you are a Non-U.S. Holder, you generally will not be subject to United States federal income or withholding tax on any gain realized on the sale or exchange of such securities unless:
| | • | such gain is effectively connected with your conduct of a trade or business in the United States (or, if required by an applicable income tax treaty, the gain is attributable to a permanent establishment or fixed base that such holder maintains in the United States); or |
| | • | you are an individual and have been present in the United States for 183 days or more in the taxable year of such sale or exchange and certain other conditions are met. |
For a cash basis taxpayer, units of foreign currency paid or received are translated into U.S. dollars at the spot rate on the settlement date of the purchase or sale. In that case, no foreign currency exchange gain or loss will result from currency fluctuations between the trade date and the settlement date of such a purchase or sale. An accrual basis taxpayer, however, may elect the same treatment required of cash basis taxpayers with respect to purchases and sales of our securities that are traded on an established securities market, provided the election is applied consistently from year to year. Such election may not be changed without the consent of the IRS. An accrual basis taxpayer who does not make such election may recognize exchange gain or loss based on currency fluctuations between the trade date and the settlement date. Any foreign currency gain or loss a U.S. Holder realizes will be U.S. source ordinary income or loss.
The determination of whether our securities are traded on an established securities market is not entirely clear under current U.S. federal income tax law. Please consult your tax advisor regarding the proper treatment of foreign currency gains or losses with respect to a sale or other disposition of our securities.
Passive foreign investment company considerations
If we were classified as a PFIC in any taxable year, a U.S. Holder would be subject to special rules with respect to distributions on and sales, exchanges and other dispositions of the securities. We will be treated as a PFIC for any taxable year in which at least 75 percent of our gross income is “passive income” or at least 50 percent of our gross assets during the taxable year, assuming we were not a controlled foreign corporation for the year being tested, based on the average of the fair market values of the assets determined at the end of each quarterly period, are assets that produce or are held for the production of passive income. Passive income for this purpose generally includes, among other things, dividends, interest, rents, royalties, gains from commodities and securities transactions, and gains from assets that produce passive income. However, rents and royalties received from unrelated parties in connection with the active conduct of a trade or business are not considered passive income for purposes of the PFIC test. In determining whether we are a PFIC, a pro rata portion of the income and assets of each corporation in which we own, directly or indirectly, at least a 25% interest (by value) is taken into account.
If we were classified as a PFIC, under Treasury Regulations, if a U.S. Holder has an option, warrant, or other right to acquire stock of a PFIC (such as the warrants being offered pursuant to this offering), such option, warrant or right is considered to be PFIC stock. Under rules described below, the holding period for the ADSs acquired upon exercise of warrants will begin on the date a U.S. Holder acquires the warrant. This will impact the availability of the QEF election and mark-to-market election with respect to the ADSs acquired upon exercise of the warrants. Thus, a U.S. Holder will have to account for ADSs acquired upon exercise of the pre-funded warrants or the warrants under the PFIC rules and the applicable elections differently.
Excess distribution rules
If we were a PFIC with respect to a U.S. Holder, then unless the holder makes one of the elections described below, a special tax regime would apply to the U.S. Holder with respect to (a) any “excess distribution” (generally, aggregate distributions in any year that are greater than 125% of the average annual distribution received by the holder in the shorter of the three preceding years or the holder’s holding period for the securities) and (b) any gain realized on the sale or other disposition of the securities. Under this regime, any excess distribution and realized gain will be treated as ordinary income and will be subject to tax as if (a) the excess distribution or gain had been realized ratably over the U.S. Holder’s holding period, (b) the amount deemed realized in each year had been subject to tax in each year of that holding period at the highest marginal rate for such year (other than income allocated to the current period or any taxable period before we became a PFIC, which would be subject to tax at the U.S. Holder’s regular ordinary income rate for the current year and would not be subject to the interest charge discussed below), and (c) the interest charge generally applicable to underpayments of tax had been imposed on the taxes deemed to have been payable in those years. In addition, dividend distributions would not qualify for the lower rates of taxation applicable to long-term capital gains discussed above under “Dividends”.
A U.S. Holder that holds the securities at any time during a taxable year in which we are classified as a PFIC generally will continue to treat such securities as securities in a PFIC, even if we no longer satisfy the income and asset tests described above, unless the U.S. Holder elects to recognize gain, which will be taxed under the excess distribution rules as if such securities had been sold on the last day of the last taxable year for which we were a PFIC.
Certain elections by a U.S. Holder would alleviate some of the adverse consequences of PFIC status and would result in an alternative treatment of the securities, as described below. However, we do not currently intend to provide the information necessary for U.S. Holders to make “QEF elections,” as described below, and the availability of a “mark-to-market election” with respect to the securities is a factual determination that will depend on the manner and quantity of trading of our securities, as described below.
QEF election
If we were a PFIC, the rules above would not apply to a U.S. Holder that makes an election to treat our shares, ADSs or pre-funded warrants as stock of a qualified electing fund. A U.S. Holder that makes a QEF election is required to include in income its pro rata share of our ordinary earnings and net capital gain as ordinary income and long-term capital gain, respectively, subject to a separate election to defer payment of taxes, which deferral is subject to an interest charge. A U.S. Holder makes a QEF election generally by attaching a completed IRS Form 8621 to a timely filed United States federal income tax return for the year beginning with which the QEF election is to be effective (taking into account any extensions). A QEF election can be revoked only with the consent of the IRS. In order for a U.S. Holder to make a valid QEF election, we must annually provide or make available to the holder certain information. We do not intend to provide to U.S. Holders the information required to make a valid QEF election and we currently make no undertaking to provide such information.
As discussed above, if we were classified as a PFIC, under Treasury Regulations, if a U.S. Holder has an option, warrant, or other right to acquire stock of a PFIC (such as the warrants being offered pursuant to this offering), such option, warrant or right is considered to be PFIC stock. However, a U.S. Holder of an option, warrant or right to acquire stock of a PFIC may not make a QEF election that will apply to the option, warrant or other right to acquire PFIC stock. In addition, under Treasury Regulations, if a U.S. Holder holds an option, warrant or other right to acquire stock of a PFIC, the holding period with respect to shares of stock of the PFIC acquired on exercise of such option, warrant or other right will include the period that the option, warrant or other right was held. Each U.S. Holder should consult its own tax advisor regarding the application of the PFIC rules to the warrants.
Mark-to-market election
If we were a PFIC, the rules above also would not apply to a U.S. Holder that makes a “mark-to-market” election with respect to the securities, but this election will be available with respect to the securities only if they meet certain minimum trading requirements to be considered “marketable stock” for purposes of the PFIC rules. Securities will be marketable stock if they are regularly traded on a national securities exchange that is registered with the SEC or on a non-U.S. exchange or market that meets certain requirements under the Treasury regulations. Securities generally will be considered regularly traded during any calendar year during which they are traded, other than in de minimis quantities, on at least 15 days during each calendar quarter. Any trades that have as their principal purpose meeting this requirement will be disregarded.
A U.S. Holder that makes a valid mark-to-market election for the first tax year in which the holder holds (or is deemed to hold) our securities and for which we are a PFIC will be required to include each year an amount equal to the excess, if any, of the fair market value of such securities the holder owns as of the close of the taxable year over the holder’s adjusted tax basis in such securities. The U.S. Holder will be entitled to a deduction for the excess, if any, of the holder’s adjusted tax basis in the securities over the fair market value of such securities as of the close of the taxable year, but only to the extent of any net mark-to-market gains with respect to such securities included by the U.S. Holder under the election for prior taxable years. The U.S. Holder’s basis in such securities will be adjusted to reflect the amounts included or deducted pursuant to the election. Amounts included in income pursuant to a mark-to-market election, as well as gain on the sale, exchange or other taxable disposition of such securities, will be treated as ordinary income. The deductible portion of any mark-to-market loss, as well as loss on a sale, exchange or other disposition of our securities to the extent that the amount of such loss does not exceed net mark-to-market gains previously included in income, will be treated as ordinary loss.
The mark-to-market election applies to the taxable year for which the election is made and all subsequent taxable years, unless the shares cease to be treated as marketable stock for purposes of the PFIC rules or the IRS consents to its revocation. The excess distribution rules described above generally will not apply to a U.S. Holder for tax years for which a mark-to-market election is in effect. However, if we were a PFIC for any year in which the U.S. Holder owns the securities but before a mark-to-market election is made, the interest charge rules described above would apply to any mark-to-market gain recognized in the year the election is made.
A mark-to-market election will be unavailable with respect to our warrants and is not expected to be available with respect to the pre-funded warrants, which are not likely to be treated as regularly traded on a qualified exchange.
PFIC reporting obligations
A U.S. Holder of PFIC shares must generally file an annual information return on IRS Form 8621 (Information Return by a Shareholder of a Passive Foreign Investment Company or Qualified Electing Fund) containing such information as the U.S. Treasury Department may require. The failure to file IRS Form 8621 could result in the imposition of penalties and the extension of the statute of limitations with respect to U.S. federal income tax.
U.S. Holders are urged to consult their tax advisors as to our status as a PFIC, and the tax consequences to them if we were a PFIC, including the reporting requirements and the desirability of making, and the availability of, a QEF election or a mark-to-market election with respect to the securities.
Medicare tax
Non-corporate U.S. Holders that are individuals, estates or trusts and whose income exceeds certain thresholds generally are subject to a 3.8% tax on all or a portion of their net investment income, which may include their gross dividend income and net gains from the disposition of securities. A United States person that is an individual, estate or trust is encouraged to consult its tax advisors regarding the applicability of this Medicare tax to its income and gains in respect of any investment in our securities.
Information reporting with respect to foreign financial assets
Individual U.S. Holders may be subject to certain reporting obligations on IRS Form 8938 (Statement of Specified Foreign Financial Asset) with respect to the securities for any taxable year during which the U.S. Holder’s aggregate value of these and certain other “specified foreign financial assets” exceed a threshold amount that varies with the filing status of the individual. This reporting obligation also applies to domestic entities formed or availed of to hold, directly or indirectly, specified foreign financial assets, including the securities. Significant penalties can apply if U.S. Holders are required to make this disclosure and fail to do so.
Information reporting and backup withholding
In general, information reporting, on IRS Form 1099, will apply to dividends in respect of shares or ADSs and the proceeds from the sale, exchange or redemption of securities that are paid to a holder within the United States (and in certain cases, outside the United States), unless such holder is an exempt recipient such as a corporation. Backup withholding (currently at a 24% rate) may apply to such payments if a holder fails to provide a taxpayer identification number (generally on an IRS Form W-9) or certification of other exempt status or fails to report in full dividend and interest income.
Backup withholding is not an additional tax. A U.S. Holder generally may obtain a refund of any amounts withheld under the backup withholding rules that exceed the U.S. Holder’s income tax liability by filing a refund claim with the IRS.
A.G.P/Global Alliance Partners., or A.G.P., is acting as the sole book-running manager and Maxim Group LLC, or Maxim, is acting as the sole book-running managerslead manager of this offering. Under the terms of an underwriting agreement, which is filed as an exhibit to the registration statement, of which this prospectus forms a part, the underwriters have agreed to purchase from us the number of ADSs and Pre-Funded Warrants shown opposite its name below:
| Name of Underwriter | | Number of
ADSs and Warrants | | | Number of Pre-Funded Warrants and Warrants | |
| A.G.P./Alliance Global Partners | | |
| | | |
| |
| Maxim Group LLC | | |
| | | | | |
The underwriters are committed to purchase all the Securities offered by this prospectus on a reasonable best-efforts basis. The Underwriters are offering the Securities, subject to prior sale, when, as and if issued to and accepted by them, subject to approval of legal matters by their counsel, and other conditions contained in the underwriting agreement, such as the receipt by the underwriters of officer’s certificates and legal opinions. The underwriting agreement provides that the underwriters’ obligation to purchase our Securities depends on the satisfaction or waiver of the conditions contained in the underwriting agreement including:
• the representations and warranties made by us to the underwriters are true;
• there is no material change in our business or the financial markets; and
• we deliver customary closing documents to the underwriters.
The underwriters reserve the right to withdraw, cancel or modify offers to the public and to reject orders in whole or in part.
Underwriting Commissions, Discounts and Expense Reimbursement
The following table shows the per Securities and total underwriting discounts and commissions we will pay to the underwriters in this offering. These amounts are shown assuming both no exercise and full exercise of the underwriters’ option to purchase additional securities.
| | | | | | Per Pre-Funded Warrant | | | Total without over-allotment option | | | Total with full over-allotment option | |
| Public offering price | | $ |
|
|
|
|
| | | $ |
| | | $ |
| |
Underwriting discounts and commissions to be paid by us (7.0%)(1) | | $ |
|
|
|
|
| | | $ |
| | | $ |
| |
| Non-accountable expense allowance ( %) | | |
|
|
|
|
| | | |
| | | |
| |
| Proceeds, before expenses, to us | | $ |
|
|
|
|
| | | $ |
| | | $ |
| |
| (1) | We have agreed to pay a non-accountable expense allowance to the underwriter up to an amount that shall not exceed $25,000, including, but not limited to, IPREO software related expenses, background check(s), tombstones, marketing related expenses; i.e. roadshow, travel, et al. and any other expenses incurred by the underwriter in connection with the offering. The total NAE allowance shall not exceed $25,000. |
We estimate that the total expenses of the offering payable by us, excluding underwriting discounts and commissions, will be approximately $ , including a % non-accountable expense allowance.
In addition to the underwriting discount, we have agreed to pay or reimburse the underwriters for reimbursement of certain expenses, including the reasonable fees of counsel of the underwriters and other expenses in an amount not to exceed $100,000. As additional compensation to A.G.P. and Maxim, upon consummation of this offering, we will issue to the underwriter or its designees warrants to purchase an aggregate number of ADSs equal to 2.5% of the number of Ordinary Shares issued in this offering, at an exercise price per share equal to 125.0% of the public offering price, or the Underwriter Warrants. The Underwriter Warrants and the underlying ADSs will not be sold, transferred, assigned, pledged, or hypothecated, or be the subject of any hedging, short sale, derivative, put, or call transaction that would result in the effective economic disposition of the Underwriter Warrants by any person for a period of 180 days beginning on the date of commencement of sales of the offering in compliance with FINRA Rule 5110.
The Underwriter Warrants will be exercisable from the date that is six months from the commencement of the sales of the offering, and will expire five years after such date in compliance with FINRA Rule 5110(g)(8)(A). Furthermore, such Underwriter’s Warrants shall be exercisable on a cash basis, provided that if a registration statement registering the Ordinary Shares underlying the Underwriter’s Warrants is not effective, the Underwriter’s Warrants may be exercised on a cashless basis and have anti-dilution terms that are consistent with FINRA Rule 5110(g)(8)(E) and (F).
Over-Allotment Option
We have granted to the underwriters an option to purchase up to additional ADSs and/or Warrants ( of the Securities sold in the offering) at the public offering price less underwriting discounts and commissions. The underwriters may exercise this option in whole or in part at any time within forty-five (45) days after the date of the offering. We will be obligated, pursuant to the option, to sell these additional Securities to the underwriters to the extent the option is exercised. If any additional Securities are purchased, the underwriters will offer the additional Securities on the same terms as those on which the other Securities are being offered hereunder.
Lock-Up Agreements
The directors, executive officers, employees and shareholders holding at least five percent (5%) of the Company’s outstanding Ordinary Shares will enter into customary “lock-up” agreements in favor of the underwriter for a period of ninety (90) days from the closing date of this offering; provided, however, that any sales by parties to the lock-ups shall be subject to the lock-up agreements and provided further, that none of such shares shall be saleable in the public market until the expiration of the ninety (90) day period described above, subject to customary exceptions.
In addition, we have agreed with the underwriter that for a 90-day “lock-up” period, commencing from the date of this prospectus, subject to specified exceptions, without the prior written consent of the underwriter, we will not offer, sell, pledge or otherwise dispose of these securities without the prior written consent of the underwriter.
Indemnification
We have agreed to indemnify the underwriter against certain liabilities, including liabilities under the Securities Act and liabilities arising from breaches of representations and warranties contained in the underwriting agreement, or to contribute to payments that the underwriter may be required to make in respect of those liabilities.
Price Stabilization, Short Positions and Penalty Bids
The underwriter has advised us that it does not intend to conduct any stabilization or over-allotment activities in connection with this offering.
Passive Market Making
In connection with this offering, the underwriter and any selling group members may engage in passive market making transactions in our common stock on Nasdaq in accordance with Rule 103 of Regulation M under the Exchange Act, as amended, during a period before the commencement of offers or sales of common stock and extending through the completion of the distribution. A passive market maker must display its bid at a price not in excess of the highest independent bid of that security.
However, if all independent bids are lowered below the passive market maker’s bid that bid must then be lowered when specified purchase limits are exceeded.
Electronic Distribution
This prospectus in electronic format may be made available on websites or through other online services maintained by the underwriter, or by its affiliates. Other than this prospectus in electronic format, the information on the underwriter’s website and any information contained in any other website maintained by the underwriter is not part of this prospectus or the registration statement of which this prospectus forms a part, has not been approved and/or endorsed by us or the underwriter in its capacity as underwriter, and should not be relied upon by investors.
Other
From time to time, the underwriter and/or its affiliates have provided, and may in the future provide, various investment banking and other financial services for us for which services they have received and, may in the future receive, customary fees. In the course of their businesses, the underwriter and its affiliates may actively trade our securities or loans for its own account or for the accounts of customers, and, accordingly, the underwriter and its affiliates may at any time hold long or short positions in such securities or loans. Except for services provided in connection with this offering, the underwriter has not provided any investment banking or other financial services to us during the 180-day period preceding the date of this prospectus, and we do not expect to retain the underwriter to perform any investment banking or other financial services for at least 90 days after the date of this prospectus.
Selling Restrictions
This prospectus does not constitute an offer to sell to, or a solicitation of an offer to buy from, anyone in any country or jurisdiction (i) in which such an offer or solicitation is not authorized, (ii) in which any person making such offer or solicitation is not qualified to do so or (iii) in which any such offer or solicitation would otherwise be unlawful. No action has been taken that would, or is intended to, permit a public offer of the securities or possession or distribution of this prospectus or any other offering or publicity material relating to the securities in any country or jurisdiction (other than the United States) where any such action for that purpose is required. Accordingly, the underwriter has undertaken that it will not, directly or indirectly, offer or sell any securities or have in its possession, distribute or publish any prospectus, form of application, advertisement or other document or information in any country or jurisdiction except under circumstances that will, to the best of its knowledge and belief, result in compliance with any applicable laws and regulations and all offers and sales of securities by it will be made on the same terms.
Israel
The Ordinary Shares offered by this prospectus have not been approved or disapproved by the Israel Securities Authority, or the ISA, nor have such Ordinary Shares been registered for sale in Israel. The Ordinary Shares offered by this prospectus may not be offered or sold to the public in Israel absent the publication of a prospectus that has been approved by the ISA. This document does not constitute a prospectus under the Israeli Securities Law and has not been filed with or approved by the ISA.
In the State of Israel, this document may be distributed only to, and may be directed only at, and any offer of the Ordinary Shares hereunder may be directed only at, (i) to the extent applicable, a limited number of persons in accordance with the Israeli Securities Law and (ii) investors listed in the first addendum to the Israeli Securities Law (the “Addendum”) consisting primarily of joint investment in trust funds, provident funds, insurance companies, banks, portfolio managers, investment advisors, members of the Tel Aviv Stock Exchange Ltd., underwriters, venture capital funds, entities with equity in excess of NIS 50 million and “qualified individuals,” each as defined in the Addendum (as it may be amended from time to time), collectively referred to as qualified investors (in each case purchasing for their own account or, where permitted under the Addendum, for the accounts of their clients who are investors listed in the Addendum). Qualified investors will be required to submit written confirmation that they fall within the scope of the Addendum, are aware of the meaning of same and agree to it.
European Economic Area
In relation to each Member State of the European Economic Area which has implemented the Prospectus Directive (each, a “Relevant Member State”) an offer to the public of any securities may not be made in that Relevant Member State, except that an offer to the public in that Relevant Member State of any securities may be made at any time under the following exemptions under the Prospectus Directive, if they have been implemented in that Relevant Member State:
| | • | to legal entities which are qualified investors as defined under the Prospectus Directive; |
| | • | by the underwriter to fewer than 150, natural or legal persons (other than qualified investors as defined in the Prospectus Directive), as permitted under the Prospectus Directive, subject to obtaining the prior consent of the representatives of the underwriter for any such offer; or |
| | • | in any other circumstances falling within Article 3(2) of the Prospectus Directive, provided that no such offer of our common stock shall result in a requirement for us or any underwriter to publish a prospectus pursuant to Article 3 of the Prospectus Directive. |
For the purposes of this provision, (1) the expression an “offer of common stock to the public” in relation to any common stock in any Relevant Member State means the communication in any form and by any means of sufficient information on the terms of the offer and any securities to be offered so as to enable an investor to decide to purchase or subscribe for the common stock, as the same may be varied in that Relevant Member State by any measure implementing the Prospectus Directive in that Relevant Member State, (2) the expression “Prospectus Directive” means Directive 2003/71/EC (and amendments thereto, including the 2010 PD Amending Directive), and includes any relevant implementing measure in each Relevant Member State and (3) the expression “2010 PD Amending Directive” means Directive 2010/73/EU.
United Kingdom
This prospectus has only been communicated or caused to have been communicated and will only be communicated or caused to be communicated as an invitation or inducement to engage in investment activity (within the meaning of Section 21 of the Financial Services and Markets Act of 2000 (the “FSMA”)) as received in connection with the issue or sale of the common stock in circumstances in which Section 21(1) of the FSMA does not apply to us. All applicable provisions of the FSMA will be complied with in respect to anything done in relation to the common stock in, from or otherwise involving the United Kingdom.
Canada
The securities may be sold only to purchasers purchasing, or deemed to be purchasing, as principal that are accredited investors, as defined in National Instrument 45-106 Prospectus Exemptions or subsection 73.3(1) of the Securities Act (Ontario), and are permitted clients, as defined in National Instrument 31-103 Registration Requirements, Exemptions and Ongoing Registrant Obligations. Any resale of the securities must be made in accordance with an exemption from, or in a transaction not subject to, the prospectus requirements of applicable securities laws.
Securities legislation in certain provinces or territories of Canada may provide a purchaser with remedies for rescission or damages if this prospectus (including any amendment thereto) contains a misrepresentation, provided that the remedies for rescission or damages are exercised by the purchaser within the time limit prescribed by the securities legislation of the purchaser’s province or territory. The purchaser should refer to any applicable provisions of the securities legislation of the purchaser’s province or territory for particulars of these rights or consult with a legal advisor.
Pursuant to section 3A.3 of National Instrument 33-105 Underwriting Conflicts (NI 33-105), the underwriter is not required to comply with the disclosure requirements of NI 33-105 regarding underwriter conflicts of interest in connection with this offering.
Australia
No placement document, prospectus, product disclosure statement or other disclosure document has been lodged with the Australian Securities and Investments Commission in relation to the offering. This prospectus does not constitute a prospectus, product disclosure statement or other disclosure document under the Corporations Act 2001, or the Corporations Act, and does not purport to include the information required for a prospectus, product disclosure statement or other disclosure document under the Corporations Act.
Any offer in Australia of the securities may only be made to persons, or the Exempt Investors, who are “sophisticated investors” (within the meaning of section 708(8) of the Corporations Act), “professional investors” (within the meaning of section 708(11) of the Corporations Act) or otherwise pursuant to one or more exemptions contained in section 708 of the Corporations Act so that it is lawful to offer the securities without disclosure to investors under Chapter 6D of the Corporations Act.
The securities applied for by Exempt Investors in Australia must not be offered for sale in Australia in the period of 12 months after the date of allotment under the offering, except in circumstances where disclosure to investors under Chapter 6D of the Corporations Act would not be required pursuant to an exemption under section 708 of the Corporations Act or otherwise or where the offer is pursuant to a disclosure document which complies with Chapter 6D of the Corporations Act. Any person acquiring securities must observe such Australian on-sale restrictions.
This prospectus contains general information only and does not take account of the investment objectives, financial situation or needs of any particular person. It does not contain any securities recommendations or financial product advice. Before making an investment decision, investors need to consider whether the information in this prospectus is appropriate to their needs, objectives and circumstances and, if necessary, seek expert advice on those matters.
Switzerland
The securities may not be publicly offered in Switzerland and will not be listed on the SIX Swiss Exchange, or SIX, or on any other stock exchange or regulated trading facility in Switzerland. This document has been prepared without regard to the disclosure standards for issuance prospectuses under art. 652a or art. 1156 of the Swiss Code of Obligations or the disclosure standards for listing prospectuses under art. 27 ff. of the SIX Listing Rules or the listing rules of any other stock exchange or regulated trading facility in Switzerland. Neither this document nor any other offering or marketing material relating to the securities or the offering may be publicly distributed or otherwise made publicly available in Switzerland.
Neither this document nor any other offering or marketing material relating to the offering, or the securities have been or will be filed with or approved by any Swiss regulatory authority. This document will not be filed with, and the offer of securities will not be supervised by, the Swiss Financial Market Supervisory Authority FINMA, and the offer of securities has not been and will not be authorized under the Swiss Federal Act on Collective Investment Schemes, or CISA. The investor protection afforded to acquirers of interests in collective investment schemes under the CISA does not extend to acquirers of securities.
Dubai International Financial Centre
This prospectus relates to an Exempt Offer in accordance with the Offered Securities Rules of the Dubai Financial Services Authority, or DFSA. This prospectus is intended for distribution only to persons of a type specified in the Offered Securities Rules of the DFSA. It must not be delivered to, or relied on by, any other person. The DFSA has no responsibility for reviewing or verifying any documents relating to Exempt Offers. The DFSA has not approved this prospectus nor taken steps to verify the information set forth herein and has no responsibility for the prospectus. The securities to which this prospectus relates may be illiquid and/or subject to restrictions on their resale. Prospective purchasers of the securities offered should conduct their own due diligence on the securities. If you do not understand the contents of this prospectus, you should consult an authorized financial advisor.
Hong Kong
The securities have not been offered or sold and will not be offered or sold in Hong Kong, by means of any document, other than (a) to “professional investors” as defined in the Securities and Futures Ordinance (Cap. 571) of Hong Kong and any rules made under that Ordinance or (b) in other circumstances which do not result in the document being a “prospectus” as defined in the Companies Ordinance (Cap. 32) of Hong Kong or which do not constitute an offer to the public within the meaning of that Ordinance. No advertisement, invitation or document relating to the securities has been or may be issued or has been or may be in the possession of any person for the purposes of issue, whether in Hong Kong or elsewhere, which is directed at, or the contents of which are likely to be accessed or read by, the public of Hong Kong (except if permitted to do so under the securities laws of Hong Kong) other than with respect to securities which are or are intended to be disposed of only to persons outside Hong Kong or only to “professional investors” as defined in the Securities and Futures Ordinance and any rules made under that Ordinance.
Japan
The securities have not been and will not be registered under the Financial Instruments and Exchange Law of Japan (Law No. 25 of 1948, as amended) and, accordingly, will not be offered or sold, directly or indirectly, in Japan, or for the benefit of any Japanese Person or to others for re-offering or resale, directly or indirectly, in Japan or to any Japanese Person, except in compliance with all applicable laws, regulations and ministerial guidelines promulgated by relevant Japanese governmental or regulatory authorities in effect at the relevant time. For the purposes of this paragraph, “Japanese Person” shall mean any person resident in Japan, including any corporation or other entity organized under the laws of Japan.
EXPENSES RELATED TO OFFERING
The following table sets forth the costs and expenses, other than underwriting discounts and commissions, payable by us in connection with the offer and sale of ADSs in this offering. All amounts listed below are estimates except the SEC registration fee and the FINRA filing fee.
| Itemized expense | | Amount | |
| SEC registration fee | | $ | | |
| FINRA filing fee | | $ | | |
| Legal fees and expenses | | $ | | |
| Transfer agent and registrar fees | | $ | | |
| Accounting fees and expenses | | $ | | |
| Miscellaneous | | $ | | |
| Total | | $ | | |
The validity of the securities offered hereby and certain matters of Israeli law will be passed upon for us by Meitar | Law Offices, Ramat Gan, Israel. Certain matters of United States federal securities law relating to this offering will be passed upon for us by Greenberg Traurig, P.A. Certain legal matters of United States federal securities law related to the offering will be passed upon for the underwriters by Sullivan & Worcester LLP, New York. Certain matters of Israeli law related to the offering will be passed upon for the underwriters by .
The consolidated financial statements of Steakholder Foods Ltd. (formerly MeaTech 3D Ltd.) as of December 31, 2021 and 2020, and for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2021, have been included herein in reliance upon the report of Somekh Chaikin, a member firm of KPMG International, independent registered public accounting firm, appearing elsewhere herein, and upon the authority of said firm as experts in accounting and auditing.
The audit report covering the December 31, 2021 consolidated financial statements contains an explanatory paragraph that states that the Company’s recurring losses from operations together with other matters described in the notes to those consolidated financial statements raise substantial doubt about the entity’s ability to continue as a going concern. The consolidated financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of that uncertainty.
ENFORCEABILITY OF CIVIL
LIABILITIES
We are incorporated under the laws of the State of Israel. Service of process upon us and upon our directors and officers and the Israeli experts named in this prospectus, substantially all of whom reside outside the United States, may be difficult to obtain within the United States. Furthermore, because substantially all of our assets and substantially all of our directors and officers are located outside the United States, any judgment obtained in the United States against us or any of our directors and officers may not be collectible within the United States.
We have irrevocably appointed Steakholder Foods USA, Inc. as our agent to receive service of process in any action against us in any U.S. federal or state court arising out of this offering or any purchase or sale of Securities in connection with this offering. The address of our agent is 1007 North Orange Street, 10th Floor, Wilmington, Delaware, 19801, United States.
We have been informed by our legal counsel in Israel, Meitar | Law Offices, that it may be difficult to initiate an action with respect to U.S. securities law in original actions instituted in Israel or obtain a judgement based on the civil liability provisions of the U.S. federal securities laws. Israeli courts may refuse to hear a claim based on an alleged violation of U.S. securities laws reasoning that Israel is not the most appropriate forum to hear such a claim. In addition, even if an Israeli court agrees to hear a claim, it may determine that Israeli law and not U.S. law is applicable to the claim. If U.S. law is found to be applicable, the content of applicable U.S. law must be proved as a fact which can be a time-consuming and costly process. Certain matters of procedure may also be governed by Israeli law.
Moreover, an Israeli court will not enforce a non-Israeli judgment if (among other things) it was given in a state whose laws do not provide for the enforcement of judgments of Israeli courts (subject to exceptional cases), or if its enforcement is likely to prejudice the sovereignty or security of the State of Israel, or if it was obtained by fraud or in absence of due process, or if it is at variance with another valid judgment that was given in the same matter between the same parties, or if a suit in the same matter between the same parties was pending before a court or tribunal in Israel, at the time the foreign action was brought.
If a foreign judgment is enforced by an Israeli court, it generally will be payable in Israeli currency, which can then be converted into non-Israeli currency and transferred out of Israel. The usual practice in an action before an Israeli court to recover an amount in a non-Israeli currency is for the Israeli court to issue a judgment for the equivalent amount in Israeli currency at the rate of exchange in force on the date of the judgment, but the judgment debtor may make payment in foreign currency. Pending collection, the amount of the judgment of an Israeli court stated in Israeli currency ordinarily will be linked to the Israeli consumer price index plus interest at the annual statutory rate set by Israeli regulations prevailing at the time. Judgment creditors must bear the risk of unfavorable exchange rates.
WHERE YOU CAN FIND ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
We are subject to the reporting requirements of the Exchange Act that are applicable to a foreign private issuer. In accordance with the Exchange Act, we file reports, including annual reports on Form 20-F, with the SEC. We also furnish to the SEC under cover of Form 6-K material information required to be made public in Israel, filed with and made public by any stock exchange or distributed by us to our shareholders. As a foreign private issuer, we are exempt from the rules under the Exchange Act prescribing the furnishing and content of proxy statements to shareholders, and our officers, directors and principal shareholders are exempt from the “short-swing profits” reporting and liability provisions contained in Section 16 of the Exchange Act and related Exchange Act rules.
The registration statement on Form F-1 of which this prospectus forms a part, including the exhibits and schedules thereto, and reports and other information are filed by us with, or furnished to, the SEC. The SEC maintains an Internet site that contains reports, proxy and information statements, and other information regarding issuers, such as us, that file electronically with the SEC (http://www.sec.gov).

MeaTech 3D Ltd.
Index to Consolidated Financial Statements
| Financial Information of MeaTech 3D Ltd. | Page |
| | |
| F-2 |
| | |
Consolidated Financial Statements: | |
| F-3 |
| F-4 |
| F-5 |
| F-6 |
| F-7 |
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting
Firm
To the Shareholders and Board of Directors
MeaTech 3D Ltd.
Opinion on the Consolidated Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated statements of financial position of MeaTech 3D Ltd. (“the Company”) as of December 31, 2021 and 2020, the related consolidated statements of income and comprehensive loss, changes in equity, and cash flows for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2021, and the related notes (collectively, the consolidated financial statements). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2021 and 2020, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2021, in conformity with International Financial Reporting Standards, as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board.
Going Concern
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared assuming that the Company will continue as a going concern. As discussed in Note 1c to the consolidated financial statements, the Company has incurred recurring losses from operations that, together with other matters described in the aforesaid note, raise substantial doubt about its ability to continue as a going concern Management’s plans in regard to these matters are also described in Note 1c. The consolidated financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of this uncertainty
Basis for Opinion
These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Company's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these consolidated financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the consolidated financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. As part of our audits, we are required to obtain an understanding of internal control over financial reporting but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion. Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the consolidated financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the consolidated financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the consolidated financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
/s/ Somekh Chaikin
Somekh Chaikin
Member Firm of KPMG International
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2020.
Tel Aviv, Israel
March 24, 2022
MeaTech 3D Ltd.
Consolidated Statements of Financial
Position
| | | | | | December 31 | | | December 31 | |
| | | | | | 2021 | | | 2020 | |
| | | | | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | |
Current assets | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | | 4 | | | | 19,176 | | | | 13,556 | |
| Other investment | | | 6 | | | | 154 | | | | 149 | |
| Receivables and prepaid expenses | | | 5 | | | | 2,782 | | | | | |
| Total current assets | | | | | | | 22,112 | | | | 13,836 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Non-current assets | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Restricted deposits | | | | | | | 405 | | | | 51 | |
| Other investment | | | 6 | | | | 1,355 | | | | 2,513 | |
| Right-of-use asset | | | 19 | | | | 407 | | | | 168 | |
| Intangible assets | | | 16 | | | | 13,453 | | | | - | |
| Fixed assets, net | | | 7 | | | | 2,922 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total non-current assets | | | | | | | 18,542 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Assets | | | | | | | 40,654 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Current liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Trade payables | | | | | | | 382 | | | | 351 | |
| Other payables | | | 8 | | | | 2,239 | | | | 996 | |
| Current maturities of lease liabilities | | | 19 | | | | 165 | | | | 180 | |
| Derivative instrument | | | | | | | - | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total current liabilities | | | | | | | 2,786 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Non-current liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Long-term lease liabilities | | | 19 | | | | 246 | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total non-current liabilities | | | | | | | 246 | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Equity | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Share capital and premium on shares | | | | | | | 69,610 | | | | 30,481 | |
| Capital reserves | | | | | | | 3,708 | | | | 3,319 | |
| Currency translation differences reserve | | | | | | | 1,275 | | | | 780 | |
| Accumulated deficit | | | | | | | (36,971 | ) | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Equity | | | | | | | 37,622 | | | | | |
| Total liabilities and Equity | | | | | | | 40,654 | | | | | |
MeaTech 3D Ltd.
Consolidated Statements of Operations and of
Comprehensive Loss
| | | | | | Year ended December 31, | | | Year ended December 31, | | | Year ended December 31, | |
| | | | | | 2021 | | | 2020 | | | 2019 | |
| | | | | | USD thousands, except share data | | | USD thousands, except share data | | | USD thousands, except share data | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Research and development expenses | | | 11 | | | | 7,594 | | | | 2,491 | | | | 166 | |
| Marketing expenses | | | 12 | | | | 1,628 | | | | 506 | | | | - | |
| General and administrative expenses | | | 13 | | | | 8,010 | | | | 5,380 | | | | 256 | |
| Public listing expenses | | | | | | | - | | | | | | | | | |
| Operating loss | | | | | | | 17,232 | | | | 18,541 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Financing income | | | 14 | | | | 509 | | | | 110 | | | | - | |
| Financing expenses | | | 14 | | | | 1,299 | | | | 93 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loss for the year | | | | | | | 18,022 | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Capital reserve for financial assets at fair value that will not be transferred to profit or loss | | | | | | | - | | | | 334 | | | | - | |
| Currency translation differences loss (income) that will not be transferred to profit or loss over ILS | | | | | | | (1,942 | ) | | | (758 | ) | | | (22 | ) |
| Currency translation differences loss (income) that might be transferred to profit or loss over EUR | | | | | | | 1,447 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total comprehensive loss for the year | | | | | | | 17,527 | | | | 18,100 | | | | 401 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loss per ordinary share, no par value (USD) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Basic and diluted loss per share (USD) | | | | | | | 0.155 | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Weighted-average number of shares outstanding - basic and diluted (shares) | | | | | | | 115,954,501 | | | | 60,112,197 | | | | 19,484,478 | |
MeaTech 3D Ltd.
Consolidated Statements of Changes in
Equity
| | | Share capital and capital premium | | | Fair value of financial assets reserve | | | Transactions with related parties reserve | | | Currency translation differences reserve | | | Share-based payments reserve | | | Accumulated deficit | | | Total | |
| | | USD thousands | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance as at January 1, 2021 | | | 30,481 | | | | (334 | ) | | | 14 | | | | 780 | | | | 3,639 | | | | (18,949 | ) | | | 15,631 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Share-based payments | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 3,965 | | | | - | | | | 3,965 | |
| Issuance of shares and warrants, net | | | 32,330 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 32,330 | |
| Exercise of options | | | 6,799 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (3,576 | ) | | | | | | | 3,223 | |
| Other comprehensive income | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 495 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 495 | |
| Loss for the year | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (18,022 | ) | | | (18,022 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance as at December 31, 2021 | | | 69,610 | | | | (334 | ) | | | 14 | | | | 1,275 | | | | 4,028 | | | | (36,971 | ) | | | 37,622 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance as at January 1, 2020 | | | 1,880 | | | | - | | | | 14 | | | | 22 | | | | - | | | | (425 | ) | | | 1,491 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Share-Based Payment | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 3,958 | | | | - | | | | 3,958 | |
| Reverse acquisition | | | 11,439 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 11,439 | |
| Issuance of shares and warrants, net | | | 14,067 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 14,067 | |
| Exercise of options - Investors | | | 2,753 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 2,753 | |
| Exercise of options – Share-Based Payment | | | 342 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (319 | ) | | | | | | | 23 | |
| Other comprehensive income (loss) | | | - | | | | (334 | ) | | | - | | | | 758 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 424 | |
| Loss for the year | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (18,524 | ) | | | (18,524 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance as at December 31, 2020 | | | 30,481 | | | | (334 | ) | | | 14 | | | | 780 | | | | 3,639 | | | | (18,949 | ) | | | 15,631 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance as at January 1, 2019 | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (2 | ) | | | (2 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Issuance of shares and warrants, net | | | 1,880 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,880 | |
| Other comprehensive income | | | | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 22 | | | | - | | | | | | | | 22 | |
| Transaction with a related party | | | - | | | | - | | | | 14 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 14 | |
| Loss for the year | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (423 | ) | | | (423 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance as at December 31, 2019 | | | 1,880 | | | | - | | | | 14 | | | | 22 | | | | - | | | | (425 | ) | | | 1,491 | |
MeaTech 3D Ltd.
Consolidated Statements of Cash
Flows
| | | | | | Year ended December 31, | | | Year ended December 31, | | | Year ended December 31, | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | 2019 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash flows - operating activities | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Net Loss for the period | |
| | | | (18,022 | ) | | | (18,524 | ) | | | (423 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Adjustments: | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Depreciation and amortization | |
| | | | 680 | | | | 213 | | | | 21 | |
| Change in fair value of derivative | |
| | | | (316 | ) | | | (36 | ) | | | 14 | |
| Change in fair value of other investment | | | 6 | | | | (193 | ) | | | (74 | ) | | | - | |
| Changes in net foreign exchange expenses | | | | | | | 1,279 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Share-based payment expenses | | | | | | | 3,965 | | | | 3,958 | | | | - | |
| Public listing expenses | | | | | | | - | | | | 10,164 | | | | - | |
| Changes in asset and liability items: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Decrease (increase) in receivables | | | | | | | (2,351 | ) | | | 5 | | | | (36 | ) |
| Increase (decrease) in trade payables | | | | | | | (97 | ) | | | 126 | | | | 66 | |
| Increase in other payables | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net cash used in operating activities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash flows - investment activities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Acquisition of fixed assets | | | | | | | (1,828 | ) | | | (681 | ) | | | (126 | ) |
| Increase in restricted deposit | | | | | | | (337 | ) | | | (6 | ) | | | (41 | ) |
| Loan provided | | | | | | | (367 | ) | | | - | | | | (86 | ) |
| Acquisition of other investments, net of cash acquired | | | 16 | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net cash used in investing activities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash flows - financing activities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Proceeds from issuance of shares and warrants | | | | | | | 29,281 | | | | 14,887 | | | | 1,670 | |
| Issuance costs | | | | | | | (3,283 | ) | | | (819 | ) | | | (8 | ) |
| Repayment of liability for lease | | | | | | | (346 | ) | | | (140 | ) | | | (14 | ) |
| Proceeds on account of other investment | | | | | | | 149 | | | | 71 | | | | - | |
| Proceeds on account of capital issuance | | | | | | | - | | | | 222 | | | | - | |
| Proceeds with regard to derivative | | | | | | | - | | | | 348 | | | | - | |
| Proceeds from exercise of share options | | | | | | | 3,222 | | | | 2,776 | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net cash from financing activities | | | | | | | 29,023 | | | | 17,345 | | | | 1,648 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Increase in cash and cash equivalents | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Effect of exchange differences on cash and cash equivalents | | | | | | | (103 | ) | | | 644 | | | | 21 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at the beginning of the period | | | | | | | 13,556 | | | | 1,274 | | | | 31 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash balance and cash equivalents at end of period | | | | | | | 19,176 | | | | 13,556 | | | | 1,274 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Non cash activities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Purchase of fixed assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Issue of shares and options against intangible asset | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
MeaTech 3D Ltd.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS AT DECEMBER 31, 2021
Note 1 – General
MeaTech 3D Ltd. (formerly Ophectra Real Estate and Investments Ltd. and Meat-Tech 3D Ltd.) (the “Company”) was incorporated in Israel on July 22, 1992 as a private company limited by shares in accordance with the Companies Ordinance, 1983, and later a publicly-traded company whose ordinary shares were listed for trade on the Tel Aviv Stock Exchange (TASE). The Company’s official address is 5 David Fikes St., Rehovot , Israel.
The Company’s foodtech activities were commenced in July 2019 by a company called MeaTech Ltd., which merged with the Company in January 2020 and became a fully-owned subsidiary, now called MeaTech MT Ltd. As the Company was the surviving entity of the merger, and continued the pre-merger business operations, utilizing the pre-merger management and employees, of MeaTech Ltd., the transaction was treated as a reverse acquisition that does not constitute a business combination.
The Company is developing a suite of advanced high-throughput manufacturing technologies to produce cell-based alternative protein products for cultivated, sustainable meat production, and focused on developing premium, center-of-plate meat products, including development of high-throughput bioprinting systems.
| | B. | Material events in the reporting period |
| (1) | Acquisition of subsidiary |
In February 2021, the Company acquired Belgian cultured fat developer Peace of Meat BV. For further details, see Note 16 below.
| (2) | Initial public offering |
On March 12, 2021, the Company completed its Initial Public Offering on the Nasdaq of 2,721,271 ADSs, each representing ten ordinary shares of the Company (in total, 27,212,710 ordinary shares), at an offering price of USD 10.30 per ADS, resulting in gross proceeds of USD 28 million and net proceeds of USD 24.7 million. The ADSs trade on the Nasdaq Capital Market under the symbol “MITC.” On August 5, 2021, the Company completed the voluntary de-listing of its ordinary shares from the TASE. A number of ordinary shares remain traded over the counter (OTC:MTTCF). Additionally, the vesting of 1,374,998 investor share rights was triggered by the IPO, and these shares were issued in return for USD 1.25 million following the IPO.
| (3) | Effects of the spread of COVID-19 |
To date, the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the Company’s operations has been mainly limited to a temporary facility closure in the context of a government-mandated general lockdown, which temporary delayed certain development activities. The Company estimates that as of the date of approval of the financial statements, the COVID-19 pandemic is not expected to affect the Company's operations. However, the Company is unable to assess with certainty the extent of future impact, in part due to the uncertainty regarding the duration of the COVID-19 pandemic, its force and its effects on the markets in which the Company operates and the effects of possible government measures to prevent the spread of the virus.
MeaTech 3D Ltd.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS AT DECEMBER 31, 2021
Note 1 - General (cont.)
Since inception, the Company has incurred significant losses and negative cash flows from operations and has an accumulated deficit of USD 37.0 million. The Company has financed its operations mainly through fundraising from various investors.
The Company’s management expects that the Company will continue to generate losses and negative cash flows from operations for the foreseeable future. Based on the projected cash flows and cash balances as of December 31, 2021, management is of the opinion that its existing cash will be sufficient to fund operations until Q4 2022. As a result, there is substantial doubt about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern.
Management’s plans include the continue securing sufficient financing through the sale of additional equity securities or capital inflows from strategic partnerships. Additional funds may not be available when the Company needs them on terms that are acceptable to it, or at all. If the Company is unsuccessful securing sufficient financing, it may need to cease operations.
The financial statements include no adjustments for measurement or presentation of assets and liabilities, which may be required should the Company fail to operate as a going concern.
In these financial statements:
(1) The Company - MeaTech 3D Ltd.
(2) The Group – The Company and its subsidiaries, MeaTech MT Ltd., formerly known as MeaTech Ltd, Meatech Europe BV and Peace of Meat B.V. (hereafter “Peace Of Meat” OR “POM”)
(3) Related Party - as defined in IAS 24 (revised).
(4) USD - United States Dollar
(5) NIS – New Israeli Shekel
(6) EUR – Euro
(7) ADS – American Depositary Shares
MeaTech 3D Ltd.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS AT DECEMBER 31, 2021
Note 2 - Basis of Preparation of the Financial Statements
| | A. | Statement of compliance with IFRS
|
The financial statements have been prepared in accordance with International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) as issued by the International Accounting Standards Board.
The financial statements were authorized for issue by the company’s board of directors on March 24, 2022.
| | B. | Functional currency and presentation currency |
The NIS is the currency that represents the primary economic environment in which the Company and its Israeli subsidiary operate, and is therefore the functional currency of their operations. The Euro is the currency that represents the primary economic environment in which the Company’s European subsidiaries operate, and is therefore the functional currency of their operations. Nonetheless, for reporting purposes, the consolidated financial statements, which were prepared on the basis of the functional currencies, were translated into US Dollars, which the Company selected as its presentation currency, as its securities are traded on the Nasdaq Capital Markets, and in order to make the Company’s financial statements more accessible to U.S.-based investors.
Assets and liabilities were translated at the exchange rate of the end of the period; expenses and income were translated at the exchange rate at the time they were generated. Exchange rate differentials generated due to such translation are attributed to the Currency translation differences reserve.
| Currency | | USD - ILS | | | USD - EUR | |
| Period | | 2021 | | | 2020 | | | 2019 | | | 2021 | |
| December 31 | | | 3.110 | | | | 3.215 | | | | 3.446 | | | | 0.883 | |
| Year Average | | | 3.230 | | | | 3.479 | | | | 3.442 | | | | 0.845 | |
The financial statements have been prepared on the historical cost basis except for provisions.
For further information regarding the measurement of these liabilities, see Note 3 regarding significant accounting policies.
The Company’s operating cycle is one year.
| E. | Use of Estimates and Judgments |
Use of estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with IFRS requires the Company’s management to make judgments, estimates and assumptions that affect the application of accounting policies and the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, income and expenses. Actual results may differ from these estimates.
MeaTech 3D Ltd.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS AT DECEMBER 31, 2021
Note 2 – Basis of Preparation of the Financial Statements (cont.)
| E. | Use of Estimates and Judgments (cont.)
|
The preparation of accounting estimates used in the preparation of the Company’s financial statements requires that the Company’s management makes assumptions regarding circumstances and events that involve considerable uncertainty. The Company’s management prepares the estimates on the basis of past experience, various facts, external circumstances, and reasonable assumptions according to the pertinent circumstances of each estimate. Estimates and underlying assumptions are reviewed on an ongoing basis. Revisions to accounting estimates are recognized in the period in which the estimates are revised and in any future periods affected.
Further information about the assumptions that were used to determine fair value is included in the following notes:
| | • | Note 6, on other investments; |
| | • | Note 10, on share-based payments; |
| | • | Note 16, on intangible assets; |
Determination of fair value
Preparation of the financial statements requires the Company to determine the fair value of certain assets and liabilities.
When determining the fair value of an asset or liability, the Company uses observable market data as much as possible. There are three levels of fair value measurements in the fair value hierarchy that are based on the data used in the measurement, as follows:
• Level 1: quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical assets or liabilities.
• Level 2: inputs other than quoted prices included within Level 1 that are observable, either directly or indirectly
• Level 3: inputs that are not based on observable market data (unobservable inputs).
MeaTech 3D Ltd.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS AT DECEMBER 31, 2021
Note 3 – Significant Accounting Policies
| (1) | Non-derivative financial assets |
Initial recognition and measurement of financial assets
The Company initially recognizes trade receivables and debt instruments issued on the date that they are created. All other financial assets are recognized initially on the trade date at which the Company becomes a party to the contractual provisions of the instrument. A financial asset is initially measured at fair value plus transaction costs that are directly attributable to the acquisition or issuance of the financial asset. A trade receivable without a significant financing component is initially measured at the transaction price. Receivables originating from contract assets are initially measured at the carrying amount of the contract assets on the date classification was changed from contract asset to receivables.
Derecognition of financial assets
Financial assets are derecognized when the contractual rights of the Company to the cash flows from the asset expire, or the Company transfers the rights to receive the contractual cash flows on the financial asset in a transaction in which substantially all the risks and rewards of ownership of the financial asset were transferred. When the Company retains substantially all of the risks and rewards of ownership of the financial asset, it continues to recognize the financial asset.
Classification of financial assets into categories and the accounting treatment of each category
Financial assets are classified at initial recognition to one of the following measurement categories: amortized cost; fair value through other comprehensive income – investments in debt instruments; fair value through other comprehensive income – investments in equity instruments; or fair value through profit or loss.
A financial asset is measured at amortized cost if it meets both of the following conditions and is not designated at fair value through profit or loss:
| - | It is held within a business model whose objective is to hold assets so as to collect contractual cash flows; and |
| - | The contractual terms of the financial asset give rise to cash flows representing solely payments of principal and interest on the principal amount outstanding on specified dates. |
| (2) | Non-derivative financial liabilities |
Non-derivative financial liabilities include finance lease liabilities, trade and other payables.
Initial recognition of financial liabilities
The Company initially recognizes financial liabilities on the trade date at which the Company becomes a party to the contractual provisions of the instrument.
Subsequent measurement of financial liabilities
Financial liabilities (other than financial liabilities at fair value through profit or loss) are recognized initially at fair value less any directly attributable transaction costs. Subsequent to initial recognition these financial liabilities are measured at amortized cost using the effective interest method.
Derecognition of financial liabilities
Financial liabilities are derecognized when the obligation of the Company, as specified in the agreement, expires or when it is discharged or cancelled.
MeaTech 3D Ltd.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS AT DECEMBER 31, 2021
Note 3 – Significant Accounting Policies (cont.)
Financial Instruments (cont.)
(3) Share capital
Ordinary shares are classified as equity. Incremental costs directly attributable to the issue of ordinary shares and share options are recognized as a deduction from equity, net of any tax effects.
(4) Issuance of securities
The consideration received from the issuance of securities is attributed initially to financial liabilities that are measured each period at fair value through profit or loss, and then to financial liabilities that are measured only upon initial recognition at fair value. The remaining amount is the value of the equity component.
Direct issuance costs are attributed to the specific securities in respect of which they were incurred, whereas joint issuance costs are attributed to the securities on a proportionate basis according to the allocation of the consideration from the issuance of the securities.
Non-financial assets
Timing of impairment testing
The carrying amounts of the Company’s non-financial assets are reviewed at each reporting date to determine whether there is any indication of impairment. If any such indication exists, then the asset’s recoverable amount is estimated.
Once a year and on the same date, or more frequently if there are indications of impairment, the Group estimates the recoverable amount of each cash generating unit that contains goodwill, or intangible assets that have indefinite useful lives or are unavailable for use.
Measurement of recoverable amount
The recoverable amount of an asset is the greater of its value in use and its fair value less costs of disposal. In assessing value in use, the estimated future cash flows are discounted to their present value using a pre-tax discount rate that reflects the assessments of market participants regarding the time value of money and the risks specific to the asset, for which the estimated future cash flows from the asset were not adjusted.
Recognition of impairment loss
An impairment loss is recognized if the carrying amount of an asset or cash-generating unit exceeds its estimated recoverable amount. Impairment losses are recognized in profit or loss.
Non-derivative financial assets
See note 6.
| | C. | Financing income and expenses |
Financing income derives from changes in fair value of financial instruments mandatorily measured at fair value through profit or loss.
Financing expenses comprise mainly from bank fee expenses and lease liabilities interest expenses, which are recognized in profit or loss.
MeaTech 3D Ltd.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS AT DECEMBER 31, 2021
Note 3 – Significant Accounting Policies (cont.)
The Company presents basic and diluted earnings or loss per share data for its ordinary shares. Basic earnings or loss per share is calculated by dividing the earnings or loss attributable to ordinary shareholders of the Company by the weighted-average number of ordinary shares outstanding during the year. Diluted earnings or loss per share is determined by adjusting the profit or loss attributable to ordinary shareholders of the Company and the weighted average-number of ordinary shares outstanding, for the effects of all dilutive potential ordinary shares, which comprise share options.
Research and development
Expenditure on research activities, undertaken with the prospect of gaining new scientific or technical knowledge and understanding, is recognized in profit or loss when incurred.
Development activities involve a plan or design for the production of new or substantially improved products and processes. Development expenditure is capitalized only if development costs can be measured reliably, the product or process is technically and commercially feasible, future economic benefits are probable, and the Company has the intention and sufficient resources to complete development and to use or sell the asset. As the Company’s development activities do not meet the standards for capitalization, research and development expenditure is recognized through profit or loss.
Subsequent expenditure
Subsequent expenditure is capitalized only when it increases the future economic benefits embodied in the specific asset to which it relates. All other expenditure, including expenditure on internally generated goodwill and brands, is recognized in profit or loss as incurred.
Other intangible assets
Other intangible assets, that are acquired by the Company, are measured at cost less accumulated amortization and accumulated impairment losses. See Note 16.
A provision is recognized if, as a result of a past event, the Company has a present legal or constructive obligation that can be estimated reliably, and it is probable that an outflow of economic benefits will be required to settle the obligation.
| (1) | Recognition and measurement |
Fixed asset items are measured at cost less accumulated depreciation and accumulated impairment losses.
The cost of a fixed asset includes expenditures that are directly attributable to the acquisition of the asset.
Depreciation is a systematic allocation of the depreciable amount of an asset over its estimated useful life. The depreciable amount is the cost of the asset or other amount that replaces the cost, less its residual value.
MeaTech 3D Ltd.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS AT DECEMBER 31, 2021
Note 3 – Significant Accounting Policies (cont.)
An asset is depreciated from the date it is ready for use, namely, the date on which it reaches the location and condition required for it to operate in the manner intended by Management.
Depreciation is recognized in the statement of income on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful lives of each part of the fixed-asset item, since this most closely reflects the expected pattern of consumption of the future economic benefits embodied in the asset.
The estimated useful lives for the current and comparative periods are as follows:
| ● Computers | 3 years |
| ● Leasehold improvements | 2 years |
| ● Laboratory equipment | 5-7 years |
| ● Machinery and Equipment | 6-10 years |
| ● Office furniture, equipment and accessories | 14 years |
Depreciation methods, useful lives and residual values are reviewed at the end of each reporting year and adjusted if appropriate.
Determining whether an arrangement contains a lease
On the inception date of the lease, the Company determines whether the arrangement is a lease or contains a lease, while examining if it conveys the right to control the use of an identified asset for a period of time in exchange for consideration. In its assessment of whether an arrangement conveys the right to control the use of an identified asset, the Company assesses whether it has the following two rights throughout the lease term:
(a) The right to obtain substantially all the economic benefits from use of the identified asset; and
(b) The right to direct the identified asset’s use.
For lease contracts that contain non-lease components, such as services or maintenance, that are related to a lease component, the company elected to account for the contract as a single lease component without separating the components.
Leased assets and lease liabilities
Contracts that award the Company control over the use of a leased asset for a period of time in exchange for consideration, are accounted for as leases. Upon initial recognition, the Company recognizes a liability at the present value of the balance of future lease payments (these payments do not include certain variable lease payments), and concurrently recognizes a right-of-use asset at the same amount of the lease liability, adjusted for any prepaid or accrued lease payments.
Since the interest rate implicit in the Company's leases is not readily determinable, the incremental borrowing rate of the lessee is used. Subsequent to initial recognition, the right-of-use asset is accounted for using the cost model and depreciated over the shorter of the lease term or useful life of the asset.
MeaTech 3D Ltd.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS AT DECEMBER 31, 2021
Note 3 – Significant Accounting Policies (cont.)
The lease term
The lease term is the non-cancellable period of the lease plus periods covered by an extension or termination option if it is reasonably certain that the lessee will or will not exercise the option, respectively.
Depreciation of right-of-use asset
After lease commencement, a right-of-use asset is measured on a cost basis less accumulated depreciation and accumulated impairment losses and is adjusted for re-measurements of the lease liability. Depreciation is calculated on a straight-line basis over the shorter of the useful life or contractual lease period. The Company’s lease of its office and laboratory space is depreciated over a period of two years.
| (1) | Post-employment benefits |
The Company has a post-employment benefit plan, financed by deposits with insurance companies or with funds managed by a trustee, and classified as a defined contribution plan, under which an entity pays fixed contributions into a separate entity and has no legal or constructive obligation to pay further amounts. Obligations for contributions to defined contribution pension plans are recognized as an expense in profit or loss in the periods during which related services are rendered by employees.
Short-term employee benefit obligations are measured on an undiscounted basis and are expensed as the related service is provided or upon the actual absence of the employee when the benefit is not accumulated.
A liability is recognized for the amount expected to be paid under short-term cash bonus if the Company has a present legal or constructive obligation to pay this amount as a result of past service provided by the employee and the obligation can be estimated reliably.
The employee benefits are classified, for measurement purposes, as short-term benefits or as other long-term benefits depending on when the Company expects the benefits to be wholly settled.
| | J. | Share-based compensation |
Share-based compensation expense related to share awards is recognized based on the fair value of the awards granted. The fair value of each option award is estimated on the grant date using the binomial option pricing model. The option pricing model requires the input of highly subjective assumptions, including the expected term of the option, the expected volatility of the price of the Company’s ordinary shares and the expected dividend yield of ordinary shares. The assumptions used to determine the fair value of the option awards represent management’s best estimates. These estimates involve inherent uncertainties and the application of management’s judgment. The Company recognizes compensation costs for awards conditioned only on continued service that have a graded vesting schedule using the accelerated method based on the multiple-option award approach. Forfeitures are accounted for as they occur.
MeaTech 3D Ltd.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS AT DECEMBER 31, 2021
Note 3 – Significant Accounting Policies (cont.)
Acquisition of a subsidiary
Upon the acquisition of a subsidiary, the Company exercises discretion when examining whether the transaction constitutes the acquisition of a business or acquisition of an asset, for the purpose of determining the accounting treatment of the transaction. Transactions in which the acquired company is not considered a business are accounted for as the acquisition of a group of assets and liabilities. In such transactions, the cost of acquisition, which includes transaction costs, is allocated proportionately to the acquired identifiable assets and liabilities, based on their proportionate fair value on the acquisition date. Furthermore, no goodwill is recognized and no deferred taxes are recognized in respect of the temporary differences existing on the acquisition date.
Consideration paid partly in the form of equity instruments, based on the quoted share price. Any additional consideration will be capitalized upon the achievement of defined milestones, which constitutes the variable consideration.
When the variable consideration depends on performance conditions, the Company has elected not to recognize the contingent consideration at the time of purchase, but rather if and when the contingent conditions occur and when the consideration is transferred or obliged to be transferred.
IFRS 3 includes a distinction between a transaction to acquire an operation is the acquisition of a "business" and the acquisition of a group of assets that according to the standard is not considered the acquisition of a "business". The aforementioned standard offers the optional concentration test so that if substantially all of the fair value of the acquired assets is attributable to a group of similar identifiable assets or to a single identifiable asset, this will not be the acquisition of a business
Transactions eliminated on consolidation
Intra-group balances and transactions, and any unrealized income and expenses arising from intra-group transactions, are eliminated in preparing the consolidated financial statements.
| | L. | Transactions with controlling shareholder |
Assets and liabilities included in a transaction with a controlling shareholder are measured at fair value on the date of the transaction. As the transaction is on the equity level, the Company includes the difference between the fair value and the consideration from the transaction in its equity.
Government grants are recognized initially at fair value when there is reasonable assurance that they will be received and the Group will comply with the conditions associated with the grant. Unconditional government grants are recognized when the Group is entitled to receive them. Grants that compensate the Group for expenses incurred are presented as a deduction from the corresponding expense. Grants that compensate the Group for the cost of an asset are presented as a deduction from the related assets and are recognized in profit or loss on a systematic basis over the useful life of the asset.
MeaTech 3D Ltd.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS AT DECEMBER 31, 2021
Note 4 – Cash and Cash Equivalents
| | | December 31 | | | December 31 | |
| | | 2021 | | | 2020 | |
| | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | |
| | | | | | | |
| Cash in USD | | | 15,596 | | | | 1,021 | |
| Cash in NIS | | | 1,688 | | | | 7,627 | |
| Cash in Euro | | | 1,892 | | | | | |
| Total cash and cash equivalents | | | 19,176 | | | | 13,556 | |
Note 5 – Receivables and Prepaid Expenses
| | | December 31 | | | December 31 | |
| | | 2021 | | | 2020 | |
| | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | |
| | | | | | | |
| Institutions | | | 301 | | | | 102 | |
| Prepaid expenses | | | 743 | | | | 20 | |
| Other | | | 1,738 | | | | | |
| | | | 2,782 | | | | 131 | |
Note 6 – Other Investments
| | | December 31 | | | December 31 | |
| | | 2021 | | | 2020 | |
| | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | |
| | | | | | | |
Separation Agreement from Therapin (A) (1) | | | 1,509 | | | | 1,414 | |
| Investment in Peace of Meat (B) | | | - | | | | | |
| Total Other Investments | | | 1,509 | | | | 2,662 | |
| Developments in Other Investment | | USD thousands | |
| | | | |
| As at January 1, 2021 | | | 2,662 | |
| Initial investment in POM transferred to intangible asset | | | (1,223 | ) |
| Proceeds from Therapin asset | | | (149 | ) |
| Profit from increase in fair value | | | 193 | |
| Effect of changes in exchange rates | | | 26 | |
As at December 31, 2021(1) | | | 1,509 | |
| (1) | USD 154 thousand are classified as a current asset. |
MeaTech 3D Ltd.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS AT DECEMBER 31, 2021
Note 6 – Other Investments (cont.)
| A. | Separation Agreement from Therapin |
On May 26, 2020, following the approval of the Company's Board of Directors, the Company engaged in a separation agreement with Therapin, in which the Company had held 14.74% of the issued and paid-up share capital. Pursuant to the separation agreement, the investment agreement under which the Company invested in Therapin an amount of USD 2.1 million (NIS 7.25 million) in return for allotment of shares and warrants of Therapin (the “Payment Amount”) was canceled, and replaced with a debt arrangement as follows:
| 1. | Therapin committed to pay to the Company an amount of USD 13 thousand (NIS 40 thousand) per month, thereafter as of August 1, 2020 over a period of 119 months (the “Payment Period”), for an aggregate total amount of USD 1.4 million (NIS 4.8 million). During the first two years from the date of the separation agreement, 50% of the payments from Therapin will be transferred to a restricted deposit and form an additional resource of the Merger settlement fund. After two years, the contents of the restricted deposit, will be released to the Company, subject to court approval. |
| | 2. | The rest of the Payment Amount will be paid to the Company if, during the Payment Period, Therapin or a subsidiary completes an exit event, including listing on a stock exchange pursuant to a merger or IPO, and the Company will be given the option to receive shares in such merged company/issue, or payment of the remaining balance in cash. |
| | 3. | During the Payment Period, if Therapin has not completed one of the transactions as set out in Section 2, then in the event that Therapin generates a distributable surplus, Therapin will pay the Company an amount equivalent to 14.74% of the surplus balance as repayment on account of the outstanding balance (but in any case no more than the outstanding balance). |
| | 4. | In the event that, during or subsequent to the end of the Payment Period, Therapin distributes a dividend to its shareholders, and on that date there is a remaining outstanding balance of the Payment Amount, Therapin will pay the Company an amount equivalent to 14.74% of the dividend distributed to shareholders as repayment on account of the outstanding balance (but in any case no more than the outstanding balance). |
| | 5. | As a result of the separation agreement, the Company is no longer a shareholder in Therapin, but rather a debtholder. |
The engagement in the separation agreement was decided in light of the Company’s change in direction to focus on the development of cultured meat technology, using three-dimensional printing.
The Company re-measured the asset using a fair value measurement at approximately USD 1.3 million (NIS 4.5 million). The fair value was assessed by capitalization of future cash flows (proceeds) at interest rates that reflect the level of risk (based on the duration of the debt) of these proceeds and were classified as Level 3 in the fair value hierarchy. The estimated capitalization interest was based on Therapin's financial statements, cash balances and liabilities, repayment dates, and analysis of the market in which Therapin operates. The expected additional payment event is 4.2 years, and the interest rate for capitalization of the debt is 10.23%-10.72%.
The revaluation was accounted for in other comprehensive income in the amount of USD 0.3 million (NIS 1.2 million). Any change in the fair value following the separation date, will be recognized through profit or loss.
During 2021, the Company received USD 149 thousand based on the agreement detailed above and recorded USD 193 thousand as re-valuation financing income in profit and loss.
| B. | Investment in Peace Of Meat (‘POM’) |
In October 2020, the Company announced that it had made an initial investment in Peace of Meat BV (POM), a leading developer of cultured fat products, in the amount of EUR 1 million (approximately USD 1.2 million) in return for approximately 5.65% of the outstanding equity of POM, post-allocation, as part of its planned full acquisition of POM, which was completed on February 10, 2021. Following the acquisition, POM was consolidated within the group, refer to Note 16.
MeaTech 3D Ltd.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS AT DECEMBER 31, 2021
Note 7 – Fixed Assets, net
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | Office furniture, equipment and accessories | | | | |
| | | USD thousands | | | | |
| Cost | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Balance as at January 1, 2020 | | | 29 | | | | 11 | | | | 89 | | | | - | | | | 1 | | | | 130 | |
| Additions during the year | | | 43 | | | | 46 | | | | 466 | | | | 243 | | | | 27 | | | | 825 | |
| Effect of changes in exchange rates | | | 2 | | | | 1 | | | | 18 | | | | - | | | | 1 | | | | 22 | |
| Dispositions in the year | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cost as at December 31, 2020 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Accumulated depreciation | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Balance as at January 1, 2020 | | | 2 | | | | - | | | | 1 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 3 | |
| Depreciation during the year | | | 15 | | | | 10 | | | | 37 | | | | 4 | | | | 1 | | | | 67 | |
| Dispositions in the year | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Accumulated depreciation as at December 31, 2020 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Depreciated balance as at December 31, 2020 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Balance as at January 1, 2021 | | | 74 | | | | 58 | | | | 573 | | | | 243 | | | | 28 | | | | 976 | |
| Additions through acquisition of a subsidiary | | | 14 | | | | 3 | | | | 556 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 573 | |
| Additions during the year | | | 98 | | | | 75 | | | | 1,608 | | | | 77 | | | | 27 | | | | 1,885 | |
| Effect of changes in exchange rates | | | 2 | | | | (1 | ) | | | (56 | ) | | | 13 | | | | 2 | | | | (40 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cost as at December 31, 2021 | | | 188 | | | | 135 | | | | 2,681 | | | | 333 | | | | 57 | | | | 3,394 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Accumulated depreciation | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Balance as at January 1, 2021 | | | 17 | | | | 10 | | | | 38 | | | | 4 | | | | 1 | | | | 70 | |
| Depreciation during the year | | | 42 | | | | 22 | | | | 296 | | | | 31 | | | | 3 | | | | 394 | |
| Effect of changes in exchange rates | | | 2 | | | | 1 | | | | 4 | | | | 1 | | | | - | | | | 8 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Accumulated depreciation as at December 31, 2021 | | | 61 | | | | 33 | | | | 338 | | | | 36 | | | | 4 | | | | 472 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Depreciated balance as at December 31, 2021 | | | 127 | | | | 102 | | | | 2,343 | | | | 297 | | | | 53 | | | | 2,922 | |
During the year ended December 31, 2021, the Company acquired fixed assets on credit in the amount of USD 57 thousand (2020: USD 143 thousand). The cost of acquisition had not yet been paid at the reporting date.
MeaTech 3D Ltd.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS AT DECEMBER 31, 2021
Note 8 – Other Payables
| | | December 31 | | | December 31 | |
| | | 2021 | | | 2020 | |
| | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | |
| | | | | | | |
| Accrued expenses | | | 459 | | | | 263 | |
| Employee benefits | | | 1,122 | | | | 503 | |
| Contingent liability | | | 217 | | | | 217 | |
| Subsidiary government grant | | | 218 | | | | - | |
| Others | | | 223 | | | | | |
| | | | 2,239 | | | | 996 | |
Note 9 – Capital and Reserves
| | | Number of Ordinary Shares (thousand) | |
| | | 2021 | | | 2020 | | | 2019 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Issued and paid-in share capital as at January 1 | | | 79,866 | | | | 19,870 | | | | 15,447 | |
| Issued in reverse merger | | | - | | | | 30,526 | | | | - | |
| Exercise of share options during the period – Investor-related | | | 3,010 | | | | 11,302 | | | | 2,255 | |
| Exercise of share options during the period – Share-Based Payment-related | | | 2,218 | | | | 294 | | | | - | |
| Issued not for cash during the period (1) | | | 12,088 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Issued for cash during the period (2) | | | 28,588 | | | | 17,874 | | | | 2,168 | |
| Issued and paid-in share capital as at December 31, 2021 | | | 125,770 | | | | 79,866 | | | | 19,870 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Authorized share capital | | | 1,000,000 | | | | 1,000,000 | | | | 1,000,000 | |
| (1) | In February 2021, the Company completed a purchase of all of the outstanding share capital not yet owned by the Company, of Belgian cultured fat developer Peace of Meat BV. See Note 16 for information regarding the issuance of shares as part of the consideration. As part of the IPO, options and rights previously held by the Company's founders and Series A Investors were issued to 6,359,480 shares.
|
| (2) | On March 12, 2021, the Company completed its Initial Public Offering (IPO) at the Nasdaq of 2,721,271 ADSs, each representing ten ordinary shares of the Company (in total, 27,212,710 ordinary shares), at an offering price of USD 10.30 per ADS, resulting in gross proceeds of USD 28 million and net proceeds of USD 24.7 million. Additionally, the vesting of 1,374,998 investor share rights was triggered by the IPO, and these shares were issued in return for USD 1.25 million following the IPO. |
MeaTech 3D Ltd.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS AT DECEMBER 31, 2021
Note 10 – Share-based payments
The terms and conditions related to the grants of the share option programs are as follows (All granted options and restricted stock units (RSU) are non-tradable and physically-settled):
| | Date of grant and eligible recipients | | | | No. of ordinary shares (thousands) | | | | Contractual duration of the instrument (years) |
| | Options awarded to employees of the Company and subsidiaries on March 25, 2021 | | Options exercisable for ordinary shares | | 2,600 | | 1/3 after one year and the balance in 8 quarterly tranches | | 4 years |
| | RSUs awarded to directors on March 25, 2021 | | The RSUs vest automatically at no exercise price | | 90 | | 1/3 after one year and the balance in 8 quarterly tranches | | 4 years |
| | Options awarded to employees of the Company and subsidiaries on April 19, 2021 | | Options exercisable for ordinary shares | | 800 | | 1/3 after one year and the balance in 8 quarterly tranches | | 4 years |
| | Options awarded to employees of the Company and subsidiaries on July 22, 2021 | | Options exercisable for ordinary shares | | 1,362.5 | | 1/3 after one year and the balance in 8 quarterly tranches | | 4 years |
| | RSUs awarded to directors on September 14, 2021 | | The RSUs vest automatically at no exercise price | | 287.5 | | 1/3 after one year and the balance in 8 quarterly tranches
| | 4 years |
| | Options awarded to directors on September 14, 2021 | | Options exercisable for ordinary shares | | 785.6 | | 1/3 after one year and the balance in 8 quarterly tranches | | 4 years |
| | Options awarded to the deputy CEO on September 14, 2021 | | Options exercisable for ordinary shares | | 250 | | 1/3 after one year and the balance in 8 quarterly tranches | | 4 years |
| | Options awarded to BlueSoundWaves on October 6, 2021 | | Options exercisable for ordinary shares | | 6,215.8 | | 1/3 after one year and the balance in 8 quarterly tranches, subject to milestone-based acceleration | | 10 years |
| | RSUs awarded to BlueSoundWaves on October 6, 2021 | | The RSUs vest automatically at no exercise price | | 1,243.1 | | 1/3 after one year and the balance in 8 quarterly tranches, subject to milestone-based acceleration
| | 10 years |
| | Options awarded to employees of the Company and subsidiaries on November 24, 2021 | | Options exercisable for ordinary shares | | 925 | | 1/3 after one year and the balance in 8 quarterly tranches | | 4 years |
| | Total options/RSUs exercisable/vesting into shares granted in the year ended December 31, 2021 | | | | 14,559.5 | | | | |
MeaTech 3D Ltd.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS AT DECEMBER 31, 2021
Note 10 – Share-based payments (cont.)
| | A. | Number and weighted average exercise prices of options and RSUs |
The number and weighted average exercise prices of options and RSUs are as follows:
| | | Number of options and RSUs | | | Weighted average exercise price 2021 | |
| | | 2021 | | | NIS | |
| Outstanding at January 1 | | | 9,505,140 | | | | 2.60 | |
| Granted during the year | | | 14,559,520 | | | | 2.06 | |
| Forfeited during the year | | | 194,673 | | | | 1.63 | |
Exercised during the year(1) | | | 4,834,730 | | | | 2.55 | |
| Outstanding at December 31 | | | 19,035,257 | | | | 2.20 | |
| Exercisable at December 31 | | | 3,562,192 | | | | 3.07 | |
| (1) | Partly executed through cashless mechanism |
Besides incentive options and RSUs, as of the balance sheet date the Company has issued securities exercisable into 22,866,787 ordinary shares to investors, former shareholders of Peace of Meat (see Note 16) and former Ophectra Real Estate and Investments Ltd. employees prior to the reverse merger (see Note 1A), including investor warrants exercisable into 20,224,191 ordinary shares with exercise prices between NIS 3.03 and NIS 6.00, earn-out rights of former shareholders of Peace of Meat, exercisable into 2,412,596 ordinary shares with no exercise price and prior Ophectra Real Estate and Investments Ltd. employees options exercisable into 230,000 ordinary shares with exercise prices between NIS 1.72 and NIS 2.50.
MeaTech 3D Ltd.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS AT DECEMBER 31, 2021
Note 10 – Share-based payments (cont.)
| | B. | Information on measurement of fair value of share-based payment plans |
The fair value at the dates the options and RSUs were awarded was estimated using a binomial option pricing model.
Breakdown of the parameters used for measuring fair value at the date the share-based payment plans were awarded:
| | | Options/RSUs |
| Fair value at date awarded | | NIS 23.0 million (USD 7.0 millions) |
| | | |
| Parameters taken into account in the fair value calculation: | | |
| Share price (NIS at date awarded) | | 2.05 - 3.53 |
| Exercise price (NIS unlinked) | | 0 - 3.68 |
| Expected volatility | | 73.84%-93.10% |
| Expected useful life | | 4 – 10 years |
| Risk-free interest rate | | 0.23%-1.97% |
| Expected rate of dividend | | 0% |
The expected volatility was determined on the basis of share price volatility in similar companies, due to the Company’s limited share price performance history since the date of the merger in January 2020 described in Note 1A above. The simplified method was used for estimating the expected useful life of the employee stock options. The estimated useful life of the options for consultants and officers is the full contractual life of the option. The risk-free interest rate was based on NIS-linked Israeli Government bonds until the time of the Company’s Nasdaq listing, and US Treasury notes thereafter, with time to maturity equivalent to the expected useful life of the options. Share price was used based on share prices on the TASE until the time of the Company’s Nasdaq Capital Markets listing, and on Nasdaq thereafter.
The total non-cashflow expenses recorded during the years ended December 31, 2021, 2020 and 2019, amounted to approximately USD 4.0 million (NIS 12.7 million), USD 4.0 million (NIS 13.1 million) and USD 0, respectively.
MeaTech 3D Ltd.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS AT DECEMBER 31, 2021
Note 11 – Research and Development Expenses
| | | Year ended December 31, | | | Year ended December 31, | | | Year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2021 | | | 2020 | | | 2019 | |
| | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
Salaries, wages and related expenses(1) | | | 3,425 | | | | 1,369 | | | | 117 | |
Share-based payment(1) | | | 911 | | | | 476 | | | | - | |
| Materials | | | 1,875 | | | | 319 | | | | 20 | |
| Professional services | | | 403 | | | | 89 | | | | 13 | |
| Registration, drafting and filing of patents | | | 0 | | | | 25 | | | | 10 | |
| Maintenance, office and software fees | | | 145 | | | | 116 | | | | - | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | | 400 | | | | 59 | | | | - | |
| Insurance | | | 332 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Others | | | 103 | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Research and Development Expenses | | | 7,594 | | | | 2,491 | | | | | |
| | (1) | Including expenses in respect of related parties - see Note 18. |
Note 12 – Marketing Expenses
| | | Year ended December 31, | | | Year ended December 31, | | | Year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2021 | | | 2020 | | | 2019 | |
| | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Salaries, wages and related expenses | | | 494 | | | | 255 | | | | - | |
Share-based payment(1) | | | 570 | | | | 139 | | | | - | |
| PR, advertisement and professional services | | | 507 | | | | 91 | | | | - | |
| Maintenance, office and software fees | | | 22 | | | | 13 | | | | - | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | | 17 | | | | 3 | | | | - | |
| Others | | | 18 | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Marketing Expenses | | | 1,628 | | | | 506 | | | | | |
MeaTech 3D Ltd.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS AT DECEMBER 31, 2021
Note 13 – General and Administrative Expenses
| | | Year ended December 31, | | | Year ended December 31, | | | Year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2021 | | | 2020 | | | 2019 | |
| | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
Salaries, wages and related expenses(1) | | | 1,328 | | | | 556 | | | | 107 | |
Share-based payment(1) | | | 2,484 | | | | 3,343 | | | | - | |
Legal and professional services(1) | | | 1,499 | | | | 991 | | | | 112 | |
| Contingent liability expenses | | | - | | | | 217 | | | | - | |
| Insurance | | | 1,837 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Corporate costs | | | 343 | | | | 60 | | | | - | |
| Maintenance, office and software fees | | | 149 | | | | 38 | | | | 10 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | | 263 | | | | 151 | | | | 20 | |
| Others | | | 107 | | | | 24 | | | | 7 | |
| Total General and Administrative Expenses | | | 8,010 | | | | 5,380 | | | | 256 | |
| | (1) | Including expenses in respect of related parties - see Note 18. |
Note 14 – Financing Income and Expenses
| | | Year ended December 31, | | | Year ended December 31, | | | Year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2021 | | | 2020 | | | 2019 | |
| | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | |
| Financing Income | | | | | | | | | |
| Net change in fair value of financial instruments mandatorily measured at fair value through profit or loss | | | 509 | | | | 110 | | | | - | |
| Financing Expenses | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net foreign exchange loss | | | 1,279 | | | | 85 | | | | - | |
| Interest expense on lease liabilities | | | 9 | | | | 5 | | | | 1 | |
| Bank interest and commission expenses | | | 11 | | | | 3 | | | | - | |
| Total Financial expenses | | | 1,299 | | | | 93 | | | | 1 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Financing expenses (income), net | | | 790 | | | | | | | | 1 | |
MeaTech 3D Ltd.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS AT DECEMBER 31, 2021
Note 15 – Income Tax
| A. | Details regarding the tax environment of the Company |
The tax rates applicable to the companies operating in Israel for the years 2020-2021 are 23%.
The tax rates applicable to the companies operating in Belgium for the years 2020-2021 are 25%.
The Company has final tax assessments through 2012.
| C. | Unrecognized carryforward losses and deferred taxes |
As at December 31, 2021, the Group has estimated business losses carried forward in the amount of USD 18.2 million. Under current tax legislation in Israel and Belgium, tax losses do not expire. Deferred tax assets have not been recognized in respect of these items, nor in respect of timing differences for research and development expenses carried forward in the amount of USD 4.3 million, since the Company has not yet established the probability that future taxable profit will be available against which the Company can utilize the benefits.
Note 16 - Subsidiaries
In February 2021, the Company completed a purchase of all of the outstanding share capital not yet owned by the Company of Belgian cultured fat developer Peace of Meat BV for total consideration of up to EUR 16.3 million (USD 19.9 million). The total consideration payable by the Company in the acquisition consists of both cash and equity instruments to be paid to Peace of Meat shareholders and in legal and finder’s fees. The total consideration is to be paid part as of the closing of the acquisition and part upon the achievement of the defined milestones and sub-milestones. Substantially all of the fair value of the gross assets acquired is concentrated in a single identifiable asset or group of similar identifiable assets (the “intangible asset” or “IPR&D”), thus the subsidiary is not considered a business and the acquisition is accounted as an asset acquisition. Contingent consideration, dependent upon the achievement of technological milestones will be recognized at the time of the achievement of each milestone on the basis of the shares and cash that are payable.
The following summarizes the major classes of consideration at the acquisition date:
Total consideration
| | | USD thousands | |
| Cash consideration at closing date | | | 4,799 | |
| Initial cash investment in acquiree | | | 1,223 | |
| Equity instruments issued (4,070,766 ordinary shares)(1) | | | 4,359 | |
| Acquisition-related costs (2) | | | 254 | |
| Total consideration as of consolidation date | | | 10,635 | |
| Contingent consideration (3) | | | 9,308 | |
| Total consideration subject to achievement of all milestones | | | 19,943 | |
MeaTech 3D Ltd.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS AT DECEMBER 31, 2021
Note 16 - Subsidiaries (cont.)
| (1) | The fair value of the ordinary shares issued was based on the share price of the Company at the closing date (February 10, 2021) of NIS 3.986 per share.
|
| (2) | Acquisition-related costs include legal expenses and finder’s fees
|
| (3) | Contingent consideration
The Company agreed to pay the selling shareholders and the finder an additional 4,070,766 rights to ordinary shares with a value of USD 4.4 million and cash consideration of USD 4.9 million upon the achievement of defined milestones related to Peace of Meat’s biomass and bioreactor size, density, capacity and production. The acquisition agreement specified that each milestone must be reached within a six-month period, over a total period of two years, which can be extended by up to nine additional months under circumstances set forth in the acquisition agreement. As of the date of approval of these financial statements, Peace of Meat had fully achieved the first two such milestones.
No liability is being provisioned before milestones achievement. |
Identifiable assets acquired and liabilities assumed:
| Peace Of Meat condensed Balance Sheet | | USD thousands | |
| Current assets | | | 425 | |
| Non-current assets | | | 588 | |
| Current liabilities | | | (578 | ) |
| Non-current liabilities | | | (16 | ) |
| Tangible assets net | | | 419 | |
MeaTech 3D Ltd.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS AT DECEMBER 31, 2021
Note 16 - Subsidiaries (cont.)
IPR&D – Intangible asset
Intangible asset that was recognized as a result of the acquisition and additions made by December 31, 2021 as follows:
| Peace Of Meat initial consolidation effect | | USD thousands | |
| Closing cash consideration and related acquisition costs | | | 5,053 | |
| Shares consideration | | | 4,359 | |
| Initial cash investment in acquiree | | | 1,223 | |
| Tangible assets, net | | | (419 | ) |
| | | | 10,216 | |
| Additional contributions post acquisition date according to milestone achievement: | | | | |
| Cash consideration | | | 1,960 | |
| Payment liabilities | | | 194 | |
| Shares consideration (1,852,730 ordinary shares) | | | 1,973 | |
| Total | | | 14,343 | |
| FX rate effect | | | (890 | ) |
| Period end intangible asset balance | | | 13,453 | |
| The aggregate cash flows for the Group as a result of the acquisition in the Year ended December 31,2021 | | USD thousands | |
| Cash and cash equivalents paid | | | (5,053 | ) |
| Cash and cash equivalents of the subsidiary | | | 205 | |
| Cash consideration for milestone achievement during the period | | | (1,960 | ) |
| | | | | |
| Net reduction of cash flow as of acquisition date | | | (6,808 | ) |
As of December 31, 2021, the recoverable amount of the in-process IPR&D was based on its value in use and was determined by discounting the future cash flows to be generated from it by using the discounted cash flows method, on the annual year test. The recoverable amount of the IPR&D exceeds their carrying amount, thus no impairment loss was recognized. The discount rate used for calculating intangible assets recoverable amount is 23.0%, in addition to taking into consideration the risks associated in small stock premium companies.
MeaTech 3D Ltd.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS AT DECEMBER 31, 2021
Note 17 – Contingent Liabilities
From time to time, the Company may be party to litigation or other legal proceedings that it considers to be a part of the ordinary course of its business. The Company is not currently involved in any legal proceedings that could reasonably be expected to have a material adverse effect on its business, prospects, financial condition or results of operations.
| A. | In November 2020, the Israeli Securities Authority, or ISA, initiated an administrative proceeding claiming negligent misstatement regarding certain immediate and periodic reports published by the Company’s predecessor (Ophectra) during the years 2017 and 2018, prior to the merger with MeaTech and prior to establishment of the settlement fund in connection with the Merger. In February 2021, the trustee of the settlement fund informed the Company that the ISA views the Company as a party to this proceeding, notwithstanding the settlement and establishment of the settlement fund. This proceeding is of an administrative nature and carries a potential penalty in the form of a monetary fine which, under applicable Israeli law, could be as high as NIS 5 million. In April 2021, following negotiations with the ISA, the Company agreed to settle the matter for $0.2 million (NIS 0.7 million), for which the Company recorded a provision. The settlement is subject to approval of the ISA’s Enforcement Committee. |
| B. | In February 2021, a civil claim was lodged against the settlement fund, relating to Ophectra's activities prior to establishment of the settlement fund, in an amount of USD $0.8 million (NIS 2.5 million). The Company believes that the probability is low of a final ruling against the settlement fund. |
MeaTech 3D Ltd.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS AT DECEMBER 31, 2021
Note 18 – Related and Interested Parties
| A. | Balances with related parties |
| | | Year ended December 31, | | | Year ended December 31, | | | Year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2021 | | | 2020 | | | 2019 | |
| | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Related companies receivables | | | - | | | | - | | | | 87 | |
| Trade and other payables | | | 261 | | | | 117 | | | | 52 | |
| B. | Expense amounts with respect to related parties |
| | | Year ended December 31, | | | Year ended December 31, | | | Year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2021 | | | 2020 | | | 2019 | |
| | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | |
| General and administrative expenses | | | | | | | | | |
| Salaries, wages and related expenses | | | 588 | | | | 316 | | | | 89 | |
| Legal and professional services | | | 301 | | | | 281 | | | | 58 | |
| Share-based payments | | | 777 | | | | 488 | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| |
| Research & Development expenses | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Salaries, wages and related | | | 338 | | | | 121 | | | | -
| |
| Share-based payments | | | 66 | | | | 64 | | | | 15 | |
| 1. | Key Management Personnel
The Company recognizes four key management personnel as related parties, namely Mr. Sharon Fima – former Chief Executive Officer (CEO), served as CEO un until January 24 2022, Mr. Omri Schanin - Deputy CEO, Mr. Guy Hefer – Chief Financial Officer (CFO) and Mr. Dan Kozlovski – Chief Technologies Officer (CTO), who served as Vice President of Research and Development (VP R&D) until February 2022.
Mr. Sharon Fima, the previous CEO and CTO, who also served as a director, was employed by the Company (including MeaTech Ltd. prior to the merger described in Note 1A above) between September 1, 2019 and January 24, 2022. Until July 2021, Mr. Fima was entitled to a gross annual salary of NIS 0.5 million (USD 0.1 million) plus generally accepted social benefit contributions for senior executives and the use of a company car, including a related tax gross-up. Commencing August 1, 2021, Mr. Fima was entitled to an annual gross salary of NIS 0.6 million (USD 0.2 million). Mr. Fima also received options valued at NIS 0.2 million (USD 0.1 million) to be recognized over three-year vesting period commencing March 2020, some of which were forfeited subsequent to the balance sheet date following the CEO replacement. |
MeaTech 3D Ltd.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS AT DECEMBER 31, 2021
Note 18 – Related and Interested Parties (cont.)
| | B. | Expense amounts with respect to related parties (cont.) |
The Deputy CEO, who also served as a director until January 2022, has been employed by the Company (including MeaTech Ltd. prior to the merger described in Note 1A above) since September 1, 2019. Mr. Schanin was entitled to a gross annual salary of NIS 0.4 million (USD 0.1 million) plus generally accepted social benefit contributions for senior executives. Commencing August 1, 2021, Mr. Schanin is entitled to an annual gross salary of NIS 0.5 million (USD 0.2 million). Mr. Schanin also received options valued at an aggregate of NIS 0.8 million (USD 0.25 million) to be recognized over three-year vesting periods commencing August 2021.
The CFO, has been employed by the Company since October 18, 2020. Mr. Hefer was entitled to a gross annual salary of NIS 0.4 million (USD 0.1) plus generally accepted social benefit contributions for senior executives. Commencing August 1, 2021, Mr. Hefer is entitled to an annual gross salary of NIS 0.5 million (USD 0.2 million). Mr. Hefer also received options valued at an aggregate of NIS 0.75 million (USD 0.23 million) to be recognized over three-year vesting periods commencing in 2021.
The CTO (previously VP R&D), has been employed by the Company (including MeaTech Ltd. prior to the merger described in Note 1A above) since December 5, 2019. Mr. Kozlovski was entitled to a gross annual salary of NIS 0.4 million (USD 0.1 million) plus generally accepted social benefit contributions for senior executives. Commencing August 1, 2021, Mr. Kozlovski is entitled to an annual gross salary of NIS 0.5 million (USD 0.2 million). Mr. Kozlovski also received options valued at of NIS 0.07 million (USD 0.02 million)to be recognized over three-year vesting period commencing in 2019.
| 2. | Directors
Mr. Steve H. Lavin served as active chairman of the Company's Board of Directors between May 2020 and January 2022, and he was entitled to an annual compensation of USD 0.2 million as well as share-based compensation.
Mr. Danny Ayalon served as director between May 2020 and January 2022, and was entitled to an annual compensation of USD 0.03 million as well as share-based compensation.
Additional non-executive directors were compensated in accordance with the terms of the Israeli Companies Regulations (Rules Regarding Payment and Expenses for External Directors), 2000, as amended until July 31, 2021 and are since entitled to annual compensation of USD 0.03 million as well as share-based compensation. |
MeaTech 3D Ltd.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS AT DECEMBER 31, 2021
Note 19 – Leases
Leases in which the Group is the lessee
| 1. | Under an office leasing agreement dated November 1, 2019, MeaTech leased office space and parking spaces, for a monthly fee of USD 10 thousand (NIS 32 thousand), including management fees, for a period of two years, with an option to extend the term of the lease by one more year. The Company initially recognized a long-term lease liability and a right-of-use asset in the amount of USD 214 thousand (NIS 743 thousand). The incremental interest rate used for estimating the liability is 2.25%. On November 2021 the Company extended the agreement for an additional period of 2.3 years. |
| 2. | Under an office leasing agreement dated August 9, 2020, the Company leased office space and parking spaces, for a monthly fee of USD 8 thousand (NIS 27 thousand), including management fees, for a period of one year, with an option to extend the term of the lease by one more year. The Company initially recognized a long-term lease liability and a right-of-use asset in the amount of USD 102 thousand (NIS 348 thousand). The incremental interest rate used for estimating the liability is 4.3%. This agreement has ended during 2021. |
| 3. | Under an office leasing agreements dated between March and October 2021 for periods of 1.5-2 years, POM and Meatech Europe BV are leasing several spaces from a shared spaces provider for a monthly aggregated fee of USD 11 thousand (EUR 10 thousand). The Company initially recognized a long-term lease liability and a right-of-use asset in the amount of USD 259 thousand (EUR 220 thousand). The incremental interest rate used for estimating the liability is 3%. |
| | | USD thousands | |
| Balance as at January 1, 2020 | | | 197 | |
| Additions during the year | | | 102 | |
| Amortization during the year | | | (146 | ) |
| Effect of changes in exchange rates | | | 15 | |
| Balance as at December 31, 2020 | | | 168 | |
| Additions following the acquisition of POM | | | 16 | |
| Additions during the year | | | 512 | |
| Amortization during the year | | | (286 | ) |
| Effect of changes in exchange rates | | | (3 | ) |
| Balance as at December 31, 2021 | | | 407 | |
| 5. | Maturity analysis of for the Company’s lease liabilities |
| | | December 31, | | | December 31, | |
| | | 2021 | | | 2020 | |
| | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | |
| | | | | | | |
| Up to one year | | | 165 | | | | 180 | |
| 1-5 years | | | 246 | | | | - | |
| Total | | | 411 | | | | 180 | |
MeaTech 3D Ltd.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS AT DECEMBER 31, 2021
Note 19 – Leases (cont.)
| 6. | Amounts recognized in the statement of operation |
| | | Year ended December 31, | | | Year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2021 | | | 2020 | |
| | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | |
| | | | | | | |
| Amortization of ROU asset | | | 286 | | | | 146 | |
| Interest expenses on lease liability | | | 9 | | | | 5 | |
Total amounts paid for leasing of the offices in the year ended December 31, 2021 and December 31, 2020, was USD 346 thousand and USD 140 thousand, respectively.
Note 20 - Employee Benefits
Employee benefits include post-employment benefits and short-term benefits.
Regarding benefits to key management employees, see Note 18(B).
The Company has a defined contribution plan in respect of its liability to pay the savings component of provident funds and in relation to employee severance pay, which is subject to Section 14 of the Israeli Severance Pay Law – 1963, according to which the Company pays fixed contributions to pension funds and/or insurance companies that release the Company from any additional severance-related liability. Expenses recognized in respect of such defined contribution plans in the years ended December 31, 2021 and December 31, 2020, amounted to USD 225 thousand and USD 121 thousand, respectively.
MeaTech 3D Ltd.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS AT DECEMBER 31, 2021
Note 21 – Loss per Share
Weighted average number of ordinary shares | |
| | | Year ended December 31, 2021 | | | Year ended December 31, 2020 | | | Year ended December 31,
2019 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Issued and paid-in share capital as at January 1 | | | 79,866,264 | | | | 19,870,337 | | | | - | |
| Weighted average of the number of ordinary shares of MeaTech 3D Ltd. issued during the year | | | 36,088,237 | | | | 40,241,860 | | | | - | |
| Weighted average of the number of ordinary shares used to calculate basic earnings per share | | | 115,954,501 | | | | 60,112,197 | | | | 19,484,478 | |
In prior periods, the weighted average number of the ordinary shares of MeaTech (now known as MeaTech MT Ltd.) was multiplied by the exchange ratio according to which ordinary shares of MeaTech 3D Ltd. were issued in return for ordinary shares of MeaTech in the 2020 reverse acquisition.
At December 31, 2021, 41,902,044 options, warrants and RSUs (in 2020 and 2019, 45,768,424 and 9,839 options respectively) were excluded from the diluted weighted average number of ordinary shares calculation, as their effect would have been anti-dilutive.
MeaTech 3D Ltd.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS AT DECEMBER 31, 2021
Note 22 – Agreements, Guarantees and Liens
| A. | To secure its undertakings in connection with its lease agreements as described in Note 19, MeaTech provided a bank guarantee in the amount of USD 27 thousand (NIS 85 thousand) For which there's a restricted deposit. MeaTech also restricted a deposit of USD 26 thousand (NIS 80 thousand) in favor of a bank to secure its liabilities with respect to credit cards. The guarantee and deposit were assigned to MeaTech 3D Ltd. upon the Merger. |
| B. | To secure its undertakings in connection with its future lease agreement, MeaTech 3D Ltd. provided a bank guarantee in the amount of USD 334 thousand (NIS 1,040 thousand) For which there's a restricted deposit. |
| C. | To secure its undertakings in connection with its lease agreements as described in Note 13, POM provided a bank guarantee in the amount of USD 18 thousand (EUR 15 thousand) For which there's a restricted deposit. |
Note 23 – Financial Instruments
The Company has exposure to the following risks from its use of financial instruments: credit, liquidity and market risks.
| A. | Framework for risk management |
The Board of Directors has overall responsibility for the establishment and oversight of the Company’s risk management framework.
The Company’s risk management policy was formulated to identify and analyze the risks that the Company faces, to set appropriate limits for the risks and controls, and to monitor the risks and their compliance with the limits. The risk policy and risk management methods are reviewed regularly to reflect changes in market conditions and in the Company’s operations. The Company acts to develop an effective control environment in which all employees understand their roles and commitment.
Credit risk is the risk of financial loss to the Company if a debtor or counterparty to a financial instrument fails to meet its contractual obligations, and arises mainly from the Company’s receivables.
The Company restricts exposure to credit risk by investing only in bank deposits.
Liquidity risk is the risk that the Company will not be able to meet its financial obligations as they fall due. The Company’s approach to managing liquidity is to ensure, as far as possible, that it will always have sufficient liquidity to meet its liabilities when due, under both normal and stressed conditions, without incurring unacceptable losses or risking damage to the Company’s reputation.
This does not take into account the potential effect of extreme circumstances that cannot reasonably be predicted.
Market risk is the risk that changes in market prices, such as foreign currency exchange rates, the CPI, interest rates and the prices of equity instruments, will influence the Company’s results or the value of its holdings in financial instruments. The objective of market risk management is to manage and control market risk exposures within acceptable parameters, while optimizing the return.
MeaTech 3D Ltd.
NOTES TO THE FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AS AT DECEMBER 31, 2021
Note 23 – Financial Instruments (cont.)
The carrying amounts of financial assets and liabilities, including cash and cash equivalents, other receivables, trade payables and other payables are the same or proximate to their fair value.
In connection with the Company’s Nasdaq public offering, all existing price protection mechanisms were eliminated, as a result of which financing income was recorded.
Note 24 – Subsequent Events
In January 2022, Mr. Sharon Fima stepped down from the positions of Chief Executive Officer, Chief Technology Officer and Director, citing the Company’s current stage of development. Messrs. Steven H. Lavin (Chairman) and Danny Ayalon also stepped down from the Board of Directors, citing the Company’s current stage of development and to pursue other ventures, and Mr. Omri Schanin stepped down from the Board of Directors and continues to serve as MeaTech’s Deputy CEO.
The Company’s Board of Directors appointed Mr. Arik Kaufman to the position of Chief Executive Officer and Mr. Yaron Kaiser to the position of Chairman of the Board of Directors.
In March 2022, the Company moved to its new headquarters at 5 David Fikes St., Rehovot, Israel, and terminated the lease at its previous headquarters. The laboratory and office space total approximately 18,300 square feet. The lease for this facility will expire in January 2026, although the Company has an option to renew it for four years. The annual rent (including parking fees) is approximately USD 0.7 million, linked to the Israeli CPI. This move is expected to affect the Company’s estimates regarding lease maturities and right-of-use assets in future reporting periods.
Steakholder Foods Ltd. (formerly known as MeaTech 3D Ltd.)
Unaudited Consolidated Interim Financial Statements As At June 30, 2022
| Financial Information of Steakholder Foods Ltd. | Page |
| | |
| Contents: | |
| F-2 |
| F-3 |
| F-5 |
| F-6 |
| F-7 |
Unaudited Condensed consolidated interim statements of
financial position
| | | | | | June 30 | | | June 30 | | | December 31 | |
| | | | | | 2022 | | | 2021 | | | 2021 | |
| | | | | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | |
Current assets | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | 4 | | | | 8,434 | | | | 30,637 | | | | 19,176 | |
| Other investment | | | | | | 137 | | | | 147 | | | | 154 | |
| Receivables | | 5 | | | | 2,237 | | | | 1,174 | | | | | |
| Total current assets | | | | | | 10,808 | | | | 31,958 | | | | 22,112 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Non-current assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Restricted deposits | | | | | | 380 | | | | 388 | | | | 405 | |
| Other investment | | | | | | 1,209 | | | | 1,264 | | | | 1,355 | |
| Right-of-use asset | | 15 | | | | 3,612 | | | | 306 | | | | 407 | |
| Intangible assets | | | | | | 12,360 | | | | 9,930 | | | | 13,453 | |
| Fixed assets, net | | | | | | 4,653 | | | | 2,206 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total non-current assets | | | | | | 22,214 | | | | 14,094 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Assets | | | | | | 33,022 | | | | 46,052 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Current liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Trade payables | | | | | | 779 | | | | 359 | | | | 382 | |
| Other payables | | 6 | | | | 2,174 | | | | 1,573 | | | | 2,239 | |
| Current maturities of lease liabilities | | 15 | | | | 428 | | | | 210 | | | | 165 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total current liabilities | | | | | | 3,381 | | | | 2,142 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Non-current liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Long-term lease liabilities | | 15 | | | | 3,247 | | | | 102 | | | | 246 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total non-current liabilities | | | | | | 3,247 | | | | 102 | | | | 246 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Capital | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Share capital and premium on shares | | | | | | 70,476 | | | | 65,283 | | | | 69,610 | |
| Capital reserves | | | | | | 3,943 | | | | 4,383 | | | | 3,708 | |
| Currency translation differences reserve | | | | | | (1,898 | ) | | | 857 | | | | 1,275 | |
| Accumulated deficit | | | | | | (46,127 | ) | | | (26,715 | ) | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total capital | | | | | | 26,394 | | | | 43,808 | | | | | |
| Total liabilities and capital | | | | | | 33,022 | | | | 46,052 | | | | | |
Unaudited Condensed consolidated interim of Income and of
Comprehensive Loss
| | | | | | Six months ended June 30, | | | Six months ended June 30, | | | Year ended December 31, | |
| | | | | | 2022 | | | 2021 | | | 2021 | |
| | | | | | USD thousands, except share data | | | USD thousands, except share data | | | USD thousands, except share data | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Research and development expenses | | 9 | | | | 4,427 | | | | 2,910 | | | | 7,594 | |
| Marketing expenses | | 10 | | | | 1,959 | | | | 605 | | | | 1,628 | |
| General and administrative expenses | | 11 | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operating loss | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Financing income | | 12 | | | | (1,062 | ) | | | (401 | ) | | | (509 | ) |
| Financing expenses | | | | | | 145 | | | | 493 | | | | | |
| Total financing (income) expenses | | | | | | (917 | ) | | | 92 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loss for the period | | | | | | 9,156 | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Currency translation differences loss (income) that might be transferred to profit or loss over ILS | | | | | | 2,326 | | | | (293 | ) | | | (1,942 | ) |
| Currency translation differences loss (income) that might be transferred to profit or loss over EUR | | | | | | 847 | | | | 216 | | | | 1,447 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total comprehensive loss for the period | | | | | | 12,329 | | | | 7,689 | | | | 17,527 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loss per ordinary share, no par value (USD) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Basic and diluted loss per share (USD) | | | | | | 0.072 | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Weighted-average number of shares outstanding - basic and diluted (shares) | | | | | | | | | | 107,189,837 | | | | 115,954,501 | |
Unaudited Condensed consolidated interim of Income and of Comprehensive Loss
| | | | | | Three months ended June 30, | | | Three months ended June 30, | |
| | | | | | 2022 | | | 2021 | |
| | | | | | USD thousands, except share data | | | USD thousands, except share data | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Research and development expenses | | 9 | | | | 2,285 | | | | 1,783 | |
| Marketing expenses | | 10 | | | | 908 | | | | 285 | |
| General and administrative expenses | | 11 | | | | | | | | | |
| Operating loss | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Financing income | | 12 | | | | (678 | ) | | | (24 | ) |
| Financing expenses | | | | | | 85 | | | | 664 | |
| Total financing (income) expenses | | | | | | (593 | ) | | | 640 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loss for the period | | | | | | 4,169 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Currency translation differences loss (income) that might be transferred to profit or loss over ILS | | | | | | 1,811
| | | | (898 | ) |
| Currency translation differences loss (income) that might be transferred to profit or loss over EUR | | | | | | 600
| | | | 33 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total comprehensive loss for the period | | | | | | 6,580 | | | | 3,242 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loss per ordinary share, no par value (USD) | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Basic and diluted loss per share (USD) | | | | | | 0.033 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Weighted-average number of shares outstanding - basic and diluted (shares) | | | | | | 126,533,200 | | | | 123,665,142 | |
Unaudited Condensed consolidated interim statements of
changes in equity
| | | Premium and Capital Share | | | Fair value of financial assets reserve | | | Transactions with related parties reserve | | | Currency translation differences reserve | | | Share-based payments reserve | | | Accumulated deficit | | | Total | |
| | | USD thousands | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance as at January 1, 2022 | | | 69,610 | | | | (334 | ) | | | 14 | | | | 1,275 | | | | 4,028 | | | | (36,971 | ) | | | 37,622 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Share-based payments | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,048 | | | | - | | | | 1,048 | |
| Exercise of options | | | 866 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (813 | ) | | | | | | | 53 | |
| Other comprehensive income (loss) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (3,173 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | (3,173 | ) |
| Loss for the period | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (9,156 | ) | | | (9,156 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance as at June 30, 2022 | | | 70,476 | | | | (334 | ) | | | 14 | | | | (1,898 | ) | | | 4,263 | | | | (46,127 | ) | | | 26,394 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance as at January 1, 2021 | | | 30,481 | | | | (334 | ) | | | 14 | | | | 780 | | | | 3,639 | | | | (18,949 | ) | | | 15,631 | |
| | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Share-Based Payment | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 2,313 | | | | | | | | 2,313 | |
| Issuance of shares and warrants, net | | | 30,357 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | 30,357 | |
| Exercise of options | | | 4,445 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (1,249 | ) | | | | | | | 3,196 | |
| Other comprehensive income (loss) | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | 77 | | | |
| | | | | | | | 77 | |
| Loss for the period | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | - | | | |
| | | | (7,766 | ) | | | (7,766 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Balance as at June 30, 2021 | | | 65,283 | | | | (334 | ) | | | 14 | | | | 857 | | | | 4,703 | | | | (26,715 | ) | | | 43,808 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance as at January 1, 2021 | | | 30,481 | | | | (334 | ) | | | 14 | | | | 780 | | | | 3,639 | | | | (18,949 | ) | | | 15,631 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Share-based payments | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 3,965 | | | | - | | | | 3,965 | |
| Issuance of shares and warrants, net | | | 32,330 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 32,330 | |
| Exercise of options | | | 6,799 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (3,576 | ) | | | | | | | 3,223 | |
| Other comprehensive income (loss) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 495 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 495 | |
| Loss for the period | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (18,022 | ) | | | (18,022 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance as at December 31, 2021 | | | 69,610 | | | | (334 | ) | | | 14 | | | | 1,275 | | | | 4,028 | | | | (36,971 | ) | | | 37,622 | |
Unaudited Condensed consolidated interim statements of
cash flows
| | | Six months ended June 30, 2022 | | |
Six months ended June 30,
| | | Year ended December 31, 2021 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
Cash flows - operating activities | | | | | | | | | |
| Net Loss for the period | | | (9,156 | ) | | | (7,766 | ) | | | (18,022 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Adjustments: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | | 722 | | | | 278 | | | | 680 | |
| Change in fair value of derivative | | | -
| | | | (311 | ) | | | (316 | ) |
| Change in fair value of other investment | | | (80 | ) | | | (90 | ) | | | (193 | ) |
| Changes in net foreign exchange expenses | | | (982 | ) | | | 485 | | | | 1,279 | |
| Expenses of interest over liability of lease | | | 137 | | | | 1 | | | | 9 | |
| Share-based payment expenses | | | 1,048 | | | | 2,313 | | | | 3,965 | |
| Changes in asset and liability items: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Decrease (increase) in receivables | | | 257 | | | | (782 | ) | | | (2,351 | ) |
| Increase (decrease) in trade payables | | | 224 | | | | 3 | | | | (97 | ) |
| Increase (decrease) in other payables | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net cash from (used in) operating activities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash flows - investment activities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Acquisition of fixed assets | | | (2,341 | ) | | | (902 | ) | | | (1,828 | ) |
| Increase in restricted deposit | | | (20 | ) | | | (337 | ) | | | (337 | ) |
| Loan provided | | | -
| | | | (367 | ) | | | (367 | ) |
| Proceeds on account of other investment* | | | 73 | | | | 73 | | | | 149 | |
| Acquisition of other investments, net of cash acquired | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net cash used in investing activities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash flows - financing activities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Proceeds from issuance of shares and warrants | | | - | | | | 29,281 | | | | 29,281 | |
| Issuance costs | | | - | | | | (3,283 | ) | | | (3,283 | ) |
| Repayment of liability for lease | | | (230 | ) | | | (134 | ) | | | (346 | ) |
| Repayment of interest over liability of lease | | | (137 | ) | | | (1 | ) | | | (9 | ) |
| Proceeds from exercise of share options | | | 53 | | | | 3,196 | | | | 3,222 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net cash from financing activities | | | (314 | ) | | | 29,059 | | | | 28,865 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Increase in cash and cash equivalents | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Effect of exchange differences on cash and cash equivalents | | | (504 | ) | | | (549 | ) | | | (103 | ) |
| Cash and cash equivalents at the beginning of the period: | | | 19,176 | | | | 13,556 | | | | 13,556 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash balance and cash equivalents at end of period | | | 8,434 | | | | 30,637 | | | | 19,176 | |
| Non-cash activities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Purchase of fixed assets yet to be paid | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Issue of shares and options against intangible asset | | | | | | | | | | | | |
*Reclassified
Steakholder Foods Ltd. (formerly Ophectra Real Estate and Investments Ltd., Meat-Tech 3D Ltd. and MeaTech 3D Ltd.) (the “Company”) was incorporated in Israel on July 22, 1992 as a private company limited by shares in accordance with the Companies Ordinance, 1983, and later a publicly-traded company whose ordinary shares were listed for trade on the Tel Aviv Stock Exchange (TASE). In March 2021, the Company completed an initial public offering on the Nasdaq Capital Market, listing American Depositary Shares (ADSs) for trade under the ticker STKH, and later voluntarily de-listed its ordinary shares from the TASE. The Company’s official address is 5 David Fikes St., Rehovot, Israel. In August 2022, the Company changed its name from MeaTech 3D Ltd. to Steakholder Foods Ltd.
The Company’s foodtech activities commenced in July 2019 by a company called MeaTech Ltd., which merged with the Company in January 2020 and became a fully-owned subsidiary, now called Steakholder Innovation Ltd. As the Company was the surviving entity of the merger, and continued the pre-merger business operations, utilizing the pre-merger management and employees, of MeaTech Ltd., the transaction was treated as a reverse acquisition that does not constitute a business combination.
The Company is developing a suite of advanced high-throughput manufacturing technologies to produce cell-based alternative protein products for cultivated, sustainable meat production, and focused on developing premium, center-of-plate meat products, including development of high-throughput bioprinting systems.
Since inception the Company has incurred significant losses and negative cash flows from operations and has an accumulated deficit of USD 46.1 million. The Company has financed its operations mainly through fundraising from various investors.
The Company’s management expects that the Company will continue to generate losses and negative cash flows from operations for the foreseeable future. Based on the projected cash flows and cash balances as of June 30, 2022, management is of the opinion that its existing cash will be sufficient to fund operations until Q2 2023. As a result, there is substantial doubt about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern.
Management’s plans include the continue securing sufficient financing through the sale of additional equity securities or capital inflows from strategic partnerships. Additional funds may not be available when the Company needs them on terms that are acceptable to it, or at all. If the Company is unsuccessful securing sufficient financing, it may need to cease operations.
The financial statements include no adjustments for measurement or presentation of assets and liabilities, which may be required should the Company fail to operate as a going concern.
Definitions:
In these financial statements:
(1) The Company - Steakholder Foods Ltd.
(2) The Group – The Company and its subsidiaries, Steakholder Innovation Ltd. (formerly known as MeaTech Ltd.), Steakholder Foods Europe BV, Peace of Meat BV (hereafter “Peace Of Meat”) and Steakholder Foods USA, Inc.
(3) Related Party - as defined in IAS 24 (revised).
(4) USD - United States Dollar
(5) NIS – New Israeli Shekel
(6) EUR – Euro
(7) ADS – American Depositary Shares
(8) GBP - British pound sterling
Note 2 - Basis of preparation of the Financial Statements
| A. | Statement of compliance with IFRS |
These interim condensed consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with IAS 34, Interim Financial Reporting, and do not include all of the information required in full annual financial statements.
The interim condensed consolidated financial statements were approved by the Company’s Board of Directors on August 24, 2022.
The main accounting policy and calculation methods applied in the preparation of these Consolidated Interim Financial Statements are consistent with those applied in the preparation of the annual financial statements of the year 2021.
B. Use of estimates and judgments
The preparation of these interim condensed consolidated financial statements in conformity with IFRS requires management to make judgments for preparing the assessments, estimates and assumptions that affect the application of accounting policies and the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, income and expenses. It should be clarified that actual results may differ from such estimates.
The judgments made by management, when applying the Group’s accounting policies and the key assumptions used in assessments that involve uncertainty, are consistent with those applied in the preparation of the Annual Financial Statements.
C. Functional currency and presentation currency
The New Israeli Shekel ("NIS") is the currency that represents the primary economic environment in which the Company and its Israeli subsidiary operate, and is therefore the functional currency of their operations. The Euro is the currency that represents the primary economic environment in which the Company’s European subsidiaries operate, and is therefore the functional currency of their operations. Nonetheless, for reporting purposes, the consolidated financial statements, which were prepared on the basis of the functional currencies, were translated into US Dollars, which the Company selected as its presentation currency, as its securities are traded on the Nasdaq Capital Markets, and in order to make the Company’s financial statements more accessible to U.S.-based investors.
Assets and liabilities were translated at the exchange rate of the end of the period; expenses and income were translated at the exchange rate at the time they were generated. Exchange rate differentials generated due to such translation are attributed to the Currency translation differences reserve.
| Currency | | USD - ILS | | | USD - EUR | |
| | | 2022 | | | 2021 | | | 2022 | | | 2021 | |
| June 30 | | | 3.500 | | | | 3.260 | | | | 0.962 | | | | 0.841 | |
| Average for six months ended June 30 | | | 3.272 | | | | 3.265 | | | | 0.915 | | | | 0.830 | |
| Average for three months ended June 30 | | | 3.341 | | | | 3.265 | | | | 0.938 | | | | 0.830 | |
| December 31 | | | - | | | | 3.110 | | | | - | | | | 0.883 | |
| Average for twelve months ended December 31 | | | - | | | | 3.230 | | | | - | | | | 0.845 | |
Note 3 – Material Events in the reporting period
In January 2022, Messrs. Steven Lavin, Daniel Ayalon, Sharon Fima and Omri Schanin stepped down as directors of the Company, and Mr. Fima also resigned as Chief Executive Officer and Chief Technology Officer. At that time, Mr. Yaron Kaiser was appointed to the Board as its Chairman, and Mr. Arik Kaufman was appointed as the Company’s Chief Executive Officer. In April 2022, Mr. Schanin resigned as Deputy Chief Executive Officer.
In March 2022, the Company’s headquarters were relocated to new, more spacious premises with state-of-the-art laboratories in Rehovot, Israel. The new space, allows the Company to enhance its cultured meat research and development, including three-dimensional bioprinting technology, and to continue growing its biology and engineering teams.
For more information, see Note 15.
Note 4 – Cash and Cash Equivalents
| | | June 30 | | | June 30 | | | December 31 | |
| | | 2022 | | | 2021 | | | 2021 | |
| | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash in USD | | | 4,260 | | | | 22,756 | | | | 15,596 | |
| Cash in NIS | | | 3,059 | | | | 6,225 | | | | 1,688 | |
| Cash in Euro | | | 1,110 | | | | 1,656 | | | | 1,892 | |
| Cash in GBP | | | 5 | | | | - | | | | | |
| Total cash and cash equivalents | | | 8,434 | | | | 30,637 | | | | 19,176 | |
Note 5 – Receivables
| | | June 30 | | | June 30 | | | December 31 | |
| | | 2022 | | | 2021 | | | 2021 | |
| | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Institutions | | | 320 | | | | 548 | | | | 301 | |
| Prepaid expenses | | | 854 | | | | 605 | | | | 743 | |
| Other | | | 1,063 | | | | 21 | | | | | |
| | | | 2,237 | | | | 1,174 | | | | 2,782 | |
Note 6 – Other Payables
| | | June 30 | | | June 30 | | | December 31 | |
| | | 2022 | | | 2021 | | | 2021 | |
| | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Accrued expenses | | | 626 | | | | 513 | | | | 459 | |
| Employee benefits | | | 1,081 | | | | 532 | | | | 1,122 | |
| Provision - see note 13 (a) | | | 200 | | | | 217 | | | | 217 | |
| Subsidiary government grant advances | | | 252 | | | | 311 | | | | 218 | |
| Others | | | 15 | | | | - | | | | | |
| | | | 2,174 | | | | 1,573 | | | | 2,239 | |
Note 7 – Capital and Reserves
| | | Thousands of Ordinary Shares | |
| | | June 30, 2022 | |
| | | | |
| Issued and paid-in share capital as at the beginning of the period | | | 125,770 | |
| Exercise of share options during the period – Share-Based Payment-related | | | 589 | |
| Issued not - for cash during the period* | | | 176 | |
| Issued and paid-in share capital as at June 30 | | | 126,535 | |
| | | | | |
| Authorized share capital | | | 1,000,000 | |
*Allocated to POM founders as part of original SPA
Note 8 – Share-based payments
New allotments during the six-month period ended June 30, 2022 that remain outstanding are set out below. All granted options and restricted stock units (RSU) are non-tradable and physically-settled:
| Date of grant and eligible recipients | | Terms of the instrument | | No. of ordinary shares (thousands) | | Vesting Conditions | | Contractual duration of the instrument (years) |
| Options awarded to CEO and Chairman on March 15, 2022 | | Options exercisable for ordinary shares | | | 850 | | 12 quarterly tranches | | 4 years |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Options awarded to employees of the Company and subsidiaries on March 24, 2022 | | Options exercisable for ordinary shares | | | 775 | | 1/3 after one year and the balance in 8 quarterly tranches | | 4 years |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Options awarded to employees of the Company on June 10, 2022 | | Options exercisable for ordinary shares | | | 2,180 | | 1/3 after one year and the balance in 8 quarterly tranches | | 4 years |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Total options exercisable into shares | | | | | 3,805 | | | | |
Note 8 – Share-based payments (Cont.)
The fair value at the dates the options were awarded was estimated using a binomial option pricing model.
Breakdown of the parameters used for measuring fair value at the date the share-based payment plans were awarded:
| | | Options |
| Fair value at date awarded | | USD 1,107 thousand |
| | | |
| Parameters taken into account in the fair value calculation: | | |
| Share price (USD at date awarded) | | 0.43-0.51 |
| Exercise price (USD unlinked) | | 0.40-0.52 |
| Expected volatility (weighted average) | | 94.87%-100.74% |
| Contractual term | | 4 years |
| Risk-free interest rate | | 2.03%-3.24% |
| Expected rate of dividend | | 0% |
The expected volatility (standard deviation) was determined on the basis of share price volatility in similar companies, due to the Company’s limited historic share price performance since the date of the merger in January 2020 described in Note 1A above. The estimated Contractual Term of the options is the full contractual life of the option. The risk-free interest rate was based on US bonds, with time to maturity equivalent to the expected useful life of the options. Share price was used according to quoted share prices on Nasdaq.
The total expense over the six and three months ended June 30, 2022, amounted to approximately USD 1.0 million (NIS 3.4 million) and USD 0.3 million (NIS 1.0 million), respectively.
Note 9 – Research and Development Expenses
| | | Six months ended June 30, | | | Six months ended June 30, | | | Year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2022 | | | 2021 | | | 2021 | |
| | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
Salaries, wages and related expenses(1) | | | 2,356 | | | | 1,354 | | | | 3,425 | |
Share-based payment(1) | | | 218 | | | | 463 | | | | 911 | |
| Materials | | | 689 | | | | 514 | | | | 1,875 | |
| Professional services | | | 315 | | | | 132 | | | | 403 | |
| Maintenance, office and software fees | | | 197 | | | | 79 | | | | 145 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | | 468 | | | | 174 | | | | 400 | |
| D&O insurance | | | 112 | | | | 119 | | | | 332 | |
| Others | | | 72 | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Research and Development Expenses | | | 4,427 | | | | 2,910 | | | | | |
(1) Including expenses in respect of related parties - see Note 14.
| | | Three months ended June 30, | | | Three months ended June 30, | |
| | | 2022 | | | 2021 | |
| | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | |
| | | | | | | |
Salaries, wages and related expenses(1) | | | 1,206 | | | | 830 | |
Share-based payment(1) | | | 193 | | | | 200 | |
| Materials | | | 295 | | | | 342 | |
| Professional services | | | 190 | | | | 86 | |
| Maintenance, office and software fees | | | 78 | | | | 42 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | | 250 | | | | 149 | |
| D&O insurance | | | 32 | | | | 66 | |
| Others | | | 41 | | | | | |
| Total Research and Development Expenses | | | 2,285 | | | | 1,783 | |
(1) Including expenses in respect of related parties - see Note 14.
Note 10 – Marketing Expenses
| | | Six months ended June 30, | | | Six months ended June 30, | | | Year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2022 | | | 2021 | | | 2021 | |
| | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
Salaries, wages and related expenses(1) | | | 445 | | | | 243 | | | | 494 | |
Share-based payment(1) | | | 528 | | | | 76 | | | | 570 | |
| PR and advertisement | | | 817 | | | | 269 | | | | 507 | |
| Maintenance, office and software fees | | | 41 | | | | 7 | | | | 22 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | | 54 | | | | 5 | | | | 17 | |
| D&O insurance | | | 43 | | | | 0 | | | | - | |
| Others | | | 31 | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Marketing Expenses | | | 1,959 | | | | 605 | | | | | |
(1) Including expenses in respect of related parties - see Note 14.
| | | Three months ended June 30, | | | Three months ended June 30, | |
| | | 2022 | | | 2021 | |
| | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | |
| | | | | | | |
Salaries, wages and related expenses(1) | | | 235 | | | | 120 | |
Share-based payment(1) | | | 71 | | | | 27 | |
| PR and advertisement | | | 523 | | | | 127 | |
| Maintenance, office and software fees | | | 14 | | | | 3 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | | 23 | | | | 7 | |
| D&O insurance | | | 18 | | | | - | |
| Others | | | 24 | | | | | |
| Total Marketing Expenses | | | 908 | | | | 285 | |
(1) Including expenses in respect of related parties - see Note 14.
Note 11 – General and Administrative Expenses
| | | Six months ended June 30, | | | Six months ended June 30, | | | Year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2022 | | | 2021 | | | 2021 | |
| | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
Salaries, wages and related expenses(1) | | | 969 | | | | 556 | | | | 1,328 | |
Share-based payment(1) | | | 302 | | | | 1,774 | | | | 2,484 | |
Legal and professional services(1) | | | 1,096 | | | | 739 | | | | 1,499 | |
| D&O insurance | | | 665 | | | | 680 | | | | 1,837 | |
| Corporate costs | | | 111 | | | | 227 | | | | 343 | |
| Maintenance, office and software fees | | | 172 | | | | 54 | | | | 149 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | | 190 | | | | 97 | | | | 263 | |
| Others | | | 182 | | | | | | | | | |
| Total General and Administrative Expenses | | | 3,687 | | | | 4,159 | | | | | |
(1) Including expenses in respect of related parties - see Note 14.
| | | Three months ended June 30, | | | Three months ended June 30, | |
| | | 2022 | | | 2021 | |
| | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | |
| | | | | | | |
Salaries, wages and related expenses(1) | | | 494 | | | | 227 | |
Share-based payment(1) | | | 75 | | | | 208 | |
Legal and professional services(1) | | | 469 | | | | 155 | |
| D&O insurance | | | 203 | | | | 565 | |
| Corporate costs | | | 64 | | | | 135 | |
| Maintenance, office and software fees | | | 79 | | | | 20 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | | 88 | | | | 78 | |
| Others | | | 97 | | | | | |
| Total General and Administrative Expenses | | | 1,569 | | | | 1,399 | |
(1) Including expenses in respect of related parties - see Note 14.
Note 12 – Financing Income and Expenses
| | | Six months ended June 30, | | | Six months ended June 30, | | | Year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2022 | | | 2021 | | | 2021 | |
| | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | |
| Financial Income | | | | | | | | | |
| Net change in fair value of financial instruments mandatorily measured at fair value through profit or loss | | | 80 | | | | 401 | | | | 509 | |
| Net foreign exchange income | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Financial Income | | | 1,062 | | | | 401 | | | | 509 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Financial Expenses | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net foreign exchange loss | | | - | | | | 485 | | | | 1,279 | |
| Interest expense on lease liabilities | | | 137 | | | | 1 | | | | 9 | |
| Bank interest and commission expenses | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Financial Expenses | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net financing expenses (income) recognized in profit or loss | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Three months ended June 30, | | | Three months ended June 30, | |
| | | 2022 | | | 2021 | |
| | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | |
| Financial Income | | | | | | |
Net change in fair value of financial instruments mandatorily measured at fair value through profit or loss(1) | | | 36 | | | | 24 | |
| Net foreign exchange income | | | | | | | | |
| Total Financial Income | | | 678 | | | | 24 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Financial Expenses | | | | | | | | |
| Net foreign exchange loss | | | - | | | | 659 | |
| Interest expense on lease liabilities | | | 81 | | | | - | |
| Bank interest and commission expenses | | | | | | | | |
| Total Financial Expenses | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Net financing expenses (income) recognized in profit or loss | | | | | | | | |
Note 13 – Contingent Liabilities
From time to time, the Company may be party to litigation or other legal proceedings that it considers to be a part of the ordinary course of its business. The Company is not currently involved in any legal proceedings that could reasonably be expected to have a material adverse effect on its business, prospects, financial condition or results of operations.
In November 2020, the Israeli Securities Authority, or ISA, initiated an administrative proceeding claiming negligent misstatement regarding certain immediate and periodic reports published by the Company’s predecessor (Ophectra) during the years 2017 and 2018, prior to the merger with MeaTech and prior to establishment of the settlement fund in connection with the Merger. In February 2021, the trustee of the settlement fund informed the Company that the ISA views the Company as a party to this proceeding, notwithstanding the settlement and establishment of the settlement fund. This proceeding is of an administrative nature and carries a potential penalty in the form of a monetary fine which, under applicable Israeli law, could be as high as NIS 5 million. In April 2021, following negotiations with the ISA, the Company agreed to settle the matter for $0.2 million (NIS 0.7 million), for which the Company recorded a provision. The settlement is subject to approval of the ISA’s Enforcement Committee. Similar proceedings were initiated with several other companies where the verdict, as of now, is that the companies are not to be held liable to the claims. There for, the Company initiated procedures to try and reclaim its innocence. As of now, due to lack of certainty, the Company keeps its provision stated above.
In February 2021, a civil claim was lodged against the settlement fund, relating to Ophectra's activities prior to establishment of the settlement fund, in an amount of USD $0.7 million (NIS 2.5 million). The Company believes that it is more likely than not that no final ruling will be decided against the settlement fund.
Note 14 – Related and Interested Parties
Balances with related parties
| | | Six months ended June 30, | | | Six months ended June 30, | | | Year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2022 | | | 2021 | | | 2021 | |
| | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Trade and other payables | | | 165 | | | | 106 | | | | 261 | |
Expense amounts with respect to related parties
| | | Period ended June 30, | | | Period ended June 30, | | | Year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2022 | | | 2021 | | | 2021 | |
| | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | |
| General and administrative expenses | | | | | | | | | |
| Salaries, wages and related expenses | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Legal and professional services | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Share-based payments | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Sales and Marketing expenses | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Salaries, wages and related expenses | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Professional services | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Share-based payments | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Research & Development expenses | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Salaries, wages and related | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Share-based payments | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Key Management Personnel
The Company recognizes three key management personnel as related parties, namely Mr. Arik Kaufman – Chief Executive Officer (CEO), Mr. Guy Hefer – Chief Financial Officer (CFO) and Mr. Dan Kozlovski – Chief Technologies Officer (CTO), who served as Vice President of Research and Development (VP R&D) until February 2022. In addition, Mr. Omri Schanin served as Deputy Chief Executive Officer until April 2022.
The CEO has been employed by the Company since January 24, 2022. He previously served as a director until May 2020 (including as interim chairman from March 2020) and a consultant of the Company until his appointment as CEO. Mr. Kaufman is entitled to a gross annual salary of NIS 0.6 million (USD 0.2 million), an annual bonus based primarily on milestone achievement, generally accepted social benefit contributions for senior executives and domestic travel expenses. Mr. Kaufman has also received options valued at an aggregate of NIS 0.46 million (USD 0.14 million) to be recognized over a three-year vesting period commencing in 2022.
Note 14 – Related and Interested Parties (Cont.)
Mr. Kaufman is a founding partner of BlueOcean Sustainability Fund, LLC, a Delaware LLC doing business as BlueSoundWaves, led by Ashton Kutcher, Guy Oseary and Effie Epstein, which provides the Company with marketing and promotional, consulting, and partner and investor engagement services in the U.S., in return for which BlueSoundWaves received warrants to purchase ordinary shares, as well as restricted share units, the expenses for which are recognized as share-based payments.
The previous CEO and CTO, who also served as a director, Mr. Sharon Fima, was employed by the Company (including MeaTech Ltd. prior to the merger described in Note 1A above) between September 1, 2019 and January 24, 2022. Mr. Fima was entitled to an annual gross salary of NIS 0.6 million (USD 0.2 million). Mr. Fima also received options valued at NIS 0.2 million (USD 0.1 million) to be recognized over three-year vesting period commencing March 2020, some of which were forfeited upon his resignation.
The former Deputy CEO, Mr. Omri Schanin, who also served as a director until January 2022, has been employed by the Company (including MeaTech Ltd. prior to the merger described in Note 1A above) since September 1, 2019. Following his notice of resignation, he no longer serves as Deputy CEO, and his resignation took effect on May 31, 2022. Mr. Schanin was entitled to an annual gross salary of NIS 0.5 million (USD 0.2 million).
The CFO has been employed by the Company since October 18, 2020. Mr. Hefer is entitled to an annual gross salary of NIS 0.5 million (USD 0.2 million). Mr. Hefer has also received options valued at an aggregate of NIS 0.75 million (USD 0.23 million) to be recognized over three-year vesting periods commencing in 2021.
The CTO (previously VP R&D), has been employed by the Company (including MeaTech Ltd. prior to the merger described in Note 1A above) since December 5, 2019. Mr. Kozlovski is entitled to an annual gross salary of NIS 0.5 million (USD 0.2 million). Mr. Kozlovski has also received options valued at of NIS 0.07 million (USD 0.02 million) to be recognized over three-year vesting period commencing in 2019.
Directors
Mr. Steve H. Lavin served as active chairman of the Company's Board of Directors between May 2020 and January 2022, and he was entitled to an annual compensation of USD 0.2 million as well as share-based compensation.
Mr. Yaron Kaiser has served as chairman of the Company’s Board of Directors since January 2022. He previously served as legal counsel to the Company and as a consultant until his appointment as Chairman. Mr. Kaiser is entitled to annual compensation of USD 0.15 million, an annual bonus equal to half the bonus awarded to the CEO, and re-imbursement of travel expenses. Mr. Kaiser is a founding partner of BlueSoundWaves, as described above.
Note 14 – Related and Interested Parties (Cont.)
Mr. Danny Ayalon served as director between May 2020 and January 2022, and was entitled to annual compensation of USD 0.03 million as well as share-based compensation.
Additional non-executive directors are since entitled to annual compensation of USD 0.03 million for their service on the Board of Directors and USD 0.005 million for service on each Board committee, as well as share-based compensation.
Note 15 – Leases
Leases in which the Group is the lessee
| 1. | Under the office leasing agreement dated May 18, 2021, the Company leased office space and parking spaces, for a monthly fee of USD 51 thousand (NIS 178 thousand) linked to the CPI, including management fees and insurance, for a period of 4 years, with an option to extend the term of the lease by an additional term of 4 years. On February 2022, after receiving the facilities, the Company initially recognized a long-term lease liability and a right-of-use asset in the amount of USD 3,625 thousand (NIS 12,687 thousand). The incremental interest rate used for estimating the liability is 8.77%.
As part of leasing these new facilities the company decided to terminate its previous leasing agreements in Israel. |
| | | USD thousands | |
| Balance as at January 1, 2020 | | | 168 | |
| Additions following the acquisition of POM | | | 16 | |
| Additions during the year | | | 512 | |
| Amortization during the year | | | (286 | ) |
| Effect of changes in exchange rates | | | (3 | ) |
| Balance as at December 31, 2021 | | | 407 | |
| Additions during the year | | | 4,127 | |
| Terminations during the year | | | (239 | ) |
| Amortization during the year | | | (281 | ) |
| Effect of changes in exchange rates | | | (402 | ) |
| Balance as at June 30, 2022 | | | 3,612 | |
Note 15 – Leases (cont.)
| 3. | Maturity analysis of for the Company’s lease liabilities |
| | | June 30, | | | June 30, | | | December 31, | |
| | | 2022 | | | 2021 | | | 2021 | |
| | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Up to one year | | | 428 | | | | 210 | | | | 165 | |
| 1-8 years | | | 3,247 | | | | 102 | | | | 246 | |
| Total | | | 3,675 | | | | 312 | | | | 411 | |
| 4. | Amounts recognized in the statement of operation |
| | | Six months ended June 30, | | | Six months ended June 30, | | | Year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2022 | | | 2021 | | | 2021 | |
| | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Amortization of ROU asset | | | 281 | | | | 131 | | | | 286 | |
| Interest expenses on lease liability | | | 137 | | | | 1 | | | | 9 | |
Total amounts paid for leasing of the offices in the period ended June 30, 2022 and December 31, 2021, was USD 367 thousand and USD 355 thousand, respectively.
Note 16 – Subsequent Event
On July 5, 2022, the Company consummated a securities purchase agreement with a single U.S. institutional investor for the purchase and sale of 600,000 American Depositary Shares (“ADSs”), each representing ten (10) ordinary shares of no par value, at a price of $3.50 per ADS, pre-funded warrants to purchase 1,257,143 ADSs at a price of $3.4999 (that were already paid) with an exercise price of $0.0001 per ADS to be paid once exercised, and warrants to purchase 1,857,143 ADSs for five years with an exercise price of $3.50 per ADS. The securities were offered in the framework of a registered direct offering. The gross proceeds were approximately $6.5 million, and the net proceeds were approximately $5.8 million.
F - 20
Steakholder Foods Ltd. (formerly known as MeaTech 3D Ltd.)
Unaudited Condensed Consolidated Interim Financial Statements As At September 30, 2022
| Financial Information of Steakholder Foods Ltd. | Page |
| | |
| | |
| | |
| Contents: | |
| | 2 |
| | 3 |
| | 5 |
| | 6 |
Unaudited Condensed consolidated interim statements of
financial position
| | | September 30 | | | September 30 | | | December 31 | |
| | | 2022 | | | 2021 | | | 2021 | |
| | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | | | USD thousands | |
Current assets | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents | | | 11,203 | | | | 25,441 | | | | 19,176 | |
| Other investment | | | 135 | | | | 149 | | | | 154 | |
| Receivables | | | 764 | | | | 1,890 | | | | | |
| Total current assets | | | 12,102 | | | | 27,480 | | | | 22,112 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Non-current assets | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Restricted deposits | | | 374 | | | | 391 | | | | 405 | |
| Other investment | | | 1,180 | | | | 1,287 | | | | 1,355 | |
| Right-of-use asset | | | 3,478 | | | | 328 | | | | 407 | |
| Intangible assets | | | 11,706 | | | | 11,362 | | | | 13,453 | |
| Fixed assets, net | | | 4,386 | | | | 2,467 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total non-current assets | | | 21,124 | | | | 15,835 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total Assets | | | 33,226 | | | | 43,315 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Current liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Trade payables | | | 581 | | | | 313 | | | | 382 | |
| Other payables | | | 2,154 | | | | 1,837 | | | | 2,239 | |
| Current maturities of lease liabilities | | | 407 | | | | 251 | | | | 165 | |
| Derivative instrument | | | 2,450 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total current liabilities | | | 5,592 | | | | 2,401 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Non-current liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Long-term lease liabilities | | | 3,195 | | | | 81 | | | | 246 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total non-current liabilities | | | 3,195 | | | | 81 | | | | 246 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Capital | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Share capital and premium on shares | | | 72,231 | | | | 68,348 | | | | 69,610 | |
| Capital reserves | | | 3,581 | | | | 2,653 | | | | 3,708 | |
| Currency translation differences reserve | | | (2,771 | ) | | | 519 | | | | 1,275 | |
| Accumulated deficit | | | (48,602 | ) | | | (30,687 | ) | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total capital | | | 24,439 | | | | 40,833 | | | | | |
| Total liabilities and capital | | | 33,226 | | | | 43,315 | | | | | |
Unaudited Condensed consolidated interim of Income and of
Comprehensive Loss
| | | Nine months ended September 30, | | | Nine months ended September 30, | | | Year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2022 | | | 2021 | | | 2021 | |
| | | USD thousands, except share data | | | USD thousands, except share data | | | USD thousands, except share data | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Research and development expenses | | | 7,219 | | | | 4,928 | | | | 7,594 | |
| Marketing expenses | | | 2,426 | | | | 872 | | | | 1,628 | |
| General and administrative expenses | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operating loss | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Financing income | | | (3,258 | ) | | | (457 | ) | | | (509 | ) |
| Financing expenses | | | 262 | | | | 434 | | | | | |
| Total financing (income) expenses | | | (2,996 | ) | | | (23 | ) | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loss for the period | | | 11,631 | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Currency translation differences loss (income) that might be transferred to profit or loss over ILS | | | 2,301 | | | | (456 | ) | | | (1,942 | ) |
| Currency translation differences loss (income) that might be transferred to profit or loss over EUR | | | 1,745 | | | | 717 | | | | 1,447 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total comprehensive loss for the period | | | 15,677 | | | | 11,999 | | | | 17,527 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loss per ordinary share, no par value (USD) | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Basic and diluted loss per share (USD) | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Weighted-average number of shares outstanding - basic and diluted (shares) | | | 132,652,822 | | | | 112,891,686 | | | | 115,954,501 | |
Unaudited Condensed consolidated interim of Income and of Comprehensive Loss
| | | Three months ended September 30, | | | Three months ended September 30, | |
| | | 2022 | | | 2021 | |
| | | USD thousands, except share data | | | USD thousands, except share data | |
| | | | | | | |
| Research and development expenses | | | 2,792 | | | | 2,018 | |
| Marketing expenses | | | 467 | | | | 267 | |
| General and administrative expenses | | | | | | | | |
| Operating loss | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Financing income | | | (2,196 | ) | | | (130 | ) |
| Financing expenses | | | 117 | | | | 15 | |
| Total financing (income) expenses | | | (2,079 | ) | | | (115 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Loss for the period | | | 2,475 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Currency translation differences loss (income) that might be transferred to profit or loss over ILS | | | (25 | ) | | | (163 | ) |
| Currency translation differences loss (income) that might be transferred to profit or loss over EUR | | | 898 | | | | 501 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Total comprehensive loss for the period | | | 3,348 | | | | 4,310 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Loss per ordinary share, no par value (USD) | | | | | | | | |
| Basic and diluted loss per share (USD) | | | 0.017 | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Weighted-average number of shares outstanding - basic and diluted (shares) | | | | | | | 124,048,833 | |
Unaudited Condensed consolidated interim statements of
changes in equity
| | | Premium and Capital Share | | | Fair value of financial assets reserve | | | Transactions with related parties reserve | | | Currency translation differences reserve | | | Share-based payments reserve | | | Accumulated deficit | | | Total | |
| | | USD thousands | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance as at January 1, 2022 | | | 69,610 | | | | (334 | ) | | | 14 | | | | 1,275 | | | | 4,028 | | | | (36,971 | ) | | | 37,622 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Share-based payments | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,092 | | | | - | | | | 1,092 | |
| Issuance of shares and warrants, net | | | 1,348 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,348 | |
| Exercise of options | | | 1,273 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (1,219 | ) | | | | | | | 54 | |
| Other comprehensive income (loss) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (4,046 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | (4,046 | ) |
| Loss for the period | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (11,631 | ) | | | (11,631 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance as at September 30, 2022 | | | 72,231 | | | | (334 | ) | | | 14 | | | | (2,771 | ) | | | 3,901 | | | | (48,602 | ) | | | 24,439 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance as at January 1, 2021 | | | 30,481 | | | | (334 | ) | | | 14 | | | | 780 | | | | 3,639 | | | | (18,949 | ) | | | 15,631 | |
| | | | 0 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 0 | | | | | | | | | |
| Share-Based Payment | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 2,829 | | | | - | | | | 2,829 | |
| Issuance of shares and warrants, net | | | 31,176 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 31,176 | |
| Exercise of options | | | 6,691 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (3,495 | ) | | | | | | | 3,196 | |
| Other comprehensive income (loss) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (261 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | (261 | ) |
| Loss for the period | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (11,738 | ) | | | (11,738 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 0 | | | | | | | | | |
Balance as at September 30, 2021 | | | 68,348 | | | | (334 | ) | | | 14 | | | | 519 | | | | 2,973 | | | | (30,687 | ) | | | 40,833 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| |
Balance as at January 1, 2021 | | | 30,481 | | | | (334 | ) | | | 14 | | | | 780 | | | | 3,639 | | | | (18,949 | ) | | | 15,631 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Share-based payments | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 3,965 | | | | - | | | | 3,965 | |
| Issuance of shares and warrants, net | | | 32,330 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 32,330 | |
| Exercise of options | | | 6,799 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (3,576 | ) | | | | | | | 3,223 | |
| Other comprehensive income (loss) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 495 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 495 | |
| Loss for the period | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (18,022 | ) | | | (18,022 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance as at December 31, 2021 | | | 69,610 | | | | (334 | ) | | | 14 | | | | 1,275 | | | | 4,028 | | | | (36,971 | ) | | | 37,622 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Unaudited Condensed consolidated interim statements of
cash flows
| | | Nine months ended September 30, | | | Nine months ended September 30,
2021 | | | Year ended December 31, 2021 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
Cash flows - operating activities | | | | | | | | | |
| Net Loss for the period | | | (11,631 | ) | | | (11,738 | ) | | | (18,022 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Adjustments: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | | 1,099 | | | | 479 | | | | 680 | |
| Change in fair value of derivative | | | (2,100 | ) | | | (312 | ) | | | (316 | ) |
| Change in fair value of other investment | | | (99 | ) | | | (138 | ) | | | (193 | ) |
| Net foreign exchange expenses | | | (901 | ) | | | 411 | | | | 1,279 | |
| Interest expense over lease liabilities | | | 250 | | | | 7 | | | | 9 | |
| Interest income over short term deposits | | | (73 | ) | | | - | | | | - | |
| Share-based payment expenses | | | 1,092 | | | | 2,829 | | | | 3,965 | |
| Changes in asset and liability items: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Decrease (increase) in receivables | | | 1,790 | | | | (1,523 | ) | | | (2,351 | ) |
| Increase (decrease) in trade payables | | | 315 | | | | (309 | ) | | | (97 | ) |
| Increase (decrease) in other payables | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net cash from (used in) operating activities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash flows - investment activities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Acquisition of fixed assets | | | (2,686 | ) | | | (1,124 | ) | | | (1,828 | ) |
| Increase in restricted deposit | | | (20 | ) | | | (337 | ) | | | (337 | ) |
| Loan provided | | | - | | | | (367 | ) | | | (367 | ) |
| Proceeds on account of other investment* | | | 110 | | | | 111 | | | | 149 | |
| Interest received over short term deposits | | | 73 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Acquisition of other investments, net of cash acquired | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net cash used in investing activities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash flows - financing activities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Proceeds from issuance of shares and warrants | | | 2,005 | | | | 29,281 | | | | 29,281 | |
| Issuance costs | | | (657 | ) | | | (3,283 | ) | | | (3,283 | ) |
| Repayment of liability for lease | | | (316 | ) | | | (222 | ) | | | (346 | ) |
| Repayment of interest over liability of lease | | | (250 | ) | | | (7 | ) | | | (9 | ) |
| Proceeds with regard to derivative | | | 4,495 | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Proceeds from exercise of share options | | | 53 | | | | 3,196 | | | | 3,222 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net cash from financing activities | | | 5,330 | | | | 28,965 | | | | 28,865 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Increase (Decrease) in cash and cash equivalents | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Effect of exchange differences on cash and cash equivalents | | | (747 | ) | | | (66 | ) | | | (103 | ) |
| Cash and cash equivalents at the beginning of the period: | | | 19,176 | | | | 13,556 | | | | 13,556 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash balance and cash equivalents at end of period | | | 11,203 | | | | 25,441 | | | | 19,176 | |
| Non-cash activities | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Purchase of fixed assets yet to be paid | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Issue of shares and options against intangible asset | | | | | | | | | | | | |
*Reclassified
6
Up to American Depositary Shares, each representing ten (10) Ordinary Shares
Warrants to Purchase American Depository Shares, each representing ten (10) Ordinary Shares
Pre-Funded Warrants to Purchase American Depositary Shares, each representing ten (10) Ordinary Shares

Steakholder Foods Ltd.
.
PROSPECTUS
, 2022
| Sole Book-Running Manager |
| |
A.G.P.
|
|
| Lead Manager |
| Maxim Group LLC |
PART II
INFORMATION NOT REQUIRED IN PROSPECTUS
Item 6. Indemnification of Office Holders (including Directors).
Under the Israeli Companies Law 5759-1999, or the Companies Law, a company may not exculpate an office holder from liability for a breach of the duty of loyalty. An Israeli company may exculpate an office holder in advance from liability to the company, in whole or in part, for damages caused to the company as a result of a breach of duty of care but only if a provision authorizing such exculpation is included in its articles of association. Our articles of association include such a provision.
Under the Companies Law, a company may indemnify an office holder in respect of the following liabilities and expenses incurred for acts performed by him or her as an office holder, pursuant to an undertaking made either in advance of an event or following an event, provided its articles of association include a provision authorizing such indemnification (ours contain such a provision):
| • | a financial liability imposed on him or her in favor of another person pursuant to a judgment, including a settlement or arbitrator’s award approved by a court. However, if an undertaking to indemnify an office holder with respect to such liability is provided in advance, then such an undertaking must be limited to events which, in the opinion of the board of directors, can be foreseen based on the company’s activities when the undertaking to indemnify is given, and to an amount or according to criteria determined by the board of directors as reasonable under the circumstances, and such undertaking shall detail the above-mentioned foreseen events and amount or criteria; |
| • | reasonable litigation expenses, including attorneys’ fees, incurred by the office holder: (i) as a result of an investigation or proceeding instituted against him or her by an authority authorized to conduct such investigation or proceeding, provided that (A) no indictment was filed against such office holder as a result of such investigation or proceeding; and (B) no financial liability, such as a criminal penalty, was imposed upon him or her as a substitute for the criminal proceeding as a result of such investigation or proceeding, or, if such financial liability was imposed, it was imposed with respect to an offense that does not require proof of criminal intent; and (ii) in connection with a monetary sanction; and |
| • | reasonable litigation expenses, including attorneys’ fees, incurred by the office holder or imposed by a court in proceedings instituted against him or her by the company, on its behalf, or by a third party, or in connection with criminal proceedings in which the office holder was acquitted, or as a result of a conviction for an offense that does not require proof of criminal intent. |
Under the Companies Law and the Israeli Securities Law 5728-1968, or the Israeli Securities Law, a company may insure an office holder against the following liabilities incurred for acts performed by him or her as an office holder if and to the extent provided in the company’s articles of association:
| • | a breach of the duty of loyalty to the company, provided that the office holder acted in good faith and had a reasonable basis to believe that the act would not harm the company; |
| • | a breach of duty of care to the company or to a third party, to the extent such a breach arises out of the negligent conduct of the office holder; and |
| • | a financial liability imposed on the office holder in favor of a third party. |
Under our articles of association, we may insure and indemnify an office holder against the aforementioned liabilities as well as the following liabilities:
| • | any breach of duty of care to us or to a third party; |
| • | any other action which is permitted by law to insure an office holder against; |
| • | any expenses incurred and/or paid by the office holder in connection with an administrative enforcement procedure under any applicable law, including the Efficiency of Enforcement Procedures in the Securities Authority Law (legislation amendments), 5771-2011, and the Israeli Securities Law, which we refer to as an Administrative Enforcement Procedure, and including reasonable litigation expenses and attorney fees; and |
| • | any financial liability in favor of a victim of a felony pursuant to Section 52ND of the Israeli Securities Law. |
Under the Companies Law, a company may not indemnify, exculpate or insure an office holder against any of the following:
| • | a breach of the duty of loyalty, except for indemnification and insurance for a breach of the duty of loyalty to the company to the extent that the office holder acted in good faith and had a reasonable basis to believe that the act would not harm the company; |
| • | a breach of duty of care committed intentionally or recklessly, excluding a breach arising solely out of the negligent conduct of the office holder; |
| • | an act or omission committed with intent to derive illegal personal benefit; or |
| • | a civil or administrative fine or forfeit levied against the office holder. |
Our articles of association permit us to exculpate, indemnify and insure our office holders to the fullest extent permitted or to be permitted by the Companies Law and the Israeli Securities Law.
Under the Companies Law, exculpation, indemnification and insurance for office holders in a public company must be approved by the compensation committee and the board of directors, and, with respect to certain office holders or under certain circumstances, also by the shareholders. We have obtained the foregoing approvals with respect to our office holders, and have entered into agreements with each of our office holders exculpating them to the fullest extent permitted by law and by our articles of association, and undertaking to indemnify them to the fullest extent permitted by law and our articles of association. This indemnification is limited to events determined as foreseeable by the board of directors based on our activities, and to an amount or according to criteria determined by the board of directors as reasonable under the circumstances.
The maximum indemnification amount set forth in such agreements is limited to the greater of (i) $20,000,000 and (ii) 25% of our Company’s shareholders’ equity set forth on our Company’s most recent consolidated balance sheet at the time that the obligation to indemnify hereunder is incurred. Such maximum amount is in addition to any amount paid (if paid) under insurance and/or by a third-party pursuant to an indemnification arrangement. In the opinion of the SEC, indemnification of directors and office holders for liabilities arising under the Securities Act, however, is against public policy and therefore unenforceable.
We have obtained directors’ and officers’ liability insurance for the benefit of our office holders and intend to continue to maintain such coverage and pay all premiums thereunder to the fullest extent permitted by the Companies Law.
Item 7. Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities.
Since inception of our predecessor entity, MeaTech Ltd. (now known as Steakholder Foods Ltd.), we have issued securities which were not registered under the Securities Act as set forth below.
The following is a summary of transactions during the preceding three years involving sales of our securities that were not registered under the Securities Act:
| | • | In September and October 2019, we issued 19,681 Ordinary Shares to certain investors at a price of $95.94 per share and 9,839 warrants exercisable into Ordinary Shares at an exercise price of $353 per warrant, for aggregate gross proceeds of $1.89 million. |
| | • | In May 2020, we issued to certain investors 1,391,794 Ordinary Shares and warrants to purchase 8,040,382 Ordinary Shares at an exercise price of NIS 3.36 per warrant, for aggregate gross proceeds of $1 million. |
| | • | In May 2020, we issued to certain investors 4,398,570 Ordinary Shares and 4,398,570 options to purchase Ordinary Shares at an exercise price of NIS 3.03, for aggregate gross proceeds of $2.4 million. |
| | • | In August 2020, we issued to certain investors 5,292,160 Ordinary Shares and warrants exercisable into 7,409,021 Ordinary Shares at an exercise price of NIS 3.95 per share, for aggregate gross proceeds of $5.8 million, as well as rights exercisable into 1,374,998 Ordinary Shares at an exercise price of NIS 3.00 per share, and rights for warrants exercisable into 1,925,000 Ordinary Shares at an exercise price of NIS 3.95 per share. |
| | • | In December 2020, we issued to certain investors 6,791,600 Ordinary Shares, warrants exercisable into 3,395,800 Ordinary Shares at an exercise price of NIS 5.00 per share and warrants exercisable into 3,395,800 Ordinary Shares at an exercise price of NIS 6.00 per share, for aggregate gross proceeds of $7.3 million. |
| | • | In February 2021, we issued 4,070,766 Ordinary Shares and rights to purchase 4,070,766 additional Ordinary Shares, vesting with no exercise price upon the achievement of certain milestones, to certain shareholders of Peace of Meat, in the course of purchasing the entire outstanding equity of Peace of Meat in return for a combination of cash and our securities. |
| • | In October 2021, we issued options to purchase 6,251,770 Ordinary Shares exercisable at a price at or above the closing price at the time of allocation (the precise price to be determined by the amount of increase in the ADS price by the time of exercise), and restricted share units vesting into 1,243,150 Ordinary Shares with no exercise price, all vesting between one and three years from the date of allocation and subject to acceleration upon milestone achievement, to our partner BlueSoundWaves in return for services related to accelerating our growth in developing and commercializing our proprietary cultured meat production technologies. |
We believe that the offers, sales and issuances of the securities described in the preceding paragraphs were exempt from registration either (a) under Section 4(a)(2) of the Securities Act and the rules and regulations promulgated thereunder (including Regulation D and Rule 506), in that the transactions were between an issuer and sophisticated investors or members of its senior executive management and did not involve any public offering within the meaning of Section 4(a)(2) or (b) under Regulation S promulgated under the Securities Act in that offers, sales and issuances were not made to persons in the United States and no directed selling efforts were made in the United States
Item 8. Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules.
EXHIBIT INDEX
| Exhibit No. | | Description |
| 1.1* | | Form of Underwriting Agreement |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
| 4.3* | | Form of Underwriter Warrant (included in Exhibit 1.1) |
4.4*
| | Form of Warrant |
4.5*
| | Form of Pre-Funded Warrant |
| 5.1* | | Opinion of Meitar | Law Offices, Israeli counsel to the registrant |
| 5.2* | | Opinion of Greenberg Traurig, P.A., U.S. counsel to the registrant |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
| 23.2* | | Consent of Meitar | Law Offices, Israeli counsel to the registrant (included in Exhibit 5.1) |
| 23.3* | | Consent of Greenberg Traurig, P.A., U.S. counsel to the registrant (included in Exhibit 5.2) |
|
| |
|
| |
* To be filed by amendment. ** Filed herewith. # English translation of original Hebrew document. | |
Financial Statement Schedules:
All Financial Statement Schedules have been omitted because either they are not required, are not applicable or the information required therein is otherwise set forth in the Registrant’s consolidated financial statements and related notes thereto.
Item 9. Undertakings.
| | (a) | The undersigned Registrant hereby undertakes: |
| | (1) | To file, during any period in which offers or sales are being made, a post-effective amendment to this registration statement: |
| | i. | To include any prospectus required by section 10(a)(3) of the Securities Act of 1933; |
| | ii. | To reflect in the prospectus any facts or events arising after the effective date of the registration statement (or the most recent post-effective amendment thereof) which, individually or in the aggregate, represent a fundamental change in the information set forth in the registration statement. Notwithstanding the foregoing, any increase or decrease in volume of securities offered (if the total dollar value of securities offered would not exceed that which was registered) and any deviation from the low or high end of the estimated maximum offering range may be reflected in the form of prospectus filed with the Commission pursuant to Rule 424(b) if, in the aggregate, the changes in volume and price represent no more than 20% change in the maximum aggregate offering price set forth in the “Calculation of Registration Fee” table in the effective registration statement; |
| | iii. | To include any material information with respect to the plan of distribution not previously disclosed in the registration statement or any material change to such information in the registration statement. |
| | (2) | That, for the purpose of determining any liability under the Securities Act of 1933, each such post-effective amendment shall be deemed to be a new registration statement relating to the securities offered therein, and the offering of such securities at that time shall be deemed to be the initial bona fide offering thereof. |
| | (3) | To remove from registration by means of a post-effective amendment any of the securities being registered which remain unsold at the termination of the offering. |
| | (4) | To file a post-effective amendment to the registration statement to include any financial statements required by Item 8.A. of Form 20-F at the start of any delayed offering or throughout a continuous offering. Financial statements and information otherwise required by Section 10(a)(3) of the Act need not be furnished, provided that the registrant includes in the prospectus, by means of a post-effective amendment, financial statements required pursuant to this paragraph (a)(4) and other information necessary to ensure that all other information in the prospectus is at least as current as the date of those financial statements. Notwithstanding the foregoing, with respect to registration statements on Form F-3, a post-effective amendment need not be filed to include financial statements and information required by Section 10(a)(3) of the Act or Rule 3-19 of this chapter if such financial statements and information are contained in periodic reports filed with or furnished to the Commission by the registrant pursuant to section 13 or section 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 that are incorporated by reference in the Form F-3. |
| | (5) | That, for the purpose of determining liability under the Securities Act of 1933 to any purchaser: |
| | i. | If the registrant is relying on Rule 430B: |
| | A. | Each prospectus filed by the registrant pursuant to Rule 424(b)(3) shall be deemed to be part of the registration statement as of the date the filed prospectus was deemed part of and included in the registration statement; and |
| | B. | Each prospectus required to be filed pursuant to Rule 424(b)(2), (b)(5), or (b)(7) as part of a registration statement in reliance on Rule 430B relating to an offering made pursuant to Rule 415(a)(1)(i), (vii), or (x) for the purpose of providing the information required by section 10(a) of the Securities Act of 1933 shall be deemed to be part of and included in the registration statement as of the earlier of the date such form of prospectus is first used after effectiveness of the date of the first contract or sale of securities in the offering described in the prospectus. As provided in Rule 430B, for liability purposes of the issuer and any person that is at that date an underwriter, such date shall be deemed to be a new effective date of the registration statement relating to the securities in the registration statement to which that prospectus relates, and the offering of such securities at that time shall be deemed to be the initial bona fide offering thereof. Provided, however, that no statement made in a registration statement or prospectus that is part of the registration statement or made in a document incorporated or deemed incorporated by reference into the registration statement or prospectus that is part of the registration statement will, as to a purchaser with a time of contract sale prior to such effective date, supersede or modify any statement that was made in the registration statement or prospectus that was part of the registration statement or made in any such document immediately prior to such effective date; or |
| | ii. | If the registrant is subject to Rule 430C, each prospectus filed pursuant to Rule 424(b) as part of a registration statement relating to an offering, other than registration statements relying on Rule 430B or other prospectuses filed in reliance on Rule 430A, shall be deemed to be part of and included in the registration statement as of the date it is first used after effectiveness. Provided, however, that no statement made in a registration statement or prospectus that is part of the registration statement or made in a document incorporated or deemed incorporated by reference into the registration statement or prospectus that is part of the registration statement will, as to a purchaser with a time of contract of sale prior to such first use, supersede or modify any statement that was made in the registration statement or prospectus that was part of the registration statement or made in any such document immediately prior to such date of first use. |
| | (6) | That, for the purpose of determining liability of the registrant under the Securities Act of 1933 to any purchaser in the initial distribution of the securities, the undersigned registrant undertakes that in a primary offering of securities of the undersigned registrant pursuant to this registration statement, regardless of the underwriting method used to sell the securities to the purchaser, if the securities are offered or sold to such purchaser by means of any of the following communications, the undersigned registrant will be a seller to the purchaser and will be considered to offer or sell securities to such purchaser: |
| | i. | Any preliminary prospectus or prospectus of the undersigned registrant relating to the offering required to be filed pursuant to Rule 424; |
| | | |
| | ii. | Any free writing prospectus relating to the offering prepared by or on behalf of the undersigned registrant or used or referred to by the undersigned registrant; |
| | | |
| | iii. | The portion of any other free writing prospectus relating to the offering containing material information about the undersigned registrant or its securities provided by or on behalf of the undersigned registrant; and |
| | | |
| | iv. | Any other communication that is an offer in the offering made by the undersigned registrant to the purchaser. |
(b) Insofar as indemnification for liabilities arising under the Securities Act of 1933 may be permitted to directors, officers and controlling persons of the registrant pursuant to the provisions described in Item 6 hereof, or otherwise, the registrant has been advised that in the opinion of the SEC such indemnification is against public policy as expressed in the Act and is, therefore, unenforceable. In the event that a claim for indemnification against such liabilities (other than the payment by the registrant of expenses incurred or paid by a director, officer or controlling person of the registrant in the successful defense of any action, suit or proceeding) is asserted by such director, officer or controlling person in connection with the securities being registered, the registrant will, unless in the opinion of its counsel the matter has been settled by controlling precedent, submit to a court of appropriate jurisdiction the question whether such indemnification by it is against public policy as expressed in the Act and will be governed by the final adjudication of such issue.
(c) The undersigned registrant hereby undertakes that:
| | (1) | That for purposes of determining any liability under the Securities Act of 1933, the information omitted from the form of prospectus filed as part of this registration statement in reliance upon Rule 430A and contained in a form of prospectus filed by the registrant pursuant to Rule 424(b)(1) or (4), or 497(h) under the Securities Act shall be deemed to be part of this registration statement as of the time it was declared effective. |
| | (2) | That for the purpose of determining any liability under the Securities Act of 1933, each post-effective amendment that contains a form of prospectus shall be deemed to be a new registration statement relating to the securities offered therein, and the offering of such securities at that time shall be deemed to be the initial bona fide offering thereof. |
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act of 1933, the registrant certifies that it has reasonable grounds to believe that it meets all of the requirements for filing on Form F-1 and has duly caused this registration statement to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized, in the City of Rehovot, State of Israel on November 23, 2022.
| | Steakholder Foods Ltd. |
| | |
| | By: | /s/ Arik Kaufman |
| | Name: | Arik Kaufman |
| | Title: | Chief Executive Officer |
The undersigned officers and directors of Steakholder Foods Ltd. hereby constitute and appoint each of Arik Kaufman and Guy Hefer with full power of substitution, each of them singly our true and lawful attorneys-in-fact and agents to take any actions to enable the Company to comply with the Securities Act, and any rules, regulations and requirements of the SEC, in connection with this registration statement on Form F-1, including the power and authority to sign for us in our names in the capacities indicated below any and all further amendments to this registration statement and any other registration statement filed pursuant to the provisions of Rule 462 under the Securities Act.
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act of 1933, this registration statement has been signed by the following persons in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| Signatures | | Title | | Date |
| | | | | |
/s/ Yaron Kaiser | | Chairman of the Board of Directors | | November 23, 2022 |
| Yaron Kaiser | | | | |
| | | | | |
/s/ Arik Kaufman | | Chief Executive Officer and Director (Principal Executive Officer) | | November 23, 2022 |
| Arik Kaufman | | | | |
| | | | | |
/s/ Guy Hefer | | Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) | | November 23, 2022 |
| Guy Hefer | | | | |
| | | | | |
/s/ Eli Arad | | Director | | November 23, 2022 |
| Eli Arad | | | | |
| | | | | |
/s/ David Gerbi | | Director | | November 23, 2022 |
| David Gerbi | | | | |
| | | | | |
/s/ Sari Singer | | Director | | November 23, 2022 |
| Sari Singer | | | | |
SIGNATURE OF AUTHORIZED REPRESENTATIVE IN THE UNITED STATES
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, the Registrant’s duly authorized representative has signed this registration statement on Form F-1 on November 23, 2022.
| | Steakholder Foods USA, Inc. |
| | |
| | Authorized U.S. Representative |
| | |
| | By: | /s/ Arik Kaufman |
| | Name: | Arik Kaufman |
| | Title: | President |
II - 8