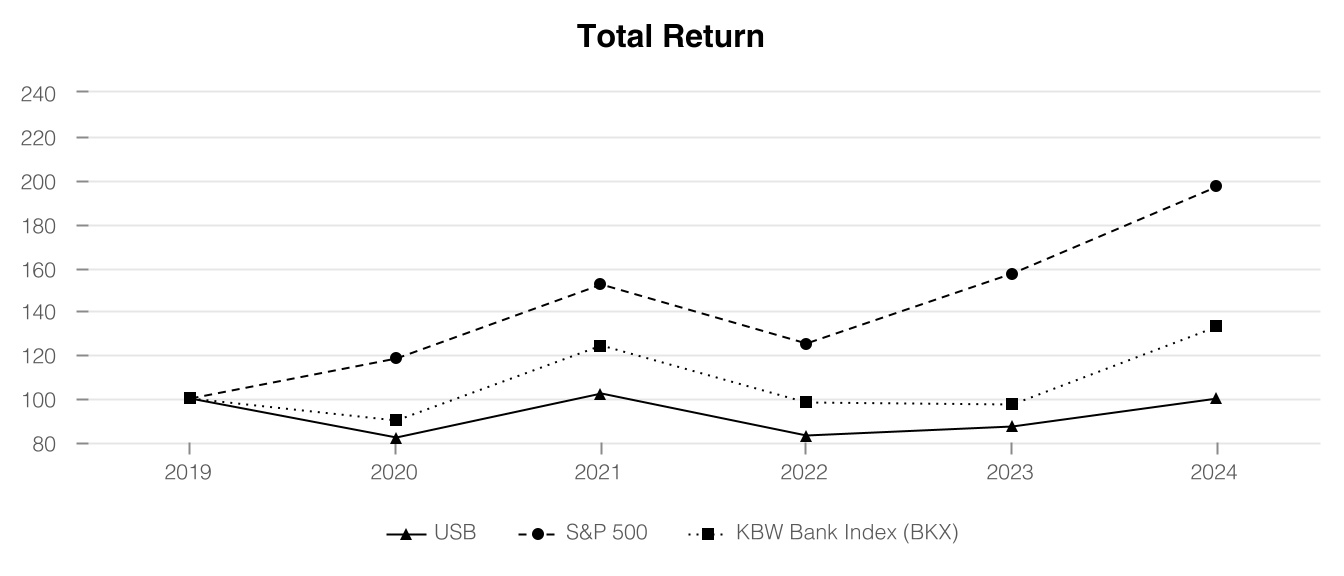
The following pages discuss in detail the financial results we achieved in 2024.
The following information appears in accordance with the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995:
This report contains forward-looking statements about U.S. Bancorp. Statements that are not historical or current facts, including statements about beliefs and expectations, are forward-looking statements and are based on the information available to, and assumptions and estimates made by, management as of the date hereof. These forward-looking statements cover, among other things, future economic conditions and the anticipated future revenue, expenses, financial condition, asset quality, capital and liquidity levels, plans, prospects and operations of U.S. Bancorp. Forward-looking statements often use words such as “anticipates,” “targets,” “expects,” “hopes,” “estimates,” “projects,” “forecasts,” “intends,” “plans,” “goals,” “believes,” “continue” and other similar expressions or future or conditional verbs such as “will,” “may,” “might,” “should,” “would” and “could.”
Forward-looking statements involve inherent risks and uncertainties that could cause actual results to differ materially from those set forth in forward-looking statements, including the following risks and uncertainties:
•Deterioration in general business and economic conditions or turbulence in domestic or global financial markets, which could adversely affect U.S. Bancorp’s revenues and the values of its assets and liabilities, reduce the availability of funding to certain financial institutions, lead to a tightening of credit, and increase stock price volatility;
•Turmoil and volatility in the financial services industry, including failures or rumors of failures of other depository institutions, which could affect the ability of depository institutions, including U.S. Bank National Association, to attract and retain depositors, and could affect the ability of financial services providers, including U.S. Bancorp, to borrow or raise capital;
•Increases in Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (“FDIC”) assessments, including due to bank failures;
•Actions taken by governmental agencies to stabilize the financial system and the effectiveness of such actions;
•Uncertainty regarding the content, timing and impact of changes to regulatory capital, liquidity and resolution-related requirements applicable to large banking organizations in response to adverse developments affecting the banking sector;
•Changes to statutes, regulations, or regulatory policies or practices, including capital and liquidity requirements, and the enforcement and interpretation of such laws and regulations, and U.S. Bancorp’s ability to address or satisfy those requirements and other requirements or conditions imposed by regulatory entities;
•Changes in trade policy, including the imposition of tariffs or the impacts of retaliatory tariffs;
•Changes in interest rates;
•Increases in unemployment rates;
•Deterioration in the credit quality of U.S. Bancorp's loan portfolios or in the value of the collateral securing those loans;
•Changes in commercial real estate occupancy rates;
•Risks related to originating and selling mortgages, including repurchase and indemnity demands, and related to U.S. Bancorp’s role as a loan servicer;
•Impacts of current, pending or future litigation and governmental proceedings;
•Increased competition from both banks and non-banks;
•Effects of climate change and related physical and transition risks;
•Changes in customer behavior and preferences and the ability to implement technological changes to respond to customer needs and meet competitive demands;
•Breaches in data security;
•Failures or disruptions in or breaches of U.S. Bancorp’s operational, technology or security systems or infrastructure, or those of third parties, including as a result of cybersecurity incidents;
•Failures to safeguard personal information;
•Impacts of pandemics, natural disasters, terrorist activities, civil unrest, international hostilities and geopolitical events;
•Impacts of supply chain disruptions, rising inflation, slower growth or a recession;
•Failure to execute on strategic or operational plans;
•Effects of mergers and acquisitions and related integration;
•Effects of critical accounting policies and judgments;
•Effects of changes in or interpretations of tax laws and regulations;
•Management’s ability to effectively manage credit risk, market risk, operational risk, compliance risk, strategic risk, interest rate risk, liquidity risk and reputation risk; and
•The risks and uncertainties more fully discussed in the section entitled “Risk Factors” of this report.
In addition, factors other than these risks also could adversely affect U.S. Bancorp’s results, and the reader should not consider these risks to be a complete set of all potential risks or uncertainties. Readers are cautioned not to place undue reliance on any forward-looking statements. Forward-looking statements speak only as of the date hereof, and U.S. Bancorp undertakes no obligation to update them in light of new information or future events.
Management’s Discussion and Analysis
Overview
U.S. Bancorp and its subsidiaries (the “Company”) continued to demonstrate financial discipline and a well-diversified business model in 2024. Financial results for 2024 included fee revenue growth, prudent expense management, stable credit quality and the accretion of common equity tier 1 capital of 70 basis points. During 2024, the Company continued to effectively manage its balance sheet while expanding interconnectedness across its businesses.
Financial Performance The Company earned $6.3 billion in 2024, or $3.79 per diluted common share, compared with $5.4 billion, or $3.27 per diluted common share in 2023.
Financial performance for 2024, compared with 2023, included the following:
•Net interest income decreased $1.1 billion (6.4 percent) due to the impact of higher interest rates on deposit mix and pricing, partially offset by modest growth in earning assets and improved asset mix;
•Noninterest income increased $429 million (4.0 percent) primarily due to higher trust and investment management fees, commercial products revenue, payment services revenue and mortgage banking revenue;
•Noninterest expense decreased $1.7 billion (8.9 percent), reflecting lower merger and integration charges and lower FDIC special assessment charges, partially offset by higher compensation and employee benefits expense;
•The provision for credit losses decreased $37 million (1.6 percent), reflecting stabilizing economic and credit trends;
•Average loans decreased $7.4 billion (1.9 percent) driven by decreases in other retail loans, commercial real estate loans and commercial loans, partially offset by increases in credit card loans and residential mortgages; and
•Average deposits increased $3.9 billion (0.8 percent), driven by increases in average total savings deposits and time deposits, partially offset by a decrease in average noninterest-bearing deposits.
Credit Quality The Company continued to prudently manage credit underwriting.
•The allowance for credit losses was $7.9 billion at December 31, 2024, an increase of $86 million (1.1 percent) compared with December 31, 2023. The increase was primarily driven by period-end loan growth.
•Nonperforming assets were $1.8 billion at December 31, 2024, an increase of $338 million (22.6 percent)
compared with December 31, 2023. The increase was primarily due to higher nonperforming commercial and commercial real estate loans.
•Net charge-offs were $2.2 billion in 2024, an increase of $247 million (13.0 percent) compared with 2023. The increase reflected higher credit card and commercial loan net charge-offs, partially offset by the impacts in the prior year of charge-offs on acquired loans and charge-offs related to balance sheet repositioning and capital management actions.
Capital Management At December 31, 2024, all of the Company’s regulatory capital ratios exceeded regulatory “well-capitalized” requirements.
•The Company’s common equity tier 1 capital ratio was 10.6 percent at December 31, 2024, an increase of 70 basis points from December 31, 2023.
•The Company resumed share repurchases in the fourth quarter of 2024, as part of a new $5.0 billion share repurchase program.
Earnings Summary The Company reported net income attributable to U.S. Bancorp of $6.3 billion in 2024, or $3.79 per diluted common share, compared with $5.4 billion, or $3.27 per diluted common share, in 2023. Return on average assets and return on average common equity were 0.95 percent and 11.7 percent, respectively, in 2024, compared with 0.82 percent and 10.8 percent, respectively, in 2023. The results for 2024 included the impact of $400 million ($300 million net-of-tax) of notable items, including $155 million of merger and integration charges associated with the 2022 acquisition of MUFG Union Bank, N.A. (“MUB”), $136 million of incremental FDIC special assessment charges and $109 million of charges related to lease impairments and operational efficiency actions. Combined, these items decreased 2024 diluted earnings per common share by $0.19. The results for 2023 included the impacts of $2.2 billion ($1.6 billion net-of-tax) of notable items, including $1.0 billion of merger and integration charges related to the MUB acquisition, $734 million of FDIC special assessment charges, $243 million of provision for credit losses related to balance sheet repositioning and capital management actions, $140 million of securities losses related to balance sheet repositioning, a $110 million charitable contribution to support a community benefit plan related to the MUB acquisition, and a $70 million discrete tax benefit. Combined, these items decreased 2023 diluted earnings per common share by $1.04.
| | |
22 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
| | | | | | | | |
| TABLE 1 | | Selected Financial Data |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Year Ended December 31 (Dollars and Shares in Millions, Except Per Share Data) | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 |
| Condensed Income Statement | | | |
| Net interest income | $ | 16,289 | | $ | 17,396 | | $ | 14,728 | |
Taxable-equivalent adjustment(a) | 120 | | 131 | | 118 | |
Net interest income (taxable-equivalent basis)(b) | 16,409 | | 17,527 | | 14,846 | |
| Noninterest income | 11,046 | | 10,617 | | 9,456 | |
| Total net revenue | 27,455 | | 28,144 | | 24,302 | |
| Noninterest expense | 17,188 | | 18,873 | | 14,906 | |
| Provision for credit losses | 2,238 | | 2,275 | | 1,977 | |
| Income before taxes | 8,029 | | 6,996 | | 7,419 | |
| Income taxes and taxable-equivalent adjustment | 1,700 | | 1,538 | | 1,581 | |
| Net income | 6,329 | | 5,458 | | 5,838 | |
| Net (income) loss attributable to noncontrolling interests | (30) | | (29) | | (13) | |
| Net income attributable to U.S. Bancorp | $ | 6,299 | | $ | 5,429 | | $ | 5,825 | |
| Net income applicable to U.S. Bancorp common shareholders | $ | 5,909 | | $ | 5,051 | | $ | 5,501 | |
| Per Common Share | | | |
| Earnings per share | $ | 3.79 | | $ | 3.27 | | $ | 3.69 | |
| Diluted earnings per share | 3.79 | | 3.27 | | 3.69 | |
| Dividends declared per share | 1.98 | | 1.93 | | 1.88 | |
Book value per share(c) | 33.19 | | 31.13 | | 28.71 | |
| Market value per share | 47.83 | | 43.28 | | 43.61 | |
| Average common shares outstanding | 1,560 | | 1,543 | | 1,489 | |
| Average diluted common shares outstanding | 1,561 | | 1,543 | | 1,490 | |
| Financial Ratios | | | |
| Return on average assets | .95 | % | .82 | % | .98 | % |
| Return on average common equity | 11.7 | | 10.8 | | 12.6 | |
Return on tangible common equity(b) | 17.2 | | 16.9 | | 17.0 | |
Net interest margin (taxable-equivalent basis)(a) | 2.70 | | 2.90 | | 2.72 | |
Efficiency ratio(b) | 62.3 | | 66.7 | | 61.4 | |
| Net charge-offs as a percent of average loans outstanding | .58 | | .50 | | .32 | |
| Average Balances | | | |
| Loans | $ | 373,875 | | $ | 381,275 | | $ | 333,573 | |
Investment securities(d) | 166,634 | | 162,757 | | 169,442 | |
| Earning assets | 606,641 | | 605,199 | | 545,343 | |
| Assets | 664,014 | | 663,440 | | 592,149 | |
| Noninterest-bearing deposits | 83,007 | | 107,768 | | 120,394 | |
| Deposits | 509,515 | | 505,663 | | 462,384 | |
| Short-term borrowings | 17,201 | | 34,141 | | 25,740 | |
| Long-term debt | 54,473 | | 44,142 | | 33,114 | |
| Total U.S. Bancorp shareholders’ equity | 57,206 | | 53,660 | | 50,416 | |
| Period End Balances | | | |
| Loans | $ | 379,832 | | $ | 373,835 | | $ | 388,213 | |
| Investment securities | 164,626 | | 153,751 | | 161,650 | |
| Assets | 678,318 | | 663,491 | | 674,805 | |
| Deposits | 518,309 | | 512,312 | | 524,976 | |
| Long-term debt | 58,002 | | 51,480 | | 39,829 | |
| Total U.S. Bancorp shareholders’ equity | 58,578 | | 55,306 | | 50,766 | |
| Asset Quality | | | |
| Nonperforming assets | $ | 1,832 | | $ | 1,494 | | $ | 1,016 | |
| Allowance for credit losses | 7,925 | | 7,839 | | 7,404 | |
| Allowance for credit losses as a percentage of period-end loans | 2.09 | % | 2.10 | % | 1.91 | % |
| Capital Ratios | | | |
| Common equity tier 1 capital | 10.6 | % | 9.9 | % | 8.4 | % |
| Tier 1 capital | 12.2 | | 11.5 | | 9.8 | |
| Total risk-based capital | 14.3 | | 13.7 | | 11.9 | |
| Leverage | 8.3 | | 8.1 | | 7.9 | |
| Total leverage exposure | 6.8 | | 6.6 | | 6.4 | |
Tangible common equity to tangible assets(b) | 5.8 | | 5.3 | | 4.5 | |
Tangible common equity to risk-weighted assets(b) | 8.5 | | 7.7 | | 6.0 | |
Common equity tier 1 capital to risk-weighted assets, reflecting the full implementation of the current expected credit losses methodology(b) | 10.5 | | 9.7 | | 8.1 | |
(a)Based on a federal income tax rate of 21 percent for those assets and liabilities whose income or expense is not included for federal income tax purposes.
(b)See Non-GAAP Financial Measures beginning on page 57. (c)Calculated as U.S. Bancorp common shareholders’ equity divided by common shares outstanding at end of the period.
(d)Excludes unrealized gains and losses on available-for-sale investment securities and any premiums or discounts recorded related to the transfer of investment securities at fair value from available-for-sale to held-to-maturity.
Total net revenue for 2024 was $689 million (2.4 percent) lower than 2023, reflecting a 6.4 percent decrease in net interest income and a 4.0 percent increase in noninterest income. The decrease in net interest income from the prior year was primarily due to the impact of higher interest rates on deposit mix and pricing, partially offset by modest growth in earning assets and improved asset mix. The increase in noninterest income was driven by higher fee revenue across most categories, partially offset by lower service charges and lower other noninterest income.
Noninterest expense in 2024 was $1.7 billion (8.9 percent) lower than 2023, primarily due to lower merger and integration charges and lower FDIC special assessment charges, partially offset by higher compensation and employee benefits expense.
Results for 2023 Compared With 2022 For discussion related to changes in financial condition and results of operations for 2023 compared with 2022, refer to “Management’s Discussion and Analysis” in the Company’s Annual Report for the year ended December 31, 2023, included as Exhibit 13 to the Company’s Form 10-K filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission ("SEC") on February 20, 2024.
Statement of Income Analysis
Net Interest Income Net interest income, on a taxable-equivalent basis, was $16.4 billion in 2024, compared with $17.5 billion in 2023. The $1.1 billion (6.4 percent) decrease in 2024 compared with 2023 was primarily due to the impact of higher interest rates on deposit mix and pricing, partially offset by modest growth in earning assets and improved asset mix. Average earning assets were $1.4 billion (0.2 percent) higher in 2024, compared with 2023, reflecting increases in investment securities, interest-bearing deposits with banks and other earning assets, partially offset by a decrease in loans. The net interest margin, on a taxable-equivalent basis, in 2024 was 2.70 percent, compared with 2.90 percent in 2023. The decrease in the net interest margin in 2024, compared with 2023, was primarily due to the impact of higher interest rates on deposit mix and pricing, partially offset by improved earning asset mix across loans and investment securities. Refer to the “Interest Rate Risk Management” section for further information on the sensitivity of the Company’s net interest income to changes in interest rates.
| | | | | | | | |
| TABLE 2 | | Analysis of Net Interest Income(a) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31 (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 | 2024
v 2023 | 2023
v 2022 |
| Components of Net Interest Income | | | | | |
| Income on earning assets (taxable-equivalent basis) | $ | 31,789 | | $ | 30,144 | | $ | 18,066 | | $ | 1,645 | | $ | 12,078 | |
| Expense on interest-bearing liabilities (taxable-equivalent basis) | 15,380 | | 12,617 | | 3,220 | | 2,763 | | 9,397 | |
Net interest income (taxable-equivalent basis)(b) | $ | 16,409 | | $ | 17,527 | | $ | 14,846 | | $ | (1,118) | | $ | 2,681 | |
| Net interest income, as reported | $ | 16,289 | | $ | 17,396 | | $ | 14,728 | | $ | (1,107) | | $ | 2,668 | |
| Average Yields and Rates Paid | | | | | |
| Earning assets yield (taxable-equivalent basis) | 5.24 | % | 4.98 | % | 3.31 | % | .26 | % | 1.67 | % |
| Rate paid on interest-bearing liabilities (taxable-equivalent basis) | 3.09 | | 2.65 | | .80 | | .44 | | 1.85 | |
| Gross interest margin (taxable-equivalent basis) | 2.15 | % | 2.33 | % | 2.51 | % | (.18) | % | (.18) | % |
| Net interest margin (taxable-equivalent basis) | 2.70 | % | 2.90 | % | 2.72 | % | (.20) | % | .18 | % |
| Average Balances | | | | | |
Investment securities(c) | $ | 166,634 | | $ | 162,757 | | $ | 169,442 | | $ | 3,877 | | $ | (6,685) | |
| Loans | 373,875 | | 381,275 | | 333,573 | | (7,400) | | 47,702 | |
| Earning assets | 606,641 | | 605,199 | | 545,343 | | 1,442 | | 59,856 | |
| Noninterest-bearing deposits | 83,007 | | 107,768 | | 120,394 | | (24,761) | | (12,626) | |
| Interest-bearing deposits | 426,508 | | 397,895 | | 341,990 | | 28,613 | | 55,905 | |
| Total deposits | 509,515 | | 505,663 | | 462,384 | | 3,852 | | 43,279 | |
| Interest-bearing liabilities | 498,182 | | 476,178 | | 400,844 | | 22,004 | | 75,334 | |
(a)Interest and rates are presented on a fully taxable-equivalent basis based on a federal income tax rate of 21 percent.
(b)See Non-GAAP Financial Measures beginning on page 57. (c)Excludes unrealized gains and losses on available-for-sale investment securities and any premiums or discounts recorded related to the transfer of investment securities at fair value from available-for-sale to held-to-maturity.
| | |
24 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
Average total loans were $373.9 billion in 2024, compared with $381.3 billion in 2023. The $7.4 billion (1.9 percent) decrease was primarily due to lower other retail loans, commercial real estate loans and commercial loans, partially offset by higher credit card loans and residential mortgages. Average other retail loans decreased $6.2 billion (12.5 percent), driven by lower automobile loans. Average commercial real estate loans decreased $3.0 billion (5.5 percent), primarily due to loan workout activities and payoffs exceeding a reduced level of new originations. Average commercial loans decreased $1.5 billion (1.1 percent), primarily due to decreased demand as corporate customers accessed the capital markets. Average credit card loans increased $2.1 billion (8.0 percent) primarily due to customer account growth and higher spend volume. Average residential mortgages increased $1.1 billion (1.0 percent), driven by originations.
Average investment securities in 2024 were $3.9 billion (2.4 percent) higher than in 2023, primarily due to balance sheet positioning and liquidity management.
Average total deposits for 2024 were $3.9 billion (0.8 percent) higher than 2023. Average total savings deposits were $18.3 billion (5.2 percent) higher in 2024, compared with 2023, driven by increases in balances within Wealth, Corporate, Commercial and Institutional Banking, along with Consumer and Business Banking. Average time deposits for 2024 were $10.3 billion (22.1 percent) higher than 2023, primarily due to increases in Consumer and Business Banking balances. Changes in time deposits are primarily related to those deposits managed as an alternative to other funding sources, based largely on relative pricing and liquidity characteristics. Average noninterest-bearing deposits were $24.8 billion (23.0 percent) lower in 2024, compared with 2023, driven by lower balances within Wealth, Corporate, Commercial and Institutional Banking, as well as Consumer and Business Banking.
| | | | | | | | |
| TABLE 3 | | Net Interest Income — Changes Due to Rate and Volume(a) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2024 v 2023 | 2023 v 2022 |
| Year Ended December 31 (Dollars in Millions) | Volume | Yield/Rate | Total | Volume | Yield/Rate | Total |
| Increase (decrease) in | | | | | | |
| Interest Income | | | | | | |
| Investment securities | $ | 109 | | $ | 514 | | $ | 623 | | $ | (136) | | $ | 1,245 | | $ | 1,109 | |
| Loans held for sale | 5 | | 21 | | 26 | | (72) | | 18 | | (54) | |
| Loans | | | | | | |
| Commercial | (94) | | 149 | | 55 | | 389 | | 3,933 | | 4,322 | |
| Commercial real estate | (185) | | 127 | | (58) | | 546 | | 1,183 | | 1,729 | |
| Residential mortgages | 41 | | 231 | | 272 | | 1,019 | | 511 | | 1,530 | |
| Credit card | 273 | | 113 | | 386 | | 340 | | 506 | | 846 | |
| Other retail | (325) | | 345 | | 20 | | (424) | | 731 | | 307 | |
| Total loans | (290) | | 965 | | 675 | | 1,870 | | 6,864 | | 8,734 | |
| Interest-bearing deposits with banks | 117 | | 46 | | 163 | | 313 | | 1,709 | | 2,022 | |
| Other earning assets | 130 | | 28 | | 158 | | 76 | | 191 | | 267 | |
| Total earning assets | 71 | | 1,574 | | 1,645 | | 2,051 | | 10,027 | | 12,078 | |
| Interest Expense | | | | | | |
| Interest-bearing deposits | | | | | | |
| Interest checking | (41) | | 212 | | 171 | | 28 | | 1,029 | | 1,057 | |
| Money market savings | 1,300 | | 626 | | 1,926 | | 388 | | 4,046 | | 4,434 | |
| Savings accounts | (26) | | 101 | | 75 | | (2) | | 82 | | 80 | |
| Time deposits | 375 | | 366 | | 741 | | 192 | | 1,140 | | 1,332 | |
| Total interest-bearing deposits | 1,608 | | 1,305 | | 2,913 | | 606 | | 6,297 | | 6,903 | |
| Short-term borrowings | (981) | | 113 | | (868) | | 186 | | 1,223 | | 1,409 | |
| Long-term debt | 436 | | 282 | | 718 | | 259 | | 826 | | 1,085 | |
| Total interest-bearing liabilities | 1,063 | | 1,700 | | 2,763 | | 1,051 | | 8,346 | | 9,397 | |
| Increase (decrease) in net interest income | $ | (992) | | $ | (126) | | $ | (1,118) | | $ | 1,000 | | $ | 1,681 | | $ | 2,681 | |
(a)This table shows the components of the change in net interest income by volume and rate on a taxable-equivalent basis based on a federal income tax rate of 21 percent. This table does not take into account the level of noninterest-bearing funding, nor does it fully reflect changes in the mix of assets and liabilities. The change in interest not solely due to changes in volume or rates has been allocated on a pro-rata basis to volume and yield/rate.
Provision for Credit Losses The provision for credit losses reflects changes in economic conditions and the size and credit quality of the entire portfolio of loans. The Company maintains an allowance for credit losses considered appropriate by management for expected losses, based on factors discussed in the “Analysis and Determination of the Allowance for Credit Losses” section.
The provision for credit losses was $2.2 billion in 2024, compared with $2.3 billion in 2023. The $37 million (1.6 percent) decrease reflects stabilizing economic and credit trends. Net charge-offs increased $247 million (13.0
percent) in 2024, compared with 2023, reflecting higher credit card and commercial loan net charge-offs, partially offset by the impacts of charge-offs in the prior year related to acquired loans and balance sheet repositioning and capital management actions.
Refer to “Corporate Risk Profile” for further information on the provision for credit losses, net charge-offs, nonperforming assets and other factors considered by the Company in assessing the credit quality of the loan portfolio and establishing the allowance for credit losses.
| | | | | | | | |
| TABLE 4 | | Noninterest Income |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31 (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 | 2024
v 2023 | 2023
v 2022 |
| Card revenue | $ | 1,679 | | $ | 1,630 | | $ | 1,512 | | 3.0 | % | 7.8 | % |
| Corporate payment products revenue | 773 | | 759 | | 698 | | 1.8 | | 8.7 | |
| Merchant processing services | 1,714 | | 1,659 | | 1,579 | | 3.3 | | 5.1 | |
| Trust and investment management fees | 2,660 | | 2,459 | | 2,209 | | 8.2 | | 11.3 | |
| Service charges | 1,253 | | 1,306 | | 1,298 | | (4.1) | | .6 | |
| Commercial products revenue | 1,523 | | 1,372 | | 1,105 | | 11.0 | | 24.2 | |
| Mortgage banking revenue | 627 | | 540 | | 527 | | 16.1 | | 2.5 | |
| Investment products fees | 330 | | 279 | | 235 | | 18.3 | | 18.7 | |
| Other | 641 | | 758 | | 273 | | (15.4) | | * |
| Total fee revenue | 11,200 | | 10,762 | | 9,436 | | 4.1 | | 14.1 | |
| Securities gains (losses), net | (154) | | (145) | | 20 | | (6.2) | | * |
| Total noninterest income | $ | 11,046 | | $ | 10,617 | | $ | 9,456 | | 4.0 | % | 12.3 | % |
*Not meaningful
Noninterest Income Noninterest income in 2024 was $11.0 billion, compared with $10.6 billion in 2023. The $429 million (4.0 percent) increase in 2024 from 2023 reflected higher trust and investment management fees, commercial products revenue, payment services revenue and mortgage banking revenue, partially offset by lower service charges and other noninterest income. Trust and investment management fees increased primarily due to business growth and favorable market conditions.
Commercial products revenue increased primarily due to higher corporate bond fees. Payment services revenue increased primarily driven by higher merchant processing services revenue due to business volume growth, along with increased card revenue due to favorable rates. Mortgage banking revenue increased primarily due to a gain on the sale of mortgage servicing rights in 2024, along with the impact of balance sheet repositioning and capital management actions taken in 2023.
| | | | | | | | |
| TABLE 5 | | Noninterest Expense |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31 (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 | 2024
v 2023 | 2023
v 2022 |
| Compensation and employee benefits | $ | 10,554 | | $ | 10,416 | | $ | 9,157 | | 1.3 | % | 13.7 | % |
| Net occupancy and equipment | 1,246 | | 1,266 | | 1,096 | | (1.6) | | 15.5 | |
| Professional services | 491 | | 560 | | 529 | | (12.3) | | 5.9 | |
| Marketing and business development | 619 | | 726 | | 456 | | (14.7) | | 59.2 | |
| Technology and communications | 2,074 | | 2,049 | | 1,726 | | 1.2 | | 18.7 | |
| Other intangibles | 569 | | 636 | | 215 | | (10.5) | | * |
| Other | 1,480 | | 2,211 | | 1,398 | | (33.1) | | 58.2 | |
| Total before merger and integration charges | 17,033 | | 17,864 | | 14,577 | | (4.7) | | 22.5 | |
| Merger and integration charges | 155 | | 1,009 | | 329 | | (84.6) | | * |
| Total noninterest expense | $ | 17,188 | | $ | 18,873 | | $ | 14,906 | | (8.9) | % | 26.6 | % |
Efficiency ratio(a) | 62.3 | % | 66.7 | % | 61.4 | % | | |
*Not meaningful
(a)See Non-GAAP Financial Measures beginning on page 57. | | |
26 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
Noninterest Expense Noninterest expense in 2024 was $17.2 billion, compared with $18.9 billion in 2023. The $1.7 billion (8.9 percent) decrease in noninterest expense in 2024, compared to 2023, reflected lower merger and integration charges, lower other noninterest expense and lower marketing and business development expense, partially offset by higher compensation and employee benefits expense. Other noninterest expense decreased primarily due to lower FDIC special assessment charges in 2024. Marketing and business development expense decreased primarily due to the impact of a charitable contribution in 2023 related to the MUB acquisition. Compensation and employee benefits expense increased primarily due to higher commissions, performance-based incentives and medical expenses.
Income Tax Expense The provision for income taxes was $1.6 billion (an effective rate of 20.0 percent) in 2024, compared with $1.4 billion (an effective rate of 20.5 percent) in 2023.
For further information on income taxes, refer to Note 18 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Balance Sheet Analysis
Average earning assets were $606.6 billion in 2024, compared with $605.2 billion in 2023. The increase in average earning assets of $1.4 billion (0.2 percent) was primarily due to increases in investment securities of $3.9 billion (2.4 percent), interest-bearing deposits with banks of $2.2 billion (4.5 percent) and other earning assets of $2.7 billion (27.5 percent), partially offset by a decrease in loans of $7.4 billion (1.9 percent).
For average balance information, refer to the "Net Interest Income" section in Statement of Income Analysis and Consolidated Daily Average Balance Sheet and Related Yields and Rates on page 134. Loans The Company’s loan portfolio was $379.8 billion at December 31, 2024, compared with $373.8 billion at December 31, 2023, reflecting an increase of $6.0 billion (1.6 percent). The increase was driven by higher commercial loans, residential mortgages and credit card loans, partially offset by lower commercial real estate loans and other retail loans. Table 6 provides a summary of the loan distribution by product type, while Table 7 provides a summary of the selected loan maturity distribution by loan category.
| | | | | | | | |
| TABLE 6 | | Loan Portfolio Distribution |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2024 | 2023 |
| At December 31 (Dollars in Millions) | Amount | Percent
of Total | Amount | Percent
of Total |
| Commercial | | | | |
| Commercial | $ | 135,254 | | 35.6 | % | $ | 127,676 | | 34.2 | % |
| Lease financing | 4,230 | | 1.1 | | 4,205 | | 1.1 | |
| Total commercial | 139,484 | | 36.7 | | 131,881 | | 35.3 | |
| Commercial Real Estate | | | | |
| Commercial mortgages | 38,619 | | 10.2 | | 41,934 | | 11.2 | |
| Construction and development | 10,240 | | 2.7 | | 11,521 | | 3.1 | |
| Total commercial real estate | 48,859 | | 12.9 | | 53,455 | | 14.3 | |
| Residential Mortgages | | | | |
| Residential mortgages | 112,806 | | 29.7 | | 108,605 | | 29.0 | |
| Home equity loans, first liens | 6,007 | | 1.6 | | 6,925 | | 1.9 | |
| Total residential mortgages | 118,813 | | 31.3 | | 115,530 | | 30.9 | |
| Credit Card | 30,350 | | 8.0 | | 28,560 | | 7.6 | |
| Other Retail | | | | |
| Retail leasing | 4,040 | | 1.0 | | 4,135 | | 1.1 | |
| Home equity and second mortgages | 13,565 | | 3.6 | | 13,056 | | 3.5 | |
| Revolving credit | 3,747 | | 1.0 | | 3,668 | | 1.0 | |
| Installment | 14,373 | | 3.8 | | 13,889 | | 3.7 | |
| Automobile | 6,601 | | 1.7 | | 9,661 | | 2.6 | |
| Total other retail | 42,326 | | 11.1 | | 44,409 | | 11.9 | |
| Total loans | $ | 379,832 | | 100.0 | % | $ | 373,835 | | 100.0 | % |
| | | | | | | | |
| TABLE 7 | | Selected Loan Maturity Distribution |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| At December 31, 2024 (Dollars in Millions) | One Year
or Less | Over One
Through
Five Years | Over Five
Through
Fifteen Years | Over Fifteen
Years | | Total |
| Commercial | $ | 40,939 | | $ | 84,587 | | $ | 13,578 | | $ | 380 | | | $ | 139,484 | |
| Commercial real estate | 14,961 | | 20,138 | | 5,274 | | 8,486 | | (a) | 48,859 | |
| Residential mortgages | 215 | | 2,282 | | 6,159 | | 110,157 | | | 118,813 | |
| Credit card | 30,350 | | — | | — | | — | | | 30,350 | |
| Other retail | 1,836 | | 9,502 | | 13,657 | | 17,331 | | | 42,326 | |
| Total loans | $ | 88,301 | | $ | 116,509 | | $ | 38,668 | | $ | 136,354 | | | $ | 379,832 | |
| | | | | |
| Total of loans due after one year with: | | | | | | |
| | | | Predetermined
Interest Rates | | Floating Interest Rates |
| Commercial | $ | 13,759 | | | $ | 84,786 | |
| Commercial real estate | 11,543 | | | 22,355 | |
| Residential mortgages | 60,578 | | | 58,020 | |
| Credit card | — | | | — | |
| Other retail | 27,870 | | | 12,620 | |
| Total | $ | 113,750 | | | $ | 177,781 | |
(a)Primarily represents construction loans for single-family residences or loans guaranteed by the Small Business Administration.
| | | | | | | | |
| TABLE 8 | | Commercial Loans by Industry Group |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2024 | 2023 |
| At December 31 (Dollars in Millions) | Loans | Percent
of Total | Loans | Percent
of Total |
| Industry Group | | | | |
| Financial institutions | $ | 25,468 | | 18.3 | % | $ | 20,016 | | 15.2 | % |
| Real-estate related | 17,446 | | 12.5 | | 19,108 | | 14.5 | |
| Automotive | 11,069 | | 7.9 | | 6,678 | | 5.1 | |
| Personal, professional and commercial services | 9,776 | | 7.0 | | 10,273 | | 7.8 | |
| Healthcare | 6,919 | | 5.0 | | 8,240 | | 6.2 | |
| Media and entertainment | 6,267 | | 4.5 | | 6,265 | | 4.8 | |
| Retail | 5,181 | | 3.7 | | 4,970 | | 3.8 | |
| Capital goods | 4,673 | | 3.3 | | 5,315 | | 4.0 | |
| Transportation | 4,591 | | 3.3 | | 4,467 | | 3.4 | |
| Power | 3,952 | | 2.8 | | 3,435 | | 2.6 | |
| Food and beverage | 3,931 | | 2.8 | | 4,053 | | 3.1 | |
| Technology | 3,693 | | 2.6 | | 3,963 | | 3.0 | |
| Energy | 3,577 | | 2.6 | | 3,744 | | 2.8 | |
| Metals and mining | 3,543 | | 2.5 | | 3,332 | | 2.5 | |
| Building materials | 3,029 | | 2.2 | | 3,008 | | 2.3 | |
| State and municipal government | 3,023 | | 2.2 | | 3,217 | | 2.4 | |
| Education and non-profit | 2,921 | | 2.1 | | 3,330 | | 2.5 | |
| Agriculture | 1,779 | | 1.3 | | 1,778 | | 1.3 | |
| Other | 18,646 | | 13.4 | | 16,689 | | 12.7 | |
| Total | $ | 139,484 | | 100.0 | % | $ | 131,881 | | 100.0 | % |
Commercial Commercial loans, including lease financing, increased $7.6 billion (5.8 percent) at December 31, 2024, compared with December 31, 2023, primarily due to growth
in corporate banking. Table 8 provides a summary of commercial loans by industry group.
| | |
28 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
| | | | | | | | |
| TABLE 9 | | Commercial Real Estate Loans by Property Type and Geography |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2024 | 2023 |
| At December 31 (Dollars in Millions) | Loans | Percent
of Total | Loans | Percent
of Total |
| Property Type | | | | |
| Multi-family | $ | 17,678 | | 36.2 | % | $ | 17,786 | | 33.3 | % |
| Business owner occupied | 10,500 | | 21.5 | | 10,795 | | 20.2 | |
| Office | 5,601 | | 11.5 | | 6,948 | | 13.0 | |
| Industrial | 4,791 | | 9.8 | | 5,608 | | 10.5 | |
| Residential land and development | 3,659 | | 7.5 | | 4,419 | | 8.3 | |
| Retail | 3,498 | | 7.1 | | 3,806 | | 7.1 | |
| Lodging | 1,156 | | 2.4 | | 1,661 | | 3.1 | |
| Other | 1,976 | | 4.0 | | 2,432 | | 4.5 | |
| Total | $ | 48,859 | | 100.0 | % | $ | 53,455 | | 100.0 | % |
| Geography | | | | |
| California | $ | 17,990 | | 36.8 | % | $ | 20,130 | | 37.7 | % |
| Washington | 4,607 | | 9.4 | | 4,245 | | 7.9 | |
| Texas | 2,366 | | 4.8 | | 2,669 | | 5.0 | |
| Florida | 1,726 | | 3.5 | | 1,843 | | 3.4 | |
| Oregon | 1,673 | | 3.4 | | 1,809 | | 3.4 | |
| Colorado | 1,515 | | 3.1 | | 1,476 | | 2.8 | |
| Illinois | 1,431 | | 2.9 | | 1,516 | | 2.8 | |
| Minnesota | 1,313 | | 2.8 | | 1,497 | | 2.8 | |
| Wisconsin | 1,177 | | 2.4 | | 1,266 | | 2.4 | |
| New York | 1,160 | | 2.4 | | 1,273 | | 2.4 | |
| All other states | 13,901 | | 28.5 | | 15,731 | | 29.4 | |
| Total | $ | 48,859 | | 100.0 | % | $ | 53,455 | | 100.0 | % |
Commercial Real Estate The Company’s portfolio of commercial real estate loans, which includes commercial mortgages and construction and development loans, decreased $4.6 billion (8.6 percent) at December 31, 2024, compared with December 31, 2023. The decrease was primarily due to loan workout activities and payoffs exceeding a reduced level of new originations. Table 9 provides a summary of commercial real estate loans by property type and geographical location.
The Company also finances the operations of real estate developers and other entities with operations related to real estate. These loans are not secured directly by real estate but have similar characteristics to commercial real estate loans. These loans were included in the commercial loan category and totaled $17.4 billion and $19.1 billion at December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively.
| | | | | | | | |
| TABLE 10 | | Residential Mortgages by Geography |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2024 | 2023 |
| At December 31 (Dollars in Millions) | Loans | Percent
of Total | Loans | Percent
of Total |
| California | $ | 53,682 | | 45.2 | % | $ | 52,584 | | 45.5 | % |
| Washington | 6,829 | | 5.8 | | 6,678 | | 5.8 | |
| Florida | 3,947 | | 3.3 | | 3,767 | | 3.3 | |
| Colorado | 3,737 | | 3.1 | | 3,881 | | 3.4 | |
| Illinois | 3,452 | | 2.9 | | 3,630 | | 3.1 | |
| Minnesota | 3,357 | | 2.9 | | 3,600 | | 3.1 | |
| Texas | 3,312 | | 2.8 | | 3,287 | | 2.8 | |
| New York | 3,129 | | 2.6 | | 2,726 | | 2.4 | |
| Arizona | 3,088 | | 2.6 | | 3,134 | | 2.7 | |
| Massachusetts | 2,737 | | 2.3 | | 2,680 | | 2.3 | |
| All other states | 31,543 | | 26.5 | | 29,563 | | 25.6 | |
| Total | $ | 118,813 | | 100.0 | % | $ | 115,530 | | 100.0 | % |
Residential Mortgages Residential mortgages held in the loan portfolio at December 31, 2024, increased $3.3 billion (2.8 percent) compared to December 31, 2023, driven by originations. Residential mortgages originated and placed in the Company’s loan portfolio include jumbo mortgages and branch-originated first lien home equity loans to borrowers with high credit quality.
Credit Card Total credit card loans increased $1.8 billion (6.3 percent) at December 31, 2024, compared with December 31, 2023, primarily driven by customer account growth and higher spend volume.
Other Retail Total other retail loans, which include retail leasing, home equity and second mortgages and other retail loans, decreased $2.1 billion (4.7 percent) at December 31, 2024, compared with December 31, 2023, driven by a decrease in automobile loans. Tables 10, 11 and 12 provide a geographic summary of residential mortgages, credit card loans and other retail loans outstanding, respectively, as of December 31, 2024 and 2023.
| | | | | | | | |
| TABLE 11 | | Credit Card Loans by Geography |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2024 | 2023 |
| At December 31 (Dollars in Millions) | Loans | Percent
of Total | Loans | Percent
of Total |
| California | $ | 3,289 | | 10.8 | % | $ | 2,928 | | 10.3 | % |
| Texas | 1,819 | | 6.0 | | 1,719 | | 6.0 | |
| Illinois | 1,557 | | 5.1 | | 1,472 | | 5.2 | |
| Florida | 1,479 | | 4.9 | | 1,363 | | 4.8 | |
| Ohio | 1,468 | | 4.8 | | 1,406 | | 4.9 | |
| Minnesota | 1,371 | | 4.5 | | 1,333 | | 4.7 | |
| Wisconsin | 1,220 | | 4.0 | | 1,177 | | 4.1 | |
| Colorado | 1,021 | | 3.4 | | 964 | | 3.3 | |
| Missouri | 960 | | 3.2 | | 918 | | 3.2 | |
| Washington | 947 | | 3.1 | | 889 | | 3.1 | |
| All other states | 15,219 | | 50.2 | | 14,391 | | 50.4 | |
| Total | $ | 30,350 | | 100.0 | % | $ | 28,560 | | 100.0 | % |
| | |
30 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
| | | | | | | | |
| TABLE 12 | | Other Retail Loans by Geography |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2024 | 2023 |
| At December 31 (Dollars in Millions) | Loans | Percent
of Total | Loans | Percent
of Total |
| California | $ | 9,179 | | 21.7 | % | $ | 9,506 | | 21.4 | % |
| Texas | 2,995 | | 7.1 | | 3,505 | | 7.9 | |
| Florida | 2,675 | | 6.3 | | 2,729 | | 6.1 | |
| Washington | 1,746 | | 4.1 | | 1,800 | | 4.1 | |
| Minnesota | 1,742 | | 4.1 | | 1,943 | | 4.4 | |
| Ohio | 1,520 | | 3.6 | | 1,752 | | 3.9 | |
| Illinois | 1,435 | | 3.4 | | 1,704 | | 3.8 | |
| Colorado | 1,340 | | 3.2 | | 1,440 | | 3.2 | |
| New York | 1,329 | | 3.1 | | 1,444 | | 3.3 | |
| Oregon | 1,259 | | 3.0 | | 1,313 | | 3.0 | |
| All other states | 17,106 | | 40.4 | | 17,273 | | 38.9 | |
| Total | $ | 42,326 | | 100.0 | % | $ | 44,409 | | 100.0 | % |
The Company generally retains portfolio loans through maturity; however, the Company’s intent may change over time based upon various factors such as ongoing asset/liability management activities, assessment of product profitability, credit risk, liquidity needs, and capital implications. If the Company’s intent or ability to hold an existing portfolio loan changes, it is transferred to loans held for sale.
Loans Held for Sale Loans held for sale, consisting primarily of residential mortgages to be sold in the
secondary market, were $2.6 billion at December 31, 2024, compared with $2.2 billion at December 31, 2023. The increase in loans held for sale was principally due to a higher level of mortgage loan closings in the fourth quarter of 2024, compared with the fourth quarter of 2023. Almost all of the residential mortgage loans the Company originates or purchases for sale follow guidelines that allow the loans to be sold into existing, highly liquid secondary markets, in particular in government agency transactions and to government sponsored enterprises (“GSEs”).
| | | | | | | | |
| TABLE 13 | | Investment Securities |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2024 | 2023 |
| At December 31 (Dollars in Millions) | Amortized
Cost | Fair Value | Weighted-
Average
Maturity in
Years | Weighted- Average Yield(e) | Amortized
Cost | Fair Value | Weighted-
Average
Maturity in
Years | Weighted- Average Yield(e) |
| Held-to-Maturity | | | | | | | | |
| U.S. Treasury and agencies | $ | 1,296 | | $ | 1,275 | | 1.3 | 2.85 | % | $ | 1,345 | | $ | 1,310 | | 2.3 | 2.85 | % |
Mortgage-backed securities(a) | 77,094 | | 64,753 | | 8.8 | 2.19 | | 82,692 | | 72,770 | | 8.8 | 2.21 | |
| Other | 244 | | 247 | | 2.2 | 2.73 | | 8 | | 8 | | 2.8 | 2.56 | |
| Total held-to-maturity | $ | 78,634 | | $ | 66,275 | | 8.7 | 2.20 | % | $ | 84,045 | | $ | 74,088 | | 8.7 | 2.22 | % |
| Available-for-Sale | | | | | | | | |
| U.S. Treasury and agencies | $ | 30,467 | | $ | 28,387 | | 5.1 | 2.98 | % | $ | 21,768 | | $ | 19,542 | | 5.9 | 2.19 | % |
Mortgage-backed securities(a) | 44,238 | | 40,638 | | 7.4 | 3.82 | | 36,895 | | 33,427 | | 6.3 | 3.09 | |
Asset-backed securities(a) | 7,136 | | 7,165 | | 3.8 | 5.56 | | 6,713 | | 6,724 | | 2.2 | 5.33 | |
Obligations of state and political subdivisions(b)(c) | 10,690 | | 9,552 | | 11.7 | 3.72 | | 10,867 | | 9,989 | | 9.9 | 3.75 | |
| Other | 249 | | 250 | | 1.5 | 4.79 | | 24 | | 24 | | 1.7 | 4.51 | |
Total available-for-sale(d) | $ | 92,780 | | $ | 85,992 | | 6.8 | 3.67 | % | $ | 76,267 | | $ | 69,706 | | 6.3 | 3.12 | % |
(a)Information related to asset and mortgage-backed securities included above is presented based upon weighted-average maturities that take into account anticipated future prepayments.
(b)Information related to obligations of state and political subdivisions is presented based upon yield to first optional call date if the security is purchased at a premium, and yield to maturity if the security is purchased at par or a discount.
(c)Maturity calculations for obligations of state and political subdivisions are based on the first optional call date for securities with a fair value above par and the contractual maturity date for securities with a fair value equal to or below par.
(d)Amortized cost excludes portfolio level basis adjustments of $13 million and $335 million at December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively.
(e)Weighted-average yields for obligations of state and political subdivisions are presented on a fully-taxable equivalent basis based on a federal income tax rate of 21 percent. Yields on investment securities are computed based on amortized cost balances, excluding any premiums or discounts recorded related to the transfer of investment securities at fair value from available-for-sale to held-to-maturity.
Investment Securities The Company uses its investment securities portfolio to manage interest rate risk, provide liquidity (including the ability to meet regulatory requirements), generate interest and dividend income, and serve as collateral for public deposits and wholesale funding sources. While the Company intends to hold its investment securities indefinitely, it may sell available-for-sale investment securities in response to structural changes in the balance sheet and related interest rate risk and to meet liquidity requirements, among other factors.
Investment securities totaled $164.6 billion at December 31, 2024, compared with $153.8 billion at December 31, 2023. The $10.9 billion (7.1 percent) increase was primarily due to net investment purchases driven by balance sheet positioning and liquidity management, along with a favorable change in net unrealized gains (losses) on available-for-sale investment securities. Investment securities by type are shown in Table 13.
The Company’s available-for-sale investment securities are carried at fair value with changes in fair value reflected in other comprehensive income (loss) unless a portion of a security’s unrealized loss is related to credit and an allowance for credit losses is necessary. At December 31, 2024, the Company’s net unrealized losses on available-for-sale investment securities were $6.8 billion ($5.1 billion net-of-tax), compared with net unrealized losses of $6.9 billion ($5.2 billion net-of-tax) at December 31, 2023. The favorable change in net unrealized gains (losses) was primarily due to increases in the fair value of U.S. treasury securities as a result of changes in interest rates. Gross unrealized losses on available-for-sale investment securities totaled $6.9 billion at December 31, 2024, compared with $7.1 billion at December 31, 2023. When evaluating credit losses, the Company considers various factors such as the nature of the investment security, the credit ratings or financial condition of the issuer, the extent of the unrealized loss, expected cash flows of the underlying collateral, the existence of any government or agency guarantees, and market conditions. At December 31, 2024, the Company had no plans to sell
securities with unrealized losses, and believes it is more likely than not that it would not be required to sell such securities before recovery of their amortized cost.
Refer to Notes 4 and 21 in the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for further information on investment securities.
Deposits Total deposits were $518.3 billion at December 31, 2024, compared with $512.3 billion at December 31, 2023. The $6.0 billion (1.2 percent) increase in total deposits reflected increases in total savings deposits and time deposits, partially offset by a decrease in noninterest-bearing deposits.
Interest-bearing savings deposits increased $9.3 billion (2.5 percent) at December 31, 2024, compared with December 31, 2023. The increase was related to higher money market and savings account deposit balances, partially offset by lower interest checking deposit balances. Money market deposit balances increased $7.4 billion (3.7 percent), primarily due to higher Wealth, Corporate, Commercial and Institutional Banking balances. Savings account balances increased $2.2 billion (5.0 percent), driven by higher Consumer and Business Banking balances. Interest checking balances decreased $265 million (0.2 percent) primarily due to lower Consumer and Business Banking balances, partially offset by higher Wealth, Corporate, Commercial and Institutional Banking balances.
Time deposits at December 31, 2024, increased $2.5 billion (4.8 percent), compared with December 31, 2023, driven by higher Consumer and Business Banking balances. Changes in time deposits are primarily related to those deposits managed as an alternative to other funding sources, based largely on relative pricing and liquidity characteristics.
Noninterest-bearing deposits at December 31, 2024, decreased $5.8 billion (6.5 percent) from December 31, 2023. The decrease was primarily driven by lower balances within Wealth, Corporate, Commercial and Institutional Banking, as well as Consumer and Business Banking, due to the impact of higher interest rates.
| | |
32 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
The composition of deposits was as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2024 | 2023 |
| At December 31 (Dollars in Millions) | Amount | Percent
of Total | Amount | Percent
of Total |
| Noninterest-bearing deposits | $ | 84,158 | | 16.2 | % | $ | 89,989 | | 17.6 | % |
| Interest-bearing deposits | | | | |
| Interest checking | 127,188 | | 24.5 | | 127,453 | | 24.9 | |
| Money market savings | 206,805 | | 39.9 | | 199,378 | | 38.9 | |
| Savings accounts | 45,389 | | 8.8 | | 43,219 | | 8.4 | |
| Total savings deposits | 379,382 | | 73.2 | | 370,050 | | 72.2 | |
| Domestic time deposits less than $250,000 | 39,297 | | 7.6 | | 35,700 | | 7.0 | |
| Domestic time deposits greater than $250,000 | 14,552 | | 2.8 | | 15,336 | | 3.0 | |
| Foreign time deposits | 920 | | .2 | | 1,237 | | .2 | |
| Total interest-bearing deposits | 434,151 | | 83.8 | | 422,323 | | 82.4 | |
Total deposits(a) | $ | 518,309 | | 100.0 | % | $ | 512,312 | | 100.0 | % |
(a)Includes $259.9 billion and $260.7 billion of deposits at December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively, that are not subject to any federal, state or foreign deposit insurance program.
The maturity of domestic time deposits in excess of the insurance limit and those time deposits not subject to any federal, state or foreign deposit insurance program at December 31, 2024 was as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars in Millions) | Domestic Time Deposits
Greater Than $250,000 | Foreign Time
Deposits | Total |
| Three months or less | $ | 6,377 | | $ | 920 | | $ | 7,297 | |
| Three months through six months | 5,950 | | — | | 5,950 | |
| Six months through one year | 1,770 | | — | | 1,770 | |
| Thereafter | 455 | | — | | 455 | |
| Total | $ | 14,552 | | $ | 920 | | $ | 15,472 | |
Borrowings The Company utilizes both short-term and long-term borrowings as part of its asset/liability management and funding strategies. Short-term borrowings, which include federal funds purchased, commercial paper, repurchase agreements, borrowings secured by high-grade assets and other short-term borrowings, were $15.5 billion at December 31, 2024, compared with $15.3 billion at December 31, 2023. The $239 million (1.6 percent) increase in short-term borrowings at December 31, 2024, compared with December 31, 2023, was primarily due to increases in repurchase agreement balances and short-term Federal Home Loan Bank (“FHLB”) advances, partially offset by lower commercial paper and other short-term borrowing balances.
Long-term debt was $58.0 billion at December 31, 2024, compared with $51.5 billion at December 31, 2023. The $6.5 billion (12.7 percent) increase was primarily due to $6.5 billion of medium-term note and $1.8 billion of bank note issuances and a $3.5 billion increase in FHLB advances, partially offset by $4.6 billion of medium-term note and $1.0 billion of subordinated note repayments.
Refer to Notes 12 and 13 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information regarding short-term borrowings and long-term debt, and the
“Liquidity Risk Management” section for discussion of liquidity management of the Company.
Corporate Risk Profile
Overview Managing risks is an essential part of successfully operating a financial services company. The Company’s Board of Directors has approved a risk management framework which establishes governance and risk management requirements for all risk-taking activities. This framework includes Company and business line risk appetite statements which set boundaries for the types and amount of risk that may be undertaken in pursuing business objectives and initiatives. The Board of Directors, primarily through its Risk Management Committee, oversees performance relative to the risk management framework, risk appetite statements, and other policy requirements.
The Executive Risk Committee (“ERC”), which is chaired by the Chief Risk Officer and includes the Chief Executive Officer and other members of the executive management team, oversees execution against the risk management framework and risk appetite statements. The ERC focuses on current and emerging risks, including strategic and reputation risks, by directing timely and comprehensive actions. Senior operating committees have also been
established, each responsible for overseeing a specified category of risk.
The Company’s most prominent risk exposures are credit, interest rate, market, liquidity, operational, compliance, strategic, and reputation. Credit risk is the risk of loss associated with a change in the credit profile or the failure of a borrower or counterparty to meet its contractual obligations. Interest rate risk is the current or prospective risk to earnings and capital, or market valuations, arising from the impact of changes in interest rates. Market risk is the risk associated with fluctuations in interest rates, foreign exchange rates, commodities and credit spreads that may result in changes in the values of financial instruments, such as trading and available-for-sale investment securities, mortgage loans held for sale (“MLHFS”), mortgage servicing rights (“MSRs”) and derivatives that are accounted for on a fair value basis. Liquidity risk is the risk that financial condition or overall safety and soundness is adversely affected by the Company’s inability, or perceived inability, to meet its cash flow obligations in a timely and complete manner in either normal or stressed conditions. Operational risk is the risk to current or projected financial condition and resilience arising from inadequate or failed internal processes or systems, people (including human errors or misconduct), or adverse external events, including the risk of loss resulting from breaches in data security. Operational risk can also include the risk of loss due to failures by third parties with which the Company does business. Compliance risk is the risk that the Company may suffer legal or regulatory sanctions, financial losses, and reputational damage if it fails to adhere to compliance requirements and the Company’s compliance policies. Strategic risk is the risk to current or projected financial condition and resilience arising from adverse business decisions, poor implementation of business decisions, or lack of responsiveness to changes in the banking industry and operating environment. Reputation risk is the risk to current or projected financial condition and resilience arising from negative public opinion. This risk may impair the Company’s competitiveness by affecting its ability to establish new relationships or services, or continue servicing existing relationships. In addition to the risks identified above, other risk factors exist that may impact the Company. Refer to “Risk Factors” beginning on page 136 for a detailed discussion of these factors. The Company’s Board and management-level governance committees are supported by a “three lines of defense” model for establishing effective checks and balances. The first line of defense, the business lines, manages risks in conformity with established limits and policy requirements. In turn, business line leaders and their risk officers establish programs to ensure conformity with these limits and policy requirements. The second line of defense, which includes the Chief Risk Officer’s organization as well as policy and oversight activities of corporate support functions, translates risk appetite and strategy into actionable risk limits and policies. The second line of defense monitors first line of defense conformity with limits and policies and provides reporting and escalation of emerging risks and other concerns to senior management
and the Risk Management Committee of the Board of Directors. The third line of defense, internal audit, is responsible for providing the Audit Committee of the Board of Directors and senior management with independent assessment and assurance regarding the effectiveness of the Company’s governance, risk management and control processes.
Management regularly provides reports to the Risk Management Committee of the Board of Directors. The Risk Management Committee discusses with management the Company’s risk management performance and provides a summary of key risks to the entire Board of Directors, covering the status of existing matters, areas of potential future concern and specific information on certain types of loss events. The Risk Management Committee considers quarterly reports by management assessing the Company’s performance relative to the risk appetite statements and the associated risk limits, including:
•Macroeconomic environment and other qualitative considerations, such as regulatory and compliance changes, litigation developments, geopolitical events, and technology and cybersecurity;
•Credit measures, including adversely rated and nonperforming loans, leveraged transactions, credit concentrations and lending limits;
•Interest rate and market risk, including market value and net income simulation, and trading-related Value at Risk (“VaR”);
•Liquidity risk, including funding projections under various stressed scenarios;
•Operational and compliance risk, including losses stemming from events such as fraud, processing errors, control breaches, breaches in data security or adverse business decisions, as well as reporting on technology performance, and various legal and regulatory compliance measures;
•Capital ratios and projections, including regulatory measures and stressed scenarios; and
•Strategic and reputation risk considerations, impacts and responses.
Credit Risk Management The Company’s strategy for credit risk management includes well-defined, centralized credit policies, uniform underwriting criteria, and ongoing risk monitoring and review processes for all commercial and consumer credit exposures. The strategy also emphasizes diversification on a geographic, industry and customer level, regular credit examinations and management reviews of loans exhibiting deterioration of credit quality. The Risk Management Committee oversees the Company’s credit risk management process.
In addition, credit quality ratings, as defined by the Company, are an important part of the Company’s overall credit risk management and evaluation of its allowance for credit losses. Loans with a pass rating represent those loans not classified on the Company’s rating scale for problem credits, as minimal credit risk has been identified. Loans with a special mention or classified rating (defined
| | |
34 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
by internally assessed rating or exception based monitoring credits in consumer lending and small business loans that are 90 days or more past due and still accruing, nonaccrual loans and loans in a junior lien position that are current but are behind a first lien position on nonaccrual), encompass all loans held by the Company that it considers to have a potential or well-defined weakness that may put full collection of contractual cash flows at risk. The Company’s internal credit quality ratings for consumer loans are primarily based on delinquency and nonperforming status. Refer to Notes 1 and 5 in the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for further discussion of the Company’s loan portfolios including internal credit quality ratings.
The Company categorizes its loan portfolio into two segments, which is the level at which it develops and documents a systematic methodology to determine the allowance for credit losses. The Company’s two loan portfolio segments are commercial lending and consumer lending.
The commercial lending segment includes loans and leases made to small business, middle market, large corporate, commercial real estate, financial institution, non-profit and public sector customers. Key risk characteristics relevant to commercial lending segment loans include the industry and geography of the borrower’s business, purpose of the loan, repayment source, borrower’s debt capacity and financial flexibility, loan covenants, and nature of pledged collateral, if any, as well as macroeconomic factors such as unemployment rates, gross domestic product levels, corporate bond spreads and long-term interest rates. These risk characteristics, among others, are considered in determining estimates about the likelihood of default by the borrowers and the severity of loss in the event of default. The Company considers these risk characteristics in assigning internal risk ratings to, or forecasting losses on, these loans, which are the significant factors in determining the allowance for credit losses for loans in the commercial lending segment.
The consumer lending segment represents loans and leases made to consumer customers, including residential mortgages, credit card loans, and other retail loans such as revolving consumer lines, auto loans and leases and home equity loans and lines. Key risk characteristics relevant to consumer lending segment loans primarily relate to the borrowers’ capacity and willingness to repay, customer payment history and credit scores and consider macroeconomic factors such as unemployment rates, consumer bankruptcy filings, household debt levels, real disposable income, effect of higher interest rates on variable rate or adjustable rate loans, and in some cases, updated loan-to-value (“LTV”) information reflecting current market conditions on secured loans. These and other risk characteristics are reflected in forecasts of delinquency levels, bankruptcies and losses which are the primary factors in determining the allowance for credit losses for the consumer lending segment.
The Company further disaggregates its loan portfolio segments into various classes based on their underlying risk characteristics. The two classes within the commercial
lending segment are commercial loans and commercial real estate loans. The three classes within the consumer lending segment are residential mortgages, credit card loans and other retail loans.
Because business processes and credit risks associated with unfunded credit commitments are essentially the same as for loans, the Company utilizes similar processes to estimate its liability for unfunded credit commitments. The Company also engages in non-lending activities that may give rise to credit risk, including derivative transactions for balance sheet hedging purposes, foreign exchange transactions, deposit overdrafts, commodity contracts and interest rate contracts for customers, investments in securities and other financial assets, and settlement risk, including Automated Clearing House transactions and the processing of credit card transactions for merchants. These activities are subject to credit review, analysis and approval processes.
During 2024, the Company continued to monitor economic uncertainty related to interest rates, inflationary pressures and other economic factors that may affect the financial strength of corporate and consumer borrowers. Beginning on January 7, 2025, wildfires generated substantial damage and disruption to the Los Angeles area. The Company has programs available to work with impacted customers and support the community. The Company continues to monitor the potential impacts on its customers and financial statements as the situation evolves. The Company does not anticipate this impact to be material to its financial statements.
Credit Diversification The Company manages its credit risk, in part, through diversification of its loan portfolio which is achieved through limit setting by product type criteria, such as industry, geography and identification of credit concentrations. As part of its normal business activities, the Company offers a broad array of traditional commercial lending products and specialized products such as asset-based lending, commercial lease financing, agricultural credit, warehouse mortgage lending, small business lending, commercial real estate lending, health care lending and correspondent banking financing. The Company also offers an array of consumer lending products, including residential mortgages, credit card loans, auto loans, retail leases, home equity loans and lines, revolving credit arrangements and other consumer loans. These consumer lending products are primarily offered through the branch office network, home mortgage and loan production offices, mobile and online banking, and indirect distribution channels, such as auto and recreational vehicle dealers. The Company monitors and manages the portfolio diversification by industry, customer and geography. The Company has significant loan exposure within California given its strategic position in those markets and size of the economy. Table 6 provides information with respect to the overall product diversification and changes in the mix during 2024.
The commercial loan class is diversified among various industries with higher percentages in financial institutions and real estate. Table 8 provides a summary of significant
industry groups of commercial loans outstanding at December 31, 2024 and 2023.
The commercial real estate loan class reflects the Company’s focus on serving business owners within its local network, as well as regional and national investment-based real estate owners and developers. Within the commercial real estate loan class, different property types have varying degrees of credit risk. Table 9 provides a summary of the significant property types and geographical locations of commercial real estate loans outstanding at December 31, 2024 and 2023. Commercial real estate loans are diversified among various property types with higher percentages in multi-family, business owner-occupied and office properties. The commercial real estate office sector, which represented 11.5 percent of commercial real estate loans at December 31, 2024, is a driver of stress in this loan class. The Company continued to monitor the commercial real estate office portfolio and maintained an allowance to loan coverage ratio of 11 percent at December 31, 2024, compared with 10 percent at December 31, 2023. Office nonperforming loans as a percent of total office loans increased to 10.9 percent at December 31, 2024, compared to 7.6 percent at December 31, 2023.
The Company’s consumer lending segment originates consumer credit through several channels, including traditional branch lending, mobile and online banking, indirect lending, alliance partnerships and correspondent banks. Each distinct underwriting and origination process within consumer lending manages unique credit risk characteristics and prices its loan production commensurate with the differing risk profiles.
Residential mortgage originations are generally limited to prime borrowers and are performed through the Company’s branches, loan production offices, mobile and online services, and a wholesale network of originators. The Company may retain residential mortgage loans it originates on its balance sheet or sell the loans into the secondary market while retaining the servicing rights and customer relationships. Utilizing the secondary markets enables the Company to effectively reduce its credit and other asset/liability risks. For residential mortgages that are retained in the Company’s portfolio and for home equity and second mortgages, credit risk is managed by adherence to LTV and borrower credit criteria during the underwriting process.
The Company estimates updated LTV information on its outstanding residential mortgages quarterly, based on a method that combines automated valuation model updates and relevant home price indices. LTV is the ratio of the loan’s outstanding principal balance to the current estimate of property value. For home equity and second mortgages, combined loan-to-value (“CLTV”) is the combination of the first mortgage original principal balance and the second lien outstanding principal balance, relative to the current estimate of property value. Certain loans do not have an LTV or CLTV, primarily due to lack of availability of relevant automated valuation model and/or home price indices values, or lack of necessary valuation data on acquired loans.
The following tables provide summary information of residential mortgages and home equity and second mortgages by LTV at December 31, 2024:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Residential Mortgages (Dollars in Millions) | Interest
Only | Amortizing | Total | Percent
of Total |
| Loan-to-Value | | | | |
| Less than or equal to 80% | $ | 13,829 | | $ | 91,554 | | $ | 105,383 | | 88.7 | % |
| Over 80% through 90% | 237 | | 4,907 | | 5,144 | | 4.3 | |
| Over 90% through 100% | 25 | | 903 | | 928 | | .8 | |
| Over 100% | 22 | | 385 | | 407 | | .3 | |
| No LTV available | — | | 6 | | 6 | | — | |
Loans purchased from GNMA mortgage pools(a) | — | | 6,945 | | 6,945 | | 5.9 | |
| Total | $ | 14,113 | | $ | 104,700 | | $ | 118,813 | | 100.0 | % |
(a)Represents loans purchased and loans that could be purchased from Government National Mortgage Association (“GNMA”) mortgage pools under delinquent loan repurchase options whose payments are primarily insured by the Federal Housing Administration or guaranteed by the United States Department of Veterans Affairs.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Home Equity and Second Mortgages
(Dollars in Millions) | Lines | Loans | Total | Percent
of Total |
| Loan-to-Value / Combined Loan-to-Value |
| Less than or equal to 80% | $ | 10,414 | | $ | 2,453 | | $ | 12,867 | | 94.9 | % |
| Over 80% through 90% | 419 | | 110 | | 529 | | 3.9 | |
| Over 90% through 100% | 71 | | 16 | | 87 | | .6 | |
| Over 100% | 56 | | 4 | | 60 | | .4 | |
| No LTV/CLTV available | 21 | | 1 | | 22 | | .2 | |
| Total | $ | 10,981 | | $ | 2,584 | | $ | 13,565 | | 100.0 | % |
Credit card and other retail loans are diversified across customer segments and geographies. Diversification in the credit card portfolio is achieved with broad customer relationship distribution through the Company’s and financial institution partners’ branches, retail and affinity partners, and digital channels.
Tables 10, 11 and 12 provide a geographical summary of the residential mortgage, credit card and other retail loan portfolios, respectively.
The following table provides a summary of the Company’s credit card loan balances disaggregated based upon updated credit score at December 31, 2024:
| | | | | |
| Percent of Total(a) |
| Credit score > 660 | 87 | % |
| Credit score < 660 | 13 | |
| No credit score | — | |
(a)Credit score distribution excludes loans serviced by others.
| | |
36 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
| | | | | | | | |
| TABLE 15 | | Delinquent Loan Ratios as a Percent of Ending Loan Balances |
| | | | | | | | |
At December 31 90 days or more past due | 2024 | 2023 |
| Commercial | | |
| Commercial | .07 | % | .09 | % |
| Lease financing | — | | — | |
| Total commercial | .07 | | .09 | |
| Commercial Real Estate | | |
| Commercial mortgages | — | | — | |
| Construction and development | .09 | | .03 | |
| Total commercial real estate | .02 | | .01 | |
Residential Mortgages(a) | .17 | | .12 | |
| Credit Card | 1.43 | | 1.31 | |
| Other Retail | | |
| Retail leasing | .05 | | .05 | |
| Home equity and second mortgages | .25 | | .26 | |
| Other | .11 | | .11 | |
| Total other retail | .15 | | .15 | |
| Total loans | .21 | % | .19 | % |
| | |
| At December 31 90 days or more past due and nonperforming loans | 2024 | 2023 |
| Commercial | .55 | % | .37 | % |
| Commercial real estate | 1.70 | | 1.46 | |
Residential mortgages(a) | .30 | | .25 | |
| Credit card | 1.43 | | 1.31 | |
| Other retail | .50 | | .46 | |
| Total loans | .69 | % | .57 | % |
(a)Delinquent loan ratios exclude $2.3 billion and $2.0 billion at December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively, of loans purchased and loans that could be purchased from GNMA mortgage pools under delinquent loan repurchase options whose repayments are primarily insured by the Federal Housing Administration or guaranteed by the United States Department of Veterans Affairs. Including these loans, the ratio of residential mortgages 90 days or more past due and nonperforming to total residential mortgages was 2.28 percent and 2.00 percent at December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively.
Loan Delinquencies Trends in delinquency ratios are an indicator, among other considerations, of credit risk within the Company’s loan portfolios. The entire balance of a loan account is considered delinquent if the minimum payment contractually required to be made is not received by the date specified on the billing statement. Delinquent loans purchased and loans that could be purchased from GNMA mortgage pools under delinquent loan repurchase options, whose repayments are primarily insured by the Federal Housing Administration or guaranteed by the United States Department of Veterans Affairs, are excluded from delinquency statistics. In addition, in certain situations, a consumer lending customer’s account may be re-aged to remove it from delinquent status. Generally, the purpose of re-aging accounts is to assist customers who have recently overcome temporary financial difficulties and have demonstrated both the ability and willingness to resume regular payments. In addition, the Company may re-age the consumer lending account of a customer who has experienced longer-term financial difficulties and apply modified, concessionary terms and conditions to the account. Commercial lending loans are generally not subject to re-aging policies.
Accruing loans 90 days or more past due totaled $810 million at December 31, 2024, compared with $698 million at December 31, 2023. Accruing loans 90 days or more past due are not included in nonperforming assets and continue to accrue interest because they are adequately secured by collateral, are in the process of collection and are reasonably expected to result in repayment or restoration to current status, or are managed in homogeneous portfolios with specified charge-off timeframes adhering to regulatory guidelines. The ratio of accruing loans 90 days or more past due to total loans was 0.21 percent at December 31, 2024, compared with 0.19 percent at December 31, 2023.
The following table provides summary delinquency information for residential mortgages, credit card and other retail loans included in the consumer lending segment:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
At December 31 (Dollars in Millions) | Amount | As a Percent of Ending
Loan Balances |
| 2024 | 2023 | 2024 | 2023 |
Residential Mortgages(a) | | | | |
| 30-89 days | $ | 188 | | $ | 169 | | .16 | % | .15 | % |
| 90 days or more | 206 | | 136 | | .17 | | .12 | |
| Nonperforming | 152 | | 158 | | .13 | | .14 | |
| Total | $ | 546 | | $ | 463 | | .46 | % | .40 | % |
| Credit Card | | | | |
| 30-89 days | $ | 428 | | $ | 406 | | 1.41 | % | 1.42 | % |
| 90 days or more | 435 | | 375 | | 1.43 | | 1.31 | |
| Nonperforming | — | | — | | — | | — | |
| Total | $ | 863 | | $ | 781 | | 2.84 | % | 2.73 | % |
| Other Retail | | | | |
| Retail Leasing | | | | |
| 30-89 days | $ | 25 | | $ | 25 | | .62 | % | .60 | % |
| 90 days or more | 2 | | 2 | | .05 | | .05 | |
| Nonperforming | 7 | | 8 | | .17 | | .19 | |
| Total | $ | 34 | | $ | 35 | | .84 | % | .85 | % |
| Home Equity and Second Mortgages | | | | |
| 30-89 days | $ | 61 | | $ | 77 | | .45 | % | .59 | % |
| 90 days or more | 34 | | 34 | | .25 | | .26 | |
| Nonperforming | 121 | | 113 | | .89 | | .87 | |
| Total | $ | 216 | | $ | 224 | | 1.59 | % | 1.72 | % |
Other(b) | | | | |
| 30-89 days | $ | 143 | | $ | 176 | | .58 | % | .65 | % |
| 90 days or more | 28 | | 31 | | .11 | | .11 | |
| Nonperforming | 19 | | 17 | | .08 | | .06 | |
| Total | $ | 190 | | $ | 224 | | .77 | % | .82 | % |
(a)Excludes $660 million of loans 30-89 days past due and $2.3.billion of loans 90 days or more past due at December 31, 2024, purchased and that could be purchased from GNMA mortgage pools under delinquent loan repurchase options that continue to accrue interest, compared with $595 million and $2.0 billion at December 31, 2023, respectively.
(b)Includes revolving credit, installment and automobile loans.
Modified Loans In certain circumstances, the Company may modify the terms of a loan to maximize the collection of amounts due when a borrower is experiencing financial difficulties or is expected to experience difficulties in the near-term. In most cases the modification is either a concessionary reduction in interest rate, extension of the maturity date or other concessionary modification of loan terms that would otherwise not be considered.
Modified loans accrue interest if the borrower complies with the revised terms and conditions and has demonstrated repayment performance at a level commensurate with the modified terms over several payment cycles, which is generally six months or greater.
The Company continues to work with borrowers who are experiencing financial difficulties to modify their loans. Many of the Company’s loan modifications are determined on a case-by-case basis in connection with ongoing loan collection processes. The modifications vary within each of the Company’s loan classes. Commercial lending segment modifications generally include extensions of the maturity date and may be accompanied by an increase or decrease to the interest rate. The Company may also work with the borrower to make other changes to the loan to mitigate losses, such as obtaining additional collateral and/or guarantees to support the loan.
The Company has also implemented certain residential mortgage loan modification programs. The Company modifies residential mortgage loans under Federal Housing Administration, United States Department of Veterans Affairs, and its own internal programs. Under these programs, the Company offers qualifying homeowners the opportunity to permanently modify their loan and achieve more affordable monthly payments. These modifications may include adjustments to interest rates, conversion of adjustable rates to fixed rates, extensions of maturity dates or deferrals of payments, capitalization of accrued interest and/or outstanding advances, or in limited situations, partial forgiveness of loan principal. In some instances, participation in residential mortgage loan modification programs requires the customer to complete a short-term trial period. A permanent loan modification is contingent on the customer successfully completing the trial period arrangement, and the loan documents are not modified until that time.
Credit card and other retail loan modifications are generally part of distinct modification programs providing customers modification solutions over a specified time period, generally up to 60 months.
The Company also makes short-term modifications, in limited circumstances, to assist borrowers experiencing temporary hardships. Short-term consumer lending modification programs include payment reductions, deferrals of up to three past due payments, and the ability to return to current status if the borrower makes required payments. The Company may also make short-term modifications to commercial lending loans, with the most common modification being an extension of the maturity date of three months or less. Such extensions generally are used when the maturity date is imminent and the borrower is experiencing some level of financial stress, but the Company believes the borrower will pay all contractual amounts owed.
Nonperforming Assets The level of nonperforming assets represents another indicator of the Company’s risk within the loan portfolio. Nonperforming assets include nonaccrual loans, modified loans not performing in accordance with modified terms and not accruing interest, modified loans that have not met the performance period required to return to accrual status, other real estate owned (“OREO”) and other nonperforming assets owned by the Company. Interest payments collected from assets on nonaccrual status are generally applied against the principal balance and not recorded as income. However, interest income may
| | |
38 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
be recognized for interest payments received if the remaining carrying amount of the loan is believed to be collectible.
At December 31, 2024, total nonperforming assets were $1.8 billion, compared with $1.5 billion at December 31, 2023. The $338 million (22.6 percent) increase in nonperforming assets, from December 31, 2023 to December 31, 2024, was primarily due to higher nonperforming commercial and commercial real estate loans. The ratio of total nonperforming assets to total loans
and other real estate was 0.48 percent at December 31, 2024, compared with 0.40 percent at December 31, 2023.
OREO was $21 million at December 31, 2024, compared with $26 million at December 31, 2023, and was related to foreclosed properties that previously secured loan balances. These balances exclude foreclosed GNMA loans whose repayments are primarily insured by the Federal Housing Administration or guaranteed by the United States Department of Veterans Affairs.
| | | | | | | | |
| TABLE 16 | | Nonperforming Assets(a) |
| | | | | | | | |
| At December 31 (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 |
| Commercial | | |
| Commercial | $ | 644 | | $ | 349 | |
| Lease financing | 26 | | 27 | |
| Total commercial | 670 | | 376 | |
| Commercial Real Estate | | |
| Commercial mortgages | 789 | | 675 | |
| Construction and development | 35 | | 102 | |
| Total commercial real estate | 824 | | 777 | |
Residential Mortgages(b) | 152 | | 158 | |
| Credit Card | — | | — | |
| Other Retail | | |
| Retail leasing | 7 | | 8 | |
| Home equity and second mortgages | 121 | | 113 | |
| Other | 19 | | 17 | |
| Total other retail | 147 | | 138 | |
Total nonperforming loans(1) | 1,793 | | 1,449 | |
Other Real Estate(c) | 21 | | 26 | |
| Other Assets | 18 | | 19 | |
| Total nonperforming assets | $ | 1,832 | | $ | 1,494 | |
Accruing loans 90 days or more past due(b) | $ | 810 | | $ | 698 | |
Period-end loans(2) | $ | 379,832 | | $ | 373,835 | |
Nonperforming assets to total loans(1)/(2) | .47 | % | .39 | % |
Nonperforming assets to total loans plus other real estate(c) | .48 | % | .40 | % |
Changes in Nonperforming Assets
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars in Millions) | Commercial and Commercial Real Estate | Residential Mortgages, Credit Card and Other Retail | Total |
| Balance December 31, 2023 | $ | 1,155 | | $ | 339 | | $ | 1,494 | |
| Additions to nonperforming assets | | | |
| New nonaccrual loans and foreclosed properties | 1,557 | | 190 | | 1,747 | |
| Advances on loans | 32 | | 1 | | 33 | |
| | | |
| Total additions | 1,589 | | 191 | | 1,780 | |
| Reductions in nonperforming assets | | | |
| Paydowns, payoffs | (516) | | (49) | | (565) | |
| Net sales | (41) | | (28) | | (69) | |
| Return to performing status | (112) | | (87) | | (199) | |
Charge-offs(d) | (581) | | (28) | | (609) | |
| Total reductions | (1,250) | | (192) | | (1,442) | |
| Net additions to (reductions in) nonperforming assets | 339 | | (1) | | 338 | |
| Balance December 31, 2024 | $ | 1,494 | | $ | 338 | | $ | 1,832 | |
(a)Throughout this document, nonperforming assets and related ratios do not include accruing loans 90 days or more past due.
(b)Excludes $2.3 billion and $2.0 billion at December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively, of loans purchased and loans that could be purchased from GNMA mortgage pools under delinquent loan repurchase options that are 90 days or more past due that continue to accrue interest, as their repayments are primarily insured by the Federal Housing Administration or guaranteed by the United States Department of Veterans Affairs.
(c)Foreclosed GNMA loans of $46 million and $47 million at December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively, continue to accrue interest and are recorded as other assets and excluded from nonperforming assets because they are insured by the Federal Housing Administration or guaranteed by the United States Department of Veterans Affairs.
(d)Charge-offs exclude actions for certain card products and loan sales that were not classified as nonperforming at the time the charge-off occurred.
| | |
40 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
| | | | | | | | |
| TABLE 17 | | Net Charge-offs as a Percent of Average Loans Outstanding |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2024 | 2023 | 2022 |
Year Ended December 31
(Dollars in Millions) | Average Loan Balance | Net Charge-offs | Percent | Average Loan Balance | Net Charge-offs | Percent | Average Loan Balance | Net Charge-offs | Percent |
| Commercial | | | | | | | | | |
| Commercial | $ | 129,235 | | $ | 523 | | .40 | % | $ | 130,544 | | $ | 293 | | .22 | % | $ | 118,967 | | $ | 211 | | .18 | % |
| Lease financing | 4,177 | | 29 | | .69 | | 4,339 | | 21 | | .48 | | 4,830 | | 16 | | .33 | |
| Total commercial | 133,412 | | 552 | | .41 | | 134,883 | | 314 | | .23 | | 123,797 | | 227 | | .18 | |
| Commercial Real Estate | | | | | | | | | |
| Commercial mortgages | 40,513 | | 163 | | .40 | | 42,894 | | 265 | | .62 | | 30,890 | | 17 | | .06 | |
| Construction | 11,144 | | 2 | | .02 | | 11,752 | | (2) | | (.02) | | 10,208 | | 20 | | .20 | |
| Total commercial real estate | 51,657 | | 165 | | .32 | | 54,646 | | 263 | | .48 | | 41,098 | | 37 | | .09 | |
| Residential Mortgages | 117,026 | | (9) | | (.01) | | 115,922 | | 109 | | .09 | | 84,749 | | (23) | | (.03) | |
| Credit Card | 28,683 | | 1,227 | | 4.28 | | 26,570 | | 849 | | 3.20 | | 23,478 | | 524 | | 2.23 | |
| Other Retail | | | | | | | | | |
| Retail leasing | 4,097 | | 21 | | .51 | | 4,665 | | 6 | | .13 | | 6,459 | | 3 | | .05 | |
| Home equity and second mortgages | 13,181 | | (1) | | (.01) | | 12,829 | | (2) | | (.02) | | 11,051 | | (7) | | (.06) | |
| Other | 25,819 | | 197 | | .76 | | 31,760 | | 366 | | 1.15 | | 42,941 | | 302 | | .70 | |
| Total other retail | 43,097 | | 217 | | .50 | | 49,254 | | 370 | | .75 | | 60,451 | | 298 | | .49 | |
| Total loans | $ | 373,875 | | $ | 2,152 | | .58 | % | $ | 381,275 | | $ | 1,905 | | .50 | % | $ | 333,573 | | $ | 1,063 | | .32 | % |
Analysis of Loan Net Charge-offs Total loan net charge-offs were $2.2 billion in 2024, compared with $1.9 billion in 2023. The $247 million (13.0 percent) increase in total net charge-offs in 2024, compared with 2023, reflected higher credit card and commercial loan net charge-offs in 2024, partially offset by the impacts in 2023 of charge-offs on acquired loans and charge-offs related to balance sheet repositioning and capital management actions. The ratio of total loan net charge-offs to average loans outstanding was 0.58 percent in 2024, compared with 0.50 percent in 2023.
Commercial and commercial real estate loan net charge-offs for 2024 were $717 million (0.39 percent of average loans outstanding), compared with $577 million (0.30 percent of average loans outstanding) in 2023. The increase in net charge-offs in 2024, compared with 2023, was driven primarily by select borrowers facing challenges from the higher interest rate and inflation environment.
Residential mortgage loan net charge-offs for 2024 reflected net recoveries of $9 million, compared with net charge-offs of $109 million (0.09 percent of average loans outstanding) in 2023. Credit card loan net charge-offs in 2024 were $1.2 billion (4.28 percent of average loans outstanding), compared with $849 million (3.20 percent of average loans outstanding) in 2023. Other retail loan net charge-offs for 2024 were $217 million (0.50 percent of average loans outstanding), compared with $370 million (0.75 percent of average loans outstanding) in 2023. The decrease in residential mortgage and other retail loan net charge-offs in 2024, compared with 2023, reflects 2023 charge-offs related to balance sheet repositioning and capital management actions. The increase in credit card net charge-offs reflects stabilizing economic and credit conditions.
Analysis and Determination of the Allowance for Credit Losses The allowance for credit losses is established for current expected credit losses on the Company’s loan and lease portfolio, including unfunded credit commitments. The allowance considers expected losses for the remaining lives of the applicable assets, inclusive of expected recoveries. The allowance for credit losses is increased through provisions charged to earnings and reduced by net charge-offs.
Management evaluates the appropriateness of the allowance for credit losses on a quarterly basis. Multiple economic scenarios are considered over a three-year reasonable and supportable forecast period, which includes increasing consideration of historical loss experience over years two and three. These economic scenarios are constructed with interrelated projections of multiple economic variables, and loss estimates are produced that consider the historical correlation of those economic variables with credit losses. After the forecast period, the Company fully reverts to long-term historical loss experience, adjusted for prepayments and characteristics of the current loan and lease portfolio, to estimate losses over the remaining life of the portfolio. The economic scenarios are updated at least quarterly and are designed to provide a range of reasonable estimates, both better and worse than current expectations. Scenarios are weighted based on the Company’s expectation of economic conditions for the foreseeable future and reflect significant judgment and consideration of economic forecast uncertainty. Final loss estimates also consider factors affecting credit losses not reflected in the scenarios, due to the unique aspects of current conditions and expectations. These factors may include, but are not limited
to, changes in borrower behavior or conditions in specific lending segments, loan servicing practices, regulatory guidance, and/or fiscal and monetary policy actions.
Because business processes and credit risks associated with unfunded credit commitments are essentially the same as for loans, the Company utilizes similar processes to estimate its liability for unfunded credit commitments, which is included in other liabilities in the Consolidated Balance Sheet. Both the allowance for loan losses and the liability for unfunded credit commitments are included in the Company’s analysis of credit losses and reported reserve ratios.
The allowance recorded for credit losses utilizes forward-looking expected loss models to consider a variety of factors affecting lifetime credit losses. These factors include, but are not limited to, macroeconomic variables such as unemployment rates, real estate prices, gross domestic product levels, interest rates, and corporate bond spreads, as well as loan and borrower characteristics, such as internal risk ratings on commercial loans and consumer credit scores, delinquency status, collateral type and available valuation information, consideration of end-of-term losses on lease residuals, and the remaining term of the loan, adjusted for expected prepayments. For each loan portfolio, including those loans modified under various loan modification programs, model estimates are adjusted as necessary to consider any relevant changes in portfolio composition, lending policies, underwriting standards, risk management practices, economic conditions or other factors that may affect the accuracy of the model. Expected credit loss estimates also include consideration of expected cash recoveries on loans previously charged-off or expected recoveries on collateral-dependent loans where recovery is expected through sale of the collateral at fair value less selling costs. Where loans do not exhibit similar risk characteristics, an individual analysis is performed to consider expected credit losses.
For loans and leases that do not share similar risk characteristics with a pool of loans, the Company establishes individually assessed reserves. Reserves for individual commercial nonperforming loans greater than $5 million in the commercial lending segment are analyzed utilizing expected cash flows discounted using the original effective interest rate, the observable market price of the loan, or the fair value of the collateral, less selling costs, for collateral-dependent loans as appropriate.
When evaluating the appropriateness of the allowance for credit losses for any loans and lines in a junior lien position, the Company considers the delinquency and modification status of the first lien, based on either servicing data for the first lien accounts serviced by the Company or the status of first lien mortgage accounts reported on customer credit bureau files when the first lien is not serviced by the Company. This information is considered within the overall assessment of economic conditions, problem loans, recent loss experience and other factors in determining the allowance for credit losses.
When a loan portfolio is purchased, the acquired loans are divided into those considered purchased with more than insignificant credit deterioration (“PCD”) and those not
considered PCD. An allowance is established for each population and considers product mix, risk characteristics of the portfolio and delinquency status and refreshed LTV ratios when possible. Considerations for PCD loans include whether the loan has experienced a charge-off, bankruptcy or significant deterioration since origination. The allowance established for purchased loans not considered PCD is recognized through provision expense upon acquisition, whereas the allowance established for loans considered PCD at acquisition is offset by an increase in the basis of the acquired loans. Any subsequent increases and decreases in the allowance related to purchased loans, regardless of PCD status, are recognized through provision expense, with charge-offs charged to the allowance. The Company had a total net book balance of $2.3 billion of PCD loans, primarily related to the MUB acquisition, included in its loan portfolio at December 31, 2024.
The Company’s methodology for determining the appropriate allowance for credit losses also considers the imprecision inherent in the methodologies used and allocated to the various loan portfolios. As a result, amounts determined under the methodologies described above are adjusted by management to consider the potential impact of other qualitative factors not captured in quantitative model adjustments which include, but are not limited to, the following: model imprecision, imprecision in economic scenario assumptions, and emerging risks related to either changes in the economic environment that are affecting specific portfolios, or changes in portfolio concentrations over time that may affect model performance. The consideration of these items results in adjustments to allowance amounts included in the Company’s allowance for credit losses for each loan portfolio. Some factors considered in 2024 that required a higher level of qualitative judgment included consideration of factors affecting commercial real estate office property values, and the effects of persisting inflationary pressures and continued elevated interest rates across commercial and consumer lending portfolios.
The results of the analysis are evaluated quarterly to confirm the estimates are appropriate for each loan portfolio. Table 19 shows the amount of the allowance for credit losses by loan class and underlying portfolio category.
Although the Company determined the amount of each element of the allowance separately and considers this process to be an important credit management tool, the entire allowance for credit losses is available for the entire loan portfolio. The actual amount of losses can vary significantly from the estimated amounts.
At December 31, 2024, the allowance for credit losses was $7.9 billion, compared with an allowance of $7.8 billion at December 31, 2023. The increase in the allowance for credit losses of $86 million (1.1 percent) at December 31, 2024, compared with December 31, 2023, was primarily driven by loan portfolio growth.
The ratio of the allowance for credit losses to period-end loans was 2.09 percent at December 31, 2024, compared with 2.10 percent at December 31, 2023. The ratio of the allowance for credit losses to nonperforming loans was 442
| | |
42 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
percent at December 31, 2024, compared with 541 percent at December 31, 2023. The ratio of the allowance for credit losses to annual loan net charge-offs at December 31, 2024, was 368 percent, compared with 411 percent at December 31, 2023.
The allowance for credit losses related to commercial lending segment loans decreased $56 million during the year ended December 31, 2024, reflecting improved credit quality and charge-offs of problem loans, partially offset by loan growth.
The allowance for credit losses related to consumer lending segment loans increased $142 million during the year ended December 31, 2024, due to credit card portfolio growth and stabilizing performance, partially offset by favorability in residential real estate secured portfolios related to strength in home values.
Economic conditions considered in estimating the allowance for credit losses at December 31, 2024 included changes in projected gross domestic product and unemployment levels. These factors were evaluated through a combination of quantitative calculations using multiple economic scenarios and additional qualitative assessments that considered the degree of economic uncertainty in the current environment. The projected unemployment rates for 2025 considered in the estimate ranged from 3.1 percent to 8.8 percent.
The following table summarizes the baseline forecast for key economic variables the Company used in its estimate of the allowance for credit losses at December 31, 2024 and 2023:
| | | | | | | | |
| December 31,
2024 | December 31,
2023 |
United States unemployment rate for the three months ending(a) | | |
| December 31, 2024 | 4.2 | % | 4.0 | % |
| June 30, 2025 | 4.4 | | 4.1 | |
| December 31, 2025 | 4.3 | | 4.0 | |
United States real gross domestic product for the three months ending(b) | | |
| December 31, 2024 | 2.3 | % | 1.3 | % |
| June 30, 2025 | 1.9 | | 1.6 | |
| December 31, 2025 | 1.7 | | 2.0 | |
(a)Reflects quarterly average of forecasted reported United States unemployment rate.
(b)Reflects year-over-year growth rates.
| | | | | | | | |
| TABLE 18 | | Summary of Allowance for Credit Losses |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 |
| Balance at beginning of year | $ | 7,839 | | $ | 7,404 | | $ | 6,155 | |
Change in accounting principle(a) | — | | (62) | | — | |
Allowance for acquired credit losses(b) | — | | 127 | | 336 | |
| Charge-Offs | | | |
| Commercial | | | |
| Commercial | 615 | | 357 | | 294 | |
| Lease financing | 37 | | 32 | | 25 | |
| Total commercial | 652 | | 389 | | 319 | |
| Commercial real estate | | | |
| Commercial mortgages | 218 | | 278 | | 28 | |
| Construction and development | 11 | | 3 | | 26 | |
| Total commercial real estate | 229 | | 281 | | 54 | |
| Residential mortgages | 13 | | 129 | | 13 | |
| Credit card | 1,406 | | 1,014 | | 696 | |
| Other retail | | | |
| Retail leasing | 35 | | 18 | | 18 | |
| Home equity and second mortgages | 9 | | 12 | | 9 | |
| Other | 269 | | 448 | | 391 | |
| Total other retail | 313 | | 478 | | 418 | |
Total charge-offs(c) | 2,613 | | 2,291 | | 1,500 | |
| Recoveries | | | |
| Commercial | | | |
| Commercial | 92 | | 64 | | 83 | |
| Lease financing | 8 | | 11 | | 9 | |
| Total commercial | 100 | | 75 | | 92 | |
| Commercial real estate | | | |
| Commercial mortgages | 55 | | 13 | | 11 | |
| Construction and development | 9 | | 5 | | 6 | |
| Total commercial real estate | 64 | | 18 | | 17 | |
| Residential mortgages | 22 | | 20 | | 36 | |
| Credit card | 179 | | 165 | | 172 | |
| Other retail | | | |
| Retail leasing | 14 | | 12 | | 15 | |
| Home equity and second mortgages | 10 | | 14 | | 16 | |
| Other | 72 | | 82 | | 89 | |
| Total other retail | 96 | | 108 | | 120 | |
| Total recoveries | 461 | | 386 | | 437 | |
| Net Charge-Offs | | | |
| Commercial | | | |
| Commercial | 523 | | 293 | | 211 | |
| Lease financing | 29 | | 21 | | 16 | |
| Total commercial | 552 | | 314 | | 227 | |
| Commercial real estate | | | |
| Commercial mortgages | 163 | | 265 | | 17 | |
| Construction and development | 2 | | (2) | | 20 | |
| Total commercial real estate | 165 | | 263 | | 37 | |
| Residential mortgages | (9) | | 109 | | (23) | |
| Credit card | 1,227 | | 849 | | 524 | |
| Other retail | | | |
| Retail leasing | 21 | | 6 | | 3 | |
| Home equity and second mortgages | (1) | | (2) | | (7) | |
| Other | 197 | | 366 | | 302 | |
| Total other retail | 217 | | 370 | | 298 | |
| Total net charge-offs | 2,152 | | 1,905 | | 1,063 | |
Provision for credit losses(d) | 2,238 | | 2,275 | | 1,977 | |
| Other changes | — | | — | | (1) | |
| Balance at end of year | $ | 7,925 | | $ | 7,839 | | $ | 7,404 | |
| Components | | | |
| Allowance for loan losses | $ | 7,583 | | $ | 7,379 | | $ | 6,936 | |
| Liability for unfunded credit commitments | 342 | | 460 | | 468 | |
Total allowance for credit losses(1) | $ | 7,925 | | $ | 7,839 | | $ | 7,404 | |
Period-end loans(2) | $ | 379,832 | | $ | 373,835 | | $ | 388,213 | |
Nonperforming loans(3) | 1,793 | | 1,449 | | 972 | |
| Allowance for Credit Losses as a Percentage of | | | |
Period-end loans(1)/(2) | 2.09 | % | 2.10 | % | 1.91 | % |
Nonperforming loans(1)/(3) | 442 | | 541 | | 762 | |
| Nonperforming and accruing loans 90 days or more past due | 304 | | 365 | | 506 | |
| Nonperforming assets | 433 | | 525 | | 729 | |
| Net charge-offs | 368 | | 411 | | 697 | |
(a)Effective January 1, 2023, the Company adopted accounting guidance which removed the separate recognition and measurement of troubled debt restructurings.
(b)Allowance for purchased credit deteriorated and charged-off loans acquired from MUB.
(c)2023 includes $91 million of charge-offs related to uncollectible amounts on acquired loans, as well as $309 million of charge-offs related to balance sheet repositioning and capital management actions. 2022 includes $179 million of charge-offs related to uncollectible amounts on acquired loans, as well as $189 million of charge-offs related to balance sheet repositioning and capital management actions.
(d)2023 includes provision for credit losses of $243 million related to balance sheet repositioning and capital management actions. 2022 includes provision for credit losses of $662 million related to the acquisition of MUB and $129 million related to balance sheet repositioning and capital management actions.
| | |
44 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
| | | | | | | | |
| TABLE 19 | | Allocation of the Allowance for Credit Losses |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Allowance Amount | Allowance as a Percent of Loans |
| At December 31 (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 | 2024 | 2023 |
| Commercial | | | | |
| Commercial | $ | 2,090 | | $ | 2,038 | | 1.55 | % | 1.60 | % |
| Lease financing | 85 | | 81 | | 2.01 | | 1.91 | |
| Total commercial | 2,175 | | 2,119 | | 1.56 | | 1.61 | |
| Commercial Real Estate | | | | |
| Commercial mortgages | 1,016 | | 1,068 | | 2.63 | | 2.55 | |
| Construction and development | 492 | | 552 | | 4.80 | | 4.79 | |
| Total commercial real estate | 1,508 | | 1,620 | | 3.09 | | 3.03 | |
| Residential Mortgages | 783 | | 827 | | .66 | | .72 | |
| Credit Card | 2,640 | | 2,403 | | 8.70 | | 8.41 | |
| Other Retail | | | | |
| Retail leasing | 93 | | 95 | | 2.30 | | 2.30 | |
| Home equity and second mortgages | 255 | | 321 | | 1.88 | | 2.46 | |
| Other | 471 | | 454 | | 1.91 | | 1.67 | |
| Total other retail | 819 | | 870 | | 1.93 | | 1.96 | |
| Total allowance | $ | 7,925 | | $ | 7,839 | | 2.09 | % | 2.10 | % |
Residual Value Risk Management The Company manages its risk to changes in the residual value of leased vehicles, office and business equipment, and other assets through disciplined residual valuation at the inception of a lease, diversification of its leased assets, regular residual asset valuation reviews and monitoring of residual value gains or losses upon the disposition of assets. Lease originations are subject to the same well-defined underwriting standards referred to in the “Credit Risk Management” section, which includes an evaluation of the residual value risk. Retail lease residual value risk is mitigated further by effective end-of-term marketing of off-lease vehicles.
Included in the retail leasing portfolio was approximately $3.1 billion of retail leasing residuals at December 31, 2024, compared with $3.4 billion at December 31, 2023. The Company monitors concentrations of leases by manufacturer and vehicle type. As of December 31, 2024, vehicle lease residuals related to sport utility vehicles were 54.1 percent of the portfolio, while auto and truck classes represented approximately 21.2 percent and 14.6 percent of the portfolio, respectively. At year-end 2024, the individual vehicle model with the largest residual value outstanding represented 23.7 percent of the aggregate residual value of all vehicles in the portfolio. At December 31, 2024 and 2023, the weighted-average origination term of the portfolio was 41 months. At December 31, 2024, the commercial leasing portfolio had $484 million of residuals, compared with $491 million at December 31, 2023. At year-end 2024, lease residuals related to trucks and other transportation equipment represented 39.4 percent of the total residual portfolio, while business and office equipment represented 27.4 percent.
Operational Risk Management The Company operates in many different businesses in diverse markets and relies on the ability of its employees and systems to process a high number of transactions. Operational risk is inherent in all business activities, and the management of this risk is important to the achievement of the Company’s objectives. Business lines have direct and primary responsibility and accountability for identifying, controlling, and monitoring operational risks embedded in their business activities, including those additional or increased risks created by economic and financial disruptions.
The Company maintains a system of controls with the objective of providing proper transaction authorization and execution, proper system operations, proper oversight of third parties with whom it does business, safeguarding of assets from misuse or theft, and ensuring the reliability and security of financial and other data. The Company also maintains a cybersecurity risk program which provides centralized planning and management of related and interdependent work with a focus on risks from cybersecurity threats. The Company's cybersecurity risk program is integrated into the Company's overall business and operational strategies and requires that the Company allocate appropriate resources to maintain the program. Refer to “Item 1C. Cybersecurity” in the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2024, for further discussion on the Company's cybersecurity risk program.
Business continuation and disaster recovery planning is also critical to effectively managing operational risks. Each business unit of the Company is required to develop, maintain and test these plans at least annually to ensure that recovery activities, if needed, can support mission critical functions, including technology, networks and data
centers supporting customer applications and business operations.
While the Company strives to design processes to minimize operational risks, there is no absolute assurance that business disruption or operational losses would not occur from an external event or internal control breakdown. On an ongoing basis, management makes process changes and investments to enhance its systems of internal controls and business continuity and disaster recovery plans.
Compliance Risk Management The Company may suffer legal or regulatory sanctions, material financial loss, or damage to its reputation if it fails to comply with laws, regulations, rules, standards of good practice, and codes of conduct, including those related to compliance with Bank Secrecy Act/anti-money laundering requirements, sanctions compliance requirements as administered by the Office of Foreign Assets Control, consumer protection and other requirements. The Company has controls and processes in place for the assessment, identification, monitoring, management and reporting of compliance risks and issues, including those created or increased by economic and financial disruptions. Refer to “Supervision and Regulation” in the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2024, for further discussion of the regulatory framework applicable to bank holding companies and their subsidiaries.
Interest Rate Risk Management In the banking industry, changes in interest rates are a significant risk that can impact earnings as well as the safety and soundness of an entity. The Company manages its exposure to changes in interest rates through asset and liability management activities within guidelines established by its Asset Liability Management Committee (“ALCO”) and approved by the Board of Directors. The ALCO has the responsibility for approving and overseeing compliance with the ALCO management policies, including interest rate risk exposure. One way the Company measures and analyzes its interest rate risk is through analysis of net interest income sensitivities across a range of scenarios.
Net interest income sensitivity analysis includes evaluating all of the Company’s assets and liabilities and off-balance sheet instruments, inclusive of new business activity, under various interest rate scenarios that differ in the direction, amount and speed of change over time, as well as the overall shape of the yield curve. The balance sheet includes assumptions regarding loan and deposit volumes and pricing which are based on quantitative analysis, historical trends and management outlook and strategies. Deposit balances, mix and pricing are dynamic
across interest rate scenarios and will change both with the absolute level of rates as well as the assumed interest rate shock. Deposit pricing changes, commonly referred to as the deposit beta, represents the amount by which the Company’s interest-bearing deposit rates have or will change given a change in short-term market rates. Base case and net interest income sensitivities are reviewed monthly by the ALCO and are used to guide asset/liability management strategies.
The Company also manages interest rate sensitivity by utilizing market value of equity modeling, which measures the degree to which the market values of the Company’s assets and liabilities and off-balance sheet instruments will change given a change in interest rates. Management measures the impact of changes in market values due to interest rates under a number of scenarios, including immediate and sustained parallel shifts, and flattening or steepening of the yield curve. The Company manages its interest rate risk position by holding assets with desired interest rate risk characteristics on its balance sheet, executing certain pricing strategies for loans and deposits and deploying investment portfolio, funding and derivative strategies.
Table 20 summarizes the projected impact to net interest income over the next 12 months of various potential interest rate changes. The sensitivity of the projected impact to net interest income over the next 12 months is dependent on balance sheet growth, product mix, customer behavior, deposit pricing and funding decisions. From December 31, 2023 to December 31, 2024, interest rate sensitivity to higher rates decreased, primarily due to deposit migration into higher yielding products. As of December 31, 2024, the Company continues to be asset sensitive to a parallel upward move in interest rates with most of that impact coming from the long end of the yield curve. Net interest income simulation incorporates rate-sensitive deposit behavior that could result in changes in both projected deposit balances and mix under the various interest rate scenarios. Higher rate scenarios result in disintermediation of bank deposits and a mix shift into higher yielding deposits. Conversely, in lower rate scenarios, the analysis assumes that deposits will shift into lower yielding products. While the Company utilizes models and assumptions based on historical information and expected behaviors, actual outcomes could vary significantly. For larger interest rate shock scenarios, mortgage assets and deposits are expected to behave in a non-linear manner resulting in varying impacts to net interest income in those scenarios.
| | | | | | | | |
| TABLE 20 | | Sensitivity of Net Interest Income |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| December 31, 2024 | December 31, 2023 |
| Down 50 bps
Immediate | Up 50 bps
Immediate | Down 200 bps
Immediate | Up 200 bps
Immediate | Down 50 bps
Immediate | Up 50 bps
Immediate | Down 200 bps
Immediate | Up 200 bps
Immediate |
| Net interest income | .25 | % | .17 | % | .01 | % | 1.05 | % | (.19) | % | .71 | % | (1.05) | % | 2.28 | % |
| | |
46 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
Use of Derivatives to Manage Interest Rate and Other Risks To manage the sensitivity of earnings and capital to interest rate, prepayment, credit, price and foreign currency fluctuations (asset and liability management positions), the Company enters into derivative transactions. The Company uses derivatives for asset and liability management purposes primarily in the following ways:
•To convert fixed-rate debt and available-for-sale investment securities from fixed-rate payments to floating-rate payments;
•To convert floating-rate loans and debt from floating-rate payments to fixed-rate payments;
•To mitigate changes in value of the Company’s unfunded mortgage loan commitments, funded MLHFS and MSRs;
•To mitigate remeasurement volatility of foreign currency denominated balances; and
•To mitigate the volatility of the Company’s net investment in foreign operations driven by fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates.
In addition, the Company enters into interest rate, foreign exchange and commodity derivative contracts to support the business requirements of its customers (customer-related positions). The Company minimizes the market, funding and liquidity risks of customer-related positions by either entering into similar offsetting positions with broker-dealers, or on a portfolio basis by entering into other derivative or non-derivative financial instruments that partially or fully offset the exposure from these customer-related positions. The Company may enter into derivative contracts that are either exchange-traded, centrally cleared through clearinghouses or over-the-counter. The Company does not utilize derivatives for speculative purposes. The Company does not designate all of the derivatives that it enters into for risk management purposes as accounting hedges because of the inefficiency of applying the accounting requirements and may instead elect fair value accounting for the related hedged items. In particular, the Company enters into interest rate swaps, swaptions, forward commitments to buy to-be-announced securities (“TBAs”), U.S. Treasury and Eurodollar futures and options on U.S. Treasury futures to mitigate fluctuations in the value of its MSRs, but does not designate those derivatives as accounting hedges. Refer to Note 9 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information regarding MSRs, including management of the changes in fair value.
Additionally, the Company uses forward commitments to sell TBAs and other commitments to sell residential mortgage loans at specified prices to economically hedge the interest rate risk in its residential mortgage loan production activities. The forward commitments to sell and the unfunded mortgage loan commitments on loans intended to be sold are considered derivatives under the accounting guidance related to accounting for derivative instruments and hedging activities. The Company has elected the fair value option for the MLHFS.
Derivatives are subject to credit risk associated with counterparties to the contracts. Credit risk associated with derivatives is measured by the Company based on the
probability of counterparty default. The Company manages the credit risk of its derivative positions by diversifying its positions among various counterparties, by entering into master netting arrangements, and, where possible, by requiring collateral arrangements. The Company may also transfer counterparty credit risk related to interest rate swaps to third parties through the use of risk participation agreements. In addition, certain interest rate swaps, interest rate forwards and credit contracts are required to be centrally cleared through clearinghouses to further mitigate counterparty credit risk. The Company also mitigates the credit risk of its derivative positions, as well as the credit risk on loans or lending portfolios, through the use of credit contracts.
For additional information on derivatives and hedging activities, refer to Notes 19 and 20 in the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Market Risk Management In addition to interest rate risk, the Company is exposed to other forms of market risk, principally related to trading activities which support customers’ strategies to manage their own foreign currency, interest rate risk, commodities risk and funding activities. For purposes of its internal capital adequacy assessment process, the Company considers risk arising from its trading activities, as well as the remeasurement volatility of foreign currency denominated balances included on its Consolidated Balance Sheet (collectively, “Covered Positions”), employing methodologies consistent with the requirements of regulatory rules for market risk. The Company’s Market Risk Committee (“MRC”), within the framework of the ALCO, oversees market risk management. The MRC monitors and reviews the Company’s Covered Positions and establishes policies for market risk management, including exposure limits for each portfolio. The Company uses a VaR approach to measure general market risk. Theoretically, VaR represents the statistical risk of loss the Company has to adverse market movements over a one-day time horizon. The Company uses the historical simulation method to calculate VaR for its Covered Positions measured at the ninety-ninth percentile using a one-year look-back period for distributions derived from past market data. The market factors used in the calculations include those pertinent to market risks inherent in the underlying trading portfolios, principally those that affect the Company’s corporate bond trading business, foreign currency transaction business, client derivatives business, loan trading business and municipal securities business, as well as those inherent in the Company’s foreign denominated balances and the derivatives used to mitigate the related measurement volatility. On average, the Company expects the one-day VaR to be exceeded by actual losses two to three times per year related to these positions. The Company monitors the accuracy of internal VaR models and modeling processes by back-testing model performance, regularly updating the historical data used by the VaR models and regular model validations to assess the accuracy of the models’ input, processing, and reporting components. All models are required to be independently reviewed and approved prior to being placed in use. If the Company were to experience market
losses in excess of the estimated VaR more often than expected, the VaR models and associated assumptions would be analyzed and adjusted.
The average, high, low and period-end one-day VaR amounts for the Company’s Covered Positions were as follows:
| | | | | | | | |
Year Ended December 31 (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 |
| Average | $ | 3 | | $ | 4 | |
| High | 4 | | 7 | |
| Low | 2 | | 2 | |
| Period-end | 2 | | 3 | |
The Company did not experience any actual losses for its combined Covered Positions that exceeded VaR during the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2023. The Company stress tests its market risk measurements to provide management with perspectives on market events that may not be captured by its VaR models, including worst case historical market movement combinations that have not necessarily occurred on the same date.
The Company calculates Stressed VaR using the same underlying methodology and model as VaR, except that a historical continuous one-year look-back period is utilized that reflects a period of significant financial stress appropriate to the Company’s Covered Positions. The period selected by the Company includes the significant market volatility of the last four months of 2008.
The average, high, low and period-end one-day Stressed VaR amounts for the Company’s Covered Positions were as follows:
| | | | | | | | |
Year Ended December 31 (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 |
| Average | $ | 10 | | $ | 10 | |
| High | 16 | | 16 | |
| Low | 7 | | 6 | |
| Period-end | 11 | | 8 | |
Valuations of positions in client derivatives and foreign currency activities are based on discounted cash flow or other valuation techniques using market-based assumptions. These valuations are compared to third-party quotes or other market prices to determine if there are significant variances. Significant variances are approved by senior management in the Company’s corporate functions. Valuation of positions in the corporate bond trading, loan trading, asset-backed securities and municipal securities businesses are based on trader marks. These trader marks are evaluated against third-party prices, with significant variances approved by senior management in the Company’s corporate functions.
The Company also measures the market risk of its hedging activities related to residential MLHFS and MSRs using the historical simulation method. The VaRs are measured at the ninety-ninth percentile and employ factors pertinent to the market risks inherent in the valuation of the
assets and hedges. A one-year look-back period is used to obtain past market data for the models.
The average, high and low VaR amounts for the residential MLHFS and related hedges and the MSRs and related hedges were as follows:
| | | | | | | | |
Year Ended December 31 (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 |
| Residential Mortgage Loans Held For Sale and Related Hedges | | |
| Average | $ | 2 | | $ | 1 | |
| High | 3 | | 2 | |
| Low | 1 | | — | |
| Mortgage Servicing Rights and Related Hedges | | |
| Average | $ | 2 | | $ | 7 | |
| High | 3 | | 12 | |
| Low | 1 | | 2 | |
Liquidity Risk Management The Company’s liquidity risk management process is designed to identify, measure, and manage the Company’s funding and liquidity risk to meet its daily funding needs and to address expected and unexpected changes in its funding requirements. The Company engages in various activities to manage its liquidity risk. These activities include diversifying its funding sources, stress testing, and holding readily-marketable assets which can be used as a source of liquidity if needed. In addition, the Company’s profitable operations, sound credit quality and strong credit ratings and capital position have enabled it to develop a large and reliable base of core deposit funding within its market areas and in domestic and global capital markets.
The Company’s Board of Directors approves the Company’s liquidity policy. The Risk Management Committee of the Company’s Board of Directors oversees the Company’s liquidity risk management process and approves a contingency funding plan. The ALCO reviews the Company’s liquidity policy and limits, and regularly assesses the Company’s ability to meet funding requirements arising from adverse company-specific or market events.
The Company’s liquidity policy requires it to maintain diversified wholesale funding sources to avoid maturity, entity and market concentrations. The Company operates a Cayman Islands branch for issuing Eurodollar time deposits. In addition, the Company has relationships with dealers to issue national market retail and institutional savings certificates and short-term and medium-term notes. The Company also maintains a significant correspondent banking network and relationships. Accordingly, the Company has access to national federal funds, funding through repurchase agreements and sources of stable certificates of deposit and commercial paper.
The Company regularly projects its funding needs under various stress scenarios and maintains a contingency funding plan consistent with the Company’s access to diversified sources of contingent funding. The Company maintains a substantial level of total available liquidity in the
| | |
48 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
form of on-balance sheet and off-balance sheet funding sources. These liquidity sources include cash at the Federal Reserve Bank and certain European central banks, unencumbered liquid assets, and capacity to borrow from the FHLB and at the Federal Reserve Bank’s Discount Window. Unencumbered liquid assets in the Company’s investment securities portfolio provide asset liquidity through the Company’s ability to sell the securities or pledge and borrow against them. Refer to Note 4 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements and “Balance Sheet Analysis” for further information on investment securities maturities and trends. Asset liquidity is further enhanced by the Company’s practice of pledging loans to access secured borrowing facilities through the FHLB and Federal Reserve Bank.
The following table summarizes the Company's total available liquidity from on-balance sheet and off-balance sheet funding sources:
| | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars in Millions) | December 31,
2024 | December 31,
2023 |
| Cash held at the Federal Reserve Bank and other central banks | $ | 47,434 | | $ | 52,403 | |
| Available investment securities | 67,910 | | 34,220 | |
| Borrowing capacity from the Federal Reserve Bank and FHLB | 171,226 | | 215,763 | |
| Total available liquidity | $ | 286,570 | | $ | 302,386 | |
Borrowing capacity from the Federal Reserve Bank and FHLB declined from December 31, 2023 to December 31, 2024 primarily due to the expiration of the Federal Reserve Bank’s Bank Term Funding Program (“BTFP”). This decline was partially offset by an increase in available investment securities as a portion of the securities previously pledged through the BTFP were made available for sale or pledging.
The Company’s diversified deposit base provides a sizeable source of relatively stable and low-cost funding, while reducing the Company’s reliance on the wholesale markets. Total deposits were $518.3 billion at December 31, 2024, compared with $512.3 billion at December 31, 2023. Average noninterest-bearing deposit balances in 2024 decreased 23 percent compared with 2023, reflecting the shift of noninterest-bearing balances into interest-bearing deposit products resulting from the higher interest rate environment. Average total deposits in 2024 and 2023 funded approximately 77 percent and 76 percent of the Company’s total assets for these same periods, respectively. Refer to Note 11 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements and “Balance Sheet Analysis” for further information on the maturities, terms and trends of the Company’s deposits.
Additional funding is provided by long-term debt and short-term borrowings. Long-term debt was $58.0 billion at December 31, 2024, and is an important funding source because of its multi-year borrowing structure. Refer to Note 13 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for information on the terms and maturities of the Company’s long-term debt issuances and “Balance Sheet Analysis” for discussion on long-term debt trends. Short-term borrowings were $15.5 billion at December 31, 2024, and supplement the Company’s other funding sources. Refer to Note 12 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements and “Balance Sheet Analysis” for further information on the terms and trends of the Company’s short-term borrowings.
The Company’s ability to raise negotiated funding at competitive prices is influenced by rating agencies’ views of the Company’s credit quality, liquidity, capital and earnings. Table 21 details the rating agencies’ most recent assessments as of December 31, 2024.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Moody's | S&P Global Ratings | Fitch Ratings | DBRS Morningstar |
| U.S. Bancorp | | | | |
| Long-term issuer rating | A3 | A | A+ | AA (low) |
| Short-term issuer rating | N/A | A-1 | F1 | R-1 (middle) |
| Senior unsecured debt | A3 | A | A | AA (low) |
| Subordinated debt | A3 | A- | A- | A (high) |
| Junior subordinated debt | Baa1 | N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Preferred stock | Baa2 | BBB | BBB | A (low) |
| Commercial paper | P-2 | N/A | F1 | R-1 (middle) |
| | | | |
| U.S. Bank National Association | | | | |
| Long-term issuer rating | A2 | A+ | A+ | AA |
| Short-term issuer rating | P-1 | A-1 | F1 | R-1 (high) |
| Long-term deposits | Aa3 | N/A | AA- | AA |
| Short-term deposits | P-1 | N/A | F1+ | N/A |
| Senior unsecured debt | A2 | A+ | A+ | AA |
| Subordinated debt | A2 | A | N/A | AA (low) |
| Commercial paper | P-1 | A-1 | N/A | R-1 (high) |
| Counterparty risk assessment | A1(cr)/P-1(cr) | | | |
| Counterparty risk rating | A2/P-1 | | | |
| Baseline credit assessment | a2 | | | |
In addition to assessing liquidity risk on a consolidated basis, the Company monitors the parent company’s liquidity. The parent company’s routine funding requirements consist primarily of operating expenses, dividends paid to shareholders, debt service, repurchases of common stock and funds used for acquisitions. The parent company obtains funding to meet its obligations from dividends collected from its subsidiaries and the issuance of debt and capital securities. The Company establishes limits for the minimal number of months into the future where the parent company can meet existing and forecasted obligations with cash and securities held that can be readily monetized. The Company measures and manages this limit in both normal and adverse conditions. The Company maintains sufficient funding to meet expected capital and debt service obligations for 24 months without the support of dividends from subsidiaries and assuming access to the wholesale markets is maintained. The Company maintains sufficient liquidity to meet its capital and debt service obligations for 12 months under adverse conditions without the support of dividends from subsidiaries or access to the wholesale markets. The parent company is currently in excess of required liquidity minimums.
Under SEC rules, the parent company is classified as a “well-known seasoned issuer,” which allows it to file a registration statement that does not have a limit on issuance capacity. “Well-known seasoned issuers” generally include those companies with outstanding common securities with a market value of at least $700 million held by non-affiliated parties or those
companies that have issued at least $1 billion in aggregate principal amount of non-convertible securities, other than common equity, in the last three years. However, the parent company’s ability to issue debt and other securities under a registration statement filed with the SEC under these rules is limited by the debt issuance authority granted by the Company’s Board of Directors and/or the ALCO policy.
At December 31, 2024, parent company long-term debt outstanding was $35.3 billion, compared with $34.3 billion at December 31, 2023. The increase was primarily due to $6.5 billion of medium-term note issuances, partially offset by $4.6 billion of medium-term note and $1.0 billion of subordinated note repayments. As of December 31, 2024, there was $2.3 billion of parent company debt scheduled to mature in 2025. Future debt maturities may be met through medium-term note and capital security issuances and dividends from subsidiaries, as well as from parent company cash and cash equivalents.
Dividend payments to the Company by its subsidiary banks are subject to regulatory review and statutory limitations and, in some instances, regulatory approval. In general, dividends to the parent company from its banking subsidiaries are limited by rules which compare dividends to net income for regulatorily-defined periods. For further information, see Note 24 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
The Company is subject to a regulatory Liquidity Coverage Ratio (“LCR”) requirement which requires large banking organizations to maintain an adequate level of unencumbered high quality liquid assets to meet estimated liquidity needs over a 30-day stressed period. For the three months ended December 31, 2024 and December 31,
| | |
50 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
2023, the Company's average daily LCR was 106.6 percent and 109.2 percent, respectively. The Company was compliant with this requirement for both of these periods.
The Company is also subject to a regulatory Net Stable Funding Ratio (“NSFR”) requirement which requires large banking organizations to maintain a minimum level of stable funding based on the liquidity characteristics of their assets, commitments, and derivative exposures over a one-year time horizon. The Company was compliant with this requirement at December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023.
European Exposures The Company provides merchant processing and corporate trust services in Europe either directly or through banking affiliations in Europe. Revenue generated from sources in Europe represented approximately 2 percent of the Company’s total net revenue for 2024. Operating cash for these businesses is deposited on a short-term basis typically with certain European central banks. For deposits placed at other European banks, exposure is mitigated by the Company placing deposits at multiple banks and managing the amounts on deposit at any bank based on institution-specific deposit limits. At December 31, 2024, the Company had an aggregate amount on deposit with European banks of approximately $6.4 billion, predominately with the Central Bank of Ireland and Bank of England.
In addition, the Company provides financing to domestic multinational corporations that generate revenue from customers in European countries, transacts with various European banks as counterparties to certain derivative-related activities, and through a subsidiary, manages money market funds that hold certain investments in European sovereign debt. Any deterioration in economic conditions in Europe, including the impacts resulting from the Russia-Ukraine conflict, is not expected to have a significant effect on the Company related to these activities.
Commitments, Contingent Liabilities and Other Contractual Obligations The Company participates in many different contractual arrangements which may or may not be recorded on its balance sheet, with unrelated or consolidated entities, under which the Company has an obligation to pay certain amounts, provide credit or liquidity enhancements or provide market risk support. These arrangements also include any obligation related to a variable interest held in an unconsolidated entity that provides financing, liquidity, credit enhancement or market risk support.
In the ordinary course of business, the Company enters into contractual obligations that may require future cash payments, including funding for customer loan requests, customer deposit maturities and withdrawals, debt service, leases for premises and equipment, and other cash commitments. Refer to Notes 6, 11, 13, 16 and 22 in the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for information on the Company’s operating lease obligations, deposits, long-term debt, benefit obligations and guarantees and other commitments, respectively.
Commitments to extend credit are legally binding and generally have fixed expiration dates or other termination
clauses. Many of the Company’s commitments to extend credit expire without being drawn and, therefore, total commitment amounts do not necessarily represent future liquidity requirements or the Company’s exposure to credit loss. Commitments to extend credit also include consumer credit lines that are cancellable upon notification to the consumer. Total contractual amounts of commitments to extend credit at December 31, 2024 were $409.4 billion. The Company also issues and confirms various types of letters of credit, including standby and commercial. Total contractual amounts of letters of credit at December 31, 2024 were $11.0 billion. For more information on the Company’s commitments to extend credit and letters of credit, refer to Note 22 in the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
The Company’s off-balance sheet arrangements with unconsolidated entities primarily consist of private investment funds or partnerships that make equity investments, provide debt financing or support community-based investments in tax-advantaged projects. In addition to providing investment returns, these arrangements in many cases assist the Company in complying with requirements of the Community Reinvestment Act. The investments in these entities generate a return primarily through the realization of federal and state income tax credits and other tax benefits, such as tax deductions from operating losses of the investments, over specified time periods. The entities in which the Company invests are generally considered variable interest entities (“VIEs”). The Company’s recorded investment in these entities, net of contractual equity investment commitments of $5.0 billion, was $3.1 billion at December 31, 2024.
The Company also has non-controlling financial investments in private funds and partnerships considered VIEs. The Company’s recorded investment in these entities was approximately $264 million at December 31, 2024, and the Company had unfunded commitments to invest an additional $118 million. For more information on the Company’s interests in unconsolidated VIEs, refer to Note 7 in the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Guarantees are contingent commitments issued by the Company to customers or other third parties requiring the Company to perform if certain conditions exist or upon the occurrence or nonoccurrence of a specified event, such as a scheduled payment to be made under contract. The Company’s primary guarantees include commitments from securities lending activities in which indemnifications are provided to customers; indemnification or buy-back provisions related to sales of loans and tax credit investments; and merchant charge-back guarantees through the Company’s involvement in providing merchant processing services. For certain guarantees, the Company may have access to collateral to support the guarantee, or through the exercise of other recourse provisions, be able to offset some or all of any payments made under these guarantees.
The Company and certain of its subsidiaries, along with other Visa U.S.A. Inc. member banks, have a contingent guarantee obligation to indemnify Visa Inc. for potential losses arising from antitrust lawsuits challenging the
practices of Visa U.S.A. Inc. and MasterCard International. The indemnification by the Company and other Visa U.S.A. Inc. member banks has no maximum amount. Refer to Note 22 in the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for further details regarding guarantees, other commitments, and contingent liabilities, including maximum potential future payments and current carrying amounts.
Capital Management The Company is committed to managing capital to maintain strong protection for depositors and creditors and for maximum shareholder benefit. The Company also manages its capital to exceed regulatory capital requirements for banking organizations. To achieve its capital goals, the Company employs a variety of capital management tools, including dividends, common share repurchases, and the issuance of subordinated debt, non-cumulative perpetual preferred stock, common stock and other capital instruments.
The Company announced on September 12, 2024 that its Board of Directors had approved a regular quarterly dividend of $0.50 per common share. This represented a 2 percent increase over the previous dividend rate per common share of $0.49 per quarter.
The Company also announced on September 12, 2024 that its Board of Directors authorized a share repurchase program to repurchase up to $5.0 billion of its common stock, effective September 13, 2024. This share repurchase program replaced the previous share repurchase program announced on December 22, 2020, which was terminated effective on September 12, 2024.
Capital distributions, including dividends and stock repurchases, are subject to the approval of the Company’s Board of Directors and compliance with regulatory requirements. For a more complete analysis of activities impacting shareholders’ equity and capital management programs, refer to Note 14 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Total U.S. Bancorp shareholders’ equity was $58.6 billion at December 31, 2024, compared with $55.3 billion
at December 31, 2023. The increase was primarily the result of corporate earnings, partially offset by dividends paid.
The regulatory capital requirements effective for the Company follow Basel III, with the Company being subject to calculating its capital adequacy as a percentage of risk-weighted assets under the standardized approach. Under Basel III, banking regulators define minimum capital requirements for banks and financial services holding companies. These requirements are expressed in the form of a minimum common equity tier 1 capital ratio, tier 1 capital ratio, total risk-based capital ratio, tier 1 leverage ratio and a tier 1 total leverage exposure, or supplementary leverage ratio. The Company’s minimum required level for the common equity tier 1 capital, tier 1 capital and total capital ratios included a stress capital buffer of 3.1 percent at December 31, 2024. The Company targets its regulatory capital levels, at both the bank and bank holding company level, to exceed the “well-capitalized” threshold for these ratios under the FDIC Improvement Act prompt corrective action provisions that are applicable to all banks. Refer to Note 14 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for further detail on the Company’s minimum required capital ratios and the minimum “well-capitalized” thresholds under the prompt corrective action framework.
Beginning in 2022, the Company began to phase into its regulatory capital requirements the cumulative deferred impact of its 2020 adoption of the accounting guidance related to the impairment of financial instruments based on the current expected credit losses (“CECL”) methodology plus 25 percent of its quarterly credit reserve increases during 2020 and 2021. This cumulative deferred impact was phased into the Company’s regulatory capital during 2022 through 2024, culminating with a fully phased in regulatory capital calculation beginning in 2025.
| | |
52 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
| | | | | | | | |
| TABLE 22 | | Regulatory Capital Ratios |
| | | | | | | | |
| At December 31 (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 |
| Basel III standardized approach: | | |
| Common shareholders’ equity | $ | 51,770 | | $ | 48,498 | |
| Less intangible assets | | |
| Goodwill (net of deferred tax liability) | (11,508) | | (11,480) | |
| Other disallowed intangible assets (net of deferred tax liability) | (1,846) | | (2,278) | |
Other(a) | 9,461 | | 10,207 | |
| Common equity tier 1 capital | 47,877 | | 44,947 | |
| Qualifying preferred stock | 6,808 | | 6,808 | |
| Noncontrolling interests eligible for tier 1 capital | 450 | | 450 | |
| Other | (6) | | (6) | |
| Tier 1 capital | 55,129 | | 52,199 | |
| Eligible portion of allowance for credit losses | 5,616 | | 5,645 | |
| Subordinated debt and noncontrolling interests eligible for tier 2 capital | 3,630 | | 4,077 | |
| Tier 2 capital | 9,246 | | 9,722 | |
| Total risk-based capital | $ | 64,375 | | $ | 61,921 | |
| Risk-weighted assets | $ | 450,498 | | $ | 453,390 | |
| Common equity tier 1 capital as a percent of risk-weighted assets | 10.6 | % | 9.9 | % |
| Tier 1 capital as a percent of risk-weighted assets | 12.2 | | 11.5 | |
| Total risk-based capital as a percent of risk-weighted assets | 14.3 | | 13.7 | |
| Tier 1 capital as a percent of adjusted quarterly average assets (leverage ratio) | 8.3 | | 8.1 | |
| Tier 1 capital as a percent of total on- and off-balance sheet leverage exposure (total leverage exposure ratio) | 6.8 | | 6.6 | |
(a)Includes the impact of items included in other comprehensive income (loss), such as unrealized gains (losses) on available-for-sale securities, accumulated net gains on cash flow hedges, pension liability adjustments, and the portion of deferred tax assets related to net operating loss and tax credit carryforwards not eligible for common equity tier 1 capital.
Table 22 provides a summary of statutory regulatory capital ratios in effect for the Company at December 31, 2024 and 2023. All regulatory ratios exceeded regulatory “well-capitalized” requirements. As of December 31, 2024, U.S. Bank National Association (“USBNA”) also met all regulatory capital ratios to be considered “well-capitalized”. There are no conditions or events since December 31, 2024 that management believes have changed the risk-based category of USBNA.
In July 2023, the U.S. federal bank regulatory authorities proposed a rule to refine the Basel III capital framework for financial institutions. The proposal incorporates elements of the international Basel Committee’s post-crisis reforms, including the Fundamental Review of the Trading Book to replace the existing market risk rule, and introduces new standardized approaches for credit risk, operational risk and credit valuation adjustment (CVA) risk. The proposal’s finalization could revise the risk-based capital measures applicable to the Company; however, until the proposal is finalized the exact impacts are unknown.
The Company believes certain other capital ratios are useful in evaluating its capital adequacy. The Company’s tangible common equity, as a percent of tangible assets and as a percent of risk-weighted assets determined in accordance with transitional regulatory capital requirements related to the CECL methodology under the standardized approach, were 5.8 percent and 8.5 percent, respectively, at December 31, 2024, compared with 5.3
percent and 7.7 percent at December 31, 2023, respectively. In addition, the Company’s common equity tier 1 capital to risk-weighted assets ratio, reflecting the full implementation of the CECL methodology, was 10.5 percent at December 31, 2024, compared with 9.7 percent at December 31, 2023. Refer to “Non-GAAP Financial Measures” beginning on page 57 for further information on these other capital ratios. As an approved mortgage seller and servicer, USBNA, through its mortgage banking division, is required to maintain various levels of shareholder’s equity, as specified by various agencies, including the United States Department of Housing and Urban Development, Government National Mortgage Association, Federal Home Loan Mortgage Corporation and the Federal National Mortgage Association. At December 31, 2024, USBNA met these requirements.
Business Segment Financial Review
The Company’s major business segments are Wealth, Corporate, Commercial and Institutional Banking, Consumer and Business Banking, Payment Services, and Treasury and Corporate Support.
Basis for Financial Presentation Business segment results are derived from the Company’s business unit profitability reporting systems by specifically attributing managed balance sheet assets, deposits and other liabilities and their related income or expense. Refer to Note 23 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for further information on the business segments’ basis for financial presentation.
Designations, assignments and allocations change from time to time as management systems are enhanced, methods of evaluating performance or product lines change or business segments are realigned to better respond to the Company’s diverse customer base. During 2024 and 2023, certain organization and methodology changes were made, including revising the Company’s business segment funds transfer-pricing methodology related to deposits and loans during the second quarter of 2024 and combining its Wealth Management and Investment Services and Corporate and Commercial Banking business segments to create the Wealth, Corporate, Commercial and Institutional Banking business segment during the third quarter of 2023. Prior period results were recast and presented on a comparable basis.
Wealth, Corporate, Commercial and Institutional Banking Wealth, Corporate, Commercial and Institutional Banking provides core banking, specialized lending, transaction and payment processing, capital markets, asset management, and brokerage and investment related services to wealth, middle market, large corporate, commercial real estate, government and institutional clients. Wealth, Corporate, Commercial and Institutional Banking contributed $4.8 billion of the Company’s net income in 2024, or an increase of $105 million (2.3 percent), compared with 2023.
Net revenue increased $190 million (1.6 percent) in 2024, compared with 2023. Net interest income, on a taxable-equivalent basis, decreased $217 million (2.8 percent) in 2024, compared with 2023, primarily due to the impact of deposit mix and pricing. Noninterest income increased $407 million (9.8 percent) in 2024, compared with 2023, primarily due to higher trust and investment management fees and commercial products revenue, both driven by business growth and favorable market conditions.
Noninterest expense increased $5 million (0.1 percent) in 2024, compared with 2023, primarily due to higher compensation and employee benefits expense. The provision for credit losses increased $45 million (13.2 percent) in 2024, compared with 2023, primarily due to higher net charge-offs.
Consumer and Business Banking Consumer and Business Banking comprises consumer banking, small business banking and consumer lending. Products and services are delivered through banking offices, telephone
servicing and sales, online services, direct mail, ATMs, mobile devices, distributed mortgage loan officers, and intermediary relationships including auto dealerships, mortgage banks, and strategic business partners. Consumer and Business Banking contributed $1.9 billion of the Company’s net income in 2024, or a decrease of $673 million (26.3 percent), compared with 2023.
Net revenue decreased $1.1 billion (10.6 percent) in 2024, compared with 2023. Net interest income, on a taxable-equivalent basis, decreased $1.0 billion (11.8 percent) in 2024, compared with 2023, due to the impact of deposit mix and pricing. Noninterest income decreased $69 million (4.1 percent) in 2024, compared with 2023, primarily due to lower service charges, partially offset by higher mortgage banking revenue.
Noninterest expense decreased $300 million (4.4 percent) in 2024, compared with 2023, primarily due to lower compensation and employee benefits expense and net shared services expense. The provision for credit losses increased $104 million in 2024, compared with 2023, primarily due to normalizing credit conditions.
Payment Services Payment Services includes consumer and business credit cards, stored-value cards, debit cards, corporate, government and purchasing card services and merchant processing. Payment Services contributed $1.0 billion of the Company’s net income in 2024, or an increase of $7 million (0.7 percent), compared with 2023.
Net revenue increased $365 million (5.5 percent) in 2024, compared with 2023. Net interest income, on a taxable-equivalent basis, increased $222 million (8.5 percent) in 2024, compared with 2023, primarily due to higher loan balances, partially offset by higher funding costs. Noninterest income increased $143 million (3.5 percent) in 2024, compared with 2023, driven by higher card revenue due to favorable rates, and higher merchant processing services revenue due to business volume growth.
Noninterest expense increased $135 million (3.4 percent) in 2024, compared with 2023, reflecting higher net shared services expense. The provision for credit losses increased $220 million (15.8 percent) in 2024, compared with 2023, primarily due to higher net charge-offs.
Treasury and Corporate Support Treasury and Corporate Support includes the Company’s investment portfolios, funding, capital management, interest rate risk management, income taxes not allocated to the business lines, including most investments in tax-advantaged projects, and the residual aggregate of those expenses associated with corporate activities that are managed on a consolidated basis. Treasury and Corporate Support recorded a net loss of $1.4 billion in 2024, compared with a net loss of $2.8 billion in 2023.
Net revenue decreased $150 million (17.0 percent) in 2024, compared with 2023. Net interest income, on a taxable-equivalent basis, decreased $98 million (6.0 percent) in 2024, compared with 2023, primarily due to higher funding costs, partially offset by higher rates on earning assets and balance sheet growth. Noninterest income decreased $52 million (7.0 percent) in 2024,
| | |
54 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
compared with 2023, primarily due to a decrease in other revenue, partially offset by the impact of a gain on the sale of mortgage servicing rights during 2024.
Noninterest expense decreased $1.5 billion (57.8 percent) in 2024, compared with 2023, primarily due to lower merger and integration charges and lower FDIC special assessment charges, partially offset by higher compensation and employee benefits expense. The provision for credit losses was $406 million (87.7 percent)
lower in 2024, compared with 2023, primarily due to the impact of balance sheet repositioning and capital management actions in 2023.
Income taxes are assessed to each business segment at a managerial tax rate of 25.0 percent with the residual tax expense or benefit to arrive at the consolidated effective tax rate included in Treasury and Corporate Support.
| | | | | | | | |
| TABLE 23 | | Business Segment Financial Performance |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Wealth, Corporate, Commercial and Institutional Banking | Consumer and Business Banking | Payment Services |
Year Ended December 31 (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 | Percent
Change | 2024 | 2023 | Percent
Change | 2024 | 2023 | Percent
Change |
| Condensed Income Statement | | | | | | | | | |
| Net interest income (taxable-equivalent basis) | $ | 7,645 | | $ | 7,862 | | (2.8) | % | $ | 7,658 | | $ | 8,683 | | (11.8) | % | $ | 2,831 | | $ | 2,609 | | 8.5 | % |
| Noninterest income | 4,548 | | 4,141 | | 9.8 | | 1,606 | | 1,675 | | (4.1) | | 4,198 | | 4,055 | | 3.5 | |
| Total net revenue | 12,193 | | 12,003 | | 1.6 | | 9,264 | | 10,358 | | (10.6) | | 7,029 | | 6,664 | | 5.5 | |
| Noninterest expense | 5,449 | | 5,444 | | .1 | | 6,569 | | 6,869 | | (4.4) | | 4,055 | | 3,920 | | 3.4 | |
| Income (loss) before provision and income taxes | 6,744 | | 6,559 | | 2.8 | | 2,695 | | 3,489 | | (22.8) | | 2,974 | | 2,744 | | 8.4 | |
| Provision for credit losses | 385 | | 340 | | 13.2 | | 182 | | 78 | | * | 1,614 | | 1,394 | | 15.8 | |
| Income (loss) before income taxes | 6,359 | | 6,219 | | 2.3 | | 2,513 | | 3,411 | | (26.3) | | 1,360 | | 1,350 | | .7 | |
| Income taxes and taxable-equivalent adjustment | 1,590 | | 1,555 | | 2.3 | | 629 | | 854 | | (26.3) | | 340 | | 337 | | .9 | |
| Net income (loss) | 4,769 | | 4,664 | | 2.3 | | 1,884 | | 2,557 | | (26.3) | | 1,020 | | 1,013 | | .7 | |
| Net (income) loss attributable to noncontrolling interests | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | |
| Net income (loss) attributable to U.S. Bancorp | $ | 4,769 | | $ | 4,664 | | 2.3 | | $ | 1,884 | | $ | 2,557 | | (26.3) | | $ | 1,020 | | $ | 1,013 | | .7 | |
| Average Balance Sheet | | | | | | | | | |
| Loans | $ | 172,466 | | $ | 175,836 | | (1.9) | | $ | 155,088 | | $ | 162,012 | | (4.3) | | $ | 41,081 | | $ | 38,471 | | 6.8 | |
| Goodwill | 4,825 | | 4,682 | | 3.1 | | 4,326 | | 4,466 | | (3.1) | | 3,357 | | 3,327 | | .9 | |
| Other intangible assets | 981 | | 1,007 | | (2.6) | | 4,539 | | 5,264 | | (13.8) | | 277 | | 352 | | (21.3) | |
| Assets | 201,362 | | 202,701 | | (.7) | | 168,913 | | 179,247 | | (5.8) | | 47,169 | | 44,291 | | 6.5 | |
| Noninterest-bearing deposits | 56,760 | | 70,908 | | (20.0) | | 20,810 | | 30,967 | | (32.8) | | 2,685 | | 2,981 | | (9.9) | |
| Interest-bearing deposits | 214,622 | | 203,038 | | 5.7 | | 200,611 | | 185,712 | | 8.0 | | 96 | | 103 | | (6.8) | |
| Total deposits | 271,382 | | 273,946 | | (.9) | | 221,421 | | 216,679 | | 2.2 | | 2,781 | | 3,084 | | (9.8) | |
| Total U.S. Bancorp shareholders’ equity | 21,438 | | 22,366 | | (4.1) | | 14,426 | | 16,026 | | (10.0) | | 10,005 | | 9,310 | | 7.5 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Treasury and Corporate Support | Consolidated Company |
Year Ended December 31 (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 | Percent
Change | 2024 | 2023 | Percent
Change |
| Condensed Income Statement | | | | | | |
| Net interest income (taxable-equivalent basis) | $ | (1,725) | | $ | (1,627) | | (6.0) | % | $ | 16,409 | | $ | 17,527 | | (6.4) | % |
| Noninterest income | 694 | | 746 | | (7.0) | | 11,046 | | 10,617 | | 4.0 | |
| Total net revenue | (1,031) | | (881) | | (17.0) | | 27,455 | | 28,144 | | (2.4) | |
| Noninterest expense | 1,115 | | 2,640 | | (57.8) | | 17,188 | | 18,873 | | (8.9) | |
| Income (loss) before provision and income taxes | (2,146) | | (3,521) | | 39.1 | | 10,267 | | 9,271 | | 10.7 | |
| Provision for credit losses | 57 | | 463 | | (87.7) | | 2,238 | | 2,275 | | (1.6) | |
| Income (loss) before income taxes | (2,203) | | (3,984) | | 44.7 | | 8,029 | | 6,996 | | 14.8 | |
| Income taxes and taxable-equivalent adjustment | (859) | | (1,208) | | 28.9 | | 1,700 | | 1,538 | | 10.5 | |
| Net income (loss) | (1,344) | | (2,776) | | 51.6 | | 6,329 | | 5,458 | | 16.0 | |
| Net (income) loss attributable to noncontrolling interests | (30) | | (29) | | (3.4) | | (30) | | (29) | | (3.4) | |
| Net income (loss) attributable to U.S. Bancorp | $ | (1,374) | | $ | (2,805) | | 51.0 | | $ | 6,299 | | $ | 5,429 | | 16.0 | |
| Average Balance Sheet | | | | | | |
| Loans | $ | 5,240 | | $ | 4,956 | | 5.7 | | $ | 373,875 | | $ | 381,275 | | (1.9) | |
| Goodwill | — | | — | | — | | 12,508 | | 12,475 | | .3 | |
| Other intangible assets | 9 | | 16 | | (43.8) | | 5,806 | | 6,639 | | (12.5) | |
| Assets | 246,570 | | 237,201 | | 3.9 | | 664,014 | | 663,440 | | .1 | |
| Noninterest-bearing deposits | 2,752 | | 2,912 | | (5.5) | | 83,007 | | 107,768 | | (23.0) | |
| Interest-bearing deposits | 11,179 | | 9,042 | | 23.6 | | 426,508 | | 397,895 | | 7.2 | |
| Total deposits | 13,931 | | 11,954 | | 16.5 | | 509,515 | | 505,663 | | .8 | |
| Total U.S. Bancorp shareholders’ equity | 11,337 | | 5,958 | | 90.3 | | 57,206 | | 53,660 | | 6.6 | |
*Not meaningful
| | |
56 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
Non-GAAP Financial Measures
In addition to capital ratios defined by banking regulators, the Company considers various other measures when evaluating capital utilization and adequacy, including:
•Tangible common equity to tangible assets,
•Tangible common equity to risk-weighted assets, and
•Common equity tier 1 capital to risk-weighted assets, reflecting the full implementation of the CECL methodology.
These capital measures are viewed by management as useful additional methods of evaluating the Company’s utilization of its capital held and the level of capital available to withstand unexpected negative market or economic conditions. Additionally, presentation of these measures allows investors, analysts and banking regulators to assess the Company’s capital position relative to other financial services companies. These capital measures are not defined in generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”), or are not currently effective or defined in banking regulations. In addition, certain of these measures differ from currently effective capital ratios defined by banking regulations principally in that the currently effective ratios, which are subject to certain transitional provisions, temporarily exclude the full impact of the 2020 adoption of accounting guidance related to impairment of financial instruments based on the CECL methodology. As a result,
these capital measures disclosed by the Company may be considered non-GAAP financial measures. Management believes this information helps investors assess trends in the Company’s capital adequacy.
The Company discloses the return on tangible common equity ratio and tangible book value per share as it believes they are useful financial measures to assess the Company's use of equity.
The Company also discloses net interest income and related ratios and analysis on a taxable-equivalent basis, which may also be considered non-GAAP financial measures. The Company believes this presentation to be the preferred industry measurement of net interest income as it provides a relevant comparison of net interest income arising from taxable and tax-exempt sources. In addition, certain performance measures utilize net interest income on a taxable-equivalent basis, including the efficiency ratio and net interest margin.
The Company also discloses percent of net revenue for its business lines excluding Treasury and Corporate Support to highlight the contributions to net revenue from the Company's core revenue-producing businesses.
There may be limits in the usefulness of these measures to investors. As a result, the Company encourages readers to consider the consolidated financial statements and other financial information contained in this report in their entirety, and not to rely on any single financial measure.
The following tables show the Company’s calculation of these non-GAAP financial measures:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| At December 31 (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 |
| Total equity | $ | 59,040 | | $ | 55,771 | | $ | 51,232 | |
| Preferred stock | (6,808) | | (6,808) | | (6,808) | |
| Noncontrolling interests | (462) | | (465) | | (466) | |
Common equity(1) | 51,770 | | 48,498 | | 43,958 | |
Goodwill (net of deferred tax liability)(a) | (11,508) | | (11,480) | | (11,395) | |
| Intangible assets (net of deferred tax liability), other than mortgage servicing rights | (1,846) | | (2,278) | | (2,792) | |
Tangible common equity(2) | 38,416 | | 34,740 | | 29,771 | |
| Common equity tier 1 capital, determined in accordance with transitional regulatory capital requirements related to the CECL methodology implementation | 47,877 | | 44,947 | | 41,560 | |
Adjustments(b) | (433) | | (866) | | (1,299) | |
Common equity tier 1 capital, reflecting the full implementation of the CECL methodology(3) | 47,444 | | 44,081 | | 40,261 | |
Total assets(4) | 678,318 | | 663,491 | | 674,805 | |
Goodwill (net of deferred tax liability)(a) | (11,508) | | (11,480) | | (11,395) | |
| Intangible assets (net of deferred tax liability), other than mortgage servicing rights | (1,846) | | (2,278) | | (2,792) | |
Tangible assets(5) | 664,964 | | 649,733 | | 660,618 | |
Risk-weighted assets, determined in accordance with prescribed regulatory capital requirements effective for the Company(6) | 450,498 | | 453,390 | | 496,500 | |
Adjustments(c) | (368) | | (736) | | (620) | |
Risk-weighted assets, reflecting the full implementation of the CECL methodology(7) | 450,130 | | 452,654 | | 495,880 | |
| Ratios | | | |
Common equity to assets(1)/(4) | 7.6 | % | 7.3 | % | 6.5 | % |
Tangible common equity to tangible assets(2)/(5) | 5.8 | | 5.3 | | 4.5 | |
Tangible common equity to risk-weighted assets(2)/(6) | 8.5 | | 7.7 | | 6.0 | |
Common equity tier 1 capital to risk-weighted assets, reflecting the full implementation of the CECL methodology(3)/(7) | 10.5 | | 9.7 | | 8.1 | |
(a)Includes goodwill related to certain investments in unconsolidated financial institutions per prescribed regulatory requirements.
(b)Includes the estimated increase in the allowance for credit losses related to the adoption of the CECL methodology net of deferred taxes.
(c)Includes the impact of the estimated increase in the allowance for credit losses related to the adoption of the CECL methodology.
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31 (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 |
| Net interest income | $ | 16,289 | | $ | 17,396 | | $ | 14,728 | |
Taxable-equivalent adjustment(a) | 120 | | 131 | | 118 | |
| Net interest income, on a taxable-equivalent basis | 16,409 | | 17,527 | | 14,846 | |
| | | |
| Net interest income, on a taxable-equivalent basis (as calculated above) | 16,409 | | 17,527 | | 14,846 | |
| Noninterest income | 11,046 | | 10,617 | | 9,456 | |
| Less: Securities gains (losses), net | (154) | | (145) | | 20 | |
Total net revenue, excluding net securities gains (losses)(1) | 27,609 | | 28,289 | | 24,282 | |
Noninterest expense(2) | 17,188 | | 18,873 | | 14,906 | |
Efficiency ratio(2)/(1) | 62.3 | % | 66.7 | % | 61.4 | % |
(a)Based on federal income tax rate of 21 percent for those assets and liabilities whose income or expense is not included for federal income tax purposes.
| | |
58 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31, 2024 (Dollars in Millions) | Net Revenue | Net Revenue as a Percent of the Consolidated Company | Net Revenue as a Percent of the Consolidated Company Excluding Treasury and Corporate Support |
| Wealth, Corporate, Commercial and Institutional Banking | $ | 12,193 | | 44 | % | 43 | % |
| Consumer and Business Banking | 9,264 | | 34 | | 32 | |
| Payment Services | 7,029 | | 26 | | 25 | |
| Treasury and Corporate Support | (1,031) | | (4) | | |
| Consolidated Company | 27,455 | | 100 | % | |
| Less: Treasury and Corporate Support | (1,031) | | | |
| Consolidated Company excluding Treasury and Corporate Support | $ | 28,486 | | | 100 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31 (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 |
| Net income applicable to U.S. Bancorp common shareholders | $ | 5,909 | | $ | 5,051 | | $ | 5,501 | |
| Intangible amortization (net-of-tax) | 450 | | 502 | | 170 | |
Net income applicable to U.S. Bancorp common shareholders, excluding intangibles amortization(1) | 6,359 | | 5,553 | | 5,671 | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| Average total equity | 57,668 | | 54,125 | | 50,882 | |
| Average preferred stock | (6,808) | | (6,808) | | (6,761) | |
| Average noncontrolling interests | (462) | | (465) | | (466) | |
Average goodwill (net of deferred tax liability)(a) | (11,485) | | (11,485) | | (9,240) | |
| Average intangible assets (net of deferred tax liability), other than mortgage servicing rights | (2,040) | | (2,480) | | (991) | |
Average tangible common equity(2) | 36,873 | | 32,887 | | 33,424 | |
Return on tangible common equity(1)/(2) | 17.2 | % | 16.9 | % | 17.0 | % |
| | | |
(a)Includes goodwill related to certain investments in unconsolidated financial institutions per prescribed regulatory requirements.
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| At December 31 (Dollars in Millions, Except Per Share Data) | 2024 | 2023 | Percent Change |
| Common equity | $ | 51,770 | | $ | 48,498 | | |
Goodwill (net of deferred tax liability)(a) | (11,508) | | (11,480) | | |
| Intangible assets (net of deferred tax liability), other than mortgage servicing rights | (1,846) | | (2,278) | | |
Tangible common equity(1) | 38,416 | | 34,740 | | |
Common shares outstanding(2) | 1,560 | | 1,558 | | |
Tangible book value per common share(1)/(2) | $ | 24.63 | | $ | 22.30 | | 10.4 | % |
(a)Includes goodwill related to certain investments in unconsolidated financial institutions per prescribed regulatory requirements.
Accounting Changes
Note 2 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements discusses accounting standards recently issued but not yet required to be adopted and the expected impact of these changes in accounting standards. To the extent the adoption of new accounting standards materially affects the Company’s financial condition or results of operations, the impacts are discussed in the applicable section(s) of the Management’s Discussion and Analysis and the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Critical Accounting Policies
The accounting and reporting policies of the Company comply with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States and conform to general practices within the banking industry. The preparation of financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires management
to make estimates and assumptions. The Company’s financial position and results of operations can be affected by these estimates and assumptions, which are integral to understanding the Company’s financial statements. Critical accounting policies are those policies management believes are the most important to the portrayal of the Company’s financial condition and results, and require management to make estimates that are difficult, subjective or complex. Most accounting policies are not considered by management to be critical accounting policies. Several factors are considered in determining whether or not a policy is critical in the preparation of financial statements. These factors include, among other things, whether the estimates are significant to the financial statements, the nature of the estimates, the ability to readily validate the estimates with other information (including third-party sources or available prices), sensitivity of the estimates to changes in economic conditions and whether alternative accounting methods may be utilized under GAAP.
Management has discussed the development and the selection of critical accounting policies with the Company’s Audit Committee.
Significant accounting policies are discussed in Note 1 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. Those policies considered to be critical accounting policies are described below.
Allowance for Credit Losses Management’s evaluation of the appropriate allowance for credit losses is often the most critical of all the accounting estimates for a banking institution. It is an inherently subjective process impacted by many factors as discussed throughout the Management’s Discussion and Analysis section of the Annual Report.
The methods utilized to estimate the allowance for credit losses, key assumptions and quantitative and qualitative information considered by management in determining the appropriate allowance for credit losses at December 31, 2024 are discussed in the “Credit Risk Management” section. Although methodologies utilized to determine each element of the allowance reflect management’s assessment of credit risk, imprecision exists in these measurement tools due in part to subjective judgments involved and an inherent lag in the data available to quantify current conditions and events that affect credit loss reserve estimates.
Given the many quantitative variables and subjective factors affecting the credit portfolio, changes in the allowance for credit losses may not directly coincide with changes in risk ratings or delinquency status within loan and lease portfolios. This is in part due to the timing of the risk rating process in relation to changes in the business cycle, the exposure and mix of loans within risk rating categories, levels of nonperforming loans and the timing of charge-offs and expected recoveries. The allowance for credit losses measures the expected loss content on the remaining portfolio exposure, while nonperforming loans and net charge-offs are measures of specific impairment events that have already been confirmed. Therefore, the degree of change in the forward-looking expected loss in the allowance may differ from the level of changes in nonperforming loans and net charge-offs. Management maintains an appropriate allowance for credit losses by updating allowance rates to reflect changes in expected losses, including expected changes in economic or business cycle conditions. Some factors considered in determining the appropriate allowance for credit losses are more readily quantifiable while other factors require extensive qualitative judgment in determining the overall level of the allowance for credit losses.
The Company considers a range of economic scenarios in its determination of the allowance for credit losses. These scenarios are constructed with interrelated projections of multiple economic variables, and loss estimates are produced that consider the historical correlation of those economic variables with credit losses, and also the expectation that conditions will eventually normalize over the longer run. Scenarios worse than the Company’s expected outcome at December 31, 2024 include risks of persisting inflationary pressures, continued elevated
interest rates, declines in residential and commercial real estate prices, high unemployment rates, supply shortages, changing fiscal policy, geopolitical risks, tightening in bank lending standards, and potential bank failures, which could all precipitate a moderate to severe recession and result in increased credit losses.
Under the range of economic scenarios considered, the allowance for credit losses would have been lower by $1.1 billion or higher by $2.0 billion. This range reflects the sensitivity of the allowance for credit losses specifically related to the range of economic scenarios considered as of December 31, 2024.
Because several quantitative and qualitative factors are considered in determining the allowance for credit losses, these sensitivity analyses do not necessarily reflect the nature and extent of future changes in the allowance for credit losses. They are intended to provide insights into the impact of adverse changes in the economy on the Company’s modeled loss estimates for the loan portfolio and do not imply any expectation of future deterioration in the risk rating or loss rates. Given current processes employed by the Company, management believes the risk ratings and loss model estimates currently assigned are appropriate. It is possible that others, given the same information, may at any point in time reach different reasonable conclusions that could be significant to the Company’s financial statements. Refer to the “Analysis and Determination of the Allowance for Credit Losses” section for further information.
Fair Value Estimates A portion of the Company’s assets and liabilities are carried at fair value on the Consolidated Balance Sheet, with changes in fair value recorded either through earnings or other comprehensive income (loss) in accordance with applicable accounting principles generally accepted in the United States. These include all of the Company’s available-for-sale investment securities, derivatives and other trading instruments, MSRs and MLHFS. The estimation of fair value also affects other loans held for sale, which are recorded at the lower-of-cost-or-fair value. The determination of fair value is important for certain other assets that are periodically evaluated for impairment using fair value estimates, including goodwill.
Fair value is generally defined as the exit price at which an asset or liability could be exchanged in a current transaction between willing, unrelated parties, other than in a forced or liquidation sale. Fair value is based on quoted market prices in an active market, or if market prices are not available, is estimated using models employing techniques such as matrix pricing or discounting expected cash flows. The significant assumptions used in the models, which include assumptions for interest rates, discount rates, prepayments and credit losses, are independently verified against observable market data where possible. Where observable market data is not available, the estimate of fair value becomes more subjective and involves a high degree of judgment. In this circumstance, fair value is estimated based on management’s judgment regarding the value that market participants would assign to the asset or liability. This valuation process takes into consideration factors such as
| | |
60 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
market illiquidity. Imprecision in estimating these factors can impact the amount recorded on the balance sheet for a particular asset or liability with related impacts to earnings or other comprehensive income (loss).
When available, trading and available-for-sale securities are valued based on quoted market prices. However, certain securities are traded less actively and, therefore, quoted market prices may not be available. The determination of fair value may require benchmarking to similar instruments or performing a discounted cash flow analysis using estimates of future cash flows and prepayment, interest and default rates. For more information on investment securities, refer to Note 4 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
As few derivative contracts are listed on an exchange, the majority of the Company’s derivative positions are valued using valuation techniques that use readily observable market inputs. Certain derivatives, however, must be valued using techniques that include unobservable inputs. For these instruments, the significant assumptions must be estimated and, therefore, are subject to judgment. Note 19 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements provides a summary of the Company’s derivative positions.
Refer to Note 21 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information regarding estimations of fair value.
Mortgage Servicing Rights MSRs are capitalized as separate assets when loans are sold and servicing is retained, or may be purchased from others. The Company records MSRs at fair value. Because MSRs do not trade in an active market with readily observable prices, the Company determines the fair value by estimating the present value of the asset’s future cash flows utilizing market-based prepayment rates, option adjusted spread, and other assumptions validated through comparison to trade information, industry surveys and independent third-party valuations. Changes in the fair value of MSRs are recorded in earnings during the period in which they occur. Risks inherent in the valuation of MSRs include higher than expected prepayment rates and/or delayed receipt of cash flows. The Company utilizes derivatives, including interest rate swaps, swaptions, forward commitments to buy TBAs, U.S. Treasury and Eurodollar futures and options on U.S. Treasury futures, to mitigate the valuation risk. Refer to Notes 9 and 21 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information on the assumptions used in determining the fair value of MSRs and an analysis of the sensitivity to changes in interest rates of the fair value of the MSRs portfolio and the related derivative instruments used to mitigate the valuation risk.
Income Taxes The Company estimates income tax expense based on amounts expected to be owed to the various tax jurisdictions in which it operates, including federal, state and local domestic jurisdictions, and an insignificant amount to foreign jurisdictions. The estimated income tax expense is reported in the Consolidated Statement of Income. Accrued taxes are reported in other assets or other liabilities on the Consolidated Balance Sheet and represent the net estimated amount due to or to
be received from taxing jurisdictions either currently or deferred to future periods. Deferred taxes arise from differences between assets and liabilities measured for financial reporting purposes versus income tax reporting purposes. Deferred tax assets are recognized if, in management’s judgment, their realizability is determined to be more likely than not. Uncertain tax positions that meet the more likely than not recognition threshold are measured to determine the amount of benefit to recognize. An uncertain tax position is measured at the largest amount of benefit management believes is more likely than not to be realized upon settlement. In estimating accrued taxes, the Company assesses the relative merits and risks of the appropriate tax treatment considering statutory, judicial and regulatory guidance in the context of the tax position. Because of the complexity of tax laws and regulations, interpretation can be difficult and subject to legal judgment given specific facts and circumstances. It is possible that others, given the same information, may at any point in time reach different reasonable conclusions regarding the estimated amounts of accrued taxes.
Changes in the estimate of accrued taxes occur periodically due to changes in tax rates, interpretations of tax laws, the status of examinations being conducted by various taxing authorities, and newly enacted statutory, judicial and regulatory guidance that impacts the relative merits and risks of tax positions. These changes, when they occur, affect accrued taxes and can be significant to the operating results of the Company. Refer to Note 18 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information regarding income taxes.
Controls and Procedures
Under the supervision and with the participation of the Company’s management, including its principal executive officer and principal financial officer, the Company has evaluated the effectiveness of the design and operation of its disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”)). Based upon this evaluation, the principal executive officer and principal financial officer have concluded that, as of the end of the period covered by this report, the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures were effective.
During the most recently completed fiscal quarter, there was no change made in the Company’s internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) under the Exchange Act) that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
The annual report of the Company’s management on internal control over financial reporting is provided on page 62. The audit report of Ernst & Young LLP, the Company’s independent accountants, regarding the Company’s internal control over financial reporting is provided on page 63.
Report of Management
Responsibility for the financial statements and other information presented throughout this Annual Report rests with the management of U.S. Bancorp. The Company believes the consolidated financial statements have been prepared in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States and present the substance of transactions based on the circumstances and management’s best estimates and judgment.
In meeting its responsibilities for the reliability of the financial statements, management is responsible for establishing and maintaining an adequate system of internal control over financial reporting as defined by Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. The Company’s system of internal control is designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of publicly filed financial statements in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States.
To test compliance, the Company carries out an extensive audit program. This program includes a review for compliance with written policies and procedures and a comprehensive review of the adequacy and effectiveness of the system of internal control. Although control procedures are designed and tested, it must be recognized that there are limits inherent in all systems of internal control, and, therefore, errors and irregularities may nevertheless occur. Projection of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
The Board of Directors of the Company has an Audit Committee composed of directors who are independent of U.S. Bancorp. The Audit Committee meets periodically with management, the internal auditors and the independent accountants to consider audit results and to discuss internal accounting control, auditing and financial reporting matters.
Management assessed the effectiveness of the Company’s system of internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2024. In making this assessment, management used the criteria set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission in its Internal Control—Integrated Framework (2013 framework). Based on its assessment and those criteria, management believes the Company maintained effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2024.
The effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2024 has been audited by Ernst & Young LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, as stated in their accompanying report appearing on page 63. | | |
62 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Shareholders and the Board of Directors of U.S. Bancorp
Opinion on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
We have audited U.S. Bancorp’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2024, based on criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 framework) (the COSO criteria). In our opinion, U.S. Bancorp (the Company) maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2024, based on the COSO criteria.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the consolidated balance sheets of the Company as of December 31, 2024 and 2023, the related consolidated statements of income, comprehensive income, shareholders’ equity and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2024, and the related notes and our report dated February 21, 2025 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
Basis for Opinion
The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting included in the accompanying Report of Management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects.
Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Definition and Limitations of Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Minneapolis, Minnesota
February 21, 2025
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Shareholders and the Board of Directors of U.S. Bancorp
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of U.S. Bancorp (the Company) as of December 31, 2024 and 2023, the related consolidated statements of income, comprehensive income, shareholders’ equity and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2024, and the related notes (collectively referred to as the “consolidated financial statements”). In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company at December 31, 2024 and 2023, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2024, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB), the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2024, based on criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (2013 framework), and our report dated February 21, 2025 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the PCAOB and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with the U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
Critical Audit Matter
The critical audit matter communicated below is a matter arising from the current period audit of the financial statements that was communicated or required to be communicated to the audit committee and that: (1) relates to accounts or disclosures that are material to the financial statements and (2) involved our especially challenging, subjective or complex judgments. The communication of the critical audit matter does not alter in any way our opinion on the consolidated financial statements, taken as a whole, and we are not, by communicating the critical audit matter below, providing a separate opinion on the critical audit matter or on the accounts or disclosures to which it relates.
| | | | | |
| Allowance for Credit Losses |
Description of the Matter | The Company’s loan and lease portfolio and the associated allowance for credit losses (ACL), were $379.8 billion and $7.9 billion as of December 31, 2024, respectively. The provision for credit losses was $2.2 billion for the year ended December 31, 2024. As discussed in Notes 1 and 5 to the financial statements, the ACL is established for current expected credit losses on the Company’s loan and lease portfolio, including unfunded credit commitments, by utilizing forward-looking expected loss models. When determining expected losses, the Company uses multiple probability weighted economic scenarios over a reasonable and supportable forecast period and then fully reverts to historical loss experience to estimate losses over the remaining asset lives. Model estimates are adjusted to consider any relevant changes in portfolio composition, lending policies, underwriting standards, risk management practices, economic conditions or other factors that would affect the accuracy of the model. Additionally, management may adjust the ACL for other qualitative factors such as model imprecision, imprecision in economic scenario assumptions, and emerging risks related to either changes in the environment that are affecting specific portfolio segments, or changes in portfolio concentrations. Auditing management’s ACL estimate and related provision for credit losses was complex due to the highly judgmental nature of the probability weighted economic scenarios, expected loss models, as well as model and qualitative factor adjustments. |
| | |
64 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
| | | | | |
How We Addressed the Matter in Our Audit | We obtained an understanding, evaluated the design and tested the operating effectiveness of the Company’s controls over the ACL process, including management’s controls over: 1) development of baseline economic scenario, selection of alternative economic scenarios and implementation of these scenarios and the probability weights assigned to them; 2) expected loss models, including model validation, implementation, monitoring, the completeness and accuracy of key inputs and assumptions used in the models, and management’s output assessment and related adjustments; 3) adjustments to reflect management’s consideration of qualitative factors; 4) the ACL methodology and governance process. With the support of specialists, we assessed the economic scenarios and related probability weights by, among other procedures, evaluating management’s methodology and agreeing a sample of key economic variables used to external sources. We also performed and considered the results of various sensitivity analyses and analytical procedures, including comparison of a sample of the key economic variables to alternative external sources, historical statistics and peer bank information. With respect to expected loss models, with the support of specialists, we evaluated model calculation design and reperformed the calculation for a sample of models. We also tested the appropriateness of key inputs and assumptions used in these models by agreeing a sample of inputs to internal and external sources. As to model adjustments, with the support of specialists, we evaluated management’s estimate methodology and assessment of factors that could potentially impact the accuracy of expected loss models. We also recalculated a sample of model adjustments and tested internal and external data used by agreeing a sample of inputs to internal and external sources. Regarding the completeness of qualitative factors identified and incorporated into measuring the ACL, with the support of specialists, we evaluated the potential impact of imprecision in the expected loss models and economic scenario assumptions; emerging risks related to changes in the environment impacting specific portfolio segments and portfolio concentrations. We also evaluated and tested internal and external data used in the qualitative adjustments by agreeing significant inputs and underlying data to internal and external sources. We evaluated the overall ACL amount, including model estimates and adjustments, qualitative factors adjustments, and whether the recorded ACL appropriately reflects expected credit losses on the loan and lease portfolio and unfunded credit commitments. We reviewed historical loss statistics, peer-bank information, subsequent events and transactions and considered whether they corroborate or contradict the Company’s measurement of the ACL. We searched for and evaluated information that corroborates or contradicts management’s forecasted assumptions and related probability weights as well as identification and measurement of adjustments to model estimates and qualitative factors. |

We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2003.
Minneapolis, Minnesota
February 21, 2025
Consolidated Financial Statements and Notes Table of Contents
| | | | | |
| Consolidated Financial Statements | |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| | |
66 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
U.S. Bancorp
Consolidated Balance Sheet
| | | | | | | | |
| At December 31 (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 |
| | | |
| Assets | | |
| Cash and due from banks | $ | 56,502 | | $ | 61,192 | |
| Investment securities | | |
| Held-to-maturity (fair value $66,275 and $74,088, respectively) | 78,634 | | 84,045 | |
Available-for-sale ($320 and $338 pledged as collateral, respectively)(a) | 85,992 | | 69,706 | |
| Loans held for sale (including $2,251 and $2,011 of mortgage loans carried at fair value, respectively) | 2,573 | | 2,201 | |
| Loans | | |
| Commercial | 139,484 | | 131,881 | |
| Commercial real estate | 48,859 | | 53,455 | |
| Residential mortgages | 118,813 | | 115,530 | |
| Credit card | 30,350 | | 28,560 | |
| Other retail | 42,326 | | 44,409 | |
| Total loans | 379,832 | | 373,835 | |
| Less allowance for loan losses | (7,583) | | (7,379) | |
| Net loans | 372,249 | | 366,456 | |
| Premises and equipment | 3,565 | | 3,623 | |
| Goodwill | 12,536 | | 12,489 | |
| Other intangible assets | 5,547 | | 6,084 | |
Other assets (including $7,501 and $3,548 of trading securities at fair value pledged as collateral, respectively)(a) | 60,720 | | 57,695 | |
| Total assets | $ | 678,318 | | $ | 663,491 | |
| | | |
| Liabilities and Shareholders’ Equity | | |
| Deposits | | |
| Noninterest-bearing | $ | 84,158 | | $ | 89,989 | |
| Interest-bearing (including $5,754 and $2,818 of time deposits carried at fair value, respectively) | 434,151 | | 422,323 | |
| Total deposits | 518,309 | | 512,312 | |
| Short-term borrowings | 15,518 | | 15,279 | |
| Long-term debt | 58,002 | | 51,480 | |
| Other liabilities | 27,449 | | 28,649 | |
| Total liabilities | 619,278 | | 607,720 | |
| Shareholders’ equity | | |
| Preferred stock | 6,808 | | 6,808 | |
| Common stock, $.01 par value per share, authorized: 4,000,000,000 shares; issued: 2024 and 2023 —2,125,725,742 shares | 21 | | 21 | |
| Capital surplus | 8,715 | | 8,673 | |
| Retained earnings | 76,863 | | 74,026 | |
| Less cost of common stock in treasury: 2024 — 565,929,654 shares; 2023 — 567,732,687 shares | (24,065) | | (24,126) | |
| Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) | (9,764) | | (10,096) | |
| Total U.S. Bancorp shareholders’ equity | 58,578 | | 55,306 | |
| Noncontrolling interests | 462 | | 465 | |
| Total equity | 59,040 | | 55,771 | |
| Total liabilities and equity | $ | 678,318 | | $ | 663,491 | |
(a)Includes only collateral pledged by the Company where counterparties have the right to sell or pledge the collateral.
See Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
U.S. Bancorp
Consolidated Statement of Income
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31 (Dollars and Shares in Millions, Except Per Share Data) | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 |
| Interest Income | | | |
| Loans | $ | 23,009 | | $ | 22,324 | | $ | 13,603 | |
| Loans held for sale | 173 | | 147 | | 201 | |
| Investment securities | 5,111 | | 4,485 | | 3,378 | |
| Other interest income | 3,373 | | 3,051 | | 763 | |
| Total interest income | 31,666 | | 30,007 | | 17,945 | |
| Interest Expense | | | |
| Deposits | 11,688 | | 8,775 | | 1,872 | |
| Short-term borrowings | 1,107 | | 1,971 | | 565 | |
| Long-term debt | 2,582 | | 1,865 | | 780 | |
| Total interest expense | 15,377 | | 12,611 | | 3,217 | |
| Net interest income | 16,289 | | 17,396 | | 14,728 | |
| Provision for credit losses | 2,238 | | 2,275 | | 1,977 | |
| Net interest income after provision for credit losses | 14,051 | | 15,121 | | 12,751 | |
| Noninterest Income | | | |
| Card revenue | 1,679 | | 1,630 | | 1,512 | |
| Corporate payment products revenue | 773 | | 759 | | 698 | |
| Merchant processing services | 1,714 | | 1,659 | | 1,579 | |
| Trust and investment management fees | 2,660 | | 2,459 | | 2,209 | |
| Service charges | 1,253 | | 1,306 | | 1,298 | |
| Commercial products revenue | 1,523 | | 1,372 | | 1,105 | |
| Mortgage banking revenue | 627 | | 540 | | 527 | |
| Investment products fees | 330 | | 279 | | 235 | |
| Securities gains (losses), net | (154) | | (145) | | 20 | |
| Other | 641 | | 758 | | 273 | |
| Total noninterest income | 11,046 | | 10,617 | | 9,456 | |
| Noninterest Expense | | | |
| Compensation and employee benefits | 10,554 | | 10,416 | | 9,157 | |
| Net occupancy and equipment | 1,246 | | 1,266 | | 1,096 | |
| Professional services | 491 | | 560 | | 529 | |
| Marketing and business development | 619 | | 726 | | 456 | |
| Technology and communications | 2,074 | | 2,049 | | 1,726 | |
| Other intangibles | 569 | | 636 | | 215 | |
| Merger and integration charges | 155 | | 1,009 | | 329 | |
| Other | 1,480 | | 2,211 | | 1,398 | |
| Total noninterest expense | 17,188 | | 18,873 | | 14,906 | |
| Income before income taxes | 7,909 | | 6,865 | | 7,301 | |
| Applicable income taxes | 1,580 | | 1,407 | | 1,463 | |
| Net income | 6,329 | | 5,458 | | 5,838 | |
| Net (income) loss attributable to noncontrolling interests | (30) | | (29) | | (13) | |
| Net income attributable to U.S. Bancorp | $ | 6,299 | | $ | 5,429 | | $ | 5,825 | |
| Net income applicable to U.S. Bancorp common shareholders | $ | 5,909 | | $ | 5,051 | | $ | 5,501 | |
| Earnings per common share | $ | 3.79 | | $ | 3.27 | | $ | 3.69 | |
| Diluted earnings per common share | $ | 3.79 | | $ | 3.27 | | $ | 3.69 | |
| Average common shares outstanding | 1,560 | | 1,543 | | 1,489 | |
| Average diluted common shares outstanding | 1,561 | | 1,543 | | 1,490 | |
See Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
| | |
68 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
U.S. Bancorp
Consolidated Statement of Comprehensive Income
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31 (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 |
| Net income | $ | 6,329 | | $ | 5,458 | | $ | 5,838 | |
| Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) | | | |
| Changes in unrealized gains (losses) on investment securities available-for-sale | (60) | | 1,500 | | (13,656) | |
| Changes in unrealized gains (losses) on derivative hedges | (676) | | (252) | | (75) | |
| Changes in debit valuation adjustments | 1 | | — | | — | |
| Foreign currency translation | 18 | | 21 | | (10) | |
| Changes in unrealized gains (losses) on retirement plans | 245 | | (262) | | 526 | |
| Reclassification to earnings of realized (gains) losses | 910 | | 748 | | 544 | |
| Income taxes related to other comprehensive income (loss) | (106) | | (444) | | 3,207 | |
| Total other comprehensive income (loss) | 332 | | 1,311 | | (9,464) | |
| Comprehensive income (loss) | 6,661 | | 6,769 | | (3,626) | |
| Comprehensive (income) loss attributable to noncontrolling interests | (30) | | (29) | | (13) | |
| Comprehensive income (loss) attributable to U.S. Bancorp | $ | 6,631 | | $ | 6,740 | | $ | (3,639) | |
See Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
U.S. Bancorp
Consolidated Statement of Shareholders’ Equity | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | U.S. Bancorp Shareholders | | |
| (Dollars and Shares in Millions, Except Per Share Data) | Common
Shares
Outstanding | Preferred
Stock | Common
Stock | Capital
Surplus | Retained
Earnings | Treasury
Stock | Accumulated
Other
Comprehensive
Income (Loss) | Total U.S.
Bancorp
Shareholders’
Equity | Noncontrolling
Interests | Total
Equity |
| Balance December 31, 2021 | 1,484 | | $ | 6,371 | | $ | 21 | | $ | 8,539 | | $ | 69,201 | | $ | (27,271) | | $ | (1,943) | | $ | 54,918 | | $ | 469 | | $ | 55,387 | |
| Net income (loss) | | | | | 5,825 | | | | 5,825 | | 13 | | 5,838 | |
| Other comprehensive income (loss) | | | | | | | (9,464) | | (9,464) | | | (9,464) | |
Preferred stock dividends(a) | | | | | (296) | | | | (296) | | | (296) | |
| Common stock dividends ($1.88 per share) | | | | | (2,829) | | | | (2,829) | | | (2,829) | |
| Issuance of preferred stock | | 437 | | | | | | | 437 | | | 437 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Issuance of common and treasury stock | 48 | | | | (32) | | | 2,071 | | | 2,039 | | | 2,039 | |
| Purchase of treasury stock | (1) | | | | | | (69) | | | (69) | | | (69) | |
| Distributions to noncontrolling interests | | | | | | | | — | | (13) | | (13) | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Net other changes in noncontrolling interests | | | | | | | | — | | (3) | | (3) | |
| Stock option and restricted stock grants | | | | 205 | | | | | 205 | | | 205 | |
| Balance December 31, 2022 | 1,531 | | $ | 6,808 | | $ | 21 | | $ | 8,712 | | $ | 71,901 | | $ | (25,269) | | $ | (11,407) | | $ | 50,766 | | $ | 466 | | $ | 51,232 | |
Change in accounting principle(b) | | | | | 46 | | | | 46 | | | 46 | |
| Net income (loss) | | | | | 5,429 | | | | 5,429 | | 29 | | 5,458 | |
| Other comprehensive income (loss) | | | | | | | 1,311 | | 1,311 | | | 1,311 | |
Preferred stock dividends(c) | | | | | (350) | | | | (350) | | | (350) | |
| Common stock dividends ($1.93 per share) | | | | | (3,000) | | | | (3,000) | | | (3,000) | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Issuance of common and treasury stock | 28 | | | | (264) | | | 1,205 | | | 941 | | | 941 | |
| Purchase of treasury stock | (1) | | | | | | (62) | | | (62) | | | (62) | |
| Distributions to noncontrolling interests | | | | | | | | — | | (29) | | (29) | |
| Net other changes in noncontrolling interests | | | | | | | | — | | (1) | | (1) | |
| Stock option and restricted stock grants | | | | 225 | | | | | 225 | | | 225 | |
| Balance December 31, 2023 | 1,558 | | $ | 6,808 | | $ | 21 | | $ | 8,673 | | $ | 74,026 | | $ | (24,126) | | $ | (10,096) | | $ | 55,306 | | $ | 465 | | $ | 55,771 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income (loss) | | | | | 6,299 | | | | 6,299 | | 30 | | 6,329 | |
| Other comprehensive income (loss) | | | | | | | 332 | | 332 | | | 332 | |
Preferred stock dividends(d) | | | | | (352) | | | | (352) | | | (352) | |
| Common stock dividends ($1.98 per share) | | | | | (3,110) | | | | (3,110) | | | (3,110) | |
| Issuance of common and treasury stock | 6 | | | | (199) | | | 234 | | | 35 | | | 35 | |
| Purchase of treasury stock | (4) | | | | | | (173) | | | (173) | | | (173) | |
| Distributions to noncontrolling interests | | | | | | | | — | | (30) | | (30) | |
| Net other changes in noncontrolling interests | | | | | | | | — | | (3) | | (3) | |
| Stock option and restricted stock grants | | | | 241 | | | | | 241 | | | 241 | |
| Balance December 31, 2024 | 1,560 | | $ | 6,808 | | $ | 21 | | $ | 8,715 | | $ | 76,863 | | $ | (24,065) | | $ | (9,764) | | $ | 58,578 | | $ | 462 | | $ | 59,040 | |
(a)Reflects dividends declared per share on the Company’s Series A, Series B, Series J, Series K, Series L, Series M, Series N, and Series O Non-Cumulative Perpetual Preferred Stock of $3,965.458, $962.487, $1,325.00, $1,375.00, $937.50, $1,000.00, $925.00, and $1,050.00, respectively.
(b)Effective January 1, 2023, the Company adopted accounting guidance which removed the separate recognition and measurement of troubled debt restructurings. Upon adoption, the Company reduced its allowance for credit losses and increased retained earnings net of deferred taxes through a cumulative-effect adjustment
(c)Reflects dividends declared per share on the Company’s Series A, Series B, Series J, Series K, Series L, Series M, Series N, and Series O Non-Cumulative Perpetual Preferred Stock of $6,439.904, $1,503.518, $1,325.00, $1,375.00, $937.50, $1,000.00, $925.00, and $1,125.00, respectively.
(d)Reflects dividends declared per share on the Company’s Series A, Series B, Series J, Series K, Series L, Series M, Series N and Series O Non-Cumulative Perpetual Preferred Stock of $6,537.806, $1,527.702, $1,325.00, $1,375.00, $937.50, $1,000.00, $925.00, and $1,125.00, respectively.
See Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
| | |
70 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
U.S. Bancorp
Consolidated Statement of Cash Flows
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31 (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 |
| Operating Activities | | | |
| Net income attributable to U.S. Bancorp | $ | 6,299 | | $ | 5,429 | | $ | 5,825 | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities | | | |
| Provision for credit losses | 2,238 | | 2,275 | | 1,977 | |
| Depreciation and amortization of premises and equipment | 370 | | 382 | | 345 | |
| Amortization of intangibles | 569 | | 636 | | 215 | |
| (Gain) loss on sale of loans held for sale | (184) | | 7 | | 387 | |
| (Gain) loss on sale of securities and other assets | 123 | | 119 | | (188) | |
| Loans originated for sale, net of repayments | (24,225) | | (26,936) | | (33,127) | |
| Proceeds from sales of loans held for sale | 24,008 | | 26,686 | | 38,895 | |
| Other, net | 2,075 | | (151) | | 6,790 | |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | 11,273 | | 8,447 | | 21,119 | |
| Investing Activities | | | |
| Proceeds from sales of available-for-sale investment securities | 13,125 | | 11,209 | | 36,391 | |
| Proceeds from maturities of held-to-maturity investment securities | 6,161 | | 6,164 | | 5,759 | |
| Proceeds from maturities of available-for-sale investment securities | 6,006 | | 6,314 | | 14,927 | |
| Purchases of held-to-maturity investment securities | (246) | | (932) | | (7,091) | |
| Purchases of available-for-sale investment securities | (35,886) | | (8,342) | | (24,592) | |
| Net (increase) decrease in loans outstanding | (7,278) | | 3,829 | | (27,318) | |
| Proceeds from sales of loans | 645 | | 5,707 | | 4,420 | |
| Purchases of loans | (1,264) | | (1,106) | | (2,113) | |
| Net (increase) decrease in securities purchased under agreements to resell | (3,859) | | (2,404) | | 252 | |
| Net cash (paid for) received from acquisitions | (103) | | (330) | | 12,257 | |
| Other, net | (1,835) | | (1,184) | | (5,392) | |
| Net cash (used in) provided by investing activities | (24,534) | | 18,925 | | 7,500 | |
| Financing Activities | | | |
| Net increase (decrease) in deposits | 6,001 | | (12,291) | | (17,215) | |
| Net increase (decrease) in short-term borrowings | 239 | | (16,508) | | 15,213 | |
| Proceeds from issuance of long-term debt | 12,017 | | 15,583 | | 8,732 | |
| Principal payments or redemption of long-term debt | (6,042) | | (4,084) | | (6,926) | |
| Proceeds from issuance of preferred stock | — | | — | | 437 | |
| Proceeds from issuance of common stock | 32 | | 951 | | 21 | |
| Repurchase of preferred stock | — | | — | | (1,100) | |
| Repurchase of common stock | (173) | | (62) | | (69) | |
| Cash dividends paid on preferred stock | (356) | | (341) | | (299) | |
| Cash dividends paid on common stock | (3,092) | | (2,970) | | (2,776) | |
| | | |
| Other, net | (55) | | — | | — | |
| Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities | 8,571 | | (19,722) | | (3,982) | |
| Change in cash and due from banks | (4,690) | | 7,650 | | 24,637 | |
| Cash and due from banks at beginning of period | 61,192 | | 53,542 | | 28,905 | |
| Cash and due from banks at end of period | $ | 56,502 | | $ | 61,192 | | $ | 53,542 | |
| | | |
| Supplemental Cash Flow Disclosures | | | |
| Cash paid for income taxes | $ | 499 | | $ | 645 | | $ | 767 | |
| Cash paid for interest | 15,382 | | 12,282 | | 2,717 | |
| Noncash transfer of available-for-sale investment securities to held-to-maturity | — | | — | | 40,695 | |
| Net noncash transfers to foreclosed property | 24 | | 26 | | 23 | |
| Acquisitions | | | |
| Assets acquired (sold) | $ | 106 | | $ | (83) | | $ | 106,209 | |
| Liabilities (assumed) sold | (3) | | 413 | | (95,753) | |
| Net | $ | 103 | | $ | 330 | | $ | 10,456 | |
See Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
| | | | | | | | |
| NOTE 1 | | Significant Accounting Policies |
U.S. Bancorp is a financial services holding company headquartered in Minneapolis, Minnesota, serving millions of local, national and global customers. U.S. Bancorp and its subsidiaries (the “Company”) provide a full range of financial services, including lending and depository services through banking offices principally in the Midwest and West regions of the United States, through online services, over mobile devices and through other distribution channels. The Company also engages in credit card, merchant, and ATM processing, mortgage banking, cash management, capital markets, insurance, trust and investment management, brokerage, and leasing activities, principally in domestic markets.
Basis of Presentation The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company and its subsidiaries and all VIEs for which the Company has both the power to direct the activities of the VIE that most significantly impact the VIE’s economic performance, and the obligation to absorb losses or right to receive benefits of the VIE that could potentially be significant to the VIE. Consolidation eliminates intercompany accounts and transactions. Certain items in prior periods have been reclassified to conform to the current period presentation.
Uses of Estimates The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the amounts reported in the financial statements and accompanying notes. Actual experience could differ from those estimates and assumptions.
Securities
Realized gains or losses on securities are determined on a trade date basis based on the specific amortized cost of the investments sold.
Trading Securities Securities held for resale are classified as trading securities and are included in other assets and reported at fair value. Changes in fair value and realized gains or losses are reported in noninterest income.
Available-for-sale Securities Debt securities that are not trading securities but may be sold before maturity in response to changes in the Company’s interest rate risk profile, funding needs, demand for collateralized deposits by public entities or other reasons, are carried at fair value with unrealized net gains or losses reported within other comprehensive income (loss). Declines in fair value related to credit, if any, are recorded through the establishment of an allowance for credit losses.
Held-to-maturity Securities Debt securities for which the Company has the positive intent and ability to hold to maturity are reported at historical cost adjusted for amortization of premiums and accretion of discounts.
Expected credit losses, if any, are recorded through the establishment of an allowance for credit losses.
Securities Purchased Under Agreements to Resell and Securities Sold Under Agreements to Repurchase Securities purchased under agreements to resell and securities sold under agreements to repurchase are accounted for as collateralized financing transactions with a receivable or payable recorded at the amounts at which the securities were acquired or sold, plus accrued interest. Collateral requirements are continually monitored and additional collateral is received or provided as required. The Company records a receivable or payable for cash collateral paid or received.
Equity Investments
Equity investments in entities where the Company has a significant influence (generally between 20 percent and 50 percent ownership), but does not control the entity, are accounted for using the equity method. Investments in limited partnerships and similarly structured limited liability companies where the Company’s ownership interest is greater than 5 percent are accounted for using the equity method. Equity investments not using the equity method are accounted for at fair value with changes in fair value and realized gains or losses reported in noninterest income, unless fair value is not readily determinable, in which case the investment is carried at cost subject to adjustments for any observable market transactions on the same or similar instruments of the investee. Most of the Company’s equity investments do not have readily determinable fair values. All equity investments are evaluated for impairment at least annually and more frequently if certain criteria are met.
Loans
The Company offers a broad array of lending products and categorizes its loan portfolio into two segments, which is the level at which it develops and documents a systematic methodology to determine the allowance for credit losses. The Company’s two loan portfolio segments are commercial lending and consumer lending. The Company further disaggregates its loan portfolio segments into various classes based on their underlying risk characteristics. The two classes within the commercial lending segment are commercial loans and commercial real estate loans. The three classes within the consumer lending segment are residential mortgages, credit card loans and other retail loans.
Originated Loans Held for Investment Loans the Company originates as held for investment are reported at the principal amount outstanding, net of unearned interest income and deferred fees and costs, and any direct principal charge-offs. Interest income is accrued on the unpaid principal balances as earned. Loan and commitment fees and certain direct loan origination costs
| | |
72 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
are deferred and recognized over the life of the loan and/or commitment period as yield adjustments.
Purchased Loans All purchased loans are recorded at fair value at the date of purchase and those acquired on or after January 1, 2020 are divided into those considered PCD and those not considered PCD. An allowance for credit losses is established for each population and considers product mix, risk characteristics of the portfolio, delinquency status and refreshed loan-to-value ratios when possible. The allowance established for purchased loans not considered PCD is recognized through provision expense upon acquisition, whereas the allowance established for loans considered PCD at acquisition is offset by an increase in the basis of the acquired loans. Any subsequent increases and decreases in the allowance related to purchased loans, regardless of PCD status, are recognized through provision expense, with charge-offs charged to the allowance.
Commitments to Extend Credit Unfunded commitments for residential mortgage loans intended to be held for sale are considered derivatives and recorded in other assets and other liabilities on the Consolidated Balance Sheet at fair value with changes in fair value recorded in noninterest income. All other unfunded loan commitments are not considered derivatives and are not reported on the Consolidated Balance Sheet. Reserves for credit exposure on all other unfunded credit commitments are recorded in other liabilities.
Allowance for Credit Losses The allowance for credit losses is established for current expected credit losses on the Company’s loan and lease portfolio, including unfunded credit commitments. The allowance considers expected losses for the remaining lives of the applicable assets, inclusive of expected recoveries. The allowance for credit losses is increased through provisions charged to earnings and reduced by net charge-offs. Management evaluates the appropriateness of the allowance for credit losses on a quarterly basis.
Multiple economic scenarios are considered over a three-year reasonable and supportable forecast period, which includes increasing consideration of historical loss experience over years two and three. These economic scenarios are constructed with interrelated projections of multiple economic variables, and loss estimates are produced that consider the historical correlation of those economic variables with credit losses. After the forecast period, the Company fully reverts to long-term historical loss experience, adjusted for prepayments and characteristics of the current loan and lease portfolio, to estimate losses over the remaining life of the portfolio. The economic scenarios are updated at least quarterly and are designed to provide a range of reasonable estimates, both better and worse than current expectations. Scenarios are weighted based on the Company’s expectation of economic conditions for the foreseeable future and reflect significant judgment and consideration of economic forecast uncertainty. Final loss estimates also consider factors affecting credit losses not reflected in the scenarios, due to the unique aspects of current conditions and
expectations. These factors may include, but are not limited to, loan servicing practices, regulatory guidance, and/or fiscal and monetary policy actions.
The allowance recorded for credit losses utilizes forward-looking expected loss models to consider a variety of factors affecting lifetime credit losses. These factors include, but are not limited to, macroeconomic variables such as unemployment rates, real estate prices, gross domestic product levels, inflation, interest rates and corporate bonds spreads, as well as loan and borrower characteristics, such as internal risk ratings on commercial loans and consumer credit scores, delinquency status, collateral type and available valuation information, consideration of end-of-term losses on lease residuals, and the remaining term of the loan, adjusted for expected prepayments. For each loan portfolio, including those loans modified under various loan modification programs, model estimates are adjusted as necessary to consider any relevant changes in portfolio composition, lending policies, underwriting standards, risk management practices, economic conditions or other factors that would affect the accuracy of the model. Expected credit loss estimates also include consideration of expected cash recoveries on loans previously charged-off or expected recoveries on collateral dependent loans where recovery is expected through sale of the collateral at fair value less selling costs. Where loans do not exhibit similar risk characteristics, an individual analysis is performed to consider expected credit losses. For loans and leases that do not share similar risk characteristics with a pool of loans, the Company establishes individually assessed reserves. Reserves for individual commercial nonperforming loans greater than $5 million in the commercial lending segment are analyzed utilizing expected cash flows discounted using the original effective interest rate, the observable market price of the loan, or the fair value of the collateral, less selling costs, for collateral-dependent loans as appropriate. For smaller commercial loans collectively evaluated for impairment, historical loss experience is also incorporated into the allowance methodology applied to this category of loans.
The Company’s methodology for determining the appropriate allowance for credit losses also considers the imprecision inherent in the methodologies used and allocated to the various loan portfolios. As a result, amounts determined under the methodologies described above are adjusted by management to consider the potential impact of other qualitative factors not captured in the quantitative model adjustments which include, but are not limited to, the following: model imprecision, imprecision in economic scenario assumptions, and emerging risks related to either changes in the environment that are affecting specific portfolios, or changes in portfolio concentrations over time that may affect model performance. The consideration of these items results in adjustments to allowance amounts included in the Company’s allowance for credit losses for each loan portfolio.
The Company also assesses the credit risk associated with off-balance sheet loan commitments, letters of credit, investment securities and derivatives. Credit risk associated with derivatives is reflected in the fair values
recorded for those positions. The liability for off-balance sheet credit exposure related to loan commitments and other credit guarantees is included in other liabilities. Because business processes and credit risks associated with unfunded credit commitments are essentially the same as for loans, the Company utilizes similar processes to estimate its liability for unfunded credit commitments.
The results of the analysis are evaluated quarterly to confirm the estimates are appropriate for each specific loan portfolio, as well as the entire loan portfolio, as the entire allowance for credit losses is available for the entire loan portfolio.
Credit Quality The credit quality of the Company’s loan portfolios is assessed as a function of net credit losses, levels of nonperforming assets and delinquencies, and credit quality ratings as defined by the Company.
For all loan portfolio classes, loans are considered past due based on the number of days delinquent except for monthly amortizing loans which are classified delinquent based upon the number of contractually required payments not made (for example, two missed payments is considered 30 days delinquent). When a loan is placed on nonaccrual status, unpaid accrued interest is reversed, reducing interest income in the current period.
Commercial lending segment loans are generally placed on nonaccrual status when the collection of principal and interest has become 90 days past due or is otherwise considered doubtful. Commercial lending segment loans are generally fully charged down if unsecured by collateral or partially charged down to the fair value of the collateral securing the loan, less costs to sell, when the loan is placed on nonaccrual.
Consumer lending segment loans are generally charged-off at a specific number of days or payments past due. Residential mortgages and other retail loans secured by 1-4 family properties are generally charged down to the fair value of the collateral securing the loan, less costs to sell, at 180 days past due. Residential mortgage loans and lines in a first lien position are placed on nonaccrual status in instances where a partial charge-off occurs unless the loan is well secured and in the process of collection. Residential mortgage loans and lines in a junior lien position secured by 1-4 family properties are placed on nonaccrual status at 120 days past due or when they are behind a first lien that has become 180 days or greater past due or placed on nonaccrual status. Any secured consumer lending segment loan whose borrower has had debt discharged through bankruptcy, for which the loan amount exceeds the fair value of the collateral, is charged down to the fair value of the related collateral and the remaining balance is placed on nonaccrual status. Credit card loans continue to accrue interest until the account is charged-off. Credit cards are charged-off at 180 days past due. Other retail loans not secured by 1-4 family properties are charged-off at 120 days past due; and revolving consumer lines are charged-off at 180 days past due. Similar to credit cards, other retail loans are generally not placed on nonaccrual status because of the relative short period of time to charge-off. Certain retail customers having financial difficulties may have the terms of their credit card
and other loan agreements modified to require only principal payments and, as such, are reported as nonaccrual.
For all loan classes, interest payments received on nonaccrual loans are generally recorded as a reduction to a loan’s carrying amount while a loan is on nonaccrual and are recognized as interest income upon payoff of the loan. However, interest income may be recognized for interest payments if the remaining carrying amount of the loan is believed to be collectible. In certain circumstances, loans in any class may be restored to accrual status, such as when a loan has demonstrated sustained repayment performance or no amounts are past due and prospects for future payment are no longer in doubt; or when the loan becomes well secured and is in the process of collection. Loans where there has been a partial charge-off may be returned to accrual status if all principal and interest (including amounts previously charged-off) is expected to be collected and the loan is current.
The Company classifies its loan portfolio classes using internal credit quality ratings on a quarterly basis. These ratings include pass, special mention and classified, and are an important part of the Company’s overall credit risk management process and evaluation of the allowance for credit losses. Loans with a pass rating represent those loans not classified on the Company’s rating scale for problem credits, as minimal credit risk has been identified. Special mention loans are those loans that have a potential weakness deserving management’s close attention. Classified loans are those loans where a well-defined weakness has been identified that may put full collection of contractual cash flows at risk. It is possible that others, given the same information, may reach different reasonable conclusions regarding the credit quality rating classification of specific loans.
Loan Modifications In certain circumstances, the Company may modify the terms of a loan to maximize the collection of amounts due when a borrower is experiencing financial difficulties or is expected to experience difficulties in the near-term. The Company recognizes interest on modified loans if full collection of contractual principal and interest is expected. The effects of modifications on credit loss expectations, such as improved payment capacity, longer expected lives and other factors, are considered when measuring the allowance for credit losses. Modification performance, including redefault rates and how these compare to historical losses, are also considered. Modifications generally do not result in significant changes to the Company’s allowance for credit losses.
For the commercial lending segment, modifications generally result in the Company working with borrowers on a case-by-case basis. Commercial and commercial real estate modifications generally include extensions of the maturity date and may be accompanied by an increase or decrease to the interest rate. In addition, the Company may work with the borrower in identifying other changes that mitigate loss to the Company, which may include additional collateral or guarantees to support the loan. To a lesser
| | |
74 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
extent, the Company may provide an interest rate reduction.
Modifications for the consumer lending segment are generally part of programs the Company has initiated. The Company modifies residential mortgage loans under Federal Housing Administration, United States Department of Veterans Affairs, or its own internal programs. Under these programs, the Company offers qualifying homeowners the opportunity to permanently modify their loan and achieve more affordable monthly payments. These modifications may include adjustments to interest rates, conversion of adjustable rates to fixed rates, extension of maturity dates or deferrals of payments, capitalization of accrued interest and/or outstanding advances, or in limited situations, partial forgiveness of loan principal. In some instances, participation in residential mortgage loan modification programs requires the customer to complete a short-term trial period. A permanent loan modification is contingent on the customer successfully completing the trial period arrangement, and the loan documents are not modified until that time.
Credit card and other retail loan modifications are generally part of distinct modification programs providing customers experiencing financial difficulty with modifications whereby balances may be amortized up to 60 months, and generally include waiver of fees and reduced interest rates.
Leases The Company, as a lessor, originates retail and commercial leases either directly to the consumer or indirectly through dealer networks. Retail leases, primarily automobiles, have terms up to 5 years. Commercial leases may include high dollar assets such as aircraft or lower cost items such as office equipment. At lease inception, retail lease customers may be provided with an end-of-term purchase option, which is based on the contractual residual value of the automobile at the expiration of the lease. Automobile leases do not typically contain options to extend or terminate the lease. Equipment leases may contain various types of purchase options. Some option amounts are a stated value, while others are determined using the fair market value at the time of option exercise.
Residual values on leased assets are reviewed regularly for impairment. Residual valuations for retail leases are based on independent assessments of expected used automobile sale prices at the end of the lease term. Impairment tests are conducted based on these valuations considering the probability of the lessee returning the asset to the Company, re-marketing efforts, insurance coverage and ancillary fees and costs. Valuations for commercial leases are based upon external or internal management appraisals. The Company manages its risk to changes in the residual value of leased vehicles, office and business equipment, and other assets through disciplined residual valuation setting at the inception of a lease, diversification of its leased assets, regular residual asset valuation reviews and monitoring of residual value gains or losses upon the disposition of assets. Retail lease residual value risk is mitigated further by the purchase of residual value insurance coverage and effective end-of-term marketing of off-lease vehicles.
The Company, as lessee, leases certain assets for use in its operations. Leased assets primarily include retail branches, operations centers and other corporate locations, and, to a lesser extent, office and computer equipment. For each lease with an original term greater than 12 months, the Company records a lease liability and a corresponding right of use (“ROU”) asset. The Company accounts for the lease and non-lease components in the majority of its lease contracts as a single lease component, with the determination of the lease liability at lease inception based on the present value of the consideration to be paid under the contract. The discount rate used by the Company is determined at commencement of the lease using a secured rate for a similar term as the period of the lease. The Company’s leases do not include significant variable lease payments.
Certain of the Company’s real estate leases include options to extend. Lease extension options are generally exercisable at market rates. Option periods that the Company is reasonably certain that it will exercise are included in the calculation of its ROU assets and lease liabilities.
Other Real Estate OREO is included in other assets, and is property acquired through foreclosure or other proceedings on defaulted loans. OREO is initially recorded at fair value, less estimated selling costs. The fair value of OREO is evaluated regularly and any decreases in value along with holding costs, such as taxes and insurance, are reported in noninterest expense.
Loans Held For Sale
Loans held for sale (“LHFS”) represent mortgage loans intended to be sold in the secondary market and other loans that management has an active plan to sell. LHFS are carried at the lower-of-cost-or-fair value as determined on an aggregate basis by type of loan with the exception of loans for which the Company has elected fair value accounting, which are carried at fair value. Any writedowns to fair value upon the transfer of loans to LHFS are reflected in loan charge-offs.
Where an election is made to carry the LHFS at fair value, any change in fair value is recognized in noninterest income. Where an election is made to carry LHFS at lower-of-cost-or-fair value, any further decreases are recognized in noninterest income and increases in fair value above the loan cost basis are not recognized until the loans are sold. Fair value elections are made at the time of origination or purchase based on the Company’s fair value election policy. The Company has elected fair value accounting for substantially all its MLHFS.
Derivative Financial Instruments
In the ordinary course of business, the Company enters into derivative transactions to manage various risks and to accommodate the business requirements of its customers. Derivative instruments are reported in other assets or other liabilities at fair value. Changes in a derivative’s fair value are recognized currently in earnings unless specific hedge accounting criteria are met.
All derivative instruments that qualify and are designated for hedge accounting are recorded at fair value and classified as either a hedge of the fair value of a recognized asset or liability (“fair value hedge”); a hedge of a forecasted transaction or the variability of cash flows to be received or paid related to a recognized asset or liability (“cash flow hedge”); or a hedge of the volatility of a net investment in foreign operations driven by changes in foreign currency exchange rates (“net investment hedge”). Changes in the fair value of a derivative that is highly effective and designated as a fair value hedge, and the offsetting changes in the fair value of the hedged item, are recorded in earnings. Changes in the fair value of a derivative that is highly effective and designated as a cash flow hedge are recorded in other comprehensive income (loss) until cash flows of the hedged item are realized. Changes in the fair value of net investment hedges that are highly effective are recorded in other comprehensive income (loss). The Company performs an assessment, at inception and, at a minimum, quarterly thereafter, to determine the effectiveness of the derivative in offsetting changes in the value or cash flows of the hedged item(s).
If a derivative designated as a cash flow hedge is terminated or ceases to be highly effective, the gain or loss in other comprehensive income (loss) is amortized to earnings over the period the forecasted hedged transactions impact earnings. If a hedged forecasted transaction is no longer probable, hedge accounting is ceased and any gain or loss included in other comprehensive income (loss) is reported in earnings immediately, unless the forecasted transaction is at least reasonably possible of occurring, whereby the amounts remain within other comprehensive income (loss).
Revenue Recognition
In the ordinary course of business, the Company recognizes income derived from various revenue generating activities. Certain revenues are generated from contracts where they are recognized when, or as services or products are transferred to customers for amounts the Company expects to be entitled. Revenue generating activities related to financial assets and liabilities are also recognized, including mortgage servicing fees, loan commitment fees, foreign currency remeasurements, and gains and losses on securities, equity investments and unconsolidated subsidiaries. Certain specific policies include the following:
Card Revenue Card revenue includes interchange from credit, debit and stored-value cards processed through card association networks, annual fees, and other transaction and account management fees. Interchange rates are generally set by the card associations and based on purchase volumes and other factors. The Company records interchange as services are provided. Transaction and account management fees are recognized as services are provided, except for annual fees which are recognized over the applicable period. Costs for rewards programs and certain payments to partners and card associations are also recorded within card revenue when services are
provided. The Company predominately records card revenue within the Payment Services business segment.
Corporate Payment Products Revenue Corporate payment products revenue primarily includes interchange from commercial card products processed through card association networks and revenue from proprietary network transactions. The Company records corporate payment products revenue as services are provided. Certain payments to card associations and customers are also recorded within corporate payment products revenue as services are provided. Corporate payment products revenue is recorded within the Payment Services business segment.
Merchant Processing Services Merchant processing services revenue consists principally of merchant discount and other transaction and account management fees charged to merchants for the electronic processing of card association network transactions, less interchange paid to the card-issuing bank, card association assessments, and revenue sharing amounts. All of these are recognized at the time the merchant’s services are performed. The Company may enter into revenue sharing agreements with referral partners or in connection with purchases of merchant contracts from sellers. The revenue sharing amounts are determined primarily on sales volume processed or revenue generated for a particular group of merchants. Merchant processing revenue also includes revenues related to point-of-sale equipment recorded as sales when the equipment is shipped or as earned for equipment rentals. The Company records merchant processing services revenue within the Payment Services business segment.
Trust and Investment Management Fees Trust and investment management fees are recognized over the period in which services are performed and are based on a percentage of the fair value of the assets under management or administration, fixed based on account type, or transaction-based fees. Services provided to clients include trustee, transfer agent, custodian, fiscal agent, escrow, fund accounting and administration services. Services provided to mutual funds may include selling, distribution and marketing services. Trust and investment management fees are predominately recorded within the Wealth, Corporate, Commercial and Institutional Banking business segment.
Service Charges Service charges include fees received on deposit accounts under depository agreements with customers to provide access to deposited funds, serve as a custodian of funds, and when applicable, pay interest on deposits. Checking or savings accounts may contain fees for various services used on a day-to-day basis by a customer. Fees are recognized as services are delivered to and consumed by the customer, or as fees are charged. Service charges also include revenue generated from ATM transaction processing and settlement services which is recognized at the time the services are performed. Certain payments to partners and card associations related to ATM processing services are also recorded within service
| | |
76 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
charges as services are provided. Further, revenue generated from treasury management services are included in service charges and include fees for a broad range of products and services that enable customers to manage their cash more efficiently. These products and services include cash and investment management, receivables management, disbursement services, funds transfer services, and information reporting. Treasury management revenue is recognized as products and services are provided to customers. The Company reflects a discount calculated on monthly average collected customer balances. Service charges are reported primarily within the Wealth, Corporate, Commercial and Institutional Banking, and Consumer and Business Banking business segments.
Commercial Products Revenue Commercial products revenue primarily includes revenue related to ancillary services provided to Wealth, Corporate, Commercial and Institutional Banking, and Consumer and Business Banking customers, including underwriting fees, standby letter of credit fees, non-yield related loan fees, loan and syndication fees, and revenue recognized on customer-related derivatives and sales of direct financing leases. The Company charges underwriting fees when leading or participating with a group of underwriters in raising investment capital on behalf of securities issuers. These fees are recognized at securities issuance. The Company, in its role as lead underwriter, arranges deal structuring and use of outside vendors for the underwriting group. The Company recognizes only those fees and expenses related to its underwriting commitment. Sales of direct financing leases are recognized at point of sale.
Mortgage Banking Revenue Mortgage banking revenue includes revenue derived from mortgages originated and subsequently sold, generally with servicing retained. The primary components include: gains and losses on mortgage sales; servicing revenue; changes in fair value for mortgage loans originated with the intent to sell and measured at fair value under the fair value option; changes in fair value for derivative commitments to purchase and originate mortgage loans; changes in the fair value of MSRs; and the impact of risk management activities associated with the mortgage origination pipeline, funded loans and MSRs. Net interest income from mortgage loans is recorded in interest income. Refer to Other Significant Policies in Note 1, as well as Note 9 and Note 21 for a further discussion of MSRs. Mortgage banking revenue is reported within the Consumer and Business Banking business segment.
Investment Products Fees Investment products fees include commissions related to the execution of requested security trades, distribution fees from sale of mutual funds, and investment advisory fees. Commissions and investment advisory fees are recognized as services are delivered to and utilized by the customer. Distribution fees are received over time, are dependent on the consumer maintaining their mutual fund asset position and the value of such position. These revenues are estimated and recognized at the point a significant reversal of revenue becomes remote.
Investment products fees are predominately reported within the Wealth, Corporate, Commercial and Institutional Banking business segment.
Other Noninterest Income Other noninterest income is primarily related to financial assets including income on unconsolidated subsidiaries and equity method investments, gains on sale of other investments and corporate owned life insurance proceeds. The Company reports other noninterest income across all business segments.
Other Significant Policies
Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets Goodwill is recorded on acquired businesses if the purchase price exceeds the fair value of the net assets acquired. Goodwill is not amortized but is subject, at a minimum, to annual tests for impairment at a reporting unit level. In certain situations, an interim impairment test may be required if events occur or circumstances change that would more likely than not reduce the fair value of a reporting unit below its carrying amount. Determining the amount of goodwill impairment, if any, includes assessing whether the carrying value of a reporting unit exceeds its fair value. Other intangible assets are recorded at their fair value upon completion of a business acquisition or certain other transactions, and include core deposits benefits and the value of customer contracts or relationships. Other intangible assets are amortized over their estimated useful lives, using straight-line and accelerated methods and are reviewed for impairment when indicators of impairment are present. Determining the amount of other intangible asset impairment, if any, includes assessing the present value of the estimated future cash flows associated with the intangible asset and comparing it to the carrying amount of the asset.
Income Taxes Deferred taxes are recorded to reflect the tax consequences on future years of differences between the tax basis of assets and liabilities and their financial reporting carrying amounts. The Company uses the deferral method of accounting on investments that generate investment tax credits. Under this method, the investment tax credits are recognized as a reduction to the related asset. For investments in qualified affordable housing projects and certain other tax-advantaged investments, the Company presents the expense in tax expense rather than noninterest expense.
Mortgage Servicing Rights MSRs are capitalized as separate assets when loans are sold and servicing is retained or if they are purchased from others. MSRs are recorded at fair value. The Company determines the fair value by estimating the present value of the asset’s future cash flows utilizing market-based prepayment rates, option adjusted spread, and other assumptions validated through comparison to trade information, industry surveys and independent third-party valuations. Changes in the fair value of MSRs are recorded in earnings as mortgage banking revenue during the period in which they occur.
Pensions For purposes of its pension plans, the Company utilizes its fiscal year-end as the measurement date. At the measurement date, plan assets are determined based on fair value, generally representing observable market prices or the net asset value provided by the funds’ trustee or administrator. The actuarial cost method used to compute the pension liabilities and related expense is the projected unit credit method. The projected benefit obligation is principally determined based on the present value of projected benefit distributions at an assumed discount rate. The discount rate utilized is based on the investment yield of high quality corporate bonds available in the marketplace with maturities equal to projected cash flows of future benefit payments as of the measurement date. Periodic pension expense (or income) includes service costs, interest costs based on the assumed discount rate, the expected return on plan assets based on an actuarially derived market-related value and amortization of actuarial gains and losses. Service cost is included in compensation and employee benefits expense on the Consolidated Statement of Income, with all other components of periodic pension expense included in other noninterest expense on the Consolidated Statement of Income.
Pension accounting reflects the long-term nature of benefit obligations and the investment horizon of plan assets, and can have the effect of reducing earnings volatility related to short-term changes in interest rates and market valuations. Actuarial gains and losses include the impact of plan amendments and various unrecognized gains and losses which are deferred, and to the extent exceed 10 percent of the greater of the projected benefit obligation or the market-related value of plan assets, are amortized over the future service periods of active employees or the remaining life expectancies of inactive participants. The market-related value utilized to determine the expected return on plan assets is based on fair value adjusted for the difference between expected returns and actual performance of plan assets. The unrealized difference between actual experience and expected returns is included in expense over a period of approximately 15 years for active employees and approximately 30 years for inactive participants. The overfunded or underfunded status of each plan is recorded as an asset or liability on the Consolidated Balance Sheet, with changes in that status recognized through other comprehensive income (loss).
Premises and Equipment Premises and equipment are stated at cost less accumulated depreciation and depreciated primarily on a straight-line basis over the estimated life of the assets. Estimated useful lives range up to 40 years for newly constructed buildings and from 3 to 25 years for furniture and equipment.
The Company, as lessee, records an ROU asset for each lease with an original term greater than 12 months. ROU assets are included in premises and equipment, with the corresponding lease liabilities included in long-term debt and other liabilities.
Capitalized Software The Company capitalizes certain costs associated with the acquisition or development of
internal-use software. Once the software is ready for its intended use, these costs are amortized on a straight-line basis over the software’s expected useful life and reviewed for impairment on an ongoing basis. Estimated useful lives are generally 3 to 5 years, but may range up to 7 years.
Stock-Based Compensation The Company grants stock-based awards, which may include restricted stock, restricted stock units and options to purchase common stock of the Company. Stock option grants are for a fixed number of shares to employees and directors with an exercise price equal to the fair value of the shares at the date of grant. Restricted stock and restricted stock unit grants are awarded at no cost to the recipient. Stock-based compensation for awards is recognized in the Company’s results of operations over the vesting period. The Company immediately recognizes compensation cost of awards to employees that meet retirement status, despite their continued active employment. The amortization of stock-based compensation reflects estimated forfeitures adjusted for actual forfeiture experience. As compensation expense is recognized, a deferred tax asset is recorded that represents an estimate of the future tax deduction from exercise or release of restrictions. At the time stock-based awards are exercised, cancelled, expire, or restrictions are released, the Company may be required to recognize an adjustment to tax expense, depending on the market price of the Company’s common stock at that time.
Per Share Calculations Earnings per common share is calculated using the two-class method under which earnings are allocated to common shareholders and holders of participating securities. Unvested stock-based compensation awards that contain nonforfeitable rights to dividends or dividend equivalents are considered participating securities under the two-class method. Net income applicable to U.S. Bancorp common shareholders is then divided by the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding to determine earnings per common share. Diluted earnings per common share is calculated by adjusting income and outstanding shares, assuming conversion of all potentially dilutive securities.
Reference Interest Rate Transition In March 2020, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued accounting guidance to ease the financial reporting burdens related to the market transition from the London Interbank Offered Rate (“LIBOR”) and other interbank offered rates to alternative reference rates. The guidance provided temporary optional expedients and exceptions to the guidance in United States generally accepted accounting principles on contract modifications and hedge accounting. The guidance was effective upon issuance and generally could be applied through December 31, 2024. The adoption of this guidance was not material to the Company's financial statements.
| | |
78 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
Income Taxes – Improvements to Income Tax Disclosures In December 2023, the FASB issued guidance, effective for the Company for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2024, related to income tax disclosures. This guidance requires additional information in income tax rate reconciliation disclosures and additional disclosures about income taxes paid. The guidance is required, at a minimum, to be adopted on a prospective basis, with an option to apply it retrospectively. The Company expects the adoption of this guidance will not be material to its financial statements.
Segment Reporting – Improvements to Reportable Segment Disclosures Effective with the 2024 annual reporting period, the Company adopted accounting guidance on a retrospective basis, issued by the FASB in November 2023, related to segment disclosures. This guidance requires disclosures of significant segment expenses and other segment items and expands interim period disclosure requirements to include segment profit or loss and assets, which were previously only required to be disclosed annually. The adoption of this guidance was not material to the Company's financial statements.
| | | | | | | | |
| NOTE 3 | | Restrictions on Cash and Due |
| | from Banks |
Banking regulators require bank subsidiaries to maintain minimum average reserve balances, either in the form of vault cash or reserve balances held with central banks or other financial institutions. The amount of required reserve balances were approximately $53 million at both December 31, 2024 and 2023. The Company held balances at central banks and other financial institutions of $48.4 billion and $49.5 billion at December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively, to meet these requirements and for other purposes. These balances are included in cash and due from banks on the Consolidated Balance Sheet.
| | | | | | | | |
| NOTE 4 | | Investment Securities |
The Company’s held-to-maturity investment securities are carried at historical cost, adjusted for amortization of premiums and accretion of discounts. The Company’s available-for-sale investment securities are carried at fair
value with unrealized net gains or losses reported within accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) in shareholders’ equity.
The amortized cost, gross unrealized holding gains and losses, and fair value of held-to-maturity and available-for-sale investment securities at December 31 were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2024 | 2023 |
| (Dollars in Millions) | Amortized Cost | Unrealized Gains | Unrealized Losses | Fair Value | Amortized Cost | Unrealized Gains | Unrealized Losses | Fair Value |
| Held-to-Maturity | | | | | | | | |
| U.S. Treasury and agencies | $ | 1,296 | | $ | — | | $ | (21) | | $ | 1,275 | | $ | 1,345 | | $ | — | | $ | (35) | | $ | 1,310 | |
| Mortgage-backed securities | | | | | | | | |
| Residential agency | 75,392 | | 3 | | (12,317) | | 63,078 | | 80,997 | | 6 | | (9,929) | | 71,074 | |
| Commercial agency | 1,702 | | — | | (27) | | 1,675 | | 1,695 | | 6 | | (5) | | 1,696 | |
| Other | 244 | | 3 | | — | | 247 | | 8 | | — | | — | | 8 | |
| Total held-to-maturity | $ | 78,634 | | $ | 6 | | $ | (12,365) | | $ | 66,275 | | $ | 84,045 | | $ | 12 | | $ | (9,969) | | $ | 74,088 | |
| Available-for-Sale | | | | | | | | |
| U.S. Treasury and agencies | $ | 30,467 | | $ | 1 | | $ | (2,081) | | $ | 28,387 | | $ | 21,768 | | $ | 8 | | $ | (2,234) | | $ | 19,542 | |
| Mortgage-backed securities | | | | | | | | |
| Residential agency | 35,558 | | 13 | | (2,290) | | 33,281 | | 28,185 | | 104 | | (2,211) | | 26,078 | |
| Commercial | | | | | | | | |
| Agency | 8,673 | | — | | (1,322) | | 7,351 | | 8,703 | | — | | (1,360) | | 7,343 | |
| Non-agency | 7 | | — | | (1) | | 6 | | 7 | | — | | (1) | | 6 | |
| Asset-backed securities | 7,136 | | 30 | | (1) | | 7,165 | | 6,713 | | 25 | | (14) | | 6,724 | |
| Obligations of state and political subdivisions | 10,690 | | 13 | | (1,151) | | 9,552 | | 10,867 | | 36 | | (914) | | 9,989 | |
| Other | 249 | | 1 | | — | | 250 | | 24 | | — | | — | | 24 | |
| Total available-for-sale, excluding portfolio level basis adjustments | 92,780 | | 58 | | (6,846) | | 85,992 | | 76,267 | | 173 | | (6,734) | | 69,706 | |
Portfolio level basis adjustments (a) | 13 | | — | | (13) | | — | | 335 | | — | | (335) | | — | |
| Total available-for-sale | $ | 92,793 | | $ | 58 | | $ | (6,859) | | $ | 85,992 | | $ | 76,602 | | $ | 173 | | $ | (7,069) | | $ | 69,706 | |
(a)Represents fair value hedge basis adjustments related to active portfolio layer method hedges of available-for-sale investment securities, which are not allocated to individual securities in the portfolio. For additional information, refer to Note 19.
Investment securities with a fair value of $18.8 billion at December 31, 2024, and $20.5 billion at December 31, 2023, were pledged to secure public, private and trust deposits, repurchase agreements and for other purposes required by contractual obligation or law. Included in these amounts were securities where the Company and certain
counterparties have agreements granting the counterparties the right to sell or pledge the securities. Investment securities securing these types of arrangements had a fair value of $320 million at December 31, 2024, and $338 million at December 31, 2023.
The following table provides information about the amount of interest income from taxable and non-taxable investment securities:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31 (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 |
| Taxable | $ | 4,808 | | $ | 4,171 | | $ | 3,081 | |
| Non-taxable | 303 | | 314 | | 297 | |
| Total interest income from investment securities | $ | 5,111 | | $ | 4,485 | | $ | 3,378 | |
| | |
80 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
The following table provides information about the amount of gross gains and losses realized through the sales of available-for-sale investment securities:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31 (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 |
| Realized gains | $ | 147 | | $ | 74 | | $ | 163 | |
| Realized losses | (301) | | (219) | | (143) | |
| Net realized gains (losses) | $ | (154) | | $ | (145) | | $ | 20 | |
| Income tax expense (benefit) on net realized gains (losses) | $ | (39) | | $ | (37) | | $ | 5 | |
The Company conducts a regular assessment of its available-for-sale investment securities with unrealized losses to determine whether all or some portion of a security’s unrealized loss is related to credit and an allowance for credit losses is necessary. If the Company intends to sell or it is more likely than not the Company will be required to sell an investment security, the amortized cost of the security is written down to fair value. When evaluating credit losses, the Company considers various factors such as the nature of the investment security, the credit ratings or financial condition of the issuer, the extent of the unrealized loss, expected cash flows of underlying
collateral, the existence of any government or agency guarantees, and market conditions. The Company measures the allowance for credit losses using market information where available and discounting the cash flows at the original effective rate of the investment security. The allowance for credit losses is adjusted each period through earnings and can be subsequently recovered. The allowance for credit losses on the Company’s available-for-sale investment securities was immaterial at December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023.
At December 31, 2024, certain investment securities had a fair value below amortized cost. The following table shows the gross unrealized losses excluding portfolio level basis adjustments and fair value of the Company’s available-for-sale investment securities with unrealized losses, aggregated by investment category and length of time the individual investment securities have been in continuous unrealized loss positions, at December 31, 2024:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Less Than 12 Months | 12 Months or Greater | Total |
| (Dollars in Millions) | Fair Value | Unrealized Losses | Fair Value | Unrealized Losses | Fair Value | Unrealized Losses |
| U.S. Treasury and agencies | $ | 9,236 | | $ | (28) | | $ | 16,978 | | $ | (2,053) | | $ | 26,214 | | $ | (2,081) | |
| Mortgage-backed securities | | | | | | |
| Residential agency | 15,369 | | (275) | | 15,738 | | (2,015) | | 31,107 | | (2,290) | |
| Commercial | | | | | | |
| Agency | — | | — | | 7,351 | | (1,322) | | 7,351 | | (1,322) | |
| Non-agency | — | | — | | 7 | | (1) | | 7 | | (1) | |
| Asset-backed securities | 35 | | — | | 1,164 | | (1) | | 1,199 | | (1) | |
| Obligations of state and political subdivisions | 1,697 | | (21) | | 7,435 | | (1,130) | | 9,132 | | (1,151) | |
| Other | 2 | | — | | 4 | | — | | 6 | | — | |
| Total investment securities | $ | 26,339 | | $ | (324) | | $ | 48,677 | | $ | (6,522) | | $ | 75,016 | | $ | (6,846) | |
These unrealized losses primarily relate to changes in interest rates and market spreads subsequent to purchase of these available-for-sale investment securities. U.S. Treasury and agencies securities and agency mortgage-backed securities are issued, guaranteed or otherwise supported by the United States government. The Company’s obligations of state and political subdivisions are generally high grade. Accordingly, the Company does not consider these unrealized losses to be credit-related and an allowance for credit losses is not necessary. In general, the issuers of the investment securities are contractually prohibited from prepayment at less than par, and the Company did not pay significant purchase premiums for these investment securities. At December 31, 2024, the Company had no plans to sell investment securities with unrealized losses, and believes it is more
likely than not it would not be required to sell such investment securities before recovery of their amortized cost.
During the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2023, the Company did not purchase any investment securities that had more-than-insignificant credit deterioration.
Predominantly all of the Company’s held-to-maturity investment securities are U.S. Treasury and agencies securities and highly rated agency mortgage-backed securities that are guaranteed or otherwise supported by the United States government and have no history of credit losses. Accordingly the Company does not expect to incur any credit losses on held-to-maturity investment securities and has no allowance for credit losses recorded for these securities.
The following table provides information about the amortized cost, fair value and yield by maturity date of the investment securities outstanding at December 31, 2024:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars in Millions) | Amortized
Cost | Fair Value | Weighted-
Average
Maturity in
Years | Weighted- Average Yield(e) |
| | | | | |
| Held-to-Maturity | | | | |
| U.S. Treasury and agencies | | | | |
| Maturing in one year or less | $ | 650 | | $ | 647 | | 0.4 | 2.71 | % |
| Maturing after one year through five years | 646 | | 628 | | 2.3 | 3.00 | |
| Maturing after five years through ten years | — | | — | | — | | — | |
| Maturing after ten years | — | | — | | — | | — | |
| Total | $ | 1,296 | | $ | 1,275 | | 1.3 | 2.85 | % |
Mortgage-backed securities(a) | | | | |
| Maturing in one year or less | $ | 42 | | $ | 41 | | 0.8 | 4.52 | % |
| Maturing after one year through five years | 2,110 | | 2,091 | | 3.5 | 4.49 | |
| Maturing after five years through ten years | 73,667 | | 61,626 | | 9.0 | 2.12 | |
| Maturing after ten years | 1,275 | | 995 | | 10.1 | 2.18 | |
| Total | $ | 77,094 | | $ | 64,753 | | 8.8 | 2.19 | % |
| Other | | | | |
| Maturing in one year or less | $ | 19 | | $ | 16 | | 0.2 | 3.24 | % |
| Maturing after one year through five years | 225 | | 231 | | 2.4 | 2.68 | |
| Maturing after five years through ten years | — | | — | | — | | — | |
| Maturing after ten years | — | | — | | — | | — | |
| Total | $ | 244 | | $ | 247 | | 2.2 | 2.73 | % |
Total held-to-maturity(b) | $ | 78,634 | | $ | 66,275 | | 8.7 | 2.20 | % |
| Available-for-Sale | | | | |
| U.S. Treasury and agencies | | | | |
| Maturing in one year or less | $ | 11 | | $ | 11 | | 0.1 | 4.64 | % |
| Maturing after one year through five years | 14,070 | | 13,335 | | 3.2 | 2.63 | |
| Maturing after five years through ten years | 15,629 | | 14,476 | | 6.5 | 3.35 | |
| Maturing after ten years | 757 | | 565 | | 10.6 | 1.92 | |
| Total | $ | 30,467 | | $ | 28,387 | | 5.1 | 2.98 | % |
Mortgage-backed securities(a) | | | | |
| Maturing in one year or less | $ | 30 | | $ | 29 | | 0.6 | 2.02 | % |
| Maturing after one year through five years | 6,028 | | 5,611 | | 3.9 | 2.87 | |
| Maturing after five years through ten years | 37,699 | | 34,560 | | 7.9 | 3.96 | |
| Maturing after ten years | 481 | | 438 | | 11.0 | 4.76 | |
| Total | $ | 44,238 | | $ | 40,638 | | 7.4 | 3.82 | % |
Asset-backed securities (a) | | | | |
| Maturing in one year or less | $ | — | | $ | — | | — | | — | % |
| Maturing after one year through five years | 3,668 | | 3,684 | | 1.7 | 4.90 | |
| Maturing after five years through ten years | 3,468 | | 3,481 | | 5.9 | 6.26 | |
| Maturing after ten years | — | | — | | — | | — | |
| Total | $ | 7,136 | | $ | 7,165 | | 3.8 | 5.56 | % |
Obligations of state and political subdivisions(c)(d) | | | | |
| Maturing in one year or less | $ | 128 | | $ | 128 | | 0.4 | 5.53 | % |
| Maturing after one year through five years | 1,698 | | 1,687 | | 2.5 | 4.67 | |
| Maturing after five years through ten years | 1,563 | | 1,474 | | 7.2 | 3.69 | |
| Maturing after ten years | 7,301 | | 6,263 | | 14.9 | 3.47 | |
| Total | $ | 10,690 | | $ | 9,552 | | 11.7 | 3.72 | % |
| Other | | | | |
| Maturing in one year or less | $ | 49 | | $ | 49 | | 0.7 | 4.66 | % |
| Maturing after one year through five years | 200 | | 201 | | 1.7 | 4.82 | |
| Maturing after five years through ten years | — | | — | | — | | — | |
| Maturing after ten years | — | | — | | — | | — | |
| Total | $ | 249 | | $ | 250 | | 1.5 | 4.79 | % |
Total available-for-sale(b)(f) | $ | 92,780 | | $ | 85,992 | | 6.8 | 3.67 | % |
(a)Information related to asset and mortgage-backed securities included above is presented based upon weighted-average maturities that take into account anticipated future prepayments.
(b)The weighted-average maturity of total held-to-maturity investment securities was 8.7 years at December 31, 2023, with a corresponding weighted-average yield of 2.22 percent. The weighted-average maturity of total available-for-sale investment securities was 6.3 years at December 31, 2023, with a corresponding weighted-average yield of 3.12 percent.
(c)Information related to obligations of state and political subdivisions is presented based upon yield to first optional call date if the security is purchased at a premium, and yield to maturity if the security is purchased at par or a discount.
(d)Maturity calculations for obligations of state and political subdivisions are based on the first optional call date for securities with a fair value above par and the contractual maturity date for securities with a fair value equal to or below par.
(e)Weighted-average yields for obligations of state and political subdivisions are presented on a fully-taxable equivalent basis based on a federal income tax rate of 21 percent. Yields on investment securities are computed based on amortized cost balances, excluding any premiums or discounts recorded related to the transfer of investment securities at fair value from available-for-sale to held-to maturity.
(f)Amortized cost excludes portfolio level basis adjustments of $13 million.
| | |
82 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
| | | | | | | | |
| NOTE 5 | | Loans and Allowance for Credit Losses |
The composition of the loan portfolio at December 31, by class and underlying specific portfolio type, was as follows:
| | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 |
| Commercial | | |
| Commercial | $ | 135,254 | | $ | 127,676 | |
| Lease financing | 4,230 | | 4,205 | |
| Total commercial | 139,484 | | 131,881 | |
| Commercial Real Estate | | |
| Commercial mortgages | 38,619 | | 41,934 | |
| Construction and development | 10,240 | | 11,521 | |
| Total commercial real estate | 48,859 | | 53,455 | |
| Residential Mortgages | | |
| Residential mortgages | 112,806 | | 108,605 | |
| Home equity loans, first liens | 6,007 | | 6,925 | |
| Total residential mortgages | 118,813 | | 115,530 | |
| Credit Card | 30,350 | | 28,560 | |
| Other Retail | | |
| Retail leasing | 4,040 | | 4,135 | |
| Home equity and second mortgages | 13,565 | | 13,056 | |
| Revolving credit | 3,747 | | 3,668 | |
| Installment | 14,373 | | 13,889 | |
| Automobile | 6,601 | | 9,661 | |
| Total other retail | 42,326 | | 44,409 | |
| Total loans | $ | 379,832 | | $ | 373,835 | |
The Company had loans of $127.6 billion at December 31, 2024, and $123.1 billion at December 31, 2023, pledged at the Federal Home Loan Bank, and loans of $85.1 billion at December 31, 2024, and $82.8 billion at December 31, 2023, pledged at the Federal Reserve Bank.
The Company offers a broad array of lending products to consumer and commercial customers, in various industries, across several geographical locations, predominately in the states in which it has Consumer and Business Banking offices. Collateral for commercial and commercial real estate loans may include marketable securities, accounts receivable, inventory, equipment, real estate, or the related property.
Originated loans are reported at the principal amount outstanding, net of unearned interest and deferred fees and costs, and any partial charge-offs recorded. Purchased loans are recorded at fair value at the date of purchase. Net unearned interest and deferred fees and costs on originated loans and unamortized premiums and discounts
on purchased loans amounted to $2.5 billion at December 31, 2024 and $2.7 billion at December 31, 2023. The Company evaluates purchased loans for more-than-insignificant deterioration at the date of purchase in accordance with applicable authoritative accounting guidance. Purchased loans that have experienced more-than-insignificant deterioration from origination are considered purchased credit deteriorated loans. All other purchased loans are considered non-purchased credit deteriorated loans.
Allowance for Credit Losses The allowance for credit losses is established for current expected credit losses on the Company’s loan and lease portfolio, including unfunded credit commitments. The allowance considers expected losses for the remaining lives of the applicable assets, inclusive of expected recoveries. The allowance for credit losses is increased through provisions charged to earnings and reduced by net charge-offs.
Activity in the allowance for credit losses by portfolio class was as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars in Millions) | Commercial | Commercial Real Estate | Residential Mortgages | Credit
Card | Other
Retail | Total
Loans |
| Balance at December 31, 2023 | $ | 2,119 | | $ | 1,620 | | $ | 827 | | $ | 2,403 | | $ | 870 | | $ | 7,839 | |
| Add | | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Provision for credit losses | 608 | | 53 | | (53) | | 1,464 | | 166 | | 2,238 | |
| Deduct | | | | | | |
| Loans charged-off | 652 | | 229 | | 13 | | 1,406 | | 313 | | 2,613 | |
| Less recoveries of loans charged-off | (100) | | (64) | | (22) | | (179) | | (96) | | (461) | |
| Net loan charge-offs (recoveries) | 552 | | 165 | | (9) | | 1,227 | | 217 | | 2,152 | |
| | | | | | |
| Balance at December 31, 2024 | $ | 2,175 | | $ | 1,508 | | $ | 783 | | $ | 2,640 | | $ | 819 | | $ | 7,925 | |
| Balance at December 31, 2022 | $ | 2,163 | | $ | 1,325 | | $ | 926 | | $ | 2,020 | | $ | 970 | | $ | 7,404 | |
| Add | | | | | | |
Change in accounting principle(a) | — | | — | | (31) | | (27) | | (4) | | (62) | |
Allowance for acquired credit losses(b) | — | | 127 | | — | | — | | — | | 127 | |
| Provision for credit losses | 270 | | 431 | | 41 | | 1,259 | | 274 | | 2,275 | |
| Deduct | | | | | | |
| Loans charged-off | 389 | | 281 | | 129 | | 1,014 | | 478 | | 2,291 | |
| Less recoveries of loans charged-off | (75) | | (18) | | (20) | | (165) | | (108) | | (386) | |
| Net loan charge-offs (recoveries) | 314 | | 263 | | 109 | | 849 | | 370 | | 1,905 | |
| | | | | | |
| Balance at December 31, 2023 | $ | 2,119 | | $ | 1,620 | | $ | 827 | | $ | 2,403 | | $ | 870 | | $ | 7,839 | |
| Balance at December 31, 2021 | $ | 1,849 | | $ | 1,123 | | $ | 565 | | $ | 1,673 | | $ | 945 | | $ | 6,155 | |
| Add | | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
Allowance for acquired credit losses(b) | 163 | | 87 | | 36 | | 45 | | 5 | | 336 | |
Provision for credit losses(c) | 378 | | 152 | | 302 | | 826 | | 319 | | 1,977 | |
| Deduct | | | | | | |
Loans charged-off(d) | 319 | | 54 | | 13 | | 696 | | 418 | | 1,500 | |
| Less recoveries of loans charged-off | (92) | | (17) | | (36) | | (172) | | (120) | | (437) | |
| Net loan charge-offs (recoveries) | 227 | | 37 | | (23) | | 524 | | 298 | | 1,063 | |
| Other Changes | — | | — | | — | | — | | (1) | | (1) | |
| Balance at December 31, 2022 | $ | 2,163 | | $ | 1,325 | | $ | 926 | | $ | 2,020 | | $ | 970 | | $ | 7,404 | |
(a)Effective January 1, 2023, the Company adopted accounting guidance which removed the separate recognition and measurement of troubled debt restructurings.
(b)Represents allowance for credit deteriorated and charged-off loans acquired from MUB.
(c)Includes $662 million of provision for credit losses related to the acquisition of MUB.
(d)Includes $179 million of total charge-offs primarily on loans previously charged-off by MUB, which were written up upon acquisition to unpaid principal balance as required by purchase accounting.
The increase in the allowance for credit losses from December 31, 2023 to December 31, 2024 was primarily driven by loan portfolio growth.
| | |
84 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
The following table provides a summary of loans charged-off by portfolio class and year of origination for the years ended December 31: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars in Millions) | Commercial | Commercial Real Estate(a) | Residential Mortgages(b) | Credit Card(c) | Other Retail(d) | Total Loans |
| 2024 | | | | | | |
| Originated in 2024 | $ | 30 | | $ | 117 | | $ | — | | $ | — | | $ | 13 | | $ | 160 | |
| Originated in 2023 | 84 | | 51 | | — | | — | | 47 | | 182 | |
| Originated in 2022 | 178 | | 55 | | 3 | | — | | 52 | | 288 | |
| Originated in 2021 | 32 | | 1 | | — | | — | | 40 | | 73 | |
| Originated in 2020 | 12 | | 1 | | — | | — | | 21 | | 34 | |
| Originated prior to 2020 | 41 | | 4 | | 10 | | — | | 35 | | 90 | |
| Revolving | 275 | | — | | — | | 1,406 | | 105 | | 1,786 | |
| | | | | | |
| Total charge-offs | $ | 652 | | $ | 229 | | $ | 13 | | $ | 1,406 | | $ | 313 | | $ | 2,613 | |
| 2023 | | | | | | |
| Originated in 2023 | $ | 48 | | $ | 63 | | $ | — | | $ | — | | $ | 57 | | $ | 168 | |
| Originated in 2022 | 63 | | 88 | | 1 | | — | | 130 | | 282 | |
| Originated in 2021 | 30 | | 69 | | 6 | | — | | 83 | | 188 | |
| Originated in 2020 | 17 | | 2 | | 8 | | — | | 38 | | 65 | |
| Originated in 2019 | 15 | | 3 | | 16 | | — | | 31 | | 65 | |
| Originated prior to 2019 | 53 | | 56 | | 98 | | — | | 31 | | 238 | |
| Revolving | 163 | | — | | — | | 1,014 | | 80 | | 1,257 | |
| Revolving converted to term | — | | — | | — | | — | | 28 | | 28 | |
| Total charge-offs | $ | 389 | | $ | 281 | | $ | 129 | | $ | 1,014 | | $ | 478 | | $ | 2,291 | |
Note: Year of origination is based on the origination date of a loan, or for existing loans the date when the maturity date, pricing or commitment amount is amended. Predominantly all current year and near term loan origination years for gross charge-offs relate to existing loans that have had recent maturity date, pricing or commitment amount amendments.
(a)Includes $91 million of 2023 charge-offs related to uncollectible amounts on acquired loans.
(b)Includes $117 million of 2023 charge-offs related to balance sheet repositioning and capital management actions.
(c)Predominantly all credit card loans are considered revolving loans. Includes an immaterial amount of charge-offs related to revolving converted to term loans.
(d)Includes $192 million of 2023 charge-offs related to balance sheet repositioning and capital management actions.
Credit Quality The credit quality of the Company’s loan portfolios is assessed as a function of net credit losses, levels of nonperforming assets and delinquencies, and credit quality ratings as defined by the Company. These credit quality ratings are an important part of the Company’s overall credit risk management process and evaluation of the allowance for credit losses.
The following table provides a summary of loans by portfolio class, including the delinquency status of those that continue to accrue interest, and those that are nonperforming:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Accruing | | |
| (Dollars in Millions) | Current | 30-89 Days Past Due | 90 Days or More Past Due | Nonperforming(b) | Total |
| December 31, 2024 | | | | | |
| Commercial | $ | 138,362 | | $ | 356 | | $ | 96 | | $ | 670 | | $ | 139,484 | |
| Commercial real estate | 47,948 | | 78 | | 9 | | 824 | | 48,859 | |
Residential mortgages(a) | 118,267 | | 188 | | 206 | | 152 | | 118,813 | |
| Credit card | 29,487 | | 428 | | 435 | | — | | 30,350 | |
| Other retail | 41,886 | | 229 | | 64 | | 147 | | 42,326 | |
| Total loans | $ | 375,950 | | $ | 1,279 | | $ | 810 | | $ | 1,793 | | $ | 379,832 | |
| December 31, 2023 | | | | | |
| Commercial | $ | 130,925 | | $ | 464 | | $ | 116 | | $ | 376 | | $ | 131,881 | |
| Commercial real estate | 52,619 | | 55 | | 4 | | 777 | | 53,455 | |
Residential mortgages(a) | 115,067 | | 169 | | 136 | | 158 | | 115,530 | |
| Credit card | 27,779 | | 406 | | 375 | | — | | 28,560 | |
| Other retail | 43,926 | | 278 | | 67 | | 138 | | 44,409 | |
| Total loans | $ | 370,316 | | $ | 1,372 | | $ | 698 | | $ | 1,449 | | $ | 373,835 | |
(a)At December 31, 2024, $660 million of loans 30–89 days past due and $2.3 billion of loans 90 days or more past due purchased and that could be purchased from GNMA mortgage pools under delinquent loan repurchase options whose repayments are insured by the Federal Housing Administration or guaranteed by the United States Department of Veterans Affairs, were classified as current, compared with $595 million and $2.0 billion at December 31, 2023, respectively.
(b)Substantially all nonperforming loans at December 31, 2024 and 2023, had an associated allowance for credit losses. The Company recognized interest income on nonperforming loans of $29 million and $22 million for the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively, compared to what would have been recognized at the original contractual terms of the loans of $66 million and $49 million, respectively.
At December 31, 2024, total nonperforming assets held by the Company were $1.8 billion, compared with $1.5 billion at December 31, 2023. Total nonperforming assets included $1.8 billion of nonperforming loans, $21 million of OREO and $18 million of other nonperforming assets owned by the Company at December 31, 2024, compared with $1.4 billion, $26 million and $19 million, respectively, at December 31, 2023.
At December 31, 2024, the amount of foreclosed residential real estate held by the Company, and included in OREO, was $21 million, compared with $26 million at December 31, 2023. These amounts excluded $46 million and $47 million at December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023, respectively, of foreclosed residential real estate
related to mortgage loans whose payments are primarily insured by the Federal Housing Administration or guaranteed by the United States Department of Veterans Affairs. In addition, the amount of residential mortgage loans secured by residential real estate in the process of foreclosure at December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023, was $576 million and $728 million, respectively, of which $354 million and $487 million, respectively, related to loans purchased and that could be purchased from GNMA mortgage pools under delinquent loan repurchase options whose repayments are insured by the Federal Housing Administration or guaranteed by the United States Department of Veterans Affairs.
| | |
86 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
The following table provides a summary of loans by portfolio class and the Company’s internal credit quality rating:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | December 31, 2024 | December 31, 2023 |
| | | Criticized | | | Criticized | |
| (Dollars in Millions) | Pass | Special Mention | Classified(a) | Total Criticized | Total | Pass | Special Mention | Classified(a) | Total Criticized | Total |
| Commercial | | | | | | | | | | |
| Originated in 2024 | $ | 57,578 | | $ | 503 | | $ | 1,034 | | $ | 1,537 | | $ | 59,115 | | $ | — | | $ | — | | $ | — | | $ | — | | $ | — | |
| Originated in 2023 | 19,128 | | 173 | | 564 | | 737 | | 19,865 | | 43,023 | | 827 | | 856 | | 1,683 | | 44,706 | |
| Originated in 2022 | 19,718 | | 231 | | 370 | | 601 | | 20,319 | | 40,076 | | 274 | | 632 | | 906 | | 40,982 | |
| Originated in 2021 | 4,677 | | 60 | | 92 | | 152 | | 4,829 | | 9,219 | | 117 | | 154 | | 271 | | 9,490 | |
| Originated in 2020 | 2,737 | | 68 | | 68 | | 136 | | 2,873 | | 3,169 | | 92 | | 71 | | 163 | | 3,332 | |
| Originated prior to 2020 | 4,075 | | 8 | | 75 | | 83 | | 4,158 | | 5,303 | | 30 | | 209 | | 239 | | 5,542 | |
Revolving(b) | 27,344 | | 169 | | 812 | | 981 | | 28,325 | | 26,213 | | 362 | | 1,254 | | 1,616 | | 27,829 | |
| Total commercial | 135,257 | 1,212 | 3,015 | 4,227 | 139,484 | 127,003 | 1,702 | 3,176 | 4,878 | 131,881 |
| Commercial real estate | | | | | | | | | | |
| Originated in 2024 | 9,652 | | 261 | | 1,772 | | 2,033 | | 11,685 | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | |
| Originated in 2023 | 5,213 | | 42 | | 760 | | 802 | | 6,015 | | 8,848 | | 465 | | 2,206 | | 2,671 | | 11,519 | |
| Originated in 2022 | 9,047 | | 661 | | 913 | | 1,574 | | 10,621 | | 11,831 | | 382 | | 1,141 | | 1,523 | | 13,354 | |
| Originated in 2021 | 6,515 | | 100 | | 196 | | 296 | | 6,811 | | 9,235 | | 500 | | 385 | | 885 | | 10,120 | |
| Originated in 2020 | 2,954 | | 29 | | 137 | | 166 | | 3,120 | | 3,797 | | 51 | | 87 | | 138 | | 3,935 | |
| Originated prior to 2020 | 7,868 | | 119 | | 471 | | 590 | | 8,458 | | 10,759 | | 458 | | 619 | | 1,077 | | 11,836 | |
| Revolving | 2,078 | | — | | 68 | | 68 | | 2,146 | | 2,613 | | 6 | | 70 | | 76 | | 2,689 | |
| Revolving converted to term | 3 | | — | | — | | — | | 3 | | 2 | | — | | — | | — | | 2 | |
| Total commercial real estate | 43,330 | | 1,212 | | 4,317 | | 5,529 | | 48,859 | | 47,085 | | 1,862 | | 4,508 | | 6,370 | | 53,455 | |
Residential mortgages(c) | | | | | | | | | | |
| Originated in 2024 | 10,291 | | — | | — | | — | | 10,291 | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | |
| Originated in 2023 | 8,764 | | — | | 11 | | 11 | | 8,775 | | 9,734 | | — | | 5 | | 5 | | 9,739 | |
| Originated in 2022 | 28,484 | | — | | 43 | | 43 | | 28,527 | | 29,146 | | — | | 17 | | 17 | | 29,163 | |
| Originated in 2021 | 34,694 | | — | | 35 | | 35 | | 34,729 | | 36,365 | | — | | 16 | | 16 | | 36,381 | |
| Originated in 2020 | 13,748 | | — | | 16 | | 16 | | 13,764 | | 14,773 | | — | | 9 | | 9 | | 14,782 | |
| Originated prior to 2020 | 22,463 | | — | | 264 | | 264 | | 22,727 | | 25,202 | | — | | 262 | | 262 | | 25,464 | |
| Revolving | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | 1 | | — | | — | | — | | 1 | |
| Total residential mortgages | 118,444 | | — | | 369 | | 369 | | 118,813 | | 115,221 | | — | | 309 | | 309 | | 115,530 | |
Credit card(d) | 29,915 | | — | | 435 | | 435 | | 30,350 | | 28,185 | | — | | 375 | | 375 | | 28,560 | |
| Other retail | | | | | | | | | | |
| Originated in 2024 | 7,398 | | — | | 3 | | 3 | | 7,401 | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | |
| Originated in 2023 | 3,966 | | — | | 9 | | 9 | | 3,975 | | 5,184 | | — | | 4 | | 4 | | 5,188 | |
| Originated in 2022 | 4,085 | | — | | 11 | | 11 | | 4,096 | | 5,607 | | — | | 12 | | 12 | | 5,619 | |
| Originated in 2021 | 6,537 | | — | | 14 | | 14 | | 6,551 | | 10,398 | | — | | 15 | | 15 | | 10,413 | |
| Originated in 2020 | 2,715 | | — | | 6 | | 6 | | 2,721 | | 4,541 | | — | | 9 | | 9 | | 4,550 | |
| Originated prior to 2020 | 2,828 | | — | | 15 | | 15 | | 2,843 | | 4,008 | | — | | 20 | | 20 | | 4,028 | |
| Revolving | 13,846 | | — | | 120 | | 120 | | 13,966 | | 13,720 | | — | | 104 | | 104 | | 13,824 | |
| Revolving converted to term | 731 | | — | | 42 | | 42 | | 773 | | 735 | | — | | 52 | | 52 | | 787 | |
| Total other retail | 42,106 | | — | | 220 | | 220 | | 42,326 | | 44,193 | | — | | 216 | | 216 | | 44,409 | |
| Total loans | $ | 369,052 | | $ | 2,424 | | $ | 8,356 | | $ | 10,780 | | $ | 379,832 | | $ | 361,687 | | $ | 3,564 | | $ | 8,584 | | $ | 12,148 | | $ | 373,835 | |
| Total outstanding commitments | $ | 778,155 | | $ | 3,875 | | $ | 10,441 | | $ | 14,316 | | $ | 792,471 | | $ | 762,869 | | $ | 5,053 | | $ | 10,470 | | $ | 15,523 | | $ | 778,392 | |
Note: Year of origination is based on the origination date of a loan, or for existing loans the date when the maturity date, pricing or commitment amount is amended. Predominantly all current year and nearer term loan origination years for criticized loans relate to existing loans that have had recent maturity date, pricing or commitment amount amendments.
(a)Classified rating on consumer loans primarily based on delinquency status.
(b)Includes an immaterial amount of revolving converted to term loans.
(c)At December 31, 2024, $2.3 billion of GNMA loans 90 days or more past due and $1.4 billion of modified GNMA loans whose repayments are insured by the Federal Housing Administration or guaranteed by the United States Department of Veterans Affairs were classified with a pass rating, compared with $2.0 billion and $1.2 billion at December 31, 2023, respectively.
(d)Predominately all credit card loans are considered revolving loans. Includes an immaterial amount of revolving converted to term loans.
Loan Modifications In certain circumstances, the Company may modify the terms of a loan to maximize the collection of amounts due when a borrower is experiencing financial difficulties or is expected to experience difficulties in the near-term. The following table provides a summary of period-end balances of loans modified during the periods presented, by portfolio class and modification granted:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31 (Dollars in Millions) | Interest Rate Reduction | Payment Delay | Term Extension | Multiple Modifications(a) | Total Modifications | Percent of Class Total |
| 2024 | | | | | | |
| Commercial | $ | 77 | | $ | 2 | | $ | 526 | | $ | — | | $ | 605 | | .4 | % |
| Commercial real estate | 43 | | — | | 1,107 | | 70 | | 1,220 | | 2.5 | |
Residential mortgages(b) | — | | 79 | | 17 | | 23 | | 119 | | .1 | |
| Credit card | 414 | | 11 | | — | | — | | 425 | | 1.4 | |
| Other retail | 7 | | 3 | | 125 | | 4 | | 139 | | .3 | |
| Total loans, excluding loans purchased from GNMA mortgage pools | 541 | | 95 | | 1,775 | | 97 | | 2,508 | | .7 | |
Loans purchased from GNMA mortgage pools(b) | 1 | | 1,215 | | 292 | | 407 | | 1,915 | | 1.6 | |
| Total loans | $ | 542 | | $ | 1,310 | | $ | 2,067 | | $ | 504 | | $ | 4,423 | | 1.2 | % |
| 2023 | | | | | | |
| Commercial | $ | 46 | | $ | — | | $ | 286 | | $ | 33 | | $ | 365 | | .3 | % |
| Commercial real estate | — | | — | | 645 | | 72 | | 717 | | 1.3 | |
Residential mortgages(b) | — | | 234 | | 26 | | 20 | | 280 | | .2 | |
| Credit card | 349 | | 1 | | — | | — | | 350 | | 1.2 | |
| Other retail | 7 | | 21 | | 144 | | 3 | | 175 | | .4 | |
| Total loans, excluding loans purchased from GNMA mortgage pools | 402 | | 256 | | 1,101 | | 128 | | 1,887 | | .5 | |
Loans purchased from GNMA mortgage pools(b) | — | | 1,263 | | 255 | | 321 | | 1,839 | | 1.6 | |
| Total loans | $ | 402 | | $ | 1,519 | | $ | 1,356 | | $ | 449 | | $ | 3,726 | | 1.0 | % |
(a)Includes $310 million of total loans receiving a payment delay and term extension, $155 million of total loans receiving an interest rate reduction and term extension and $39 million of total loans receiving an interest rate reduction, payment delay and term extension for the year ended December 31, 2024, compared with $329 million, $112 million and $8 million for the year ended December 31, 2023, respectively.
(b)Percent of class total amounts expressed as a percent of total residential mortgage loan balances.
Loan modifications included in the table above exclude trial period arrangements offered to customers and secured loans to consumer borrowers that have had debt discharged through bankruptcy where the borrower has not reaffirmed the debt during the periods presented. At
December 31, 2024, the balance of loans modified in trial period arrangements was $189 million, while the balance of secured loans to consumer borrowers that have had debt discharged through bankruptcy was not material.
| | |
88 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
The following table summarizes the effects of loan modifications made to borrowers on loans modified:
| | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31 | Weighted-Average Interest Rate Reduction | Weighted-Average Months of Term Extension |
| 2024 | | |
Commercial(a) | 20.3 | % | 11 |
| Commercial real estate | 3.2 | | 13 |
| Residential mortgages | 1.1 | | 90 |
| Credit card | 16.4 | | — | |
| Other retail | 7.7 | | 5 |
| Loans purchased from GNMA mortgage pools | .6 | | 110 |
| 2023 | | |
Commercial(a) | 13.0 | | 12 |
| Commercial real estate | 3.5 | | 11 |
| Residential mortgages | 1.2 | | 98 |
| Credit card | 15.4 | | — | |
| Other retail | 7.9 | | 4 |
| Loans purchased from GNMA mortgage pools | .6 | | 103 |
Note: The weighted-average payment deferral for all portfolio classes was less than $1 million for the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2023. Forbearance payments are required to be paid at the end of the original term loan.
(a)The weighted-average interest rate reduction was primarily driven by commercial cards.
Loans that receive a forbearance plan generally remain in default until they are no longer delinquent as the result of the payment of all past due amounts or the borrower
receiving a term extension or modification. Therefore, loans only receiving forbearance plans are not included in the table below.
The following table provides a summary of loan balances as of December 31, which were modified during the prior twelve months, by portfolio class and delinquency status:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars in Millions) | Current | 30-89 Days Past Due | 90 Days or More Past Due | Total |
| 2024 | | | | |
| Commercial | $ | 395 | | $ | 26 | | $ | 167 | | $ | 588 | |
| Commercial real estate | 875 | | 26 | | 319 | | 1,220 | |
Residential mortgages(a) | 1,469 | | 4 | | 6 | | 1,479 | |
| Credit card | 302 | | 73 | | 39 | | 414 | |
| Other retail | 112 | | 19 | | 6 | | 137 | |
| Total loans | $ | 3,153 | | $ | 148 | | $ | 537 | | $ | 3,838 | |
| 2023 | | | | |
| Commercial | $ | 255 | | $ | 12 | | $ | 98 | | $ | 365 | |
| Commercial real estate | 524 | | — | | 193 | | 717 | |
Residential mortgages(a) | 1,385 | | 24 | | 16 | | 1,425 | |
| Credit card | 251 | | 67 | | 32 | | 350 | |
| Other retail | 133 | | 21 | | 8 | | 162 | |
| Total loans | $ | 2,548 | | $ | 124 | | $ | 347 | | $ | 3,019 | |
(a)At December 31, 2024, $442 million of loans 30-89 days past due and $324 million of loans 90 days or more past due purchased and that could be purchased from GNMA mortgage pools under delinquent loan repurchase options whose payments are insured by the Federal Housing Administration or guaranteed by the United States Department of Veterans Affairs, were classified as current, compared with $372 million and $175 million at December 31, 2023, respectively.
The following table provides a summary of loans that defaulted (fully or partially charged-off or became 90 days or more past due) that were modified within twelve months prior to default.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31 (Dollars in Millions) | Interest Rate Reduction | Payment Delay | Term Extension | Multiple Modifications(a) |
| 2024 | | | | |
| Commercial | $ | 30 | | $ | — | | $ | 45 | | $ | — | |
| Commercial real estate | 43 | | — | | 137 | | — | |
| Residential mortgages | — | | 3 | | — | | 3 | |
| Credit card | 128 | | — | | — | | — | |
| Other retail | 2 | | — | | 20 | | — | |
| Total loans, excluding loans purchased from GNMA mortgage pools | 203 | | 3 | | 202 | | 3 | |
| Loans purchased from GNMA mortgage pools | 1 | | 168 | | 78 | | 89 | |
| Total loans | $ | 204 | | $ | 171 | | $ | 280 | | $ | 92 | |
(a)Includes $81 million of total loans receiving a payment delay and term extension, $8 million of total loans receiving an interest rate reduction and term extension and $3 million of total loans receiving an interest rate reduction, payment delay and term extension.
The following table provides a summary of loans that defaulted (fully or partially charged-off or became 90 days or more past due) that were modified on or after January 1, 2023, the date the Company adopted accounting guidance which removed the separate recognition and measurement of troubled debt restructurings, through December 31, 2023:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31 (Dollars in Millions) | Interest Rate Reduction | Payment Delay | Term Extension | Multiple Modifications(a) |
| 2023 | | | | |
| Commercial | $ | 7 | | $ | — | | $ | — | | $ | — | |
| Commercial real estate | — | | — | | 1 | | — | |
| Residential mortgages | — | | 8 | | 2 | | 1 | |
| Credit card | 35 | | — | | — | | — | |
| Other retail | 1 | | 1 | | 11 | | — | |
| Total loans, excluding loans purchased from GNMA mortgage pools | 43 | | 9 | | 14 | | 1 | |
| Loans purchased from GNMA mortgage pools | — | | 67 | | 30 | | 37 | |
| Total loans | $ | 43 | | $ | 76 | | $ | 44 | | $ | 38 | |
(a)Represents loans receiving a payment delay and term extension.
As of December 31, 2024, the Company had $510 million of commitments to lend additional funds to borrowers whose terms of their outstanding owed balances have been modified.
| | |
90 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
The Company, as a lessor, originates retail and commercial leases either directly to the consumer or indirectly through dealer networks. Retail leases consist primarily of automobiles, while commercial leases may include high
dollar assets such as aircraft or lower cost items such as office equipment.
The components of the net investment in sales-type and direct financing leases, at December 31, were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | | 2023 |
| Lease receivables | $ | 7,328 | | | $ | 7,239 | |
| Unguaranteed residual values accruing to the lessor’s benefit | 911 | | | 1,082 | |
| Total net investment in sales-type and direct financing leases | $ | 8,239 | | | $ | 8,321 | |
The Company, as a lessor, recorded $775 million, $738 million and $764 million of revenue on its Consolidated Statement of Income for the years ended December 31,
2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively, primarily consisting of interest income on sales-type and direct financing leases.
The contractual future lease payments to be received by the Company, at December 31, 2024, were as follows:
| | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars in Millions) | Sales-type and Direct Financing Leases | Operating Leases |
| 2025 | $ | 2,758 | | $ | 143 | |
| 2026 | 2,142 | | 104 | |
| 2027 | 1,804 | | 77 | |
| 2028 | 865 | | 52 | |
| 2029 | 269 | | 32 | |
| Thereafter | 335 | | 54 | |
| Total lease payments | 8,173 | | $ | 462 | |
| Amounts representing interest | (845) | | |
| Lease receivables | $ | 7,328 | | |
The Company, as lessee, leases certain assets for use in its operations. Leased assets primarily include retail branches, operations centers and other corporate locations, and, to a lesser extent, office and computer equipment. For each lease with an original term greater than 12 months, the Company records a lease liability and a corresponding ROU asset. At December 31, 2024, the Company’s ROU assets included in premises and equipment and lease liabilities included in long-term debt and other liabilities, were $1.4 billion and $1.5 billion,
respectively, compared with $1.4 billion of ROU assets and $1.6 billion of lease liabilities at December 31, 2023, respectively.
Total costs incurred by the Company, as a lessee, were $529 million, $496 million and $390 million for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively, and principally related to contractual lease payments on operating leases. The Company’s leases do not impose significant covenants or other restrictions on the Company.
The following table presents amounts relevant to the Company’s assets leased for use in its operations for the years ended December 31:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 |
| Cash paid for amounts included in the measurement of lease liabilities | | | |
| Operating cash flows from operating leases | $ | 389 | | $ | 409 | | $ | 294 | |
| Operating cash flows from finance leases | 7 | | 7 | | 4 | |
| Financing cash flows from finance leases | 62 | | 49 | | 14 | |
| Right of use assets obtained in exchange for new operating lease liabilities | 268 | | 230 | | 239 | |
| Right of use assets obtained in exchange for new finance lease liabilities | 59 | | 25 | | 91 | |
The following table presents the weighted-average remaining lease terms and discount rates of the Company’s assets leased for use in its operations at December 31:
| | | | | | | | |
| | 2024 | 2023 |
| Weighted-average remaining lease term of operating leases (in years) | 6.7 | 6.4 |
| Weighted-average remaining lease term of finance leases (in years) | 8.1 | 8.3 |
| Weighted-average discount rate of operating leases | 4.0 | % | 3.7 | % |
| Weighted-average discount rate of finance leases | 7.3 | % | 7.7 | % |
The contractual future lease obligations of the Company at December 31, 2024, were as follows:
| | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars in Millions) | Operating Leases | Finance
Leases |
| 2025 | $ | 324 | | $ | 38 | |
| 2026 | 291 | | 37 | |
| 2027 | 248 | | 34 | |
| 2028 | 195 | | 26 | |
| 2029 | 147 | | 8 | |
| Thereafter | 382 | | 24 | |
| Total lease payments | 1,587 | | 167 | |
| Amounts representing interest | (218) | | (18) | |
| Lease liabilities | $ | 1,369 | | $ | 149 | |
| | | | | | | | |
| NOTE 7 | | Accounting for Transfers and Servicing of Financial Assets and Variable Interest Entities |
| | |
The Company transfers financial assets in the normal course of business. The majority of the Company’s financial asset transfers are residential mortgage loan sales primarily to GSEs, transfers of tax-advantaged investments, commercial loan sales through participation agreements, and other individual or portfolio loan and securities sales. In accordance with the accounting guidance for asset transfers, the Company considers any ongoing involvement with transferred assets in determining whether the assets can be derecognized from the balance sheet. Guarantees provided to certain third parties in connection with the transfer of assets are further discussed in Note 22.
For loans sold under participation agreements, the Company also considers whether the terms of the loan participation agreement meet the accounting definition of a participating interest. With the exception of servicing and certain performance-based guarantees, the Company’s continuing involvement with financial assets sold is minimal and generally limited to market customary representation and warranty clauses. Any gain or loss on sale depends on the previous carrying amount of the transferred financial assets, the consideration received, and any liabilities incurred in exchange for the transferred assets. Upon transfer, any servicing assets and other interests that continue to be held by the Company are initially recognized at fair value. For further information on MSRs, refer to Note 9. On a limited basis, the Company may acquire and package high-grade corporate bonds for select corporate customers, in which the Company generally has no continuing involvement with these transactions. Additionally, the Company is an authorized GNMA issuer and issues GNMA securities on a regular basis. The Company has no other asset securitizations or similar
asset-backed financing arrangements that are off-balance sheet.
The Company previously provided financial support primarily through the use of waivers of trust and investment management fees associated with various unconsolidated registered money market funds it manages. The Company discontinued providing this support beginning in the third quarter of 2022 due to rising interest rates in 2022. The Company provided $65 million of support to the funds during the year ended December 31, 2022.
The Company is involved in various entities that are considered to be VIEs. The Company’s investments in VIEs are primarily related to investments promoting affordable housing, community development and renewable energy sources. Some of these tax-advantaged investments support the Company’s regulatory compliance with the Community Reinvestment Act. The Company’s investments in these entities generate a return primarily through the realization of federal and state income tax credits, and other tax benefits, such as tax deductions from operating losses of the investments, over specified time periods. These tax credits are recognized as a reduction of tax expense or, for investments qualifying as investment tax credits, as a reduction to the related investment asset. The Company recognized federal and state income tax credits related to its affordable housing and other tax-advantaged investments in tax expense of $585 million, $576 million and $461 million for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively. The Company recognized $573 million, $582 million and $424 million of expenses related to all of these investments for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively, which were primarily included in tax expense.
| | |
92 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
The Company is not required to consolidate VIEs in which it has concluded it does not have a controlling financial interest, and thus is not the primary beneficiary. In such cases, the Company does not have both the power to direct the entities’ most significant activities and the obligation to absorb losses or the right to receive benefits that could potentially be significant to the VIEs.
The Company’s investments in these unconsolidated VIEs are carried in other assets on the Consolidated Balance Sheet. The Company’s unfunded capital and other commitments related to these unconsolidated VIEs are generally carried in other liabilities on the Consolidated Balance Sheet. The Company’s maximum exposure to loss from these unconsolidated VIEs include the investment recorded on the Company’s Consolidated Balance Sheet, net of unfunded capital commitments, and previously recorded tax credits which remain subject to recapture by taxing authorities based on compliance features required to be met at the project level. While the Company believes potential losses from these investments are remote, the maximum exposure was determined by assuming a scenario where the community-based business and housing projects completely fail and do not meet certain government compliance requirements resulting in recapture of the related tax credits.
The following table provides a summary of investments in community development and tax-advantaged VIEs that the Company has not consolidated:
| | | | | | | | |
| At December 31 (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 |
| Investment carrying amount | $ | 8,107 | | $ | 6,659 | |
| Unfunded capital and other commitments | 5,032 | | 3,619 | |
| Maximum exposure to loss | 8,435 | | 9,002 | |
The Company also has noncontrolling financial investments in private investment funds and partnerships considered to be VIEs, which are not consolidated. The Company’s recorded investment in these entities, carried in other assets on the Consolidated Balance Sheet, was approximately $264 million at December 31, 2024 and $219 million at December 31, 2023. The maximum exposure to loss related to these VIEs was $382 million at December 31, 2024 and $319 million at December 31, 2023, representing the Company’s investment balance and its unfunded commitments to invest additional amounts.
The Company also held senior notes of $3.2 billion as available-for-sale investment securities at December 31, 2024, compared with $5.3 billion at December 31, 2023. These senior notes were issued by third-party securitization vehicles that held $3.6 billion at December 31, 2024 and $6.1 billion at December 31, 2023 of indirect auto loans that collateralize the senior notes. These VIEs are not consolidated by the Company.
The Company’s individual net investments in unconsolidated VIEs, which exclude any unfunded capital commitments, ranged from less than $1 million to $79 million at December 31, 2024, compared with less than $1 million to $86 million at December 31, 2023.
The Company is required to consolidate VIEs in which it has concluded it has a controlling financial interest. The Company sponsors entities to which it transfers its interests in tax-advantaged investments to third parties. At December 31, 2024, approximately $6.4 billion of the Company’s assets and $4.2 billion of its liabilities included on the Consolidated Balance Sheet were related to community development and tax-advantaged investment VIEs which the Company has consolidated, primarily related to these transfers. These amounts compared to $6.1 billion and $4.4 billion, respectively, at December 31, 2023. The majority of the assets of these consolidated VIEs are reported in other assets, and the liabilities are reported in long-term debt and other liabilities. The assets of a particular VIE are the primary source of funds to settle its obligations. The creditors of the VIEs do not have recourse to the general credit of the Company. The Company’s exposure to the consolidated VIEs is generally limited to the carrying value of its variable interests plus any related tax credits previously recognized or transferred to others with a guarantee.
During 2024 the Company ended its previously sponsored municipal bond securities tender option bond program. The Company controlled the activities of the program’s entities and was entitled to the residual returns and provided liquidity and remarketing arrangements to the program. The Company had previously consolidated the program’s entities, and at December 31, 2023, included $607 million of available-for-sale investment securities and $381 million of short-term borrowings on the Consolidated Balance Sheet related to this program.
| | | | | | | | |
| NOTE 8 | | Premises and Equipment |
Premises and equipment at December 31 consisted of the following:
| | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 |
| Land | $ | 498 | | $ | 515 | |
| Buildings and improvements | 3,121 | | 3,239 | |
| Furniture, fixtures and equipment | 3,010 | | 3,013 | |
| Right of use assets on operating leases | 1,114 | | 1,149 | |
| Right of use assets on finance leases | 314 | | 275 | |
| Construction in progress | 96 | | 68 | |
| Total premises and equipment, gross | 8,153 | | 8,259 | |
| Less accumulated depreciation and amortization | (4,588) | | (4,636) | |
| Total premises and equipment, net | $ | 3,565 | | $ | 3,623 | |
| | | | | | | | |
| NOTE 9 | | Mortgage Servicing Rights |
The Company capitalizes MSRs as separate assets when loans are sold and servicing is retained. MSRs may also be purchased from others. The Company carries MSRs at fair value, with changes in the fair value recorded in earnings during the period in which they occur. The Company serviced $216.6 billion of residential mortgage loans for others at December 31, 2024, and $233.4 billion at December 31, 2023, including subserviced mortgages with no corresponding MSR asset. Included in mortgage banking revenue are the MSR fair value changes arising
from market rate and model assumption changes, net of the value change in derivatives used to economically hedge MSRs. These changes resulted in net losses of $2 million, $41 million and $45 million for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively. Loan servicing and ancillary fees, not including valuation changes, included in mortgage banking revenue were $699 million, $733 million and $754 million for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively.
Changes in fair value of capitalized MSRs are summarized as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 |
| Balance at beginning of period | $ | 3,377 | | $ | 3,755 | | $ | 2,953 | |
| Rights purchased | 1 | | 5 | | 156 | |
| Rights capitalized | 276 | | 373 | | 590 | |
| Rights sold | (188) | | (440) | | (255) | |
| Changes in fair value of MSRs | | | |
Due to fluctuations in market interest rates(a) | 235 | | 66 | | 804 | |
Due to revised assumptions or models(b) | 43 | | 12 | | (29) | |
Other changes in fair value(c) | (375) | | (394) | | (464) | |
| Balance at end of period | $ | 3,369 | | $ | 3,377 | | $ | 3,755 | |
(a)Includes changes in MSR value associated with changes in market interest rates, including estimated prepayment rates and anticipated earnings on escrow deposits.
(b)Includes changes in MSR value not caused by changes in market interest rates, such as changes in assumed cost to service, ancillary income and option adjusted spread, as well as the impact of any model changes.
(c)Primarily the change in MSR value from passage of time and cash flows realized (decay), but also includes the impact of changes to expected cash flows not associated with changes in market interest rates, such as the impact of delinquencies.
The estimated sensitivity to changes in interest rates of the fair value of the MSR portfolio and the related derivative instruments as of December 31 follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2024 | 2023 |
| (Dollars in Millions) | Down
100 bps | Down
50 bps | Down
25 bps | Up
25 bps | Up
50 bps | Up
100 bps | Down
100 bps | Down
50 bps | Down
25 bps | Up
25 bps | Up
50 bps | Up
100 bps |
| MSR portfolio | $ | (310) | | $ | (144) | | $ | (69) | | $ | 63 | | $ | 120 | | $ | 217 | | $ | (370) | | $ | (173) | | $ | (84) | | $ | 77 | | $ | 147 | | $ | 268 | |
| Derivative instrument hedges | 325 | | 147 | | 69 | | (61) | | (118) | | (220) | | 381 | | 178 | | 86 | | (79) | | (152) | | (289) | |
| Net sensitivity | $ | 15 | | $ | 3 | | $ | — | | $ | 2 | | $ | 2 | | $ | (3) | | $ | 11 | | $ | 5 | | $ | 2 | | $ | (2) | | $ | (5) | | $ | (21) | |
| | |
94 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
The fair value of MSRs and their sensitivity to changes in interest rates is influenced by the mix of the servicing portfolio and characteristics of each segment of the portfolio. The Company’s servicing portfolio consists of the distinct portfolios of government-insured mortgages, conventional mortgages and Housing Finance Agency (“HFA”) mortgages. The servicing portfolios are predominantly comprised of fixed-rate agency loans with
limited adjustable-rate or jumbo mortgage loans. The HFA servicing portfolio is comprised of loans originated under state and local housing authority program guidelines which assist purchases by first-time or low- to moderate-income homebuyers through a favorable rate subsidy, down payment and/or closing cost assistance on government- and conventional-insured mortgages.
A summary of the Company’s MSRs and related characteristics by portfolio as of December 31 follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2024 | 2023 |
| (Dollars in Millions) | HFA | Government | Conventional(d) | Total | HFA | Government | Conventional(d) | Total |
Servicing portfolio(a) | $ | 52,807 | | $ | 25,139 | | $ | 138,428 | | $ | 216,374 | | $ | 48,286 | | $ | 25,996 | | $ | 151,056 | | $ | 225,338 | |
| Fair value | $ | 856 | | $ | 512 | | $ | 2,001 | | $ | 3,369 | | $ | 769 | | $ | 507 | | $ | 2,101 | | $ | 3,377 | |
Value (bps)(b) | 162 | | 204 | | 145 | | 156 | | 159 | | 195 | | 139 | | 150 | |
| Weighted-average servicing fees (bps) | 35 | | 45 | | 25 | | 30 | | 36 | | 44 | | 26 | | 30 | |
| Multiple (value/servicing fees) | 4.57 | | 4.56 | | 5.69 | | 5.17 | | 4.45 | | 4.41 | | 5.41 | | 5.00 | |
| Weighted-average note rate | 4.92 | % | 4.35 | % | 3.87 | % | 4.18 | % | 4.56 | % | 4.23 | % | 3.81 | % | 4.02 | % |
| Weighted-average age (in years) | 4.5 | 6.1 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 4.3 | 5.5 | 4.3 | 4.4 |
| Weighted-average expected prepayment (constant prepayment rate) | 9.9 | % | 10.2 | % | 7.8 | % | 8.6 | % | 10.5 | % | 11.1 | % | 9.1 | % | 9.6 | % |
| Weighted-average expected life (in years) | 7.5 | 6.8 | 7.4 | 7.4 | 7.2 | 6.5 | 7.0 | 7.0 |
Weighted-average option adjusted spread(c) | 5.8 | % | 6.2 | % | 5.6 | % | 5.7 | % | 5.4 | % | 5.9 | % | 4.6 | % | 4.9 | % |
(a)Represents principal balance of mortgages having corresponding MSR asset.
(b)Calculated as fair value divided by the servicing portfolio.
(c)Option adjusted spread is the incremental spread added to the risk-free rate to reflect optionality and other risk inherent in the MSRs.
(d)Represents loans sold primarily to GSEs.
Intangible assets consisted of the following:
| | | | | | | | |
| At December 31 (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 |
| Goodwill | $ | 12,536 | | $ | 12,489 | |
| Core deposit benefits | 1,702 | | 2,134 | |
| Mortgage servicing rights | 3,369 | | 3,377 | |
| Other identified intangibles | 476 | | 573 | |
| Total | $ | 18,083 | | $ | 18,573 | |
Aggregate amortization expense consisted of the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31 (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 |
| Core deposit benefits | $ | 432 | | $ | 481 | | $ | 53 | |
| Other identified intangibles | 137 | | 155 | | 162 | |
| Total | $ | 569 | | $ | 636 | | $ | 215 | |
The estimated amortization expense for the next five years is as follows:
| | | | | |
| (Dollars in Millions) | |
| 2025 | $ | 489 | |
| 2026 | 422 | |
| 2027 | 353 | |
| 2028 | 290 | |
| 2029 | 223 | |
The following table reflects the changes in the carrying value of goodwill for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars in Millions) | Wealth, Corporate, Commercial and Institutional Banking | Consumer and Business Banking | Payment Services | Treasury and Corporate Support | Consolidated Company |
| Balance at December 31, 2021 | $ | 3,673 | | $ | 3,245 | | $ | 3,344 | | $ | — | | $ | 10,262 | |
| Goodwill acquired | 918 | | 1,220 | | 11 | | — | | 2,149 | |
| Foreign exchange translation and other | (2) | | — | | (36) | | — | | (38) | |
| Balance at December 31, 2022 | $ | 4,589 | | $ | 4,465 | | $ | 3,319 | | $ | — | | $ | 12,373 | |
| Goodwill acquired | 235 | | (139) | | — | | — | | 96 | |
| Foreign exchange translation and other | 1 | | — | | 19 | | — | | 20 | |
| Balance at December 31, 2023 | $ | 4,825 | | $ | 4,326 | | $ | 3,338 | | $ | — | | $ | 12,489 | |
| Goodwill acquired | — | | — | | 80 | | — | | 80 | |
| Foreign exchange translation and other | (2) | | — | | (31) | | — | | (33) | |
| Balance at December 31, 2024 | $ | 4,823 | | $ | 4,326 | | $ | 3,387 | | $ | — | | $ | 12,536 | |
The composition of deposits at December 31 was as follows:
| | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 |
| Noninterest-bearing deposits | $ | 84,158 | | $ | 89,989 | |
| Interest-bearing deposits | | |
| Interest checking | 127,188 | | 127,453 | |
| Money market savings | 206,805 | | 199,378 | |
| Savings accounts | 45,389 | | 43,219 | |
| Time deposits | 54,769 | | 52,273 | |
| Total interest-bearing deposits | 434,151 | | 422,323 | |
| Total deposits | $ | 518,309 | | $ | 512,312 | |
The maturities of time deposits outstanding at December 31, 2024 were as follows:
| | | | | |
| (Dollars in Millions) | |
| 2025 | $ | 51,876 | |
| 2026 | 2,045 | |
| 2027 | 310 | |
| 2028 | 149 | |
| 2029 | 387 | |
| Thereafter | 2 | |
| Total | $ | 54,769 | |
| | |
96 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
| | | | | | | | |
| NOTE 12 | | Short-Term Borrowings |
Short-term borrowings at December 31 consisted of the following:
| | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 |
| Federal funds purchased | $ | 252 | | $ | 248 | |
| Securities sold under agreements to repurchase | 7,642 | | 3,576 | |
| Commercial paper | 4,288 | | 7,773 | |
| Other short-term borrowings | 3,336 | | 3,682 | |
| Total | $ | 15,518 | | $ | 15,279 | |
Long-term debt (debt with original maturities of more than one year) at December 31 consisted of the following:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars in Millions) | Rate Type | Rate(a) | Maturity Date | 2024 | 2023 |
| U.S. Bancorp (Parent Company) | | | | | |
| Subordinated notes | Fixed | 3.600 | % | 2024 | $ | — | | $ | 1,000 | |
| Fixed | 7.500 | % | 2026 | 199 | | 199 | |
| Fixed | 3.100 | % | 2026 | 1,000 | | 1,000 | |
| Fixed | 3.000 | % | 2029 | 1,000 | | 1,000 | |
| Fixed | 4.967 | % | 2033 | 1,300 | | 1,300 | |
| Fixed | 2.491 | % | 2036 | 1,300 | | 1,300 | |
| Medium-term notes | Fixed | 1.375% - 6.787% | 2025 - 2039 | 27,939 | | 26,618 | |
| Floating | 3.813 | % | 2028 | 519 | | — | |
Other(b) | | | | 2,000 | | 1,915 | |
| Subtotal | | | | 35,257 | | 34,332 | |
| Subsidiaries | | | | | |
| Federal Home Loan Bank advances | Fixed | 1.860% - 8.250% | 2025 - 2027 | 12,550 | | 9,051 | |
| Floating | 5.190% - 5.210% | 2025 - 2026 | 3,000 | | 3,000 | |
| Bank notes | Fixed | 2.050% - 5.550% | 2025 - 2032 | 3,405 | | 2,289 | |
| Floating | —% - 4.588% | 2027 - 2062 | 1,813 | | 1,324 | |
Other(c) | | | | 1,977 | | 1,484 | |
| Subtotal | | | | 22,745 | | 17,148 | |
| Total | | | | $ | 58,002 | | $ | 51,480 | |
(a)Weighted-average interest rates of medium-term notes, Federal Home Loan Bank advances and bank notes were 4.40 percent, 4.63 percent and 3.08 percent, respectively.
(b)Includes $2.2 billion and $2.1 billion at December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively, of discounted noninterest-bearing additional cash received by the Company upon close of its 2022 acquisition of MUB from Mitsubishi UFJ Financial Group ("MUFG") to be delivered to MUFG on or prior to December 1, 2027, discounted at the Company’s 5-year unsecured borrowing rate as of the acquisition date, as well as debt issuance fees and unrealized gains and losses and deferred amounts relating to derivative instruments.
(c)Includes consolidated community development and tax-advantaged investment VIEs, finance lease obligations, debt issuance fees, and unrealized gains and losses and deferred amounts relating to derivative instruments.
The Company has arrangements with the Federal Home Loan Bank and Federal Reserve Bank whereby the Company could have borrowed an additional $171.2 billion and $215.8 billion at December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively.
Maturities of long-term debt outstanding at December 31, 2024, were: | | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars in Millions) | Parent Company | Consolidated |
| 2025 | $ | 2,106 | | $ | 8,199 | |
| 2026 | 3,917 | | 13,471 | |
| 2027 | 4,757 | | 10,045 | |
| 2028 | 4,402 | | 4,430 | |
| 2029 | 4,472 | | 4,480 | |
| Thereafter | 15,603 | | 17,377 | |
| Total | $ | 35,257 | | $ | 58,002 | |
| | | | | | | | |
| NOTE 14 | | Shareholders' Equity |
At December 31, 2024 and 2023, the Company had authority to issue 4 billion shares of common stock and 50 million shares of preferred stock. The Company had 1.6 billion shares of common stock outstanding at
December 31, 2024 and 2023. The Company had 59 million shares reserved for future issuances, primarily under its stock incentive plans at December 31, 2024.
The number of shares issued and outstanding and the carrying amount of each outstanding series of the Company’s preferred stock at December 31 were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2024 | 2023 |
| (Dollars in Millions) | Shares
Issued and
Outstanding | Liquidation
Preference | Discount | Carrying
Amount | Shares
Issued and
Outstanding | Liquidation
Preference | Discount | Carrying
Amount |
| Series A | 12,510 | $ | 1,251 | | $ | 145 | | $ | 1,106 | | 12,510 | $ | 1,251 | | $ | 145 | | $ | 1,106 | |
| Series B | 40,000 | 1,000 | | — | | 1,000 | | 40,000 | 1,000 | | — | | 1,000 | |
| Series J | 40,000 | 1,000 | | 7 | | 993 | | 40,000 | 1,000 | | 7 | | 993 | |
| Series K | 23,000 | 575 | | 10 | | 565 | | 23,000 | 575 | | 10 | | 565 | |
| Series L | 20,000 | 500 | | 14 | | 486 | | 20,000 | 500 | | 14 | | 486 | |
| Series M | 30,000 | 750 | | 21 | | 729 | | 30,000 | 750 | | 21 | | 729 | |
| Series N | 60,000 | 1,500 | | 8 | | 1,492 | | 60,000 | 1,500 | | 8 | | 1,492 | |
| Series O | 18,000 | 450 | | 13 | | 437 | | 18,000 | 450 | | 13 | | 437 | |
Total preferred stock(a) | 243,510 | $ | 7,026 | | $ | 218 | | $ | 6,808 | | 243,510 | $ | 7,026 | | $ | 218 | | $ | 6,808 | |
(a)The par value of all shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2024 and 2023, was $1.00 per share.
During 2022, the Company issued depositary shares representing an ownership interest in 18,000 shares of Series O Non-Cumulative Perpetual Preferred Stock with a liquidation preference of $25,000 per share (the “Series O Preferred Stock”). The Series O Preferred Stock has no stated maturity and will not be subject to any sinking fund or other obligation of the Company. Dividends, if declared, will accrue and be payable quarterly, in arrears, at a rate per annum equal to 4.50 percent. The Series O Preferred Stock is redeemable at the Company’s option, in whole or in part, on or after April 15, 2027. The Series O Preferred Stock is redeemable at the Company’s option, in whole, but not in part, prior to April 15, 2027 within 90 days following an official administrative or judicial decision, amendment to, or change in the laws or regulations that would not allow the Company to treat the full liquidation value of the Series O Preferred Stock as Tier 1 capital for purposes of the capital adequacy guidelines of the Federal Reserve Board.
During 2021, the Company issued depositary shares representing an ownership interest in 60,000 shares of Series N Fixed Rate Reset Non-Cumulative Perpetual Preferred Stock with a liquidation preference of $25,000 per share (the “Series N Preferred Stock”). The Series N Preferred Stock has no stated maturity and will not be subject to any sinking fund or other obligation of the Company. Dividends, if declared, will accrue and be payable quarterly, in arrears, at a rate per annum equal to 3.70 percent from the date of issuance to, but excluding, January 15, 2027, and thereafter will accrue and be payable quarterly at a floating rate per annum equal to the five-year treasury rate plus 2.541 percent. The Series N Preferred Stock is redeemable at the Company’s option, in whole or in part, on or after January 15, 2027. The Series N Preferred Stock is redeemable at the Company’s option, in whole, but not in part, prior to January 15, 2027 within 90
days following an official administrative or judicial decision, amendment to, or change in the laws or regulations that would not allow the Company to treat the full liquidation value of the Series N Preferred Stock as Tier 1 capital for purposes of the capital adequacy guidelines of the Federal Reserve Board.
During 2021, the Company issued depositary shares representing an ownership interest in 30,000 shares of Series M Non-Cumulative Perpetual Preferred Stock with a liquidation preference of $25,000 per share (the “Series M Preferred Stock”). The Series M Preferred Stock has no stated maturity and will not be subject to any sinking fund or other obligation of the Company. Dividends, if declared, will accrue and be payable quarterly, in arrears, at a rate per annum equal to 4.00 percent. The Series M Preferred Stock is redeemable at the Company’s option, in whole or in part, on or after April 15, 2026. The Series M Preferred Stock is redeemable at the Company’s option, in whole, but not in part, prior to April 15, 2026 within 90 days following an official administrative or judicial decision, amendment to, or change in the laws or regulations that would not allow the Company to treat the full liquidation value of the Series M Preferred Stock as Tier 1 capital for purposes of the capital adequacy guidelines of the Federal Reserve Board.
During 2020, the Company issued depositary shares representing an ownership interest in 20,000 shares of Series L Non-Cumulative Perpetual Preferred Stock with a liquidation preference of $25,000 per share (the “Series L Preferred Stock”). The Series L Preferred Stock has no stated maturity and will not be subject to any sinking fund or other obligation of the Company. Dividends, if declared, will accrue and be payable quarterly, in arrears, at a rate per annum equal to 3.75 percent. The Series L Preferred Stock is redeemable at the Company’s option, in whole or in part, on or after January 15, 2026. The Series L Preferred
| | |
98 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
Stock is redeemable at the Company’s option, in whole, but not in part, prior to January 15, 2026 within 90 days following an official administrative or judicial decision, amendment to, or change in the laws or regulations that would not allow the Company to treat the full liquidation value of the Series L Preferred Stock as Tier 1 capital for purposes of the capital adequacy guidelines of the Federal Reserve Board.
During 2018, the Company issued depositary shares representing an ownership interest in 23,000 shares of Series K Non-Cumulative Perpetual Preferred Stock with a liquidation preference of $25,000 per share (the “Series K Preferred Stock”). The Series K Preferred Stock has no stated maturity and will not be subject to any sinking fund or other obligation of the Company. Dividends, if declared, will accrue and be payable quarterly, in arrears, at a rate per annum equal to 5.50 percent. The Series K Preferred Stock is redeemable at the Company’s option, in whole or in part.
During 2017, the Company issued depositary shares representing an ownership interest in 40,000 shares of Series J Non-Cumulative Perpetual Preferred Stock with a liquidation preference of $25,000 per share (the “Series J Preferred Stock”). The Series J Preferred Stock has no stated maturity and will not be subject to any sinking fund or other obligation of the Company. Dividends, if declared, will accrue and be payable semiannually, in arrears, at a rate per annum equal to 5.30 percent from the date of issuance to, but excluding, April 15, 2027, and thereafter will accrue and be payable quarterly at a floating rate per annum equal to 2.914 percent above the three-month CME Term Secured Overnight Financing Rate (“SOFR”) plus a credit spread adjustment of 0.26161 percent. The Series J Preferred Stock is redeemable at the Company’s option, in whole or in part, on or after April 15, 2027. The Series J Preferred Stock is redeemable at the Company’s option, in whole, but not in part, prior to April 15, 2027 within 90 days following an official administrative or judicial decision, amendment to, or change in the laws or regulations that would not allow the Company to treat the full liquidation value of the Series J Preferred Stock as Tier 1 capital for purposes of the capital adequacy guidelines of the Federal Reserve Board.
During 2010, the Company issued depositary shares representing an ownership interest in 5,746 shares of Series A Non-Cumulative Perpetual Preferred Stock (the “Series A Preferred Stock”) to investors, in exchange for their portion of USB Capital IX Income Trust Securities. During 2011, the Company issued depositary shares representing an ownership interest in 6,764 shares of
Series A Preferred Stock to USB Capital IX, thereby settling the stock purchase contract established between the Company and USB Capital IX as part of the 2006 issuance of USB Capital IX Income Trust Securities. The preferred shares were issued to USB Capital IX for the purchase price specified in the stock forward purchase contract. The Series A Preferred Stock has a liquidation preference of $100,000 per share, no stated maturity and will not be subject to any sinking fund or other obligation of the Company. Dividends, if declared, will accrue and be payable quarterly, in arrears, at a rate per annum equal to the greater of 1.02 percent above three-month CME Term SOFR plus a credit spread adjustment of 0.26161 percent, or 3.50 percent. The Series A Preferred Stock is redeemable at the Company’s option, subject to prior approval by the Federal Reserve Board.
During 2006, the Company issued depositary shares representing an ownership interest in 40,000 shares of Series B Non-Cumulative Perpetual Preferred Stock with a liquidation preference of $25,000 per share (the “Series B Preferred Stock”). The Series B Preferred Stock has no stated maturity and will not be subject to any sinking fund or other obligation of the Company. Dividends, if declared, will accrue and be payable quarterly, in arrears, at a rate per annum equal to the greater of 0.60 percent above three-month CME Term SOFR plus a credit spread adjustment of 0.26161 percent, or 3.50 percent. The Series B Preferred Stock is redeemable at the Company’s option, subject to the prior approval of the Federal Reserve Board.
During 2024, 2023 and 2022, the Company repurchased shares of its common stock under various authorizations approved by its Board of Directors. As of December 31, 2024, the approximate dollar value of shares that may yet be purchased by the Company under the current Board of Directors approved authorization was $4.9 billion. Share repurchases are subject to the approval of the Company's Board of Directors and compliance with regulatory requirements.
The following table summarizes the Company’s common stock repurchased in each of the last three years:
| | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars and Shares in Millions) | Shares | Value |
| 2024 | 4 | $ | 173 | |
| 2023 | 1 | 62 | |
| 2022 | 1 | 69 | |
Shareholders’ equity is affected by transactions and valuations of asset and liability positions that require adjustments to accumulated other comprehensive income (loss). The reconciliation of the transactions affecting accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) included in shareholders’ equity for the years ended December 31, is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars in Millions) | Unrealized Gains (Losses) on Investment Securities Available-For-Sale | Unrealized Gains (Losses) on Investment Securities Transferred From Available-For-Sale to Held-To-Maturity | Unrealized Gains (Losses) on Derivative Hedges | Unrealized Gains (Losses) on Retirement Plans | Debit Valuation Adjustments | Foreign Currency Translation | Total |
| 2024 | | | | | | | |
| Balance at beginning of period | $ | (5,151) | | $ | (3,537) | | $ | (242) | | $ | (1,138) | | $ | — | | $ | (28) | | $ | (10,096) | |
| Changes in unrealized gains (losses) | (60) | | — | | (676) | | 245 | | 1 | | — | | (490) | |
| | | | | | | |
Foreign currency translation adjustment(a) | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | 18 | | 18 | |
| Reclassification to earnings of realized (gains) losses | 154 | | 499 | | 258 | | (1) | | — | | — | | 910 | |
| Applicable income taxes | (21) | | (127) | | 107 | | (61) | | — | | (4) | | (106) | |
| Balance at end of period | $ | (5,078) | | $ | (3,165) | | $ | (553) | | $ | (955) | | $ | 1 | | $ | (14) | | $ | (9,764) | |
| 2023 | | | | | | | |
| Balance at beginning of period | $ | (6,378) | | $ | (3,933) | | $ | (114) | | $ | (939) | | $ | — | | $ | (43) | | $ | (11,407) | |
| Changes in unrealized gains (losses) | 1,500 | | — | | (252) | | (262) | | — | | — | | 986 | |
| | | | | | | |
Foreign currency translation adjustment(a) | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | 21 | | 21 | |
| Reclassification to earnings of realized (gains) losses | 145 | | 530 | | 80 | | (7) | | — | | — | | 748 | |
| Applicable income taxes | (418) | | (134) | | 44 | | 70 | | — | | (6) | | (444) | |
| Balance at end of period | $ | (5,151) | | $ | (3,537) | | $ | (242) | | $ | (1,138) | | $ | — | | $ | (28) | | $ | (10,096) | |
| 2022 | | | | | | | |
| Balance at beginning of period | $ | 540 | | $ | (935) | | $ | (85) | | $ | (1,426) | | $ | — | | $ | (37) | | $ | (1,943) | |
| Changes in unrealized gains and losses | (13,656) | | — | | (75) | | 526 | | — | | — | | (13,205) | |
| Transfer of securities from available-for-sale to held-to-maturity | 4,413 | | (4,413) | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | |
Foreign currency translation adjustment(a) | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | (10) | | (10) | |
| Reclassification to earnings of realized (gains) losses | (20) | | 400 | | 36 | | 128 | | — | | — | | 544 | |
| Applicable income taxes | 2,345 | | 1,015 | | 10 | | (167) | | — | | 4 | | 3,207 | |
| Balance at end of period | $ | (6,378) | | $ | (3,933) | | $ | (114) | | $ | (939) | | $ | — | | $ | (43) | | $ | (11,407) | |
(a)Represents the impact of changes in foreign currency exchange rates on the Company’s investment in foreign operations and related hedges.
| | |
100 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
Additional detail about the impact to net income for items reclassified out of accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) and into earnings for the years ended December 31 is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Impact to Net Income | Affected Line Item in the Consolidated Statement of Income |
| (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 |
| Unrealized gains (losses) on investment securities available-for-sale | | | | |
| Realized gains (losses) on sales of investment securities | $ | (154) | | $ | (145) | | $ | 20 | | Securities gains (losses), net |
| 39 | | 37 | | (5) | | Applicable income taxes |
| (115) | | (108) | | 15 | | Net-of-tax |
| Unrealized gains (losses) on investment securities transferred from available-for-sale to held-to-maturity | | | | |
| Amortization of unrealized gains (losses) | (499) | | (530) | | (400) | | Interest income |
| 127 | | 134 | | 119 | | Applicable income taxes |
| (372) | | (396) | | (281) | | Net-of-tax |
| Unrealized gains (losses) on derivative hedges | | | | |
| Realized gains (losses) on derivative hedges | (258) | | (80) | | (36) | | Net interest income |
| 66 | | 21 | | 9 | | Applicable income taxes |
| (192) | | (59) | | (27) | | Net-of-tax |
| Unrealized gains (losses) on retirement plans | | | | |
| Actuarial gains (losses) and prior service cost (credit) amortization | 1 | | 7 | | (128) | | Other noninterest expense |
| — | | (2) | | 33 | | Applicable income taxes |
| 1 | | 5 | | (95) | | Net-of-tax |
| Total impact to net income | $ | (678) | | $ | (558) | | $ | (388) | | |
Regulatory Capital The Company uses certain measures defined by bank regulatory agencies to assess its capital. The regulatory capital requirements effective for the Company follow Basel III, with the Company being subject to calculating its capital adequacy as a percentage of risk-weighted assets under the standardized approach.
Tier 1 capital is considered core capital and includes common shareholders’ equity adjusted for the aggregate impact of certain items included in other comprehensive income (loss) (“common equity tier 1 capital”), plus qualifying preferred stock, trust preferred securities and noncontrolling interests in consolidated subsidiaries subject to certain limitations. Total risk-based capital includes Tier 1 capital and other items such as subordinated debt and the allowance for credit losses. Capital measures are stated as a percentage of risk-weighted assets, which are measured based on their perceived credit risks and include certain off-balance sheet exposures, such as unfunded loan
commitments, letters of credit, and derivative contracts. Beginning in 2022, the Company began to phase into its regulatory capital requirements the cumulative deferred impact of its 2020 adoption of the accounting guidance related to the impairment of financial instruments based on the CECL methodology plus 25 percent of its quarterly credit reserve increases during 2020 and 2021. This cumulative deferred impact was phased into the Company’s regulatory capital during 2022 through 2024, culminating with a fully phased in regulatory capital calculation beginning in 2025.
The Company is also subject to leverage ratio requirements, which is defined as Tier 1 capital as a percentage of adjusted average assets under the standardized approach and Tier 1 capital as a percentage of total on- and off-balance sheet leverage exposure under more risk-sensitive advanced approaches.
The following table provides a summary of the regulatory capital requirements in effect, along with the actual components and ratios for the Company and its bank subsidiaries:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| U.S. Bancorp | U.S. Bank National Association |
| At December 31 (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 | 2024 | 2023 |
| Basel III Standardized Approach: | | | | |
| Common equity tier 1 capital | $ | 47,877 | | $ | 44,947 | | $ | 59,866 | | $ | 58,194 | |
| Tier 1 capital | 55,129 | | 52,199 | | 60,311 | | 58,638 | |
| Total risk-based capital | 64,375 | | 61,921 | | 69,947 | | 68,817 | |
| Risk-weighted assets | 450,498 | | 453,390 | | 443,426 | | 445,829 | |
| Common equity tier 1 capital as a percent of risk-weighted assets | 10.6 | % | 9.9 | % | 13.5 | % | 13.1 | % |
| Tier 1 capital as a percent of risk-weighted assets | 12.2 | | 11.5 | | 13.6 | | 13.2 | |
| Total risk-based capital as a percent of risk-weighted assets | 14.3 | | 13.7 | | 15.8 | | 15.4 | |
| Tier 1 capital as a percent of adjusted quarterly average assets (leverage ratio) | 8.3 | | 8.1 | | 9.3 | | 9.2 | |
| Tier 1 capital as a percent of total on- and off-balance sheet leverage exposure (total leverage exposure ratio) | 6.8 | | 6.6 | | 7.6 | | 7.5 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| U.S. Bancorp | U.S. Bank National Association |
| December 31, 2024 | Minimum(a) | Well- Capitalized | Minimum(a) | Well- Capitalized |
| Bank Regulatory Capital Requirements | | | | |
| Common equity tier 1 capital as a percent of risk-weighted assets | 7.6 | % | 6.5 | % | 7.0 | % | 6.5 | % |
| Tier 1 capital as a percent of risk-weighted assets | 9.1 | | 8.0 | | 8.5 | | 8.0 | |
| Total risk-based capital as a percent of risk-weighted assets | 11.1 | | 10.0 | | 10.5 | | 10.0 | |
| Tier 1 capital as a percent of adjusted quarterly average assets (leverage ratio) | 4.0 | | 5.0 | | 4.0 | | 5.0 | |
Tier 1 capital as a percent of total on- and off-balance sheet leverage exposure (total leverage exposure ratio)(b) | 3.0 | | | 3.0 | | 3.0 | |
(a)The minimum common equity tier 1 capital, tier 1 capital and total risk-based capital ratio requirements reflect a capital conservation buffer. Banks and financial services holding companies must maintain minimum capital levels, including a capital conservation buffer, to avoid limitations on capital distributions and certain discretionary compensation payments. At December 31, 2024, U.S. Bancorp had a capital conservation buffer requirement of 3.1 percent, resulting from the Federal Reserve’s stress capital buffer requirement determined during its 2024 stress testing process, while U.S. Bank National Association had a capital conservation buffer requirement of 2.5 percent. U.S. Bancorp and U.S. Bank National Association were both subject to a capital conservation buffer requirement of 2.5 percent at December 31, 2023.
(b)A minimum "well-capitalized" threshold does not apply to U.S. Bancorp for this ratio as it is not formally defined under applicable banking regulations for bank holding companies.
Noncontrolling interests principally represent third-party investors’ interests in consolidated entities, including preferred stock of consolidated subsidiaries. During 2006, the Company’s banking subsidiary formed USB Realty Corp., a real estate investment trust, for the purpose of issuing 5,000 shares of Fixed-to-Floating Rate Exchangeable Non-cumulative Perpetual Series A Preferred Stock with a liquidation preference of $100,000 per share (“Series A Preferred Securities”) to third-party investors. Dividends on the Series A Preferred Securities, if declared, will accrue and be payable quarterly, in arrears, at a rate per annum equal to 1.147 percent above three-month CME Term SOFR plus a credit spread adjustment of 0.26161 percent. If USB Realty Corp. has not declared a dividend on the Series A Preferred Securities before the dividend payment date for any dividend period, such dividend shall not be cumulative and shall cease to accrue and be payable, and USB Realty Corp. will have no obligation to pay dividends accrued for such dividend period, whether or not dividends on the Series A Preferred Securities are declared for any future dividend period.
The Series A Preferred Securities will be redeemable, in whole or in part, at the option of USB Realty Corp. on each fifth anniversary after the dividend payment date occurring in January 2012. Any redemption will be subject to the approval of the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (“OCC”). During 2016, the Company purchased 500 shares of the Series A Preferred Securities held by third-party investors. As of December 31, 2024, 4,500 shares of the Series A Preferred Securities remain outstanding.
| | |
102 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
| | | | | | | | |
| NOTE 15 | | Earnings Per Share |
The components of earnings per share were:
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Year Ended December 31 (Dollars and Shares in Millions, Except Per Share Data) | 2024 | 2023 | | 2022 |
| Net income attributable to U.S. Bancorp | $ | 6,299 | | $ | 5,429 | | | $ | 5,825 | |
| Preferred dividends | (352) | | (350) | | | (296) | |
| | | | |
| Earnings allocated to participating stock awards | (38) | | (28) | | | (28) | |
| Net income applicable to U.S. Bancorp common shareholders | $ | 5,909 | | $ | 5,051 | | | $ | 5,501 | |
| Average common shares outstanding | 1,560 | | 1,543 | | | 1,489 | |
| Net effect of the exercise and assumed purchase of stock awards | 1 | | — | | | 1 | |
| Average diluted common shares outstanding | 1,561 | | 1,543 | | | 1,490 | |
| Earnings per common share | $ | 3.79 | | $ | 3.27 | | | $ | 3.69 | |
| Diluted earnings per common share | $ | 3.79 | | $ | 3.27 | | | $ | 3.69 | |
Options outstanding at December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, to purchase 1 million, 3 million and 1 million common shares, respectively, were not included in the computation of diluted earnings per share for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, because they were antidilutive.
Employee Retirement Savings Plan The Company has a defined contribution retirement savings plan that covers substantially all its employees. Qualified employees are allowed to contribute up to 75 percent of their annual compensation, subject to Internal Revenue Service limits, through salary deductions under Section 401(k) of the Internal Revenue Code. Employee contributions are invested at their direction among a variety of investment alternatives. Employee contributions are 100 percent matched by the Company, up to four percent of each employee’s eligible annual compensation. The Company’s matching contribution vests immediately and is invested in the same manner as each employee’s future contribution elections. Total expense for the Company’s matching contributions was $262 million, $254 million and $211 million in 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively.
Pension and Postretirement Welfare Plans The Company has tax qualified noncontributory defined benefit pension plans, nonqualified pension plans and postretirement welfare plans.
Pension Plans The funded tax qualified noncontributory defined benefit pension plans provide benefits to substantially all the Company’s employees. Participants receive annual cash balance pay credits based on eligible
pay multiplied by a percentage determined by their age and/or years of service, as defined by the plan documents. Participants also receive an annual interest credit. Generally, employees become vested upon completing three years of vesting service. The Company did not contribute to its qualified pension plans in 2024 and 2023 and does not expect to contribute to the plans in 2025.
The Company also maintains two non-qualified plans that are unfunded and provide benefits to certain employees. The assumptions used in computing the accumulated benefit obligation, the projected benefit obligation and net pension expense are substantially consistent with those assumptions used for the funded qualified plans. In 2025, the Company expects to contribute approximately $49 million to its non-qualified pension plans, which equals the 2025 expected benefit payments.
Postretirement Welfare Plans In addition to providing pension benefits, the Company has a funded postretirement welfare plan available to certain eligible participants based on their hire or retirement date. The plan is closed to new participants. In 2025, the Company does not expect to contribute to its postretirement welfare plan.
The following table summarizes the changes in benefit obligations and plan assets for the years ended December 31, and the funded status and amounts recognized in the Consolidated Balance Sheet at December 31 for the pension plans:
| | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 |
Change In Projected Benefit Obligation(a) | | |
| Benefit obligation at beginning of measurement period | $ | 7,278 | | $ | 6,617 | |
| Service cost | 219 | | 223 | |
| Interest cost | 376 | | 370 | |
| | |
| Plan amendments | — | | (23) | |
| Actuarial (gain) loss | (443) | | 398 | |
| Lump sum settlements | (118) | | (94) | |
| Benefit payments | (243) | | (213) | |
Benefit obligation at end of measurement period(b) | $ | 7,069 | | $ | 7,278 | |
| Change In Fair Value Of Plan Assets | | |
| Fair value at beginning of measurement period | $ | 7,779 | | $ | 7,375 | |
| Actual return on plan assets | 381 | | 658 | |
| Employer contributions | 35 | | 28 | |
| | |
| Lump sum settlements | (118) | | (94) | |
| Benefit payments | (243) | | (213) | |
Acquisitions(c) | — | | 25 | |
| Fair value at end of measurement period | $ | 7,834 | | $ | 7,779 | |
| Funded Status | $ | 765 | | $ | 501 | |
| Components Of The Consolidated Balance Sheet | | |
| Noncurrent benefit asset | $ | 1,329 | | $ | 1,072 | |
| Current benefit liability | (48) | | (26) | |
| Noncurrent benefit liability | (516) | | (545) | |
| Recognized amount | $ | 765 | | $ | 501 | |
| Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss), Pretax | | |
| Net actuarial loss | $ | (1,359) | | $ | (1,607) | |
| Net prior service credit | 30 | | 34 | |
| Recognized amount | $ | (1,329) | | $ | (1,573) | |
Note: At December 31, 2024 and 2023, the postretirement welfare plans projected benefit obligation was $41 million and $49 million, respectively, the fair value of plan assets was $47 million and $45 million, respectively, and the amount recognized in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss), pretax was $51 million and $52 million, respectively.
(a)The decrease in the projected benefit obligation for 2024 was primarily due to a higher discount rate and the increase for 2023 was primarily due to a lower discount rate.
(b)At December 31, 2024 and 2023, the accumulated benefit obligation for all pension plans was $6.6 billion and $6.8 billion, respectively.
(c)The increase in 2023 plan assets was related to the 2022 MUB acquisition.
The following table provides information for pension plans with benefit obligations in excess of plan assets at December 31:
| | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 |
| Plans with Projected Benefit Obligations in Excess of Plan Assets | | |
| Projected benefit obligation | $ | 564 | | $ | 571 | |
| Fair value of plan assets | — | | — | |
| Plans with Accumulated Benefit Obligations in Excess of Plan Assets | | |
| Accumulated benefit obligation | $ | 525 | | $ | 530 | |
| Fair value of plan assets | — | | — | |
| | |
104 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
The following table sets forth the components of net periodic pension cost and other amounts recognized in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) for the years ended December 31 for the pension plans:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 |
| Components Of Net Periodic Pension Cost | | | |
| Service cost | $ | 219 | | $ | 223 | | $ | 280 | |
| Interest cost | 376 | | 370 | | 248 | |
| Expected return on plan assets | (585) | | (546) | | (481) | |
| Prior service credit amortization | (4) | | (1) | | (2) | |
| Actuarial loss amortization | 9 | | 5 | | 140 | |
| Net periodic pension cost | $ | 15 | | $ | 51 | | $ | 185 | |
| Other Changes In Plan Assets And Benefit Obligations Recognized In Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) | | | |
| Net actuarial (loss) gain arising during the year | $ | 239 | | $ | (286) | | $ | 523 | |
| Net actuarial loss amortized during the year | 9 | | 5 | | 140 | |
| Net prior service credit (cost) arising during the year | — | | 23 | | (2) | |
| Net prior service credit amortized during the year | (4) | | (1) | | (2) | |
| Total recognized in other comprehensive income (loss) | $ | 244 | | $ | (259) | | $ | 659 | |
| Total recognized in net periodic pension cost and other comprehensive income (loss) | $ | 229 | | $ | (310) | | $ | 474 | |
Note: The net periodic benefit for the postretirement welfare plans was $7 million, $10 million and $9 million for the years end December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively. The total of other amounts recognized as other comprehensive loss was $1 million, $10 million and $5 million for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively.The following table sets forth weighted-average assumptions used to determine the pension plans projected benefit obligations at December 31:
| | | | | | | | |
| 2024 | 2023 |
| Discount rate | 5.77 | % | 5.12 | % |
| Cash balance interest crediting rate | 3.71 | | 3.04 | |
Rate of compensation increase(a) | 3.52 | | 3.72 | |
(a)Determined on an active liability-weighted basis.
The following table sets forth weighted-average assumptions used to determine net periodic pension cost for the years ended December 31:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2024 | 2023 | 2022 |
| Discount rate | 5.12 | % | 5.55 | % | 3.00 | % |
| Cash balance interest crediting rate | 3.04 | | 3.36 | | 3.00 | |
Expected return on plan assets(a) | 7.00 | | 6.75 | | 6.50 | |
Rate of compensation increase(b) | 3.72 | | 4.13 | | 3.56 | |
(a)With the help of an independent pension consultant, the Company considers several sources when developing its expected long-term rates of return on plan assets assumptions, including, but not limited to, past returns and estimates of future returns given the plans' asset allocation, economic conditions, and peer group long-term rate of return information. The Company determines its expected long-term rates of return reflecting current economic conditions and plan assets.
(b)Determined on an active liability-weighted basis.
Investment Policies and Asset Allocation In establishing its investment policies and asset allocation strategies, the Company considers expected returns and the volatility associated with different strategies. An independent consultant performs modeling that projects numerous outcomes using a broad range of possible scenarios, including a mix of possible rates of inflation and economic growth. Starting with current economic information, the model bases its projections on past relationships between inflation, fixed income rates and equity returns when these types of economic conditions have existed over the previous 30 years, both in the United States and in foreign countries. Estimated future returns and other actuarially determined adjustments are also considered in calculating the estimated return on assets.
Generally, based on historical performance of the various investment asset classes, investments in equities have outperformed other investment classes but are
subject to higher volatility. In an effort to minimize volatility, while recognizing the long-term up-side potential of investing in equities, the Company’s Compensation and Human Resources Committee has determined that a target asset allocation of 35 percent long duration bonds, 30 percent global equities, 10 percent real assets, 10 percent private equity funds, 5 percent domestic mid-small cap equities, 5 percent emerging markets equities, and 5 percent hedge funds is appropriate.
At both December 31, 2024 and 2023, plan assets included an asset management arrangement with a related party totaling approximately $63 million.
In addition to cash and cash equivalents, the qualified pension plans invest in funds that do not have readily determinable fair values. These funds are valued based on net asset values provided by the fund trustee or administrator as a practical expedient.
The following table summarizes the pension plans investment assets at December 31:
| | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 |
| Cash and cash equivalents | $ | 63 | | $ | 68 | |
| Collective investment funds | | |
| Domestic equity securities | 1,788 | | 1,546 | |
| Mid-small cap equity securities | 474 | | 406 | |
| International equity securities | 968 | | 981 | |
| Real estate securities | 171 | | 142 | |
| Fixed income | 1,958 | | 2,295 | |
Real estate funds(a) | 733 | | 746 | |
Hedge funds(b) | 354 | | 412 | |
Private equity funds(c) | 1,325 | | 1,183 | |
| Total plan investment assets at fair value | $ | 7,834 | | $ | 7,779 | |
(a)This category consists of several investment strategies diversified across several real estate managers.
(b)This category consists of several investment strategies diversified across several hedge fund managers.
(c)This category consists of several investment strategies diversified across several private equity fund managers.
The following benefit payments are expected to be paid from the pension plans for the years ended December 31:
| | | | | |
| (Dollars in Millions) | |
| 2025 | $ | 386 | |
| 2026 | 394 | |
| 2027 | 428 | |
| 2028 | 451 | |
| 2029 | 470 | |
| 2030-2034 | 2,623 | |
| | |
106 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
| | | | | | | | |
| NOTE 17 | | Stock-Based Compensation |
As part of its employee and director compensation programs, the Company currently may grant certain stock awards under the provisions of its stock incentive plan. The plan provides for grants of options to purchase shares of common stock at a fixed price equal to the fair value of the underlying stock at the date of grant. Option grants are generally exercisable up to ten years from the date of grant. In addition, the plan provides for grants of shares of common stock or stock units that are subject to restriction on transfer prior to vesting. Most stock and unit awards vest over three to five years and are subject to forfeiture if
certain vesting requirements are not met. Stock incentive plans of acquired companies are generally terminated at the merger closing dates. Participants under such plans receive the Company’s common stock, options to buy the Company’s common stock, or long term cash incentives, based on the conversion terms of the various merger agreements. At December 31, 2024, there were 46 million shares (subject to adjustment for forfeitures) available for grant under the Company’s stock incentive plan.
Stock Option Awards
The following is a summary of stock options outstanding and exercised under prior and existing stock incentive plans of the Company:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31 | Stock
Options/Shares | Weighted- Average Exercise Price | Weighted-Average Remaining Contractual Term | Aggregate Intrinsic Value (in millions) |
| | | | | |
| 2024 | | | | |
| Number outstanding at beginning of period | 2,838,285 | | $ | 45.28 | | | |
| Exercised | (769,636) | | 42.04 | | | |
Cancelled(a) | (20,402) | | 46.15 | | | |
Number outstanding at end of period(b) | 2,048,247 | | $ | 46.49 | | 1.4 | $ | 3 | |
| Exercisable at end of period | 2,048,247 | | $ | 46.49 | | 1.4 | $ | 3 | |
| 2023 | | | | |
| Number outstanding at beginning of period | 3,253,090 | | $ | 44.42 | | | |
| Exercised | (399,329) | | 38.15 | | | |
Cancelled(a) | (15,476) | | 47.88 | | | |
Number outstanding at end of period(b) | 2,838,285 | | $ | 45.28 | | 2.0 | $ | — | |
| Exercisable at end of period | 2,838,285 | | $ | 45.28 | | 2.0 | $ | — | |
| 2022 | | | | |
| Number outstanding at beginning of period | 3,890,131 | | $ | 42.58 | | | |
| Exercised | (624,729) | | 32.87 | | | |
Cancelled(a) | (12,312) | | 50.97 | | | |
Number outstanding at end of period(b) | 3,253,090 | | $ | 44.42 | | 2.7 | $ | — | |
| Exercisable at end of period | 3,253,090 | | $ | 44.42 | | 2.7 | $ | — | |
Note: The Company did not grant any stock option awards during 2024, 2023, and 2022.
(a)Options cancelled include both non-vested (i.e., forfeitures) and vested options.
(b)Outstanding options include stock-based awards that may be forfeited in future periods. The impact of the estimated forfeitures is reflected in compensation expense.
Stock-based compensation expense is based on the estimated fair value of the award at the date of grant or modification. The fair value of each option award is estimated on the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model, requiring the use of subjective assumptions. Because employee stock options have characteristics that differ from those of traded options,
including vesting provisions and trading limitations that impact their liquidity, the determined value used to measure compensation expense may vary from the actual fair value of the employee stock options. To satisfy option exercises, the Company predominantly uses treasury stock.
The following summarizes certain stock option activity of the Company:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31 (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 |
| Fair value of options vested | $ | — | | $ | — | | $ | — | |
| Intrinsic value of options exercised | 3 | | 2 | | 15 | |
| Cash received from options exercised | 32 | | 15 | | 21 | |
| Tax benefit realized from options exercised | 1 | | 1 | | 4 | |
Additional information regarding stock options outstanding as of December 31, 2024, is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Outstanding Options | Exercisable Options |
| Range of Exercise Prices | Shares | Weighted- Average Remaining Contractual Life (Years) | Weighted- Average Exercise Price | Shares | Weighted- Average Exercise Price |
| $35.01—$40.00 | 915,364 | 1.1 | $ | 39.49 | | 915,364 | $ | 39.49 | |
| $40.01—$45.00 | 299,092 | 0.1 | 44.30 | | 299,092 | 44.30 | |
| $45.01—$50.00 | — | — | — | — | — | |
| $50.01—$55.01 | 833,791 | 2.1 | 54.96 | | 833,791 | 54.96 | |
| | 2,048,247 | 1.4 | $ | 46.49 | | 2,048,247 | $ | 46.49 | |
Restricted Stock and Unit Awards
A summary of the status of the Company’s restricted shares of stock and unit awards is presented below:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 |
| Year Ended December 31 | Shares | Weighted-Average Grant-Date Fair Value | Shares | Weighted-Average Grant-Date Fair Value | Shares | Weighted-Average Grant-Date Fair Value |
| Outstanding at beginning of period | 8,316,571 | | $ | 48.42 | | 6,880,826 | | $ | 52.59 | | 6,812,753 | | $ | 51.04 | |
| Granted | 6,107,976 | | 42.12 | | 5,565,634 | | 45.87 | | 4,109,793 | | 55.62 | |
| Vested | (4,680,480) | | 48.52 | | (3,872,874) | | 52.05 | | (3,690,666) | | 52.88 | |
| Cancelled | (502,680) | | 44.06 | | (257,015) | | 50.00 | | (351,054) | | 54.95 | |
| Outstanding at end of period | 9,241,387 | | $ | 44.45 | | 8,316,571 | | $ | 48.42 | | 6,880,826 | | $ | 52.59 | |
The total fair value of shares vested was $208 million, $180 million and $198 million for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively. Stock-based compensation expense was $232 million, $224 million and $202 million for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively. On an after-tax basis, stock-based compensation was $173 million, $167 million
and $152 million for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively. As of December 31, 2024, there was $169 million of total unrecognized compensation cost related to nonvested share-based arrangements granted under the plans. That cost is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of 1.8 years as compensation expense.
| | |
108 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
The components of income tax expense were:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31 (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 |
| Federal | | | |
| Current | $ | 1,272 | | $ | 1,434 | | $ | 1,366 | |
| Deferred | (6) | | (326) | | (108) | |
| Federal income tax | 1,266 | | 1,108 | | 1,258 | |
| State | | | |
| Current | 279 | | 482 | | 401 | |
| Deferred | 35 | | (183) | | (196) | |
| State income tax | 314 | | 299 | | 205 | |
| Total income tax provision | $ | 1,580 | | $ | 1,407 | | $ | 1,463 | |
A reconciliation of expected income tax expense at the federal statutory rate of 21 percent to the Company’s applicable income tax expense follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31 (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 |
| Tax at statutory rate | $ | 1,661 | | $ | 1,442 | | $ | 1,533 | |
| State income tax, at statutory rates, net of federal tax benefit | 385 | | 322 | | 305 | |
| Tax effect of | | | |
| Tax credits and benefits, net of related expenses | (393) | | (272) | | (273) | |
| Tax-exempt income | (144) | | (142) | | (121) | |
| Exam Resolutions | (106) | | (35) | | — | |
Revaluation of tax related assets and liabilities(a) | (8) | | 15 | | (79) | |
| Nondeductible legal and regulatory expenses | 57 | | 76 | | 37 | |
| Other items | 128 | | 1 | | 61 | |
| Applicable income taxes | $ | 1,580 | | $ | 1,407 | | $ | 1,463 | |
(a)The 2022 acquisition of MUB resulted in an increase in the Company’s state effective tax rate, requiring the Company to revalue its state deferred tax assets and liabilities. As a result of this revaluation, the Company recorded an estimated net tax benefit of $79 million during 2022.
The tax effects of fair value adjustments on securities available-for-sale, derivative instruments in cash flow hedges, foreign currency translation adjustments, and pension and post-retirement plans are recorded directly to shareholders’ equity as part of other comprehensive income (loss).
In preparing its tax returns, the Company is required to interpret complex tax laws and regulations and utilize income and cost allocation methods to determine its taxable income. On an ongoing basis, the Company is subject to examinations by federal, state, local and foreign taxing authorities that may give rise to differing
interpretations of these complex laws, regulations and methods. Due to the nature of the examination process, it generally takes years before these examinations are completed and matters are resolved. Federal tax examinations for all years ending through December 31, 2020 are completed and resolved. The Company’s tax returns for the years ended December 31, 2021 through December 31, 2022 are under examination by the Internal Revenue Service. The years open to examination by foreign, state and local government authorities vary by jurisdiction.
A reconciliation of the changes in the federal, state and foreign uncertain tax position balances are summarized as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31 (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 |
| Balance at beginning of period | $ | 350 | | $ | 513 | | $ | 487 | |
| Additions for tax positions taken in prior years | 32 | | 141 | | 35 | |
| Additions for tax positions taken in the current year | 6 | | 3 | | 3 | |
| Exam resolutions | (131) | | (302) | | (8) | |
| Statute expirations | (1) | | (5) | | (4) | |
| Balance at end of period | $ | 256 | | $ | 350 | | $ | 513 | |
The total amount of uncertain tax positions that, if recognized, would impact the effective income tax rate as of December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, were $206 million, $276 million and $294 million, respectively. The Company classifies interest and penalties related to uncertain tax positions as a component of income tax expense. At December 31, 2024, the Company’s uncertain tax position balance included $27 million of accrued interest and penalties. During the years ended December 31, 2024,
2023 and 2022 the Company recorded approximately $(13) million, $(11) million and $7 million, respectively, in interest and penalties on uncertain tax positions.
Deferred income tax assets and liabilities reflect the tax effect of estimated temporary differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities for financial reporting purposes and the amounts used for the same items for income tax reporting purposes.
The significant components of the Company’s net deferred tax asset (liability) follows:
| | | | | | | | |
| At December 31 (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 |
| Deferred Tax Assets | | |
| Securities available-for-sale and financial instruments | $ | 3,129 | | $ | 3,231 | |
| Federal, state and foreign net operating loss, credit carryforwards and other carryforwards | 2,772 | | 2,836 | |
| Allowance for credit losses | 2,086 | | 2,051 | |
| Loans | 869 | | 1,013 | |
| Accrued expenses | 767 | | 838 | |
| Obligation for operating leases | 341 | | 348 | |
| Partnerships and other investment assets | 264 | | 271 | |
| Stock compensation | 89 | | 87 | |
| Other deferred tax assets, net | 383 | | 370 | |
| Gross deferred tax assets | 10,700 | | 11,045 | |
| Deferred Tax Liabilities | | |
| Goodwill and other intangible assets | (1,362) | | (1,450) | |
| Leasing activities | (1,273) | | (1,455) | |
| Mortgage servicing rights | (789) | | (758) | |
| Right of use operating leases | (297) | | (301) | |
| Pension and postretirement benefits | (184) | | (115) | |
| Fixed assets | (28) | | (44) | |
| Other deferred tax liabilities, net | (125) | | (168) | |
| Gross deferred tax liabilities | (4,058) | | (4,291) | |
| Valuation allowance | (389) | | (364) | |
| Net Deferred Tax Asset | $ | 6,253 | | $ | 6,390 | |
The Company has approximately $3.0 billion of federal, state and foreign net operating loss carryforwards which expire at various times beginning in 2025. A substantial portion of these carryforwards relate to state-only net operating losses, for which the related deferred tax asset is subject to a full valuation allowance as the carryforwards are not expected to be realized within the carryforward period. Management has determined it is more likely than not the other net deferred tax assets could be realized through carry back to taxable income in prior years, future reversals of existing taxable temporary differences and future taxable income.
In addition, the Company has $1.2 billion of federal credit carryforwards which expire at various times through 2044 which are not subject to a valuation allowance as management believes that it is more likely than not that the credits will be utilized within the carryforward period.
At December 31, 2024, retained earnings included approximately $102 million of base year reserves of acquired thrift institutions, for which no deferred federal income tax liability has been recognized. These base year reserves would be recaptured if certain subsidiaries of the Company cease to qualify as a bank for federal income tax purposes. The base year reserves also remain subject to income tax penalty provisions that, in general, require recapture upon certain stock redemptions of, and excess distributions to, stockholders.
| | |
110 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
| | | | | | | | |
| NOTE 19 | | Derivative Instruments |
In the ordinary course of business, the Company enters into derivative transactions to manage various risks and to accommodate the business requirements of its customers. The Company recognizes all derivatives on the Consolidated Balance Sheet at fair value in other assets or in other liabilities. On the date the Company enters into a derivative contract, the derivative is designated as either a fair value hedge, cash flow hedge, net investment hedge, or a designation is not made as it is a customer-related transaction, an economic hedge for asset/liability risk management purposes or another stand-alone derivative created through the Company’s operations (“free-standing derivative”). When a derivative is designated as a fair value, cash flow or net investment hedge, the Company performs an assessment, at inception and, at a minimum, quarterly thereafter, to determine the effectiveness of the derivative in offsetting changes in the value or cash flows of the hedged item(s).
Fair Value Hedges These derivatives are interest rate swaps the Company uses to hedge the change in fair value related to interest rate changes of its underlying available-for-sale investment securities and fixed-rate debt. Changes in the fair value of derivatives designated as fair value hedges, and changes in the fair value of the hedged items, are recorded in earnings.
Cash Flow Hedges These derivatives are interest rate swaps the Company uses to hedge the forecasted cash flows from its underlying variable-rate loans and debt. Changes in the fair value of derivatives designated as cash flow hedges are recorded in other comprehensive income (loss) until the cash flows of the hedged items are realized. If a derivative designated as a cash flow hedge is terminated or ceases to be highly effective, the gain or loss in other comprehensive income (loss) is amortized to earnings over the period the forecasted hedged transactions impact earnings. If a hedged forecasted transaction is no longer probable, hedge accounting is ceased and any gain or loss included in other comprehensive income (loss) is reported in earnings immediately, unless the forecasted transaction is at least reasonably possible of occurring, whereby the amounts remain within other comprehensive income (loss). At December 31, 2024, the Company had $553 million (net-of-tax) of realized and unrealized losses on derivatives classified as cash flow hedges recorded in other comprehensive income (loss), compared with $242 million (net-of-tax) of realized and unrealized losses at December 31, 2023. The estimated amount to be reclassified from other comprehensive income (loss) into earnings during the next 12 months is a loss of $222 million
(net-of-tax). All cash flow hedges were highly effective for the year ended December 31, 2024.
Net Investment Hedges The Company uses forward commitments to sell specified amounts of certain foreign currencies, and non-derivative debt instruments, to hedge the volatility of its net investment in foreign operations driven by fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates. The carrying amount of non-derivative debt instruments designated as net investment hedges was $1.3 billion at December 31, 2024 and December 31, 2023.
Other Derivative Positions The Company enters into free-standing derivatives to mitigate interest rate risk and for other risk management purposes. These derivatives include forward commitments to sell TBAs and other commitments to sell residential mortgage loans, which are used to economically hedge the interest rate risk related to MLHFS and unfunded mortgage loan commitments. The Company also enters into interest rate swaps, swaptions, forward commitments to buy TBAs, U.S. Treasury and Eurodollar futures and options on U.S. Treasury futures to economically hedge the change in the fair value of the Company’s MSRs. The Company enters into foreign currency forwards to economically hedge remeasurement gains and losses the Company recognizes on foreign currency denominated assets and liabilities. The Company also enters into interest rate swaps as economic hedges of fair value option elected deposits and long-term debt. In addition, the Company acts as a seller and buyer of interest rate, foreign exchange and commodity contracts for its customers. The Company mitigates the market, funding and liquidity risk associated with these customer derivatives by entering into similar offsetting positions with broker-dealers, or on a portfolio basis by entering into other derivative or non-derivative financial instruments that partially or fully offset the exposure to earnings from these customer-related positions. The Company’s customer derivatives and related hedges are monitored and reviewed by the Company’s Market Risk Committee, which establishes policies for market risk management, including exposure limits for each portfolio. The Company also has derivative contracts that are created through its operations, including certain unfunded mortgage loan commitments and swap agreements related to the sale of a portion of its Class B common and preferred shares of Visa Inc. Refer to Note 22 for further information on these swap agreements. The Company uses credit derivatives to economically hedge the credit risk on its derivative positions and loan portfolios.
The following table summarizes the asset and liability management derivative positions of the Company at December 31:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2024 | 2023 |
| | Notional Value | Fair Value | Notional Value | Fair Value |
| (Dollars in Millions) | Assets | Liabilities | Assets | Liabilities |
| Fair value hedges | | | | | | |
| Interest rate contracts | | | | | | |
| Receive fixed/pay floating swaps | $ | 10,600 | | $ | — | | $ | — | | $ | 12,100 | | $ | — | | $ | 16 | |
| Pay fixed/receive floating swaps | 29,739 | | — | | — | | 24,139 | | — | | — | |
| Cash flow hedges | | | | | | |
| Interest rate contracts | | | | | | |
| Receive fixed/pay floating swaps | 28,550 | | — | | — | | 18,400 | | — | | — | |
| Net investment hedges | | | | | | |
| Foreign exchange forward contracts | 870 | | 7 | | — | | 854 | | — | | 10 | |
| Other economic hedges | | | | | | |
| Interest rate contracts | | | | | | |
| Futures and forwards | | | | | | |
| Buy | 5,436 | | 8 | | 30 | | 5,006 | | 29 | | 5 | |
| Sell | 2,711 | | 10 | | 1 | | 4,501 | | 7 | | 34 | |
| Options | | | | | | |
| Purchased | 7,810 | | 186 | | — | | 6,085 | | 237 | | — | |
| Written | 1,991 | | 8 | | 47 | | 3,696 | | 14 | | 75 | |
| Receive fixed/pay floating swaps | 9,977 | | 45 | | 23 | | 7,029 | | 9 | | 3 | |
| Pay fixed/receive floating swaps | 2,371 | | — | | — | | 3,801 | | — | | — | |
| Foreign exchange forward contracts | 702 | | 4 | | 4 | | 734 | | 2 | | 5 | |
| Equity contracts | 293 | | — | | 9 | | 227 | | 2 | | — | |
| Credit contracts | 3,558 | | — | | 29 | | 2,620 | | 1 | | — | |
Other (a) | 1,084 | | 7 | | 78 | | 2,136 | | 11 | | 93 | |
| Total | $ | 105,692 | | $ | 275 | | $ | 221 | | $ | 91,328 | | $ | 312 | | $ | 241 | |
(a)Includes derivative liability swap agreements related to the sale of a portion of the Company’s Class B common and preferred shares of Visa Inc. The Visa swap agreements had a total notional value and fair value of $1.0 billion and $78 million at December 31, 2024, respectively, compared to $2.0 billion and $91 million at December 31, 2023, respectively. In addition, includes short-term underwriting purchase and sale commitments with total notional value of $28 million at December 31, 2023.
| | |
112 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
The following table summarizes the customer-related derivative positions of the Company at December 31:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2024 | 2023 |
| | Notional Value | Fair Value | Notional Value | Fair Value |
| (Dollars in Millions) | Assets | Liabilities | Assets | Liabilities |
| Interest rate contracts | | | | | | |
| Receive fixed/pay floating swaps | $ | 413,841 | | $ | 462 | | $ | 4,485 | | $ | 363,375 | | $ | 791 | | $ | 4,395 | |
| Pay fixed/receive floating swaps | 363,837 | | 2,342 | | 153 | | 330,539 | | 1,817 | | 280 | |
Other(a) | 72,503 | | 17 | | 34 | | 82,209 | | 17 | | 51 | |
| Options | | | | | | |
| Purchased | 96,238 | | 414 | | 2 | | 102,423 | | 1,026 | | 18 | |
| Written | 90,572 | | 12 | | 574 | | 97,690 | | 20 | | 1,087 | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | |
| Foreign exchange rate contracts | | | | | | |
| Forwards, spots and swaps | 113,718 | | 2,441 | | 2,232 | | 121,119 | | 2,252 | | 1,942 | |
| Options | | | | | | |
| Purchased | 497 | | 14 | | — | | 1,532 | | 28 | | — | |
| Written | 497 | | — | | 14 | | 1,532 | | — | | 28 | |
| Commodity contracts | | | | | | |
| Swaps | 8,224 | 199 | 180 | 2,498 | 116 | 110 |
| Options | | | | | | |
| Purchased | 3,921 | 233 | 2 | 1,936 | 151 | — |
| Written | 3,921 | 3 | 233 | 1,936 | — | 151 |
| Futures | | | | | | |
| Buy | 1 | — | — | — | — | — |
| Sell | 166 | 25 | 27 | — | — | — |
| | | | | | |
| Credit contracts | 13,670 | | — | | 3 | | 13,053 | | 1 | | 6 | |
| Total | $ | 1,181,606 | | $ | 6,162 | | $ | 7,939 | | $ | 1,119,842 | | $ | 6,219 | | $ | 8,068 | |
(a)Primarily represents floating rate interest rate swaps that pay based on differentials between specified interest rate indexes.
The table below shows the effective portion of the gains (losses) recognized in other comprehensive income (loss) and the gains (losses) reclassified from other comprehensive income (loss) into earnings (net-of-tax) for the years ended December 31:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Gains (Losses) Recognized in Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) | Gains (Losses) Reclassified from Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) into Earnings |
| (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 |
| Asset and Liability Management Positions | | | | | | |
| Cash flow hedges | | | | | | |
| Interest rate contracts | $ | (503) | | $ | (187) | | $ | (56) | | $ | (192) | | $ | (59) | | $ | (27) | |
| Net investment hedges | | | | | | |
| Foreign exchange forward contracts | 121 | | (11) | | 42 | | — | | — | | — | |
| Non-derivative debt instruments | 85 | | (33) | | 59 | | — | | — | | — | |
Note: The Company does not exclude components from effectiveness testing for cash flow and net investment hedges.
The table below shows the effect of fair value and cash flow hedge accounting on the Consolidated Statement of Income for the years ended December 31:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Interest Income | Interest Expense |
| (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 |
| Total amount of income and expense line items presented in the Consolidated Statement of Income in which the effects of fair value or cash flow hedges are recorded | $ | 31,666 | | $ | 30,007 | | $ | 17,945 | | $ | 15,377 | | $ | 12,611 | | $ | 3,217 | |
| Asset and Liability Management Positions | | | | | | |
| Fair value hedges | | | | | | |
| Interest rate contract derivatives | 508 | | (430) | | 138 | | 95 | | (458) | | 482 | |
| Hedged items | (508) | | 427 | | (139) | | (98) | | 461 | | (486) | |
| Cash flow hedges | | | | | | |
| Interest rate contract derivatives | (230) | | (52) | | — | | 28 | | 28 | | — | |
Note: The Company does not exclude components from effectiveness testing for fair value and cash flow hedges. The Company reclassified losses of $28 million, $28 million and $36 million into earnings during the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively, as a result of realized cash flows on discontinued cash flow hedges. No amounts were reclassified into earnings on discontinued cash flow hedges because it is probable the original hedged forecasted cash flows will not occur.
The table below shows cumulative hedging adjustments and the carrying amount of assets and liabilities currently designated in fair value hedges at December 31:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Carrying Amount of the Hedged Assets and Liabilities | Cumulative Hedging Adjustment |
| (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 | 2024 | 2023 |
| Line Item in the Consolidated Balance Sheet | | | | |
Available-for-sale investment securities(a) | $ | 29,005 | | $ | 23,924 | | $ | (464) | | $ | (93) | |
| Long-term debt | 10,632 | | 12,034 | | 39 | | (32) | |
Note: The table above excludes the cumulative hedging adjustment related to discontinued hedging relationships on available-for-sale investment securities and long-term debt of $(72) million and $(149) million, respectively, at December 31, 2024, compared with $(18) million and $(116) million at December 31, 2023, respectively. The carrying amount of available-for-sale investment securities and long-term debt related to discontinued hedging relationships was $6.8 billion and $14.9 billion, respectively, at December 31, 2024, compared with $830 million and $7.2 billion at December 31, 2023, respectively.
(a)Includes amounts related to available-for-sale investment securities currently designated as the hedged item in a fair value hedge using the portfolio layer method. At December 31, 2024, the amortized cost of the closed portfolios used in these hedging relationships was $17.5 billion, of which $11.6 billion was designated as hedged. At December 31, 2024, the cumulative amount of basis adjustments associated with these hedging relationships was $13 million. At December 31, 2023, the amortized cost of the closed portfolios used in these hedging relationships was $15.6 billion, of which $9.6 billion was designated as hedged. At December 31, 2023, the cumulative amount of basis adjustments associated with these hedging relationships was $335 million.
| | |
114 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
The table below shows the gains (losses) recognized in earnings for other economic hedges and the customer-related positions for the years ended December 31:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars in Millions) | Location of Gains (Losses) Recognized in Earnings | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 |
| Asset and Liability Management Positions | | | | |
| Other economic hedges | | | | |
| Interest rate contracts | | | | |
| Futures and forwards | Mortgage banking revenue | $ | 5 | | $ | 71 | | $ | 407 | |
| Purchased and written options | Mortgage banking revenue | 195 | | 89 | | 1 | |
| Swaps | Mortgage banking revenue/Other noninterest income/Interest expense | (201) | | (19) | | (1,010) | |
| Foreign exchange forward contracts | Other noninterest income | 23 | | (7) | | (1) | |
| Equity contracts | Compensation expense | (4) | | (8) | | (8) | |
| Credit contracts | Commercial products revenue | (21) | | — | | — | |
| Other | Other noninterest income | (147) | | 1 | | (181) | |
| Customer-Related Positions | | | | |
| Interest rate contracts | | | | |
| Swaps | Commercial products revenue | 280 | | 185 | | 98 | |
| Purchased and written options | Commercial products revenue | (58) | | 45 | | 20 | |
| Futures | Commercial products revenue | — | | (1) | | 30 | |
| Foreign exchange rate contracts | | | | |
| Forwards, spots and swaps | Commercial products revenue | 215 | | 195 | | 100 | |
| Purchased and written options | Commercial products revenue | — | | 1 | | 1 | |
| Commodity contracts | | | | |
| Swaps | Commercial products revenue | 16 | | 6 | | — | |
| Purchased and written options | Commercial products revenue | 6 | | — | | — | |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| Credit contracts | Commercial products revenue | (3) | | 1 | | 20 | |
Derivatives are subject to credit risk associated with counterparties to the derivative contracts. The Company measures that credit risk using a credit valuation adjustment and includes it within the fair value of the derivative. The Company manages counterparty credit risk through diversification of its derivative positions among various counterparties, by entering into derivative positions that are centrally cleared through clearinghouses, by entering into master netting arrangements and, where possible, by requiring collateral arrangements. A master netting arrangement allows two counterparties, who have multiple derivative contracts with each other, the ability to net settle amounts under all contracts, including any related collateral, through a single payment and in a single currency. Collateral arrangements generally require the counterparty to deliver collateral (typically cash or U.S. Treasury and agency securities) equal to the Company’s net derivative receivable, subject to minimum transfer and credit rating requirements.
The Company’s collateral arrangements are predominately bilateral and, therefore, contain provisions that require collateralization of the Company’s net liability derivative positions. Required collateral coverage is based on net liability thresholds and may be contingent upon the Company’s credit rating from two of the nationally recognized statistical rating organizations. If the Company’s credit rating were to fall below credit ratings thresholds established in the collateral arrangements, the counterparties to the derivatives could request immediate additional collateral coverage up to and including full collateral coverage for derivatives in a net liability position. The aggregate fair value of all derivatives under collateral arrangements that were in a net liability position at December 31, 2024, was $2.3 billion. At December 31, 2024, the Company had $1.9 billion of cash posted as collateral against this net liability position.
| | | | | | | | |
| NOTE 20 | | Netting Arrangements for Certain Financial Instruments and Securities Financing Activities |
| |
The Company’s derivative portfolio consists of bilateral over-the-counter trades, certain interest rate derivatives and credit contracts required to be centrally cleared through clearinghouses per current regulations, and exchange-traded positions which may include U.S. Treasury and Eurodollar futures or options on U.S. Treasury futures. Of the Company’s $1.3 trillion total notional amount of derivative positions at December 31, 2024, $576.7 billion related to bilateral over-the-counter trades, $709.5 billion related to those centrally cleared through clearinghouses and $1.2 billion related to those that were exchange-traded. The Company’s derivative contracts typically include offsetting rights (referred to as netting arrangements), and depending on expected volume, credit risk, and counterparty preference, collateral maintenance may be required. For all derivatives under collateral support arrangements, fair value is determined daily and, depending on the collateral maintenance requirements, the Company and a counterparty may receive or deliver collateral, based upon the net fair value of all derivative positions between the Company and the counterparty. Collateral is typically cash, but securities may be allowed under collateral arrangements with certain counterparties. Receivables and payables related to cash collateral are included in other assets and other liabilities on the Consolidated Balance Sheet, along with the related derivative asset and liability fair values. Any securities pledged to counterparties as collateral remain on the Consolidated Balance Sheet. Securities received from counterparties as collateral are not recognized on the Consolidated Balance Sheet, unless the counterparty defaults. In general, securities used as collateral can be sold, repledged or otherwise used by the party in possession. No restrictions exist on the use of cash collateral by either party. Refer to Note 19 for further discussion of the Company’s derivatives, including collateral arrangements.
As part of the Company’s treasury and broker-dealer operations, the Company executes transactions that are treated as securities sold under agreements to repurchase or securities purchased under agreements to resell, both of
which are accounted for as collateralized financings. Securities sold under agreements to repurchase include repurchase agreements and securities loaned transactions. Securities purchased under agreements to resell include reverse repurchase agreements and securities borrowed transactions. For securities sold under agreements to repurchase, the Company records a liability for the cash received, which is included in short-term borrowings on the Consolidated Balance Sheet. For securities purchased under agreements to resell, the Company records a receivable for the cash paid, which is included in other assets on the Consolidated Balance Sheet.
Securities transferred to counterparties under repurchase agreements and securities loaned transactions continue to be recognized on the Consolidated Balance Sheet, are measured at fair value, and are included in investment securities or other assets. Securities received from counterparties under reverse repurchase agreements and securities borrowed transactions are not recognized on the Consolidated Balance Sheet unless the counterparty defaults. The securities transferred under repurchase and reverse repurchase transactions typically are U.S. Treasury and agency securities, residential agency mortgage-backed securities, corporate debt securities or asset-backed securities. The securities loaned or borrowed typically are corporate debt securities traded by the Company’s primary broker-dealer subsidiary. In general, the securities transferred can be sold, repledged or otherwise used by the party in possession. No restrictions exist on the use of cash collateral by either party. Repurchase/reverse repurchase and securities loaned/borrowed transactions expose the Company to counterparty risk. The Company manages this risk by performing assessments, independent of business line managers, and establishing concentration limits on each counterparty. Additionally, these transactions include collateral arrangements that require the fair values of the underlying securities to be determined daily, resulting in cash being obtained from or refunded to counterparties to maintain specified collateral levels.
| | |
116 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
The following table summarizes the maturities by category of collateral pledged for repurchase agreements and securities loaned transactions:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars in Millions) | Overnight and Continuous | Less Than 30 Days | 30-89 Days | Greater Than 90 Days | Total |
| December 31, 2024 | | | | | |
| Repurchase agreements | | | | | |
| U.S. Treasury and agencies | $ | 5,918 | | $ | — | | $ | — | | $ | — | | $ | 5,918 | |
| Residential agency mortgage-backed securities | 319 | | — | | — | | — | | 319 | |
| Corporate debt securities | 1,116 | | — | | — | | — | | 1,116 | |
| Asset-backed securities | 270 | | 22 | | — | | — | | 292 | |
| Total repurchase agreements | 7,623 | | 22 | | — | | — | | 7,645 | |
| Securities loaned | | | | | |
| Corporate debt securities | 90 | | — | | — | | — | | 90 | |
| Total securities loaned | 90 | | — | | — | | — | | 90 | |
| Gross amount of recognized liabilities | $ | 7,713 | | $ | 22 | | $ | — | | $ | — | | $ | 7,735 | |
| December 31, 2023 | | | | | |
| Repurchase agreements | | | | | |
| U.S. Treasury and agencies | $ | 2,375 | | $ | — | | $ | — | | $ | — | | $ | 2,375 | |
| Residential agency mortgage-backed securities | 338 | | — | | — | | — | | 338 | |
| Corporate debt securities | 821 | | — | | — | | — | | 821 | |
| Asset-backed securities | — | | 45 | | — | | — | | 45 | |
| Total repurchase agreements | 3,534 | | 45 | | — | | — | | 3,579 | |
| Securities loaned | | | | | |
| Corporate debt securities | 290 | | — | | — | | — | | 290 | |
| Total securities loaned | 290 | | — | | — | | — | | 290 | |
| Gross amount of recognized liabilities | $ | 3,824 | | $ | 45 | | $ | — | | $ | — | | $ | 3,869 | |
The Company executes its derivative, repurchase/reverse repurchase and securities loaned/borrowed transactions under the respective industry standard agreements. These agreements include master netting arrangements that allow for multiple contracts executed with the same counterparty to be viewed as a single arrangement. This allows for net settlement of a single amount on a daily basis. In the event of default, the master netting arrangement provides for close-out netting, which allows all of these positions with the defaulting counterparty to be terminated and net settled with a single payment amount.
The Company has elected to offset the assets and liabilities under netting arrangements for the balance sheet presentation of the majority of its derivative counterparties. The netting occurs at the counterparty level, and includes all assets and liabilities related to the derivative contracts, including those associated with cash collateral received or delivered. The Company has not elected to offset the assets and liabilities under netting arrangements for the balance sheet presentation of repurchase/reverse repurchase and securities loaned/borrowed transactions.
The following tables provide information on the Company’s netting adjustments, and items not offset on the Consolidated Balance Sheet but available for offset in the event of default:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars in Millions) | Gross Recognized Assets | Gross Amounts Offset on the Consolidated Balance Sheet(a) | Net Amounts Presented on the Consolidated Balance Sheet | Gross Amounts Not Offset on the Consolidated Balance Sheet | |
Financial Instruments(b) | Collateral Received(c) | Net Amount |
| December 31, 2024 | | | | | | |
Derivative assets(d) | $ | 6,422 | | $ | (2,979) | | $ | 3,443 | | $ | (177) | | $ | (5) | | $ | 3,261 | |
| Reverse repurchase agreements | 6,383 | | — | | 6,383 | | (851) | | (5,508) | | 24 | |
| Securities borrowed | 1,516 | | — | | 1,516 | | — | | (1,453) | | 63 | |
| Total | $ | 14,321 | | $ | (2,979) | | $ | 11,342 | | $ | (1,028) | | $ | (6,966) | | $ | 3,348 | |
| December 31, 2023 | | | | | | |
Derivative assets(d) | $ | 6,504 | | $ | (3,666) | | $ | 2,838 | | $ | (141) | | $ | (3) | | $ | 2,694 | |
| Reverse repurchase agreements | 2,513 | | — | | 2,513 | | (568) | | (1,941) | | 4 | |
| Securities borrowed | 1,802 | | — | | 1,802 | | (14) | | (1,717) | | 71 | |
| Total | $ | 10,819 | | $ | (3,666) | | $ | 7,153 | | $ | (723) | | $ | (3,661) | | $ | 2,769 | |
(a)Includes $1.9 billion and $1.6 billion of cash collateral related payables that were netted against derivative assets at December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively.
(b)For derivative assets this includes any derivative liability fair values that could be offset in the event of counterparty default; for reverse repurchase agreements this includes any repurchase agreement payables that could be offset in the event of counterparty default; for securities borrowed this includes any securities loaned payables that could be offset in the event of counterparty default.
(c)Includes the fair value of securities received by the Company from the counterparty. These securities are not included on the Consolidated Balance Sheet unless the counterparty defaults.
(d)Excludes $15 million and $27 million at December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively, of derivative assets not subject to netting arrangements.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars in Millions) | Gross Recognized Liabilities | Gross Amounts Offset on the Consolidated Balance Sheet(a) | Net Amounts Presented on the Consolidated Balance Sheet | Gross Amounts Not Offset on the Consolidated Balance Sheet | Net Amount |
Financial Instruments(b) | Collateral Pledged(c) |
| December 31, 2024 | | | | | | |
Derivative liabilities(d) | $ | 8,081 | | $ | (2,949) | | $ | 5,132 | | $ | (177) | | $ | — | | $ | 4,955 | |
| Repurchase agreements | 7,645 | | — | | 7,645 | | (851) | | (6,787) | | 7 | |
| Securities loaned | 90 | | — | | 90 | | — | | (88) | | 2 | |
| Total | $ | 15,816 | | $ | (2,949) | | $ | 12,867 | | $ | (1,028) | | $ | (6,875) | | $ | 4,964 | |
| December 31, 2023 | | | | | | |
Derivative liabilities(d) | $ | 8,217 | | $ | (3,720) | | $ | 4,497 | | $ | (141) | | $ | — | | $ | 4,356 | |
| Repurchase agreements | 3,579 | | — | | 3,579 | | (568) | | (3,008) | | 3 | |
| Securities loaned | 290 | | — | | 290 | | (14) | | (270) | | 6 | |
| Total | $ | 12,086 | | $ | (3,720) | | $ | 8,366 | | $ | (723) | | $ | (3,278) | | $ | 4,365 | |
(a)Includes $1.9 billion and $1.7 billion of cash collateral related receivables that were netted against derivative liabilities at December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively.
(b)For derivative liabilities this includes any derivative asset fair values that could be offset in the event of counterparty default; for repurchase agreements this includes any reverse repurchase agreement receivables that could be offset in the event of counterparty default; for securities loaned this includes any securities borrowed receivables that could be offset in the event of counterparty default.
(c)Includes the fair value of securities pledged by the Company to the counterparty. These securities are included on the Consolidated Balance Sheet unless the Company defaults.
(d)Excludes $79 million and $92 million at December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively, of derivative liabilities not subject to netting arrangements.
| | |
118 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
| | | | | | | | |
| NOTE 21 | | Fair Values of Assets and Liabilities |
The Company uses fair value measurements for the initial recording of certain assets and liabilities, periodic remeasurement of certain assets and liabilities, and disclosures. Derivatives, trading and available-for-sale investment securities, MSRs, certain time deposits and structured long-term notes, and substantially all MLHFS are recorded at fair value on a recurring basis. Additionally, from time to time, the Company may be required to record at fair value other assets on a nonrecurring basis, such as loans held for sale, loans held for investment and certain other assets. These nonrecurring fair value adjustments typically involve application of lower-of-cost-or-fair value accounting or impairment write-downs of individual assets. Other financial instruments, such as held-to-maturity investment securities, loans, the majority of time deposits, short-term borrowings and long-term debt, are accounted for at amortized cost. See “Fair Value of Financial Instruments” in this Note for further information on the estimated fair value of these other financial instruments. In accordance with disclosure guidance, certain financial instruments, such as deposits with no defined or contractual maturity, receivables and payables due in one year or less, insurance contracts and equity investments not accounted for at fair value, are excluded from this Note.
Fair value is defined as the exchange price that would be received for an asset or paid to transfer a liability (an exit price) in the principal or most advantageous market for the asset or liability in an orderly transaction between market participants on the measurement date. A fair value measurement reflects all of the assumptions that market participants would use in pricing the asset or liability, including assumptions about the risk inherent in a particular valuation technique, the effect of a restriction on the sale or use of an asset and the risk of nonperformance.
The Company groups its assets and liabilities measured at fair value into a three-level hierarchy for valuation techniques used to measure financial assets and financial liabilities at fair value. This hierarchy is based on whether the valuation inputs are observable or unobservable. These levels are:
•Level 1 — Quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities. Level 1 includes U.S. Treasury securities, as well as exchange-traded instruments.
•Level 2 — Observable inputs other than Level 1 prices, such as quoted prices for similar assets or liabilities; quoted prices in markets that are not active; or other inputs that are observable or can be corroborated by observable market data for substantially the full term of the assets or liabilities. Level 2 includes debt securities that are traded less frequently than exchange-traded instruments and which are typically valued using third party pricing services; derivative contracts and other assets and liabilities, including securities, and certain time deposits, and structured long-term notes, whose value is determined using a pricing model with inputs that are observable in the market or can be derived principally from or corroborated by observable market
data; and MLHFS whose values are determined using quoted prices for similar assets or pricing models with inputs that are observable in the market or can be corroborated by observable market data.
•Level 3 — Unobservable inputs that are supported by little or no market activity and that are significant to the fair value of the assets or liabilities. Level 3 assets and liabilities include financial instruments whose values are determined using pricing models, discounted cash flow methodologies, or similar techniques, as well as instruments for which the determination of fair value requires significant management judgment or estimation. This category includes MSRs and certain derivative contracts.
Valuation Methodologies
The valuation methodologies used by the Company to measure financial assets and liabilities at fair value are described below. In addition, the following section includes an indication of the level of the fair value hierarchy in which the assets or liabilities are classified. Where appropriate, the descriptions include information about the valuation models and key inputs to those models. During the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, there were no significant changes to the valuation techniques used by the Company to measure fair value.
Available-for-Sale Investment Securities When quoted market prices for identical securities are available in an active market, these prices are used to determine fair value and these securities are classified within Level 1 of the fair value hierarchy. Level 1 investment securities include U.S. Treasury and exchange-traded securities.
For other securities, quoted market prices may not be readily available for the specific securities. When possible, the Company determines fair value based on market observable information, including quoted market prices for similar securities, inactive transaction prices, and broker quotes. These securities are classified within Level 2 of the fair value hierarchy. Level 2 valuations are generally provided by a third-party pricing service. Level 2 investment securities are predominantly agency mortgage-backed securities, certain other asset-backed securities, obligations of state and political subdivisions and agency debt securities.
Mortgage Loans Held For Sale MLHFS measured at fair value, for which an active secondary market and readily available market prices exist, are initially valued at the transaction price and are subsequently valued by comparison to instruments with similar collateral and risk profiles. MLHFS are classified within Level 2. Included in mortgage banking revenue were net losses of $15 million, $46 million and $450 million for the years ended December 31, 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively, from the changes to fair value of these MLHFS under fair value option accounting guidance. Changes in fair value due to instrument specific credit risk were immaterial. Interest
income for MLHFS is measured based on contractual interest rates and reported as interest income on the Consolidated Statement of Income. Electing to measure MLHFS at fair value reduces certain timing differences and better matches changes in fair value of these assets with changes in the value of the derivative instruments used to economically hedge them without the burden of complying with the requirements for hedge accounting.
Time Deposits The Company elects the fair value option to account for certain time deposits that are hedged with derivatives that do not qualify for hedge accounting. Electing to measure these time deposits at fair value reduces certain timing differences and better matches changes in fair value of these deposits with changes in the value of the derivative instruments used to economically hedge them. The time deposits measured at fair value are valued using a discounted cash flow model that utilizes market observable inputs and are classified within Level 2. Included in interest expense on deposits were net gains of $4 million for both the years ended December 31, 2024 and 2023, from the changes in fair value of time deposits under fair value option accounting guidance.
Long-term Debt The Company elects the fair value option to account for certain structured notes that are hedged with derivatives that do not qualify for hedge accounting. Electing to measure these structured notes at fair value reduces certain timing differences and better matches changes in fair value of these notes with changes in the value of the derivative instruments use to economically hedge them. The structured notes measured at fair value are valued using a discounted cash flow model that utilizes market observable inputs and are classified within Level 2. The discount rate used in the discounted cash flow model incorporates the impact of the Company's credit spread, which is based on observable spreads in the secondary bond market. Changes in fair value attributable to instrument specific credit risk are recorded as debit valuation adjustments (“DVA”) in other comprehensive income (loss) with all other changes in fair value recorded in interest expense. Included in other comprehensive income (loss) and interest expense on long-term debt were net DVA gains of $1 million and net gains of $17 million, respectively, for the year ended December 31, 2024 from the changes in fair value of structured notes under fair value option account guidance.
Mortgage Servicing Rights MSRs are valued using a discounted cash flow methodology, and are classified within Level 3. The Company determines fair value of the MSRs by projecting future cash flows for different interest rate scenarios using prepayment rates and other assumptions, and discounts these cash flows using a risk adjusted rate based on option adjusted spread levels. There is minimal observable market activity for MSRs on comparable portfolios and, therefore, the determination of fair value requires significant management judgment. Refer to Note 9 for further information on MSR valuation assumptions.
Derivatives The majority of derivatives held by the Company are executed over-the-counter or centrally cleared through clearinghouses and are valued using market standard cash flow valuation techniques. The models incorporate inputs, depending on the type of derivative, including interest rate curves, foreign exchange rates and volatility. All derivative values incorporate an assessment of the risk of counterparty nonperformance, measured based on the Company’s evaluation of credit risk including external assessments of credit risk. The Company monitors and manages its nonperformance risk by considering its ability to net derivative positions under master netting arrangements, as well as collateral received or provided under collateral arrangements. Accordingly, the Company has elected to measure the fair value of derivatives, at a counterparty level, on a net basis. The majority of the derivatives are classified within Level 2 of the fair value hierarchy, as the significant inputs to the models, including nonperformance risk, are observable. However, certain derivative transactions are with counterparties where risk of nonperformance cannot be observed in the market and, therefore, the credit valuation adjustments result in these derivatives being classified within Level 3 of the fair value hierarchy.
The Company also has other derivative contracts that are created through its operations, including commitments to purchase and originate mortgage loans and swap agreements executed in conjunction with the sale of a portion of its Class B common and preferred shares of Visa Inc. (the “Visa swaps”). The mortgage loan commitments are valued by pricing models that include market observable and unobservable inputs, which result in the commitments being classified within Level 3 of the fair value hierarchy. The unobservable inputs include assumptions about the percentage of commitments that actually become a closed loan and the MSR value that is inherent in the underlying loan value. The Visa swaps require payments by either the Company or the purchaser of the Visa Inc. Class B common and preferred shares when there are changes in the conversion rate of the Visa Inc. Class B common and preferred shares to Visa Inc. Class A common and preferred shares, respectively, as well as quarterly payments to the purchaser based on specified terms of the agreements. Management reviews and updates the Visa swaps fair value in conjunction with its review of Visa Inc. related litigation contingencies, and the associated escrow funding. The expected litigation resolution impacts the Visa Inc. Class B common share to Visa Inc. Class A common share conversion rate, as well as the ultimate termination date for the Visa swaps. Accordingly, the Visa swaps are classified within Level 3. Refer to Note 22 for further information on the Visa Inc. restructuring and related card association litigation.
| | |
120 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
Significant Unobservable Inputs of Level 3 Assets and Liabilities
The following section provides information to facilitate an understanding of the uncertainty in the fair value measurements for the Company’s Level 3 assets and liabilities recorded at fair value on the Consolidated Balance Sheet. This section includes a description of the significant inputs used by the Company and a description of any interrelationships between these inputs. The discussion below excludes nonrecurring fair value measurements of collateral value used for impairment measures for loans and OREO. These valuations utilize third party appraisal or broker price opinions, and are classified as Level 3 due to the significant judgment involved.
Mortgage Servicing Rights The significant unobservable inputs used in the fair value measurement of the Company’s MSRs are expected prepayments and the option adjusted spread that is added to the risk-free rate to discount projected cash flows. Significant increases in either of these inputs in isolation would have resulted in a significantly lower fair value measurement. Significant decreases in either of these inputs in isolation would have resulted in a significantly higher fair value measurement. There is no direct interrelationship between prepayments and option adjusted spread. Prepayment rates generally move in the opposite direction of market interest rates. Option adjusted spread is generally impacted by changes in market return requirements.
The following table shows the significant valuation assumption ranges for MSRs at December 31, 2024:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Minimum | Maximum | Weighted- Average(a) |
| Expected prepayment | 6 | % | 18 | % | 9 | % |
| Option adjusted spread | 5 | | 11 | | 6 | |
(a)Determined based on the relative fair value of the related mortgage loans serviced.
Derivatives The Company has two distinct Level 3 derivative portfolios: (i) the Company’s commitments to purchase and originate mortgage loans that meet the requirements of a derivative and (ii) the Company’s asset/liability and customer-related derivatives that are Level 3 due to unobservable inputs related to measurement of risk of nonperformance by the counterparty. In addition, the Company’s Visa swaps are classified within Level 3.
The significant unobservable inputs used in the fair value measurement of the Company’s derivative commitments to purchase and originate mortgage loans
are the percentage of commitments that actually become a closed loan and the MSR value that is inherent in the underlying loan value. A significant increase in the rate of loans that close would have resulted in a larger derivative asset or liability. A significant increase in the inherent MSR value would have resulted in an increase in the derivative asset or a reduction in the derivative liability. Expected loan close rates and the inherent MSR values are directly impacted by changes in market rates and will generally move in the same direction as interest rates.
The following table shows the significant valuation assumption ranges for the Company’s derivative commitments to purchase and originate mortgage loans at December 31, 2024:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Minimum | Maximum | Weighted- Average(a) |
| Expected loan close rate | 25 | % | 100 | % | 83 | % |
| Inherent MSR value (basis points per loan) | 63 | | 196 | | 116 | |
(a)Determined based on the relative fair value of the related mortgage loans.
The significant unobservable input used in the fair value measurement of certain of the Company’s asset/liability and customer-related derivatives is the credit valuation adjustment related to the risk of counterparty nonperformance. A significant increase in the credit valuation adjustment would have resulted in a lower fair value measurement. A significant decrease in the credit valuation adjustment would have resulted in a higher fair value measurement. The credit valuation adjustment is impacted by changes in market rates, volatility, market implied credit spreads, and loss recovery rates, as well as the Company’s assessment of the counterparty’s credit position. At December 31, 2024, the minimum, maximum and weighted-average credit valuation adjustment as a
percentage of the net fair value of the counterparty’s derivative contracts prior to adjustment was 0 percent, 6,313 percent and 2 percent, respectively.
The significant unobservable inputs used in the fair value measurement of the Visa swaps are management’s estimate of the probability of certain litigation scenarios occurring, and the timing of the resolution of the related litigation loss estimates in excess, or shortfall, of the Company’s proportional share of escrow funds. An increase in the loss estimate or a delay in the resolution of the related litigation would have resulted in an increase in the derivative liability. A decrease in the loss estimate or an acceleration of the resolution of the related litigation would have resulted in a decrease in the derivative liability.
The following table summarizes the balances of assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars in Millions) | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Netting | Total |
| December 31, 2024 | | | | | |
| Available-for-sale securities | | | | | |
| U.S. Treasury and agencies | $ | 23,891 | | $ | 4,496 | | $ | — | | $ | — | | $ | 28,387 | |
| Mortgage-backed securities | | | | | |
| Residential agency | — | | 33,281 | | — | | — | | 33,281 | |
| Commercial | | | | | |
| Agency | — | | 7,351 | | — | | — | | 7,351 | |
| Non-agency | — | | 6 | | — | | — | | 6 | |
| Asset-backed securities | — | | 7,165 | | — | | — | | 7,165 | |
| Obligations of state and political subdivisions | — | | 9,552 | | — | | — | | 9,552 | |
| Other | — | | 250 | | — | | — | | 250 | |
| Total available-for-sale | 23,891 | | 62,101 | | — | | — | | 85,992 | |
| Mortgage loans held for sale | — | | 2,251 | | — | | — | | 2,251 | |
| Mortgage servicing rights | — | | — | | 3,369 | | — | | 3,369 | |
| Derivative assets | 27 | | 5,208 | | 1,202 | | (2,979) | | 3,458 | |
| Other assets | 420 | | 1,769 | | — | | — | | 2,189 | |
| Total | $ | 24,338 | | $ | 71,329 | | $ | 4,571 | | $ | (2,979) | | $ | 97,259 | |
| Time deposits | $ | — | | $ | 5,754 | | $ | — | | $ | — | | $ | 5,754 | |
| Long-term debt | — | | 391 | | — | | — | | 391 | |
| Derivative liabilities | 27 | | 5,131 | | 3,002 | | (2,949) | | 5,211 | |
Short-term borrowings and other liabilities(a) | 475 | | 1,460 | | — | | — | | 1,935 | |
| Total | $ | 502 | | $ | 12,736 | | $ | 3,002 | | $ | (2,949) | | $ | 13,291 | |
| December 31, 2023 | | | | | |
| Available-for-sale securities | | | | | |
| U.S. Treasury and agencies | $ | 14,787 | | $ | 4,755 | | $ | — | | $ | — | | $ | 19,542 | |
| Mortgage-backed securities | | | | | |
| Residential agency | — | | 26,078 | | — | | — | | 26,078 | |
| Commercial | | | | | |
| Agency | — | | 7,343 | | — | | — | | 7,343 | |
| Non-agency | — | | 6 | | — | | — | | 6 | |
| Asset-backed securities | — | | 6,724 | | — | | — | | 6,724 | |
| Obligations of state and political subdivisions | — | | 9,989 | | — | | — | | 9,989 | |
| Other | — | | 24 | | — | | — | | 24 | |
| Total available-for-sale | 14,787 | | 54,919 | | — | | — | | 69,706 | |
| Mortgage loans held for sale | — | | 2,011 | | — | | — | | 2,011 | |
| Mortgage servicing rights | — | | — | | 3,377 | | — | | 3,377 | |
| Derivative assets | — | | 5,078 | | 1,453 | | (3,666) | | 2,865 | |
| Other assets | 550 | | 1,991 | | — | | — | | 2,541 | |
| Total | $ | 15,337 | | $ | 63,999 | | $ | 4,830 | | $ | (3,666) | | $ | 80,500 | |
| Time Deposits | $ | — | | $ | 2,818 | | $ | — | | $ | — | | $ | 2,818 | |
| Derivative liabilities | 16 | | 4,955 | | 3,338 | | (3,720) | | 4,589 | |
Short-term borrowings and other liabilities(a) | 517 | | 1,786 | | — | | — | | 2,303 | |
| Total | $ | 533 | | $ | 9,559 | | $ | 3,338 | | $ | (3,720) | | $ | 9,710 | |
Note: Excluded from the table above are equity investments without readily determinable fair values. The Company has elected to carry these investments at historical cost, adjusted for impairment and any changes resulting from observable price changes for identical or similar investments of the issuer. The aggregate carrying amount of these equity investments was $159 million and $133 million at December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively, and reflect no impairment or observable price change adjustment at December 31, 2024, compared with a cumulative impairment of $5 million and no observable price change adjustment at December 31, 2023. The Company recorded a $5 million impairment on these equity investments during 2023. The Company did not record any adjustments for observable price changes during 2024 and 2023.
(a)Primarily represents the Company’s obligation on securities sold short required to be accounted for at fair value per applicable accounting guidance.
| | |
122 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
The following table presents the changes in fair value for all assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis using significant unobservable inputs (Level 3) for the years ended December 31:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars in Millions) | Beginning of Period Balance | Net Gains (Losses) Included in Net Income | | Net Gains (Losses) Included in Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) | Purchases | Sales | Principal Payments | Issuances | | Settlements | | End of Period Balance | Net Change in Unrealized Gains (Losses) Relating to Assets and Liabilities Held at End of Period |
| 2024 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Mortgage servicing rights | $ | 3,377 | | $ | (97) | | (a) | $ | — | | $ | 1 | | $ | (188) | | $ | — | | $ | 276 | | (c) | $ | — | | | $ | 3,369 | | $ | (97) | | (a) |
| Net derivative assets and liabilities | (1,885) | | (3,829) | | (b) | — | | 1,076 | | (18) | | — | | 1 | | | 2,855 | | | (1,800) | | (492) | | (d) |
| 2023 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Available-for-sale securities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Obligations of state and political subdivisions | $ | 1 | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | $ | — | | $ | — | | $ | (1) | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | $ | — | | |
| Total available-for-sale | 1 | | — | | | — | | — | | — | | (1) | | — | | | — | | | — | | — | | |
| Mortgage servicing rights | 3,755 | | (316) | | (a) | — | | 5 | | (440) | | — | | 373 | | (c) | — | | | 3,377 | | (316) | | (a) |
| Net derivative assets and liabilities | (3,199) | | (2,696) | | (e) | — | | 552 | | (45) | | — | | 1 | | | 3,502 | | | (1,885) | | (183) | | (f) |
| 2022 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Available-for-sale securities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Asset-backed securities | $ | 7 | | $ | — | | | $ | (3) | | $ | — | | $ | (4) | | $ | — | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | | $ | — | | $ | — | | |
| Obligations of state and political subdivisions | 1 | | — | | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | | — | | | 1 | | — | | |
| Total available-for-sale | 8 | | — | | | (3) | | — | | (4) | | — | | — | | | — | | | 1 | | — | | |
| Mortgage servicing rights | 2,953 | | 311 | | (a) | — | | 156 | | (255) | | — | | 590 | | (c) | — | | | 3,755 | | 311 | | (a) |
| Net derivative assets and liabilities | 799 | | (5,940) | | (g) | — | | 716 | | (36) | | — | | 11 | | | 1,251 | | | (3,199) | | (3,538) | | (h) |
(a)Included in mortgage banking revenue.
(b)Approximately $200 million, $(3.9) billion and $(147) million included in mortgage banking revenue, commercial products revenue and other non-interest income, respectively.
(c)Represents MSRs capitalized during the period.
(d)Approximately $7 million, $(352) million and $(147) million included in mortgage banking revenue, commercial products revenue and other non-interest income, respectively.
(e)Approximately $182 million, $(2.9) billion and $1 million included in mortgage banking revenue, commercial products revenue and other non-interest income, respectively.
(f)Approximately $15 million, $(199) million and $1 million included in mortgage banking revenue, commercial products revenue and other non-interest income, respectively.
(g)Approximately $(141) million, $(5.6) billion and $(181) million included in mortgage banking revenue, commercial products revenue and other non-interest income, respectively.
(h)Approximately $5 million, $(3.4) billion and $(181) million included in mortgage banking revenue, commercial products revenue and other non-interest income, respectively.
The Company is also required periodically to measure certain other financial assets at fair value on a nonrecurring basis. These measurements of fair value usually result from the application of lower-of-cost-or-fair value accounting or write-downs of individual assets.
The following table summarizes the balances as of the measurement date of assets measured at fair value on a nonrecurring basis, and still held as of December 31:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2024 | 2023 |
| (Dollars in Millions) | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total |
Loans(a) | $ | — | | $ | — | | $ | 636 | | $ | 636 | | $ | — | | $ | — | | $ | 354 | | $ | 354 | |
Other assets(b) | — | | — | | 25 | | 25 | | — | | — | | 27 | | 27 | |
(a)Represents the carrying value of loans for which adjustments were based on the fair value of the collateral, excluding loans fully charged-off.
(b)Primarily represents the fair value of foreclosed properties that were measured at fair value based on an appraisal or broker price opinion of the collateral subsequent to their initial acquisition.
The following table summarizes losses recognized related to nonrecurring fair value measurements of individual assets or portfolios for the years ended December 31:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 |
Loans(a) | $ | 399 | | $ | 368 | | $ | 40 | |
Other assets(b) | 12 | | 32 | | 20 | |
(a)Represents write-downs of loans which were based on the fair value of the collateral, excluding loans fully charged-off.
(b)Primarily represents related losses of foreclosed properties that were measured at fair value subsequent to their initial acquisition.
Fair Value Option
The following table summarizes the differences between the aggregate fair value carrying amount of the assets and liabilities for which the fair value option has been elected and the aggregate remaining contractual principal balance outstanding as of December 31:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2024 | 2023 |
| (Dollars in Millions) | Fair Value Carrying Amount | Contractual Principal Outstanding | Carrying Amount Over (Under) Contractual Principal Outstanding | Fair Value Carrying Amount | Contractual Principal Outstanding | Carrying Amount Over (Under) Contractual Principal Outstanding |
Total loans(a) | $ | 2,251 | | $ | 2,243 | | $ | 8 | | $ | 2,011 | | $ | 1,994 | | $ | 17 | |
| Time deposits | 5,754 | | 5,762 | | (8) | | 2,818 | | 2,822 | | (4) | |
| Long-term debt | 391 | | 409 | | (18) | | — | | — | | — | |
(a)Includes nonaccrual loans of $1 million carried at fair value with contractual principal outstanding of $1 million at December 31, 2024 and $1 million carried at fair value with contractual principal outstanding of $1 million at December 31, 2023. Includes loans 90 days or more past due of $4 million carried at fair value with contractual principal outstanding of $4 million at December 31, 2024 and $4 million carried at fair value with contractual principal outstanding of $4 million at December 31, 2023.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
The following section summarizes the estimated fair value for financial instruments accounted for at amortized cost as of December 31, 2024 and 2023. In accordance with disclosure guidance related to fair values of financial instruments, the Company did not include assets and liabilities that are not financial instruments, such as the value of goodwill, long-term relationships with deposit,
credit card, merchant processing and trust customers, other purchased intangibles, premises and equipment, deferred taxes and other liabilities. Additionally, in accordance with the disclosure guidance, receivables and payables due in one year or less, insurance contracts, equity investments not accounted for at fair value, and deposits with no defined or contractual maturities are excluded.
The estimated fair values of the Company’s financial instruments as of December 31, are shown in the table below:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2024 | 2023 |
| | Carrying Amount | Fair Value | Carrying Amount | Fair Value |
| (Dollars in Millions) | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total |
| Financial Assets | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and due from banks | $ | 56,502 | | $ | 56,502 | | $ | — | | $ | — | | $ | 56,502 | | $ | 61,192 | | $ | 61,192 | | $ | — | | $ | — | | $ | 61,192 | |
| Federal funds sold and securities purchased under resale agreements | 6,380 | | — | | 6,380 | | — | | 6,380 | | 2,543 | | — | | 2,543 | | — | | 2,543 | |
| Investment securities held-to-maturity | 78,634 | | 1,275 | | 65,000 | | — | | 66,275 | | 84,045 | | 1,310 | | 72,778 | | — | | 74,088 | |
Loans held for sale(a) | 322 | | — | | — | | 322 | | 322 | | 190 | | — | | — | | 190 | | 190 | |
| Loans, net of allowance for losses | 372,249 | | — | | — | | 365,628 | | 365,628 | | 366,456 | | — | | — | | 362,849 | | 362,849 | |
Other(b) | 2,482 | | — | | 1,767 | | 715 | | 2,482 | | 2,377 | | — | | 1,863 | | 514 | | 2,377 | |
| Financial Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | |
Time deposits(c) | 49,015 | | — | | 49,156 | | — | | 49,156 | | 49,455 | | — | | 49,607 | | — | | 49,607 | |
Short-term borrowings(d) | 13,583 | | — | | 13,419 | | — | | 13,419 | | 12,976 | | — | | 12,729 | | — | | 12,729 | |
Long-term debt(e) | 57,611 | | — | | 56,441 | | — | | 56,441 | | 51,480 | | — | | 49,697 | | — | | 49,697 | |
Other(f) | 5,220 | | — | | 1,369 | | 3,851 | | 5,220 | | 5,432 | | — | | 1,406 | | 4,026 | | 5,432 | |
(a)Excludes mortgages held for sale for which the fair value option under applicable accounting guidance was elected.
(b)Includes investments in Federal Reserve Bank and Federal Home Loan Bank stock and tax-advantaged investments.
(c)Excludes time deposits for which the fair value option under applicable accounting guidance was elected.
(d)Excludes the Company’s obligation on securities sold short required to be accounted for at fair value per applicable accounting guidance.
(e)Excludes structured long-term notes for which the fair value option under applicable accounting guidance was elected.
(f)Includes operating lease liabilities and liabilities related to tax-advantaged investments.
The fair value of unfunded commitments, deferred non-yield related loan fees, standby letters of credit and other guarantees is approximately equal to their carrying value. The carrying value of unfunded commitments, deferred non-yield related loan fees and standby letters of credit was
$376 million and $489 million at December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively. The carrying value of other guarantees was $194 million and $198 million at December 31, 2024 and 2023, respectively.
| | |
124 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
| | | | | | | | |
NOTE 22 | | Guarantees and Contingent Liabilities |
Visa Restructuring and Card Association Litigation The Company’s Payment Services business issues credit and debit cards and acquires credit and debit card transactions through the Visa U.S.A. Inc. card association or its affiliates (collectively “Visa”). In 2007, Visa completed a restructuring and issued shares of Visa Inc. common stock to its financial institution members in contemplation of its initial public offering (“IPO”) completed in the first quarter of 2008 (the “Visa Reorganization”). As a part of the Visa Reorganization, the Company received its proportionate number of shares of Visa Inc. common stock, which were subsequently converted to Class B shares of Visa Inc. (“Class B shares”). As of December 31, 2024, the Company has sold substantially all of its Class B shares.
Visa U.S.A. Inc. (“Visa U.S.A.”) and MasterCard International (collectively, the “Card Brands”) are defendants in antitrust lawsuits challenging the practices of the Card Brands (the “Visa Litigation”). Visa U.S.A. member banks have a contingent obligation to indemnify Visa Inc. under the Visa U.S.A. bylaws (which were modified at the time of the restructuring in October 2007) for potential losses arising from the Visa Litigation. The indemnification by the Visa U.S.A. member banks has no specific maximum amount. Using proceeds from its IPO and through reductions to the conversion ratio applicable to the Class B shares held by Visa U.S.A. member banks, Visa Inc. has funded an escrow account for the benefit of member financial institutions to fund their indemnification obligations associated with the Visa Litigation. The receivable related to the escrow account is classified in other liabilities and fully offsets the related Visa Litigation contingent liability.
In October 2012, Visa signed a settlement agreement to resolve merchant class action claims associated with the multidistrict interchange litigation pending in the United States District Court for the Eastern District of New York (the “Multi-District Litigation”). The U.S. Court of Appeals for the Second Circuit reversed the approval of that settlement and remanded the matter to the district court. Thereafter, the case was split into two putative class actions, one seeking damages (the “Damages Action”) and a separate class action seeking injunctive relief only (the “Injunctive Action”). The Damages Action was settled and is fully resolved. A number of merchants opted out of the Damages Action class settlement and filed individual cases in various federal district courts. Some of those cases have been settled and others are still being litigated. In March 2024, Visa signed a settlement agreement to resolve the Injunctive Action. In June 2024, the court declined to grant preliminary approval of the proposed settlement, which provided for lower interchange fees and various other rule changes for U.S. merchants. Accordingly, the Injunctive Action continues.
Commitments to Extend Credit Commitments to extend credit are legally binding and generally have fixed expiration dates or other termination clauses. The contractual amount represents the Company’s exposure to credit loss, in the event of default by the borrower. The Company manages this credit risk by using the same credit
policies it applies to loans. Collateral is obtained to secure commitments based on management’s credit assessment of the borrower. The collateral may include marketable securities, receivables, inventory, equipment and real estate. Since the Company expects many of the commitments to expire without being drawn, total commitment amounts do not necessarily represent the Company’s future liquidity requirements. In addition, the commitments include consumer credit lines that are cancelable upon notification to the consumer.
The contract or notional amounts of unfunded commitments to extend credit at December 31, 2024, excluding those commitments considered derivatives, were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Term | |
| (Dollars in Millions) | Less Than One Year | Greater Than One Year | Total |
| Commercial and commercial real estate loans | $ | 46,760 | | $ | 138,973 | | $ | 185,733 | |
Corporate and purchasing card loans(a) | 35,687 | | — | | 35,687 | |
| Residential mortgages | 226 | | — | | 226 | |
Retail credit card loans(a) | 137,404 | | — | | 137,404 | |
| Other retail loans | 16,460 | | 26,145 | | 42,605 | |
| Other | 7,736 | | — | | 7,736 | |
(a)Primarily cancellable at the Company’s discretion.
Other Guarantees and Contingent Liabilities
The following table is a summary of other guarantees and contingent liabilities of the Company at December 31, 2024:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| (Dollars in Millions) | Collateral Held | Carrying Amount | Maximum Potential Future Payments |
| Standby letters of credit | $ | — | | $ | 23 | | $ | 10,522 | |
| Third party borrowing arrangements | — | | — | | 1 | |
| Securities lending indemnifications | 6,862 | | — | | 6,681 | |
| Asset sales | — | | 112 | | 12,650 | |
| Merchant processing | 816 | | 61 | | 144,713 | |
| Other | — | | 21 | | 3,245 | |
Letters of Credit Standby letters of credit are commitments the Company issues to guarantee the performance of a customer to a third party. The guarantees frequently support public and private borrowing arrangements, including commercial paper issuances, bond financings and other similar transactions. The Company also issues and confirms commercial letters of credit on behalf of customers to ensure payment or collection in connection with trade transactions. In the event of a customer’s or
counterparty’s nonperformance, the Company’s credit loss exposure is similar to that in any extension of credit, up to the letter’s contractual amount. Management assesses the borrower’s credit to determine the necessary collateral, which may include marketable securities, receivables, inventory, equipment and real estate. Since the conditions requiring the Company to fund letters of credit may not occur, the Company expects its liquidity requirements to be less than the total outstanding commitments. The maximum potential future payments guaranteed by the Company under standby letter of credit arrangements at December 31, 2024, were approximately $10.5 billion with a weighted-average term of approximately 14 months. The estimated fair value of standby letters of credit was approximately $23 million at December 31, 2024.
The contract or notional amount of letters of credit at December 31, 2024, were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Term | |
| (Dollars in Millions) | Less Than One Year | Greater Than One Year | Total |
| Standby | $ | 7,105 | | $ | 3,417 | | $ | 10,522 | |
| Commercial | 441 | | 21 | | 462 | |
Guarantees Guarantees are contingent commitments issued by the Company to customers or other third parties. The Company’s guarantees primarily include parent guarantees related to subsidiaries’ third party borrowing arrangements; third party performance guarantees inherent in the Company’s business operations, such as indemnified securities lending programs and merchant charge-back guarantees; and indemnification or buy-back provisions related to certain asset sales. For certain guarantees, the Company has recorded a liability related to the potential obligation, or has access to collateral to support the guarantee or through the exercise of other recourse provisions can offset some or all of the maximum potential future payments made under these guarantees.
Third Party Borrowing Arrangements The Company provides guarantees to third parties as a part of certain subsidiaries’ borrowing arrangements. The maximum potential future payments guaranteed by the Company under these arrangements were approximately $1 million at December 31, 2024.
Commitments from Securities Lending The Company participates in securities lending activities by acting as the customer’s agent involving the loan of securities. The Company indemnifies customers for the difference between the fair value of the securities lent and the fair value of the collateral received. Cash collateralizes these transactions. The maximum potential future payments guaranteed by the Company under these arrangements were approximately $6.7 billion at December 31, 2024, and represent the fair value of the securities lent to third parties. At December 31, 2024, the Company held $6.9 billion of cash as collateral for these arrangements.
Asset Sales The Company has provided guarantees to certain third parties in connection with the sale or
syndication of certain assets, primarily loan portfolios and tax-advantaged investments. These guarantees are generally in the form of asset buy-back or make-whole provisions that are triggered upon a credit event or a change in the tax-qualifying status of the related projects, as applicable, and remain in effect until the loans are collected or final tax credits are realized, respectively. The maximum potential future payments guaranteed by the Company under these arrangements were approximately $12.7 billion at December 31, 2024, and represented the proceeds received from the buyer or the guaranteed portion in these transactions where the buy-back or make-whole provisions have not yet expired. At December 31, 2024, the Company had reserved $103 million for potential losses related to the sale or syndication of tax-advantaged investments.
The maximum potential future payments do not include loan sales where the Company provides standard representations and warranties to the buyer against losses related to loan underwriting documentation defects that may have existed at the time of sale that generally are identified after the occurrence of a triggering event such as delinquency. For these types of loan sales, the maximum potential future payments is generally the unpaid principal balance of loans sold measured at the end of the current reporting period. Actual losses will be significantly less than the maximum exposure, as only a fraction of loans sold will have a representation and warranty breach, and any losses on repurchase would generally be mitigated by any collateral held against the loans.
The Company regularly sells loans to GSEs as part of its mortgage banking activities. The Company provides customary representations and warranties to GSEs in conjunction with these sales. These representations and warranties generally require the Company to repurchase assets if it is subsequently determined that a loan did not meet specified criteria, such as a documentation deficiency or rescission of mortgage insurance. If the Company is unable to cure or refute a repurchase request, the Company is generally obligated to repurchase the loan or otherwise reimburse the GSE for losses. At December 31, 2024, the Company had reserved $9 million for potential losses from representation and warranty obligations, compared with $13 million at December 31, 2023. The Company’s reserve reflects management’s best estimate of losses for representation and warranty obligations. The Company’s repurchase reserve is modeled at the loan level, taking into consideration the individual credit quality and borrower activity that has transpired since origination. The model applies credit quality and economic risk factors to derive a probability of default and potential repurchase that are based on the Company’s historical loss experience, and estimates loss severity based on expected collateral value. The Company also considers qualitative factors that may result in anticipated losses differing from historical loss trends.
As of December 31, 2024 and 2023, the Company had $15 million and $18 million, respectively, of unresolved representation and warranty claims from GSEs. The
| | |
126 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
Company does not have a significant amount of unresolved claims from investors other than GSEs.
Merchant Processing The Company, through its subsidiaries, provides merchant processing services. Under the rules of credit card associations, a merchant processor retains a contingent liability for credit card transactions processed. This contingent liability arises in the event of a billing dispute between the merchant and a cardholder that is ultimately resolved in the cardholder’s favor. In this situation, the transaction is “charged-back” to the merchant and the disputed amount is credited or otherwise refunded to the cardholder. If the Company is unable to collect this amount from the merchant, it bears the loss for the amount of the refund paid to the cardholder.
A cardholder, through its issuing bank, generally has until the later of up to four months after the date the transaction is processed or the receipt of the product or service to present a charge-back to the Company as the merchant processor. The absolute maximum potential liability is estimated to be the total volume of credit card transactions that meet the associations’ requirements to be valid charge-back transactions at any given time. Management estimates that the maximum potential exposure for charge-backs would approximate the total amount of merchant transactions processed through the credit card associations for the last four months. For the last four months of 2024 this amount totaled approximately $144.7 billion. In most cases, this contingent liability is unlikely to arise, as most products and services are delivered when purchased and amounts are refunded when items are returned to merchants. However, where the product or service has been purchased but is not provided until a future date (“future delivery”), the potential for this contingent liability increases. To mitigate this risk, the Company may require the merchant to make an escrow deposit, place maximum volume limitations on future delivery transactions processed by the merchant at any point in time, or require various credit enhancements (including letters of credit and bank guarantees). Also, merchant processing contracts may include event triggers to provide the Company more financial and operational control in the event of financial deterioration of the merchant.
The Company currently processes card transactions in the United States, Canada and Europe through wholly-owned subsidiaries. In the event a merchant was unable to fulfill product or services subject to future delivery, such as airline tickets, the Company could become financially liable for refunding the purchase price of such products or services purchased through the credit card associations under the charge-back provisions. Charge-back risk related to these merchants is evaluated in a manner similar to credit risk assessments and, as such, merchant processing contracts contain various provisions to protect the Company in the event of default. At December 31, 2024, the value of airline tickets purchased to be delivered at a future date through card transactions processed by the Company was $12.0 billion. The Company held collateral of $689 million in escrow deposits, letters of credit and indemnities from financial institutions, and liens on various
assets related to these airline processing arrangements. In addition to specific collateral or other credit enhancements, the Company maintains a liability for its implied guarantees associated with future delivery. At December 31, 2024, the liability was $40 million primarily related to these airline processing arrangements.
In the normal course of business, the Company has unresolved charge-backs. The Company assesses the likelihood of its potential liability based on the extent and nature of unresolved charge-backs and its historical loss experience. At December 31, 2024, the Company held $127 million of merchant escrow deposits as collateral and had a recorded liability for potential losses of $21 million related to these charge-backs.
Tender Option Bond Program Guarantee As discussed in Note 7, the Company previously sponsored a municipal bond securities tender option bond program and consolidated the program’s entities on its Consolidated Balance Sheet. The Company provided financial performance guarantees related to the program’s entities. During 2024, the Company ended this arrangement, effectively eliminating any outstanding related guarantees.
Other Guarantees and Commitments As of December 31, 2024, the Company sponsored, and owned 100 percent of the common equity of, USB Capital IX, a wholly-owned unconsolidated trust, formed for the purpose of issuing redeemable Income Trust Securities (“ITS”) to third-party investors, originally investing the proceeds in junior subordinated debt securities (“Debentures”) issued by the Company and entering into stock purchase contracts to purchase the Company’s preferred stock in the future. As of December 31, 2024, all of the Debentures issued by the Company have either matured or been retired. Total assets of USB Capital IX were $685 million at December 31, 2024, consisting primarily of the Company’s Series A Preferred Stock. The Company’s obligations under the transaction documents, taken together, have the effect of providing a full and unconditional guarantee by the Company, on a junior subordinated basis, of the payment obligations of the trust to third-party investors totaling $684 million at December 31, 2024.
The Company has also made other financial performance guarantees and commitments primarily related to the operations of its subsidiaries. At December 31, 2024, the maximum potential future payments guaranteed or committed by the Company under these arrangements were approximately $2.6 billion.
Litigation and Regulatory Matters
The Company is subject to various litigation and regulatory matters that arise from the conduct of its business activities. The Company establishes reserves for such matters when potential losses become probable and can be reasonably estimated. The Company believes the ultimate resolution of existing legal and regulatory matters will not have a material adverse effect on the financial condition, results of operations or cash flows of the Company. However, in light of the uncertainties inherent in these matters, it is possible that the ultimate resolution of one or more of these matters
may have a material adverse effect on the Company’s results of operations for a particular period, and future changes in circumstances or additional information could result in additional accruals or resolution in excess of established accruals, which could adversely affect the Company’s results of operations, potentially materially.
Residential Mortgage-Backed Securities Litigation Starting in 2011, the Company and other large financial institutions have been sued in their capacity as trustee for residential mortgage–backed securities trusts for losses arising out of the 2008 financial crisis. In the lawsuits brought against the Company, the investors allege that the Company’s banking subsidiary, USBNA, as trustee caused them to incur substantial losses by failing to enforce loan repurchase obligations and failing to abide by appropriate standards of care after events of default allegedly occurred. The plaintiffs in these matters seek monetary damages in unspecified amounts and most also seek equitable relief.
Regulatory Matters The Company is continually subject to examinations, inquiries, investigations and other forms of regulatory and governmental inquiry or scrutiny covering a wide range of issues in its financial services businesses including in areas of heightened regulatory scrutiny, such as compliance, risk management, third-party risk management and consumer protection. In some cases, these matters are part of reviews of specified activities at multiple industry participants; in others, they are directed at the Company individually. For example, the Division of Enforcement of the SEC has investigated U.S. Bancorp Fund Services, LLC (“USBFS”), a subsidiary of USBNA, relating to its role providing fund administration services to a third-party investment fund. This investment fund was
advised by an investment adviser who engaged in fraud, and USBFS was not affiliated with the investment adviser and did not provide any advisory services to the fund. The Division of Enforcement made a preliminary determination to recommend that the SEC file an enforcement action against USBFS, and USBFS has engaged in discussions with the SEC on this matter. The Company is cooperating fully with all pending examinations, inquiries and investigations, any of which could lead to administrative or legal proceedings or settlements. Remedies in these proceedings or settlements may include fines, penalties, restitution or alterations in the Company’s business practices (which may increase the Company’s operating expenses and decrease its revenue).
Outlook Due to their complex nature, it can be years before litigation and regulatory matters are resolved. The Company may be unable to develop an estimate or range of loss where matters are in early stages, there are significant factual or legal issues to be resolved, damages are unspecified or uncertain, or there is uncertainty as to a litigation class being certified or the outcome of pending motions, appeals or proceedings. For those litigation and regulatory matters where the Company has information to develop an estimate or range of loss, the Company believes the upper end of the range of reasonably possible losses in aggregate, in excess of any reserves established for matters where a loss is considered probable, will not be material to its financial condition, results of operations or cash flows. The Company’s estimates are subject to significant judgment and uncertainties, and the matters underlying the estimates will change from time to time. Actual results may vary significantly from the current estimates.
The Company's management reporting is organized into three reportable operating segments aligned by major lines of business based on the products and services provided to customers through its distribution channels. All other business activities not included in the reportable operating segments are included in the Treasury and Corporate Support business segment. The chief operating decision maker uses net interest income on a taxable-equivalent basis, noninterest income and net income (loss) before income taxes for all reportable segments in deciding how to allocate resources during the annual budget and monthly forecasting process. The chief operating decision maker considers variances in reported results to forecasts and variances to prior periods to assess performance. The Company’s chief operating decision maker is the Chief Executive Officer. The Company has the following reportable operating and other business segments:
Wealth, Corporate, Commercial and Institutional Banking Wealth, Corporate, Commercial and Institutional Banking provides core banking, specialized lending, transaction and payment processing, capital markets, asset management, and brokerage and investment related
services to wealth, middle market, large corporate, commercial real estate, government and institutional clients.
Consumer and Business Banking Consumer and Business Banking comprises consumer banking, small business banking and consumer lending. Products and services are delivered through banking offices, telephone servicing and sales, online services, direct mail, ATMs, mobile devices, distributed mortgage loan officers, and intermediary relationships including auto dealerships, mortgage banks, and strategic business partners.
Payment Services Payment Services includes consumer and business credit cards, stored-value cards, debit cards, corporate, government and purchasing card services and merchant processing.
Treasury and Corporate Support Treasury and Corporate Support includes the Company’s investment portfolios, funding, capital management, interest rate risk management, income taxes not allocated to business segments, including most investments in tax-advantaged projects, and the residual aggregate of those expenses
| | |
128 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
associated with corporate activities that are managed on a consolidated basis.
Basis of Presentation Business segment results are derived from the Company’s business unit profitability reporting systems by specifically attributing managed balance sheet assets, deposits and other liabilities and their related income or expense. The allowance for credit losses and related provision expense are allocated to the business segments according to the volume and credit quality of the loan balances managed, but with the impact of changes in economic forecasts recorded in Treasury and Corporate Support. Goodwill and other intangible assets are assigned to the business segments based on the mix of business of an entity acquired by the Company. Within the Company, capital levels are evaluated and managed centrally; however, capital is allocated to the business segments to support evaluation of business performance. Business segments are allocated capital on a risk-adjusted basis considering economic and regulatory capital requirements. Generally, the determination of the amount of capital allocated to each business segment includes credit allocations following a Basel III regulatory framework. Interest income and expense is determined based on the assets and liabilities managed by the business segment. Because funding and asset/liability management is a central function, funds transfer-pricing methodologies are utilized to allocate a cost of funds used or credit for funds provided to all business segment assets and liabilities, respectively, using a matched funding concept. Also, each business unit is allocated the taxable-equivalent benefit of tax-exempt products. The residual effect on net interest income of asset/liability management activities is included in Treasury and Corporate Support. Noninterest income and expenses directly managed by each business segment, including fees, service charges, salaries and benefits, and other direct revenues and costs are accounted for within each segment’s financial results in a manner similar to the consolidated financial statements.
Occupancy costs are allocated based on utilization of facilities by the business segments. Generally, operating losses are charged to the business segment when the loss event is realized in a manner similar to a loan charge-off. Noninterest expenses incurred by centrally managed operations or business segments that directly support another business segment’s operations are charged to the applicable business segment based on its utilization of those services, primarily measured by the volume of customer activities, number of employees or other relevant factors. These allocated expenses are reported as net shared services expense within noninterest expense. Certain activities that do not directly support the operations of the business segments or for which the business segments are not considered financially accountable in evaluating their performance are not charged to the business segments. The income or expenses associated with these corporate activities, including merger and integration charges, are reported within the Treasury and Corporate Support business segment. Income taxes are assessed to each business segment at a standard tax rate with the residual tax expense or benefit to arrive at the consolidated effective tax rate included in Treasury and Corporate Support.
Designations, assignments and allocations change from time to time as management systems are enhanced, methods of evaluating performance or product lines change or business segments are realigned to better respond to the Company’s diverse customer base. During 2024 and 2023, certain organization and methodology changes were made, including revising the Company’s business segment funds transfer-pricing methodology related to deposits and loans during the second quarter of 2024 and combining its Wealth Management and Investment Services and Corporate and Commercial Banking business segments to create the Wealth, Corporate, Commercial and Institutional Banking business segment during the third quarter of 2023. Prior period results were recast and presented on a comparable basis.
Condensed income statement results by business segment for the years ended December 31 were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Wealth, Corporate, Commercial and Institutional Banking | Consumer and Business Banking | Payment Services |
| (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 |
Net interest income (taxable-equivalent basis)(a) | $ | 7,645 | | $ | 7,862 | | $ | 5,680 | | $ | 7,658 | | $ | 8,683 | | $ | 7,266 | | $ | 2,831 | | $ | 2,609 | | $ | 2,504 | |
Noninterest income(b)(c) | 4,548 | | 4,141 | | 3,561 | | 1,606 | | 1,675 | | 1,536 | | 4,198 | | 4,055 | | 3,794 | |
| Total net revenue | 12,193 | | 12,003 | | 9,241 | | 9,264 | | 10,358 | | 8,802 | | 7,029 | | 6,664 | | 6,298 | |
| Compensation and employee benefits | 2,191 | | 2,151 | | 1,803 | | 2,221 | | 2,305 | | 2,041 | | 906 | | 869 | | 835 | |
| Other intangibles | 206 | | 230 | | 37 | | 266 | | 292 | | 42 | | 97 | | 114 | | 136 | |
| Net shared services | 2,116 | | 2,132 | | 1,547 | | 2,800 | | 2,956 | | 2,655 | | 2,126 | | 2,017 | | 1,656 | |
Other direct expenses(d) | 936 | | 931 | | 748 | | 1,282 | | 1,316 | | 1,041 | | 926 | | 920 | | 898 | |
| Total noninterest expense | 5,449 | | 5,444 | | 4,135 | | 6,569 | | 6,869 | | 5,779 | | 4,055 | | 3,920 | | 3,525 | |
| Income (loss) before provision and income taxes | 6,744 | | 6,559 | | 5,106 | | 2,695 | | 3,489 | | 3,023 | | 2,974 | | 2,744 | | 2,773 | |
| Provision for credit losses | 385 | | 340 | | 154 | | 182 | | 78 | | 75 | | 1,614 | | 1,394 | | 980 | |
| Income (loss) before income taxes | 6,359 | | 6,219 | | 4,952 | | 2,513 | | 3,411 | | 2,948 | | 1,360 | | 1,350 | | 1,793 | |
| Income taxes and taxable-equivalent adjustment | 1,590 | | 1,555 | | 1,239 | | 629 | | 854 | | 738 | | 340 | | 337 | | 448 | |
| Net income (loss) | 4,769 | | 4,664 | | 3,713 | | 1,884 | | 2,557 | | 2,210 | | 1,020 | | 1,013 | | 1,345 | |
| Net (income) loss attributable to noncontrolling interests | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | | — | |
| Net income (loss) attributable to U.S. Bancorp | $ | 4,769 | | $ | 4,664 | | $ | 3,713 | | $ | 1,884 | | $ | 2,557 | | $ | 2,210 | | $ | 1,020 | | $ | 1,013 | | $ | 1,345 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | Treasury and Corporate Support | Consolidated Company | | |
| (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 | | | |
Net interest income (taxable-equivalent basis)(a) | $ | (1,725) | | $ | (1,627) | | $ | (604) | | $ | 16,409 | | $ | 17,527 | | $ | 14,846 | | | | |
Noninterest income(b)(c) | 694 | | 746 | | 565 | | 11,046 | | 10,617 | | 9,456 | | | | |
| Total net revenue | (1,031) | | (881) | | (39) | | 27,455 | | 28,144 | | 24,302 | | | | |
| Compensation and employee benefits | 5,236 | | 5,091 | | 4,478 | | 10,554 | | 10,416 | | 9,157 | | | | |
| Other intangibles | — | | — | | — | | 569 | | 636 | | 215 | | | | |
| Net shared services | (7,042) | | (7,105) | | (5,858) | | — | | — | | — | | | | |
Other direct expenses(d) | 2,921 | | 4,654 | | 2,847 | | 6,065 | | 7,821 | | 5,534 | | | | |
| Total noninterest expense | 1,115 | | 2,640 | | 1,467 | | 17,188 | | 18,873 | | 14,906 | | | | |
| Income (loss) before provision and income taxes | (2,146) | | (3,521) | | (1,506) | | 10,267 | | 9,271 | | 9,396 | | | | |
| Provision for credit losses | 57 | | 463 | | 768 | | 2,238 | | 2,275 | | 1,977 | | | | |
| Income (loss) before income taxes | (2,203) | | (3,984) | | (2,274) | | 8,029 | | 6,996 | | 7,419 | | | | |
| Income taxes and taxable-equivalent adjustment | (859) | | (1,208) | | (844) | | 1,700 | | 1,538 | | 1,581 | | | | |
| Net income (loss) | (1,344) | | (2,776) | | (1,430) | | 6,329 | | 5,458 | | 5,838 | | | | |
| Net (income) loss attributable to noncontrolling interests | (30) | | (29) | | (13) | | (30) | | (29) | | (13) | | | | |
| Net income (loss) attributable to U.S. Bancorp | $ | (1,374) | | $ | (2,805) | | $ | (1,443) | | $ | 6,299 | | $ | 5,429 | | $ | 5,825 | | | | |
(a)Total net interest income includes a taxable-equivalent adjustment of $120 million, $131 million and $118 million for 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively. See Non-GAAP Financial Measures beginning on page 57. (b)Payment services noninterest income presented net of related rewards and rebate costs and certain partner payments of $3.1 billion, $3.0 billion and $2.9 billion for 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively.
(c)Total noninterest income includes revenue generated from certain contracts with customers of $9.2 billion, $8.8 billion and $8.0 billion for 2024, 2023 and 2022, respectively.
(d)Other direct expenses for each reportable segment includes: net occupancy and equipment, professional services, marketing and business development, technology and communications, and other.
| | |
130 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
Average balances by business segment for the years ended December 31 were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Wealth, Corporate, Commercial and Institutional Banking | Consumer and Business Banking | Payment Services |
| (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 |
| Loans | $ | 172,466 | | $ | 175,836 | | $ | 150,512 | | $ | 155,088 | | $ | 162,012 | | $ | 144,441 | | $ | 41,081 | | $ | 38,471 | | $ | 34,627 | |
| Other earning assets | 10,122 | | 6,613 | | 4,771 | | 2,410 | | 2,388 | | 3,117 | | 142 | | 97 | | 634 | |
| Goodwill | 4,825 | | 4,682 | | 3,634 | | 4,326 | | 4,466 | | 3,250 | | 3,357 | | 3,327 | | 3,305 | |
| Other intangible assets | 981 | | 1,007 | | 365 | | 4,539 | | 5,264 | | 3,784 | | 277 | | 352 | | 423 | |
| Assets | 201,362 | | 202,701 | | 169,554 | | 168,913 | | 179,247 | | 160,174 | | 47,169 | | 44,291 | | 41,072 | |
| Noninterest-bearing deposits | 56,760 | | 70,908 | | 82,671 | | 20,810 | | 30,967 | | 31,719 | | 2,685 | | 2,981 | | 3,410 | |
| Interest-bearing deposits | 214,622 | | 203,038 | | 175,345 | | 200,611 | | 185,712 | | 163,190 | | 96 | | 103 | | 162 | |
| Total deposits | 271,382 | | 273,946 | | 258,016 | | 221,421 | | 216,679 | | 194,909 | | 2,781 | | 3,084 | | 3,572 | |
| Total U.S. Bancorp shareholders’ equity | 21,438 | | 22,366 | | 18,159 | | 14,426 | | 16,026 | | 12,678 | | 10,005 | | 9,310 | | 8,233 | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Treasury and Corporate Support | Consolidated Company | | | |
| (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 | | | |
| Loans | $ | 5,240 | | $ | 4,956 | | $ | 3,993 | | $ | 373,875 | | $ | 381,275 | | $ | 333,573 | | | | |
| Other earning assets | 220,092 | | 214,826 | | 203,248 | | 232,766 | | 223,924 | | 211,770 | | | | |
| Goodwill | — | | — | | — | | 12,508 | | 12,475 | | 10,189 | | | | |
| Other intangible assets | 9 | | 16 | | 5 | | 5,806 | | 6,639 | | 4,577 | | | | |
| Assets | 246,570 | | 237,201 | | 221,349 | | 664,014 | | 663,440 | | 592,149 | | | | |
| Noninterest-bearing deposits | 2,752 | | 2,912 | | 2,594 | | 83,007 | | 107,768 | | 120,394 | | | | |
| Interest-bearing deposits | 11,179 | | 9,042 | | 3,293 | | 426,508 | | 397,895 | | 341,990 | | | | |
| Total deposits | 13,931 | | 11,954 | | 5,887 | | 509,515 | | 505,663 | | 462,384 | | | | |
| Total U.S. Bancorp shareholders’ equity | 11,337 | | 5,958 | | 11,346 | | 57,206 | | 53,660 | | 50,416 | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| NOTE 24 | | U.S. Bancorp (Parent Company) |
Condensed Balance Sheet
| | | | | | | | |
| At December 31 (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 |
| Assets | | |
| Due from banks, principally interest-bearing | $ | 9,377 | | $ | 11,585 | |
| Available-for-sale investment securities | 649 | | 662 | |
| Investments in bank subsidiaries | 63,680 | | 61,495 | |
| Investments in nonbank subsidiaries | 4,031 | | 3,884 | |
| Advances to bank subsidiaries | 16,100 | | 12,100 | |
| Advances to nonbank subsidiaries | 401 | | 159 | |
| Other assets | 945 | | 974 | |
| Total assets | $ | 95,183 | | $ | 90,859 | |
| Liabilities and Shareholders’ Equity | | |
| Long-term debt | $ | 35,257 | | $ | 34,332 | |
| Other liabilities | 1,348 | | 1,221 | |
| Shareholders’ equity | 58,578 | | 55,306 | |
| Total liabilities and shareholders’ equity | $ | 95,183 | | $ | 90,859 | |
Condensed Income Statement
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31 (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 |
| Income | | | |
| Dividends from bank subsidiaries | $ | 4,800 | | $ | 4,869 | | $ | 4,750 | |
| Dividends from nonbank subsidiaries | 11 | | 11 | | 105 | |
| Interest from subsidiaries | 1,224 | | 606 | | 119 | |
| Other income | 24 | | 51 | | 31 | |
| Total income | 6,059 | | 5,537 | | 5,005 | |
| Expense | | | |
| Interest expense | 1,663 | | 1,336 | | 505 | |
| Other expense | 178 | | 137 | | 162 | |
| Total expense | 1,841 | | 1,473 | | 667 | |
| Income before income taxes and equity in undistributed income of subsidiaries | 4,218 | | 4,064 | | 4,338 | |
| Applicable income taxes | (95) | | (170) | | (138) | |
| Income of parent company | 4,313 | | 4,234 | | 4,476 | |
| Equity in undistributed income of subsidiaries | 1,986 | | 1,195 | | 1,349 | |
| Net income attributable to U.S. Bancorp | $ | 6,299 | | $ | 5,429 | | $ | 5,825 | |
| | |
132 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
Condensed Statement of Cash Flows
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Year Ended December 31 (Dollars in Millions) | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 |
| Operating Activities | | | |
| Net income attributable to U.S. Bancorp | $ | 6,299 | | $ | 5,429 | | $ | 5,825 | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities | | | |
| Equity in undistributed income of subsidiaries | (1,986) | | (1,195) | | (1,349) | |
| Other, net | 385 | | 83 | | (398) | |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | 4,698 | | 4,317 | | 4,078 | |
| Investing Activities | | | |
| Proceeds from sales and maturities of investment securities | 11 | | 25 | | 423 | |
| Investments in subsidiaries | — | | — | | (5,030) | |
| Net (increase) decrease in short-term advances to subsidiaries | (242) | | (9) | | 557 | |
| Long-term advances to subsidiaries | (5,500) | | (7,500) | | (2,000) | |
| Principal collected on long-term advances to subsidiaries | 1,500 | | 4,500 | | 2,500 | |
| Cash paid for acquisition | — | | — | | (5,500) | |
| Other, net | 16 | | 172 | | (173) | |
| Net cash used in investing activities | (4,215) | | (2,812) | | (9,223) | |
| Financing Activities | | | |
| Proceeds from issuance of long-term debt | 6,516 | | 8,150 | | 8,150 | |
| Principal payments or redemption of long-term debt | (5,618) | | (936) | | (2,300) | |
| Proceeds from issuance of preferred stock | — | | — | | 437 | |
| Proceeds from issuance of common stock | 32 | | 951 | | 21 | |
| Repurchase of preferred stock | — | | — | | (1,100) | |
| Repurchase of common stock | (173) | | (62) | | (69) | |
| Cash dividends paid on preferred stock | (356) | | (341) | | (299) | |
| Cash dividends paid on common stock | (3,092) | | (2,970) | | (2,776) | |
| Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities | (2,691) | | 4,792 | | 2,064 | |
| Change in cash and due from banks | (2,208) | | 6,297 | | (3,081) | |
| Cash and due from banks at beginning of year | 11,585 | | 5,288 | | 8,369 | |
| Cash and due from banks at end of year | $ | 9,377 | | $ | 11,585 | | $ | 5,288 | |
Transfer of funds (dividends, loans or advances) from bank subsidiaries to the Company is restricted. Federal law requires loans to the Company or its affiliates to be secured and generally limits loans to the Company or an individual affiliate to 10 percent of each bank’s unimpaired capital and surplus. In the aggregate, loans to the Company and all affiliates cannot exceed 20 percent of each bank’s unimpaired capital and surplus.
Dividend payments to the Company by its subsidiary bank are subject to regulatory review and statutory limitations and, in some instances, regulatory approval. In general, dividends by the Company’s bank subsidiary to the parent company are limited by rules which compare dividends to net income for regulatorily-defined periods. Furthermore, dividends are restricted by minimum capital constraints for all national banks.
The Company has evaluated the impact of events that have occurred subsequent to December 31, 2024 through the date the consolidated financial statements were filed with the SEC. Based on this evaluation, the Company has determined none of these events were required to be recognized or disclosed in the consolidated financial statements and related notes.
U.S. Bancorp
Consolidated Daily Average Balance Sheet and Related Yields and Rates(a) (Unaudited)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2024 | 2023 | 2022 |
Year Ended December 31
(Dollars in Millions) | Average Balances | Interest | Yields
and
Rates | Average
Balances | Interest | Yields
and
Rates | Average Balances | Interest | Yields
and
Rates |
| Assets | | | | | | | | | |
Investment securities(b) | $ | 166,634 | | $ | 5,189 | | 3.11 | % | $ | 162,757 | | $ | 4,566 | | 2.81 | % | $ | 169,442 | | $ | 3,457 | | 2.04 | % |
| Loans held for sale | 2,539 | | 173 | | 6.82 | | 2,461 | | 147 | | 5.98 | | 3,829 | | 201 | | 5.26 | |
Loans(c) | | | | | | | | | |
| Commercial | 133,412 | | 8,717 | | 6.53 | | 134,883 | | 8,662 | | 6.42 | | 123,797 | | 4,340 | | 3.51 | |
| Commercial real estate | 51,657 | | 3,326 | | 6.44 | | 54,646 | | 3,384 | | 6.19 | | 41,098 | | 1,655 | | 4.03 | |
| Residential mortgages | 117,026 | | 4,577 | | 3.91 | | 115,922 | | 4,305 | | 3.71 | | 84,749 | | 2,775 | | 3.27 | |
| Credit card | 28,683 | | 3,815 | | 13.30 | | 26,570 | | 3,429 | | 12.91 | | 23,478 | | 2,583 | | 11.00 | |
| Other retail | 43,097 | | 2,619 | | 6.08 | | 49,254 | | 2,599 | | 5.28 | | 60,451 | | 2,292 | | 3.79 | |
| Total loans | 373,875 | | 23,054 | | 6.17 | | 381,275 | | 22,379 | | 5.87 | | 333,573 | | 13,645 | | 4.09 | |
| Interest-bearing deposits with banks | 51,215 | | 2,744 | | 5.36 | | 49,000 | | 2,581 | | 5.27 | | 31,425 | | 559 | | 1.78 | |
| Other earning assets | 12,378 | | 629 | | 5.08 | | 9,706 | | 471 | | 4.85 | | 7,074 | | 204 | | 2.89 | |
| Total earning assets | 606,641 | | 31,789 | | 5.24 | | 605,199 | | 30,144 | | 4.98 | | 545,343 | | 18,066 | | 3.31 | |
| Allowance for loan losses | (7,541) | | | | (7,138) | | | | (5,880) | | | |
| Unrealized gain (loss) on investment securities | (6,820) | | | | (7,985) | | | | (6,914) | | | |
| Other assets | 71,734 | | | | 73,364 | | | | 59,600 | | | |
| Total assets | $ | 664,014 | | | | $ | 663,440 | | | | $ | 592,149 | | | |
| Liabilities and Shareholders’ Equity | | | | | | | | | |
| Noninterest-bearing deposits | $ | 83,007 | | | | $ | 107,768 | | | | $ | 120,394 | | | |
| Interest-bearing deposits | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest checking | 125,365 | | 1,505 | | 1.20 | | 129,341 | | 1,334 | | 1.03 | | 117,471 | | 277 | | .24 | |
| Money market savings | 204,509 | | 7,580 | | 3.71 | | 166,272 | | 5,654 | | 3.40 | | 126,221 | | 1,220 | | .97 | |
| Savings accounts | 39,625 | | 165 | | .42 | | 55,590 | | 90 | | .16 | | 67,722 | | 10 | | .02 | |
| Time deposits | 57,009 | | 2,438 | | 4.28 | | 46,692 | | 1,697 | | 3.63 | | 30,576 | | 365 | | 1.19 | |
| Total interest-bearing deposits | 426,508 | | 11,688 | | 2.74 | | 397,895 | | 8,775 | | 2.21 | | 341,990 | | 1,872 | | .55 | |
| Short-term borrowings | | | | | | | | | |
| Federal funds purchased | 330 | | 16 | | 4.88 | | 435 | | 21 | | 4.72 | | 687 | | 8 | | 1.12 | |
| Securities sold under agreements to repurchase | 6,658 | | 326 | | 4.89 | | 3,103 | | 125 | | 4.04 | | 2,037 | | 20 | | 1.00 | |
| Commercial paper | 6,718 | | 258 | | 3.85 | | 7,800 | | 268 | | 3.44 | | 7,186 | | 69 | | .96 | |
Other short-term borrowings(d) | 3,495 | | 509 | | 14.56 | | 22,803 | | 1,563 | | 6.85 | | 15,830 | | 471 | | 2.98 | |
| Total short-term borrowings | 17,201 | | 1,109 | | 6.45 | | 34,141 | | 1,977 | | 5.79 | | 25,740 | | 568 | | 2.21 | |
| Long-term debt | 54,473 | | 2,583 | | 4.74 | | 44,142 | | 1,865 | | 4.22 | | 33,114 | | 780 | | 2.35 | |
| Total interest-bearing liabilities | 498,182 | | 15,380 | | 3.09 | | 476,178 | | 12,617 | | 2.65 | | 400,844 | | 3,220 | | .80 | |
| Other liabilities | 25,157 | | | | 25,369 | | | | 20,029 | | | |
| Shareholders’ equity | | | | | | | | | |
| Preferred equity | 6,808 | | | | 6,808 | | | | 6,761 | | | |
| Common equity | 50,398 | | | | 46,852 | | | | 43,655 | | | |
| Total U.S. Bancorp shareholders’ equity | 57,206 | | | | 53,660 | | | | 50,416 | | | |
| Noncontrolling interests | 462 | | | | 465 | | | | 466 | | | |
| Total equity | 57,668 | | | | 54,125 | | | | 50,882 | | | |
| Total liabilities and equity | $ | 664,014 | | | | $ | 663,440 | | | | $ | 592,149 | | | |
| Net interest income | | $ | 16,409 | | | | $ | 17,527 | | | | $ | 14,846 | | |
| Gross interest margin | | | 2.15 | % | | | 2.33 | % | | | 2.51 | % |
| Gross interest margin without taxable-equivalent increments | | | 2.13 | % | | | 2.31 | % | | | 2.49 | % |
| Percent of Earning Assets | | | | | | | | | |
| Interest income | | | 5.24 | % | | | 4.98 | % | | | 3.31 | % |
| Interest expense | | | 2.54 | | | | 2.08 | | | | .59 | |
| Net interest margin | | | 2.70 | % | | | 2.90 | % | | | 2.72 | % |
| Net interest margin without taxable-equivalent increments | | | 2.68 | % | | | 2.88 | % | | | 2.70 | % |
(a)Interest and rates are presented on a fully taxable-equivalent basis based on a federal income tax rate of 21 percent.
(b)Yields on investment securities are computed based on amortized cost balances, excluding any premiums or discounts recorded related to the transfer of investment securities at fair value from available-for-sale to held-to-maturity. Yields include impacts of hedge accounting, including portfolio level basis adjustments.
(c)Interest income and rates on loans include loan fees. Nonaccrual loans are included in average loan balances.
(d)Interest expense and rates includes interest paid on collateral associated with derivative positions.
| | |
134 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
U.S. Bancorp
Supplemental Financial Data (Unaudited) | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Earnings Per Common Share Summary | 2024 | 2023 | 2022 |
| Earnings per common share | $ | 3.79 | | $ | 3.27 | | $ | 3.69 | |
| Diluted earnings per common share | 3.79 | 3.27 | 3.69 |
| Dividends declared per common share | 1.98 | 1.93 | 1.88 |
| Other Statistics (Dollars and Shares in Millions) | | | |
Common shares outstanding(a) | 1,560 | 1,558 | 1,531 |
| Average common shares outstanding and common stock equivalents | | | |
| Earnings per common share | 1,560 | | 1,543 | | 1,489 | |
| Diluted earnings per common share | 1,561 | | 1,543 | | 1,490 | |
Number of shareholders(b) | 27,517 | 29,094 | 30,280 |
| Common dividends declared | $ | 3,110 | | $ | 3,000 | | $ | 2,829 | |
(a)Defined as total common shares issued less common stock held in treasury at December 31.
(b)Based on number of common stock shareholders of record at December 31.
The common stock of U.S. Bancorp is traded on the New York Stock Exchange, under the ticker symbol “USB.” At January 31, 2025, there were 27,433 holders of record of the Company’s common stock.
Stock Performance Chart
The following chart compares the cumulative total shareholder return on the Company’s common stock during the five years ended December 31, 2024, with the cumulative total return on the Standard & Poor’s 500 Index and the KBW Bank Index. The comparison assumes $100 was invested on December 31, 2019, in the Company’s common stock and in each of the foregoing indices and assumes the reinvestment of all dividends. The comparisons in the graph are based upon historical data and are not indicative of, nor intended to forecast, future performance of the Company’s common stock.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 | |
| USB | 100 | | 82 | | 102 | | 83 | | 87 | | 100 | | |
| S&P 500 | 100 | | 118 | | 152 | | 125 | | 157 | | 197 | | |
| BKX | 100 | | 90 | | 124 | | 98 | | 97 | | 133 | | |
Company Information
General Business Description U.S. Bancorp is a financial services holding company headquartered in Minneapolis, Minnesota, serving millions of local, national and global customers. U.S. Bancorp is registered as a bank holding company under the Bank Holding Company Act of 1956 (the “BHC Act”), and has elected to be treated as a financial holding company under the BHC Act. The Company provides a full range of financial services, including lending and depository services, cash management, capital markets, and trust and investment management services. It also engages in credit card services, merchant and ATM processing, mortgage banking, insurance, brokerage and leasing.
U.S. Bancorp’s banking subsidiary, USBNA, is engaged in the general banking business, principally in domestic markets, and holds all of the Company’s consolidated deposits of $518.3 billion at December 31, 2024. USBNA provides a wide range of products and services to individuals, businesses, institutional organizations, governmental entities and other financial institutions. Commercial and consumer lending services are principally offered to customers within the Company’s domestic markets, to domestic customers with foreign operations and to large national customers operating in specific industries targeted by the Company, such as healthcare, utilities, oil and gas, and state and municipal government. Lending services include traditional credit products as well as credit card services, lease financing and import/export trade, asset-backed lending, agricultural finance and other products. Depository services include checking accounts, savings accounts and time certificate contracts. Ancillary services such as capital markets, treasury management and receivable lock-box collection are provided to corporate and governmental entity customers. U.S. Bancorp’s bank and trust subsidiaries provide a full range of asset management and fiduciary services for individuals, estates, foundations, business corporations and charitable organizations.
Other U.S. Bancorp non-banking subsidiaries offer investment and insurance products to the Company’s customers principally within its domestic markets, and fund administration services to a broad range of mutual and other funds.
Banking and investment services are provided through a network of branches and banking offices across the United States, primarily in the Midwest and West regions, including 2,165 branches across 26 states as of December 31, 2024. A significant percentage of consumer transactions are completed using USBNA's digital banking services, both online and through its digital app. The Company operates a network of 4,489 ATMs as of December 31, 2024, and provides 24-hour, seven day a week telephone customer service. Mortgage banking services are provided through banking offices and loan production offices throughout the Company’s domestic markets. Lending products may be originated through banking offices, indirect correspondents, brokers or other lending sources. The Company is also one of the largest providers of corporate
and purchasing card services and corporate trust services in the United States. The Company’s subsidiaries provide domestic merchant processing services directly to merchants, as well as similar merchant services in Canada and segments of Europe. The Company also provides corporate trust and fund administration services in Europe. These foreign operations are not significant to the Company.
As of December 31, 2024, U.S. Bancorp employed more than 70,000 people.
Risk Factors
An investment in the Company involves risk, including the possibility that the value of the investment could fall substantially and that dividends or other distributions on the investment could be reduced or eliminated. Below are material risk factors that make an investment in the Company speculative or risky.
Economic and Market Conditions Risk
Deterioration in business and economic conditions could adversely affect the Company’s lending business and the value of loans and debt securities it holds The Company’s business activities and earnings are affected by general business conditions in the United States and abroad, including factors such as the level and volatility of short-term and long-term interest rates, inflation, home prices, unemployment and under-employment levels, bankruptcies, household income, consumer spending, fluctuations in both debt and equity capital markets, liquidity of the global financial markets, the availability and cost of capital and credit, investor sentiment and confidence in the financial markets, the strength of the domestic and global economies in which the Company operates, and customer deposit behavior. These conditions can change suddenly and negatively. For example, volatility due to failures of other banks or general uncertainty regarding the health of banks may affect customer deposit behavior and cause deposit withdrawals, even in situations where USBNA is not itself experiencing the same uncertainty. Other future changes in these conditions, whether related to a pandemic, geopolitical conflict, the threat or occurrence of a U.S. sovereign default or government shutdown, bank failures, other disruptions in the financial services industry or otherwise, could have adverse effects on the Company and its businesses.
Given the high percentage of the Company’s assets represented directly or indirectly by loans, and the importance of lending to its overall business, weak economic conditions have in the past negatively affected, and may in the future negatively affect, the Company’s business and results of operations, including new loan origination activity, existing loan utilization rates and delinquencies, defaults and the ability of customers to meet obligations under the loans. The value to the Company of other assets such as investment securities, most of which are debt securities or other financial instruments supported by loans, similarly have been, and would be, negatively impacted by widespread deterioration in credit quality resulting from a weakening of the economy.
| | |
136 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
In addition, volatility and uncertainty related to inflation or a possible recession and their effects may contribute to or enhance some of the risks described herein. For example, higher inflation, slower growth or a recession has in the past reduced demand for borrowing from both corporate and consumer customers and could in the future reduce demand for the Company’s products, adversely affect the creditworthiness of its borrowers or result in lower values for its interest-earning assets and investment securities. Any of these effects, or others that the Company is not able to predict, could adversely affect its financial condition or results of operations.
Any deterioration in global economic conditions could damage the domestic economy or negatively affect the Company’s borrowers or other counterparties that have direct or indirect exposure to these regions. Such global disruptions, including disruptions in supply chains or geopolitical risk, can undermine investor confidence, cause a contraction of available credit, or create market volatility, any of which could have material adverse effects on the Company’s businesses, results of operations, financial condition and liquidity, even if the Company’s direct exposure to the affected region is limited. Global political trends toward nationalism and isolationism could increase the probability of a deterioration in global economic conditions.
Changes in domestic economic, labor, trade or tax policies may arise from recent transitions in political leadership in the United States. Such policy changes could disrupt economic conditions, cause uncertainty, negatively affect some sectors of the domestic market more than others, erode consumer confidence levels, cause adverse changes in payment patterns, lead to increases in delinquencies and default rates in certain industries or regions, or have other negative market or customer impacts. Any of these developments could increase the Company’s loan charge-offs and provision for credit losses. Any future economic deterioration that affects household or corporate incomes, or that causes or amplifies concerns regarding the possibility of a return to recessionary conditions, could also result in reduced demand for credit or fee-based products and services.
Changes in interest rates have in the past reduced, and could in the future reduce, the Company’s net interest income The Company’s earnings are dependent to a large degree on net interest income, which is the difference between interest income from loans and investments and interest expense on deposits and borrowings. Net interest income is significantly affected by market rates of interest, which in turn are affected by prevailing economic conditions, by the fiscal and monetary policies of the federal government and by the policies of various regulatory agencies. Volatility in interest rates can also result in the flow of funds away from financial institutions into direct investments. Direct investments, such as United States government and corporate securities and other investment vehicles (including mutual funds), generally pay higher rates of return than financial institutions. In order to prevent outflows and compete for a shrinking pool of deposits, banks, including USBNA, have historically and
may in the future increase deposit rates, which could decrease net interest income. All of these factors may cause USBNA to lose some of its low-cost deposit funding. Customers may also continue to move noninterest-bearing deposits into interest-bearing accounts, thus increasing overall deposit costs. Higher funding costs reduce the Company’s net interest margin and net interest income. A prolonged period of high or increasing interest rates may cause the Company to experience an acceleration of deposit migration, which could adversely affect the Company’s operations and liquidity. This risk is exacerbated by technological developments and trends in customer behavior, including the ease and speed with which deposits may be transferred electronically, particularly by a growing number of customers who maintain accounts with multiple banks.
The Federal Reserve Board raised benchmark interest rates throughout 2022 and 2023 in response to economic conditions, particularly inflationary pressures, and in 2024 began to lower interest rates. Meanwhile, longer-term interest rates, while volatile, have remained elevated.
Historically, when interest rates are increasing, or when long-term rates are elevated relative to short-term rates, the Company has earned higher net interest income, and conversely, decreasing interest rates, or situations when long-term rates are compressed relative to, or lower than, short-term rates, have adversely impacted the Company's net interest income. However, higher interest rates can also lead to fewer originations of loans, less liquidity in the financial markets, and higher funding costs, each of which could adversely affect the Company’s revenues and its liquidity and capital levels. Higher interest rates could also negatively affect the payment performance on loans that are scheduled to mature or are linked to variable interest rates. If borrowers of variable rate loans are unable to afford higher interest payments, those borrowers may reduce or stop making payments, thereby causing the Company to incur losses and increased operational costs related to servicing a higher volume of delinquent loans. In 2022 and 2023, as a result of the high interest rate environment, the Company earned higher net interest income but experienced fewer originations of mortgage loans and higher funding costs. During the first half of 2024, interest rates remained elevated, which drove funding costs higher, but over the second half of the year, net interest income began to expand as funding costs stabilized and began to decrease.
The Company’s results may be materially affected by market fluctuations and significant changes in the value of financial instruments The value of securities, derivatives and other financial instruments which the Company owns or in which it makes markets can be materially affected by market fluctuations. Market volatility, illiquid market conditions and other disruptions in the financial markets may make it extremely difficult to value certain financial instruments. Subsequent valuations of financial instruments in future periods, in light of factors then prevailing, may result in significant changes in the value of these instruments. In addition, at the time of any disposition of these financial instruments, the price that the
Company ultimately realizes will depend on the demand and liquidity in the market at that time and may be materially lower than their current fair value. Any of these factors could cause a decline in the value of financial instruments that the Company owns or in which it makes markets, which may have an adverse effect on the Company’s results of operations. In addition, losses in the value of the Company’s investment securities or loan portfolio could affect market perception of the Company and create volatility in the Company’s stock price. Losses in the value of the Company’s investment securities, even if they do not affect earnings or capital, could also cause some depositors, particularly those who maintain uninsured and uncollateralized deposits, to question the stability of USBNA and to move their deposits away from USBNA. Such events could negatively affect the Company’s liquidity, financial condition and results of operations.
Changes in United States trade policies, including the imposition of tariffs and retaliatory tariffs, may adversely impact the Company’s business, financial condition and results of operations There have been recent changes to United States trade policies and tariffs, including trade policies and tariffs affecting China, Canada and Mexico, and the imposition of, or the potential for the imposition of, retaliatory tariffs by such countries. There could be additional changes to trade policies, tariffs and treaties with these and other countries in the future. Such tariffs, retaliatory tariffs or other trade restrictions on products and materials that the Company’s customers import or export could cause the prices of its customers’ products to increase, which could reduce demand for, or margins on, such products. Any of these effects could adversely affect the ability of the Company’s customers to service debt. Additionally, if prices of consumer goods increase materially as a result of tariffs, the ability of individual households to service debt may be negatively affected. If the Company’s customers are unable to service their debt, it would adversely affect the Company’s financial condition and results of operations. At this time, the Company and others are unable to predict whether and to what extent further tariffs and retaliatory tariffs may be imposed or what effect changes in the U.S. political administration may have on existing international trade agreements and policies. This uncertainty complicates business planning for the Company’s customers in certain industries, which may adversely affect the Company’s financial results if such customers change their spending and borrowing patterns in response to the current uncertainty.
Operations and Business Risk
A breach in the security of the Company’s information systems, or the information systems of certain third parties, or a critical technology failure could disrupt the Company’s businesses, result in the disclosure of confidential information, damage its reputation and create significant financial and legal risk The Company continues to experience an increasing number of attempted attacks on its information systems, software, networks and other technologies. The Company’s security measures may
not be effective against all threats, including new and emerging threats. Malicious actors continue to develop increasingly sophisticated methods of attack that could impact the Company, including attack methods that are aided by advanced artificial intelligence (“AI”) models and other tools. Many financial institutions, retailers and other companies engaged in data processing and collection, including software and information technology service providers, have reported cyber attacks, some of which involved sophisticated and targeted attacks intended to obtain unauthorized access to confidential information, destroy or ransom data, disable or degrade service, or sabotage systems, often through the introduction of software that is intentionally included or inserted in an information system for a harmful purpose (malware).
Attacks on government institutions, financial institutions, technology service providers, or other institutions important to the overall functioning of the financial system could also adversely affect, directly or indirectly, aspects of the Company’s businesses. The increasing consolidation, interdependence and complexity of financial entities and technology systems increases the risk of operational failure, both for the Company and on an industry-wide basis, and means that a technology failure, cyber attack, or other breach that significantly degrades, deletes or compromises the systems or data of one or more financial entities could materially affect the Company, its counterparties or other market participants.
Third parties that facilitate the Company’s business activities, including exchanges, clearinghouses, payment and ATM networks, financial intermediaries and vendors that provide services or technology solutions for the Company’s operations, are also sources of operational and security risks to the Company due to operational or technical failures of their systems, misconduct or negligence by their employees or cyber attacks that could affect their ability to deliver a product or service to the Company, resulting in lost or compromised Company or customer information. Furthermore, a third party may not reveal an attack or system failure to the Company in a timely manner, which could compromise the Company’s ability to respond effectively. Some of these third parties may engage vendors of their own, which introduces the risk that the third party’s vendors and subcontractors could be the source of operational and security failures. In addition, if a third party obtains access to the customer account data on the Company’s systems, and that party experiences a breach via an external or internal threat or misappropriates such data, the Company and its customers could suffer material harm, including heightened risk of fraudulent transactions, losses from fraudulent transactions, increased operational costs to remediate any security breach and legal and reputational harm. These risks are expected to continue to increase as the Company expands its interconnectivity with its customers and other third parties.
Within the past several years, multiple companies have disclosed significant cybersecurity incidents affecting debit and credit card accounts of their customers, some of whom were the Company’s cardholders and who may experience fraud on their card accounts because of the breach. The
| | |
138 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
Company has suffered, and expects to suffer in the future, losses associated with reimbursing its customers for such fraudulent transactions and for other costs related to data security compromise events, such as replacing cards associated with compromised card accounts. These attacks involving Company cards are expected to continue and could, individually or in the aggregate, have a material adverse effect on the Company’s financial condition or results of operations.
The Company may not be able to anticipate or to implement effective preventive measures against all cyber attacks because malicious actor methods and techniques change frequently, increase in sophistication, often are not recognized until launched, sometimes go undetected even when successful, and originate from a wide variety of sources, including organized crime, hackers, terrorists, activists, hostile foreign governments and other external parties. Those parties may attempt to place their information technology workers as employees or contractors of the Company or the Company’s third-party vendors to attempt to gain access to the Company’s systems. Those parties may also attempt to fraudulently induce employees, customers or other users of the Company’s systems to disclose sensitive information to gain access to the Company’s data or that of its customers or clients, such as through “phishing” and other social engineering schemes. For example, recent advances in AI may allow a bad actor to create so-called “deep fakes” to impersonate the voice or likeness of another individual, which could be used in social engineering schemes that may be more difficult to detect than other social engineering efforts. Attack methods may include the introduction of computer viruses and/or malicious or destructive code, denial-of-service attacks (DDoS), and cyber extortion with accompanying ransom demands. The Company’s information security risks may increase in the future as the Company continues to increase its mobile and internet-based product offerings and expands its internal usage of web-based products, data storage and other applications. In addition, the Company’s customers often use their own devices, such as computers, smart phones and tablets, to make payments and manage their accounts, and are subject to social engineering schemes, scam websites, and other attempts from cyber criminals to compromise or deny access to their accounts. The Company has limited ability to assure the safety and security of its customers’ transactions with the Company to the extent they are using their own devices, which have been, and likely will continue to be, subject to such threats.
If the Company’s physical or cybersecurity systems are penetrated or circumvented, or an authorized user intentionally or unintentionally removes, loses or destroys critical business data, serious negative consequences for the Company can follow, including significant disruption of the Company’s operations, misappropriation of confidential Company and/or customer information, or damage to the Company’s, customers’ or counterparties’ computers or systems. These consequences could result in violations of privacy and other applicable laws; financial loss to the Company or to its customers; loss of confidence in the
Company’s security measures; customer dissatisfaction; significant litigation exposure; regulatory investigations, fines, penalties or intervention; reimbursement or other compensatory costs (including the costs of credit monitoring services); additional compliance costs; and harm to the Company’s reputation, all of which could adversely affect the Company.
Because the investigation of any cybersecurity incident is inherently unpredictable and would require substantial time to complete, the Company may not be able to quickly remediate the consequences of any incident, which may increase the costs of, and enhance the negative consequences associated with, an incident. In addition, to the extent the Company’s insurance covers aspects of any cybersecurity incident, such insurance may not be sufficient to cover all the Company’s losses.
The Company relies on its employees, systems and third parties to conduct its business, and certain failures by systems or misconduct by employees or third parties could adversely affect its operations The Company operates in many different businesses in diverse markets and relies on the ability of its employees and systems to process a high number of transactions. The Company’s business, financial, accounting, data processing, and other operating systems and facilities may stop operating properly or become disabled or damaged due to a number of factors, including events that are out of its control. In addition to the risks posed by cybersecurity incidents, as discussed above, such systems could be compromised because of spikes in transaction volume, electrical or telecommunications outages, critical technology failures, degradation or loss of internet or website availability, natural disasters, political or social unrest, and terrorist acts. The Company’s business operations may be adversely affected by significant disruption to the operating systems that support its businesses and customers. The Company’s resiliency systems could become compromised, which could negatively impact the ability to back up data.
The Company could also incur losses resulting from the risk of human error by employees, misconduct or fraud by employees or persons outside the Company, unauthorized access to its computer systems, the execution of unauthorized transactions by employees, errors relating to transaction processing and technology, breaches of the internal control system and compliance requirements, and failures of business continuation and disaster recovery processes and systems. This risk of loss also includes customer remediation costs, potential legal actions, fines or civil money penalties that could arise resulting from an operational deficiency or noncompliance with applicable regulatory standards, adverse business decisions or their implementation, reputational harm, and customer attrition due to potential negative publicity.
Third parties provide key components of the Company’s business infrastructure, such as internet connections, cloud services, network access and mutual fund distribution. Any problems caused by third-party service providers, including failing to comply with their contractual obligations or performing their services negligently, which could cause
critical technology failures, could adversely affect the Company’s ability to deliver products and services to the Company’s customers and otherwise conduct its business. Replacing third-party service providers could also entail significant delay and expense. In addition, failure of third-party service providers to handle current or higher volumes of use could adversely affect the Company’s ability to deliver products and services to clients and otherwise conduct its business. Technological or financial difficulties of a third-party service provider could adversely affect the Company’s businesses to the extent those difficulties result in the interruption or discontinuation of services provided by that party.
Operational risks for large financial institutions such as the Company have generally increased in recent years, in part because of the proliferation of new technologies, implementation of work-from-home and hybrid work arrangements, the use of internet services and telecommunications technologies to conduct financial transactions, the increased number and complexity of transactions being processed, and the increased sophistication and activities of organized crime, hackers, terrorists, activists, and other external parties. In the event of a breakdown in the Company’s internal control systems, improper operation of systems or improper employee or third-party actions, the Company could suffer financial loss, face legal or regulatory action and suffer damage to its reputation.
The Company could face material legal and reputational harm if it fails to safeguard personal information The Company is subject to complex and evolving laws and regulations, both inside and outside the United States, governing the privacy and protection of personal information. Individuals whose personal information may be protected by law include the Company’s customers and their customers, prospective customers, job applicants, current and former employees, employees of the Company’s suppliers, and other individuals. Complying with laws and regulations applicable to the Company’s collection, use, transfer and storage of personal information can increase operating costs, impact the development and marketing of new products or services, and reduce operational efficiency. Mishandling or misuse of personal information by the Company or its suppliers, including data breaches at third parties exposing personal information that have occurred and could occur in the future, have resulted in litigation against the Company and could result in additional litigation or regulatory fines, penalties or other sanctions in the future. For example, in 2024, a state attorney general filed a claim in federal court against a bank for alleged failure to protect consumer accounts from fraud.
In the United States, several states have enacted consumer privacy laws that impose compliance obligations with respect to personal information. In particular, the California Consumer Privacy Act (the ”CCPA”), as amended by the California Privacy Rights Act, and its implementing regulations impose significant requirements on covered businesses with respect to consumer data privacy rights. Compliance with the CCPA and other state statutes,
common law, or regulations designed to protect personal information could potentially require substantial technology infrastructure and process changes across many of the Company’s businesses. Non-compliance with the CCPA or similar laws and regulations could lead to substantial regulatory fines and penalties, damages from private causes of action, compelled changes to the Company’s business practices, and/or reputational harm. The Company cannot predict whether any pending or future state or federal legislation will be adopted, or the impact of any such adopted legislation on the Company. Future legislation could result in substantial costs to the Company and could have an adverse effect on its business, financial condition, and results of operations.
In addition, legal requirements for cross-border personal data transfers vary across jurisdictions, such as in the European Economic Area and the United Kingdom, and are evolving rapidly. Compliance with this changing landscape of privacy requirements could potentially compel the Company to make significant technological and operational changes, any of which could result in substantial costs to the Company, and failure to comply with applicable data transfer or privacy requirements could subject the Company to fines or regulatory investigation or oversight.
Additional risks could arise from the failure of the Company or third parties to provide adequate notice to the Company’s customers about the personal information collected from them and the use of such information; to receive, document, and honor the privacy preferences expressed by the Company’s customers; to protect personal information from unauthorized disclosure; or to maintain proper training on privacy practices for all employees or third parties who have access to personal information. Concerns regarding the effectiveness of the Company’s measures to safeguard personal information and abide by privacy preferences, or even the perception that those measures are inadequate or that the Company does not abide by such privacy preferences, could cause the Company to lose existing or potential customers and thereby reduce its revenues. In addition, any failure or perceived failure by the Company to comply with applicable privacy or data protection laws and regulations has subjected, and may in the future subject, the Company to litigation and could result in requirements to modify or cease certain operations or practices, and/or incur material liabilities or regulatory fines, penalties, or other sanctions. Refer to “Supervision and Regulation” in the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for additional information regarding data privacy laws and regulations. Any of these outcomes could materially damage the Company’s reputation and otherwise adversely affect its business.
The Company could lose market share and experience increased costs if it does not effectively develop and implement new technology The financial services industry is continually undergoing rapid technological change with frequent introductions of new technology-driven products and services, including innovative ways that customers can make payments or manage their accounts, such as through the use of mobile payments, digital wallets or digital currencies. The Company believes its success depends, in
| | |
140 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
part, upon its ability to address customer needs by using technology to provide products and services and create additional efficiencies in the Company’s operations. When launching a new product or service or introducing a new platform for the delivery of products and services, the Company might not identify or fully appreciate the operational risks arising from those innovations or might inadvertently fail to implement adequate controls to mitigate those risks. Developing and deploying new technology-driven products and services can also involve costs that the Company may not recover and divert resources away from other product development efforts. The Company’s products and services may also rely on certain hardware, software, or service companies for which there are few alternatives, and the costs charged by these vendors may increase significantly year to year. In addition to the risk posed by critical technology failures, the Company may not be able to effectively develop and implement profitable new technology-driven products and services or be successful in marketing these products and services to its customers. Failure to successfully keep pace with technological change affecting the financial services industry, including because competitors may spend more resources on developing new technologies or because non-bank competitors have a lower cost structure and more flexibility, could harm the Company’s competitive position and negatively affect its revenue and profit.
The use of new technologies, including AI and machine learning, may result in reputational harm, increased regulatory scrutiny and increased liability The banking industry is subject to rapid and significant technological change. To compete effectively, the Company uses new and evolving technologies, including AI and machine learning, to help improve its customer service, marketing, and products, to increase productivity for internal code development and testing, and to automate certain business decisions and risk management practices, such as fraud identification. The Company's use of AI and machine learning is subject to risks that algorithms and datasets are flawed or may be insufficient or contain biased information. In addition, the models and processes relating to AI and machine learning are not always transparent, which could increase the risk of unintended deficiencies. These deficiencies could result in inaccurate or ineffective decisions, predictions or analysis, which could subject the Company to competitive harm, legal liability, increased regulatory scrutiny, reputational harm or other consequences that the Company may not be able to predict, any of which could negatively affect the Company's financial condition and results of operations. Furthermore, the legal and regulatory landscape impacting new technologies such as AI is evolving rapidly, and the inability to predict how this regulation will take shape and the absence of a uniform regulatory framework for AI may present unforeseen challenges in applying and relying on existing compliance systems. Complying with existing and new AI and data usage laws, and inconsistencies in regulation from jurisdiction to jurisdiction, could increase expenses and exposure to legal or regulatory proceedings.
Damage to the Company’s reputation could adversely impact its business and financial results Reputation risk, or the risk to the Company’s business, earnings and capital from negative public opinion, is inherent in the Company’s business. Negative public opinion about the financial services industry generally or the Company specifically could adversely affect the Company’s ability to retain and attract stakeholders such as customers, investors, and employees and could expose the Company to litigation and regulatory action. Negative public opinion can result from the Company’s actual or alleged conduct in any number of activities, including lending practices, cybersecurity incidents, misuse or failure to safeguard personal information, inability to meet community and other stakeholder commitments, discriminating or harassing behavior of employees toward other employees or customers, mortgage servicing and foreclosure practices, compensation practices, sales practices, regulatory compliance, mergers and acquisitions, and actions taken by government regulators and community organizations in response to that conduct. Additionally, the Company’s stakeholders often hold differing views on how the Company should address environmental, social and sustainability matters, including diversity-related matters, and the Company may not be able to meet the diverging expectations of different stakeholder groups, which could result in negative attention in traditional and social media, resulting in a negative perception of the Company depending on an individual’s view. In addition, failure to make accurate disclosures on these or other topics, or to deliver against announced goals, commitments and plans on these or other topics, could present reputational, legal and financial harm to the Company. If the Company is unable to design or execute against business strategies, including with respect to environmental, social or sustainability matters, reputational damage could result, leading to a loss of customers or negative investor sentiment.
The Company’s business and financial performance could be adversely affected, directly or indirectly, by natural disasters, pandemics, terrorist activities, civil unrest or international hostilities Neither the occurrence nor the potential impact of natural disasters, pandemics, terrorist activities, civil unrest or international hostilities can be predicted. However, these occurrences could impact the Company directly (for example, by interrupting the Company’s systems, which could prevent the Company from obtaining deposits, originating loans and processing and controlling its flow of business; causing significant damage to the Company’s facilities; or otherwise preventing the Company from conducting business in the ordinary course), or indirectly as a result of their impact on the Company’s borrowers, depositors, other customers, vendors or other counterparties (for example, by damaging properties pledged as collateral for the Company’s loans or impairing the ability of certain borrowers to repay their loans). The Company has also suffered, and could in the future suffer, adverse consequences to the extent that natural disasters, pandemics, terrorist activities, civil unrest or international hostilities, including the ongoing war in
Ukraine and conflict in the Middle East, affect the financial markets or the economy in general or in any particular region. These occurrences have caused, and may in the future cause, operational disruptions and increases in delinquencies, bankruptcies or defaults that could result in the Company experiencing higher levels of nonperforming assets, net charge-offs and provisions for credit losses.
The United States has in recent years faced periods of significant civil unrest. Although civil unrest has not materially affected the Company’s businesses to date, similar events could, directly or indirectly, have a material adverse effect on the Company’s operations (for example, by causing shutdowns of branches or working locations of vendors or other counterparties or damaging property pledged as collateral for the Company’s loans).
The Company’s ability to mitigate the adverse consequences of these occurrences is in part dependent on the quality of the Company’s resiliency planning and the Company’s ability, if any, to anticipate the nature of any such event that occurs. The adverse effects of natural disasters, pandemics, terrorist activities, civil unrest or international hostilities also could be increased to the extent there is a lack of preparedness on the part of national or regional emergency responders or on the part of other organizations and businesses that the Company transacts with, particularly those that it depends upon, but has no control over.
The Company’s business strategy, operations, financial performance and customers could be materially adversely affected by the impacts related to climate change Risks associated with climate change have affected, and may continue to affect, the Company and its customers and communities. The physical risks of climate change include chronic shifts in the climate, such as increasing average global temperatures, rising sea levels and an increase in the frequency and severity of extreme weather events and natural disasters, including wildfires, floods, tornadoes and hurricanes. The financial costs related to natural disasters have increased in recent years and may continue to do so in the future based on multiple factors. Such chronic shifts and disasters could disrupt the Company’s businesses and operations or the businesses and operations of the Company’s customers, vendors or counterparties, particularly with respect to those located in low-lying areas and coastlines that are more prone to flooding or other areas that are prone to wildfires and other disasters. Such chronic shifts and disasters could also adversely affect the Company’s business strategy and financial performance by, among other impacts, resulting in market volatility, negatively impacting customers’ ability to pay outstanding loans or fulfill other contractual obligations, damaging collateral or resulting in the deterioration of the value of collateral, or reducing availability or increasing costs of insurance, including insurance that protects property pledged as collateral for Company loans.
To the extent the United States and global economies continue to transition to a low-carbon economy, transition risks may arise from changes in consumer preferences, technologies, public policies, and legal and regulatory requirements. New laws and regulations could result in
significant costs as the Company implements compliance, disclosure and other programs. Failure to comply with any applicable laws or regulations could result in legal or regulatory sanctions and harm to the Company’s reputation. Failure to adequately consider transition risks in the Company’s operations could lead to a loss of market share, lower revenues, decreased asset values and higher credit costs. For example, a transition to a low-carbon economy could negatively affect the business of customers in carbon-intensive industries and reduce their creditworthiness.
These physical risks and transition risks could increase expenses or otherwise adversely impact the Company’s business strategy, operations, financial performance and customers. In particular, new laws, regulations or guidance, or the attitudes of regulators, shareholders, employees and customers regarding climate change, may affect the activities in which the Company engages and the products that the Company offers. An inability to adjust the Company’s business to mitigate the effects of physical and transition risks could result in higher operational and credit losses. In addition, the Company’s stakeholders’ views on climate change are diverse, dynamic, and rapidly changing, and the Company may not be able to meet the diverging expectations and priorities of different stakeholder groups, including regulators in different jurisdictions as further discussed in the risk factor “The Company is subject to significant financial and reputation risks from potential legal liability and governmental actions”. The Company could also experience increased expenses resulting from strategic planning, litigation and technology and market changes, and reputational harm as a result of negative public sentiment, regulatory scrutiny and reduced investor and stakeholder confidence due to the Company’s response to climate change and the Company’s climate change strategy.
Risks associated with climate change are continuing to evolve rapidly, making it difficult to assess the effects of climate change on the Company, and the Company expects that climate change-related risks will continue to evolve and increase over time.
Regulatory and Legal Risk
The Company is subject to extensive and evolving government regulation and supervision, which can increase the cost of doing business, limit the Company’s ability to make investments and generate revenue, and lead to costly enforcement actions Banking regulations are primarily intended to protect depositors’ funds, the federal Deposit Insurance Fund, and the United States financial system as a whole, and not the Company’s debt holders or shareholders. These regulations, and the Company’s inability to act in certain instances without receiving prior regulatory approval, affect the Company’s lending practices, capital structure, investment practices, dividend policy, ability to repurchase common stock, and ability to pursue strategic acquisitions, among other activities.
The Company expects that its business will remain subject to extensive regulation and supervision and that the
| | |
142 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
level of scrutiny and the enforcement environment may fluctuate over time, based on numerous factors, including bank failures, changes in the United States presidential administration or one or both houses of Congress and public sentiment regarding financial institutions (which can be influenced by scandals and other incidents that involve participants in the industry). In particular, recent changes in national political leadership have introduced uncertainty into the direction and timing of any future regulation. The Company expects the Trump administration will seek to implement a regulatory reform agenda that is significantly different than that of the Biden administration, impacting the rulemaking, supervision, examination and enforcement priorities of the federal banking agencies. Any potential new regulations or modifications to existing regulations and supervisory expectations may necessitate changes to the Company’s existing regulatory compliance and risk management infrastructure. In addition, changes in key personnel at the agencies that regulate the Company, including federal banking regulators, may result in differing interpretations of existing rules and guidelines and potentially more stringent enforcement and more severe penalties than previously experienced. In June 2024, the U.S. Supreme Court reversed its longstanding approach under the Chevron doctrine, which provided for judicial deference to regulatory agencies. As a result of this decision, there may be increased challenges to existing agency regulations, and it is uncertain how lower courts will apply the decision in the context of other regulatory schemes.
New regulations or modifications to existing regulations and supervisory expectations have increased, and may in the future increase, the Company’s costs over time and necessitate changes to the Company’s existing regulatory compliance and risk management infrastructure. In addition, regulatory changes may reduce the Company’s revenues (including by limiting the fees the Company may charge), limit the types of financial services and products it may offer, alter the investments it makes, affect the manner in which it operates its businesses, increase its litigation and regulatory costs should it fail to appropriately comply with new or modified laws and regulatory requirements, and increase the ability of non-banks to offer competing financial services and products.
Changes to statutes, regulations or regulatory policies, or their interpretation or implementation, and/or regulatory practices, requirements or expectations, could affect the Company in substantial and unpredictable ways. Complying with regulatory changes has at times resulted in significant expense for the Company, and these and other future regulatory changes could result in further significant expenses which could materially affect the Company’s financial condition and results of operations. In particular, regulators have proposed a number of regulations that, if they were to become effective, would affect the Company’s fee revenues and increase compliance costs for the Company. The potential effects on the Company remain uncertain due to legal challenges to many of the regulations as well as the recent changes in the U.S. presidential administration and control of the U.S. Senate, which are
likely to result in changing federal or state regulatory priorities. Any shifts in state or federal regulatory priorities may also result in increased compliance costs and regulatory risks as new regulations are issued and enforcement priorities shift. Failure to comply with any new law or regulation could result in litigation, regulatory enforcement actions and harm to the Company’s reputation.
General regulatory practices, such as longer time frames to obtain regulatory approvals for acquisitions and other activities (and the resultant impact on businesses the Company may seek to acquire) and initiatives to reduce fees on certain products, could affect the Company’s ability or willingness to make certain acquisitions or introduce new products or services. These could affect the Company’s ability or willingness to provide certain products or services, necessitate changes to the Company’s business practices or reduce the Company’s revenues.
Federal law grants substantial supervisory and enforcement powers to federal banking regulators and law enforcement agencies, including, among other things, the ability to assess significant civil or criminal monetary penalties, fines, or restitution; to issue cease and desist or removal orders; and to initiate injunctive actions against banking organizations and institution-affiliated parties. The financial services industry continues to face scrutiny from bank supervisors in the examination process and stringent enforcement of regulations on both the federal and state levels, including with respect to mortgage-related practices, fair lending practices, fees charged by banks, student lending practices, sales practices and related incentive compensation programs, and other consumer compliance matters, as well as compliance with Bank Secrecy Act/anti-money laundering (“BSA/AML”) requirements and sanctions compliance requirements as administered by the Office of Foreign Assets Control, and consumer protection issues more generally. This regulatory scrutiny, or the results of an investigation or examination, may lead to additional regulatory investigations or enforcement actions. There is no assurance that those actions will not result in regulatory settlements or other enforcement actions against the Company or any of the Company’s subsidiaries (including USBNA), which could cause the Company material financial and reputational harm. Furthermore, a single event involving a potential violation of law or regulation may give rise to numerous and overlapping investigations and proceedings, either by multiple federal and state agencies and officials in the United States or, in some instances, regulators and other governmental officials in foreign jurisdictions. In addition, another financial institution’s violation of law or regulation relating to a business activity or practice often will give rise to an investigation of the same or similar activities or practices of the Company.
In general, the amounts paid by financial institutions in settlement of proceedings or investigations and the severity of other terms of regulatory settlements are likely to remain elevated. In some cases, governmental authorities have required criminal pleas or other extraordinary terms, including admissions of wrongdoing and the imposition of
monitors, as part of such settlements, which could have significant consequences for a financial institution, including loss of customers, reputational harm, increased exposure to civil litigation, restrictions on the ability to access the capital markets, and the inability to operate certain businesses or offer certain products for a period of time.
Non-compliance with sanctions laws and/or BSA/AML laws or failure to maintain an adequate BSA/AML compliance program can lead to significant monetary penalties and reputational damage. In addition, federal regulators evaluate the effectiveness of an applicant in combating money laundering when determining whether to approve a proposed bank merger, acquisition, restructuring, or other expansionary activity. There have been a number of significant enforcement actions against banks, broker-dealers and non-bank financial institutions with respect to sanctions laws and BSA/AML laws, and some have resulted in substantial penalties, including against the Company and USBNA in 2018. The adoption of cryptocurrency and blockchain technology has rapidly expanded in recent years, and future regulatory changes may lead to additional growth of digital assets. Cryptocurrency and other new forms of payment have resulted in increased BSA/AML compliance risks, particularly with respect to “know-your-customer” and transaction monitoring requirements.
Violations of laws and regulations or deemed deficiencies in risk management practices or consumer compliance also may be incorporated into the Company’s confidential supervisory ratings. A downgrade in these ratings, or these or other regulatory actions and settlements, could limit the Company’s ability to conduct expansionary activities for a period of time and require new or additional regulatory approvals before engaging in certain other business activities.
Differences in regulation can affect the Company’s ability to compete effectively The content and application of laws and regulations applicable to financial institutions vary according to the size of the institution, the jurisdictions in which the institution is organized and operates and other factors. Large institutions, such as the Company, often are subject to more stringent regulatory requirements and supervision than smaller institutions. In addition, financial technology companies and other non-bank competitors may not be subject to the prudential and consumer protection regulatory framework that applies to banks, or may be regulated by a national or state agency that does not have the same regulatory priorities or supervisory requirements as the Company’s regulators. These differences in regulation can impair the Company’s ability to compete effectively with competitors that are less regulated and that do not have similar compliance costs or restrictions on activities.
Stringent requirements related to capital and liquidity are applicable to larger banking organizations, including the Company, that may limit the Company’s ability to return earnings to shareholders or operate or invest in its business If enacted as proposed, the “Basel
III Endgame” rules would result in significant changes to regulatory capital rules applicable to the Company. The Company expects that, if adopted, the final rules will result in requirements for the Company to maintain increased levels of regulatory capital. These and other future changes to the implementation of these rules including the stress capital buffer, or additional capital- and liquidity-related rules, could require the Company to take further steps to increase its capital, increase its investment security holdings, divest assets or operations, or otherwise change aspects of its capital and/or liquidity measures, including in ways that may be dilutive to shareholders or could limit the Company’s ability to pay common stock dividends, repurchase its common stock, invest in its businesses or provide loans to its customers.
The effects of external events and actions by the Federal Reserve Board have in the past limited and may in the future limit capital distributions, including suspension of the Company’s share repurchase program or reduction or suspension of the Company’s common stock dividend. In addition, bank failures in 2023 and the results of regulatory investigations into the failures has resulted in, and could result in further, increased regulatory scrutiny and heightened regulatory requirements, any of which could require the Company to expend significant time and effort to implement appropriate compliance procedures or to incur other expenses, and could negatively affect the Company’s financial condition or results of operations.
Further, in August 2023, the Federal Reserve Board, OCC and FDIC issued a proposed rule that would require, among other institutions, each Category III U.S. bank holding company, including the Company, and each insured depository institution with $100 billion or more in total consolidated assets that is a consolidated subsidiary of a Category III U.S. bank holding company, such as USBNA, to have minimum levels of outstanding long-term debt. The proposed rule is intended to improve the resolvability of the banking organizations covered by the rule. Any effects on the Company and USBNA will depend on the final form of any rulemaking, and may require the Company to change its current funding mix, including being required to raise additional long-term debt, which could adversely impact net interest margin and net interest income.
Refer to “Supervision and Regulation” in the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for additional information regarding the Company’s capital and liquidity requirements.
The Company is subject to significant financial and reputation risks from potential legal liability and governmental actions The Company faces significant legal risks in its businesses, and the volume of claims and amount of damages and penalties claimed in litigation and governmental proceedings against it and other financial institutions are substantial. Customers, clients and other counterparties make claims for substantial or indeterminate amounts of damages, while banking regulators and certain other governmental authorities have focused on enforcement. The Company is named as a defendant or is otherwise involved in many legal proceedings, including
| | |
144 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
class actions and other litigation. As a participant in the financial services industry, it is likely that the Company will continue to experience a high level of litigation and government scrutiny related to its businesses and operations in the future. Substantial legal liability or significant governmental action against the Company could materially impact the Company’s financial condition and results of operations (including because such matters may be resolved for amounts that exceed established accruals for a particular period) or cause significant reputational harm to the Company.
For example, banking organizations have been subject to claims regarding patent infringement or other violations of intellectual property rights in recent years which, in some cases, have resulted in large judgments against the banks. Such claims have in the past been brought against the Company, and if the Company is not successful in defending such claims or if new claims are brought or damages sought increase, the Company may incur substantial costs in defending such claims, regardless of their merit. If such claims are successful, the Company could be required to pay substantial damages and could suffer reputational and other harm.
In addition, lawmakers and regulators have proposed or adopted expansive requirements on environmental, social and sustainability matters. These requirements are emerging and evolving rapidly, and some have been subject to judicial challenges, leading to significant legal uncertainty. The diverging approach of lawmakers and regulators on these matters further amplify such uncertainty. For example, some states in which the Company does business have implemented “anti-ESG” measures and may seek to implement additional measures in the future. Such measures may conflict with other regulatory requirements, including requirements to enhance environmental, social and sustainability-related disclosures and efforts imposed by other jurisdictions in which the Company operates, or be inconsistent with the expectations of certain Company customers and shareholders. If the Company fails to comply with evolving, and possibly conflicting, legal and regulatory requirements, it could harm the Company’s ability to continue to conduct business in one or more of the jurisdictions in which the Company currently operates, or could otherwise harm the Company’s business.
The Company may be required to repurchase mortgage loans or indemnify mortgage loan purchasers as a result of breaches in contractual representations and warranties When the Company sells mortgage loans that it has originated to various parties, including GSEs, it is required to make customary representations and warranties to the purchaser about the mortgage loans and the manner in which they were originated. The Company may be required to repurchase mortgage loans or be subject to indemnification claims in the event of a breach of contractual representations or warranties that is not remedied within a certain period. Contracts for residential mortgage loan sales to the GSEs include various types of specific remedies and penalties that could be applied if the Company does not adequately respond to repurchase
requests. If economic conditions and the housing market deteriorate or the GSEs increase their claims for breached representations and warranties, the Company could have increased repurchase obligations and increased losses on repurchases, requiring material increases to its repurchase reserve.
The Company’s failure to satisfy its obligations as servicer for consumer loan securitizations and residential mortgage loans owned by other entities, and other losses the Company could incur as servicer, could adversely impact the Company’s reputation, servicing costs or results of operations The Company services both automobile and unsecured consumer installment loans on behalf of third-party securitization vehicles and also acts as servicer and master servicer for mortgage loans included in securitizations and for unsecuritized mortgage loans owned by investors. As a servicer or master servicer for those loans, the Company has certain contractual obligations to the securitization trusts, investors, or other third parties. As a servicer, the Company’s obligations include collecting all payments due by the borrower consistent with accepted servicing practices and applicable law, which in the case of borrower delinquency or default may include, as applicable to the loan, considering alternatives to repossession or foreclosure upon the collateral securing the loan, such as loan modifications or short sales. In the Company’s capacity as a master servicer, obligations include overseeing the servicing of mortgage loans by the servicer. Generally, the Company’s servicing obligations are set by contract, for which the Company receives a contractual fee. However, with respect to mortgage loans, GSEs can amend their servicing guidelines, which can increase the scope or costs of the services required without any corresponding increase in the Company’s servicing fee. As a servicer, the Company also advances expenses on behalf of investors which it may be unable to collect. A material breach of the Company’s obligations as servicer or master servicer may result in contract termination if the breach is not cured within a specified period of time following notice which would negatively impact the Company’s ongoing servicing fee compensation and could adversely impact the Company’s reputation. In addition, the Company may be required to indemnify the securitization trustee against losses from any failure by the Company, as a servicer or master servicer, to perform the Company’s servicing obligations or any act or omission on the Company’s part that involves willful misfeasance, bad faith, or gross negligence. For certain investors and certain transactions, the Company may be contractually obligated to repurchase a loan or reimburse the investor for credit losses incurred on the loan as a remedy for servicing errors with respect to the loan or a result of claims made that the Company did not satisfy its obligations as a servicer or master servicer. The Company may also experience increased loss severity on repurchases, which may require a material increase to the Company’s repurchase reserve. The Company has and may continue to receive indemnification requests related to the Company’s servicing of mortgage loans owned or insured by other parties, primarily GSEs.
Credit and Mortgage Business Risk
Heightened credit risk could require the Company to increase its provision for credit losses, which could have a material adverse effect on the Company’s results of operations and financial condition When the Company lends money, or enters into commitments to lend money, it incurs credit risk, or the risk of loss if its borrowers do not repay their loans. The credit performance of the Company’s loan portfolios significantly affects its financial results and condition. If the current economic environment were to worsen, the Company’s customers may have more difficulty in repaying their loans or other obligations, which could result in a higher level of credit losses and higher provisions for credit losses. Stress on the United States economy or the local economies in which the Company does business, including the economic stress caused by high commercial real estate vacancy rates, escalating geopolitical tensions, trade tariffs or other fiscal policies, and elevated interest rates and inflation has resulted, and in the future may result, in, among other things, borrowers’ inability to refinance loans at maturity and unexpected deterioration in credit quality of the loan portfolio or in the value of collateral securing those loans, which has caused, and in the future could cause, the Company to establish higher provisions for credit losses.
The Company reserves for credit losses by establishing an allowance through a charge to earnings to provide for loan defaults and nonperformance. The Company’s allowance for credit losses is compliant with CECL accounting guidance, under which the allowance for credit losses reflects the Company’s expected lifetime loss estimates of the portfolio. The allowance for credit losses is constructed based on an evaluation of the risks associated with its loan portfolio, including the size and composition of the loan portfolio, the portfolio’s historical loss experience, current and foreseeable economic conditions and borrower financial condition and collateral value. These forecasts and estimates require difficult, subjective, and complex judgments, including forecasts of economic conditions and how these economic predictions might impair the ability of the Company’s borrowers to repay their loans. The Company may not be able to accurately predict these economic conditions and/or some or all of their effects, which may, in turn, negatively impact the reliability of the process. The Company also makes loans to borrowers where it does not have or service the loan with the first lien on the property securing its loan. For loans in a junior lien position, the Company may not have access to information on the position or performance of the first lien when it is held and serviced by a third party, which may adversely affect the accuracy of the loss estimates for loans of these types. Increases in the Company’s allowance for loan losses may not be adequate to cover actual loan losses, and future provisions for loan losses could materially and adversely affect its financial results. In addition, the Company’s ability to assess the creditworthiness of its customers may be impaired if the models and approaches it uses to select, manage, and underwrite its customers become less predictive of future behaviors.
A concentration of credit and market risk in the Company’s loan portfolio could increase the potential for significant losses The Company may have higher credit risk, or experience higher credit losses, to the extent its loans are concentrated by loan type, industry segment, borrower type, or location of the borrower or collateral. For example, high vacancy rates in commercial properties may affect the value of commercial real estate, including by causing the value of properties securing commercial real estate loans to be less than the amounts owed on such loans. In addition, elevated interest rates may make it more difficult for borrowers to refinance maturing loans. Any of these or other events could increase the level of defaults and result in higher credit losses to the Company. The Company’s credit risk and credit losses can also increase if borrowers who engage in similar activities are uniquely or disproportionately affected by economic or market conditions, or by regulation, such as regulation related to climate change. Deterioration in economic conditions or real estate values in states or regions where the Company has relatively larger concentrations of residential or commercial real estate could result in higher credit costs. For example, the Company’s acquisition of MUB increased the Company’s exposure to the markets in California. Deterioration in real estate or collateral values and underlying economic conditions in California, including as a result of wildfires, could result in higher credit losses to the Company.
Changes in interest rates can impact the value of the Company’s mortgage servicing rights and mortgages held for sale, and can make its mortgage banking revenue volatile from quarter to quarter, which can reduce its earnings The Company has a portfolio of MSRs, which is the right to service a mortgage loan—collect principal, interest and escrow amounts—for a fee. The Company’s MSR portfolio had a fair value of $3.4 billion as of December 31, 2024. The Company initially carries its MSRs using a fair value measurement of the present value of the estimated future net servicing income, which includes assumptions about the likelihood of prepayment by borrowers. Changes in interest rates can affect prepayment assumptions and thus fair value. When interest rates fall, prepayments tend to increase as borrowers refinance, and the fair value of MSRs can decrease, which in turn reduces the Company’s earnings. Further, it is possible that, because of economic conditions such as a weak or deteriorating housing market, even when interest rates fall, mortgage originations may fall or any increase in mortgage originations may not be enough to offset the decrease in the MSRs’ value caused by the lower rates.
Decreased purchase volume by GSEs or limits on the Company’s access to the mortgage secondary market and GSEs could adversely affect the Company’s revenue and capacity to fund new loans The Company sells a portion of the mortgage loans that it originates to increase revenue through origination fees and ongoing servicing of such loans and to provide funding capacity for originating additional loans. GSEs could limit their purchases of conforming loans due to capital constraints,
| | |
146 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
other changes in their criteria for conforming loans or other reasons. This potential reduction in purchases could limit the Company’s ability to fund new loans. In addition, if GSEs limit their purchases of conforming loans, the Company may limit its originations of mortgage loans that it intends to sell, which could reduce the Company’s revenue from origination fees of such loans and the ongoing servicing fees it receives from such loans. Proposals have been presented to reform the housing finance market in the U.S., including the role of the GSEs in the residential finance market. The extent and timing of any such regulatory reform of the housing finance market and the GSEs, as well as any effect on the Company’s business and financial results, are uncertain.
A decline in the soundness, strength or stability of other financial institutions could adversely affect the Company’s results of operations Actual or perceived issues with, or rumors or questions about, one or more financial institutions, or about the financial services industry more generally, have led to, and may in the future lead to, among other things: market-wide liquidity problems; rapid and significant deposit withdrawals at certain institutions, particularly those with elevated levels of uninsured deposits; losses or defaults by certain institutions, up to and including failures of banks; significant volatility in the stock of financial services institutions; and an increase in fear or skepticism of the safety of banks generally. In addition, the Company’s ability to engage in routine funding or settlement transactions could be adversely affected by any of these events or by other events that affect the commercial soundness of other domestic or foreign financial institutions. Failures of banks that are unrelated to USBNA have increased, and may in the future increase, USBNA’s deposit insurance assessments, such as the FDIC’s special assessment relating to bank failures that occurred in 2023. In addition, customers and others may seek to make comparisons between failed or failing banks and USBNA, which, even if unfounded, can spread quickly through social media or other online channels. Such comparisons could affect customer confidence in USBNA and lead to deposit withdrawals or other negative effects the Company is unable to predict, any of which could materially and negatively affect the Company’s results of operations and financial condition. In addition, due to the prevalence of mobile banking and the ease with which customers can withdraw funds, deposits can now be withdrawn at a significantly faster pace than in the past (as was evidenced in the 2023 bank failures).
Financial services institutions are interrelated as a result of trading, clearing, counterparty or other relationships. The Company has exposure to many different counterparties, and the Company routinely executes and settles transactions with counterparties in the financial services industry, including brokers and dealers, commercial banks, investment banks, mutual and hedge funds, and other institutional counterparties. As a result, defaults by, or even rumors or questions about the soundness, strength or stability of, one or more financial services institutions, or the financial services industry generally, could lead to losses or defaults by the Company or by other institutions and impact
the Company’s predominately United States–based businesses or the merchant processing, corporate trust and fund administration services businesses it operates in foreign countries. Many of these transactions expose the Company to credit risk in the event of a default by a counterparty or client. In addition, the Company’s credit risk may be further increased when the collateral held by the Company cannot be realized upon or is liquidated at prices not sufficient to recover the full amount of the financial instrument exposure due the Company. Any such losses could adversely affect the Company’s results of operations.
Change in residual value of leased assets may have an adverse impact on the Company’s financial results The Company engages in leasing activities and is subject to the risk that the residual value of the property under lease will be less than the Company’s recorded asset value. Adverse changes in the residual value of leased assets can have a negative impact on the Company’s financial results. The risk of changes in the realized value of the leased assets compared to recorded residual values depends on many factors outside of the Company’s control, including supply and demand for the assets, condition of the assets at the end of the lease term, and other economic factors.
Liquidity Risk
If the Company does not effectively manage its liquidity, its business could suffer The Company’s liquidity is essential for the operation of its businesses. Market conditions, the threat or occurrence of a U.S. sovereign default, unforeseen outflows of funds or other events could negatively affect the Company’s level or cost of funding, in turn affecting its ongoing ability to accommodate liability maturities and deposit withdrawals, meet contractual obligations, and fund asset growth and new business transactions at a reasonable cost and in a timely manner. If the Company’s access to stable and low-cost sources of funding, such as customer deposits, is reduced, the Company might need to use alternative funding, which could be more expensive or of limited availability. Any substantial, unexpected or prolonged changes in the level or cost of liquidity could materially and adversely affect the Company’s businesses.
In addition, bank failures in 2023 led to significant volatility in the financial services industry and to liquidity problems at certain institutions. Although governmental support was provided in connection with these bank failures, including the FDIC invoking the systemic risk exception to guarantee uninsured deposits, there can be no guarantee that the FDIC will invoke the systemic risk exception in connection with any future bank failures or that the government would otherwise take any action to provide liquidity to troubled institutions. Further, even if governmental support for financial institutions is available in the future, it may not be sufficient to address systemic risks.
Loss of customer deposits could increase the Company’s funding costs The Company relies on customer deposits as a low-cost and stable source of funding. The Company competes with banks and other financial services companies for deposits, including those that offer online channels. Recent declines in short-term
interest rates have generally lowered the Company’s deposit funding costs. However, competition for deposits could increase to the extent the Federal Reserve continues the normalization of its balance sheet through quantitative tightening. Increased competition could negatively impact the Company’s ability to realize further improvement in deposit funding costs, even if short-term rates continue to decline. If short-term interest rates were to increase, the Company would expect more intense competition in deposit pricing. Competition and higher short-term interest rates may cause the Company to increase the interest rates it pays on deposits. If the Company’s competitors raise the interest rates they pay on deposits, or lower the interest rates they pay on deposits by less than the Company, the Company’s funding costs may increase, either because the Company raises the interest rates it pays on deposits to avoid losing deposits to competitors or because the Company loses deposits to competitors and must rely on more expensive sources of funding. Higher funding costs reduce the Company’s net interest margin and net interest income.
Checking and savings account balances and other forms of customer deposits may decrease when customers perceive alternative investments, such as the stock market, as providing a better risk/return tradeoff. When customers move money out of bank deposits and into other investments, the Company may lose a relatively low-cost source of funds, increasing the Company’s funding costs and reducing the Company’s net interest income. In addition, mass withdrawals of deposits occurred at certain banks that failed in 2023, seemingly triggered by losses in the banks’ investment securities portfolios and concerns about uninsured and uncollateralized deposits. A loss in the value of the Company’s investment or loan portfolio, perceived concerns regarding the Company’s and USBNA’s capital positions or perceived concerns regarding the level of USBNA’s uninsured and uncollateralized deposits could cause rapid and significant deposit outflows. This risk is exacerbated by technological developments and changes in banking relationships, such as customers maintaining accounts at multiple banks, which increase the ease and speed with which depositors are able to move their deposits. The potential speed of deposit withdrawals may be further accelerated due to the way information, including false information or unfounded rumors, can be spread quickly through social media and other online channels. If USBNA were to experience a significant outflow of deposits, the Company may face increased funding costs, suffer losses and have a reduced ability to raise new capital.
The Company could lose access to sources of liquidity if it were to experience financial or regulatory issues The Company has access to sources of liquidity provided by the Federal Reserve Bank, such as the Federal Reserve Bank discount window and other liquidity facilities that the Federal Reserve Board may establish from time to time, as well as liquidity provided by the FHLB. To access these sources of liquidity, the Federal Reserve Board or FHLB may impose conditions that the Company and USBNA are in sound financial condition (as determined by the Federal
Reserve Board or FHLB) or that the Company and USBNA maintain minimum supervisory ratings. If the Company or USBNA were to experience financial or regulatory issues, it could affect the Company’s or USBNA's ability to access liquidity facilities, including at times when the Company or USBNA needs additional liquidity for the operation of its business. If the Company or USBNA were to lose access to these liquidity sources, it could have a material adverse effect on the Company’s operations and financial condition.
The Company relies on dividends from its subsidiaries for its liquidity needs, and the payment of those dividends is limited by laws and regulations The Company is a separate and distinct legal entity from USBNA and the Company’s non-bank subsidiaries. The Company receives a significant portion of its cash from dividends paid by its subsidiaries. These dividends are the principal source of funds to pay dividends on the Company’s stock and interest and principal on its debt. Various federal and state laws and regulations limit the amount of dividends that USBNA and certain of the Company’s non-bank subsidiaries may pay to the Company without regulatory approval. Also, the Company’s right to participate in a distribution of assets upon a subsidiary’s liquidation or reorganization is subject to prior claims of the subsidiary’s creditors, except to the extent that any of the Company’s claims as a creditor of that subsidiary may be recognized. Refer to “Supervision and Regulation” in the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for additional information regarding limitations on the amount of dividends USBNA may pay.
Competitive and Strategic Risk
The financial services industry is highly competitive, and competitive pressures could intensify and adversely affect the Company’s financial results The Company operates in a highly competitive industry that could become even more competitive as a result of legislative, regulatory and technological changes, as well as continued industry consolidation. This consolidation may produce larger, better-capitalized and more geographically diverse companies that are capable of offering a wider array of financial products and services at more competitive prices. The Company competes with other commercial banks, savings and loan associations, mutual savings banks, finance companies, mortgage banking companies, credit unions, investment companies, credit card companies, and a variety of other financial services and advisory companies. Legislative or regulatory changes also could lead to increased competition in the financial services sector.
The adoption and rapid growth of new technologies, including generative AI, cryptocurrencies and blockchain and other distributed ledger technologies, have required the Company to invest resources to adapt its systems, products and services, and it expects to continue to make similar investments. In addition, technology has lowered barriers to entry and made it possible for non-banks to offer products and services, such as loans and payment services, that traditionally were banking products, and made it possible for technology companies to compete with
| | |
148 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
financial institutions in providing electronic, internet-based, and mobile phone–based financial solutions. Competition with non-banks, including technology companies, to provide financial products and services is intensifying. In particular, the activity of financial technology companies (“fintechs”) has grown significantly over recent years and is expected to continue to grow. Fintechs have and may continue to offer bank or bank-like products. For example, a number of fintechs have applied for bank or industrial loan charters, which, in some cases, have been granted. In addition, other fintechs have partnered with existing banks to allow them to offer deposit products or payment services to their customers. Many of these companies, including the Company’s competitors, have fewer regulatory constraints, and some have lower cost structures, in part due to lack of physical structures. In addition, future regulatory developments may increase the ability of fintechs and other competitors to compete with traditional banks, including through the use of cryptocurrency and other digital assets or alternative payment systems. Also, the potential need to adapt to industry changes in information technology systems, including potential upgrades relating to digital assets, on which the Company and financial services industry are highly dependent, could present operational issues and require capital spending. The Company’s ability to compete successfully depends on a number of factors, including, among others, its ability to develop and execute strategic plans and initiatives; developing, maintaining and building long-term customer relationships based on quality service, competitive prices, high ethical standards and safe, sound assets; and industry and general economic trends. A failure to compete effectively could contribute to downward price pressure on the Company’s products or services or a loss of market share.
The Company may need to lower prices on existing products and services and develop and introduce new products and services to maintain market share The Company’s success depends, in part, on its ability to adapt its products and services to evolving customer preferences and industry standards. There is increasing pressure to provide products and services at lower prices. Lower prices can reduce the Company’s net interest margin and revenues from its fee-based products and services. In addition, the adoption of new technologies or further developments in current technologies require the Company to make substantial expenditures to modify or adapt its existing products and services. Also, these and other capital investments in the Company’s businesses may not produce expected growth in earnings anticipated at the time of the expenditure. The Company might not be successful in developing or introducing new products and services, adapting to changing customer preferences and spending and saving habits (which may be altered significantly and with little warning), achieving market acceptance of its products and services, or sufficiently developing and maintaining loyal customer relationships.
The Company may not realize the full value of its strategic plans and initiatives As the Company develops its strategic initiatives, it reviews the internal and external
environment to inform any changes required, take advantage of new opportunities and/or respond to unexpected challenges. Initiatives include focusing on customer growth with tailored products and experiences that meet customer needs; executing disciplined strategies to grow and maintain sufficient capital levels as part of preserving the Company’s financial position and risk appetite; and partnering with or acquiring and integrating financial services businesses or assets. The Company’s initiatives are impacted by internal factors, rapid pace of change from an evolving competitive landscape, increased cybersecurity threats, accelerated digitalization, and emerging technologies. Execution of these initiatives is also impacted by the Company’s response to external economic conditions, global political and economic uncertainty, and regulatory factors that are beyond its control. The Company’s future growth and the value of its businesses will depend, in part, on its ability to effectively implement its business strategy. If the Company is not able to successfully execute its business strategy, then the Company’s competitive position, reputation, prospects for growth, and results of operations may be adversely affected.
The Company may not be able to complete future acquisitions, and completed acquisitions may not produce revenue enhancements or cost savings at levels or within timeframes originally anticipated, may result in unforeseen integration difficulties, and may dilute existing shareholders’ interests The Company regularly explores opportunities to acquire financial services businesses or assets and may also consider opportunities to acquire other banks or financial institutions. The Company cannot predict the number, size or timing of acquisitions it might pursue.
The Company must generally receive federal regulatory approval before it can acquire a bank or bank holding company. The Company’s ability to pursue or complete an attractive acquisition could be negatively impacted by regulatory delay or other regulatory issues. The Company cannot be certain when or if, or on what terms and conditions, any required regulatory approvals will be granted. For example, the Company may be required to sell branches as a condition to receiving regulatory approval for bank acquisitions. In addition, in 2024 the OCC issued a policy statement on bank mergers that may result in more scrutiny being applied to mergers with a resulting institution with $50 billion or more in total assets. The Company is unable to predict at this time what effects the OCC’s policy statement may have on mergers involving USBNA, but it may result in extended timelines for merger approvals. If the Company commits certain regulatory violations, including those that result in a downgrade in certain of the Company’s bank regulatory ratings, governmental authorities could, as a consequence, preclude it from pursuing future acquisitions for a period of time. In addition, the Company’s ability to complete future acquisitions may depend on factors outside its control, including changes in the presidential administration or in one or both houses of Congress and public sentiment regarding bank mergers. Acquisition activity by large banking organizations, such as
the Company, continues to draw regulatory and policy focus, and future changes could impact consideration of and regulatory approval processes for certain acquisitions. In addition, acquisitions by large banking organizations such as the Company may receive negative coverage in the media or negative attention by certain members of Congress or other policymakers. If the Company were to receive significant negative publicity in connection with a proposed acquisition, it could damage the Company’s reputation and impede the Company’s ability to complete the acquisition.
There can be no assurance that acquisitions the Company completes will have the anticipated positive results, including results related to expected revenue increases, cost savings, increases in geographic or product presence, and/or other projected benefits. The Company may incur substantial expenses related to acquisitions and integration of acquired companies. Successful integration of an acquired company has in the past presented and may in the future present challenges due to differences in systems, operations, policies and procedures, management teams and corporate cultures and may be more costly or difficult to complete than anticipated or have unanticipated adverse results. Integration efforts could divert management’s attention and resources, which could adversely affect the Company’s operations or results. Integration efforts could result in higher than expected customer loss, deposit attrition, loss of key employees, issues with systems and technology, disruption of the Company’s businesses or the businesses of the acquired company, or otherwise adversely affect the Company’s ability to maintain relationships with customers and employees or achieve the anticipated benefits of the acquisition. Also, the negative effect of any divestitures required by regulatory authorities in acquisitions or business combinations may be greater than expected. In addition, future acquisitions may also expose the Company to increased legal or regulatory risks. Finally, future acquisitions could be material to the Company, and it may issue additional shares of stock to pay for those acquisitions, which would dilute current shareholders’ ownership interests.
Accounting and Tax Risk
The Company’s reported financial results depend on management’s selection of accounting methods and certain assumptions and estimates, which, if incorrect, could cause unexpected losses in the future The Company’s accounting policies and methods are fundamental to how the Company records and reports its financial condition and results of operations. The Company’s management must exercise judgment in selecting and applying many of these accounting policies and methods, so they comply with generally accepted accounting principles and reflect management’s judgment regarding the most appropriate manner to report the Company’s financial condition and results of operations. In some cases, management must select the accounting policy or method to apply from two or more alternatives, any of which might be reasonable under the
circumstances, yet might result in the Company’s reporting materially different results than would have been reported under a different alternative.
Certain accounting policies are critical to presenting the Company’s financial condition and results of operations. They require management to make difficult, subjective or complex judgments about matters that are uncertain. Materially different amounts could be reported under different conditions or using different assumptions or estimates. These critical accounting policies include the allowance for credit losses, estimations of fair value, the valuation of MSRs, and income taxes. Because of the uncertainty of estimates involved in these matters, the Company may be required to do one or more of the following: significantly increase the allowance for credit losses and/or sustain credit losses that are significantly higher than the reserve provided, recognize significant losses on the remeasurement of certain asset and liability balances, or significantly increase its accrued taxes liability. For more information, refer to “Critical Accounting Policies” in this Annual Report. In addition, the FASB, SEC and other regulatory agencies may issue new or amend existing accounting and reporting standards or change existing interpretations of those standards that could materially affect the Company's financial statements.
The Company’s investments in certain tax-advantaged projects may not generate returns as anticipated and may have an adverse impact on the Company’s financial results The Company invests in certain tax-advantaged projects promoting affordable housing, community development and renewable energy resources. The Company’s investments in these projects are designed to generate a return primarily through the realization of federal and state income tax credits, and other tax benefits, over specified time periods. The Company is subject to the risk that previously recorded tax credits, which remain subject to recapture by taxing authorities based on compliance features required to be met at the project level, will fail to meet certain government compliance requirements and will not be able to be realized. The possible inability to realize these tax credit and other tax benefits can have a negative impact on the Company’s financial results. The risk of not being able to realize the tax credits and other tax benefits depends on many factors outside of the Company’s control, including changes in the applicable tax code and the ability of the projects to be completed.
General Risk Factors
The Company’s framework for managing risks may not be effective in mitigating risk and loss to the Company The Company’s risk management framework seeks to mitigate risk and loss. The Company has established processes and procedures intended to identify, measure, monitor, report, and analyze the types of risk to which it is subject, including liquidity risk, credit risk, market risk, interest rate risk, compliance risk, strategic risk, reputation risk, and operational risk related to its employees, systems and vendors, among others. However, as with any risk management framework, there are inherent limitations to
| | |
150 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
the Company’s risk management strategies as there may exist, or develop in the future, risks that it has not appropriately anticipated or identified. In addition, the Company relies on quantitative models to measure certain risks and to estimate certain financial values, and these models could fail to predict future events or exposures accurately. The Company must also develop and maintain a culture of risk management among its employees, as well as manage risks associated with third parties, and could fail to do so effectively. If the Company’s risk management framework proves ineffective, the Company could incur litigation and negative regulatory consequences and suffer unexpected losses that could affect its financial condition or results of operations.
The Company’s business could suffer if it fails to attract and retain skilled employees The Company’s success depends, in large part, on its ability to attract and retain key employees. Competition for the best people in most activities the Company engages in can be intense.
The employment market has continued to evolve, influenced by macroeconomic shifts, changes in social norms post-pandemic and technology advancements. Continued pressures on competitive compensation, benefits and flexible work arrangements continue to be focus areas.
Employees have also continued to shift their focus to better work-life balance, improved advancement opportunities and skill specific development, and many businesses, including the Company, have had to adapt quickly to the changing environment. The Company’s ability to compete successfully for talent has been and may continue to be affected by its ability to adapt quickly to such shifts in employee focus, and there is no assurance that these developments will not cause increased turnover or impede the Company’s ability to retain and attract high caliber employees.
A downgrade in the Company’s credit ratings could have a material adverse effect on its liquidity, funding costs and access to capital markets The Company’s credit ratings, which are subject to credit agencies’ ongoing review of a number of factors, including factors not within the Company’s control, are important to the Company’s liquidity. A reduction in one or more of the Company’s credit ratings could adversely affect its liquidity, increase its funding costs or limit its access to the capital markets. Further, a downgrade could decrease the number of investors and counterparties willing or able, contractually or otherwise, to do business with or lend to the Company, thereby adversely affecting the Company’s competitive position. There can be no assurance that the Company will maintain its current ratings and outlooks or whether or when any downgrades could occur.
Managing Committee
Andrew Cecere
Mr. Cecere, 64, is Chairman and Chief Executive Officer of U.S. Bancorp. Mr. Cecere has served as Chief Executive Officer since April 2017 and Chairman since April 2018. He also served as President from January 2016 to May 2024. In April 2025, he will serve as Executive Chairman of U.S. Bancorp’s Board of Directors, continuing to lead the Board and supporting Gunjan Kedia as she assumes the role of Chief Executive Officer.
Souheil S. Badran
Mr. Badran, 60, is Senior Executive Vice President and Chief Operations Officer of U.S. Bancorp. Mr. Badran has served in this position since joining U.S. Bancorp in December 2022. From January 2019 until November 2022, he served as Executive Vice President and Chief Operating Officer at Northwestern Mutual, having also served as Chief Innovation Officer from January 2019 until September 2019.
Elcio R.T. Barcelos
Mr. Barcelos, 54, is Senior Executive Vice President and Chief Human Resources Officer of U.S. Bancorp. Mr. Barcelos has served in this position since joining U.S. Bancorp in September 2020. Prior to joining U.S. Bancorp, he served in a leadership role at Federal National Mortgage Association (Fannie Mae).
James L. Chosy
Mr. Chosy, 61, is Senior Executive Vice President and General Counsel of U.S. Bancorp. Mr. Chosy has served in this position since March 2013. He also served as Corporate Secretary of U.S. Bancorp from June 2022 until December 2023 and from March 2013 until April 2016.
Gregory G. Cunningham
Mr. Cunningham, 61, is Senior Executive Vice President and Chief Diversity Officer of U.S. Bancorp. Mr. Cunningham has served in this position since July 2020. From July 2019 until July 2020, he served as Senior Vice President and Chief Diversity Officer of U.S. Bancorp, having served as Vice President of Customer Engagement of U.S. Bancorp from October 2015, when he joined U.S. Bancorp, until July 2019.
Venkatachari Dilip
Mr. Dilip, 65, is Senior Executive Vice President and Chief Information and Technology Officer of U.S. Bancorp. Mr. Dilip previously was an Executive Vice President from September 2018 to April 2023 and has served as Chief Information and Technology Officer since September 2018, when he joined U.S. Bancorp.
Terrance R. Dolan
Mr. Dolan, 63, is Vice Chair and Chief Administration Officer of U.S. Bancorp. Mr. Dolan has served in this position since September 2023. From August 2016 to August 2023, he served as Vice Chair and Chief Financial Officer of U.S. Bancorp.
Revathi N. Dominski
Ms. Dominski, 54, is Senior Executive Vice President and Chief Social Responsibility Officer of U.S. Bancorp and President of the U.S. Bank Foundation. Ms. Dominski has served as Senior Executive Vice President and Chief Social Responsibility Officer since April 2023. She joined U.S. Bancorp in June 2015 as President of the U.S. Bank Foundation and Senior Vice President of Corporate Social Responsibility.
Sekou Kaalund
Mr. Kaalund, 49, is Senior Executive Vice President, Head of Branch and Small Business Banking of U.S. Bancorp. Mr Kaalund previously was Executive Vice President from December 2022 to January 2025 and has served as Head of Branch and Small Business Banking since joining U.S. Bancorp in December 2022. Prior to joining U.S. Bancorp, he served as the Head of Consumer Banking for the Northeast Division at JPMorgan Chase from September 2020 to December 2022. He served as Managing Director and Head of Advancing Black Pathways at JPMorgan Chase from August 2018 to September 2020 and was a Managing Director across several areas in the Corporate Investment Bank at JPMorgan Chase, including U.S. Public and Corporate Pensions and Global Private Equity and Real Estate Fund Services, from July 2007 to September 2020.
Gunjan Kedia
Ms. Kedia, 54, is President of U.S. Bancorp and a member of U.S. Bancorp’s Board of Directors. Ms. Kedia has served as President since May 2024. From June 2023 to May 2024, she served as Vice Chair, Wealth, Corporate, Commercial and Institutional Banking, of U.S. Bancorp. From December 2016 to June 2023, she served as Vice Chair, Wealth Management and Investment Services, of U.S. Bancorp. In April 2025, she will assume the additional role of Chief Executive Officer.
Courtney Kelso
Ms. Kelso, 47, is Senior Executive Vice President, Head of Payments: Consumer and Small Business of U.S. Bancorp. Ms. Kelso has served in this position since joining U.S. Bancorp in February 2025. Prior to joining U.S. Bancorp, she served as Executive Vice President and Head of Card Products, Global Commercial Services at American Express from February 2021 to February 2024. From February 2018 to February 2021, she served as Senior Vice President of US Small Business, Co-Brand and Corporate Cards, Global Commercial Services at American Express.
| | |
152 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|
Felicia La Forgia
Ms. La Forgia, 56, is Senior Executive Vice President, Head of the Institutional Client Group (ICG) of U.S. Bancorp. Ms. La Forgia previously was Executive Vice President from July 2016 to January 2025 and has served as Head of ICG since June 2024. From June 2020 to June 2024, she served as Head of Corporate Banking of U.S. Bancorp.
Stephen L. Philipson
Mr. Philipson, 46, is Senior Executive Vice President, Head of Wealth, Corporate, Commercial and Institutional Banking (WCIB). Mr. Philipson has served as Head of WCIB since June 2024 and Senior Executive Vice President since April 2023. From April 2023 to June 2024, he served as Head of Global Markets and Specialized Finance of U.S. Bancorp. From October 2017 to April 2023, he served as Head of Fixed Income and Capital Markets of U.S. Bancorp.
Jodi L. Richard
Ms. Richard, 56, is Vice Chair and Chief Risk Officer of U.S. Bancorp. Ms. Richard has served in this position since October 2018. She served as Executive Vice President and Chief Operational Risk Officer of U.S. Bancorp from January 2018 until October 2018.
Arijit Roy
Mr. Roy, 48, is Senior Executive Vice President, Head of Consumer and Business Banking Products of U.S. Bancorp. Mr. Roy previously was an Executive Vice President from August 2023 to October 2024 and has served as Head of Consumer and Business Banking Products since July 2024. Prior to July 2024, he served as Head of Consumer and Segment Solutions since joining U.S. Bancorp in July 2022. Prior to joining U.S. Bancorp, he held various leadership positions at Truist, including Executive Vice President and Head of Consumer Products from April 2022 to July 2022, Executive Vice President of Deposits, Small Business Banking, Strategy and Analytics from July 2021 to April 2022, and Senior Vice President of Strategy, Digital Integration and Transformation from September 2019 to July 2021.
Mark G. Runkel
Mr. Runkel, 48, is Senior Executive Vice President, Head of Payments: Merchant and Institutional. Mr. Runkel has served in this position since January 2025. From August 2021 to January 2025, he served as Chief Transformation Officer of U.S. Bancorp. From December 2013 to August 2021, he served as Senior Executive Vice President and Chief Credit Officer of U.S. Bancorp.
John C. Stern
Mr. Stern, 46, is Senior Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer of U.S. Bancorp. Mr. Stern has served as Senior Executive Vice President since April 2023 and Chief Financial Officer since September 2023. He also served as Head of Finance of U.S. Bancorp from May 2023 to August 2023. He served as Executive Vice President of U.S. Bancorp from July 2013 through April 2023. From May 2021 until May 2023, he served as President of the Global Corporate Trust and Custody business of U.S. Bancorp. Previously, he served as Treasurer of U.S. Bancorp from July 2013 to May 2021.
Dominic V. Venturo
Mr. Venturo, 58, is Senior Executive Vice President and Chief Digital Officer of U.S. Bancorp. Mr. Venturo has served in this position since July 2020. From January 2015 until July 2020, he served as Executive Vice President and Chief Innovation Officer of U.S. Bancorp.
Directors
Andrew Cecere1,6
Chairman and Chief Executive Officer
U.S. Bancorp
Warner L. Baxter1,2,3
Retired Executive Chairman and Former Chairman,
President and Chief Executive Officer
Ameren Corporation
(Energy)
Dorothy Bridges1,5,6
Chief Executive Officer
Metropolitan Economic Development Association (Meda)
(Economic Development)
Elizabeth L. Buse2,6
Former Chief Executive Officer
Monitise plc
(Financial services)
Alan B. Colberg2,5
Retired President and Chief Executive Officer
Assurant, Inc.
(Financial services and specialty insurance)
Kimberly N. Ellison-Taylor2,5
Founder and Chief Executive Officer
KET Solutions, LLC
(Technology)
Aleem Gillani2,6
Retired Corporate Executive Vice President and
Chief Financial Officer
SunTrust Banks, Inc.
(Financial services)
Kimberly J. Harris1,3,4
Retired President and Chief Executive Officer
Puget Energy, Inc.
(Energy)
Roland A. Hernandez1,3,4
Founding Principal and Chief Executive Officer
Hernandez Media Ventures
(Media)
Gunjan Kedia1
President
U.S. Bancorp
Richard P. McKenney4,6
President and Chief Executive Officer
Unum Group
(Financial protection benefits)
Yusuf I. Mehdi5,6
Executive Vice President,
Consumer Chief Marketing Officer
Microsoft Corporation
(Technology)
Loretta E. Reynolds5,6
Founder and Chief Executive Officer
LEReynolds Group, LLC
(Information Technology)
John P. Wiehoff1,6
Retired Chairman and Chief Executive Officer
C.H. Robinson Worldwide, Inc.
(Transportation and logistics services)
Scott W. Wine1,3,4
Former Chief Executive Officer
CNH Industrial N.V.
(Agricultural machinery)
1.Executive Committee
2.Audit Committee
3.Compensation and Human Resources Committee
4.Governance Committee
5.Public Responsibility Committee
6.Risk Management Committee
| | |
154 U.S. Bancorp 2024 Annual Report |
|