Exhibit 1
Japan Finance Organization
for Municipalities
This description of Japan Finance Organization for Municipalities is dated April 16, 2010 and appears as Exhibit 1 to its Annual Report on Form 18-K to the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission.
THE DELIVERY OF THIS DOCUMENT AT ANY TIME DOES NOT IMPLY THAT THE INFORMATION IS CORRECT AS OF ANY TIME SUBSEQUENT TO ITS DATE. THIS DOCUMENT (OTHERWISE THAN AS PART OF A PROSPECTUS CONTAINED IN A REGISTRATION STATEMENT FILED UNDER THE U.S. SECURITIES ACT OF 1933) DOES NOT CONSTITUTE AN OFFER TO SELL OR THE SOLICITATION OF AN OFFER TO BUY ANY SECURITIES OF JAPAN FINANCE ORGANIZATION FOR MUNICIPALITIES.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
| | | | | |
| | | Page | |
| JAPAN FINANCE ORGANIZATION FOR MUNICIPALITIES | | | 3 | |
| CAPITALIZATION | | | 3 | |
| RECENT DEVELOPMENTS | | | 4 | |
| BUSINESS | | | 6 | |
| Purpose and Authority | | | 6 | |
| Government Control and Supervision | | | 6 | |
| Loan Operations | | | 8 | |
| Loan Terms | | | 9 | |
| Funds Available for Lending | | | 11 | |
| Risk Management | | | 11 | |
| MANAGEMENT | | | 15 | |
| DEBT RECORD | | | 16 | |
| FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF THE PREDECESSOR | | | 16 | |
| FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF JFM | | | 21 | |
| SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE | | | 45 | |
FURTHER INFORMATION
This document appears as an exhibit to the Annual Report on Form 18-K of Japan Finance Organization for Municipalities (“JFM”) filed with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (the Commission). Additional information with respect to JFM is available in such Annual Report, in the other exhibits to such Annual Report and in amendments thereto. Such Annual Report, exhibits and amendments may be inspected and copied at the public reference room maintained by the Commission at: 100 F Street, N.E., Washington, D.C. 20549. Information regarding the operations of the Commission’s public reference room can be obtained by calling the Commission at 1-800-SEC-0330. Copies of such documents may also be obtained from JFM by telephoning 81-3-3539-2690. The Annual Report and its exhibits and amendments are also available through the Commission’s Internet website at http://www.sec.gov.
In this document all amounts are expressed in Japanese Yen (“¥” or “yen”), except as otherwise specified. The spot buying rate quoted on the Tokyo Foreign Exchange Market on April 14, 2010, as reported by The Bank of Japan at 5:00 p.m., Tokyo time, was ¥93.47 = $1.00, and the noon buying rate on April 9, 2010 for cable transfers in New York City payable in yen, as reported by the Federal Reserve Bank of New York, was ¥93.28 =$1.00.
References to fiscal years of JFM are to the 12-month periods commencing on April 1 of the year indicated, except that references to the fiscal year 2008 refer to (1) the six-month fiscal period ended September 30, 2008 of Japan Finance Corporation for Municipal Enterprises (the predecessor to JFM) (the “Predecessor”), which was its last fiscal period, and (2) the eight-month fiscal period ended March 31, 2009 of JFM, which was its first fiscal period.
Unless otherwise indicated, all amounts relating to JFM are presented on a basis consistent with the audited financial statements of JFM, which have been prepared in accordance with the Japan Finance Organization for Municipalities Law (Law No. 64 of May 30, 2007), as amended (the “JFM Law”), and which are included in this document.
Figures in tables may not add up to totals due to rounding.
JAPAN FINANCE ORGANIZATION FOR MUNICIPALITIES
JFM was established on August 1, 2008, initially under the name “Japan Finance Organization for Municipal Enterprises,” by local governments as an autonomously managed organization. JFM started its business on October 1, 2008, at which time JFM succeeded to substantially all of the rights and assets of the Predecessor and assumed all of the obligations of the Predecessor and the Predecessor was dissolved. Whereas the Predecessor’s capital was contributed entirely by the national government, JFM’s capital was provided by Japan’s local governments. At the time of JFM’s establishment, JFM received contributions in the amount of ¥16.6 billion from all of the local governments (prefectures, government-designated cities, cities, special wards of Tokyo, towns and villages – 1,857 in total as of August 1, 2008).
On June 1, 2009, the amended JFM Law went into effect, which provided for the change of JFM’s name, expansion of the scope of its lending and flexibility of its lending terms. See “Recent Developments – Reorganization from Japan Finance Organization for Municipal Enterprises to Japan Finance Organization for Municipalities”. Among other changes, the name of JFM was changed from “Japan Finance Organization for Municipal Enterprises” to “Japan Finance Organization for Municipalities”.
Under the JFM Law, JFM is supervised by the Representative Board, a committee composed of representatives of Japan’s local governments and individuals who are knowledgeable in economics, finance, law and accounting as well as the affairs of local administrations and their finances, with respect to such matters as appointment of management, business plans and annual budget.
CAPITALIZATION
The capitalization of JFM as of March 31, 2009 was as follows:
| | | | | |
| | | (in millions) | |
| Domestic bonds: | | | | |
| Government guaranteed bonds: | | | | |
| 0.5%-2.2% Guaranteed Bonds due 2008-2022 | | ¥ | 11,922,460 | |
| Non-government guaranteed private placement bonds | | | 3,492,453 | |
| Non-government guaranteed public offering bonds | | | 2,297,830 | |
| Government guaranteed bonds issued overseas | | | 1,126,160 | |
| | | | |
| | | | | |
| Total long-term bonds (1) | | | 18,838,903 | |
| | | | |
| | | | | |
| Net Assets: | | | | |
| Capital | | | 16,602 | |
| Retained earnings | | | 1,295 | |
| General account surplus reserve | | | 1,295 | |
| Management account surplus reserve | | | 35,190 | |
| | | | |
| | | | | |
| Total net assets | | | 53,087 | |
| | | | |
| | | | | |
| Total capitalization | | ¥ | 18,891,990 | |
| | | | |
| | | |
| (1) | | Includes current maturities. For additional information relating to long-term bonds, see Note 6 to JFM’s audited financial statements included elsewhere in this document. |
-3-
RECENT DEVELOPMENTS
Trends in Lending Operations
The outstanding loan balances of the Predecessor reached ¥1 trillion in 1974, ¥5 trillion in 1981, ¥10 trillion in 1986, ¥20 trillion in 1997, ¥25 trillion in 2004, and in October 2008, JFM inherited the loan balance of ¥22,458.6 billion from the Predecessor. In fiscal year 2008, the Predecessor and JFM made long-term loans in the amount of ¥1,108.8 billion. As of September 30, 2009, the outstanding loan balance was ¥21,845.1 billion. As of March 31, 2009, the number of local governments borrowing from JFM totaled 2,079, including all prefectures. Cities and special wards of Tokyo had the highest balance of ¥15,451.0 billion and accounted for 71% of the total outstanding loan balance. Next were prefectures with a balance of ¥3,900.4 billion and an 18% share of the total. Finally, towns, villages, local government associations and others had a balance of ¥2,493.8 billion and accounted for 11% of the total balance.
In terms of project type, water supply, electricity supply and port facilities projects were the primary targets of the Predecessor’s loans during the mid-1950s to mid-1960s. The targets shifted to water supply, regional development and sewerage projects in the mid-1960s to mid-1970s, and from the mid-1970s to the mid-1980s, the major targets were sewerage, water supply and three types of “special projects” (i.e., projects of great urgency and necessity to respond appropriately to the issues of the regional community). Recently, sewerage and three types of special projects accounted for a high share of the total. As of September 30, 2009, of the outstanding loan balance of ¥21,845.1 billion, sewerage projects accounted for the largest share at 41.9%, followed by three types of special projects (primarily local road construction) at 22.2%, and water supply at 19.3% of the total.
Reorganization from Japan Finance Organization for Municipal Enterprises to Japan Finance Organization for Municipalities
Shortly after JFM began operations, the proposal for the “creation of a financial organization jointly owned by local governments for the purpose of providing long-term and low-interest funds for local governments (general account)” was incorporated into the economic policy package put together by the national government and the ruling party on October 30, 2008. As a result of deliberations on this proposal within the national government, a bill, which included the provisions for expansion of JFM’s scope of lending and a change in the organization name, was submitted to the Diet, and was passed in March 2009. As a result, on June 1, 2009, JFM was reorganized, changing its name from “Japan Financial Organization for Municipal Enterprises” to “Japan Finance Organization for Municipalities”, and the scope of lending was expanded to include the general account of local governments, in addition to municipal enterprises as in the past. Moreover, in response to the requests of local governments, JFM has improved the terms of lending, including extension of terms to maturity and increased application of special interest rates.
As an organization owned jointly by local governments, JFM can now operate more independently than the Predecessor, and as a result of the expansion of scope of lending, JFM is now able to respond to the funding needs of local governments in a more timely and appropriate manner.
Name Change
JFM’s name has been changed from “Japan Finance Organization for Municipal Enterprises” to “Japan Finance Organization for Municipalities” to reflect the fact that it can now provide funds not only for projects of municipal enterprises, but also for overall operations of local governments, as a result of the expansion of the scope of lending to include the general account.
-4-
Expansion of the Scope of Lending
JFM, main target of lending was originally municipal enterprises, while lending for general account-related projects was limited to the three categories of local road construction, improvement of rivers and other waterways, and high school construction. Now, with the inclusion of the general account into the scope of lending, JFM can respond to the financing needs of local governments in a timely and appropriate manner. JFM can also respond flexibly to extraordinary financial countermeasure funding needs of local governments to cover shortfalls caused by disruption in domestic and international financial systems, or changes in economic conditions. During fiscal year 2009, specific targets of lending include independent general account-related projects initiated autonomously by local governments, such as regional revitalization projects, disaster prevention projects and special municipal merger projects, in addition to the existing three special projects (primarily local road construction). As for extraordinary financial countermeasure funding, which is expected to increase rapidly, JFM plans to lend mainly to cities, towns and villages, which face difficulties in raising long-term funds.
Improved Lending Terms
As a joint organization of local governments, JFM is now able to act more flexibly than the Predecessor in setting loan maturities and interest rates based on local governments’ needs. At the time of the reorganization, the maximum term to maturity was extended from 28 years to 30 years. The extra special interest rates will be applied to loans for general account-related projects including the existing three special projects.
-5-
BUSINESS
Purpose and Authority
Under the JFM Law, JFM’s objective is to contribute to the sound financial operation of local governments and to improve the welfare of local residents by providing long-term funding at low interest rates to local governments with respect to their general account-related projects as well as to municipal enterprises, and also by supporting funding by local governments from capital markets, in order to efficiently and effectively acquire such funding. Municipal enterprises are departments within local governments which undertake public service activities, such as water supply, sewerage, hospital facilities and transportation, which are accounted for independently from general services like social welfare and education.
Government Control and Supervision
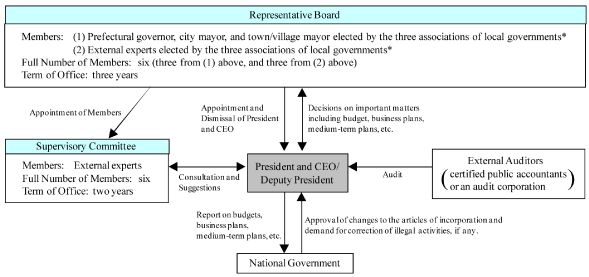
JFM’s capital is contributed by all of Japan’s local governments – 47 prefectures as well as government-designated cities, special wards of Tokyo, towns and villages. JFM is subject to control and supervision of the local governments through the Representative Board, which consists of members nominated by the local governments. There are six members, three of which are heads of local governments (governors of prefectures or mayors of cities, towns or villages) and the other three are individuals knowledgeable in economics, finance, law and accounting as well as the affairs of local administrations and their finances. The term of each member is three years. The Representative Board appoints JFM’s President and Chief Executive Officer and Corporate Auditors. The Representative Board is authorized to approve such key management matters as appointment of management, business plans and annual budget. The Representative Board is also authorized to obtain from JFM’s management information relating to JFM’s operations and financial condition, and to order JFM’s management to take corrective actions with respect to any illegal or other inappropriate activities.
To ensure adequate third-party monitoring of JFM’s business activities, JFM has a Supervisory Committee (the “Committee”). The members of the Committee are appointed by the Representative Board, and are individuals knowledgeable in economics, finance, law and accounting as well as the affairs of local administrations and their finances. The Committee is authorized to monitor JFM’s annual budgets and business plans and to provide its opinions and recommendations to JFM’s management with respect to key matters on JFM’s business and operations. JFM’s management is required to report to the Representative Board, and to give due regard to, such opinions and recommendations of the Committee.
Under the JFM Law, JFM is required to report to the national government (the Minister for Internal Affairs and Communications) its annual budgets, business plans and financial statements. Changes to JFM’s articles of incorporation require the approval of the Minister for Internal Affairs and Communications. The Minister for Internal Affairs and Communications is authorized to request JFM to take corrective actions with respect to any illegal or other inappropriate activities.
-6-
The following diagram summarizes the governance structure of JFM:
Corporate Governance System
| | | |
| * | | Three associations of local governments are National Governors’ Association, Japan Association of City Mayors and National Association of Towns and Villages. |
-7-
Loan Operations
JFM’s loan operations can be broadly divided into general loans and entrusted loans. General loans are loans to local governments. Entrusted loans are loans from funds entrusted to JFM by The Japan Finance Corporation (“JFC”), a governmental financial institution, which are used for on-lending to local governments for financing maintenance of public forests and improvements of pastures.
The following tables give details of the loans extended by the Predecessor and JFM during each of the four years in the period ended March 31, 2008 and six months ended September 30, 2008, March 31, 2009 and September 30, 2009.
Loans Extended
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | The Predecessor | | | JFM | |
| | | Years ended March 31, | | | Six months ended | |
| | | 2005 | | | 2006 | | | 2007 | | | 2008 | | | September 30, 2008 | | | March 31, 2009 | | | September 30, 2009 | |
| | | (in billions) |
| General Loans And Loans To Local Public Corporations | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Community facilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Water supply | | ¥ | 231 | | | | 14.0 | % | | ¥ | 186 | | | | 13.3 | % | | ¥ | 164 | | | | 13.4 | % | | ¥ | 156 | | | | 13.9 | % | | ¥ | 20 | | | | 3.1 | % | | ¥ | 131 | | | | 27.6 | % | | ¥ | 21 | | | | 5.8 | % |
| Gas supply | | | 3 | | | | 0.2 | | | | 1 | | | | 0.1 | | | | 1 | | | | 0.1 | | | | 1 | | | | 0.1 | | | | 0 | | | | 0.0 | | | | 1 | | | | 0.2 | | | | 0 | | | | 0.0 | |
| Sewerage | | | 576 | | | | 35.0 | | | | 497 | | | | 35.5 | | | | 446 | | | | 36.6 | | | | 437 | | | | 38.8 | | | | 265 | | | | 41.9 | | | | 193 | | | | 40.6 | | | | 202 | | | | 56.6 | |
| Public housing | | | 34 | | | | 2.1 | | | | 28 | | | | 2.0 | | | | 24 | | | | 2.0 | | | | 16 | | | | 1.5 | | | | 14 | | | | 2.2 | | | | 3 | | | | 0.5 | | | | 14 | | | | 3.9 | |
High school construction(1) | | | 6 | | | | 0.4 | | | | 4 | | | | 0.3 | | | | 6 | | | | 0.5 | | | | 2 | | | | 0.2 | | | | 2 | | | | 0.3 | | | | 0 | | | | 0.0 | | | | 8 | | | | 2.1 | |
Improvement of rivers and other waterways(1) | | | 19 | | | | 1.1 | | | | 5 | | | | 0.4 | | | | 6 | | | | 0.5 | | | | 7 | | | | 0.6 | | | | 5 | | | | 0.7 | | | | 1 | | | | 0.1 | | | | | | | |
| Hospitals | | | 97 | | | | 5.9 | | | | 74 | | | | 5.3 | | | | 57 | | | | 4.7 | | | | 50 | | | | 4.5 | | | | 4 | | | | 0.6 | | | | 64 | | | | 13.5 | | | | 3 | | | | 0.7 | |
| Elderly care | | | 5 | | | | 0.3 | | | | 7 | | | | 0.5 | | | | 4 | | | | 0.3 | | | | 3 | | | | 0.2 | | | | 1 | | | | 0.1 | | | | 1 | | | | 0.2 | | | | 0 | | | | 0.1 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | 971 | | | | 59.0 | | | | 802 | | | | 57.3 | | | | 708 | | | | 58.0 | | | | 672 | | | | 59.7 | | | | 311 | | | | 48.9 | | | | 394 | | | | 82.7 | | | | 248 | | | | 69.2 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Road construction and transportation facilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Transportation (excluding subways) | | | 6 | | | | 0.4 | | | | 5 | | | | 0.4 | | | | 10 | | | | 0.8 | | | | 9 | | | | 0.8 | | | | 0 | | | | 0.0 | | | | 2 | | | | 0.5 | | | | 0 | | | | 0.0 | |
| Subways | | | 134 | | | | 8.1 | | | | 97 | | | | 6.9 | | | | 64 | | | | 5.2 | | | | 53 | | | | 4.7 | | | | 1 | | | | 0.1 | | | | 48 | | | | 10.1 | | | | 3 | | | | 0.9 | |
| Local road construction | | | 368 | | | | 22.4 | | | | 261 | | | | 18.6 | | | | 209 | | | | 17.1 | | | | 166 | | | | 14.8 | | | | 118 | | | | 18.6 | | | | 18 | | | | 3.8 | | | | 100 | | | | 28.1 | |
| Toll roads and parking facilities | | | 2 | | | | 0.1 | | | | 4 | | | | 0.3 | | | | 2 | | | | 0.1 | | | | 1 | | | | 0.1 | | | | 1 | | | | 0.2 | | | | 0 | | | | 0.0 | | | | 0 | | | | 0.0 | |
| Recreation facilities | | | 1 | | | | 0.1 | | | | 0 | | | | 0.0 | | | | 0 | | | | 0.0 | | | | 0 | | | | 0.0 | | | | 0 | | | | 0.0 | | | | 0 | | | | 0.0 | | | | 0 | | | | 0.1 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | 511 | | | | 31.1 | | | | 367 | | | | 26.1 | | | | 285 | | | | 23.3 | | | | 229 | | | | 20.4 | | | | 120 | | | | 18.9 | | | | 68 | | | | 14.4 | | | | 103 | | | | 29.1 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Industry and distribution-related facilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Industrial water supply | | | 11 | | | | 0.7 | | | | 8 | | | | 0.5 | | | | 7 | | | | 0.5 | | | | 8 | | | | 0.8 | | | | 0 | | | | 0.0 | | | | 12 | | | | 2.5 | | | | 0 | | | | 0.1 | |
| Electricity supply | | | 1 | | | | 0.1 | | | | 1 | | | | 0.1 | | | | 1 | | | | 0.1 | | | | 1 | | | | 0.1 | | | | 0 | | | | 0.0 | | | | 0 | | | | 0.1 | | | | 0 | | | | 0.1 | |
| Port facilities | | | 13 | | | | 0.8 | | | | 8 | | | | 0.6 | | | | 6 | | | | 0.5 | | | | 5 | | | | 0.4 | | | | 3 | | | | 0.5 | | | | 1 | | | | 0.2 | | | | 3 | | | | 1.0 | |
| Regional development | | | 1 | | | | 0.1 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 1 | | | | 0.1 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | _— | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
| Industrial waste disposal | | | 5 | | | | 0.3 | | | | 4 | | | | 0.3 | | | | 4 | | | | 0.3 | | | | 0 | | | | 0.0 | | | | 0 | | | | 0.0 | | | | 0 | | | | 0.0 | | | | 0 | | | | 0.0 | |
| Markets | | | 6 | | | | 0.3 | | | | 7 | | | | 0.5 | | | | 4 | | | | 0.4 | | | | 4 | | | | 0.3 | | | | 1 | | | | 0.1 | | | | 1 | | | | 0.1 | | | | 1 | | | | 0.4 | |
| Slaughterhouse | | | 1 | | | | 0.1 | | | | 1 | | | | 0.1 | | | | 0 | | | | 0.0 | | | | 0 | | | | 0.0 | | | | 0 | | | | 0.0 | | | | 0 | | | | 0.0 | | | | 0 | | | | 0.0 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | 38 | | | | 2.4 | | | | 29 | | | | 2.0 | | | | 23 | | | | 1.8 | | | | 18 | | | | 1.6 | | | | 4 | | | | 0.6 | | | | 14 | | | | 2.9 | | | | 4 | | | | 1.6 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Others | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Regional revitalization projects | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 0 | | | | 0.0 | |
| Disaster prevention projects | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 0 | | | | 0.0 | |
| Special municipal merger projects | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 0 | | | | 0.0 | |
| Extraordinary financial countermeasures funding | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 0 | | | | 0.0 | |
| Refinance loans | | | 110 | | | | 6.7 | | | | 200 | | | | 14.3 | | | | 200 | | | | 16.4 | | | | 200 | | | | 17.8 | | | | 199 | | | | 31.4 | | | | 0 | | | | 0.0 | | | | 0 | | | | 0.0 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| General Loans (subtotal) | | | 1,630 | | | | 99.2 | | | | 1,398 | | | | 99.7 | | | | 1,216 | | | | 99.6 | | | | 1,120 | | | | 99.4 | | | | 633 | | | | 100.0 | | | | 475 | | | | 100.0 | | | | 357 | | | | 100.0 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Local toll road public corporations | | | 14 | | | | 0.8 | | | | 5 | | | | 0.3 | | | | 5 | | | | 0.4 | | | | 6 | | | | 0.6 | | | | 0 | | | | 0.0 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
| Local land development public corporations | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loans to local public corporations (subtotal) | | | 14 | | | | 0.8 | | | | 5 | | | | 0.3 | | | | 5 | | | | 0.4 | | | | 6 | | | | 0.6 | | | | 0 | | | | 0.0 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total | | ¥ | 1,644 | | | | 100.0 | % | | ¥ | 1,402 | | | | 100.0 | % | | ¥ | 1,221 | | | | 100.0 | % | | ¥ | 1,126 | | | | 100.0 | % | | ¥ | 633 | | | | 100.0 | % | | ¥ | 475 | | | | 100.0 | % | | ¥ | 357 | | | | 100.0 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Entrusted Loans | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Forests | | ¥ | 42 | | | | 98.7 | % | | ¥ | 16 | | | | 98.2 | % | | ¥ | 13 | | | | 98.4 | % | | ¥ | 13 | | | | 98.3 | % | | ¥ | 4 | | | | 96.3 | % | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
| Pastures | | | 1 | | | | 1.3 | | | | 0 | | | | 1.8 | | | | 0 | | | | 1.6 | | | | 0 | | | | 1.7 | | | | 0 | | | | 3.7 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total | | ¥ | 43 | | | | 100.0 | % | | ¥ | 17 | | | | 100.0 | % | | ¥ | 13 | | | | 100.0 | % | | ¥ | 13 | | | | 100.0 | % | | ¥ | 4 | | | | 100.0 | % | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
______________
Note (1) Accounts consolidated since June 1, 2009
-8-
Loans Outstanding
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | The Predecessor | | | JFM | |
| | | As of March 31, | | | As of September 30, | | | As of March 31, | | | As of September 30, | |
| | | 2005 | | | 2006 | | | 2007 | | | 2008 | | | 2008 | | | 2009 | | | 2009 | |
| | | (in billions) | |
| General Loans And Loans To Local Public Corporations | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Community facilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Water supply | | ¥ | 5,077 | | | | 20.3 | % | | ¥ | 4,974 | | | | 20.1 | % | | ¥ | 4,848 | | | | 20.0 | % | | ¥ | 4,600 | | | | 19.8 | % | | ¥ | 4,313 | | | | 19.2 | % | | ¥ | 4,326 | | | | 19.5 | % | | ¥ | 4,225 | | | | 19.3 | % |
| Gas supply | | | 76 | | | | 0.3 | | | | 70 | | | | 0.3 | | | | 63 | | | | 0.3 | | | | 56 | | | | 0.2 | | | | 51 | | | | 0.2 | | | | 48 | | | | 0.2 | | | | 44 | | | | 0.2 | |
| Sewerage | | | 9,741 | | | | 38.9 | | | | 9,779 | | | | 39.5 | | | | 9,736 | | | | 40.1 | | | | 9,423 | | | | 40.6 | | | | 9,240 | | | | 41.2 | | | | 9,199 | | | | 41.4 | | | | 9,160 | | | | 41.9 | |
| Public housing | | | 858 | | | | 3.4 | | | | 820 | | | | 3.3 | | | | 777 | | | | 3.2 | | | | 719 | | | | 3.1 | | | | 691 | | | | 3.1 | | | | 663 | | | | 3.0 | | | | 646 | | | | 3.0 | |
| High school construction | | | 115 | | | | 0.5 | | | | 110 | | | | 0.4 | | | | 107 | | | | 0.4 | | | | 98 | | | | 0.4 | | | | 96 | | | | 0.4 | | | | 91 | | | | 0.4 | | | | 90 | | | | 0.4 | |
| Improvement of rivers and other waterways | | | 355 | | | | 1.4 | | | | 330 | | | | 1.3 | | | | 308 | | | | 1.3 | | | | 284 | | | | 1.2 | | | | 273 | | | | 1.2 | | | | 260 | | | | 1.2 | | | | 251 | | | | 1.1 | |
| Hospitals | | | 406 | | | | 1.6 | | | | 457 | | | | 1.8 | | | | 484 | | | | 2.0 | | | | 503 | | | | 2.2 | | | | 492 | | | | 2.2 | | | | 541 | | | | 2.4 | | | | 527 | | | | 2.4 | |
| Elderly care | | | 15 | | | | 0.1 | | | | 21 | | | | 0.1 | | | | 24 | | | | 0.1 | | | | 26 | | | | 0.1 | | | | 26 | | | | 0.1 | | | | 26 | | | | 0.1 | | | | 26 | | | | 0.1 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | 16,643 | | | | 66.5 | | | | 16,561 | | | | 66.9 | | | | 16,347 | | | | 67.4 | | | | 15,709 | | | | 67.6 | | | | 15,182 | | | | 67.6 | | | | 15,154 | | | | 68.2 | | | | 14,969 | | | | 68.4 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Road construction and transportation facilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Transportation (excluding subways) | | | 24 | | | | 0.1 | | | | 25 | | | | 0.1 | | | | 29 | | | | 0.1 | | | | 32 | | | | 0.1 | | | | 28 | | | | 0.1 | | | | 27 | | | | 0.1 | | | | 23 | | | | 0.1 | |
| Subways | | | 1,613 | | | | 6.5 | | | | 1,622 | | | | 6.5 | | | | 1,599 | | | | 6.6 | | | | 1,558 | | | | 6.7 | | | | 1,477 | | | | 6.6 | | | | 1,481 | | | | 6.7 | | | | 1,440 | | | | 6.6 | |
| Local road construction | | | 5,434 | | | | 21.7 | | | | 5,330 | | | | 21.5 | | | | 5,153 | | | | 21.2 | | | | 4,900 | | | | 21.1 | | | | 4,793 | | | | 21.4 | | | | 4,615 | | | | 20.8 | | | | 4,514 | | | | 20.7 | |
| Toll roads and parking facilities | | | 146 | | | | 0.6 | | | | 136 | | | | 0.5 | | | | 126 | | | | 0.5 | | | | 114 | | | | 0.5 | | | | 109 | | | | 0.5 | | | | 103 | | | | 0.5 | | | | 97 | | | | 0.4 | |
| Recreation facilities | | | 23 | | | | 0.1 | | | | 20 | | | | 0.1 | | | | 17 | | | | 0.1 | | | | 11 | | | | 0.0 | | | | 10 | | | | 0.0 | | | | 9 | | | | 0.0 | | | | 8 | | | | 0.0 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | 7,240 | | | | 28.9 | | | | 7,133 | | | | 28.8 | | | | 6,924 | | | | 28.5 | | | | 6,615 | | | | 28.5 | | | | 6,418 | | | | 28.6 | | | | 6,235 | | | | 28.1 | | | | 6,082 | | | | 27.8 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Industry and distribution-related facilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Industrial water supply | | | 383 | | | | 1.5 | | | | 357 | | | | 1.4 | | | | 328 | | | | 1.4 | | | | 308 | | | | 1.3 | | | | 280 | | | | 1.3 | | | | 281 | | | | 1.3 | | | | 270 | | | | 1.2 | |
| Electricity supply | | | 110 | | | | 0.5 | | | | 102 | | | | 0.4 | | | | 93 | | | | 0.4 | | | | 84 | | | | 0.4 | | | | 80 | | | | 0.4 | | | | 76 | | | | 0.4 | | | | 72 | | | | 0.3 | |
| Port facilities | | | 135 | | | | 0.5 | | | | 133 | | | | 0.5 | | | | 129 | | | | 0.5 | | | | 123 | | | | 0.5 | | | | 120 | | | | 0.5 | | | | 115 | | | | 0.5 | | | | 113 | | | | 0.5 | |
| Regional development | | | 143 | | | | 0.6 | | | | 122 | | | | 0.5 | | | | 104 | | | | 0.4 | | | | 68 | | | | 0.3 | | | | 67 | | | | 0.3 | | | | 56 | | | | 0.3 | | | | 56 | | | | 0.3 | |
| Industrial waste disposal | | | 6 | | | | 0.0 | | | | 10 | | | | 0.0 | | | | 14 | | | | 0.1 | | | | 14 | | | | 0.1 | | | | 13 | | | | 0.0 | | | | 12 | | | | 0.0 | | | | 12 | | | | 0.1 | |
| Markets | | | 120 | | | | 0.5 | | | | 117 | | | | 0.5 | | | | 112 | | | | 0.5 | | | | 106 | | | | 0.5 | | | | 102 | | | | 0.5 | | | | 97 | | | | 0.4 | | | | 94 | | | | 0.4 | |
| Slaughterhouse | | | 8 | | | | 0.0 | | | | 8 | | | | 0.0 | | | | 8 | | | | 0.0 | | | | 7 | | | | 0.0 | | | | 7 | | | | 0.0 | | | | 7 | | | | 0.0 | | | | 7 | | | | 0.0 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | 905 | | | | 3.6 | | | | 849 | | | | 3.4 | | | | 788 | | | | 3.2 | | | | 710 | | | | 3.1 | | | | 669 | | | | 3.0 | | | | 644 | | | | 2.9 | | | | 624 | | | | 2.8 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| General Loans (subtotal) | | | 24,788 | | | | 99.1 | | | | 24,543 | | | | 99.1 | | | | 24,059 | | | | 99.1 | | | | 23,033 | | | | 99.2 | | | | 22,270 | | | | 99.2 | | | | 22,036 | | | | 99.2 | | | | 21,675 | | | | 99.2 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Local toll road public corporations | | | 235 | | | | 0.9 | | | | 222 | | | | 0.9 | | | | 209 | | | | 0.9 | | | | 197 | | | | 0.8 | | | | 188 | | | | 0.8 | | | | 179 | | | | 0.8 | | | | 170 | | | | 0.8 | |
| Local land development public corporations | | | 1 | | | | 0.0 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loans to local public corporations (subtotal) | | | 236 | | | | 0.9 | | | | 222 | | | | 0.9 | | �� | | 209 | | | | 0.9 | | | | 197 | | | | 0.8 | | | | 188 | | | | 0.8 | | | | 179 | | | | 0.8 | | | | 170 | | | | 0.8 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total | | ¥ | 25,024 | | | | 100.0 | % | | ¥ | 24,765 | | | | 100.0 | % | | ¥ | 24,268 | | | | 100.0 | % | | ¥ | 23,230 | | | | 100.0 | % | | ¥ | 22,459 | | | | 100.0 | % | | ¥ | 22,215 | | | | 100.0 | % | | ¥ | 21,845 | | | | 100.0 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Entrusted Loans | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Forests | | ¥ | 373 | | | | 92.0 | % | | ¥ | 365 | | | | 92.3 | % | | ¥ | 358 | | | | 92.6 | % | | ¥ | 351 | | | | 93.0 | % | | ¥ | 348 | | | | 93.5 | % | | ¥ | 344 | | | | 93.4 | % | | ¥ | 341 | | | | 93.9 | % |
| Pastures | | | 32 | | | | 8.0 | | | | 30 | | | | 7.7 | | | | 28 | | | | 7.4 | | | | 26 | | | | 7.0 | | | | 24 | | | | 6.5 | | | | 24 | | | | 6.6 | | | | 22 | | | | 6.1 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total | | ¥ | 405 | | | | 100.0 | % | | ¥ | 395 | | | | 100.0 | % | | ¥ | 386 | | | | 100.0 | % | | ¥ | 377 | | | | 100.0 | % | | ¥ | 372 | | | | 100.0 | % | | ¥ | 369 | | | | 100.0 | % | | ¥ | 364 | | | | 100.0 | % |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Loan Terms
The terms and conditions applicable to JFM’s loans other than entrusted loans are determined by JFM in accordance with the costs of funds procured by JFM. The terms and conditions of entrusted loans are determined by JFC.
Interest Rates
Loan interest rates consist of three types: standard interest rate; special interest rate; and extra-special interest rate.
Standard Interest Rate. The standard interest rate represents the rate at which the discounted present value of cash flows of the fund raised by JFM to make loans equals the discounted present value of cash flows generated by those loans with their respective terms to maturity, grace periods and repayment methods.
-9-
Special Interest Rate. The special interest rate is set at a discount on the standard rate (0.3% below standard rate) for projects that are particularly important to the livelihood of residents.
Extra-Special Interest Rate. The extra-special interest rate is set at a further discount on the standard rate (0.35% below standard rate) for special projects of great urgency and necessity to respond appropriately to the issues of the regional community.
The trend of loan interest rates for fiscal year 2008 and the six months ended September 30, 2009 is shown below. During this period, extra-special interest rates were at the same level as the rates of the Fiscal Loan Fund provided by the national government.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Month/Year | | October ’08 | | | November ’08 | | | December ’08 | | | January ’09 | | | February ’09 | | | March ’09 | |
| Interest Rate Reset Date | | Oct.28 | | | Nov.20 | | | Dec.17 | | | Jan.22 | | | Feb.19 | | | Mar.19 | |
| Standard Interest Rate | | | 2.25 | % | | | 2.35 | % | | | 2.30 | % | | | 2.05 | % | | | 2.10 | % | | | ® | |
| Special Interest Rate | | | 2.10 | % | | | ® | | | | 2.00 | % | | | 1.80 | % | | | 1.90 | % | | | ® | |
| Extra-Special Interest Rate | | | ® | | | | ® | | | | 2.00 | % | | | 1.80 | % | | | 1.90 | % | | | ® | |
| Interest Rate of Fiscal Loan Fund | | | ® | | | | ® | | | | 2.00 | % | | | 1.80 | % | | | 1.90 | % | | | ® | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Month/Year | | April ’09 | | | May ’09 | | | June ’09 | | | July ’09 | | | August ’09 | | | September ’09 | |
| Interest Rate Reset Date | | Apr 20 | | | May 25 | | | Jun 17 | | | Jul 21 | | | Aug 19 | | | Sep 17 | |
| Standard Interest Rate | | | 2.20 | | | | 2.20 | | | | 2.25 | | | | 2.05 | | | | 2.20 | | | | 2.10 | |
| Special Interest Rate | | | 2.00 | | | | 2.10 | | | | 2.20 | | | | 2.00 | | | | 2.10 | | | | 2.00 | |
| Extra-Special Interest Rate | | | 2.00 | | | | 2.10 | | | | 2.20 | | | | 2.00 | | | | 2.10 | | | | 2.00 | |
| Interest Rate of Fiscal Loan Fund | | | 2.00 | | | | 2.10 | | | | 2.20 | | | | 2.00 | | | | 2.10 | | | | 2.00 | |
| | | |
| * | | The figures for October 2008 through May 2009 are fixed interest rates for loans with 28-year maturity and 5-year grace period. The figures for June 2009 through September 2009 are fixed interest rates for loans with 30-year maturity and 5-year grace period. The interest rates of the Fiscal Loan Fund are based on the same conditions. |
Maturities
The loan maturity, which is set according to the purpose of the loan, was previously 28 years at the maximum (25 years on average). As a result of the review of the loan maturity for each purpose, which was conducted at the time of the reorganization of JFM (see “Recent Developments – Reorganization from Japan Finance Organization for Municipal Enterprises to Japan Finance Organization for Municipalities”), the maximum term to maturity was set at 30 years for fiscal 2009 loans with consent (approval). The new loan maturities for major purposes are shown below.
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Loans with Consent (Approval) | | | Loans with Consent (Approval) | |
| | | up to Fiscal 2008 | | | from Fiscal 2009 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | Adjustable Interest | | | | | | | | | | | Adjustable Interest | |
| | | Fixed Interest Rate | | | Rate* | | | Fixed Interest Rate | | | Rate* | |
| Loan Purpose | | | | | | Grace | | | | | | | Grace | | | | | | | Grace | | | | | | | Grace | |
| by Project | | Maturity | | | Period | | | Maturity | | | Period | | | Maturity | | | Period | | | Maturity | | | Period | |
| Public Housing | | | 20 | | | | 5 | | | | 20 | | | | 5 | | | | 25 | | | | 5 | | | | 25 | | | | 5 | |
| Water supply | | | 28 | | | | 5 | | | | 28 | | | | 5 | | | | 30 | | | | 5 | | | | 30 | | | | 5 | |
| Transportation | | | 28 | | | | 5 | | | | 28 | | | | 5 | | | | 30 | | | | 5 | | | | 30 | | | | 5 | |
| Hospitals | | | 28 | | | | 5 | | | | 28 | | | | 5 | | | | 30 | | | | 5 | | | | 30 | | | | 5 | |
| Sewerage | | | 28 | | | | 5 | | | | 28 | | | | 5 | | | | 30 | | | | 5 | | | | 30 | | | | 5 | |
| Industrial Water Supply | | | 25 | | | | 5 | | | | 25 | | | | 5 | | | | 30 | | | | 5 | | | | 30 | | | | 5 | |
| Electricity Supply | | | 25 | | | | 5 | | | | 28 | | | | 5 | | | | 30 | | | | 5 | | | | 30 | | | | 5 | |
| Gas Supply | | | 20 | | | | 3 | | | | 20 | | | | 3 | | | | 25 | | | | 5 | | | | 25 | | | | 5 | |
| Port Facilities | | | 18 | | | | 5 | | | | 28 | | | | 5 | | | | 20 | | | | 5 | | | | 30 | | | | 5 | |
| Markets | | | 20 | | | | 5 | | | | 20 | | | | 5 | | | | 25 | | | | 5 | | | | 25 | | | | 5 | |
| Slaughterhouses | | | 18 | | | | 3 | | | | 18 | | | | 3 | | | | 20 | | | | 5 | | | | 20 | | | | 5 | |
| | | |
| (* | | Note: Reviewed every 10 years) |
-10-
The following table sets forth information concerning the maturities of JFM’s outstanding loans as of March 31, 2009.
Loans Outstanding by Maturity
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | (in millions) | |
| 5 years or less | | ¥ | 1,304,232 | | | | 5.9 | % |
| More than 5 years to 10 years | | | 3,613,489 | | | | 16.2 | % |
| More than 10 years to 20 years | | | 11,097,149 | | | | 50.0 | % |
| More than 20 years | | | 6,200,418 | | | | 27.9 | % |
| | | | | | | |
| Total | | ¥ | 22,215,288 | | | | 100.0 | % |
| | | | | | | |
Funds Available for Lending
The following table gives details of the Predecessor’s and JFM’s funds available for lending for the past four fiscal years in the period ended March 31, 2008 and for six months ended September 30, 2008, March 31, 2009 and September 30, 2009 (other than funds entrusted by JFC).
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | The Predecessor | | | JFM | |
| | | Years ended March 31, | | | Six months ended | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | September 30, | | | March 31, | | | September 30, | |
| | | 2005 | | | 2006 | | | 2007 | | | 2008 | | | 2008 | | | 2009 | | | 2009 | |
| | | (in billions) | |
| Cash and deposits at the beginning of the year | | ¥ | 716 | | | ¥ | 666 | | | ¥ | 721 | | | ¥ | 768 | | | ¥ | 1,122 | | | ¥ | 17 | | | ¥ | 1,130 | |
| Government guaranteed bonds (domestic) | | | 1,130 | | | | 951 | | | | 739 | | | | 650 | | | | 220 | | | | 720 | | | | 419 | |
| Government guaranteed bonds (foreign) | | | 122 | | | | 128 | | | | 120 | | | | 119 | | | | 75 | | | | 0 | | | | 0 | |
| Non-guaranteed public offering bonds (domestic) | | | 400 | | | | 399 | | | | 360 | | | | 370 | | | | 150 | | | | 160 | | | | 322 | |
| Non-guaranteed private placement bonds | | | 408 | | | | 335 | | | | 334 | | | | 255 | | | | 127 | | | | 0 | | | | 150 | |
| Contributions of the proceeds from public races | | | 11 | | | | 9 | | | | 11 | | | | 14 | | | | 2 | | | | (10 | ) | | | 0 | |
| Proceeds from collection of loans | | | 1,508 | | | | 1,663 | | | | 1,716 | | | | 2,164 | | | | 1,405 | | | | 719 | | | | 727 | |
| Other | | | 825 | | | | 780 | | | | 734 | | | | 693 | | | | 315 | | | | 1,715 | | | | 282 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Subtotal | | ¥ | 5,120 | | | ¥ | 4,932 | | | ¥ | 4,734 | | | ¥ | 5,032 | | | ¥ | 3,416 | | | ¥ | 3,320 | | | ¥ | 3,030 | |
| Bonds redeemed and other outflows | | | 2,810 | | | | 2,806 | | | | 2,748 | | | | 2,783 | | | | 1,358 | | | | 1,397 | | | | 1,257 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Funds available for lending | | | 2,310 | | | | 2,126 | | | | 1,986 | | | | 2,249 | | | | 2,058 | | | | 1,605 | | | | 1,774 | |
| Total loan funds | | ¥ | 1,644 | | | ¥ | 1,405 | | | ¥ | 1,218 | | | ¥ | 1,126 | | | ¥ | 633 | | | ¥ | 475 | | | ¥ | 357 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and deposits at the end of the year | | | 666 | | | | 721 | | | | 768 | | | | 1,122 | | | | 1,425 | | | | 1,130 | | | | 1,417 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
JFM raises funds for its loan operations mainly by issuing non-guaranteed bonds to capital markets. JFM is permitted to issue Japanese government-guaranteed bonds to refinance previously-issued Japanese government-guaranteed bonds (including those issued by the Predecessor). The national government draws up a plan for its Fiscal Investment and Loan Program (Zaito plan) each year. The annual Zaito plan, which is subject to approval by the Diet, determines the allocation of funds and extent of government guarantees for institutions like JFM.
Contributions of the proceeds from horse, bicycle, motorcycle and boat races, operated exclusively by local governments, are forwarded to JFM in accordance with the Local Finance Law. The contributions are accumulated in a separate account (Fund for Improvement of Operations of Municipalities) and monies transferred from returns from the management of the Fund to the accounts are applied to contribute to the reduction of interest rates on loans to local governments.
Risk Management
JFM established the Integrated Risk Management Committee as part of its efforts to identify and formulate appropriate responses to the various risks JFM must deal with in the course of operations, including interest rate risk. In addition, JFM is promoting more advanced analytical procedures for its asset and liability management.
-11-
Credit Risk
Credit risk is the risk of loss arising from a credit event, such as deterioration in the financial condition of a borrower, that causes an asset to lose value or become worthless. In addition to credit risk associated with loans, market transactions also involve credit risk.
Credit Risk for Loans. JFM makes loans exclusively to local governments. There have been no default on loans made to local governments for the reasons outlined below. JFM and the Predecessor have never experienced any loan losses.
The national government includes local government debt servicing costs in the expenditure of the Local Government Finance Program, and secures the total amount of local allocation tax which balances local governments’ total expenditures including debt servicing costs and total revenue. Thus, the national government effectively secures revenue sources for principal and interest payments for local governments. The national government also secures revenue sources for debt service for individual local governments by including a portion of local government debt servicing costs in the Standard Financial Needs when calculating local allocation tax.
Under the consultation system for local government bonds and loans, credit reviews must include checks on situations of local government debt servicing, and tax revenue and necessary revenue sources to be secured. Additionally, under the Early Warning System, the local governments whose debt servicing costs and financial deficits exceed a certain level must apply for approval to issue bonds or obtain loans, so that the credit standing of local government bonds and loans is maintained.
Under the Law Relating to the Financial Soundness of Local Governments, which was promulgated in June 2007, local governments whose fiscal indicators exceed the early warning limits must make their own efforts toward achieving fiscal soundness, and local governments whose fiscal indicators exceed the reconstruction limits must take necessary actions to restore their finances under the oversight of the national government with regard to redemption of local government bonds and loans, and other operations.
As of September 30, 2009, JFM’s total outstanding loans stood at ¥21,845.1 billion. The amount of outstanding loans made to local government road corporations by the former JFM was ¥179.4 billion, which accounted for slightly less than 1% of the total loans.
JFM is not subject to Japan’s Banking Law or Financial Reconstruction Law, but performs self-assessment of loans made to local government road corporations in accordance with the “Financial Inspection Manual” of the Financial Services Agency of Japan. All of these loans have been classified as normal assets based on the self-assessment.
The amount of loans made to local governments whose fiscal indicators exceeded the early warning limits or the reconstruction limits accounted for slightly more than 1% of the total loans.
Credit Risk Associated with Market Transactions. JFM is exposed to the risk of loss arising from a credit event, such as deterioration in the financial condition of a counter-party, which causes an asset to lose value or become worthless. However, JFM appropriately manages credit risk of this type by constantly monitoring counter-parties’ financial standing and limiting them to financial institutions that meet the credit rating and other criteria.
Market Risk
Market risk is the risk of loss resulting from changes in the value of assets and liabilities due to fluctuations in risk factors such as interest rates, securities prices and foreign exchange rates, or the risk of loss resulting from changes in earnings generated from assets and liabilities. Market risk includes interest rate risk, foreign exchange risk, inflation risk and price change risk.
Interest Rate Risk. Interest rate risk is the risk of loss resulting from fluctuations in interest rates. More specifically, it is the risk of losses incurred or decrease in profits, which would arise from fluctuations in interest rates when there is an interest rate or maturity gap between assets and liabilities.
-12-
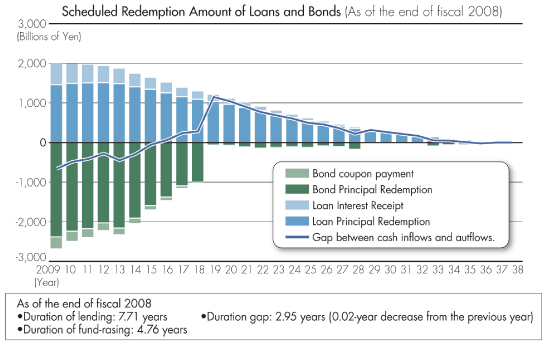
JFM makes loans to local governments. The maximum term to maturity is 30 years, and the average maturity about 25 years. On the other hand, the majority of the funds for these loans is raised mainly through issuance of 10-year bonds, which creates interest rate risk associated with bond refinance.
JFM takes the following measures to address the interest rate risk resulting from a duration gap between lending and fund-raising.
| | • | | JFM maintains necessary reserves for interest rate volatility to cope with the interest rate risk resulting from a duration gap between lending and fund-raising. The amount of the above reserves stood at ¥3,294.7 billion at the end of March 2009. |
| | • | | As assets and liabilities in JFM’s General account are expected to expand, JFM carries out an ALM analysis of this account in a timely and appropriate manner to further enhance the effectiveness of its management of interest rate risk. JFM also endeavors to reduce its exposure to interest rate risk by setting the following medium-term management target (by the end of fiscal year 2013), by continuously issuing longer-term bonds with maturities exceeding 10 years, and by utilizing interest rate swaps. |
| | (1) | | Keep the “outlier ratio” below approximately 20%. “Outlier ratio” is the ratio of “decline in economic value” as a result of interest rate shocks to net assets including reserves for interest rate volatility. “Decline in economic value” is the decline of present value after interest rate shocks (an upward and downward 200-basis point parallel shift of the yield curve). |
| | (2) | | Keep a duration gap below approximately 2 years. |
Foreign Exchange and Other Risks. Various risks associated with bond principal and interest payments are hedged by swap transactions. These risks include foreign exchange risk related to foreign currency-denominated bonds, interest rate risk related to floating rate notes, and risk of fluctuations in the amounts of principal and interest of inflation-indexed bonds.
JFM’s policy for investing surplus funds gives priority to short-term financial products with stable returns, such as Treasury Bills, which creates little price change risk. Additionally, foreign exchange risk related to foreign currency-denominated bank deposits is hedged by foreign exchange contracts.
Liquidity Risk
Liquidity risk is the risk that JFM will incur losses because it finds it difficult to secure the necessary funds or is forced to obtain funds at far higher interest rates than under normal conditions due to a mismatch between the maturities of assets and liabilities or an unexpected outflow of funds (funding-liquidity risk). It also includes the risk that JFM will incur losses because it is unable to conduct market transactions or is forced to conduct transactions at far more unfavorable prices than under normal conditions due to market disruption or other difficult situations (market-liquidity risk).
-13-
JFM’s exposure to liquidity risk is extremely low because loans are made to local governments according to a pre-set schedule, and the daily cash and liquidity management is carried out based on a quarterly plan for fund management. Moreover, JFM has entered into overdraft agreements with several financial institutions to prepare for the unexpected, and invests surplus funds only in short-term financial products.
Operational Risk
Operational risk is the risk of loss resulting from inadequate operation processes, inadequate activities by management and staff, and inadequate computer systems, or from external events.
Administrative Risk. Administrative risk is the risk of loss resulting from the neglect by management and staff to properly conduct administrative work, accidents caused by them and violation of laws conducted by them in the course of the administrative work process.
JFM endeavors to mitigate its exposure to administrative risk by preparing operational manuals, holding educational seminars and reducing operational workload through systematization.
Systems Risk. Systems risk is the risk that the confidentiality, integrity and availability of information assets will be impaired as a result of computer system inadequacies or the fraudulent use of computer systems.
JFM has established and implemented the “Systems Risk Management Policy” and the “Systems Risk Management Standard” to appropriately manage systems risk and ensure smooth business operations.
JFM has also prepared the “Contingency Plan” to minimize the scope of losses and the impact on operations and restore normal operations promptly and efficiently in the event that computer systems break down or cannot be used due to unexpected accidents, disasters or malfunctions.
Other Risks. In addition to the aforementioned risks, JFM appropriately identifies and addresses other risks, such as legal risk, personnel risk, physical asset risk and reputation risk.
-14-
MANAGEMENT
JFM is managed by the President and Chief Executive Officer, one Deputy President and up to three Senior Executive Directors. In addition, it has two Corporate Auditors. The President and Chief Executive Officer and the Corporate Auditors are appointed by the Representative Board. The Deputy President and the Senior Executive Directors are appointed by the President and Chief Executive Officer with the approval of the Representative Board. When the Representative Board or the President and Chief Executive Officer has appointed an officer, JFM is required to notify the officer’s name and address to the Minister for Internal Affairs and Communications.
The President and Chief Executive Officer has the authority to manage all operations and holds the right of final decision and representation on all matters related to JFM. The Deputy President and Senior Executive Directors assist the President and Chief Executive Officer in the performance of his duties.
The Corporate Auditors are responsible for auditing the accounts of JFM, and may, at their discretion, submit reports to the Representative Board, the President and Chief Executive Officer and the Ministers of Internal Affairs and Communications.
The officers of JFM as of the date of this Exhibit are as follows:
| | | |
| President and Chief Executive Officer | | Yuji Watanabe |
| | | |
| Deputy President | | Masamichi Fukunaga |
| | | |
| Senior Executive Directors | | Takeji Takei |
| | | Senior Executive Director (in charge of overall coordination, Corporate Planning Department, Administration Department and Loan Department) |
| | | Yoji Ninomiya |
| | | Senior Executive Director (in charge of Finance Department) |
| | | Takao Kodama |
| | | Senior Executive Director (part-time) |
| | | |
| Corporate Auditors | | Shuichi Kadowaki
Nadamu Takata (part-time) |
-15-
DEBT RECORD
There has been no default of interest or principal on any obligation of JFM or the Predecessor.
FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF THE PREDECESSOR
Set forth below are the Predecessor’s unaudited financial statements for the six months ended September 30, 2008. The Predecessor’s financial statements below were prepared in accordance with the Japan Finance Corporation for Municipal Enterprises Law and the Law Concerning the Budget and Settlement of Accounts of Public Corporations and the regulations thereunder, as well as with accounting principles and procedures generally followed by governmental financial institutions in Japan.
Statements of Income
Set forth below are the Predecessor’s unaudited financial statements for the six months ended September 30, 2008. The following statements of income should be read in conjunction with the other financial statements and “Notes to Financial Statements” included in this Annual Report.
| | | | | |
| | | Six months ended | |
| | | September, 30 | |
| | | 2008 | |
| | | (in millions) | |
| Revenues | | | | |
| Interest on loans | | | | |
| Interest on long-term loans | | ¥ | 309,721 | |
| Interest on loans in process | | | — | |
| Interest on short-term loans | | | — | |
| | | | |
| | | | 309,721 | |
| | | | |
| | | | | |
| Fees for entrusted loans | | | 119 | |
| Interest on deposits | | | 1,871 | |
| Profit on securities sold | | | 139 | |
| Miscellaneous income | | | 306 | |
| Transfer from fund for the improvement of operations of municipal enterprises | | | — | |
| Gains on sales of fixed assets | | | — | |
| Reversal of reserves for reduced interest loans | | | 15,549 | |
| | | | |
| Total revenues | | ¥ | 327,704 | |
| | | | |
| | | | | |
| Expenses | | | | |
| Interest on bonds | | | 158,055 | |
| Interest on short-term borrowing | | | — | |
| Miscellaneous interest payments | | | 172 | |
| Office expenses | | | 1,179 | |
| Bond-issue costs | | | 204 | |
| Depreciation | | | 30 | |
| Amortization of deferred bond expenses | | | 1,544 | |
| Miscellaneous losses | | | 1 | |
| Loss on disposal of fixed assets | | | — | |
| Provision for fund for the improvement of operations of municipal enterprises | | | 1,296 | |
| Loss of bond redemption | | | — | |
| Provision for reserves for reduced interest loans | | | 2,075 | |
| Provision for reserves for loss on refinance of bonds | | | — | |
| | | | |
| Net income | | | 163,148 | |
| Total expenses | | ¥ | 327,704 | |
| | | | |
-16-
Balance Sheet
| | | | | |
| | | Six months ended | |
| | | September, 30 | |
| | | 2008 | |
| | | (in millions) | |
Assets | | | | |
| Long-term loans | | ¥ | 22,458,657 | |
| Entrusted loans | | | 372,301 | |
| Cash and deposits | | | 1,424,899 | |
| Securities | | | — | |
| Accrued income | | | 15,718 | |
| Fixed assets | | | 2,410 | |
| | | | |
| Total assets | | ¥ | 24,273,985 | |
| | | | |
| | | | | |
Liabilities and Capital | | | | |
| Bonds | | | 19,352,644 | |
| Entrusted funds | | | 105 | |
| Obligations for entrusted loans | | | 372,301 | |
| Accrued expenses | | | 14,335 | |
| Deferred income | | | 1,291 | |
| Other payables | | | 4 | |
| Fund for the improvement of operations of municipal enterprises | | | 903,355 | |
| Reserves for reduced interest loans | | | 136,767 | |
| Reserves for loss on refinance of bonds | | | 2,955,650 | |
| Capital | | | 16,600 | |
| Surplus reserve | | | 357,786 | |
| Net income | | | 163,148 | |
| | | | |
| Total liabilities and capital | | ¥ | 24,273,985 | |
| | | | |
See “Notes to Financial Statements”.
-17-
Notes to Financial Statements
The following notes to the financial statements include information which is not required under accounting principles and procedures generally followed by governmental financial institutions in Japan but is presented herein as additional information.
1. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies:
Basis of presentation
Pursuant to the Japan Finance Corporation for Municipal Enterprises Law and the Law Concerning the Budget and Settlement of Accounts of Public Corporations, the Predecessor prepares annual financial statements and fiscal year-end results for each fiscal year.
The financial statements are submitted to the Minister of Finance for approval through the designated government ministers. The Predecessor’s fiscal year-end results are submitted to the Minister of Finance without delay through the designated government ministers once the Minister of Finance has approved the financial statements.
Once the financial statements and the fiscal year-end results have been submitted to the Cabinet, they are submitted to the Board of Audit, a supervisory body established under the Constitution of Japan. The fiscal year-end results are then inspected by the Board of Audit and submitted by the Cabinet together with the financial statements to the Diet.
The financial statements and fiscal year-end results are prepared in accordance with accounting principles and procedures generally followed by governmental financial institutions in Japan.
Securities
Securities are stated at cost. Earnings from securities are recorded on a cash basis. The effect of the departure from the accrual basis is immaterial.
Method of Depreciation
The straight-line method is applied based on the standards laid out by the Corporation Tax Law. The cumulative depreciation amount for fixed assets as of September 30, 2008 is ¥ 567,357,282.
Criteria for Appropriation of Reserves
Reserves for Reduced Interest Loans
Among projects financed by loans, the Predecessor provides loans at the Special Rate or the Temporary Special Rate that is lower than the Standard Rate and is applied to projects closely related to residents’ lives and welfare.
To cover losses that arise from providing funds at reduced interest rates, the Predecessor sets aside Reserves for Reduced Interest Loans in the amount calculated in accordance with the relevant ministry ordinance. This amount is basically a portion of the interest that is reduced for the reduced-interest loan and is added to the reserve during the fiscal year in which the loan is made.
-18-
Notes to Financial Statements — (Continued)
Reserves for Loss on Refinance of Bonds
The Predecessor makes loans mainly to local governments at a fixed rate of interest with maturities of up to 28 years. Most of the funding for such loans comes from the issuance of bonds, consisting mainly of bonds with 10 years’ maturity. As a result of this type of funding, any loans having maturities in excess of 10 years will expose the Predecessor to interest rate risks associated with the refinance of 10-year bonds. In the event that any profits, determined in accordance with methods of computation provided by the designated government ministers, are made in a fiscal year as a result of the refinance of the Predecessor’s outstanding bonds, the Predecessor sets aside as Reserves for Loss on Refinance of Bonds for that fiscal year an amount determined by the Predecessor with the consent of the designated government ministers provided that the total amount of the Reserve for Loss on Refinance of Bonds for the related fiscal year is no greater than a maximum of 12.5% of the aggregate amount at the end of the related fiscal year of loans made by the Predecessor to local governments and subscriptions by the Predecessor for local loans.
Other Material Factors in Preparing Financial Statements:
Consumption tax
Income and expense subject to consumption tax include related consumption taxes paid or received.
Deferred accounts
Amortization methods of deferred accounts are as follows:
| | | | Expenses for bond issues |
| |
| | | | Amortized based on ministry ordinances designated by the Minister of Finance in accordance with laws and regulations. |
Loans
There are no loans which are past due for six months or more.
2. Translation of foreign currencies
All of the Predecessor’s foreign currency bonds are covered by currency swaps or long-term forward exchange contracts. The discount on forward exchange contracts has been recorded in deferred income and amortized over the period of related bonds. The amortized deduction income is recorded as a deduction of interest on bonds each fiscal year.
3. Entrusted loans
Entrusted loans are loans from funds entrusted by the Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries Finance Corporation (a governmental financial institution) to the Predecessor, which are used for secondary lending to local governments for financing maintenance of public forests and improvements of pastures. Loans made and collected are for the account of such corporation. While the amounts of such entrusted funds are recorded as a liability of the Predecessor, with the loans made from such funds correspondingly recorded as an asset of the Predecessor, the financial statements of the Predecessor do not reflect interest received on such funds or the costs associated with such funds, except lending-management fees received from the entrustor.
4. Fund for the Improvement of Operations of Municipal Enterprises
This Fund is accounted for separately from the accounts of the Predecessor. Contributions of the proceeds from public races, together with interest on investments, accumulate in the Fund. Monies are transferred from returns from the management of the Fund to the accounts of the Predecessor to contribute to the reduction of interest rates on loans to local governments.
-19-
Notes to Financial Statements — (Continued)
5. Reserves for Possible Loan Losses
The Predecessor has never experienced any loan losses. Accordingly, no reserves for loan losses have been maintained.
6. Appropriation of Profits
The Predecessor is exempted from income tax on its earnings under Japan’s Corporate Tax law.
7. Bonds Issued and Outstanding
The Predecessor bonds issued, as of September 30, 2008, including bonds due within one year, consisted of the following:
| | | | | |
| | | September 30, | |
| | | 2008 | |
| | | (in millions) | |
| Government guaranteed bonds (domestic) | | ¥ | 12,069,650 | |
| Non-guaranteed private placement bonds | | | 3,865,071 | |
| Non-guaranteed public offering bonds | | | 2,298,698 | |
| | | | |
| | | | | |
| Government guaranteed bonds (foreign-DM) | | | 0 | |
| Government guaranteed bonds (foreign-U.S. dollar) | | | 444,599 | |
| Government guaranteed bonds (foreign-£) | | | 27,585 | |
| Government guaranteed bonds (foreign-Euro) | | | 122,040 | |
| Government guaranteed bonds (non-domestic Yen) | | | 525,000 | |
| | | | |
| Total | | ¥ | 19,352,643 | |
| | | | |
The aggregate annual maturities of bonds outstanding, including bonds due within one year, as of March 31, 2008 were as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Years ended March 31, | | Domestic | | | Foreign | | | Total | |
| | | (in millions) | |
| 2009 | | | 2,401,576 | | | | 38,196 | | | | 2,439,772 | |
| 2010 | | | 2,307,173 | | | | 78,319 | | | | 2,385,492 | |
| 2011 | | | 2,124,870 | | | | 116,780 | | | | 2,241,650 | |
| 2012 | | | 1,976,130 | | | | 200,000 | | | | 2,176,130 | |
| 2013 | | | 1,730,560 | | | | — | | | | 1,730,560 | |
| Thereafter | | | 8,353,390 | | | | 649,125 | | | | 9,002,515 | |
8. Capital
In accordance with the provisions of the Japan Finance Corporation for Municipal Enterprises Law, all of the capital of JFM has been contributed in cash by the central government. The cumulative capital contribution as of September 30, 2008 was ¥16,600 million.
-20-
FINANCIAL STATEMENTS OF JFM
Set forth below are JFM’s audited financial statements for its first fiscal period (ended March 31, 2009) and unaudited financial statements for the six months ended September 30, 2009.
-21-
Audited Financial Statements of JFM for the fiscal period ended March 31, 2009
Report of Independent Auditors
To the President of Japan Finance Organization for Municipalities
We have audited the accompanying balance sheet of Japan Finance Organization for Municipal Enterprises as of March 31, 2009, and the related statements of operations, changes in net assets, appropriation of profit and cash flows for the year then ended, all expressed in yen. These financial statements are the responsibility of the President. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with auditing standards generally accepted in Japan. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of Japan Finance Organization for Municipal Enterprises at March 31, 2009, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for the year then ended in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in Japan (refer to Note 1 of the Notes to Financial Statements).
The U.S. dollar amounts in the accompanying financial statements with respect to the year ended March 31, 2009 are presented solely for convenience. Our audit also included the translation of yen amounts into U.S. dollar amounts and, in our opinion, such translation has been made on the basis described in Note 1.
/s/ Ernst & Young ShinNihon LLC
June 5, 2009
-22-
Balance Sheet (As of March 31, 2009)
(Millions of Yen) (Thousands of US dollars)
| | | | | | | | | |
| Item | | Amount | |
Assets | | | | | | | | |
| Loans (Note 3) | | ¥ | 22,215,288 | | | $ | 225,535,921 | |
| Securities (Note 15) | | | 874,832 | | | | 8,881,550 | |
| Cash and bank deposits | | | 255,591 | | | | 2,594,836 | |
| Other assets | | | 20,051 | | | | 203,570 | |
| Tangible fixed assets (Note 4) | | | 3,010 | | | | 30,560 | |
| Intangible fixed assets (Note 4) | | | 842 | | | | 8,558 | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Total assets | | ¥ | 23,369,616 | | | $ | 237,254,995 | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Liabilities | | | | | | | | |
| Bonds (Note 5 and 6) | | ¥ | 18,978,163 | | | $ | 192,671,714 | |
| Other liabilities | | | 19,756 | | | | 200,578 | |
| Reserve for bonuses (Note 7) | | | 47 | | | | 485 | |
| Reserve for directors’ bonuses (Note 7) | | | 7 | | | | 81 | |
| Reserve for retirement benefits (Note 7 and 10) | | | 202 | | | | 2,058 | |
| Reserve for retirement benefits for directors and corporate auditors (Note 7) | | | 51 | | | | 519 | |
| Fund for improvement of operations of municipal enterprises | | | 894,675 | | | | 9,083,004 | |
| Basic fund for improvement of operations of municipal enterprises (Note 9) | | | 892,875 | | | | 9,064,728 | |
| Additional fund for improvement of operations of municipal enterprises (Note 9) | | | 1,800 | | | | 18,276 | |
| Reserve under special laws | | | 3,423,622 | | | | 34,757,593 | |
| Reserve for interest rate volatility (Note 8) | | | 220,000 | | | | 2,233,503 | |
| Management account reserve for interest rate volatility (Note 8) | | | 3,074,728 | | | | 31,215,519 | |
| Reserve for interest rate reduction | | | 128,894 | | | | 1,308,571 | |
| | | | | | | |
| Total liabilities | | | 23,316,529 | | | | 236,716,032 | |
| | | | | | | |
Net Assets | | | | | | | | |
| Capital | | | 16,602 | | | | 168,549 | |
| Retained earnings | | | 1,295 | | | | 13,153 | |
| General account surplus reserve | | | 1,295 | | | | 13,153 | |
| Management account surplus reserve | | | 35,190 | | | | 357,261 | |
| | | | | | | |
| Total net assets | | | 53,087 | | | | 538,963 | |
| | | | | | | |
Total liabilities and net assets | | ¥ | 23,369,616 | | | $ | 237,254,995 | |
| | | | | | | |
-23-
Statement of Income (From August 1, 2008 through March 31, 2009)
(Millions of Yen) (Thousands of US dollars)
| | | | | | | | | |
| Item | | Amount | |
| Income | | ¥ | 291,330 | | | $ | 2,957,666 | |
| Interest income | | | 291,288 | | | | 2,957,240 | |
| Fees and commissions | | | 33 | | | | 342 | |
| Other income | | | 8 | | | | 84 | |
| | | | | | | |
| Expenses | | | 160,632 | | | | 1,630,790 | |
| Interest expenses | | | 155,235 | | | | 1,575,992 | |
| Fees and commissions | | | 134 | | | | 1,366 | |
| Other operating expenses | | | 2,233 | | | | 22,673 | |
| General and administrative expenses | | | 1,203 | | | | 12,218 | |
| Other expenses | | | 1,826 | | | | 18,541 | |
| Transfer to fund for improvement of operations of municipal enterprises (Note 9) | | | 1,800 | | | | 18,276 | |
| Others | | | 26 | | | | 265 | |
| | | | | | | |
| Ordinary income | | | 130,697 | | | | 1,326,876 | |
| | | | | | | |
| Special gains | | | 307,872 | | | | 3,125,611 | |
| Reversal of management account reserve for interest rate volatility (Note 8) | | | 300,000 | | | | 3,045,685 | |
| Reversal of reserve for interest rate reduction | | | 7,872 | | | | 79,926 | |
| | | | | | | |
| Special losses | | | 418,144 | | | | 4,245,125 | |
| Provision for management account reserve for interest rate volatility (Note 8) | | | 118,144 | | | | 1,199,440 | |
| Payment to national treasury (Note 8) | | | 300,000 | | | | 3,045,685 | |
| | | | | | | |
| Net income | | ¥ | 20,425 | | | $ | 207,362 | |
| | | | | | | |
-24-
Appropriation of Profit [General Account] (March 31, 2009)
(Millions of Yen)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| I Profit to be appropriated | | | | | | | | | | | 1,295 | |
| Net income | | | | | | | 1,295 | | | | | |
| Accumulated deficit brought down | | | — | | | | | | | | | |
| II Profit appropriated | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Surplus reserve | | | | | | | 1,295 | | | | 1,295 | |
(Thousands of US dollars)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| I Profit to be appropriated | | | | | | | | | | | 13,153 | |
| Net income | | | | | | | 13,153 | | | | | |
| Accumulated deficit brought down | | | — | | | | | | | | | |
| II Profit appropriated | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Surplus reserve | | | | | | | 13,153 | | | | 13,153 | |
| | | |
| Notes: | 1. | Profit was appropriated at the end of this fiscal year in accordance with the provisions of Article 39, Section 1 of the Japan Finance Organization for Municipal Enterprises Law (Law No. 64, 2007). |
| |
| 2. | Surplus reserve appropriated was posted as General account surplus reserve on the Balance Sheet. |
Appropriation of Profits [Management Account] (March 31, 2009)
(Millions of Yen)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| I Profit to be appropriated | | | | | | | | | | | 19,129 | |
| Net income | | | | | | | 19,129 | | | | | |
| Accumulated deficit brought down | | | — | | | | | | | | | |
| II Profit appropriated | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Surplus reserve | | | | | | | 19,129 | | | | 19,129 | |
(Thousands of US dollars)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| I Profit to be appropriated | | | | | | | | | | | 194,209 | |
| Net income | | | | | | | 194,209 | | | | | |
| Accumulated deficit brought down | | | — | | | | | | | | | |
| II Profit appropriated | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Surplus reserve | | | | | | | 194,209 | | | | 194,209 | |
| | | |
| Notes:1. | | Profit was appropriated at the end of this fiscal year in accordance with the provisions of Article 13, Section 8 of the supplementary provisions of the Japan Finance Organization for Municipal Enterprises Law (Law No. 64, 2007). |
| |
| 2. | | Surplus reserve appropriated was posted as Management account surplus reserve on the Balance Sheet. |
-25-
Statement of Changes in Net Assets (From August 1, 2008 through March 31, 2009)
(Millions of Yen)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Stockholders’ equity | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | Retained earnings | | | Total | | | Management | | | | |
| | | | | | | General account | | | Total retained | | | stockholders’ | | | account surplus | | | | |
| | | Capital | | | surplus reserve | | | earnings | | | equity | | | reserve | | | Total net assets | |
| Balance at end of previous fiscal year | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
| Changes during accounting period | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Contribution to capital | | | 16,602 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 16,602 | | | | — | | | | 16,602 | |
| Succession to assets and liabilities of Japan Finance Corporation for Municipal Enterprises | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 16,060 | | | | 16,060 | |
| Net income | | | — | | | | 1,295 | | | | 1,295 | | | | 1,295 | | | | 19,129 | | | | 20,425 | |
| Net changes during accounting period | | | 16,602 | | | | 1,295 | | | | 1,295 | | | | 17,897 | | | | 35,190 | | | | 53,087 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Balance at March 31, 2009 | | | 16,602 | | | | 1,295 | | | | 1,295 | | | | 17,897 | | | | 35,190 | | | | 53,087 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
(Thousands of US dollars)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Stockholders’ equity | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | Retained earnings | | | Total | | | Management | | | | |
| | | | | | | General account | | | Total retained | | | stockholders’ | | | account surplus | | | | |
| | | Capital | | | surplus reserve | | | earnings | | | equity | | | reserve | | | Total net assets | |
| Balance at end of previous fiscal year | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | |
| Changes during accounting period | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Contribution to capital | | | 168,549 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 168,549 | | | | — | | | | 168,549 | |
| Succession to assets and liabilities of Japan Finance Corporation for Municipal Enterprises | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 163,052 | | | | 163,052 | |
| Net income | | | — | | | | 13,153 | | | | 13,153 | | | | 13,153 | | | | 194,209 | | | | 207,362 | |
| Net changes during accounting period | | | 168,549 | | | | 13,153 | | | | 13,153 | | | | 181,702 | | | | 357,261 | | | | 538,963 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Balance at March 31, 2009 | | | 168,549 | | | | 13,153 | | | | 13,153 | | | | 181,702 | | | | 357,261 | | | | 538,963 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
-26-
Statement of Cash Flows (From August 1, 2008 through March 31, 2009)
(Millions of Yen) (Thousands of US dollars)
| | | | | | | | | |
| Item | | Amount | |
| I Cash flows from operating activities | | | | | | | | |
| Net income | | ¥ | 20,425 | | | $ | 207,362 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | | 123 | | | | 1,253 | |
| Interest income | | | (291,288 | ) | | | (2,957,240 | ) |
| Interest expenses | | | 155,235 | | | | 1,575,991 | |
| Decrease in reserve for bonuses | | | (5 | ) | | | (58 | ) |
| Increase in reserve for directors’ bonuses | | | 6 | | | | 71 | |
| Increase in reserve for retirement benefits | | | 10 | | | | 105 | |
| Increase in reserve for retirement benefits for directors and corporate auditors | | | 26 | | | | 269 | |
| Increase in fund for improvement of operations of municipal enterprises | | | 1,800 | | | | 18,276 | |
| Increase in management account reserve for interest rate volatility | | | 118,144 | | | | 1,199,440 | |
| Decrease in reserve for interest rate reduction | | | (7,872 | ) | | | (79,926 | ) |
| Net increase/decrease in loans | | | 243,369 | | | | 2,470,753 | |
| Net increase/decrease in bonds | | | (363,477 | ) | | | (3,690,123 | ) |
| Interest received | | | 289,975 | | | | 2,943,913 | |
| Interest paid | | | (151,043 | ) | | | (1,533,439 | ) |
| Others | | | (40 | ) | | | (416 | ) |
| | | | | | | |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | | | 15,388 | | | | 156,231 | |
| | | | | | | |
| II Cash flows from investing activities | | | | | | | | |
| Proceeds from redemption of securities | | | 2,895,550 | | | | 29,396,447 | |
| Purchases of securities | | | (2,422,893 | ) | | | (24,597,907 | ) |
| Purchases of intangible fixed assets | | | (20 | ) | | | (206 | ) |
| | | | | | | |
| Net cash provided by investing activities | | | 472,635 | | | | 4,798,334 | |
| | | | | | | |
| III Cash flows from financing activities | | | | | | | | |
| Payment to national treasury | | | (300,000 | ) | | | (3,045,685 | ) |
| Refund of contributions made from municipally operated racing | | | (10,479 | ) | | | (106,387 | ) |
| Proceeds from contribution to capital | | | 16,602 | | | | 168,549 | |
| Others (Note 12) | | | (16,455 | ) | | | (167,056 | ) |
| | | | | | | |
| Net cash provided by financing activities | | | (310,332 | ) | | | (3,150,579 | ) |
| | | | | | | |
| IV Effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | |
| V Net increase in cash and cash equivalents | | | 177,692 | | | | 1,803,986 | |
| | | | | | | |
| VI Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | |
| VII Net increase in cash by succession to assets and liabilities | | | 77,898 | | | | 790,850 | |
| | | | | | | |
| VIII Cash and cash equivalents at end of year | | | 255,591 | | | | 2,594,836 | |
| | | | | | | |
-27-
Notes to Financial Statements
| | | Japan Finance Organization for Municipalities (hereinafter, “JFM”) has prepared financial statements pursuant to the following law and ministerial ordinances: |
| | • | | The Japan Finance Organization for Municipal Enterprises Law (Law No. 64, 2007; hereinafter, “Law”), which was subsequently amended by the provisions of Article 5 of the Law on the partial provision of Local Allocation Tax Law (Law No. 10, 2009). |
| | • | | The Ministerial Ordinance on Finance and Accounting of Japan Finance Organization for Municipal Enterprises (Ordinance No.87 of the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications, 2008), which was subsequently amended in accordance with the provisions of Article 2 of the Ministerial Ordinance on preparation for relevant ministerial ordinances of the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications for partial enforcement of the Law on partial revision of the Local Allocation Tax Law (Ordinance No.49 of the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications, 2009; hereinafter, “Preparation Ministerial Ordinance”). |
| | • | | The Ministerial Ordinance on Finance and Accounting of Japan Finance Organization for Municipalities amended in accordance with the provisions of Article 2 of the Preparation Ministerial Ordinance where applied to the financial statements with respect to the year ended March 31, 2009 in accordance with the supplementary provisions of Article 2, Section 1 of the Preparation Ministerial Ordinance. |
Since JFM does not have any subsidiaries or affiliates, it does not prepare consolidated financial statements.
Amounts less than one million yen have been omitted. As a result, the totals in Japanese yen shown in the financial statements do not necessarily agree with the sum of the individual amounts.
The translation of the Japanese yen amounts into U.S. Dollars is included solely for the convenience of readers outside Japan, using the prevailing exchange rate as of March 31, 2009, the final business day of the fiscal year, which was ¥98.50 to US$1.
| 2. | | Significant Accounting Policies |
| | (1) | | Securities |
| |
| | | | As for security valuation, held-to-maturity securities are carried at amortized cost (straight-line method). |
| |
| | (2) | | Derivative transactions |
| |
| | | | Derivative transactions are carried at fair value with changes in unrealized gain or loss charged or credited to operations, except for those which meet the criteria for hedge accounting. |
-28-
| | (a) | | Tangible fixed assets |
| |
| | | | Depreciation of tangible fixed assets is calculated by the straight-line method based on the estimated useul lives and the residual value determined by management. The estimated useful lives of major items are as follows: |
| |
| | | | Buildings: 20 to 41 years Others: 2 to 19 years |
| |
| | (b) | | lntangible fixed assets |
| |
| | | | Depreciation of intangible fixed assets is calculated by the straight-line method based on the estimated useul lives and the residual value determined by management. Software for internal use owned by JFM is depreciated over 5 years. |
| | (4) | | Deferred assets
Bond issuance costs are expensed in full when incurred. |
| | (5) | | Translation of assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies into Japanese yen
Monetary assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies, for which foreign currency swaps or foreign exchange forward contracts are used to hedge the foreign currency fluctuation, are translated at the contracted rate as the swap contracts or the forward contracts qualify for deferral hedge accounting. |
| | (a) | | Reserve for possible loan losses |
| |
| | | | JFM has never experienced any loan losses. Accordingly, no reserve for loan losses has been maintained. |
| |
| | (b) | | Reserve for bonuses |
| |
| | | | Reserve for bonuses is provided for payment of bonuses to employees, in the amount of estimated bonuses, which are attributable to the fiscal year. |
| |
| | (c) | | Reserve for directors’ bonuses |
| |
| | | | Reserve for directors’ bonuses is provided for payment of bonuses to directors, in the amount of estimated bonuses, which are attributable to the fiscal year. |
| |
| | (d) | | Reserve for retirement benefits |
| |
| | | | Reserve for retirement benefits is provided for payment of retirement benefits to employees, in the amount deemed accrued at the fiscal year-end, based on the projected retirement benefit obligation and fair value of plan assets at the fiscal year-end. |
| | (e) | | Reserve for retirement benefits for directors and corporate auditors
Reserve for retirement benefits for directors and corporate auditors is provided for payment of retirement benefits to directors and corporate auditors, in the amount deemed accrued at the fiscal year-end based on the internal policies. |
-29-
| | (a) | | Hedge accounting method |
| |
| | | | If swap contracts or forward contracts used to hedge the foreign currency fluctuation qualify for deferral hedge accounting, foreign currency-denominated assets and liabilities are translated at the contracted rate. Interest rate swaps which qualify for hedge accounting and meet specific matching criteria are not measured at market value, but the differential paid or received under the swap agreements is recognized and included in interest expense or income. |
| | (b) | | Hedging instruments and hedged items |
| | | | | | | |
| | | (i) | | Hedging instrument | | Currency swap |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | Hedged items | | Payment of interest and principle of foreign currency-denominated bonds |
| | | | | | | |
| | | (ii) | | Hedging instrument | | Interest rate swap |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | Hedged items | | Payment of interest and principle of inflation-indexed bonds, and payment of interest of floating rate bonds |
| | | | | | | |
| | | (iii) | | Hedging instrument | | Foreign exchange forward contract |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | Hedged items | | Receipt of interest and principal of foreign currency-denominated bank deposits |
| | (c) | | Hedging policy |
| |
| | | | JFM uses hedging instruments as a means of hedging exposure to foreign exchange risk on foreign currency-denominated bonds, and interest rate risk on inflation-indexed bonds and floating rate bonds. The terms and notional amounts of these hedging instruments are set within those of the underlying transactions. |
| |
| | (d) | | Assessment of hedge effectiveness |
| |
| | | | A periodic assessment of hedge effectiveness for currency swaps is omitted since major terms of the hedging instruments and the underlying transactions are the same and the foreign currency fluctuations are therefore expected to be fully hedged at the beginning and throughout the hedging periods. |
A periodic assessment of hedge effectiveness for interest rate swaps is omitted when the exceptional accrual method is applied.
-30-
| | (8) | | Cash and cash equivalents |
| |
| | | | Cash and cash equivalents in the Statement of Cash Flows consist of “Cash and bank deposits” on the Balance Sheet. |
| |
| | (9) | | Fund for improvement of operations of municipal enterprises |
| |
| | | | In accordance with the provisions of Article 46, Section 1 of the Law, JFM has established the Fund for improvement of operations of municipal enterprises to reserve contributions as stipulated in Article 32-2 of the Local Finance Law (Law No. 109, 1948). Also, pursuant to the provisions of Article 46, Section 5 of the Law, income arising from the investment of the Fund (hereinafter, “investment income”) is used to reduce interest rates of the loans to municipalities, and if there is any surplus in the investment income after this interest rates reduction process, the surplus amount is added to the Fund. Further, pursuant to the provisions of Article 46, Section 6 of the Law, if there is any shortfall after the interest rates reduction process, the shortfall is covered by withdrawal of the Fund within the limits of the total of the additional portion to the Fund made up to the previous fiscal year and the contributions made in the relative fiscal year. |
As for the current fiscal year, JFM refunded the contributions in accordance with the provisions of Article 2, Section 7 of the supplementary provisions of the Enforcement Ordinance of the Local Finance Law (Government Ordinance No. 267, 1948), which was subsequently amended by the Government Ordinance on partial revision of the Enforcement Ordinance of the Local Finance Law (Government Ordinance No. 398, 2007).
| | (10) | | Reserve for interest rate volatility and Management account reserve for interest rate volatility |
| |
| | | | Reserve for interest rate volatility is set aside to prepare for interest rate risk associated with refinancing of our bonds (excluding the bonds issued by the former Japan Finance Corporation for Municipal Enterprises) pursuant to the provisions of Article 38, Sections 1 and 3 of the Law, and Article 9, Section 8 of the supplementary provisions of the Law, and is calculated and accounted for based on the provisions of Article 34 of the Ministerial Ordinance on Finance and Accounting of Japan Finance Organization for Municipal Enterprises (Ordinance No. 87 of the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications, 2008) and Article 22 of the Government Ordinance on preparation of relevant government ordinances and provisional measures for the abolishment of the Japan Finance Corporation for Municipal Enterprises Law (Government Ordinance No. 226, 2008; hereinafter, “Preparation Ordinance”). |
Management account reserve for interest rate volatility is set aside to prepare for interest rate risk associated with refinancing of the bonds issued by the former Japan Finance Corporation for Municipal Enterprises pursuant to the provisions of Article 9, Sections 9 and 10, and Article 13, Sections 5 and 7 of the supplementary provisions of the Law, and is calculated and accounted for based on the provisions of Articles 1 through 3 of the Ministerial Ordinance on the operations of the Management Account at Japan Finance Organization for Municipal Enterprises (Ordinance No. 2 of the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communication, and the Ministry of Finance, 2008; hereinafter, “Management Account Operations Ordinance”) and Articles 3 and 5 of the supplementary provisions of the above ordinance.
-31-
| | (11) | | Reserve for interest rate reduction |
| |
| | | | Reserve for interest rate reduction is set aside to reduce interest rates on the loans made by the former Japan Finance Corporation for Municipal Enterprises to local governments pursuant to the provisions of Article 9, Section 13, and Article 13, Section 8 of the supplementary provisions of the Law, and Article 26, Sections 1, 3 and 4 of the Preparation Ordinance, and is calculated and accounted for based on the provisions of Article 5 of the Management Account Operations Ordinance. |
| | (12) | | Management account surplus reserve |
| |
| | | | Profits generated in the Management account are accounted for as Management account surplus reserve separately from retained earnings in accordance with the provisions of Article 13, Section 8 of the supplementary provisions of the Law and Article 26, Section 2 of the Preparation Ordinance. |
| | (13) | | Consumption taxes |
| |
| | | | National and local consumption taxes are accounted for using the tax-excluded method. |
| 3. | | Loans |
| |
| | | There are no bankrupt loans, non-accrual loans, past due loans (3 months or more), or restructured loans. Since JFM has never experienced loan losses in the past, it does not account for loan loss reserves. |
Bankrupt loans represent loans to borrowers as defined in Articles 96, Section 1, Clause 3 (a) through (e) and Clause 4 of the Enforcement Ordinance of the Corporate Income Tax Law (Government Ordinance No. 97, 1965), and on which accrued interest is not accounted in revenue as there is no expectation of collection of either principal or interest because they are past due for a considerable period of time or for other reasons (excluding loans on which bad debts are written off; hereinafter, “Non-accrual loans”).
Non-accrual loans represent loans on which accrued interest is not accounted in revenue, excluding loans to bankrupt borrowers and loans with grace for interest payment to assist in corporate reorganization or to support business.
Past due loans (3 months or more) represent loans on which payment of principal or interest is in arrears for more than 3 months, calculated from the day following the contractual due date, excluding bankrupt loans and non-accrual loans.
Restructured loans represent loans which are given certain favorable terms and conditions, such as reduction or exemption of interest, grace for interest or principal payment, and debt waiver, to assist borrowers in corporate rehabilitation or to support business, excluding bankrupt loans, non-accrual loans and past due loans (3 months or more).
| 4. | | Tangible and Intangible Fixed Assets |
| |
| | | Tangible and intangible fixed assets at March 31, 2009 consisted of the following: |
(Millions of Yen)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Balance at end | | | Increase | | | Decrease | | | Balance | | | Accumulated depreciation | | | Depreciation | | | Balance | |
| | | of previous | | | during the | | | during the | | | at March 31, | | | at March 31, 2009 or | | | during the | | | at March 31, | |
| Type of assets | | fiscal year | | | year | | | year | | | 2009 | | | accumulated amortization | | | year | | | 2009 | |
| Tangible fixed assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Buildings | | | — | | | | 551 | | | | — | | | | 551 | | | | 21 | | | | 21 | | | | 529 | |
| Land | | | — | | | | 2,403 | | | | — | | | | 2,403 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 2,403 | |
| Other tangible fixed assets | | | — | | | | 91 | | | | — | | | | 91 | | | | 13 | | | | 13 | | | | 77 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total tangible fixed assets | | | — | | | | 3,045 | | | | — | | | | 3,045 | | | | 35 | | | | 35 | | | | 3,010 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Intangible fixed assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Software | | | — | | | | 910 | | | | — | | | | 910 | | | | 88 | | | | 88 | | | | 822 | |
| Other intangible fixed assets | | | — | | | | 20 | | | | — | | | | 20 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 20 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total intangible fixed assets | | | — | | | | 931 | | | | — | | | | 931 | | | | 88 | | | | 88 | | | | 842 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
-32-
(Thousands of US dollars)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Balance at end | | | Increase | | | Decrease | | | Balance | | | Accumulated depreciation | | | Depreciation | | | Balance | |
| | | of previous | | | during the | | | during the | | | at March 31, | | | at March 31, 2009 or | | | during the | | | at March 31, | |
| Type of assets | | fiscal year | | | year | | | year | | | 2009 | | | accumulated amortization | | | year | | | 2009 | |
| Tangible fixed assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Buildings | | | — | | | | 5,595 | | | | — | | | | 5,595 | | | | 221 | | | | 221 | | | | 5,374 | |
| Land | | | — | | | | 24,398 | | | | — | | | | 24,398 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 24,398 | |
| Other tangible fixed assets | | | — | | | | 925 | | | | — | | | | 925 | | | | 137 | | | | 137 | | | | 788 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total tangible fixed assets | | | — | | | | 30,918 | | | | — | | | | 30,918 | | | | 358 | | | | 358 | | | | 30,560 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Intangible fixed assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Software | | | — | | | | 9,246 | | | | — | | | | 9,246 | | | | 894 | | | | 894 | | | | 8,352 | |
| Other intangible fixed assets | | | — | | | | 206 | | | | — | | | | 206 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 206 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total intangible fixed assets | | | — | | | | 9,452 | | | | — | | | | 9,452 | | | | 894 | | | | 894 | | | | 8,558 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | |
| Notes: 1. | | “Increase during the year” includes the amount of the fixed assets inherited from the former Japan Finance Corporation for Municipal Enterprises on October 1, 2008, in accordance with the provisions of Article 10, Sections 1 and 2 of the supplemental provisions of the Law. |
| |
| 2. | | Accumulated depreciation of tangible fixed assets amounted to 35 million yen (358 thousand dollars) as of March 31, 2009. |
| 5. | | Assets Pledged as Collateral |
| |
| | | Pursuant to the provisions of Article 40, Section 2 of the Law, JFM’s total assets are pledged as general collateral for JFM bonds for 18,978,163 million yen (192,671,714 thousand dollars). |
| 6. | | Bonds |
| |
| | | Bonds at March 31, 2009 consisted of the following: |
(Millions of Yen) (Thousands of US dollars)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | Outstanding amount | | | Coupon rate | | | | |
| Type of bond | | Date of issue | | at March 31, 2009 | | | (%) | | | Maturity | |
| Government-guaranteed bond (domestic) 1st 4-year JFM bond | | 2/27/2009 | | ¥ | 299,827 | | | $ | 3,043,934 | | | | 0.7 | | | | 4Y | |
| Government-guaranteed bonds (domestic) 1st-6th JFM bonds | | 10/16/2008-3/17/2009 | | | 420,057 | | | | 4,264,545 | | | | 1.3~1.6 | | | | 10Y | |
| Public offering bond without government guarantee 1st 5-year JFM bond | | 2/24/2009 | | | 29,991 | | | | 304,481 | | | | 1.01 | | | | 5Y | |
| Public offering bonds without government guarantee 1st-2nd JFM bonds | | 11/25/2008-2/20/2009 | | | 79,952 | | | | 811,701 | | | | 1.59 ~1.77 | | | | 10Y | |
| Public offering bond without government guarantee 1st 20-year JFM bond | | 1/26/2009 | | | 49,940 | | | | 507,013 | | | | 2.07 | | | | 20Y | |
| JFM bonds - Sub-total | | — | | | 879,769 | | | | 8,931,674 | | | | — | | | | — | |
| Government-guaranteed bonds (domestic) 775th-886th former JFM bonds | | 4/28/1999- | | | 10,999,234 | | | | 111,667,358 | | | | | | | | | |
| | | 6/19/2008 | | | (1,782,750 | ) | | | (18,098,985 | ) | | | 0.5 ~2.0 | | | | 10Y | |
| Government-guaranteed (domestic) 1st-5th 15-year former JFM bonds | | 6/22/2005-7/18/2007 | | | 184,615 | | | | 1,874,266 | | | | 1.6 ~2.2 | | | | 15Y | |
| Government-guaranteed bonds (foreign) 13th Eurodollar former JFM bond - 5th Global Yen former JFM bond | | 5/7/1999-6/25/2008 | | | 1,125,217 | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | (81,740 | ) | | | 11,423,523 | | | | 1.350 | | | | 10Y | |
| | | | | [US dollars 3,900,000 thousand] | | | | (829,848 | ) | | | ~6.000 | | | | ~20Y | |
| | | | | [Euro 900,000 thousand] | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | [Pound sterling 150,000 thousand] | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Public offering bond without government guarantee 1st 5-year former JFM bond | | 2/29/2008 | | | 129,950 | | | | 1,319,291 | | | | 1.14 | | | | 5Y | |
(Continued)
-33-
(Millions of Yen) (Thousands of US dollars)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | Outstanding amount | | | Coupon rate | | | | |
| Type of bond | | Date of issue | | | at March 31, 2009 | | | (%) | | | Maturity | |
| Public offering bonds without government guarantee 1st-30th former JFM bonds | | | 12/26/2001-6/16/2008 | | | ¥ | 1,279,743 | | | $ | 12,992,317 | | | | 0.64~2.07 | | | | 10Y | |
| Public offering bonds without government guarantee 1st-25th 20-year former JFM bonds | | | 7/30/2002-6/16/2008 | | | | 569,587 | | | | 5,782,612 | | | | 1.03~2.58 | | | | 20Y | |
| Public offering bonds without government guarantee 1st-10th 30-year former JFM bonds | | | 1/29/2004-9/20/2006 | | | | 189,842 | | | | 1,927,339 | | | | 2.39~2.95 | | | | 30Y | |
| Public offering bond without government guarantee 1st floating rate former JFM bond | | | 10/31/2002 | | | | 20,000 | | | | 203,046 | | | Floating | | | 15Y | |
| Public offering bonds without government guarantee 1st-2nd inflation-indexed former JFM bonds | | | 3/2/2005-7/19/2005 | | | | 40,000 | | | | 406,091 | | | | 1.248~1.408 | | | | 10Y | |
| Public offering bonds without government guarantee 1st-3rd former JFM bonds with scheduled repayment | | | 2/14/2003-6/9/2004 | | | | 47,830 (2,170 | ) | | | 485,584 (22,030 | ) | | | 1.39~2.01 | | | | 28Y | |
| Public offering bond without government guarantee 1st CMS-linked floating rate former JFM bond | | | 9/13/2006 | | | | 20,000 | | | | 203,045 | | | | 1.894 | | | | 10Y | |
| Private placement bonds A series 52nd — Special No. 1 series 31st former JFM bonds | | | 7/30/1999-7/31/2008 | | | | 3,492,373 (522,253 | ) | | | 35,455,568 (5,302,063 | ) | | | 0.67~2.18 | | | | 10Y | |
| Former JFM bonds — Sub-total | | | — | | | | 18,098,393 (2,388,913 | ) | | | 183,740,040 (24,252,926 | ) | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total | | | — | | | ¥ | 18,978,163 (2,388,913 | ) | | $ | 192,671,714 (24,252,926 | ) | | | — | | | | — | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | |
| Notes: 1. | | Pursuant to the provisions of Article 40, Section 2 of the Law, JFM’s total assets are pledged as general collateral for JFM bonds for 18,978,163 million yen (192,671,714 thousand dollars). |
| |
| 2. | | Amounts posted in brackets “[___]” in the column of “Outstanding amount at March 31, 2009” for “Government-guaranteed bond (foreign) — 13th Eurodollar former JFM bond — 5th Global Yen former JFM bond” are denominated in foreign currencies. |
| |
| 3. | | Amounts posted in parentheses “(___)” in the column of “Outstanding amount at March 31, 2009” are the amounts to be repaid within one year. |
| |
| 4. | | The repayment schedule for the five years from the end of this fiscal year is as follows. |
(Millions of Yen)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Within 1 year | | After 1 year through 2 years | | | After 2 years through 3 years | | | After 3 years through 4 years | | | After 4 years through 5 years | |
| 2,388,913 | | | 2,244,370 | | | | 2,176,130 | | | | 2,030,560 | | | | 2,160,070 | |
(Thousands of US dollars)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Within 1 year | | After 1 year through 2 years | | | After 2 years through 3 years | | | After 3 years through 4 years | | | After 4 years through 5 years | |
| 24,252,926 | | | 22,785,482 | | | | 22,092,690 | | | | 20,614,822 | | | | 21,929,645 | |
Reserves at March 31, 2009 consisted of the following:
(Millions of Yen)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Balance at end | | | | | | | Decrease during | | | | | | | |
| | | of previous fiscal | | | Increase | | | the year (for | | | Decrease during | | | Balance at | |
| Type of reserve | | year | | | during the year | | | intended purposes) | | | the year (Others) | | | March 31, 2009 | |
| Reserve for bonuses | | | — | | | | 101 | | | | 53 | | | | — | | | | 47 | |
| Reserve for directors’ bonuses | | | — | | | | 8 | | | | 0 | | | | — | | | | 7 | |
| Reserve for retirement benefits | | | — | | | | 202 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 202 | |
| Reserve for retirement benefits for directors and corporate auditors | | | — | | | | 51 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 51 | |
-34-
(Thousands of US dollars)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Balance at end | | | | | | | Decrease during | | | | | | | |
| | | of previous fiscal | | | Increase | | | the year (for | | | Decrease during | | | Balance at | |
| Type of reserve | | year | | | during the year | | | intended purposes) | | | the year (Others) | | | March 31, 2009 | |
| Reserve for bonuses | | | — | | | | 1,028 | | | | 543 | | | | — | | | | 485 | |
| Reserve for directors’ bonuses | | | — | | | | 90 | | | | 9 | | | | — | | | | 81 | |
| Reserve for retirement benefits | | | — | | | | 2,058 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 2,058 | |
| Reserve for retirement benefits for directors and corporate auditors | | | — | | | | 519 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 519 | |
| 8. | | Reserve for Interest Rate Volatility |
| | (1) | | Reserve for interest rate volatility at March 31, 2009 consisted of the following: |
(Millions of Yen)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Balance at | | | Increase during the year | | | Decrease during the year | | | | |
| | | end of previous | | | | | | | Amount | | | | | | | Amount | | | Balance at | |
| Type of reserve | | fiscal year | | | | | | | provided | | | | | | | withdrawn | | | March 31, 2009 | |
| Reserve for interest rate volatility | | | — | | | | 220,000 | | | | 220,000 | | | | — | | | | | | | | 220,000 | |
| Management account reserve for interest rate volatility | | | — | | | | 3,374,728 | | | | | | | | 300,000 | | | | — | | | | 3,074,728 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total | | | — | | | | 3,594,728 | | | | 220,000 | | | | 300,000 | | | | — | | | | 3,294,728 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
(Thousands of US dollars)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Balance at | | | Increase during the year | | | Decrease during the year | | | | |
| | | end of previous | | | | | | | Amount | | | | | | | Amount | | | Balance at | |
| Type of reserve | | fiscal year | | | | | | | provided | | | | | | | withdrawn | | | March 31, 2009 | |
| Reseve for interest rate volatility | | | — | | | | 2,233,503 | | | | 2,233,503 | | | | — | | | | | | | | 2,233,503 | |
| Management account reserve for interest rate volatility | | | — | | | | 34,261,204 | | | | | | | | 3,045,685 | | | | — | | | | 31,215,519 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total | | | — | | | | 36,494,707 | | | | 2,233,503 | | | | 3,045,685 | | | | — | | | | 33,449,022 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | (2) | | During this fiscal year, Management account reserve for interest rate volatility was reversed in the amount of 300,000 million yen (3,045,685 thousand dollars) and paid to the national treasury in accordance with the Ministerial Ordinance on determination of the amount attributable to the national government for fiscal 2008 pursuant to the provisions of Article 14 of the supplementary provisions of the Law (Ordinance No. 1 of the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications, and the Ministry of Finance, 2009). |
| 9. | | Fund for Improvement of Operations of Municipal Enterprises |
Fund for improvement of operations of municipal enterprises at March 31, 2009 consisted of the following:
(Millions of Yen)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | Increase during the year | | | Decrease during the year | | | | |
| | | Balance at end of | | | | | | | Amount | | | Amount | | | | | | | Balance at | |
| Type of fund | | Previous fiscal year | | | Amount of reserve | | | transferred | | | withdrawn | | | Others | | | March 31, 2009 | |
| Basic fund for improvement of operations of municipal enterprises | | | — | | | | 903,354 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 10,479 | | | | 892,875 | |
| Additional fund for improvement of operations of municipal enterprises | | | — | | | | — | | | | 1,800 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 1,800 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total | | | — | | | | 903,354 | | | | 1,800 | | | | — | | | | 10,479 | | | | 894,675 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
-35-
(Thousands of US dollars)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | Increase during the year | | | Decrease during the year | | | | |
| | | Balance at end | | | | | | | Amount | | | Amount | | | | | | | Balance at | |
| Type of fund | | of previous fiscal year | | | Amount of reserve | | | transferred | | | withdrawn | | | Others | | | March 31, 2009 | |
| Basic fund for improvement of operations of municipal enterprises | | | — | | | | 9,171,115 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 106,387 | | | | 9,064,728 | |
| Additional fund for improvement of operations of municipal enterprises | | | — | | | | — | | | | 18,276 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 18,276 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total | | | — | | | | 9,171,115 | | | | 18,276 | | | | — | | | | 106,387 | | | | 9,083,004 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | |
| Notes: 1. | | “Amount of reserve” of “Basic fund for improvement of operations of municipal enterprises” represents the amount that JFM inherited from the former Japan Finance Corporation for Municipal Enterprises in accordance with the provisions of Article 9, Section 11 of the supplementary provisions of the Law. |
| |
| 2. | | The full amount of “Others” posted in “Decrease during the year” for “Basic fund for improvement of operations of municipal enterprises” represents the amount which was refunded in accordance with the provisions of Article 2, Section 7 of the supplementary provisions of the Enforcement ordinance of the Local Finance Law, which was subsequently amended by the Government Ordinance. |
| |
| 3. | | “Amount transferred” posted in “Increase during the year” for “Additional fund for improvement of operations of municipal enterprises” represents the amount transferred to Additional fund for improvement of operations of municipal enterprises pursuant to the provisions of Article 46, Section 5 of the Law. |
| | | |
| 10. | | Reserve for Employee Retirement Benefits |
| | | | | | |
| | (1) | | Outline of retirement benefits system employed
JFM has a defined benefit plan that contributes to the Employees’ Pension Fund and offers lump-sum payments upon retirement. |
| | | | | | |
| | (2) | | Projected benefit obligation | | |
| |
| | | | Projected benefit obligation | | 316 million yen (3,210 thousand dollars) |
| | | | Plan assets | | 113 million yen (1,152 thousand dollars) |
| | | | Reserve for employee retirement benefits | | 202 million yen (2,058 thousand dollars) |
| | | | | | |
| | (3) | | Pension expenses | | |
| |
| | | | Pension expenses | | 14 million yen (143 thousand dollars) |
| | | | Pension expenses related to lump-sum payments upon retirement | | 2 million yen (22 thousand dollars) |
| | | | Pension expenses related to the Employees’ Pension Fund | | 11 million yen (121 thousand dollars) |
| | | | | | |
| | (4) | | Basis of calculation of projected benefit obligation | | |
| |
| | | | Projected benefit obligation is calculated by the simple method. | | |
| | | |
| 11. | | Net Income by Account |
Net income of General account was 1,295 million yen (13,153 thousand dollars), while net income of Management account was 19,129 million yen (194,209 thousand dollars).
| | (1) | | “Others” in III Cash flows from financing activities section |
This represents capital of the former Japan Finance Corporation for Municipal Enterprises contributed by the national government, and expenses related to Other Liabilities on the Balance Sheet of Succeeded Assets and Liabilities.
| | (2) | | Significant non-cash transaction |
On October 1, 2008, JFM succeeded to assets and liabilities of the former Japan Finance Corporation for Municipal Enterprises in accordance with the provisions of Article 9, Section 1 and Article 10, Sections 1 and 2 of the supplementary provisions of the Law.
-36-
| | | |
| 13. | | Information by Account (Balance Sheet) |
Balance sheet of General account and Management account at March 31, 2009 was as follows:
(Millions of Yen)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | Management | | | | | | | |
| Item | | General account | | | account | | | Offset | | | Total | |
Assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loans | | | 475,313 | | | | 21,739,974 | | | | | | | | 22,215,288 | |
| Securities | | | 874,832 | | | | | | | | | | | | 874,832 | |
| Cash and bank deposits | | | 255,591 | | | | | | | | | | | | 255,591 | |
| Other assets | | | 2,543 | | | | 17,508 | | | | | | | | 20,051 | |
| Tangible fixed assets | | | 3,010 | | | | | | | | | | | | 3,010 | |
| Intangible fixed assets | | | 842 | | | | | | | | | | | | 842 | |
| Due from general account | | | | | | | 1,209,333 | | | | (1,209,333 | ) | | | | |
| Due from management account for fund for improvement of operations of municipal enterprises | | | 892,875 | | | | | | | | (892,875 | ) | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total assets | | | 2,505,009 | | | | 22,966,816 | | | | (2,102,209 | ) | | | 23,369,616 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Bonds | | | 159,884 | | | | 18,818,279 | | | | | | | | 18,978,163 | |
| Other liabilities | | | 2,908 | | | | 16,848 | | | | | | | | 19,756 | |
| Reserve for bonuses | | | 47 | | | | | | | | | | | | 47 | |
| Reserve for directors’ bonuses | | | 7 | | | | | | | | | | | | 7 | |
| Reserve for retirement benefits | | | 202 | | | | | | | | | | | | 202 | |
| Reserve for retirement benefits for directors and corporate auditors | | | 51 | | | | | | | | | | | | 51 | |
| Fund for improvement of operations of municipal enterprises | | | 894,675 | | | | | | | | | | | | 894,675 | |
| Basic fund for improvement of operations of municipal enterprises | | | 892,875 | | | | | | | | | | | | 892,875 | |
| Additional fund for improvement of operations of municipal enterprises | | | 1,800 | | | | | | | | | | | | 1,800 | |
| Due to management account | | | 1,209,333 | | | | | | | | (1,209,333 | ) | | | | |
| Due to general account for fund for improvement of operations of municipal enterprises | | | | | | | 892,875 | | | | (892,875 | ) | | | | |
| Reserve under special laws | | | 220,000 | | | | 3,203,622 | | | | | | | | 3,423,622 | |
| Reserve for interest rate volatility | | | 220,000 | | | | | | | | | | | | 220,000 | |
| Management account reserve for interest rate volatility | | | | | | | 3,074,728 | | | | | | | | 3,074,728 | |
| Reserve for interest rate reduction | | | | | | | 128,894 | | | | | | | | 128,894 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total liabilities | | | 2,487,111 | | | | 22,931,626 | | | | (2,102,209 | ) | | | 23,316,529 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net Assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Capital | | | 16,602 | | | | | | | | | | | | 16,602 | |
| Retained earnings | | | 1,295 | | | | | | | | | | | | 1,295 | |
| General account surplus reserve | | | 1,295 | | | | | | | | | | | | 1,295 | |
| Management account surplus reserve | | | | | | | 35,190 | | | | | | | | 35,190 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total net assets | | | 17,897 | | | | 35,190 | | | | | | | | 53,087 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total liabilities and net assets | | | 2,505,009 | | | | 22,966,816 | | | | (2,102,209 | ) | | | 23,369,616 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
-37-
(Thousands of US dollars)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | Management | | | | | | | |
| Item | | General account | | | account | | | Offset | | | Total | |
Assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loans | | | 4,825,515 | | | | 220,710,406 | | | | | | | | 225,535,921 | |
| Securities | | | 8,881,550 | | | | | | | | | | | | 8,881,550 | |
| Cash and bank deposits | | | 2,594,836 | | | | | | | | | | | | 2,594,836 | |
| Other assets | | | 25,823 | | | | 177,747 | | | | | | | | 203,570 | |
| Tangible fixed assets | | | 30,560 | | | | | | | | | | | | 30,560 | |
| Intangible fixed assets | | | 8,558 | | | | | | | | | | | | 8,558 | |
| Due from general account | | | | | | | 12,277,496 | | | | (12,277,496 | ) | | | | |
| Due from management account for fund for improvement of operations of municipal enterprises | | | 9,064,728 | | | | | | | | (9,064,728 | ) | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total assets | | | 25,431,570 | | | | 233,165,649 | | | | (21,342,224 | ) | | | 237,254,995 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Bonds | | | 1,623,194 | | | | 191,048,520 | | | | | | | | 192,671,714 | |
| Other liabilities | | | 29,528 | | | | 171,050 | | | | | | | | 200,578 | |
| Reserve for bonuses | | | 485 | | | | | | | | | | | | 485 | |
| Reserve for directors’ bonuses | | | 81 | | | | | | | | | | | | 81 | |
| Reserve for retirement benefits | | | 2,058 | | | | | | | | | | | | 2,058 | |
| Reserve for retirement benefits for directors and corporate auditors | | | 519 | | | | | | | | | | | | 519 | |
| Fund for improvement of operations of municipal enterprises | | | 9,083,004 | | | | | | | | | | | | 9,083,004 | |
| Basic fund for improvement of operations of municipal enterprises | | | 9,064,728 | | | | | | | | | | | | 9,064,728 | |
| Additional fund for improvement of operations of municipal enterprises | | | 18,276 | | | | | | | | | | | | 18,276 | |
| Due to management account | | | 12,277,496 | | | | | | | | (12,277,496 | ) | | | | |
| Due to general account for fund for improvement of operations of municipal enterprises | | | | | | | 9,064,728 | | | | (9,064,728 | ) | | | | |
| Reserve under special laws | | | 2,233,503 | | | | 32,524,090 | | | | | | | | 34,757,593 | |
| Reserve for interest rate volatility | | | 2,233,503 | | | | | | | | | | | | 2,233,503 | |
| Management account reserve for interest rate volatility | | | | | | | 31,215,519 | | | | | | | | 31,215,519 | |
| Reserve for interest rate reduction | | | | | | | 1,308,571 | | | | | | | | 1,308,571 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total liabilities | | | 25,249,868 | | | | 232,808,388 | | | | (21,342,224 | ) | | | 236,716,032 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net Assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Capital | | | 168,549 | | | | | | | | | | | | 168,549 | |
| Retained earnings | | | 13,153 | | | | | | | | | | | | 13,153 | |
| General account surplus reserve | | | 13,153 | | | | | | | | | | | | 13,153 | |
| Management account surplus reserve | | | | | | | 357,261 | | | | | | | | 357,261 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total net assets | | | 181,702 | | | | 357,261 | | | | | | | | 538,963 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total liabilities and net assets | | | 25,431,570 | | | | 233,165,649 | | | | (21,342,224 | ) | | | 237,254,995 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
-38-
| | | |
| Notes: 1. | | General account and Management account |
| |
| | | In accordance with the provisions of Article 13, Section 1 of the supplementary provisions of the Law, Management account is used to conduct administration, collection and other related operations of the assets that JFM inherited from the former Japan Finance Corporation for Municipal Enterprises (management of the assets of the former Japan Finance Corporation for Municipal Enterprises). Management account is separated from the other account (General account) pursuant to the provisions of Article 13, Section 3 of the supplementary provisions of the Law. |
| |
| 2. | | General account surplus reserve and Management account surplus reserve |
| |
| | | “Net income” of General account is posted as “General account surplus reserve” in accordance with the provisions of Article 39, Section 1 of the Law, while “Net income” of Management account is posted as “Management account surplus reserve” in accordance with the provisions of Article 13, Section 8 of the supplementary provisions the Law. |
| |
| 3. | | Due from General account and Due to Management account |
| |
| | | These figures represent the amount of funds lent between General account and Management account pursuant to the provisions of Article 13, Section 4 of the supplementary provisions of the Law. |
| |
| 4. | | Due to General account for Fund for improvement of operations of municipal enterprises and Due from Management account for Fund for improvement of operations of municipal enterprises |
| |
| | | These figures represent the amount of cash received for “Fund for improvement of operations of municipal enterprises,” which was lent to Management account from General account pursuant to the provisions of Article 9, Section 12 of the supplementary provisions of the Law. |
-39-
| 14. | | Information by Account (Statement of Income) |
| |
| | | Statement of income of General account and Management account from August 1, 2008 through March 31, 2009 was as follows: |
(Millions of Yen)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | Management | | | | | | | |
| Item | | General account | | | account | | | Offset | | | Total | |
Income | | | 17,807 | | | | 298,791 | | | | (25,269 | ) | | | 291,330 | |
| Interest income | | | 5,016 | | | | 286,271 | | | | | | | | 291,288 | |
| Fees and commissions | | | 33 | | | | | | | | | | | | 33 | |
| Other income | | | 6 | | | | 1 | | | | | | | | 8 | |
| Administrative fee for management account | | | 571 | | | | | | | | (571 | ) | | | | |
| Interest on fund for improvement of operations of municipal enterprises | | | 12,179 | | | | | | | | (12,179 | ) | | | | |
| Interest on due from general account | | | | | | | 2,154 | | | | (2,154 | ) | | | | |
| Transfer from general account for fund for improvement of operations of municipal enterprises | | | | | | | 10,363 | | | | (10,363 | ) | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Expenses | | | 16,512 | | | | 169,389 | | | | (25,269 | ) | | | 160,632 | |
| Interest expenses | | | 572 | | | | 154,662 | | | | | | | | 155,235 | |
| Fees and commissions | | | 0 | | | | 134 | | | | | | | | 134 | |
| Other operating expenses | | | 485 | | | | 1,747 | | | | | | | | 2,233 | |
| General and administrative expenses | | | 1,109 | | | | 94 | | | | | | | | 1,203 | |
| Other expenses | | | 1,826 | | | | | | | | | | | | 1,826 | |
| Transfer to fund for improvement of operations of municipal enterprises | | | 1,800 | | | | | | | | | | | | 1,800 | |
| Others | | | 26 | | | | | | | | | | | | 26 | |
| Interest on due to management account | | | 2,154 | | | | | | | | (2,154 | ) | | | | |
| Transfer to management account for fund for improvement of operations of municipal enterprises | | | 10,363 | | | | | | | | (10,363 | ) | | | | |
| Administrative fee for management account | | | | | | | 571 | | | | (571 | ) | | | | |
| Interest on fund for improvement of operations of municipal enterprises | | | | | | | 12,179 | | | | (12,179 | ) | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Ordinary income | | | 1,295 | | | | 129,401 | | | | | | | | 130,697 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Special gains | | | | | | | 307,872 | | | | | | | | 307,872 | |
| Reversal of management account reserve for interest rate volatility | | | | | | | 300,000 | | | | | | | | 300,000 | |
| Reversal of reserve for interest rate reduction | | | | | | | 7,872 | | | | | | | | 7,872 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Special losses | | | | | | | 418,144 | | | | | | | | 418,144 | |
| Provision for management account reserve for interest rate volatility | | | | | | | 118,144 | | | | | | | | 118,144 | |
| Payment to national treasury | | | | | | | 300,000 | | | | | | | | 300,000 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income | | | 1,295 | | | | 19,129 | | | | | | | | 20,425 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
-40-
(Thousands of US dollars)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | Management | | | | | | | |
| Item | | General account | | | account | | | Offset | | | Total | |
Income | | | 180,790 | | | | 3,033,415 | | | | (256,539 | ) | | | 2,957,666 | |
| Interest income | | | 50,928 | | | | 2,906,312 | | | | | | | | 2,957,240 | |
| Fees and commissions | | | 342 | | | | | | | | | | | | 342 | |
| Other income | | | 69 | | | | 15 | | | | | | | | 84 | |
| Administrative fee for management account | | | 5,797 | | | | | | | | (5,797 | ) | | | | |
| Interest on fund for improvement of operations of municipal enterprises | | | 123,654 | | | | | | | | (123,654 | ) | | | | |
| Interest on due from general account | | | | | | | 21,878 | | | | (21,878 | ) | | | | |
| Transfer from general account for fund for improvement of operations of municipal enterprises | | | | | | | 105,210 | | | | (105,210 | ) | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Expenses | | | 167,637 | | | | 1,719,692 | | | | (256,539 | ) | | | 1,630,790 | |
| Interest expenses | | | 5,814 | | | | 1,570,178 | | | | | | | | 1,575,992 | |
| Fees and commissions | | | 4 | | | | 1,362 | | | | | | | | 1,366 | |
| Other operating expenses | | | 4,927 | | | | 17,746 | | | | | | | | 22,673 | |
| General and administrative expenses | | | 11,263 | | | | 955 | | | | | | | | 12,218 | |
| Other expenses | | | 18,541 | | | | | | | | | | | | 18,541 | |
| Transfer to fund for improvement of operations of municipal enterprises | | | 18,276 | | | | | | | | | | | | 18,276 | |
| Others | | | 265 | | | | | | | | | | | | 265 | |
| Interest on due to management account | | | 21,878 | | | | | | | | (21,878 | ) | | | | |
| Transfer to management account for fund for improvement of operations of municipal enterprises | | | 105,210 | | | | | | | | (105,210 | ) | | | | |
| Administrative fee for management account | | | | | | | 5,797 | | | | (5,797 | ) | | | | |
| Interest on fund for improvement of operations of municipal enterprises | | | | | | | 123,654 | | | | (123,654 | ) | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Ordinary income | | | 13,153 | | | | 1,313,723 | | | | | | | | 1,326,876 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Special gains | | | | | | | 3,125,611 | | | | | | | | 3,125,611 | |
| Reversal of management account reserve for interest rate volatility | | | | | | | 3,045,685 | | | | | | | | 3,045,685 | |
| Reversal of reserve for interest rate reduction | | | | | | | 79,926 | | | | | | | | 79,926 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Special losses | | | | | | | 4,245,125 | | | | | | | | 4,245,125 | |
| Provision for management account reserve for interest rate volatility | | | | | | | 1,199,440 | | | | | | | | 1,199,440 | |
| Payment to national treasury | | | | | | | 3,045,685 | | | | | | | | 3,045,685 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income | | | 13,153 | | | | 194,209 | | | | | | | | 207,362 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
-41-
| 15. | | Market Value of Marketable Securities |
| | (1) | | Marketable held-to-maturity securities at March 31, 2009 consisted of the following: |
(Millions of Yen)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Balance sheet
amount | | | Market value | | | Net unrealized
gains (losses) | | | Unrealized
gains | | | Unrealized
losses | |
| Financial bills | | | 193,958 | | | | 193,954 | | | | (4 | ) | | | — | | | | (4 | ) |
| Treasury discount bills | | | 411,873 | | | | 411,865 | | | | (8 | ) | | | — | | | | (8 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total | | | 605,832 | | | | 605,819 | | | | (12 | ) | | | — | | | | (12 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
(Thousands of US dollars)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Balance sheet
amount | | | Market value | | | Net unrealized
gains (losses) | | | Unrealized
gains | | | Unrealized
losses | |
| Financial bills | | | 1,969,125 | | | | 1,969,078 | | | | (47 | ) | | | — | | | | (47 | ) |
| Treasury discount bills | | | 4,181,461 | | | | 4,181,373 | | | | (88 | ) | | | — | | | | (88 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total | | | 6,150,586 | | | | 6,150,451 | | | | (135 | ) | | | — | | | | (135 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | |
| Notes: | 1. | Market value is based on market prices at the end of the fiscal year. |
| |
| 2. | “Unrealized gains” and “Unrealized losses” are components of Net unrealized gains (losses). |
| | | |
| (2) | Securities with no available market value at March 31, 2009 were as follows: |
(Millions of Yen) (Thousands of US dollars)
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | Amount | |
| Negotiable certificate of deposits | | ¥ | 269,000 | | | $ | 2,730,964 | |
-42-
| 16. | | Derivative Information |
| | (1) | | Types of derivative transactions |
| |
| | | | Derivative transactions conducted by JFM are interest rate swaps for interest rate related transactions, and currency swaps for currency related transactions. |
| |
| | (2) | | Policies and purposes of derivative transactions |
| |
| | | | JFM uses interest rate swaps and currency swaps as a means of hedging exposure to interest rate and foreign exchange fluctuation risks, and does not enter into derivatives for speculative purposes. |
Interest rate swaps are used to hedge exposure to interest rate risk on fund raising operations. Currency swaps are used to hedge exposure to foreign exchange risk associated with issuance of foreign currency-denominated bonds.
Hedge accounting is applied to interest rate swaps and currency swaps.
| | (a) | | Hedge accounting method |
| |
| | | | If derivatives used to hedge the foreign currency fluctuation qualify for deferral hedge accounting, foreign currency-denominated assets and liabilities are translated at the contracted rate. Interest rate swaps which qualify for hedge accounting and meet specific matching criteria are not measured at market value, but the differential paid or received under the swap agreements is recognized and included in interest expense or income. |
| |
| | (b) | | Hedging instruments and hedged items |
| | (i) | Hedging instrument | | Currency swap |
| |
| | | Hedged items | | Payment of interest and principal of foreign currency-denominated bonds |
| |
| | (ii) | Hedging instrument | | Interest rate swap |
| |
| | | Hedged items | | Payment of interest and principal of inflation-indexed bonds, and payment of interest of floating rate bonds |
| |
| | (iii) | Hedging instrument | | Foreign exchange forward contract |
| |
| | | Hedged items | | Receipt of interest and principal of foreign currency-denominated bank deposits |
| | (c) | | Hedging policy |
| |
| | | | JFM uses hedging instruments as a means of hedging exposure to foreign exchange risk on foreign currency-denominated bonds and interest rate risk on inflation-indexed bonds and floating rate bonds. The terms and notional amounts of these hedging instruments are set within those of the underlying transactions. |
| |
| | (d) | | Assessment of hedge effectiveness |
| |
| | | | A periodic assessment of hedge effectiveness for currency swaps is omitted since major terms of the hedging instruments and the underlying transactions are the same and the foreign currency fluctuations are therefore expected to be fully hedged at the beginning and throughout the hedging periods. |
A periodic assessment of hedge effectiveness for interest rate swaps is omitted when the exceptional accrual method is applied.
-43-
| | (3) | | Risks on derivative transactions |
| |
| | | | Major risks on derivative transactions are market risk and credit risk. Market risk is the risk of future revenue fluctuations due to market value changes. Credit risk is the risk of losses incurred when counterparties are unable to fulfill their contracts due to bankruptcy or other reasons. |
As for derivative transactions used for hedging purposes, market risk is offset by market risk on underlying transactions. Regarding credit risk, JFM limits counterparties to the financial institutions with high credit standing, constantly monitors their credit profiles, and deals with multiple counterparties.
| | (4) | | Risk management system for derivative transactions |
| |
| | | | Execution and management of derivative transactions are conducted by the Finance Department of JFM with the approval of persons in charge in accordance with the operational guidelines which specify transaction authority. |
Additionally, the total amount of derivative transactions, the status of risks and the credit risk on counterparties are reported to executive officers periodically.
| | (5) | | Supplementary information on market value of transactions |
| |
| | | | Since hedge accounting is applied to all the derivatives transactions conducted by JFM, description of the above is not included in Notes. |
| 17. | | Succession to Assets and Liabilities |
| |
| | | Shown below are assets and liabilities that JFM inherited from the former Japan Finance Corporation for Municipal Enterprises in accordance with the provisions of Article 9, Section 1 and Article 10, Sections 1 and 2 of the supplementary provisions of the Law, and Management account surplus reserve is also shown based on Article 21 of the Preparation Ordinance. |
Balance Sheet of Succeeded Assets and Liabilities (As of October 1, 2008)
(Millions of Yen) (Thousands of US dollars)
| | | | | | | | | |
| Item | | Amount | |
Assets | | | | | | | | |
| Loans | | ¥ | 22,458,657 | | | $ | 228,006,674 | |
| Securities | | | 1,347,000 | | | | 13,675,127 | |
| Cash and bank deposits | | | 77,898 | | | | 790,850 | |
| Other assets | | | 17,179 | | | | 174,412 | |
| Tangible fixed assets | | | 3,045 | | | | 30,918 | |
| Intangible fixed assets | | | 654 | | | | 6,645 | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Total assets | | ¥ | 23,904,435 | | | $ | 242,684,626 | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Liabilities | | | | | | | | |
| Bonds | | ¥ | 19,339,289 | | | $ | 196,337,962 | |
| Other liabilities | | | 32,108 | | | | 325,976 | |
| Reserve for bonuses | | | 54 | | | | 552 | |
| Reserve for retirement benefits | | | 217 | | | | 2,204 | |
| Fund for improvement of operations of municipal enterprises | | | 903,354 | | | | 9,171,115 | |
| Basic fund for improvement of operations of municipal enterprises | | | 903,354 | | | | 9,171,115 | |
| Reserve under special laws | | | 3,613,350 | | | | 36,683,765 | |
| Reserve for interest rate volatility | | | 220,000 | | | | 2,233,502 | |
| Management account reserve for interest rate volatility | | | 3,256,583 | | | | 33,061,765 | |
| Reserve for interest rate reduction | | | 136,767 | | | | 1,388,498 | |
| | | | | | | |
Total liabilities | | | 23,888,375 | | | | 242,521,574 | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Net Assets | | | | | | | | |
| Management account surplus reserve | | | 16,060 | | | | 163,052 | |
| | | | | | | |
Total net assets | | | 16,060 | | | | 163,052 | |
| | | | | | | |
Total liabilities and net assets | | ¥ | 23,904,435 | | | $ | 242,684,626 | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | |
| Note: | | “Other liabilities” includes liabilities for 16,455 million yen (167,056 thousand dollars) that is related to repayment of the capital of the former Japan Finance Corporation for Municipal Enterprises contributed by the national government. |
-44-
SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE
Long-term bonds of JFM as of March 31, 2009 (1):
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | (in millions) | |
| Domestic bonds: | | | | | | | | |
| Government guaranteed bonds: | | | | | | | | |
| 0.5%-2.2% Guaranteed Bonds due 2008-2022 issued in 1998-2008 | | | | | | ¥ | 11,922,460 | |
| Non-guaranteed private placement bonds: | | | | | | | | |
| Bonds 10 years due 2008-2017 issued in 1998-2008 | | | | | | | 3,492,453 | |
| Non-guaranteed public offering bonds due 2008-2036 issued in 2001-2008 | | | | | | | 2,297,830 | |
| | | | | | | | |
| Total domestic bonds | | | | | | ¥ | 17,712,743 | |
| Government guaranteed bonds issued overseas (2): | | | | | | | | |
| U.S. Dollar bonds: | | | | | | | | |
| 6.000% Guaranteed Bonds due 2009 ($700,000) issued in 1999 and 2000 | | | | | | | 81,740 | |
| 5.875% Guaranteed Bonds due 2011 ($1,000,000) issued in 2001 | | | | | | | 119,500 | |
| 4.625% Guaranteed Bonds due 2015 ($1,200,000) issued in 2005 | | | | | | | 129,720 | |
| 5.000% Guaranteed Bonds due 2017 ($1,000,000) issued in 2007 | | | | | | | 119,780 | |
| | | | | | | | |
| Subtotal | | $ | (3,200,000 | ) | | ¥ | 450,740 | |
| Pound Sterling bonds: | | | | | | | | |
| 5.750% Guaranteed Bonds due 2019 (£150,000) issued in 1999 | | | | | | | 28,380 | |
| Yen bonds: | | | | | | | | |
| 1.550% Guaranteed Bonds due 2012 issued in 2002 | | | | | | | 200,000 | |
| 1.350% Guaranteed Bonds due 2013 issued in 2003 | | | | | | | 130,000 | |
| 2.000% Guaranteed Bonds due 2016 issued in 2006 | | | | | | | 120,000 | |
| 1.900% Guaranteed Bonds due 2017 issued in 2008 | | | | | | | 75,000 | |
| | | | | | | | |
| Subtotal | | | | | | | 525,000 | |
| | | | | | | | |
| Euro bonds: | | | | | | | | |
4.500% Guaranteed Bonds due 2014 (€900,000) issued in 2004 | | | | | | | 122,040 | |
| Total government guaranteed bonds sold in foreign markets | | | | | | ¥ | 1,126,160 | |
| | | | | | | | |
| Total long-term bonds | | | | | | ¥ | 18,838,903 | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | |
| (1) | | Includes current maturities. |
| |
| (2) | | The actual foreign currency amounts of bonds are set forth in parentheses (in thousands of units of the relevant foreign currency) for bonds issued in foreign currencies. Translations of actual foreign currency amounts into yen amounts have been made in accordance with the method stated in Note 2 of the Notes to Financial Statements. |
-45-
Unaudited financial statements of JFM for the six months ended September 30, 2009
Interim Balance Sheet (As of September 30, 2009)
(Millions of Yen)
| | | | | |
| Item | | Amount | |
Assets | | | | |
| Loans (Note 3) | | ¥ | 21,845,150 | |
| Securities (Note 9) | | | 1,168,780 | |
| Cash and bank deposits | | | 247,956 | |
| Other assets | | | 18,312 | |
| Tangible fixed assets (Note 4) | | | 2,980 | |
| Intangible fixed assets | | | 853 | |
| | | | |
| | | | | |
Total assets | | ¥ | 23,284,034 | |
| | | | |
| | | | | |
Liabilities | | | | |
| Bonds (Note 5) | | ¥ | 18,765,647 | |
| Other liabilities | | | 17,785 | |
| Reserve for bonuses | | | 54 | |
| Reserve for directors’ bonuses | | | 8 | |
| Reserve for retirement benefits | | | 209 | |
| Reserve for retirement benefits for directors and corporate auditors | | | 53 | |
| Fund for improvement of operations of municipalities | | | 896,345 | |
| Basic fund for improvement of operations of municipalities | | | 892,875 | |
| Additional fund for improvement of operations of municipalities | | | 3,469 | |
| Reserve under special laws | | | 3,545,611 | |
| Reserve for interest rate volatility | | | 440,000 | |
| Management account reserve for interest rate volatility | | | 2,984,345 | |
| Reserve for interest rate reduction | | | 121,265 | |
| | | | |
| Total liabilities | | | 23,225,715 | |
| | | | |
Net Assets | | | | |
| Capital | | | 16,602 | |
| Retained earnings | | | 4,163 | |
| General account surplus reserve | | | 1,295 | |
| General account interim unappropriated retained earnings | | | 2,868 | |
| Valuation and translation adjustments | | | (1,163 | ) |
| Management account surplus reserve | | | 38,716 | |
| Management account surplus reserve | | | 35,190 | |
| Management account interim unappropriated retained earnings | | | 3,526 | |
| | | | |
| Total net assets | | | 58,318 | |
| | | | |
Total liabilities and net assets | | ¥ | 23,284,034 | |
| | | | |
-46-
Interim Statement of Income (From April 1, 2009 through September 30, 2009)
(Millions of Yen)
| | | | | |
| Item | | Amount |
| Income | | ¥ | 280,672 | |
| Interest income | | | 280,558 | |
| Fees and commissions | | | 107 | |
| Other income | | | 6 | |
| | | | |
| Expenses | | | 152,290 | |
| Interest expenses | | | 146,978 | |
| Fees and commissions | | | 136 | |
| Other operating expenses | | | 2,300 | |
| General and administrative expenses | | | 1,204 | |
| Other expenses | | | 1,669 | |
| Transfer to fund for improvement of operations of municipalities | | | 1,669 | |
| | | | |
| Ordinary income | | | 128,382 | |
| | | | |
| Special gains | | | 227,628 | |
| Reversal of management account reserve for interest rate volatility | | | 220,000 | |
| Reversal of reserve for interest rate reduction | | | 7,628 | |
| | | | |
| Special losses | | | 349,616 | |
| Provision for reserve for interest rate volatility | | | 220,000 | |
| Provision for management account reserve for interest rate volatility | | | 129,616 | |
| | | | |
| Interim net income | | ¥ | 6,394 | |
| | | | |
-47-
Interim Statement of Changes in Net Assets (From April 1, 2009 through September 30, 2009)
(Millions of Yen)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Stockholders’ equity | | | Valuation | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | Retained earnings | | | | | | | and translation | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | General account | | | | | | | adjustments | | | | | | | Management | |
| | | | | | | | | | | interim | | | Total | | | Deferred gains | | | Management | | | account interim | |
| | | | | | | General account | | | unappropriated | | | stockholders’ | | | or losses | | | account surplus | | | unappropriated | |
| | | Capital | | | surplus reserve | | | retained earnings | | | equity | | | on hedges | | | reserve | | | retained earnings | |
| Balance at end of previous fiscal year | | | 16,602 | | | | 1,295 | | | | — | | | | 17,897 | | | | — | | | | 35,190 | | | | — | |
| Changes during interim accounting period | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Interim net income | | | — | | | | — | | | | 2,868 | | | | 2,868 | | | | — | | | | — | | | | 3,526 | |
| Changes of items other than stockholders’ equity during interim accounting period | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | — | | | | (1,163 | ) | | | — | | | | — | |
| Net changes during interim accounting period | | | — | | | | — | | | | 2,868 | | | | 2,868 | | | | (1,163 | ) | | | — | | | | 3,526 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Balance at September 30, 2009 | | | 16,602 | | | | 1,295 | | | | 2,868 | | | | 20,765 | | | | (1,163 | ) | | | 35,190 | | | | 3,526 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
-48-
Interim Statement of Cash Flows (From April 1, 2009 through September 30, 2009)
(Millions of Yen)
| | | | | |
| Item | | Amount |
| I Cash flows from operating activities | | | | |
| Interim net income | | ¥ | 6,394 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | | 137 | |
| Interest income | | | (280,558 | ) |
| Interest expenses | | | 146,978 | |
| Increase in reserve for bonuses | | | 6 | |
| Increase in reserve for directors’ bonuses | | | 0 | |
| Increase in reserve for retirement benefits | | | 6 | |
| Increase in reserve for retirement benefits for directors and corporate auditors | | | 2 | |
| Increase in fund for improvement of operations of municipalities | | | 1,669 | |
| Increase in reserve for interest rate volatility | | | 220,000 | |
| Decrease in management account reserve for interest rate volatility | | | (90,383 | ) |
| Decrease in reserve for interest rate reduction | | | (7,628 | ) |
| Net increase/decrease in loans | | | 370,137 | |
| Net increase/decrease in bonds | | | (214,613 | ) |
| Interest received | | | 281,665 | |
| Interest paid | | | (147,483 | ) |
| Others | | | (314 | ) |
| | | | |
| Net cash provided by operating activities | | | 286,017 | |
| | | | |
| II Cash flows from investing activities | | | | |
| Proceeds from redemption of securities | | | 2,566,000 | |
| Purchases of securities | | | (2,859,533 | ) |
| Purchase of tangible fixed assets | | | (6 | ) |
| Purchases of intangible fixed assets | | | (112 | ) |
| | | | |
| Net cash provided by investing activities | | | (293,651 | ) |
| | | | |
| III Cash flows from financing activities | | | — | |
| IV Effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents | | | — | |
| | | | |
| V Net decrease in cash and cash equivalents | | | (7,634 | ) |
| | | | |
| VI Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year | | | 255,591 | |
| | | | |
| VII Cash and cash equivalents at September 30, 2009 | | | 247,956 | |
| | | | |
-49-
Notes to Financial Statements
| | | Japan Finance Organization for Municipalities (hereinafter, “JFM”) has prepared financial statements pursuant to the following law and ministerial ordinances: |
| | • | | The Japan Finance Organization for Municipal Enterprises Law (Law No. 64, 2007; hereinafter, “Law”), which was subsequently amended by the provisions of Article 5 of the Law on the partial provision of Local Allocation Tax Law (Law No. 10, 2009). |
| | • | | The Ministerial Ordinance on Finance and Accounting of Japan Finance Organization for Municipal Enterprises (Ordinance No.87 of the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications, 2008), which was subsequently amended in accordance with the provisions of Article 2 of the Ministerial Ordinance on preparation for relevant ministerial ordinances of the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications for partial enforcement of the Law on partial revision of the Local Allocation Tax Law (Ordinance No.49 of the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications, 2009; hereinafter, “Preparation Ministerial Ordinance”). |
| | • | | The Ministerial Ordinance on Finance and Accounting of Japan Finance Organization for Municipalities amended in accordance with the provisions of Article 2 of the Preparation Ministerial Ordinance where applied to the financial statements with respect to the year ended March 31, 2009 in accordance with the supplementary provisions of Article 2, Section 1 of the Preparation Ministerial Ordinance. |
Since JFM does not have any subsidiaries or affiliates, it does not prepare consolidated financial statements.
Amounts less than one million yen have been omitted. As a result, the totals in Japanese yen shown in the financial statements do not necessarily agree with the sum of the individual amounts.
| 2. | | Significant Accounting Policies |
| | (1) | | Securities |
| |
| | | | As for security valuation, held-to-maturity securities are carried at amortized cost (straight-line method). |
| |
| | (2) | | Derivative transactions |
| |
| | | | Derivative transactions are carried at fair value with changes in unrealized gain or loss charged or credited to operations, except for those which meet the criteria for hedge accounting. |
| |
| | (3) | | Depreciation |
| | (a) | | Tangible fixed assets |
| |
| | | | Depreciation of tangible fixed assets is calculated by the straight-line method based on the estimated useul lives and the residual value determined by management. The estimated useful lives of major items are as follows: |
| |
| | | | Buildings: 20 to 41 years Others: 2 to 19 years |
| |
| | (b) | | lntangible fixed assets |
| |
| | | | Depreciation of intangible fixed assets is calculated by the straight-line method based on the estimated useul lives and the residual value determined by management. Software for internal use owned by JFM is depreciated over 5 years. |
| | (4) | | Deferred assets
Bond issuance costs are expensed in full when incurred. |
-50-
| | (5) | | Translation of assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies into Japanese yen
Monetary assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies, for which foreign currency swaps or foreign exchange forward contracts are used to hedge the foreign currency fluctuation, are translated at the contracted rate as the swap contracts or the forward contracts qualify for deferral hedge accounting. |
| | (a) | | Reserve for possible loan losses |
| |
| | | | JFM has never experienced any loan losses. Accordingly, no reserve for loan losses has been maintained. |
| |
| | (b) | | Reserve for bonuses |
| |
| | | | Reserve for bonuses is provided for payment of bonuses to employees, in the amount of estimated bonuses, which are attributable to the fiscal year. |
| |
| | (c) | | Reserve for directors’ bonuses |
| |
| | | | Reserve for directors’ bonuses is provided for payment of bonuses to directors, in the amount of estimated bonuses, which are attributable to the fiscal year. |
| |
| | (d) | | Reserve for retirement benefits |
| |
| | | | Reserve for retirement benefits is provided for payment of retirement benefits to employees, in the amount deemed accrued at the fiscal year-end, based on the projected retirement benefit obligation and fair value of plan assets at the fiscal year-end. |
| | (e) | | Reserve for retirement benefits for directors and corporate auditors
Reserve for retirement benefits for directors and corporate auditors is provided for payment of retirement benefits to directors and corporate auditors, in the amount deemed accrued at the fiscal year-end based on the internal policies. |
| | (a) | | Hedge accounting method |
Interest rate swaps to be used to hedge the interest rate risk, which qualify for hedge accounting and meet specific matching criteria, are not measured at market value, but the differential paid or received under the swap agreements is recognized and included in interest expense or income, and otherwise, deferral hedge accounting is applied. Designation transactions are applied to debts and credits in foreign currency which conform to requirement of hedge accounting.
-51-
| | (b) | | Hedging instruments and hedged items |
| | | |
| (i) | Hedging instrument | Interest rate swap |
| | | |
| | Hedged items | Bonds |
| | | |
| (ii) | Hedging instrument | Currency swap |
| | | |
| | Hedged items | Foreign currency-denominated bonds |
| | | |
| (iii) | Hedging instrument | Foreign exchange forward contract |
| | | |
| | Hedged items | Receipt of interest and principal of foreign currency-denominated bank deposits |
JFM uses interest rate swaps and currency swaps as a means of hedging exposure to interest rate risk and foreign exchange risk associated with the issuance of bonds. Hedged items are identified for each contract.
| | (d) | | Assessment of hedge effectiveness |
Hedging to offset the foreign currency fluctuations of bonds is considered to be highly effective since major terms of the underlying transactions and the hedging instruments are almost the same, which is used as an assessment of hedge effectiveness.
An assessment of hedge effectiveness for interest rate swaps that qualify for hedge accounting and meet specific matching criteria, and for currency swaps and foreign exchange forward contracts that qualify for deferral hedge accounting, is omitted.
| | (8) | | Cash and cash equivalents |
| |
| | | | Cash and cash equivalents in the Interim Statement of Cash Flows consist of “Cash and bank deposits” on the Interim Balance Sheet. |
| | (9) | | Fund for improvement of operations of municipalities |
In accordance with the provisions of Article 46, Section 1 of the Japan Finance Organization for Municipalities Law (Law No. 64, 2007, the “Laws”), JFM has established the Fund for improvement of operations of municipalities to reserve contributions as stipulated in Article 32-2 of the Local Finance Law (Law No. 109, 1948). Also, pursuant to the provisions of Article 46, Section 5 of the Law, income arising from the investment of the Fund (hereinafter “investment income”) is used to reduce interest rates of the loans to municipalities, and if there is any surplus in the investment income after this interest rates reduction process, the surplus amount is added to the fund, Further, pursuant to the provisions of Article 46, Section 6 of the Law, if there is any shortfall after the interest rates reduction process, the shortfall is covered by withdrawal of the Fund within the limits of the total of the additional portion to the Fund made up to the previous fiscal year and the contributions made in the relative fiscal year.
-52-
| | (10) | | Reserve for interest rate volatility and Management account reserve for interest rate volatility |
Reserve for interest rate volatility is set aside to prepare for interest rate risk associated with refinancing of our bonds (excluding the bonds issued by the former Japan Finance Corporation for Municipal Enterprises), and is calculated and accounted for pursuant to the provisions of Article 38, Sections 1 and 3 of the Law, and Article 9, Section 8 of the supplementary provisions of the Law, Article 34 of the Ministerial Ordinance on Finance and Accounting of Japan Finance Organization for Municipalities (Ordinance No. 87 of the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications, 2008) and Article 22 of the Government Ordinance on preparation of relevant government ordinances and provisional measures for the abolishment of the Japan Finance Corporation for Municipal Enterprises Law (Government Ordinance No. 226, 2008; hereinafter, “Preparation Ordinance”).
Management account reserve for interest rate volatility is set aside to prepare for interest rate risk associated with refinancing of the bonds issued by the former Japan Finance Corporation for Municipal Enterprises, and is calculated and accounted for pursuant to the provisions of Article 9, Sections 9 and 10, and Article 13, Sections 5 and 7 of the supplementary provisions of the Law, Articles 1 through 3 of the Ministerial Ordinance on the operations of the Management Account at Japan Finance Organization for Municipalities (Ordinance No. 2 of the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communication, and the Ministry of Finance, 2008; hereinafter, “Management Account Operations Ordinance”) and Articles 3 and 5 of the supplementary provisions of the above ordinance.
| | (11) | | Reserve for interest rate reduction |
| |
| | | | Reserve for interest rate reduction is set aside to reduce interest rates on the loans made by the former Japan Finance Corporation for Municipal Enterprises to local governments pursuant to the provisions of Article 9, Section 13, and Article 13, Section 8 of the supplementary provisions of the Law, and Article 26, Sections 1, 3 and 4 of the Preparation Ordinance, and is calculated and accounted for based on the provisions of Article 5 of the Management Account Operations Ordinance. |
| | (12) | | Consumption taxes |
| |
| | | | National and local consumption taxes are accounted for using the tax-excluded method. |
| 3. | | Loans |
| |
| | | There are no bankrupt loans, non-accrual loans, past due loans (3 months or more), or restructured loans. Since JFM has never experienced loan losses in the past, it does not account for loan loss reserves. |
Bankrupt loans represent loans to borrowers as defined in Articles 96, Section 1, Clause 3 (a) through (e) and Clause 4 of the Enforcement Ordinance of the Corporate Income Tax Law (Government Ordinance No. 97, 1965), and on which accrued interest is not accounted in revenue as there is no expectation of collection of either principal or interest because they are past due for a considerable period of time or for other reasons (excluding loans on which bad debts are written off; hereinafter, “Non-accrual loans”).
Non-accrual loans represent loans on which accrued interest is not accounted in revenue, excluding loans to bankrupt borrowers and loans with grace for interest payment to assist in corporate reorganization or to support business.
Past due loans (3 months or more) represent loans on which payment of principal or interest is in arrears for more than 3 months, calculated from the day following the contractual due date, excluding bankrupt loans and non-accrual loans.
Restructured loans represent loans which are given certain favorable terms and conditions, such as reduction or exemption of interest, grace for interest or principal payment, and debt waiver, to assist borrowers in corporate rehabilitation or to support business, excluding bankrupt loans, non-accrual loans and past due loans (3 months or more).
| | | |
| 4. | | Accumulated depreciation of tangible fixed assets amounted to 70 million yen as of September 30, 2009. |
| 5. | | Assets Pledged as Collateral |
| |
| | | Pursuant to the provisions of Article 40, Section 2 of the Law, JFM’s total assets are pledged as general collateral for JFM bonds for 18,765,647 million yen. |
Net income of General account was 2,868 million yen, while interim net income of Management account was 3,526 million yen.
-53-
| | | |
| 7. | | Information by Account (Interim Balance Sheet) |
Interim balance sheet of General account and Management account at September 30, 2009 was as follows:
(Millions of Yen)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | Management | | | | | | | |
| Item | | General account | | | account | | | Offset | | | Total | |
Assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Loans | | | 830,292 | | | | 21,014,857 | | | | | | | | 21,845,150 | |
| Securities | | | 1,168,780 | | | | | | | | | | | | 1,168,780 | |
| Cash and bank deposits | | | 247,956 | | | | | | | | | | | | 247,956 | |
| Other assets | | | 3,061 | | | | 15,251 | | | | | | | | 18,312 | |
| Tangible fixed assets | | | 2,980 | | | | | | | | | | | | 2,980 | |
| Intangible fixed assets | | | 853 | | | | | | | | | | | | 853 | |
| Due from general account | | | | | | | 1,154,285 | | | | (1,154,285 | ) | | | | |
| Due from management account for fund for improvement of operations of municipalities | | | 892,875 | | | | | | | | (892,875 | ) | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total assets | | | 3,146,800 | | | | 22,184,394 | | | | (2,047,160 | ) | | | 23,284,034 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Liabilities | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Bonds | | | 631,889 | | | | 18,133,758 | | | | | | | | 18,765,647 | |
| Other liabilities | | | 4,352 | | | | 13,432 | | | | | | | | 17,785 | |
| Reserve for bonuses | | | 54 | | | | | | | | | | | | 54 | |
| Reserve for directors’ bonuses | | | 8 | | | | | | | | | | | | 8 | |
| Reserve for retirement benefits | | | 209 | | | | | | | | | | | | 209 | |
| Reserve for retirement benefits for directors and corporate auditors | | | 53 | | | | | | | | | | | | 53 | |
| Fund for improvement of operations of municipalities | | | 896,345 | | | | | | | | | | | | 896,345 | |
| Basic fund for improvement of operations of municipalities | | | 892,875 | | | | | | | | | | | | 892,875 | |
| Additional fund for improvement of operations of municipalities | | | 3,469 | | | | | | | | | | | | 3,469 | |
| Due to management account | | | 1,154,285 | | | | | | | | (1,154,285 | ) | | | | |
| Due to general account for fund for improvement of operations of municipalities | | | | | | | 892,875 | | | | (892,875 | ) | | | | |
| Reserve under special laws | | | 440,000 | | | | 3,105,611 | | | | | | | | 3,545,611 | |
| Reserve for interest rate volatility | | | 440,000 | | | | | | | | | | | | 440,000 | |
| Management account reserve for interest rate volatility | | | | | | | 2,984,345 | | | | | | | | 2,984,345 | |
| Reserve for interest rate reduction | | | | | | | 121,265 | | | | | | | | 121,265 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total liabilities | | | 3,127,198 | | | | 22,145,677 | | | | (2,047,160 | ) | | | 23,225,715 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net Assets | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Capital | | | 16,602 | | | | | | | | | | | | 16,602 | |
| Retained earnings | | | 4,163 | | | | | | | | | | | | 4,163 | |
| General account surplus reserve | | | 1,295 | | | | | | | | | | | | 1,295 | |
| General account interim unappropriated retained earnings | | | 2,868 | | | | | | | | | | | | 2,868 | |
| Valuation and translation adjustments | | | (1,163 | ) | | | | | | | | | | | (1,163 | ) |
| Management account surplus reserve | | | | | | | 38,716 | | | | | | | | 38,716 | |
| Management account surplus reserve | | | | | | | 35,190 | | | | | | | | 35,190 | |
| Management account interim unappropriated retained earnings | | | | | | | 3,526 | | | | | | | | 3,526 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total net assets | | | 19,602 | | | | 38,716 | | | | | | | | 58,318 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total liabilities and net assets | | | 3,146,800 | | | | 22,184,394 | | | | (2,047,160 | ) | | | 23,284,034 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
-54-
| | | |
| Notes: 1. | | General account and Management account |
| |
| | | In accordance with the provisions of Article 13, Section 1 of the supplementary provisions of the Law, Management account is used to conduct administration, collection and other related operations of the assets that JFM inherited from the former Japan Finance Corporation for Municipal Enterprises (management of the assets of the former Japan Finance Corporation for Municipal Enterprises). Management account is separated from the other account (General account) pursuant to the provisions of Article 13, Section 3 of the supplementary provisions of the Law. |
| |
| 2. | | General account surplus reserve and Management account surplus reserve |
| |
| | | “Interim net income” of General account is posted as “General account interim unappropriated earnings” in accordance with the provisions of Article 39, Section 1 of the Law, while “Interim net income” of Management account is posted as “Management account interim unappropriated earnings” in accordance with the provisions of Article 13, Section 8 of the supplementary provisions the Law. |
| |
| 3. | | Due from General account and Due to Management account |
| |
| | | These figures represent the amount of funds lent between General account and Management account pursuant to the provisions of Article 13, Section 4 of the supplementary provisions of the Law. |
| |
| 4. | | Due to General account for Fund for improvement of operations of municipalities and Due from Management account for Fund for improvement of operations of municipalities |
| |
| | | These figures represent the amount of cash received for “Fund for improvement of operations of municipalities,” which was lent to Management account from General account pursuant to the provisions of Article 9, Section 12 of the supplementary provisions of the Law. |
-55-
| 8. | | Information by Account (Interim Statement of Income) |
| |
| | | Interim statement of income of General account and Management account from April 1, 2009 through September 30, 2009 was as follows: |
(Millions of Yen)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | Management | | | | | | | |
| Item | | General account | | | account | | | Offset | | | Total | |
Income | | | 20,505 | | | | 282,867 | | | | (22,701 | ) | | | 280,672 | |
| Interest income | | | 7,890 | | | | 272,668 | | | | | | | | 280,558 | |
| Fees and commissions | | | 107 | | | | | | | | | | | | 107 | |
| Other income | | | 6 | | | | | | | | | | | | 6 | |
| Administrative fee for management account | | | 479 | | | | | | | | (479 | ) | | | | |
| Interest on fund for improvement of operations of municipalities | | | 12,021 | | | | | | | | (12,021 | ) | | | | |
| Interest on due from general account | | | | | | | 388 | | | | (388 | ) | | | | |
| Transfer from general account for fund for improvement of operations of municipalities | | | | | | | 9,811 | | | | (9,811 | ) | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Expenses | | | 17,637 | | | | 157,353 | | | | (22,701 | ) | | | 152,290 | |
| Interest expenses | | | 3,581 | | | | 143,397 | | | | | | | | 146,978 | |
| Fees and commissions | | | 3 | | | | 133 | | | | | | | | 136 | |
| Other operating expenses | | | 1,048 | | | | 1,252 | | | | | | | | 2,300 | |
| General and administrative expenses | | | 1,135 | | | | 69 | | | | | | | | 1,204 | |
| Other expenses | | | 1,669 | | | | | | | | | | | | 1,669 | |
| Transfer to fund for improvement of operations of municipal enterprises | | | 1,669 | | | | | | | | | | | | 1,669 | |
| Interest on due to management account | | | 388 | | | | | | | | (388 | ) | | | | |
| Transfer to management account for fund for improvement of operations of municipalities | | | 9,811 | | | | | | | | (9,811 | ) | | | | |
| Administrative fee for management account | | | | | | | 479 | | | | (479 | ) | | | | |
| Interest on fund for improvement of operations of municipalities | | | | | | | 12,021 | | | | (12,021 | ) | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Ordinary income | | | 2,868 | | | | 125,514 | | | | | | | | 128,382 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Special gains | | | 220,000 | | | | 227,628 | | | | (220,000 | ) | | | 227,628 | |
| Reversal of management account reserve for interest rate volatility | | | | | | | 220,000 | | | | | | | | 220,000 | |
| Reversal of reserve for interest rate reduction | | | | | | | 7,628 | | | | | | | | 7,628 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Transfer from management account | | | 220,000 | | | | | | | | (220,000 | ) | | | | |
Special losses | | | 220,000 | | | | 349,616 | | | | (220,000 | ) | | | 349,616 | |
| Provision for reserve for interest rate volatility | | | 220,000 | | | | | | | | | | | | 220,000 | |
| Provision for management account reserve for interest rate volatility | | | | | | | 129,616 | | | | | | | | 129,616 | |
| Transfer to general account | | | | | | | 220,000 | | | | (220,000 | ) | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Interim net income | | | 2,868 | | | | 3,526 | | | | | | | | 6,394 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
-56-
| 9. | | Market Value of Marketable Securities |
| | (1) | | Marketable held-to-maturity securities at September 30, 2009 consisted of the following: |
(Millions of Yen)
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | Interim balance
sheet amount | | | Market value | | | Net unrealized
gains (losses) | | | Unrealized
gains | | | Unrealized
losses | |
| Treasury discount bills | | | 816,780 | | | | 816,737 | | | | (42 | ) | | | — | | | | (42 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | |
| Notes: | 1. | Market value is based on market prices at the end of the interim period. |
| |
| 2. | “Unrealized gains” and “Unrealized losses” are components of Net unrealized gains (losses). |
| | (2) | | Securities with no available market value at September 30, 2009 were as follows: |
(Millions of Yen)
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | Amount | |
| Negotiable certificate of deposits | | ¥ | 352,000 | |
| 10. | | Derivative Information |
| | (1) | | Types of derivative transactions |
Derivative transactions conducted by JFM are interest rate swaps for interest rate related transactions, and currency swaps and foreign exchange forward contracts for currency related transactions.
| | (2) | | Policies and purposes of derivative transactions |
JFM uses interest rate swaps, currency swaps and foreign exchange forward contracts as a means of hedging exposure to interest rate and foreign exchange fluctuation risks, and does not enter into derivatives for speculative purposes.
Interest rate swaps are used to hedge exposure to interest rate risk on fund raising operations. Currency swaps and foreign exchange forward contracts are used to hedge exposure to foreign exchange risk associated with issuance of foreign currency-denominated bonds and foreign currency-denominated bank deposits.
Hedge accounting is applied to interest rate swaps, currency swaps and foreign exchange forward contracts.
| | (a) | | Hedge accounting method |
Interest rate swaps to be used to hedge the interest rate risk, which qualify for hedge accounting and meet specific matching criteria, are not measured at market value, but the differential paid or received under the swap agreements is recognized and included in interest expense or income, and otherwise, deferral hedge accounting is applied. Designation transactions are applied to debts and credits in foreign currency which conform to requirement of hedge accounting.
| | (b) | | Hedging instruments and hedged items |
| | | |
| (i) | Hedging instrument | Interest rate swap |
| | | |
| | Hedged items | Bonds |
| | | |
| (ii) | Hedging instrument | Currency swap |
| | | |
| | Hedged items | Foreign currency-denominated bonds |
| | | |
| (iii) | Hedging instrument | Foreign exchange forward contract |
| | | |
| | Hedged items | Receipt of interest and principal of foreign currency-denominated bank deposits |
JFM uses interest rate swaps and currency swaps as a means of hedging exposure to interest rate risk and foreign exchange risk associated with the issuance of bonds. Hedged items are identified for each contract.
-57-
| | (d) | | Assessment of hedge effectiveness |
Hedging to offset the foreign currency fluctuations of bonds is considered to be highly effective since major terms of the underlying transactions and the hedging instruments are almost the same, which is used as an assessment of hedge effectiveness.
An assessment of hedge effectiveness for interest rate swaps that qualify for hedge accounting and meet specific matching criteria, and for currency swaps and foreign exchange forward contracts that qualify for deferral hedge accounting, is omitted.
| | (3) | | Risks on derivative transactions |
Major risks on derivative transactions are market risk and credit risk. Market risk is the risk of future revenue fluctuations due to market value changes. Credit risk is the risk of losses incurred when counterparties are unable to fulfill their contracts due to bankruptcy or other reasons.
As for derivative transactions used for hedging purposes, market risk is offset by market risk on underlying transactions.
Regarding credit risk, JFM limits counterparties to the financial institutions with high credit standing, constantly monitors cost of restructuring of transactions and their credit profiles, and deals with multiple counterparties.
| | (4) | | Risk management system for derivative transactions |
Execution and management of derivative transactions are conducted by the Finance Department of JFM with the approval of persons in charge in accordance with the operational guidelines which specify transaction authority and limit of transaction value.
Additionally, the total amount of derivative transactions, the status of risks, market value and the credit risk on counterparties are reported to Integrated Risk Management Committee periodically.
| | (5) | | Supplementary information on market value of transactions |
Since hedge accounting is applied to all the derivatives transactions conducted by JFM, description of the above is not included in Notes.
-58-