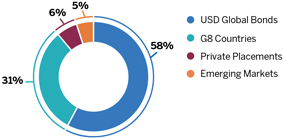
Actuarial Gains or Losses – Changes in the value of the defined benefit obligation and the plan assets due to differences between actuarial assumptions and what has actually occurred and due to changes in actuarial assumptions.
Actuarial Valuation (re: Pension Benefit Plans) – An assessment of the financial status of a benefit plan performed by an independent actuary. It includes the valuation of any plan assets and the defined benefit obligation using estimates of future events that will affect the costs and obligation for employee benefits plans.
Amortized Cost – The amount at which the financial asset or financial liability is measured at initial recognition minus principal repayments, plus or minus the cumulative amortization using the effective interest method of any difference between that initial amount and the maturity amount and minus any reduction (directly or through the use of an allowance account) for impairment or uncollectability.
Basis Point – One one-hundredth of a percentage point.
Capital Adequacy – A measurement of the amount of capital required to cover the credit, market, operational, pension and business/strategic risks we have undertaken compared to the existing capital base.
CDOR – Canadian Dollar Offered Rate – An industry determined financial benchmark and the recognized benchmark index for Canadian bankers’ acceptances with a term to maturity of one year or less.
Claims Ratio – Net claims incurred as a percentage of net written premium.
Co-insurance – Leveraging another insurer’s capacity by jointly sharing the risk of the original insurance policy.
Contingent Liability – Potential debt which arises from past events and may become an actual obligation if certain events occur or fail to occur. Contingent liability is also referred to as insurance policies and guarantees outstanding.
Credit Risk – The risk of loss incurred if a counterparty fails to meet its financial commitments.
Cross Currency Interest Rate Swaps – Transactions in which two parties exchange currencies at inception and at maturity, as well as interest flows on the exchanged amounts on predetermined dates for a specified period of time using agreed-upon fixed or floating rates of interest.
Defined Benefit Obligation – The actuarial present value, without deducting any plan assets, of expected future payments required to settle the obligation resulting from employee service in the current and prior periods.
Derivative Instruments – Financial contracts that derive their value from changes in interest rates, foreign exchange rates, credit spreads, commodity prices, equities, market indexes or other financial measures. Such instruments include futures, interest rate, foreign exchange, equity, commodity and credit default swaps.
Effective Interest Rate – The rate that exactly discounts estimated future cash payments or receipts through the expected life of the financial instrument or, when appropriate, a shorter period, to the net carrying amount of the financial asset or financial liability.
Exposure at Default – Generally represents the expected gross exposure – outstanding amount for on-balance sheet exposure and loan equivalent amount for off-balance sheet exposure.
Facultative Reinsurance – Reinsurance provided on a transactional basis.
Foreign Exchange Forwards – Commitments to exchange cash flows in different currencies, for which the foreign exchange rate is predetermined, at a specified date in the future.
Foreign Exchange Risk – The risk of loss or harm due to changes in spot and forward prices, and/or volatility of currency exchange rates.
Foreign Exchange Swaps – Commitments to exchange cash flows in different currencies where there are two exchanges; the first is made at the spot rate at inception and the second at a predetermined rate on a specified date in the future.
Gross Loans Receivable – Principal amounts outstanding under existing loan agreements.
Hedge – A risk management practice used to manage interest rate or foreign exchange exposures arising from the normal course of business operations.
Individually Impaired Loans – Loans where there is objective evidence that an impairment loss has occurred.
Insurance Risk – The risk of loss or harm due to actual experience being different from that assumed when an insurance product was designed and priced.
Interest Rate Risk – The risk that the fair value or future cash flows of a financial instrument will fluctuate because of changes in market interest rates.
Interest Rate Swaps – Transactions in which two parties exchange interest flows on a specified notional amount on predetermined dates for a specified period of time using agreed-upon fixed or floating rates of interest. Notional amounts upon which interest payments/receipts are based are not exchanged.
LIBOR – London Inter-Bank Offered Rate – The interest rate at which banks in London are prepared to lend funds to first-class banks.
Liquidity Risk – The risk that we would be unable to honour daily cash commitments or the risk that we would have to obtain funds rapidly, possibly at an excessively high premium during severe market conditions.
Loss Given Default – Measures the severity of loss on a facility in the event of a borrower’s default, expressed as a percentage of exposure at default.
Market Risk – The risk of loss or harm due to adverse movements in market prices, interest rates and/or foreign exchange rates.
Net Finance Margin – Net financing and investment income expressed as a percentage of average income earning assets.
Net Financing and Investment Income – Loan, marketable securities and investment revenues net of interest expense and financing related expenses.
Net Revenue – Net income excluding the provision for credit losses, claims-related expenses, unrealized gains and losses, and administrative expenses.
Operational Risk – The risk of loss or harm resulting from inadequate or failed internal processes, people and systems or from external events.
Performing Loans – Loans for which there is reasonable assurance that EDC can collect the principal and interest on time.
Probability of Default – The likelihood that a borrower will not be able to meet its scheduled repayments.
Productivity Ratio – Administrative expenses expressed as a percentage of net revenue excluding the impact due to fluctuations in the exchange rate from the rate projected in the Corporate Plan.
Structured Entity (SE) – An entity created to accomplish a narrow and well-defined objective. The SE is designed so that voting or similar rights are not the dominant factor in deciding who controls the entity.
Structured Notes – Hybrid securities that combine debt instruments with derivative components.
Undisbursed Loan Commitments – A contractual amount under an existing loan agreement that has yet to be advanced to the borrower.


















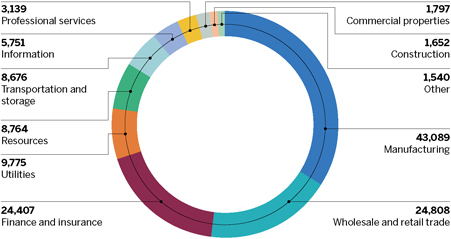
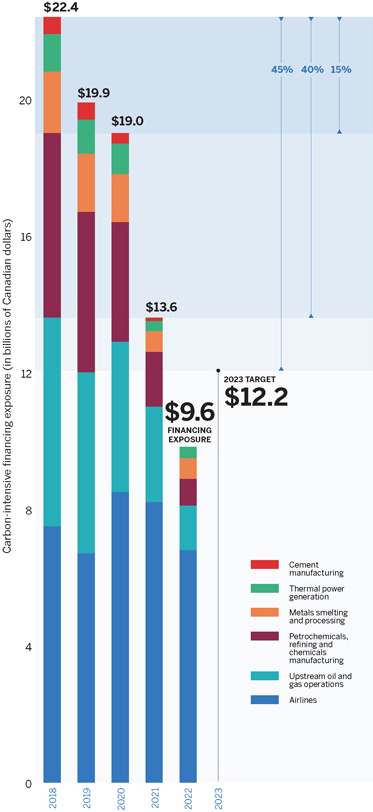
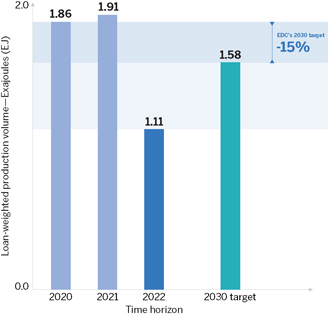




































 ASSURED
ASSURED