EXHIBIT (17)(a)(i)

Eaton Vance Hawaii Municipals Fund
Eaton Vance Insured Municipals Fund
Eaton Vance Kansas Municipals Fund
| Mutual funds providing tax-exempt income |
Prospectus Dated
June 1, 2009
The Securities and Exchange Commission has not approved or disapproved these securities or
determined whether this prospectus is truthful or complete. Any representation to the contrary is a
criminal offense. |
| | | |
| Information in this prospectus | | | |
| | Page | | Page |
| Fund Summaries | 2 | Sales Charges | 15 |
| Investment Objectives & Principal Policies and Risks | 9 | Redeeming Shares | 17 |
| Management and Organization | 11 | Shareholder Account Features | 18 |
| Valuing Shares | 12 | Tax Information | 19 |
| Purchasing Shares | 12 | Financial Highlights | 21 |
This prospectus contains important information about the Funds and the services
available to shareholders. Please save it for reference. |
Fund Summaries
This section summarizes the investment objectives and principal strategies and risks of investing in an Eaton Vance Municipals Funds. You will find more specific information about each Fund in the pages that follow.
Investment Objectives and Principal Strategies
The investment objective of each Fund is to provide current income exempt from regular federal income tax and, in the case of the Hawaii Fund and Kansas Fund, from particular state taxes. Under normal market circumstances, each Fund will invest at least 80% of its net assets in municipal obligations that are exempt from such taxes. The Hawaii Fund and Kansas Fund primarily invest in investment grade municipal obligations (those rated BBB or Baa or higher), but may also invest in lower rated obligations. The Insured Fund primarily invests in municipal obligations that are insured as to principal and interest payments by insurers having a claims-paying ability rated at least investment grade, provided that at least 50% of such assets is invested in obligations insured by insurers having a claims-paying ability rated at least A. Each Fund normally acquires municipal obligations with maturities of ten years or more.
Each Fund may concentrate in certain types of municipal obligations (such as industrial development bonds, housing bonds, hospital bonds or utility bonds), so Fund shares could be affected by events that adversely affect a particular sector. Each Fund may purchase derivative instruments (such as inverse floaters, futures contracts and options thereon, interest rate swaps, and forward rate contracts), bonds that do not make regular payments of interest, bonds issued on a when-issued basis and municipal leases. The portfolio managers may also trade securities to minimize taxable capital gains to shareholders. A portion of the Insured and Hawaii Funds’ distributions generally will be subject to the federal alternative minimum tax.
Principal Risk Factors
Obligations with maturities of ten years or more may offer higher yields than obligations with shorter maturities, but they are subject to greater fluctuations in value when interest rates change. When interest rates rise, the value of Fund shares typically will decline. A Fund’s yield will also fluctuate over time. The Hawaii and Kansas Funds invest a significant portion of assets in obligations of issuers located in a single state and are sensitive to factors affecting that state, such as changes in the economy, decreases in tax collection or the tax base, legislation which limits taxes and changes in issuer credit ratings.
Because obligations rated BBB or Baa and obligations rated below BBB or Baa (so-called “junk bonds”) are more sensitive to the financial soundness of their issuers than higher quality obligations, Fund shares, as a general matter, may fluctuate more in value than shares of a fund investing solely in higher quality obligations. Obligations rated BBB or Baa have speculative characteristics, while lower rated obligations are predominately speculative.
A Fund’s use of derivatives may expose the Fund to increased risk of principal loss due to imperfect correlation, failure of the counterparty and unexpected price or interest rate movements. Inverse floaters are volatile and involve leverage risk. Bonds that do not make regular interest payments may experience greater volatility in response to interest rate changes. When-issued securities are subject to the risk that when delivered to the Fund they will be worth less than the price the Fund agreed to pay for them. Municipal leases often require a legislative appropriation of funds for payment. If the necessary appropriation is not made, the issuer of the lease may not be able to meet its obligations.
As non-diversified funds, each Fund may invest a larger portion of their assets in the obligations of a limited number of issuers than may a diversified fund. This makes each Fund more susceptible to adverse economic, business or other developments affecting such issuers. Each Fund may invest, with respect to 50% of its total assets, more than 5% (but not more than 25%) of its total assets in securities of any one issuer, other than U.S. Government securities.
No Fund is a complete investment program and you may lose money by investing in a Fund. There is no guarantee that a Fund will be able to achieve its investment objective. An investment in a Fund is not a deposit in a bank and is not insured or guaranteed by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation or any other government agency.
2
| Eaton Vance Hawaii Municipals Fund |
The Hawaii Fund’s investment objective is to provide current income exempt from regular federal income tax and Hawaii state individual income taxes.
The Board of Trustees of the Hawaii Fund has voted to recommend that shareholders approve the merger of the Hawaii Fund into Eaton Vance National Municipals Fund (the "National Fund"), a diversified national municipal bond fund with substantially similar investment objectives and policies to the Fund (with the exception of policies to avoid particular state income taxes). Shareholders of the Fund will be asked to approve the merger at a special meeting scheduled to be held on September 25, 2009. If approved, the Fund will transfer its assets to the National Fund in exchange for shares of the National Fund, and the National Fund will assume the liabilities of the Fund. Immediately following this exchange, which will be effected on the basis of the relative net asset value of the Fund, the Fund will distribute shares of National Fund to its shareholders pro rata in liquidation of the Fund.
Performance Information. The following bar chart and table provide information about the Hawaii Fund’s performance for each calendar year through December 31, 2008. The returns in the bar chart are for Class B shares and do not reflect a sales charge. If the sales charge was reflected, the returns would be lower. The table contains returns for each Class of shares and a comparison to two national indices of municipal bonds. Returns in the table for Class B shares are shown before and after the reduction of taxes. Although past performance (both before and after taxes) is no guarantee of future results, this performance information demonstrates the risk that the value of your investment will change.
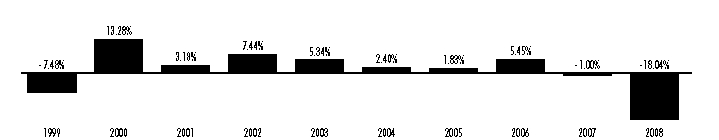
During the ten years ended December 31, 2008, the highest quarterly total return for Class B was 5.72% for the quarter ended December 31, 2000, and the lowest quarterly return was –9.87% for the quarter ended December 31,2008. The year-to-date total return through the end of the most recent calendar quarter (December 31, 2008 to March 31, 2009) was 6.89%. For the 30 days ended January 31, 2009, the SEC yield and SEC tax-equivalent yield (assuming a combined state and federal income tax rate of 40.36%) for Class A shares were 3.84% and 6.44%, respectively, for Class B shares were 3.44% and 5.77%, respectively, and for Class C shares were 3.56% and 5.97%, respectively. A lower tax rate would result in lower tax-equivalent yields. For current yield information call 1-800-262-1122.
| | | |
| | One | Five | Ten |
| Average Annual Total Return as of December 31, 2008 | Year | Years | Years |
| Class A Return Before Taxes | –21.34% | –2.52% | 1.13% |
| Class B Return Before Taxes | –21.99% | –2.58% | 0.88% |
| Class B Return After Taxes on Distributions | –22.00% | –2.61% | 0.85% |
| Class B Return After Taxes on Distributions and the Sale of Class B Shares | –13.10% | –1.58% | 1.34% |
| Class C Return Before Taxes | –18.74% | –2.26% | 0.88% |
| Barclays Capital Municipal Bond Index (reflects no deduction for fees, expenses or taxes) | –2.47% | 2.71% | 4.26% |
| Barclays Capital Long (22+) Municipal Bond Index (reflects no deduction for fees, expenses or taxes) | –14.68% | 0.82% | 3.35% |
These returns reflect the maximum sales charge for Class A (4.75%) and any applicable contingent deferred sales charge ("CDSC") for Class B and Class C. The Class C performance shown above for the period prior to October 1, 2007 is the performance of Class B shares, adjusted for the sales change that applies to Class C (but not adjusted for any other differences in the expenses of the two classes). Barclays Capital Municipal Bond Index (formerly, Lehman Brothers Municipal Bond Index) is an unmanaged index of municipal bonds. Barclays Capital Long (22+) Municipal Bond Index (formerly Lehman Brothers Municipal Bond Long 22+ Index) is the long bond component of the Barclays Capital Municipal Bond Index. Investors cannot invest directly in an Index. (Source for Barclays Capital Municipal Bond Index and Barclays Capital Long (22+) Municipal Bond Index is Lipper, Inc.)
Total returns are historical and are calculated by determining the percentage change in net asset value or public offering price with all distributions reinvested. The Fund's past performance (both before and after taxes) is no guarantee of future results. Investment return and principal value of Fund shares will fluctuate so that shares, when redeemed, may be worth more or less than their original cost. Performance is for the stated time period only; due to market volatility, the Fund's current performance may be lower or higher than the quoted return. For the Fund’s performance as of the most recent month-end, please refer to www.eatonvance.com.
After-tax returns are calculated using certain assumptions. After-tax returns are calculated using the highest historical individual federal income tax rate and do not reflect the impact of state and local taxes. Actual after-tax returns depend on a shareholder’s tax situation and the actual characterization of distributions, and may differ from those shown. After-tax returns are not relevant to shareholders who hold shares in tax-deferred accounts or to shares held by non-taxable entities. After-tax returns for other Classes of shares will vary from after-tax returns presented for Class B shares. Return After Taxes on Distributions for a period may be the same as Return Before Taxes for that period because no taxable distributions were made during that period. Also, Return After Taxes on Distributions and the Sale of Fund Shares for a period may be greater than or equal to Return After Taxes on Distributions for the same period because of losses realized on the sale of Fund s hares.
3
Hawaii Fund Fees and Expenses. These tables describe the fees and expenses that you may pay if you buy and hold shares. Annual Fund Operating Expenses are stated as a percentage of the Fund’s average daily net assets for its most recently completed fiscal year. In general, Annual Fund Operating Expenses as a percentage of Fund average daily net assets will change as Fund assets increase and decrease, and Annual Fund Operating Expenses may differ in the future. The net assets of the Fund as of its last five fiscal year ends are included in the Financial Highlights in this prospectus.
| | | | | | | | |
| Shareholder Fees | | | | | Annual Fund Operating Expenses | | | |
| (fees paid directly from your investment) | Class A | Class B | Class C | | (expenses that are deducted from Fund assets) | Class A | Class B | Class C |
| Maximum Sales Charge (Load) (as a percentage of offering price) | 4.75% | None | None | | Management Fees | 0.15% | 0.15% | 0.15% |
| Maximum Deferred Sales Charge (Load) (as a percentage of the | | | | | Distribution and Service (12b-1) Fees | 0.20% | 0.95% | 0.95% |
| lower of net asset value at time of purchase or redemption) | None | 5.00% | 1.00% | | Other Expenses (total including Interest Expense)(1) | 0.72% | 0.71% | 0.72% |
| Maximum Sales Charge (Load) Imposed on Reinvested Distributions | None | None | None | | Interest Expense | 0.14% | 0.14% | 0.14% |
| | | | | | Other Expenses (excluding Interest Expense) | 0.58% | 0.57% | 0.58% |
| | | | | | Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses | 1.07% | 1.81% | 1.82% |
| (1) | “Other Expenses” includes interest expense relating to the Fund’s liability with respect to floating rate notes held by third parties in conjunction with inverse floater securities transactions by the Fund. The Fund also records offsetting interest income in an amount equal to this expense relating to the municipal obligations underlying such transactions, and as a result net asset value and performance have not been affected by this expense. Had this expense not been included, total “Other Expenses” would have been in the amounts described in the table above as “Other Expenses (excluding Interest Expense)”. See “Investment Objectives & Principal Policies and Risks” for a description of these transactions. |
Example. This Example is intended to help you compare the cost of investing in the Fund with the cost of investing in other mutual funds. The Example assumes that you invest $10,000 in the Fund for the time periods indicated and then redeem all of your shares at the end of those periods. The Example also assumes that your investment has a 5% return each year and that the operating expenses remain the same as stated in the Fund Fees and Expenses tables above. Although your actual costs may be higher or lower, based on these assumptions your costs would be:
| | | | |
| | 1 Year | 3 Years | 5 Years | 10 Years |
| Class A shares | $579 | $799 | $1,037 | $1,719 |
| Class B shares* | $684 | $969 | $1,180 | $1,932 |
| Class C shares | $285 | $573 | $985 | $2,137 |
You would pay the following expenses if you did not redeem your shares:
| | | | |
| | 1 Year | 3 Years | 5 Years | 10 Years |
| Class A shares | $579 | $799 | $1,037 | $1,719 |
| Class B shares* | $184 | $569 | $980 | $1,932 |
| Class C shares | $185 | $573 | $985 | $2,137 |
| * | Reflects the expenses of Class A shares after eight years because Class B shares automatically convert to Class A shares after eight years. |
4
| Eaton Vance Insured Municipals Fund |
The Insured Fund’s investment objective is to provide current income exempt from regular federal income tax.
Performance Information. The following bar chart and table provide information about the Insured Fund’s performance for each calendar year through December 31, 2008. The returns in the bar chart are for Class B shares and do not reflect a sales charge. If the sales charge was reflected, the returns would be lower. The table contains returns for each Class of shares and a comparison to two national indices of municipal bonds. Returns in the table for Class B shares are shown before and after the reduction of taxes. Although past performance (both before and after taxes) is no guarantee of future results, this performance information demonstrates the risk that the value of your investment will change.
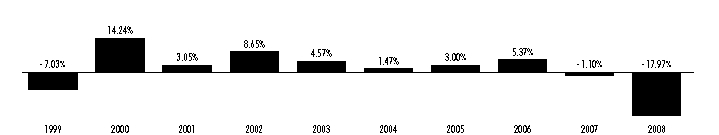
During the ten years ended December 31, 2008, the highest quarterly total return for Class B was 6.25% for the quarter ended December 31, 2000, and the lowest quarterly return was –8.42% for the quarter ended September 30, 2008. The year-to-date total return through the end of the most recent calendar quarter (December 31, 2008 to March 31, 2009) was 7.70%. For the 30 days ended January 31, 2009, the SEC yield and SEC tax-equivalent yield (assuming a federal income tax rate of 35.00%) for Class A shares were 4.24% and 6.52%, respectively, for Class B shares were 3.69% and 5.68%, respectively, and for Class C shares were 3.76% and 5.78%, respectively. A lower tax rate would result in lower tax-equivalent yields. For current yield information call 1-800-262-1122.
| | | |
| | One | Five | Ten |
| Average Annual Total Return as of December 31, 2008 | Year | Years | Years |
| Class A Return Before Taxes | –21.15% | –2.45% | 1.32% |
| Class B Return Before Taxes | –21.91% | –2.55% | 1.06% |
| Class B Return After Taxes on Distributions | –21.91% | –2.55% | 1.05% |
| Class B Return After Taxes on Distributions and the Sale of Class B Shares | –12.97% | –1.50% | 1.54% |
| Class C Return Before Taxes | –18.74% | –2.20% | 1.07% |
| Barclays Capital Municipal Bond Index (reflects no deduction for fees, expenses or taxes) | –2.47% | 2.71% | 4.26% |
| Barclays Capital Long (22+) Municipal Bond Index (reflects no deduction for fees, expenses or taxes) | –14.68% | 0.82% | 3.35% |
These returns reflect the maximum sales charge for Class A (4.75%) and any applicable CDSC for Class B and Class C. The Class C performance shown above for the period prior to June 2, 2006 is the performance of Class B shares, adjusted for the sales charge that applies to Class C shares (but not adjusted for any other differences in the expenses of the two classes). Barclays Capital Municipal Bond Index (formerly, Lehman Brothers Municipal Bond Index) is an unmanaged index of municipal bonds. Barclays Capital Long (22+) Municipal Bond Index (formerly Lehman Brothers Municipal Bond Long 22+ Index) is the long bond component of the Barclays Capital Municipal Bond Index. Investors cannot invest directly in an Index. (Source for Barclays Capital Municipal Bond Index and Barclays Capital (Long 22+) Municipal Bond Index is Lipper, Inc.)
Total returns are historical and are calculated by determining the percentage change in net asset value or public offering price with all distributions reinvested. The Fund's past performance (both before and after taxes) is no guarantee of future results. Investment return and principal value of Fund shares will fluctuate so that shares, when redeemed, may be worth more or less than their original cost. Performance is for the stated time period only; due to market volatility, the Fund's current performance may be lower or higher than the quoted return. For the Fund’s performance as of the most recent month-end, please refer to www.eatonvance.com.
After-tax returns are calculated using certain assumptions. After-tax returns are calculated using the highest historical individual federal income tax rate and do not reflect the impact of state and local taxes. Actual after-tax returns depend on a shareholder’s tax situation and the actual characterization of distributions, and may differ from those shown. After-tax returns are not relevant to shareholders who hold shares in tax-deferred accounts or to shares held by non-taxable entities. After-tax returns for other Classes of shares will vary from after-tax returns presented for Class B shares. Return After Taxes on Distributions for a period may be the same as Return Before Taxes for that period because no taxable distributions were made during that period. Also, Return After Taxes on Distributions and the Sale of Fund Shares for a period may be greater than or equal to Return After Taxes on Distributions for the same period because of losses realized on the sale of Fund s hares.
5
Insured Fund Fees and Expenses. These tables describe the fees and expenses that you may pay if you buy and hold shares. Annual Fund Operating Expenses are stated as a percentage of the Fund’s average daily net assets for its most recently completed fiscal year. In general, Annual Fund Operating Expenses as a percentage of Fund average daily net assets will change as Fund assets increase and decrease, and Annual Fund Operating Expenses may differ in the future. The net assets of the Fund as of its last five fiscal year ends are included in the Financial Highlights in this prospectus.
| | | | | | | | |
| Shareholder Fees | | | | | Annual Fund Operating Expenses | | | |
| (fees paid directly from your investment) | Class A | Class B | Class C | | (expenses that are deducted from Fund assets) | Class A | Class B | Class C |
| Maximum Sales Charge (Load) (as a percentage of offering price) | 4.75% | None | None | | Management Fees | 0.23% | 0.23% | 0.23% |
| Maximum Deferred Sales Charge (Load) (as a percentage of the | | | | | Distribution and Service (12b-1) Fees | 0.20% | 0.95% | 0.95% |
| lower of net asset value at time of purchase or redemption) | None | 5.00% | 1.00% | | Other Expenses (total including Interest Expense)(1) | 0.64% | 0.64% | 0.63% |
| Maximum Sales Charge (Load) Imposed on Reinvested Distributions | None | None | None | | Interest Expense | 0.17% | 0.17% | 0.17% |
| | | | | | Other Expenses (excluding Interest Expense) | 0.47% | 0.47% | 0.46% |
| | | | | | Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses | 1.07% | 1.82% | 1.81% |
| (1) | “Other Expenses” includes interest expense relating to the Fund’s liability with respect to floating rate notes held by third parties in conjunction with inverse floater securities transactions by the Fund. The Fund also records offsetting interest income in an amount equal to this expense relating to the municipal obligations underlying such transactions, and as a result net asset value and performance have not been affected by this expense. Had this expense not been included, total “Other Expenses” would have been in the amounts described in the table above as “Other Expenses (excluding Interest Expense)”. See “Investment Objectives & Principal Policies and Risks” for a description of these transactions. |
Example. This Example is intended to help you compare the cost of investing in the Fund with the cost of investing in other mutual funds. The Example assumes that you invest $10,000 in the Fund for the time periods indicated and then redeem all of your shares at the end of those periods. The Example also assumes that your investment has a 5% return each year and that the operating expenses remain the same as stated in the Fund Fees and Expenses tables above. Although your actual costs may be higher or lower, based on these assumptions your costs would be:
| | | | |
| | 1 Year | 3 Years | 5 Years | 10 Years |
| Class A shares | $579 | $799 | $1,037 | $1,719 |
| Class B shares* | $685 | $973 | $1,185 | $1,940 |
| Class C shares | $284 | $569 | $980 | $2,127 |
You would pay the following expenses if you did not redeem your shares:
| | | | |
| | 1 Year | 3 Years | 5 Years | 10 Years |
| Class A shares | $579 | $799 | $1,037 | $1,719 |
| Class B shares* | $185 | $573 | $985 | $1,940 |
| Class C shares | $184 | $569 | $980 | $2,127 |
* Reflects the expenses of Class A shares after eight years because Class B shares automatically convert to Class A shares after eight years.
6
| Eaton Vance Kansas Municipals Fund |
The Kansas Fund’s investment objective is to provide current income exempt from regular federal income tax and Kansas state individual income taxes.
Performance Information. The following bar chart and table provide information about the Kansas Fund’s performance for each calendar year through December 31, 2008. The returns in the bar chart are for Class B shares and do not reflect a sales charge. If the sales charge was reflected, the returns would be lower. The table contains returns for each Class of shares and a comparison to two national indices of municipal bonds. Returns in the table for Class B shares are shown before and after the reduction of taxes. Although past performance (both before and after taxes) is no guarantee of future results, this performance information demonstrates the risk that the value of your investment will change.
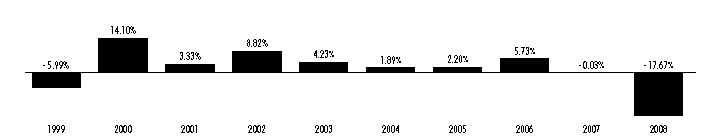
During the ten years ended December 31, 2008, the highest quarterly total return for Class B was 6.06% for the quarter ended December 31, 2000, and the lowest quarterly return was –10.52% for the quarter ended December 31, 2008. The year-to-date total return through the end of the most recent calendar quarter (December 31, 2008 to March 31, 2009) was 9.10%. For the 30 days ended January 31, 2009, the SEC yield and SEC tax-equivalent yield (assuming a combined state and federal income tax rate of 39.19%) for Class A shares were 3.86% and 6.35%, respectively, for Class B shares were 3.35% and 5.51%, respectively, and for Class C shares were 3.35% and 5.51%, respectively. A lower tax rate would result in lower tax-equivalent yields. For current yield information call 1-800-262-1122.
| | | |
| | One | Five | Ten |
| Average Annual Total Return as of December 31, 2008 | Year | Years | Years |
| Class A Return Before Taxes | –20.99% | –2.22% | 1.55% |
| Class B Return Before Taxes | –21.64% | –2.28% | 1.31% |
| Class B Return After Taxes on Distributions | –21.64% | –2.28% | 1.31% |
| Class B Return After Taxes on Distributions and the Sale of Class B Shares | –12.88% | –1.31% | 1.72% |
| Class C Return Before Taxes | –18.46% | –1.95% | 1.31% |
| Barclays Capital Municipal Bond Index (reflects no deduction for fees, expenses or taxes) | –2.47% | 2.71% | 4.26% |
| Barclays Capital Long (22+) Municipal Bond Index (reflects no deduction for fees, expenses or taxes) | –14.68% | 0.82% | 3.35% |
These returns reflect the maximum sales charge for Class A (4.75%) and any applicable CDSC for Class B and Class C. The Class C performance shown above for the period prior to June 2, 2006 is the performance of Class B shares, adjusted for the sales charge that applies to Class C shares (but not adjusted for any other differences in the expenses of the two classes). Barclays Capital Municipal Bond Index (formerly, Lehman Brothers Municipal Bond Index) is an unmanaged index of municipal bonds. Barclays Capital Long (22+) Municipal Bond Index (formerly Lehman Brothers Municipal Bond Long 22+ Index) is the long bond component of the Barclays Capital Municipal Bond Index. Investors cannot invest directly in an Index. (Source for Barclays Capital Municipal Bond Index and Barclays Capital Long (22+) Municipal Bond Index is Lipper, Inc.)
Total returns are historical and are calculated by determining the percentage change in net asset value or public offering price with all distributions reinvested. The Fund's past performance (both before and after taxes) is no guarantee of future results. Investment return and principal value of Fund shares will fluctuate so that shares, when redeemed, may be worth more or less than their original cost. Performance is for the stated time period only; due to market volatility, the Fund's current performance may be lower or higher than the quoted return. For the Fund’s performance as of the most recent month-end, please refer to www.eatonvance.com.
After-tax returns are calculated using certain assumptions. After-tax returns are calculated using the highest historical individual federal income tax rate and do not reflect the impact of state and local taxes. Actual after-tax returns depend on a shareholder’s tax situation and the actual characterization of distributions, and may differ from those shown. After-tax returns are not relevant to shareholders who hold shares in tax-deferred accounts or to shares held by non-taxable entities. After-tax returns for other Classes of shares will vary from after-tax returns presented for Class B shares. Return After Taxes on Distributions for a period may be the same as Return Before Taxes for that period because no taxable distributions were made during that period. Also, Return After Taxes on Distributions and the Sale of Fund Shares for a period may be greater than or equal to Return After Taxes on Distributions for the same period because of losses realized on the sale of Fund s hares.
7
Kansas Fund Fees and Expenses. These tables describe the fees and expenses that you may pay if you buy and hold shares. Annual Fund Operating Expenses are stated as a percentage of the Fund’s average daily net assets for its most recently completed fiscal year. In general, Annual Fund Operating Expenses as a percentage of Fund average daily net assets will change as Fund assets increase and decrease, and Annual Fund Operating Expenses may differ in the future. The net assets of the Fund as of its last five fiscal year ends are included in the Financial Highlights in this prospectus.
| | | | | | | | |
| Shareholder Fees | | | | | Annual Fund Operating Expenses | | | |
| (fees paid directly from your investment) | Class A | Class B | Class C | | (expenses that are deducted from Fund assets) | Class A | Class B | Class C |
| Maximum Sales Charge (Load) (as a percentage of offering price) | 4.75% | None | None | | Management Fees | 0.21% | 0.21% | 0.21% |
| Maximum Deferred Sales Charge (Load) (as a percentage of the | | | | | Distribution and Service (12b-1) Fees | 0.20% | 0.95% | 0.95% |
| lower of net asset value at time of purchase or redemption) | None | 5.00% | 1.00% | | Other Expenses (total including Interest Expense)(1) | 0.42% | 0.42% | 0.42% |
| Maximum Sales Charge (Load) Imposed on Reinvested Distributions | None | None | None | | Interest Expense | 0.06% | 0.06% | 0.06% |
| | | | | | Other Expenses (excluding Interest Expense) | 0.36% | 0.36% | 0.36% |
| | | | | | Total Annual Fund Operating Expenses | 0.83% | 1.58% | 1.58% |
| (1) | “Other Expenses” includes interest expense relating to the Fund’s liability with respect to floating rate notes held by third parties in conjunction with inverse floater securities transactions by the Fund. The Fund also records offsetting interest income in an amount equal to this expense relating to the municipal obligations underlying such transactions, and as a result net asset value and performance have not been affected by this expense. Had this expense not been included, total “Other Expenses” would have been in the amounts described in the table above as “Other Expenses (excluding Interest Expense)”. See “Investment Objectives & Principal Policies and Risks” for a description of these transactions. |
Example. This Example is intended to help you compare the cost of investing in the Fund with the cost of investing in other mutual funds. The Example assumes that you invest $10,000 in the Fund for the time periods indicated and then redeem all of your shares at the end of those periods. The Example also assumes that your investment has a 5% return each year and that the operating expenses remain the same as stated in the Fund Fees and Expenses tables above. Although your actual costs may be higher or lower, based on these assumptions your costs would be:
| | | | |
| | 1 Year | 3 Years | 5 Years | 10 Years |
| Class A shares | $556 | $727 | $914 | $1,452 |
| Class B shares* | $661 | $899 | $1,060 | $1,677 |
| Class C shares | $261 | $499 | $860 | $1,878 |
You would pay the following expenses if you did not redeem your shares:
| | | | |
| | 1 Year | 3 Years | 5 Years | 10 Years |
| Class A shares | $556 | $727 | $914 | $1,452 |
| Class B shares* | $161 | $499 | $860 | $1,677 |
| Class C shares | $161 | $499 | $860 | $1,878 |
* Reflects the expenses of Class A shares after eight years because Class B shares automatically convert to Class A shares after eight years.
8
Investment Objectives & Principal Policies and Risks
The investment objective of each Fund is to provide current income exempt from regular federal income tax and, in the case of the Hawaii Fund and Kansas Fund, from particular state taxes. Each Fund seeks to achieve its objective by investing primarily (i.e., at least 80% of its net assets during periods of normal market conditions) in municipal obligations, the interest on which is exempt from regular federal income tax and from the state taxes which, in accordance with the Fund’s investment objective, the Fund seeks to avoid. This is a fundamental policy of each Fund which only may be changed with shareholder approval. For purposes of the policy, “net assets” include any assets purchased with borrowings for investment purposes. Each Fund’s investment objective and certain other policies may be changed by the Trustees without shareholder approval. There is no present intention to make any such change and shareholders will receive at least 60 days’ notice of any material change in the Fund’s investment objective.
At least 75% of the Hawaii Fund’s and the Kansas Fund’s net assets will normally be invested in municipal obligations rated at least investment grade at the time of investment (which are those rated Baa or higher by Moody’s Investors Services, Inc. ("Moody’s"), or BBB or higher by either Standard & Poor’s Ratings Group ("S&P") or Fitch Ratings ("Fitch")) or, if unrated, determined by the investment adviser to be of at least investment grade quality. The balance of the Hawaii Fund’s and the Kansas Fund’s net assets may be invested in municipal obligations rated below investment grade and in unrated municipal obligations considered to be of comparable quality by the investment adviser. Municipal obligations rated Baa or BBB or below have speculative characteristics, while lower-quality obligations are predominately speculative. Also, changes in economic conditions or other circumstances are more likely to reduce the capacity of issuers of lower-rated obligations to make principal and interest payments. Lower-rated obligations also, as a general matter, may be subject to greater price volatility than higher rated obligations. No Fund will invest more than 10% of its net assets in obligations rated below B by Moody’s, S&P or Fitch, or in unrated obligations considered to be of comparable quality by the investment adviser. A credit rating may have a modifier (such as plus, minus or a numerical modifier) to denote its relative status within the rating. The presence of a modifier does not change the security’s credit rating (meaning that BBB- and Baa3 are within the investment grade rating).
At least 80% of the Insured Fund’s net assets will normally be invested in obligations that are insured as to principal and interest payments by insurers having a claims-paying ability rated at least Baa by Moody’s or BBB by S&P or Fitch, provided that at least 50% of such net assets is invested in obligations insured by insurers having a claims-paying ability rated at least A by Moody’s, S&P or Fitch. Ratings of Baa or higher by Moody’s or BBB or higher by S&P or Fitch are considered to be of investment grade quality. The Insured Fund may invest up to 20% of its net assets in unrated obligations deemed by the investment adviser to be of investment grade quality and obligations that are uninsured. This insurance does not protect the market value of such obligations or the net asset value of the Insured Fund. The value of an obligation will be affected by the credit standing of its insurer.
Municipal obligations include bonds, notes and commercial paper issued by a municipality, a group of municipalities or participants in qualified issues of tax-exempt debt for a wide variety of both public and private purposes. Municipal obligations also include municipal leases and participations in municipal leases. An issuer’s obligation under such leases is often subject to the appropriation by the appropriate legislative body, on an annual or other basis, of funds for the payment of the obligations. Certain municipal obligations may be purchased on a “when-issued” basis, which means that payment and delivery occur on a future settlement date. The price and yield of such securities are generally fixed on the date of commitment to purchase.
The investment adviser’s process for selecting securities for purchase and sale is research intensive and emphasizes the creditworthiness of the issuer or other person obligated to repay the obligation. Although the investment adviser considers ratings when making investment decisions, it performs its own credit and investment analysis and does not rely primarily on the ratings assigned by the rating services. Credit ratings are based largely on the rating agency’s investment analysis at the time of rating and the rating assigned to any particular security is not necessarily a reflection of the issuer’s current financial condition. The rating assigned to a security by a rating agency does not necessarily reflect its assessment of the volatility of the security’s market value or of the liquidity of an investment in the security.
The interest on municipal obligations is (in the opinion of the issuer’s counsel) exempt from regular federal income tax. Interest income from certain types of municipal obligations generally will be subject to the federal alternative minimum tax (the “AMT”) for individuals. Distributions to corporate investors may also be subject to the AMT. The Insured and Hawaii Funds may not be suitable for investors subject to the AMT. The Kansas Fund will not invest in an obligation if the interest on that obligation is subject to the AMT.
Although each Fund may invest in securities of any maturity, it is expected that the Fund will normally acquire securities with maturities of ten years or more at the time of investment. Many obligations permit the issuer at its option to “call,”
9
or redeem, its securities. As such, the effective maturity of an obligation may be less than ten years as the result of call provisions. The effective maturity of an obligation is its likely redemption date after consideration of any call or redemption features. If an issuer calls securities during a time of declining interest rates, it may not be possible to reinvest the proceeds in securities providing the same investment return as the securities redeemed. The average maturity of the Fund’s holdings may vary depending on market conditions.
Under normal conditions, each of the Hawaii Fund and Kansas Fund invests at least 65% of its total assets in obligations issued by its respective state or its political subdivisions, agencies, authorities and instrumentalities. Municipal obligations of issuers in a single state may be adversely affected by economic developments (including insolvency of an issuer) and by legislation and other governmental activities in that state. Each Fund may also invest up to 35% of its net assets in municipal obligations issued by the governments of Puerto Rico, the U.S. Virgin Islands and Guam.
Each Fund may invest 25% or more of its total assets in municipal obligations in the same sector (such as leases, housing finance, public housing, municipal utilities, hospital and health facilities or industrial development). This may make the Fund more susceptible to adverse economic, political or regulatory occurrences or adverse court decisions affecting a particular sector.
The net asset value of the Fund’s shares will change in response to changes in prevailing interest rates and changes in the value of securities held by the Fund. The value of securities held will be affected by the credit quality of the issuer of the obligation, and general economic and business conditions that affect the specific economic sector of the issuer as well as any actual or anticipated change to the tax treatment of securities held by the Fund. Changes by rating agencies in the rating assigned to an obligation may also affect the value of that obligation. To the extent that securities held by the Fund are insured as to principal and interest payments by insurers whose claims-paying ability or other rating is downgraded by a ratings agency, the value of such securities may be affected. When the supply of municipal obligations exceeds demand, the value of Fund shares may decline. The increased presence of non-traditional participants in the municipal markets may lead to greater volatility in the markets.
A Fund may purchase derivative instruments, which derive their value from another instrument, security or index. For example, the Fund may invest in residual interests of a trust (the ”trust”) that holds municipal securities (“inverse floaters”). The trust will also issue floating rate notes to third parties that may be senior to the inverse floaters held by a Fund. The Fund receives interest payments on inverse floaters that bear an inverse relationship to the interest rate paid on the floating rate notes. As a result of Financial Accounting Standards Statement No. 140 (“FAS 140”), interest paid by the trust to the floating rate note holders may be reflected as income in the Fund’s financial statements with an offsetting expense for the interest paid by the trust to the floating rate note holders. Inverse floaters involve leverage risk and will involve greater risk than an investment in a fixed rate bond. Because changes in the interest rate paid to the floating rate note holders inversely affects the interest paid on the inverse floater, the value and income of an inverse floater are generally more volatile than that of a fixed rate bond. Inverse floaters have varying degrees of liquidity, and the market for these securities is relatively volatile. These securities tend to underperform the market for fixed rate bonds in a rising long-term interest rate environment, but tend to outperform the market for fixed rate bonds when long-term interest rates decline. While inverse floaters expose the Fund to leverage risk, they do not constitute borrowings for purposes of the Fund’s restrictions on borrowings.
Each Fund may also purchase and sell various kinds of financial futures contracts and options thereon to hedge against changes in interest rates or as a substitute for the purchase of portfolio securities. Each Fund may also enter into interest rate swaps, forward rate contracts and credit derivatives, which may include credit default swaps, total return swaps or credit options, as well as purchase an instrument that has greater or lesser credit risk than the municipal bonds underlying the instrument. The use of derivative instruments for both hedging and investment purposes involves a risk of loss or depreciation due to a variety of factors including counterparty risk, unexpected market, interest rate or securities price movements, and tax and regulatory constraints. The use of derivatives is highly specialized and engaging in derivative transactions for purposes other than hedging is speculative. Derivative hedging transactions may not be effective because of imperfect correlations, i.e. offsetting markets which do not experience price changes in perfect correlation with each other, and other factors.
Each Fund may invest in zero coupon bonds, which do not require the issuer to make periodic interest payments. The values of these bonds are subject to greater fluctuation in response to changes in market interest rates than bonds which pay interest currently. Each Fund accrues income on these investments and is required to distribute that income each year. Each Fund may be required to sell securities to obtain cash needed for income distributions.
The limited liquidity of certain securities in which each Fund may invest (including those eligible for resale under Rule 144A of the Securities Act of 1933) could affect their market prices, thereby adversely affecting net asset value and the
10
ability to pay income. The amount of publicly available information about certain municipal obligations may be limited and the investment performance of the Fund may be more dependent on the portfolio manager’s analysis than if this were not the case.
Each Fund may borrow amounts up to one-third of the value of its total assets (including assets acquired using borrowings), but it will not borrow more than 5% of the value of its total assets except to satisfy redemption requests or for other temporary purposes. Such borrowings would result in increased expense to the Fund and, while they are outstanding, would magnify increases or decreases in the value of Fund shares. No Fund will purchase additional investment securities while outstanding borrowings exceed 5% of the value of its total assets.
During unusual market conditions, each Fund may temporarily invest up to 50% of its total assets in cash or cash equivalents, including short-term municipal securities, which is not consistent with the Fund’s investment objective. While temporarily invested, the Fund may not achieve its objective, and interest income from temporary investments may be taxable. Each Fund might not use all of the strategies and techniques or invest in all of the types of securities described in this Prospectus or the Statement of Additional Information. While at times the Fund may use alternative investment strategies in an effort to limit its losses, it may choose not to do so.
Each Fund’s investment policies include a fundamental investment provision allowing the Fund to invest substantially all of its investable assets in one or more open-end management investment companies having substantially the same investment policies and restrictions as the Fund. Any such company or companies would be advised by the Fund’s investment adviser (or an affiliate) and the Fund would not pay directly any advisory fee with respect to the assets so invested. The Fund will indirectly bear its proportionate share of any management fees paid by investment companies in which it invests in addition to the advisory fee paid by the Fund. The Fund may initiate investments in one or more investment companies at any time without shareholder approval.
Management and Organization
Management. Each Fund’s investment adviser is Boston Management and Research (“BMR”), a subsidiary of Eaton Vance Management (“Eaton Vance”), with offices at Two International Place, Boston, MA 02110. Eaton Vance has been managing assets since 1924 and managing mutual funds since 1931. Eaton Vance and its affiliates currently manage approximately $120 billion on behalf of mutual funds, institutional clients and individuals.
The investment adviser manages the investments of each Fund. Under its investment advisory agreement with each Fund, BMR receives a monthly advisory fee equal to the aggregate of a daily asset based fee and a daily income based fee. The fees are applied on the basis of the following categories.
| | | |
| | | Annual | Daily |
| Category | Daily Net Assets | Asset Rate | Income Rate |
| 1 | up to $20 million | 0.100% | 1.00% |
| 2 | $20 million but less than $40 million | 0.200% | 2.00% |
| 3 | $40 million but less than $500 million | 0.300% | 3.00% |
| 4 | $500 million but less than $1 billion | 0.275% | 2.75% |
| 5 | $1 billion but less than $1.5 billion | 0.250% | 2.50% |
| 6 | $1.5 billion but less than $2 billion | 0.225% | 2.25% |
| 7 | $2 billion but less than $3 billion | 0.200% | 2.00% |
| 8 | $3 billion and over | 0.175% | 1.75% |
For the fiscal year ended January 31, 2009, the effective annual rate of advisory fees paid to BMR, based on average daily net assets, was equivalent to the percentage of average daily net assets stated below.
| | |
| | Net Assets on | |
| | January 31, 2009 | Advisory Fee |
| Hawaii | $17,007,671 | 0.15% |
| Insured | $47,481,275 | 0.23% |
| Kansas | $32,936,994 | 0.21% |
Each Fund’s most recent shareholder report provides information regarding the basis for the Trustees’ approval of each Fund’s investment advisory agreement.
11
Robert B. MacIntosh is the portfolio manager of the Hawaii Fund (since it commenced operations). Craig R. Brandon is the portfolio manager of the Insured Fund (since September 13, 2004). Adam A. Weigold is the portfolio manager of the Kansas Fund (since October 1, 2007). Each portfolio manager is a Vice President of Eaton Vance and BMR and also manages other Eaton Vance portfolios, and Mr. MacIntosh has been an Eaton Vance portfolio manager for more than five years. Mr. Brandon and Mr. Weigold were appointed portfolio managers in 2004 and 2007, respectively, and have been municipal credit analysts at Eaton Vance for more than five years.
The Statement of Additional Information provides additional information about each portfolio manager’s compensation, other accounts managed by each portfolio manager, and each portfolio manager’s ownership of Fund shares with respect to which that portfolio manager has management responsibilities.
Eaton Vance serves as the administrator of each Fund, providing each Fund with administrative services and related office facilities. Eaton Vance does not currently receive a fee for serving as administrator.
Eaton Vance also serves as the sub-transfer agent for each Fund. For the sub-transfer agency services it provides, Eaton Vance receives an aggregate fee based upon the actual expenses it incurs in the performance of sub-transfer agency services. This fee is paid to Eaton Vance by the Fund’s transfer agent from the fees the transfer agent receives from the Eaton Vance funds.
Organization. Each Fund is a series of Eaton Vance Municipals Trust II (the "Trust"), a Massachusetts business trust. Each Fund offers multiple classes of shares. Each Class represents a pro rata interest in the Fund but is subject to different expenses and rights. The Funds do not hold annual shareholder meetings but may hold special meetings for matters that require shareholder approval (such as electing or removing trustees, approving management or advisory contracts or changing investment policies that may only be changed with shareholder approval).
Because the Funds use this combined prospectus, a Fund could be held liable for a misstatement or omission made about another Fund. The Trust’s Trustees considered this risk in approving the use of a combined prospectus.
Valuing Shares
Each Fund values its shares once each day only when the New York Stock Exchange (the "Exchange") is open for trading (typically Monday through Friday), as of the close of regular trading on the Exchange (normally 4:00 p.m. eastern time). The purchase price of Fund shares is their net asset value (plus a sales charge for Class A shares), which is derived from the value of Fund holdings. When purchasing or redeeming Fund shares through an investment dealer, your investment dealer must communicate your order to the principal underwriter by a specific time each day in order for the purchase price or the redemption price to be based on that day’s net asset value per share. It is the investment dealer’s responsibility to transmit orders promptly. Each Fund may accept purchase and redemption orders as of the time of their receipt by certain investment dealers (or their designated intermediaries).
The Trustees have adopted procedures for valuing investments and have delegated to the investment adviser the daily valuation of such investments. Municipal obligations owned by the Funds are normally valued on the basis of valuations furnished by a pricing service. The pricing service considers various factors relating to bonds and market transactions to determine value. In certain situations, the investment adviser may use the fair value of a security if market prices are unavailable or deemed unreliable. A security that is fair valued may be valued at a price higher or lower than actual market quotations or the value determined by other funds using their own fair valuation procedures. The investment adviser expects to use fair value pricing for municipal obligations under limited circumstances, such as when an obligation is not priced by the pricing service or is in default. Eaton Vance has established a Valuation Committee that oversees the valuation of investments.
Purchasing Shares
You may purchase shares through your investment dealer or by mailing an account application form to the transfer agent (see back cover for address). Purchases will be executed at the net asset value (plus any applicable sales charge) next determined after their receipt in good order by the Fund’s transfer agent. A Fund’s transfer agent or your investment dealer must receive your purchase in good order no later than the close of regular trading on the Exchange (normally 4:00 p.m. eastern time) for your purchase to be effected at that day’s net asset value. If you purchase shares through an investment dealer, that dealer may charge you a fee for executing the purchase for you. Each Fund may suspend the sale of its shares at any time and any purchase order may be refused for any reason. The Funds do not issue share certificates.
Your initial investment must be at least $1,000. After your initial investment, additional investments may be made in any amount at any time by sending a check payable to the order of the Fund or the transfer agent directly to the transfer agent
12
(see back cover for address). Please include your name and account number and the name of the Fund and Class of shares with each investment.
You may make automatic investments of $50 or more each month or each quarter from your bank account. You can establish bank automated investing on the account application or by providing written instructions. Please call 1-800-262-1122 Monday through Friday, 8:00 a.m. to 6:00 p.m. (eastern time) for further information. The minimum initial investment amount and Fund policy of redeeming accounts with low account balances are waived for bank automated investing accounts (other than for Class I), certain group purchase plans (including proprietary fee-based programs sponsored by broker-dealers) and for persons affiliated with Eaton Vance, its affiliates and certain Fund service providers (as described in the Statement of Additional Information).
Restrictions on Excessive Trading and Market Timing. The Funds are not intended for excessive trading or market timing. Market timers seek to profit by rapidly switching money into a fund when they expect the share price of the fund to rise and taking money out of the fund when they expect those prices to fall. By realizing profits through short-term trading, shareholders that engage in rapid purchases and sales or exchanges of a fund’s shares may dilute the value of shares held by long-term shareholders. Volatility resulting from excessive purchases and sales or exchanges of fund shares, especially involving large dollar amounts, may disrupt efficient portfolio management. In particular, excessive purchases and sales or exchanges of a fund’s shares may cause a fund to have difficulty implementing its investment strategies, may force the fund to sell portfolio securities at inopportune times to raise cash or may cause increased expenses (such as increa sed brokerage costs, realization of taxable capital gains without attaining any investment advantage or increased administrative costs).
A fund that invests in securities that are, among other things, thinly traded, traded infrequently or relatively illiquid (including certain municipal obligations) is susceptible to the risk that the current market price for such securities may not accurately reflect current market values. A shareholder may seek to engage in short-term trading to take advantage of these pricing differences (commonly referred to as “price arbitrage”). The investment adviser is authorized to use the fair value of a security if prices are unavailable or are deemed unreliable (see “Valuing Shares”). The use of fair value pricing and the restrictions on excessive trading and market timing described below are intended to reduce a shareholder’s ability to engage in price arbitrage to the detriment of the Funds.
The Boards of Trustees of the Eaton Vance funds have adopted policies to discourage short-term trading and market timing and to seek to minimize their potentially detrimental effects. Pursuant to these policies, if an investor (through one or more accounts) makes more than one round-trip exchange (exchanging from one fund to another fund and back again) within 90 days, it will be deemed to constitute market timing or excessive trading. Under the policies, each Fund or its principal underwriter will reject or cancel a purchase order, suspend or terminate the exchange privilege or terminate the ability of an investor to invest in the Eaton Vance funds if the Fund or the principal underwriter determines that a proposed transaction involves market timing or excessive trading that it believes is likely to be detrimental to the Fund. Each Fund and its principal underwriter use reasonable efforts to detect market timing and excessive trading activity, but they cannot ensure that they will be able to identify all cases of market timing and excessive trading. Each Fund or its principal underwriter may also reject or cancel any purchase order (including an exchange) from an investor or group of investors for any other reason. Decisions to reject or cancel purchase orders (including exchanges) in the Fund are inherently subjective and will be made in a manner believed to be in the best interest of a Fund’s shareholders. No Eaton Vance fund has any arrangement to permit market timing.
The following fund share transactions generally are exempt from the market timing and excessive trading policy described above because each Fund and the principal underwriter believe they generally do not raise market timing or excessive trading concerns:
| •transactions made pursuant to a systematic purchase plan or as the result of automatic reinvestment of dividends or distributions, or initiated by the Fund (e.g., for failure to meet applicable account minimums); |
| •transactions made by participants in employer sponsored retirement plans involving participant payroll or employer contributions or loan repayments, redemptions as part of plan terminations or at the direction of the plan, mandatory retirement distributions, or rollovers; |
| •transactions made by asset allocation and wrap programs where the adviser to the program directs transactions in the accounts participating in the program in concert with changes in a model portfolio; or |
| •transactions in shares of Eaton Vance Cash Management Fund, Eaton Vance Money Market Fund, Eaton Vance Tax Free Reserves and Eaton Vance Institutional Short Term Income Fund. |
It may be difficult for the Fund or the principal underwriter to identify market timing or excessive trading in omnibus accounts traded through financial intermediaries. The Funds and the principal underwriter have provided guidance to
13
financial intermediaries (such as banks, broker-dealers, insurance companies and retirement administrators) concerning the application of the Eaton Vance funds’ market timing and excessive trading policies to Fund shares held in omnibus accounts maintained and administered by such intermediaries, including guidance concerning situations where market timing or excessive trading is considered to be detrimental to the Fund. Each Fund or its principal underwriter may rely on a financial intermediary’s policy to restrict market timing and excessive trading if it believes that policy is likely to prevent market timing that is likely to be detrimental to the Fund. Such policy may be more or less restrictive than the Fund’s policy. Although each Fund or the principal underwriter reviews trading activity at the omnibus account level for activity that indicates potential market timing or excessive trading activity, the Funds and the principal underwriter typically will not req uest or receive individual account data unless suspicious trading activity is identified. Each Fund and the principal underwriter generally rely on financial intermediaries to monitor trading activity in omnibus accounts in good faith in accordance with their own or Fund policies. Each Fund and the principal underwriter cannot ensure that these financial intermediaries will in all cases apply the policies of the Fund or their own policies, as the case may be, to accounts under their control.
Choosing a Share Class. Each Fund offers different classes of shares. The different classes of shares represent investments in the same portfolio of securities, but the classes are subject to different sales charges and expenses and will likely have different share prices due to differences in class expenses. In choosing the class of shares that suits your investment needs, you should consider:
- how long you expect to own your shares;
- how much you intend to invest;
- the sales charge and total operating expenses associated with owning each class; and
- whether you qualify for a reduction or waiver of any applicable sales charges (see “Reducing or Eliminating Class A Sales Charges” under “Sales Charges” below).
Each investor’s considerations are different. You should speak with your investment dealer to help you decide which class of shares is best for you. Set forth below is a brief description of each class of shares offered by the Funds.
| Class A shares are offered at net asset value plus a front-end sales charge of up to 4.75%. This charge is deducted from the amount you invest. The Class A sales charge is reduced for purchases of $25,000 or more. The sales charge applicable to your purchase may be reduced under the right of accumulation or a statement of intention, which are described in “Reducing or Eliminating Class A Sales Charges” under “Sales Charges” below. Some investors may be eligible to purchase Class A shares at net asset value under certain circumstances, which are also described below. Class A shares pay distribution and service fees equal to 0.20% annually of average daily net assets. Returns on Class A shares are generally higher than returns on Class B and Class C shares because Class A has lower annual expenses than those classes. |
| Class B shares are offered at net asset value with no front-end sales charge. If you sell your Class B shares within six years of purchase, you generally will be subject to a contingent deferred sales charge or “CDSC”. The amount of the CDSC applicable to a redemption of Class B shares decreases over six years, as described in the CDSC schedule in “Contingent Deferred Sales Charge” under “Sales Charges” below. The CDSC is deducted from your redemption proceeds. Under certain circumstances, the Class B CDSC may be waived (such as in the case of the death of the shareholder). See “CDSC Waivers” under “Sales Charges” below. Class B shares pay distribution fees and service fees equal to 0.95% annually of average daily net assets. Returns on Class B shares are generally lower than returns on Class A shares because Class B has higher annual expenses than Class A. Class B shares automatically convert to Class A shares after eight years. Because the sales charge applicable to Class A shares is reduced for larger purchases and Class A has lower operating expenses, purchasing Class B shares may not be appropriate if you are investing a large amount. |
| Orders for Class B shares of one or more Eaton Vance funds will be refused when the total value of the purchase (including the aggregate value of all Eaton Vance fund shares held within the purchasing shareholder’s account) is $100,000 or more. Investors considering cumulative purchases of $100,000 or more, or who, after a purchase of shares, would own shares of Eaton Vance funds with a current market value of $100,000 or more, should consider whether Class A shares would be more advantageous and consult their investment dealer. |
| Class C shares are offered at net asset value with no front-end sales charge. If you sell your Class C shares within one year of purchase, you generally will be subject to a CDSC. The CDSC is deducted from your redemption proceeds. Under certain circumstances, the Class C CDSC may be waived (such as certain redemptions from tax-deferred retirement plan accounts). See “CDSC Waivers” under “Sales Charges” below. Class C shares pay |
14
| distribution fees and service fees equal to 0.95% annually of average daily net assets. Returns on Class C shares are generally lower than returns on Class A shares because Class C has higher annual expenses than Class A. |
| Orders for Class C shares of one or more Eaton Vance funds will be refused when the total value of the purchase (including the aggregate value of all Eaton Vance fund shares held within the purchasing shareholder’s account) is $1,000,000 or more. Investors considering cumulative purchases of $1,000,000 or more, or who, after a purchase of shares, would own shares of Eaton Vance funds with a current market value of $1,000,000 or more, should consider whether Class A shares would be more advantageous and consult their investment dealer. |
Payments to Investment Dealers. In addition to payments disclosed under "Sales Charges" below, the principal underwriter, out of its own resources, may make cash payments to certain investment dealers who provide marketing support, transaction processing and/or administrative services and, in some cases, include some or all Eaton Vance funds in preferred or specialized selling programs. Payments made by the principal underwriter to an investment dealer may be significant and are typically in the form of fees based on Fund sales, assets, transactions processed and/or accounts attributable to that investment dealer. Investment dealers also may receive amounts from the principal underwriter in connection with educational or due diligence meetings that include information concerning Eaton Vance funds. The principal underwriter may pay or allow other promotional incentives or payments to investment dealers to the extent permitted by applicable laws and regulations.
Certain investment dealers that maintain fund accounts for the benefit of their customers provide sub-accounting, recordkeeping and/or administrative services to the Eaton Vance funds and are compensated for such services by the funds. As used in this prospectus, the term “investment dealer” includes any broker, dealer, bank (including bank trust departments), registered investment adviser, financial planner, a retirement plan and/or its administrator, their designated intermediaries and any other firm having a selling, administration or similar agreement with the principal underwriter or its affiliates.
Sales Charges
Class A Front-End Sales Charge. Class A shares are offered at net asset value per share plus a sales charge that is determined by the amount of your investment. The current sales charge schedule is:
| | | |
| | Sales Charge* | Sales Charge* | Dealer Commission |
| | as Percentage of | as Percentage of Net | as Percentage of |
| Amount of Purchase | Offering Price | Amount Invested | Offering Price |
| Less than $25,000 | 4.75% | 4.99% | 4.50% |
| $25,000 but less than $100,000 | 4.50% | 4.71% | 4.25% |
| $100,000 but less than $250,000 | 3.75% | 3.90% | 3.50% |
| $250,000 but less than $500,000 | 3.00% | 3.09% | 2.75% |
| $500,000 but less than $1,000,000 | 2.00% | 2.04% | 2.00% |
| $1,000,000 or more | 0.00** | 0.00** | 0.75% |
| * | Because the offering price per share is rounded to two decimal places, the actual sales charge you pay on a purchase of Class A shares may be more or less than your total purchase amount multiplied by the applicable sales charge percentage. |
| ** | No sales charge is payable at the time of purchase on investments of $1 million or more. A CDSC of 1.00% will be imposed on such investments (as described below) in the event of redemptions within 18 months of purchase. |
Reducing or Eliminating Class A Charges. Front-end sales charges on purchases of Class A shares may be reduced under the right of accumulation or under a statement of intention. To receive a reduced sales charge, you must inform your investment dealer or the Fund at the time you purchase shares that you qualify for such a reduction. If you do not let your investment dealer or the Fund know you are eligible for a reduced sales charge at the time of purchase, you will not receive the discount to which you may otherwise be entitled.
| Right of Accumulation. Under the right of accumulation, the sales charge you pay is reduced if the current market value of your holdings in the Fund or any other Eaton Vance fund (based on the current maximum public offering price) plus your new purchase total $25,000 or more. Shares of Eaton Vance Cash Management Fund and Eaton Vance Tax Free Reserves cannot be included under the right of accumulation. Shares owned by you, your spouse and children under age twenty-one may be combined for purposes of the right of accumulation, including shares held for the benefit of any of you in omnibus or “street name” accounts. In addition, shares held in a trust or fiduciary account of which any of the foregoing persons is the sole beneficiary (including retirement accounts) may be combined for purposes of |
15
| the right of accumulation. Shares purchased and/or owned in a SEP, SARSEP and SIMPLE IRA plan also may be combined for purposes of the right of accumulation for the plan and its participants. You may be required to provide documentation to establish your ownership of shares included under the right of accumulation (such as account statements for you, your spouse and children or marriage certificates, birth certificates and/or trust or other fiduciary-related documents). |
| Statement of Intention. Under a statement of intention, purchases of $25,000 or more made over a 13-month period are eligible for reduced sales charges. Shares eligible under the right of accumulation (other than those included in employer-sponsored retirement plans) may be included to satisfy the amount to be purchased under a statement of intention. Under a statement of intention, the principal underwriter may hold 5% of the dollar amount to be purchased in escrow in the form of shares registered in your name until you satisfy the statement or the 13-month period expires. A statement of intention does not obligate you to purchase (or the Fund to sell) the full amount indicated in the statement. |
Class A shares are offered at net asset value (without a sales charge) to clients of financial intermediaries who (i) charge an ongoing fee for advisory, investment, consulting or similar services, or (ii) have entered into an agreement with the principal underwriter to offer Class A shares through a no-load network or platform. Such clients may include individuals, corporations, foundations and endowments. Class A shares also are offered at net asset value to investment and institutional clients of Eaton Vance and its affiliates; certain persons affiliated with Eaton Vance; and to certain fund service providers as described in the Statement of Additional Information. Class A shares may also be purchased at net asset value pursuant to the reinvestment privilege and exchange privilege and when distributions are reinvested. See “Shareholder Account Features” for details.
Contingent Deferred Sales Charge. Each Class of shares is subject to a CDSC on certain redemptions. Class A shares purchased at net asset value in amounts of $1 million or more are subject to a 1.00% CDSC if redeemed within 18 months of purchase. Class C shares are subject to a 1.00% CDSC if redeemed within one year of purchase. Class B shares are subject to the following CDSC schedule:
| | |
| Year of Redemption After Purchase | CDSC | |
| First or Second | 5% | CDSCs are based on the lower of the net asset value at |
| Third | 4% | the time of purchase or at the time of redemption. |
| Fourth | 3% | Shares acquired through the reinvestment of |
| Fifth | 2% | distributions are exempt from the CDSC. Redemptions |
| Sixth | 1% | are made first from shares that are not subject to a |
| Seventh or following | 0% | CDSC. |
The sales commission payable to investment dealers in connection with sales of Class B and Class C shares is described under “Distribution and Service Fees” below.
CDSC Waivers. CDSCs are waived for certain redemptions pursuant to a Withdrawal Plan (see “Shareholder Account Features”). The CDSC is also waived following the death of a beneficial owner of shares (a death certificate and other applicable documents may be required).
Conversion Feature. After eight years, Class B shares automatically convert to Class A shares. Class B shares acquired through the reinvestment of distributions convert in proportion to shares not so acquired.
Distribution and Service Fees. Class A, Class B and Class C shares have in effect plans under Rule 12b-1 that allows each Fund to pay distribution fees for the sale and distribution of shares (so-called “12b-1 fees”) and service fees for personal and/or shareholder account services. Class B and Class C shares pay distribution fees to the principal underwriter of 0.75% of average daily net assets annually. Because these fees are paid from Fund assets on an ongoing basis, they will increase your cost over time and may cost you more than paying other types of sales charges. The principal underwriter compensates investment dealers on sales of Class B and Class C shares (except exchange transactions and reinvestments) in an amount equal to 4% and 1%, respectively, of the purchase price of the shares. After the first year, investment dealers also receive 0.75% of the value of Class C shares in annual distribution fees. Class B and Class C shares also pay ser vice fees to the principal underwriter equal to 0.20% of average daily net assets annually. Class A shares pay distribution and service fees equal to 0.20% of average daily net assets annually. After the sale of shares, the principal underwriter receives the Class A distribution and service fees and the Class B and Class C service fees for one year and thereafter investment dealers generally receive them based on the value of shares sold by such dealers for shareholder servicing performed by such investment dealers. Although there is no present intention to do so, Class A, Class B and Class C could pay service
16
fees of up to 0.25% annually upon Trustee approval. Distribution and service fees are subject to the limitations contained in the sales charge rule of the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority.
More information about sales charges is available free of charge on the Eaton Vance website at www.eatonvance.com and in the Statement of Additional Information. Please consult the Eaton Vance website for any updates to sales charge information before making a purchase of Fund shares.
Redeeming Shares
You can redeem shares in any of the following ways:
| |
| By Mail | Send your request to the transfer agent along with any certificates and stock |
| | powers. The request must be signed exactly as your account is registered (for |
| | instance, a joint account must be signed by all registered owners to be accepted) |
| | and a signature guarantee may be required. Call 1-800-262-1122 for additional |
| | information. You can obtain a signature guarantee at banks, savings and loan |
| | institutions, credit unions, securities dealers, securities exchanges, clearing |
| | agencies and registered securities associations that participate in The Securities |
| | Transfer Agents Medallion Program, Inc. (STAMP, Inc.). Only signature |
| | guarantees issued in accordance with STAMP, Inc. will be accepted. You may be |
| | asked to provide additional documents if your shares are registered in the name of |
| | a corporation, partnership or fiduciary. |
| | |
| By Telephone | You can redeem up to $100,000 per account (which may include shares of one or |
| | more Eaton Vance funds) per day by calling 1-800-262-1122 Monday through |
| | Friday, 8:00 a.m. to 6:00 p.m. (eastern time). Proceeds of a telephone redemption |
| | can be sent only to the account address or to a bank pursuant to prior instructions. |
| | Shares held by corporations, trusts or certain other entities and shares that are |
| | subject to fiduciary arrangements cannot be redeemed by telephone. |
| | |
| Through an Investment Dealer | Your investment dealer is responsible for transmitting the order promptly. An |
| | investment dealer may charge a fee for this service. |
If you redeem shares, your redemption price will be based on the net asset value per share next computed after the redemption request is received in good order by the Fund’s transfer agent. Your redemption proceeds normally will be paid in cash within seven days, reduced by the amount of any applicable CDSC and any federal income tax required to be withheld. Payments will be sent by regular mail. However, if you have given complete written authorization in advance, you may request that the redemption proceeds be wired directly to your bank account. The bank designated may be any bank in the United States. The request may be made by calling 1-800-262-1122 or by sending a signature guaranteed letter of instruction to the transfer agent (see back cover for address). Corporations, trusts and other entities may need to provide additional documentation. You may be required to pay the costs of such transaction by the Fund or your bank. No costs are currently charged by the Fund. Howe ver, charges may apply for expedited mail delivery services. Each Fund may suspend or terminate the expedited payment procedure upon at least 30 days’ notice.
If you recently purchased shares, the proceeds of a redemption will not be sent until the purchase check (including a certified or cashier’s check) has cleared. If the purchase check has not cleared, redemption proceeds may be delayed up to 15 days from the purchase date. If your account value falls below $750 (other than due to market decline), you may be asked either to add to your account or redeem it within 60 days. If you take no action, your account will be redeemed and the proceeds sent to you.
While redemption proceeds are normally paid in cash, redemptions may be paid by distributing marketable securities. If you receive securities, you could incur brokerage or other charges in converting the securities to cash.
17
Shareholder Account Features
Distributions. You may have your Fund distributions paid in one of the following ways:
| |
| •Full Reinvest Option | Distributions are reinvested in additional shares. This option will be assigned if you do not specify an option. |
| | |
| •Partial Reinvest Option | Dividends are paid in cash and capital gains are reinvested in additional shares. |
| | |
| •Cash Option | Distributions are paid in cash. |
| | |
| •Exchange Option | Distributions are reinvested in additional shares of any class of another Eaton |
| | Vance fund chosen by you, subject to the terms of that fund’s prospectus. Before |
| | selecting this option, you must obtain a prospectus of the other fund and consider |
| | its objectives, risks, and charges and expenses carefully. |
Information about the Funds. From time to time, you may receive the following:
| •Semiannual and annual reports containing a list of portfolio holdings as of the end of the second and fourth fiscal quarters, respectively, performance information and financial statements. |
| •Periodic account statements, showing recent activity and total share balance. |
| •Tax information needed to prepare your income tax returns. |
| •Proxy materials, in the event a shareholder vote is required. |
| •Special notices about significant events affecting your Fund. |
Most fund information (including semiannual and annual reports, prospectuses and proxy statements) as well as your periodic account statements can be delivered electronically. For more information please go to www.eatonvance.com. Select “Mutual Funds” then “Electronic Delivery”.
Each Fund will file with the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) a list of its portfolio holdings as of the end of the first and third fiscal quarters on Form N-Q. Each Fund’s annual and semiannual reports (as filed on Form N-CSR) and each Form N-Q may be viewed on the SEC’s website (www.sec.gov). The most recent fiscal and calendar quarter end holdings may also be viewed on the Eaton Vance website (www.eatonvance.com). Portfolio holdings information that is filed with the SEC is posted on the Eaton Vance website approximately 60 days after the end of the quarter to which it relates. Portfolio holdings information as of each calendar quarter end is posted to the website 30 days after such quarter end. Each Fund also posts information about certain portfolio characteristics (such as top ten holdings and asset allocation) as of the most recent calendar quarter end on the Eaton Vance website approximately ten business days after the calendar quarter end.
The Eaton Vance funds have established policies and procedures with respect to the disclosure of portfolio holdings and other information concerning Fund characteristics. A description of these policies and procedures is provided in the Statement of Additional Information. Such policies and procedures regarding disclosure of portfolio holdings are designed to prevent the misuse of material, non-public information about the funds.
Withdrawal Plan. You may redeem shares on a regular periodic basis by establishing a systematic withdrawal plan. Withdrawals will not be subject to any applicable CDSC if they are, in the aggregate, less than or equal to 12% annually of the greater of either the initial account balance or the current account balance. Because purchases of Class A shares are generally subject to an initial sales charge, Class A shareholders should not make withdrawals from their accounts while also making purchases.
Exchange Privilege. You may exchange your Fund shares for shares of the same Class of another Eaton Vance fund or, in the case of Class B and Class C shares, Eaton Vance Money Market Fund. Exchanges are made at net asset value. If your shares are subject to a CDSC, the CDSC will continue to apply to your new shares at the same CDSC rate. For purposes of the CDSC, your shares will continue to age from the date of your original purchase of Fund shares.
Before exchanging, you should read the prospectus of the new fund carefully. Exchanges are subject to the terms applicable to purchases of the new fund’s shares as set forth in its prospectus. If you wish to exchange shares, write to the transfer agent (see back cover for address) or call 1-800-262-1122. Periodic automatic exchanges are also available. The exchange privilege may be changed or discontinued at any time. You will receive at least 60 days’ notice of any material change to the privilege. This privilege may not be used for “market timing” and may be terminated for market timing accounts or for
18
any other reason. For additional information, see "Restrictions on Excessive Trading and Market Timing" under "Purchasing Shares".
Reinvestment Privilege. If you redeem shares, you may reinvest at net asset value all or any portion of the redemption proceeds in the same class of shares of the Fund you redeemed from, provided that the reinvestment occurs within 60 days of the redemption, and the privilege has not been used more than once in the prior 12 months. Under these circumstances your account will be credited with any CDSC paid in connection with the redemption. Any CDSC period applicable to the shares you acquire upon reinvestment will run from the date of your original share purchase. Reinvestment requests must be in writing. At the time of a reinvestment, you or your financial intermediary must notify the Fund or the transfer agent that you are reinvesting redemption proceeds in accordance with this privilege. If you reinvest, your purchase will be at the next determined net asset value following receipt of your request.
Telephone and Electronic Transactions. You can redeem or exchange shares by telephone as described in this Prospectus. In addition, certain transactions may be conducted through the Eaton Vance website. The transfer agent and the principal underwriter have procedures in place to authenticate telephone and electronic instructions (such as using security codes or verifying personal account information). As long as the transfer agent and principal underwriter follow reasonable procedures, they will not be responsible for unauthorized telephone or electronic transactions and you bear the risk of possible loss resulting from these transactions. You may decline the telephone redemption option on the account application. Telephone instructions are recorded.
“Street Name” Accounts. If your shares are held in a “street name” account at an investment dealer, that dealer (and not the Fund or its transfer agent) will perform all recordkeeping, transaction processing and distribution payments. Because the Fund will have no record of your transactions, you should contact your investment dealer to purchase, redeem or exchange shares, to make changes in your account, or to obtain account information. You will not be able to utilize a number of shareholder features, such as telephone transactions, directly with the Fund. If you transfer shares in a “street name” account to an account with another investment dealer or to an account directly with the Fund, you should obtain historical information about your shares prior to the transfer.
Procedures for Opening New Accounts. To help the government fight the funding of terrorism and money laundering activities, federal law requires financial institutions to obtain, verify and record information that identifies each new customer who opens a Fund account and to determine whether such person’s name appears on government lists of known or suspected terrorists or terrorist organizations. When you open an account, the transfer agent or your investment dealer will ask you for your name, address, date of birth (for individuals), residential or business street address (although post office boxes are still permitted for mailing) and social security number, taxpayer identification number, or other government-issued identifying number. You also may be asked to produce a copy of your driver’s license, passport or other identifying documents in order to verify your identity. In addition, it may be necessary to verify your identity by cross-referencing your identification information with a consumer report or other electronic databases. Other information or documents may be required to open accounts for corporations and other entities. Federal law prohibits the Fund and other financial institutions from opening a new account unless they receive the minimum identifying information described above. If a person fails to provide the information requested, any application by that person to open a new account will be rejected. Moreover, if the transfer agent or the investment dealer is unable to verify the identity of a person based on information provided by that person, it may take additional steps including, but not limited to, requesting additional information or documents from the person, closing the person’s account or reporting the matter to the appropriate federal authorities. If your account is closed for this reason, your shares may be automatically redeemed at the net asset value next determined. If the Fund’s net asset value has decreased since your purchase, you will lose money as a result of this redemption. Each Fund has also designated an anti-money laundering compliance officer.
Account Questions. If you have any questions about your account or the services available, please call Eaton Vance Shareholder Services at 1-800-262-1122 Monday through Friday, 8:00 a.m. to 6:00 p.m. (eastern time), or write to the transfer agent (see back cover for address).
Tax Information
Each Fund declares dividends daily and ordinarily pays distributions monthly. Different Classes of the Fund may distribute different dividend amounts. Your account will be credited with dividends beginning on the business day after the day when the funds used to purchase your Fund shares are collected by the transfer agent. For tax purposes, the entire monthly distribution of the Fund’s daily dividends ordinarily will constitute tax-exempt income to you. Distributions of net realized gains, if any, will be made at least annually (usually in December). The exemption of “exempt-interest dividend” income
19
from regular federal income taxation does not necessarily result in similar exemptions from such income under the state or local tax laws.
A Fund may invest a portion of its assets in securities that generate income that is not exempt from federal income tax. Taxes on distributions of capital gains are determined by how long the Fund owned the investments that generated them, rather than how long a shareholder has owned his or her shares in the Fund. Distributions of any taxable income and net short-term capital gains will be taxable as ordinary income. Distributions of any long-term capital gains are taxable as long-term capital gains. Distributions of interest on certain municipal obligations are a tax preference item under the AMT provisions applicable to individuals and corporations, and all tax-exempt distributions may affect a corporation’s AMT liability. Each Fund’s distributions will be treated as described above for federal income tax purposes whether they are paid in cash or reinvested in additional shares. A redemption of Fund shares, including an exchange for shares of another fund, is a taxable transaction.
Shareholders, particularly corporations, recipients of social security or railroad retirement benefits and those subject to the AMT, should consult with their advisers concerning the applicability of federal, state, local and other taxes to an investment. Additional information about state taxes is provided below.
Hawaii Taxes. In the opinion of special tax counsel to the Hawaii Fund, distributions paid by the Fund will generally be exempt from Hawaii income tax to the extent that they are derived from interest on obligations of the State of Hawaii or any of its political subdivisions or authorities or obligations issued by certain other government authorities (for example, U.S. territories). Distributions derived from the Fund’s other investment income and short-term capital gains will be subject to Hawaii income tax as ordinary income and distributions from net realized long-term capital gains will be subject to Hawaii income tax as capital gains.
Capital gains or losses realized from a redemption, sale or exchange of shares of the Fund by a Hawaii resident will be taken into account for Hawaii individual income tax purposes.
Kansas Taxes. In the opinion of special tax counsel to the Kansas Fund, individuals, trusts, estates and corporations will not be subject to the Kansas income tax on the portion of exempt-interest dividends derived from interest on obligations of Kansas and its political subdivisions issued after December 31, 1987, and interest on obligations issued before January 1, 1988 where the laws of the State of Kansas authorizing the issuance of such obligations specifically exempt the interest on such obligations from income tax under the laws of the State of Kansas. All remaining dividends (except for dividends, if any, derived from debt obligations issued by the governments of Puerto Rico, the U.S. Virgin Islands and Guam and which are exempt from federal and state income taxes pursuant to federal law), including dividends derived from capital gains, will be includable in the Kansas taxable income of individuals, trusts, estates and corporations. Distributions treated as long-term capital gains for federal income tax purposes will generally receive the same characterization under Kansas law. Capital gains or losses realized from a redemption, sale or exchange of shares of the Fund by a Kansas taxpayer will be taken into account for Kansas income tax purposes.
The above exemptions do not apply to the privilege tax imposed on banks, banking associations, trust companies, savings and loan associations, and insurance companies, or the franchise tax imposed on corporations. Banks, banking associations, trust companies, savings and loan associations, insurance companies and corporations are urged to consult their own tax advisors regarding the effects of theses taxes before investing in the Fund.
The Kansas Fund has been advised by the Kansas Department of Revenue that dividends derived from shares of the Fund are not subject to the local intangibles tax imposed by certain Kansas counties, cities and townships pursuant to existing Kansas law.
20
Financial Highlights
The financial highlights are intended to help you understand the Fund’s financial performance for the period(s) indicated. Certain information in the tables reflects the financial results for a single Fund share. The total returns in the tables represent the rate an investor would have earned (or lost) on an investment in the Fund (assuming reinvestment of all distributions at net asset value). This information has been audited by Deloitte & Touche LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm. The report of Deloitte & Touche LLP and each Fund’s financial statements are incorporated herein by reference and included in the Fund’s annual report, which is available on request.
| | | | | | | | |
| | Hawaii Fund |
| | Year Ended January 31, |
| | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 |
| | Class A | Class B | Class C | Class A | Class B | Class C(13) | Class A | Class B |
| Net asset value - Beginning of period | $ 9.370 | $9.490 | $9.490 | $9.770 | $9.890 | $ 9.700 | $9.670 | $9.780 |
| |
| Income (loss) from operations | | | | | | | | |
| Net investment income(1) | $ 0.376 | $0.318 | $0.297 | $0.390 | $0.324 | $ 0.105 | $0.406 | $0.340 |
| Net realized and unrealized gain (loss) | (1.448) | (1.477) | (1.446) | (0.398) | (0.402) | (0.208) | 0.096 | 0.102 |
| Total income (loss) from operations | $ (1.072) | $(1.159) | $(1.149) | $ (0.008) | $(0.078) | $(0.103) | $0.502 | $0.442 |
| |
| Less distributions | | | | | | | | |
| From net investment income | $ (0.388) | $(0.321) | $(0.321) | $ (0.392) | $(0.322) | $(0.107) | $ (0.402) | $(0.332) |
| Total distributions | $ (0.388) | $(0.321) | $(0.321) | $ (0.392) | $(0.322) | $(0.107) | $ (0.402) | $(0.332) |
| Net asset value - End of period | $ 7.910 | $8.010 | $8.020 | $9.370 | $9.490 | $ 9.490 | $9.770 | $9.890 |
| Total return (2) | (11.62)% | (12.37)% | (12.37)% | (0.09)% | (0.81)% | (1.06)%(11) | 5.28% | 4.58% |
| |
| Ratios/Supplemental Data | | | | | | | | |
| Net assets, end of period (000’s omitted) | $14,319 | $2,572 | $116 | $15,720 | $3,872 | $34 | $13,856 | $5,504 |
| Ratios (As a percentage of average daily net assets): | | | | | | | | |
| Expenses excluding interest and fees | 0.93% | 1.67% | 1.68% | 0.83%(3) | 1.58%(3) | 1.58%(9) | 0.82% | 1.57% |
| Interest and fee expense(5) | 0.14% | 0.14% | 0.14% | 0.31% | 0.31% | 0.31%(9) | 0.35% | 0.35% |
| Total expenses before custodian fee reduction | 1.07% | 1.81% | 1.82% | 1.14%(3) | 1.89%(3) | 1.89%(9) | 1.17% | 1.92% |
| Expenses after custodian fee reduction excluding interest and fees | 0.90% | 1.65% | 1.65% | 0.75%(3) | 1.50%(3) | 1.50%(9) | 0.78% | 1.53% |
| Net investment income | 4.39% | 3.65% | 3.56% | 4.06% | 3.33% | 3.26%(9) | 4.16% | 3.45% |
| Portfolio Turnover | 12% | 12% | 12% | 20% | 20% | 20%(14) | 28% | 28% |
| (See footnotes on last page.) |
21
| Financial Highlights (continued) |
| | | | |
| | Hawaii Fund |
| | Year Ended January 31, |
| | 2006 | 2005 |
| | Class A | Class B | Class A | Class B |
| Net asset value - Beginning of year | $9.850 | $9.970 | $ 9.910 | $10.040 |
| |
| Income (loss) from operations | | | | |
| Net investment income(1) | $0.408 | $0.344 | $ 0.444 | $0.379 |
| Net realized and unrealized gain (loss) | (0.172) | (0.187) | (0.069) | (0.083) |
| Total income (loss) from operations | $0.236 | $0.157 | $ 0.375 | $0.296 |
| |
| Less distributions | | | | |
| From net investment income | $ (0.416) | $(0.347) | $(0.435) | $ (0.366) |
| Total distributions | $ (0.416) | $(0.347) | $(0.435) | $ (0.366) |
| Net asset value - End of year | $9.670 | $9.780 | $ 9.850 | $9.970 |
| Total return (2) | 2.46%(12) | 1.62%(12) | 3.91% | 3.21%(7) |
| |
| Ratios/Supplemental Data | | | | |
| Net assets, end of period(000’s omitted) | $10,239 | $6,681 | $ 8,394 | $10,063 |
| Ratios (As a percentage of average daily net assets): | | | | |
| Expenses excluding interest and fees | 0.88% | 1.63% | 0.80%(4) | 1.55%(4) |
| Interest and fee expense(5) | 0.18% | 0.18% | 0.10%(4) | 0.10%(4) |
| Total expenses before custodian fee reduction | 1.06% | 1.81% | 0.90%(4) | 1.65%(4) |
| Expenses after custodian fee reduction excluding interest and fees | 0.86% | 1.61% | 0.79%(4) | 1.54%(4) |
| Net investment income | 4.20% | 3.49% | 4.55% | 3.83% |
| Portfolio Turnover of the Portfolio | — | — | 19%(6) | 19%(6) |
| Portfolio Turnover of the Fund | 22% | 22% | 7% | 7% |
| (See footnotes on last page.) |
22
| Financial Highlights (continued) |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | Insured Fund |
| | Year Ended January 31, |
| | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 |
| | Class A | Class B | Class C | Class A | Class B | Class C | Class A | Class B | Class C(8) |
| Net asset value - Beginning of period | $10.760 | $10.640 | $10.650 | $11.320 | $11.190 | $11.190 | $11.170 | $11.040 | $11.040 |
| |
| Income (loss) from operations | | | | | | | | | |
| Net investment income(1) | $ 0.423 | $ 0.348 | $0.341 | $0.474 | $ 0.388 | $ 0.383 | $0.483 | $0.396 | $ 0.202 |
| Net realized and unrealized gain (loss) | (1.555) | (1.545) | (1.538) | (0.565) | (0.558) | (0.543) | 0.148 | 0.146 | 0.209 |
| Total income (loss) from operations | $ (1.132) | $ (1.197) | $ (1.197) | $ (0.091) | $ (0.170) | $ (0.160) | $0.631 | $0.542 | $ 0.411 |
| |
| Less distributions | | | | | | | | | |
| From net investment income | $ (0.468) | $ (0.383) | $ (0.383) | $ (0.469) | $ (0.380) | $ (0.380) | $ (0.481) | $ (0.392) | $ (0.261) |
| Total distributions | $ (0.468) | $ (0.383) | $ (0.383) | $ (0.469) | $ (0.380) | $ (0.380) | $ (0.481) | $ (0.392) | $ (0.261) |
| Net asset value - End of period | $ 9.160 | $ 9.060 | $9.070 | $10.760 | $10.640 | $10.650 | $11.320 | $11.190 | $11.190 |
| Total return (2) | (10.69)% | (11.40)% | (11.39)% | (0.85)% | (1.57)% | (1.48)% | 5.76% | 4.99% | 3.76%(11) |
| |
| Ratios/Supplemental Data | | | | | | | | | |
| Net assets, end of period(000’s omitted) | $36,305 | $ 5,929 | $5,248 | $29,433 | $ 7,998 | $ 1,144 | $30,822 | $10,421 | $26 |
| Ratios (As a percentage of average daily net assets): | | | | | | | | | |
| Expenses excluding interest and fees | 0.90% | 1.65% | 1.64% | 0.71%(3) | 1.46%(3) | 1.45%(3) | 0.73% | 1.48% | 1.48%(9) |
| Interest and fee expense(5) | 0.17% | 0.17% | 0.17% | 0.56% | 0.56% | 0.56% | 0.39% | 0.39% | 0.39%(9) |
| Total expenses | 1.07% | 1.82% | 1.81% | 1.27%(3) | 2.02%(3) | 2.01%(3) | 1.12% | 1.87% | 1.87%(9) |
| Expenses after custodian fee reduction excluding interest and | | | | | | | | | |
| fees | 0.86% | 1.61% | 1.60% | 0.69%(3) | 1.44%(3) | 1.43%(3) | 0.71% | 1.46% | 1.46%(9) |
| Net investment income | 4.31% | 3.55% | 3.65% | 4.27% | 3.52% | 3.53% | 4.29% | 3.56% | 2.70%(9) |
| Portfolio Turnover | 79% | 79% | 79% | 34% | 34% | 34% | 33% | 33% | 33%(10) |
| (See footnotes on last page.) |
23
| Financial Highlights (continued) |
| | | | |
| | | Insured Fund | |
| | | Year Ended January 31, | |
| | 2006 | 2005 |
| | Class A | Class B | Class A | Class B |
| Net asset value - Beginning of year | $11.380 | $11.250 | $11.540 | $11.420 |
| |
| Income (loss) from operations | | | | |
| Net investment income(1) | $0.490 | $0.406 | $ 0.524 | $0.436 |
| Net realized and unrealized gain (loss) | (0.204) | (0.209) | (0.155) | (0.167) |
| Total income (loss) from operations | $0.286 | $0.197 | $ 0.369 | $0.269 |
| |
| Less distributions | | | | |
| From net investment income | $ (0.496) | $ (0.407) | $ (0.529) | $ (0.439) |
| Total distributions | $ (0.496) | $ (0.407) | $ (0.529) | $ (0.439) |
| Net asset value - End of year | $11.170 | $11.040 | $11.380 | $11.250 |
| Total return (2) | 2.58% | 1.78% | 3.34% | 2.64%(7) |
| |
| Ratios/Supplemental Data | | | | |
| Net assets, end of year (000’s omitted) | $30,896 | $13,650 | $25,848 | $18,170 |
| Ratios (As a percentage of average daily net assets): | | | | |
| Expenses excluding interest and fees | 0.72% | 1.47% | 0.70%(4) | 1.45%(4) |
| Interest and fee expense(5) | 0.20% | 0.20% | 0.23%(4) | 0.23%(4) |
| Total expenses | 0.92% | 1.67% | 0.93%(4) | 1.68%(4) |
| Expenses after custodian fee reduction excluding interest and fees | 0.70% | 1.45% | 0.69%(4) | 1.44%(4) |
| Net investment income | 4.36% | 3.64% | 4.64% | 3.89% |
| Portfolio Turnover of the Portfolio | — | — | 0%(6) | 0%(6) |
| Portfolio Turnover of the Fund | 28% | 28% | 12% | 12% |
| (See footnotes on last page.) |
24
| Financial Highlights (continued) |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | Kansas Fund |
| | Year Ended January 31, |
| | | 2009 | | | 2008 | | | 2007 | |
| | Class A | Class B | Class C | Class A | Class B | Class C | Class A | Class B | Class C(8) |
| Net asset value - Beginning of period | $10.180 | $10.100 | $10.100 | $10.520 | $10.430 | $10.430 | $10.360 | $10.280 | $10.260 |
| |
| Income (loss) from operations | | | | | | | | | |
| Net investment income(1) | $ 0.407 | $0.335 | $0.333 | $0.416 | $ 0.337 | $ 0.337 | $0.426 | $0.348 | $ 0.211 |
| Net realized and unrealized gain (loss) | (1.251) | (1.246) | (1.234) | (0.338) | (0.331) | (0.331) | 0.163 | 0.150 | 0.191 |
| Total income (loss) from operations | $ (0.844) | $ (0.911) | $ (0.901) | $0.078 | $ 0.006 | $ 0.006 | $0.589 | $0.498 | $ 0.402 |
| |
| Less distributions | | | | | | | | | |
| From net investment income | $ (0.416) | $ (0.339) | $ (0.339) | $ (0.418) | $ (0.336) | $ (0.336) | $ (0.429) | $ (0.348) | $ (0.232) |
| Total distributions | $ (0.416) | $ (0.339) | $ (0.339) | $ (0.418) | $ (0.336) | $ (0.336) | $ (0.429) | $ (0.348) | $ (0.232) |
| Net asset value - End of period | $ 8.920 | $8.850 | $8.860 | $10.180 | $10.100 | $10.100 | $10.520 | $10.430 | $10.430 |
| Total return (2) | (8.39)% | (9.11)% | (9.00)% | 0.74% | 0.05% | 0.05% | 5.79% | 4.92% | 3.95%(11) |
| |
| Ratios/Supplemental Data | | | | | | | | | |
| Net assets, end of year (000’s omitted) | $27,768 | $2,993 | $2,176 | $30,715 | $ 3,729 | $ 1,648 | $23,177 | $4,221 | $ 723 |
| Ratios (As a percentage of average daily net assets): | | | | | | | | | |
| Expenses excluding interest and fees | 0.77% | 1.52% | 1.52% | 0.72%(3) | 1.48%(3) | 1.47%(3) | 0.77% | 1.52% | 1.52%(9) |
| Interest and fee expense(5) | 0.06% | 0.06% | 0.06% | 0.15% | 0.15% | 0.15% | 0.25% | 0.25% | 0.25%(9) |
| Total expenses before custodian fee reduction | 0.83% | 1.58% | 1.58% | 0.87%(3) | 1.63%(3) | 1.62%(3) | 1.02% | 1.77% | 1.77%(9) |
| Expenses after custodian fee reduction excluding interest and fees | 0.74% | 1.50% | 1.49% | 0.66%(3) | 1.41%(3) | 1.40%(3) | 0.73% | 1.48% | 1.48%(9) |
| Net investment income | 4.31% | 3.57% | 3.57% | 4.01% | 3.27% | 3.28% | 4.08% | 3.37% | 3.01%(9) |
| Portfolio Turnover | 29% | 29% | 29% | 20% | 20% | 20% | 12% | 12% | 12%(10) |
| (See footnotes on last page.) |
25
| Financial Highlights (continued) |
| | | | |
| | Kansas Fund |
| | Year Ended January 31, |
| | 2006 | 2005 |
| | Class A | Class B | Class A | Class B |
| Net asset value - Beginning of year | $10.560 | $10.470 | $10.680 | $10.590 |
| |
| Income (loss) from operations | | | | |
| Net investment income(1) | $ 0.434 | $ 0.355 | $ 0.470 | $ 0.394 |
| Net realized and unrealized gain (loss) | (0.200) | (0.192) | (0.114) | (0.120) |
| Total income from operations | $ 0.234 | $ 0.163 | $ 0.356 | $ 0.274 |
| |
| Less distributions | | | | |
| From net investment income | $ (0.434) | $ (0.353) | $ (0.476) | $ (0.394) |
| Total distributions | $ (0.434) | $ (0.353) | $ (0.476) | $ (0.394) |
| Net asset value - End of year | $10.360 | $10.280 | $10.560 | $10.470 |
| Total return (2) | 2.28% | 1.60% | 3.46% | 2.84%(15) |
| |
| Ratios/Supplemental Data | | | | |
| Net assets, end of year (000’s omitted) | $17,112 | $ 5,071 | $15,920 | $ 6,158 |
| Ratios (As a percentage of average daily net assets): | | | | |
| Expenses excluding interest and fees | 0.83% | 1.58% | 0.77%(4) | 1.52%(4) |
| Interest and fee expense(5) | 0.23% | 0.23% | 0.12%(4) | 0.12%(4) |
| Total expenses before custodian fee reduction | 1.06% | 1.81% | 0.89%(4) | 0.64%(4) |
| Expenses after custodian fee reduction excluding interest and fees | 0.82% | 1.57% | 0.76%(4) | 1.51%(4) |
| Net investment income | 4.17% | 3.44% | 4.48% | 3.77% |
| Portfolio Turnover of the Portfolio | — | — | 10%(6) | 10%(6) |
| Portfolio Turnover of the Fund | 17% | 17% | 8% | 8% |
| (1) | Computed using average shares outstanding. |
| (2) | Returns are historical and are calculated by determining the percentage change in net asset value with all distributions reinvested. |
| (3) | The investment adviser was allocated a portion of the Fund’s operating expenses (equal to 0.01% of average daily net assets for the year ended January 31, 2008). Absent this allocation, total return would be lower. |
| (4) | Includes the Fund’s share of its corresponding Portfolio’s allocated expenses while the Fund was making investments directly into the Portfolio. |
| (5) | Interest and fee expense relates to the liability for floating rate notes issued in conjunction with inverse floater securities transactions (see Note 1I to the Fund’s audited financial statements). |
| (6) | Portfolio turnover represents the rate of portfolio activity for the period while the Fund was making investments directly into the Portfolio. |
| (7) | Total return reflects an increase of 0.13% due to a change in the timing of the payment and reinvestment of distributions. |
| (8) | For the period from the start of business, June 2, 2006, to January 31, 2007. |
| (9) | Annualized. |
| (10) | For the year ended January 31, 2007. |
| (11) | Not annualized. |
| (12) | During the year ended January 31, 2006, the Fund realized a gain on the disposal of investment security which did not meet investment guidelines. The gain was less than $0.01 per share and had no effect on total return. |
| (13) | For the period from the start of business, October 1, 2007, to January 31, 2008. |
| (14) | For the year ended January 31, 2008. |
| (15) | Total return reflects an increase of 0.12% due to a change in the timing of the payment and reinvestment of distributions. |
26
This Page Intentionally Left Blank

About the Funds: More information is available in the statement of additional information. The statement of additional information is incorporated by reference into this prospectus. Additional information about each Fund’s investments is available in the annual and semiannual reports to shareholders. In the annual report, you will find a discussion of the market conditions and investment strategies that significantly affected each Fund’s performance during the past fiscal year. You may obtain free copies of the statement of additional information and the shareholder reports on Eaton Vance’s website at www.eatonvance.com or by contacting the principal underwriter:
Eaton Vance Distributors, Inc.
Two International Place
Boston, MA 02110
1-800-262-1122
website: www.eatonvance.com |
You will find and may copy information about each Fund (including the statement of additional information and shareholder reports): at the Securities and Exchange Commission’s public reference room in Washington, DC (call 1-202-551-8090 for information on the operation of the public reference room); on the EDGAR Database on the SEC’s Internet site (http://www.sec.gov); or, upon payment of copying fees, by writing to the SEC’s public reference section, 100 F Street NE, Washington, DC 20549-0102, or by electronic mail at publicinfo@sec.gov.
Shareholder Inquiries: You can obtain more information from Eaton Vance Shareholder Services or the Fund transfer agent, PNC Global Investment Servicing. If you own shares and would like to add to, redeem or change your account, please write or call below:
| | |
| Regular Mailing Address: | Overnight Mailing Address: | Phone Number: |
| Eaton Vance Funds | Eaton Vance Funds | 1-800-262-1122 |
| PO Box 9653 | 101 Sabin Street | Monday - Friday |
| Providence, RI 02940-9653 | Pawtucket, RI 02860 | 8 a.m. - 6 p.m. ET |
| | |
| The Funds’ Investment Company Act No. is 811-08134. | | TFC6/1P |
| 543-6/09 | © 2009 Eaton Vance Management | |
| | STATEMENT OF
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
June 1, 2009 |
Eaton Vance Hawaii Municipals Fund
Eaton Vance Insured Municipals Fund
Eaton Vance Kansas Municipals Fund |
Two International Place
Boston, Massachusetts 02110
1-800-262-1122 |
This Statement of Additional Information (“SAI”) provides general information about the Funds. The Hawaii and Kansas Funds are non-diversified, open-end management investment companies. The Insured Fund is a diversified open-end management investment company. Each Fund is a series of Eaton Vance Municipals Trust II (the “Trust”). Capitalized terms used in this SAI and not otherwise defined have the meanings given to them in the prospectus. This SAI contains additional information about:
| | | | | |
| | | Page | | | Page |
| Strategies and Risks | 2 | Purchasing and Redeeming Shares | 20 |
| Investment Restrictions | 9 | Sales Charges | 21 |
| Management and Organization | 11 | Performance | | 23 |
| Investment Advisory and Administrative Services | 16 | Taxes | | 26 |
| Other Service Providers | 19 | Portfolio Securities Transactions | 29 |
| Calculation of Net Asset Value | 20 | Financial Statements | 31 |
| |
| Appendix A: | Class A Fees, Performance and Ownership | 32 | Appendix E: | Ratings | 41 |
| Appendix B: | Class B Fees, Performance and Ownership | 34 | Appendix F: | Insurance | 50 |
| Appendix C: | Class C Fees, Performance and Ownership | 36 | Appendix G: | Eaton Vance Funds Proxy Voting Policy and Procedures | 52 |
| Appendix D: | State Specific Information | 38 | Appendix H: | Adviser Proxy Voting Policies and Procedures | 54 |
Although each Fund offers only its shares of beneficial interest, it is possible that a Fund (or Class) might become liable for a misstatement or omission in this SAI regarding another Fund (or Class) because the Funds use this combined SAI. The Trustees of the Trust have considered this factor in approving the use of a combined SAI.
This SAI is NOT a prospectus and is authorized for distribution to prospective investors only if preceded or accompanied by the Fund prospectus dated June 1, 2009, as supplemented from time to time, which is incorporated herein by reference. This SAI should be read in conjunction with the prospectus, which may be obtained by calling 1-800-262-1122.
2009 Eaton Vance Management
The following defined terms may be used herein: “SEC” for the Securities and Exchange Commission; “CFTC” for the Commodities Futures Trading Commission; “IRS” for the Internal Revenue Service; “Code” for the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended; “1940 Act” for the Investment Company Act of 1940, as amended; “1933 Act” for the Securities Act of 1933, as amended; and “FINRA” for the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority.
Primary strategies are defined in the prospectus. The following is a description of the various investment practices that may be engaged in, whether as a primary or secondary strategy, and a summary of certain attendant risks. The investment adviser(s) may not buy any of the following instruments or use any of the following techniques unless it believes that doing so will help achieve the investment objective(s).
Municipal Obligations. Municipal obligations are issued to obtain funds for various public and private purposes. Municipal obligations include bonds as well as tax-exempt commercial paper, project notes and municipal notes such as tax, revenue and bond anticipation notes of short maturity, generally less than three years. While most municipal bonds pay a fixed rate of interest semiannually in cash, there are exceptions. Some bonds pay no periodic cash interest, but rather make a single payment at maturity representing both principal and interest. Bonds may be issued or subsequently offered with interest coupons materially greater or less than those then prevailing, with price adjustments reflecting such deviation.
In general, there are three categories of municipal obligations, the interest on which is exempt from federal income tax and is not a tax preference item for purposes of the alternative minimum tax ("AMT"): (i) certain “public purpose” obligations (whenever issued), which include obligations issued directly by state and local governments or their agencies to fulfill essential governmental functions; (ii) certain obligations issued before August 8, 1986 for the benefit of non-governmental persons or entities; and (iii) certain “private activity bonds” issued after August 7, 1986 which include “qualified Section 501(c)(3) bonds” or refundings of certain obligations included in the second category. In assessing the federal income tax treatment of interest on any municipal obligation, each Fund will rely on an opinion of the issuer’s counsel (when available) and will not undertake any independent verification of the basis for the opinion.
Interest on certain “private activity bonds” issued after August 7, 1986 is exempt from regular federal income tax, but such interest (including a distribution by a Fund derived from such interest) is treated as a tax preference item which could subject the recipient to or increase the recipient’s liability for the AMT. For corporate shareholders, a Fund’s distributions derived from interest on all municipal obligations (whenever issued) are included in “adjusted current earnings” for purposes of the AMT as applied to corporations (to the extent not already included in alternative minimum taxable income as income attributable to private activity bonds).
The two principal classifications of municipal bonds are “general obligation” and “revenue” bonds. Issuers of general obligation bonds include states, counties, cities, towns and regional districts. The proceeds of these obligations are used to fund a wide range of public projects, including the construction or improvement of schools, highways and roads, water and sewer systems and a variety of other public purposes. The basic security of general obligation bonds is the issuer’s pledge of its faith, credit, and taxing power for the payment of principal and interest. The taxes that can be levied for the payment of debt service may be limited or unlimited as to rate and amount.
Revenue bonds are generally secured by the net revenues derived from a particular facility or group of facilities or, in some cases, from the proceeds of a special excise or other specific revenue source. Revenue bonds have been issued to fund a wide variety of capital projects including: electric, gas, water, sewer and solid waste disposal systems; highways, bridges and tunnels; port, airport and parking facilities; transportation systems; housing facilities, colleges and universities and hospitals. Although the principal security behind these bonds varies widely, many provide additional security in the form of a debt service reserve fund whose monies may be used to make principal and interest payments on the issuer’s obligations. Housing finance authorities have a wide range of security including partially or fully insured, rent subsidized and/or collateralized mortgages, and/or the net revenues from housing or other public projects. In addition to a debt service reserve fun d, some authorities provide further security in the form of a state’s ability (without legal obligation) to make up deficiencies in the debt service reserve fund. Lease rental revenue bonds issued by a state or local authority for capital projects are normally secured by annual lease rental payments from the state or locality to the authority sufficient to cover debt service on the authority’s obligations. Such payments are usually subject to annual appropriations by the state or locality. Industrial development and pollution control bonds, although nominally issued by municipal authorities, are in most cases revenue bonds and are generally not secured by the taxing power of the municipality, but are usually secured by the revenues derived by the authority from payments of the industrial user or users. Each Fund may on occasion acquire revenue bonds which carry warrants or similar rights covering equity securities. Such warrants or rights may be held indefinitely, but if exercised, each Fund antici pates that it would, under normal circumstances, dispose of any equity securities so acquired within a reasonable period of time.
2
The obligations of any person or entity to pay the principal of and interest on a municipal obligation are subject to the provisions of bankruptcy, insolvency and other laws affecting the rights and remedies of creditors, such as the Federal Bankruptcy Act, and laws, if any, which may be enacted by Congress or state legislatures extending the time for payment of principal or interest, or both, or imposing other constraints upon enforcement of such obligations. Certain bond structures may be subject to the risk that a taxing authority may issue an adverse ruling regarding tax-exempt status. There is also the possibility that as a result of adverse economic conditions (including unforeseen financial events, natural disasters and other conditions that may affect an issuer’s ability to pay its obligations), litigation or other conditions, the power or ability of any person or entity to pay when due principal of and interest on a municipal obligation may be materially affected or interest and principal previously paid may be required to be refunded. There have been recent instances of defaults and bankruptcies involving municipal obligations which were not foreseen by the financial and investment communities. Each Fund will take whatever action it considers appropriate in the event of anticipated financial difficulties, default or bankruptcy of either the issuer of any municipal obligation or of the underlying source of funds for debt service. Such action may include retaining the services of various persons or firms (including affiliates of the investment adviser) to evaluate or protect any real estate, facilities or other assets securing any such obligation or acquired by a Fund as a result of any such event, and a Fund may also manage (or engage other persons to manage) or otherwise deal with any real estate, facilities or other assets so acquired. Each Fund anticipates that real estate consulting and management services may be required with respect to properties securing various municipal obligations in its portfolio or subsequently acquired by each Fund. Each Fund will incur additional expenditures in taking protective action with respect to portfolio obligations in (or anticipated to be in) default and assets securing such obligations.
The yields on municipal obligations will be dependent on a variety of factors, including purposes of issue and source of funds for repayment, general money market conditions, general conditions of the municipal bond market, size of a particular offering, maturity of the obligation and rating of the issue. The ratings of Moody’s, S&P and Fitch represent their opinions as to the quality of the municipal obligations which they undertake to rate, and in the case of insurers, other factors including the claims-paying ability of such insurer. It should be emphasized, however, that ratings are based on judgment and are not absolute standards of quality. Consequently, municipal obligations with the same maturity, coupon and rating may have different yields while obligations of the same maturity and coupon with different ratings may have the same yield. In addition, the market price of such obligations will normally fluctuate with changes in interest rates, and therefore the net asset value of a Fund will be affected by such changes.
State-Specific Concentration. For a discussion of the risks associated with investing in municipal obligations of a particular state’s issuers, see “Risks of Concentration” in Appendix D. Each Fund may also invest a total of up to 35% of its net assets in the obligations of Puerto Rico, the U.S. Virgin Islands and Guam. Accordingly, a Fund may be adversely affected by local political and economic conditions and developments within Puerto Rico, the U.S. Virgin Islands and Guam affecting the issuers of such obligations. Each Fund may also invest to a limited extent in obligations issued by the N. Mariana Territories and American Samoa. Information about some of these conditions and developments is included in Appendix D.
Sector Concentration. Each Fund may invest 25% or more of its total assets in municipal obligations in certain sectors. There could be economic, business or political developments or court decisions that adversely affect all municipal obligations in the same sector. In particular, investments in revenue bonds might involve (without limitation) the following risks.
Hospital bond ratings are often based on feasibility studies which contain projections of expenses, revenues and occupancy levels. Among the influences affecting a hospital’s gross receipts and net income available to service its debt are demand for hospital services, the ability of the hospital to provide the services required, management capabilities, economic developments in the service area, efforts by insurers and government agencies to limit rates and expenses, confidence in the hospital, service area economic developments, competition, availability and expense of malpractice insurance, Medicaid and Medicare funding and possible federal legislation limiting the rates of increase of hospital charges.
Electric utilities face problems in financing large construction programs in an inflationary period, cost increases and delay occasioned by safety and environmental considerations (particularly with respect to nuclear facilities), difficulty in obtaining fuel at reasonable prices, and in achieving timely and adequate rate relief from regulatory commissions, effects of energy conservation and limitations on the capacity of the capital market to absorb utility debt.
Industrial development bonds (“IDBs”) are normally secured only by the revenues from the project and not by state or local government tax payments, they are subject to a wide variety of risks, many of which relate to the nature of the specific project. Generally, IDBs are sensitive to the risk of a slowdown in the economy.
Standard tobacco bonds are secured by a single source of revenue, installment payments made by tobacco companies stemming from the settlement of lawsuits brought against them by various states (the “Master Settlement Agreement”).
3
Appropriation backed tobacco bonds are supported by the same Master Settlement Agreement payments as standard tobacco bonds, but are also subject to a state’s pledge that the governor will request an appropriation of funds in its annual budget for debt service if Master Settlement Agreement revenues are insufficient. These payments are not generally fixed but rather are tied to the volume of the company’s U.S. sales of cigarettes. Tobacco bonds are subject to several risks, including the risk that cigarette consumption declines or that a tobacco company defaults on its obligation to make payments to the state. Escrowed tobacco bonds no longer rely on Master Settlement Agreement revenue as security, and are backed by a variety of government securities.
In addition, the airline industry continues to evolve. A number of major carriers have either emerged from bankruptcy or are currently in bankruptcy. Recent problems include, but are not limited to, increased competition, labor and union conflicts, greater security costs and fluctuating jet fuel prices. Court rulings have given some guidance to the viability of collateral structures. However, there is still uncertainty as to the strength of collateral pledged under various security systems.
Certain tax-exempt bonds issued by Native American tribes may be subject to the risk that a taxing authority would determine that the income from such bonds is not eligible for tax-exempt status. In the event of any final adverse ruling to this effect, holders of such bonds may be subject to penalties.
Insured Obligations. Insured municipal obligations held by the Insured Fund (“Insured Fund obligations”) will be insured as to their scheduled payment of principal and interest under (i) an insurance policy obtained by the issuer or underwriter of the obligation at the time of its original issuance (“Issue Insurance”), (ii) an insurance policy obtained by the Insured Fund or a third party subsequent to the obligation’s original issuance (“Secondary Market Insurance”) or (iii) a municipal insurance policy purchased by the Insured Fund (“Mutual Fund Insurance”). Each type of insurance insures the timely payment of interest and principal of the obligation but does not protect the market value of such obligation or the net asset value of the Insured Fund.
Issue Insurance is generally purchased by the issuer or underwriter of the obligation and is non cancellable and effective as long as the securities are unpaid and the insurer remains in business. Secondary Market Insurance allows the Insured Fund or a third party to pay a single premium to insure a obligation as to principal and interest until maturity and to transfer the insurance benefit with the underlying security. Secondary Market Insurance premiums do not result in an expense to the Insured Fund, but are added to the cost basis of the obligation so insured. Mutual Fund Insurance may be purchased from insurance companies that guarantee the timely payment of interest and principal when due on certain Insured obligations that are designated by the insurer as eligible for such insurance. Mutual Fund Insurance may terminate upon the Insured Fund’s sale of the obligation or it may be extended to enhance the marketability of the obligation. To extend a policy, the Insured Fund will pay a single, predetermined premium payable from the proceeds of the sale of that obligation. It is expected that the Insured Fund will extend a policy only if, in the opinion of the Investment Adviser, the net proceeds from the sale of the obligation, as insured, would exceed the proceeds from the sale of that obligation without insurance. The price of Insured Fund obligations insured by Mutual Fund Insurance is expected to be more volatile than the price of Insured Fund obligations insured by Issue or Secondary Market Insurance. To the extent the Insured Fund’s obligations are insured by Mutual Fund Insurance, the price of the Insured Fund’s shares, will be more volatile than if such obligations were otherwise insured.
With respect to the 80% of its net assets which will be insured, the obligations held by the Insured Fund will be insured by insurers having a financial strength rating at least Baa by Moody’s or BBB by S&P or Fitch, provided at least 50% of such net assets is invested in obligations insured by insurers having a financial strength rating at least A by Moody’s, S&P or Fitch. See Appendix D for a brief description of the financial strength ratings. Insured Fund will invest at least 65% of its total assets in insured obligations. For purposes of these limitations, the Insured Fund’s investment adviser considers that insurance passes through to any residual interest in a trust that holds such insured municipal securities ("inverse floaters").
The Insured Fund anticipates that under normal conditions all or substantially all of its insured obligations will be subject to Issue Insurance or Secondary Market Insurance. If the Insured Fund purchases Mutual Fund Insurance, premiums are paid by the Insured Fund. These premiums are based on the credit quality and principal amount of the obligation to be insured. If the issuer, underwriter, or other third party purchases the insurance for the obligation, the value of such insurance is generally reflected in a higher market value or purchase price for the obligation. While insurance is intended to reduce financial risk, the cost of such insurance (from higher purchase prices of securities or the payment of insurance premiums) will result in lower yields on the Insured obligations so insured.
The Insured Fund may also invest in municipal obligations that are secured by an escrow or trust account which contains securities issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government, its agencies or instrumentalities, that are backed by the full faith and credit of the United States, and sufficient, in combination with available trustee-held funds, in amount to ensure the
4
payment of interest on and principal of the secured obligation (“collateralized obligations”). Collateralized obligations generally are regarded as having the credit characteristics of the underlying U.S. Government, agency or instrumentality securities. These obligations will not be subject to Issue Insurance, Secondary Market Insurance or Mutual Fund Insurance, but will be considered to be insured obligations for purposes of the Insured Fund’s policy of investing at least 80% of its net assets in insured obligations (but such obligations will not constitute more than 15% of the insured portion of the Insured Fund).
The credit quality of companies which provide such credit enhancements will affect the value of those securities. Although the insurance feature reduces certain financial risks, the premiums for insurance and the higher market price paid for insured obligations may reduce a Fund’s current yield. Insurance generally will be obtained from insurers with a financial strength rating at least Baa by Moody’s or BBB by S&P or Fitch, provided that at least 50% of such net assets is invested in obligations insured by insurers having a financial strength rating at least A by Moody’s, S&P or Fitch. The insurance does not guarantee the market value of the insured obligation or the net asset value of a Fund’s shares. The Hawaii and Kansas Funds may also purchase municipal bonds that are additionally secured by insurance, bank credit agreements, or escrow accounts.
Credit Quality. While municipal obligations rated investment grade or below and comparable unrated municipal obligations may have some quality and protective characteristics, these characteristics can be expected to be offset or outweighed by uncertainties or major risk exposures to adverse conditions. Lower rated and comparable unrated municipal obligations are subject to the risk of an issuer’s inability to meet principal and interest payments on the obligations (credit risk) and may also be subject to greater price volatility due to such factors as interest rate sensitivity, market perception of the creditworthiness of the issuer and general market liquidity (market risk). Lower rated or unrated municipal obligations are also more likely to react to real or perceived developments affecting market and credit risk than are more highly rated obligations, which react primarily to movements in the general level of interest rates.
Municipal obligations held by a Fund which are rated below investment grade but which, subsequent to the assignment of such rating, are backed by escrow accounts containing U.S. Government obligations may be determined by the investment adviser to be of investment grade quality for purposes of the Fund’s investment policies. A Fund may retain in its portfolio an obligation whose rating drops after its acquisition, including defaulted obligations, if such retention is considered desirable by the investment adviser; provided, however, that holdings of obligations rated below Baa or BBB will be no more than 35% of net assets and holdings rated below B will be less than 10% of net assets. In the event the rating of an obligation held by a Fund is downgraded, causing the Fund to exceed this limitation, the investment adviser will (in an orderly fashion within a reasonable period of time) dispose of such obligations as it deems necessary in order to comply with each Fund’s credit quality limitations. In the case of a defaulted obligation, a Fund may incur additional expense seeking recovery of its investment. See “Portfolio of Investments” in the “Financial Statements” incorporated by reference into this SAI with respect to any defaulted obligations held by a Fund.
When a Fund invests in lower rated or unrated municipal obligations, the achievement of the Fund’s goals is more dependent on the investment adviser’s ability than would be the case if the Fund were investing in municipal obligations in the higher rating categories. In evaluating the credit quality of a particular issue, whether rated or unrated, the investment adviser may take into consideration, among other things, the financial resources of the issuer (or, as appropriate, of the underlying source of funds for debt service), its sensitivity to economic conditions and trends, any operating history of and the community support for the facility financed by the issue, the ability of the issuer’s management and regulatory matters. The investment adviser may also purchase structured derivative products with greater or lesser credit risk than the underlying bonds. Such bonds may be rated investment grade, as well as below investment grade. For a description of municipal bond ratings, see Appendix E.
Municipal Leases. Each Fund may invest in municipal leases and participations therein, which arrangements frequently involve special risks. Municipal leases are obligations in the form of a lease, installment purchase or conditional sales contract (which typically provide for the title to the leased asset to pass to the governmental issuer) which is issued by state or local governments to acquire equipment and facilities. Interest income from such obligations is generally exempt from local and state taxes in the state of issuance. “Participations” in such leases are undivided interests in a portion of the total obligation. Participations entitle their holders to receive a pro rata share of all payments under the lease. The obligation of the issuer to meet its obligations under such leases is often subject to the appropriation by the appropriate legislative body, on an annual or other basis, of funds for the payment of the obligations. Investments in municipal leases are thus subject to the risk that the legislative body will not make the necessary appropriation and the issuer will not otherwise be willing or able to meet its obligation.
Certain municipal lease obligations owned by a Fund may be deemed illiquid for the purpose of the Fund’s 15% limitation on investments in illiquid securities, unless determined by the investment adviser, pursuant to guidelines adopted by the
5
Trustees, to be liquid securities for the purpose of such limitation. In determining the liquidity of municipal lease obligations, the investment adviser will consider the factors it believes are relevant to the marketability of the obligation, to the extent that information regarding such factor is available to the investment adviser and pertinent to the liquidity determination, which may include: (1) the willingness of dealers to bid for the obligation; (2) the number of dealers willing to purchase or sell the obligation and the number of other potential buyers; (3) the frequency of trades and quotes for the obligation; (4) the nature of the marketplace trades, including the time needed to dispose of the obligation, the method of soliciting offers, and the mechanics of transfer; (5) the willingness of the governmental issuer to continue to appropriate funds for the payment of the obligation; (6) how likely or remote an event of nonappropriation may be, which depends in varying degrees on a variety of factors, including those relating to the general creditworthiness of the governmental issuer, its dependence on its continuing access to the credit markets, and the importance to the issuer of the equipment, property or facility covered by the lease or contract; (7) the rating, if any, assigned to the obligation and/or the governmental issuer by any nationally recognized statistical rating organization; (8) whether the obligation is insured as to the timely payment of principal and interest; and (9) all factors and information unique to the obligation in determining its liquidity. If the municipal lease obligation is insured as to the timely payment of principal and interest, or if the obligation has an investment grade rating (rated BBB or Baa or higher), the investment adviser will consider the obligation to be liquid. In the event a Fund acquires an unrated municipal lease obligation, the investment adviser will be responsible for determining the credit quality of such obligation on an ongoing basis, including an assessment of the likelihood that the lease may or may not be cancelled.
Zero Coupon Bonds. Zero coupon bonds are debt obligations which do not require the periodic payment of interest and are issued at a significant discount from face value. The discount approximates the total amount of interest the bonds will accrue and compound over the period until maturity at a rate of interest reflecting the market rate of the security at the time of issuance. Each Fund is required to accrue income from zero coupon bonds on a current basis, even though it does not receive that income currently in cash, and each Fund is required to distribute that income for each taxable year. Thus, a Fund may have to sell other investments to obtain cash needed to make income distributions.
When-Issued Securities. New issues of municipal obligations are sometimes offered on a “when-issued” basis, that is, delivery and payment for the securities normally take place within a specified number of days after the date of a Fund’s commitment and are subject to certain conditions such as the issuance of satisfactory legal opinions. Each Fund may also purchase securities on a when-issued basis pursuant to refunding contracts in connection with the refinancing of an issuer’s outstanding indebtedness. Refunding contracts generally require the issuer to sell and a Fund to buy such securities on a settlement date that could be several months or several years in the future. Each Fund may also purchase instruments that give the Fund the option to purchase a municipal obligation when and if issued.
Each Fund will make commitments to purchase when-issued securities only with the intention of actually acquiring the securities, but may sell such securities before the settlement date if it is deemed advisable as a matter of investment strategy. The payment obligation and the interest rate that will be received on the securities are fixed at the time a Fund enters into the purchase commitment. When a Fund commits to purchase a security on a when-issued basis it records the transaction and reflects the value of the security in determining its net asset value. Securities purchased on a when-issued basis and the securities held by a Fund are subject to changes in value based upon the perception of the creditworthiness of the issuer and changes in the level of interest rates (i.e., appreciation when interest rates decline and depreciation when interest rates rise). Therefore, to the extent that a Fund remains substantially fully invested at the same time that it has purchased securities on a when-issued basis, there will be greater fluctuations in the Fund’s net asset value than if it solely set aside cash to pay for when-issued securities.
Credit Derivatives. Each Fund may invest in credit default swaps, total return swaps or credit options. In a credit default swap, the buyer of credit protection (or seller of credit risk) agrees to pay the counterparty a fixed, periodic premium for a specified term. In return, the counterparty agrees to pay a contingent payment to the buyer in the event of an agreed upon credit occurrence with respect to a particular reference entity. In a total return swap, the buyer receives a periodic return equal to the total economic return of a specified security, securities or index, for a specified period of time. In return, the buyer pays the counterparty a variable stream of payments, typically based upon short term interest rates, possibly plus or minus an agreed upon spread. Credit options are options whereby the purchaser has the right, but not the obligation, to enter into a transaction involving either an asset with inherent credit risk or a credit derivative, at terms specified at the initiation of the option. Transactions in derivative instruments involve a risk of loss or depreciation due to: unanticipated adverse changes in securities prices, interest rates, indices, the other financial instruments’ prices or currency exchange rates; the inability to close out a position; default by the counterparty; imperfect correlation between a position and the desired hedge; tax constraints on closing out positions; and portfolio management constraints on securities subject to such transactions. Derivative instruments may sometimes increase or leverage exposure to a particular market risk, thereby increasing price volatility. The counterparties to many derivatives transactions are investment banks (or, if recently
6
restructured, formerly categorized as investment banks), an industry that has recently experienced higher than normal bankruptcies. The risk of counterparty default increases in the event such counterparties undergo bankruptcy or are otherwise part of an industry affected by increased bankruptcy activity.
Redemption, Demand and Put Features and Put Options. Issuers of municipal obligations reserve the right to call (redeem) the bond. If an issuer redeems securities held by a Fund during a time of declining interest rates, the Fund may not be able to reinvest the proceeds in securities providing the same investment return as the securities redeemed. Also, some bonds may have “put” or “demand” features that allow early redemption by the bondholder. Longer term fixed-rate bonds may give the holder a right to request redemption at certain times (often annually after the lapse of an intermediate term). These bonds are more defensive than conventional long term bonds (protecting to some degree against a rise in interest rates) while providing greater opportunity than comparable intermediate term bonds, because a Fund may retain the bond if interest rates decline.
Liquidity and Protective Put Options. Each Fund may enter into a separate agreement with the seller of the security or some other person granting the Fund the right to put the security to the seller thereof or the other person at an agreed upon price. Each Fund intends to limit this type of transaction to institutions (such as banks or securities dealers) which the investment adviser believes present minimal credit risks and would engage in this type of transaction to facilitate portfolio liquidity or (if the seller so agrees) to hedge against rising interest rates. There is no assurance that this kind of put option will be available to a Fund or that selling institutions will be willing to permit a Fund to exercise a put to hedge against rising interest rates. A Fund does not expect to assign any value to any separate put option which may be acquired to facilitate portfolio liquidity, inasmuch as the value (if any) of the put will be reflected in the value assigned to the associated security; any put acquired for hedging purposes would be valued in good faith under methods or procedures established by the Trustees after consideration of all relevant factors, including its expiration date, the price volatility of the associated security, the difference between the market price of the associated security and the exercise price of the put, the creditworthiness of the issuer of the put and the market prices of comparable put options. Interest income generated by certain bonds having put or demand features may be taxable.
OTC Options. Each Fund may enter into an agreement with a potential buyer of a municipal obligation that gives the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to purchase a municipal obligation held by the Fund at a particular price in the future and is commonly referred to as an over-the-counter option or OTC option. Such agreements will be entered solely to help facilitate the selling of municipal obligations, for instance, if the buyer wishes to lock in a price for a particular municipal obligation subject to performing due diligence on the issue or issuer. The buyer may not pay a premium for such option. Each Fund may enter into such arrangements on up to 5% of the value of such Fund’s assets. There is a risk that the value of a municipal obligation underlying an option may appreciate above the value that the buyer has agreed to pay for the municipal obligation and therefore the Fund would not be entitled to the appreciation above such price.
Variable Rate Obligations. Each Fund may purchase variable rate obligations. Variable rate instruments provide for adjustments in the interest rate at specified intervals (daily, weekly, monthly, semiannually, etc.). The revised rates are usually set at the issuer’s discretion in which case the investor normally enjoys the right to “put” the security back to the issuer or his agent. Rate revisions may alternatively be determined by formula or in some other contractual fashion. Variable rate obligations normally provide that the holder can demand payment of the obligation on short notice at par with accrued interest and which are frequently secured by letters of credit or other support arrangements provided by banks. To the extent that such letters of credit or other arrangements constitute an unconditional guarantee of the issuer’s obligations, a bank may be treated as the issuer of a security for the purposes of complying with the diversification requirements set forth in Section 5(b) of the 1940 Act and Rule 5b-2 thereunder. A Fund would anticipate using these bonds as cash equivalents pending longer term investment of its funds.
Inverse Floaters. Each Fund may invest in residual interests in a trust that holds municipal securities (“inverse floaters”). The interest rate payable on an inverse floater bears an inverse relationship to the interest rate on another security issued by the trust. Because changes in the interest rate on the other security inversely affect the interest paid on the inverse floater, the value and income of an inverse floater is generally more volatile than that of a fixed rate bond. Inverse floaters have interest rate adjustment formulas which generally reduce or, in the extreme, eliminate the interest paid to a Fund when short-term interest rates rise, and increase the interest paid to a Fund when short-term interest rates fall. Inverse floaters have varying degrees of liquidity, and the market for these securities is relatively volatile. These securities tend to underperform the market for fixed rate bonds in a rising long-term interest rate environment, but tend to outperform the market for fixed rate bonds when long-term interest rates decline. Although volatile, inverse floaters typically offer the potential for yields exceeding the yields available on fixed rate bonds with comparable credit quality and maturity. These securities usually permit the investor to convert the floating rate to a fixed rate (normally adjusted downward), and this optional conversion feature may provide a partial hedge against rising rates if exercised at an opportune time. While
7
inverse floaters expose a Fund to leverage risk because they provide two or more dollars of bond market exposure for every dollar invested, they are not subject to a Fund’s restrictions on borrowings.
Under certain circumstances, a Fund may enter into a so-called shortfall and forbearance agreement with the sponsor of an inverse floater held by the Fund. Such agreements commit a Fund to reimburse the sponsor of such inverse floater, upon the termination of the trust issuing the inverse floater, the difference between the liquidation value of the underlying security (which is the basis of the inverse floater) and the principal amount due to the holders of the floating rate security issued in conjunction with the inverse floater. Absent a shortfall and forebearance agreement, a Fund would not be required to make such a reimbursement. If a Fund chooses not to enter into such an agreement, the inverse floater could be terminated and the Fund could incur a loss.
Interest Rate Swaps and Forward Rate Contracts. Interest rate swaps involve the exchange by a Fund with another party of their respective commitments to pay or receive interest, e.g., an exchange of fixed rate payments for floating rate payments. A Fund will only enter into interest rate swaps on a net basis, i.e., the two payment streams are netted out with the Fund receiving or paying, as the case may be, only the net amount of the two payments. Each Fund may also enter forward rate contracts. Under these contracts, the buyer locks in an interest rate at a future settlement date. If the interest rate on the settlement date exceeds the lock rate, the buyer pays the seller the difference between the two rates. If the lock rate exceeds the interest rate on the settlement date, the seller pays the buyer the difference between the two rates. Any such gain received by the Fund would be taxable.
If the other party to an interest rate swap or forward rate contract defaults, a Fund’s risk of loss consists of the net amount of payments that the Fund is contractually entitled to receive. The net amount of the excess, if any, of a Fund’s obligations over its entitlements will be maintained in a segregated account by the Fund’s custodian. No Fund will enter into any interest rate swap or forward rate contract unless the claims-paying ability of the other party thereto is considered to be investment grade by the investment adviser. If there is a default by the other party to such a transaction, a Fund will have contractual remedies pursuant to the agreements related to the transaction. These instruments are traded in the over-the-counter market.
Illiquid Obligations. At times, a substantial portion of a Fund’s assets may be invested in securities as to which the Fund, by itself or together with other accounts managed by the investment adviser and its affiliates, holds a major portion or all of such securities. Under adverse market or economic conditions or in the event of adverse changes in the financial condition of the issuer, a Fund could find it more difficult to sell such securities when the investment adviser believes it advisable to do so or may be able to sell such securities only at prices lower than if such securities were more widely held. Under such circumstances, it may also be more difficult to determine the fair value of such securities for purposes of computing a Fund’s net asset value. Illiquid securities may also include those legally restricted as to resale, and securities eligible for resale pursuant to Rule 144A thereunder. Rule 144A securities may be treated as liquid securities if the investment adviser determines that such treatment is warranted. Even if determined to be liquid, holdings of these securities may increase the level of Fund illiquidity if eligible buyers become uninterested in purchasing them.
The secondary market for some municipal obligations issued within a state (including issues which are privately placed with a Fund) is less liquid than that for taxable debt obligations or other more widely traded municipal obligations. No Fund will purchase illiquid securities if more than 15% of its net assets would be invested in securities that are not readily marketable. No established resale market exists for certain of the municipal obligations in which a Fund may invest. The market for obligations rated below investment grade is also likely to be less liquid than the market for higher rated obligations. As a result, a Fund may be unable to dispose of these municipal obligations at times when it would otherwise wish to do so at the prices at which they are valued.
Futures Contracts and Options on Futures Contracts. A change in the level of interest rates may affect the value of the securities held by a Fund (or of securities that a Fund expects to purchase). To hedge against changes in rates or as a substitute for the purchase of securities, a Fund may enter into (i) futures contracts for the purchase or sale of debt securities and (ii) futures contracts on securities indices. All futures contracts entered into by a Fund are traded on exchanges or boards of trade that are licensed and regulated by the CFTC and must be executed through a futures commission merchant or brokerage firm which is a member of the relevant exchange. Each Fund may purchase and write call and put options on futures contracts which are traded on a United States exchange or board of trade. Each Fund will be required, in connection with transactions in futures contracts and the writing of options on futures, to make margin deposits, which will be held by the futures commission merchant through whom the Fund engages in such futures and options transactions.
Some futures contracts and options thereon may become illiquid under adverse market conditions. In addition, during periods of market volatility, a commodity exchange may suspend or limit transactions in an exchange-traded instrument, which may make the instrument temporarily illiquid and difficult to price. Commodity exchanges may also establish daily
8
limits on the amount that the price of a futures contract or futures option can vary from the previous day’s settlement price. Once the daily limit is reached, no trades may be made that day at a price beyond the limit. This may prevent a Fund from closing out positions and limiting its losses.
Each Fund will engage in futures and related options transactions for either hedging or non-hedging purposes. Each Fund will determine that the price fluctuations in the futures contracts and options on futures used for hedging purposes are substantially related to price fluctuations in securities held by the Fund or which it expects to purchase. Each Fund will engage in transactions in futures and related options contracts only to the extent such transactions are consistent with the requirements of the Code, for maintaining qualification of a Fund as a regulated investment company for federal income tax purposes. Each Fund has claimed an exclusion from the definition of a Commodity Pool Operator (“CPO”) under the Commodity Exchange Act and therefore are not subject to registration or regulation as a CPO.
Asset Coverage. To the extent required by SEC guidelines, each Fund will only engage in transactions that expose it to an obligation to another party if it owns either (1) an offsetting (“covered”) position for the same type of financial asset, or (2) cash or liquid securities, segregated with its custodian, with a value sufficient at all times to cover its potential obligations not covered as provided in (1). Assets used as cover or segregated with the custodian cannot be sold while the position(s) requiring cover is open unless replaced with other appropriate assets. As a result, if a large portion of assets is segregated or committed as cover, it could impede portfolio management or the ability to meet redemption requests or other current obligations.
ReFlow Liquidity Program. Each Fund may participate in the ReFlow liquidity program, which is designed to provide an alternative liquidity source for mutual funds experiencing net redemptions of their shares. Pursuant to the program, ReFlow Fund, LLC ("ReFlow") provides participating mutual funds with a source of cash to meet net shareholder redemptions by standing ready each business day to purchase fund shares up to the value of the net shares redeemed by other shareholders that are to settle the next business day. Following purchases of fund shares, ReFlow then generally redeems those shares when the fund experiences net sales, at the end of a maximum holding period determined by ReFlow (currently 28 days) or at other times at ReFlow’s discretion. While ReFlow holds fund shares, it will have the same rights and privileges with respect to those shares as any other shareholder. For use of the ReFlow service, a fund pays a fee to ReFlow each time it purchas es fund shares, calculated by applying to the purchase amount a fee rate determined through an automated daily auction among participating mutual funds. The current minimum fee rate is 0.15% of the value of the fund shares purchased by ReFlow although the fund may submit a bid at a higher fee rate if it determines that doing so is in the best interest of fund shareholders. Such fee is allocated among a fund’s share classes based on relative net assets. ReFlow’s purchases of fund shares through the liquidity program are made on an investment-blind basis without regard to the fund’s objective, policies or anticipated performance. ReFlow will purchase Class A shares at net asset value and will not be subject to any sales charge, investment minimum or redemption fee applicable to such shares. Investments in a Fund by ReFlow in connection with the ReFlow liquidity program are not subject to the round trip limitation described in "Restrictions on Excessive Trading and Market Timing" under "Purchasin g Shares" in the prospectus. In accordance with federal securities laws, ReFlow is prohibited from acquiring more than 3% of the outstanding voting securities of a fund. The investment adviser believes that the program assists in stabilizing a Fund’s net assets to the benefit of the Fund and its shareholders. To the extent a Fund’s net assets do not decline, the investment adviser may also benefit.
Temporary Investments. Cash equivalents are highly liquid, short-term securities such as commercial paper, time deposits, certificates of deposit, short-term notes and short-term U.S. Government obligations. These securities may be subject to federal income, state income and/or other taxes.
Portfolio Turnover. Each Fund may sell (and later purchase) securities in anticipation of a market decline (a rise in interest rates) or purchase (and later sell) securities in anticipation of a market rise (a decline in interest rates). Securities may also be purchased and sold based on their relative value in the marketplace. A Fund cannot accurately predict its portfolio turnover rate, but it is anticipated that the annual portfolio turnover rate will generally not exceed 100% (excluding turnover of securities having a maturity of one year or less). A 100% annual turnover rate could occur, for example, if all the securities held by a Fund were replaced once in a period of one year. A high turnover rate (100% or more) necessarily involves greater expenses to a Fund. Historical turnover rate(s) are included in the Financial Highlights table(s) in the Prospectus.
The following investment restrictions of each Fund are designated as fundamental policies and as such cannot be changed without the approval of the holders of a majority of a Fund’s outstanding voting securities, which as used in this SAI means the lesser of: (a) 67% of the shares of a Fund present or represented by proxy at a meeting if the holders of more than 50%
9
of the outstanding shares are present or represented at the meeting; or (b) more than 50% of the outstanding shares of a Fund. Accordingly, each Fund may not:
| |
| (1) | Borrow money or issue senior securities except as permitted by the 1940 Act; |
| |
| (2) | Purchase securities on margin (but the Fund may obtain such short-term credits as may be necessary for the |
| | clearance of purchases and sales of securities). The deposit or payment by the Fund of initial or maintenance |
| | margin in connection with futures contracts or related options transactions is not considered the purchase of a |
| | security on margin; |
| |
| (3) | Underwrite or participate in the marketing of securities of others, except insofar as it may technically be deemed |
| | to be an underwriter in selling a portfolio security under circumstances which may require the registration of |
| | the same under the 1933 Act; |
| |
| (4) | Purchase or sell real estate, although it may purchase and sell securities which are secured by real estate and |
| | securities of companies which invest or deal in real estate; |
| |
| (5) | Purchase or sell physical commodities or contracts for the purchase or sale of physical commodities; or |
| |
| (6) | Make loans to any person except by (a) the acquisition of debt instruments and making portfolio investments, |
| | (b) entering into repurchase agreements and (c) lending portfolio securities. |
In connection with Restriction (1) above, the 1940 Act currently permits investment companies to borrow money so long as there is 300% asset coverage of the borrowing (i.e., borrowings do not exceed one-third of the investment company’s total assets after subtracting liabilities other than the borrowings). There is no current intent to borrow money except for the limited purposes described in the prospectus.
Notwithstanding the investment policies and restrictions of each Fund, the Fund may invest all of its investable assets in an open-end management investment company with substantially the same investment objective, policies and restrictions as the Fund.
The following nonfundamental investment policies have been adopted by each Fund. A nonfundamental investment policy may be changed by the Trustees with respect to a Fund without approval by the Fund’s shareholders. Each Fund will not:
- make short sales of securities or maintain a short position, unless at all times when a short position is open (i) it owns an equal amount of such securities or securities convertible into or exchangeable, without payment of any further consideration, for securities of the same issue as, and equal in amount to, the securities sold short or (ii) it holds in a segregated account cash or other liquid securities (to the extent required under the 1940 Act) in an amount equal to the current market value of the securities sold short, and unless not more than 25% of its net assets (taken at current value) is held as collateral for such sales at any one time; or
- invest more than 15% of net assets in investments which are not readily marketable, including restricted securities and repurchase agreements maturing in more than seven days. Restricted securities for the purposes of this limitation do not include securities eligible for resale pursuant to Rule 144A under the 1933 Act and commercial paper issued pursuant to Section 4(2) of said Act that the Board of Trustees, or its delegate, determines to be liquid. Any such determination by a delegate will be made pursuant to procedures adopted by the Board. When investing in Rule 144A securities, the level of portfolio illiquidity may be increased to the extent that eligible buyers become uninterested in purchasing such securities.
No Fund will invest 25% or more of its total assets in any one industry. For purposes of the foregoing policy, securities of the U.S. Government, its agencies, or instrumentalities are not considered to represent industries. Municipal obligations backed by the credit of a governmental entity are also not considered to represent industries. However, municipal obligations backed only by the assets and revenues of non-governmental users may for this purpose be deemed to be issued by such non-governmental users. The foregoing 25% limitation would apply to these issuers. As discussed in the prospectus and this SAI, a Fund may invest more than 25% of its total assets in certain economic sectors, such as revenue bonds, housing, hospitals and other health care facilities, utilities and industrial development bonds. Each Fund reserves the right to invest more than 25% of total assets in each of these sectors.
For purposes of a Fund’s investment restrictions and diversification status, the determination of the “issuer” of any obligation, including inverse floaters, will be made by the Fund’s investment adviser on the basis of the characteristics of the obligation and other relevant factors, the most significant of which is the source of funds committed to meeting interest and principal payments of such obligations. A Fund’s investments in inverse floaters and similar securities described in the
10
prospectus and this SAI will not be considered borrowing for purposes of a Fund’s restrictions on borrowing described herein and in the prospectus.
Whenever an investment policy or investment restriction set forth in the prospectus or this SAI states a maximum percentage of assets that may be invested in any security or other asset, or describes a policy regarding quality standards, such percentage limitation or standard shall be determined immediately after and as a result of the acquisition by a Fund of such security or asset. Accordingly, any later increase or decrease resulting from a change in values, assets or other circumstances or any subsequent rating change made by a rating service (or as determined by the investment adviser if the security is not rated by a rating agency), will not compel a Fund to dispose of such security or other asset. However, a Fund must always be in compliance with the borrowing policy and limitation on investing in illiquid securities set forth above. If a sale of securities is required to comply with the 15% limit on illiquid securities, such sales will be made in an orderly manner with cons ideration of the best interests of shareholders.
| MANAGEMENT AND ORGANIZATION |
Fund Management. The Trustees of the Trust are responsible for the overall management and supervision of the affairs of the Trust. The Trustees and officers of the Trust are listed below. Except as indicated, each individual has held the office shown or other offices in the same company for the last five years. Trustees and officers of the Trust hold indefinite terms of office. The “Noninterested Trustees” consist of those Trustees who are not “interested persons” of the Trust, as that term is defined under the 1940 Act. The business address of each Trustee and officer is Two International Place, Boston, Massachusetts 02110. As used in this SAI, “EVC” refers to Eaton Vance Corp., “EV” refers to Eaton Vance, Inc. and “EVD” refers to Eaton Vance Distributors, Inc. (see "Principal Underwriter" under "Other Service Providers"). EVC and EV are the corporate parent and trustee, respectively, of Eaton Vance and BMR. Eac h officer affiliated with Eaton Vance may hold a position with other Eaton Vance affiliates that is comparable to his or her position with Eaton Vance listed below.
| | | | Number of Portfolios | |
| | | | | in Fund Complex | |
| | Trust | Term of Office and | | Overseen By | |
| Name and Date of Birth | Position(s) | Length of Service | Principal Occupation(s) During Past Five Years | Trustee(1) | Other Directorships Held |
| |
| Interested Trustee | | | | | |
| |
| THOMAS E. FAUST JR. | Trustee | Since 2007 | Chairman, Chief Executive Officer and President of EVC, Director and | 175 | Director of EVC |
| 5/31/58 | | | President of EV, Chief Executive Officer and President of Eaton Vance | | |
| | | | and BMR, and Director of EVD. Trustee and/or officer of 175 registered | | |
| | | | investment companies and 4 private investment companies managed | | |
| | | | by Eaton Vance or BMR. Mr. Faust is an interested person because of | | |
| | | | his positions with BMR, Eaton Vance, EVC, EVD and EV, which are | | |
| | | | affiliates of the Trust. | | |
| |
| Noninterested Trustees | | | | | |
| |
| BENJAMIN C. ESTY | Trustee | Since 2005 | Roy and Elizabeth Simmons Professor of Business Administration, | 175 | None |
| 1/2/63 | | | Harvard University Graduate School of Business Administration. | | |
| |
| |
| ALLEN R. FREEDMAN | Trustee | Since 2007 | Former Chairman (2002-2004) and a Director (1983-2004) of | 175 | Director of Assurant, Inc. |
| 4/3/40 | | | Systems & Computer Technology Corp. (provider of software to higher | | (insurance provider), and |
| | | | education). Formerly, a Director of Loring Ward International (fund | | Stonemor Partners L.P. (owner |
| | | | distributor) (2005-2007). Formerly, Chairman and a Director of Indus | | and operator of cemeteries) |
| | | | International, Inc. (provider of enterprise management software to the | | |
| | power generating industry) (2005-2007). | | |
| |
| WILLIAM H. PARK | Trustee | Since 2003 | Vice Chairman, Commercial Industrial Finance Corp. (specialty finance | 175 | None |
| 9/19/47 | | | company) (since 2006). Formerly, President and Chief Executive | | |
| | | | Officer, Prizm Capital Management, LLC (investment management | | |
| | | | firm) (2002-2005). | | |
| |
| RONALD A. PEARLMAN | Trustee | Since 2003 | Professor of Law, Georgetown University Law Center. | 175 | None |
| 7/10/40 | | | | | |
11
| | | | Number of Portfolios | |
| | | | | in Fund Complex | |
| | Trust | Term of Office and | | Overseen By | |
| Name and Date of Birth | Position(s) | Length of Service | Principal Occupation(s) During Past Five Years | Trustee(1) | Other Directorships Held |
| |
| HELEN FRAME PETERS | Trustee | Since 2008 | Professor of Finance, Carroll School of Management, Boston College. | 175 | Director of Federal Home Loan |
| 3/22/48 | | | Adjunct Professor of Finance, Peking University, Beijing, China (since | | Bank of Boston (a bank for |
| | | | 2005). | | banks) and BJ’s Wholesale |
| | | | | | Club, Inc. (wholesale club |
| | | | | | retailer); Trustee of SPDR Index |
| | | | | | Shares Funds and SPDR Series |
| | | | | | Trust (exchange traded funds) |
| |
| HEIDI L. STEIGER | Trustee | Since 2007 | Managing Partner, Topridge Associates LLC (global wealth | 175 | Director of Nuclear Electric |
| 7/8/53 | | | management firm) (since 2008); Senior Adviser (since 2008), | | Insurance Ltd. (nuclear |
| | | | President (2005-2008), Lowenhaupt Global Advisors, LLC (global | | insurance provider) and Aviva |
| | | | wealth management firm). Formerly, President and Contributing | | USA (insurance provider) |
| | | | Editor, Worth Magazine (2004-2005). Formerly, Executive Vice | | |
| | | | President and Global Head of Private Asset Management (and various | | |
| | | | other positions), Neuberger Berman (investment firm) (1986-2004). | | |
| |
| LYNN A. STOUT | Trustee | Since 1998 | Paul Hastings Professor of Corporate and Securities Law (since 2006) | 175 | None |
| 9/14/57 | | | and Professor of Law (2001-2006), University of California at Los | | |
| | | | Angeles School of Law. | | |
| |
| RALPH F. VERNI | Chairman of the | Chairman of the | Consultant and private investor. | 175 | None |
| 1/26/43 | Board and Trustee | Board since 2007 | | | |
| | | and Trustee since | | | |
| | | 2005 | | | |
(1)Includes both master and feeder funds in a master-feeder structure.
| | | | |
| Principal Officers who are not Trustees | | | | |
| | | Term of Office and | | |
| Name and Date of Birth | Trust Position(s) | Length of Service | Principal Occupation(s) During Past Five Years |
| |
| |
| CYNTHIA J. CLEMSON | President | Since 2005 | Vice President of Eaton Vance and BMR. Officer of 92 registered investment companies managed |
| 3/2/63 | | | by Eaton Vance or BMR. | |
| |
| |
| WILLIAM H. AHERN, JR. | Vice President | Since 2004 | Vice President of Eaton Vance and BMR. Officer of 76 registered investment companies managed |
| 7/28/59 | | | by Eaton Vance or BMR. | |
| |
| |
| CRAIG R. BRANDON | Vice President | Since 2004 | Vice President of Eaton Vance and BMR. Officer of 45 registered investment companies managed |
| 12/21/66 | | | by Eaton Vance or BMR. | |
| |
| |
| JAMES H. EVANS | Vice President | Since 2009 | Vice President of Eaton Vance and BMR since December 2008. Formerly, Senior Vice President and |
| 11/18/59 | | | Senior Portfolio Manager, Tax-Exempt Fixed Income at M.D. Sass (1990 - 2008). Officer of 6 |
| | | | registered investment companies managed by Eaton Vance or BMR. |
| |
| |
| ROBERT B. MACINTOSH | Vice President | Since 1993 | Vice President of Eaton Vance and BMR. Officer of 92 registered investment companies managed |
| 1/22/57 | | | by Eaton Vance or BMR. | |
| |
| |
| THOMAS M. METZOLD | Vice President | Since 2004 | Vice President of Eaton Vance and BMR. Officer of 46 registered investment companies managed |
| 8/3/58 | | | by Eaton Vance or BMR. | |
| |
| |
| ADAM A. WEIGOLD | Vice President | Since 2007 | Vice President of Eaton Vance and BMR. Officer of 72 registered investment companies managed |
| 3/22/75 | | | by Eaton Vance or BMR. | |
12
| | | | |
| | | Term of Office and | | |
| Name and Date of Birth | Trust Position(s) | Length of Service | Principal Occupation(s) During Past Five Years |
| |
| BARBARA E. CAMPBELL | Treasurer | Since 2005 | Vice President of Eaton Vance and BMR. Officer of 175 registered investment companies managed |
| 6/19/57 | | | by Eaton Vance or BMR. | |
| |
| |
| MAUREEN A. GEMMA | Secretary and Chief Legal Officer | Secretary since 2007 and Chief | Vice President of Eaton Vance and BMR. Officer of 175 registered investment companies managed |
| 5/24/60 | | Legal Officer since 2008 | by Eaton Vance or BMR. | |
| |
| |
| PAUL M. O’NEIL | Chief Compliance Officer | Since 2004 | Vice President of Eaton Vance and BMR. Officer of 175 registered investment companies managed |
| 7/11/53 | | | by Eaton Vance or BMR. | |
The Board of Trustees of the Trust have several standing Committees, including the Governance Committee, the Audit Committee, the Portfolio Management Committee, the Compliance Reports and Regulatory Matters Committee and the Contract Review Committee (formerly, the Special Committee). Each of the Committees are comprised of only noninterested Trustees.
Mmes. Stout (Chair), Peters and Steiger, and Messrs. Esty, Freedman, Park, Pearlman and Verni are members of the Governance Committee. The purpose of the Governance Committee is to consider, evaluate and make recommendations to the Board of Trustees with respect to the structure, membership and operation of the Board of Trustees and the Committees thereof, including the nomination and selection of noninterested Trustees and a Chairperson of the Board of Trustees and the compensation of such persons. During the fiscal year ended January 31, 2009, the Governance Committee convened seven times.
The Governance Committee will, when a vacancy exists or is anticipated, consider any nominee for noninterested Trustee recommended by a shareholder if such recommendation is submitted in writing to the Governance Committee, contains sufficient background information concerning the candidate, including evidence the candidate is willing to serve as a noninterested Trustee if selected for the position, and is received in a sufficiently timely manner.
Messrs. Park (Chair) and Verni, and Mmes. Steiger and Stout are members of the Audit Committee. The Board of Trustees has designated Mr. Park, a noninterested Trustee, as audit committee financial expert. The Audit Committee’s purposes are to (i) oversee each Fund’s accounting and financial reporting processes, its internal control over financial reporting, and, as appropriate, the internal control over financial reporting of certain service providers; (ii) oversee or, as appropriate, assist Board oversight of the quality and integrity of each Fund’s financial statements and the independent audit thereof; (iii) oversee, or, as appropriate, assist Board oversight of, each Fund’s compliance with legal and regulatory requirements that relate to each Fund’s accounting and financial reporting, internal control over financial reporting and independent audits; (iv) approve prior to appointment the engagement and, when appropriate, replacement of the independent re gistered public accounting firm, and, if applicable, nominate the independent registered public accounting firm to be proposed for shareholder ratification in any proxy statement of a Fund; (v) evaluate the qualifications, independence and performance of the independent registered public accounting firm and the audit partner in charge of leading the audit; and (vi) prepare, as necessary, audit committee reports consistent with the requirements of applicable SEC and stock exchange rules for inclusion in the proxy statement of a Fund. During the fiscal year ended January 31, 2009, the Audit Committee convened five times.
Messrs. Verni (Chair), Esty, Freedman, Park and Pearlman, and Ms. Peters are currently members of the Contract Review Committee. The purposes of the Contract Review Committee are to consider, evaluate and make recommendations to the Board of Trustees concerning the following matters: (i) contractual arrangements with each service provider to the Funds, including advisory, sub-advisory, transfer agency, custodial and fund accounting, distribution services and administrative services; (ii) any and all other matters in which any service provider (including Eaton Vance or any affiliated entity thereof) has an actual or potential conflict of interest with the interests of the Fund or investors therein; and (iii) any other matter appropriate for review by the noninterested Trustees, unless the matter is within the responsibilities of the other Committees of the Board of Trustees. During the fiscal year ended January 31, 2009, the Contract Review Committee convened nine times.
Messrs. Esty (Chair) and Freedman, and Ms. Peters are currently members of the Portfolio Management Committee. The purposes of the Portfolio Management Committee are to: (i) assist the Board of Trustees in its oversight of the portfolio management process employed by the Funds and their investment adviser and sub-adviser(s), if applicable, relative to the Funds’ stated objective(s), strategies and restrictions; (ii) assist the Board of Trustees in its oversight of the trading policies
13
and procedures and risk management techniques applicable to the Funds; and (iii) assist the Board of Trustees in its monitoring of the performance results of all Funds, giving special attention to the performance of certain Funds that it or the Board of Trustees identifies from time to time. During the fiscal year ended January 31, 2009, the Portfolio Management Committee convened five times.
Mr. Pearlman (Chair) and Mmes. Steiger and Stout are currently members of the Compliance Reports and Regulatory Matters Committee. The purposes of the Compliance Reports and Regulatory Matters Committee are to: (i) assist the Board of Trustees in its oversight role with respect to compliance issues and certain other regulatory matters affecting the Funds; (ii) serve as a liaison between the Board of Trustees and the Funds’ Chief Compliance Officer (the “CCO”); and (iii) serve as a “qualified legal compliance committee” within the rules promulgated by the SEC. During the fiscal year ended January 31, 2009, the Compliance Reports and Regulatory Matters Committee convened four times.
Share Ownership. The following table shows the dollar range of equity securities beneficially owned by each Trustee in each Fund and in all Eaton Vance Funds overseen by the Trustee as of December 31, 2008.
| | | | | | | | | |
| | Dollar Range of Equity Securities Owned by |
| | Benjamin C. | Thomas E. | Allen R. | William H. | Ronald A. | Helen Frame | Heidi L. | Lynn A. | Ralph F. |
| Fund Name | Esty(2) | Faust Jr.(1) | Freedman(2) | Park(2) | Pearlman(2) | Peters(2) | Steiger(2) | Stout(2) | Verni(2) |
| Hawaii Fund | None | None | None | None | None | None | None | None | None |
| Insured Fund | None | None | None | None | None | None | None | None | None |
| Kansas Fund | None | None | None | None | None | None | None | None | None |
| Aggregate Dollar | | | | | | | | | |
| Range of Equity | | | | | | | | | |
| Securities Owned in | | | | | | | | | |
| all Registered Funds | | | | | | | | | |
| Overseen by Trustee | | | | | | | | | |
| in the Eaton Vance | | | | | | | | | |
| Family of Funds | over $100,000 | over $100,000 | over $100,000 | over $100,000(3) | over $100,000 | None | None | over $100,000(3) | over $100,000(3) |
| (1) | Interested Trustee. |
| (2) | Noninterested Trustees. |
| (3) | Includes shares which may be deemed to be beneficially owned through the Trustee Deferred Compensation Plan. |
As of December 31, 2008, no noninterested Trustee or any of their immediate family members owned beneficially or of record any class of securities of EVC, EVD or any person controlling, controlled by or under common control with EVC or EVD.
During the calendar years ended December 31, 2007 and December 31, 2008, no noninterested Trustee (or their immediate family members) had:
| 1. | Any direct or indirect interest in Eaton Vance, EVC, EVD or any person controlling, controlled by or under common control with EVC or EVD; |
| 2. | Any direct or indirect material interest in any transaction or series of similar transactions with (i) the Trust or any Fund; (ii) another fund managed by EVC, distributed by EVD or a person controlling, controlled by or under common control with EVC or EVD; (iii) EVC or EVD; (iv) a person controlling, controlled by or under common control with EVC or EVD; or (v) an officer of any of the above; or |
| 3. | Any direct or indirect relationship with (i) the Trust or any Fund; (ii) another fund managed by EVC, distributed by EVD or a person controlling, controlled by or under common control with EVC or EVD; (iii) EVC or EVD; (iv) a person controlling, controlled by or under common control with EVC or EVD; or (v) an officer of any of the above. |
During the calendar years ended December 31, 2007 and December 31, 2008, no officer of EVC, EVD or any person controlling, controlled by or under common control with EVC or EVD served on the Board of Directors of a company where a noninterested Trustee of the Trust or any of their immediate family members served as an officer.
Trustees of the Funds who are not affiliated with the investment adviser may elect to defer receipt of all or a percentage of their annual fees in accordance with the terms of a Trustees Deferred Compensation Plan (the “Trustees’ Plan”). Under the Trustees’ Plan, an eligible Trustee may elect to have his or her deferred fees invested by the Funds in the shares of one or more funds in the Eaton Vance Family of Funds, and the amount paid to the Trustees under the Trustees’ Plan will be determined based upon the performance of such investments. Deferral of Trustees’ fees in accordance with the Trustees’
14
Plan will have a negligible effect on the assets, liabilities, and net income per share of the Funds, and will not obligate the Funds to retain the services of any Trustee or obligate the Funds to pay any particular level of compensation to the Trustee. The Trust does not have a retirement plan for Trustees.
The fees and expenses of the Trustees of the Trust are paid by the Fund (and other series of the Trust). (A Trustee of the Trust who is a member of the Eaton Vance organization receives no compensation from the Trust.) During the fiscal year ended January 31, 2009, the Trustees of the Trust earned the following compensation in their capacities as Trustees from the Trust. For the year ended December 31, 2008, the Trustees earned the following compensation in their capacities as Trustees of the funds in the Eaton Vance fund complex(1):
| | | | | | | | |
| | Benjamin C. | Allen R. | William H. | Ronald A. | Helen Frame | Heidi L. | Lynn A. | Ralph F. |
| Source of Compensation | Esty | Freedman | Park | Pearlman | Peters(1) | Steiger | Stout | Verni |
| Trust(2) | $3,588 | $3,337 | $3,550 | $3,588 | $1,229 | $3,337 | $3,607 | $4,890 |
| Trust and Fund Complex(1) | $212,500 | $204,167 | $209,167(3) | $212,500 | $204,167 | $204,167 | $224,167(4) | $319,167(5) |
| (1) | As of June 1,2009, the Eaton Vance fund complex consists of 175 registered investment companies or series thereof. Ms. Peters was elected as a Trustee effective November 17, 2008, and thus the compensation figures listed for the Trust and Fund Complex are estimated for the calendar year ended December 31, 2008 based on amounts she would have received if she had been a Trustee for the full 2008 calendar year. Norton H. Reamer retired as a Trustee on July 1, 2008. For the fiscal year ended January 31, 2009, Mr. Reamer received Trustees fees of $1,156 from the Trust. For the calendar year ended December 31, 2008, Mr. Reamer received $166,667 from the Trust and Fund Complex. |
| (2) | The Trust consisted of 4 Funds as of January 31, 2009. |
| (3) | Includes $80,000 of deferred compensation. |
| (4) | Includes $45,000 of deferred compensation. |
| (5) | Includes $157,500 of deferred compensation. |
Organization. Each Fund is a series of the Trust, which was organized under Massachusetts law on October 25, 1993 and is operated as an open-endmanagement investment company. The Trust may issue an unlimited number of shares of beneficial interest (no par value per share) in one or more series (such as a Fund). The Trustees of the Trust have divided the shares of each Fund into multiple classes. Each class represents an interest in a Fund, but is subject to different expenses, rights and privileges. The Trustees have the authority under the Declaration of Trust to create additional classes of shares with differing rights and privileges. When issued and outstanding, shares are fully paid and nonassessable by the Trust. Shareholders are entitled to one vote for each full share held. Fractional shares may be voted proportionately. Shares of a Fund will be voted together except that only shareholders of a particular class may vote on matters affecting only that clas s. Shares have no preemptive or conversion rights and are freely transferable. In the event of the liquidation of a Fund, shareholders of each class are entitled to share pro rata in the net assets attributable to that class available for distribution to shareholders.
As permitted by Massachusetts law, there will normally be no meetings of shareholders for the purpose of electing Trustees unless and until such time as less than a majority of the Trustees of the Trust holding office have been elected by shareholders. In such an event the Trustees then in office will call a shareholders’ meeting for the election of Trustees. Except for the foregoing circumstances and unless removed by action of the shareholders in accordance with the Trust’s By-laws, the Trustees shall continue to hold office and may appoint successor Trustees. The Trust’s By-laws provide that no person shall serve as a Trustee if shareholders holding two-thirds of the outstanding shares have removed him or her from that office either by a written declaration filed with the Trust’s custodian or by votes cast at a meeting called for that purpose. The By-laws further provide that under certain circumstances the shareholders may call a meeting to remove a Trustee and that the Trust is required to provide assistance in communication with shareholders about such a meeting.
The Trust’s Declaration of Trust may be amended by the Trustees when authorized by vote of a majority of the outstanding voting securities of the Trust, the financial interests of which are affected by the amendment. The Trustees may also amend the Declaration of Trust without the vote or consent of shareholders to change the name of the Trust or any series or to make such other changes (such as reclassifying series or classes of shares or restructuring the Trust) as do not have a materially adverse effect on the financial interests of shareholders or if they deem it necessary to conform it to applicable federal or state laws or regulations. The Trust’s By-laws provide that the Trust will indemnify its Trustees and officers against liabilities and expenses incurred in connection with any litigation or proceeding in which they may be involved because of their offices with the Trust. However, no indemnification will be provided to any Trustee or officer for any liability to the Trust or shareholders by reason of willful misfeasance, bad faith, gross negligence or reckless disregard of the duties involved in the conduct of his or her office.
The Trust or any series or class thereof may be terminated by: (1) the affirmative vote of the holders of not less than two-thirds of the shares outstanding and entitled to vote at any meeting of shareholders of the Trust or the appropriate series or class thereof, or by an instrument or instruments in writing without a meeting, consented to by the holders of two-thirds
15
of the shares of the Trust or a series or class thereof, provided, however, that, if such termination is recommended by the Trustees, the vote of a majority of the outstanding voting securities of the Trust or a series or class thereof entitled to vote thereon shall be sufficient authorization; or (2) by means of an instrument in writing signed by a majority of the Trustees, to be followed by a written notice to shareholders stating that a majority of the Trustees has determined that the continuation of the Trust or a series or a class thereof is not in the best interest of the Trust, such series or class or of their respective shareholders.
Under Massachusetts law, if certain conditions prevail, shareholders of a Massachusetts business trust (such as the Trust) could be deemed to have personal liability for the obligations of the Trust. Numerous investment companies registered under the 1940 Act have been formed as Massachusetts business trusts, and management is not aware of an instance where such liability has been imposed. The Trust’s Declaration of Trust contains an express disclaimer of liability on the part of Fund shareholders and the Trust’s By-laws provide that the Trust shall assume the defense on behalf of any Fund shareholders. The Declaration of Trust also contains provisions limiting the liability of a series or class to that series or class. Moreover, the Trust’s By-laws also provide for indemnification out of Fund property of any shareholder held personally liable solely by reason of being or having been a shareholder for all loss or expense arising from such liability. The assets of eac h Fund are readily marketable and will ordinarily substantially exceed its liabilities. In light of the nature of each Fund’s business and the nature of its assets, management believes that the possibility of the Fund’s liability exceeding its assets, and therefore the shareholder’s risk of personal liability, is remote.
Proxy Voting Policy. The Board of Trustees of the Trust have adopted a proxy voting policy and procedures (the “Fund Policy”), pursuant to which the Trustees have delegated proxy voting responsibility to the investment adviser and adopted the proxy voting policies and procedures of the investment adviser (the “Policies”). An independent proxy voting service has been retained to assist in the voting of Fund proxies through the provision of vote analysis, implementation and recordkeeping and disclosure services. The Trustees will review each Fund’s proxy voting records from time to time and will annually consider approving the Policies for the upcoming year. For a copy of the Fund Policy and Adviser Policies, see Appendix G and Appendix H, respectively. Information on how each Fund voted proxies relating to portfolio securities during the most recent 12-month period ended June 30 is available (1) without charge, upon request, by calling 1- 800-262-1122, and (2) on the SEC’s website at http://www.sec.gov.
INVESTMENT ADVISORY AND ADMINISTRATIVE SERVICES
Investment Advisory Services. The investment adviser manages the investments and affairs of each Fund and provides related office facilities and personnel subject to the supervision of the Trust’s Board of Trustees. The investment adviser furnishes investment research, advice and supervision, furnishes an investment program and determines what securities will be purchased, held or sold by each Fund and what portion, if any, of the Fund’s assets will be held uninvested. Each Investment Advisory Agreement requires the investment adviser to pay the salaries and fees of all officers and Trustees of the Trust who are members of the investment adviser’s organization and all personnel of the investment adviser performing services relating to research and investment activities.
For a description of the compensation that each Fund pays the investment adviser, see the prospectus. The following table sets forth the net assets of each Fund and the advisory fees for the three fiscal years ended January 31, 2009.
| | | | |
| | | Advisory Fee for Fiscal Years Ended |
| Fund | Net Assets at 1/31/09 | 1/31/09 | 1/31/08 | 1/31/07 |
| Hawaii | $17,007,671 | $26,795 | $31,186 | $26,448 |
| Insured | 47,481,275 | 86,722 | 91,029 | 103,599 |
| Kansas | 32,936,994 | 74,983 | 68,067 | 43,449 |
Each Investment Advisory Agreement with the investment adviser continues in effect from year to year so long as such continuance is approved at least annually (i) by the vote of a majority of the noninterested Trustees of the Trust cast in person at a meeting specifically called for the purpose of voting on such approval and (ii) by the Board of Trustees of the Trust or by vote of a majority of the outstanding voting securities of the Fund. Each Agreement may be terminated at any time without penalty on sixty (60) days’ written notice by the Board of Trustees of either party, or by vote of the majority of the outstanding voting securities of the Fund, and the Agreement will terminate automatically in the event of its assignment. Each Agreement provides that the investment adviser may render services to others. Each Agreement also provides that the investment adviser shall not be liable for any loss incurred in connection with the performance of its duties, or action taken or o mitted under the Agreement, in the absence of willful misfeasance, bad faith, gross negligence in the performance of its duties or by reason of its reckless disregard of its obligations and duties thereunder, or for any losses sustained in the acquisition, holding or disposition of any security or other investment.
16
Information About BMR and Eaton Vance. BMR and Eaton Vance are business trusts organized under the laws of The Commonwealth of Massachusetts. Eaton Vance, Inc. (“EV”) serves as trustee of BMR and Eaton Vance. EV and Eaton Vance are wholly-owned subsidiaries of Eaton Vance Corp. (“EVC”), a Maryland corporation and publicly-held holding company. BMR is an indirect subsidiary of EVC. EVC through its subsidiaries and affiliates engages primarily in investment management, administration and marketing activities. The Directors of EVC are Thomas E. Faust Jr., Ann E. Berman, Leo I. Higdon, Jr., Dorothy E. Puhy, Duncan W. Richardson, Winthrop H. Smith, Jr. and Richard A. Spillane Jr. All shares of the outstanding Voting Common Stock of EVC are deposited in a Voting Trust, the Voting Trustees of which are Mr. Faust, Jeffrey P. Beale, Cynthia J. Clemson, Maureen A. Gemma, Lisa Jones, Brian D. Langstraat, Michael R. Mach, Robert B. MacIntosh, Frederick S . Marius, Thomas M. Metzold, Scott H. Page, Mr. Richardson, Walter A. Row, III, G. West Saltonstall, Judith A. Saryan, David M. Stein, Payson F. Swaffield, Mark S. Venezia, Michael W. Weilheimer, Robert J. Whelan and Matthew J. Witkos (all of whom are officers of Eaton Vance or its affiliates). The Voting Trustees have unrestricted voting rights for the election of Directors of EVC. All of the outstanding voting trust receipts issued under said Voting Trust are owned by certain of the officers of BMR and Eaton Vance who are also officers, or officers and Directors of EVC and EV. As indicated under “Management and Organization,” all of the officers of the Trust (as well as Mr. Faust who is also a Trustee) hold positions in the Eaton Vance organization.
Code of Ethics. The investment adviser, principal underwriter, and each Fund have adopted Codes of Ethics governing personal securities transactions. Under the Codes, employees of Eaton Vance and the principal underwriter may purchase and sell securities (including securities held or eligible for purchase by a Fund) subject to the provisions of the Codes and certain employees are also subject to pre-clearance, reporting requirements and other procedures.
Portfolio Managers. The portfolio manager of each Fund is listed below. Each portfolio manager manages other investment companies and/or investment accounts in addition to a Fund. The following tables show, as of a Fund’s most recent fiscal year end, the number of accounts each portfolio manager managed in each of the listed categories and the total assets in the accounts managed within each category. The table also shows the number of accounts with respect to which the advisory fee is based on the performance of the account, if any, and the total assets in those accounts.
| | | | |
| | Number of | Total Assets of | Number of Accounts | Total Assets of Accounts |
| Hawaii Fund | All Accounts | All Accounts* | Paying a Performance Fee | Paying a Performance Fee* |
| Robert B. MacIntosh | | | | |
| Registered Investment Companies | 10 | $2,078.7 | 0 | $0 |
| Other Pooled Investment Vehicles | 0 | $ 0 | 0 | $0 |
| Other Accounts | 307 | $ 268.7 | 0 | $0 |
| | | | | |
| | Number of | Total Assets of | Number of Accounts | Total Assets of Accounts |
| Insured Fund | All Accounts | All Accounts* | Paying a Performance Fee | Paying a Performance Fee |
| Craig R. Brandon | | | | |
| Registered Investment Companies | 11 | $1,208.8 | 0 | $0 |
| Other Pooled Investment Vehicles | 0 | $ 0 | 0 | $0 |
| Other Accounts | 0 | $ 0 | 0 | $0 |
| | | | | |
| | Number of | Total Assets of | Number of Accounts | Total Assets of Accounts |
| Kansas Fund | All Accounts | All Accounts* | Paying a Performance Fee | Paying a Performance Fee |
| Adam A. Weigold | | | | |
| Registered Investment Companies | 12 | $945.9 | 0 | $0 |
| Other Pooled Investment Vehicles | 0 | $ 0 | 0 | $0 |
| Other Accounts | 0 | $ 0 | 0 | $0 |
* In millions of dollars.
The following table shows the dollar range of shares beneficially owned of a Fund by its portfolio manager as of the Fund’s most recent fiscal year ended January 31, 2009 and in the Eaton Vance Family of Funds as of December 31, 2008. The purpose of the Hawaii Municipals Fund and Kansas Municipals Fund is to provide tax-exempt income to persons subject
17
to taxation in those states. In most cases, each Fund’s portfolio manager is not subject to such taxation. In addition, in most cases, Fund shares are not registered for sale in the state of the portfolio manager’s residence.
| | |
| | | Aggregate Dollar Range of Equity |
| | Dollar Range of Equity Securities | Securities Owned in all Registered Funds in |
| Fund Name and Portfolio Manager | Owned in the Fund | the Eaton Vance Family of Funds |
| Hawaii Municipals Fund | | |
| Robert B. MacIntosh | None | $500,001-$1,000,000 |
| Insured Municipals Fund | | |
| Craig R. Brandon | None | $100,001 - $500,000 |
| Kansas Municipals Fund | | |
| Adam A. Weigold | None | $100,001 – $500,000 |
It is possible that conflicts of interest may arise in connection with a portfolio manager’s management of a Fund’s investments on the one hand and the investments of other accounts for which the portfolio manager is responsible on the other. For example, a portfolio manager may have conflicts of interest in allocating management time, resources and investment opportunities among the Fund and other accounts he advises. In addition, due to differences in the investment strategies or restrictions between a Fund and the other accounts, a portfolio manager may take action with respect to another account that differs from the action taken with respect to the Fund. In some cases, another account managed by a portfolio manager may compensate the investment adviser based on the performance of the securities held by that account. The existence of such a performance based fee may create additional conflicts of interest for the portfolio manager in the allocation of management time, resources and investment opportunities. Whenever conflicts of interest arise, the portfolio manager will endeavor to exercise his discretion in a manner that he believes is equitable to all interested persons. The investment adviser has adopted several policies and procedures designed to address these potential conflicts including a code of ethics and policies that govern the investment adviser’s trading practices, including among other thing the aggregation and allocation of trades among clients, brokerage allocation, cross trades and best execution.
Compensation Structure for BMR. Compensation of the investment adviser’s portfolio managers and other investment professionals has three primary components: (1) a base salary, (2) an annual cash bonus, and (3) annual stock-based compensation consisting of options to purchase shares of EVC’s nonvoting common stock and restricted shares of EVC’s nonvoting common stock. The investment adviser’s investment professionals also receive certain retirement, insurance and other benefits that are broadly available to the investment adviser’s employees. Compensation of the investment adviser’s investment professionals is reviewed primarily on an annual basis. Cash bonuses, stock-based compensation awards, and adjustments in base salary are typically paid or put into effect at or shortly after the October 31st fiscal year end of EVC.
Method to Determine Compensation. The investment adviser compensates its portfolio managers based primarily on the scale and complexity of their portfolio responsibilities and the total return performance of managed funds and accounts versus appropriate peer groups or benchmarks. In addition to rankings within peer groups of funds on the basis of absolute performance, consideration may also be given to relative risk-adjusted performance. Risk-adjusted performance measures include, but are not limited to, the Sharpe Ratio. Performance is normally based on periods ending on the September 30th preceding fiscal year end. Fund performance is normally evaluated primarily versus peer groups of funds as determined by Lipper Inc. and/or Morningstar, Inc. When a fund’s peer group as determined by Lipper or Morningstar is deemed by the investment adviser’s management not to provide a fair comparison, performance may instead be evaluated primarily against a custom peer group. In evaluating the performance of a fund and its manager, primary emphasis is normally placed on three-year performance, with secondary consideration of performance over longer and shorter periods. For funds that are tax-managed or otherwise have an objective of after-tax returns, performance is measured net of taxes. For other funds, performance is evaluated on a pre-tax basis. For funds with an investment objective other than total return (such as current income), consideration will also be given to the fund’s success in achieving its objective. For managers responsible for multiple funds and accounts, investment performance is evaluated on an aggregate basis, based on averages or weighted averages among managed funds and accounts. Funds and accounts that have performance-based advisory fees are not accorded disproportionate weightings in measuring aggregate portfolio manager performance.
The compensation of portfolio managers with other job responsibilities (such as heading an investment group or providing analytical support to other portfolios) will include consideration of the scope of such responsibilities and the managers’ performance in meeting them.
18
The investment adviser seeks to compensate portfolio managers commensurate with their responsibilities and performance, and competitive with other firms within the investment management industry. The investment adviser participates in investment-industry compensation surveys and utilizes survey data as a factor in determining salary, bonus and stock-based compensation levels for portfolio managers and other investment professionals. Salaries, bonuses and stock-based compensation are also influenced by the operating performance of the investment adviser and its parent company. The overall annual cash bonus pool is based on a substantially fixed percentage of pre-bonus operating income. While the salaries of the investment adviser’s portfolio managers are comparatively fixed, cash bonuses and stock-based compensation may fluctuate significantly from year to year, based on changes in manager performance and other factors as described herein. For a high performing portfolio manage r, cash bonuses and stock-based compensation may represent a substantial portion of total compensation.
Administrative Services. As indicated in the prospectus, Eaton Vance serves as administrator of each Fund, but currently receives no compensation for providing administrative services to the Fund. Under its Administrative Services Agreement, Eaton Vance has been engaged to administer each Fund’s affairs, subject to the supervision of the Trustees of the Trust, and shall furnish office space and all necessary office facilities, equipment and personnel for administering the affairs of each Fund.
Sub-Transfer Agency Services. Eaton Vance also serves as sub-transfer agent for each Fund. As sub-transfer agent, Eaton Vance performs the following services directly on behalf of a Fund: (1) provides call center services to financial intermediaries and shareholders; (2) answers written inquiries related to shareholder accounts (matters relating to portfolio management, distribution of shares and other management policy questions will be referred to a Fund); (3) furnishes an SAI to any shareholder who requests one in writing or by telephone from a Fund; and (4) processes transaction requests received via telephone. For the sub-transfer agency services it provides, Eaton Vance receives an aggregate annual fee equal to the lesser of $2.5 million or the actual expenses incurred by Eaton Vance in the performance of those services. This fee is paid to Eaton Vance by a Fund’s transfer agent from fees it receives from the Eaton Vance funds. Each Fund will pay a pr o rata share of such fee. For the fiscal year ended January 31, 2009, the transfer agent accrued for or paid to Eaton Vance the following amounts for sub-transfer agency services performed on behalf of each Fund:
| | |
| Hawaii | Insured | Kansas |
| $504 | $641 | $872 |
Expenses. Each Fund is responsible for all expenses not expressly stated to be payable by another party (such as expenses required to be paid pursuant to an agreement with the investment adviser, the principal underwriter or the administrator). In the case of expenses incurred by the Trust, each Fund is responsible for its pro rata share of those expenses. The only expenses of a Fund allocated to a particular class are those incurred under the Distribution Plan applicable to that class, the fee paid to the principal underwriter for handling repurchase transactions and certain other class-specific expenses.
Principal Underwriter. Eaton Vance Distributors, Inc. (“EVD”), Two International Place, Boston, MA 02110 is the principal underwriter of each Fund. The principal underwriter acts as principal in selling shares under a Distribution Agreement with the Trust. The expenses of printing copies of prospectuses used to offer shares and other selling literature and of advertising are borne by the principal underwriter. The fees and expenses of qualifying and registering and maintaining qualifications and registrations of a Fund and its shares under federal and state securities laws are borne by the Fund. The Distribution Agreement is renewable annually by the Trust’s Board of Trustees (including a majority of the noninterested Trustees who have no direct or indirect financial interest in the operation of the Distribution Plan or the Distribution Agreement), may be terminated on sixty days’ notice either by such Trustees or by vote of a majority of the outstanding Class A, Class B and Class C shares or on six months’ notice by the principal underwriter and is automatically terminated upon assignment. The principal underwriter distributes shares on a “best efforts” basis under which it is required to take and pay for only such shares as may be sold. EVD is a direct, wholly-owned subsidiary of EVC. Mr. Faust is a Director of EVD.
Custodian. State Street Bank and Trust Company (“State Street“), 200 Clarendon Street, Boston, MA 02116, serves as custodian to each Fund. State Street has custody of all cash and securities of a Fund, maintains the general ledger of each Fund and computes the daily net asset value of shares of each Fund. In such capacity it attends to details in connection with the sale, exchange, substitution, transfer or other dealings with each Fund’s investments, receives and disburses all funds and performs various other ministerial duties upon receipt of proper instructions from the Trust. State Street provides services in connection with the preparation of shareholder reports and the electronic filing of such reports with the SEC. EVC and its affiliates and their officers and employees from time to time have transactions with various banks, including
19
State Street. It is Eaton Vance’s opinion that the terms and conditions of such transactions were not and will not be influenced by existing or potential custodial or other relationships between each Fund and such banks.
Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm. Deloitte & Touche LLP, 200 Berkeley Street, Boston, MA 02116, is the independent registered public accounting firm of each Fund, providing audit services and assistance and consultation with respect to the preparation of filings with the SEC.
Transfer Agent. PNC Global Investment Servicing, P.O. Box 9653, Providence, RI 02940-9653, serves as transfer and dividend disbursing agent for each Fund.
| CALCULATION OF NET ASSET VALUE |
The net asset value of each Fund is computed by State Street (as agent and custodian for each Fund) by subtracting the liabilities of the Fund from the value of its total assets. Each Fund will be closed for business and will not price their respective shares on the following business holidays and any other business day that the New York Stock Exchange (the "Exchange") is closed: New Year’s Day, Martin Luther King, Jr. Day, Presidents’ Day, Good Friday, Memorial Day, Independence Day, Labor Day, Thanksgiving Day and Christmas Day.
Inasmuch as the market for municipal obligations is a dealer market with no central trading location or continuous quotation system, it is not feasible to obtain last transaction prices for most municipal obligations held by a Fund, and such obligations, including those purchased on a when-issued basis, will normally be valued on the basis of valuations furnished by a pricing service. The pricing service uses information with respect to transactions in bonds, quotations from bond dealers, market transactions in comparable securities, various relationships between securities, and yield to maturity in determining value. Taxable obligations, if any, are normally valued on the basis of valuations furnished by a pricing service. Open futures positions on debt securities are valued at the most recent settlement prices, unless such price does not reflect the fair value of the contract, in which case the positions will be valued by or at the direction of the Trustees. Other assets are valu ed at fair value using methods determined in good faith by or at the direction of the Trustees considering relevant factors, data and information including the market value of freely tradable securities of the same class in the principal market on which such securities are normally traded.
| PURCHASING AND REDEEMING SHARES |
Additional Information About Purchases. Fund shares are offered for sale only in states where they are registered. Fund shares are continuously offered through investment dealers which have entered into agreements with the principal underwriter. Shares of a Fund are sold at the offering price, which is the net asset value plus the initial sales charge, if any. The Fund receives the net asset value. The principal underwriter receives the sales charge, all or a portion of which may be reallowed to the investment dealers responsible for selling Fund shares. The sales charge table in the prospectus is applicable to purchases of a Fund alone or in combination with purchases of certain other funds offered by the principal underwriter, made at a single time by (i) an individual, or an individual, his or her spouse and their children under the age of twenty-one, purchasing shares for his or their own account, and (ii) a trustee or other fiduciary purchasing shares for a single trust estate or a single fiduciary account. The table is also presently applicable to (1) purchases of Class A shares pursuant to a written Statement of Intention; or (2) purchases of Class A shares pursuant to the Right of Accumulation and declared as such at the time of purchase. See “Sales Charges”.
In connection with employee benefit or other continuous group purchase plans, a Fund may accept initial investments of less than the minimum investment amount on the part of an individual participant. In the event a shareholder who is a participant of such a plan terminates participation in the plan, his or her shares will be transferred to a regular individual account. However, such account will be subject to the right of redemption by a Fund as described below.
Suspension of Sales. The Trust may, in its absolute discretion, suspend, discontinue or limit the offering of one or more of its classes of shares at any time. In determining whether any such action should be taken, the Trust’s management intends to consider all relevant factors, including (without limitation) the size of a Fund or class, the investment climate and market conditions, the volume of sales and redemptions of shares, and (if applicable) the amount of uncovered distribution charges of the principal underwriter. The Class A, Class B and Class C Distribution Plans may continue in effect and payments may be made under the Plans following any such suspension, discontinuance or limitation of the offering of shares; however, there is no contractual obligation to continue any Plan for any particular period of time. Suspension of the offering of shares would not, of course, affect a shareholder’s ability to redeem shares.
Additional Information About Redemptions. The right to redeem shares of a Fund can be suspended and the payment of the redemption price deferred when the Exchange is closed (other than for customary weekend and holiday closings), during periods when trading on the Exchange is restricted as determined by the SEC, or during any emergency as
20
determined by the SEC which makes it impracticable for a Fund to dispose of its securities or value its assets, or during any other period permitted by order of the SEC for the protection of investors.
Due to the high cost of maintaining small accounts, the Trust reserves the right to redeem accounts with balances of less than $750. Prior to such a redemption, shareholders will be given 60 days’ written notice to make an additional purchase. However, no such redemption would be required by the Trust if the cause of the low account balance was a reduction in the net asset value of shares. No CDSC or redemption fees, if applicable, will be imposed with respect to such involuntary redemptions.
While normally payments will be made in cash for redeemed shares, the Trust, subject to compliance with applicable regulations, has reserved the right to pay the redemption price of shares of a Fund, either totally or partially, by a distribution in kind of readily marketable securities. The securities so distributed would be valued pursuant to the valuation procedures described in this SAI. If a shareholder received a distribution in kind, the shareholder could incur brokerage or other charges in converting the securities to cash.
Systematic Withdrawal Plan. The transfer agent will send to the shareholder regular monthly or quarterly payments of any permitted amount designated by the shareholder based upon the value of the shares held. The checks will be drawn from share redemptions and hence, may require the recognition of taxable gain or loss. Income dividends and capital gains distributions in connection with withdrawal plan accounts will be credited at net asset value as of the record date for each distribution. Continued withdrawals in excess of current income will eventually use up principal, particularly in a period of declining market prices. A shareholder may not have a withdrawal plan in effect at the same time he or she has authorized Bank Automated Investing or is otherwise making regular purchases of Fund shares. The shareholder, the transfer agent or the principal underwriter may terminate the withdrawal plan at any time without penalty.
Other Information. A Fund’s net asset value per share is normally rounded to two decimal places. In certain situations (such as a merger, share split or a purchase or sale of shares that represents a significant portion of a share class), the administrator may determine to extend the calculation of the net asset value per share to additional decimal places to ensure that neither the value of the Fund nor a shareholder’s shares is diluted materially as the result of a purchase or sale or other transaction.
In circumstances where a financial intermediary has entered into an agreement with a Fund or its principal underwriter to exchange shares from one class of the Fund to another, such exchange shall be permitted and any applicable redemption fee will not be imposed in connection with such transaction, provided that the class of shares acquired in the exchange is subject to the same redemption fee. In connection with the exemption from the Funds’ policies to discourage short-term trading and market timing and the applicability of any redemption fee to a redemption, asset allocation programs include an investment vehicle that allocates its assets among investments in concert with changes in a model portfolio.
Dealer Commissions. The principal underwriter may, from time to time, at its own expense, provide additional incentives to investment dealers which employ registered representatives who sell Fund shares and/or shares of other funds distributed by the principal underwriter. In some instances, such additional incentives may be offered only to certain investment dealers whose representatives sell or are expected to sell significant amounts of shares. In addition, the principal underwriter may from time to time increase or decrease the sales commissions payable to investment dealers. The principal underwriter may allow, upon notice to all investment dealers with whom it has agreements, discounts up to the full sales charge during the periods specified in the notice. During periods when the discount includes the full sales charge, such investment dealers may be deemed to be underwriters as that term is defined in the 1933 Act.
Purchases at Net Asset Value. Class A shares may be sold at net asset value to current and retired Directors and Trustees of Eaton Vance funds and portfolios; to clients (including custodial, agency, advisory and trust accounts) and current and retired officers and employees of Eaton Vance, its affiliates and other investment advisers and sub-advisers of Eaton Vance sponsored funds; and to such persons’ spouses, parents, siblings and lineal descendants and their beneficial accounts. Such shares may also be issued at net asset value (1) in connection with the merger (or similar transaction) of an investment company (or series or class thereof) or personal holding company with a Fund (or class thereof), (2) to investors making an investment as part of a fixed fee program whereby an entity unaffiliated with the investment adviser provides investment services, such as management, brokerage and custody, (3) to investment advisors, financial planners or other int ermediaries who place trades for their own accounts or the accounts of their clients and who charge a management, consulting or similar ongoing fee for their services; clients of such investment advisors, financial planners or other intermediaries who place trades for their own accounts if the accounts are linked to the master account of such investment advisor, financial planner or other intermediary on the books and records of the broker or agent; financial intermediaries who have entered into an agreement with the principal underwriter to offer Class A shares through a no-load platform, (4)
21
to officers and employees of the Fund custodian and the transfer agent and (5) in connection with the ReFlow liquidity program. Class A shares may also be sold at net asset value to registered representatives and employees of investment dealers. Sales charges generally are waived because either (i) there is no sales effort involved in the sale of shares or (ii) the investor is paying a fee (other than the sales charge) to the investment dealer involved in the sale. Any new or revised sales charge or CDSC waiver will be prospective only.
Waiver of Investment Minimums. In addition to waivers described in the prospectus, minimum investment amounts are waived for current and retired Directors and Trustees of Eaton Vance funds and portfolios, clients (including custodial, agency, advisory and trust accounts), current and retired officers and employees of Eaton Vance, its affiliates and other investment advisers and sub-advisers of Eaton Vance sponsored funds, and for such persons’ spouses, parents, siblings and lineal descendants and their beneficial accounts. The minimum initial investment amount is also waived for officers and employees of a Fund’s custodian and transfer agent. Investments in a Fund by ReFlow in connection with the ReFlow liquidity program are also not subject to the minimum investment amount.
Statement of Intention. If it is anticipated that $25,000 or more of Class A shares and shares of other funds exchangeable for Class A shares of another Eaton Vance fund will be purchased within a 13-month period, the Statement of Intention section of the account application should be completed so that shares may be obtained at the same reduced sales charge as though the total quantity were invested in one lump sum. Shares eligible for the right of accumulation (see below) as of the date of the Statement and purchased during the 13-month period will be included toward the completion of the Statement. If you make a Statement of Intention, the transfer agent is authorized to hold in escrow sufficient shares (5% of the dollar amount specified in the Statement) which can be redeemed to make up any difference in sales charge on the amount intended to be invested and the amount actually invested. A Statement of Intention does not obligate the shareholder to purchase or the Fund to sell the full amount indicated in the Statement.
If the amount actually purchased during the 13-month period is less than that indicated in the Statement, the shareholder will be requested to pay the difference between the sales charge applicable to the shares purchased and the sales charge paid under the Statement of Intention. If the payment is not received in 20 days, the appropriate number of escrowed shares will be redeemed in order to realize such difference. If the total purchases during the 13-month period are large enough to qualify for a lower sales charge than that applicable to the amount specified in the Statement, all transactions will be computed at the expiration date of the Statement to give effect to the lower sales charge. Any difference will be refunded to the shareholder in cash or applied to the purchase of additional shares, as specified by the shareholder. This refund will be made by the investment dealer and the principal underwriter. If at the time of the recomputation, the investment dealer for the account has changed, the adjustment will be made only on those shares purchased through the current investment dealer for the account.
Right of Accumulation. Under the right of accumulation, the applicable sales charge level is calculated by aggregating the dollar amount of the current purchase and the value (calculated at the maximum current offering price) of shares owned by the shareholder. Shares of Eaton Vance Cash Management Fund and Eaton Vance Tax Free Reserves cannot be accumulated for purposes of this privilege. The sales charge on the shares being purchased will then be applied at the rate applicable to the aggregate. Share purchases eligible for the right of accumulation are described under "Sales Charges" in the prospectus. For any such discount to be made available at the time of purchase a purchaser or his or her investment dealer must provide the principal underwriter (in the case of a purchase made through an investment dealer) or the transfer agent (in the case of an investment made by mail) with sufficient information to permit verification that the purchase order qualifies for the accumulation privilege. Confirmation of the order is subject to such verification. The right of accumulation privilege may be amended or terminated at any time as to purchases occurring thereafter.
Conversion Feature. Class B shares held for eight years will automatically convert to Class A shares. For purposes of this conversion, all distributions paid on Class B shares which the shareholder elects to reinvest in Class B shares will be considered to be held in a separate sub-account. Upon the conversion of Class B shares not acquired through the reinvestment of distributions, a pro rata portion of the Class B shares held in the sub-account will also convert to Class A shares. This portion will be determined by the ratio that the Class B shares being converted bears to the total of Class B shares (excluding shares acquired through reinvestment) in the account. This conversion feature is subject to the continuing availability of a ruling from the Internal Revenue Service or an opinion of counsel that the conversion is not taxable for federal income tax purposes.
Distribution Plans
The Trust has in effect a compensation-type Distribution Plan (the “Class A Plan”) pursuant to Rule 12b-1 under the 1940 Act for Class A shares. The Class A Plan is designed to (i) finance activities which are primarily intended to result in the distribution and sales of Class A shares and to make payments in connection with the distribution of such shares and (ii)
22
pay service fees for personal services and/or the maintenance of shareholder accounts to the principal underwriter, investment dealers and other persons. The distribution and service fees payable under the Class A Plan shall not exceed 0.25% of the average daily net assets attributable to Class A shares for any fiscal year. Class A distribution and service fees are paid monthly in arrears. For the distribution and service fees paid by Class A shares, see Appendix A.
The Trust also has in effect compensation-type Distribution Plans (the “Class B and Class C Plans“) pursuant to Rule 12b-1 under the 1940 Act for each Fund’s Class B and Class C shares. On each sale of shares (excluding reinvestment of distributions) a Class will pay the principal underwriter amounts representing (i) sales commissions equal to 5% for Class B shares and 6.25% for Class C shares of the amount received by a Fund for each Class share sold and (ii) interest at the rate of 1% over the prime rate then reported in The Wall Street Journal applied to the outstanding amounts owed to the principal underwriter, so-called “uncovered distribution charges”. Each Class pays the principal underwriter a distribution fee, accrued daily and paid monthly, at an annual rate not exceeding 0.75% of its average daily net assets to finance the distribution of its shares. Such fees compensate the principal underwriter for the sales commissions paid by it to investment dealers on the sale of shares, for other distribution expenses (such as personnel, overhead, travel, printing and postage) and for interest expenses. The principal underwriter currently pays an up-front sales commission (except on exchange transactions and reinvestments) of 4% of the purchase price of Class B shares and 0.80% of the purchase price of Class C shares, and an up-front service fee of 0.20% on Class C shares. Distribution fees paid by a Class and CDSCs paid to the Fund by redeeming Class shareholders reduce the outstanding uncovered distribution charges of the Class. Whenever there are no outstanding uncovered distribution charges of a Class, the Class discontinues payment of distribution fees.
The Trustees of the Trust believe that each Plan will be a significant factor in the expected growth of each Fund’s assets, and will result in increased investment flexibility and advantages which have benefited and will continue to benefit the Fund and its shareholders. The Eaton Vance organization will profit by reason of the operation of each Class B and Class C Plan through an increase in Fund assets and if at any point in time the aggregate amounts received by the principal underwriter pursuant to the Plans and from CDSCs have exceeded the total expenses incurred in distributing Class B and Class C shares. Because payments to the principal underwriter under the Class B and Class C Plans are limited, uncovered distribution charges (sales expenses of the principal underwriter plus interest, less the above fees and CDSCs received by it) may exist indefinitely. For sales commissions, CDSCs and uncovered distribution charges, see Appendix B and Appendix C.
The Class B and Class C Plans also authorize the payment of service fees to the principal underwriter, investment dealers and other persons in amounts not exceeding an annual rate of 0.25% of its average daily net assets for personal services, and/or the maintenance of shareholder accounts. For Class B, this fee is paid monthly in arrears based on the value of shares sold by such persons. For Class C, investment dealers currently receive (a) a service fee (except on exchange transactions and reinvestments) at the time of sale equal to 0.20% of the purchase price of Class C shares sold by such dealer, and (b) monthly service fees approximately equivalent to 1/12 of 0.20% of the value of Class C shares sold by such dealer. During the first year after a purchase of Class C shares, the principal underwriter will retain the service fee as reimbursement for the service fee payment made to investment dealers at the time of sale. For the service fees paid, see Appendix B and Appendix C.
A Plan continues in effect from year to year so long as such continuance is approved at least annually by the vote of both a majority of (i) the noninterested Trustees of the Trust who have no direct or indirect financial interest in the operation of the Plan or any agreements related to the Plan (the “Plan Trustees”) and (ii) all of the Trustees then in office. A Plan may be terminated at any time by vote of a majority of the Plan Trustees or by a vote of a majority of the outstanding voting securities of the applicable Class. Quarterly Trustee review of a written report of the amount expended under the Plan and the purposes for which such expenditures were made is required. A Plan may not be amended to increase materially the payments described therein without approval of the shareholders of the affected Class and the Trustees. So long as a Plan is in effect, the selection and nomination of the noninterested Trustees shall be committed to the discretion of such Trustees . The Trustees, including the Plan Trustees, initially approved the current Plan(s) on June 23, 1997 (November 14, 2005 in the case of the Class C Plan for the Insured and Kansas Funds and August 6, 2007 in the case of the Class C Plan for the Hawaii Fund). Any Trustee of the Trust who is an “interested” person of the Trust has an indirect financial interest in a Plan because his or her employer (or affiliates thereof) receives distribution and/or service fees under the Plan or agreements related thereto.
Performance Calculations. Average annual total return before deduction of taxes (“pre-tax return”) is determined by multiplying a hypothetical initial purchase order of $1,000 by the average annual compound rate of return (including capital appreciation/depreciation, and distributions paid and reinvested) for the stated period and annualizing the result. The calculation assumes (i) that all distributions are reinvested at net asset value on the reinvestment dates during the period, (ii) the deduction of the maximum of any initial sales charge from the initial $1,000 purchase, (iii) a complete
23
redemption of the investment at the end of the period, and (iv) the deduction of any applicable CDSC at the end of the period.
Average annual total return after the deduction of taxes on distributions is calculated in the same manner as pre-tax return except the calculation assumes that any federal income taxes due on distributions are deducted from the distributions before they are reinvested. Average annual total return after the deduction of taxes on distributions and taxes on redemption also is calculated in the same manner as pre-tax return except the calculation assumes that (i) any federal income taxes due on distributions are deducted from the distributions before they are reinvested and (ii) any federal income taxes due upon redemption are deducted at the end of the period. After-tax returns are based on the highest federal income tax rates in effect for individual taxpayers as of the time of each assumed distribution and redemption (taking into account their tax character), and do not reflect the impact of state and local taxes. In calculating after-tax returns, the net value of any federal income tax credits available to shareholders is applied to reduce federal income taxes payable on distributions at or near year-end and, to the extent the net value of such credits exceeds such distributions, is then assumed to be reinvested in additional Fund shares at net asset value on the last day of the fiscal year in which the credit was generated or, in the case of certain tax credits, on the date on which the year-end distribution is paid. For pre-tax and after-tax total return information, see Appendix A, Appendix B and Appendix C.
In addition to the foregoing total return figures, each Fund may provide pre-tax and after-tax annual and cumulative total return, as well as the ending redeemable cash value of a hypothetical investment. If shares are subject to a sales charge, total return figures may be calculated based on reduced sales charges or at net asset value. These returns would be lower if the full sales charge was imposed. After-tax returns may also be calculated using different tax rate assumptions and taking into account state and local income taxes as well as federal taxes.
Yield is computed pursuant to a standardized formula by dividing the net investment income per share earned during a recent thirty-day period by the maximum offering price (including the maximum of any initial sales charge) per share on the last day of the period and annualizing the resulting figure. Net investment income per share is calculated from the yields to maturity of all debt obligations held based on prescribed methods, reduced by accrued expenses for the period with the resulting number being divided by the average daily number of shares outstanding and entitled to receive distributions during the period. Yield figures do not reflect the deduction of any applicable CDSC, but assume the maximum of any initial sales charge. (Actual yield may be affected by variations in sales charges on investments.) A tax-equivalent yield is computed by using the tax-exempt yield and dividing by one minus a stated tax rate. The stated tax rate will reflect the federal income and certain s tate (if any) taxes applicable to investors in a particular tax bracket and may reflect certain assumptions relating to tax exemptions and deductions. The tax-equivalent yield will differ for investors in other tax brackets or for whom the assumed exemptions and deductions are not available. Tax-equivalent yield is designed to show the approximate yield a taxable investment would have to earn to produce an after-tax yield equal to the tax-exempt yield.
Disclosure of Portfolio Holdings and Related Information. The Board of Trustees has adopted policies and procedures (the “Policies”) with respect to the disclosure of information about portfolio holdings of each Fund. Pursuant to the Policies, information about portfolio holdings of a Fund may not be disclosed to any party except as follows:
| • Disclosure made in filings with the SEC and posted on the Eaton Vance website: In accordance with rules established by the SEC, each Fund sends semiannual and annual reports to shareholders that contain a complete list of portfolio holdings as of the end of the second and fourth fiscal quarters, respectively, within 60 days of quarter-end. Each Fund also discloses complete portfolio holdings as of the end of the first and third fiscal quarters on Form N-Q, which is filed with the SEC within 60 days of quarter-end. Each Fund’s complete portfolio holdings as reported in annual and semiannual reports and on Form N-Q are available for viewing on the SEC website at http:// www.sec.gov and may be reviewed and copied at the SEC’s public reference room (information on the operation and terms of usage of the SEC public reference room is available at http://www.sec.gov/info/edgar/prrrules.htm or by calling 1-800-SEC-0330). Generally within five business days of filing with the SEC, each Fund’s portfolio holdings as reported in annual and semiannual reports and on Form N-Q also are available on Eaton Vance’s website at www.eatonvance.com and are available upon request at no cost by contacting Eaton Vance at 1-800-262-1122. Each Fund also will post a complete list of its portfolio holdings as of each calendar quarter end on the Eaton Vance website within 30 days of calendar quarter end. |
| • Disclosure of certain portfolio characteristics: Each Fund may also post information about certain portfolio characteristics (such as top ten holdings and asset allocation information) as of the most recent calendar quarter end on the Eaton Vance website approximately ten business days after the calendar quarter end. Such information is also available upon request by contacting Eaton Vance at 1-800-262-1122. |
24
- Confidential disclosure for a legitimate Fund purpose: Portfolio holdings may be disclosed, from time to time as necessary, for a legitimate business purpose of a Fund, believed to be in the best interests of the Fund and its shareholders, provided there is a duty or an agreement that the information be kept confidential. Any such confidentiality agreement includes provisions intended to impose a duty not to trade on the non-public information. The Policies permit disclosure of portfolio holdings information to the following: 1) affiliated and unaffiliated service providers that have a legal or contractual duty to keep such information confidential, such as employees of the investment adviser (including portfolio managers and, in the case of a Portfolio, the portfolio manager of any account that invests in the Portfolio), the a dministrator, custodian, transfer agent, principal underwriter, etc. described herein and in the prospectus; 2) other persons who owe a fiduciary or other duty of trust or confidence to the Fund (such as Fund legal counsel and independent registered public accounting firm); or 3) persons to whom the disclosure is made in advancement of a legitimate business purpose of a Fund and who have expressly agreed in writing to maintain the disclosed information in confidence and to use it only in connection with the legitimate business purpose underlying the arrangement. Such persons may include securities lending agents which may receive information from time to time regarding selected holdings which may be loaned by a Fund, credit rating agencies (such as Moody’s Investor Services, Inc. and Standard & Poor’s Ratings Group), statistical ratings agencies (such as Morningstar, Inc.), analytical service providers engaged by the investment adviser (such as Advent, Bloomberg L.P., Evare, Factset, McMunn Associates, Inc. and The Yield Book, Inc.), proxy evaluation vendors (such as Institutional Shareholder Servicing Inc.), pricing services (such as LSTA/ LPC Mark-to-Market Pricing Service, WM Company Reuters Information Services, Pricing Direct, State Street Derivatives Pricing Service, FT Interactive Data Corp. and Standard & Poor’s Securities Evaluation Service, Inc.), which receive information as needed to price a particular holding, translation services, lenders under Fund credit facilities (such as Citibank, N.A.), consultants and, for purposes of facilitating portfolio transactions, investment dealers and other intermediaries (such as national and regional municipal bond dealers and mortgage-backed securities dealers). These entities receive portfolio information on an as needed basis in order to perform the service for which they are being engaged. If required in order to perform their duties, this information will be provided in real time or as soon as practical thereafter. Additional categories of disclosure involving a legitimate business purpose may be added to this list upon the authorization of a Fund’s Board of Trustees. In addition, in connection with a redemption in kind, the redeeming shareholder may be required to agree to keep the information about the securities to be so distributed confidential, except to the extent necessary to dispose of the securities.
- Historical portfolio holdings information: From time to time, each Fund may be requested to provide historic portfolio holdings information that has not been made public previously. In such case, the requested information may be provided if: the information is requested for due diligence or another legitimate purpose; the requested portfolio holdings are for a period that is no more recent than the date of the portfolio holdings posted to the Eaton Vance website; a Fund’s portfolio manager and Eaton Vance’s Chief Equity or Chief Income Investment Officer (as appropriate) have reviewed the request and do not believe the dissemination of the information requested would disadvantage Fund shareholders; and the Chief Compliance Officer ("CCO") has reviewed the request to ensure that the disclosure of the requested informat ion does not give rise to a conflict of interest between Fund shareholders and an affiliated service provider.
The Funds, the investment adviser and principal underwriter will not receive any monetary or other consideration in connection with the disclosure of information concerning a Fund’s portfolio holdings.
The Policies may not be waived, or exception made, without the consent of the CCO of the Funds. The CCO may not waive or make exception to the Policies unless such waiver or exception is consistent with the intent of the Policies, which is to ensure that disclosure of portfolio information is in the best interest of Fund shareholders. In determining whether to permit a waiver of or exception to the Policies, the CCO will consider whether the proposed disclosure serves a legitimate purpose of a Fund, whether it could provide the recipient with an advantage over Fund shareholders or whether the proposed disclosure gives rise to a conflict of interest between a Fund’s shareholders and its investment adviser, principal underwriter or other affiliated person. The CCO will report all waivers of or exceptions to the Policies to the Trustees at their next meeting. The Trustees may impose additional restrictions on the disclosure of portfolio holdings information at any time.
The Policies are designed to provide useful information concerning a Fund to existing and prospective Fund shareholders while at the same time inhibiting the improper use of portfolio holdings information in trading Fund shares and/or portfolio securities held by a Fund. However, there can be no assurance that the provision of any portfolio holdings information is not susceptible to inappropriate uses (such as the development of “market timing” models), particularly in the hands of highly sophisticated investors, or that it will not in fact be used in such ways beyond the control of the Funds.
25
Each series of the Trust is treated as a separate entity for federal income tax purposes. Each Fund has elected to be treated and intends to qualify each year as a regulated investment company (“RIC”) under Subchapter M of the Code. Accordingly, each Fund intends to satisfy certain requirements relating to sources of its income and diversification of its assets and to distribute substantially all of its net investment income (including tax-exempt income) and net short-term and long-term capital gains (after reduction by any available capital loss carryforwards) in accordance with the timing requirements imposed by the Code, so as to maintain its RIC status and to avoid paying any federal income tax. If a Fund qualifies for treatment as a RIC and satisfies the above-mentioned distribution requirements, it will not be subject to federal income tax on income paid to its shareholders in the form of dividends or capital gain distributions. Each Fund qualified as a RIC for its fiscal year ended January 31, 2009. Each Fund also seeks to avoid payment of federal excise tax. However, if a Fund fails to distribute in a calendar year substantially all of its ordinary income for such year and substantially all of its capital gain net income for the one-year period ending October 31 (or later if the Fund is permitted so to elect and so elects), plus any retained amount from the prior year, the Fund will be subject to a 4% excise tax on the undistributed amounts.
In order to avoid incurring a federal excise tax obligation, the Code requires that a Fund distribute (or be deemed to have distributed) by December 31 of each calendar year (i) at least 98% of its ordinary income (not including tax-exempt income) for such year, (ii) at least 98% of its capital gain net income (which is the excess of its realized capital gains over its realized capital losses), generally computed on the basis of the one-year period ending on October 31 of such year, after reduction by any available capital loss carryforwards and (iii) 100% of any income and capital gains from the prior year (as previously computed) that was not paid out during such year and on which the Fund paid no federal income tax. If a Fund fails to meet these requirements it will be subject to a nondeductible 4% excise tax on the undistributed amounts. Under current law, provided that a Fund qualifies as a RIC for federal tax purposes, the Fund should not be liable for any income, corporate e xcise or franchise tax in the Commonwealth of Massachusetts.
If a Fund does not qualify as a RIC for any taxable year, the Fund’s taxable income will be subject to corporate income taxes, and all distributions from earnings and profits, including distributions of net capital gain (if any), will be taxable to the shareholder as ordinary income. However, such distributions will be eligible (i) to be treated as qualified dividend income in the case of shareholders taxed as individuals and (ii) for the dividends received deduction in the case of corporate shareholders. In addition, in order to requalify for taxation as a RIC, the Fund may be required to recognize unrealized gains, pay substantial taxes and interest, and make substantial distributions.
A Fund’s investment in zero coupon and certain other securities will cause it to realize income prior to the receipt of cash payments with respect to these securities. Such income will be accrued daily by the Fund and, in order to avoid a tax payable by the Fund, the Fund may be required to liquidate securities that it might otherwise have continued to hold in order to generate cash so that the Fund may make required distributions to its shareholders.
A Fund may invest to a significant extent in debt obligations that are in the lowest rating categories (with the exception of the Insured Fund which may not invest in obligations rated lower than BBB or Baa) or are unrated, including debt obligations of issuers not currently paying interest or who are in default. Investments in debt obligations that are at risk of or in default present special tax issues for a Fund. Tax rules are not entirely clear about issues such as when a Fund may cease to accrue interest, original issue discount or market discount, when and to what extent deductions may be taken for bad debts or worthless securities and how payments received on obligations in default should be allocated between principal and income.
Distributions by a Fund of net tax-exempt interest income that are properly designated as “exempt-interest dividends” may be treated by shareholders as interest excludable from gross income for federal income tax purposes under Section 103(a) of the Code. In order for a Fund to be entitled to pay the tax-exempt interest income as exempt-interest dividends to its shareholders, the Fund must and intends to satisfy certain requirements, including the requirement that, at the close of each quarter of its taxable year, at least 50% of the value of its total assets consists of obligations the interest on which is exempt from regular federal income tax under Code Section 103(a). Interest on certain municipal obligations may be taxable for purposes of the federal AMT and for state and local purposes. In addition, corporate shareholders must include the full amount of exempt-interest dividends in computing the preference items for the purposes of the AMT. Shareholders of a Fund ar e required to report tax-exempt interest on their federal income tax returns.
For taxable years beginning on or before December 31, 2010, distributions of investment income designated by a Fund as derived from “qualified dividend income” will be taxed in the hands of individual shareholders at the rates applicable to long-term capital gains, provided holding period and other requirements are met at both the shareholder and Fund level. It is not expected a significant portion of Fund distributions would be derived from qualified dividend income.
26
Tax-exempt distributions received from a Fund are taken into account in determining, and may increase, the portion of social security and certain railroad retirement benefits that may be subject to federal income tax.
Interest on indebtedness incurred or continued by a shareholder to purchase or carry shares of a Fund is not deductible to the extent it is deemed related to the Fund’s distributions of tax-exempt interest. Further, entities or persons who are “substantial users” (or persons related to “substantial users”) of facilities financed by industrial development or private activity bonds should consult their tax advisers before purchasing shares of a Fund. “Substantial user” is defined in applicable Treasury regulations to include a “non-exempt person” who regularly uses in its trade or business a part of a facility financed from the proceeds of industrial development bonds, and the same definition should apply in the case of private activity bonds.
Any recognized gain or income attributable to market discount on long-term tax-exempt municipal obligations (i.e., obligations with a term of more than one year) purchased after April 30, 1993 (except to the extent of a portion of the discount attributable to original issue discount), is taxable as ordinary income. A long-term debt obligation is generally treated as acquired at a market discount if purchased after its original issue at a price less than (i) the stated principal amount payable at maturity, in the case of an obligation that does not have original issue discount or (ii) in the case of an obligation that does have original issue discount, the sum of the issue price and any original issue discount that accrued before the obligation was purchased, subject to a de minimis exclusion.
From time to time proposals have been introduced before Congress for the purpose of restricting or eliminating the federal income tax exemption for interest on certain types of municipal obligations, and it can be expected that similar proposals may be introduced in the future. Under federal tax legislation enacted in 1986, the federal income tax exemption for interest on certain municipal obligations was eliminated or restricted. As a result of any such future legislation, the availability of municipal obligations for investment by a Fund and the value of the securities held by it may be affected. It is possible that events occurring after the date of issuance of municipal obligations, or after a Fund’s acquisition of such an obligation, may result in a determination that the interest paid on that obligation is taxable, even retroactively.
In the course of managing its investments, a Fund may realize some short-term and long-term capital gains (and/or losses) as well as other taxable income. Any distributions by a Fund of its share of such capital gains (after reduction by any capital loss carryforwards) or other taxable income would be taxable to shareholders of the Fund. However, it is expected that such amounts, if any, would normally be insubstantial in relation to the tax-exempt interest earned by the Fund.
A Fund’s investments in options, futures contracts, hedging transactions, forward contracts (to the extent permitted) and certain other transactions will be subject to special tax rules (including mark-to-market, constructive sale, straddle, wash sale, short sale and other rules), the effect of which may be to accelerate income to a Fund, defer Fund losses, cause adjustments in the holding periods of Fund securities, convert capital gain into ordinary income and convert short-term capital losses into long-term capital losses. These rules could therefore affect the amount, timing and character of distributions to investors.
As a result of entering into swap contracts, a Fund may make or receive periodic net payments. A Fund may also make or receive a payment when a swap is terminated prior to maturity through an assignment of the swap or other closing transaction. Periodic net payments will generally constitute ordinary income or deductions, while termination of a swap will generally result in capital gain or loss (which will be a long-term capital gain or loss if a Fund has been a party to a swap for more than one year). With respect to certain types of swaps, a Fund may be required to currently recognize income or loss with respect to future payments on such swaps or may elect under certain circumstances to mark such swaps to market annually for tax purposes as ordinary income or loss. The tax treatment of many types of credit default swaps is uncertain.
Any loss realized upon the sale or exchange of Fund shares with a tax holding period of six months or less will be disallowed to the extent of any distributions treated as tax-exempt interest with respect to such shares and if the loss exceeds the disallowed amount, will be treated as a long-term capital loss to the extent of any distributions treated as long-term capital gain with respect to such shares. In addition, all or a portion of a loss realized on a redemption or other disposition of Fund shares may be disallowed under “wash sale” rules to the extent the shareholder acquired other shares of the same Fund (whether through the reinvestment of distributions or otherwise) within the period beginning 30 days before the redemption of the loss shares and ending 30 days after such date. Any disallowed loss will result in an adjustment to the shareholder’s tax basis in some or all of the other shares acquired.
Sales charges paid upon a purchase of shares subject to a front-end sales charge cannot be taken into account for purposes of determining gain or loss on a redemption or exchange of the shares before the 91st day after their purchase to the extent a sales charge is reduced or eliminated in a subsequent acquisition of Fund shares (or shares of another fund) pursuant to
27
the reinvestment or exchange privilege. Any disregarded amounts will result in an adjustment to the shareholder’s tax basis in some or all of any other shares acquired.
Dividends and distributions on a Fund’s shares are generally subject to federal income tax as described herein to the extent they do not exceed the Fund’s realized income and gains, even though such dividends and distributions may economically represent a return of a particular shareholder’s investment. Such distributions are likely to occur in respect of shares purchased at a time when the Fund’s net asset value reflects gains that are either unrealized, or realized but not distributed. Such realized gains may be required to be distributed even when a Fund’s net asset value also reflects unrealized losses. Certain distributions declared in October, November or December and paid in the following January will be taxed to shareholders as if received on December 31 of the year in which they were declared.
In general, dividends (other than capital gain dividends and exempt-interest dividends) paid to a shareholder that is not a “U.S. person” within the meaning of the Code (a “foreign person”) are subject to withholding of U.S. federal income tax at a rate of 30% (or lower applicable treaty rate).
For taxable years beginning before January 1, 2010, properly-designated dividends are generally exempt from U.S. federal withholding tax where they (i) are paid in respect of a Fund’s “qualified net interest income” (generally, a Fund’s U.S. source interest income, other than certain contingent interest and interest from obligations of a corporation or partnership in which the Fund is at least a 10% shareholder, reduced by expenses that are allocable to such income) or (ii) are paid in respect of a Fund’s “qualified short-term capital gains” (generally, the excess of a Fund’s net short-term capital gain over the Fund’s long-term capital loss for such taxable year). However, depending on its circumstances, a Fund may designate all, some or none of its potentially eligible dividends as such qualified net interest income or as qualified short-term capital gains and/or treat such dividends, in whole or in part, as ineligible for this exemption from withholding. In order to qualify for this exemption from withholding, a non-U.S. shareholder will need to comply with applicable certification requirements relating to its non-U.S. status (including, in general, furnishing an IRS Form W-8BEN or substitute Form). In the case of shares held through an intermediary, the intermediary may withhold even if a Fund designates the payment as qualified net interest income or qualified short-term capital gain. Non-U.S. shareholders should contact their intermediaries with respect to the application of these rules to their accounts.
For taxable years beginning before January 1, 2010, distributions that a Fund designates as “short-term capital gain dividends” or “long-term capital gain dividends” may not be treated as such to a recipient foreign shareholder if the distribution is attributable to gain received from the sale or exchange of U.S. real property or an interest in a U.S. real property holding corporation and the foreign shareholder has not owned more than 5% of the outstanding shares of a Fund at any time during the one-year period ending on the date of distribution. Such distributions will be subject to 30% withholding by a Fund and will be treated as ordinary dividends to the foreign shareholder.
If a Fund’s direct or indirect interests in U.S. real property were to exceed certain levels, a foreign shareholder realizing gains upon redemption from a Fund could be subject to the 35% withholding tax and U.S. filing requirements unless more than 50% of the Fund’s shares were owned by U.S. persons at such time or unless the foreign person had not held more than 5% of the Fund’s outstanding shares throughout either such person’s holding period for the redeemed shares or, if shorter, the previous five years. It is not expected that a significant portion of the Fund’s distributions will be attributable to gains from sale or exchange of U.S. real property interests.
Amounts paid by a Fund to individuals and certain other shareholders who have not provided the Fund with their correct taxpayer identification number (“TIN”) and certain certifications required by the IRS as well as shareholders with respect to whom the Fund has received certain information from the IRS or a broker, may be subject to “backup” withholding of federal income tax arising from the Fund’s taxable dividends and other distributions as well as the proceeds of redemption transactions (including repurchases and exchanges), at a rate of 28% for amounts paid through 2010. The backup withholding rate will be 31% for amounts paid thereafter. An individual’s TIN is generally his or her social security number. Backup withholding is not an additional tax and any amount withheld may be credited against a shareholder’s U.S. federal income tax liability.
Under Treasury regulations, if a shareholder realizes a loss on disposition of a Fund’s shares of $2 million or more for an individual shareholder or $10 million or more for a corporate shareholder, the shareholder must file with the IRS a disclosure statement on Form 8886. Direct shareholders of portfolio securities are in many cases excepted from this reporting requirement, but under current guidance, shareholders of a RIC are not excepted. The fact that a loss is reportable under these regulations does not affect the legal determination of whether the taxpayer’s treatment of the loss is proper. Shareholders should consult their tax advisors to determine the applicability of these regulations in light of their individual circumstances. Under certain circumstances, certain tax-exempt entities and their managers may be subject to excise tax if they are parties to certain reportable transactions.
28
The foregoing discussion does not address all of the special tax rules applicable to certain classes of investors, such as tax-exempt entities, foreign investors, insurance companies and financial institutions. Shareholders should consult their own tax advisers with respect to special tax rules that may apply in their particular situations, as well as the federal, state, local, and, where applicable, foreign tax consequences of investing in a Fund.
See Appendix D for state tax information for certain states.
| PORTFOLIO SECURITIES TRANSACTIONS |
Decisions concerning the execution of portfolio security transactions, including the selection of the market and the broker-dealer firm, are made by BMR, each Fund’s investment adviser. Each Fund is responsible for the expenses associated with its portfolio transactions. The investment adviser is also responsible for the execution of transactions for all other accounts managed by it. The investment adviser places the portfolio security transactions for execution with one or more broker-dealer firms. The investment adviser uses its best efforts to obtain execution of portfolio security transactions at prices which in the investment adviser’s judgment are advantageous to the client and at a reasonably competitive spread or (when a disclosed commission is being charged) at reasonably competitive commission rates. In seeking such execution, the investment adviser will use its best judgment in evaluating the terms of a transaction, and will give consideration to various releva nt factors, including without limitation the full range and quality of the broker-dealer firm’s services including the responsiveness of the firm to the investment adviser, the size and type of the transaction, the nature and character of the market for the security, the confidentiality, speed and certainty of effective execution required for the transaction, the general execution and operational capabilities of the broker-dealer firm, the reputation, reliability, experience and financial condition of the firm, the value and quality of the services rendered by the firm in other transactions, and the reasonableness of the spread or commission, if any. In addition, the investment adviser may consider the receipt of Proprietary Research Services (as defined below), provided it does not compromise the investment adviser’s obligation to seek best overall execution for a Fund. The investment adviser may engage in portfolio brokerage transactions with a broker-dealer firm that sells shares of Eaton Vance funds, provided such transactions are not directed to that firm as compensation for the promotion or sale of such shares.
Municipal obligations, including state obligations, purchased and sold by each Fund are generally traded in the over-the-counter market on a net basis (i.e., without commission) through broker-dealers and banks acting for their own account rather than as brokers, or otherwise involve transactions directly with the issuer of such obligations. Such firms attempt to profit from such transactions by buying at the bid price and selling at the higher asked price of the market for such obligations, and the difference between the bid and asked price is customarily referred to as the spread. Each Fund may also purchase municipal obligations from underwriters, and dealers in fixed-price offerings, the cost of which may include undisclosed fees and concessions to the underwriters. On occasion it may be necessary or appropriate to purchase or sell a security through a broker on an agency basis, in which case the Fund will incur a brokerage commiss ion. Although spreads or commissions on portfolio security transactions will, in the judgment of the investment adviser, be reasonable in relation to the value of the services provided, spreads or commissions exceeding those which another firm might charge may be paid to firms who were selected to execute transactions on behalf of each Fund and the investment adviser’s other clients for providing brokerage and research services to the investment adviser.
Pursuant to the safe harbor provided in Section 28(e) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, a broker or dealer who executes a portfolio transaction may receive a commission that is in excess of the amount of commission another broker or dealer would have charged for effecting that transaction if the investment adviser determines in good faith that such compensation was reasonable in relation to the value of the brokerage and research services provided. This determination may be made either on the basis of that particular transaction or on the basis of the overall responsibility which the investment adviser and its affiliates have for accounts over which they exercise investment discretion. Brokerage and research services may include advice as to the value of securities, the advisability of investing in, purchasing, or selling securities, and the availability of securities or purchasers or sellers of securities; furnishing analyses and reports concerning issuers, indus tries, securities, economic factors and trends, portfolio strategy and the performance of accounts; effecting securities transactions and performing functions incidental thereto (such as clearance and settlement); and the “Research Services” referred to in the next paragraph. The investment adviser may also receive Research Services from underwriters and dealers in fixed-price offerings.
It is a common practice of the investment advisory industry and of the advisers of investment companies, institutions and other investors to receive research, analytical, statistical and quotation services, data, information and other services, products and materials which assist such advisers in the performance of their investment responsibilities (“Research Services”) from broker-dealer firms that execute portfolio transactions for the clients of such advisers and from affiliates of executing broker-dealers. Investment advisers also commonly receive Research Services from research providers that are not affiliated with an executing broker-dealer, but which have entered into payment arrangements involving an executing
29
broker-dealer (“Third Party Research Services”). In a typical Third Party Research Services arrangement involving transactions in municipal obligations, an executing broker-dealer enters into an arrangement with an investment adviser pursuant to which the investment adviser receives a credit for portfolio transactions executed for its clients through that broker-dealer. These credits are referred to herein as “research credits” and are primarily generated as the result of acquisitions of new issuances of municipal obligations in fixed-price offerings. The amount of the research credit generated as the result of a particular transaction is typically a negotiated percentage of the offering price of the municipal obligations. The investment adviser may use research credits to acquire Third Party Research Services, which are then paid for by the executing broker-dealer. The investment adviser may receive Research Services and Third Party Research Services consistent with the foregoing.
Research Services received by the investment adviser may include, but are not limited to, such matters as general economic, political, business and market information, industry and company reviews, evaluations of securities and portfolio strategies and transactions, technical analysis of various aspects of the securities markets, recommendations as to the purchase and sale of securities and other portfolio transactions, certain financial, industry and trade publications, certain news and information services, and certain research oriented computer software, data bases and services. Any particular Research Service obtained through a broker-dealer may be used by the investment adviser in connection with client accounts other than those accounts which pay commissions to such broker-dealer. Any such Research Service may be broadly useful and of value to the investment adviser in rendering investment advisory services to all or a significant portion of its clients, or may be relevant and useful for the management of only one client’s account or of a few clients’ accounts, or may be useful for the management of merely a segment of certain clients’ accounts, regardless of whether any such account or accounts paid commissions to the broker-dealer through which such Research Service was obtained. The investment adviser evaluates the nature and quality of the various Research Services obtained through broker-dealer firms and may attempt to allocate sufficient portfolio security transactions to such firms to ensure the continued receipt of Research Services which the investment adviser believes are useful or of value to it in rendering investment advisory services to its clients.
Since May 1, 2004, if the investment adviser uses research credits generated from a Fund securities transactions to pay for Third Party Research Services (as described above), the investment adviser has agreed to reduce the advisory fee payable by a Fund by the amount of such research credits. However, the investment adviser generally does not expect to acquire Third Party Research Services with research credits.
Some executing broker-dealers develop and make available directly to their brokerage customers proprietary Research Services (“Proprietary Research Services”). As a general matter, broker-dealers bundle the cost of Proprietary Research Services with trade execution services rather than charging separately for each. In such circumstances, the cost or other value of the Proprietary Research Services cannot be determined. The advisory fee paid by a Fund will not be reduced in connection with the receipt of Proprietary Research Services by the investment adviser.
The investment companies sponsored by the investment adviser or its affiliates may allocate trades in such offerings to acquire information relating to the performance, fees and expenses of such companies and other mutual funds, which information is used by the Trustees of such companies to fulfill their responsibility to oversee the quality of the services provided by various entities, including the investment adviser, to such companies. Such companies may also pay cash for such information.
Municipal obligations considered as investments for a Fund may also be appropriate for other investment accounts managed by the investment adviser or its affiliates. Whenever decisions are made to buy or sell securities by a Fund and one or more of such other accounts simultaneously, the investment adviser will allocate the security transactions (including “new” issues) in a manner which it believes to be equitable under the circumstances. As a result of such allocations, there may be instances where a Fund will not participate in a transaction that is allocated among other accounts. If an aggregated order cannot be filled completely, allocations will generally be made on a pro rata basis. An order may not be allocated on a pro rata basis where, for example: (i) consideration is given to portfolio managers who have been instrumental in developing or negotiating a particular investment; (ii) consideration is given to an account with specialized investment policies that coincide with the particulars of a specific investment; (iii) pro rata allocation would result in odd-lot or de minimis amounts being allocated to a portfolio or other client; or (iv) where the investment adviser reasonably determines that departure from a pro rata allocation is advisable. While these aggregation and allocation policies could have a detrimental effect on the price or amount of the securities available to a Fund from time to time, it is the opinion of the Trustees of the Trust that the benefits from the investment adviser organization outweigh any disadvantage that may arise from exposure to simultaneous transactions.
The following table shows brokerage commissions paid during each of the three fiscal years ended January 31, 2009, 2008 and 2007, as well as the amount of Fund security transactions for the most recent fiscal year (if any) that were directed to firms that provided some Research Services to the investment adviser or its affiliates, and the commissions paid in
30
connection therewith. As described above, the investment adviser may consider the receipt of Research Services in selecting a broker-dealer firm, provided it does not compromise the investment adviser’s obligation to seek best overall execution.
| | | | | |
| | | | | | Commissions Paid on |
| | | | | Amount of Transactions | Transactions |
| | | | | Directed to Firms | Directed to Firms |
| | Brokerage Commissions Paid for the Fiscal Year Ended | Providing Research | Providing Research |
| Fund | 1/31/09 | 1/31/08 | 1/31/07 | 1/31/09 | 1/31/09 |
| Hawaii | $161 | $1,096 | $1,891 | $0 | $0 |
| Insured | $427 | 2,026 | 3,602 | 0 | 0 |
| Kansas | $805 | 858 | 1,644 | 0 | 0 |
As of January 31, 2009, each Fund held no securities of its “regular brokers or dealers”, as that term is defined in Rule 10b-1 of the 1940 Act.
The audited financial statements of, and the report of the independent registered public accounting firm for the Funds, appear in the Funds’ most recent annual report to shareholders and are incorporated by reference into this SAI. A copy of the annual report accompanies this SAI.
Householding. Consistent with applicable law, duplicate mailings of shareholder reports and certain other Fund information to shareholders residing at the same address may be eliminated.
31
Class A Fees, Performance & Ownership
Sales Charges and Distribution and Service Fees. For the fiscal year ended January 31, 2009, the following table shows (1) total sales charges paid by each Fund, (2) sales charges paid to investment dealers, (3) sales charges paid to the principal underwriter, (4) CDSC payments to the principal underwriter, (5) total distribution and service fees paid by each Fund, and (6) distribution and service fees paid to investment dealers. Distribution and service fees that were not paid to investment dealers were retained by the principal underwriter.
| | | | | | |
| | | | | | Total Distribution and | Total Distribution and |
| | Total Sales | Sales Charges to | Sales Charges to | CDSC Paid to | Service | Service Fees Paid |
| Fund | Charges Paid | Investment Dealers | Principal Underwriter | Principal Underwriter | Fees Paid | to Investment Dealers |
| Hawaii | $44,756 | $43,849 | $ 907 | $9,000 | $28,384 | $21,642 |
| Insured | 125,876 | 120,657 | 5,219 | 17,000 | 58,941 | 47,823 |
| Kansas | 86,030 | 80,764 | 5,266 | 8,000 | 59,187 | 41,356 |
For the fiscal years ended January 31, 2008 and January 31, 2007, the following total sales charges were paid on sales of Class A, of which the principal underwriter received the following amounts.
| | | | |
| | January 31, 2008 | January 31, 2008 | January 31, 2007 | January 31, 2007 |
| | Total Sales | Sales Charges to | Total Sales | Sales Charges to |
| Fund | Charges Paid | Principal Underwriter | Charges Paid | Principal Underwriter |
| Hawaii | $127,434 | $5,103 | $46,606 | $2,243 |
| Insured | 89,632 | 5,112 | 80,303 | 4,522 |
| Kansas | 106,151 | 5,437 | 98,566 | 4,095 |
Performance Information. The tables below indicate the average annual total return (both before and after taxes) on a hypothetical investment of $1,000 in this Class of shares for the periods shown in each table. Any performance presented with an asterisk (*) includes the effect of subsidizing expenses. Performance would have been lower without subsidies.
Total returns are historical and are calculated by determining the percentage change in net asset value or public offering price with all distributions reinvested. Each Fund’s past performance (both before and after taxes) is no guarantee of future results. Investment return and principal value of Fund shares will fluctuate so that shares, when redeemed, may be worth more or less than their original cost. Performance is for the stated time period only; due to market volatility, a Fund’s current performance may be lower or higher than the quoted return. For the Fund’s performance as of the most recent month-end, please refer to www.eatonvance.com.
About Returns After Taxes. After-tax returns are calculated using certain assumptions. After-tax returns are calculated using the highest historical individual federal income tax rates and do not reflect the impact of state and local taxes. Actual after-tax returns depend on a shareholder’s tax situation and the actual characterization of distributions, and may differ from those shown. After-tax returns are not relevant to shareholders who hold shares in tax-deferred accounts or to shares held by non-taxable entities. Return After Taxes on Distributions for a period may be the same as Return Before Taxes for that period because no taxable distributions were made during that period, or because the taxable portion of distributions made during the period was insignificant. Also, Return After Taxes on Distributions and the Sale of Fund Shares for a period may be greater than or equal to Return After Taxes on Distributions for the same period because of l osses realized on the sale of Fund shares. A portion of the distributions made in the current year may be recharacterized as taxable after year-end.
| | | |
| Hawaii Fund | Length of Period Ended January 31, 2009 |
| Average Annual Total Return: | One Year | Five Years | Ten Years |
| Before Taxes and Excluding Maximum Sales Charge | –11.62% | –0.21% | 2.20% |
| Before Taxes and Including Maximum Sales Charge | –15.84% | –1.17% | 1.71% |
| After Taxes on Distributions and Excluding Maximum Sales Charge | –11.64% | –0.23% | 2.17% |
| After Taxes on Distributions and Including Maximum Sales Charge | –15.86% | –1.19% | 1.67% |
| After Taxes on Distributions and Redemption and Excluding Maximum Sales Charge | –6.09% | 0.49% | 2.54% |
| After Taxes on Distributions and Redemption and Including Maximum Sales Charge | –8.91% | –0.33% | 2.11% |
32
| | | |
| Insured Fund | Length of Period Ended January 31, 2009 |
| Average Annual Total Return: | One Year | Five Years | Ten Years |
| Before Taxes and Excluding Maximum Sales Charge | –10.69% | –0.15% | 2.41% |
| Before Taxes and Including Maximum Sales Charge | –14.96% | –1.12% | 1.91% |
| After Taxes on Distributions and Excluding Maximum Sales Charge | –10.69% | –0.15% | 2.39% |
| After Taxes on Distributions and Including Maximum Sales Charge | –14.96% | –1.12% | 1.89% |
| After Taxes on Distributions and Redemption and Excluding Maximum Sales Charge | –5.39% | 0.59% | 2.75% |
| After Taxes on Distributions and Redemption and Including Maximum Sales Charge | –8.24% | –0.24% | 2.31% |
| | |
| Kansas Fund | Length of Period Ended January 31, 2009 |
| Average Annual Total Return: | One Year | Five Years | Ten Years |
| Before Taxes and Excluding Maximum Sales Charge | –8.39% | 0.65% | 2.94% |
| Before Taxes and Including Maximum Sales Charge | –12.76% | –0.31% | 2.44% |
| After Taxes on Distributions and Excluding Maximum Sales Charge | –8.39% | 0.65% | 2.93% |
| After Taxes on Distributions and Including Maximum Sales Charge | –12.76% | –0.31% | 2.44% |
| After Taxes on Distributions and Redemption and Excluding Maximum Sales Charge | –3.99% | 1.22% | 3.18% |
| After Taxes on Distributions and Redemption and Including Maximum Sales Charge | –6.90% | 0.39% | 2.74% |
Control Persons and Principal Holders of Securities. At May 1, 2009, the Trustees and officers of the Trust, as a group, owned in the aggregate less than 1% of the outstanding shares of this Class of a Fund. In addition, as of the same date, the following person(s) held the share percentage indicated below, which was owned either (i) beneficially by such person(s) or (ii) of record by such person(s) on behalf of customers who are the beneficial owners of such shares and as to which such record owner(s) may exercise voting rights under certain limited circumstances:
| | | |
| Hawaii | Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith, Inc. | Jacksonville, FL | 14.6% |
| | Morgan Stanley | Jersey City, NJ | 9.1% |
| | First Clearing, LLC | Kailua, HI | 8.4% |
| | Charles Schwab & Co., Inc. | San Francisco, CA | 7.2% |
| | Citigroup Global Markets, Inc. | New York, NY | 6.7% |
| | Penson Financial Services, Inc. | Dallas, TX | 5.2% |
| Insured | Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith, Inc. | Jacksonville, FL | 17.9% |
| | Morgan Stanley | Jersey City, NJ | 11.8% |
| Kansas | Charles Schwab & Co., Inc. | San Francisco, CA | 8.3% |
| | Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith, Inc. | Jacksonville, FL | 7.3% |
To the knowledge of the Trust, no other person owned of record or beneficially 5% or more of the outstanding shares of this Class of a Fund as of such date.
33
| Class B Fees, Performance & Ownership |
Distribution and Service Fees. For the fiscal year ended January 31, 2009, the following table shows (1) sales commissions paid by the principal underwriter to investment dealers on sales of Class B shares, (2) distribution fees paid to the principal underwriter under the Distribution Plan, (3) CDSC payments to the principal underwriter, (4) uncovered distribution charges under the Distribution Plan (dollar amount and as a percentage of net assets attributable to Class B), (5) service fees paid under the Distribution Plan, and (6) service fees paid to investment dealers. The service fees paid by the Funds that were not paid to investment dealers were retained by the principal underwriter.
| | | | | | |
| | Commission Paid | | | | | |
| | by Principal | Distribution Fee | CDSC Paid to | Uncovered Distribution | | Service Fees |
| | Underwriter to | Paid to | Principal | Charges (as a % of Class | Service | Paid t |
| Fund | Investment Dealers | Principal Underwriter | Underwriter | Net Assets) | Fees | Investment Dealers |
| |
| Hawaii | $6,333 | $24,853 | $6,000 | $395,000 (15.4%) | $6,627 | $6,177 |
| |
| Insured | 12,995 | 50,767 | 7,000 | 444,000 (7.5%) | 13,538 | 13,347 |
| |
| Kansas | 6,603 | 24,953 | 4,000 | 212,000 (7.1%) | 6,654 | 6,494 |
Performance Information. The tables below indicate the average annual total return (both before and after taxes) on a hypothetical investment of $1,000 in this Class of shares for the periods shown in each table. Any performance presented with an asterisk (*) includes the effect of subsidizing expenses. Performance would have been lower without subsidies.
Total returns are historical and are calculated by determining the percentage change in net asset value or public offering price with all distributions reinvested. Each Fund’s past performance (both before and after taxes) is no guarantee of future results. Investment return and principal value of Fund shares will fluctuate so that shares, when redeemed, may be worth more or less than their original cost. Performance is for the stated time period only; due to market volatility, a Fund’s current performance may be lower or higher than the quoted return. For the Fund’s performance as of the most recent month-end, please refer to www.eatonvance.com.
About Returns After Taxes. After-tax returns are calculated using certain assumptions. After-tax returns are calculated using the highest historical individual federal income tax rates and do not reflect the impact of state and local taxes. Actual after-tax returns depend on a shareholder’s tax situation and the actual characterization of distributions, and may differ from those shown. After-tax returns are not relevant to shareholders who hold shares in tax-deferred accounts or to shares held by non-taxable entities. Return After Taxes on Distributions for a period may be the same as Return Before Taxes for that period because no taxable distributions were made during that period, or because the taxable portion of distributions made during the period was insignificant. Also, Return After Taxes on Distributions and the Sale of Fund Shares for a period may be greater than or equal to Return After Taxes on Distributions for the same period because of l osses realized on the sale of Fund shares. A portion of the distributions made in the current year may be recharacterized as taxable after year-end.
| | | |
| Hawaii Fund | Length of Period Ended January 31, 2009 |
| Average Annual Total Return: | One Year | Five Years | Ten Years |
| Before Taxes and Excluding Maximum Sales Charge | –12.37% | –0.95% | 1.44% |
| Before Taxes and Including Maximum Sales Charge | –16.59% | –1.28% | 1.44% |
| After Taxes on Distributions and Excluding Maximum Sales Charge | –12.39% | –0.97% | 1.41% |
| After Taxes on Distributions and Including Maximum Sales Charge | –16.61% | –1.31% | 1.41% |
| After Taxes on Distributions and Redemption and Excluding Maximum Sales Charge | –6.85% | –0.25% | 1.79% |
| After Taxes on Distributions and Redemption and Including Maximum Sales Charge | –9.60% | –0.52% | 1.79% |
34
| | | |
| Insured Fund | Length of Period Ended January 31, 2009 |
| Average Annual Total Return: | One Year | Five Years | Ten Years |
| Before Taxes and Excluding Maximum Sales Charge | –11.40% | –0.88% | 1.65% |
| Before Taxes and Including Maximum Sales Charge | –15.66% | –1.21% | 1.65% |
| After Taxes on Distributions and Excluding Maximum Sales Charge | –11.40% | –0.89% | 1.65% |
| After Taxes on Distributions and Including Maximum Sales Charge | –15.66% | –1.22% | 1.65% |
| After Taxes on Distributions and Redemption and Excluding Maximum Sales Charge | –6.13% | –0.15% | 2.01% |
| After Taxes on Distributions and Redemption and Including Maximum Sales Charge | –8.90% | –0.42% | 2.01% |
| | |
| Kansas Fund | Length of Period Ended January 31, 2009 |
| Average Annual Total Return: | One Year | Five Years | Ten Years |
| Before Taxes and Excluding Maximum Sales Charge | –9.11% | –0.06% | 2.19% |
| Before Taxes and Including Maximum Sales Charge | –13.49% | –0.40% | 2.19% |
| After Taxes on Distributions and Excluding Maximum Sales Charge | –9.01% | –0.04% | 2.19% |
| After Taxes on Distributions and Including Maximum Sales Charge | –13.39% | –0.38% | 2.19% |
| After Taxes on Distributions and Redemption and Excluding Maximum Sales Charge | –4.66% | 0.52% | 2.44% |
| After Taxes on Distributions and Redemption and Including Maximum Sales Charge | –7.51% | 0.24% | 2.44% |
Control Persons and Principal Holders of Securities. At May 1, 2009, the Trustees and officers of the Trust, as a group, owned in the aggregate less than 1% of the outstanding shares of this Class of a Fund. In addition, as of the same date, the following person(s) held the share percentage indicated below, which was owned either (i) beneficially by such person(s) or (ii) of record by such person(s) on behalf of customers who are the beneficial owners of such shares and as to which such record owner(s) may exercise voting rights under certain limited circumstances:
| | | |
| Hawaii | Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith, Inc. | Jacksonville, FL | 19.3% |
| | Citigroup Global Markets, Inc. | New York, NY | 12.4% |
| | Stifel Nicolaus & Co. Inc. | St. Louis, MO | 9.7% |
| | Morgan Stanley | Jersey City, NJ | 8.7% |
| Insured | Morgan Stanley | Jersey City, NJ | 16.5% |
| | Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith, Inc. | Jacksonville, FL | 15.3% |
| Kansas | Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith, Inc. | Jacksonville, FL | 7.7% |
| | Edward D. Jones & Co. | Maryland Hts., MO | 5.2% |
| | First Clearing, LLC | Leawood, KS | 5.1% |
To the knowledge of the Trust, no other person owned of record or beneficially 5% or more of the outstanding shares of this Class of a Fund as of such date.
35
| Class C Fees, Performance & Ownership |
Distribution and Service Fees. For the fiscal year ended January 31, 2009, the following table shows (1) sales commissions paid by the principal underwriter to investment dealers on sales of Class C shares, (2) distribution fees paid to the principal underwriter under the Distribution Plan, (3) CDSC payments to the principal underwriter, (4) uncovered distribution charges under the Distribution Plan (dollar amount and as a percentage of net assets attributable to Class C), (5) service fees paid under the Distribution Plan, and (6) service fees paid to investment dealers. The service fees paid by the Funds that were not paid to investment dealers were retained by the principal underwriter.
| | | | | | |
| | Commission Paid | | | | | |
| | by Principal | Distribution Fee | | Uncovered Distribution | | Service Fees |
| | Underwriter to | Paid to | CDSC Paid to | Charges (as a % of Class | Service | Paid to |
| Fund | Investment Dealers | Principal Underwriter | Principal Underwriter | Net Assets) | Fees | Investment Dealers |
| |
| Hawaii | $ 768 | $ 361 | $ 0 | $ 4,000 (3.4%) | $ 96 | $ 240 |
| |
| Insured | $20,720 | $14,219 | 13,000 | 108,000 (2.1%) | $3,790 | $6,706 |
| |
| Kansas | $15,914 | $14,885 | 0 | 182,000 (8.4%) | $3,969 | $4,859 |
Performance Information. The tables below indicate the average annual total return (both before and after taxes) on a hypothetical investment in shares of $1,000. Total return for the period prior to the date this Class of each Fund was first offered, reflects the total return of Class B, adjusted to reflect the Class C CDSC. The total return has not been adjusted to reflect certain other expenses (such as distribution and service fees). If such adjustments were made, the Class C total return would be different. Any performance presented with an asterisk (*) includes the effect of subsidizing expenses. Performance would have been lower without subsidies.
Total returns are historical and are calculated by determining the percentage change in net asset value or public offering price with all distributions reinvested. Each Fund’s past performance (both before and after taxes) is no guarantee of future results. Investment return and principal value of Fund shares will fluctuate so that shares, when redeemed, may be worth more or less than their original cost. Performance is for the stated time period only; due to market volatility, a Fund’s current performance may be lower or higher than the quoted return. For the Fund’s performance as of the most recent month-end, please refer to www.eatonvance.com.
About Returns After Taxes. After-tax returns are calculated using certain assumptions. After-tax returns are calculated using the highest historical individual federal income tax rates and do not reflect the impact of state and local taxes. Actual after-tax returns depend on a shareholder’s tax situation and the actual characterization of distributions, and may differ from those shown. After-tax returns are not relevant to shareholders who hold shares in tax-deferred accounts or to shares held by non-taxable entities. Return After Taxes on Distributions for a period may be the same as Return Before Taxes for that period because no taxable distributions were made during that period, or because the taxable portion of distributions made during the period was insignificant. Also, Return After Taxes on Distributions and the Sale of Fund Shares for a period may be greater than or equal to Return After Taxes on Distributions for the same period because of l osses realized on the sale of Fund shares. A portion of the distributions made in the current year may be recharacterized as taxable after year-end.
| | | |
| Hawaii Fund | Length of Period Ended January 31, 2009 |
| Average Annual Total Return: | One Year | Five Years | Ten Years |
| Before Taxes and Excluding Maximum Sales Charge | –12.37% | –0.95% | 1.44% |
| Before Taxes and Including Maximum Sales Charge | –13.22% | –0.95% | 1.44% |
| After Taxes on Distributions and Excluding Maximum Sales Charge | –12.39% | –0.97% | 1.41% |
| After Taxes on Distributions and Including Maximum Sales Charge | –13.23% | –0.97% | 1.41% |
| After Taxes on Distributions and Redemption and Excluding Maximum Sales Charge | –6.85% | –0.25% | 1.79% |
| After Taxes on Distributions and Redemption and Including Maximum Sales Charge | –7.40% | –0.25% | 1.79% |
| Class C commenced operations October 1, 2007. | | | |
36
| | | |
| Insured Fund | Length of Period Ended January 31, 2009 |
| Average Annual Total Return: | One Year | Five Years | Ten Years |
| Before Taxes and Excluding Maximum Sales Charge | –11.39% | –0.86% | 1.66% |
| Before Taxes and Including Maximum Sales Charge | –12.24% | –0.86% | 1.66% |
| After Taxes on Distributions and Excluding Maximum Sales Charge | –11.39% | –0.87% | 1.66% |
| After Taxes on Distributions and Including Maximum Sales Charge | –12.24% | –0.87% | 1.66% |
| After Taxes on Distributions and Redemption and Excluding Maximum Sales Charge | –6.12% | –0.13% | 2.02% |
| After Taxes on Distributions and Redemption and Including Maximum Sales Charge | –6.67% | –0.13% | 2.02% |
| Class C commenced operations June 2, 2006. | | | |
| | |
| Kansas Fund | Length of Period Ended January 31, 2009 |
| Average Annual Total Return: | One Year | Five Years | Ten Years |
| Before Taxes and Excluding Maximum Sales Charge | –9.00% | –0.04% | 2.20% |
| Before Taxes and Including Maximum Sales Charge | –9.88% | –0.04% | 2.20% |
| After Taxes on Distributions and Excluding Maximum Sales Charge | –9.11% | –0.06% | 2.18% |
| After Taxes on Distributions and Including Maximum Sales Charge | –9.98% | –0.06% | 2.18% |
| After Taxes on Distributions and Redemption and Excluding Maximum Sales Charge | –4.72% | 0.50% | 2.43% |
| After Taxes on Distributions and Redemption and Including Maximum Sales Charge | –5.29% | 0.50% | 2.43% |
| Class C commenced operations June 2, 2006. | | | |
Control Persons and Principal Holders of Securities. At May 1, 2009, the Trustees and officers of the Trust, as a group, owned in the aggregate less than 1% of the outstanding shares of this Class of a Fund. In addition, as of the same date, the following person(s) held the share percentage indicated below, which was owned either (i) beneficially by such person(s) or (ii) of record by such person(s) on behalf of customers who are the beneficial owners of such shares and as to which such record owner(s) may exercise voting rights under certain limited circumstances:
| | | |
| Hawaii | First Clearing, LLC | Keneohe, HI | 22.7% |
| | American Enterprise Investment Services | Minneapolis, MN | 17.5% |
| | American Enterprise Investment Services | Minneapolis, MN | 17.0% |
| | First Clearing, LLC | Pearl City, HI | 16.8% |
| | Edward D Jones & CO. | Maryland Hts, MO | 14.6% |
| | First Clearing, LLC | Pearl City, HI | 9.8% |
| Insured | Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith, Inc. | Jacksonville, FL | 35.7% |
| | Special Custody Acct. FEBO Customers Omnibus Account | Louisville, KY | 8.8% |
| | First Clearing, LLC | Mount Dora, FL | 5.0% |
| Kansas | NFS LLC FEBO Bernice Williamson Trust | Bedford, TX | 13.1% |
| | Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith, Inc. | Jacksonville, FL | 11.8% |
| | Pershing LLC | Jersey City, NJ | 9.1% |
| | Citigroup Global Markets, Inc. | New York, NY | 6.1% |
| | Gary L. Adams and Betty L. Adams JTWROS | Manter, KS | 5.5% |
Beneficial owners of 25% or more of this Class are presumed to be in control of the Class for purposes of voting on certain matters submitted to shareholders.
To the knowledge of the Trust, no other person owned of record or beneficially 5% or more of the outstanding shares of this Class of a Fund as of such date.
37
| STATE SPECIFIC INFORMATION |
Risks of Concentration. The following information as to certain state specific considerations is given to investors in view of a Fund’s policy of concentrating its investments in particular state issuers. Such information supplements the information in the prospectus. It is derived from sources that are generally available to investors and is believed to be accurate. Such information constitutes only a brief summary, does not purport to be a complete description and is based on information from official statements relating to securities offerings of issuers of each particular state. The Trust has not independently verified this information.
The bond ratings provided in the prospectus are current as of the date of the prospectus and are based on economic conditions which may not continue; moreover, there can be no assurance that particular bond issues may not be adversely affected by changes in economic, political or other conditions. Unless stated otherwise, the ratings indicated are for obligations of the state. A state’s political subdivisions may have different ratings which are unrelated to the ratings assigned to state obligations.
After showing mixed results during the first two quarters of 2008, Hawaii’s economy slowed in the third and fourth quarters, primarily the result of worsening national economic conditions and the decline of visitor industry activity in the State. According to the State Department of Business, Economic Development & Tourism, total civilian employment, tax collections distributed to the State general fund revenues, visitor arrivals and visitor expenditures, and new private building authorizations all declined in the fourth quarter of 2008 from the same quarter in 2007. Only the value of government contracts awarded increased in the fourth quarter of 2008, although total personal income also showed positive growth in the third quarter of 2008, the most recent period for which data is available.
The civilian labor force in Hawaii grew to 659,800 in the fourth quarter of 2008, an increase of 12,700 people or 2.0 percent from the fourth quarter of 2007. Civilian employment, however, decreased by 1,400 people or 0.2 percent from the same quarter in 2007. As a result, the average number of civilian unemployed for the quarter increased to 32,100, 78.3 percent higher than the year before. This pushed the unemployment rate to 4.9 percent in the fourth quarter of 2008, compared with the 2.8 percent a year earlier. The unemployment rate averaged 4.0 percent for all of 2008, 1.4 percentage points higher than in 2007. The number of wage and salary jobs fell to 628,600 in the fourth quarter of 2008, a decrease of 7,200 jobs or 1.1 percent from the same quarter of 2007. For the full year in 2008, the average jobs in Hawaii totaled 630,050, which is the same as the average jobs in 2007.
Total nominal personal income (i.e., not adjusted for inflation) increased by $1.999 billion, or 4.0 percent, in the third quarter of 2008 (the period for which the latest data are available from the U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis) compared to the third quarter of 2007. For the full year in 2007, total personal income increased 5.9 percent from 2006, compared to a 7.3 percent increase in 2006 over 2005. Wage and salary disbursements, which make up about 57 percent of total personal income, increased $952 million or 3.3 percent in the third quarter of 2008 from the same quarter of 2007. For the year of 2007, wage and salary disbursements grew 5.6 percent from 2006, lower than the 6.7 percent growth between 2005 and 2006. Honolulu’s Consumer Price Index increased 3.6 percent in the second half of 2008 from the same period in 2007 compared to the national average of 3.4 percent. Combined with a 4.9 percent increase in the first hal f of 2008, this produced a 4.3 percent increase for the year compared to a 3.8 percent national average.
Tax revenue distributed to the State general fund totaled nearly $1.077 billion in the fourth quarter of 2008, an decrease of $48.2 million or 4.3 percent from the fourth quarter of 2007. Revenues from the general excise and use tax (excluding a 0.5 percent Honolulu County surcharge) decreased by 9.1 percent, net individual income tax collections increased 4.3 percent, and transient accommodation tax revenues decreased 11.5 percent in the quarter compared to the same quarter of 2007. For the full year in 2008, State general fund tax revenues totaled $4.611 billion, down $71.8 million or 1.5 percent from 2007. General excise and use taxes were down 2.0 percent, net individual income tax collections were down 0.9 percent, and the transient accommodation tax collections were down 3.6 percent for the year.
In the fourth quarter of 2008, Hawaii’s tourism sector continued the negative growth started in the second quarter of 2008. The total number of visitors arriving by air decreased by 15.5 percent in the fourth quarter of 2008 compared to the same quarter of 2007, with domestic arrivals down 17.2 percent and international arrivals down 10.9 percent. The average daily visitor census decreased by 13.5 percent for the quarter. In 2008, total arrivals were down 10.9 percent and the average daily census decreased by 8.1 percent from the prior year. Nominal visitor expenditures by air totaled $2.618 billion in the fourth quarter of 2008, down 17.4 percent from the same quarter of 2007. In 2008, visitor expenditures decreased by $1.242 billion or 9.9 percent from 2007. Hotel occupancy rates decreased 8.3 percentage points to 63.7 percent for the
38
fourth quarter of 2008 compared with the same quarter of 2007. For all of 2008, hotel occupancy averaged 70.4 percent, down 4.6 percentage points from 2007.
The fourth quarter indicators of Hawaii’s construction industry were mostly negative. Construction jobs showed a significant decline from a previous year’s comparable quarter, down 5.9 percent or 2,350 jobs. Construction jobs decreased by 0.1 percent for all of 2008 compared to 2007. The total value of private building authorizations decreased by $439.5 million or 50.7 percent in the fourth quarter of 2008 compared to the same quarter of 2007. For the full year in 2008, the total value of private building permits decreased $678.9 million or 18.9 percent from 2007. Government contracts awarded increased $155.4 million or 133.4 percent in the fourth quarter of 2008 compared to the same quarter of 2007. In 2008, government contracts awarded increased $83.3 million or 9.6 percent compared with that of 2007. State government CIP expenditures, however, were down $304.3 million or 46.6 percent in the fourth quarter of 2008 from the same quarter in 2007. CIP expenditures increase d $72.1 million or 4.9 percent for the year compared to 2007.
In the fourth quarter of 2008, Honolulu’s median price for single family resales was $610,000, a 2.4 percent decrease from the same quarter of 2007. The fourth quarter median price for condominium resales decreased 1.6 percent to $315,000 from the same quarter in 2007. In the fourth quarter of 2008, the numbers of single-family unit and condominium unit resales were down 19.1 percent and 34.2 percent, respectively, from the same quarter of 2007.
Traditionally a farm-based economy, growth in the trade, services and manufacturing sectors has decreased Kansas' strong dependence on agriculture. At present, the Kansas economy has four major economic sectors (manufacturing, wholesale and retail trade, government, and services) which respectively employ from 14 to 33 percent of the labor force.
Primary sources of state revenue are a 5.3% sales tax, a corporate income tax between 4% and 7.10% and an individual income tax between 3.5% and 6.45%. In 2008, the sales tax constituted 38.1% of taxes collected. The largest percentage of expenditures from all state funds are in the areas of education and research (public schools, state universities, state board of education) and human resources (assistance programs). General property taxes generate a large portion of local tax revenue. Local sales and use taxes have provided an increased amount of revenue, from $30 million in 1980 to $750.58 million in 2008, as voters in more cities and counties have elected to impose the tax or to raise the tax rate to the maximum permitted by state law.
The State's 2008 General Fund showed total revenues of $5.693 billion against total expenditures of $6.102 billion. In 1990, the Kansas legislature approved House Bill 2867 which established ending balances as a mechanism to hold state expenditure growth to the level of revenue growth. House Bill 2867 requires that in each fiscal year certain funds be transferred from the state General Fund to the newly created cash operating reserve fund. The reserve fund is designed to be available in the event that revenues in the General Fund are insufficient to meet budgeted expenditures. House Bill 2867 also provides that state General Fund balances in addition to the cash operating reserve fund must be one percent of expenditures in fiscal year 1993, two percent of expenditures in fiscal year 1994 and 2.5 percent in 1995 and each fiscal year thereafter.
PUERTO RICO, THE U.S. VIRGIN ISLANDS AND GUAM
Puerto Rico. Puerto Rico has a diversified economy dominated by the manufacturing and service sectors. The Commonwealth of Puerto Rico differs from the states in its relationship with the federal government. Most federal taxes, except those such as social security taxes that are imposed by mutual consent, are not levied in Puerto Rico. Section 936 of the Code has provided a tax credit for certain qualified U.S. corporations electing “possessions corporation” status. However, in 1993, Section 936 was amended to provide for two alternative limitations on the Section 936 credit attributable to certain active business income. The first limitation was based on the economic activity of the Section 936 possessions corporation. The second limited the credit to a specified percentage of the credit allowed under prior law. In 1996, Section 936 credit was repealed except that the credit attributable to possessions source business income with respect to certain ex isting credit claimants was subjected to a phase out over a ten year period (subject to additional caps).
Also in 1996, a new Section 30A was added to the Code. Section 30A permits a “qualifying domestic corporation” that meets certain gross income tests to claim a credit against the federal income tax in an amount equal to the portion of the tax which is attributable to the taxable income from sources outside of the United States, from the active conduct of a trade or business in Puerto Rico or from the sale of substantially all the assets used in such a trade or business. Section 30A was phased out January 1, 2006.
During the mid and late 1990s the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico benefited from a robust U.S. economy, more aggressive tax collections and low oil prices. This created an expanded employment base, job growth, reduction in unemployment, increase in tourism spending, real GDP growth in the 3.1% to 3.5% range and significant increases in General Fund cash
39
balances from fiscal year end 1997 to fiscal year end 1999. These factors, combined with minimal negative impact from the 1996 federal legislation phasing out Section 936 tax benefits to Puerto Rico subsidiaries of U.S. Corporations, created a positive outlook for the credit in the late 1990s.
In fiscal year 2000, the outlook on the credit turned negative due to the slowdown in the U.S. economy (88% of Puerto Rico’s exports go to the U.S.), uncertainty regarding increasing oil prices, failure of the government to reign in health care costs, expense overruns in education and a decreasing rate of employment growth. As a result, the General Fund recorded a $268 million deficit in fiscal year 2000 due to increased education and health care spending.
A new administration, the Popular Democratic Party that favors Puerto Rico’s commonwealth status over a potential statehood status, took office in January, 2001. It was not long before they realized the presence of continued fiscal stress and estimated a fiscal year 2001 budget shortfall of $700 million. The shortfall was stated to be caused by weakened revenue growth due to the slowing pace of employment and a softening U.S. economy.
On May 30, 2001, S&P downgraded the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico to an A- from an A due to continued years of operating deficits and the use of borrowing to cover the deficits. Puerto Rico continued to use deficit financing and cash transfers from other accounts to fill budget deficits for fiscal years 2002 - 2006. In fiscal year 2006, the Commonwealth hoped to balance the budget with cost saving measures and new excise taxes, but the deficit ballooned to $1.1 billion. As a result of continued annual deficits, and the 2 week shut down of non-essential government employees in May 2006, Moody’s lowered the rating on Puerto Rico to Baa3 from Baa2 on May 8, 2006. S&P rates Puerto Rico BBB- after a downgrade from BBB in May 2007 and A- in September 2005. In 2007, the government made progress toward structural balance by instituting a sales tax and flat spending. As a result, Moody’s changed their outlook from negative to stable last fall. However, due to the weakened economies of Puerto Rico and the U.S., Puerto Rico is estimating bigger budget shortfalls in fiscal years 2008 and 2009. The fiscal year 2009 shortfall is estimated at 33% general fund expenditures. The new administration that took office in January 2009 has proposed many spending cuts to combat the shortfall and is expecting $5.5 billion in federal stimulus dollars to spark the economy over the next few years.
The U.S. Virgin Islands. The United States Virgin Islands (“USVI”) is heavily reliant on the tourism industry, with roughly 43% of non-agricultural employment in tourist-related trade and services. The tourism industry is economically sensitive and is adversely affected by the recession in the United States and Europe. The attacks of September 11, 2001 also had an adverse affect on tourism. For 2001, air passengers to the USVI were down 2.9% after increasing 12% in 2000. However, supported by an increase in cruise passengers, total visitors increased by 4.4% in 2001. An important component of the USVI revenue base is the federal excise tax on rum exports. Tax revenues rebated by the federal government to the USVI provide the primary security of many outstanding USVI bonds. Since more than 90% of the rum distilled in the USVI is distilled at one plant, any interruption in its operations (as occurred after Hurricane Hugo in 1989) would adversely affect these revenues. The last major hurricane to impact the USVI was Hurricane Marilyn on September 15, 1995. Consequently, there can be no assurance that rum exports to the United States and the rebate of tax revenues to the USVI will continue at their present levels. The preferential tariff treatment the USVI rum industry currently enjoys could be reduced under NAFTA. Increased competition from Mexican rum producers could reduce USVI rum imported to the U.S., decreasing excise tax revenues generated.
The USVI is periodically hit by hurricanes. Several hurricanes have caused extensive damage, which has had a negative impact on revenue collections. In addition, eventual elimination of the Section 936 tax credit for those companies with operations in USVI may lead to slower growth in the future. Moody’s assigned a Baa3 rating to the territory and S&P a BBB- in September 2006.
Guam. The U.S. territory of Guam derives a substantial portion of its economic base from Japanese tourism. With a reduced U.S. military presence on the island, Guam has relied more heavily on tourism in past years. During 1998, the Japanese recession combined with the impact of typhoon Paka resulted in a budget deficit of $21 million. Based on these factors, S&P downgraded Guam's rating to BBB- from BBB with a negative outlook on May 26, 1999. Although total visitors improved in 1999 and 2000, they were weakened by economic slowdowns and the effects of the September 11th terrorist attacks in 2001. In 2002 Guam was hit with two major typhoons and impacted by the global economic slowdown. These negative trends have had an unfavorable effect on Guam’s financial position with consistent general fund deficits from 1997-2002 with the exception of a small surplus in 2000. Guam also has a high debt burden with outstanding debt per capita of $2,700 and debt service representing 16% of expenditures. These factors caused S&P to downgrade Guam’s rating to BB (below investment grade) from BBB– on March 25, 2002. Due to continued economic weakness and the negative effects of the typhoons in 2002, S&P further downgraded Guam’s debt to B from BB on May 6, 2003. Guam is not rated by Moody’s.
40
The ratings indicated herein are believed to be the most recent ratings available at the date of this SAI for the securities listed. Ratings are generally given to securities at the time of issuance. While the rating agencies may from time to time revise such ratings, they undertake no obligation to do so, and the ratings indicated do not necessarily represent ratings which would be given to these securities on a particular date.
MOODY’S INVESTORS SERVICE, INC. (“Moody’s”)
LONG-TERM CORPORATE OBLIGATIONS RATINGS
Moody’s long-term obligation ratings are opinions of the relative credit risk of fixed-income obligations with an original maturity of one year or more. They address the possibility that a financial obligation will not be honored as promised. Such ratings use Moody’s Global Scale and reflect both the likelihood of default and any financial loss suffered in the event of default.
Aaa: Obligations rated Aaa are judged to be of the highest quality, with minimal credit risk. Aa: Obligations rated Aa are judged to be of high quality and are subject to very low risk.
A: Obligations rated A are considered upper-medium grade and are subject to low credit risk.
Baa: Obligations rated Baa are subject to moderate credit risk. They are considered medium grade and as such may possess certain speculative characteristics.
Ba: Obligations rated Ba are judged to have speculative elements and are subject to substantial credit risk. B: Obligations rated B are considered speculative and are subject to high credit risk.
Caa: Obligations rated Caa are judged to be of poor standing and are subject to very high credit risk.
Ca: Obligations rated Ca are highly speculative and are likely in, or very near, default, with some prospect of recovery of principal and interest.
C: Obligations rated C are the lowest rated class of bonds and are typically in default, with little prospect for recovery of principal or interest.
Note: Moody’s appends numerical modifiers, 1, 2, and 3 to each generic rating classification from Aa through Caa. The modifier 1 indicates that the obligation ranks in the higher end of its generic rating category; the modifier 2 indicates a midrange ranking; and the modifier 3 indicates a ranking in the lower end of that generic rating category.
SHORT-TERM CORPORATE OBLIGATION RATINGS
Moody’s short term ratings are opinions of the ability of issuers to honor short-term financial obligations. Ratings may be assigned to issuers, short-term programs or to individual short-term debt instruments. Such obligations generally have an original maturity not exceeding thirteen months, unless explicitly noted.
P-1: Issuers (or supporting institutions) rated Prime-1 have a superior ability to repay short-term debt obligations.
P-2: Issuers (or supporting institutions) rated Prime-2 have a strong ability to repay short-term debt obligations.
P-3: Issuers (or supporting institutions) rated Prime-3 have an acceptable ability tot repay short-term obligations.
NP: Issuers (or supporting institutions) rated Not Prime do not fall within any of the Prime ratings categories.
ISSUER RATINGS
Issuer Ratings are opinions of the ability of entities to honor senior unsecured financial obligations and contracts. Moody’s expresses Issuer Ratings on its general long-term and short-term scales.
US MUNICIPAL RATINGS
Moody’s municipal ratings are opinions of the investment quality of issuers and issues in the U.S. municipal market. As such, these ratings incorporate assessment of the default probability and loss severity of these issuers and issues. The default and loss content for Moody’s municipal long-term rating scale differs from Moody’s general long-term scale. Historical default and loss rates for obligations rated on the US Municipal Scale are significantly lower that for similarly rated corporate obligations. It is important that users of Moody’s ratings understand these differences when making rating comparisons between the Municipal and Global scales.
41
US MUNICIPAL LONG-TERM DEBT RATINGS
Municipal Ratings are based upon the analysis of five primary factors related to municipal finance: market position, financial position, debt levels, governance, and covenants. Each of the factors is evaluated individually and for its effect on the other factors in the context of the municipality’s ability to repay its debt.
Aaa: Issuers or issues rated Aaa demonstrate the strongest creditworthiness relative to other US municipal or tax-exempt issuers or issues.
Aa: Issuers or issues rated Aa demonstrate very strong creditworthiness relative to other US municipal and tax-exempt issuers.
A: Issuers or issues rated A present above-average creditworthiness relative to other US municipal or tax-exempt issuers or issues.
Baa: Issuers or issues rated Baa represent average creditworthiness relative to other US municipal or tax-exempt issuers or issues.
Ba: Issuers or issues rated Ba demonstrate below-average creditworthiness relative to other US municipal or tax-exempt issuers or issues.
B: Issuers or issues rated B demonstrate weak creditworthiness relative to other US municipal or tax-exempt issuers or issues.
Caa: Issuers or issues rated Caa demonstrate very weak creditworthiness relative to other US municipal or tax-exempt issuers or issues.
Ca: Issuers or issues rated Ca demonstrate extremely weak creditworthiness relative to other US municipal or tax-exempt issuers or issues.
C: Issuers or issues rated Caa demonstrate the weakest creditworthiness relative to other US municipal or tax-exempt issuers or issues.
Note: Moody’s appends numerical modifiers, 1, 2, and 3 to each generic rating classification from Aa through Caa. The modifier 1 indicates that the obligation ranks in the higher end of its generic rating category; the modifier 2 indicates a midrange ranking; and the modifier 3 indicates a ranking in the lower end of that generic rating category.
US MUNICIPAL SHORT-TERM OBLIGATION RATINGS AND DEMAND OBLIGATION RATINGS
Short-Term Obligation Ratings
There are three rating categories for short-term municipal obligations that are considered investment grade. These ratings are designated as Municipal Investment Grade (MIG) and are divided into three levels--MIG 1 through MIG 3. In addition, those short-term obligations that are of speculative quality are designated SG, or speculative grade. MIG ratings expires at the maturity of the obligation.
MIG 1: This designation denotes superior credit quality. Excellent protection is afforded by established cash flows, highly reliable liquidity support, or demonstrated broad-band access to the market for refinancing.
MIG 2: This designation denotes strong credit quality. Margins of protection are ample, although not as large as in the preceding group/
MIG 3: This designation denotes acceptable credit quality. Liquidity and cash-flow protection may be narrow, and market access for refinancing is likely to be less well-established.
SG: This designation denotes speculative-grade credit quality. Debt instruments in this category may lack sufficient margins or protection.
Demand Obligation Ratings
In the case of variable rate demand obligations (VRDOs), a two-component rating is assigned; a long or short-term rating and demand obligation rating. The first element represents Moody’s evaluation of the degree of risk associated with scheduled principal and interest payments. The second element represents Moody’s evaluation of the degree of risk associated with the ability to receive purchase price upon demand (“demand feature”), using a variation of the MIG rating scale, the Variable Municipal Investment Grade or VMIG rating.
When either the long- or short-term aspect of a VRDO is not rated, that piece is designated NR., e.g., Aaa/NR or NR/VMIG.
42
VMIG rating expirations are a function of each issue’s specific structural or credit features.
VMIG 1: This designation denotes superior credit quality. Excellent protection is afforded by the superior short-term credit strength of the liquidity provider and structural and legal protections that ensure the timely payment of purchase price upon demand.
VMIG 2: This designation denotes strong credit quality. Good protection is afforded by the strong short-term credit strength of the liquidity provider and structural and legal protections that ensure the timely payment of purchase price upon demand.
VMIG 3: This designation denotes acceptable credit quality. Adequate protection is afforded by the satisfactory short-term credit strength of the liquidity provider and structural and legal protections that ensure the timely payment of purchase price upon demand.
SG: This designation denotes speculative-grade credit quality. Demand features rated in this category may be supported by a liquidity provider that does not have an investment grade short-term rating or may lack the structural and/or legal protections necessary to ensure the timely payment of purchase price upon demand.
STANDARD & POOR’S RATINGS GROUP (“S&P”)
ISSUE CREDIT RATINGS DEFINITIONS |
Issue credit ratings can be either long or short term. Short-term ratings are generally assigned to those obligations considered short-term in the relevant market. In the U.S., for example, that means obligations with an original maturity of no more than 365 days--including commercial paper. Short-term ratings are also used to indicated the creditworthiness of an obligor with respect to put-features on long-term obligations. The result is a dual rating, in which the short-term rating addresses the put feature, in addition to the usual long-term rating. Medium-term notes are assigned long-term ratings.
Issue credit ratings are based in varying degrees on the following considerations:
Likelihood of payment-- capacity and willingness of the obligor to meet its financial commitment on an obligation in accordance with the terms of the obligation.
Nature of and provisions of the obligations;
Protection afforded by, and relative position of, the obligation in the event of bankruptcy, reorganization, or other arrangement under the laws of bankruptcy and other laws affecting creditors’ rights.
Issue ratings are an assessment of default risk, but may incorporate an assessment of relative seniority or ultimate recovery in the event of default. Junior obligations are typically rated lower than senior obligations, to reflect the lower priority in bankruptcy, as noted above. (Such differentiation may apply when an entity has both senior and subordinated obligations, secured and unsecured obligations, or operating company and holding company obligations.)
LONG-TERM ISSUE CREDIT RATINGS:
AAA: An obligation rated ‘AAA’ has the highest rating assigned by S&P. The obligor’s capacity to meet its financial commitment on the obligation is extremely strong.
AA: An obligation rated ‘AA’ differs from the highest-rated obligors only to a small degree. The obligor’s capacity to meet its financial commitments on the obligation is very strong.
A: An obligation rated ‘A’ is somewhat more susceptible to the adverse effects of changes in circumstances and economic conditions than obligations in higher-rated categories. However, the obligor’s capacity to meet its financial commitments on the obligation is still strong.
BBB: An obligation rated ‘BBB’ exhibits adequate protection parameters. However, adverse economic conditions or changing circumstances are more likely to lead to a weakened capacity of the obligor to meet its financial commitment on the obligation.
BB, B, CCC, and CC and C
Obligations rated ‘BB’, ‘B’, ‘CCC’, ‘CC’, and ‘C’ are regarded as having significant speculative characteristics. ‘BB’ indicates the least degree of speculation and ‘C’ the highest. While such obligations will likely have some quality and protective characteristics, these may be outweighed by large uncertainties or major exposures to adverse conditions.
43
BB: An obligation rated ‘BB’ is less vulnerable to non-payment than other speculative issues. However, it faces major ongoing uncertainties or exposure to adverse business, financial, or economic conditions which could lead to the obligor’s inadequate capacity to meet its financial commitment on the obligation.
B: An obligation rated ‘B’ is more vulnerable than obligations rated ‘BB’, but the obligor currently has the capacity to meet its financial commitment on the obligation. Adverse business, financial or economic conditions will likely impair the obligor’s capacity or willingness to meet its financial commitment on the obligation.
CCC: An obligation rated ‘CCC’ is currently vulnerable to nonpayment, and is dependent upon favorable business, financial, and economic conditions for the obligor to meet its financial commitment on the obligation. In the event of adverse business, financial or, economic conditions, the obligor is not likely to have the capacity to meet its financial commitment on the obligation.
CC: An obligation rated ‘CC’ is currently highly vulnerable to nonpayment.
C: A subordinated debt or preferred stock obligation rated ‘C’ is currently highly vulnerable to nonpayment. The ‘C’ rating may be used to cover a situation where a bankruptcy petition has been filed or similar action taken, but payments on this obligation are being continued. A ‘C’ also will be assigned to a preferred stock issue in arrears on dividends or sinking fund payments, but that is currently paying.
D: A obligation rated ‘D’ is in payment default. The ‘D’ rating category is used when payments on an obligation are not made on the date due even if the applicable grace period has not expired, unless S&P believes that such payments will be made during such grace period. The ‘D’ rating also will be used upon the filing of a bankruptcy petition or the taking of a similar action if payments on an obligation are jeopardized.
Plus (+) or Minus (-): The ratings from ‘AA’ to’ CCC’ may be modified by the addition of a plus (+) or minus (-) sign to show relative standing within the major rating categories.
NR: This indicates that no rating has been requested, that there is insufficient information on which to base a rating, or that S&P does not rate a particular obligation as a matter of policy.
SHORT-TERM ISSUE CREDIT RATINGS
A-1: A short-term obligation rated ‘A-1’ is rated in the highest category by S&P. The obligor’s capacity to meet its financial commitment on the obligation is strong. Within this category, certain obligations are designated with a plus sign (+). This indicates that the obligor’s capacity to meet its financial commitments on these obligation is extremely strong.
A-2: A short-term obligation rated ‘A-2’ is somewhat more susceptible to the adverse effects of changes in circumstances and economic conditions than obligations in higher rating categories. However, the obligor’s capacity to meet its financial commitment on the obligation is satisfactory.
A-3: A short-term obligation rated ‘A-3’ exhibits adequate protection parameters. However, adverse economic conditions or changing circumstances are more likely to lead to a weakened capacity of the obligor to meet its financial commitment on the obligation.
B: A short-term obligation rated ‘B’ is regarded as having significant speculative characteristics. Ratings of ‘B-1’, ‘B-2’, and ‘B-3’ may be assigned to indicate finer distinctions within the ‘B’ category. The obligor currently has the capacity to meet its financial commitment on the obligation; however, it faces major ongoing uncertainties which could lead to the obligor’s inadequate capacity to meet its financial commitment on the obligation.
B-1: A short-term obligation rated ‘B-1’ is regarded as having significant speculative characteristics, but the obligor has a relatively stronger capacity to meet their financial commitments over the short-term compared to other speculative-grade obligors.
B-2: A short-term obligation rated ‘B-2’ is regarded as having significant speculative characteristics, and the obligor has an average speculative-grade capacity to meet its financial commitments over the short-term compared to other speculative-grade obligors.
B-3: A short-term obligation rated ‘B-3’ is regarded as having significant speculative characteristics, and the obligor has a relatively weaker capacity to meet its financial commitments over the short-term compared to other speculative-grade obligors.
C: A short-term obligation rated ‘C’ is currently vulnerable to nonpayment and is dependent upon favorable business, financial and economic conditions for the obligor to meet its financial commitment on the obligation.
44
D: A short-term obligation rated ‘D’ is in payment default. The ‘D’ rating category is used when payments on an obligation are not made on the date due even if the applicable grace period has not expired, unless S&P believes that such payments will be made during such grace period. The ‘D’ rating also will be used upon the filing of a bankruptcy petition or the taking of a similar action if payments on an obligation are jeopardized.
ISSUER CREDIT RATINGS DEFINTIONS
Issuer credit ratings are based on current information furnished by obligors or obtained by S&P from other sources it considers reliable. S&P does not perform an audit in connection with any issuer credit rating and may, on occasion, rely on unaudited financial information. Issuer credit ratings may be changed, suspended, or withdrawn as a result of changes in, or unavailability of, such information, or based on other circumstances. Issuer credit ratings can either be long or short term. Short-term issuer credit ratings reflect the obligor’s creditworthiness over a short-term horizon.
LONG-TERM ISSUER CREDIT RATINGS
AAA: An obligor rated ‘AAA’ has extremely strong capacity to meet its financial commitments. ‘AAA’ is the highest issuer credit rating assigned by S&P.
AA: An obligor rated ‘AA’ has very strong capacity to meet its financial commitments. It differs from the highest-rated obligors only to a small degree.
A: An obligor rated ‘A’ has strong capacity to meet its financial commitments but is somewhat more susceptible to the adverse effects of changes in circumstances and economic conditions than obligors in higher-rated categories.
BBB: An obligor rated ‘BBB’ has adequate capacity to meet its financial commitments. However, adverse economic conditions or changing circumstances are more likely to lead to a weakened capacity of the obligor to meet its financial commitments.
BB, B, CCC, and CC
Obligors rated ‘BB’, ‘B’, ‘CCC’, and ‘CC’ are regarded as having significant speculative characteristics. ‘BB’ indicates the least degree of speculation and ‘CC’ the highest. While such obligors will likely have some quality and protective characteristics, these may be outweighed by large uncertainties or major exposures to adverse conditions.
BB: An obligor ‘BB’ is less vulnerable in the near term than other lower-rated obligors. However, it faces major ongoing uncertainties and exposure to adverse business, financial, or economic conditions which could lead to the obligor’s inadequate capacity to meet its financial commitments.
B: An obligor rated ‘B’ is more vulnerable than the obligors rated ‘BB’, but the obligor currently has the capacity to meet its financial commitments. Adverse business, financial, or economic conditions will likely impair the obligor’s capacity or willingness to meets its financial commitments.
CCC: An obligor rated ‘CCC’ is currently vulnerable, and is dependent upon favorable business, financial, and economic conditions to meet its financial commitments.
CC: An obligor rated ‘CC’ is currently highly vulnerable.
Plus (+) or Minus (-): The ratings from ‘AA’ to’ CCC’ may be modified by the addition of a plus (+) or minus (-) sign to show relative standing within the major rating categories.
R: An obligor rated ‘R’ is under regulatory supervision owing to its financial condition. During the pendency of the regulatory supervision the regulators may have the power to favor one class of obligations over others or pay some obligations and not others. Please see S&P’s issue credit ratings for a more detailed description of the effects of regulatory supervision on specific issues or classes of obligations.
SD and D: An obligor rated ‘SD’ (selective default) or ‘D’ has failed to pay one or more of its obligations (rated or unrated) when it came due. A ‘D’ rating is assigned when S&P believes that the default will be a general default and that the obligor will fail to pay all or substantially all of its obligations as they come due. An ‘SD’ rating is assigned when S&P believes that the obligor has selectively defaulted on a specific issue or class of obligations but it will continue to meet its payment obligations on other issues or classes of obligations in a timely manner. Please see S&P’s issue credit ratings for a more detailed description of the effects of a default on specific issues or classes of obligations.
NR: An issuer designated NR is not rated.
SHORT-TERM ISSUER CREDIT RATINGS
45
A-1: An obligor rated ‘A-1’ has strong capacity to meet its financial commitments. It is rated in the highest category by S&P. Within this category, certain obligors are designated with a plus sign (+). This indicates that the obligor’s capacity to meet its financial commitments is extremely strong.
A-2: An obligor rated ‘A-2’ has satisfactory capacity to meet its financial commitments. However, it is somewhat more susceptible to the adverse effects of changes in circumstances and economic conditions than obligors in the highest rating category.
A-3: An obligor rated ‘A-3’ has adequate capacity to meet its financial obligations. However, adverse economic conditions or changing circumstances are more likely to lead to a weakened capacity of the obligor to meet its financial commitments.
B: An obligor rated ‘B’ is regarded as vulnerable and has significant speculative characteristics. Ratings ‘B-1’, ‘B-2’, and ‘B-3’ may be assigned to indicate finer distinctions within the ‘B’ category. The obligor currently has the capacity to meet its financial commitments; however, it faces major ongoing uncertainties which could lead to the obligor’s inadequate capacity to meet its financial commitments.
B-1: Obligors with a ‘B-1’ short-term rating have a relatively stronger capacity to meet their financial commitments over the short-term compared to other speculative-grade obligors.
B-2: Obligors with a ‘B-2’ short-term rating have an average speculative-grade capacity to meet their financial commitments over the short-term compared to other speculative-grade obligors.
B-3: Obligors with a ‘B-3’ short-term rating have a relatively weaker capacity to meet their financial commitments over the short-term compared to other speculative-grade obligors.
C: An obligor rated ‘C’ is currently vulnerable to nonpayment and is dependent upon favorable business, financial, and economic conditions for it to meet its financial commitments.
R: An obligor rated ‘R’ is under regulatory supervision owing to its financial condition. During the pendency of the regulatory supervision the regulators may have the power to favor one class of obligations over others or pay some obligations and not others. Please see S&P’s issue credit ratings for a more detailed description of the effects of regulatory supervision on specific issues or classes of obligations.
SD and D: An obligor rated ‘SD’ (selective default) or ‘D’ has failed to pay one or more of its obligations (rated or unrated) when it came due. A ‘D’ rating is assigned when S&P believes that the default will be a general default and that the obligor will fail to pay all or substantially all of its obligations as they come due. An ‘SD’ rating is assigned when S&P believes that the obligor has selectively defaulted on a specific issue or class of obligations but it will continue to meet its payment obligations on other issues or classes of obligations in a timely manner. Please see S&P’s issue credit ratings for a more detailed description of the effects of a default on specific issues or classes of obligations.
NR: An issuer designated as NR is not rated.
MUNICIPAL RATINGS
SHORT-TERM NOTES: An S&P U.S. municipal note ratings reflects the liquidity factors and market access risks unique to notes. Notes due in three years or less will likely receive a note rating. Notes maturing beyond three years will most likely receive a long-term debt rating. The following criteria will be used in making that assessment:
| Amortization schedule--the larger the final maturity relative to other maturities, the more likely it will be treated as a note; and |
| Source of payment--the more dependent the issue is on the market for its refinancing, the more likely it will be treated as a note. |
Note rating symbols are as follows:
SP-1: Strong capacity to pay principal and interest. An issue determined to possess a very strong capacity to pay debt will be given a plus(+) designation.
SP-2: Satisfactory capacity to pay principal and interest, with some vulnerability to adverse financial and economic changes over the term of the notes.
SP-3: Speculative capacity to pay principal and interest.
FITCH RATINGS
LONG-TERM CREDIT RATINGS |
46
Investment Grade
AAA: Highest credit quality ‘AAA’ ratings denote the lowest expectation of credit risk. They are assigned only in case of exceptionally strong capacity for payment of financial commitments. The capacity is highly unlikely to be adversely affected by foreseeable events.
AA: Very high credit quality. ‘AA’ ratings denote expectations of very low credit risk. They indicate very strong capacity for payment of financial commitments. This capacity is not significantly vulnerable to foreseeable events.
A: High credit quality. ‘A’ ratings denote expectations of low credit risk. The capacity for payment of financial commitments is considered strong. The capacity may, nevertheless, be more vulnerable to changes in circumstances or in economic conditions that is the case for higher ratings.
BBB: Good credit quality. ‘BBB’ ratings indicate that they are currently expectations of low credit risk. The capacity for payment of financial commitments is considered adequate but adverse changes in circumstances and economic conditions are more likely to impair this capacity. This is the lowest investment grade category.
Speculative Grade
BB: Speculative. ‘BB’ ratings indicate that there is a possibility of credit risk developing, particularly as the result of adverse economic change over time; however, business or financial alternatives may be available to allow financial commitments to be met. Securities rated in this category are not investment grade. The obligor’s ability to pay interest and repay principal may be affected over time by adverse economic changes. However, business and financial alternatives can be identified that could assist the obligor in satisfying its debt service requirements.
B: Highly speculative. For issuers and performing obligations, ‘B’ ratings indicate that significant credit risk is present, but a limited margin of safety remains. Financial commitments are currently being met; however, capacity for continued payment is contingent upon a sustained, favorable business and economic environment.
For individual obligations, may indicate distressed or defaulted obligations with potential for extremely high recoveries. Such obligations would possess a Recovery of Rating ‘RR1’ (outstanding).
CCC: For issuers and performing obligations, default is a real possibility. Capacity for meeting financial commitments is solely reliant upon sustained, favorable business or economic conditions.
For individual obligations, may indicate distressed or defaulted obligations with potential for average to superior levels of recovery. Differences in credit quality may be denoted by plus/minus distinctions. Such obligations typically would possess a Recovery Rating of ‘RR2’ (superior), ‘RR3’ (good) or ‘RR4’ (average).
CC: For issuers and performing obligations, default of some kind appears probable.
For individual obligations, may indicate distressed or defaulted obligations with a Recovery Rating of 'RR4' (average) or 'RR5' (below average).
C: For issuers performing obligations, default is imminent.
For individual obligations, may indicate distressed or defaulted obligations with potential for below-average to poor recoveries. Such obligations would possess a Recovery Rating of ‘RR6’ (poor).
RD: Indicates an entity that has failed to make due payments (within the applicable grace period) on some but not all material financial obligations, but continues to honor other classes of obligations.
D: Indicates an entity or sovereign that has defaulted on all of its financial obligations. Default generally is defined as one of the following:
Failure of an obligor to make timely payment of principal and/or interest under the contractual terms of any financial obligation; The bankruptcy filings, administration, receivership, liquidation or other winding-up or cessation of business of an obligor; The distressed or other coercive exchange of an obligation, where creditors were offered securities with diminished structural or economic terms compared with the existing obligation.
Default ratings are not assigned prospectively; within this context, non-payment on an instrument that contains a deferral feature or grace period will not be considered a default until after the expiration of the deferral or grace period.
Issuers will be rated 'D' upon a default. Defaulted and distressed obligations typically are rated along the continuum of 'C' to 'B' ratings categories, depending upon their recovery prospects and other relevant characteristics. Additionally, in structured finance transactions, where analysis indicates that an instrument is irrevocably impaired such that it is not
47
expected to meet pay interest and/or principal in full in accordance with the terms of the obligation's documentation during the life of the transaction, but where no payment default in accordance with the terms of the documentation is imminent, the obligation may be rated in the 'B' or 'CCC-C' categories.
Default is determined by reference to the terms of the obligations' documentation. Fitch will assign default ratings where it has reasonably determined that payment has not been made on a material obligation in accordance with the requirements of the obligation's documentation, or where it believes that default ratings consistent with Fitch's published definition of default are the most appropriate ratings to assign.
Notes to Long-Term ratings:
The modifiers "+" or "-" may be appended to a rating to denote relative status within major rating categories. Such suffixes are not added to the 'AAA' Long-term rating category, to categories below 'CCC', or to Short-term ratings other than 'F1'. (The +/- modifiers are only used to denote issues within the CCC category, whereas issuers are only rated CCC without the use of modifiers.)
Short-Term Credit Ratings
The following ratings scale applies to foreign currency and local currency ratings. A Short-term rating has a time horizon of less than 13 months for most obligations, or up to three years for US public finance, in line with industry standards, to reflect unique risk characteristics of bond, tax and revenue anticipation notes that are commonly issued with terms up to three years. Short-term ratings thus place greater emphasis on the liquidity necessary to meet financial commitments in a timely manner.
F1: Highest credit quality. Indicates the strongest capacity for timely payment of financial commitments; may have an added "+" to denote any exceptionally strong credit feature.
F2: Good credit quality. A satisfactory capacity for timely payment of financial commitments, but the margin of safety is not as great as in the case of the higher ratings.
F3: Fair credit quality. The capacity for timely payment of financial commitments is adequate; however, near term adverse changes could result in a reduction to non investment grade.
B: Speculative. Minimal capacity for timely payment of financial commitments, plus vulnerability to near term adverse changes in financial and economic conditions.
C: High default risk. Default is a real possibility. Capacity for meeting financial commitments is solely reliant upon a sustained, favorable business and economic environment.
D: Indicates an entity or sovereign that has defaulted on all of its financial obligations.
Notes to Short-Term ratings:
The modifiers "+" or "-" may be appended to a rating to denote relative status within major rating categories. Such suffixes are not added to the 'AAA' Long-term rating category, to categories below 'CCC', or to Short-term ratings other than 'F1'. (The +/- modifiers are only used to denote issues within the CCC category, whereas issuers are only rated CCC without the use of modifiers.)
48
DESCRIPTION OF INSURANCE FINANCIAL STRENGTH RATINGS
Moody’s Investors Service, Inc. Insurance Financial Strength Ratings
Moody’s Insurance Financial Strength Ratings are opinions of the ability of insurance companies to repay punctually senior policyholder claims and obligations. Specific obligations are considered unrated unless they are individually rated because the standing of a particular insurance obligation would depend on an assessment of its relative standing under those laws governing both the obligation and the insurance company. Insurance Companies rated Aaa offer exceptional financial security. While the credit profile of these companies is likely to change, such changes as can be visualized are most unlikely to impair their fundamentally strong position.
Standard &Poor’s Insurance Financial Strength Ratings
A S&P insurer financial strength rating is a current opinion of the financial security characteristics of an insurance organization with respect to its ability to pay under its insurance policies and contracts in accordance with their terms. Insurer financial strength ratings are also assigned to health maintenance organizations and similar health plans with respect to their ability to pay under their policies and contracts in accordance with their terms. This opinion is not specific to any particular policy or contract, nor does it address the suitability of a particular policy or contract for a specific purpose or purchaser. Furthermore, the opinion does not take into account deductibles, surrender or cancellation penalties, timeliness of payment, nor the likelihood of the use of a defense such as fraud to deny claims. For organizations with cross-border or multinational operations, including those conducted by subsidiaries or branch offices, the ratings do not take into acco unt potential that may exist for foreign exchange restrictions to prevent financial obligations from being met. Insurer financial strength ratings are based on information furnished by rated organizations or obtained by S&P from other sources it considers reliable. S&P does not perform an audit in connection with any rating and may on occasion rely on unaudited financial information. Ratings may be changed, suspended, or withdrawn as a result of changes in, or unavailability of such information or based on other circumstances. Insurer financial strength ratings do not refer to an organization's ability to meet nonpolicy (i.e. debt) obligations. Assignment of ratings to debt issued by insurers or to debt issues that are fully or partially supported by insurance policies, contracts, or guarantees is a separate process from the determination of insurer financial strength ratings, and follows procedures consistent with issue credit rating definitions and practices. Insurer financial strength ratings are not a recommendation to purchase or discontinue any policy or contract issued by an insurer or to buy, hold, or sell any security issued by an insurer. A rating is not a guaranty of an insurer's financial strength or security. An insurer rated ‘AAA’ has extremely strong financial security characteristics. ‘AAA’ is the highest insurer financial strength rating assigned by S&P.
Fitch Insurer Financial Strength Ratings
The Fitch Insurer Financial Strength (“IFS”) Rating provides an assessment of the financial strength of an insurance organization. The IFS Rating is assigned to the insurance company's policyholder obligations, including assumed reinsurance obligations and contract holder obligations, such as guaranteed investment contracts. The IFS Rating reflects both the ability of the insurer to meet these obligations on a timely basis, and expected recoveries received by claimants in the event the insurer stops making payments or payments are interrupted, due to either the failure of the insurer or some form of regulatory intervention. In the context of the IFS Rating, the timeliness of payments is considered relative to both contract and/or policy terms but also recognizes the possibility of reasonable delays caused by circumstances common to the insurance industry, including claims reviews, fraud investigations and coverage disputes. The IFS Rating does not encompass policyholder o bligations residing in separate accounts, unit-linked products or segregated funds, for which the policyholder bears investment or other risks. However, any guarantees provided to the policyholder with respect such obligations are included in the IFS Rating. Expected recoveries are based on Fitch's assessments of the sufficiency of an insurance company's assets to fund policyholder obligations, in a scenario in which payments have been ceased or interrupted. Accordingly, expected recoveries exclude the impact of recoveries obtained from any government sponsored guaranty or policyholder protection funds. Expected recoveries also exclude the impact of collateralizing or security, such as letters of credit or trusteed assets, supporting select reinsurance obligations. IFS Ratings can be assigned to insurance and reinsurance companies in any insurance sector, including the life & annuity, non-life, property/casualty, health, mortgage, financial guaranty, residual value and title insurance sectors, as well as to managed care companies such as health maintenance organizations. The IFS Rating does not address the quality of an insurer's claims handling services or the relative value of products sold. ‘AAA’ IFS Rating is exceptional strong. ‘AAA’ IFS Rating denotes the lowest exception of ceased or interrupted payments. They are assigned only in the case of exceptionally strong capacity to meet policyholder and contract obligations on a timely basis. This capacity is highly unlikely to be adversely affected by foreseeable events.
49
The following information relates to the Insured Fund and supplements the information contained under “Additional Information about Investment Policies -- Insurance.”
In General. Insured obligations held by the Fund will be insured as to their scheduled payment of principal and interest under (i) an insurance policy obtained by the issuer or underwriter of the obligation at the time of its original issuance (“Issue Insurance”), (ii) an insurance policy obtained by the Fund or a third party subsequent to the obligation's original issuance (“Secondary Market Insurance”) or (iii) a municipal insurance policy purchased by the Fund (“Mutual Fund Insurance”). The Fund anticipates that all or substantially all of its insured obligations will be subject to Issue Insurance or Secondary Market Insurance. Although the insurance feature reduces certain financial risks, the premiums for Mutual Fund Insurance (which, if purchased by the Fund, are paid from the Fund's assets) and the higher market price paid for obligations covered by Issue Insurance or Secondary Market Insurance reduce the Fund's curren t yield.
Insurance will cover the timely payment of interest and principal on obligations and will be obtained from insurers with a claims-paying ability rated at least Baa by Moody's or BBB by S&P or Fitch, provided that at least 50% of such net assets is invested in obligations insured by insurers having a claims-paying ability rated at least A by Moody’s, S&P or Fitch. Obligations insured by any insurer with such a claims-paying ability rating will generally carry the same rating or credit risk as the insurer. See the Appendix in Part I for a brief description of Moody's, Fitch's and S&P's claims-paying ability ratings. Such insurers must guarantee the timely payment of all principal and interest on obligations as they become due. Such insurance may, however, provide that in the event of non-payment of interest or principal when due with respect to an insured obligation, the insurer is not obligated to make such payment until a specified time period has lapsed (which may be 30 days or more after it has been notified by the Fund that such non-payment has occurred). For these purposes, a payment of principal is due only at final maturity of the obligation and not at the time any earlier sinking fund payment is due. While the insurance will guarantee the timely payment of principal and interest, it does not guarantee the market value of the obligations or the net asset value of the Fund.
Obligations are generally eligible to be insured under Mutual Fund Insurance if, at the time of purchase by the Fund, they are identified separately or by category in qualitative guidelines furnished by the mutual fund insurer and are in compliance with the aggregate limitations on amounts set forth in such guidelines. Premium variations are based, in part, on the rating of the obligations being insured at the time the Fund purchases the obligations. The insurer may prospectively withdraw particular obligations from the classifications of securities eligible for insurance or change the aggregate amount limitation of each issue or category of eligible obligations. The insurer must, however, continue to insure the full amount of the obligations previously acquired which the insurer has indicated are eligible for insurance, so long as they continue to be held by the Fund. The qualitative guidelines and aggregate amount limitations established by the insurer from time to time will not necessarily be the same as those the Fund would use to govern selection of obligations for the Fund. Therefore, from time to time such guidelines and limitations may affect investment decisions in the event the Fund's securities are insured by Mutual Fund Insurance.
For Mutual Fund Insurance that terminates upon the sale of the insured security, the insurance does not have any effect on the resale value of such security. Therefore, the Fund will generally retain any insured obligations which are in default or, in the judgment of the Investment Adviser, are in significant risk of default and place a value on the insurance. This value will be equal to the difference between the market value of the defaulted insured obligations and the market value of similar obligations which are not in default. As a result, the Investment Adviser may be unable to manage the securities held by the Fund to the extent the Fund holds defaulted insured obligations, which will limit its ability in certain circumstances to purchase other obligations. While a defaulted insured obligation is held by the Fund, the Fund will continue to pay the insurance premium thereon but will also collect interest payments from the insurer and retain the right to collect the full amoun t of principal from the insurer when the insured obligation becomes due. The Fund expects that the market value of a defaulted insured obligation covered by Issue Insurance or Secondary Market Insurance will generally be greater than the market value of an otherwise comparable defaulted obligation covered by Mutual Fund Insurance.
The Fund may also invest in obligations that are secured by an escrow or trust account which contains securities issued or guaranteed by the U.S. Government, its agencies or instrumentalities, that are backed by the full faith and credit of the United States, and sufficient in amount to ensure the payment of interest on and principal of the secured obligation (“collateralized obligations”). Collateralized obligations generally are regarded as having the credit characteristics of the underlying U.S. Government, agency or instrumentality securities. These obligations will not be subject to Issue Insurance, Secondary Market Insurance or Mutual Fund Insurance, but will be considered to be insured obligations for purposes of the Fund's policy of investing at least 80% of its net assets in insured obligations (but such obligations shall not constitute more than 15% of the insured portion of the Fund).
50
Principal Insurers. Currently, Municipal Bond Investors Assurance Corporation (“MBIA”), Financial Guaranty Insurance Company (“FGIC”), AMBAC Indemnity Corporation (“AMBAC”), Radian Asset Assurance (“Radian”), XL Capital Assurance (“XL Capital”), Financial Security Assurance Corp., together with its affiliated insurance companies--Financial Security Assurance International Inc. and Financial Security Assurance of Oklahoma, Inc. (collectively, “FSA”)and CIFG North America (“CIFG NA”), are considered to have a high claims-paying ability and, therefore, are eligible insurers for the Fund's obligations. Additional insurers may be added without further notification. The following information concerning these eligible insurers is based upon information provided by such insurers or information filed with certain state insurance regulators. Neither the Fund nor the Trust has independently verified such information and make no representations as to the accuracy and adequacy of such information or as to the absence of material adverse changes subsequent to the date thereof.
MBIA is a monoline financial guaranty insurance company created from an unincorporated association (the Municipal Bond Insurance Association), through which its members wrote municipal bond insurance on a several and joint-basis through 1986. Since then MBIA has expanded its bond insurance business to include asset-backed securities, corporate debt through Collateralized Debt Obligations (“CDOs”) and commercial real estate. MBIA issues municipal bond insurance policies guarantying the timely payment of principal and interest on new municipal bond issues and leasing obligations of municipal entities, secondary market insurance of such instruments and insurance on such instruments held in unit investment trusts and mutual funds. As of December 31, 2007, MBIA had total assets of approximately $47.4 billion and approximately $14.6 billion of claims paying resources. MBIA has a claims-paying ability rating of “AAA” by S&P, “Aaa” by Moody's and “AA” by Fitch.
Financial Guaranty Insurance Corporation, a wholly owned subsidiary of FGIC Corporation, which prior to December 18, 2003 was a wholly-owned subsidiary of General Electric Capital Corporation and was sold on that date for approximately $2.18 billion to an investor group consisting of The PMI Group, The Blackstone Group, The Cypress Group and CIVC Partners L.P., is an insurer of municipal securities, including new issues, securities held in unit investment trusts and mutual funds, and those traded on secondary markets. The investors in FGIC Corporation are not obligated to pay the debts of or claims against FGIC. As of December 31, 2007, FGIC had total assets of approximately $6.4 billion and approximately $5.4 billion of claims paying resources. FGIC has a claims-paying ability rating of “BB” by S&P, “BBB” by Fitch, and “Baa3” by Moody's.
AMBAC, a wholly owned subsidiary of AMBAC Inc., is a monoline insurance company whose policies guaranty the payment of principal and interest on municipal obligations issues. As of December 31, 2007, AMBAC had assets of approximately $23.6 billion and claims paying resources of approximately $14.5 billion. AMBAC has a claims-paying ability rating of “AAA” by S&P, “Aaa” by Moody's and “AA” by Fitch.
Radian is a wholly owned subsidiary of Radian Group Inc. Radian is rated AA by Standard & Poor’s and Aa3 by Moody’s. The Fitch Rating was withdrawn recently upon request of Radian. The company provides financial guaranty insurance and reinsurance for debt and asset backed securities. Radian was formerly known as Asset Guarantee Company and was purchased by Radian Group for $518 million in February 2001. As of December 31, 2007 Radian had assets of $8.2 billion and claims paying resources of $3.2 billion.
XL Capital is a financial guarantor and wholly owned subsidiary of property casualty insurer XL Capital Ltd. XL Capital began transactions in January of 2001 and is rated A3/A- by Moody’s and S&P respectively while Fitch rates XL Capital at BB. XL Financial Assurance guarantees 100% of XL Capital exposure with $3.6 billion in claims paying resources and $3.6 billion in assets as of December 31, 2007.
FSA purchased Capital Guaranty Insurance Company including its book of business and reserves effective December 20, 1995. FSA is a monoline insurer whose policies guaranty the timely payment of principal and interest on new issue and secondary market issue municipal securities transactions, among other financial obligations. On March 14, 2000, Dexia, Europe's largest municipal lender with assets in excess of $230 billion announced that it had signed a definitive agreement providing for the acquisition of FSA Holdings, holding company for FSA, Inc. Dexia acquired the company in the second quarter of 2000, for $2.6 billion in cash, or $76 per share. As of December 31, 2007, FSA had total assets of approximately $28 billion and claims paying resources of $6.7 billion. FSA has a claims-paying ability rating of “AAA” by S&P and Fitch and “Aaa” by Moody's.
CIFG is owned by France based Caisse Nationale des Caisses d’Epargne (CNCE) and Banque Federale des Banques Populaires (BFBP). CIFG NA insures primary and secondary market transactions in North America, primarily in the CDO and municipal market. CIFG is rated “Ba2” by Moody’s, “A+” by S&P and “A-” by Fitch. As of March 31, 2007, CIFG has claims paying resources of $1.4 billion and total assets of $1 billion.
51
EATON VANCE FUNDS
PROXY VOTING POLICY AND PROCEDURES |
I. Overview
The Boards of Trustees (the “Boards”) of the Eaton Vance Funds (the “Funds”) recognize that it is their fiduciary responsibility to actively monitor the Funds’ operations. The Boards have always placed paramount importance on their oversight of the implementation of the Funds’ investment strategies and the overall management of the Funds’ investments. A critical aspect of the investment management of the Funds continues to be the effective assessment and voting of proxies relating to the Funds’ portfolio securities. While the Boards will continue to delegate the day-to-day responsibilities relating to the management of the proxy-voting process to the relevant investment adviser or sub-adviser, if applicable, of the Fund (or its underlying portfolio in the case of a master-feeder arrangement), the Boards have determined that it is in the interests of the Funds’ shareholders to adopt these written proxy voting policy and procedures (the &# 147;Policy”). For purposes of this Policy the term “Fund” shall include a Fund’s underlying portfolio in the case of a master-feeder arrangement and the term “Adviser” shall mean the adviser to a Fund or its sub-adviser if a sub-advisory relationship exists.
II. Delegation of Proxy Voting Responsibilities
Pursuant to investment advisory agreements between each Fund and its Adviser, the Adviser has long been responsible for reviewing proxy statements relating to Fund investments and, if the Adviser deems it appropriate to do so, to vote proxies on behalf of the Funds. The Boards hereby formally delegate this responsibility to the Adviser, except as otherwise described in this Policy. In so doing, the Boards hereby adopt on behalf of each Fund the proxy voting policies and procedures of the Adviser(s) to each Fund as the proxy voting policies and procedures of the Fund. The Boards recognize that the Advisers may from time to time amend their policies and procedures. The Advisers will report material changes to the Boards in the manner set forth in Section V below. In addition, the Boards will annually review and approve the Advisers’ proxy voting policies and procedures.
III. Delegation of Proxy Voting Disclosure Responsibilities
The Securities and Exchange Commission (the “Commission”) recently enacted certain new reporting requirements for registered investment companies. The Commission’s new regulations require that funds (other than those which invest exclusively in non-voting securities) make certain disclosures regarding their proxy voting activities. The most significant disclosure requirement for the Funds is the duty pursuant to Rule 30b1-4 promulgated under the Investment Company Act of 1940, as amended (the “1940 Act”), to file Form N-PX no later than August 31st of each year beginning in 2004. Under Form N-PX, each Fund will be required to disclose, among other things, information concerning proxies relating to the Fund’s portfolio investments, whether or not the Fund (or its Adviser) voted the proxies relating to securities held by the Fund and how it voted in the matter and whether it voted for or against manageme nt.
The Boards hereby delegate to each Adviser the responsibility for recording, compiling and transmitting in a timely manner all data required to be filed on Form N-PX to Eaton Vance Management, which acts as administrator to each of the Funds (the “Administrator”), for each Fund that such Adviser manages. The Boards hereby delegate the responsibility to file Form N-PX on behalf of each Fund to the Administrator.
IV. Conflicts of Interest
The Boards expect each Adviser, as a fiduciary to the Fund(s) it manages, to put the interests of each Fund and its shareholders above those of the Adviser. In the event that in connection with its proxy voting responsibilities a material conflict of interest arises between a Fund’s shareholders and the Fund’s Adviser or the Administrator (or any of their affiliates) or any affiliated person of the Fund, and the Proxy Administrator intends to vote the proxy in a manner inconsistent with the guidelines approved by the Board, the Adviser, to the extent it is aware or reasonably should have been aware of the material conflict, will refrain from voting any proxies related to companies giving rise to such material conflict until it notifies and consults with the appropriate Board(s), or a committee or sub-committee of such Board concerning the material conflict.
Once the Adviser notifies the relevant Board(s), committee or sub-committee of the Board, of the material conflict, the Board(s), committee or sub-committee, shall convene a meeting to review and consider all relevant materials related to the
52
proxies involved. In considering such proxies, the Adviser shall make available all materials requested by the Board, committee or sub-committee and make reasonably available appropriate personnel to discuss the matter upon request. The Board, committee or sub-committee will instruct the Adviser on the appropriate course of action. If the Board, committee or sub-committee is unable to meet and the failure to vote a proxy would have a material adverse impact on the Fund(s) involved, each Adviser will have the right to vote such proxy, provided that it discloses the existence of the material conflict to the Board, committee or sub-committee at its next meeting. Any determination regarding the voting of proxies of each Fund that is made by the committee or sub-committee shall be deemed to be a good faith determination regarding the voting of proxies by the full Board.
V. Reports
The Administrator shall make copies of each Form N-PX filed on behalf of the Funds available for the Boards’ review upon the Boards’ request. The Administrator (with input from the Adviser for the relevant Fund(s)) shall also provide any reports reasonably requested by the Boards regarding the proxy voting records of the Funds.
Each Adviser shall annually report any material changes to such Adviser’s proxy voting policies and procedures to the relevant Board(s) and the relevant Board(s) will annually review and approve the Adviser’s proxy voting policies and procedures. Each Adviser shall report any changes to such Adviser’s proxy voting policies and procedures to the Administrator prior to implementing such changes in order to enable the Administrator to effectively coordinate the Funds’ disclosure relating to such policies and procedures.
53
EATON VANCE MANAGEMENT
BOSTON MANAGEMENT AND RESEARCH
PROXY VOTING POLICIES AND PROCEDURES |
I. Introduction
Eaton Vance Management, Boston Management and Research and Eaton Vance Investment Counsel (each an “Adviser” and collectively the “Advisers”) have each adopted and implemented policies and procedures that each Adviser believes are reasonably designed to ensure that proxies are voted in the best interest of clients, in accordance with its fiduciary duties and Rule 206(4)-6 under the Investment Advisers Act of 1940, as amended. The Advisers’ authority to vote the proxies of their clients is established by their advisory contracts or similar documentation, such as the Eaton Vance Funds Proxy Voting Policy and Procedures. These proxy policies and procedures reflect the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) requirements governing advisers and the long-standing fiduciary standards and responsibilities for ERISA accounts set out in the Department of Labor Bulletin 94-2 C.F.R. 2509.94-2 (July 29, 1994).
II. Overview
Each Adviser manages its clients’ assets with the overriding goal of seeking to provide the greatest possible return to such clients consistent with governing laws and the investment policies of each client. In pursuing that goal, each Adviser seeks to exercise its clients’ rights as shareholders of voting securities to support sound corporate governance of the companies issuing those securities with the principle aim of maintaining or enhancing the companies’ economic value.
The exercise of shareholder rights is generally done by casting votes by proxy at shareholder meetings on matters submitted to shareholders for approval (for example, the election of directors or the approval of a company’s stock option plans for directors, officers or employees). Each Adviser is adopting the formal written Guidelines described in detail below and will utilize such Guidelines in voting proxies on behalf of its clients. These Guidelines are designed to promote accountability of a company’s management and board of directors to its shareholders and to align the interests of management with those of shareholders.
Each Adviser will vote any proxies received by a client for which it has sole investment discretion through a third-party proxy voting service (“Agent”) in accordance with customized policies, as approved by the Boards of Trustees of the Eaton Vance Funds and, with respect to proxies referred back to the Adviser by the Agent pursuant to the Guidelines, in a manner that is reasonably designed to eliminate any potential conflicts of interest, as described more fully below. The Agent is currently Institutional Shareholder Services Inc. Proxies will be voted in accordance with client-specific guidelines and an Eaton Vance Fund’s sub-adviser’s proxy voting policies and procedures, if applicable.
No set of guidelines can anticipate all situations that may arise. In special cases, the Proxy Administrator (the person specifically charged with the responsibility to oversee the Agent and coordinate the voting of proxies referred back to the Adviser by the Agent) may seek insight from the Proxy Group established by the Advisers. The Proxy Group will assist in the review of the Agent’s recommendation when a proxy voting issue is referred to the Proxy Group through the Proxy Administrator. The members of the Proxy Group, which may include employees of the Advisers’ affiliates, may change at the Advisers’ discretion.
III. Roles and Responsibilities
| The Proxy Administrator will assist in the coordination of the voting of each client’s proxy in accordance with the Guidelines below and the Funds’ Proxy Voting Policy and Procedures. The Proxy Administrator is authorized to direct the Agent to vote a proxy in accordance with the Guidelines. Responsibilities assigned herein to the Proxy Administrator, or activities in support thereof, may be performed by such members of the Proxy Group or employees of the Advisers’ affiliates as are deemed appropriate by the Proxy Group. |
| An independent proxy voting service (the “Agent”), as approved by the Board of each Fund, shall be engaged to assist in the voting of proxies. The Agent is currently Institutional Shareholder Services Inc. The Agent is responsible for coordinating with the clients’ custodians and the Advisers to ensure that all proxy materials received by the custodians relating to the portfolio securities are processed in a timely fashion. The Agent is required to vote and/or refer all proxies in accordance with the Guidelines below. The Agent shall retain a record of all proxy votes handled by the Agent. Such record must reflect all of the information required to be disclosed in a Fund’s Form N-PX pursuant |
54
| to Rule 30b1-4 under the Investment Company Act of 1940. In addition, the Agent is responsible for maintaining copies of all proxy statements received by issuers and to promptly provide such materials to an Adviser upon request. |
| Subject to the oversight of the Advisers, the Agent shall establish and maintain adequate internal controls and policies in connection with the provision of proxy voting services to the Advisers, including methods to reasonably ensure that its analysis and recommendations are not influenced by a conflict of interest, and shall disclose such controls and policies to the Advisers when and as provided for herein. Unless otherwise specified, references herein to recommendations of the Agent shall refer to those in which no conflict of interest has been identified. |
| The Adviser shall establish a Proxy Group which shall assist in the review of the Agent’s recommendations when a proxy voting issue has been referred to the Proxy Administrator by the Agent. The members of the Proxy Group, which may include employees of the Advisers’ affiliates, may be amended from time to time at the Advisers’ discretion. |
| For each proposal referred to the Proxy Group, the Proxy Group will review the (i) Guidelines, (ii) recommendations of the Agent, and (iii) any other resources that any member of the Proxy Group deems appropriate to aid in a determination of the recommendation. |
| If the Proxy Group recommends a vote in accordance with the Guidelines, or the recommendation of the Agent, where applicable, it shall instruct the Proxy Administrator to so advise the Agent. |
| If the Proxy Group recommends a vote contrary to the Guidelines, or the recommendation of the Agent, where applicable, or if the proxy statement relates to a conflicted company of the Agent, as determined by the Advisers, it shall follow the procedures for such voting outlined below. |
| The Proxy Administrator shall use best efforts to convene the Proxy Group with respect to all matters requiring its consideration. In the event the Proxy Group cannot meet in a timely manner in connection with a voting deadline, the Proxy Administrator shall follow the procedures for such voting outlined below. |
IV. Proxy Voting Guidelines (“Guidelines”)
| It shall generally be the policy of the Advisers to take no action on a proxy for which no client holds a position or otherwise maintains an economic interest in the relevant security at the time the vote is to be cast. |
| In all cases except those highlighted below, it shall generally be the policy of the Advisers to vote in accordance with the recommendation by the Agent, Institutional Shareholder Services Inc. |
| When a fund client participates in the lending of its securities and the securities are on loan at the record date, proxies related to such securities generally will not be forwarded to the relevant Adviser by the fund’s custodian and therefore will not be voted. In the event that the Adviser determines that the matters involved would have a material effect on the applicable fund’s investment in the loaned securities, the fund will exercise its best efforts to terminate the loan in time to be able to cast such vote or exercise such consent. |
| Interpretation and application of these Guidelines is not intended to supersede any law, regulation, binding agreement or other legal requirement to which an issuer may be or become subject. The Guidelines relate to the types of proposals that are most frequently presented in proxy statements to shareholders. Absent unusual circumstances, each Adviser will utilize these Guidelines when voting proxies on behalf of its clients. The Guidelines may be revised at any time, provided such revisions are reported to the Boards of Trustees of the Eaton Vance Funds. |
| B. Proposals Regarding Mergers and Corporate Restructurings |
| The Agent shall be directed to refer proxy proposals accompanied by its written analysis and voting recommendation to the Proxy Administrator for all proposals relating to Mergers and Corporate Restructurings. |
| C. Proposals Regarding Mutual Fund Proxies – Disposition of Assets/Termination/Liquidation and Mergers |
| The Agent shall be directed to refer proxy proposals accompanied by its written analysis and voting recommendation to the Proxy Administrator for all proposals relating to the Disposition of Assets/Termination/Liquidation and Mergers contained in mutual fund proxies. |
| D. Corporate Structure Matters/Anti-Takeover Defenses |
| As a general matter, the Advisers will normally vote against anti-takeover measures and other proposals designed to limit the ability of shareholders to act on possible transactions (except in the case of closed-end management investment companies). |
55
| E. Social and Environmental Issues |
| The Advisers generally support management on social and environmental proposals. |
| Upon receipt of a referral from the Agent or upon advice from an Eaton Vance investment professional, the Proxy Administrator may solicit additional research from the Agent, as well as from any other source or service. |
| 1. WITHIN-GUIDELINES VOTES: Votes in Accordance with the Guidelines and/or, where applicable, Agent Recommendation |
| In the event the Proxy Administrator recommends a vote within Guidelines and/or, where applicable, in accordance with the Agent’s recommendation, the Proxy Administrator will instruct the Agent to vote in this manner. |
| 2. NON-VOTES: Votes in Which No Action is Taken |
| The Proxy Administrator may recommend that a client refrain from voting under the following circumstances: (i) if the economic effect on shareholders' interests or the value of the portfolio holding is indeterminable or insignificant, e.g., proxies in connection with securities no longer held in the portfolio of a client or proxies being considered on behalf of a client that is no longer in existence; or (ii) if the cost of voting a proxy outweighs the benefits, e.g., certain international proxies, particularly in cases in which share blocking practices may impose trading restrictions on the relevant portfolio security. In such instances, the Proxy Administrator may instruct the Agent not to vote such proxy. |
| Reasonable efforts shall be made to secure and vote all other proxies for the clients, but, particularly in markets in which shareholders' rights are limited, Non-Votes may also occur in connection with a client's related inability to timely access ballots or other proxy information in connection with its portfolio securities. |
| Non-Votes may also result in certain cases in which the Agent's recommendation has been deemed to be conflicted, as provided for herein. |
| 3. OUT-OF-GUIDELINES VOTES: Votes Contrary to Guidelines, or Agent Recommendation, where applicable, Where No Recommendation is Provided by Agent, or Where Agent's Recommendation is Conflicted |
| If the Proxy Administrator recommends that a client vote contrary to the Guidelines, or the recommendation of the Agent, where applicable, if the Agent has made no recommendation on a matter requiring case-by-case consideration and the Guidelines are silent, or the Agent's recommendation on a matter requiring case-by-case consideration is deemed to be conflicted, the Proxy Administrator will forward the Agent’s analysis and recommendation and any research obtained from the Agent or any other source to the Proxy Group. The Proxy Group may consult with the Agent as it deems necessary. The Proxy Administrator will instruct the Agent to vote the proxy as recommended by the Proxy Group. The Adviser will provide a report to the Boards of Trustees of the Eaton Vance Funds reflecting any votes cast contrary to the Guidelines or Agent Recommendation, as applicable, and shall do so no less than annually. |
The Proxy Administrator will maintain a record of all proxy questions that have been referred by the Agent, all applicable recommendations, analysis and research received and any resolution of the matter.
V. Recordkeeping
The Advisers will maintain records relating to the proxies they vote on behalf of their clients in accordance with Section 204-2 of the Investment Advisers Act of 1940, as amended. Those records will include:
- A copy of the Advisers’ proxy voting policies and procedures;
- Proxy statements received regarding client securities. Such proxy statements received from issuers are either in the SEC’s EDGAR database or are kept by the Agent and are available upon request;
- A record of each vote cast;
- A copy of any document created by the Advisers that was material to making a decision on how to vote a proxy for a client or that memorializes the basis for such a decision; and
- Each written client request for proxy voting records and the Advisers’ written response to any client request (whether written or oral) for such records.
All records described above will be maintained in an easily accessible place for five years and will be maintained in the offices of the Advisers or their Agent for two years after they are created.
56
VI. Assessment of Agent and Identification and Resolution of Conflicts with Clients
| The Advisers shall establish that the Agent (i) is independent from the Advisers, (ii) has resources that indicate it can competently provide analysis of proxy issues, and (iii) can make recommendations in an impartial manner and in the best interests of the clients and, where applicable, their beneficial owners. The Advisers shall utilize, and the Agent shall comply with, such methods for establishing the foregoing as the Advisers may deem reasonably appropriate and shall do so not less than annually as well as prior to engaging the services of any new proxy voting service. The Agent shall also notify the Advisers in writing within fifteen (15) calendar days of any material change to information previously provided to an Adviser in connection with establishing the Agent's independence, competence or impartiality. |
| As fiduciaries to their clients, each Adviser puts the interests of its clients ahead of its own. In order to ensure that relevant personnel of the Advisers are able to identify potential material conflicts of interest, each Adviser will take the following steps: |
| • Quarterly, the Eaton Vance Legal and Compliance Department will seek information from the department heads of each department of the Advisers and of Eaton Vance Distributors, Inc. (“EVD”) (an affiliate of the Advisers and principal underwriter of certain Eaton Vance Funds). Each department head will be asked to provide a list of significant clients or prospective clients of the Advisers or EVD. |
| • A representative of the Legal and Compliance Department will compile a list of the companies identified (the “Conflicted Companies”) and provide that list to the Proxy Administrator. |
| • The Proxy Administrator will compare the list of Conflicted Companies with the names of companies for which he or she has been referred a proxy statement (the “Proxy Companies”). If a Conflicted Company is also a Proxy Company, the Proxy Administrator will report that fact to the Proxy Group. |
| • If the Proxy Administrator expects to instruct the Agent to vote the proxy of the Conflicted Company strictly according to the Guidelines contained in these Proxy Voting Policies and Procedures (the “Policies”) or the recommendation of the Agent, as applicable, he or she will (i) inform the Proxy Group of that fact, (ii) instruct the Agent to vote the proxies and (iii) record the existence of the material conflict and the resolution of the matter. |
| • If the Proxy Administrator intends to instruct the Agent to vote in a manner inconsistent with the Guidelines contained herein or the recommendation of the Agent, as applicable, the Proxy Group, in consultation with Eaton Vance senior management, will then determine if a material conflict of interest exists between the relevant Adviser and its clients. If the Proxy Group, in consultation with Eaton Vance senior management, determines that a material conflict exists, prior to instructing the Agent to vote any proxies relating to these Conflicted Companies the Adviser will seek instruction on how the proxy should be voted from: |
| • The client, in the case of an individual or corporate client; |
| • In the case of a Fund, its board of directors, or any committee or sub-committee identified by the board; or |
| • The adviser, in situations where the Adviser acts as a sub-adviser to such adviser. |
The Adviser will provide all reasonable assistance to each party to enable such party to make an informed decision.
If the client, Fund board or adviser, as the case may be, fails to instruct the Adviser on how to vote the proxy, the Adviser will generally instruct the Agent, through the Proxy Administrator, to abstain from voting in order to avoid the appearance of impropriety. If however, the failure of the Adviser to vote its clients’ proxies would have a material adverse economic impact on the Advisers’ clients’ securities holdings in the Conflicted Company, the Adviser may instruct the Agent, through the Proxy Administrator, to vote such proxies in order to protect its clients’ interests. In either case, the Proxy Administrator will record the existence of the material conflict and the resolution of the matter.
The Advisers shall also identify and address conflicts that may arise from time to time concerning the Agent. Upon the Advisers’ request, which shall be not less than annually, and within fifteen (15) calendar days of any material change to such information previously provided to an Adviser, the Agent shall provide the Advisers with such information as the Advisers deem reasonable and appropriate for use in determining material relationships of the Agent that may pose a conflict of interest with respect to the Agent’s proxy analysis or recommendations. Such information shall include, but is not limited to, a monthly report from the Agent detailing the Agent’s Corporate Securities Division clients and related revenue data. The Advisers shall review such information on a monthly basis. The Proxy Administrator shall instruct the Agent to refer any proxies for which a material conflict of the Agent is deemed to be present to the Proxy Administrator. Any such proxy referr ed by the Agent shall be referred to the Proxy Group for consideration accompanied by the Agent’s written analysis and voting recommendation. The Proxy Administrator will instruct the Agent to vote the proxy as recommended by the Proxy Group.
57




