On February 12, 2008, we sold our aluminum extrusions business in Canada for an estimated purchase price of $25.5 million to an affiliate of H.I.G. Capital. The final purchase price is subject to increase or decrease to the extent that actual working capital, cash and indebtedness (as defined) as of February 12, 2008 are above or below the estimated amounts used to determine the estimated purchase price. We expect to realize cash income tax benefits in 2008 from the sale of approximately $11.4 million, which we recognized as a deferred income tax asset in our consolidated balance sheet at December 31, 2007. All historical results for the Canadian business have been reflected as discontinued operations; however, cash flows for discontinued operations have not been separately disclosed in the consolidated statements of cash flows (see Note 17 to the notes to financial statements for more information).
The sale of our aluminum extrusions business in Canada, which was suffering from operating losses driven by lower volume and higher conversion costs from appreciation of the Canadian dollar, allows us to focus on our U.S. aluminum extrusions operations where we have more control over costs and profitability.
Net sales from continuing operations in Aluminum Extrusions were $371.8 million in 2007, down 7.9% from $403.8 million in 2006. Operating profit from ongoing U.S. operations decreased to $16.5 million in 2007, down 9.8% from $18.3 million in 2006. Volume from continuing operations decreased to 155.8 million pounds in 2007, down 15.9% from 185.2 million pounds in 2006.
The decreases in net sales and ongoing operating profit from continuing operations were mainly due to lower volume, partially offset by higher selling prices. Shipments declined in most markets, especially extrusions used in hurricane protection products and residential construction. In addition, we began experiencing a softening of markets for extrusions used in non-residential construction in the fourth quarter of 2007. Overall backlog for continuing operations in Aluminum Extrusions at December 31, 2007 was down by approximately 7% compared with December 31, 2006.
Capital expenditures for continuing operations in Aluminum Extrusions were $4.4 million in 2007, down from $6.6 million in 2006, and are projected to be approximately $21 million in 2008. In January, we announced plans to spend approximately $24 million over the next 18 months to expand the capacity at our plant in Carthage, Tennessee. Approximately 65% of our sales of aluminum extrusions from our U.S. operations are related to non-residential construction, and this additional capacity will increase our capabilities in this sector. Depreciation expense for continuing operations was $8.5 million in 2007, up slightly from $8.4 million in 2006, and is projected to be $8.5 million in 2008.
Net pension income from continuing operations was $2.8 million in 2007, a favorable change of $4.5 million (8 cents per share after taxes) from amounts recognized 2006. Most of the favorable changes relate to a pension plan that is reflected in “Corporate expenses, net” in the operating profit by segment table presented on page 14. Net pension income from continuing operations is expected to be $5.5 million in 2008. We contributed approximately $167,000 to our pension plans for continuing operations in 2007 and expect to contribute a similar amount in 2008.
Interest expense was $2.7 million in 2007, a decline $2.8 million (5 cents per share after taxes) versus 2006 due to lower average debt outstanding.
The effective tax rate used to compute income taxes from continuing operations was 41.1% in 2007 compared with 35.9% in 2006. The increase in the effective tax rate for continuing manufacturing operations for 2007 versus 2006, which had an unfavorable impact of approximately 8 cents per share, was mainly due to a valuation allowance for possible deferred tax benefits on capital loss carry-forwards and lower income tax benefits expected for the Extraterritorial Income Exclusion and Domestic Production Activities Deduction and the research and development (“R&D”) tax credit.
During the first quarter of 2007, we adopted new accounting standards for maintenance costs and uncertain income tax positions, neither of which had a material impact on Tredegar’s results of operations or financial condition.
In addition, we adopted new accounting standards on fair value measurements and the fair value option for financial assets and liabilities, neither of which had an impact on historical results at the date of adoption.
On April 2, 2007, we invested $10 million in Harbinger Capital Partners Special Situations Fund, L.P. (“Harbinger”), a fund that seeks to achieve superior absolute returns by participating primarily in medium to long-term investments involving distressed/high yield debt securities, special situation equities and private loans and notes. The fund is a highly speculative investment subject to a two-year lock-up and additional limitations on withdrawal. There is no secondary market for interests in the fund. Our investment in Harbinger, which represents less than 2% of Harbinger’s total partnership capital, is accounted for under the cost method. At December 31, 2007, Harbinger reported our capital account value at $23.0 million reflecting $13.0 million of unrealized appreciation ($8.3 million or 22 cents per share after taxes) versus the carrying value in our consolidated balance sheet of $10 million.
On August 31, 2007, we invested $6.5 million in a privately held drug delivery company representing ownership on a fully diluted basis of approximately 23%. This company is developing and commercializing state of the art drug delivery systems designed to improve patient compliance and outcomes. During 2007, we invested $6.2 million in real estate. At December 31, 2007, the carrying value in Tredegar’s balance sheet of its investments in this real estate and the drug delivery company equaled the respective amounts invested.
During 2007 we used a portion of a standing authorization from our board of directors to repurchase approximately 4.8 million shares of our stock at an average price of $16.00 per share. Despite the significant funds used for this program, our net debt (total debt less cash and cash equivalents) at December 31, 2007 increased by only $12.2 million to $33.8 million due to strong cash flow from operations and lower capital expenditures (net debt is not intended to represent debt as defined by generally accepted accounting principles, but is utilized by management in evaluating financial leverage and equity valuation and we believe that investors also may find net debt helpful for the same purposes). On January 7, 2008, we announced that our board of directors approved a share repurchase program whereby we are authorized at our discretion to purchase, in the open market or in privately negotiated transactions, up to 5 million shares of our outstanding common stock. This share repurchase program replaces our previous share repurchase authorization. The authorization has no time limit. Consolidated net capitalization and other credit measures are provided in the financial condition section beginning on page 25.
Critical Accounting Policies
In the ordinary course of business, we make a number of estimates and assumptions relating to the reporting of results of operations and financial position in the preparation of financial statements in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles. Actual results could differ significantly from those estimates under different assumptions and conditions. We believe the following discussion addresses our critical accounting policies. These policies require management to exercise judgments that are often difficult, subjective and complex due to the necessity of estimating the effect of matters that are inherently uncertain.
Impairment and Useful Lives of Long-lived Identifiable Assets and Goodwill
We regularly assess our long-lived identifiable assets for impairment when events or circumstances indicate that their carrying value may not be recoverable from future cash flows. Any necessary impairment charges are recorded when we do not believe the carrying value of the long-lived asset will be recoverable. We also reassess the useful lives of our long-lived assets based on changes in our business and technologies.
We assess goodwill for impairment when events or circumstances indicate that the carrying value may not be recoverable, or, at a minimum, on an annual basis (December 1 of each year). We have made determinations as to what our reporting units are and what amounts of goodwill and intangible assets should be allocated to those reporting units.
In assessing the recoverability of long-lived identifiable assets and goodwill, we must make assumptions regarding estimated future cash flows, discount rates and other factors to determine if impairment tests are met or the fair value of the respective assets. If these estimates or their related assumptions change in the future, we may be required to record additional impairment charges. Based upon assessments performed, we recorded asset impairment losses for
19
continuing operations related to long-lived identifiable assets of $594,000 in 2007, $1.2 million in 2006 and $8.4 million in 2005. For asset impairments relating to discontinued operations, see Note 17 to the notes to financial statements.
Investment Accounted for Under the Fair Value Method
On August 31, 2007, we invested $6.5 million in a privately held drug delivery company representing ownership on a fully diluted basis of approximately 23%. This investment is accounted for under the fair value method. We elected the fair value option over the equity method of accounting since our investment objectives are similar to those of venture capitalists, which typically do not have controlling financial interests (venture capital funds use the fair value method to account for their investment portfolios). At December 31, 2007, the fair value of our investment (included in “Other assets and deferred charges” in our consolidated balance sheet) equaled the amount invested.
Statement of Financial Accounting Standards (“SFAS”) No. 157, Fair Value Measurements, requires disclosure of the level within the fair value hierarchy in which fair value measurements in their entirety fall, segregating fair value measurements using quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities (Level 1), significant other observable inputs (Level 2), and significant unobservable inputs (Level 3). On the date of our investment (August 31, 2007), we believe that the amount we paid for our ownership interest and liquidation preferences was based on Level 2 inputs, including investments by other investors. Subsequent to August 31, 2007, and until the next round of financing, we believe fair value estimates drop to Level 3 inputs since there is no secondary market for our ownership interest. In addition, the company currently has no product sales. Accordingly, after the latest financing and until the next round of financing or other significant financial transaction, value estimates will primarily be based on assumptions relating to meeting product development and commercialization milestones, cash flow projections (projections of sales, costs, expenses, capital expenditures and working capital investment) and discounting of these factors for the high degree of risk. As a result, an increase in our estimate of the fair value of our ownership interest is unlikely unless a significant new round of financing, merger or initial public offering indicates a higher value. However, if the company does not meet its development and commercialization milestones and there are indications that the amount or timing of its projected cash flows or related risks are unfavorable versus plans as of August 31, 2007, or a new round of financing or other significant financial transaction indicates a lower value, then our estimate of the fair value of our ownership interest in the company is likely to decline.
Pension Benefits
We have noncontributory defined benefit (pension) plans in our continuing operations that have significant net pension income developed from actuarial valuations. Inherent in these valuations are key assumptions including discount rates, expected return on plan assets and rate of future compensation increases. We are required to consider current market conditions, including changes in interest rates and plan asset investment returns, in determining these assumptions. Actuarial assumptions may differ materially from actual results due to changing market and economic conditions, higher or lower withdrawal rates or longer or shorter life spans of participants. These differences may result in a significant impact to the amount of net pension income recorded in future periods.
The discount rate is used to determine the present value of future payments. The discount rate is the single rate that, when applied to expected benefit payments, provides a present value equal to the present value of expected benefit payments determined by using the AA-rated bond yield curve. In general, our liability increases as the discount rate decreases and vice versa. Our weighted average discount rate for continuing operations was 6.25% at the end of 2007, 5.75% at the end of 2006 and 5.75% at the end of 2005, with changes between periods due to changes in market interest rates. The compensation increase assumption affects the estimate of future payments, and was 4% at the end of 2007, 2006 and 2005. A lower expected return on plan assets increases the amount of expense and vice versa. Decreases in the level of actual plan assets will also serve to increase the amount of pension expense. Since 2003, the value of our plan assets relating to continuing operations has increased due to improved general market conditions after declining from 2000 to 2002. Our expected long-term return on plan assets relating to continuing operations has been 8.5% since 2004 based on market and economic conditions and asset mix (our expected return was 8.75% in 2003 and 9% in 2002 and prior years). See page 64 for more information on expected long-term return on plan assets and asset mix.
See the executive summary beginning on page 17 for further discussion regarding the financial impact of our pension plans.
20
Income Taxes
On a quarterly basis, we review our judgments regarding uncertain tax positions and the likelihood that the benefits of a deferred tax asset will be realized. As circumstances change, we reflect in earnings any adjustments to unrecognized benefits for uncertain tax positions and valuation allowances for deferred tax assets.
For financial reporting purposes, we had unrecognized tax benefits on uncertain tax positions of $3.3 million as of December 31, 2007. Included in this amount were $2.3 million for tax positions for which ultimate deductibility is highly certain but for which the timing of deductibility is uncertain. Because of the impact of deferred income tax accounting, other than interest, penalties and deductions not related to timing, a longer deductibility period would not affect the total income tax expense or the annual effective tax rate shown for financial reporting purposes, but would accelerate payments to the taxing authority. Tax payments resulting from the successful challenge by the taxing authority for accelerated deductions taken by us would possibly result in the payment of interest and penalties. Accordingly, we also accrue for possible interest and penalties on uncertain tax positions. The balance of accrued interest and penalties on deductions taken relating to uncertain tax positions was approximately $1.2 million at December 31, 2007 ($759,000 net of corresponding federal and state income tax benefits). Accruals for possible interest and penalties on uncertain tax positions are reflected in income tax expense for financial reporting purposes.
We anticipate that by December 31, 2008, we will settle several disputed issues raised by the Internal Revenue Service (the “IRS”) during its examination of our U.S. income tax returns for 2001-2003, the most significant of which regards the recognition of our captive insurance subsidiary as an insurance company for U.S. income tax purposes. It is reasonably possible that a settlement with the IRS for the disputed issues would cost us $1.4 million, which would be applied against the balance of unrecognized tax benefits and accrued interest and penalties.
Tredegar and its subsidiaries file income tax returns in U.S., state and foreign jurisdictions. Tredegar is no longer subject to U.S. federal income tax examinations by tax authorities for years before 2001. With few exceptions, Tredegar and its subsidiaries are no longer subject to state or non-U.S. income tax examinations by tax authorities for years before 2004.
As of December 31, 2007, we had valuation allowances relating to deferred tax assets of $4.0 million. For more information on deferred income tax assets and liabilities, see Note 14 of the notes to financial statements.
Recently Issued Accounting Standards
In December 2007, the Financial Accounting Standards Board issued SFAS No. 141(R), Business Combinations, and SFAS No. 160, Noncontrolling Interests in Consolidated Financial Statements. SFAS No. 141 is applied prospectively to business combinations for which the acquisition date is on or after the beginning of the first annual reporting period beginning on or after December 15, 2008. The new accounting standard for noncontrolling interests (sometimes referred to as minority interests) applies to all fiscal years and interim periods beginning on or after December 15, 2008. Early application is prohibited for both standards. We currently do not have noncontrolling or minority interests in our consolidated financial statements. We will apply the new standards when required and applicable.
Results of Continuing Operations
2007 versus 2006
Revenues. Overall, sales in 2007 decreased by 1.6% compared with 2006, primarily due to a decline in sales in Aluminum Extrusions. For more information on net sales and volume, see the executive summary beginning on page 17.
Operating Costs and Expenses. Consolidated gross profit (sales minus cost of goods sold and freight) as a percentage of sales was 15.3% in 2007 and 14.5% in 2006. The gross profit margin increased in Film Products but decreased in
21
Aluminum Extrusions primarily because of the changes in sales and volume. In addition, gross profit improvement in Film Products was partially offset by an estimated negative impact in 2007 of $2.5 million from the lag in the pass-through of changes in average resin costs and year-end adjustments for LIFO. In 2006, we estimated a favorable impact of $4.5 million from the lag in the pass-through of changes in average resin costs and year-end adjustments for LIFO.
As a percentage of sales, selling, general and administrative and R&D expenses were 8.3% in 2007, up from 7.7% in 2006. The increase is primarily due to higher costs in Film Products, including costs associated with a new information system and a reorganization that resulted in the hiring of additional personnel.
Losses associated with plant shutdowns, asset impairments and restructurings in 2007 totaled $4.1 million ($2.8 million after taxes) and included:
| |
• | A fourth quarter charge of $1.2 million ($780,000 after taxes), a third quarter charge of $1.2 million ($793,000 after taxes) and a first quarter charge of $366,000 ($238,000 after taxes) related to the estimated loss on the sublease of a portion of the AFBS (formerly Therics) facility in Princeton, New Jersey; |
| |
• | A fourth quarter charge of $256,000 ($256,000 after taxes) and a first quarter charge of $338,000 ($284,000 after taxes) for asset impairments in Film Products; |
| |
• | A third quarter charge of $493,000 ($309,000 after taxes) and a second quarter charge of $99,000 ($62,000 after taxes) for severance and other employee-related costs in Aluminum Extrusions; |
| |
• | A second quarter charge of $26,000 ($16,000 after taxes) and a first quarter charge of $29,000 ($17,000 after taxes) for costs related to the shutdown of the films manufacturing facility in LaGrange, Georgia; and |
| |
• | A third quarter charge of $42,000 ($26,000 after taxes) related to expected future environmental costs at the aluminum extrusions facility in Newnan, Georgia (included in “Cost of goods sold” in the consolidated statements of income). |
Results in 2007 include a fourth-quarter gain of $2.7 million ($1.7 million after taxes) on the sale of corporate real estate (proceeds of $3.8 million) and a third-quarter loss from the write-down of an investment of $2.1 million ($1.3 million after taxes). The pretax amounts for both of these items are included in “Other income (expense), net” in the consolidated statements of income and separately shown in the segment operating profit table on page 14. Income taxes in 2007 include the recognition of a valuation allowance against deferred tax assets of $1.1 million in the third quarter for expected limitations on the utilization of certain assumed capital losses.
For more information on costs and expenses, see the executive summary beginning on page 17.
Interest Income and Expense. Interest income, which is included in “Other income (expense), net” in the consolidated statements of income, was $1.2 million in 2007 and $1.2 million in 2006. Our policy permits investment of excess cash in marketable securities that have the highest credit ratings and maturities of less than one year with the primary objectives being safety of principal and liquidity.
Interest expense decreased to $2.7 million in 2007, a decline of $2.8 million versus 2006 due to lower average debt outstanding. Average debt outstanding and interest rates were as follows:
| | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(In Millions) | | 2007 | | 2006 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Floating-rate debt with interest charged on a rollover
basis at one-month LIBOR plus a credit spread: | | | | | | | |
Average outstanding debt balance | | $ | 41.5 | | $ | 91.0 | |
Average interest rate | | | 6.0 | % | | 5.9 | % |
Fixed-rate and other debt: | | | | | | | |
Average outstanding debt balance | | $ | 2.2 | | $ | 4.4 | |
Average interest rate | | | 3.8 | % | | 6.5 | % |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total debt: | | | | | | | |
Average outstanding debt balance | | $ | 43.7 | | $ | 95.4 | |
Average interest rate | | | 5.9 | % | | 5.9 | % |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
22
Income Taxes. The effective tax rate increased to 41.1% in 2007 compared with 35.9% in 2006 mainly due to a valuation allowance for possible deferred tax benefits on capital loss carry-forwards and lower income tax benefits expected for the Extraterritorial Income Exclusion and Domestic Production Activities Deduction and the research and development (“R&D”) tax credit. For more information on the variances in our effective tax rate between years, see Note 14 of the notes to financial statements.
2006 versus 2005
Revenues. Sales in 2006 increased by 16.0% compared with 2005. Net sales (sales less freight) increased 11.1% in Film Products primarily due to growth in higher value-added products, including surface protection, elastic and apertured materials, and higher selling prices, which were driven by higher raw material costs. Net sales increased 23.2% in Aluminum Extrusions due to higher volume (up 4.6%) and selling prices. For more information on net sales and volume, see the business segment review beginning on page 33.
Operating Costs and Expenses. Gross profit (sales minus cost of goods sold and freight) as a percentage of sales increased to 14.5% in 2006 from 14.3% in 2005. At Film Products, a higher gross profit margin was driven primarily by growth in higher value-added products, including surface protection, elastic and apertured materials, partially offset by the effects of higher average selling prices to cover higher average resin costs. Margins in Film Products also improved in 2006 versus 2005 from a favorable lag in the pass-through to customers of changes in resin costs and income from LIFO inventory liquidations of approximately $7.4 million in 2006 (including $2.9 million of income shown in “Cost of goods sold” in the consolidated statements of income from LIFO liquidations related to the shutdown of the facility in LaGrange, Georgia) compared with an unfavorable net lag and LIFO adjustment in 2005 of approximately $4.0 million. At Aluminum Extrusions, a lower gross profit margin was primarily due to the effects of higher selling prices to cover higher aluminum costs, partially offset by higher volume and selling prices and lower energy costs.
As a percentage of sales, selling, general and administrative and R&D expenses decreased to 7.7% in 2006 compared with 8.7% in 2005 due primarily to higher sales and the divestiture of substantially all of our interest in AFBS, Inc. (formerly known as Therics, Inc.) at the end of the second quarter of 2005. For more information on this divestiture, see the business segment review beginning on page 33.
Losses associated with plant shutdowns, asset impairments and restructurings, net of gains on sale of related assets and related income from LIFO inventory liquidations, in 2006 totaled $1.9 million ($1.4 million after taxes) and included:
| |
• | A fourth quarter net gain of $14,000 ($8,000 after taxes), a third-quarter net gain of $1 million ($615,000 after taxes), a second-quarter net gain of $822,000 ($494,000 after taxes) and a first-quarter pretax charge of $404,000 ($243,000 after taxes) associated with the shutdown of the films manufacturing facility in LaGrange, Georgia, including a pretax gain of $2.9 million for related LIFO inventory liquidations (included in “Cost of goods sold” in the consolidated statements of income), severance and other costs of $1.6 million, asset impairment charges of $130,000 and a gain on the disposal of equipment of $261,000 (included in “Other income (expense), net” in the consolidated statements of income); |
| |
• | A third-quarter charge of $920,000 ($566,000 after taxes) related to expected future environmental costs at the aluminum extrusions facility in Newnan, Georgia (included in “Cost of goods sold” in the consolidated statements of income); |
| |
• | A fourth quarter charge of $143,000 ($93,000 after taxes) and a third quarter charge of $494,000 ($321,000 after taxes) related to the estimated loss on the sub-lease of a portion of the AFBS facility in Princeton, New Jersey; |
| |
• | Second-quarter charges of $459,000 ($289,000 after taxes) and first-quarter charges of $268,000 ($170,000 after taxes) for severance and other employee-related costs in connection with restructurings in Aluminum Extrusions ($514,000) and Film Products ($213,000); and |
| |
• | First-quarter charges of $1 million ($876,000 after taxes) for asset impairments relating to machinery & equipment in Film Products. |
In 2006, a pretax gain on the sale of public equity securities of $56,000 (proceeds also of $56,000) is
23
included in “Other income (expense), net” in the consolidated statements of income and “Gain on the sale of corporate assets” in the segment operating profit table on page 14. Income taxes in 2006 include a reversal of a valuation allowance of $577,000 for deferred tax assets associated with capital loss carry-forwards recorded with the write-down of an investment.
For more information on costs and expenses, see the executive summary beginning on page 17.
Interest Income and Expense. Interest income, which is included in “Other income (expense), net” in the consolidated statements of income, was $1.2 million in 2006 and $586,000 in 2005. Interest income was up primarily due to a higher average yield earned on cash equivalents.
Interest expense increased to $5.5 million in 2006 compared with $4.6 million in 2005. Average debt outstanding and interest rates were as follows:
| | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(In Millions) | | 2006 | | 2005 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Floating-rate debt with interest charged on a rollover basis at one-month LIBOR plus a credit spread: | | | | | | | |
Average outstanding debt balance | | $ | 91.0 | | $ | 110.0 | |
Average interest rate | | | 5.9 | % | | 4.5 | % |
Fixed-rate and other debt: | | | | | | | |
Average outstanding debt balance | | $ | 4.4 | | $ | 5.9 | |
Average interest rate | | | 6.5 | % | | 5.5 | % |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total debt: | | | | | | | |
Average outstanding debt balance | | $ | 95.4 | | $ | 115.9 | |
Average interest rate | | | 5.9 | % | | 4.6 | % |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Income Taxes. The effective tax rate declined to 35.9% in 2006 compared with 41.5% in 2005 due to the numerous variances between years that are shown in the effective tax rate reconciliation provided in Note 14 of the notes to financial statements.
24
Financial Condition
Assets and Liabilities
Changes in assets and liabilities from continuing operations from December 31, 2006 to December 31, 2007 are summarized below:
| | |
• | Accounts receivable decreased $9.9 million (9.2%). |
| |
| – | Accounts receivable in Film Products increased by $510,000 due mainly to higher sales. Days sales outstanding (“DSO”) was 45 at December 31, 2007 compared with 46 at December 31, 2006. |
| | |
| – | Accounts receivable for continuing operations in Aluminum Extrusions decreased by $10.4 million. DSO was 40 at December 31, 2007 compared with 42 at December 31, 2006. |
| | |
• | Inventories were relatively flat. |
| |
| ��� | Inventories in Film Products decreased by approximately $800,000. Inventory days were 43 at December 31, 2007 and 2006. |
| | |
| – | Inventories for continuing operations of Aluminum Extrusions increased by approximately $800,000. Inventory days increased to 35 at December 31, 2007 compared with 28 at December 31, 2006, primarily due to cyclical fluctuations. |
| | |
• | Net property, plant and equipment was down $18.4 million (6.4%) due primarily to depreciation for continuing operations of $42.5 million compared with capital expenditures of $19.7 million, reductions of $5.2 million for property disposals and reimbursements from a customer for purchases of equipment (proceeds of $7.9 million less net gains recognized of $2.7 million) and asset impairments in Film Products of $594,000, partially offset by appreciation of foreign currencies relative to the U.S. Dollar (favorable impact of $10.4 million). |
| |
• | Accounts payable increased by $13.1 million (24.3%). |
| |
| – | Accounts payable in Film Products increased by $2.9 million due mainly to higher sales. Accounts payable days were 30 at December 31, 2007 compared with 29 at December 31, 2006. |
| | |
| – | Accounts payable for continuing operations in Aluminum Extrusions increased by $5.7 million. Accounts payable days were 37 at December 31, 2007 compared with 23 days at December 31, 2006, primarily due to seasonal fluctuations and consistent with the increase in inventory days. |
| | |
| – | Accounts payable increased at corporate by $3.4 million for amounts payable to a securities broker relating to our repurchase of Tredegar common stock. |
| | |
• | Accrued expenses decreased by $5.1 million (13.2%) due primarily to lower incentive compensation accruals, revenue received in advance in 2006 recognized in 2007, reclassification of certain items from current to noncurrent liabilities and the timing of payments, partially offset by an unrealized loss on futures contracts that hedge fixed-priced customer contracts in Aluminum Extrusions (at December 31, 2006, there was an unrealized gain on futures contracts reflected in current assets) and a higher estimated loss related to a lease associated with AFBS (formerly Therics). |
25
Net capitalization and indebtedness as defined under our revolving credit agreement as of December 31, 2007 were as follows:
| | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
Net Capitalization and Indebtedness as of Dec. 31, 2007 | |
(In Thousands) | |
|
|
Net capitalization: | | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 48,217 | |
Debt: | | | | |
$300 million revolving credit agreement maturing
December 15, 2010 | | | 80,000 | |
Other debt | | | 2,056 | |
| |
|
| |
Total debt | | | 82,056 | |
| |
|
| |
Debt net of cash and cash equivalents | | | 33,839 | |
Shareholders’ equity | | | 491,328 | |
| |
|
| |
Net capitalization | | $ | 525,167 | |
| |
|
| |
Indebtedness as defined in revolving credit agreement: | | | | |
Total debt | | $ | 82,056 | |
Face value of letters of credit | | | 5,957 | |
Liabilities relating to derivative financial instruments | | | 1,815 | |
| |
|
| |
Indebtedness | | $ | 89,828 | |
|
|
|
|
|
Under the revolving credit agreement, borrowings are permitted up to $300 million, and $219 million was available to borrow at December 31, 2007. The credit spread and commitment fees charged on the unused amount under the revolving credit agreement at various indebtedness-to-adjusted EBITDA levels are as follows:
| | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pricing Under Revolving Credit Agreement (Basis Points) | |
|
|
Indebtedness-to-Adjusted
EBITDA Ratio | | Credit Spread
Over LIBOR | | Commitment
Fee | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
> 2.50x but <= 3x | | | 125 | | | 25 | |
> 1.75x but <= 2.50x | | | 100 | | | 20 | |
> 1x but <=1.75x | | | 87.5 | | | 17.5 | |
<= 1x | | | 75 | | | 15 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
At December 31, 2007, the interest rate on debt under the revolving credit agreement was priced at one-month LIBOR plus the applicable credit spread of 75 basis points.
26
The computations of adjusted EBITDA, adjusted EBIT, the leverage ratio and interest coverage ratio as defined in the credit agreement are presented below along with the related most restrictive covenants. Adjusted EBITDA and adjusted EBIT as defined in the credit agreement are not intended to represent cash flow from operations as defined by GAAP and should not be considered as either an alternative to net income or to cash flow.
| | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
Computations of Adjusted EBITDA, Adjusted EBIT, Leverage Ratio and | |
Interest Coverage Ratio as Defined in Revolving Credit Agreement Along with Related Most | |
Restrictive Covenants | |
As of and For the Year Ended December 31, 2007 (In Thousands) | |
|
|
|
|
|
Computations of adjusted EBITDA and adjusted EBIT as defined in revolving credit agreement for the twelve months ended December 31, 2007: | | | | |
Net income | | $ | 15,249 | |
Plus: | | | | |
After-tax losses related to discontinued operations | | | 19,681 | |
Total income tax expense for continuing operations | | | 24,366 | |
Interest expense | | | 2,721 | |
Charges related to stock option grants and awards accounted for under the fair value-based method | | | 978 | |
Losses related to the application of the equity method of accounting | | | — | |
Depreciation and amortization expense for continuing operations | | | 42,655 | |
All non-cash losses and expenses, plus cash losses and expenses not to exceed $10,000, for continuing operations that are classified as unusual, extraordinary or which are related to plant shutdowns, asset impairments and/or restructurings (cash-related of $3,475) | | | 6,164 | |
Minus: | | | | |
After-tax income related to discontinued operations | | | — | |
Total income tax benefits for continuing operations | | | — | |
Interest income | | | (1,212 | ) |
All non-cash gains and income, plus cash gains and income not to exceed $10,000, for continuing operations that are classified as unusual, extraordinary or which are related to plant shutdowns, asset impairments and/or restructurings (all cash-related) | | | (2,699 | ) |
Plus or minus, as applicable, pro forma EBITDA adjustments associated with acquisitions and asset dispositions | | | — | |
| |
|
| |
Adjusted EBITDA as defined in revolving credit agreement | | | 107,903 | |
Less: Depreciation and amortization expense for continuing operations (including pro forma for acquisitions and asset dispositions) | | | (42,655 | ) |
| |
|
| |
Adjusted EBIT as defined in revolving credit agreement | | $ | 65,248 | |
| |
|
| |
Shareholders’ equity at December 31, 2007 | | $ | 491,328 | |
Computations of leverage and interest coverage ratios as defined in revolving credit agreement: | | | | |
Leverage ratio (indebtedness-to-adjusted EBITDA) | | | .83 | x |
Interest coverage ratio (adjusted EBIT-to-interest expense) | | | 23.98 | x |
Most restrictive covenants as defined in revolving credit agreement: | | | | |
Maximum permitted aggregate amount of dividends that can be paid by Tredegar during the term of the revolving credit agreement ($100,000 plus 50% of net income generated after October 1, 2005) | | $ | 127,170 | |
Minimum adjusted shareholders’ equity permitted ($351,918 plus 50% of net income generated after October 1, 2005) | | $ | 388,276 | |
Maximum leverage ratio permitted: | | | | |
Ongoing | | | 3.00 | x |
Pro forma for acquisitions | | | 2.50 | x |
Minimum interest coverage ratio permitted | | | 2.50 | x |
|
|
|
|
|
27
Noncompliance with any one or more of the debt covenants may have a material adverse effect on financial condition or liquidity in the event such noncompliance cannot be cured or should we be unable to obtain a waiver from the lenders. Renegotiation of the covenant(s) through an amendment to the credit agreement may effectively cure the noncompliance, but may have an effect on financial condition or liquidity depending upon how the covenant is renegotiated.
We are obligated to make future payments under various contracts as set forth below:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| | Payments Due by Period | |
|
|
| |
(In Millions) | | 2008 | | 2009 | | 2010 | | 2011 | | 2012 | | Remainder | | Total | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Debt | | $ | .5 | | $ | .6 | | $ | 80.5 | | $ | .3 | | $ | .1 | | | $ | .1 | | | $ | 82.1 | |
Operating leases: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
AFBS (formerly Therics) | | | 1.6 | | | 1.6 | | | 1.6 | | | .4 | | | — | | | | — | | | | 5.2 | |
Other | | | .9 | | | 1.3 | | | 1.4 | | | 1.3 | | | 1.3 | | | | .6 | | | | 6.8 | |
Capital expenditure commitments (1) | | | 3.0 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | — | | | | 3.0 | |
Estimated obligations relating to uncertain tax positions (2) | | | 2.2 | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | 2.3 | | | | 4.5 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Total | | $ | 8.2 | | $ | 3.5 | | $ | 83.5 | | $ | 2.0 | | $ | 1.4 | | | $ | 3.0 | | | $ | 101.6 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| |
(1) | Represents contractual obligations for plant construction and purchases of real property and equipment. See Note 13 on page 65. |
| |
(2) | Amounts for which reasonable estimates about the timing of payments cannot be made are included in the remainder column. |
We believe that existing borrowing availability, our current cash balances and our cash flow from operations will be sufficient to satisfy our working capital, capital expenditure and dividend requirements for the foreseeable future.
From time to time, we enter into transactions with third parties in connection with the sale of assets or businesses in which we agree to indemnify the buyers or third parties involved in the sale for certain liabilities or risks related to the assets or business. Also, in the ordinary course of our business, we may enter into agreements with third parties for the sale of goods or services that may contain indemnification provisions. In the event that an indemnification claim is asserted, liability for indemnification would be subject to an assessment of the underlying facts and circumstances under the terms of the applicable agreement. Further, any indemnification payments may be limited or barred by a monetary cap, a time limitation, or a deductible or basket. For these reasons, we are unable to estimate the maximum potential amount of the potential future liability under the indemnity provisions of these agreements. We do, however, accrue for losses for any known contingent liability, including those that may arise from indemnification provisions, when future payment is probable. We disclose contingent liabilities if the probability of loss is reasonably possible and significant.
Shareholders’ Equity
At December 31, 2007, we had 34,765,450 shares of common stock outstanding and a total market capitalization of $559.0 million, compared with 39,286,079 shares of common stock outstanding and a total market capitalization of $888.3 million at December 31, 2006.
During 2006 and 2005 we did not purchase any shares of our common stock in the open market. See the issuer purchases of equity securities section of Item 5 on page 8 regarding purchases of our common stock in 2007 and our standing authorization permitting additional purchases.
Cash Flows
The discussion in this section supplements the information presented in the consolidated statements of cash flows on page 43. Cash flows for discontinued operations have not been separately disclosed in the consolidated statements of cash flows.
Cash provided by operating activities was $95.6 million in 2007 compared with $104.6 million in 2006. The decrease is due primarily to higher income tax payments (income tax payments were approximately $17.0 million
28
in 2007 compared with $7.8 million in 2006) and a decline in operating results in Aluminum Extrusions (mainly operations in Canada divested on February 12, 2008), partially offset by lower incremental working capital investment (see assets and liabilities section on page 25 for discussion of working capital trends and Note 17 to the notes to financial statements for discussion of discontinued aluminum extrusion operations in Canada).
Cash used in investing activities declined to $36.3 million in 2007 compared with $40.6 million in 2006 due to lower capital expenditures and proceeds from property disposals and reimbursements from a customer for purchases of equipment, partially offset by higher investments. Capital expenditures in 2007 primarily included the normal replacement of machinery and equipment and continued expansion of capacity for surface protection films and elastic materials. See the executive summary beginning on page 17 and the business segment review beginning on page 33 for more information on capital expenditures.
Net cash flow used in financing activities was $54.1 million in 2007 and included the use of cash generated from operating activities in excess of investing activities, additional borrowings under our revolving credit facility and proceeds from the exercise of stock options to pay dividends and purchase Tredegar common stock.
Cash provided by operating activities was $104.6 million in 2006 compared with $53.7 million in 2005. The increase is due primarily to improved operating results, higher deferred income taxes and lower incremental working capital investment.
Cash used in investing activities was $40.6 million in 2006 compared with $55.0 million in 2005 due primarily to lower capital expenditures. Capital expenditures in 2006 in Film Products of $33.2 million (down from $50.5 million in 2005 and $1.5 million in excess of 2006 depreciation) primarily included the continued expansion of capacity for surface protection films and elastic materials, a new information system and normal replacement of machinery and equipment. Capital expenditures in Aluminum Extrusions were $7.4 million in 2006 compared to $12 million in 2005 and depreciation in 2006 of $12.3 million. See the business segment review beginning on page 33 for more information on capital expenditures.
Net cash flow used in financing activities was $47.0 million in 2006 and included the use of cash generated from operating activities in excess of investing activities to pay dividends and repay amounts outstanding under our revolving credit facility. In addition, financing activities in 2006 included proceeds from the exercise of stock options of $9.7 million, including $8.5 million in the fourth quarter of 2006 due to an increase in our stock price and certain stock option expiration dates in early 2007.
Cash provided by operating activities was $53.7 million in 2005 compared with $93.8 million in 2004. The decrease is due primarily to the income tax refund received in 2004 related to the sale in 2003 of our venture capital portfolio, partially offset by lower working capital investment in 2005 compared with 2004.
Cash used in investing activities was $55.0 million in 2005 compared with $52.2 million in 2004. The change is primarily attributable to higher capital expenditures (up $6.9 million) and lower proceeds from the sale of assets and property disposals (down $2.2 million), partially offset by a small acquisition in Film Products in 2004 ($1.4 million) and higher investment in Novalux, Inc. in 2004 ($5.0 million invested in 2004 compared with $1.1 million invested in 2005).
Net cash provided by financing activities was $3.6 million in 2005 and included the refinancing of our debt in December 2005.
29
Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk
Tredegar has exposure to the volatility of interest rates, polyethylene and polypropylene resin prices, aluminum ingot and scrap prices, energy prices, foreign currencies and emerging markets. See the assets and liabilities section beginning on page 25 regarding credit agreements and interest rate exposures.
Changes in resin prices, and the timing of those changes, could have a significant impact on profit margins in Film Products. Profit margins in Aluminum Extrusions are sensitive to fluctuations in aluminum ingot and scrap prices as well as natural gas prices (natural gas is the principal energy source used to operate our casting furnaces). There is no assurance of our ability to pass through higher raw material and energy costs to our customers.
See the executive summary beginning on page 17 and the business segment review beginning on page 33 for discussion regarding the impact of the lag in the pass-through of resin price changes. The volatility of average quarterly prices of low density polyethylene resin in the U.S. (a primary raw material for Film Products) is shown in the chart below.

Source: Quarterly averages computed by Tredegar using monthly data provided by Chemical Data Inc. (“CDI”). In January 2005, CDI reflected a 4 cents per pound non-market adjustment based on their estimate of the growth of discounts over the 2000 to 2003 period. The 4th quarter 2004 average rate of 67 cents per pound is shown on a pro forma basis as if the non-market adjustment was made in October 2004.
Resin prices in Europe, Asia and South America have exhibited similar trends. The price of resin is driven by several factors including supply and demand and the price of oil, ethylene and natural gas. To address fluctuating resin prices, Film Products has index-based pass-through raw material cost agreements for the majority of its business. However, under certain agreements, changes in resin prices are not passed through for an average period of 90 days.
30
In the normal course of business, we enter into fixed-price forward sales contracts with certain customers for the sale of fixed quantities of aluminum extrusions at scheduled intervals. In order to hedge our exposure to aluminum price volatility (see the chart below) under these fixed-price arrangements, which generally have a duration of not more than 12 months, we enter into a combination of forward purchase commitments and futures contracts to acquire or hedge aluminum, based on the scheduled deliveries. See Note 6 on page 55 for more information.
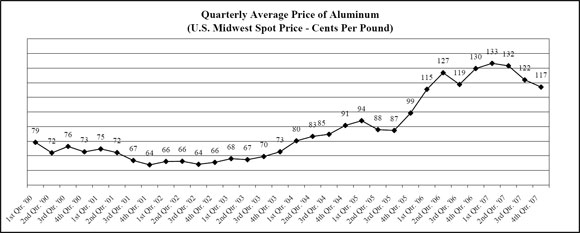
Source: Quarterly averages computed by Tredegar using daily closing data provided by Bloomberg.
In Aluminum Extrusions, we hedge from time-to-time a portion of our exposure to natural gas price volatility by entering into fixed-price forward purchase contracts with our natural gas suppliers. We estimate that, in an unhedged situation, every $1 per mmBtu per month change in the market price of natural gas has a $95,000 impact on the continuing monthly operating profit for our U.S. operations in Aluminum Extrusions. In September 2005, we announced an energy surcharge for our aluminum extrusions business in the U.S. to be applied when the previous quarter’s NYMEX natural gas average settlement price is in excess of $8.85 per mmBtu.

Source: Quarterly averages computed by Tredegar using monthly NYMEX settlement prices.
31
We sell to customers in foreign markets through our foreign operations and through exports from U.S. plants. The percentage of sales and total assets for continuing manufacturing operations related to foreign markets for 2007 and 2006 are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
Tredegar Corporation - Continuing Manufacturing Operations
Percentage of Net Sales and Total Assets Related to Foreign Markets | |
|
|
|
|
| | 2007 | | 2006 | |
| |
| |
| |
| | % of Total
Net Sales * | | % Total
Assets-
Foreign
Oper-
ations * | | % of Total
Net Sales * | | % Total
Assets -
Foreign
Oper-
ations * | |
| | | | | |
| |
| | |
| | |
| | Exports
From
U.S. | | Foreign
Oper-
ations | | | Exports
From
U.S. | | Foreign
Oper-
ations | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
Canada | | | 5 | | | — | | | — | | | 5 | | | — | | | — | |
Europe | | | 1 | | | 17 | | | 16 | | | 1 | | | 15 | | | 16 | |
Latin America | | | — | | | 3 | | | 2 | | | — | | | 3 | | | 2 | |
Asia | | | 3 | | | 6 | | | 7 | | | 5 | | | 5 | | | 8 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total % exposure to foreign markets | | | 9 | | | 26 | | | 25 | | | 11 | | | 23 | | | 26 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | |
* | | The percentages for foreign markets are relative to Tredegar’s total net sales and total assets from manufacturing operations (consolidated net sales and total assets from continuing operations excluding cash and cash equivalents and AFBS (formerly Therics)). |
We attempt to match the pricing and cost of our products in the same currency and generally view the volatility of foreign currencies (see trends for the Euro and Chinese Yuan in the chart below) and emerging markets, and the corresponding impact on earnings and cash flow, as part of the overall risk of operating in a global environment. Exports from the U.S. are generally denominated in U.S. Dollars. Our foreign currency exposure on income from continuing foreign operations relates to the Euro, the Chinese Yuan, the Hungarian Forint and the Brazilian Real.
In Film Products, where we are typically able to match the currency of our sales and costs, we estimate that the change in value of foreign currencies relative to the U.S. Dollar had a positive impact on operating profit of approximately $3 million in 2007 compared with 2006, $500,000 in 2006 compared with 2005, and $600,000 in 2005 compared with 2004.
In 2007, we used currency options to hedge a portion of our exposure to changes in exchange rates. Results for continuing operations include realized losses of $239,000 on currency hedges of royalties relating to our operations in Europe and results from discontinued operations include realized gains of $1.3 million on currency hedges of our exposure to the Canadian Dollar. There were no derivatives outstanding at December 31, 2007 relating to currency hedges. Trends for the Euro and Chinese Yuan are shown in the chart below:

Source: Quarterly averages computed by Tredegar using daily closing data provided by Bloomberg.
32
Business Segment Review
Net sales (sales less freight) and operating profit from ongoing operations are the measures of sales and operating profit used by the chief operating decision maker for purposes of assessing performance.
Film Products
Net Sales. See the executive summary beginning on page 17 for the discussion of net sales (sales less freight) in Film Products in 2007 compared with 2006.
Net sales in Film Products were $511.2 million in 2006 and $460.3 million in 2005. The increase in net sales in Film Products in 2006 is primarily due to growth in higher value-added products, including surface protection films, elastic materials and new apertured materials. Selling price and net sales are also affected by the pass-through of changes in raw material costs and changes in currency exchange rates (see the qualitative and quantitative disclosures about market risks section beginning on page 30). Total volume was 253.5 million pounds in 2006 and 261.1 million pounds in 2005. We estimate that the growth in net sales excluding the effects of the pass-through of resin price changes and currency exchange rate changes was about 6% in 2006 and 7% in 2005. Volume declines in 2006 compared with 2005 were mainly due to lower sales of certain commodity barrier films that were dropped in conjunction with the shutdown of the plant in LaGrange, Georgia. The plant was shut down in the first half of 2006 and had sales of commodity barrier films of approximately $20 million in 2005.
Operating Profit. See the executive summary beginning on page 17 for the discussion of operating profit in Film Products in 2007 compared with 2006.
Operating profit from ongoing operations in Film Products was $57.6 million in 2006 and $44.9 million in 2005. Operating profit from ongoing operations excluding the estimated effects of resin pass-through lag and year-end LIFO adjustments was $53.1 million in 2006 and $48.9 million in 2005. The increase in operating profit in 2006 excluding the impact of resin pass-through lag and LIFO adjustments was driven by growth in the sale of higher value surface protection films, elastic materials and new apertured topsheets.
Identifiable Assets. Identifiable assets in Film Products decreased to $488.0 million at December 31, 2007, from $499.0 million at December 31, 2006, due primarily to depreciation of $33.9 million compared with capital expenditures of $15.3 million and asset impairments during the year totaling $594,000, partially offset by the effects of currency rate changes on property, plant and equipment and goodwill of approximately $11.3 million. See page 25 for further discussion on changes in assets and liabilities.
Identifiable assets in Film Products increased to $499.0 million at December 31, 2006, from $479.3 million at December 31, 2005, due primarily to the effects of currency rate changes of $9.0 million, higher accounts receivable (up $6.5 million) due to higher sales and higher inventories (up $3.4 million) and asset impairments during 2006 totaling $1.2 million.
Depreciation, Amortization and Capital Expenditures. Depreciation and amortization for Film Products was $34.1 million in 2007, $31.7 million in 2006 and $26.7 million in 2005. The increase in 2007 compared with 2006 is primarily due to capital expenditures in 2006 and 2007 and appreciation of the U.S. Dollar value of currencies for operations outside of the U.S. The increase in 2006 compared with 2005 is mainly due to the relatively high level of capital expenditures from 2003-2005. We expect depreciation and amortization expense for Film Products to be approximately $33 million in 2008.
Capital expenditures declined to $15.3 million in 2007 compared with $33.2 million in 2006. Capital expenditures in 2008 are expected to be approximately $33 million. Capital expenditures in 2007 primarily included the normal replacement of machinery and equipment and continued expansion of capacity for surface protection films and elastic materials.
33
Capital expenditures declined to $33.2 million in 2006 compared with $50.5 million in 2005. Approximately half of the capital expenditures in 2006 related to expanding the production capacity for surface protection films. Other capital expenditures in 2006 included capacity additions for elastic materials and continued costs associated with a new information system, which was rolled out in U.S. locations.
Aluminum Extrusions (Continuing Operations)
Net Sales and Operating Profit. See the executive summary beginning on page 17 for the discussion of net sales (sales less freight) and operating profit for the continuing operations of Aluminum Extrusions in 2007 compared with 2006.
Net sales were $403.8 million in 2006, up 23.2% versus $327.7 million in 2005. Operating profit from continuing ongoing operations was $18.3 million in 2006, up 7.1% compared to $17.1 million in 2005. Volume increased to 185.2 million pounds in 2006, up 4.6% compared to 177.0 million pounds in 2005. Growth in shipments in 2006 was driven by demand for extrusions used in commercial construction and hurricane protection products, partially offset by a decline in extrusions used in residential construction. The increase in operating profit during 2006 was primarily due to higher volume and selling prices and lower energy costs, partially offset by higher charges for possible uncollectible accounts ($1.4 million).
Identifiable Assets. Identifiable assets in Aluminum Extrusions were $115.2 million at December 31, 2007, $129.0 million at December 31, 2006 and $130.4 million at December 31, 2005. The decline of $13.8 million at the end of 2007 compared with 2006 is mainly due to lower accounts receivable of $10.4 million (see page 25 for further discussion) and depreciation of $8.5 million compared with capital expenditures of $4.4 million. Changes between 2006 and 2005 are primarily due to sales-driven fluctuations in accounts receivable and inventory levels.
Depreciation, Amortization and Capital Expenditures. Depreciation and amortization for Aluminum Extrusions was $8.5 million in 2007, $8.4 million in 2006 and $8 million in 2005. We expect depreciation and amortization expense for Aluminum Extrusions to be $8.5 million in 2008.
Capital expenditures totaled $4.4 million in 2007, $6.6 million in 2006 and $5.8 million in 2005, and reflect the normal replacement of machinery and equipment. Capital expenditures are expected to be approximately $21 million in 2008. In January, we announced plans to spend approximately $24 million over the next 18 months to expand the capacity at our plant in Carthage, Tennessee. Approximately 65% of our sales of aluminum extrusions from our U.S. operations are related to non-residential construction, and this additional capacity will increase our capabilities in this sector.
AFBS
On June 30, 2005, substantially all of the assets of AFBS, Inc. (formerly known as Therics, Inc.), a wholly-owned subsidiary of Tredegar, were sold or assigned to a newly-created limited liability company, Therics, LLC, which is controlled and managed by an individual not affiliated with Tredegar. AFBS received a 17.5% equity interest in Therics, LLC, then valued at $170,000 and a 3.5% interest in Theken Spine, LLC, then valued at $800,000, along with potential future payments based on the sale of certain products by Therics, LLC. AFBS retained substantially all of its liabilities in the transaction, which included customary indemnification provisions for pre-transaction liabilities. Tredegar has no obligation or intent to fund any future losses that may occur at Therics, LLC or Theken Spine, LLC. The ownership interest in Therics, LLC is accounted for under the equity method of accounting with losses limited to its initial carrying value of $170,000. The ownership interest in Theken Spine, LLC is accounted for under the cost method, with an impairment loss recognized and a new cost basis established for any write-down to estimated fair value, if necessary. The payments due from Therics, LLC that are based on the sale of certain products are recognized as income when earned. AFBS had operating losses of $3.5 million during the first six months of 2005 and $9.8 million in 2004. Results of operations for AFBS since June 30, 2005 are immaterial.
34
| |
Item 7A. | QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK |
See discussion of quantitative and qualitative disclosures about market risk beginning on page 30 in Management’s Discussion and Analysis.
| |
Item 8. | FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA |
See the index on page 39 for references to the report of the independent registered public accounting firm, the consolidated financial statements and selected quarterly financial data.
| |
Item 9. | CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE |
None.
| |
Item 9A. | CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES |
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Pursuant to Rule 13a-15(b) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”), we carried out an evaluation, with the participation of our management, including our principal executive officer and principal financial officer, of the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures (as defined under Rule 13a-15(e) under the Exchange Act) as of the end of the period covered by this report. Based upon that evaluation, our principal executive officer and principal financial officer concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures are effective to ensure that information required to be disclosed by us in the reports that we file or submit under the Exchange Act, is recorded, processed, summarized and reported, within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms, and that such information is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our principal executive officer and principal financial officer, as appropriate, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting, as such term is defined in Rule 13a-15(f) under the Exchange Act. The Company’s internal control over financial reporting is designed to provide reasonable assurance to the Company’s management and board of directors regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation and fair presentation of published financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States of America and includes policies and procedures that:
| |
• | Pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of our assets; |
| |
• | Provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States of America, and that our receipts and expenditures are being made only in accordance with authorization of our management and directors; and |
| |
• | Provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of our assets that could have a material effect on the consolidated financial statements. |
Internal control over financial reporting includes the controls themselves, monitoring (including internal auditing practices) and actions taken to correct deficiencies as identified.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies
35
or procedures may deteriorate.
Management conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting based on the framework in Internal Control - Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. Based on their evaluation under the framework in Internal Control — Integrated Framework, our management concluded that our internal control over financial reporting was effective as of December 31, 2007.
The effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2007 has been audited by PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, as stated in their report which is included on pages 39-40.
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
There has been no change in our internal control over financial reporting during the quarter ended December 31, 2007, that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
| |
Item 9B. | OTHER INFORMATION |
None.
PART III
| |
Item 10. | DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE |
The information concerning directors and persons nominated to become directors of Tredegar included in the Proxy Statement under the headings “Election of Directors” and “Tredegar’s Board of Directors” is incorporated herein by reference.
The information concerning corporate governance included in the Proxy Statement under the heading “Board Meetings, Meetings of Non-Management Directors and the Board Committees” is incorporated herein by reference.
The information included in the Proxy Statement under the heading “Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Requirements” is incorporated herein by reference.
36
Set forth below are the names, ages and titles of our executive officers:
| | | | | | |
Name | | | Age | | Title | |
| | |
| |
| |
| | | | |
John D. Gottwald | | 53 | | President and Chief Executive |
| | | | |
Nancy M. Taylor | | 48 | | President, Tredegar Film Products and Corporate Senior Vice President |
| | | | |
D. Andrew Edwards | | 49 | | Vice President, Chief Financial Officer and Treasurer |
| | | | |
McAlister C. Marshall, II | | 38 | | Vice President, General Counsel and Corporate Secretary |
| | | | |
Larry J. Scott | | 57 | | Vice President, Audit |
John D. Gottwald. On January 16, 2006, Mr. Gottwald was elected President and Chief Executive Officer effective March 1, 2006. Mr. Gottwald had served as Chairman of the Board of Directors since September 10, 2001. Mr. Gottwald served as President and Chief Executive Officer from July 10, 1989 until September 10, 2001.
Nancy M. Taylor. Ms. Taylor was elected President of Tredegar Film Products effective April 5, 2005. She was elected Senior Vice President effective November 1, 2004. Ms. Taylor served as Senior Vice President, Strategy and Special Projects from November 1, 2004 until April 5, 2005. Ms. Taylor served as Managing Director, European Operations, of Tredegar Film Products from January 1, 2003 until November 1, 2004. Ms. Taylor served as Vice President, Administration and Corporate Development from September 10, 2001 until February 12, 2003. Ms. Taylor served as Secretary from February 24, 1994 until February 12, 2003. She served as Vice President, Law, from November 18, 1998 until September 10, 2001, and served as General Counsel from May 22, 1997 until July 25, 2000.
D. Andrew Edwards. Mr. Edwards was elected Vice President, Chief Financial Officer and Treasurer on August 28, 2003. Mr. Edwards has served as Vice President, Finance since November 18, 1998. Mr. Edwards has served as Treasurer since May 22, 1997. From October 19, 1992 until July 10, 2000, Mr. Edwards served as Controller.
McAlister C. Marshall, II. Mr. Marshall was elected Vice President, General Counsel and Corporate Secretary on October 1, 2006, the date that he joined Tredegar. From July 2000 until September 2006, he served as Assistant General Counsel at The Brink’s Company. He was an Associate at the law firm of Hunton & Williams LLP from 1996 until 2000.
Larry J. Scott. Mr. Scott was elected Vice President, Audit, on May 24, 2000. Mr. Scott served as Director of Internal Audit from February 24, 1994 until May 24, 2000.
We have adopted a Code of Conduct that applies to all of our directors, officers and employees (including our Chief Executive Officer, Chief Financial Officer and principal accounting officer) and have posted the Code of Conduct on our web site. We intend to satisfy the disclosure requirement under Item 10 of Form 8-K relating to amendments to or waivers from any provision of our Code of Conduct applicable to Chief Executive Officer, Chief Financial Officer and principal accounting officer by posting this information on our website. Our Internet address is www.tredegar.com. The information on or that can be accessed through our website is not, and shall not be deemed to be, a part of this report or incorporated into other filings we make with the SEC.
Because our common stock is listed on the NYSE, our chief executive officer is required to make, and he has made, an annual certification to the NYSE stating that he was not aware of any violation by us of the corporate governance listing standards of the NYSE. Our chief executive officer made his annual certification to that effect to the NYSE as of May 25, 2007. In addition, we have filed, as exhibits to this Annual Report on Form 10-K, the certifications of our principal executive officer and principal financial officer required under Section 302 of the Sarbanes Oxley Act of 2002 to be filed with the SEC regarding the quality of our public disclosure.
37
| |
Item 11. | EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION |
The information included in the Proxy Statement under the headings “Compensation of Directors”, “Board Meetings of Non-Management Directors and Board Committees - Executive Compensation Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation”, “Compensation Discussion and Analysis”, “Executive Compensation Committee Report” and “Compensation of Executive Officers” is incorporated herein by reference.
| |
Item 12. | SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS |
The information included in the Proxy Statement under the heading “Stock Ownership” is incorporated herein by reference. The following table summarizes information with respect to equity compensation plans under which securities are authorized for issuance as of December 31, 2007.
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Column (a) | | Column (b) | | Column (c) | | Column (d) | |
| | | | | | | |
Plan Category | | Number of Securities
to be Issued Upon
Exercise of
Outstanding Options,
Warrants and Rights | | Weighted Average
Exercise Price of
Outstanding Options,
Warrants and Rights | | Number of Securities
Remaining Available for
Future Issuance Under
Equity Compensation Plans,
Excluding Securities
Reflected in Column | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Equity compensation plans approved by security holders | | 1,009,858 | * | | | $ | 17.90 | | | 1,412,232 | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Equity compensation plans not approved by security holders | | — | | | | | — | | | — | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total | | 1,009,858 | | | | $ | 17.90 | | | 1,412,232 | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Includes performance stock units that give the holder the right to receive shares of Tredegar common stock upon the satisfaction of certain performance criteria.
| |
Item 13. | CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE |
The information included in the Proxy Statement under the headings “Certain Relationships and Related Transactions” and “Tredegar’s Board of Directors” is incorporated herein by reference.
| |
Item 14. | PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING FEES AND SERVICES |
The following is incorporated herein by reference:
| |
• | Information on accounting fees and services included in the Proxy Statement under the heading “Audit Fees;” and |
| |
• | Information on the Audit Committee’s procedures for pre-approving certain audit and non-audit services included in the Proxy Statement under the heading “Board Meetings, Meetings of Non-Management Directors and Board Committees - Audit Committee Matters”. |
38
PART IV
| | | |
Item 15. | EXHIBITS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES |
| | | |
| (a) | List of documents filed as a part of the report: |
| | | |
| | (1) | Financial statements: |
Tredegar Corporation
Index to Financial Statements and Supplementary Data
| | |
| (2) | Financial statement schedules: |
| | |
| | None. |
| | |
| (3) | Exhibits: |
| | |
| | See Exhibit Index on pages 80-81. |
|
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM |
|
To the Board of Directors and Shareholders of
Tredegar Corporation:
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements listed in the index appearing under Item 15(a)(1) present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of Tredegar Corporation and its subsidiaries at December 31, 2007 and December 31, 2006, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2007 in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. Also in our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2007, based on criteria established in Internal Control - Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). The Company’s management is responsible for these financial statements, for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting appearing under Item 9A. Our responsibility is to express opinions on these financial statements, and on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our integrated audits. We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable
39
assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement and whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audits of the financial statements included examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, and evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audits also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinions.
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (i) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (ii) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (iii) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
As discussed in Note 1 to the consolidated financial statements, the Company changed the way in which it accounts for uncertain tax positions effective January 1, 2007, share-based compensation effective January 1, 2006, and defined benefit pension and other postretirement plans effective December 31, 2006.
PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP
Richmond, Virginia
March 4, 2008
40
|
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF INCOME |
|
Tredegar Corporation and Subsidiaries |
| | | | | | | | | | |
Years Ended December 31 | | 2007 | | 2006 | | 2005 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(In Thousands, Except Per-Share Data) | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
Revenues and other: | | | | | | | | | | |
Sales | | $ | 922,583 | | $ | 937,561 | | $ | 808,464 | |
Other income (expense), net | | | 1,782 | | | 1,444 | | | (2,211 | ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | 924,365 | | | 939,005 | | | 806,253 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
Costs and expenses: | | | | | | | | | | |
Cost of goods sold | | | 761,509 | | | 779,376 | | | 672,465 | |
Freight | | | 19,808 | | | 22,602 | | | 20,276 | |
Selling, general and administrative | | | 68,501 | | | 64,082 | | | 61,007 | |
Research and development | | | 8,354 | | | 8,088 | | | 8,982 | |
Amortization of intangibles | | | 149 | | | 149 | | | 299 | |
Interest expense | | | 2,721 | | | 5,520 | | | 4,573 | |
Asset impairments and costs associated with exit and disposal activities | | | 4,027 | | | 4,080 | | | 15,782 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total | | | 865,069 | | | 883,897 | | | 783,384 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Income from continuing operations before income taxes | | | 59,296 | | | 55,108 | | | 22,869 | |
Income taxes | | | 24,366 | | | 19,791 | | | 9,497 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Income from continuing operations | | | 34,930 | | | 35,317 | | | 13,372 | |
Income (loss) from discontinued operations | | | (19,681 | ) | | 2,884 | | | 2,857 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net income | | $ | 15,249 | | $ | 38,201 | | $ | 16,229 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Earnings (loss) per share: | | | | | | | | | | |
Basic: | | | | | | | | | | |
Continuing operations | | $ | .91 | | $ | .92 | | $ | .35 | |
Discontinued operations | | | (.51 | ) | | .07 | | | .07 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net income | | $ | .40 | | $ | .99 | | $ | .42 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Diluted: | | | | | | | | | | |
Continuing operations | | $ | .90 | | $ | .91 | | $ | .35 | |
Discontinued operations | | | (.51 | ) | | .07 | | | .07 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net income | | $ | .39 | | $ | .98 | | $ | .42 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
See accompanying notes to financial statements.
41
|
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS |
|
Tredegar Corporation and Subsidiaries |
| | | | | | | |
December 31 | | 2007 | | 2006 | |
|
(In Thousands, Except Share Data) | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
Assets | | | | | | | |
Current assets: | | | | | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 48,217 | | $ | 40,898 | |
| | | | | | | |
Accounts and notes receivable, net of allowance for doubtful accounts and sales returns of $5,198 in 2007 and $7,388 in 2006 | | | 97,064 | | | 106,955 | |
Income taxes recoverable | | | 323 | | | 10,975 | |
Inventories | | | 48,666 | | | 48,664 | |
Deferred income taxes | | | 9,172 | | | 6,055 | |
Prepaid expenses and other | | | 4,077 | | | 4,428 | |
Current assets of discontinued operation | | | 37,750 | | | 35,275 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total current assets | | | 245,269 | | | 253,250 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Property, plant and equipment, at cost: | | | | | | | |
Land and land improvements | | | 7,278 | | | 8,497 | |
Buildings | | | 81,449 | | | 77,804 | |
Machinery and equipment | | | 548,961 | | | 521,650 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total property, plant and equipment | | | 637,688 | | | 607,951 | |
Less accumulated depreciation | | | 368,605 | | | 320,516 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net property, plant and equipment | | | 269,083 | | | 287,435 | |
Other assets and deferred charges | | | 116,759 | | | 63,712 | |
Goodwill and other intangibles (other intangibles of $464 in 2007 and $581 in 2006) | | | 135,907 | | | 132,237 | |
Noncurrent assets of discontinued operation | | | 17,460 | | | 45,153 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total assets | | $ | 784,478 | | $ | 781,787 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Liabilities and Shareholders’ Equity | | | | | | | |
Current liabilities: | | | | | | | |
Accounts payable | | $ | 67,161 | | $ | 54,020 | |
Accrued expenses | | | 33,676 | | | 38,790 | |
Current portion of long-term debt | | | 540 | | | 678 | |
Current liabilities of discontinued operation | | | 17,152 | | | 18,522 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total current liabilities | | | 118,529 | | | 112,010 | |
Long-term debt | | | 81,516 | | | 61,842 | |
Deferred income taxes | | | 68,625 | | | 65,732 | |
Other noncurrent liabilities | | | 15,662 | | | 14,299 | |
Noncurrent liabilities of discontinued operation | | | 8,818 | | | 11,309 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total liabilities | | | 293,150 | | | 265,192 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Commitments and contingencies (Notes 13 and 16) | | | | | | | |
Shareholders’ equity: | | | | | | | |
Common stock (no par value): | | | | | | | |
Authorized 150,000,000 shares; | | | | | | | |
Issued and outstanding - 34,765,450 shares in 2007 and 39,286,079 in 2006 (including restricted stock) | | | 51,444 | | | 120,508 | |
Common stock held in trust for savings restoration plan (59,222 shares in 2007 and 58,632 in 2006) | | | (1,303 | ) | | (1,291 | ) |
Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss): | | | | | | | |
Foreign currency translation adjustment | | | 40,610 | | | 21,522 | |
Gain (loss) on derivative financial instruments | | | (1,204 | ) | | 654 | |
Pension and other postretirement benefit adjustments | | | (3,767 | ) | | (21,211 | ) |
Retained earnings | | | 405,548 | | | 396,413 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total shareholders’ equity | | | 491,328 | | | 516,595 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total liabilities and shareholders’ equity | | $ | 784,478 | | $ | 781,787 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
See accompanying notes to financial statements.
42
|
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS |
|
Tredegar Corporation and Subsidiaries |
| | | | | | | | | | |
Years Ended December 31 | | 2007 | | 2006 | | 2005 | |
|
(In Thousands) | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
Cash flows from operating activities: | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income | | $ | 15,249 | | $ | 38,201 | | $ | 16,229 | |
Adjustments for noncash items: | | | | | | | | | | |
Depreciation | | | 45,892 | | | 44,132 | | | 38,490 | |
Amortization of intangibles | | | 149 | | | 149 | | | 299 | |
Deferred income taxes | | | (24,241 | ) | | 10,155 | | | 9,217 | |
Accrued pension and postretirement benefits | | | (1,735 | ) | | 3,178 | | | (1,979 | ) |
Stock option-based compensation expense | | | 978 | | | 970 | | | — | |
Loss from write-down of investment | | | 2,095 | | | — | | | 5,000 | |
Gain on sale of assets | | | (2,699 | ) | | (317 | ) | | (4,174 | ) |
Loss on asset impairments and divestitures | | | 32,287 | | | 1,150 | | | 9,378 | |
Changes in assets and liabilities, net of effects of acquisitions and divestitures: | | | | | | | | | | |
Accounts and notes receivable | | | 15,786 | | | 151 | | | (3,361 | ) |
Inventories | | | 4,099 | | | (5,080 | ) | | 2,803 | |
Income taxes recoverable | | | 10,478 | | | 1,991 | | | (12,966 | ) |
Prepaid expenses and other | | | 764 | | | (275 | ) | | 530 | |
Accounts payable and accrued expenses | | | (2,932 | ) | | 11,592 | | | (3,590 | ) |
Other, net | | | (616 | ) | | (1,392 | ) | | (2,173 | ) |
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
Net cash provided by operating activities | | | 95,554 | | | 104,605 | | | 53,703 | |
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
Cash flows from investing activities: | | | | | | | | | | |
Capital expenditures | | | (20,643 | ) | | (40,573 | ) | | (62,543 | ) |
Investments, including Harbinger ($10 million), a drug delivery company ($6.5 million) and real estate ($6.2 million) in 2007 | | | (23,513 | ) | | (542 | ) | | (1,095 | ) |
Proceeds from the sale of assets and property disposals and reimbursements from customers for purchases of equipment | | | 7,871 | | | 475 | | | 8,018 | |
Other, net | | | — | | | — | | | 636 | |
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
|
Net cash used in investing activities | | | (36,285 | ) | | (40,640 | ) | | (54,984 | ) |
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
|
Cash flows from financing activities: | | | | | | | | | | |
Dividends paid | | | (6,126 | ) | | (6,221 | ) | | (6,190 | ) |
Debt principal payments | | | (39,964 | ) | | (54,530 | ) | | (147,846 | ) |
Borrowings | | | 59,500 | | | 4,000 | | | 156,500 | |
Repurchases of Tredegar common stock, net of settlement payable of $3,368 | | | (73,959 | ) | | — | | | — | |
Proceeds from exercise of stock options | | | 6,471 | | | 9,702 | | | 1,130 | |
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
|
Net cash used in financing activities | | | (54,078 | ) | | (47,049 | ) | | 3,594 | |
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
|
Effect of exchange rate changes on cash | | | 2,128 | | | 548 | | | (1,873 | ) |
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
|
Increase in cash and cash equivalents | | | 7,319 | | | 17,464 | | | 440 | |
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period | | | 40,898 | | | 23,434 | | | 22,994 | |
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents at end of period | | $ | 48,217 | | $ | 40,898 | | $ | 23,434 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Supplemental cash flow information: | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest payments (net of amount capitalized) | | $ | 2,712 | | $ | 5,734 | | $ | 4,388 | |
Income tax payments (refunds), net | | | 16,989 | | | 7,828 | | | 14,915 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
See accompanying notes to financial statements.
43
|
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY |
|
Tredegar Corporation and Subsidiaries |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | Accumulated Other
Comprehensive Income (Loss) | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | |
| | | | | | | | | | Unrealized
Gain on
Available-
for-Sale
Securities | | | | Gain
(Loss) on
Derivative
Financial
Instruments | | Pension &
Other Post-
retirement
Benefit
Adjust. | | | |
| | | | | | Trust for
Savings
Restora-
tion Plan | | Unearned
Restricted
Stock
Compensation | | | Foreign
Currency
Trans-
lation | | | | Total
Share-
holders’
Equity | |
| | Common Stock | | | | | | | | | | |
| |
| | Retained
Earnings | | | | | | | | |
| | Shares | | Amount | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(In Thousands, Except Share
and Per-Share Data) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance December 31, 2004 | | 38,597,522 | | $ | 109,450 | | $ | 354,378 | | $ | (1,274 | ) | | $ | (1,402 | ) | | | $ | — | | | $ | 19,562 | | $ | 884 | | $ | (1,156 | ) | $ | 480,442 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Comprehensive income (loss): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income | | — | | | — | | | 16,229 | | | — | | | | — | | | | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 16,229 | |
Other comprehensive income (loss): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Available-for-sale securities adjustment, net of reclassification adjustment (net of tax of $13) | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | — | | | | | 23 | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 23 | |
Foreign currency translation adjustment (net of tax of $2,933) | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | — | | | | | — | | | | (5,448 | ) | | — | | | — | | | (5,448 | ) |
Derivative financial instruments adjustment (net of tax of $60) | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | — | | | | | — | | | | — | | | (108 | ) | | — | | | (108 | ) |
Minimum pension liability adjustment (net of tax of $630) | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | — | | | | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | (1,278 | ) | | (1,278 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
Comprehensive income | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 9,418 | |
Cash dividends declared
($.16 per share) | | — | | | — | | | (6,190 | ) | | — | | | | — | | | | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (6,190 | ) |
Restricted stock grant, net of forfeitures and vested shares | | (11,000 | ) | | (49 | ) | | — | | | — | | | | 49 | | | | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
Restricted stock amortization | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | 387 | | | | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 387 | |
Issued upon exercise of stock options (including related income tax benefits of $175) & other | | 150,494 | | | 1,305 | | | — | | | — | | | | — | | | | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 1,305 | |
Tredegar common stock purchased by trust for savings restoration plan | | — | | | — | | | 10 | | | (10 | ) | | | — | | | | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance December 31, 2005 | | 38,737,016 | | | 110,706 | | | 364,427 | | | (1,284 | ) | | | (966 | ) | | | | 23 | | | | 14,114 | | | 776 | | | (2,434 | ) | | 485,362 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Comprehensive income (loss): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income | | — | | | — | | | 38,201 | | | — | | | | — | | | | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 38,201 | |
Other comprehensive income (loss): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Available-for-sale securities adjustment, net of reclassification adjustment (net of tax of $13) | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | — | | | | | (23 | ) | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (23 | ) |
Foreign currency translation adjustment (net of tax of $3,921) | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | — | | | | | — | | | | 7,408 | | | — | | | — | | | 7,408 | |
Derivative financial instruments adjustment (net of tax of $60) | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | — | | | | | — | | | | — | | | (122 | ) | | — | | | (122 | ) |
Minimum pension liability adjustment (net of tax of $422) | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | — | | | | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | 821 | | | 821 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
Comprehensive income | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 46,285 | |
Cumulative adjustment for the adoption of SFAS No. 158 relating to pension and other postretirement benefits (net of tax of $11,354) | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | — | | | | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | (19,598 | ) | | (19,598 | ) |
Cash dividends declared
($.16 per share) | | — | | | — | | | (6,221 | ) | | — | | | | — | | | | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (6,221 | ) |
Stock-based compensation expense | | (25,500 | ) | | 1,066 | | | — | | | — | | | | — | | | | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 1,066 | |
Restricted stock amortization | | — | | | (966 | ) | | — | | | — | | | | 966 | | | | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
Issued upon exercise of stock options (including related income tax benefits of $678) & other | | 574,563 | | | 9,702 | | | — | | | — | | | | — | | | | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 9,702 | |
Tredegar common stock purchased by trust for savings restoration plan | | — | | | — | | | 6 | | | (7 | ) | | | — | | | | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (1 | ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance December 31, 2006 | | 39,286,079 | | | 120,508 | | | 396,413 | | | (1,291 | ) | | | — | | | | | — | | | | 21,522 | | | 654 | | | (21,211 | ) | | 516,595 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Comprehensive income (loss): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net income | | — | | | — | | | 15,249 | | | — | | | | — | | | | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 15,249 | |
Other comprehensive income (loss): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Foreign currency translation adjustment (net of tax of $10,428) | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | — | | | | | — | | | | 19,088 | | | — | | | — | | | 19,088 | |
Derivative financial instruments adjustment (net of tax of $1,166) | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | — | | | | | — | | | | — | | | (1,858 | ) | | — | | | (1,858 | ) |
Net actuarial gains or losses and prior service costs (net of tax of $10,209) | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | — | | | | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | 16,218 | | | 16,218 | |
Amortization of net actuarial gains or losses and prior service costs (net of tax of $702) | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | | — | | | | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | 1,226 | | | 1,226 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
Comprehensive income | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 49,923 | |
Cash dividends declared
($.16 per share) | | — | | | — | | | (6,126 | ) | | — | | | | — | | | | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (6,126 | ) |
Stock-based compensation expense | | (10,000 | ) | | 1,654 | | | — | | | — | | | | — | | | | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 1,654 | |
Issued upon exercise of stock options (including related income tax benefits of $491) & other | | 322,871 | | | 6,609 | | | — | | | — | | | | — | | | | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | 6,609 | |
Repurchases of Tredegar common stock | | (4,833,500 | ) | | (77,327 | ) | | — | | | — | | | | — | | | | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (77,327 | ) |
Tredegar common stock purchased by trust for savings restoration plan | | — | | | — | | | 12 | | | (12 | ) | | | — | | | | | — | | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance December 31, 2007 | | 34,765,450 | | $ | 51,444 | | $ | 405,548 | | $ | (1,303 | ) | | $ | — | | | | $ | — | | | $ | 40,610 | | $ | (1,204 | ) | $ | (3,767 | ) | $ | 491,328 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
See accompanying notes to financial statements.
44
|
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS |
|
Tredegar Corporation and Subsidiaries
(In thousands, except Tredegar share and per-share amounts and unless otherwise stated) |
|
1 SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES |
|
Organization and Nature of Operations. Tredegar Corporation and subsidiaries (collectively “Tredegar,” “we,” “us” or “our”) are engaged in the manufacture of plastic films and aluminum extrusions. See Note 15 regarding restructurings and Note 17 regarding discontinued operations.
Basis of Presentation. The consolidated financial statements include the accounts and operations of Tredegar and all of its majority-owned subsidiaries. Intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated. Prior periods have been reclassified to conform to the current period presentation of discontinued operations.
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles requires us to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of revenues, expenses, assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Foreign Currency Translation. The financial statements of foreign subsidiaries, where the local currency is the functional currency, are translated into U.S. Dollars using exchange rates in effect at the period end for assets and liabilities and average exchange rates during each reporting period for results of operations. Adjustments resulting from the translation of these financial statements are reflected as a separate component of shareholders’ equity. We have no foreign subsidiaries where the U.S. Dollar is the functional currency.
Transaction and remeasurement gains or losses included in income were not material in 2007, 2006 and 2005. These amounts do not include the effects between reporting periods that exchange rate changes have on income of our foreign locations that result from translation into U.S. Dollars.
Cash and Cash Equivalents. Cash and cash equivalents consist of cash on hand in excess of daily operating requirements and highly liquid investments with original maturities of three months or less. At December 31, 2007 and 2006, Tredegar had cash and cash equivalents of $48,217 and $40,898, respectively, including funds held in foreign locations of $24,559 and $19,118, respectively.
Our policy permits investment of excess cash in marketable securities that have the highest credit ratings and maturities of less than one year. The primary objectives of the policy are safety of principal and liquidity.
Accounts and Notes Receivable. Accounts receivable are stated at the amount invoiced to customers less allowances for doubtful accounts and sales returns. Accounts receivable are non-interest bearing and arise from the sale of product to customers under typical industry trade terms. Notes receivable are not significant. Past due amounts are determined based on established terms and charged-off when deemed uncollectible. The allowance for doubtful accounts is determined based on our assessment of probable losses taking into account past due amounts, customer credit profile, historical experience and current economic conditions. Other receivables include insurance recoveries due within one year and value-added taxes related to certain foreign subsidiaries.
Inventories. Inventories are stated at the lower of cost or market, with cost determined on the last-in, first-out (“LIFO”) basis, the weighted average cost or the first-in, first-out basis. Cost elements included in work-in-process and finished goods inventories are raw materials, direct labor and manufacturing overhead.
Property, Plant and Equipment. Accounts include costs of assets constructed or purchased, related delivery and installation costs and interest incurred on significant capital projects during their construction periods. Expenditures for renewals and betterments also are capitalized, but expenditures for repairs and maintenance are expensed as incurred. The cost and accumulated depreciation applicable to assets retired or sold are removed from the respective accounts, and gains or losses thereon are included in income.
45
On January 1, 2007, we adopted Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) Staff Position (“FSP”) No. AUG AIR-1, Accounting for Planned Major Maintenance Activities, which had no impact on our results of operations or financial condition reported in prior periods. The FSP eliminates the accrual method of accounting for major maintenance activities, but continues to permit the use of the direct expensing, built-in overhaul and deferral methods.
Property, plant and equipment include capitalized interest of $577 in 2007, $885 in 2006 and $1,179 in 2005.
Depreciation is computed primarily by the straight-line method based on the estimated useful lives of the assets, which range from 15 to 25 years for buildings and land improvements and 3 to 11 years for machinery and equipment. The average depreciation period for machinery and equipment is approximately 10 years in Film Products and for the continuing operations of Aluminum Extrusions.
Investments in Private Entities with Less Than or Equal to 50% Voting Ownership Interest. We account for our investments in private entities where our voting ownership is less than or equal to 50% based on the facts and circumstances surrounding the investment at the time the investment is made. We are required to account for investments under the consolidation method in situations where we are the primary beneficiary of a variable interest entity (we have no investments that meet this condition). The primary beneficiary is the party in a variable interest entity that will absorb a majority of the entity’s expected losses, receive a majority of the entity’s expected residual returns, or both. If we are not deemed the primary beneficiary in an investment in a private entity then we select either: (i) the fair value method or (ii) either the (a) the cost method if we do not have significant influence over operating and financial policies of the company or (b) the equity method if we do have significant influence.
FASB Statement No. 157, Fair Value Measurements, requires disclosure of the level within the fair value hierarchy in which fair value measurements in their entirety fall, segregating fair value measurements using quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities (Level 1), significant other observable inputs (Level 2), and significant unobservable inputs (Level 3).
Goodwill and Other Intangibles. The excess of the purchase price over the fair value of identifiable net assets of acquired companies is allocated to goodwill. We assess goodwill for impairment when events or circumstances indicate the carrying value may not be recoverable, or, at a minimum, on an annual basis as of December 1 of each year. Impairment reviews may result in recognition of losses. We have made determinations as to what our reporting units are and what amounts of goodwill, intangible assets, other assets and liabilities should be allocated to those reporting units.
The components of goodwill and other intangibles at December 31, 2007 and 2006, and related amortization periods for continuing operations are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
December 31 | | 2007 | | 2006 | | | Amortization Periods | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Carrying value of goodwill: | | | | | | | | | | |
Film Products | | $ | 104,507 | | $ | 103,562 | | | Not amortized | |
Aluminum Extrusions | | | 30,935 | | | 28,094 | | | Not amortized | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total carrying value of goodwill | | | 135,442 | | | 131,656 | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Carrying value of other intangibles: | | | | | | | | | | |
Film Products (cost basis of $1,172 in 2007 and 2006) | | | 465 | | | 581 | | | Not more than 17 yrs. | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total carrying value of other intangibles | | | 465 | | | 581 | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total carrying value of goodwill and other intangibles | | $ | 135,907 | | $ | 132,237 | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Excluded from the table above is goodwill for the Aluminum Extrusions reporting unit of $6,459 which was allocated to discontinued aluminum extrusions operations in Canada. This goodwill was allocated using the estimated fair value of the aluminum extrusions business in Canada (the after-tax cash flow expected from disposal of approximately $30,000 when it was classified as held for sale at the end of December 2007), and the estimated fair value of the aluminum extrusions business in the U.S. retained. The fair value of the aluminum extrusions business in the U.S. was estimated at approximately $145,000 using comparable enterprise value-to-EBITDA multiples as of December 31, 2007. See Note 17 for more information on discontinued operations.
46
A reconciliation of the beginning and ending balances of goodwill and other intangibles for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2007 is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | 2007 | | 2006 | | 2005 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Goodwill and other intangibles: | | | | | | | | | | |
Net carrying value, beginning of year | | $ | 132,237 | | $ | 131,529 | | $ | 136,524 | |
Amortization | | | (149 | ) | | (149 | ) | | (299 | ) |
Decrease due to sale of AFBS (formerly Therics) assets | | | — | | | — | | | (4,329 | ) |
Increase (decrease) due to foreign currency translation and other | | | 3,819 | | | 857 | | | (367 | ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total carrying value of goodwill and other intangibles | | $ | 135,907 | | $ | 132,237 | | $ | 131,529 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets. We review long-lived assets for possible impairment when events indicate that impairment may exist. For assets to be held and used in operations, if events indicate that an asset may be impaired, we estimate the future unlevered pre-tax cash flows expected to result from the use of the asset and its eventual disposition. Assets are grouped for this purpose at the lowest level for which there are identifiable and independent cash flows. If the sum of these undiscounted pre-tax cash flows is less than the carrying amount of the asset, an impairment loss is recognized. Measurement of the impairment loss is based on the estimated fair value of the asset, generally determined on a discounted after-tax cash flow basis.
Assets to be disposed of are reported at the lower of their carrying amount or estimated fair value less cost to sell, with an impairment loss recognized for any writedown required.
Pension Costs and Postretirement Benefit Costs Other than Pensions. Pension costs and postretirement benefit costs other than pensions are accrued over the period employees provide service to the company. Our policy is to fund our pension plans at amounts not less than the minimum requirements of the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974 and to fund postretirement benefits other than pensions when claims are incurred. In September 2006, the FASB issued Statement of Financial Accounting Standards (“SFAS”) No. 158, Employers’ Accounting for Defined Benefit Pension and Other Postretirement Plans, an amendment of FASB Statements No 87, 88, 106 and 132(R), effective for public companies for fiscal years ending after December 15, 2006. Accordingly, we were required to recognize the funded status of our pension and other postretirement plans in our December 31, 2006 financial statements, which resulted in a reduction of prepaid pension cost of $27,651, an increase in related liabilities of $3,301, a decrease in noncurrent deferred income liabilities of $11,354 and a decrease in shareholders’ equity of $19,598. See Note 11 for more information.
Postemployment Benefits. We periodically provide certain postemployment benefits purely on a discretionary basis. Related costs for these programs are accrued when it is probable that benefits will be paid and amounts can be reasonably estimated. All other postemployment benefits are either accrued under current benefit plans or are not material to our financial position or results of operations.
Revenue Recognition. Revenue from the sale of products, which is shown net of estimated sales returns and allowances, is recognized when title has passed to the customer, the price of the product is fixed and determinable, and collectibility is reasonably assured. Amounts billed to customers related to freight have been classified as sales in the accompanying consolidated statements of income. The cost of freight has been classified as a separate line in the accompanying consolidated statements of income. Taxes assessed by a governmental authority that are both imposed on and concurrent with a specific revenue-producing transaction between Tredegar and its customers (such as value-added taxes) are accounted for on a net basis and therefore excluded from revenues.
Research & Development (“R&D”) Costs. R&D costs are expensed as incurred and include primarily salaries, wages, employee benefits, equipment depreciation, facility costs and the cost of materials consumed relating to R&D efforts. R&D costs include a reasonable allocation of indirect costs.
47
Income Taxes. Income taxes are recognized during the period in which transactions enter into the determination of income for financial reporting purposes, with deferred income taxes being provided at enacted statutory tax rates on the differences between the financial reporting and tax bases of assets and liabilities (see Note 14). We accrue U.S. federal income taxes on unremitted earnings of our foreign subsidiaries.
On January 1, 2007, we adopted a new accounting standard for uncertain tax positions (FASB Interpretation No. 48, Accounting for Uncertainty in Income Taxes), which had no impact on our results of operations or financial condition reported in prior periods. Under the new standard, in order to report the benefit of a tax position in our financial statements, we must determine that it is more likely than not that the position will be sustained, based on the technical merits of the position, if the taxing authority examines the position and the dispute is litigated. The determination is made on the basis of all the facts, circumstances and information available as of the reporting date.
Earnings Per Share. Basic earnings per share is computed using the weighted average number of shares of common stock outstanding. Diluted earnings per share is computed using the weighted average common and potentially dilutive common equivalent shares outstanding, determined as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | 2007 | | 2006 | | 2005 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted average shares outstanding used to compute basic earnings per share | | | 38,532,036 | | | 38,670,757 | | | 38,471,348 | |
Incremental shares attributable to stock options and restricted stock | | | 156,467 | | | 260,305 | | | 125,356 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shares used to compute diluted earnings per share | | | 38,688,503 | | | 38,931,062 | | | 38,596,704 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Incremental shares attributable to stock options and restricted stock are computed using the average market price during the related period. During 2007, 2006 and 2005, 184,960, 1,128,393 and 2,024,690 of average out-of-the-money options to purchase shares were excluded from the calculation of incremental shares attributable to stock options and restricted stock.
Stock-Based Employee Compensation Plans. Effective January 1, 2006, we adopted SFAS No. 123(R), Share-Based Payment (“SFAS 123(R)”). SFAS 123(R) requires us to record compensation expense for all share-based awards. Because we used the modified prospective method in adopting SFAS 123(R), prior periods have not been restated. In addition, the cumulative adjustment (estimated forfeitures) relating to the adoption of SFAS 123(R) in the first quarter of 2006 of $96,000 has not been separately shown in the income statement due to immateriality.
For periods presented prior to 2006, we applied Accounting Principles Board (“APB”) Opinion No. 25, Accounting for Stock Issued to Employees, and related interpretations and provided the required pro forma disclosures of SFAS No. 123, Accounting for Stock-Based Compensation (“SFAS 123”). Stock options, stock appreciation rights (“SARs”) and restricted stock grants are accounted for using the intrinsic value method under APB Opinion No. 25 and related interpretations whereby:
| |
• | No compensation cost is recognized for fixed stock option or restricted stock grants unless the quoted market price of the stock at the measurement date (ordinarily the date of grant or award) is in excess of the amount the employee is required to pay; and |
| |
• | Compensation cost for SARs is recognized and adjusted up through the date of exercise or forfeiture based on the estimated number of SARs expected to be exercised multiplied by the difference between the market price of our stock and the amount the employee is required to pay (there were no SARs outstanding at December 31, 2005). |
48
Had compensation cost for stock option grants been determined in 2005 based on the fair value at the grant dates, our income and diluted earnings per share from continuing operations would have been reduced to the pro forma amounts indicated below:
| | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
| | 2005 | |
|
|
|
|
Income from continuing operations: | | | | |
As reported | | $ | 13,372 | |
Pro forma for stock option-based employee compensation cost, net of tax, based on the fair value method | | | (1,073 | ) |
|
|
|
|
|
Pro forma income from continuing operations | | $ | 12,299 | |
|
|
|
|
|
Basic earnings per share from continuing operations: | | | | |
As reported | | $ | .35 | |
Pro forma | | | .32 | |
|
|
|
|
|
Diluted earnings per share from continuing operations: | | | | |
As reported | | $ | .35 | |
Pro forma | | | .32 | |
|
|
|
|
|
Stock option-based compensation expense included in determining net income under SFAS 123(R) was $978 ($629 after taxes or 2 cents per share) in 2007 and $970 ($676 after taxes or 2 cents per share) in 2006. Compensation cost related to restricted and other stock-based awards included in determining net income from continuing operations was $713 in 2007, $188 in 2006 and $386 in 2005.
The fair value of each option was estimated as of the grant date using the Black-Scholes options-pricing model. The assumptions used in this model for valuing Tredegar stock options granted in 2007 and 2006 are as follows (there were no Tredegar stock options granted in 2005):
| | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | 2007 | | 2006 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dividend yield | | | 1.1 | % | | 1.1 | % |
Weighted average volatility percentage | | | 33.1 | % | | 38.3 | % |
Weighted average risk-free interest rate | | | 3.3 | % | | 4.7 | % |
Holding period (years): | | | | | | | |
Officers | | | n/a | | | 6.0 | |
Management | | | 5.0 | | | 5.0 | |
Other employees | | | n/a | | | n/a | |
Weighted average excercise price at date of grant (also weighted average market price at date of grant): | | | | | | | |
Officers | | | n/a | | $ | 15.22 | |
Management | | $ | 14.40 | | | 15.32 | |
Other employees | | | n/a | | | n/a | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The dividend yield is the dividend yield on our common stock at the date of grant, which we believe is a reasonable estimate of the expected yield during the holding period. We calculate expected volatility based on the historical volatility of our common stock using a sequential period of historical data equal to the expected holding period of the option. We have no reason to believe that future volatility is likely to differ from the past. The assumed risk-free interest rate is based on observed interest rates (zero coupon U.S. Treasury debt securities) appropriate for the expected holding period. The expected holding period and forfeiture assumptions are based on historical experience. Estimated forfeiture assumptions are reviewed through the vesting period. Adjustments are made if actual forfeitures differ from previous estimates. The cumulative effect of a change in estimated forfeitures is recognized in the period of the change.
49
Tredegar stock options granted during 2007 and 2006 (there were no Tredegar stock options granted in 2005), and related estimated fair value at the date of grant, are as follows:
| | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | 2007 | | 2006 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Stock options granted (number of shares): | | | | | |
Officers | | n/a | | 107,500 | |
Management | | 4,000 | | 342,300 | |
Other employees | | n/a | | n/a | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total | | 4,000 | | 449,800 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Estimated weighted average fair value of options per share at date of grant: | | | | | |
Officers | | n/a | | $ 6.26 | |
Management | | $ 4.91 | | 5.69 | |
Other employees | | n/a | | n/a | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total estimated fair value of stock options granted (in thousands) | | $ 20 | | $2,620 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Additional disclosure of Tredegar stock options is included in Note 10.
Financial Instruments. We use derivative financial instruments for the purpose of hedging aluminum price volatility and interest rate and currency exchange rate exposures that exist as part of ongoing business operations. Our derivative financial instruments are designated as and qualify as cash flow hedges and are recognized in the balance sheet at fair value. A change in the fair value of the derivative that is highly effective as and that is designated and qualifies as a cash flow hedge is recorded in other comprehensive income. Gains and losses reported in other comprehensive income are reclassified to earnings in the periods in which earnings are affected by the variability of cash flows of the hedged transaction. Such gains and losses are reported on the same line as the underlying hedged item. Any hedge ineffectiveness (which represents the amount by which the changes in the fair value of the derivative exceed the variability in the cash flows of the forecasted transaction) is recorded in current period earnings. The amount of gains and losses recognized for hedge ineffectiveness was immaterial in 2007, 2006 and 2005.
Our policy requires that we formally document all relationships between hedging instruments and hedged items, as well as our risk management objective and strategy for undertaking various hedge transactions. We also formally assess (both at the hedge’s inception and on an ongoing basis) whether the derivatives that are used in hedging transactions have been highly effective in offsetting changes in the fair value or cash flows of hedged items and whether those derivatives may be expected to remain highly effective in future periods. When it is determined that a derivative is not (or has ceased to be) highly effective as a hedge, we discontinue hedge accounting prospectively.
As a policy, we do not engage in speculative or leveraged transactions, nor do we hold or issue financial instruments for trading purposes.
The cash flows related to financial instruments are classified in the statements of cash flows in a manner consistent with those of the transactions being hedged.
Comprehensive Income. Comprehensive income, which is included in the consolidated statement of shareholders’ equity, is defined as net income and other comprehensive income. Other comprehensive income includes changes in unrealized gains and losses on available-for-sale securities, foreign currency translation adjustments, unrealized gains and losses on derivative financial instruments and minimum pension liability adjustments, all recorded net of deferred income taxes directly in shareholders’ equity.
50
The available-for-sale securities adjustment included in the consolidated statement of shareholders’ equity is comprised of the following components:
| | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | 2006 | | | 2005 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Available-for-sale securities adjustment: | | | | | | | |
Unrealized net holding gains (losses)
arising during the period | | $ | 20 | | $ | 36 | |
Income taxes | | | (7 | ) | | (13 | ) |
Reclassification adjustment for net
losses (gains) realized in income | | | (56 | ) | | — | |
Income taxes | | | 20 | | | — | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Available-for-sale securities adjustment | | $ | (23 | ) | $ | 23 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Recently Issued Accounting Standards. In December 2007, the FASB issued SFAS No. 141(R), Business Combinations, and SFAS No. 160, Noncontrolling Interests in Consolidated Financial Statements. SFAS No. 141 is applied prospectively to business combinations for which the acquisition date is on or after the beginning of the first annual reporting period beginning on or after December 15, 2008. The new accounting standard for noncontrolling interests (sometimes referred to as minority interests) applies to all fiscal years and interim periods beginning on or after December 15, 2008. Early application is prohibited for both standards. We currently do not have noncontrolling or minority interests in our consolidated financial statements. We will apply the new standards when required and applicable.
During the third quarter of 2007, we invested $6,500 in a privately held drug delivery company representing ownership on a fully diluted basis of approximately 23%. The company is developing and commercializing state of the art drug delivery systems designed to improve patient compliance and outcomes. The investment is accounted for under the fair value method. We elected the fair value option over the equity method of accounting since our investment objectives are similar to those of venture capitalists, which typically do not have controlling financial interests (venture capital funds use the fair value method to account for their investment portfolios). At December 31, 2007, the fair value of our investment (also the carrying value included in “Other assets and deferred charges” in our balance sheet) equaled the amount invested.
On the date of our investment (August 31, 2007), we believe that the amount we paid for our ownership interest and liquidation preferences was based on Level 2 inputs, including investments by other investors. Subsequent to August 31, 2007, and until the next round of financing, we believe fair value estimates drop to Level 3 inputs since there is no secondary market for our ownership interest. In addition, the company currently has no product sales. Accordingly, after the latest financing and until the next round of financing or other significant financial transaction, value estimates will primarily be based on assumptions relating to meeting product development and commercialization milestones, cash flow projections (projections of sales, costs, expenses, capital expenditures and working capital investment) and discounting of these factors for the high degree of risk. As a result, an increase in our estimate of the fair value of our ownership interest is unlikely unless a significant new round of financing, merger or initial public offering indicates a higher value. However, if the company does not meet its development and commercialization milestones and there are indications that the amount or timing of its projected cash flows or related risks are unfavorable versus plans as of August 31, 2007, or a new round of financing or other significant financial transaction indicates a lower value, then our estimate of the fair value of our ownership interest in the company is likely to decline.
Had we not elected to account for our investment under the fair value method, we would have been required to use the equity method of accounting.
51
Our valuation of intangibles indicates that there were no in-process research & development costs that would have been written off in applying the purchase accounting and the equity method at August 31, 2007. We would not have been allocated any profits or losses for the year ended December 31, 2007 based on the formulas contained in the company’s operating agreement. The condensed balance sheets for the drug delivery company at August 31, 2007 (shown on a pro forma basis for a second closing of its recent financing in September 2007) and December 31, 2007 and related condensed statements of income for the year and four months ended December 31, 2007, adjusted on a purchase accounting basis to the valuation implied by the latest round of financing in August-September 2007, are provided below:
| | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(Unaudited) | | Pro Forma 8/31/07 | | 12/31/07 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Assets | | | | | | | |
Cash & ownership subscriptions
receivables | | $ | 8,557 | | $ | 6,781 | |
Other tangible assets | | | 278 | | | 1,253 | |
Identifiable intangibles (15 year life) | | | 3,967 | | | 3,901 | |
Goodwill | | | 10,194 | | | 10,194 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total assets | | $ | 22,996 | | $ | 22,129 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | Pro Forma 8/31/07 | | 12/31/07 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Liabilities & Members’ Equity | | | | | | | |
Liabilities | | $ | 1,503 | | $ | 1,494 | |
Contributed capital | | | 12,233 | | | 12,354 | |
Net equity appreciation implied from
purchase accounting adjustments | | | 12,805 | | | 12,805 | |
Accumulated losses | | | (3,545 | ) | | (4,524 | ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total liabilities & members’ equity | | $ | 22,996 | | $ | 22,129 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | |
| | | 2007 | | Sept.-Dec. ‘07 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Revenues & Expenses | | | | | | | |
Revenues | | $ | — | | $ | — | |
Costs & expenses | | | 2,445 | | | 800 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss | | $ | (2,445 | ) | $ | (800 | ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
On April 2, 2007, we invested $10,000 in Harbinger Capital Partners Special Situations Fund, L.P. (“Harbinger”), a fund that seeks to achieve superior absolute returns by participating primarily in medium to long-term investments involving distressed/high yield debt securities, special situation equities and private loans and notes. The fund is a highly speculative investment subject to a two-year lock-up and additional limitations on withdrawal. There is no secondary market for interests in the fund. Our investment in Harbinger, which represents less than 2% of Harbinger’s total partnership capital, is accounted for under the cost method. At December 31, 2007, Harbinger reported our capital account value at $23,000 reflecting $13,000 of unrealized appreciation versus the carrying value in our balance sheet of $10,000 (included in “Other assets and deferred charges”).
During 2007, we invested approximately $6,200 in real estate. At December 31, 2007, the carrying value in our balance sheet of investments in this real estate (included in “Other assets and deferred charges”) equaled the amount invested.
In August of 2004, we invested $5,000 in Novalux, Inc., a developer of laser technology for potential use in a variety of applications. We made additional investments in Novalux based on its prospects at the time of $1,095 in October 2005, $400 in May 2006, $142 in September 2006, $458 in July 2007 and $404 in November 2007. We wrote down our investment in Novalux and recognized losses of $5,000 in the December 2005 and $2,095 in September 2007 based on anticipated delays in bringing the company’s technology to market and liquidity issues. Our carrying value in Novalux of $404 and $1,637 at December 31, 2007 and 2006, respectively, is included in “Other assets and deferred charges” in the consolidated balance sheet. Novalux assets were sold in January 2008 in exchange for certain unrestricted and restricted common shares of a public company in Australia. We expect to recover our remaining carrying value of $404 upon the liquidation by Novalux of its remaining assets, which primarily consists of the common shares referred to above.
52
Information by business segment and geographic area for the last three years is provided below. There are no accounting transactions between segments and no allocations to segments. Net sales (sales less freight) and operating profit from ongoing operations are the measures of sales and operating profit used by the chief operating decision maker for purposes of assessing performance. Film Products’ net sales to The Procter & Gamble Company (“P&G”) totaled $258,602 in 2007, $255,414 in 2006 and $236,554 in 2005. These amounts include plastic film sold to others that convert the film into materials used with products manufactured by P&G.
| | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
| | Net Sales | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | | | 2005 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Film Products | | $ | 530,972 | | $ | 511,169 | | $ | 460,277 | |
Aluminum Extrusions | | | 371,803 | | | 403,790 | | | 327,659 | |
AFBS (formerly Therics) | | | — | | | — | | | 252 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total net sales | | | 902,775 | | | 914,959 | | | 788,188 | |
Add back freight | | | 19,808 | | | 22,602 | | | 20,276 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sales as shown in consolidated statements of income | | $ | 922,583 | | $ | 937,561 | | $ | 808,464 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | Operating Profit | |
| | | 2007 | | | 2006 | | | 2005 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Film Products: | | | | | | | | | | |
Ongoing operations | | $ | 59,423 | | $ | 57,645 | | $ | 44,946 | |
Plant shutdowns, asset impairments and restructurings, net of gains on the sale of assets (a) | | | (649 | ) | | 221 | | | (3,955 | ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aluminum Extrusions: | | | | | | | | | | |
Ongoing operations | | | 16,516 | | | 18,302 | | | 17,084 | |
Plant shutdowns, asset impairments and restructurings, net of gains on the sale of assets (a) | | | (634 | ) | | (1,434 | ) | | (993 | ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AFBS (formerly Therics): | | | | | | | | | | |
Ongoing operations | | | — | | | — | | | (3,467 | ) |
Loss on investment in Therics, LLC | | | — | | | (25 | ) | | (145 | ) |
Restructurings (a) | | | (2,786 | ) | | (637 | ) | | (10,318 | ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total | | | 71,870 | | | 74,072 | | | 43,152 | |
Interest income | | | 1,212 | | | 1,240 | | | 586 | |
Interest expense | | | 2,721 | | | 5,520 | | | 4,573 | |
Gain on sale of corporate assets (a) | | | 2,699 | | | 56 | | | 61 | |
Loss from write-down of investment in Novalux (a) | | | 2,095 | | | — | | | 5,000 | |
Stock option-based compensation expense | | | 978 | | | 970 | | | — | |
Corporate expenses, net (a) | | | 10,691 | | | 13,770 | | | 11,357 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Income from continuing operations before income taxes | | | 59,296 | | | 55,108 | | | 22,869 | |
Income taxes (a) | | | 24,366 | | | 19,791 | | | 9,497 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Income from continuing operations | | | 34,930 | | | 35,317 | | | 13,372 | |
Income (loss) from discontinued operations (a) | | | (19,681 | ) | | 2,884 | | | 2,857 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net income | | $ | 15,249 | | $ | 38,201 | | $ | 16,229 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
(a) | See Notes 2 and 15 for more information on losses associated with plant shutdowns, asset impairments and restructurings, unusual items, gains from sale of assets, investment write-down and other items, and Note 17 for more information on discontinued operations. |
| |
(b) | The difference between total consolidated sales as reported in the consolidated statements of income and segment and geographic net sales reported in this note is freight of $19,808 in 2007, $22,602 in 2006, and $20,276 in 2005. |
| |
(c) | Information on exports and foreign operations are provided on the next page. Cash and cash equivalents includes funds held in foreign locations of $24,559, $19,118 and $14,890 at December 31, 2007, 2006, and 2005, respectively. Export sales relate almost entirely to Film Products. Foreign operations in The Netherlands, Hungary, China, Italy and Brazil also relate to Film Products. Sales from our locations in The Netherlands, Hungary and Italy are primarily to customers located in Europe. Sales from our locations in China (Guangzhou and Shanghai) are primarily to customers located in China, but also include other customers in Asia. |
53
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | Identifiable Assets | | | | | | | | | | |
December 31 | | 2007 | | 2006 | | 2005 | | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
Film Products | | $ | 488,035 | | $ | 498,961 | | $ | 479,286 | | | | | | | | | | |
Aluminum Extrusions | | | 115,223 | | | 128,967 | | | 130,448 | | | | | | | | | | |
AFBS (formerly Therics) | | | 2,866 | | | 2,420 | | | 2,759 | | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
Subtotal | | | 606,124 | | | 630,348 | | | 612,493 | | | | | | | | | | |
General corporate | | | 74,927 | | | 30,113 | | | 61,905 | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents (c) | | | 48,217 | | | 40,898 | | | 23,434 | | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
Continuing operations | | | 729,268 | | | 701,359 | | | 697,832 | | | | | | | | | | |
Discontinued aluminum extrusions business in Canada (a) | | | 55,210 | | | 80,428 | | | 83,926 | | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
Total | | $ | 784,478 | | $ | 781,787 | | $ | 781,758 | | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
| |
| | Depreciation and Amortization | | Capital Expenditures | |
| | 2007 | | 2006 | | 2005 | | 2007 | | 2006 | | 2005 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Film Products | | $ | 34,092 | | $ | 31,847 | | $ | 26,673 | | $ | 15,304 | | $ | 33,168 | | $ | 50,466 | |
Aluminum Extrusions | | | 8,472 | | | 8,378 | | | 7,996 | | | 4,391 | | | 6,609 | | | 5,750 | |
AFBS (formerly Therics) | | | — | | | — | | | 437 | | | — | | | — | | | 36 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Subtotal | | | 42,564 | | | 40,225 | | | 35,106 | | | 19,695 | | | 39,777 | | | 56,252 | |
General corporate | | | 91 | | | 111 | | | 195 | | | 6 | | | 24 | | | 73 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Continuing operations | | | 42,655 | | | 40,336 | | | 35,301 | | | 19,701 | | | 39,801 | | | 56,325 | |
Discontinued aluminum extrusions business in Canada (a) | | | 3,386 | | | 3,945 | | | 3,488 | | | 942 | | | 772 | | | 6,218 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Total | | $ | 46,041 | | $ | 44,281 | | $ | 38,789 | | $ | 20,643 | | $ | 40,573 | | $ | 62,543 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Net Sales by Geographic Area (c) | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2007 | | 2006 | | 2005 | | | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
United States | | $ | 577,824 | | $ | 606,411 | | $ | 495,900 | | | | | | | | | | | |
Exports from the United States to: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Canada | | | 46,243 | | | 42,669 | | | 44,870 | | | | | | | | | | | |
Latin America | | | 1,188 | | | 4,364 | | | 9,428 | | | | | | | | | | | |
Europe | | | 9,856 | | | 8,944 | | | 8,311 | | | | | | | | | | | |
Asia | | | 31,432 | | | 50,096 | | | 40,476 | | | | | | | | | | | |
Foreign operations: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
The Netherlands | | | 104,379 | | | 91,476 | | | 83,649 | | | | | | | | | | | |
Hungary | | | 35,286 | | | 29,152 | | | 33,573 | | | | | | | | | | | |
China | | | 57,252 | | | 42,460 | | | 36,823 | | | | | | | | | | | |
Italy | | | 13,359 | | | 14,323 | | | 15,866 | | | | | | | | | | | |
Brazil | | | 25,956 | | | 25,064 | | | 19,292 | | | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Total (b) | | $ | 902,775 | | $ | 914,959 | | $ | 788,188 | | | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
| | Identifiable Assets
by Geographic Area (c) | | Property, Plant & Equipment,
Net by Geographic Area (c) | |
December 31 | | 2007 | | 2006 | | 2005 | | 2007 | | 2006 | | 2005 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
United States | | $ | 429,376 | | $ | 454,931 | | $ | 452,546 | | $ | 163,130 | | $ | 175,983 | | $ | 177,956 | |
Foreign operations: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
The Netherlands | | | 73,658 | | | 70,609 | | | 67,683 | | | 52,383 | | | 53,905 | | | 54,331 | |
Hungary | | | 20,178 | | | 20,039 | | | 18,505 | | | 10,952 | | | 12,475 | | | 12,787 | |
China | | | 49,696 | | | 53,633 | | | 40,599 | | | 33,192 | | | 34,671 | | | 26,104 | |
Italy | | | 17,378 | | | 16,734 | | | 17,997 | | | 3,580 | | | 3,565 | | | 3,093 | |
Brazil | | | 15,838 | | | 14,402 | | | 15,163 | | | 5,055 | | | 4,892 | | | 5,205 | |
General corporate | | | 74,927 | | | 30,113 | | | 61,905 | | | 791 | | | 1,944 | | | 1,994 | |
Cash and cash equivalents (c) | | | 48,217 | | | 40,898 | | | 23,434 | | | n/a | | | n/a | | | n/a | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Continuing operations | | | 729,268 | | | 701,359 | | | 697,832 | | | 269,083 | | | 287,435 | | | 281,470 | |
Discontinued aluminum extrusions business in Canada (a) | | | 55,210 | | | 80,428 | | | 83,926 | | | 11,001 | | | 38,328 | | | 41,406 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Total | | $ | 784,478 | | $ | 781,787 | | $ | 781,758 | | $ | 280,084 | | $ | 325,763 | | $ | 322,876 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
See footnotes on prior page and a reconciliation of net sales to sales as shown in the consolidated statements of income.
54
| |
4 | ACCOUNTS AND NOTES RECEIVABLE |
|
|
|
| Accounts and notes receivable consist of the following: |
| | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
December 31 | | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Trade, less allowance for doubtful
accounts and sales returns of $5,198
in 2007 and $7,388 in 2006 | | $ | 94,699 | | $ | 102,062 | |
Other | | | 2,365 | | | 4,893 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total | | $ | 97,064 | | $ | 106,955 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The allowance for doubtful accounts and sales returns decreased by $2,190 in 2007 and increased by $2,515 in 2006 and $164 in 2005. The changes in 2007, 2006 and 2005 were comprised of increases to the allowance for charges to expense of $3,001, $3,236 and $366, respectively, decreases in the allowance for income from recoveries of $1,442, $57 and $15, respectively, decreases in the allowance for write-offs of $3,780, $680 and $62, respectively, and foreign exchange and other adjustments to the allowance of plus $31, plus $16 and minus $125, respectively.
| |
5 | INVENTORIES |
|
|
|
| Inventories consist of the following: |
| | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
December 31 | | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Finished goods | | $ | 10,004 | | $ | 9,182 | |
Work-in-process | | | 3,624 | | | 3,495 | |
Raw materials | | | 19,369 | | | 21,773 | |
Stores, supplies and other | | | 15,669 | | | 14,214 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total | | $ | 48,666 | | $ | 48,664 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Inventories stated on the LIFO basis amounted to $17,774 at December 31, 2007 and $17,230 at December 31, 2006, which are below replacement costs by approximately $25,845 at December 31, 2007 and $26,139 at December 31, 2006. During 2006, inventories accounted for on a LIFO basis declined, which resulted in cost of goods sold being stated at below current replacement costs by approximately $5,400 ($5,300 in Film Products, including $2,900 associated with the shutdown of the films manufacturing facility in LaGrange, Georgia, and $100 in Aluminum Extrusions). During 2005, inventories accounted for on a LIFO basis declined, which resulted in cost of goods sold being stated at below current replacement costs by approximately $2,300 ($2,100 in Film Products and $200 in Aluminum Extrusions).
In the normal course of business, we enter into fixed-price forward sales contracts with certain customers for the sale of fixed quantities of aluminum extrusions at scheduled intervals. In order to hedge our exposure to aluminum price volatility under these fixed-price arrangements, which generally have a duration of not more than 12 months, we enter into a combination of forward purchase commitments and futures contracts to acquire or hedge aluminum, based on the scheduled deliveries. The futures contracts are designated as and accounted for as cash flow hedges. These contracts involve elements of credit and market risk that are not reflected on our balance sheet, including the risk of dealing with counterparties and their ability to meet the terms of the contracts. The counterparties to our forward purchase commitments are major aluminum brokers and suppliers, and the counterparties to our futures contracts are major financial institutions. Fixed-price forward sales contracts are only made available to our best and most credit-worthy customers. The notional amount of aluminum futures contracts that hedged fixed-price forward sales contracts was $36,369 (32,762 pounds of aluminum) at December 31, 2007 and $15,865 (13,016 pounds of aluminum) at December 31, 2006. Unrealized losses in excess of gains on aluminum futures contracts that hedge fixed-price forward sales contracts of $1,815 ($1,204 after taxes) at December 31, 2007, and unrealized gains in excess of losses on
55
aluminum futures contracts that hedge fixed-price forward sales contracts of $1,184 ($728 after taxes) at December 31, 2006, are included as a separate component of shareholders’ equity for the respective periods. The portion of aluminum futures contracts that was ineffective in hedging fixed-price forward sales contracts was immaterial in 2007, 2006 and 2005.
In the past we have used interest rate swaps with large major financial institutions to manage interest rate exposure, but there have been no interest rate swaps outstanding since 2003.
In 2007, we used zero cost collar currency options to hedge a portion of our exposure to changes in exchange rates. Results for continuing operations include realized losses of $239,000 on currency hedges of royalties relating to our operations in Europe and results from discontinued operations include realized gains of $1,311 on currency hedges of our exposure to the Canadian Dollar (see Note 17 for more information). There were no derivatives outstanding at December 31, 2007 relating to currency hedges.
After-tax gains of $731 in 2007, $1,104 in 2006 and $939 in 2005 were reclassified from other comprehensive income to earnings and were offset by losses, respectively, from transactions relating to the underlying hedged item. As of December 31, 2007, we expect $1,204 of unrealized after-tax losses on derivative instruments reported in accumulated other comprehensive income to be reclassified to earnings within the next twelve months. We also expect that these losses will be offset by gains from transactions relating to the underlying hedged item.
| |
7 | ACCRUED EXPENSES |
|
|
| Accrued expenses consist of the following: |
| | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
December 31 | | | 2007 | | | 2006 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Payrolls, related taxes and medical and
other benefits | | $ | 7,921 | | $ | 8,209 | |
Workmen’s compensation and disabilities | | | 4,159 | | | 4,334 | |
Vacation | | | 3,636 | | | 3,592 | |
Plant shutdowns and divestitures | | | 6,201 | | | 5,058 | |
Incentive compensation | | | 1,880 | | | 4,075 | |
Other | | | 9,879 | | | 13,522 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total | | $ | 33,676 | | $ | 38,790 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
56
A reconciliation of the beginning and ending balances of accrued expenses associated with plant shutdowns and divestitures for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2007 is as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | Severance | | Asset
Impairments | Accelerated
Depreciation (a) | Other (b) | | Total | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance at December 31, 2004 | | $ | 2,457 | | $ | — | | $ | — | | $ | 3,394 | | $ | 5,851 | |
2005: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Charges | | | 3,470 | | | 8,433 | | | 353 | | | 5,442 | | | 17,698 | |
Cash spent | | | (3,887 | ) | | — | | | — | | | (3,179 | ) | | (7,066 | ) |
Charged against assets | | | — | | | (8,433 | ) | | (353 | ) | | — | | | (8,786 | ) |
Foreign currency translation | | | (8 | ) | | — | | | — | | | — | | | (8 | ) |
Reversed to income | | | (562 | ) | | — | | | — | | | (170 | ) | | (732 | ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance at December 31, 2005 | | | 1,470 | | | — | | | — | | | 5,487 | | | 6,957 | |
2006: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Charges | | | 1,371 | | | 1,150 | | | — | | | 1,607 | | | 4,128 | |
Cash spent | | | (2,405 | ) | | — | | | — | | | (2,472 | ) | | (4,877 | ) |
Charged against assets | | | — | | | (1,150 | ) | | — | | | — | | | (1,150 | ) |
Foreign currency translation | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
Reversed to income | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance at December 31, 2006 | | | 436 | | | — | | | — | | | 4,622 | | | 5,058 | |
2007: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Charges | | | 592 | | | 594 | | | — | | | 2,841 | | | 4,027 | |
Cash spent | | | (665 | ) | | — | | | — | | | (1,625 | ) | | (2,290 | ) |
Charged against assets | | | — | | | (594 | ) | | — | | | — | | | (594 | ) |
Foreign currency translation | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
Reversed to income | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Balance at December 31, 2007 | | $ | 363 | | $ | — | | $ | — | | $ | 5,838 | | $ | 6,201 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
(a) | Represents depreciation accelerated due to plant shutdowns based on a remaining useful life of less than one year. |
| |
(b) | Other includes primarily accrued losses on a sub-lease at a facility in Princeton New, Jersey. |
See Note 15 for more information on plant shutdowns, asset impairments and restructurings of continuing operations.
57
| |
8 | DEBT AND CREDIT AGREEMENTS |
|
On December 15, 2005, we refinanced our debt with a new $300,000, five-year unsecured revolving credit agreement (the “Credit Agreement”). At December 31, 2007, available credit under the Credit Agreement was approximately $219,000. Total debt due and outstanding at December 31, 2007 is summarized below:
| | | | | | | | | | |
|
Debt Due and Outstanding at December 31, 2007 |
|
|
Year
Due | | Credit
Agreement | | Other | | Total Debt
Due | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2008 | | $ | — | | $ | 540 | | $ | 540 | |
2009 | | | — | | | 552 | | | 552 | |
2010 | | | 80,000 | | | 463 | | | 80,463 | |
2011 | | | — | | | 247 | | | 247 | |
2012 | | | — | | | 126 | | | 126 | |
Remainder | | | — | | | 128 | | | 128 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total | | $ | 80,000 | | $ | 2,056 | | $ | 82,056 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The credit spread over LIBOR and commitment fees charged on the unused amount under the Credit Agreement at various indebtedness-to-adjusted EBITDA levels are as follows:
| | | | | | | |
|
Pricing Under Credit Agreement (Basis Points) |
|
| | Credit Spread
Over LIBOR | | | | |
| |
| | | | |
Indebtedness-to-
Adjusted EBITDA
Ratio | | ($80 Million
Outstanding
at 12/31/07) | | Commitment
Fee | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
> 2.50x but <= 3x | | 125 | | | 25 | | |
> 1.75x but <= 2.50x | | 100 | | | 20 | | |
> 1x but <= 1.75x | | 87.5 | | | 17.5 | | |
<= 1x | | 75 | | | 15 | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
At December 31, 2007, the interest cost on debt was priced at one-month LIBOR plus the applicable credit spread of 75 basis points.
The most restrictive covenants in the Credit Agreement include:
| |
• | Maximum aggregate dividends over the term of the Credit Agreement of $100,000 plus, beginning October 1, 2005, 50% of net income ($127,170 as of December 31, 2007); |
| |
• | Minimum shareholders’ equity ($388,276 as of December 31, 2007); |
| |
• | Maximum indebtedness-to-adjusted EBITDA through December 31, 2008 of 3x and 2.75x thereafter (2.5x on a pro forma basis for acquisitions); and |
| |
• | Minimum adjusted EBIT-to-interest expense of 2.5x. |
We believe we were in compliance with all of our debt covenants as of December 31, 2007. Noncompliance with any one or more of the debt covenants may have a material adverse effect on financial condition or liquidity in the event such noncompliance cannot be cured or should we be unable to obtain a waiver from the lenders. Renegotiation of the covenant through an amendment to the Credit Agreement may effectively cure the noncompliance, but may have an effect on financial condition or liquidity depending upon how the covenant is renegotiated.
In the past we have used interest rate swaps with large major financial institutions to manage interest rate exposure, but there have been no interest rate swaps outstanding since 2003.
58
| |
9 | SHAREHOLDER RIGHTS AGREEMENT |
|
Pursuant to a Rights Agreement dated as of June 30, 1999 (as amended), between Tredegar and National City Bank as Rights Agent, one right is attendant to each share of our common stock (“Right”). Each Right entitles the registered holder to purchase from Tredegar one one-hundredth of a share of Participating Cumulative Preferred Stock, Series A (the “Preferred Stock”), at an exercise price of $150 (the “Purchase Price”). The Rights will become exercisable, if not earlier redeemed, only if a person or group acquires 10% or more of the outstanding shares of our common stock or announces a tender offer which would result in ownership by a person or group of 10% or more of our common stock. Any action by a person or group whose beneficial ownership was reported on Amendment No. 4 to the Schedule 13D filed with respect to Tredegar on March 20, 1997, cannot cause the Rights to become exercisable.
Each holder of a Right, upon the occurrence of certain events, will become entitled to receive, upon exercise and payment of the Purchase Price, Preferred Stock (or in certain circumstances, cash, property or other securities of Tredegar or a potential acquirer) having a value equal to twice the amount of the Purchase Price.
The Rights will expire on June 30, 2009.
| |
10 | STOCK OPTION AND STOCK AWARD PLANS |
|
We have two stock option plans under which stock options may be granted to purchase a specified number of shares of common stock at a price no lower than the fair market value on the date of grant and for a term not to exceed 10 years. One of those option plans is a directors’ stock plan. In addition, we have three other stock option plans under which there are options that remain outstanding, but no future grants can be made. Employee options ordinarily vest one to two years from the date of grant. The option plans also permit the grant of stock appreciation rights (“SARs”), stock, restricted stock, stock unit awards and incentive awards. No SARs have been granted since 1992. All SARs outstanding at December 31, 2001, were exercised during 2002.
A summary of our stock options outstanding at December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005, and changes during those years, is presented below:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
|
| | | | | Option Exercise Price/Share | |
| | | | |
| |
| | Number of
Options | | | | | Range | | | | | Wgted.
Ave. | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Outstanding at 12/31/04 | | | 2,661,990 | | $ | 4.17 | | | to | | $ | 46.63 | | $ | 22.01 | |
Granted | | | — | | | n/a | | | to | | | n/a | | | n/a | |
Forfeited and Expired | | | (274,575 | ) | | 13.95 | | | to | | | 46.63 | | | 21.90 | |
Exercised | | | (137,075 | ) | | 4.17 | | | to | | | 16.55 | | | 7.51 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Outstanding at 12/31/05 | | | 2,250,340 | | | 7.38 | | | to | | | 46.63 | | | 22.90 | |
Granted | | | 449,800 | | | 15.11 | | | to | | | 19.52 | | | 15.30 | |
Forfeited and Expired | | | (874,525 | ) | | 7.38 | | | to | | | 46.63 | | | 29.73 | |
Exercised | | | (578,442 | ) | | 7.38 | | | to | | | 19.75 | | | 16.47 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Outstanding at 12/31/06 | | | 1,247,173 | | | 13.95 | | | to | | | 29.94 | | | 18.16 | |
Granted | | | 4,000 | | | 14.40 | | | to | | | 14.40 | | | 14.40 | |
Forfeited and Expired | | | (184,065 | ) | | 13.95 | | | to | | | 29.94 | | | 20.68 | |
Exercised | | | (364,125 | ) | | 13.95 | | | to | | | 22.72 | | | 18.58 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Outstanding at 12/31/07 | | | 702,983 | | $ | 13.95 | | | to | | $ | 29.94 | | $ | 17.25 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
59
The following table summarizes additional information about stock options outstanding and exercisable and non-vested restricted stock outstanding at December 31, 2007:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
|
| | | | | | | | Options Outstanding at
December 31, 2007 | | Options Exercisable at
December 31, 2007 | |
| | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | Weighted Average | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Range of
Exercise Prices | | | Shares | | Remaining
Contract-
ual Life
(Years) | | Exercise
Price | | Aggregate
Intrinsic
Value
(In Thousands) | | Shares | | Weighted
Average
Exercise
Price | | Aggregate
Intrinsic
Value
(In Thousands) | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ 13.95 | | | to | | $ | 17.88 | | | 420,943 | | | 4.8 | | $ | 14.95 | | $ | 781 | | | 86,643 | | $ | 13.95 | | $ | 247 | | |
17.89 | | | to | | | 19.75 | | | 235,750 | | | 1.2 | | | 18.91 | | | — | | | 224,250 | | | 18.88 | | | — | | |
19.76 | | | and over | | | | | | 46,290 | | | .5 | | | 29.78 | | | — | | | 46,290 | | | 29.78 | | | — | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total | | | | | | | | | 702,983 | | | 3.3 | | $ | 17.25 | | $ | 781 | | | 357,183 | | $ | 19.09 | | $ | 247 | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | Non-vested Restricted Stock | | Maximum Non-vested Restricted
Stock Units Issuable Upon Satis-
faction of Certain Performance Criteria | |
| |
|
|
|
|
| | Number
of Shares | | Wgtd. Ave.
Grant Date
Fair Value/Sh. | | Grant Date
Fair Value
(In Thousands) | | Number
of Shares | | Wgtd. Ave.
Grant Date
Fair Value/Sh. | | Grant Date
Fair Value
(In Thousands) | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Outstanding at 12/30/04 | | | 120,000 | | $ | 13.95 | | | $ | 1,674 | | | | — | | $ | — | | $ | — | |
Granted | | | 7,000 | | | 12.92 | | | | 90 | | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
Vested | | | (8,000 | ) | | 13.95 | | | | (111 | ) | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
Forfeited | | | (10,000 | ) | | 13.95 | | | | (140 | ) | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Outstanding at 12/30/05 | | | 109,000 | | | 13.88 | | | | 1,513 | | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
Granted | | | 2,000 | | | 16.31 | | | | 33 | | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
Vested | | | (17,333 | ) | | 13.95 | | | | (242 | ) | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
Forfeited | | | (24,167 | ) | | 13.80 | | | | (333 | ) | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Outstanding at 12/31/06 | | | 69,500 | | | 13.97 | | | | 971 | | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
Granted | | | — | | | — | | | | — | | | | 233,375 | | | 20.80 | | | 4,854 | |
Vested | | | (6,000 | ) | | 13.95 | | | | (84 | ) | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
Forfeited | | | (4,000 | ) | | 13.95 | | | | (56 | ) | | | (56,500 | ) | | 23.00 | | | (1,300) | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Outstanding at 12/31/07 | | | 59,500 | | $ | 13.97 | | | $ | 831 | | | | 176,875 | | $ | 20.09 | | $ | 3,554 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The total intrinsic value of stock options exercised was $1,455 in 2007 and $2,174 in 2006. The grant-date fair value of stock option-based awards vested was $1,323 in 2006 (none in 2007). As of December 31, 2007, there was $260 and approximately $1,700 of unrecognized compensation cost related to stock option-based awards and non-vested restricted stock and other stock-based awards, respectively. This cost is expected to be recognized over the remaining weighted average period of .26 years for stock option-based awards and 1.4 years for non-vested restricted stock and other stock-based awards. Compensation costs for non-vested restricted stock is subject to accelerated vesting based on meeting certain financial targets.
Stock options exercisable totaled 851,873 shares at December 31, 2006 and 1,983,440 shares at December 31, 2005. Stock options available for grant totaled 1,412,232 shares at December 31, 2007, 1,601,700 shares at December 31, 2006 and 1,998,300 shares at December 31, 2005.
| |
11 | RETIREMENT PLANS AND OTHER POSTRETIREMENT BENEFITS |
|
|
We have noncontributory defined benefit (pension) plans covering most employees. The plans for salaried and hourly employees currently in effect are based on a formula using the participant’s years of service and compensation or using the participant’s years of service and a dollar amount.
On October 26, 2006, we announced changes to our U.S. defined benefit (pension) and savings plans covering salaried and certain other employees. The changes had no impact on our net income or earnings per share in 2006. The changes relating to the pension plan reduced our projected benefit obligation by approximately $10,000 as of
60
December 31, 2006. In 2007, the changes to the pension plan reduced our service cost, interest cost and amortization of prior service cost components of pension expense by approximately $600, $600 and $1,500, respectively, and the savings plan changes (see Note 12) increased charges for company matching contributions by approximately $700.
In addition to providing pension benefits, we provide postretirement life insurance and health care benefits for certain groups of employees. Tredegar and retirees share in the cost of postretirement health care benefits, with employees hired on or before January 1, 1993, receiving a fixed subsidy to cover a portion of their health care premiums. On December 8, 2003, the Medicare Prescription Drug Improvement and Modernization Act of 2003 (the “Act”) was signed into law. We eliminated prescription drug coverage for Medicare-eligible retirees as of January 1, 2006. Consequently, we are not eligible for any federal subsidies.
Assumptions used for financial reporting purposes to compute net benefit income or cost and benefit obligations for continuing operations, and the components of net periodic benefit income or cost for continuing operations, are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | Pension Benefits | | Other Post-
Retirement Benefits | |
| |
| |
|
|
| | 2007 | | 2006 | | 2005 | | 2007 | | 2006 | | 2005 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted-average assumptions used to determine benefit obligations: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Discount rate | | | 6.25 | % | | 5.75 | % | | 5.75 | % | | 6.25 | % | | 5.75 | % | | 5.75 | % |
Rate of compensation increases | | | 4.00 | % | | 4.00 | % | | 4.00 | % | | 4.00 | % | | 4.00 | % | | 4.00 | % |
Weighted-average assumptions used to determine net periodic benefit cost: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Discount rate | | | 5.75 | % | | 5.75 | % | | 6.00 | % | | 5.75 | % | | 5.75 | % | | 6.00 | % |
Rate of compensation increases | | | 4.00 | % | | 4.00 | % | | 4.00 | % | | 4.00 | % | | 4.00 | % | | 4.00 | % |
Expected long-term return on plan assets, during the year | | | 8.50 | % | | 8.50 | % | | 8.50 | % | | n/a | | | n/a | | | n/a | |
Rate of increase in per-capita cost of covered health care benefits: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Indemnity plans, end of year | | | n/a | | | n/a | | | n/a | | | 6.00 | % | | 6.00 | % | | 6.00 | % |
Managed care plans, end of year | | | n/a | | | n/a | | | n/a | | | 6.00 | % | | 6.00 | % | | 6.00 | % |
Components of net periodic benefit income (cost): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Service cost | | $ | (4,232 | ) | $ | (4,933 | ) | $ | (5,334 | ) | $ | (106 | ) | $ | (70 | ) | $ | (90 | ) |
Interest cost | | | (11,447 | ) | | (12,079 | ) | | (11,377 | ) | | (503 | ) | | (513 | ) | | (556 | ) |
Expected return on plan assets | | | 20,372 | | | 19,820 | | | 20,564 | | | — | | | — | | | — | |
Amortization of prior service costs and gains or losses | | | (1,819 | ) | | (4,476 | ) | | (655 | ) | | — | | | 14 | | | (7 | ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net periodic benefit income (cost) | | $ | 2,874 | | $ | (1,668 | ) | $ | 3,198 | | $ | (609 | ) | $ | (569 | ) | $ | (653 | ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
61
The following tables reconcile the changes in benefit obligations and plan assets in 2007 and 2006, and reconcile the funded status to prepaid or accrued cost at December 31, 2007 and 2006:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | Pension Benefits | | Other Post-
Retirement Benefits | |
| |
| |
|
|
| | 2007 | | 2006 | | 2007 | | 2006 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Change in benefit obligation: | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Benefit obligation, beginning of year | | $ | 205,588 | | $ | 211,701 | | $ | 9,366 | | $ | 9,623 | |
Service cost | | | 4,232 | | | 4,933 | | | 106 | | | 70 | |
Interest cost | | | 11,447 | | | 12,079 | | | 503 | | | 513 | |
Plan amendments | | | 23 | | | (10,039 | ) | | — | | | — | |
Effect of discount rate change | | | (12,318 | ) | | — | | | (467 | ) | | — | |
Other | | | 775 | | | (3,426 | ) | | (377 | ) | | 80 | |
Benefits paid | | | (9,618 | ) | | (9,660 | ) | | (441 | ) | | (920 | ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Benefit obligation, end of year | | $ | 200,129 | | $ | 205,588 | | $ | 8,690 | | $ | 9,366 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Change in plan assets: | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Plan assets at fair value, | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
beginning of year | | $ | 256,669 | | $ | 232,624 | | $ | — | | $ | — | |
Actual return on plan assets | | | 36,883 | | | 33,538 | | | — | | | — | |
Employer contributions | | | 167 | | | 167 | | | 441 | | | 920 | |
Benefits paid | | | (9,619 | ) | | (9,660 | ) | | (441 | ) | | (920 | ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Plan assets at fair value, end of year | | $ | 284,100 | | $ | 256,669 | | $ | — | | $ | — | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Funded status of the plans | | $ | 83,971 | | $ | 51,081 | | $ | (8,690 | ) | $ | (9,366 | ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Amounts recognized in the consolidated | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
balance sheets: | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Prepaid benefit cost | | $ | 86,295 | | $ | 53,619 | | $ | — | | $ | — | |
Accrued benefit liability | | | (2,324 | ) | | (2,538 | ) | | (8,690 | ) | | (9,366 | ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net amount recognized | | $ | 83,971 | | $ | 51,081 | | $ | (8,690 | ) | $ | (9,366 | ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net benefit income or cost is determined using assumptions at the beginning of each year. Funded status is determined using assumptions at the end of each year. Prepaid pension costs for continuing operations of $86,295 and $53,619 are included in “Other assets and deferred charges” in the consolidated balance sheets at December 31, 2007 and 2006, respectively. Pension and postretirement liabilities for continuing operations of $11,014 and $11,904 are included in “Other noncurrent liabilities” in the consolidated balance sheets at December 31, 2007 and 2006, respectively. The amount of our accumulated benefit obligation is the same as our projected benefit obligation.
At December 31, 2007, the effect of a 1% change in the health care cost trend rate assumptions would be immaterial.
62
Expected benefit payments for continuing operations over the next five years and in the aggregate for 2013-2017 are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Years | | Pension
Benefits | | Other
Post-
Retirement
Benefits | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2008 | | $ | 10,621 | | | $ | 492 | | |
2009 | | | 11,104 | | | | 537 | | |
2010 | | | 11,564 | | | | 579 | | |
2011 | | | 12,074 | | | | 609 | | |
2012 | | | 12,766 | | | | 641 | | |
2013 - 2017 | | | 72,202 | | | | 3,556 | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
The incremental impact for continuing and discontinued operations of adopting SFAS No. 158 as of December 31, 2006 (see the pension costs and postretirement benefit costs other than pensions section of Note 1 for further information on this new standard) and recognizing an additional minimum liability (the “AML”) is shown in the table below:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
As of December 31, 2006 | | Prior to AML &
SFAS No. 158
Adjustments | | AML
Adjustment | | SFAS No. 158
Adjustment | | Post AML
& SFAS No. 158
Adjustments | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Prepaid pension costs | | | $ | 80,442 | | | | $ | 1,243 | | | | $ | (27,651 | ) | | | $ | 54,034 | | |
Pension liabilities | | | | — | | | | | — | | | | | 3,619 | | | | | 3,619 | | |
Postretirement liabilities | | | | 9,740 | | | | | — | | | | | (318 | ) | | | | 9,422 | | |
Decrease (increase) in deferred income tax liabilities relating to accumulated other comprehensive loss | | | | 1,252 | | | | | (422 | ) | | | | 11,354 | | | | | 12,184 | | |
Accumulated other comprehensive loss | | | | 2,434 | | | | | (821 | ) | | | | 19,598 | | | | | 21,211 | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
Amounts recognized in 2007 and 2006 before related deferred income taxes in accumulated other comprehensive income consist of:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | Pension | | Other Post -
Retirement | |
| |
| |
|
|
| | 2007 | | 2006 | | 2007 | | 2006 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Continuing operations: | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Prior service cost (benefit) | | $ | (6,140 | ) | $ | (7,200 | ) | $ | — | | $ | — | |
Net actuarial (gain) loss | | | 5,194 | | | 36,103 | | | (682 | ) | | 161 | |
Discontinued operations: | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Prior service cost (benefit) | | | 1,108 | | | 1,002 | | | — | | | — | |
Net actuarial (gain) loss | | | 6,008 | | | 3,807 | | | (445 | ) | | (478 | ) |
Total: | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Prior service cost (benefit) | | | (5,032 | ) | | (6,198 | ) | | — | | | — | |
Net actuarial (gain) loss | | | 11,202 | | | 39,910 | | | (1,127 | ) | | (317 | ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
63
The amounts before related deferred income taxes in accumulated other comprehensive income that are expected to be recognized as components of net periodic benefit or cost during 2008 are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | Pension | | Other Post
Retirement | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Continuing operations: | | | | | | | |
Prior service cost (benefit) | | | $ | (1,049 | ) | | | $ | — | | |
Net actuarial (gain) loss | | | | 344 | | | | | (1 | ) | |
Discontinued operations: | | | | | | | | | | | |
Prior service cost (benefit) | | | | 83 | | | | | — | | |
Net actuarial (gain) loss | | | | 187 | | | | | (43 | ) | |
Total: | | | | | | | | | | | |
Prior service cost (benefit) | | | | (966 | ) | | | | — | | |
Net actuarial (gain) loss | | | | 531 | | | | | (44 | ) | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The percentage composition of assets held by pension plans for continuing operations at December 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005, and the current expected long-term return on assets are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | % Composition | | Expected
Long-term | |
| | of Plan Assets | | |
| |
| | |
December 31 | | 2007 | | 2006 | | 2005 | | Return % | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pension plans related to continuing operations: | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Low-risk fixed income securities | | 8.5 | % | | 11.4 | % | | 15.6 | % | | 4.3 | % | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Large capitalization equity securities | | 20.7 | | | 22.4 | | | 21.1 | | | 8.1 | | |
Mid-capitalization equity securities | | 7.4 | | | 8.8 | | | 8.0 | | | 9.1 | | |
Small-capitalization equity securities | | 4.7 | | | 5.1 | | | 4.7 | | | 9.5 | | |
International equity securities | | 22.6 | | | 27.4 | | | 24.8 | | | 10.4 | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total equity securities | | 55.4 | | | 63.7 | | | 58.6 | | | 9.4 | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hedge and private equity funds | | 33.9 | | | 22.5 | | | 23.3 | | | 8.8 | | |
Other assets | | 2.2 | | | 2.4 | | | 2.5 | | | 3.6 | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total for continuing operations | | 100.0 | % | | 100.0 | % | | 100.0 | % | | 8.5 | % | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Our targeted allocation percentage for pension plan assets is in the range of the percentage composition that existed at December 31, 2007. Expected long-term returns are estimated by asset class and generally are based on inflation-adjusted historical returns, volatilities, risk premiums and managed asset premiums. The portfolio of fixed income securities is structured with maturities that generally match estimated benefit payments over the next 1-2 years. We believe that over the long term a diversified portfolio of equity securities, hedge funds and private equity funds have a better risk-return profile than fixed income securities. The average remaining duration of benefit payments for our pension plans is about 12 years. We expect our required contributions to approximate $167 in 2008.
The estimate of the fair value of assets held by our pension plans is provided by third parties not affiliated with Tredegar. The fair value of low-risk fixed income securities and equity securities are typically based on Level 1 inputs. The fair value of the ownership interests held by our pension plans in hedge and private equity funds is reported by the funds. While the fair value of the underlying assets in these funds may be substantially based on Level 1 and Level 2 inputs, we believe that the ownership interests held by our pension plans in these funds are based on Level 3 inputs since there is no secondary market for the ownership interests and there are restrictions on withdrawals. Other assets are primarily comprised of cash and insurance contracts.
We also have a non-qualified supplemental pension plan covering certain employees. Effective December 31, 2005, further participation in this plan was terminated and benefit accruals for existing participants were frozen. The plan was designed to restore all or a part of the pension benefits that would have been payable to designated participants from our principal pension plans if it were not for limitations imposed by income tax regulations. The
64
projected benefit obligation relating to this unfunded plan was $2,324 at December 31, 2007 and $2,537 at December 31, 2006. Pension expense recognized was $161 in 2007, $355 in 2006 and $256 in 2005. This information has been included in the preceding pension benefit tables.
Approximately 135 employees at our films manufacturing facility in Kerkrade, The Netherlands are covered by a collective bargaining agreement that includes participation in a multi-employer pension plan. Pension expense recognized for participation in this plan, which is equal to required contributions, was $868 in 2007, $807 in 2006 and $364 in 2005. This information has been excluded from the preceding pension benefit tables.
We have a savings plan that allows eligible employees to voluntarily contribute a percentage of their compensation up to Internal Revenue Service (“IRS”) limitations. Under the provisions of the plan on or before December 31, 2006, we matched a portion (generally 50 cents for every $1 of employee contribution, up to a maximum of 10% of base pay) of the employee’s contribution to the plan with shares of our common stock. Effective January 1, 2007, and in conjunction with certain pension plan changes (see Note 11), the following changes were made to the savings plan for salaried and certain hourly employees:
| |
• | The company makes matching contributions to the savings plan of $1 for every $1 of employee contribution. The maximum matching contribution is 6% of base pay for 2007-2009 and 5% of base pay thereafter. |
|
• | The savings plan includes immediate vesting for active employees of past matching contributions as well as future matching contributions when made (compared with the previous 5-year graded vesting) and automatic enrollment at 3% of base pay unless the employee opts out or elects a different percentage. |
We also have a non-qualified plan that restores matching benefits for employees suspended from the savings plan due to certain limitations imposed by income tax regulations. Charges recognized for these plans were $2,828 in 2007, $2,770 in 2006 and $1,889 in 2005. The savings plan changes effective January 1, 2007 increased charges for company matching contributions by approximately $700. Our liability under the restoration plan was $1,027 at December 31, 2007 (consisting of 63,852 phantom shares of common stock) and $1,332 at December 31, 2006 (consisting of 58,931 phantom shares of common stock) valued at the closing market price on those dates.
The Tredegar Corporation Benefits Plan Trust (the “Trust”) purchased 7,200 shares of our common stock in 1998 for $192 and 46,671 shares of our common stock in 1997 for $1,020, as a partial hedge against the phantom shares held in the restoration plan. There have been no shares purchased since 1997 except for
re-invested dividends. The cost of the shares held by the Trust is shown as a reduction to shareholders’ equity in the consolidated balance sheets.
| |
13 | RENTAL EXPENSE AND CONTRACTUAL COMMITMENTS |
|
Rental expense for continuing operations was $3,873 in 2007, $3,859 in 2006 and $3,811 in 2005. Rental commitments under all non-cancelable operating leases for continuing operations as of December 31, 2007, are as follows:
| | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
Year | | Amount | |
|
2008 | | $ | 2,461 | |
2009 | | | 2,929 | |
2010 | | | 2,959 | |
2011 | | | 1,757 | |
2012 | | | 1,322 | |
Remainder | | | 595 | |
|
Total | | $ | 12,023 | |
|
|
|
|
|
AFBS, Inc. (formerly known as Therics, Inc. - see Note 15 for additional information regarding its restructuring in 2005), a wholly-owned subsidiary of Tredegar, has future rental commitments under noncancelable
65
operating leases through 2011 (most of which contain sublease options) totaling approximately $5,200. These future rental commitments are included in the above table. Sublease rental commitments relating to excess space at AFBS total $632 (excluded from the above table).
Contractual obligations for plant construction and purchases of real property and equipment amounted to $2,965 at December 31, 2007 and $5,992 at December 31, 2006.
Income from continuing operations before income taxes and income taxes are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | 2007 | | 2006 | | 2005 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Income from continuing operations | | | | | | | | | | |
before income taxes: | | | | | | | | | | |
Domestic | | $ | 50,942 | | $ | 48,850 | | $ | 16,031 | |
Foreign | | | 8,354 | | | 6,258 | | | 6,838 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total | | $ | 59,296 | | $ | 55,108 | | $ | 22,869 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current income taxes: | | | | | | | | | | |
Federal | | $ | 24,698 | | $ | 5,165 | | $ | 1,592 | |
State | | | 856 | | | 840 | | | 811 | |
Foreign | | | 4,351 | | | 4,223 | | | (422 | ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total | | | 29,905 | | | 10,228 | | | 1,981 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Deferred income taxes: | | | | | | | | | | |
Federal | | | (4,009 | ) | | 9,030 | | | 6,928 | |
State | | | 316 | | | 687 | | | 600 | |
Foreign | | | (1,846 | ) | | (154 | ) | | (12 | ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total | | | (5,539 | ) | | 9,563 | | | 7,516 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total income taxes | | $ | 24,366 | | $ | 19,791 | | $ | 9,497 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The significant differences between the U.S. federal statutory rate and the effective income tax rate for continuing operations are as follows:
| | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | Percent of Income Before Income
Taxes for Continuing Operations | |
| |
|
|
|
|
| | 2007 | | 2006 | | 2005 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Income tax expense at federal statutory rate | | | | 35.0 | | | | | 35.0 | | | | 35.0 | |
State taxes, net of federal income tax benefit | | | | 1.3 | | | | | 1.8 | | | | 4.0 | |
Unremitted earnings from foreign operations | | | | 2.2 | | | | | 1.2 | | | | 2.7 | |
Valuation allowance for capital loss
carry-forwards | | | | 1.8 | | | | | (1.1 | ) | | | 2.5 | |
Valuation allowance for foreign operating
loss carry-forwards | | | | 1.4 | | | | | 1.9 | | | | 1.8 | |
Non-deductible expenses | | | | .2 | | | | | .3 | | | | .6 | |
Research and development tax credit | | | | (.1 | ) | | | | (.9 | ) | | | (1.8 | ) |
Extraterritorial Income Exclusion and
Domestic Production Activities Deduction | | | | (.5 | ) | | | | (1.8 | ) | | | (2.8 | ) |
Foreign rate differences | | | | (1.1 | ) | | | | (.3 | ) | | | (.9 | ) |
Other | | | | .9 | | | | | (.2 | ) | | | .4 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Effective income tax rate | | | | 41.1 | | | | | 35.9 | | | | 41.5 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
66
Deferred tax liabilities and deferred tax assets at December 31, 2007 and 2006, are as follows:
| | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
December 31 | | 2007 | | 2006 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Deferred tax liabilities: | | | | | | | |
Depreciation | | $ | 29,105 | | $ | 30,077 | |
Pensions | | | 31,693 | | | 19,584 | |
Amortization of goodwill | | | 18,059 | | | 15,318 | |
Foreign currency translation gain adjustment | | | 13,497 | | | 7,402 | |
Derivative financial instruments | | | — | | | 480 | |
Other | | | 1,152 | | | 1,490 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total deferred tax liabilities | | | 93,506 | | | 74,351 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Deferred tax assets: | | | | | | | |
Excess of tax basis over financial reporting basis for the aluminum extrusions business in Canada | | | 11,428 | | | — | |
Employee benefits | | | 6,543 | | | 5,945 | |
Tax in excess of book basis for venture capital and other investments
(net of valuation allowance of $1,066 in 2007) | | | 5,805 | | | 2,547 | |
Asset write-offs, divestitures and environmental accruals | | | 3,274 | | | 2,851 | |
Timing adjustment for unrecognized tax benefits on uncertain tax positions, including portion relating to interest and penalties | | | 2,761 | | | — | |
Allowance for doubtful accounts and sales returns | | | 1,237 | | | 1,209 | |
Tax benefit on state credits and foreign NOL carryforwards | | | 954 | | | 731 | |
Derivative financial instruments | | | 464 | | | — | |
Inventory | | | 70 | | | 640 | |
Other (net of valuation allowance of $2,947 in 2007and $2,120 in 2006) | | | 1,517 | | | 750 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total deferred tax assets | | | 34,053 | | | 14,673 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net deferred tax liability | | $ | 59,453 | | $ | 59,678 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Included in the balance sheet: | | | | | | | |
Noncurrent deferred tax liabilities in excess of assets | | $ | 68,625 | | $ | 65,732 | |
Current deferred tax assets in excess of liabilities | | | 9,172 | | | 6,055 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net deferred tax liability | | $ | 59,453 | | $ | 59,677 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Except as noted below, we believe that it is more likely than not that future taxable income will exceed future tax deductible amounts thereby resulting in the realization of deferred tax assets. A valuation allowance of $2,947 at December 31, 2007 is included in other deferred tax assets that offsets an amount included in that line item relating to possible future tax benefits on operating losses generated by certain foreign subsidiaries that may not be recoverable in the carry-forward period. In addition, a valuation allowance of $1,066 at December 31, 2007 was established in the third quarter of 2007 due to expected limitations on the utilization of assumed capital losses.
67
A reconciliation of our unrecognized uncertain tax positions since January 1, 2007, is shown below:
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | Increase
(Decrease)
Due to
Settlements
with
Taxing
Authorities | | | | | | | |
| | | | | Increase (Decrease)
Due to Tax Positions
Taken in | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | Reductions
Due to
Lapse of
Statute of
Limitations | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | Balance at
Jan. 1,
2007 | |
| | | | Balance at
Dec. 31,
2007 | |
| | | Current
Period | | Prior
Period | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gross unrecognized tax benefits on uncertain tax positions (reflected in current income tax and other noncurrent liability accounts in the balance sheet) | | | $ | 3,393 | | | | $ | 566 | | | | $ | (506 | ) | | | $ | — | | | | $ | (185 | ) | | | $ | 3,268 | | |
Deferred income tax assets related to unrecognized tax benefits on uncertain tax positions for which ultimate deductibility is highly certain but for which the timing of the deduction is uncertain (reflected in deferred income tax accounts in the balance sheet) | | | | (2,733 | ) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (2,325 | ) | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net unrecognized tax benefits on uncertain tax positions, which would impact the effective tax rate if recognized | | | | 660 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 943 | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest and penalties accrued on deductions taken relating to uncertain tax positions (approximately $300, $300 and $100 reflected in income tax expense in the income statement in 2007, 2006 and 2005, respectively, with the balance shown in current income tax and other noncurrent liability accounts in the balance sheet) | | | | 891 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 1,195 | | |
Related deferred income tax assets recognized on interest and penalties | | | | (327 | ) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | (436 | ) | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest and penalties accrued on uncertain tax positions net of related deferred income tax benefits, which would impact the effective tax rate if recognized | | | | 564 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | 759 | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total net unrecognized tax benefits on uncertain tax positions reflected in the balance sheet, which would impact the effective tax rate if recognized | | | $ | 1,224 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | $ | 1,702 | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
We anticipate that by December 31, 2008, we will settle several disputed issues raised by the IRS during its examination of our U.S. income tax returns for 2001-2003, the most significant of which regards the recognition of our captive insurance subsidiary as an insurance company for U.S. income tax purposes. It is reasonably possible that a settlement with the IRS for the disputed issues would cost us $1,400, which would be applied against the balance of unrecognized tax benefits and accrued interest and penalties.
Tredegar and its subsidiaries file income tax returns in U.S., state and foreign jurisdictions. Tredegar is no longer subject to U.S. federal income tax examinations by tax authorities for years before 2001. With few exceptions, Tredegar and its subsidiaries are no longer subject to state or non-U.S. income tax examinations by tax authorities for years before 2004.
| |
15 | LOSSES ASSOCIATED WITH PLANT SHUTDOWNS, ASSET IMPAIRMENTS AND RESTRUCTURINGS, UNUSUAL ITEMS, GAINS FROM SALE OF ASSETS AND OTHER ITEMS |
|
|
Losses associated with plant shutdowns, asset impairments and restructurings for continuing operations in 2007 totaled $4,069 ($2,781 after taxes) and included:
| |
• | A fourth quarter charge of $1,200 ($780 after taxes), a third quarter charge of $1,220 ($793 after taxes) and a first quarter charge of $366 ($238 after taxes) related to the estimated loss on the sub-lease of a portion of the AFBS (formerly Therics) facility in Princeton, New Jersey; |
| |
• | A fourth quarter charge of $256 ($256 after taxes) and a first quarter charge of $338 ($284 after taxes) for asset impairments in Film Products; |
68
| |
• | A third quarter charge of $493 ($309 after taxes) and a second quarter charge of $99 ($62 after taxes) for severance and other employee-related costs in Aluminum Extrusions; |
| |
• | A second quarter charge of $26 ($16 after taxes) and a first quarter charge of $29 ($17 after taxes) for costs related to the shutdown of the films manufacturing facility in LaGrange, Georgia; and |
| |
• | A third quarter charge of $42 ($26 after taxes) related to expected future environmental costs at the aluminum extrusions facility in Newnan, Georgia (included in “Cost of goods sold” in the consolidated statements of income). |
| |
Results in 2007 also include a fourth-quarter gain of $2,699 ($1,737 after taxes) on the sale of corporate real estate (proceeds of approximately $3,800) and a third-quarter loss from the write-down of Novalux of $2,095 ($1,341 after taxes). See Note 2 for more information on Novalux. The pretax amounts for both of these items are included in “Other income (expense), net” in the consolidated statements of income and separately shown in the segment operating profit table in Note 3. Income taxes in 2007 include the recognition of a valuation allowance against deferred tax assets of $1,066 in the third quarter for expected limitations on the utilization of assumed capital losses (see Note 14). |
| |
Losses associated with plant shutdowns, asset impairments and restructurings for continuing operations, net of gains on sale of related assets, in 2006 totaled $1,850 ($1,441 after taxes) and include: |
| |
• | A fourth quarter net gain of $14 ($8 after taxes), a third-quarter net gain of $1,022 ($615 after taxes), a second-quarter net gain of $822 ($494 after taxes) and a first-quarter pretax charge of $404 ($243 after taxes) associated with the shutdown of the films manufacturing facility in LaGrange, Georgia, including a pretax gain of $2,889 for related LIFO inventory liquidations (included in “Cost of goods sold” in the consolidated statements of income), severance and other costs of $1,566, asset impairment charges of $130 and a gain on the disposal of equipment of $261 (included in “Other income (expense), net” in the consolidated statements of income); |
| |
• | A third-quarter charge of $920 ($566 after taxes) related to expected future environmental costs at the aluminum extrusions facility in Newnan, Georgia (included in “Cost of goods sold” in the consolidated statements of income); |
| |
• | A fourth quarter charge of $143 ($93 after taxes) and a third quarter charge of $494 ($321 after taxes) related to the estimated loss on the sublease of a portion of the AFBS facility in Princeton, New Jersey; |
| |
• | Second-quarter charges of $459 ($289 after taxes) and first-quarter charges of $268 ($170 after taxes) for severance and other employee-related costs in connection with restructurings in Aluminum Extrusions ($514) and Film Products ($213); and |
| |
• | First-quarter charges of $1,020 ($876 after taxes) for asset impairments relating to machinery & equipment in Film Products. |
| |
In 2006, a pretax gain on the sale of public equity securities of $56 (proceeds also of $56) is included in “Other income (expense), net” in the consolidated statements of income and “Gain on the sale of corporate assets” in the segment operating profit table in Note 3. Income taxes in 2006 include a reversal of a valuation allowance of $577 for deferred tax assets associated with capital loss carry-forwards recorded with the write-down of the investment in Novalux (see Notes 2 and 14). |
| |
Losses associated with plant shutdowns, asset impairments and restructurings for continuing operations, net of gains on sale of related assets, in 2005 totaled $15,721 ($10,087 after taxes) and include: |
| |
• | A fourth-quarter charge of $269 ($174 after taxes) and a second-quarter charge of $10,049 ($6,532 after taxes) related to the sale or assignment of substantially all of the assets of AFBS, Inc. (formerly known as Therics, Inc. - see below for additional information regarding its restructuring in 2005), including asset impairment charges of $5,638, lease-related losses of $3,326 and severance (31 people) and other transaction-related costs of $1,354 (see below for additional information on the transaction); |
| |
• | Fourth-quarter charges of $397 ($256 after taxes), third-quarter charges of $756 ($474 after taxes), second-quarter charges of $500 ($317 after taxes) and first-quarter charges of $418 ($266 after taxes) related to severance and other employee-related costs associated with restructurings in Film Products ($1,118 before taxes) and Aluminum Extrusions ($498 before taxes) and at corporate headquarters ($455 before taxes; included in “Corporate expenses, net” in the segment operating profit table in Note 3) (an aggregate of 19 people were affected by these restructurings); |
69
| |
• | A fourth-quarter charge of $2,101 ($1,263 after taxes) related to the shutdown of the films manufacturing facility in LaGrange, Georgia, including asset impairment charges of $1,615 and severance (15 people) and other costs of $486; |
| |
• | A second-quarter charge of $27 ($16 after taxes) and a first-quarter gain of $1,618 ($973 after taxes) related to the shutdown of the films manufacturing facility in New Bern, North Carolina, including a $1,816 gain on the sale of the facility (included in “Other income (expense), net” in the consolidated statements of income), partially offset by shutdown-related expenses of $225; |
| |
• | A first-quarter charge of $1,019 ($653 after taxes) for process reengineering costs associated with the implementation of an information system in Film Products (included in “Costs of goods sold” in the consolidated statements of income); |
| |
• | Fourth-quarter charges of $118 ($72 after taxes), third-quarter charges of $595 ($359 after taxes), second-quarter charges of $250 ($150 after taxes) partially offset by a net first-quarter gain of $120 ($72 after taxes) related to severance and other employee-related accruals associated with the restructuring of the research and development operations in Film Products (of this amount, $1,366 in pretax charges for employee relocation and recruitment is included in SG&A expenses in the consolidated statements of income); |
| |
• | A second-quarter gain of $653 ($392 after taxes) related to the shutdown of the films manufacturing facility in Carbondale, Pennsylvania, including a $630 gain on the sale of the facility (included in “Other income (expense), net” in the consolidated statements of income), and the reversal to income of certain shutdown-related accruals of $23; |
| |
• | Fourth-quarter charges of $583 ($351 after taxes) for asset impairments in Film Products; |
| |
• | A net fourth-quarter charge of $495 ($310 after taxes) in Aluminum Extrusions, including an asset impairment of $597, partially offset by the reversal to income of certain shutdown-related accruals of $102; |
| |
• | Fourth-quarter charges of $31 ($19 after taxes), third-quarter charges of $117 ($70 after taxes), second-quarter charges of $105 ($63 after taxes) and first-quarter charges of $100 ($60 after taxes) for accelerated depreciation related to restructurings in Film Products; and |
| |
• | A fourth-quarter charge of $182 ($119 after taxes) in Film Products related to the write-off of an investment. |
On June 30, 2005, substantially all of the assets of AFBS, Inc. (formerly known as Therics, Inc.), a wholly-owned subsidiary of Tredegar, were sold or assigned to a newly-created limited liability company, Therics, LLC, which is controlled and managed by an individual not affiliated with Tredegar. AFBS received a 17.5% equity interest in Therics, LLC, then valued at $170 and a 3.5% interest in Theken Spine, LLC, then valued at $800, along with potential future payments based on the sale of certain products by Therics, LLC. AFBS retained substantially all of its liabilities in the transaction, which included customary indemnification provisions for pre-transaction liabilities. Tredegar has no obligation or intent to fund any future losses that may occur at Therics, LLC or Theken Spine, LLC. The ownership interest in Therics, LLC is accounted for under the equity method of accounting with losses limited to its initial carrying value of $170. The ownership interest in Theken Spine, LLC is accounted for under the cost method, with an impairment loss recognized and a new cost basis established for any write-down to estimated fair value, if necessary. The payments due from Therics, LLC that are based on the sale of certain products are recognized as income when earned. AFBS had operating losses of $3,467 during the first six months of 2005 and $9,763 in 2004. Results of operations for AFBS since June 30, 2005 are immaterial.
See Note 2 for information regarding the write-down in 2005 of our investment in Novalux, Inc.
Gain on sale of corporate assets in 2005 includes a pretax gain of $61 related to the sale of corporate real estate. This gain is included in “Other income (expense), net” in the consolidated statements of income and separately shown in the operating profit by segment table in Note 3.
During the first quarter of 2005, we recognized a pretax gain for interest receivable on tax refund claims of $508 ($327 after taxes) (included in “Other income (expense), net” in the consolidated statements of income and “Corporate expenses, net” in the segment operating profit table in Note 3).
We are involved in various stages of investigation and remediation relating to environmental matters at certain
70
current and former plant locations. Where we have determined the nature and scope of any required environmental remediation activity, estimates of cleanup costs have been obtained and accrued. As we continue efforts to maintain compliance with applicable environmental laws and regulations, additional contingencies may be identified. If additional contingencies are identified, our practice is to determine the nature and scope of those contingencies, obtain and accrue estimates of the cost of remediation, and perform remediation. We do not believe that additional costs that could arise from those activities will have a material adverse effect on our financial position. However, those costs could have a material adverse effect on quarterly or annual operating results at that time.
We are involved in various other legal actions arising in the normal course of business. After taking into consideration information we deemed relevant, we believe that we have sufficiently accrued for probable losses and that the actions will not have a material adverse effect on our financial position. However, the resolution of the actions in a future period could have a material adverse effect on quarterly or annual operating results at that time.
From time to time, we enter into transactions with third parties in connection with the sale of assets or businesses in which we agree to indemnify the buyers or third parties involved in the sale for certain liabilities or risks related to the assets or business. Also, in the ordinary course of our business, we may enter into agreements with third parties for the sale of goods or services that may contain indemnification provisions. In the event that an indemnification claim is asserted, liability for indemnification would be subject to an assessment of the underlying facts and circumstances under the terms of the applicable agreement. Further, any indemnification payments may be limited or barred by a monetary cap, a time limitation, or a deductible or basket. For these reasons, we are unable to estimate the maximum potential amount of the potential future liability under the indemnity provisions of these agreements. We do, however, accrue for losses for any known contingent liability, including those that may arise from indemnification provisions, when future payment is probable. We disclose contingent liabilities if the probability of loss is reasonably possible and significant.
| |
17 | DISCONTINUED OPERATIONS |
|
|
On February 12, 2008, and pursuant to the terms and conditions of a purchase agreement dated January 6, 2008, we sold our aluminum extrusions business in Canada for an estimated purchase price of approximately $25,500 to an affiliate of H.I.G. Capital. The final purchase price is subject to increase or decrease to the extent that actual working capital, cash and indebtedness (as defined) as of February 12, 2008 are above or below the estimated amounts used to determine the estimated purchase price.
The sale of our aluminum extrusions business in Canada, which was suffering from operating losses driven by lower volume and higher conversion costs from appreciation of the Canadian dollar, allows us to focus on our U.S. aluminum extrusions operations where we have more control over costs and profitability. The business was classified as held for sale at the end of December 2007 when it became probable that the business would be sold. All historical results for this business have been reflected as discontinued operations; however, cash flows for discontinued operations have not been separately disclosed in the consolidated statements of cash flows.
During September 2007, we recognized a charge of $27,550 ($22,744 after taxes) for impairment of property, plant and equipment (“PP&E”) related to the aluminum extrusions operations in Canada. The impairment of PP&E was due to deteriorating business conditions and financial results. The combination of lower volume and appreciation of the Canadian dollar, which impacted our costs, caused a shift from overall profitability in 2006 to losses in 2007. In addition, our projections of the future unlevered pretax cash flows for this business indicated that the carrying value of its net assets at September 30, 2007 of approximately $71,700 (tangible assets in excess of liabilities excluding deferred income taxes) before the impairment would not be recovered. As a result, in accordance with SFAS No. 144, Accounting for the Impairment or Disposal of Long-Lived Assets, we recognized the impairment charge to write down the individual components of long-lived assets (PP&E) to the lower of their carrying value or estimated fair value. Our estimates of real property values were based on a commonly used valuation methodology in real estate whereby projected net operating income for the property (projected earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization that could be earned from rent) is divided by a related risk-adjusted expected rate of return (referred to as the capitalization rate). The estimated fair value of machinery and equipment was based on our estimates of the proceeds that we would receive if they were sold. Our estimates of the value of real estate and machinery and equipment were based on Level 2 inputs as defined by SFAS No. 157, Fair Value Measurements.
71
During December 2007, we recognized an additional impairment charge of $4,143 ($4,143 after taxes) to write down the remaining carrying value of the aluminum extrusions operations in Canada to estimated fair value less cost to sell in accordance with SFAS No. 144. In addition, in December 2007 we recognized income tax benefits of $11,428 relating to a worthless stock deduction for the business that will be recognized in Tredegar’s 2008 consolidated income tax return (included in discontinued operations in the consolidated statement of income in 2007 but reflected as a deferred income tax asset for continuing operations in our consolidated balance sheet at December 31, 2007). This tax benefit is expected to be realized by a reduction of Tredegar’s quarterly estimated income tax payments by the end of the third quarter of 2008.
Goodwill for the Aluminum Extrusions reporting unit of $6,459 has been allocated to the discontinued aluminum extrusions operations in Canada using the estimated fair value of the business sold (the after-tax cash flow expected from disposal of approximately $30,000 when it was classified as held for sale at the end of December 2007), and the estimated fair value of the aluminum extrusions business in the U.S. retained. The fair value of the aluminum extrusions business in the U.S. was estimated at approximately $145,000 using comparable enterprise value-to-EBITDA multiples as of December 31, 2007.
The statements of income for 2007, 2006 and 2005 and balance sheets as of December 31, 2007 and 2006 for the aluminum extrusions business in Canada are shown below:
|
|
Aluminum Extrusions Business in Canada |
Statements of Income |
|
|
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | 2007 | | 2006 | | 2005 | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Revenues and other items: | | | | | | | | | | | |
Sales | | $ | 157,691 | | $ | 178,965 | | $ | 148,505 | | |
Other income (expense), net | | | — | | | — | | | 1,667 | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | 157,691 | | | 178,965 | | | 150,172 | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Costs and expenses: | | | | | | | | | | | |
Cost of goods sold | | | 156,700 | | | 165,465 | | | 138,156 | | |
Freight | | | 4,969 | | | 5,494 | | | 4,415 | | |
Selling, general and administrative | | | 2,389 | | | 4,277 | | | 3,716 | | |
Asset impairments and costs associated with exit and disposal activities | | | 31,754 | | | — | | | 552 | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total | | | 195,812 | | | 175,236 | | | 146,839 | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Income (loss) before income taxes | | | (38,121 | ) | | 3,729 | | | 3,333 | | |
Income taxes | | | (18,440 | ) | | 845 | | | 476 | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net income (loss) | | $ | (19,681 | ) | $ | 2,884 | | $ | 2,857 | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aluminum Extrusions Business in Canada
Balance Sheets
| | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
December 31 | | 2007 | | 2006 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Assets | | | | | | | |
Current assets: | | | | | | | |
Accounts and notes receivable, net | | $ | 15,470 | | $ | 14,879 | |
Inventories | | | 22,089 | | | 20,266 | |
Prepaid expenses and other | | | 191 | | | 130 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total current assets | | | 37,750 | | | 35,275 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Noncurrent assets: | | | | | | | |
Net property, plant and equipment | | | 11,001 | | | 38,328 | |
Other assets and deferred charges | | | — | | | 366 | |
Goodwill and other intangibles | | | 6,459 | | | 6,459 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total noncurrent assets | | | 17,460 | | | 45,153 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | |
|
Total assets | | $ | 55,210 | | $ | 80,428 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
December 31 | | 2007 | | 2006 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Liabilities and Carrying Value of | | | | | | | |
Tredegar’s Net Advances & Investment | | | | | | | |
Current liabilities: | | | | | | | |
Accounts payable | | $ | 13,528 | | $ | 15,406 | |
Accrued expenses | | | 3,624 | | | 3,116 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total current liabilities | | | 17,152 | | | 18,522 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Noncurrent liabilities: | | | | | | | |
Deferred income taxes | | | 6,048 | | | 10,040 | |
Other noncurrent liabilities | | | 2,770 | | | 1,269 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total noncurrent liabilities | | | 8,818 | | | 11,309 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accumul. other comprehensive income (loss): | | | | | | | |
Foreign currency translation adjust. | | | 15,700 | | | 7,821 | |
Gain (loss) on derivatives | | | (465 | ) | | 47 | |
Pension and other postret. benefit adjust. | | | (4,871 | ) | | (2,877 | ) |
Carrying value of Tredegar’s net advances & investment | | | 18,876 | | | 45,606 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Liabilities and carrying value of Tredegar’s net advances & investment | | $ | 55,210 | | $ | 80,428 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
72
| |
SELECTED QUARTERLY FINANCIAL DATA | |
|
Tredegar Corporation and Subsidiaries | |
(In thousands, except per-share amounts) | |
(Unaudited) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| | First
Quarter | | Second
Quarter | | Third
Quarter | | Fourth
Quarter | | Year | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2007 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sales | | $ | 244,887 | | $ | 234,882 | | $ | 234,352 | | $ | 208,462 | | $ | 922,583 | |
Gross profit | | | 37,180 | | | 35,075 | | | 36,297 | | | 32,714 | | | 141,266 | |
Income from continuing operations | | | 11,135 | | | 10,564 | | | 6,195 | | | 7,036 | | | 34,930 | |
Income (loss) from discontinued operations | | | (802 | ) | | (629 | ) | | (24,571 | ) | | 6,321 | | | (19,681 | ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net income (loss) | | | 10,333 | | | 9,935 | | | (18,376 | ) | | 13,357 | | | 15,249 | |
Earnings (loss) per share: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Basic | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Continuing operations | | | .28 | | | .27 | | | .16 | | | .19 | | | .91 | |
Discontinued operations | | | (.02 | ) | | (.02 | ) | | (.63 | ) | | .17 | | | (.51 | ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net income (loss) | | | .26 | | | .25 | | | (.47 | ) | | .36 | | | .40 | |
Diluted | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Continuing operations | | | .28 | | | .27 | | | .16 | | | .19 | | | .90 | |
Discontinued operations | | | (.02 | ) | | (.02 | ) | | (.63 | ) | | .17 | | | (.51 | ) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net income (loss) | | | .26 | | | .25 | | | (.47 | ) | | .36 | | | .39 | |
Shares used to compute earnings per share: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Basic | | | 39,272 | | | 39,402 | | | 38,985 | | | 36,494 | | | 38,532 | |
Diluted | | | 39,487 | | | 39,584 | | | 39,119 | | | 36,587 | | | 38,688 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2006 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sales | | $ | 228,518 | | $ | 234,491 | | $ | 247,557 | | $ | 226,995 | | $ | 937,561 | |
Gross profit | | | 32,404 | | | 33,303 | | | 35,800 | | | 34,076 | | | 135,583 | |
Income from continuing operations | | | 7,104 | | | 8,494 | | | 9,883 | | | 9,836 | | | 35,317 | |
Income (loss) from discontinued operations | | | 1,111 | | | 756 | | | (193 | ) | | 1,210 | | | 2,884 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net income (loss) | | | 8,215 | | | 9,250 | | | 9,690 | | | 11,046 | | | 38,201 | |
Earnings (loss) per share: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Basic | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Continuing operations | | | .18 | | | .22 | | | .25 | | | .25 | | | .92 | |
Discontinued operations | | | .03 | | | .02 | | | — | | | .03 | | | .07 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net income (loss) | | | .21 | | | .24 | | | .25 | | | .28 | | | .99 | |
Diluted | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Continuing operations | | | .18 | | | .22 | | | .25 | | | .25 | | | .91 | |
Discontinued operations | | | .03 | | | .02 | | | — | | | .03 | | | .07 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net income (loss) | | | .21 | | | .24 | | | .25 | | | .28 | | | .98 | |
Shares used to compute earnings per share: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Basic | | | 38,602 | | | 38,632 | | | 38,654 | | | 38,793 | | | 38,671 | |
Diluted | | | 38,664 | | | 38,837 | | | 39,123 | | | 39,092 | | | 38,931 | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
73
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| | |
| TREDEGAR CORPORATION
(Registrant) |
| | |
Dated: March 4, 2008 | By | /s/ John D. Gottwald |
| |
|
| | John D. Gottwald |
| | President and Chief Executive |
| | Officer |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities indicated on March 4, 2008.
| | | |
| Signature | | Title |
| | | |
/s/ | John D. Gottwald | | President, Chief Executive Officer and Director |
|
| | (Principal Executive Officer) |
| (John D. Gottwald) | | |
| | | |
/s/ | D. Andrew Edwards | | Vice President, Chief Financial Officer and Treasurer |
|
| | (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) |
| (D. Andrew Edwards) | | |
| | | |
/s/ | Richard L. Morrill | | Chairman of the Board of Directors |
|
| | |
| (Richard L. Morrill) | | |
| | | |
/s/ | William M. Gottwald | | Vice Chairman of the Board of Directors |
|
| | |
| (William M. Gottwald) | | |
| | | |
/s/ | N. A. Scher | | Vice Chairman of the Board of Directors |
|
| | |
| (Norman A. Scher) | | |
| | | |
/s/ | Horst R. Adam | | Director |
|
| | |
| (Horst R. Adam) | | |
| | | |
/s/ | Austin Brockenbrough, III | | Director |
|
| | |
| (Austin Brockenbrough, III) | | |
| | | |
/s/ | Donald T. Cowles | | Director |
|
| | |
| (Donald T. Cowles) | | |
74
| | | |
/s/ | Thomas G. Slater, Jr. | | Director |
|
| | |
| (Thomas G. Slater, Jr.) | | |
| | | |
/s/ | R. Gregory Williams | | Director |
|
| | |
| (R. Gregory Williams) | | |
| | | |
75
EXHIBIT INDEX
| |
3.1 | Amended and Restated Articles of Incorporation of Tredegar (filed as Exhibit 3.1 to Tredegar’s Annual Report on Form 10-K (File No. 1-10258) for the year ended December 31, 2004, and incorporated herein by reference) |
| |
3.2 | Amended and Restated By-laws of Tredegar (filed as Exhibit 3.2 to Tredegar’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 1-10258), filed November 6, 2007, and incorporated herein by reference) |
| |
3.3 | Articles of Amendment (filed as Exhibit 3.3 to Tredegar’s Annual Report on Form 10-K (File No. 1-10258) for the year ended December 31, 2004, and incorporated herein by reference) |
| |
4.1 | Form of Common Stock Certificate (filed as Exhibit 4.1 to Tredegar’s Annual Report on Form 10-K (File No. 1-10258) for the year ended December 31, 2004, and incorporated herein by reference) |
| |
4.2 | Rights Agreement, dated as of June 30, 1999, by and between Tredegar and American Stock Transfer & Trust Company, as Rights Agent (filed as Exhibit 4.2 to Tredegar’s Annual Report on Form 10-K (File No. 1-10258) for the year ended December 31, 2004, and incorporated herein by reference) |
| |
4.2.1 | Amendment and Substitution Agreement (Rights Agreement) dated as of December 11, 2002, by and among Tredegar, American Stock Transfer and Trust Company and National City Bank (filed as Exhibit 4.2.1 to Tredegar’s Annual Report on Form 10-K (File No. 1-10258) for the year ended December 31, 2002, and incorporated herein by reference) |
| |
4.3 | Credit Agreement among Tredegar Corporation, as borrower, the domestic subsidiaries of Tredegar that from time to time become parties thereto, as guarantors, the several banks and other financial institutions as may from time to time become parties thereto, Wachovia Bank, National Association, as administrative agent, SunTrust Bank, as syndication agent, and Bank of America, N.A., KeyBank National Association, and JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as documentation agents, dated as of December 15, 2005 (filed as Exhibit 10.16 to Tredegar’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 1-10258), filed December 20, 2005, and incorporated herein by reference) |
| |
10.1 | Reorganization and Distribution Agreement dated as of June 1, 1989, between Tredegar and Ethyl (filed as Exhibit 10.1 to Tredegar’s Annual Report on Form 10-K (File No. 1-10258) for the year ended December 31, 2004, and incorporated herein by reference) |
| |
*10.2 | Employee Benefits Agreement dated as of June 1, 1989, between Tredegar and Ethyl (filed as Exhibit 10.2 to Tredegar’s Annual Report on Form 10-K (File No. 1-10258) for the year ended December 31, 2004, and incorporated herein by reference) |
| |
10.3 | Tax Sharing Agreement dated as of June 1, 1989, between Tredegar and Ethyl (filed as Exhibit 10.3 to Tredegar’s Annual Report on Form 10-K (File No. 1-10258) for the year ended December 31, 2004, and incorporated herein by reference) |
| |
10.4 | Indemnification Agreement dated as of June 1, 1989, between Tredegar and Ethyl (filed as Exhibit 10.4 to Tredegar’s Annual Report on Form 10-K (File No. 1-10258) for the year ended December 31, 2004, and incorporated herein by reference) |
| |
*10.5 | Tredegar Industries, Inc. Retirement Benefit Restoration Plan (filed as Exhibit 10.7 to Tredegar’s Annual Report on Form 10-K (File No. 1-10258) for the year ended December 31, 2004, and incorporated herein by reference) |
| |
*10.5.1 | Amendment to the Tredegar Retirement Benefit Restoration Plan (filed as Exhibit 10.7.1 to Tredegar’s Annual Report on Form 10-K (File No. 1-10258) for the year ended December 31, 2004, and incorporated herein by reference) |
| |
*10.6 | Tredegar Industries, Inc. Savings Plan Benefit Restoration Plan (filed as Exhibit 10.8 to Tredegar’s Annual Report on Form 10-K (File No. 1-10258) for the year ended December 31, 2004, and incorporated herein by reference) |
| |
*10.6.1 | Resolutions of the Executive Committee of the Board of Directors of Tredegar Corporation adopted on December 28, 2004 (effective as of December 31, 2004) amending the Tredegar Corporation Retirement Savings Plan Benefit Restoration Plan (filed as Exhibit 10.9.1 to Tredegar’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 1-10258), filed on December 30, 2004, and incorporated herein by reference) |
| |
*10.7 | Tredegar Industries, Inc. Amended and Restated Incentive Plan (filed as Exhibit 10.9 to Tredegar’s Annual Report on Form 10-K (File No. 1-10258) for the year ended December 31, 2005, and incorporated herein by reference) |
| |
*10.8 | Tredegar Industries, Inc. Directors’ Stock Plan (filed as Exhibit 10.11 to Tredegar’s Annual Report on Form 10-K (File No. 1-10258) for the year ended December 31, 2004, and incorporated herein by reference) |
| |
*10.9 | Tredegar Corporation’s 2004 Equity Incentive Plan (filed as Exhibit 10.13 to the Form S-8 Registration Statement No. 333-115423, filed on May 12, 2004 (incorporating from the Annex to Tredegar Corporation’s Definitive Proxy Statement on Schedule 14A filed on March 4, 2004 (File No. 1-10258) and incorporated herein by reference) |
76
| |
| |
*10.10 | Transfer Agreement, by and between Old Therics and New Therics, dated as of June 30, 2005 (filed as Exhibit 10.17 to Tredegar’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 1-10258), filed July 1, 2005, and incorporated herein by reference) |
| |
10.11 | Intellectual Property Transfer Agreement, by and between Old Therics and New Therics, dated as of June 30, 2005 (filed as Exhibit 10.18 to Tredegar’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 1-10258), filed July 1, 2005, and incorporated herein by reference) |
| |
10.12 | Unit Purchase Agreement, by and between Old Therics, New Therics and Randall R. Theken, dated as of June 30, 2005 (filed as Exhibit 10.19 to Tredegar’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 1-10258), filed July 1, 2005, and incorporated herein by reference) |
| |
10.13 | Payment Agreement, by and between Old Therics and New Therics, dated as of June 30, 2005 (filed as Exhibit 10.20 to Tredegar’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 1-10258), filed July 1, 2005, and incorporated herein by reference) |
| |
*10.14 | Form of Notice of Nonstatutory Stock Option Grant and Nonstatutory Stock Option Terms and Conditions (filed as Item 1.01 to Tredegar’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 1-10258), filed on March 10, 2006, and incorporated herein by reference) |
| |
*10.15 | Form of Notice of Stock Unit Award and Stock Unit Award Terms and Conditions (filed as Exhibit 10.21 to Tredegar’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 1-10258), filed on February 27, 2007, and incorporated herein by reference) |
| |
*10.16 | Form of Notice of Stock Unit Award and Stock Unit Award Terms and Conditions (2007 EPA) (filed as Exhibit 10.22 to Tredegar’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 1-10258), filed on June 26, 2007, and incorporated herein by reference) |
| |
*10.17 | Form of Notice of Stock Unit Award and Stock Unit Award Terms and Conditions (2008 EPA) (filed as Exhibit 10.23 to Tredegar’s Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 1-10258), filed on June 26, 2007, and incorporated herein by reference) |
| |
+*10.18 | Summary of Director Compensation for Fiscal 2008 |
| |
+21 | Subsidiaries of Tredegar |
| |
+23.1 | Consent of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm |
| |
+31.1 | Section 302 Certification of Principal Executive Officer |
| |
+31.2 | Section 302 Certification of Principal Financial Officer |
| |
+32.1 | Section 906 Certification of Principal Executive Officer |
| |
+32.2 | Section 906 Certification of Principal Financial Officer |
* Denotes compensatory plans or arrangements or management contracts.
+ Filed herewith
77




