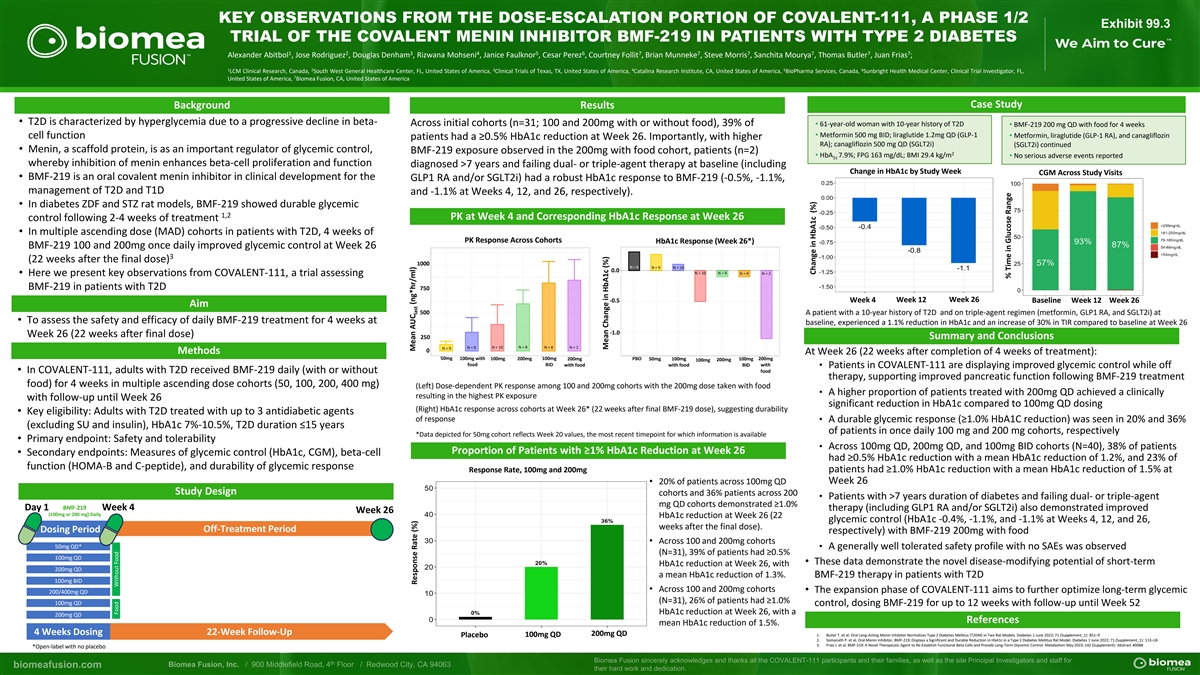
KEY OBSERVATIONS FROM THE DOSE-ESCALATION PORTION OF COVALENT-111, A PHASE 1/2 Exhibit 99.3 TRIAL OF THE COVALENT MENIN INHIBITOR BMF-219 IN PATIENTS WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 7 7 7 7 7 Alexander Abitbol , Jose Rodriguez , Douglas Denham , Rizwana Mohseni , Janice Faulknor , Cesar Perez , Courtney Follit , Brian Munneke , Steve Morris , Sanchita Mourya , Thomas Butler , Juan Frias ; 1 2 3 4 5 6 LCM Clinical Research, Canada, South West General Healthcare Center, FL, United States of America, Clinical Trials of Texas, TX, United States of America, Catalina Research Institute, CA, United States of America, BioPharma Services, Canada, Sunbright Health Medical Center, Clinical Trial Investigator, FL, 7 United States of America, Biomea Fusion, CA, United States of America Case Study Background Results • T2D is characterized by hyperglycemia due to a progressive decline in beta- Across initial cohorts (n=31; 100 and 200mg with or without food), 39% of • 61-year-old woman with 10-year history of T2D • BMF-219 200 mg QD with food for 4 weeks • Metformin 500 mg BID; liraglutide 1.2mg QD (GLP-1 cell function • Metformin, liraglutide (GLP-1 RA), and canagliflozin patients had a ≥0.5% HbA1c reduction at Week 26. Importantly, with higher RA); canagliflozin 500 mg QD (SGLT2i) (SGLT2i) continued • Menin, a scaffold protein, is as an important regulator of glycemic control, BMF-219 exposure observed in the 200mg with food cohort, patients (n=2) 2 • HbA 7.9%; FPG 163 mg/dL; BMI 29.4 kg/m • No serious adverse events reported 1c whereby inhibition of menin enhances beta-cell proliferation and function diagnosed >7 years and failing dual- or triple-agent therapy at baseline (including Change in HbA1c by Study Week CGM Across Study Visits • BMF-219 is an oral covalent menin inhibitor in clinical development for the GLP1 RA and/or SGLT2i) had a robust HbA1c response to BMF-219 (-0.5%, -1.1%, management of T2D and T1D and -1.1% at Weeks 4, 12, and 26, respectively). • In diabetes ZDF and STZ rat models, BMF-219 showed durable glycemic 1,2 PK at Week 4 and Corresponding HbA1c Response at Week 26 control following 2-4 weeks of treatment • In multiple ascending dose (MAD) cohorts in patients with T2D, 4 weeks of PK Response Across Cohorts HbA1c Response (Week 26*) BMF-219 100 and 200mg once daily improved glycemic control at Week 26 3 (22 weeks after the final dose) 1000 N = 6 N = 9 N = 10 0.0 N = 10 N = 9 N = 9 N = 2 • Here we present key observations from COVALENT-111, a trial assessing BMF-219 in patients with T2D 750 -0.5 Week 4 Week 12 Week 26 Baseline Week 12 Week 26 Aim 500 A patient with a 10-year history of T2D and on triple-agent regimen (metformin, GLP1 RA, and SGLT2i) at • To assess the safety and efficacy of daily BMF-219 treatment for 4 weeks at baseline, experienced a 1.1% reduction in HbA1c and an increase of 30% in TIR compared to baseline at Week 26 -1.0 Week 26 (22 weeks after final dose) 250 Summary and Conclusions N = 8 N = 10 N = 8 N = 8 N = 2 N = 9 0 Methods At Week 26 (22 weeks after completion of 4 weeks of treatment): 50mg 100mg with 100mg 200mg 100mg 200mg PBO 50mg 100mg 100mg 200mg 100mg 200mg food BID with food with food BID with • Patients in COVALENT-111 are displaying improved glycemic control while off • In COVALENT-111, adults with T2D received BMF-219 daily (with or without food therapy, supporting improved pancreatic function following BMF-219 treatment food) for 4 weeks in multiple ascending dose cohorts (50, 100, 200, 400 mg) (Left) Dose-dependent PK response among 100 and 200mg cohorts with the 200mg dose taken with food • A higher proportion of patients treated with 200mg QD achieved a clinically resulting in the highest PK exposure with follow-up until Week 26 significant reduction in HbA1c compared to 100mg QD dosing (Right) HbA1c response across cohorts at Week 26* (22 weeks after final BMF-219 dose), suggesting durability • Key eligibility: Adults with T2D treated with up to 3 antidiabetic agents of response • A durable glycemic response (≥1.0% HbA1C reduction) was seen in 20% and 36% (excluding SU and insulin), HbA1c 7%-10.5%, T2D duration ≤15 years of patients in once daily 100 mg and 200 mg cohorts, respectively *Data depicted for 50mg cohort reflects Week 20 values, the most recent timepoint for which information is available • Primary endpoint: Safety and tolerability • Across 100mg QD, 200mg QD, and 100mg BID cohorts (N=40), 38% of patients Proportion of Patients with ≥1% HbA1c Reduction at Week 26 • Secondary endpoints: Measures of glycemic control (HbA1c, CGM), beta-cell had ≥0.5% HbA1c reduction with a mean HbA1c reduction of 1.2%, and 23% of function (HOMA-B and C-peptide), and durability of glycemic response Response Rate, 100mg and 200mg patients had ≥1.0% HbA1c reduction with a mean HbA1c reduction of 1.5% at • 20% of patients across 100mg QD Week 26 Study Design cohorts and 36% patients across 200 • Patients with >7 years duration of diabetes and failing dual- or triple-agent mg QD cohorts demonstrated ≥1.0% BMF-219 Day 1 Week 4 therapy (including GLP1 RA and/or SGLT2i) also demonstrated improved Week 26 (100mg or 200 mg) Daily HbA1c reduction at Week 26 (22 glycemic control (HbA1c -0.4%, -1.1%, and -1.1% at Weeks 4, 12, and 26, weeks after the final dose). Dosing Period Off-Treatment Period respectively) with BMF-219 200mg with food • Across 100 and 200mg cohorts 50mg QD* • A generally well tolerated safety profile with no SAEs was observed (N=31), 39% of patients had ≥0.5% 100mg QD • These data demonstrate the novel disease-modifying potential of short-term HbA1c reduction at Week 26, with 200mg QD a mean HbA1c reduction of 1.3%. BMF-219 therapy in patients with T2D 100mg BID • Across 100 and 200mg cohorts • The expansion phase of COVALENT-111 aims to further optimize long-term glycemic 200/400mg QD (N=31), 26% of patients had ≥1.0% 100mg QD control, dosing BMF-219 for up to 12 weeks with follow-up until Week 52 HbA1c reduction at Week 26, with a 200mg QD References mean HbA1c reduction of 1.5%. 4 Weeks Dosing 22-Week Follow-Up 200mg QD 1. Butler T. et al. Oral Long-Acting Menin Inhibitor Normalizes Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) in Two Rat Models. Diabetes 1 June 2022; 71 (Supplement_1): 851–P. Placebo 100mg QD 2. Somanath P. et al. Oral Menin Inhibitor, BMF-219, Displays a Significant and Durable Reduction in HbA1c in a Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Rat Model. Diabetes 1 June 2022; 71 (Supplement_1): 113–LB. 3. Frias J. et al. BMF-219: A Novel Therapeutic Agent to Re-Establish Functional Beta Cells and Provide Long-Term Glycemic Control. Metabolism May 2023; 142 (Supplement): Abstract #0088 *Open-label with no placebo Food Without Food Mean AUC (ng*hr/ml) Response Rate (%) last Mean Change in HbA1c (%) Change in HbA1c (%) % Time in Glucose Range
