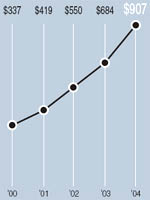
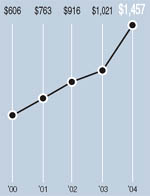
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION
AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS This Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations should be read in conjunction with the Company’s historical Consolidated Financial Statements and Notes thereto included in this Report. The Company’s operations are conducted through its operating subsidiaries. Its two primary operating subsidiaries, Kinro, Inc. and its subsidiaries (“Kinro”) and Lippert Components, Inc. and its subsidiaries (“Lippert”) have operations in both the recreational vehicle (“RV”) and manufactured housing (“MH”) segments. At December 31, 2004, the Company’s subsidiaries operated 50 plants in the United States and one in Canada. The RV segment accounted for 65 percent of consolidated net sales for 2004 and 62 percent of consolidated net sales for 2003. The RV segment manufactures a variety of products used in the production of recreational vehicles, including windows, doors, chassis, chassis parts, slide-out mechanisms and related power units, and electric stabilizer jacks. The RV segment also manufactures specialty trailers for equipment hauling, boats, personal watercraft and snowmobiles. The Company’s RV products are used primarily in travel trailers and fifth wheel RVs. Travel trailers and fifth wheel RVs accounted for 69 percent of all RVs shipped by the industry in 2004, up from 61 percent in 2001. In recent months, the Company has begun to focus its efforts on expanding its market share for products used in motorhomes, and began selling slide-out mechanisms for motorhomes in the second quarter of 2004. The Company is also introducing leveling devices, axles, steps and bath products for RVs. The MH segment, which accounted for 35 percent of consolidated net sales for 2004 and 38 percent of consolidated net sales for 2003, manufactures a variety of products used in the construction of manufactured homes, and to a lesser extent, modular housing and office units, including vinyl and aluminum windows and screens, chassis, chassis parts, and thermo-formed bath and shower units. On May 4, 2004, the Company acquired California-based Zieman Manufacturing Company (“Zieman”). Zieman is a manufacturer of specialty trailers for equipment hauling, boats, personal watercraft and snowmobiles, and chassis and chassis parts for towable recreational vehicles and manufactured homes. The purchase price was $21.4 million, plus $5.2 million of Zieman’s debt which the Company assumed. The purchase price was funded with borrowings under the Company’s credit agreement. Zieman had 10 plants in 4 states in the western United States. The results of the acquired Zieman business have been included in the Company’s Consolidated Statements of Income beginning May 4, 2004. Zieman’s sales for its fiscal year ended December 31, 2003 were approximately $42 million, and for the year ended December 31, 2004 Zieman’s sales were $58 million, including $40 million subsequent to its acquisition by the Company. In 2003, Zieman had approximately $12 million in sales of RV chassis and chassis parts, approximately $19 million in sales of marine and leisure trailers, and $11 million of MH chassis and chassis parts. The operations of Zieman are being integrated with those of Lippert. The production processes and raw materials used by Zieman are substantially similar to those of Lippert, and it is expected that the operating margins achieved by this newly-acquired business will, over time, approximate those achieved by Lippert. Until the second quarter of 2004, the Company’s RV segment included only recreational vehicle products, however, with the Company’s acquisition of Zieman, the specialty trailer business of Zieman has been added to the RV segment. Other than sales of specialty trailers, which aggregated approximately $17.5 million in 2004, sales to industries other than manufacturers of RVs and manufactured homes are not significant. Inter-seg-ment sales are insignificant. INDUSTRY BACKGROUND Recreational Vehicle Industry The Recreational Vehicle Industrial Association (“RVIA”) reported a 15 percent increase in total industry shipments, to 370,100 RVs in 2004, from 320,800 in 2003. Shipments of travel trailers and fifth wheel RVs, the Company’s primary market, increased 19 percent in 2004. It has been reported by analysts that industry-wide shipments included approximately 13,500 travel trailers, consisting of only the essential components, purchased by the Federal Emergency Management Agency (“FEMA”) to provide emergency housing to hurricane victims in the southeastern United States. It is not expected that these units will be resold to traditional RV consumers. Without the FEMA units, the increase in industry shipments would have been 11 percent. The RVIA is projecting a 2.5 percent decline in wholesale shipments of all types of RVs in 2005, but they are forecasting that shipments of travel trailers and fifth wheel RVs will be approximately the same as in 2004. In the long term, increasing industry RV sales are expected to continue to be driven by positive demographics, as demand for RVs is strongest from the over-50 age group, which is the fastest growing segment of the population. According to US Census Bureau projections, 10 years from now there will be in excess of 20 million more people over the age of 50. Industry growth also continues to be bolstered by the preference for domestic vacations, rather than foreign travel, and low interest rates. In recent years, the RVIA has employed an advertising campaign to attract customers in the 35 to 54 age group, and the number of RVs owned by those 35 to 54 grew faster than all other age groups. Manufactured Housing Industry As a result of (i) limited credit availability for purchases of manufactured homes, (ii) high interest rate spreads between conventional mortgages on site built homes and chattel loans for manufactured homes (chattel loans have been used to finance approximately 30 percent of manufactured homes purchased this year), and (iii) unusually high repossessions of manufactured homes, industry production declined approximately 65 percent since 1998, to 131,000 homes in 2003, the lowest |