UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
(Mark One)
| [X] | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
| | For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2014 OR |
| [ ] | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
| | For the transition period from to |
Commission file number 0-24960
COVENANT TRANSPORTATION GROUP, INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| Nevada | | 88-0320154 |
| (State / other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) | | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
| 400 Birmingham Hwy. | | |
| Chattanooga, TN | | 37419 |
| (Address of principal executive offices) | | (Zip Code) |
| Registrant's telephone number, including area code: | 423 - 821-1212 |
| | |
| Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act: | $0.01 Par Value Class A Common Stock – The NASDAQ Global Select Market |
| | (Title of class) |
| | |
| Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: | None |
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act.
[ ] Yes [X] No
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Act.
[ ] Yes [X] No
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days.
[X] Yes [ ] No
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Website, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files).
[X] Yes [ ] No
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant's knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendments to this Form 10-K. [ ]
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See definitions of "accelerated filer, "large accelerated filer," and "smaller reporting company" in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| Large accelerated filer | [ ] | Accelerated filer | [ ] |
| Non-accelerated filer | [ ] (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) | Smaller reporting company | [X] |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act).
[ ] Yes [X] No
The aggregate market value of the common equity held by non-affiliates of the registrant as of June 30, 2014, was approximately $107.0 million (based upon the $12.88 per share closing price on that date as reported by NASDAQ). In making this calculation the registrant has assumed, without admitting for any purpose, that all executive officers, directors, and affiliated holders of more than 10% of a class of outstanding common stock, and no other persons, are affiliates.
As of March 2, 2015, the registrant had 15,790,902 shares of Class A common stock and 2,350,000 shares of Class B common stock outstanding.
Portions of the materials from the registrant's definitive proxy statement for the 2015 Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be held on May 14, 2015, have been incorporated by reference into Part III of this Form 10-K.
| Part I | | |
| | Item 1. | Business | |
| | Item 1A. | Risk Factors | |
| | Item 1B. | Unresolved Staff Comments | |
| | Item 2. | Properties | |
| | Item 3. | Legal Proceedings | |
| | Item 4. | Mine Safety Disclosures | |
| | | | |
| Part II | | |
| | Item 5. | Market for Registrant's Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities | |
| | Item 6. | Selected Financial Data | |
| | Item 7. | Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations | |
| | Item 7A. | Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk | |
| | Item 8. | Financial Statements and Supplementary Data | |
| | Item 9. | Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure | |
| | Item 9A. | Controls and Procedures | |
| | Item 9B. | Other Information | |
| | | | |
| Part III | | |
| | Item 10. | Directors, Executive Officers, and Corporate Governance | |
| | Item 11. | Executive Compensation | |
| | Item 12. | Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters | |
| | Item 13. | Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence | |
| | Item 14. | Principal Accounting Fees and Services | |
| | | | |
| Part IV | | |
| | Item 15. | Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules | |
| Signatures | |
| | |
| Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm | |
| | |
| Financial Data | |
| | Consolidated Balance Sheets | |
| | Consolidated Statements of Operations | |
| | Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income | |
| | Consolidated Statements of Stockholders' Equity | |
| | Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows | |
| | Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements | |
PART I
This Annual Report on Form 10-K contains certain statements that may be considered forward-looking statements within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended and such statements are subject to the safe harbor created by those sections and the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995, as amended. All statements, other than statements of historical or current fact, are statements that could be deemed forward-looking statements, including without limitation: any projections of earnings, revenues, or other financial items; any statement of plans, strategies, and objectives of management for future operations; any statements concerning proposed new services or developments; any statements regarding future economic conditions or performance; and any statements of belief and any statement of assumptions underlying any of the foregoing. In this Annual Report, statements relating to the ability of our infrastructure to support future growth, our ability to recruit and retain qualified drivers, our ability to react to market conditions, our ability to gain market share, future tractor and trailer prices, expected functioning of our information technology systems, expected liquidity and methods for achieving sufficient liquidity, future fuel prices, future inflation, future third-party service provider relationships and availability, future compensation arrangements with independent contractors and drivers, expected owner operator usage, future driver market, planned allocation of capital, future equipment costs, expected settlement of operating lease obligations, future asset sales, future tax expense and deductions, future effectiveness of fuel surcharge programs and price hedges, expected capital expenditures (including the future mix of lease and purchase obligations), future asset utilization, future trucking capacity, expected freight demand and volumes, future rates, future depreciation and amortization, and future purchased transportation expense, among others, are forward-looking statements. Such statements may be identified by their use of terms or phrases such as "believe," "may," "could," "expects," "estimates," "projects," "anticipates," "plans," "intends," and similar terms and phrases. Forward-looking statements are based on currently available operating, financial, and competitive information. Forward-looking statements are inherently subject to risks and uncertainties, some of which cannot be predicted or quantified, which could cause future events and actual results to differ materially from those set forth in, contemplated by, or underlying the forward-looking statements. Factors that could cause or contribute to such differences include, but are not limited to, those discussed in the section entitled "Item 1A. Risk Factors," set forth below. Readers should review and consider the factors discussed in "Item 1A. Risk Factors," along with various disclosures in our press releases, stockholder reports, and other filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission.
All such forward-looking statements speak only as of the date of this Annual Report. You are cautioned not to place undue reliance on such forward-looking statements. We expressly disclaim any obligation or undertaking to release publicly any updates or revisions to any forward-looking statements contained herein to reflect any change in our expectations with regard thereto or any change in the events, conditions, or circumstances on which any such statement is based.
References in this Annual Report to "we," "us," "our," or the "Company" or similar terms refer to Covenant Transportation Group, Inc. and its subsidiaries.
GENERAL
Background and Strategy
We were founded in 1986 as a provider of expedited long haul freight transportation, primarily using two-person driver teams in transcontinental lanes. Since that time, we have grown from 25 trucks to approximately 2,700 trucks and expanded our services from predominantly long haul dry van to include refrigerated, dedicated, cross-border, regional, brokerage, and other offerings. The expansion of our fleet and service offerings have placed us among the nation's largest truckload transportation companies.
Generally, we transport full trailer loads of freight from origin to destination without intermediate stops or handling. We provide truckload transportation services throughout the continental United States, into and out of Mexico, and into and out of portions of Canada. Our truckload freight services utilize equipment we own or lease or equipment owned by independent contractors for the pick-up and delivery of freight. In most of our truckload business, we transport freight over nonroutine routes. Our dedicated freight service offering provides similar transportation services, but does so pursuant to agreements whereby we make our equipment available to a specific customer for shipments over particular routes at specified times. To complement our truckload operations, we provide freight brokerage services and accounts receivable factoring services. Through our asset based and non-asset based capabilities, we transport many types of freight for a diverse customer base.
We concentrate on market sectors where we believe our capacity in relation to sector size and our operating proficiency can make a meaningful difference to customers. The primary sectors in which we operate are as follows:
● Expedited / Long haul: In our expedited / long haul business, we operate approximately 1,070 tractors, approximately 690 of which are driven by two-person driver teams. Our expedited operations primarily involve high service freight with delivery standards, such as 1,000 miles in 22 hours, or 15-minute delivery windows, that are difficult for competitors to satisfy with solo-driven tractors or rail-intermodal service. Our expedited services often involve high value, high security, or time-definite loads for integrated global freight companies, less-than-truckload carriers, manufacturers, and retailers. We believe we are one of the five largest team expedited providers, and that growth in omni-channel, organic food, manufacturing, and e-commerce freight make this an attractive sector.
● Temperature-Controlled: In our temperature-controlled business, we operate approximately 970 tractors, approximately 200 of which are driven by two-person driver teams, and also offer intermodal service in longer haul lanes. The temperature-controlled sector includes fresh and frozen foods, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and other freight where extreme heat or cold could cause damage. We believe we are among the ten largest temperature-controlled providers, and that factors such as United States population growth, increasing consumer preference for fresh and organic produce, and demographic trends requiring more pharmaceuticals make this an attractive sector.
● Dedicated: In our dedicated contract business, we operate approximately 510 tractors, approximately 20 of which are driven by two-person driver teams, primarily for manufacturers located in the southeastern United States. The dedicated sector typically involves longer-term contracts that allocate a specified number of tractors and trailers to a specific customer, with fixed and variable compensation. Many of our dedicated contract customers are automotive companies or tier one suppliers to the auto industry, with high service standards. We believe this sector is growing because of an improved manufacturing environment in the United States, particularly in the Southeast, customer concerns about trucking capacity, and a need for dependable service at plants.
● Capacity Provider Solutions and Services / Equipment Sales and Leasing: We primarily provide freight brokerage capacity to customers when the freight does not fit our network or profitability requirements. In addition, we participate in the market for used equipment sales and leasing through our 49% ownership of Transport Enterprise Leasing, LLC ("TEL"), and we assist current and potential capacity providers with improving their cash flows through secure invoice factoring services. We believe this suite of services links our interests with those of our customers and current and potential third party capacity providers. We intend to expand our presence in these sectors, which we believe offer attractive growth opportunities with a lower capital investment than our asset-based truckload operations.
As our fleet has grown over three decades and our service platform matured, several important trends dramatically affected the truckload industry and our business. First, supply chain patterns became more fluid in response to dynamic changes in labor and transportation costs, ocean freight and rail-intermodal service standards, retail distribution center networks, governmental regulations, and other industry-wide factors. Second, the cost structure of the truckload business, particularly equipment and fuel prices, rose dramatically, impacting us and our customers' freight decisions. Third, customers used technology to constantly optimize their supply chains, which necessitated expanding our own technological capability to optimize our asset allocation, manage yields, and drive operational efficiency. Fourth, a confluence of regulatory constraints, safety and security demands, and scarcity of qualified applicants, negatively impacted our asset productivity and reinforced what a precious resource professional truck drivers are (and we believe increasingly will be) in our industry.
In the fourth quarter of 2011, we began examining the key components of each of our business units, including: market trends and our relative positioning in the market; leadership and our personnel's ability to execute; financial results, investment returns, and capital requirements; importance of our service to our customers; and growth prospects.
As a result of the assessment process, we developed the Company's first formal strategic plan. Each year since, we have updated the plan via formal process, selecting initiatives and setting goals that both our Board of Directors and management believe are key to ensuring "continuous improvement" for our shareholders, customers, employees, vendors and the motoring public.
The key elements of our current strategic plan are:
● Organizational Excellence and Entrepreneurial Spirit. We have re-aligned our management team, added talent, and implemented best practices in part through using Franklin Covey's Four Disciplines of Execution® to bring a new focus to metrics, accountability, and incentive compensation. Through multiple programs recognizing individual initiative, we have also been instilling an ownership culture throughout our company. We also implemented a single enterprise management system across all subsidiaries to improve visibility and coordination of customers, operations, and financial activities.
● Focus on the Driver. Drivers are the lifeblood of our company and our industry. We employ a broad range of safety, lifestyle, compensation, equipment technology, and personal recognition methods to convey our respect and appreciation for our drivers and to improve their careers. A portion of these techniques involve sophisticated analytics to identify likely candidates, match teams, evaluate recruiting spending, deliver training content to drivers, and design tractor specifications. Over the past three years, our driver turnover percentage has improved toward the industry average after starting significantly higher.
● Focus on the Customer Experience. Our mission statement begins: "CTG's mission is to be a problem solver for every customer…" We offer premium service in sectors where we can make a difference, and we use our brokerage subsidiary, Covenant Transport Solutions, Inc., to cover loads that do not meet our requirements. With each interaction, we seek to enhance the value we bring to the customer relationship.
● Rigorous Capital Allocation Process and Reduce Leverage. Our senior management annually ranks capital investment opportunities against available capital and debt reduction goals, and material investments must pass return on investment and capital investment committee approval processes. In addition, reducing our total leverage has been a primary strategic goal. We believe our disciplined investment review has contributed to our improved results by allocating capital to more profitable business units and downsizing other units into greater profitability.
● Risk Management—Assess and Mitigate. We consistently evaluate risk areas with significant volatility, as well as the costs and benefits associated with mitigating the volatility. Diesel fuel prices, insurance and claims cost, and used equipment prices are all areas where we identified significant risk and volatility for our business. To manage these risks, we have employed fuel hedging contracts on a portion of our fuel usage not covered by customer fuel surcharges, lowered our self-insured accident liability retention, and expanded our ability to sell our used equipment to increase bargaining power with the tractor and trailer manufacturers.
● Technology. We purchase and deploy technology that we believe will allow us to operate more safely, securely, and efficiently. Our information systems are integrated into a single platform that represents a multi-year investment to upgrade the hardware and software of our information systems. This technology was purchased off the shelf, which minimizes our fixed cost investment, and enables us to stay current with the latest developments.
We believe the ongoing execution of our strategic plan has contributed to the substantial improvement in operating results and profitability we have generated over the past several years. In 2014, the results of our strategic plan are evident in that we successfully completed a follow-on stock offering that helped significantly deleverage our balance sheet; enhanced our recruiting, retention, and business intelligence; further upgraded our information technology; focused on service and on time delivery; and enhanced cross-marketing opportunities between our subsidiaries. Each of these accomplishments positively impacted the success of the key initiatives identified above, our overarching financial goals, and ultimately, the Company.
Fiscal 2014 marks the best annual results we have experienced since 1999. Additionally, fiscal 2014 is our third consistent year of profitability, noting only one year between fiscal 2006-2011 produced a profit. We believe the return to profitability on a consistent basis is the result of certain initiatives we put in place that are providing positive results. However, we still have significant work ahead to achieve our goals, deliver a strong and stable product for our customers, provide a bright future for our employees and owner-operators, and create meaningful value for our stockholders.
The Company
We operate a relatively new tractor fleet and employ sophisticated truck technology that enhances our operational efficiencies and our drivers' safety. Our company-owned tractor fleet has an average age of approximately 1.6 years, which compares favorably to an average U.S. Class 8 tractor age of approximately 6.5 years in 2013. Some of the technologies we employ include the following: (1) freight optimization software that can perform sophisticated analyses of profitability and other measures on each customer, route, and load; (2) routing software that selects the best route, identifies fuel stops, and warns of deviations from routing instructions; (3) a tracking and communications system that permits direct communication between drivers and fleet managers, as well as constant location and delivery updates; (4) electronic logging devices in all of our tractors; (5) aerodynamics and other fuel efficiency systems that have significantly improved fuel mileage; and (6) safety technology, including rollover stability control, collision mitigation, and lane-change warning. We believe our modern fleet lowers maintenance costs, improves fuel mileage, improves safety, contributes to better customer service, and assists with driver retention.
Business Units
We have one reportable segment, our asset-based truckload services ("Truckload").
The Truckload segment consists of three asset-based operating fleets that are aggregated because they have similar economic characteristics and meet the aggregation criteria. The three operating fleets that comprise our Truckload segment are as follows: (i) Covenant Transport, Inc. ("Covenant Transport"), our historical flagship operation, which provides expedited long haul, dedicated, temperature-controlled, and regional solo-driver service; (ii) Southern Refrigerated Transport, Inc. ("SRT"), which provides primarily long haul and regional temperature-controlled service; and (iii) Star Transportation, Inc. ("Star"), which provides regional solo-driver and dedicated services, primarily in the southeastern United States.
In addition, our Covenant Transport Solutions, Inc. ("Solutions") subsidiary has service offerings ancillary to our Truckload operations, including: freight brokerage service through freight brokerage agents, who are paid a commission for the freight they provide, and accounts receivable factoring. These operations consist of several operating segments, which neither individually nor in the aggregate meet the quantitative or qualitative reporting thresholds.
The following charts reflect the size of each of our subsidiaries measured by 2014 total revenue, net of fuel surcharge revenue, which we refer to as "freight revenue":
Distribution of Freight Revenue Among Subsidiaries |
| Covenant Transport | 55% |
| SRT | 28% |
| Star | 7% |
| Solutions | 10% |
Our Truckload segment comprised approximately 90%, 93%, and 95% of our total freight revenue in 2014, 2013, and 2012, respectively.
In our Truckload segment, we primarily generate revenue by transporting freight for our customers. Generally, we are paid a predetermined rate per mile for our truckload services. We enhance our truckload revenue by charging for tractor and trailer detention, loading and unloading activities, and other specialized services, as well as through the collection of fuel surcharges to mitigate the impact of increases in the cost of fuel. The main factors that affect our Truckload revenue are the revenue per mile we receive from our customers, the percentage of miles for which we are compensated, and the number of shipments and miles we generate. These factors relate, among other things, to the general level of economic activity in the United States, inventory levels, specific customer demand, the level of capacity in the trucking industry, and driver availability.
The main expenses that impact the profitability of our Truckload segment are the variable costs of transporting freight for our customers. These costs include fuel expenses, driver-related expenses, such as wages, benefits, training, and recruitment, and purchased transportation expenses, which primarily include compensating independent contractors. Expenses that have both fixed and variable components include maintenance and tire expense and our total cost of insurance and claims. These expenses generally vary with the miles we travel, but also have a controllable component based on safety, self-insured retention versus insurance premiums, fleet age, efficiency, and other factors. Our main fixed costs include rentals and depreciation of long-term assets, such as revenue equipment and terminal facilities, and the compensation of non-driver personnel.
We measure the productivity of our Truckload segment with three key performance metrics: average freight revenue per total mile (excluding fuel surcharges), average miles per tractor, and average freight revenue per tractor per week (excluding fuel surcharges). A description of each follows:
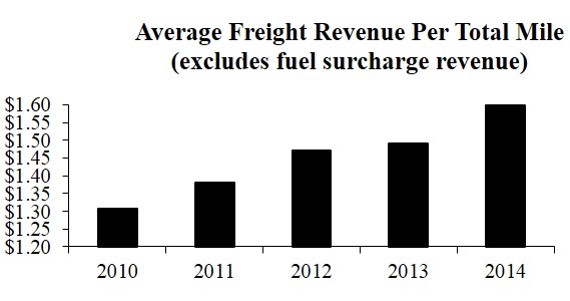
Average Freight Revenue Per Total Mile. Our average freight revenue per total mile is primarily a function of 1) the allocation of assets among our subsidiaries and 2) the macro U.S. economic environment including supply/demand of freight and carriers. The year-over-year increase from 2010 to 2014 is a result of allocating more tractors to our niche/specialized service offerings that provide higher rates (including expedited/critical freight, high-value/constant security, temperature-controlled, and cross border service). Also, tighter capacity in the truckload freight market, especially for expedited/team transit, and shipper concerns about the prospect of tighter capacity considering the regulatory and driver market, afforded an environment more conducive to rate increases. | |
| Average Freight Revenue Per Total Mile (excludes fuel surcharge revenue) | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | | 2014 |
| $1.31 | $1.38 | $1.47 | $1.49 | | $1.60 |
Average Miles Per Tractor. Average miles per tractor reflect economic demand, driver availability, regulatory constraints, and the allocation of tractors among the service offerings. Utilization in 2014 improved from that of 2013 primarily due to an increase on the number of team-driven tractors as a percentage of our fleet partially offset by a lower seated truck percentage. All years were an improvement as compared to 2011, when we experienced issues with the system conversion and were lower than 2010, which benefited from fewer regulations and better driver availability. |  |
| Average Miles Per Tractor | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | |
| 125,178 | 115,775 | 118,103 | 119,375 | 123,275 | |
Average Freight Revenue Per Tractor Per Week. We use average freight revenue per tractor per week as our main measure of asset productivity. This operating metric takes into account the effects of freight rates, non-revenue miles, and miles per tractor. In addition, because we calculate average freight revenue per tractor using all of our trucks, it takes into account the percentage of our fleet that is unproductive due to lack of drivers, repairs, and other factors. The increase in average freight revenue per tractor per week in 2014 is primarily due to increased rate and allocation of tractors to more productive service offerings, which further contributed to higher rates and utilization. | 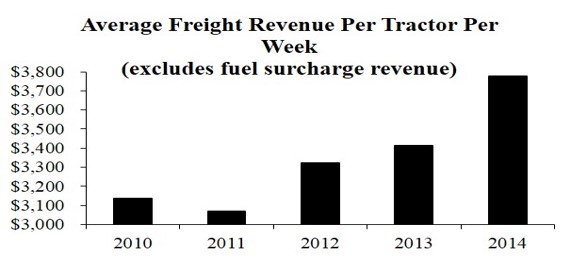 |
| Average Freight Revenue Per Tractor Per Week (excludes fuel surcharge revenue) | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | |
| $3,137 | $3,069 | $3,320 | $3,411 | $3,777 | |
Our Solutions subsidiary comprised approximately 10%, 7%, and 5% of our total operating revenue in 2014, 2013, and 2012, respectively. Solutions derives revenue from arranging transportation services for customers through relationships with thousands of third-party carriers and integration with our Truckload segment. Solutions provides freight brokerage services through freight brokerage agents, who are paid a commission for the freight brokerage service they provide and accounts receivable factoring. The main factors that impact profitability in terms of expenses are the variable costs of outsourcing the transportation freight for our customers and managing fixed costs, including salaries and selling, general, and administrative expenses. Our brokerage loads decreased to 34,091 in 2014, from 37,884 in 2013, while average revenue per load increased approximately 49% to $1,575 in 2014, from $1,060 in 2013, primarily due to additional peak-season freight opportunities during the fourth quarter of 2014, improved coordination with our Truckload segment, and additional business from new customers added during the year partially offset by the discontinuation of an underperforming location in June of 2014. Additionally, revenue from Solutions' accounts receivable factoring improved by more than 30% year-over-year to $2.3 million in 2014 from $1.7 million in 2013.
In May 2011, we acquired a 49.0% interest in TEL. TEL is a tractor and trailer equipment leasing company and used equipment reseller. We have accounted for our investment in TEL using the equity method of accounting and thus our financial results include our proportionate share of TEL's net income since May 2011, or $3.7 million in 2014, $2.8 million in 2013, and $1.9 million in 2012. As a result, TEL's results and growth are significant to our current year results and, in our estimation, to our longer-term vision.
Refer to Note 16, "Segment Information," of the accompanying consolidated financial statements for further information about our reporting segment's operating and financial results for 2014, 2013, and 2012.
Customers and Operations
We focus on targeted markets throughout the United States where we believe our service standards can provide a competitive advantage. We are a major carrier for transportation companies such as freight forwarders, less-than-truckload carriers, and third-party logistics providers that require a high level of service to support their businesses, as well as for traditional truckload customers such as manufacturers, retailers, and food and beverage shippers. All of our asset-based subsidiaries are truckload carriers and as such we generally dedicate an entire trailer to one customer from origin to destination. We also generate revenue through providing ancillary services, including freight brokerage services and accounts receivable factoring.
In 2014, one customer accounted for more than 10% of our consolidated revenue. UPS, our largest customer, was serviced by both our Truckload segment and our Solutions subsidiary providing for $82.5 million of total revenue. No customer accounted for more than 10% of our consolidated revenue in 2013 or 2012. Our top five customers accounted for approximately 29%, 25%, and 24% of our total revenue in 2014, 2013, and 2012, respectively.
We operate tractors driven by a single driver and also tractors assigned to two-person driver teams. Our single driver tractors generally operate in shorter lengths of haul, generate fewer miles per tractor, and experience more non-revenue miles, but the lower productive miles are expected to be offset by generally higher revenue per loaded mile and the reduced employee expense of compensating only one driver. In contrast, our two-person driver tractors generally operate in longer lengths of haul, generate greater miles per tractor, and experience fewer non-revenue miles, but we typically receive lower revenue per loaded mile and incur higher employee expenses of compensating both drivers. We expect operating statistics and expenses to shift with the mix of single and team operations.
We operate throughout the U.S. and in parts of Canada and Mexico, with substantially all of our revenue generated from within the U.S. All of our tractors are domiciled in the U.S., and we have generated less than two percent of our revenue in Canada and Mexico in 2014, 2013 and 2012. We do not separately track domestic and foreign revenue from customers, and providing such information would not be meaningful. All of our long-lived assets are, and have been for the last three fiscal years, located within the United States.
In 2009, we began a multi-year project to upgrade the hardware and software of our information systems. The goal upon completion of the project was to have uniform operational and financial systems across the entire Company as we believe this provides improved customer service, utilization, and enhances our visibility into and across the organization. All of our operating subsidiaries are now operating on the new system. We encountered difficulties when we converted our Covenant Transport subsidiary to the new system in the third quarter of 2011, which disrupted our operations and impacted our customer service, driver relations, and results of operations. All significant problems associated with the Covenant Transport conversion were addressed by the end of January 2012 and efficiencies from the new system were realized by Covenant Transport in 2012. We implemented the new operating system at SRT in February 2014. As expected with any large conversion project, SRT experienced inefficiencies that resulted in a reduction in average miles per tractor in February and March of this year. As a result of the system conversion, SRT experienced a year-over-year reduction in first quarter profitability; however, by the second quarter of 2014 those inefficiencies were largely resolved. We are excited to have all subsidiaries on one operating platform and are evaluating where we can leverage the system to add efficiencies across the Company.
Drivers and Other Personnel
Driver recruitment, retention, and satisfaction are essential to our success, and we have made each of these factors a primary element of our strategy. We recruit both experienced and student drivers as well as independent contractor drivers who own and drive their own tractor and provide their services to us under contract. We conduct recruiting and/or driver orientation efforts from five of our locations, and we offer ongoing training throughout our terminal network. We emphasize driver-friendly operations throughout our organization. We have implemented automated programs to signal when a driver is scheduled to be routed toward home, and we assign fleet managers specific tractor units, regardless of geographic region, to foster positive relationships between the drivers and their principal contact with us.
The truckload industry has periodically experienced difficulty in attracting and retaining enough qualified truck drivers. It is also common for the driver turnover rate of individual carriers to exceed 100% in a year. At times, there are driver shortages in the trucking industry. In past years, when there were driver shortages, the number of qualified drivers had not kept pace with freight growth because of (i) changes in the demographic composition of the workforce; (ii) alternative employment opportunities other than truck driving that became available in a growing economy; and (iii) individual drivers' desire to be home more often.
Driver retention was challenging in 2014 as economic growth provided more employment opportunities that attracted professional drivers, especially during the first half of the year; however, due to certain of our initiatives during the second half of the year, we increased the number of drivers as of December 31, 2014 by approximately 3.0% year-over-year through improved recruiting and retention. Despite the increase in number of drivers as of December 31, 2014, our average truck count for the year was reduced as compared to December 31, 2013, as a result of open trucks, including wrecked units, averaging approximately 5.1% for the year ended December 31, 2014, compared to approximately 4.8% for the year ended December 31, 2013.
We believe having a happy, healthy, and safe driver is the key to our success, both in the short term and over a longer period. As a result, we are actively working to enhance our drivers' experience in an effort to recruit and retain more drivers.
Independent contractors provide a tractor and a driver and are responsible for all operating expenses in exchange for a fixed payment per mile. We do not have the capital outlay of purchasing the tractor. The payments to independent contractors are recorded in revenue equipment rentals and purchased transportation. When independent contractor tractors are utilized, we avoid expenses generally associated with company-owned equipment, such as driver compensation, fuel, interest, and depreciation. Obtaining equipment from independent contractors and under operating leases effectively shifts financing expenses from interest to "above the line" operating expenses.
Internal education and evaluation of the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration ("FMCSA") Compliance Safety Accountability program ("CSA") (formerly Comprehensive Safety Analysis 2010) are priorities as we develop plans to keep our top talent and challenge those drivers that need improvement. Overall, we believe this regulation will bring challenges as well as opportunities for truckload carriers. CSA, in conjunction with the new U.S. Department of Transportation ("DOT") reductions in hours-of-service for drivers, has reduced and will likely continue to impact effective capacity in our industry as well as negatively impact equipment utilization. Nevertheless, for carriers that successfully manage the new environment with driver-friendly equipment, compensation, and operations, we believe opportunities to increase market share may be available. Driver pay may increase as a result of regulation and economic expansion, which could provide more alternative employment opportunities. If economic growth is sustained, however, we expect the supply/demand environment to be favorable enough for us to offset expected compensation increases with better freight pricing.
We use driver teams in a substantial portion of our tractors. Driver teams permit us to provide expedited service on selected long haul lanes because teams are able to handle longer routes and drive more miles while remaining within DOT hours-of-service rules. The use of teams contributes to greater equipment utilization of the tractors they drive than obtained with single drivers. The use of teams, however, increases the accumulation of miles on tractors and trailers as well as personnel costs as a percentage of revenue and the number of drivers we must recruit. At December 31, 2014 and 2013, teams operated approximately 32% of our tractors.
We are not a party to any collective bargaining agreement. At December 31, 2014, we employed approximately 3,600 drivers and approximately 800 non-driver personnel. At December 31, 2014, we also contracted with 195 independent contractors.
Revenue Equipment
At December 31, 2014, we operated 2,665 tractors and 6,722 trailers. Of these tractors, 2,320 were owned, 150 were financed under operating leases, and 195 were provided by independent contractors, who own and drive their own tractors. Of these trailers, 2,916 were owned, 2,904 were financed under operating leases, and 902 were financed under capital leases. Furthermore, at December 31, 2014, approximately 66% of our trailers were dry vans and the remaining trailers were refrigerated vans.
We believe that operating high quality, late-model equipment contributes to operating efficiency, helps us recruit and retain drivers, and is an important part of providing excellent service to customers. We operate a modern fleet of tractors, with the majority of units under warranty, to minimize repair and maintenance costs and reduce service interruptions caused by breakdowns. We also order most of our equipment with uniform specifications to reduce our parts inventory and facilitate maintenance. At December 31, 2014, our tractor fleet had an average age of approximately 1.6 years, and our trailer fleet had an average age of approximately 5.4 years. As of December 31, 2014, 100% of our tractor fleet had engines compliant with stricter regulations regarding emissions that became effective in 2007 and 97.4% of our tractor fleet had engines compliant with stricter regulations regarding emissions that became effective in 2010. We equip our tractors with a satellite-based tracking and communications system that permits direct communication between drivers and fleet managers. We believe that this system enhances our operating efficiency and improves customer service and fleet management. This system also updates the tractor's position every thirty minutes, which allows us and our customers to locate freight and accurately estimate pick-up and delivery times. We also use the system to monitor engine idling time, speed, performance, and other factors that affect operating efficiency. At December 31, 2014, 100% of our fleet was equipped with electronic on board recorders ("EOBRs," now referred to as electronic logging devices, or "ELDs"), which electronically monitor truck miles and enforce hours-of-service regulations.
Over the past decade, the price of new tractors has risen dramatically and there has been significant volatility in the used equipment market. This has substantially increased our costs of operation.
Industry and Competition
Truckload is the largest segment of the for-hire ground freight transportation market based on revenue, surpassing the combined market size of less-than-truckload, railroad, intermodal, and parcel delivery combined. The truckload market is further segmented into sectors such as regional dry van, temperature-controlled van, flatbed, dedicated contract, expedited, and irregular route.
The U.S. trucking industry is highly competitive and includes thousands of "for-hire" motor carriers, none of which dominate the market. Service and price are the principal means of competition in the trucking industry. We compete to some extent with railroads and rail-truck intermodal service but attempt to differentiate ourselves from our competition on the basis of service. Rail and rail-truck intermodal movements are more often subject to delays and disruptions arising from rail yard congestion, which reduce the effectiveness of such service to customers with time-definite pick-up and delivery schedules. In times of high fuel prices or decreased consumer demand, however, rail-intermodal competition becomes more significant.
Our industry is subject to dynamic factors that significantly affect our operating results. These factors include the availability of qualified truck drivers, the volume of freight in the sectors we serve, the price of diesel fuel, and government regulations that impact productivity and costs. Recently, our industry has experienced increased freight volumes, scarcity of qualified truck drivers, and new regulations that limit productivity. These factors have contributed to an environment of tight trucking capacity and rising freight rates for many trucking companies, including us. Based on our assessment of future regulatory changes, driver demographics, and expected growth rates of our major customers and sectors, we expect a favorable pricing environment to continue for the next several years, offset in part by higher driver pay and other inflationary costs. We believe large and diversified companies, like ourselves, are best positioned to capitalize on the current industry environment, because we can offer significant capacity commitments to major customers, safe and comfortable new equipment to drivers, and optimized routing and other business analytics to make the most of our drivers' federally limited operating hours.
We believe that the cost and complexity of operating trucking fleets are increasing and that economic and competitive pressures are likely to force many smaller competitors and private fleets to consolidate or exit the industry. As a result, we believe that larger, better-capitalized companies, like us, will have opportunities to increase profit margins and gain market share. In the market for dedicated services, we believe that truckload carriers, like us, have a competitive advantage over truck lessors, which are the other major participants in the market, because we can offer lower prices by utilizing back-haul freight within our network that traditional lessors may not have.
Regulation
Our operations are regulated and licensed by various U.S. agencies. Our Canadian business activities are subject to similar requirements imposed by the laws and regulations of Canada, as well as its provincial laws and regulations. We operate within Mexico by utilizing third-party carriers within that country. Our Company drivers and independent contractors also must comply with the safety and fitness regulations of the DOT, including those relating to drug and alcohol testing and hours-of-service. Such matters as weight and equipment dimensions are also subject to U.S. regulations. We also may become subject to new or more restrictive regulations relating to fuel emissions, drivers' hours-of-service, ergonomics, or other matters affecting safety or operating methods. Other agencies, such as the Environmental Protection Agency ("EPA") and the Department of Homeland Security ("DHS") also regulate our equipment, operations, and drivers.
The DOT, through the FMCSA, imposes safety and fitness regulations on us and our drivers, including rules that restrict driver hours-of-service. In December 2011, the FMCSA published its 2011 Hours-of-Service Final Rule (the "2011 Rule"). The 2011 Rule requires drivers to take 30-minute breaks after eight hours of consecutive driving and reduces the total number of hours a driver is permitted to work during each week from 82 hours to 70 hours. The 2011 Rule also modified the requirements for when the weekly hours-of-service limit can be reset by having the driver refrain from working for a period of 34 hours, known as a "34-hour restart." The 2011 Rule also provides that the 34-hour restart may only be used once per week and must include two rest periods between one a.m. and five a.m. (together, the “2011 Restart Restrictions”). These rule changes became effective July 1, 2013. We believe the 2011 Rule has decreased productivity and caused some loss of efficiency, as drivers and shippers have needed supplemental training, computer programming has required modifications, additional drivers have been employed or engaged, additional equipment has been acquired, and shipping lanes have been reconfigured.
On December 13, 2014, Congress passed the 2015 Omnibus Appropriations bill, which was signed into law December 16, 2014. Among other things, the legislation provides relief from the 2011 Restart Restrictions, which essentially reverts back to the more straight forward 34-hour restart that was in effect before the 2011 Rule became effective.
The FMCSA also is considering revisions to the existing rating system and the safety labels assigned to motor carriers evaluated by the DOT. We currently have a "satisfactory" DOT rating, which is the highest available rating under the current safety rating scale. If we were to receive a conditional or unsatisfactory DOT safety rating, it could adversely affect our business because some of our customer contracts require a satisfactory DOT safety rating. Under the revised rating system being considered by the FMCSA, our safety rating would be evaluated more regularly, and our safety rating would reflect a more in-depth assessment of safety-based violations.
CSA introduced a new enforcement and compliance model that evaluates and ranks both fleets and individual drivers on certain safety-related standards. The methodology for determining a carrier's DOT safety rating has been expanded to include the on-road safety performance of the carrier's drivers. As a result, certain current and potential drivers may no longer be eligible to drive for us, our fleet could be ranked poorly as compared to our peer firms, and our safety rating could be adversely impacted. The occurrence of future deficiencies could affect driver recruiting and retention by causing high-quality drivers to seek employment with other carriers, or could cause our customers to direct their business away from us and to carriers with higher fleet safety rankings, either of which would adversely affect our results of operations and productivity. Additionally, we may incur greater than expected expenses in our attempts to improve our scores as a result of those scores.
Certain of our subsidiaries have exceeded the established intervention thresholds in several of the seven safety-related standards of CSA. Based on these unfavorable ratings, we may be prioritized for an intervention action or roadside inspection, either of which could adversely affect our results of operations. We have put new maintenance procedures in place in an attempt to address maintenance issues that were cited. Additionally, we have reduced the maximum speed on a large portion of our fleet and enhanced programs that reward drivers for positive safety behavior.
The FMCSA proposed new rules that would require nearly all carriers, including us, to install and use EOBRs in their tractors to electronically monitor truck miles and enforce hours-of-service. These rules were vacated by the Seventh Circuit Court of Appeals in August 2011. In July 2012, Congress passed a federal transportation bill that requires promulgation of rules mandating the use of EOBRs (now referred to as ELDs) by July 2013 with full adoption by all trucking companies no later than July 2015. It is uncertain if this adoption date will be challenged or extended. We believe the pending ELD mandate, together with the revised hours-of-service rules and other regulations, could result in a reduction in effective trucking capacity to service increased demand. We have proactively installed ELDs on 100% of our owned tractors.
In the aftermath of the September 11, 2001 terrorist attacks, the DHS and other federal, state, and municipal authorities implemented and continue to implement various security measures, including checkpoints and travel restrictions on large trucks. The U.S. Transportation Security Administration ("TSA") adopted regulations that require determination by the TSA that each driver who applies for or renews his or her license for carrying hazardous materials is not a security threat. This could reduce the pool of qualified drivers who are permitted to transport hazardous waste, which could require us to increase driver compensation, limit our fleet growth, or result in trucks sitting idle. These regulations also could complicate the matching of available equipment with hazardous material shipments, thereby increasing our response time on customer orders and our non-revenue miles. As a result, it is possible we could fail to meet the needs of our customers or could incur increased expenses to do so.
We are subject to various environmental laws and regulations dealing with the hauling and handling of hazardous materials, fuel storage tanks, air emissions from our vehicles and facilities, engine idling, and discharge and retention of storm water. Our truck terminals often are located in industrial areas where groundwater or other forms of environmental contamination could occur. Our operations involve the risks of fuel spillage or seepage, environmental damage, and hazardous waste disposal, among others. Certain of our facilities have waste oil or fuel storage tanks and fueling islands. A small percentage of our freight consists of low-grade hazardous substances, which subjects us to a wide array of regulations. Additionally, increasing efforts to control emissions of greenhouse gases may have an adverse effect on us. Although we have instituted programs to monitor and control environmental risks and promote compliance with applicable environmental laws and regulations, if we are involved in a spill or other accident involving hazardous substances, if there are releases of hazardous substances we transport, if soil or groundwater contamination is found at our facilities or results from our operations, or if we are found to be in violation of applicable laws or regulations, we could be subject to cleanup costs and liabilities, including substantial fines or penalties or civil and criminal liability, any of which could have a materially adverse effect on our business and operating results.
The EPA adopted a series of emissions control regulations that require progressive reductions in exhaust emissions from new diesel engines manufactured on or after October 2002, January 2007, and January 2010. Compliance with these regulations increased our new tractor costs and operating expenses and reduced our fuel economy. In May 2010, President Obama signed an executive memorandum directing the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration ("NHTSA") and the EPA to develop new, stricter fuel efficiency standards for heavy tractors. In August 2011, the NHTSA and EPA adopted a new rule that established the first-ever fuel economy and greenhouse gas standards for medium- and heavy-duty vehicles, which include tractors we utilize. These standards apply to model years 2014 to 2018, which are required to achieve an approximate 20 percent reduction in fuel consumption by 2018, which equates to approximately four gallons of fuel for every 100 miles traveled. In addition, in February 2014 President Obama announced that his administration will begin developing the next phase of tighter fuel efficiency standards for medium and heavy-duty vehicles, including tractors we utilize, and directed the EPA and NHTSA to develop new fuel-efficiency and greenhouse gas standards by March 31, 2016. We believe that the foregoing requirements could result in increased new tractor prices and additional parts and maintenance costs incurred to retrofit our tractors with technology to achieve compliance with such standards, which could adversely affect our operating results and profitability, particularly if such costs are not offset by potential fuel savings. We cannot predict, however, the extent to which our operations and productivity will be impacted.
The California Air Resources Board ("CARB") also adopted emission control regulations that will be applicable to all heavy-duty tractors that pull 53-foot or longer box-type trailers within the State of California. The tractors and trailers subject to these CARB regulations must be either EPA SmartWay certified or equipped with low-rolling, resistance tires and retrofitted with SmartWay-approved aerodynamic technologies. Enforcement of these CARB regulations for model year 2011 equipment began in January 2010 and will be phased in over several years for older equipment. In order to comply with the CARB regulations, we submitted a large fleet compliance plan to CARB in 2010. We will continue monitoring our compliance with the CARB regulations. As of January 1, 2014, CARB regulations require certain drayage trucks with 2006 or older model year engines to upgrade to 2007 or newer model year engines. We believe some industry participants may have difficulty complying with this new requirement, which may tighten drayage freight capacity and decrease drayage competition in California. Federal and state lawmakers also are considering a variety of climate-change proposals. Compliance with such regulations could increase the cost of new tractors and trailers, impair equipment productivity, and increase operating expenses. These effects, combined with the uncertainty as to the operating results that will be produced by the newly designed diesel engines and the residual values of these vehicles, could increase our costs or otherwise adversely affect our business or operations.
In order to reduce exhaust emissions, some states and municipalities have begun to restrict the locations and amount of time where diesel-powered tractors, such as ours, may idle. These restrictions could force us to alter our drivers' behavior, purchase on-board power units that do not require the engine to idle, or face a decrease in productivity.
Beginning October 2013, any entity acting as a broker or a freight forwarder is required to obtain authority from the FMCSA, and is subject to a minimum $75,000 financial security requirement, increased from the previous requirement of $10,000. We are licensed by the FMCSA as a property broker and are in compliance with the financial security requirement. This new requirement may limit entry of new brokers into the market or cause current brokers to exit the market. Such persons may seek agent relationships with companies such as us to avoid this increased cost. If they do not seek out agent relationships, the number of brokers in the industry could decrease.
Fuel Availability and Cost
The cost of fuel trended lower in 2014, compared to 2013 and 2012, as demonstrated by a decrease in the Department of Energy ("DOE") national average for diesel of approximately 9.7 cents per gallon for 2014 compared to 2013. Our fuel cost was further decreased in 2014 due to an increase in our average fuel miles per gallon during 2014 as a result of purchasing equipment with more fuel-efficient engines.
We actively manage our fuel costs by routing our drivers through fuel centers with which we have negotiated volume discounts and through jurisdictions with lower fuel taxes, where possible. We have also reduced the maximum speed of many of our trucks, implemented strict idling guidelines for our drivers, purchased technology to enhance our management and monitoring of out-of-route miles, encouraged the use of shore power units in truck stops, and imposed standards for accepting broker freight that includes minimum rates and fuel surcharges. These initiatives have contributed to significant improvements in fleet wide average fuel mileage. Moreover, we have a fuel surcharge program in place with the majority of our customers, which has historically enabled us to recover some of the higher fuel costs. However, even with the fuel surcharges, the price of fuel has affected our profitability. Our fuel surcharges are billed on a lagging basis, meaning we typically bill customers in the current week based on a previous week's applicable index. Therefore, in times of increasing fuel prices, we do not recover as much as we are currently paying for fuel. In periods of declining prices, the opposite is true. In addition, we incur additional costs when fuel prices rise that cannot be fully recovered due to our engines being idled during cold or warm weather, empty or out-of-route miles, and for fuel used by refrigerated trailer units that generally is not billed to customers. In addition, from time-to-time customers attempt to modify their surcharge programs, some successfully, which can result in recovery of a smaller portion of fuel price increases. Rapid increases in fuel costs or shortages of fuel could have a materially adverse effect on our operations or future profitability.
To reduce the variability of the ultimate cash flows associated with fluctuations in diesel fuel prices, we periodically enter into various derivative instruments, including forward futures swap contracts. Historically diesel fuel has not been a traded commodity on the futures market so heating oil has been used as a substitute, as prices for both generally move in similar directions. Recently, however, we have been able to enter into hedging contracts with respect to both heating oil and ultra low sulfur diesel ("ULSD"). Under these contracts, we pay a fixed rate per gallon of heating oil or ULSD and receive the monthly average price of New York heating oil per the New York Mercantile Exchange ("NYMEX") and Gulf Coast ULSD, respectively. Because the fixed price is determined based on market prices at the time we enter into the hedge, in times of increasing fuel prices the hedge contracts become more valuable, whereas in times of decreasing fuel prices the opposite is true. At December 31, 2014, we had forward futures swap contracts on approximately 12.6 million, 12.1 million, and 3.0 million gallons of diesel to be purchased in 2015, 2016, and 2017, respectively, or approximately 23%, 22%, and 5% of our projected annual 2015, 2016, and 2017 fuel requirements, respectively. Due to declining petroleum prices in 2014, the fair value of our fuel hedging contracts at December 31, 2014, represented a $22.7 million liability.
Seasonality
In the trucking industry, revenue generally decreases as customers reduce shipments following the winter holiday season and as inclement weather impedes operations. At the same time, operating expenses generally increase, with fuel efficiency declining because of engine idling and weather, creating more physical damage equipment repairs. For the reasons stated, first quarter results historically have been lower than results in each of the other three quarters of the year, excluding charges. Over the past several years, we have seen increases in demand at varying times, specifically May through October, based primarily on restocking required to replenish inventories that have been held significantly lower than historical averages. Additionally, we have seen surges between Thanksgiving and Christmas resulting from holiday shopping trends toward delivery of gifts purchased over the internet, as well as the impact of shorter holiday seasons.
Additional Information
At December 31, 2014, our corporate structure included Covenant Transportation Group, Inc., a Nevada holding company organized in May 1994, and its wholly owned subsidiaries: Covenant Transport, Inc., a Tennessee corporation; Southern Refrigerated Transport, Inc., an Arkansas corporation; Star Transportation, Inc., a Tennessee corporation; Covenant Transport Solutions, Inc., a Nevada corporation; Covenant Logistics, Inc., a Nevada corporation; Covenant Asset Management, Inc., a Nevada corporation; CTG Leasing Company, a Nevada corporation; and IQS Insurance Retention Group, Inc., a Vermont corporation.
Our headquarters is located at 400 Birmingham Highway, Chattanooga, Tennessee 37419, and our website address is www.ctgcompanies.com. Our Annual Report on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K, and all other reports we file with the SEC pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the "Exchange Act") are available free of charge through our website. Information contained in or available through our website is not incorporated by reference into, and you should not consider such information to be part of, this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Additionally, you may read all of the materials that we file with the SEC by visiting the SEC's Public Reference Room at 100 F Street, N.E., Washington, D.C. 20549. If you would like information about the operation of the Public Reference Room, you may call the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330. You may also visit the SEC's website at www.sec.gov. This site contains reports, proxy and information statements and other information regarding the Company and other companies that file electronically with the SEC.
Our future results may be affected by a number of factors over which we have little or no control. The following discussion of risk factors contains forward-looking statements as discussed in Item 1 above. The following issues, uncertainties, and risks, among others, should be considered in evaluating our business and growth outlook.
Our business is subject to general economic and business factors affecting the trucking industry that are largely out of our control, any of which could have a materially adverse effect on our operating results.
The truckload industry is highly cyclical, and our business is dependent on a number of factors that may have a negative impact on our results of operations, many of which are beyond our control. We believe that some of the most significant of these factors are economic changes that affect supply and demand in transportation markets, such as:
| ● | recessionary economic cycles, such as the period from 2007 through 2009; |
| | |
| ● | changes in customers' inventory levels and in the availability of funding for their working capital; |
| | |
| ● | excess tractor capacity in comparison with shipping demand; and |
| | |
| ● | downturns in customers' business cycles. |
Economic conditions that decrease shipping demand or increase the supply of tractors and trailers can exert downward pressure on rates and equipment utilization, thereby decreasing asset productivity. The risks associated with these factors are heightened when the U.S. economy is weakened. Some of the principal risks during such times, which risks we experienced during prior recessionary times, are as follows:
| ● | we may experience a reduction in overall freight levels, which may impair our asset utilization; |
| | |
| ● | certain of our customers may face credit issues and could experience cash flow problems that may lead to payment delays, increased credit risk, bankruptcies, and other financial hardships that could result in even lower freight demand and may require us to increase our allowance for doubtful accounts; |
| | |
| ● | freight patterns may change as supply chains are redesigned, resulting in an imbalance between our capacity and our customers' freight demand; |
| | |
| ● | customers may solicit bids for freight from multiple trucking companies or select competitors that offer lower rates from among existing choices in an attempt to lower their costs, and we might be forced to lower our rates or lose freight; and |
| | |
| ● | we may be forced to accept more freight from freight brokers, where freight rates are typically lower, or may be forced to incur more non-revenue miles to obtain loads. |
We also are subject to potential increases in various costs and other events that are outside of our control that could materially reduce our profitability if we are unable to increase our rates sufficiently. Such cost increases include, but are not limited to, fuel and energy prices, taxes and interest rates, tolls, license and registration fees, insurance premiums, revenue equipment and related maintenance costs, and healthcare and other benefits for our employees. We could be affected by strikes or other work stoppages at our service centers or at customer, port, border, or other shipping locations. Changing impacts of regulatory measures could impair our operating efficiency and productivity, decrease our revenues and profitability, and result in higher operating costs. In addition, declines in the resale value of revenue equipment can also affect our profitability and cash flows. From time to time, various federal, state, or local taxes may also increase, including taxes on fuels. We cannot predict whether, or in what form, any such cost increase or event could occur. Any such cost increase or event could adversely affect our profitability.
In addition, we cannot predict future economic conditions, fuel price fluctuations, or how consumer confidence could be affected by actual or threatened armed conflicts or terrorist attacks, government efforts to combat terrorism, military action against a foreign state or group located in a foreign state, or heightened security requirements. Enhanced security measures could impair our operating efficiency and productivity and result in higher operating costs.
We may not be successful in achieving our strategic plan.
Our current strategic plan includes instilling an enterprise-wide culture, allocating our available capital toward business units we expect to generate acceptable returns, improving the career and experience of our professional drivers, offering our customers significant value in markets and sectors where we can make a difference, and effectively managing the risks associated with our business. To this end, several of our initiatives include growing our expedited dry van and temperature-controlled teams, increasing the number of tractors and trailers allocated toward dedicated contract operations in targeted markets, effectively managing the attraction, development, and retention of qualified drivers, capitalizing on our enterprise management system including improving the performance at SRT, our most recent (and final) subsidiary to implement this technology, and continuing to manage our exposures to fluctuations in fuel prices, claims, interest rates, used truck prices, and other potentially volatile expenses through a variety of hedging, insurance, contractual, and other methods. Such initiatives will require time, management and financial resources, changes in our operations and sales functions, and monitoring and implementation of technology. We may be unable to effectively and successfully implement, or achieve sustainable improvement from, our strategic plan and initiatives or achieve these objectives. In addition, our operating margins could be adversely affected by future changes in and expansion of our business, including the expected expansion of expedited dry van and temperature-controlled teams. Further, our operating results may be negatively affected by a failure to further penetrate our existing customer base, cross-sell our services, pursue new customer opportunities, or manage the operations and expenses of new or growing services. There is no assurance that we will be successful in achieving our strategic plan and initiatives. If we are unsuccessful in implementing our strategic plan and initiatives, our financial condition, results of operations, and cash flows could be adversely affected.
We operate in a highly competitive and fragmented industry, and numerous competitive factors could impair our ability to improve our profitability.
| ● | we compete with many other truckload carriers of varying sizes and, to a lesser extent, with less-than-truckload carriers, railroads, intermodal companies, and other transportation companies, many of which have more equipment and greater capital resources than we do; |
| | |
| ● | many of our competitors periodically reduce their freight rates to gain business, especially during times of reduced growth rates in the economy, which may limit our ability to maintain or increase freight rates or maintain significant growth in our business; |
| | |
| ● | many of our customers, including several in our top ten, are other transportation companies, and they may decide to transport their own freight; |
| | |
| ● | many customers reduce the number of carriers they use by selecting "core carriers" as approved service providers, and in some instances we may not be selected; |
| | |
| ● | many customers periodically accept bids from multiple carriers for their shipping needs, and this process may depress freight rates or result in the loss of some business to competitors; |
| | |
| ● | the trend toward consolidation in the trucking industry may create other large carriers with greater financial resources and other competitive advantages relating to their size; |
| | |
| ● | advances in technology require increased investments to remain competitive, and our customers may not be willing to accept higher freight rates to cover the cost of these investments; and |
| | |
| ● | competition from non-asset-based logistics and freight brokerage companies may adversely affect our customer relationships and freight rates. |
We have a history of net losses and may be unsuccessful in improving our profitability.
We have generated a profit in only four of the last seven years and our aggregate net losses during the seven year period are significantly more than our aggregate net income. We may not be able to sustain or increase profitability in the future. Achieving profitability depends upon numerous factors, including our ability to effectively and successfully implement other strategic plans and initiatives, increase our average revenue per tractor, improve driver retention, and control expenses. If we are unable to improve our profitability, then our liquidity, financial position, and results of operations may be adversely affected.
We self-insure for a significant portion of our claims exposure, which could significantly increase the volatility of, and decrease the amount of, our earnings.
Our future insurance and claims expense could reduce our earnings and make our earnings more volatile. We self-insure for a significant portion of our claims exposure and related expenses. We accrue amounts for liabilities based on our assessment of claims that arise and our insurance coverage for the periods in which the claims arise, and we evaluate and revise these accruals from time to time based on additional information. Due to our significant self-insured amounts, we have significant exposure to fluctuations in the number and severity of claims and the risk of being required to accrue or pay additional amounts if our estimates are revised or the claims ultimately prove to be more severe than originally assessed. Historically, we have had to significantly adjust our reserves on several occasions, and future significant adjustments may occur. For example, in the third quarter of 2014, there was an unfavorable judgment against one of our subsidiaries for a cargo claim and we had to record a significant additional reserve of $7.5 million for this claim. Further, our self-insured retention levels could change and result in more volatility than in recent years.
We maintain insurance above the amounts for which we self-insure with licensed insurance carriers. Although we believe our aggregate insurance limits are sufficient to cover reasonably expected claims, it is possible that one or more claims could exceed those limits. If any claim was to exceed our coverage, we would bear the excess, in addition to our other self-insured amounts. Our insurance and claims expense could increase, or we could find it necessary to again raise our self-insured retention or decrease our aggregate coverage limits when our policies are renewed or replaced. Our operating results and financial condition may be adversely affected if these expenses increase, if we experience a claim in excess of our coverage limits, if we experience a claim for which we do not have coverage, if we experience an increase in number of claims, or if we have to increase our reserves.
Our auto liability insurance policy contains a provision under which we have the option, on a retroactive basis, to assume responsibility for the entire cost of covered claims during the policy period in exchange for a refund of a portion of the premiums we paid for the policy. This is referred to as "commuting" the policy. We have elected to commute policies in one of the past five years. We have received approximately $3.5 million in policy premiums, net of additional reserves for claims commuted, in respect of commuting these policies. In exchange, we have assumed the risk for all claims during the years for the policies commuted. Our subsequent payouts for the claims assumed have been less than the refunds. We expect the total refunds to exceed the total payouts; however, not all of the claims have been finally resolved and we cannot assure you of the result. We may continue to commute policies for certain years in the future. To the extent we do so, and one or more claims result in large payouts, we will not have insurance, and our financial condition, results of operation, and liquidity could be materially and adversely affected.
Our self-insurance for auto liability at one of our subsidiaries and our use of a captive insurance company could adversely impact our operations.
Covenant Transport, Inc. has been approved to self-insure for auto liability by the FMCSA. We believe this status, along with the use of a captive insurance company, allows us to post substantially lower aggregate letters of credit and restricted cash than we would be required to post without this status or the use of a captive insurance company. Our wholly owned captive insurance subsidiary is a regulated insurance company through which we insure a portion of our auto liability claims in certain states. An increase in the number or severity of auto liability claims for which we self-insure through Covenant Transport, Inc. or insure through the captive insurance company or pressure in the insurance and reinsurance markets could adversely impact our earnings and results of operations. Further, both arrangements increase the possibility that our expenses will be volatile.
To comply with certain state insurance regulatory requirements, cash and cash equivalents must be paid to our captive insurance subsidiary as capital investments and insurance premiums, which are restricted as collateral for anticipated losses. Significant future increases in the amount of collateral required by third-party insurance carriers and regulators would reduce our liquidity and could adversely affect our results of operations and capital resources. Further, regulations applicable to the captive insurance subsidiary may increase our costs, limit our ability to change premiums, restrict our ability to access cash held by this subsidiary, and otherwise impede our ability to take actions we deem advisable.
Fluctuations in the price or availability of fuel, hedging activities, the volume and terms of diesel fuel purchase commitments, and surcharge collection and surcharge policies approved by customers may increase our costs of operation, which could materially and adversely affect our profitability.
Fuel is one of our largest operating expenses. Diesel fuel prices fluctuate greatly due to economic, political, weather, and other factors beyond our control, each of which may lead to an increase in the cost of fuel. Fuel also is subject to regional pricing differences and often costs more on the West Coast, where we have significant operations. Additionally, fuel pricing can be affected by the rising demand in developing countries and could be adversely impacted by the use of crude oil and oil reserves for other purposes and diminished drilling activity. Such events may lead not only to increases in fuel prices, but also to fuel shortages and disruptions in the fuel supply chain. Because our operations are dependent upon diesel fuel, significant diesel fuel cost increases, shortages, or supply disruptions could materially and adversely affect our results of operations and financial condition.
From time to time, we use hedging contracts and volume purchase arrangements to attempt to limit the effect of price fluctuations. We may be forced to make cash payments under the hedging arrangements. Our hedging arrangements effectively allow us to pay a fixed rate for fuel that is determined based on the market rate at the time we enter into the hedge. In times of falling diesel fuel prices, including recently, our costs will not be reduced to the same extent they would have reduced if we had not entered into the hedging contracts and we may incur significant expense in connection with our obligation to make cash payments under such contracts. Accordingly, in times of falling diesel fuel prices, our profitability and cash flows may be negatively impacted to a greater extent than if we had not entered into the hedging contracts.
We use a fuel surcharge program to recapture a portion of the increases in fuel prices over a base rate negotiated with our customers. Our fuel surcharge program does not protect us against the full effect of increases in fuel prices. The terms of each customer's fuel surcharge program vary and certain customers have sought to modify the terms of their fuel surcharge programs to minimize recoverability for fuel price increases. A failure to improve our fuel price protection through these measures, increases in fuel prices, a shortage or rationing of diesel fuel, or significant payments under hedging arrangements, could materially and adversely affect our results of operations.
We depend on the proper functioning and availability of our information systems and a system failure or unavailability or an inability to effectively upgrade our information systems could cause a significant disruption to our business and have a materially adverse effect on our results of operation.
We depend on the proper functioning and availability of our information systems, including financial reporting and operating systems, in operating our business. Our operating system is critical to understanding customer demands, accepting and planning loads, dispatching equipment and drivers, and billing and collecting for our services. Our financial reporting system is critical to producing accurate and timely financial statements and analyzing business information to help us manage effectively. We recently finished implementing a multi-year project to upgrade the hardware and software of our information systems with respect to most of our subsidiaries. We have experienced difficulties in converting portions of our operations, including inefficiencies resulting in a reduction in average miles per tractor and increased driver turnover. While not as significant as experienced with Covenant Transport, Inc.'s system conversion in 2011, SRT's conversion to the new system in early 2014 provided some of the aforementioned difficulties.
Our operations and those of our technology and communications service providers are vulnerable to interruption by fire, earthquake, power loss, telecommunications failure, terrorist attacks, Internet failures, computer viruses, and other events beyond our control. Although we attempt to reduce the risk of disruption to our business operations should a disaster occur through redundant computer systems and networks and backup systems, there can be no assurance that such measures will be effective. If any of our critical information systems fail or become otherwise unavailable, whether as a result of the upgrade project or otherwise, we would have to perform the functions manually, which could temporarily impact our ability to manage our fleet efficiently, to respond to customers' requests effectively, to maintain billing and other records reliably, and to bill for services and prepare financial statements accurately or in a timely manner. Our business interruption insurance may be inadequate to protect us in the event of an unforeseeable and extreme catastrophe. Any significant system failure, upgrade complication, security breach, or other system disruption could interrupt or delay our operations, damage our reputation, cause us to lose customers, or impact our ability to manage our operations and report our financial performance, any of which could have a materially adverse effect on our business.
Our Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement (our "Credit Facility") and other financing arrangements contain certain covenants, restrictions, and requirements, and we may be unable to comply with such covenants, restrictions, and requirements. A default could result in the acceleration of all or part of our outstanding indebtedness, which could have an adverse effect on our financial condition, liquidity, results of operations, and the market price of our Class A common stock.
We have a $95.0 million Credit Facility with a group of banks and numerous other financing arrangements. Our Credit Facility contains certain restrictions and covenants relating to, among other things, dividends, liens, acquisitions and dispositions outside of the ordinary course of business, affiliate transactions, and a fixed charge coverage ratio, if availability is below a certain threshold. We have had difficulty meeting budgeted results and have had to request amendments or waivers in the past. If we are unable to meet budgeted results or otherwise comply with our Credit Facility, we may be unable to obtain amendments or waivers under our Credit Facility, or we may incur fees in doing so.
Certain other financing arrangements contain certain restrictions and non-financial covenants, in addition to those contained in our Credit Facility. In addition, certain of our fuel hedging contracts are with lenders under our Credit Facility and could be terminated by such lenders if the Credit Facility is terminated or replaced. If we fail to comply with any of our financing arrangement covenants, restrictions, and requirements, we will be in default under the relevant agreement, which could cause cross-defaults under our other financing arrangements. In the event of any such default, if we failed to obtain replacement financing, amendments to, or waivers under the applicable financing arrangements, our lenders could cease making further advances, declare our debt to be immediately due and payable, fail to renew letters of credit, impose significant restrictions and requirements on our operations, institute foreclosure procedures against their collateral, or impose significant fees and transaction costs. If acceleration occurs, economic conditions such as the recent credit market crisis may make it difficult or expensive to refinance the accelerated debt or we may have to issue equity securities, which would dilute stock ownership. Even if new financing is made available to us, credit may not be available to us on acceptable terms. A default under our financing arrangements could result in a materially adverse effect on our liquidity, financial condition, and results of operations.
Our substantial indebtedness and capital and operating lease obligations could adversely affect our ability to respond to changes in our industry or business.
As a result of our level of debt, capital leases, operating leases, and encumbered assets, we believe:
| ● | our vulnerability to adverse economic conditions and competitive pressures is heightened; |
| | |
| ● | we will continue to be required to dedicate a substantial portion of our cash flows from operations to lease payments and repayment of debt, limiting the availability of cash for other purposes; |
| | |
| ● | our flexibility in planning for, or reacting to, changes in our business and industry will be limited; |
| | |
| ● | our profitability is sensitive to fluctuations in interest rates because some of our debt obligations are subject to variable interest rates, and future borrowings and lease financing arrangements will be affected by any such fluctuations; |
| | |
| ● | our ability to obtain additional financing in the future for working capital, capital expenditures, acquisitions, or other purposes may be limited; and |
| | |
| ● | we may be required to issue additional equity securities to raise funds, which would dilute the ownership position of our stockholders. |
Our financing obligations could negatively impact our future operations, our ability to satisfy our capital needs, or our ability to engage in other business activities. We also cannot assure you that additional financing will be available to us when required or, if available, will be on terms satisfactory to us.
We have significant ongoing capital requirements that could affect our profitability if we are unable to generate sufficient cash from operations and obtain financing on favorable terms.
The truckload industry is capital intensive, and our policy of operating newer equipment requires us to expend significant amounts annually. We expect to pay for projected capital expenditures with cash flows from operations, borrowings under our Credit Facility, proceeds from the sale of our used revenue equipment, proceeds under other financing facilities, and leases of revenue equipment. If we are unable to generate sufficient cash from operations and obtain financing on favorable terms in the future, we may have to limit our fleet size, enter into less favorable financing arrangements, or operate our revenue equipment for longer periods, any of which could have a materially adverse effect on our profitability.
We derive a significant portion of our revenue from our major customers, the loss of one or more of which could have a materially adverse effect on our business.
A significant portion of our revenue is generated from our major customers. In 2014, one customer accounted for more than 10% of our consolidated revenue. This customer was serviced by both our Truckload segment and our Solutions subsidiary providing for $82.5 million of total revenue. Our top five customers accounted for approximately 29%, 25%, and 24% of our total revenue in 2014, 2013, and 2012, respectively. Generally, we do not have long-term contractual relationships with our major customers. Accordingly, in response to economic conditions, supply and demand in our industry, our performance, our customers' internal initiatives, or other factors, our customers may reduce or eliminate their use of our services, or threaten to do so to gain pricing or other concessions from us.
Economic conditions and capital markets may adversely affect our customers and their ability to remain solvent. Our customers' financial difficulties can negatively impact our results of operations and financial condition, especially if our customers were to delay or default on payments to us. For some of our customers, we have entered into multi-year contracts, and the rates we charge may not remain advantageous. A reduction in or termination of our services, by one or more of our major customers, could have a materially adverse effect on our business and operating results.
We depend on third-parties, particularly in our brokerage business, and service instability from these providers could increase our operating costs and reduce our ability to offer brokerage services, which could adversely affect our revenue, results of operations, and customer relationships.
Our brokerage business is dependent upon the services of third-party capacity providers, including other truckload carriers. For this business, we do not own or control the transportation assets that deliver our customers' freight, and we do not employ the people directly involved in delivering the freight. This reliance could also cause delays in reporting certain events, including recognizing revenue and claims. These third-party providers seek other freight opportunities and may require increased compensation in times of improved freight demand or tight trucking capacity. Our inability to secure the services of these third-parties could significantly limit our ability to serve our customers on competitive terms. Additionally, if we are unable to secure sufficient equipment or other transportation services to meet our commitments to our customers or provide our services on competitive terms, our operating results could be materially and adversely affected. Our ability to secure sufficient equipment or other transportation services is affected by many risks beyond our control, including equipment shortages in the transportation industry, particularly among contracted truckload carriers, interruptions in service due to labor disputes, changes in regulations impacting transportation, and changes in transportation rates.
Increases in driver compensation or difficulty in attracting and retaining qualified drivers could adversely affect our profitability.
Like many truckload carriers, we experience substantial difficulty in attracting and retaining sufficient numbers of qualified drivers, including independent contractors. Our industry periodically experiences a shortage of qualified drivers, particularly during periods of economic expansion, in which alternative employment opportunities are more plentiful and freight demand increases, or during periods of economic downturns, in which unemployment benefits might be extended and financing is limited for independent contractors who seek to purchase equipment or for students who seek financial aid for driving school. Regulatory requirements, including CSA and hours-of-service changes, and an improved economy could further reduce the number of eligible drivers or force us to increase driver compensation to attract and retain drivers. We have seen evidence that stricter hours-of-service regulations adopted by the DOT have tightened, and may continue to tighten, the market for eligible drivers. A shortage of qualified drivers and intense competition for drivers from other trucking companies will create difficulties in maintaining or increasing the number of our drivers, including independent contractor drivers. The compensation we offer our drivers and independent contractors is subject to market conditions, and we may find it necessary to increase driver and independent contractor compensation in future periods. In addition, we and our industry suffer from a high turnover rate of drivers. The high turnover rate requires us to continually recruit a substantial number of drivers in order to operate existing revenue equipment. Our use of team-driven tractors in our expedited business requires two drivers per tractor, which further increases the number of drivers we must recruit and retain in comparison to operations that require one driver per tractor. If we are unable to continue to attract and retain a sufficient number of drivers, we could be forced to, among other things, adjust our compensation packages, increase the number of our tractors without drivers, or operate with fewer trucks and face difficulty meeting shipper demands, any of which could adversely affect our growth and profitability.
If our independent contractor drivers are deemed by regulators or judicial process to be employees, our business and results of operations could be adversely affected.
Tax and other regulatory authorities have asserted that independent contractor drivers in the trucking industry are employees rather than independent contractors. Federal legislators have introduced legislation in the past to make it easier for tax and other authorities to reclassify independent contractor drivers as employees, including legislation to increase the recordkeeping requirements for those that engage independent contractor drivers and to heighten the penalties of companies who misclassify their employees and are found to have violated employees' overtime and/or wage requirements. Additionally, federal legislators have sought to abolish the current safe harbor allowing taxpayers meeting certain criteria to treat individuals as independent contractors if they are following a long-standing, recognized practice, extend the Fair Labor Standards Act to independent contractors, and impose notice requirements based upon employment or independent contractor status and fines for failure to comply. Some states have put initiatives in place to increase their revenues from items such as unemployment, workers' compensation, and income taxes, and a reclassification of independent contractor drivers as employees would help states with this initiative. Taxing and other regulatory authorities and courts apply a variety of standards in their determination of independent contractor status. Our classification of independent contractors has been the subject of audits by such authorities from time to time. While we have been successful in continuing to classify our independent contractor drivers as independent contractors and not employees, we may be unsuccessful in defending that position in the future. If our independent contractor drivers are determined to be our employees, we would incur additional exposure under federal and state tax, workers' compensation, unemployment benefits, labor, employment, and tort laws, including for prior periods, as well as potential liability for employee benefits and tax withholdings.
We operate in a highly regulated industry, and changes in existing regulations or violations of existing or future regulations could have a materially adverse effect on our operations and profitability.
We operate in the U.S. pursuant to operating authority granted by the DOT and in various Canadian provinces pursuant to operating authority granted by the Ministries of Transportation and Communications in such provinces. We operate within Mexico by utilizing third-party carriers within that country. Our company drivers and independent contractors also must comply with the safety and fitness regulations of the DOT, including those relating to drug and alcohol testing and hours-of-service. Such matters as weight and equipment dimensions also are subject to government regulations. We also may become subject to new or more restrictive regulations relating to exhaust emissions, drivers' hours-of-service, ergonomics, on-board reporting of operations, collective bargaining, security at ports, and other matters affecting safety or operating methods. Future laws and regulations may be more stringent and require changes in our operating practices, influence the demand for transportation services, or require us to incur significant additional costs. Higher costs incurred by us or by our suppliers who pass the costs onto us through higher prices could adversely affect our results of operations.
Safety-related evaluations and rankings under CSA could adversely affect our profitability and operations, our ability to maintain or grow our fleet, and our customer relationships.
Under CSA, drivers and fleets are evaluated and ranked based on certain safety-related standards. The methodology for determining a carrier's DOT safety rating has been expanded to include on-road safety performance of the carrier's drivers. As a result, certain current and potential drivers may no longer be eligible to drive for us, our fleet could be ranked poorly as compared to our peer carriers, and our safety rating could be adversely impacted. We recruit and retain first-time drivers to be part of our fleet, and these drivers may have a higher likelihood of creating adverse safety events under CSA. The occurrence of future deficiencies could affect driver recruitment by causing high-quality drivers to seek employment with other carriers or could cause our customers to direct their business away from us and to carriers with higher fleet safety rankings, either of which would adversely affect our results of operations. Additionally, competition for drivers with favorable safety ratings may increase and thus could necessitate increases in driver-related compensation costs. Further, we may incur greater than expected expenses in our attempts to improve our scores or as a result of those scores.
Certain of our subsidiaries have exceeded the established intervention thresholds in a number of the seven safety-related standards. Based on these unfavorable ratings, we may be prioritized for an intervention action or roadside inspection, either of which could adversely affect our results of operations. In addition, customers may be less likely to assign loads to us. We have put new procedures in place in an attempt to address areas where we have exceeded the thresholds. However, we cannot assure you these measures will be effective.
The FMCSA also is considering revisions to the existing rating system and the safety labels assigned to motor carriers evaluated by the DOT. We currently have a satisfactory DOT rating, which is the highest available rating under the current safety rating scale. If we were to receive a conditional or unsatisfactory DOT safety rating, it could adversely affect our business as customer contracts may require a satisfactory DOT safety rating, and a conditional or unsatisfactory rating could negatively impact or restrict our operations.
Increased prices, reduced productivity, and scarcity of financing for new revenue equipment may adversely affect our earnings and cash flows.
We are subject to risk with respect to higher prices for new tractors. Prices have increased and may continue to increase, due, in part, to government regulations applicable to newly manufactured tractors and diesel engines and due, in part, to the pricing discretion of equipment manufacturers. In addition, we have recently equipped our tractors with safety, aerodynamics, and other options that increase the price of the tractors. More restrictive U.S. Environmental Protection Agency emissions standards have required vendors to introduce new engines. Compliance with such regulations has increased the cost of our new tractors and could impair equipment productivity, lower fuel mileage, and increase our operating expenses. These adverse effects, combined with the uncertainty as to the reliability of the vehicles equipped with the newly designed diesel engines and the residual values realized from the disposition of these vehicles, could increase our costs or otherwise adversely affect our business or operations as the regulations become effective.
The market for used equipment is cyclical and can be volaltile, and any downturn in the market could negatively impact our earnings and cash flows. We have a combination of agreements and non-binding statements of indicative trade values covering the terms of trade-in commitments from our primary equipment vendors for disposal of a portion of our revenue equipment. From time to time, prices we expect to receive under these arrangements may be higher than the prices we would receive in the open market. We may suffer a financial loss upon disposition of our equipment if these vendors refuse or are unable to meet their financial obligations under these agreements, if we do not enter into definitive agreements consistent with the indicative trade values, if we fail to or are unable to enter into similar arrangements in the future, or if we do not purchase the number of replacement units from the vendors required for such trade-ins.
If we are unable to retain our key employees, our business, financial condition, and results of operations could be harmed.
We are highly dependent upon the services of the following key employees: David R. Parker, our Chairman of the Board, Chief Executive Officer, and President and Joey B. Hogan, our Senior Executive Vice President and Chief Operating Officer. We currently do not have employment agreements with Messrs. Parker or Hogan. The loss of any of their services could negatively impact our operations and future profitability. We must continue to develop and retain a core group of managers and attract, develop, and retain sufficient additional managers if we are to continue to improve our profitability and have appropriate succession planning for key management personnel.
We may not make acquisitions in the future, or if we do, we may not be successful in our acquisition strategy.
We made ten acquisitions between 1996 and 2006. Accordingly, acquisitions have provided a substantial portion of our growth. We may not have the financial capacity or be successful in identifying, negotiating, or consummating any future acquisitions. If we fail to make any future acquisitions, our historical growth rate could be materially and adversely affected. Any acquisitions we undertake could involve the dilutive issuance of equity securities and/or incurring indebtedness. In addition, acquisitions involve numerous risks, including difficulties in assimilating or integrating the acquired company's operations or assets into our business, the diversion of our management's attention from other business concerns, risks of entering into markets in which we have had no or only limited direct experience, and the potential loss of customers, key employees, and drivers of the acquired company, all of which could have a materially adverse effect on our business and operating results.
Our 49% owned subsidiary, TEL, faces certain additional risks particular to its operations, any one of which could adversely affect our operating results.
In May 2011, we acquired a 49% interest in TEL, a used equipment leasing company and reseller. We account for our investment in TEL using the equity method of accounting. TEL faces several risks similar to those we face and additional risks particular to its business and operations. The ability to secure financing and market fluctuations in interest rates could impact TEL's ability to grow its leasing business and its margins on leases. Adverse economic activity may restrict the number of used equipment buyers and their ability to pay prices for used equipment that we find acceptable. In addition, TEL's leasing customers are typically small trucking companies without substantial financial resources, and TEL is subject to risk of loss should those customers be unable to make their lease payments. Further, we believe the used equipment market will significantly impact TEL's results of operations and such market has been volatile in the past. There can be no assurance that TEL will experience gains on sale similar to those it has experienced in the past and it may incur losses on sale. As regulations change, the market for used equipment may be impacted as such regulatory changes may make used equipment costly to upgrade to comply with such regulations or we may be forced to scrap equipment if such regulations eliminate the market for particular used equipment. Further, there is an overlap in providers of equipment financing to TEL and our wholly owned operations and those providers may consider the combined exposure and limit the amount of credit available to us.
Under the purchase agreement we entered into, we have an option to acquire 100% of TEL through May 2016. If we exercise the option, our consolidated indebtedness would increase. If we fail to exercise the option, the counterparties have the right to purchase our 49% ownership at a defined price. Further, the other owners of TEL and we have discussed amending the option price formula (in each direction) to reflect changes in the business since inception of our investment. We expect any revision to result in an increase in the amount we would have to pay to exercise the option. There is no assurance that we will be able to agree on a revised formula or that TEL's ownership incentives will not be changed as a result of this process.
Finally, we do not control TEL's ownership or management. Our investment in TEL is subject to the risk that TEL's management and controlling members may make business, financial, or management decisions with which we do not agree or that the management or controlling members may take risks or otherwise act in a manner that does not serve our interests. If any of the foregoing were to occur, the value of our investment in TEL could decrease, and our financial condition, results of operations, and cash flow could suffer as a result.
We are exposed to risks related to our receivables factoring arrangements.
We engage in receivables factoring arrangements pursuant to which our clients, consisting of smaller trucking companies, factor their receivables to us for a fee to facilitate faster cash flow. We advance 85% to 95% of each receivable factored and retain the remainder as collateral for collection issues that might arise. The retained amounts are returned to the clients after the related receivable has been collected. We evaluate each client's customer base under predefined criteria. These factored receivables are generally unsecured, except when personal guarantees are received. While we have procedures to monitor and limit exposure to credit risk on these receivables, there can be no assurance such procedures will continue to effectively limit collection risk and avoid losses. We periodically assess the credit risk of our client's customers and regularly monitor the timeliness of payments. Slowdowns, bankruptcies, or financial difficulties within the markets our clients serve may impair the financial condition of one or more of our client's customers and may hinder such customers' ability to pay the factored receivables on a timely basis or at all. If any of these difficulties are encountered, our cash flows and results of operations could be adversely impacted.
Our Chairman of the Board, Chief Executive Officer, and President and his wife control a large portion of our stock and have substantial control over us, which could limit other stockholders' ability to influence the outcome of key transactions, including changes of control.
Our Chairman of the Board, Chief Executive Officer, and President, David Parker, and his wife, Jacqueline Parker, beneficially own or have sole voting and dispositive power over approximately 21% of our outstanding Class A common stock and 100% of our Class B common stock. On all matters with respect to which our stockholders have a right to vote, including the election of directors, each share of Class A common stock is entitled to one vote, while each share of Class B common stock is entitled to two votes. All outstanding shares of Class B common stock are owned by the Parkers and are convertible to Class A common stock on a share-for-share basis at the election of the Parkers or automatically upon transfer to someone outside of the Parker family. This voting structure gives the Parkers approximately 39% of the voting power of all of our outstanding stock. As such, the Parkers are able to substantially influence decisions requiring stockholder approval, including the election of our entire board of directors, the adoption or extension of anti-takeover provisions, mergers, and other business combinations. This concentration of ownership could limit the price that some investors might be willing to pay for the Class A common stock, and could allow the Parkers to prevent or could discourage or delay a change of control, which other stockholders may favor. The interests of the Parkers may conflict with the interests of other holders of Class A common stock, and they may take actions affecting us with which other stockholders disagree.
Seasonality and the impact of weather affect our operations and profitability.
Our tractor productivity decreases during the winter season because inclement weather impedes operations, and some customers reduce their shipments after the winter holiday season. Our expedited operations, which is a growing part of our business, historically have experienced a greater reduction in first quarter demand than our other operations. Revenue also can be affected by bad weather and holidays, since revenue is directly related to available working days of shippers. At the same time, operating expenses increase due to declining fuel efficiency because of engine idling and higher fuel prices and due to harsh weather creating higher accident frequency, increased claims, and more equipment repairs. We also could suffer short-term impacts from weather-related events such as hurricanes, blizzards, ice storms, and floods that could harm our results or make our results more volatile. Weather and other seasonal events could adversely affect our operating results.
None.
Our corporate headquarters and main terminal are located on approximately 180 acres of property in Chattanooga, Tennessee. This facility includes an office building of approximately 182,000 square feet, a maintenance facility of approximately 65,000 square feet, a body shop of approximately 60,000 square feet, and a truck wash. Our Solutions subsidiary is also operated and managed out of the Chattanooga facility. We maintain seven terminals, which are utilized by our Truckload segment located on our major traffic lanes in or near the cities listed below. These terminals provide a base for drivers in proximity to their homes, a transfer location for trailer relays on transcontinental routes, parking space for equipment dispatch, and the other uses indicated below.
| | | | |
| Chattanooga, Tennessee | x | x | x | Leased |
| Texarkana, Arkansas | x | x | x | Owned |
| Hutchins, Texas | x | x | | Owned |
| Pomona, California | | x | | Owned |
| Allentown, Pennsylvania | | | | Owned |
| LaVergne, Tennessee | x | x | x | Owned |
| Orlando, Florida | | | | Owned |
On August 26, 2014, the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of Ohio issued a pre-trial decision in a lawsuit against SRT relating to a cargo claim incurred in 2008. The court awarded the plaintiff approximately $5.9 million plus prejudgment interest and costs and denied a cross-motion for summary judgment by SRT. Previously, the court had ruled in favor of SRT on all but one count before overturning its earlier decision and ruling in favor of the plaintiff. SRT filed a Notice of Appeal with the U.S. Sixth Circuit Court of Appeals on September 24, 2014 and that appeal is currently being briefed by the parties with oral arguments to be scheduled in the months ahead. As a result of this decision and pending final outcome of the appeal, we increased the reserve for this claim by approximately $7.5 million to approximately $8.1 million during the third quarter of 2014.
From time-to-time we are a party to routine litigation arising in the ordinary course of business, most of which involves claims for personal injury and property damage incurred in connection with the transportation of freight. We maintain insurance to cover liabilities arising from the transportation of freight for amounts in excess of certain self-insured retentions.
None.
PART II
ITEM 5. MARKET FOR REGISTRANT'S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES
Price Range of Common Stock
Our Class A common stock is traded on the NASDAQ Global Select Market, under the symbol "CVTI." The following table sets forth, for the calendar periods indicated, the range of high and low sales price for our Class A common stock as reported by NASDAQ from January 1, 2013, to December 31, 2014.
| Period | High | | Low |
| | | | |
| Calendar Year 2013: | | | |
| | | | |
1st Quarter | $6.55 | | $5.00 |
2nd Quarter | $6.30 | | $4.85 |
3rd Quarter | $7.50 | | $5.13 |
4th Quarter | $8.30 | | $6.10 |
| | | | |
| Calendar Year 2014: | | | |
| | | | |
1st Quarter | $12.29 | | $7.85 |
2nd Quarter | $12.96 | | $8.88 |
3rd Quarter | $19.30 | | $11.05 |
4th Quarter | $29.10 | | $15.63 |
On March 2, 2015, the last reported sale price of our Class A common stock on the NASDAQ Global Select Market was $30.73.
As of March 2, 2015, we had approximately 93 stockholders of record of our Class A common stock; however, we estimate our actual number of stockholders is much higher because a substantial number of our shares are held of record by brokers or dealers for their customers in street names. As of March 2, 2015, Mr. Parker, together with certain of his family members, owned all of the outstanding Class B common stock.
Dividend Policy
We have never declared and paid a cash dividend on our Class A or Class B common stock. It is the current intention of our Board of Directors to continue to retain earnings to finance our business and reduce our indebtedness rather than to pay dividends. The payment of cash dividends is currently limited by our financing arrangements. Future payments of cash dividends will depend upon our financial condition, results of operations, capital commitments, restrictions under then-existing agreements, and other factors deemed relevant by our Board of Directors.
See "Equity Compensation Plan Information" under Item 12 in Part III of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for certain information concerning shares of our Class A common stock authorized for issuance under our equity compensation plans.
Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
The table below sets forth the information with respect to purchases of our Class A common stock made by or on behalf of us during the quarter ended December 31, 2014:
| (a) Total Number of Shares Purchased (1) | (b) Average Price Paid per Share | (c) Total Number of Shares Purchased as Part of Publicly Announced Plans or Programs | (d) Maximum Number of Class A Shares that May Yet Be Purchased Under the Publicly Announced Plans or Programs |
| October 1-31, 2014 | - | - | - | - |
| November 1-30, 2014 | - | - | - | - |
| | | | |
| | | | |
| (1) | Includes 271 shares of Class A common stock withheld at an average price of $26.76 per share and 24,017 shares of Class A common stock withheld at an average price of $27.11 per share (under the terms of grants under the Covenant Transportation Group, Inc. Third Amended and Restated 2006 Omnibus Incentive Plan) to offset tax withholding obligations that occurred upon vesting and release of restricted shares. The withholding of shares was permitted under the applicable award agreements and was not part of any stock repurchase plan. |
| (In thousands, except per share and operating data amounts) | |
| | | Years Ended December 31, | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Statement of Operations Data: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Freight revenue | | $ | 578,569 | | | $ | 538,933 | | | $ | 527,435 | | | $ | 512,026 | | | $ | 546,320 | |
| Fuel surcharge revenue | | | 140,411 | | | | 145,616 | | | | 146,819 | | | | 140,601 | | | | 103,429 | |
Total revenue | | $ | 718,980 | | | $ | 684,549 | | | $ | 674,254 | | | $ | 652,627 | | | $ | 649,749 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operating expenses: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Salaries, wages, and related expenses | | | 231,761 | | | | 218,946 | | | | 217,080 | | | | 211,169 | | | | 216,316 | |
Fuel expense | | | 168,856 | | | | 186,002 | | | | 194,841 | | | | 208,693 | | | | 177,239 | |
Operations and maintenance | | | 47,251 | | | | 50,043 | | | | 45,839 | | | | 43,862 | | | | 42,050 | |
Revenue equipment rentals and purchased transportation | | | 111,772 | | | | 102,954 | | | | 85,010 | | | | 63,353 | | | | 71,474 | |
Operating taxes and licenses | | | 10,960 | | | | 10,969 | | | | 11,043 | | | | 12,148 | | | | 11,090 | |
Insurance and claims (2) | | | 39,594 | | | | 30,305 | | | | 33,133 | | | | 35,886 | | | | 32,648 | |
Communications and utilities | | | 5,806 | | | | 5,240 | | | | 4,809 | | | | 5,137 | | | | 4,974 | |
General supplies and expenses | | | 16,950 | | | | 16,002 | | | | 16,068 | | | | 15,627 | | | | 16,143 | |
Depreciation and amortization, including gains and losses on disposition of equipment and impairment of assets | | | 46,384 | | | | 43,694 | | | | 43,222 | | | | 46,274 | | | | 51,807 | |
Goodwill impairment charge (1) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 11,539 | | | | - | |
| Total operating expenses | | | 679,334 | | | | 664,155 | | | | 651,045 | | | | 653,688 | | | | 623,741 | |
| Operating income (loss) | | | 39,646 | | | | 20,394 | | | | 23,209 | | | | (1,061 | ) | | | 26,008 | |
| Other expense (income): | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest expense | | | 10,807 | | | | 10,400 | | | | 12,697 | | | | 16,208 | | | | 16,566 | |
Other | | | (13 | ) | | | (3 | ) | | | (13 | ) | | | (155 | ) | | | (22 | ) |
| Other expenses, net | | | 10,794 | | | | 10,397 | | | | 12,684 | | | | 16,053 | | | | 16,544 | |
| Equity in income of affiliate | | | 3,730 | | | | 2,750 | | | | 1,875 | | | | 675 | | | | - | |
| Income (loss) before income taxes | | | 32,582 | | | | 12,747 | | | | 12,400 | | | | (16,439 | ) | | | 9,464 | |
| Income tax expense (benefit) | | | 14,774 | | | | 7,503 | | | | 6,335 | | | | (2,172 | ) | | | 6,175 | |
| Net income (loss) | | $ | 17,808 | | | $ | 5,244 | | | $ | 6,065 | | | $ | (14,267 | ) | | $ | 3,289 | |
| (1) | Represents non-cash impairment charges to write off the goodwill in our Truckload segment. |
| (2) | 2014 insurance and claims expense includes $7.5 million additional reserves for 2008 cargo claim. |
| Basic income (loss) per share | | $ | 1.17 | | | $ | 0.35 | | | $ | 0.41 | | | $ | (0.97 | ) | | $ | 0.23 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | �� | | | | | | | | | | |
| Diluted income (loss) per share | | $ | 1.15 | | | $ | 0.35 | | | $ | 0.41 | | | $ | (0.97 | ) | | $ | 0.23 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Basic weighted average common shares outstanding | | | 15,250 | | | | 14,837 | | | | 14,742 | | | | 14,689 | | | | 14,374 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Diluted weighted average common shares outstanding | | | 15,517 | | | | 15,039 | | | | 14,808 | | | | 14,689 | | | | 14,505 | |
| | | Years Ended December 31, | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Selected Balance Sheet Data: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net property and equipment | | $ | 382,491 | | | $ | 329,608 | | | $ | 279,017 | | | $ | 322,303 | | | $ | 323,954 | |
| Total assets | | $ | 554,017 | | | $ | 466,422 | | | $ | 400,232 | | | $ | 439,825 | | | $ | 441,179 | |
| Long-term debt and capital lease obligations, less current maturities | | $ | 172,903 | | | $ | 182,677 | | | $ | 109,217 | | | $ | 144,296 | | | $ | 155,381 | |
| Total stockholders' equity | | $ | 169,204 | | | $ | 100,360 | | | $ | 94,673 | | | $ | 87,055 | | | $ | 100,698 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Selected Operating Data: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Capital expenditures (proceeds), net (1) | | $ | 89,455 | | | $ | 91,976 | | | $ | (15,738 | ) | | $ | 54,402 | | | $ | 84,677 | |
| Average freight revenue per loaded mile (2) | | $ | 1.77 | | | $ | 1.66 | | | $ | 1.63 | | | $ | 1.53 | | | $ | 1.45 | |
| Average freight revenue per total mile (2) | | $ | 1.60 | | | $ | 1.49 | | | $ | 1.47 | | | $ | 1.38 | | | $ | 1.31 | |
| Average freight revenue per tractor per week (2) | | $ | 3,777 | | | $ | 3,411 | | | $ | 3,320 | | | $ | 3,069 | | | $ | 3,137 | |
| Average miles per tractor per year | | | 123,275 | | | | 119,375 | | | | 118,103 | | | | 115,775 | | | | 125,178 | |
| Weighted average tractors for year (3) | | | 2,609 | | | | 2,777 | | | | 2,895 | | | | 3,029 | | | | 3,099 | |
| Total tractors at end of period (3) | | | 2,665 | | | | 2,688 | | | | 2,884 | | | | 2,978 | | | | 3,087 | |
| Total trailers at end of period (4) | | | 6,722 | | | | 6,861 | | | | 6,904 | | | | 7,361 | | | | 7,332 | |
| Team-driven tractors as percentage of fleet | | | 32.1 | % | | | 29.2 | % | | | 28.1 | % | | | 27.3 | % | | | 28.0 | % |
| (1) | Includes equipment purchased under capital leases. |
| (2) | Excludes fuel surcharge revenue. |
| (3) | Includes monthly rental tractors and tractors provided by independent contractors. |
| (4) | Excludes monthly rental trailers. |
The information set forth above should be read in conjunction with "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations" and the Company's consolidated financial statements and notes thereto included in Items 7 and 8, respectively, of this Form 10-K.
ITEM 7. MANAGEMENT'S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
Cautionary Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements
Item 7, as well as other items of this Annual Report, contains certain statements that may be considered forward-looking statements within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, and such statements are subject to the safe harbor created by those sections and the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995, as amended. All statements, other than statements of historical or current fact, are statements that could be deemed forward-looking statements, including without limitation: any projections of earnings, revenues, or other financial items; any statement of plans, strategies, and objectives of management for future operations; any statements concerning proposed new services or developments; any statements regarding future economic conditions or performance; and any statements of belief and any statements of assumptions underlying any of the foregoing. In this Item 7, statements relating to expected sources of working capital, liquidity and funds for meeting equipment purchase obligations, expected capital expenditures (including the future mix of lease and purchase obligations), future trucking capacity, expected freight demand and volumes, future rates and prices, future depreciation and amortization, expected tractor and trailer count, future driver market, expected driver compensation, expected owner operator usage, planned allocation of capital, future equipment costs, expected settlement of operating lease obligations, future asset sales, future insurance and claims, future tax expense and deductions, future fuel expense and the future effectiveness of fuel surcharge programs and price hedges, among others, are forward-looking statements. Such statements may be identified by their use of terms or phrases such as "believe," "may," "could," "expects," "estimates," "projects," "anticipates," "plans," "intends," and similar terms and phrases. Forward-looking statements are based on currently available operating, financial, and competitive information. Forward-looking statements are inherently subject to risks and uncertainties, some of which cannot be predicted or quantified, which could cause future events and actual results to differ materially from those set forth in, contemplated by, or underlying the forward-looking statements. Factors that could cause or contribute to such differences include, but are not limited to, those discussed in the section entitled "Item 1A. Risk Factors," set forth above. Readers should review and consider the factors discussed in "Item 1A. Risk Factors," along with various disclosures in our press releases, stockholder reports, and other filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission.
All such forward-looking statements speak only as of the date of this Annual Report. You are cautioned not to place undue reliance on such forward-looking statements. We expressly disclaim any obligation or undertaking to release publicly any updates or revisions to any forward-looking statements contained herein to reflect any change in our expectations with regard thereto or any change in the events, conditions, or circumstances on which any such statement is based.
EXECUTIVE OVERVIEW
The fourth quarter of 2013 was a tipping point in the supply versus demand equation for Truckload freight. Demand began to exceed supply, especially for the niche markets we serve and specifically expedited/team and temperature-controlled. While the harsh winter weather and SRT system conversion negatively impacted the first quarter of 2014, beginning in March 2014 we saw the truckload freight balance dynamics start shifting again, such that demand again exceeded supply. This trend stayed consistent throughout most of the remainder of 2014, such that we began planning for the peak shipping seasons (from Thanksgiving to Christmas) months in advance. This planning allowed precise execution, as measured by on-time deliveries, for both our customers and the ultimate consumers of our freight. When combined with the demand provided by the growth in holiday shopping over the Internet and the resulting volumes carried for our less-than-truckload ("LTL"), parcel delivery, and omni-channel shipping customers, the execution boosted the fourth quarter of 2014 to be our most profitable quarter since inception.
Fiscal 2014 marks the best annual results we have experienced since 1999. Additionally, 2014 is our third consistent year of profitability, after experiencing only one year of profitability between fiscal 2006-2011.
While there are many accomplishments to celebrate in 2014, those that are specifically noteworthy were 1) a 7.2% increase in average freight revenue per total mile and 3.3% increase in average miles per truck, 2) a significant improvement in fuel economy and resulting decrease in net fuel expense, and 3) a successful follow-on stock offering and related decrease in our total indebtedness. The main negatives were 1) increased operating costs on a per mile basis, 2) increase in driver turnover compared to 2013, and 3) the increase in our frequency of accidents, as measured by DOT accidents per million miles.
Additional items of note for 2014 include the following:
| ● | Total revenue was $719.0 million, compared with $684.5 million for 2013, and freight revenue (excludes revenue from fuel surcharge) was $578.6 million, compared with $538.9 million for 2013; |
| ● | Operating income was $39.6 million, compared with an operating income of $20.4 million for 2013; |
| ● | Net income was $17.8 million, or $1.17 per basic share and $1.15 per diluted share, compared with net income of $5.2 million, or $0.35 per basic and diluted share, for 2013. Net income for 2014 includes an unfavorable after-tax impact of approximately $4.6 million, or $0.30 per diluted share, attributable to an adverse 2008 cargo claim judgment; |
| ● | Solutions' revenue increased by 39.4% to $56.0 million, compared to $40.1 million for 2013. Solutions' gross margin (purchased transportation divided by revenue) was 77.0% in 2014 from 76.4% for 2013, while its other operating costs improved to 16.0% of revenue from 20.5% in 2013; |
| ● | Since December 31, 2013, aggregate lease-adjusted indebtedness (which includes the present value of off-balance sheet lease obligations), net of cash, decreased by $78.5 million to $226.7 million; |
| ● | With available borrowing capacity of approximately $60.7 million under our Credit Facility, we do not expect to be required to test our fixed charge covenant in the foreseeable future; |
| ● | Our equity investment in TEL provided $3.7 million of pre-tax earnings in 2014 compared to $2.8 million for 2013; and |
| ● | Stockholders' equity at December 31, 2014, was $169.2 million and our tangible book value was $169.0 million, or $9.34 per basic share. |
As we look forward to 2015 and beyond, a continued focus on the disciplined approach we have forged as a result of our strategic planning and continuous improvement processes will be key to ensuring we align ourselves with freight that complements our core competencies and markets we serve. Moreover, growing our partner carrier businesses (TEL and Solutions) and maintaining cost control and operational discipline will be keys to success.
Our outlook for 2015 is positive. We expect our average truck count to grow over the course of the year, starting with a year-over-year increase in the first quarter of 2015. In addition, we expect to report positive first quarter earnings for the first time since 2004. For the full year, we expect earnings per diluted share to increase modestly over 2014, even if adding back the approximately $0.30 per share unfavorable cargo claim reserve adjustment we recorded in the third quarter of 2014 and taking into consideration approximately 19.0% more estimated annual weighted average diluted shares. Achieving year-over-year improvements may become more challenging in the second half of the year depending on the level of involvement of our asset-based and Solutions subsidiaries in the supply chains of our LTL, parcel, and omni-channel shipping customers during the peak freight season. However, additional growth of e-commerce retail freight could assist with continued year-over-year improvements even in the second half of the year.
RESULTS OF CONSOLIDATED OPERATIONS
The following table sets forth total revenue and freight revenue (total revenue less fuel surcharge revenue) for the periods indicated:
Revenue
| | | Year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | | | 2012 | |
| Revenue: | | | | | | | | | |
| Freight revenue | | $ | 578,569 | | | $ | 538,933 | | | $ | 527,435 | |
| Fuel surcharge revenue | | | 140,411 | | | | 145,616 | | | | 146,819 | |
| Total revenue | | $ | 718,980 | | | $ | 684,549 | | | $ | 674,254 | |
For 2014, total revenue increased $34.4 million, or 5.0%, to $719.0 million from $684.5 million in 2013. Freight revenue increased $39.6 million, or 7.4%, to $578.6 million for 2014, from $538.9 million in 2013, while fuel surcharge revenue decreased $5.2 million year-over-year. The increase in freight revenue resulted from a $23.8 million increase in freight revenue from our Truckload segment and a $15.9 million increase in revenues from Solutions.
The increase in 2014 Truckload revenue relates to an increase in average freight revenue per tractor per week of 10.7% compared to 2013 and a $4.1 million increase in freight revenue contributed by our temperature-controlled intermodal service offering. These improvements were partially offset by a decrease in our average tractor fleet of 6.1% from 2013. The increase in average freight revenue per tractor per week is the result of a 7.2% increase, or 10.7 cents per mile, in average rate per total mile, as well as a 3.3% increase in average miles per unit when compared to 2013.
The increase in Solutions' revenue is primarily the result of additional peak-season freight opportunities during the fourth quarter of 2014, improved coordination with our Truckload segment, and additional business from new customers added during the year, partially offset by the discontinuation of an underperforming location in June of 2014.
For the year ended December 31, 2013, total revenue increased $10.3 million, or 1.5%, to $684.5 million from $674.3 million in 2012. Freight revenue increased $11.5 million, or 2.2%, to $538.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2013, from $527.4 million in 2012, while fuel surcharge revenue decreased $1.2 million year-over-year. The increase in freight revenue resulted from a $13.9 million increase in revenue from Solutions offset by a $2.4 million decrease in freight revenue from our Truckload segment.
The decrease in 2013 Truckload revenue relates to a decrease in our average tractor fleet of 4.1% from 2012, as well as a decrease of 3.0% in our total miles from 2012. These declines were partially offset by an increase in average freight revenue per total mile of 2.4 cents per mile, or 1.7%, compared to 2012 and an increase in utilization of 1.1% year-over-year. The main factors impacting the increased utilization were an increase in the percentage of our fleet comprised of team-driven tractors and unusually strong fourth quarter 2013 seasonal business, partially offset by the new hours-of-service regulations.
The increase in Solutions' revenue is primarily due to the growth of certain newer service offerings, including less-than-truckload consolidation services and accounts receivable factoring, as well as efficiencies gained in capturing the additional freight revenue from overflow freight from our Truckload operations.
Based on the capacity constraints in the market, primarily resulting from a shortage of professional drivers and an increased demand arising from improving economic conditions and e-commerce trends, we expect continued positive rate trends in the future.
For comparison purposes in the discussion below, we use total revenue and freight revenue (total revenue less fuel surcharge revenue) when discussing changes as a percentage of revenue. As it relates to the comparison of expenses to freight revenue, we believe removing fuel surcharge revenue, which is sometimes a volatile source of revenue, affords a more consistent basis for comparing the results of operations from period-to-period. Nonetheless, freight revenue represents a non-GAAP financial measure. Accordingly, undue reliance should not be placed on the discussion of freight revenue, and discussions of freight revenue should be considered in combination with discussions of total revenue. For each expense item discussed below, we have provided a table setting forth the relevant expense first as a percentage of total revenue, and then as a percentage of freight revenue.
Salaries, wages, and related expenses
| | | Year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | | | 2012 | |
| Salaries, wages, and related expenses | | $ | 231,761 | | | $ | 218,946 | | | $ | 217,080 | |
| % of total revenue | | | 32.2 | % | | | 32.0 | % | | | 32.2 | % |
| % of freight revenue | | | 40.1 | % | | | 40.6 | % | | | 41.2 | % |
Salaries, wages, and related expenses increased approximately $12.8 million, or 5.9%, for the year ended December 31, 2014, compared with 2013. As a percentage of total revenue, salaries, wages, and related expenses remained relatively even at 32.2% of total revenue for the year ended December 31, 2014, as compared to 32.0% in 2013. As a percentage of freight revenue, salaries, wages, and related expenses declined to 40.1% of freight revenue for the year ended December 31, 2014, from 40.6% in 2013. Salaries, wages, and related expenses increased approximately 5.7 cents per mile primarily due to pay adjustments for both driver and non-drivers since 2013, as well as increased non-driver incentive compensation tied to our results of operations. Additionally, group insurance costs increased approximately $1.7 million from 2013 as a result of more participants and fees directly related to the Affordable Care Act. We also had higher workers' compensation expense in 2014 at 3.4 cents per company mile compared to 3.0 cents in 2013 due to an increase in our DOT accidents and increased development of prior period claims. Additionally, we had a reduction in the percentage of our fleet comprised of independent contractors, whose costs are included in the purchased transportation line item.
For the year ended December 31, 2013, salaries, wages, and related expenses increased approximately $1.9 million, or 0.9%, compared with 2012. As a percentage of total revenue, salaries, wages, and related expenses remained relatively even at 32.0% of total revenue for the year ended December 31, 2013, as compared to 32.2% in 2012. As a percentage of freight revenue, salaries, wages, and related expenses declined to 40.6% of freight revenue for the year ended December 31, 2013, from 41.2% in 2012. Salaries, wages, and related expenses increased approximately 2.5 cents per mile due to pay adjustments since 2012 and higher workers' compensation expense in 2013 of 3.0 cents per company mile compared to 2.8 cents in 2012, partially offset by an increase in the percentage of our fleet comprised of independent contractors, whose costs are included in the purchased transportation line item. Additionally, non-driver wages decreased as a result of decreased incentive compensation tied to our results of operations.
Going forward, we believe we expect driver pay to increase as we look to reduce the number of unseated trucks in our fleet in a tight market for drivers. In addition, salaries, wages, and related expenses will increase as a result of wage inflation, higher healthcare costs, and increased incentive compensation due to better performance. As a percentage of total revenue and freight revenue, salaries, wages, and related expenses will fluctuate to some extent based on the percentage of revenue generated by independent contractors and our Solutions business, for which payments are reflected in the purchased transportation line item.
Fuel expense
| | | Year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | | | 2012 | |
| Fuel expense | | $ | 168,856 | | | $ | 186,002 | | | $ | 194,841 | |
| % of total revenue | | | 23.5 | % | | | 27.2 | % | | | 28.9 | % |
We receive a fuel surcharge on our loaded miles from most shippers; however, this does not cover the entire increase in fuel prices for several reasons, including the following: surcharges cover only loaded miles we operate; surcharges do not cover miles driven out-of-route by our drivers; and surcharges typically do not cover refrigeration unit fuel usage or fuel burned by tractors while idling. Moreover, most of our business relating to shipments obtained from freight brokers does not carry a fuel surcharge. Finally, fuel surcharges vary in the percentage of reimbursement offered, and not all surcharges fully compensate for fuel price increases even on loaded miles.
The rate of fuel price changes also can have an impact on results. Most fuel surcharges are based on the average fuel price as published by the DOE for the week prior to the shipment, meaning we typically bill customers in the current week based on the previous week's applicable index. Therefore, in times of increasing fuel prices, we do not recover as much as we are currently paying for fuel. In periods of declining prices, the opposite is true. Fuel prices as measured by the DOE averaged approximately 9.7 cents per gallon lower in 2014 compared with 2013 and 4.6 cents per gallon lower in 2013 compared to 2012.
Additionally, $3.1 million of 2014 losses and $0.6 million and $5.0 million of 2013 and 2012 gains, respectively, were reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive (loss) income to our results from operations for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013, and 2012, respectively, related to fuel hedging. Of the $3.1 million of losses reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive loss for the year ended December 31, 2014, approximately $1.8 million related to losses on contracts that expired or were sold and for which we completed the forecasted transaction by purchasing the hedged diesel fuel, approximately $1.4 million was recorded as additional fuel expense related to contracts for which the hedging relationship was no longer deemed to be effective on a prospective basis, and approximately $0.2 million was recorded as unfavorable ineffectiveness on the contracts that existed at December 31, 2014. The ineffectiveness was calculated using the cumulative dollar offset method as an estimate of the difference in the expected cash flows of the respective fuel hedge contracts compared to the changes in the all-in cash outflows required for the diesel fuel purchases. The calculation of ineffectiveness excludes approximately $0.1 million from the assessment of hedge ineffectiveness as a result of the related contracts being in an under-hedged position as of the date of the calculation.
To measure the effectiveness of our fuel surcharge program, we subtract fuel surcharge revenue (other than the fuel surcharge revenue we reimburse to independent contractors and other third parties, which is included in purchased transportation) from our fuel expense. The result is referred to as net fuel expense. Our net fuel expense as a percentage of freight revenue is affected by the cost of diesel fuel net of fuel surcharge collection, the percentage of miles driven by company trucks, our fuel economy, and our percentage of deadhead miles, for which we do not receive fuel surcharge revenues. Net fuel expense is shown below:
| | | Year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | | | 2012 | |
| Total fuel surcharge | | $ | 140,411 | | | $ | 145,616 | | | $ | 146,819 | |
| Less: Fuel surcharge revenue reimbursed to independent contractors and other third parties | | | 10,837 | | | | 12,863 | | | | 12,195 | |
| Company fuel surcharge revenue | | $ | 129,574 | | | $ | 132,753 | | | $ | 134,624 | |
| Total fuel expense | | $ | 168,856 | | | $ | 186,002 | | | $ | 194,841 | |
| Less: Company fuel surcharge revenue | | | 129,574 | | | | 132,753 | | | | 134,624 | |
| Net fuel expense | | $ | 39,282 | | | $ | 53,249 | | | $ | 60,217 | |
| % of freight revenue | | | 6.8 | % | | | 9.9 | % | | | 11.4 | % |
Total fuel expense decreased approximately $17.1 million, or 9.2%, for the year ended December 31, 2014, compared with 2013. As a percentage of total revenue, total fuel expense decreased to 23.5% of total revenue for the year ended December 31, 2014, from 27.2% in 2013. As a percentage of freight revenue, total fuel expense decreased to 29.2% of freight revenue for year ended December 31, 2014, from 34.5% in 2013. These decreases are primarily related to an increase in our average fuel miles per gallon during 2014 as a result of purchasing equipment with more fuel-efficient engines and improved fuel pricing.
Net fuel expense decreased $14.0 million, or 26.2%, for the year ended December 31, 2014 compared to 2013. As a percentage of freight revenue, net fuel expense decreased 3.1% for the year ended December 31, 2014 compared to 2013. These decreases are primarily the result of improved miles per gallon due to new engine technology, improved fuel surcharge recovery, and improved fuel pricing, in each case, net of gains and losses on fuel hedging contracts.
Net fuel expense decreased $7.0 million, or 11.6%, for the year ended December 31, 2013 compared to 2012. As a percentage of freight revenue, net fuel expense decreased 1.5% for the year ended December 31, 2013 compared to 2012. These decreases were primarily the result of improved miles per gallon due to new engine technology, improved fuel surcharge recovery on certain customers, and an increase in the average percentage of our fleet comprised of independent contractors.
For the year ended December 31, 2013, total fuel expense decreased approximately $8.8 million, or 4.5%, compared with 2012. As a percentage of total revenue, total fuel expense decreased to 27.2% of total revenue for the year ended December 31, 2013, from 28.9% in 2012. As a percentage of freight revenue, total fuel expense decreased to 34.5% of freight revenue for the year ended December 31, 2013, from 36.9% in 2012. These decreases are primarily related to the increase in the percentage of our fleet comprised of independent contractors, since they generate a similar amount of revenue per truck, while they pay the cost of their fuel. Additionally, we have experienced an increase in our average fuel miles per gallon during 2013 as a result of purchasing equipment with more fuel-efficient engines.
We expect to continue managing our idle time and truck speeds, investing in more fuel-efficient tractors to improve our miles per gallon, locking in fuel hedges when deemed appropriate, and partnering with customers to adjust fuel surcharge programs that are inadequate to recover a fair portion of fuel costs. Going forward, our net fuel expense is expected to fluctuate as a percentage of revenue based on factors such as diesel fuel prices, percentage recovered from fuel surcharge programs, percentage of uncompensated miles, percentage of revenue generated by team-driven tractors (which tend to generate higher miles and lower revenue per mile, thus proportionately more fuel cost as a percentage of revenue), percentage of revenue generated by refrigerated operation (which uses diesel fuel for refrigeration, but usually does not recover fuel surcharges on refrigeration fuel), percentage of revenue generated from independent contractors, the success of fuel efficiency initiatives, and gains and losses on fuel hedging contracts. We have focused our efforts on increasing our ability to recover fuel surcharges under our customer contracts for fuel used in refrigeration units. If these efforts are successful, they could give rise to an increase in fuel surcharges recovered and a corresponding decrease in net fuel expense. Additionally, in recent months petroleum based markets have experienced rapid declines such that current pricing has reached four-year lows and, at current prices, we would experience fuel hedging losses over the next several years. The amount of these losses would vary depending on market fuel prices. Finally, we believe fuel prices could increase going forward based upon the recent significant decline in prices. As such, there has been significant volatility in our net fuel expense, and we would expect such volatility to continue.
Operations and maintenance
| | | Year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | | | 2012 | |
| Operations and maintenance | | $ | 47,251 | | | $ | 50,043 | | | $ | 45,839 | |
| % of total revenue | | | 6.6 | % | | | 7.3 | % | | | 6.8 | % |
| % of freight revenue | | | 8.2 | % | | | 9.3 | % | | | 8.7 | % |
Operations and maintenance decreased $2.8 million, or 5.6%, for the year ended December 31, 2014, compared with 2013. As a percentage of total revenue, operations and maintenance decreased to 6.6% of total revenue in 2014, from 7.3% in 2013. As a percentage of freight revenue, operations and maintenance decreased to 8.2% of freight revenue for 2014, from 9.3% in 2013. These decreases were primarily the result of reduced parts and vehicle maintenance expense related to the fleet reduction, removing older, higher maintenance units from the fleet, and a decline in the average age of our revenue equipment, partially offset by an increase in recruiting.
For the year ended December 31, 2013, operations and maintenance increased approximately $4.2 million, or 9.2%, compared with 2012. As a percentage of total revenue, operations and maintenance increased to 7.3% of total revenue in 2013, from 6.8% in 2012. As a percentage of freight revenue, operations and maintenance increased to 9.3% of freight revenue for 2013, from 8.7% in 2012. These increases were due primarily to additional repair expense for replacing diesel exhaust fluid particulate filters, an increase in the average age of tractors and trailers, and higher driver recruiting expenses. Recruiting costs were higher in 2013 than in 2012 as a result of the tight capacity in the driver market and our efforts to fill unseated trucks.
Revenue equipment rentals and purchased transportation
| | | Year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | | | 2012 | |
| Revenue equipment rentals and purchased transportation | | $ | 111,772 | | | $ | 102,954 | | | $ | 85,010 | |
| % of total revenue | | | 15.5 | % | | | 15.0 | % | | | 12.6 | % |
| % of freight revenue | | | 19.3 | % | | | 19.1 | % | | | 16.1 | % |
Revenue equipment rentals and purchased transportation increased approximately $8.8 million, or 8.6%, for the year ended December 31, 2014, compared with 2013. As a percentage of total revenue, revenue equipment rentals and purchased transportation increased to 15.5% of total revenue for the year ended December 31, 2014, from 15.0% in 2013. As a percentage of freight revenue, revenue equipment rentals and purchased transportation increased to 19.3% of freight revenue for the year ended December 31, 2014, from 19.1% in 2013. These increases were primarily the result of increased costs related to a $12.4 million increase in payments to third-party transportation providers related to increased revenues at our Solutions subsidiary and growth of our temperature-controlled intermodal service offering, partially offset by a decrease in leased equipment rental payments and a decrease in payments to independent contractors, which comprised a smaller percentage of our total fleet. For the year ended December 31, 2014, miles run by independent contractors decreased to 8.2% of our total miles from 9.2% for 2013 and leased units decreased to 150 units from 650 units in 2013. We expect revenue equipment rentals to decrease going forward as a result of our increase in acquisition of revenue equipment through purchases rather than operating leases. As discussed below, this decrease may be partially or fully offset by an increase in purchased transportation.
For the year ended December 31, 2013, revenue equipment rentals and purchased transportation increased approximately $17.9 million, or 21.1%, compared with 2012. As a percentage of total revenue, revenue equipment rentals and purchased transportation increased to 15.0% of total revenue for the year ended December 31, 2013, from 12.6% in 2012. As a percentage of freight revenue, revenue equipment rentals and purchased transportation increased to 19.1% of freight revenue for the year ended December 31, 2013, from 16.1% in 2012. These increases were primarily the result of an $8.9 million increase in payments to third-party transportation providers related to growth of our Solutions subsidiary's less-than-truckload consolidation service offering, a $2.5 million increase in payments to independent contractors, and a $3.1 million increase in tractor and trailer equipment rental expense. Payments to independent contractors increased year-over-year due to the increase in the average size of the independent contractor fleet and fuel surcharges passed through to independent contractors that are a component of the related expense, and increased miles per unit. For the year ended December 31, 2013, miles run by independent contractors increased to 9.2% of our total miles from 8.7% for 2012.
This expense category will fluctuate with the number of loads hauled by independent contractors and handled by Solutions and the percentage of our fleet financed with operating leases, as well as the amount of fuel surcharge revenue passed through to the third party carriers and independent contractors. If capacity remains tight, we believe we may need to increase the amounts we pay to third-party transportation providers and independent contractors, which would increase this expense category as a percentage of freight revenue absent an offsetting increase in revenue. Additionally, we have enhanced our independent contractor lease purchase program and are actively recruiting independent contractors. As such, we expect the percentage of independent contractors in our fleet to grow, which could increase this line item as a percentage of revenue.
Operating taxes and licenses
| | | Year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | | | 2012 | |
| Operating taxes and licenses | | $ | 10,960 | | | $ | 10,969 | | | $ | 11,043 | |
| % of total revenue | | | 1.5 | % | | | 1.6 | % | | | 1.6 | % |
| % of freight revenue | | | 1.9 | % | | | 2.0 | % | | | 2.1 | % |
For the periods presented, the change in operating taxes and licenses was not significant as either a percentage of total revenue or freight revenue.
Insurance and claims
| | | Year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | | | 2012 | |
| Insurance and claims | | $ | 39,594 | | | $ | 30,305 | | | $ | 33,133 | |
| % of total revenue | | | 5.5 | % | | | 4.4 | % | | | 4.9 | % |
| % of freight revenue | | | 6.8 | % | | | 5.6 | % | | | 6.3 | % |
Insurance and claims, consisting primarily of premiums and deductible amounts for liability, physical damage, and cargo damage insurance and claims, increased approximately $9.3 million, or 30.7%, for year ended December 31, 2014, compared to 2013. As a percentage of total revenue, insurance and claims increased to 5.5% of total revenue for the year ended December 31, 2014, from 4.4% in 2013. As a percentage of freight revenue, insurance and claims increased to 6.8% of freight revenue for the year ended December 31, 2014, from 5.6% in 2013. These increases are primarily related to approximately $7.5 million of additional reserves related to the adverse judgment in 2014 regarding a 2008 cargo claim. Excluding this cargo claim, insurance and claims cost per mile increased to 9.9 cents per mile in 2014 from 9.1 cents per mile in 2013, primarily due to a decline in safety performance, as measured by accidents per million miles, partially offset by a reduction in loss development factors resulting from more disciplined claims management.
For the year ended December 31, 2013, insurance and claims decreased approximately $2.8 million, or 8.5%, compared to 2012. As a percentage of total revenue, insurance and claims decreased to 4.4% of total revenue for the year ended December 31, 2013, from 4.9% in 2012. As a percentage of freight revenue, insurance and claims decreased to 5.6% of freight revenue for the year ended December 31, 2013, from 6.3% in 2012. Insurance and claims cost per mile decreased to 9.1 cents per mile in 2013 from 9.7 cents per mile in 2012 due to improved safety performance, measured by accidents per million miles, and a reduction in loss development factors resulting from more disciplined claims management, while 2012 included a $4.0 million credit of previously expensed premium from our commutation of the April 1, 2011 through March 31, 2012 policy for our primary auto liability insurance. We did not commute the April 1, 2012 through March 31, 2013 policy.
With our significant self-insured retention, insurance and claims expense may fluctuate significantly from period-to-period, and any increase in frequency or severity of claims could adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations. We are appealing the judgment on the 2008 cargo claim. A successful appeal or mediation could significantly reduce insurance and claims expense in the period in which the appeal is resolved. On the other hand, if we are not successful in such an appeal or mediation, insurance and claims expense may increase as a result of continuing litigation expenses, including pre and post judgment interest. We are always evaluating strategies to efficiently reduce our insurance and claims expense, which in the past has included the commutation of our auto liability insurance policy. We intend to evaluate our ability to commute the current policy and any such commutation could significantly impact insurance and claims expense.
Communications and utilities
| | | Year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | | | 2012 | |
| Communications and utilities | | $ | 5,806 | | | $ | 5,240 | | | $ | 4,809 | |
| % of total revenue | | | 0.8 | % | | | 0.8 | % | | | 0.7 | % |
| % of freight revenue | | | 1.0 | % | | | 1.0 | % | | | 0.9 | % |
For the periods presented, the change in communications and utilities was not significant as either a percentage of total revenue or freight revenue.
General supplies and expenses
| | | Year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | | | 2012 | |
| General supplies and expenses | | $ | 16,950 | | | $ | 16,002 | | | $ | 16,068 | |
| % of total revenue | | | 2.4 | % | | | 2.3 | % | | | 2.4 | % |
| % of freight revenue | | | 2.9 | % | | | 3.0 | % | | | 3.0 | % |
For the periods presented, the change in general supplies and expenses was not significant as either a percentage of total revenue or freight revenue.
Depreciation and amortization
| | | Year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | | | 2012 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | $ | 46,384 | | | $ | 43,694 | | | $ | 43,222 | |
| % of total revenue | | | 6.5 | % | | | 6.4 | % | | | 6.4 | % |
| % of freight revenue | | | 8.0 | % | | | 8.1 | % | | | 8.2 | % |
Depreciation and amortization in 2014 increased $2.7 million, or 6.2%, compared with 2013. As a percentage of total revenue, depreciation and amortization remained relatively even with 2013 at 6.5% of total revenue for the year ended December 31, 2014 compared to 6.4% for 2013. As a percentage of freight revenue, depreciation and amortization decreased slightly to 8.0% of freight revenue for the year ended December 31, 2014, from 8.1% in 2013. Depreciation, consisting primarily of depreciation of revenue equipment and excluding gains and losses, increased $4.7 million in 2014 from 2013, primarily because owned tractors increased by approximately 500 due to a reduction in use of operating leases to finance revenue equipment as well the increased cost of new tractors. Gains on the disposal of property and equipment, totaling $2.7 million in 2014, were $1.9 million higher than 2013 due to the type and mileage of the equipment sold. We expect to see an increase in depreciation and amortization going forward as a result of our expected increase in acquisition of revenue equipment through purchases rather than operating leases.
For the year ended December 31, 2013, depreciation and amortization increased $0.5 million, or 1.1%, compared with 2012. As a percentage of total revenue, depreciation and amortization remained even with 2012 at 6.4% of total revenue for the year ended December 31, 2013. As a percentage of freight revenue, depreciation and amortization decreased slightly to 8.1% of freight revenue for the year ended December 31, 2013, from 8.2% in 2012. Depreciation, consisting primarily of depreciation of revenue equipment and excluding gains and losses, decreased $3.6 million in 2013 from 2012, primarily because owned tractors decreased by 224 due to the use of operating leases and a reduction in our fleet size. This was partially offset by increased cost of new tractors. Gains on the disposal of property and equipment, totaling $0.8 million in 2013 were $4.1 million lower than 2012 due to a $2.4 million gain on the sale of a terminal in 2012 and the used equipment market being less robust in 2013.
Other expense, net
| | | Year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | | | 2012 | |
| Other expense, net | | $ | 10,794 | | | $ | 10,397 | | | $ | 12,684 | |
| % of total revenue | | | 1.5 | % | | | 1.5 | % | | | 1.9 | % |
| % of freight revenue | | | 1.9 | % | | | 1.9 | % | | | 2.4 | % |
Other expense, net includes interest expense, interest income, and other miscellaneous non-operating items, which decreased approximately $0.4 million, or 3.8%, for the year ended December 31, 2014, compared with 2013. As a percentage of total revenue, other expense, net remained even with 2013 at 1.5% for the year ended December 31, 2014. As a percentage of freight revenue, other expense, net remained even with 2013 at 1.9% of freight revenue for the year ended December 31, 2014. We expect other expense, net to decrease as compared to prior years as a result of the repayments of debt and leases from the proceeds of our late November 2014 follow-on stock offering. This decrease could be partially offset by the incurrence of balance sheet debt as we expect to transition away from operating leases and towards equipment notes as a means of financing revenue equipment.
For the year ended December 31, 2013, other expense, net, decreased approximately $2.3 million, or 18.0%, compared with 2012. As a percentage of total revenue, other expense, net decreased to 1.5% of total revenue for the year ended December 31, 2013, from 1.9% in 2012. As a percentage of freight revenue, other expense, net decreased to 1.9% of freight revenue for the year ended December 31, 2013, from 2.4% in 2012. The increased use of leases as opposed to on-balance sheet financing in the past twelve months resulted in less net debt (debt less cash) throughout the majority of the year ended December 31, 2013 and when combined with a reduced weighted average interest rate resulting from the amendment to our Credit Facility in January 2013, interest expense decreased year-over-year.
This line item will fluctuate based on our decision with respect to purchasing revenue equipment with balance sheet debt versus operating leases as well as our ability to continue to generate profitable results and reduce our leverage.
Equity in income of affiliate
| | | Year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | | | 2012 | |
| Equity in income of affiliate | | $ | 3,730 | | | $ | 2,750 | | | $ | 1,875 | |
We have accounted for our investment in TEL using the equity method of accounting and thus our financial results include our proportionate share of TEL's net income. For the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, the increase in TEL's contributions to our results is due to their growth in both leasing and truck sales. Given TEL's growth over the past three years and volatility in the used and leased equipment markets in which TEL operates, we expect the impact on our earnings resulting from our investment and TEL's profitability to become more significant over the next twelve months. Additionally, should we exercise our option to purchase the remaining 51% of TEL, the consolidation of TEL's results and balance sheet would provide for a significant fluctuation to our presentation and amounts reported. The extent of such fluctuation could depend on a number of factors, including the exercise price, the amount of TEL's debt upon exercise, how TEL is financing their fleet of tractors and trailers (which would impact depreciation, amortization, and revenue equipment rentals), and compensation and benefits at TEL.
Income tax expense
| | | Year ended December 31, | |
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | | | 2012 | |
| Income tax expense | | $ | 14,774 | | | $ | 7,503 | | | $ | 6,335 | |
| % of total revenue | | | 2.1 | % | | | 1.1 | % | | | 0.9 | % |
| % of freight revenue | | | 2.6 | % | | | 1.4 | % | | | 1.2 | % |
Income tax expense increased approximately $7.3 million, or 96.9%, for the year ended December 31, 2014, compared with 2013. As a percentage of total revenue, income tax expense increased to 2.1% of total revenue for 2014 from 1.1% in 2013. As a percentage of freight revenue, income tax expense increased to 2.6% of freight revenue for 2014 compared to 1.4% in 2013. These increases were primarily related to the $19.8 million increase in the pre-tax income in 2014 compared to 2013 resulting from the improvements in operating income noted above and the increase in the contribution from TEL's earnings.
For the year ended December 31, 2013, income tax expense increased approximately $1.2 million, or 19.0%, compared with 2013. As a percentage of total revenue, income tax expense increased to 1.1% of total revenue for 2013 from 0.9% in 2012. As a percentage of freight revenue, income tax expense increased to 1.4% of freight revenue for 2013 compared to 1.2% in 2012. The difference in income tax expense recognized in the 2012 period is primarily related to adding $0.8 million to the valuation allowance in 2013 versus relieving the valuation allowance by $0.3 million in 2012, partially offset by increased pre-tax income in 2012.
The effective tax rate is different from the expected combined tax rate due primarily to permanent differences related to our per diem pay structure for drivers. Due to the partial nondeductible effect of the per diem payments, our tax rate will fluctuate in future periods as income fluctuates. We are currently evaluating several tax planning opportunities and credits that if determined to be both applicable and to meet the recognition criteria provided by ASC 740, could reduce our future tax expense.
RESULTS OF SEGMENT OPERATIONS
We have one reportable segment, asset-based truckload services, which we refer to as Truckload. In addition, our Solutions subsidiary has service offerings ancillary to our asset-based Truckload services, including: freight brokerage service directly and through freight brokerage agents who are paid a commission for the freight they provide and accounts receivable factoring. These operations consist of several operating segments, which neither individually nor in the aggregate meet the quantitative or qualitative reporting thresholds. As a result, these operations are grouped in "Other". The operation of each of these businesses is described in our notes to Item 1 of Part 1 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
"Unallocated Corporate Overhead" includes costs that are incidental to our activities and are not specifically allocated to one of the segments. The following table summarizes financial and operating data by segment:
| | | Year ended | |
| (in thousands) | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenues: | | | | | | | | | |
| Truckload | | $ | 663,001 | | | $ | 644,403 | | | $ | 647,986 | |
| Other | | | 55,979 | | | | 40,146 | | | | 26,268 | |
| Total | | $ | 718,980 | | | $ | 684,549 | | | $ | 674,254 | |
| Operating Income (loss): | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Truckload | | $ | 54,151 | | | $ | 27,746 | | | $ | 34,185 | |
| Other | | | 3,894 | | | | 1,271 | | | | (741 | ) |
| Unallocated Corporate Overhead | | | (18,399 | ) | | | (8,623 | ) | | | (10,235 | ) |
| Total | | $ | 39,646 | | | $ | 20,394 | | | $ | 23,209 | |
Comparison of Year Ended December 31, 2014 to Year Ended December 31, 2013
Our Truckload revenue increased $18.6 million, as freight revenue increased $23.8 million and fuel surcharge revenue decreased $5.2 million. The increase in freight revenue resulted largely from a more favorable rate and demand environment, reflected by an increase in average freight revenue per tractor per week of 10.7% compared to 2013, and a $4.1 million increase of freight revenue contributed from our temperature-controlled intermodal service, partially offset by a decrease in our average tractor fleet of 6.1% from 2013 as well as the first quarter challenges of the harsh winter weather and the expected unfavorable impact of the February 2014 implementation of our enterprise management system at our SRT subsidiary. Additionally, 5.1% of our fleet lacked drivers during 2014, compared with approximately 4.8% during 2013.
Our Truckload operating income was $26.4 million higher in 2014 than 2013 due to the increase in rates and utilization, partially offset by $7.5 million of additional reserves related to a 2008 cargo claim, as previously discussed. Additionally, net fuel costs were lower due to improved miles per gallon due to new engine technology, improved fuel surcharge recovery, and improved fuel pricing, in each case, net of gains and losses on fuel hedging contracts, partially offset by an increase in operating costs per mile net of surcharge revenue primarily due to higher wages and capital costs.
Other total revenue increased $15.8 million in 2014 compared to 2013 and operating income increased $2.6 million for the same period. These improvements are primarily the result of additional peak season freight opportunities during the fourth quarter of 2014, improved coordination with our Truckload segment, and additional business from new customers added during the year, partially offset by the discontinuation of an underperforming location in June of 2014.
The fluctuation in unallocated corporate overhead is primarily the result of increased incentive compensation, headcount, claims development above the subsidiaries' retention, and expense related to the fuel hedge contracts.
Comparison of Year Ended December 31, 2013 to Year Ended December 31, 2012
For the twelve months ended December 31, 2013, our Truckload revenue decreased $3.6 million compared to 2012, as freight revenue declined $2.4 million and fuel surcharge revenue decreased $1.2 million. These decreases were the result of a 4.1% decrease in our average tractor fleet, partially offset by average freight revenue per total mile increasing by 2.4 cents per mile compared to 2012. Truckload operating costs per mile increased approximately 3.3 cents per mile compared to 2012, even considering the $2.4 million related to the gain on sale of a terminal in 2012 and operating income of $27.7 million in 2013 ($6.4 million lower than 2012).
Other total revenue increased $13.9 million in 2013 compared to 2012 and operating income increased $2.0 million for the same period. These improvements are primarily due to the growth of certain newer service offerings, including less-than-truckload consolidation services and accounts receivable factoring, as well as efficiencies gained in capturing the additional freight revenue from overflow freight from our Truckload operations.
The fluctuation in unallocated corporate overhead is primarily the result of the policy release credit recorded in the second quarter of 2012, related to our commutation of the April 1, 2011 through March 31, 2012 policy year of our primary auto liability insurance policy.
LIQUIDITY AND CAPITAL RESOURCES
Our business requires significant capital investments over the short-term and the long-term. Recently, we have financed our capital requirements with borrowings under our Credit Facility, cash flows from operations, long-term operating leases, capital leases, secured installment notes with finance companies, proceeds from our November 2014 follow-on stock offering, and proceeds from the sale of our used revenue equipment. We had working capital (total current assets less total current liabilities) of $52.7 million and $14.1 million at December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively. Based on our expected financial condition, net capital expenditures, results of operations, related net cash flows, installment notes, and other sources of financing, we believe our working capital and sources of liquidity will be adequate to meet our current and projected needs and we do not expect to experience material liquidity constraints in the foreseeable future.
We had no borrowings outstanding under the Credit Facility as of December 31, 2014, undrawn letters of credit outstanding of approximately $34.3 million, and available borrowing capacity of $60.7 million. Fluctuations in the outstanding balance and related availability under our Credit Facility are driven primarily by cash flows from operations and the timing and nature of property and equipment additions that are not funded through notes payable, as well as the nature and timing of receipt of proceeds from disposals of property and equipment.
With an average tractor fleet age of 1.6 years, we believe we have flexibility to manage our fleet and we plan to regularly evaluate our tractor replacement cycle, new tractor purchase requirements, and financing options.
Cash Flows
Net cash flows provided by operating activities were $73.7 million in 2014 compared with $40.4 million in 2013 primarily due to net income of $17.8 million in 2014 compared to $5.2 million in 2013, depreciation and amortization increasing approximately $4.6 in 2014 due to more expensive revenue equipment and having more owned units, a $12.4 million increase in insurance and claims accruals primarily relating to the $7.5 million increase to insurance reserves stemming from a cargo loss in 2008 and increased accidents in 2014 compared to 2013, and an $11.8 million increase in accounts payable and accrued expenses primarily related to increased incentive compensation accruals for achievement of 2014 performance targets. These increases were partially offset by an increase in accounts receivable primarily related to increased year-over-year end-of-year seasonal revenue for our Solutions subsidiary, including its accounts receivable factoring business, and higher freight revenue for our Truckload segment and cash collateral of $5.0 million, which was provided by the Company related to the net liability position of certain of its fuel derivative instruments.
Net cash flows used in investing activities during 2014 were relatively even with that of 2013 as we continued to acquire newer revenue equipment and dispose of older, less efficient units. We received an equity distribution from TEL for $0.3 million and $0.1 million during 2014 and 2013, respectively, that was distributed to us based on our ownership percentage in order to satisfy estimated tax payments resulting from TEL's earnings. Additionally, during 2013 we paid out $0.5 million in earn-out payments to TEL, with no corresponding payment in 2014. We expect net capital expenditures to decrease somewhat for 2015 as we plan to take delivery of approximately 580 new company tractors and dispose of approximately 505 used tractors compared to the approximately 945 new company tractors we took delivery of and the approximately 1,300 used tractors we disposed of during 2014. Additionally, the purchase option associated with our investment in TEL could impact our cash flows from investing activities, should it be exercised.
The changes in net cash flows provided by financing activities were primarily the result of proceeds from our follow-on stock offering partially offset by net repayments of $7.0 million of borrowings on our Credit Facility in 2014 compared to net borrowings of $7.0 million in 2013 and a year-over-year change in net repayments of notes payable and capital leases net of new notes payable from $45.5 million to $30.7 million.
Material Debt Agreements
In September 2008, we and substantially all of our subsidiaries (collectively, the "Borrowers") entered into a Credit Facility with Bank of America, N.A., as agent (the "Agent") and JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A. ("JPM," and together with the Agent, the "Lenders").
The Credit Facility was originally structured as an $85.0 million revolving credit facility, with an accordion feature that, so long as no event of default exists, allows us to request an increase in the revolving credit facility of up to $50.0 million. The Credit Facility includes, within our $85.0 million revolving credit facility, a letter of credit sub facility in an aggregate amount of $85.0 million and a swing line sub facility in an aggregate amount equal to the greater of $10.0 million or 10% of the Lenders' aggregate commitments under the Credit Facility from time-to-time.
In January 2013, we entered into an eighth amendment, which was effective December 31, 2012, to the Credit Facility which, among other things, (i) increased the revolver commitment to $95.0 million, (ii) extended the maturity date from September 2014 to September 2017, (iii) eliminated the availability block of $15.0 million, (iv) improved pricing for revolving borrowings by amending the applicable margin as set forth below (beginning January 1, 2013), (v) improved the unused line fee pricing to 0.375% per annum when availability is less than $50.0 million and 0.5% per annum when availability is at or over such amount (beginning January 1, 2013), (vi) provided that the fixed charge coverage ratio covenant will be tested only during periods that commence when availability is less than or equal to the greater of 12.5% of the revolver commitment or $11.9 million, (vii) eliminated the consolidated leverage ratio covenant, (viii) reduced the level of availability below which cash dominion applies to the greater of 15% of the revolver commitment or $14.3 million, (ix) added deemed amortization of real estate and eligible revenue equipment included in the borrowing base to the calculation of fixed charge coverage ratio, (x) amended certain types of permitted debt to afford additional flexibility, and (xi) allowed for stock repurchases in an aggregate amount not exceeding $5.0 million, and (xii) removed certain restrictions relating to the purchase of up to the remaining 51% equity interest in TEL, provided that certain conditions are met. In exchange for these amendments, the Borrowers agreed to pay fees of $0.3 million. Based on availability as of December 31, 2014, there was no fixed charge coverage requirement.
In August 2014, we obtained a ninth amendment to the Credit Facility, which allows for the disposition of certain parcels of real property and the acquisition of other real property. Additionally, in September 2014, we obtained a tenth amendment to the Credit Facility, which, among other things, amended certain provisions of the Credit Facility and related security documents to facilitate our entry into fuel hedging arrangements.
Borrowings under the Credit Facility are classified as either "base rate loans" or "LIBOR loans." Base rate loans accrue interest at a base rate equal to the greater of the Agent's prime rate, the federal funds rate plus 0.5%, or LIBOR plus 1.0%, plus an applicable margin ranging from 0.5% to 1.25%; while LIBOR loans accrue interest at LIBOR, plus an applicable margin ranging from 1.5% to 2.25%. The applicable rates are adjusted quarterly based on average pricing availability. The unused line fee is also adjusted quarterly between 0.375% and 0.5% based on the average daily amount by which the Lenders' aggregate revolving commitments under the Credit Facility exceed the outstanding principal amount of revolver loans and the aggregate undrawn amount of all outstanding letters of credit issued under the Credit Facility. The obligations under the Credit Facility are guaranteed by us and secured by a pledge of substantially all of our assets, with the notable exclusion of any real estate or revenue equipment pledged under other financing agreements, including revenue equipment installment notes and capital leases.
Borrowings under the Credit Facility are subject to a borrowing base limited to the lesser of (A) $95.0 million, minus the sum of the stated amount of all outstanding letters of credit; or (B) the sum of (i) 85% of eligible accounts receivable, plus (ii) the lesser of (a) 85% of the appraised net orderly liquidation value of eligible revenue equipment, (b) 95% of the net book value of eligible revenue equipment, or (c) 35% of the Lenders' aggregate revolving commitments under the Credit Facility, plus (iii) the lesser of (a) $25.0 million or (b) 65% of the appraised fair market value of eligible real estate. We had no borrowings outstanding under the Credit Facility as of December 31, 2014, undrawn letters of credit outstanding of approximately $34.3 million, and available borrowing capacity of $60.7 million.
The Credit Facility includes usual and customary events of default for a facility of this nature and provides that, upon the occurrence and continuation of an event of default, payment of all amounts payable under the Credit Facility may be accelerated, and the Lenders' commitments may be terminated. If an event of default occurs under the Credit Facility and the Lenders cause all of the outstanding debt obligations under the Credit Facility to become due and payable, this could result in a default under other debt instruments that contain acceleration or cross-default provisions. The Credit Facility contains certain restrictions and covenants relating to, among other things, debt, dividends, liens, acquisitions and dispositions outside of the ordinary course of business, and affiliate transactions. Failure to comply with the covenants and restrictions set forth in the Credit Facility could result in an event of default.
Capital lease obligations are utilized to finance a portion of our revenue equipment and are entered into with certain finance companies who are not parties to our Credit Facility. The leases in effect at December 31, 2014 terminate in January 2015 through December 2021 and contain guarantees of the residual value of the related equipment by us. As such, the residual guarantees are included in the related debt balance as a balloon payment at the end of the related term as well as included in the future minimum capital lease payments. These lease agreements require us to pay personal property taxes, maintenance, and operating expenses.
Pricing for the revenue equipment installment notes is quoted by the respective financial affiliates of our primary revenue equipment suppliers and other lenders at the funding of each group of equipment acquired and include fixed annual rates for new equipment under retail installment contracts. The notes included in the funding are due in monthly installments with final maturities at various dates ranging from January 2015 to January 2022. The notes contain certain requirements regarding payment, insuring of collateral, and other matters, but do not have any financial or other material covenants or events of default, except that certain notes totaling $174.6 million are cross-defaulted with the Credit Facility. Additionally, a portion of the abovementioned fuel hedge contracts totaling $12.8 million at December 31, 2014, is cross-defaulted with the Credit Facility. Additional borrowings from the financial affiliates of our primary revenue equipment suppliers and other lenders are available to fund most new tractors expected to be delivered in 2015, while any other property and equipment purchases, including trailers, will be funded with a combination of available cash, notes, operating leases, capital leases, and/or from the Credit Facility.
Contractual Obligations and Commercial Commitments
The following table sets forth our contractual cash obligations and commitments as of December 31, 2014:
Payments due by period: (in thousands) | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenue equipment and property installment notes, including interest (1) | | $ | 206,746 | | | $ | 34,388 | | | $ | 39,804 | | | $ | 42,719 | | | $ | 55,574 | | | $ | 26,201 | | | $ | 8,060 | |
| Operating leases (2) | | $ | 61,481 | | | $ | 13,589 | | | $ | 11,927 | | | $ | 8,487 | | | $ | 5,599 | | | $ | 3,737 | | | $ | 18,142 | |
| Capital leases (3) | | $ | 16,916 | | | $ | 2,096 | | | $ | 4,336 | | | $ | 1,507 | | | $ | 1,507 | | | $ | 1,507 | | | $ | 5,963 | |
| Lease residual value guarantees | | $ | 3,968 | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | 2,961 | | | $ | 1,007 | | | $ | - | |
| Purchase obligations (4) | | $ | 116,849 | | | $ | 116,849 | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | |
| Total contractual cash obligations (5) | | $ | 405,960 | | | $ | 166,922 | | | $ | 56,067 | | | $ | 52,713 | | | $ | 65,641 | | | $ | 32,452 | | | $ | 32,165 | |
| (1) | Represents principal and interest payments owed at December 31, 2014. The borrowings consist of installment notes with finance companies, with fixed borrowing amounts and fixed interest rates, except for a variable rate real estate note, for which the interest rate and principal amount in place at December 31, 2014, was utilized. The table assumes these installment notes are held to maturity. Refer to Note 7, "Debt" of the accompanying consolidated financial statements for further information. |
| (2) | Represents future monthly rental payment obligations under operating leases for tractors, trailers, office and terminal properties, and computer and office equipment. Substantially all lease agreements for revenue equipment have fixed payment terms based on the passage of time. The tractor lease agreements generally stipulate maximum miles and provide for mileage penalties for excess miles. These leases generally run for a period of three to five years for tractors and five to seven years for trailers. Refer to Note 8, "Leases" of the accompanying consolidated financial statements for further information. |
| (3) | Represents principal and interest payments owed at December 31, 2014. The borrowings consist of capital leases with several finance companies, with fixed borrowing amounts and fixed interest rates. Borrowings in 2014 and thereafter include the residual value guarantees on the related equipment as balloon payments. Refer to Note 7, "Debt" of the accompanying consolidated financial statements for further information. |
| (4) | Represents purchase obligations for revenue equipment totaling approximately $116.8 million in 2015. These commitments are cancelable, subject to certain adjustments in the underlying obligations and benefits. These purchase commitments are expected to be financed by operating leases, capital leases, long-term debt, proceeds from sales of existing equipment, and/or cash flows from operations. Refer to Notes 7 and 8, "Debt" and "Leases," respectively, of the accompanying consolidated financial statements for further information. |
| (5) | Excludes any amounts accrued for unrecognized tax benefits as we are unable to reasonably predict the ultimate amount or timing of settlement of such unrecognized tax benefits. |
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
Operating leases are an important source of financing for our revenue equipment, computer equipment, and certain real estate. At December 31, 2014, we had financed 150 tractors and 2,904 trailers under operating leases. Vehicles held under operating leases are not carried on our consolidated balance sheets, and lease payments, in respect of such vehicles, are reflected in our consolidated statements of operations in the line item "Revenue equipment rentals and purchased transportation." Our revenue equipment rental expense was $21.0 million in 2014, compared with $22.8 million in 2013, primarily due to repayments of debt and leases with proceeds from our follow-on stock offering in late November 2014. The total present value of remaining payments under operating leases as of December 31, 2014, was approximately $45.7 million. In connection with various operating leases, we issued residual value guarantees, which provide that if we do not purchase the leased equipment from the lessor at the end of the lease term, we are liable to the lessor for an amount equal to the shortage (if any) between the proceeds from the sale of the equipment and an agreed value. The undiscounted value of the residual guarantees are approximately $4.0 million and $9.9 million at December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively. The residual guarantees at December 31, 2014 expire between August 2018 and February 2019. We expect our residual guarantees to approximate the market value at the end of the lease term. We believe that proceeds from the sale of equipment under operating leases would exceed the payment obligation on substantially all operating leases.
CRITICAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES AND ESTIMATES
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the U.S. requires us to make decisions based upon estimates, assumptions, and factors we consider as relevant to the circumstances. Such decisions include the selection of applicable accounting principles and the use of judgment in their application, the results of which impact reported amounts and disclosures. Changes in future economic conditions or other business circumstances may affect the outcomes of our estimates and assumptions. Accordingly, actual results could differ from those anticipated. A summary of the significant accounting policies followed in preparation of the financial statements is contained in Note 1, "Summary of Significant Accounting Policies," of the consolidated financial statements attached hereto. The following discussion addresses our most critical accounting policies, which are those that are both important to the portrayal of our financial condition and results of operations and that require significant judgment or use of complex estimates.
Revenue Recognition
Revenue, drivers' wages, and other direct operating expenses generated by our Truckload reportable segment are recognized on the date shipments are delivered to the customer. Revenue includes transportation revenue, fuel surcharges, loading and unloading activities, equipment detention, and other accessorial services.
Revenue generated by our Solutions subsidiary is recognized upon completion of the services provided. Revenue is recorded on a gross basis, without deducting third party purchased transportation costs, as we act as a principal with substantial risks as primary obligor, except for transactions whereby equipment from our Truckload segment perform the related services, which we record on a net basis in accordance with the related authoritative guidance. Solutions revenue includes $2.3 million and $1.7 million of revenue in 2014 and 2013, respectively, related to an accounts receivable factoring business started in 2013 to supplement several aspects of our non-asset operations. Revenue for this business is recognized on a net basis, given we are acting as an agent and are not the primary obligor in these transactions.
Depreciation of Revenue Equipment
Property and equipment is stated at cost less accumulated depreciation. Depreciation for book purposes is determined using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets, while depreciation for tax purposes is generally recorded using an accelerated method. Depreciation of revenue equipment is our largest item of depreciation. We generally depreciate new tractors (excluding day cabs) over five years to salvage values of approximately 25% of their cost and new trailers over six years for refrigerated trailers and ten years for dry van trailers to salvage values of approximately 38% of their cost. We annually review the reasonableness of our estimates regarding useful lives and salvage values of our revenue equipment and other long-lived assets based upon, among other things, our experience with similar assets, conditions in the used revenue equipment market, and prevailing industry practice. Over the past several years, the price of new tractors has risen dramatically and there has been significant volatility in the used equipment market. Changes in the useful life or salvage value estimates, or fluctuations in market values that are not reflected in our estimates, could have a material effect on our results of operations. Gains and losses on the disposal of revenue equipment are included in depreciation expense in the consolidated statements of operations.
In 2014, 2013, and 2012, we generated net gains on revenue equipment, including assets held for sale, of $2.7 million, $0.8 million, and $4.9 million (including a $2.4 million gain on the sale of a terminal property), respectively. We review salvage values of our revenue equipment annually and adjust as needed based on trends in the used equipment market, to ensure the assets are being depreciated to amounts that represent updated estimates of their fair value at disposal.
We lease certain revenue equipment under capital leases with terms of 60 to 84 months. Amortization of leased assets is included in depreciation and amortization expense.
Pursuant to applicable accounting standards, revenue equipment and other long-lived assets are tested for impairment whenever an event occurs that indicates impairment may exist. Expected future cash flows are used to analyze whether an impairment has occurred. If the sum of expected undiscounted cash flows is less than the carrying value of the long-lived asset, then an impairment loss is recognized. We measure the impairment loss by comparing the fair value of the asset to its carrying value. Fair value is determined based on a discounted cash flow analysis or the appraised value of the assets, as appropriate.
Although a portion of our tractors are protected by non-binding indicative trade-in values or binding trade-back agreements with the manufacturers, some tractors and substantially all of our owned trailers continue to be subject to fluctuations in market prices for used revenue equipment. Moreover, our trade-back agreements are contingent upon reaching acceptable terms for the purchase of new equipment. Further declines in the price of used revenue equipment or failure to reach agreement for the purchase of new tractors with the manufacturers issuing trade-back agreements could result in impairment of, or losses on the sale of, revenue equipment. Historically, only a de minimus percentage of our equipment has been sold back to the dealers pursuant to the trade back agreements as we have generally found that market prices exceeded the trade back allowances, although in recent years, trade back allowances have increased as a result of the increasing cost of the underlying equipment.
Assets Held For Sale
Assets held for sale include property and revenue equipment no longer utilized in continuing operations which are available and held for sale. Assets held for sale are no longer subject to depreciation, and are recorded at the lower of depreciated book value or fair market value less selling costs. We periodically review the carrying value of these assets for possible impairment. We expect to sell the majority of these assets within twelve months.
Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets
We classify intangible assets into two categories: (i) intangible assets with definite lives subject to amortization and (ii) goodwill. We have no goodwill on our consolidated balance sheet for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013. We test intangible assets with definite lives for impairment if conditions exist that indicate the carrying value may not be recoverable. Such conditions may include an economic downturn in a geographic market or a change in the assessment of future operations. We record an impairment charge when the carrying value of the definite lived intangible asset is not recoverable by the cash flows generated from the use of the asset.
We determine the useful lives of our identifiable intangible assets after considering the specific facts and circumstances related to each intangible asset. Factors we consider when determining useful lives include the contractual term of any agreement, the history of the asset, our long-term strategy for the use of the asset, any laws or other local regulations which could impact the useful life of the asset, and other economic factors, including competition and specific market conditions. Intangible assets that are deemed to have definite lives are amortized, generally on a straight-line basis, over their useful lives, ranging from 4 to 20 years.
Insurance and Other Claims
The primary claims arising against us consist of cargo, liability, personal injury, property damage, workers' compensation, and employee medical expenses. Our insurance program involves self-insurance with high risk retention levels. Due to our significant self-insured retention amounts, we have exposure to fluctuations in the number and severity of claims and to variations between our estimated and actual ultimate payouts. We accrue the estimated cost of the uninsured portion of pending claims and an estimate for allocated loss adjustment expenses including legal and other direct costs associated with a claim. Estimates require judgments concerning the nature and severity of the claim, historical trends, advice from third-party administrators and insurers, the size of any potential damage award based on factors such as the specific facts of individual cases, the jurisdictions involved, the prospect of punitive damages, future medical costs, and inflation estimates of future claims development, and the legal and other costs to settle or defend the claims. We have significant exposure to fluctuations in the number and severity of claims. If there is an increase in the frequency and severity of claims, or we are required to accrue or pay additional amounts if the claims prove to be more severe than originally assessed, or any of the claims would exceed the limits of our insurance coverage, our profitability could be adversely affected.
In addition to estimates within our self-insured retention layers, we also must make judgments concerning claims where we have third party insurance and for claims outside our coverage limits. Upon settling claims and expenses associated with claims where we have third party coverage, we are generally required to initially fund payment to the claimant and seek reimbursement from the insurer. Receivables from insurers for claims and expenses we have paid on behalf of insurers total $0.1 million and $1.0 million at December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively, and are included in drivers' advances and other receivables on our consolidated balance sheet. Additionally, we accrue claims above our self-insured retention and record a corresponding receivable for amounts we expect to collect from insurers upon settlement of such claims. We have $0.6 million at December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively, as a receivable in other assets and as a corresponding accrual in the long-term portion of insurance and claims accruals on our consolidated balance sheet for claims above our self-insured retention for which we believe it is reasonably assured that the insurers will provide their portion of such claims. We evaluate collectability of the receivables based on the credit worthiness and surplus of the insurers, along with our prior experience and contractual terms with each. If any claim occurrence were to exceed our aggregate coverage limits, we would have to accrue for the excess amount. Our critical estimates include evaluating whether a claim may exceed such limits and, if so, by how much. If one or more claims were to exceed our then effective coverage limits, our financial condition and results of operations could be materially and adversely affected.
Our casualty insurance self-insured retention limit for the primary excess layer of casualty is no more than $1.0 million. Effective April 1, 2013, the policy includes a limit for a single loss of $9.0 million, an aggregate of $18.0 million for each policy year, and a $30.0 million aggregate for the three-year period ended March 31, 2016. Our prior aggregate casualty policy for the three years ended March 31, 2013, included a similar $9.0 million limit per claim and $18.0 million annual limit, with a $27.0 million limit for the three years. Our excess policies cover up to $40.0 million per claim, subject to certain aggregate limits. In addition, our current auto liability policy includes a policy release premium refund of $13.0 million, less any amounts paid on claims by the insurer, for the three years ended March 31, 2016, if we were to commute the policy for the entire three years. A decision with respect to commutation of the policy cannot be made before April 1, 2016 and must be made by June 30, 2016, unless both we and the insurance carrier agree to a commutation prior to the end of the policy term. Management cannot predict whether or not future claims or the development of existing claims will justify a commutation, and accordingly, no related amounts were recorded in 2014. The previous three-year casualty policy, which expired on March 31, 2013, provided for an annual commutation if certain losses were not met and we elected to commute the policy. The policy for the twelve months ended March 31, 2013 was not commuted; however, in June 2012 we commuted the policy for the April 1, 2011 through March 31, 2012 policy year and as such are responsible for all claims that occurred during that policy year, excluding any claims between $10.0 million and $20.0 million, should such a claim develop. We received a $4.0 million non-cash credit in 2012 related to the commutation, that off-set premiums in 2013 and accordingly reduced our insurance and claims expense
We are self-insured on an occurrence/per claim basis for workers' compensation up to the first $1.3 million. We purchase coverage on an occurrence/per claim basis for any cargo losses in the $0.3 million to $2.0 million layer, with our contracts generally excluding the value of any cargo in excess of $2.0 million. We also maintain a self-insured group medical plan for our Covenant Transport, Solutions, Star, and corporate employees, with annual per individual claimant stop-loss deductible of $0.4 million, while SRT offers a fully insured group health program to its employees. We are completely self-insured for physical damage to our own tractors and trailers.
If claims development factors that are based upon historical experience change by 10%, our claims accrual as of December 31, 2014, would change by approximately $4.1 million.
Lease Accounting and Off-Balance Sheet Transactions
We issue residual value guarantees in connection with the operating leases we enter into for certain of our revenue equipment. These leases provide that if we do not purchase the leased equipment from the lessor at the end of the lease term, then we are liable to the lessor for an amount equal to the shortage (if any) between the proceeds from the sale of the equipment and an agreed value. To the extent the expected value at the lease termination date is lower than the residual value guarantee, we would accrue for the difference over the remaining lease term. We believe that proceeds from the sale of equipment under operating leases would exceed the payment obligation on substantially all operating leases. The estimated values at lease termination involve management judgments. As leases are entered into, determination as to the classification as an operating or capital lease involves management judgments on residual values and useful lives.
Accounting for Income Taxes
Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the future tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax basis. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in income in the period that includes the enactment date. We have reflected the necessary deferred tax assets and liabilities in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets. We believe the future tax deductions will be realized principally through future reversals of existing taxable temporary differences and future taxable income, except for when a valuation allowance has been provided.
In the ordinary course of business there is inherent uncertainty in quantifying our income tax positions. We assess our income tax positions and record tax benefits for all years subject to examination based upon management's evaluation of the facts, circumstances, and information available at the reporting dates. For those tax positions where it is more likely than not that a tax benefit will be sustained, we have recorded the largest amount of tax benefit with a greater than 50% likelihood of being realized upon ultimate settlement with a taxing authority that has full knowledge of all relevant information. For those income tax positions where it is not more likely than not that a tax benefit will be sustained, no tax benefit has been recognized in the financial statements. Potential accrued interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits are recognized as a component of income tax expense.
Stock-Based Employee Compensation
We issue several types of stock-based compensation, including awards that vest based on service and performance conditions or a combination of the conditions. Performance-based awards vest contingent upon meeting certain performance criteria established by the Compensation Committee. All awards require future service and thus forfeitures are estimated based on historical forfeitures and the remaining term until the related award vests. Determining the appropriate amount to expense in each period is based on likelihood and timing of achieving the stated targets for performance-based awards and requires judgment, including forecasting future financial results. The estimates are revised periodically based on the probability and timing of achieving the required performance targets and adjustments are made as appropriate. Awards that are only subject to time vesting provisions are amortized using the straight-line method.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
Our financial instruments consist primarily of cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable, commodity contracts, accounts payable, and debt. The carrying amount of cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable, accounts payable, and current debt approximates their fair value because of the short-term maturity of these instruments. Included in accounts receivable is $15.8 million of factoring receivables at December 31, 2014, net of a $0.2 million allowance for bad debts. We advance approximately 85% to 95% of each receivable factored and retain the remainder as collateral for collection issues that might arise. The retained amounts are returned to the clients after the related receivable has been collected. At December 31, 2014, the retained amounts related to factored receivables totaled $0.3 million and were included in accounts payable in the consolidated balance sheet. Our clients are smaller trucking companies that factor their receivables to us for a fee to facilitate faster cash flow. We evaluate each client's customer base under predefined criteria. The carrying value of the factored receivables approximates the fair value, as the receivables are generally repaid directly to us by the client's customer within 30-40 days due to the combination of the short-term nature of the financing transaction and the underlying quality of the receivables. Interest rates that are currently available to us for issuance of long-term debt with similar terms and remaining maturities are used to estimate the fair value of our long-term debt, which primarily consists of revenue equipment installment notes. The fair value of our revenue equipment installment notes approximated the carrying value at December 31, 2014, as the weighted average interest rate on these notes approximates the market rate for similar debt. Borrowings under our revolving Credit Facility approximate fair value due to the variable interest rate on the facility. Additionally, commodity contracts, which are accounted for as hedge derivatives, are valued based on the forward rate of the specific indices upon which the contract is being settled and adjusted for counterparty credit risk using available market information and valuation methodologies.
Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities
We periodically utilize derivative instruments to manage exposure to changes in fuel prices. At inception of a derivative contract, we document relationships between derivative instruments and hedged items, as well as our risk-management objective and strategy for undertaking various derivative transactions, and assess hedge effectiveness. We record derivative financial instruments in the balance sheet as either an asset or liability at fair value. Changes in the fair values of these instruments can vary dramatically based on changes in the underlying commodity prices, as has been evident in the second half of 2014. For example, during 2014, market "spot" prices for ultra-low sulfur diesel peaked at a high of approximately $3.08 per gallon and hit a low price of approximately $1.58 per gallon. During 2013, market spot prices ranged from a high of $3.29 per gallon to a low of $2.72 per gallon. Market price changes can be driven by factors such as supply and demand, inventory levels, weather events, refinery capacity, political agendas, the value of the U.S. dollar, geopolitical events, and general economic conditions, among other items.
If it is determined that a derivative is not highly effective as a hedge, or if a derivative ceases to be a highly effective hedge, we discontinue hedge accounting prospectively. The effective portion of changes in the fair value of derivatives are recorded in other comprehensive income and reclassified into earnings in the same period during which the hedged transaction affects earnings. The ineffective portion is recorded in other income or expense. Based on the amounts in accumulated other comprehensive loss as of December 31, 2014, and the expected timing of the purchases of the diesel hedged, we expect to reclassify approximately $8.0 million, net of tax, on derivative instruments from accumulated other comprehensive loss into our results from operations during the next year due to actual diesel fuel purchases. The amounts actually realized will be dependent on the fair values as of the date of settlement. At December 31, 2014, we had forward futures swap contracts on approximately 12.6 million, 12.1 million, and 3.0 million gallons of diesel to be purchased in 2015, 2016, and 2017, respectively, or approximately 23%, 22%, and 5% of our projected annual 2015, 2016, and 2017 fuel requirements, respectively. While the value of our hedges was a liability of approximately $22.7 million at December 31, 2014, there has been volatility in the petroleum markets, which we expect to continue into 2014. As a result, we expect volatility in the price we pay for fuel and the value of the hedges. Additionally, we had provided $5.0 million of cash collateral which was provided by the Company related to the net liability position of certain of its fuel derivative instruments.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
On May 28, 2014, the Financial Accounting Standards Board and the International Accounting Standards Board issued converged guidance on recognizing revenue in contracts with customers. The new guidance establishes a single core principle in the Accounting Standards Update ("ASU") No. 2014-09, which is the recognition of revenue to depict the transfer of promised goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the entity expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services. This guidance will affect any reporting organization that either enters into contracts with customers to transfer goods or services or enters into contracts for the transfer of non-financial assets. This ASU is effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those years, beginning on or after December 15, 2016, and early adoption is not permitted. The Company is continuing to evaluate the new guidance and plans to provide additional information about its expected financial impact at a future date.
On August 27, 2014, the Financial Accounting Standards Board issued ASU No. 2014-15. This standard provides guidance on determining when and how to disclose going-concern uncertainties in the financial statements. The new standard requires management to perform interim and annual assessments of an entity's ability to continue as a going concern within one year of the date the financial statements are issued. This ASU is effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those years, beginning on or after December 15, 2016, with early adoption permitted. The Company is evaluating the new guidance and plans to provide additional information about its expected impact at a future date.
INFLATION, NEW EMISSIONS CONTROL REGULATIONS, AND FUEL COSTS
Most of our operating expenses are inflation-sensitive, with inflation generally producing increased costs of operations. During the past four years, the most significant effects of inflation have been on revenue equipment prices and fuel prices. New emissions control regulations and increases in commodity prices, wages of manufacturing workers, and other items have resulted in higher tractor prices. The cost of fuel has been extremely volatile over the
last several years, with costs decreasing significantly in 2014 from 2013 after trending upward in 2013, 2012, and 2010 following a reprieve in 2009 from the record high prices in 2008. We believe at least some of this volatility reflects the fluctuations in the U.S. dollar and global demand for petroleum products, unrest in certain oil-producing countries, improved fuel efficiency due to technological advancements, and an increase in domestic supply. As the United States and global economies recover, we believe that prices will likely increase as a result of inflationary pressure. We have attempted to limit the effects of inflation through certain cost control efforts and limiting the effects of fuel prices through fuel surcharges. Fluctuations in the price or availability of fuel, as well as hedging activities, surcharge collection, the percentage of freight we obtain through brokers, and the volume and terms of diesel fuel purchase commitments may increase our costs of operation, which could materially and adversely affect our profitability. We impose fuel surcharges on substantially all accounts. These arrangements generally do not fully protect us from fuel price increases and also may prevent us from receiving the full benefit of any fuel price decreases. We may be forced to make cash payments under our hedging arrangements and the absence of meaningful fuel price protection through these arrangements could adversely affect our profitability. The cost of engines used in our tractors are subject to emissions control regulations, which have substantially increased our capital costs since additional and more stringent regulation began in 2002. As of December 31, 2014, 100% of our tractor fleet had engines compliant with stricter regulations regarding emissions that became effective in 2007 and 97.4% of our tractor fleet had engines compliant with stricter regulations regarding emissions that became effective in 2010. Compliance with such regulations has increased and in our estimation will continue to increase the cost of new tractors, may not provide fuel mileage increases proportionate to the increase in the cost of equipment, and could increase our operations and maintenance expense. These adverse effects and the residual values that will be realized from the disposition of these vehicles could increase our costs or otherwise adversely affect our business or operations as the regulations impact our business through new tractor purchases.
SEASONALITY
In the trucking industry, revenue generally decreases as customers reduce shipments following the winter holiday season and as inclement weather impedes operations. At the same time, operating expenses generally increase, with fuel efficiency declining because of engine idling and weather, creating more physical damage equipment repairs. For the reasons stated, first quarter results historically have been lower than results in each of the other three quarters of the year, excluding charges. Over the past several years, we have seen increases in demand at varying times, specifically May through October, based primarily on restocking required to replenish inventories that have been held significantly lower than historical averages. Additionally, we have seen surges between Thanksgiving and Christmas resulting from holiday shopping trends toward delivery of gifts purchased over the internet, as well as the impact of shorter holiday seasons.
ITEM 7A. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
We experience various market risks, including changes in interest rates and fuel prices. We do not enter into derivatives or other financial instruments for trading or speculative purposes, or when there are no underlying related exposures. Because our operations are mostly confined to the United States, we are not subject to a material amount of foreign currency risk.
COMMODITY PRICE RISK
We engage in activities that expose us to market risks, including the effects of changes in fuel prices. Financial exposures are evaluated as an integral part of our risk management program, which seeks, from time-to-time, to reduce the potentially adverse effects that the volatility of fuel markets may have on operating results. In an effort to seek to reduce the variability of the ultimate cash flows associated with fluctuations in diesel fuel prices, we periodically enter into various derivative instruments, including forward futures swap contracts (which we refer to as "fuel hedge contracts"). Historically diesel fuel has not been a traded commodity on the futures market so heating oil has been used as a substitute, as prices for both generally move in similar directions. Recently, however, we have been able to enter into hedging contracts with respect to both heating oil and ULSD. Under these contracts, we pay a fixed rate per gallon of heating oil or ULSD and receive the monthly average price of New York heating oil per the NYMEX and Gulf Coast ULSD, respectively. The retrospective and prospective regression analyses provided that changes in the prices of diesel fuel and heating oil and diesel fuel and ULSD were each deemed to be highly effective based on the relevant authoritative guidance except for a small portion of our hedge contracts, which we determined to be ineffective on a prospective basis. Consequently, we recognized approximately $1.4 million of additional fuel expense in 2014 to mark the related liability to market. We do not engage in speculative transactions, nor do we hold or issue financial instruments for trading purposes.
We recognize all derivative instruments at fair value on our consolidated balance sheets. Our derivative instruments are designated as cash flow hedges, thus the effective portion of the gain or loss on the derivatives is reported as a component of accumulated other comprehensive (loss) income and will be reclassified into earnings in the same period during which the hedged transaction affects earnings. The effective portion of the derivative represents the change in fair value of the hedge that offsets the change in fair value of the hedged item. To the extent the change in the fair value of the hedge does not perfectly offset the change in the fair value of the hedged item, the ineffective portion of the hedge is immediately recognized in our consolidated statements of operations. Ineffectiveness is calculated using the cumulative dollar offset method as an estimate of the difference in the expected cash flows of the respective fuel hedge contracts (heating oil or ULSD) compared to the changes in the all-in cash outflows required for the diesel fuel purchases.
At December 31, 2014, we had fuel hedge contracts on approximately 12.6 million, 12.1 million, and 3.0 million gallons of diesel to be purchased in 2015, 2016, and 2017, respectively, or approximately 23%, 22%, and 5% of our projected annual 2015, 2016, and 2017 fuel requirements, respectively.
The fair value of the contracts that were in effect at December 31, 2014 and 2013, of approximately $(22.7) million and $1.4 million, respectively, are included in other liabilities and other assets, respectively, in the consolidated balance sheet, and are included in accumulated other comprehensive (loss) income, net of tax. Additionally, $3.1 million of 2014 losses and $0.6 million and $5.0 million of 2013 and 2012 gains, respectively, were reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive (loss) income to our results from operations for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013, and 2012, respectively, related to fuel hedging. Of the $3.1 million of losses reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive loss for the year ended December 31, 2014, approximately $1.8 million related to losses on contracts that expired or were sold and for which we completed the forecasted transaction by purchasing the hedged diesel fuel, approximately $1.4 million was recorded as additional fuel expense related to contracts for which the hedging relationship was no longer deemed to be effective on a prospective basis, and approximately $0.2 million was recorded as unfavorable ineffectiveness on the contracts that existed at December 31, 2014. The ineffectiveness was calculated using the cumulative dollar offset method as an estimate of the difference in the expected cash flows of the respective fuel hedge contracts compared to the changes in the all-in cash outflows required for the diesel fuel purchases. The calculation of ineffectiveness excludes approximately $0.1 million from the assessment of hedge ineffectiveness as a result of the related contracts being in an under-hedged position as of the date of the calculation.
Based on the amounts in accumulated other comprehensive loss as of December 31, 2014 and the expected timing of the purchases of the diesel hedged, we expect to reclassify approximately $8.0 million, net of tax, on derivative instruments from accumulated other comprehensive loss into our results from operations during the next year due to the actual diesel fuel purchases. The amounts actually realized will be dependent on the fair values as of the date of settlement.
We perform both a prospective and retrospective assessment of the effectiveness of our hedge contracts at inception and quarterly, including assessing the possibility of counterparty default. If we determine that a derivative is no longer expected to be highly effective, we discontinue hedge accounting prospectively and recognize subsequent changes in the fair value of the hedge in earnings. As a result of our effectiveness assessment at inception, quarterly, and at December 31, 2014 and 2013, we believe our hedge contracts have been and will continue to be highly effective in offsetting changes in cash flows attributable to the hedged risk, with the exception of the abovementioned contracts.
Outstanding financial derivative instruments expose us to credit loss in the event of nonperformance by the counterparties to the agreements. We do not expect any of the counterparties to fail to meet their obligations. Our credit exposure related to these financial instruments is represented by the fair value of contracts reported as assets. To manage credit risk, we review each counterparty's audited financial statements and credit ratings and obtain references.
If our fuel derivative instruments are in a net liability position with the counterparty and cash collateral is required, the cash collateral amounts provided are netted against the fair value of current outstanding derivative instruments. At December 31, 2014, and December 31, 2013, $5.0 million and $0.0 cash collateral deposits, respectively, were provided by us in connection with our outstanding fuel derivative instruments.
Based on our expected fuel consumption for 2014, a one dollar change in the related price of heating oil or diesel per gallon would change our net income by less than $0.1 million, assuming no further changes to our fuel hedging program or our fuel surcharge recovery. This sensitivity analysis considers that we purchase approximately 4.6 million gallons of diesel annually, on which we recovered 84.7% of the cost in 2014. Assuming our fuel surcharge recovery is consistent in 2014, this leaves 8.4 million gallons that are not covered by the natural hedge created by our fuel surcharges.
INTEREST RATE RISK
Our market risk is also affected by changes in interest rates. Historically, we have used a combination of fixed-rate and variable-rate obligations to manage our interest rate exposure. Fixed-rate obligations expose us to the risk that interest rates might fall. Variable-rate obligations expose us to the risk that interest rates might rise. Of our total $202.3 million of debt and capital leases, we had $3.4 million of variable rate debt outstanding at December 31, 2014, including both our Credit Facility and a real-estate note, whereas at December 31, 2013, of our total $235.5 million of debt, we had $10.9 million of variable rate debt outstanding, including our Credit Facility and a real-estate note. The interest rates applicable to these agreements are based on either the prime rate or LIBOR. Our earnings would be affected by changes in these short-term interest rates. Risk can be quantified by measuring the financial impact of a near-term adverse increase in short-term interest rates. At our December 31, 2014 level of borrowing, a 1% increase in our applicable rate would reduce annual net income by a de minimus amount. Our remaining debt is fixed rate debt, and therefore changes in market interest rates do not directly impact our interest expense. As of December 31, 2014, we had no derivative financial instruments to reduce our exposure to interest rate fluctuations.
ITEM 8. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
The consolidated financial statements of Covenant Transportation Group, Inc. and subsidiaries, including the consolidated balance sheets as of December 31, 2014 and 2013, and the related statements of operations, statements of comprehensive income, statements of stockholders' equity, and statements of cash flows for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2014, together with the related notes, and the report of KPMG LLP, our independent registered public accounting firm as of December 31, 2014 and 2013, and for each of the years in the three year period ended December 31, 2014 are set forth at pages 56 through 83 elsewhere in this report.
ITEM 9. CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE
There has been no change in or disagreement with accountants on accounting or financial disclosure during our two most recent fiscal years.
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
We have established disclosure controls and procedures to ensure that material information relating to us and our consolidated subsidiaries is made known to the officers who certify our financial reports and to other members of senior management and the Board of Directors.
Based on their evaluation as of December 31, 2014, our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer have concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rule 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Exchange Act) are effective at a reasonable assurance level to ensure that the information required to be disclosed by us in the reports that we file or submit under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized, and reported within the time periods specified in SEC rules and forms and that such information is accumulated and communicated to our management, including our Chief Executive Officer, as appropriate, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
Management's Annual Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting. Internal control over financial reporting is defined in Rule 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) promulgated under the Exchange Act as a process designed by, or under the supervision of, the principal executive and principal financial officers and effected by the board of directors, management, and other personnel, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles and includes those policies and procedures that:
| ● | pertain to the maintenance of records, that in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of our assets; |
| ● | provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that our receipts and expenditures are being made only in accordance with authorizations of our management and directors; and |
| ● | provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of our assets that could have a material effect on our financial statements. |
We have confidence in our internal controls and procedures. Nevertheless, our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, does not expect that our disclosure procedures and controls or our internal controls will prevent all errors or intentional fraud. An internal control system, no matter how well-conceived and operated, can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurance that the objectives of such internal controls are met. Further, the design of an internal control system must reflect the fact that there are resource constraints, and the benefits of controls must be considered relative to their costs. As a result of the inherent limitations in all internal control systems, no evaluation of controls can provide absolute assurance that all our control issues and instances of fraud, if any, have been detected.
Management assessed the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2014. In making this assessment, management used the criteria set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission, an Internal Control-Integrated Framework (1992 Framework). Based on its assessment, management believes that, as of December 31, 2014, our internal control over financial reporting is effective based on those criteria.
KPMG LLP, the independent registered public accounting firm who audited the Company's Consolidated Financial Statements included in this From 10-K, has issued a report on the Company's internal control over financial reporting which is included herein.
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
There were no changes in our internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the quarter ended December 31, 2014, that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
None.
PART III
ITEM 10. DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS, AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE
We incorporate by reference the information respecting executive officers and directors set forth under the captions "Proposal 1 - Election of Directors", "Corporate Governance – Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance", "Corporate Governance – Our Executive Officers", "Corporate Governance – Code of Conduct and Ethics", and "Corporate Governance – Committees of the Board of Directors – The Audit Committee" in our Proxy Statement for the 2015 annual meeting of stockholders, which will be filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission in accordance with Rule 14a-6 promulgated under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the "Proxy Statement"); provided, that the section entitled "Corporate Governance – Committees of the Board of Directors – The Audit Committee – Report of the Audit Committee" contained in the Proxy Statement is not incorporated by reference.
We incorporate by reference the information set forth under the sections entitled "Executive Compensation", "Corporate Governance – Committees of the Board of Directors – The Compensation Committee – Compensation Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation", and "Corporate Governance – Committees of the Board of Directors – The Compensation Committee – Report of the Compensation Committee" in the Proxy Statement; provided, that the section entitled "Corporate Governance – Committees of the Board of Directors – The Compensation Committee – Report of the Compensation Committee" contained in the Proxy Statement is not incorporated by reference.
ITEM 12. SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS
The following table provides certain information, as of December 31, 2014, with respect to our compensation plans and other arrangements under which shares of our Class A common stock are authorized for issuance.
Equity Compensation Plan Information
| | Number of securities to be issued upon exercise of outstanding options, warrants and rights | | | Weighted average exercise price of outstanding options, warrants and rights | | | Number of securities remaining eligible for future issuance under equity compensation plans (excluding securities reflected in column (a)) | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
Equity compensation plans approved by security holders | | | 76,325 642,438 | (1) (2) | | $ $ | 14.73 - | | | | - 675,021 | |
| Equity compensation plans not approved by security holders | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
| Total | | | 718,763 | | | $ | 14.73 | | | | 675,021 | |
| (1) | Stock options granted under our 2003 and 2006 Incentive Plans. |
| (2) | Restricted shares granted under the 2006 Omnibus Incentive Plan, as amended. |
We incorporate by reference the information set forth under the section entitled "Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management" in the Proxy Statement.
ITEM 13. CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE
We incorporate by reference the information set forth under the sections entitled "Corporate Governance – Board of Directors and Its Committees" and "Certain Relationships and Related Transactions" in the Proxy Statement.
ITEM 14. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING FEES AND SERVICES
We incorporate by reference the information set forth under the section entitled "Relationships with Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm – Principal Accountant Fees and Services" in the Proxy Statement.
PART IV
ITEM 15. EXHIBITS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES
| (a) | 1. | Financial Statements. | |
| | | | |
| | | Our audited consolidated financial statements are set forth at the following pages of this report: | |
| | | Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm | |
| | | Consolidated Balance Sheets | |
| | | Consolidated Statements of Operations | |
| | | Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income | |
| | | Consolidated Statements of Stockholders' Equity | |
| | | Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows | |
| | | Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements | |
| | | | |
| | 2. | Financial Statement Schedules. | |
| | | | |
| | | Financial statement schedules are not required because all required information is included in the financial statements or is not applicable. | |
| | | | |
| | 3. | Exhibits. | |
| | | | |
| | | The exhibits required to be filed by Item 601 of Regulation S-K are listed under paragraph (b) below and on the Exhibit Index appearing at the end of this report. Management contracts and compensatory plans or arrangements are indicated by an asterisk. | |
| | | | |
| (b) | | Exhibits. | |
| | | | |
| | | The following exhibits are filed with this Form 10-K or incorporated by reference to the document set forth next to the exhibit listed below. | |
Exhibit Number | Reference | Description |
| 3.1 | | Amended and Restated Articles of Incorporation (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99.2 to the Company's Report on Form 8-K, filed May 29, 2007) |
| 3.2 | | Second Amended and Restated Bylaws (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.2 to the Company's Form 10-Q, filed May 13, 2011) |
| 4.1 | | Amended and Restated Articles of Incorporation (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99.2 to the Company's Report on Form 8-K, filed May 29, 2007) |
| 4.2 | | Second Amended and Restated Bylaws (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.2 to the Company's Form 10-Q, filed May 13, 2011) |
| 10.1 | | Master Lease Agreement, dated April 15, 2003, between Transport International Pool, Inc. and Covenant Transport, Inc. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to the Company's Form 10-Q/A, filed October 31, 2003) |
| 10.2 | * | Form of Indemnification Agreement between Covenant Transport, Inc. and each officer and director, effective May 1, 2004 (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Company's Form 10-Q, filed August 5, 2004) |
| 10.3 | | Lease Agreement, dated April 3, 2006, between Covenant Transport, Inc., a Tennessee corporation, and CT Chattanooga TN, LLC (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to the Company's Form 10-K, filed March 30, 2010) |
| 10.4 | | Lease Guaranty, dated April 3, 2006, by Covenant Transport, Inc., a Tennessee corporation, for the benefit of CT Chattanooga TN, LLC (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.20 to the Company's Report on Form 8-K, filed April 7, 2006) |
| 10.5 | * | Form of Restricted Stock Award Notice under the Covenant Transportation Group, Inc. Third Amended and Restated 2006 Omnibus Incentive Plan (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.22 to the Company's Form 10-Q, filed August 9, 2006) |
| 10.6 | * | Form of Restricted Stock Special Award Notice under the Covenant Transportation Group, Inc. Third Amended and Restated 2006 Omnibus Incentive Plan (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.23 to the Company's Form 10-Q, filed August 9, 2006) |
| 10.7 | * | Form of Incentive Stock Option Award Notice under the Covenant Transportation Group, Inc. Third Amended and Restated 2006 Omnibus Incentive Plan (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.24 to the Company's Form 10-Q, filed August 9, 2006) |
| 10.8 | | Form of Lease Agreement (Open End) used in connection with Daimler Facility (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the Company's Form 10-Q, filed August 11, 2008) |
| 10.9 | | Amendment to Lease Agreement (Open End) used in connection with Daimler Facility (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to the Company's Form 10-Q, filed August 11, 2008) |
| 10.10 | | Form of Direct Purchase Money Loan and Security Agreement used in connection with Daimler Facility (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to the Company's Form 10-Q, filed August 11, 2008) |
| 10.11 | | Amendment to Direct Purchase Money Loan and Security Agreement used in connection with Daimler Facility (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.6 to the Company's Form 10-Q, filed August 11, 2008) |
| 10.12 | | Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, dated September 23, 2008, among Covenant Transportation Group, Inc., Covenant Transport, Inc., CTG Leasing Company, Covenant Asset Management, Inc., Southern Refrigerated Transport, Inc., Covenant Transport Solutions, Inc., Star Transportation, Inc., Bank of America, N.A., JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., and Textron Financial Corporation (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.14 to the Company's Form 10-K, filed March 30, 2010) |
| 10.13 | * | Covenant Transportation Group, Inc. Third Amended and Restated 2006 Omnibus Incentive Plan (Incorporated by reference to Appendix A to the Company's Schedule 14A, filed April 19, 2013) |
| 10.14 | | Amendment No. 1 to Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, dated March 27, 2009 among Covenant Transportation Group, Inc., Covenant Transport, Inc., CTG Leasing Company, Covenant Asset Management, Inc., Southern Refrigerated Transport, Inc., Covenant Transport Solutions, Inc., Star Transportation, Inc., Bank of America, N.A., JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., and Textron Financial Corporation (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company's Form 10-Q, filed May 15, 2009) |
| 10.15 | | Second Amendment to Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, dated February 25, 2010, among Covenant Transportation Group, Inc., Covenant Transport, Inc., CTG Leasing Company, Covenant Asset Management, Inc., Southern Refrigerated Transport, Inc., Covenant Transport Solutions, Inc., Star Transportation, Inc., Bank of America, N.A., JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., and Textron Financial Corporation (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company's Form 10-Q, filed May 17, 2010) |
| 10.16 | | Third Amendment to Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement dated July 30, 2010 among Covenant Transportation Group, Inc., Covenant Transport, Inc., CTG Leasing Company, Covenant Asset Management, Inc., Southern Refrigerated Transport, Inc., Covenant Transport Solutions, Inc., Star Transportation, Inc., Bank of America, N.A., and JP Morgan Chase Bank, N.A. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company's Form 10-Q, filed November 9, 2010) |
| 10.17 | | Fourth Amendment to Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement dated August 31, 2010 among Covenant Transportation Group, Inc., Covenant Transport, Inc., CTG Leasing Company, Covenant Asset Management, Inc., Southern Refrigerated Transport, Inc., Covenant Transport Solutions, Inc., Star Transportation, Inc., Bank of America, N.A., and JP Morgan Chase Bank, N.A. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Company's Form 10-Q, filed November 9, 2010) |
| 10.18 | | Letter Agreement, dated October 28, 2010, among Transport International Pool, Inc., Covenant Transport, Inc. and CTG Leasing Company (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.22 to the Company's Form 10-K, filed March 1, 2011) |
| 10.19 | | Fifth Amendment to Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement dated September 1, 2011 among Covenant Transportation Group, Inc., Covenant Transport, Inc., CTG Leasing Company, Covenant Asset Management, Inc., Southern Refrigerated Transport, Inc., Covenant Transport Solutions, Inc., Star Transportation, Inc., Bank of America, N.A., and JP Morgan Chase Bank, N.A. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company's Report on Form 8-K, filed October 28, 2011) |
| 10.20 | | Sixth Amendment to Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement dated effective as of October 24, 2011 among Covenant Transportation Group, Inc., Covenant Transport, Inc., CTG Leasing Company, Covenant Asset Management, Inc., Southern Refrigerated Transport, Inc., Covenant Transport Solutions, Inc., Star Transportation, Inc., Bank of America, N.A., and JP Morgan Chase Bank, N.A. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Company's Report on Form 8-K, filed October 28, 2011) |
| 10.21 | | Seventh Amendment to Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement dated effective as of March 29, 2012 among Covenant Transportation Group, Inc., Covenant Transport, Inc., CTG Leasing Company, Covenant Asset Management, Inc., Southern Refrigerated Transport, Inc., Covenant Transport Solutions, Inc., Star Transportation, Inc., Bank of America, N.A., and JP Morgan Chase Bank, N.A. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company's Report on Form 8-K, filed April 2, 2012) |
| 10.22 | | Eighth Amendment to Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement dated effective as of December 31, 2012 among Covenant Transportation Group, Inc., Covenant Transport, Inc., CTG Leasing Company, Covenant Asset Management, Inc., Southern Refrigerated Transport, Inc., Covenant Transport Solutions, Inc., Star Transportation, Inc., Bank of America, N.A., and JP Morgan Chase Bank, N.A. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company's Report on Form 8-K, filed January 31, 2013) |
| 10.23 | * | Description of Director Compensation Program (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.27 to the Company's Form 10-K, filed March 28, 2013) |
| 10.24 | * | Description of 2014 Bonus Plan (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company's Form 10-Q, filed May 13, 2014) |
| 10.25 | | Ninth Amendment to Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement and Related Security Documents dated effective as of August 6, 2014 among Covenant Transportation Group, Inc., Covenant Transport, Inc., CTG Leasing Company, Covenant Asset Management, Inc., Southern Refrigerated Transport, Inc., Covenant Transport Solutions, Inc., Star Transportation, Inc., Bank of America, N.A., and JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Company's Form 10-Q, filed November 13, 2014) |
| 10.26 | | Tenth Amendment to Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement and Related Security Documents dated effective as of September 8, 2014 among Covenant Transportation Group, Inc., Covenant Transport, Inc., CTG Leasing Company, Covenant Asset Management, Inc., Southern Refrigerated Transport, Inc., Covenant Transport Solutions, Inc., Star Transportation, Inc., Bank of America, N.A., and JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A. (Incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Company's Form 10-Q, filed November 13, 2014) |
| # | List of Subsidiaries |
| # | Consent of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm – KPMG LLP |
| # | Consent of Independent Auditor – Lattimore Black Morgan & Cain, PC |
| # | Certification pursuant to Item 601(b)(31) of Regulation S-K, as adopted pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, by David R. Parker, the Company's Principal Executive Officer |
| # | Certification pursuant to Item 601(b)(31) of Regulation S-K, as adopted pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, by Richard B. Cribbs, the Company's Principal Financial Officer |
| # | Certification pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, by David R. Parker, the Company's Chief Executive Officer |
| # | Certification pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, by Richard B. Cribbs, the Company's Chief Financial Officer |
| # | Financial Statements of Transport Enterprise Leasing, LLC |
| 101.INS | ** | XBRL Instance Document |
| 101.SCH | ** | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document |
| 101.CAL | ** | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document |
| 101.DEF | ** | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document |
| 101.LAB | ** | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Labels Linkbase Document |
| 101.PRE | ** | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document |
References:
| # | Filed herewith. |
| * | Management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement. |
| ** | In accordance with Regulation S-T, the XBRL-related information in Exhibit 101 to this Annual Report on Form 10-K shall be deemed to be "furnished" and not "filed." |
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| | COVENANT TRANSPORTATION GROUP, INC. |
| | |
| | |
| Date: March 3, 2015 | By: | /s/ Richard B. Cribbs |
| | | Richard B. Cribbs |
| | | Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer in his capacity as such and on behalf of the issuer. |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| Signature and Title | | Date |
| | | |
| /s/ David R. Parker | | March 3, 2015 |
| David R. Parker | | |
Chairman of the Board, President, and Chief Executive Officer (principal executive officer) | | |
| | | |
| /s/ Richard B. Cribbs | | March 3, 2015 |
| Richard B. Cribbs | | |
Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer (principal financial officer) | | |
| | | |
| /s/ M. Paul Bunn | | March 3, 2015 |
| M. Paul Bunn | | |
Chief Accounting Officer (principal accounting officer) | | |
| | | |
| /s/ Bradley A. Moline | | March 2, 2015 |
| Bradley A. Moline | | |
| Director | | |
| | | |
| /s/ William T. Alt | | March 2, 2015 |
| William T. Alt | | |
| Director | | |
| | | |
| /s/ Robert E. Bosworth | | March 2, 2015 |
| Robert E. Bosworth | | |
| Director | | |
| /s/ Herbert J. Schmidt | | March 2, 2015 |
| Herbert J. Schmidt | | |
| Director | | |
The Board of Directors and Stockholders
Covenant Transportation Group, Inc.:
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Covenant Transportation Group, Inc. and subsidiaries as of December 31, 2014 and 2013, and the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive income, stockholders’ equity, and cash flows for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2014. We also have audited Covenant Transportation Group, Inc.’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2014, based on criteria established in Internal Control – Integrated Framework (1992) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). Covenant Transportation Group Inc.’s management is responsible for these consolidated financial statements, for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting, and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these consolidated financial statements and an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement and whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audits of the consolidated financial statements included examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, and evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audits also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinions.
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of Covenant Transportation Group, Inc. and subsidiaries as of December 31, 2014 and 2013, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2014, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles. Also in our opinion, Covenant Transportation Group, Inc. maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2014, based on criteria established in Internal Control – Integrated Framework (1992) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO).
/s/ KPMG LLP
Atlanta, Georgia
March 3, 2015
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS DECEMBER 31, 2014 AND 2013 (In thousands, except share data) | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| ASSETS | | | | | | |
| Current assets: | | | | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents | | $ | 21,330 | | | $ | 9,263 | |
Accounts receivable, net of allowance of $1,767 in 2014 and $1,736 in 2013 | | | 95,943 | | | | 81,242 | |
Drivers' advances and other receivables, net of allowance of $1,290 in 2014 and $1,337 in 2013 | | | 5,770 | | | | 5,356 | |
Inventory and supplies | | | 4,402 | | | | 4,718 | |
Prepaid expenses | | | 9,028 | | | | 10,418 | |
Assets held for sale | | | 4,268 | | | | 7,073 | |
Deferred income taxes | | | 14,713 | | | | 5,234 | |
Income taxes receivable | | | 1,309 | | | | 146 | |
| Total current assets | | | 156,763 | | | | 123,450 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Property and equipment, at cost | | | 505,345 | | | | 462,376 | |
| Less: accumulated depreciation and amortization | | | (122,854 | ) | | | (132,768 | ) |
Net property and equipment | | | 382,491 | | | | 329,608 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Other assets, net | | | 14,763 | | | | 13,364 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Total assets | | $ | 554,017 | | | $ | 466,422 | |
| LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY | | | | | | | | |
| Current liabilities: | | | | | | | | |
Checks outstanding in excess of bank balances | | $ | - | | | $ | 2,918 | |
Accounts payable | | | 9,623 | | | | 8,322 | |
Accrued expenses | | | 39,470 | | | | 28,185 | |
Current maturities of long-term debt | | | 27,824 | | | | 44,070 | |
Current portion of capital lease obligations | | | 1,606 | | | | 8,732 | |
Current portion of insurance and claims accrual | | | 17,565 | | | | 17,151 | |
Other short-term liabilities | | | 7,999 | | | | - | |
| Total current liabilities | | | 104,087 | | | | 109,378 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Long-term debt | | | 159,531 | | | | 169,491 | |
Long-term portion of capital lease obligations | | | 13,372 | | | | 13,186 | |
Insurance and claims accrual | | | 23,173 | | | | 13,601 | |
Deferred income taxes | | | 73,717 | | | | 59,077 | |
Other long-term liabilities | | | 10,933 | | | | 1,329 | |
| Total liabilities | | | 384,813 | | | | 366,062 | |
| Commitments and contingent liabilities | | | - | | | | - | |
| Stockholders' equity: | | | | | | | | |
Class A common stock, $.01 par value; 20,000,000 shares authorized; 15,746,609 shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2014; and 13,469,090 issued and 12,559,703 outstanding as of December 31, 2013 | | | 168 | | | | 145 | |
Class B common stock, $.01 par value; 5,000,000 shares authorized; 2,350,000 shares issued and outstanding | | | 24 | | | | 24 | |
Additional paid-in-capital | | | 141,248 | | | | 88,620 | |
Treasury stock at cost; 0 and 909,387 shares as of December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively | | | - | | | | (12,319 | ) |
Accumulated other comprehensive (loss) income | | | (13,101 | ) | | | 833 | |
Retained earnings | | | 40,865 | | | | 23,057 | |
| Total stockholders' equity | | | 169,204 | | | | 100,360 | |
| Total liabilities and stockholders' equity | | $ | 554,017 | | | $ | 466,422 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2014, 2013, AND 2012 (In thousands, except per share data) |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenues | | | | | | | | | |
Freight revenue | | $ | 578,569 | | | $ | 538,933 | | | $ | 527,435 | |
Fuel surcharge revenue | | | 140,411 | | | | 145,616 | | | | 146,819 | |
| Total revenue | | $ | 718,980 | | | $ | 684,549 | | | $ | 674,254 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Operating expenses: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Salaries, wages, and related expenses | | | 231,761 | | | | 218,946 | | | | 217,080 | |
Fuel expense | | | 168,856 | | | | 186,002 | | | | 194,841 | |
Operations and maintenance | | | 47,251 | | | | 50,043 | | | | 45,839 | |
Revenue equipment rentals and purchased transportation | | | 111,772 | | | | 102,954 | | | | 85,010 | |
Operating taxes and licenses | | | 10,960 | | | | 10,969 | | | | 11,043 | |
Insurance and claims | | | 39,594 | | | | 30,305 | | | | 33,133 | |
Communications and utilities | | | 5,806 | | | | 5,240 | | | | 4,809 | |
General supplies and expenses | | | 16,950 | | | | 16,002 | | | | 16,068 | |
Depreciation and amortization, including gains and losses on disposition of equipment | | | 46,384 | | | �� | 43,694 | | | | 43,222 | |
| Total operating expenses | | | 679,334 | | | | 664,155 | | | | 651,045 | |
| Operating income | | | 39,646 | | | | 20,394 | | | | 23,209 | |
| Other expenses (income): | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Interest expense | | | 10,807 | | | | 10,400 | | | | 12,697 | |
Other | | | (13 | ) | | | (3 | ) | | | (13 | ) |
| Other expenses, net | | | 10,794 | | | | 10,397 | | | | 12,684 | |
| Equity in income of affiliate | | | 3,730 | | | | 2,750 | | | | 1,875 | |
| Income before income taxes | | | 32,582 | | | | 12,747 | | | | 12,400 | |
| Income tax expense | | | 14,774 | | | | 7,503 | | | | 6,335 | |
| Net income | | $ | 17,808 | | | $ | 5,244 | | | $ | 6,065 | |
| Income per share: | | | | | | | | | |
| Basic income per share: | | $ | 1.17 | | | $ | 0.35 | | | $ | 0.41 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Diluted income per share: | | $ | 1.15 | | | $ | 0.35 | | | $ | 0.41 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Basic weighted average shares outstanding | | | 15,250 | | | | 14,837 | | | | 14,742 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Diluted weighted average shares outstanding | | | 15,517 | | | | 15,039 | | | | 14,808 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
FOR THE YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2014, 2013, AND 2012
(In thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income | | $ | 17,808 | | | $ | 5,244 | | | $ | 6,065 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Other comprehensive (loss) income: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Unrealized (loss) gain on effective portion of fuel hedges, net of tax of $9,892, $567, and $2,100 in 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively | | | (15,869 | ) | | | 909 | | | | 3,369 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Reclassification of fuel hedge losses (gains) into statement of operations, net of tax of $1,206, $247, and $1,932 in 2014, 2013, and 2012, respectively | | | 1,935 | | | | (396 | ) | | | (3,099 | ) |
| Total other comprehensive (loss) income | | | (13,934 | ) | | | 513 | | | | 270 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Comprehensive income | | $ | 3,874 | | | $ | 5,757 | | | $ | 6,335 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF STOCKHOLDERS' EQUITY
FOR THE YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2014, 2013, AND 2012
(In thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | | | Accumulated | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | Additional | | | | | | Other | | | | | | Total | |
| | | Common Stock | | | Paid-In | | | Treasury | | | Comprehensive | | | Retained | | | Stockholders' | |
| | | Class A | | | Class B | | | Capital | | | Stock | | | (Loss) Income | | | Earnings | | | Equity | |
| Balances at December 31, 2011 | | $ | 143 | | | $ | 24 | | | $ | 89,535 | | | $ | (14,445 | ) | | $ | 50 | | | $ | 11,748 | | | $ | 87,055 | |
| Net income | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 6,065 | | | | 6,065 | |
| Other comprehensive income | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 270 | | | | - | | | | 270 | |
| Stock-based employee compensation cost | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,184 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,184 | |
| Issuance of restricted shares, net | | | - | | | | - | | | | (391 | ) | | | 490 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 99 | |
| Balances at December 31, 2012 | | $ | 143 | | | $ | 24 | | | $ | 90,328 | | | $ | (13,955 | ) | | $ | 320 | | | $ | 17,813 | | | $ | 94,673 | |
| Net income | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 5,244 | | | | 5,244 | |
| Other comprehensive income | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 513 | | | | - | | | | 513 | |
| Stock-based employee compensation cost | | | - | | | | - | | | | 690 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 690 | |
| Reversal of previously recognized stock-based employee compensation expense | | | - | | | | - | | | | (409 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (409 | ) |
| Issuance of restricted shares, net | | | 2 | | | | - | | | | (1,878 | ) | | | 1,636 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (240 | ) |
| Income tax deficit arising from restricted share vesting | | | - | | | | - | | | | (111 | ) | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (111 | ) |
| Balances at December 31, 2013 | | $ | 145 | | | $ | 24 | | | $ | 88,620 | | | $ | (12,319 | ) | | $ | 833 | | | $ | 23,057 | | | $ | 100,360 | |
| Net income | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 17,808 | | | | 17,808 | |
| Other comprehensive loss | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (13,934 | ) | | | - | | | | (13,934 | ) |
| Follow-on stock offering | | | 22 | | | | - | | | | 51,498 | | | | 11,464 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 62,984 | |
| Stock-based employee compensation expense | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,286 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 1,286 | |
| Exercise of stock options | | | - | | | | - | | | | 190 | | | | 408 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 598 | |
| Issuance of restricted shares, net | | | 1 | | | | - | | | | (1,180 | ) | | | 447 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | (732 | ) |
| Income tax benefit arising from restricted share vesting and option exercises | | | - | | | | - | | | | 834 | | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | | | | 834 | |
| Balances at December 31, 2014 | | $ | 168 | | | $ | 24 | | | $ | 141,248 | | | $ | - | | | $ | (13,101 | ) | | $ | 40,865 | | | $ | 169,204 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
FOR THE YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2014, 2013, AND 2012
(In thousands)
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash flows from operating activities: | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income | | $ | 17,808 | | | $ | 5,244 | | | $ | 6,065 | |
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Provision for losses on accounts receivable | | | 774 | | | | 457 | | | | 904 | |
(Realized gain) deferred gain on sales of equipment to affiliate, net | | | (33 | ) | | | 81 | | | | 198 | |
Depreciation and amortization | | | 49,043 | | | | 44,457 | | | | 48,135 | |
Amortization of deferred financing fees | | | 256 | | | | 245 | | | | 492 | |
Unrealized loss (gain) on ineffective portion of fuel hedges | | | 1,510 | | | | (55 | ) | | | - | |
Cash collateral on fuel hedge | | | (5,000 | ) | | | - | | | | - | |
Deferred income tax expense | | | 14,681 | | | | 8,217 | | | | 6,735 | |
Income tax (benefit) deficit arising from restricted share vesting | | | (834 | ) | | | 111 | | | | - | |
Casualty premium credit | | | - | | | | - | | | | (4,000 | ) |
Equity in income of affiliate | | | (3,730 | ) | | | (2,750 | ) | | | (1,875 | ) |
Gain on disposition of property and equipment | | | (2,659 | ) | | | (763 | ) | | | (4,913 | ) |
Stock-based compensation expense | | | 1,386 | | | | 381 | | | | 1,284 | |
Changes in operating assets and liabilities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Receivables and advances | | | (16,996 | ) | | | (4,312 | ) | | | (10,415 | ) |
Prepaid expenses and other assets | | | 1,680 | | | | (2,014 | ) | | | 4,630 | |
Inventory and supplies | | | 316 | | | | (168 | ) | | | 61 | |
Insurance and claims accrual | | | 9,986 | | | | (2,399 | ) | | | 3,979 | |
Accounts payable and accrued expenses | | | 5,556 | | | | (6,287 | ) | | | 3,821 | |
| Net cash flows provided by operating activities | | | 73,744 | | | | 40,445 | | | | 55,101 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash flows from investing activities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Acquisition of property and equipment | | | (163,679 | ) | | | (135,896 | ) | | | (41,787 | ) |
Investment in affiliated company | | | - | | | | (500 | ) | | | (2,900 | ) |
Return of investment in affiliated company | | | 307 | | | | 65 | | | | 316 | |
Proceeds from disposition of property and equipment | | | 78,776 | | | | 51,930 | | | | 57,525 | |
| Net cash flows (used in) provided by investing activities | | | (84,596 | ) | | | (84,401 | ) | | | 13,154 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash flows from financing activities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Change in checks outstanding in excess of bank balances | | | (2,918 | ) | | | (5,343 | ) | | | 2,298 | |
Debt refinancing costs | | | (49 | ) | | | (356 | ) | | | (26 | ) |
Payment of minimum tax withholdings on stock compensation | | | (832 | ) | | | (340 | ) | | | (9 | ) |
(Repayments) proceeds of/from borrowings under revolving credit facility, net | | | (7,010 | ) | | | 7,005 | | | | (15,885 | ) |
Repayments of capital lease obligation | | | (11,492 | ) | | | (2,186 | ) | | | (1,992 | ) |
Proceeds from issuance of notes payable | | | 115,364 | | | | 134,192 | | | | 26,395 | |
Repayments of notes payable | | | (134,560 | ) | | | (86,488 | ) | | | (76,085 | ) |
Proceeds from exercise of stock options | | | 598 | | | | - | | | | - | |
Proceeds from issuance of stock in follow-on offering, net of offering costs | | | 62,984 | | | | - | | | | - | |
Income tax benefit (deficit) arising from restricted share vesting | | | 834 | | | | (111 | ) | | | - | |
| Net cash flows provided by (used in) financing activities | | | 22,919 | | | | 46,373 | | | | (65,304 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net change in cash and cash equivalents | | | 12,067 | | | | 2,417 | | | | 2,951 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year | | | 9,263 | | | | 6,846 | | | | 3,895 | |
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of year | | $ | 21,330 | | | $ | 9,263 | | | $ | 6,846 | |
| Supplemental disclosure of cash flow information: | | | | | | | | | |
Cash paid during the year for: | | | | | | | | | |
Interest, net of capitalized interest | | $ | 10,919 | | | $ | 10,328 | | | $ | 12,967 | |
Income taxes | | $ | 571 | | | $ | 320 | | | $ | 342 | |
Equipment purchased under capital leases | | $ | 4,552 | | | $ | 8,010 | | | $ | - | |
Accrued investment in TEL | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | 500 | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2014, 2013, AND 2012
1. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Nature of Business and Segments
Covenant Transportation Group, Inc., a Nevada holding company, together with its wholly-owned subsidiaries offers truckload transportation and brokerage services to customers throughout the continental United States.
We have one reportable segment, our asset-based truckload services ("Truckload").
The Truckload segment consists of three asset-based operating fleets that are aggregated because they have similar economic characteristics and meet the aggregation criteria. The three operating fleets that comprise our Truckload segment are as follows: (i) Covenant Transport, Inc. ("Covenant Transport"), our historical flagship operation, which provides expedited long haul, dedicated, temperature-controlled, and regional solo-driver service; (ii) Southern Refrigerated Transport, Inc. ("SRT"), which provides primarily long haul and regional temperature-controlled service; and (iii) Star Transportation, Inc. ("Star"), which provides regional solo-driver and dedicated services, primarily in the southeastern United States.
In addition, our Covenant Transport Solutions, Inc. ("Solutions") subsidiary has service offerings ancillary to our asset-based Truckload services, including: freight brokerage service through freight brokerage agents who are paid a commission for the freight they provide and accounts receivable factoring. The operations consist of several operating segments, which neither individually nor in the aggregate meet the quantitative or qualitative reporting thresholds.
Principles of Consolidation
The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of Covenant Transportation Group, Inc., a holding company incorporated in the state of Nevada in 1994, and its wholly-owned subsidiaries: Covenant Transport, Inc., a Tennessee corporation; Southern Refrigerated Transport, Inc., an Arkansas corporation; Star Transportation, Inc., a Tennessee corporation; Covenant Transport Solutions, Inc., a Nevada corporation; Covenant Logistics, Inc., a Nevada corporation; Covenant Asset Management, Inc., a Nevada corporation; CTG Leasing Company, a Nevada corporation; and IQS Insurance Retention Group, Inc., a Vermont corporation.
References in this report to "it," "we," "us," "our," the "Company," and similar expressions refer to Covenant Transportation Group, Inc. and its subsidiaries. All significant intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
Investment in Transport Enterprise Leasing, LLC
Transport Enterprise Leasing, LLC ("TEL") is a tractor and trailer equipment leasing company and used equipment reseller. We evaluated our investment in TEL to determine whether it should be recorded on a consolidated basis. Our percentage of ownership interest (49%), an evaluation of control, and whether a variable interest entity ("VIE") existed were all considered in our consolidation assessment. The analysis provided that we do not control TEL and that TEL is not deemed a VIE. We have accounted for our investment in TEL using the equity method of accounting given our 49% ownership interest and ability to exercise significant influence over operating and financial policies. Under the equity method, the cost of our investment is adjusted for our share of equity in the earnings of TEL and reduced by distributions received and our proportionate share of TEL's net income is included in our earnings.
On a periodic basis, we assess whether there are any indicators that the fair value of our investment in TEL may be impaired. The investment is impaired only if the estimate of the fair value of the investment is less than the carrying value of the investment, and such decline in value is deemed to be other than temporary. To the extent impairment has occurred, the loss would be measured as the excess of the carrying amount of the investment over the fair value of the investment. As a result of TEL's earnings, no impairment indicators were noted that would provide for impairment of our investment.
Revenue Recognition
Revenue, drivers' wages, and other direct operating expenses generated by our Truckload reportable segment are recognized on the date shipments are delivered to the customer. Revenue includes transportation revenue, fuel surcharges, loading and unloading activities, equipment detention, and other accessorial services.
Revenue generated by our Solutions subsidiary is recognized upon completion of the services provided. Revenue is recorded on a gross basis, without deducting third party purchased transportation costs, as we act as a principal with substantial risks as primary obligor, except for transactions whereby equipment from our Truckload segment perform the related services, which we record on a net basis in accordance with the related authoritative guidance. Solutions' revenue includes $2.3 million and $1.7 million of revenue in 2014 and 2013, respectively, related to an accounts receivable factoring business started in 2013 to supplement several aspects of our non-asset operations. Revenue for this business is recognized on a net basis after giving effect to receivables payments we make to the factoring client, given we are acting as an agent and are not the primary generator of the factored receivables in these transactions.
Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America requires us to make decisions based upon estimates, assumptions, and factors we consider as relevant to the circumstances. Such decisions include the selection of applicable accounting principles and the use of judgment in their application, the results of which impact reported amounts and disclosures. Changes in future economic conditions or other business circumstances may affect the outcomes of our estimates and assumptions. Accordingly, actual results could differ from those anticipated.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
We consider all highly liquid investments with a maturity of three months or less at acquisition to be cash equivalents. Additionally, we are also subject to concentrations of credit risk related to deposits in banks in excess of the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation limits.
Accounts Receivable and Concentration of Credit Risk
We extend credit to our customers in the normal course of business. We perform ongoing credit evaluations and generally do not require collateral. Trade accounts receivable are recorded at their invoiced amounts, net of allowance for doubtful accounts. We evaluate the adequacy of our allowance for doubtful accounts quarterly. Accounts outstanding longer than contractual payment terms are considered past due and are reviewed individually for collectability. We maintain reserves for potential credit losses based upon its loss history and specific receivables aging analysis. Receivable balances are written off when collection is deemed unlikely.
Accounts receivable are comprised of a diversified customer base that results in a lack of concentration of credit risk. During 2014, 2013, and 2012, our top ten customers generated 38%, 34%, and 32% of total revenue, respectively. In 2014, one customer accounted for more than 10% of our consolidated revenue. This customer was serviced by both our Truckload segment and our Solutions subsidiary providing for $82.5 million of total revenue. No customer accounted for more than 10% of our consolidated revenue in 2013 or 2012. The carrying amount reported in the consolidated balance sheet for accounts receivable approximates fair value based on the fact that the receivables collection averaged approximately 36 days in 2014 and 2013, respectively.
Included in accounts receivable is $15.8 million of factoring receivables at December 31, 2014, net of a $0.2 million allowance for bad debts. We advance approximately 85% to 95% of each receivable factored and retain the remainder as collateral for collection issues that might arise. The retained amounts are returned to the clients after the related receivable has been collected. At December 31, 2014, the retained amounts related to factored receivables totaled $0.3 million and were included in accounts payable in the consolidated balance sheet. Our clients are smaller trucking companies that factor their receivables to us for a fee to facilitate faster cash flow. We evaluate each client's customer base and only factor specific receivables that meet predefined criteria. The carrying value of the factored receivables approximates the fair value, as the receivables are generally repaid directly to us by the client's customer within 30-40 days due to the combination of the short-term nature of the financing transaction and the underlying quality of the receivables.
The following table provides a summary (in thousands) of the activity in the allowance for doubtful accounts for 2014, 2013, and 2012:
Years ended December 31: | | Beginning balance January 1, | | | Additional provisions to allowance | | | Write-offs and other deductions | | | Ending balance December 31, | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2014 | | $ | 1,736 | | | $ | 774 | | | $ | (743 | ) | | $ | 1,767 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2013 | | $ | 1,729 | | | $ | 457 | | | $ | (450 | ) | | $ | 1,736 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2012 | | $ | 1,711 | | | $ | 904 | | | $ | (886 | ) | | $ | 1,729 | |
Inventories and Supplies
Inventories and supplies consist of parts, tires, fuel, and supplies. Tires on new revenue equipment are capitalized as a component of the related equipment cost when the tractor or trailer is placed in service and recovered through depreciation over the life of the vehicle. Replacement tires and parts on hand at year end are recorded at the lower of cost or market with cost determined using the first-in, first-out (FIFO) method. Replacement tires are expensed when placed in service.
Assets Held for Sale
Assets held for sale include property and revenue equipment no longer utilized in continuing operations which are available and held for sale. Assets held for sale are no longer subject to depreciation, and are recorded at the lower of depreciated book value or fair market value less selling costs. We periodically review the carrying value of these assets for possible impairment. We expect to sell the majority of these assets within twelve months.
Property and Equipment
Property and equipment is stated at cost less accumulated depreciation. Depreciation for book purposes is determined using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets, while depreciation for tax purposes is generally recorded using an accelerated method. Depreciation of revenue equipment is our largest item of depreciation. We generally depreciate new tractors (excluding day cabs) over five years to salvage values of approximately 25% of their cost. We generally depreciate new trailers over six years for refrigerated trailers and ten years for dry van trailers to salvage values of approximately 38% of their cost. We annually review the reasonableness of our estimates regarding useful lives and salvage values of our revenue equipment and other long-lived assets based upon, among other things, our experience with similar assets, conditions in the used revenue equipment market, and prevailing industry practice. Changes in the useful life or salvage value estimates, or fluctuations in market values that are not reflected in our estimates, could have a material effect on our results of operations. Gains and losses on the disposal of revenue equipment are included in depreciation expense in the consolidated statements of operations.
We lease certain revenue equipment under capital leases with terms of 60 to 84 months. Amortization of leased assets is included in depreciation and amortization expense.
Although a portion of our tractors are protected by non-binding indicative trade-in values or binding trade-back agreements with the manufacturers, substantially all of our owned trailers are subject to fluctuations in market prices for used revenue equipment. Moreover, our trade-back agreements are contingent upon reaching acceptable terms for the purchase of new equipment. Declines in the price of used revenue equipment or failure to reach agreement for the purchase of new tractors with the manufacturers issuing trade-back agreements could result in impairment of, or losses on the sale of, revenue equipment.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
Pursuant to applicable accounting standards, revenue equipment and other long-lived assets are tested for impairment whenever an event occurs that indicates an impairment may exist. Expected future cash flows are used to analyze whether an impairment has occurred. If the sum of expected undiscounted cash flows is less than the carrying value of the long-lived asset, then an impairment loss is recognized. We measure the impairment loss by comparing the fair value of the asset to its carrying value. Fair value is determined based on a discounted cash flow analysis or the appraised value of the assets, as appropriate.
Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets
We classify intangible assets into two categories: (i) intangible assets with definite lives subject to amortization and (ii) goodwill. We have no goodwill on our consolidated balance sheet for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013. We test intangible assets with definite lives for impairment if conditions exist that indicate the carrying value may not be recoverable. Such conditions may include an economic downturn in a geographic market or a change in the assessment of future operations. We record an impairment charge when the carrying value of the definite lived intangible asset is not recoverable by the cash flows generated from the use of the asset.
We determine the useful lives of our identifiable intangible assets after considering the specific facts and circumstances related to each intangible asset. Factors we consider when determining useful lives include the contractual term of any agreement, the history of the asset, our long-term strategy for the use of the asset, any laws or other local regulations which could impact the useful life of the asset, and other economic factors, including competition and specific market conditions. Intangible assets that are deemed to have definite lives are amortized, generally on a straight-line basis, over their useful lives, ranging from 4 to 20 years.
Insurance and Other Claims
The primary claims arising against us consist of cargo, liability, personal injury, property damage, workers' compensation, and employee medical expenses. Our insurance program involves self-insurance with high risk retention levels. Due to our significant self-insured retention amounts, we have exposure to fluctuations in the number and severity of claims and to variations between our estimated and actual ultimate payouts. We accrue the estimated cost of the uninsured portion of pending claims and an estimate for allocated loss adjustment expenses including legal and other direct costs associated with a claim. Estimates require judgments concerning the nature and severity of the claim, historical trends, advice from third-party administrators and insurers, the size of any potential damage award based on factors such as the specific facts of individual cases, the jurisdictions involved, the prospect of punitive damages, future medical costs, and inflation estimates of future claims development, and the legal and other costs to settle or defend the claims. We have significant exposure to fluctuations in the number and severity of claims. If there is an increase in the frequency and severity of claims, or we are required to accrue or pay additional amounts if the claims prove to be more severe than originally assessed, or any of the claims would exceed the limits of our insurance coverage, our profitability could be adversely affected.
In addition to estimates within our self-insured retention layers, we also must make judgments concerning claims where we have third party insurance and for claims outside our coverage limits. Upon settling claims and expenses associated with claims where we have third party coverage, we are generally required to initially fund payment to the claimant and seek reimbursement from the insurer. Receivables from insurers for claims and expenses we have paid on behalf of insurers total $0.1 million and $1.0 million at December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively, and are included in drivers' advances and other receivables on our consolidated balance sheet. Additionally, we accrue claims above our self-insured retention and record a corresponding receivable for amounts we expect to collect from insurers upon settlement of such claims. We have $0.6 million at December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively, as a receivable in other assets and as a corresponding accrual in the long-term portion of insurance and claims accruals on our consolidated balance sheet for claims above our self-insured retention for which we believe it is reasonably assured that the insurers will provide their portion of such claims. We evaluate collectability of the receivables based on the credit worthiness and surplus of the insurers, along with our prior experience and contractual terms with each. If any claim occurrence were to exceed our aggregate coverage limits, we would have to accrue for the excess amount. Our critical estimates include evaluating whether a claim may exceed such limits and, if so, by how much. If one or more claims were to exceed our then effective coverage limits, our financial condition and results of operations could be materially and adversely affected
Our casualty insurance self-insured retention limit for the primary excess layer of casualty is no more than $1.0 million. Effective April 1, 2013, the policy includes a limit for a single loss of $9.0 million, an aggregate of $18.0 million for each policy year, and a $30.0 million aggregate for the three-year period ended March 31, 2016. Our prior aggregate casualty policy for the three years ended March 31, 2013, included a similar $9.0 million limit per claim and $18.0 million annual limit, with a $27.0 million limit for the three years. Our excess policies cover up to $40.0 million per claim, subject to certain aggregate limits. In addition, our current auto liability policy includes a policy release premium refund of $13.0 million, less any amounts paid on claims by the insurer, for the three years ended March 31, 2016, if we were to commute the policy for the entire three years. A decision with respect to commutation of the policy cannot be made before April 1, 2016 and must be made by June 30, 2016, unless both we and the insurance carrier agree to a commutation prior to the end of the policy term. Management cannot predict whether or not future claims or the development of existing claims will justify a commutation, and accordingly, no related amounts were recorded in 2014. The previous three-year casualty policy, which expired on March 31, 2013, provided for an annual commutation if certain losses were not met and we elected to commute the policy. The policy for the twelve months ended March 31, 2013 was not commuted; however, in June 2012 we commuted the policy for the April 1, 2011 through March 31, 2012 policy year and as such are responsible for all claims that occurred during that policy year, excluding any claims between $10.0 million and $20.0 million, should such a claim develop. We received a $4.0 million non-cash credit in 2012 related to the commutation, that off-set premiums in 2013 and accordingly reduced our insurance and claims expense.
We are self-insured on an occurrence/per claim basis for workers' compensation up to the first $1.3 million. We purchase coverage on an occurrence/per claim basis for any cargo losses in the $0.3 million to $2.0 million layer, with our contracts generally excluding the value of any cargo in excess of $2.0 million. We also maintain a self-insured group medical plan for our Covenant Transport, Solutions, Star, and corporate employees, with annual per individual claimant stop-loss deductible of $0.4 million, while SRT offers a fully insured group health program to its employees. We are completely self-insured for physical damage to our own tractors and trailers.
Interest
We capitalize interest on major projects during construction. Interest is capitalized based on the average interest rate on related debt. Capitalized interest was less than $0.1 million in 2014, 2013, and 2012.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
Our financial instruments consist primarily of cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable, commodity contracts, accounts payable, and debt. The carrying amount of cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable, accounts payable, and current debt approximates their fair value because of the short-term maturity of these instruments. The carrying value of the factored receivables approximates the fair value, as the receivables are generally repaid directly to us by the client's customer within 30-40 days due to the combination of the short-term nature of the financing transaction and the underlying quality of the receivables. Interest rates that are currently available to us for issuance of long-term debt with similar terms and remaining maturities are used to estimate the fair value of our long-term debt, which primarily consists of revenue equipment installment notes. The fair value of our revenue equipment installment notes approximated the carrying value at December 31, 2014, as the weighted average interest rate on these notes approximates the market rate for similar debt. Borrowings under our revolving Credit Facility approximate fair value due to the variable interest rate on the facility. Additionally, commodity contracts, which are accounted for as hedge derivatives, as discussed in Note 13, are valued based on the forward rate of the specific indices upon which the contract is being settled and adjusted for counterparty credit risk using available market information and valuation methodologies.
Income Taxes
Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the future tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax basis. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in income in the period that includes the enactment date. We have reflected the necessary deferred tax assets and liabilities in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets. We believe the future tax deductions will be realized principally through future reversals of existing taxable temporary differences and future taxable income, except for when a valuation allowance has been provided as discussed in Note 9.
In the ordinary course of business there is inherent uncertainty in quantifying our income tax positions. We assess our income tax positions and record tax benefits for all years subject to examination based upon management's evaluation of the facts, circumstances, and information available at the reporting dates. For those tax positions where it is more likely than not that a tax benefit will be sustained, we have recorded the largest amount of tax benefit with a greater than 50% likelihood of being realized upon ultimate settlement with a taxing authority that has full knowledge of all relevant information. For those income tax positions where it is not more likely than not that a tax benefit will be sustained, no tax benefit has been recognized in the financial statements. Potential accrued interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits are recognized as a component of income tax expense.
Our policy is to recognize income tax benefit arising from the exercise of stock options and restricted share vesting based on the ordering provisions of the tax law as prescribed by the Internal Revenue Code, including indirect tax effects, if any.
Lease Accounting and Off-Balance Sheet Transactions
We issue residual value guarantees in connection with the operating leases we enter into for certain of our revenue equipment. These leases provide that if we do not purchase the leased equipment from the lessor at the end of the lease term, then we are liable to the lessor for an amount equal to the shortage (if any) between the proceeds from the sale of the equipment and an agreed value. To the extent the expected value at the lease termination date is lower than the residual value guarantee, we would accrue for the difference over the remaining lease term. We believe that proceeds from the sale of equipment under operating leases would exceed the payment obligation on substantially all operating leases. The estimated values at lease termination involve management judgments. As leases are entered into, determination as to the classification as an operating or capital lease involves management judgments on residual values and useful lives.
Capital Structure
The shares of Class A and B common stock are substantially identical except that the Class B shares are entitled to two votes per share and immediately convert to Class A shares if beneficially owned by anyone other than our Chief Executive Officer or certain members of his immediate family, while Class A shares are entitled to one vote per share. The terms of any future issuances of preferred shares will be set by our Board of Directors.
Comprehensive Income
Comprehensive income generally includes all changes in equity during a period except those resulting from investments by owners and distributions to owners. Comprehensive income for 2014, 2013, and 2012 was comprised of the net income plus the unrealized gain or loss on the effective portion of diesel fuel hedges and the reclassified fuel hedge gains or losses into earnings.
Basic income per share excludes dilution and is computed by dividing earnings available to common stockholders by the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding for the period. Diluted income per share reflects the dilution that could occur if securities or other contracts to issue common stock were exercised or converted into common stock or resulted in the issuance of common stock that then shared in our earnings. The calculation of diluted earnings per share excludes a de minimus number of unexercised options and a de minimus number of unvested shares since the effect of any assumed exercise of the related awards would be anti-dilutive for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013, and 2012, respectively. Income per share is the same for both Class A and Class B shares.
The following table sets forth the calculation of net income per share included in the consolidated statements of operations for each of the three years ended December 31:
| (in thousands except per share data) | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Numerator: | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
Net income | | $ | 17,808 | | | $ | 5,244 | | | $ | 6,065 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Denominator: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Denominator for basic income per share – weighted-average shares | | | 15,250 | | | | 14,837 | | | | 14,742 | |
| Effect of dilutive securities: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Equivalent shares issuable upon conversion of unvested restricted shares | | | 266 | | | | 202 | | | | 66 | |
| Equivalent shares issuable upon conversion of unvested employee stock options | | | 1 | | | | - | | | | - | |
Denominator for diluted income per share adjusted weighted-average shares and assumed conversions | | | 15,517 | | | | 15,039 | | | | 14,808 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Net income per share: | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Basic income per share | | $ | 1.17 | | | $ | 0.35 | | | $ | 0.41 | |
| Diluted income per share | | $ | 1.15 | | | $ | 0.35 | | | $ | 0.41 | |
Stock-Based Employee Compensation
We issue several types of stock-based compensation, including awards that vest based on service and performance conditions or a combination of the conditions. Performance-based awards vest contingent upon meeting certain performance criteria established by the Compensation Committee. All awards require future service and thus forfeitures are estimated based on historical forfeitures and the remaining term until the related award vests. Determining the appropriate amount to expense in each period is based on likelihood and timing of achieving the stated targets for performance-based awards and requires judgment, including forecasting future financial results. The estimates are revised periodically based on the probability and timing of achieving the required performance and adjustments are made as appropriate. Awards that are only subject to time vesting provisions are amortized using the straight-line method.
Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities
We periodically utilize derivative instruments to manage exposure to changes in fuel prices. At inception of a derivative contract, we document relationships between derivative instruments and hedged items, as well as our risk-management objective and strategy for undertaking various derivative transactions, and assess hedge effectiveness. We record derivative financial instruments in the balance sheet as either an asset or liability at fair value. If it is determined that a derivative is not highly effective as a hedge, or if a derivative ceases to be a highly effective hedge, we discontinue hedge accounting prospectively. The effective portion of changes in the fair value of derivatives are recorded in other comprehensive income, and reclassified into earnings in the same period during which the hedged transaction affects earnings. The ineffective portion is recorded in other income or expense.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
On May 28, 2014, the Financial Accounting Standards Board and the International Accounting Standards Board issued converged guidance on recognizing revenue in contracts with customers. The new guidance establishes a single core principle in the Accounting Standards Update ("ASU") No. 2014-09, which is the recognition of revenue to depict the transfer of promised goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the entity expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services. This guidance will affect any reporting organization that either enters into contracts with customers to transfer goods or services or enters into contracts for the transfer of non-financial assets. This ASU is effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those years, beginning on or after December 15, 2016, and early adoption is not permitted. The Company is continuing to evaluate the new guidance and plans to provide additional information about its expected financial impact at a future date.
On August 27, 2014, the Financial Accounting Standards Board issued ASU No. 2014-15. This standard provides guidance on determining when and how to disclose going-concern uncertainties in the financial statements. The new standard requires management to perform interim and annual assessments of an entity's ability to continue as a going concern within one year of the date the financial statements are issued. This ASU is effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those years, beginning on or after December 15, 2016, with early adoption permitted. The Company is evaluating the new guidance and plans to provide additional information about its expected impact at a future date.
2. LIQUIDITY
Our business requires significant capital investments over the short-term and the long-term. Recently, we have financed our capital requirements with borrowings under our Third Amended and Restated Credit Facility (“Credit Facility”), cash flows from operations, long-term operating leases, capital leases, secured installment notes with finance companies, proceeds from our follow-on stock offering, and proceeds from the sale of our used revenue equipment in 2014 and 2013. We had working capital (total current assets less total current liabilities) of $52.7 million and $14.1 million at December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively. Based on our expected financial condition, net capital expenditures, and results of operations and related net cash flows, we believe our working capital and sources of liquidity will be adequate to meet our current and projected needs for at least the next year.
We had no borrowings outstanding under the Credit Facility as of December 31, 2014, undrawn letters of credit outstanding of approximately $34.3 million, and available borrowing capacity of $60.7 million. We do not expect to experience material liquidity constraints in the foreseeable future or on a long-term basis, based on our anticipated financial condition, results of operations, cash flows, continued availability of our Credit Facility, secured installment notes, and other sources of financing that we expect will be available to us.
3. FAIR VALUE OF FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS
Fair value is defined as an exit price, representing the amount that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants. Accordingly, fair value is a market-based measurement that is determined based on assumptions that market participants would use in pricing an asset or liability. The fair value of the hedge derivative asset was determined based on quotes from the counterparty which were verified by comparing them to the exchange on which the related futures are traded, adjusted for counterparty credit risk. A three-tier fair value hierarchy is used to prioritize the inputs in measuring fair value as follows:
| ● | Level 1. Observable inputs such as quoted prices in active markets; |
| ● | Level 2. Inputs, other than the quoted prices in active markets, that are observable either directly or indirectly; and |
| ● | Level 3. Unobservable inputs in which there is little or no market data, which require the reporting entity to develop its own assumptions. |
Assets and Liabilities Measured at Fair Value on a Recurring Basis
| (in thousands) | | December 31, | |
Hedge derivative (liability) asset | | | | | | |
| Fair Value of Derivative | | $ | (22,720 | ) | | $ | 1,412 | |
| Quoted Prices in Active Markets (Level 1) | | | - | | | | - | |
| Significant Other Observable Inputs (Level 2) | | $ | (22,720 | ) | | $ | 1,412 | |
| Significant Unobservable Inputs (Level 3) | | | - | | | | - | |
| (1) | Excludes cash collateral of $5.0 million provided by the Company to the counterparty. |
4. STOCK-BASED COMPENSATION
On February 21, 2014, the Compensation Committee of our Board of Directors approved, subject to stockholder approval, a third amendment (the "Third Amendment") to the 2006 Omnibus Incentive Plan (the "Incentive Plan"). The Third Amendment (i) provides that the maximum aggregate number of shares of Class A common stock available for grant of awards under the Incentive Plan from and after May 29, 2014, shall not exceed 750,000, plus any remaining available shares of the 800,000 shares previously made available under the second amendment to the Incentive Plan (the "Second Amendment"), and any expirations, forfeitures, cancellations, or certain other terminations of shares approved for grant under the Third Amendment or the Second Amendment previously reserved, plus any remaining expirations, forfeitures, cancellations, or certain other terminations of such shares, and (ii) re-sets the term of the Incentive Plan to expire with respect to the ability to grant new awards on March 31, 2023. The Compensation Committee also re-approved, subject to stockholder re-approval, the material terms of the performance-based goals under the Incentive Plan so that certain incentive awards granted thereunder would continue to qualify as exempt "performance-based compensation" under Internal Revenue Code Section 162(m). The Company's stockholders approved the adoption of the Third Amendment and re-approved the material terms of the performance-based goals under the Incentive Plan at the Company's 2014 Annual Meeting held on May 29, 2014.
The Incentive Plan permits annual awards of shares of our Class A common stock to executives, other key employees, non-employee directors, and eligible participants under various types of options, restricted share awards, or other equity instruments. At December 31, 2014, 675,021 of the aforementioned 1,550,000 shares were available for award under the amended Incentive Plan. No participant in the Incentive Plan may receive awards of any type of equity instruments in any calendar-year that relates to more than 200,000 shares of our Class A common stock. No awards may be made under the Incentive Plan after March 31, 2023. To the extent available, we have issued treasury stock to satisfy all share-based incentive plans.
Included in salaries, wages, and related expenses within the consolidated statements of operations is stock-based compensation expense of $1.3 million, $0.3 million, and $1.2 million in 2014, 2013, and 2012, respectively. Included in general supplies and expenses within the consolidated statements of operations is stock-based compensation expenses for non-employee directors of $0.1 million in 2014, 2013, and 2012. All stock compensation expense recorded in 2014, 2013, and 2012 relates to restricted shares given no options were granted during these periods. Associated with stock compensation expense was $0.8 million income tax benefit, $0.1 million income tax deficit, and less than $0.1 million income tax benefit in 2014, 2013, and 2012, respectively, related to the exercise of stock options and restricted share vesting, resulting in related changes in taxable income and offsetting changes to additional paid in capital.
The Incentive Plan allows participants to pay the federal and state minimum statutory tax withholding requirements related to awards that vest or allows the participant to deliver to us shares of Class A common stock having a fair market value equal to the minimum amount of such required withholding taxes. To satisfy withholding requirements for shares that vested, certain participants elected to deliver to us 39,676, 53,188, and 1,940 Class A common stock shares, which were withheld at weighted average per share prices of $20.97, $6.41, and $4.60 based on the closing prices of our Class A common stock on the dates the shares vested in 2014, 2013, and 2012, respectively, in lieu of the federal and state minimum statutory tax withholding requirements. We remitted $0.8 million, $0.3 million, and less than $0.1 million in 2014, 2013, and 2012, respectively, to the proper taxing authorities in satisfaction of the employees' minimum statutory withholding requirements. The payment of minimum tax withholdings on stock compensation are reflected within the issuances of restricted shares from treasury stock in the accompanying consolidated statement of stockholders' equity.
The following table summarizes our restricted share award activity for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2014, 2013, and 2012:
| | | Number of stock awards (in thousands) | | | Weighted average grant date fair value | |
| | | | | | | |
| Unvested at December 31, 2011 | | | 468 | | | $ | 8.27 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Granted | | | 383 | | | $ | 4.48 | |
Vested | | | (40 | ) | | $ | 4.19 | |
Forfeited | | | (47 | ) | | $ | 7.64 | |
| Unvested at December 31, 2012 | | | 764 | | | $ | 6.62 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Granted | | | 263 | | | $ | 5.60 | |
Vested | | | (200 | ) | | $ | 8.12 | |
Forfeited | | | (50 | ) | | $ | 5.56 | |
| Unvested at December 31, 2013 | | | 777 | | | $ | 5.95 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
Granted | | | 136 | | | $ | 12.27 | |
Vested | | | (137 | ) | | $ | 7.43 | |
Forfeited | | | (134 | ) | | $ | 7.80 | |
| Unvested at December 31, 2014 | | | 642 | | | $ | 6.60 | |
The unvested shares at December 31, 2014 will vest based on when and if the related vesting criteria are met for each award. All awards require continued service to vest, noting that 276,321 of these awards vest solely based on continued service, which vest in varying increments between 2015 and 2017. Performance based awards account for 366,117 of the unvested shares at December 31, 2014, of which 256,684 shares have no unrecognized compensation cost as they relate to performance for the year ended December 31, 2014 and 32,463 shares relate to performance for the year ended December 31, 2016 and accordingly have no unrecognized compensation cost as they have not yet been evaluated for likelihood of vesting for purposes of compensation cost recognition.
The fair value of restricted share awards that vested in 2014, 2013, and 2012 was approximately $2.9 million, $1.2 million, and $0.1 million, respectively. As of December 31, 2014, we had approximately $1.6 million of unrecognized compensation expense related to 276,321 service-based and 76,970 2015 performance-based restricted share awards, which is probable to be recognized over a weighted average period of approximately 20 months. All restricted shares awarded to executives and other key employees pursuant to the Incentive Plan have voting and other stockholder-type rights, but will not be issued until the relevant restrictions are satisfied.
The following table summarizes our stock option activity for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2014, 2013, and 2012:
| | | Number of options (in thousands) | | | Weighted average exercise price | | Weighted average remaining contractual term | | Aggregate intrinsic value (in thousands) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| Outstanding at December 31, 2011 | | | 437 | | | $ | 14.66 | | 2.1 years | | $ | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Options granted | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | |
| Options exercised | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | |
| Options forfeited | | | (104 | ) | | $ | 12.27 | | | | | | |
| Outstanding at December 31, 2012 | | | 333 | | | $ | 15.67 | | 1.5 years | | $ | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Options granted | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | |
| Options exercised | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | |
| Options forfeited | | | (112 | ) | | $ | 17.14 | | | | | | |
| Outstanding at December 31, 2013 | | | 221 | | | $ | 14.98 | | 1.0 years | | $ | - | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Options granted | | | - | | | | - | | | | | | |
| Options exercised | | | (45 | ) | | $ | 13.64 | | | | | | |
| Options forfeited | | | (100 | ) | | $ | 21.71 | | | | | | |
| Outstanding at December 31, 2014 | | | 76 | | | $ | 14.73 | | 0.5 years | | $ | 945 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Exercisable at December 31, 2014 | | | 76 | | | $ | 14.73 | | 0.5 years | | $ | 945 | |
5. PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT
A summary of property and equipment, at cost, as of December 31, 2014 and 2013 is as follows:
| (in thousands) | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenue equipment | | 3-10 years | | | $ | 418,574 | | | $ | 372,968 | |
| Communications equipment | | 5-10 years | | | | 8,248 | | | | 9,084 | |
| Land and improvements | | 0-10 years | | | | 18,820 | | | | 19,009 | |
| Buildings and leasehold improvements | | 7-40 years | | | | 37,217 | | | | 41,876 | |
| Construction in-progress | | | - | | | | 2,976 | | | | 1,859 | |
| Other | | 2-7 years | | | | 19,510 | | | | 17,580 | |
| | | | | | | $ | 505,345 | | | $ | 462,376 | |
Depreciation expense was $49.0 million, $44.2 million, and $47.8 million, in 2014, 2013, and 2012, respectively. The aforementioned depreciation expense excludes net gains on the sale of property and equipment totaling $2.7 million, $0.8 million, and $4.9 million in 2014, 2013, and 2012, respectively, which are presented net in depreciation and amortization expense in the consolidated statements of operations.
We lease certain revenue equipment under capital leases with terms of 60 to 84 months. At December 31, 2014 and 2013, property and equipment included capitalized leases, which had capitalized costs of $33.8 million and $29.4 million and accumulated amortization of $10.6 million and $7.6 million, respectively. Amortization of these leased assets is included in depreciation and amortization expense in the consolidated statement of operations and totaled $3.0 million, $2.2 million, and $2.1 million during 2014, 2013, and 2012, respectively.
6. GOODWILL AND OTHER ASSETS
We have no goodwill on our consolidated balance sheet.
A summary of other assets as of December 31, 2014 and 2013 is as follows:
| (in thousands) | | | | | | |
| Customer relationships | | | 3,490 | | | | 3,490 | |
| Less: accumulated amortization of intangibles | | | (3,255 | ) | | | (3,164 | ) |
Net intangible assets | | | 235 | | | | 326 | |
| Investment in TEL | | | 12,192 | | | | 8,737 | |
| Other long-term receivables | | | 575 | | | | 631 | |
| Deposits | | | 546 | | | | 732 | |
| Deferred loan costs, net | | | 724 | | | | 931 | |
| Hedge derivative asset | | | - | | | | 1,412 | |
| Other, net | | | 491 | | | | 595 | |
| | | $ | 14,763 | | | $ | 13,364 | |
Amortization expenses of intangible assets were $0.1 million, $0.2 million, and $0.3 million for 2014, 2013, and 2012, respectively. Approximate intangible amortization expense for the next five years is as follows:
| | | (In thousands) | |
| 2015 | | $ | 66 | |
| 2016 | | | 48 | |
| 2017 | | | 35 | |
| 2018 | | | 25 | |
| 2019 | | | 18 | |
| Thereafter | | $ | 43 | |
7. DEBT
Current and long-term debt consisted of the following at December 31, 2014 and 2013:
| (in thousands) | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Borrowings under Credit Facility | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | - | | | $ | 7,010 | |
| Revenue equipment installment notes; weighted average interest rate of 3.8% at December 31, 2014, and 4.7% December 31, 2013, due in monthly installments with final maturities at various dates ranging from January 2015 to January 2022, secured by related revenue equipment | | | 27,550 | | | | 155,832 | | | | 43,745 | | | | 158,596 | |
| Real estate note; interest rate of 2.5% and 2.4% at December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively, due in monthly installments with fixed maturity at December 2018, secured by related real-estate | | | 166 | | | | 3,608 | | | | 217 | | | | 3,693 | |
| Other note payable, interest rate of 3.0% at December 31, 2014 and 2013, with fixed maturity at November 2016 | | | 108 | | | | 91 | | | | 108 | | | | 192 | |
| Total debt | | | 27,824 | | | | 159,531 | | | | 44,070 | | | | 169,491 | |
| Principal portion of capital lease obligations, secured by related revenue equipment | | | 1,606 | | | | 13,372 | | | | 8,732 | | | | 13,186 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total debt and capital lease obligations | | $ | 29,430 | | | $ | 172,903 | | | $ | 52,802 | | | $ | 182,677 | |
In September 2008, we and substantially all of our subsidiaries (collectively, the "Borrowers") entered into a Third Amended and Restated Credit Facility with Bank of America, N.A., as agent (the "Agent") and JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A. ("JPM," and together with the Agent, the "Lenders").
The Credit Facility was originally structured as an $85.0 million revolving credit facility, with an accordion feature that, so long as no event of default exists, allows us to request an increase in the revolving credit facility of up to $50.0 million. The Credit Facility includes, within our $85.0 million revolving credit facility, a letter of credit sub facility in an aggregate amount of $85.0 million and a swing line sub facility in an aggregate amount equal to the greater of $10.0 million or 10% of the Lenders' aggregate commitments under the Credit Facility from time-to-time.
In January 2013, we entered into an eighth amendment, which was effective December 31, 2012, to the Credit Facility which, among other things, (i) increased the revolver commitment to $95.0 million, (ii) extended the maturity date from September 2014 to September 2017, (iii) eliminated the availability block of $15.0 million, (iv) improved pricing for revolving borrowings by amending the applicable margin as set forth below (beginning January 1, 2013), (v) improved the unused line fee pricing to 0.375% per annum when availability is less than $50.0 million and 0.5% per annum when availability is at or over such amount (beginning January 1, 2013), (vi) provided that the fixed charge coverage ratio covenant will be tested only during periods that commence when availability is less than or equal to the greater of 12.5% of the revolver commitment or $11.9 million, (vii) eliminated the consolidated leverage ratio covenant, (viii) reduced the level of availability below which cash dominion applies to the greater of 15% of the revolver commitment or $14.3 million, (ix) added deemed amortization of real estate and eligible revenue equipment included in the borrowing base to the calculation of fixed charge coverage ratio, (x) amended certain types of permitted debt to afford additional flexibility, and (xi) allowed for stock repurchases in an aggregate amount not exceeding $5.0 million, and (xii) removed certain restrictions relating to the purchase of up to the remaining 51% equity interest in TEL, provided that certain conditions are met. In exchange for these amendments, the Borrowers agreed to pay fees of $0.3 million. Based on availability as of December 31, 2014, there was no fixed charge coverage requirement
In August 2014, we obtained a ninth amendment to the Credit Facility, which allows for the disposition of certain parcels of real property and the acquisition of other real property. Additionally, in September 2014, we obtained a tenth amendment to the Credit Facility, which, among other things, amended certain provisions of the Credit Facility and related security documents to facilitate the Borrowers' entry into fuel hedging arrangements.
Borrowings under the Credit Facility are classified as either "base rate loans" or "LIBOR loans." Base rate loans accrue interest at a base rate equal to the greater of the Agent's prime rate, the federal funds rate plus 0.5%, or LIBOR plus 1.0%, plus an applicable margin ranging from 0.5% to 1.25%; while LIBOR loans accrue interest at LIBOR, plus an applicable margin ranging from 1.5% to 2.25%. The applicable rates are adjusted quarterly based on average pricing availability. The unused line fee is also adjusted quarterly between 0.375% and 0.5% based on the average daily amount by which the Lenders' aggregate revolving commitments under the Credit Facility exceed the outstanding principal amount of revolver loans and the aggregate undrawn amount of all outstanding letters of credit issued under the Credit Facility. The obligations under the Credit Facility are guaranteed by us and secured by a pledge of substantially all of our assets, with the notable exclusion of any real estate or revenue equipment pledged under other financing agreements, including revenue equipment installment notes and capital leases.
Borrowings under the Credit Facility are subject to a borrowing base limited to the lesser of (A) $95.0 million, minus the sum of the stated amount of all outstanding letters of credit; or (B) the sum of (i) 85% of eligible accounts receivable, plus (ii) the lesser of (a) 85% of the appraised net orderly liquidation value of eligible revenue equipment, (b) 95% of the net book value of eligible revenue equipment, or (c) 35% of the Lenders' aggregate revolving commitments under the Credit Facility, plus (iii) the lesser of (a) $25.0 million or (b) 65% of the appraised fair market value of eligible real estate. We had no borrowings outstanding under the Credit Facility as of December 31, 2014, undrawn letters of credit outstanding of approximately $34.3 million, and available borrowing capacity of $60.7 million.
The Credit Facility includes usual and customary events of default for a facility of this nature and provides that, upon the occurrence and continuation of an event of default, payment of all amounts payable under the Credit Facility may be accelerated, and the Lenders' commitments may be terminated. If an event of default occurs under the Credit Facility and the Lenders cause all of the outstanding debt obligations under the Credit Facility to become due and payable, this could result in a default under other debt instruments that contain acceleration or cross-default provisions. The Credit Facility contains certain restrictions and covenants relating to, among other things, debt, dividends, liens, acquisitions and dispositions outside of the ordinary course of business, and affiliate transactions. Failure to comply with the covenants and restrictions set forth in the Credit Facility could result in an event of default.
Capital lease obligations are utilized to finance a portion of our revenue equipment and are entered into with certain finance companies who are not parties to our Credit Facility. The leases in effect at December 31, 2014 terminate in January 2015 through December 2021 and contain guarantees of the residual value of the related equipment by us. As such, the residual guarantees are included in the related debt balance as a balloon payment at the end of the related term as well as included in the future minimum capital lease payments. These lease agreements require us to pay personal property taxes, maintenance, and operating expenses.
Pricing for the revenue equipment installment notes is quoted by the respective financial affiliates of our primary revenue equipment suppliers and other lenders at the funding of each group of equipment acquired and include fixed annual rates for new equipment under retail installment contracts. The notes included in the funding are due in monthly installments with final maturities at various dates ranging from January 2015 to January 2022. The notes contain certain requirements regarding payment, insuring of collateral, and other matters, but do not have any financial or other material covenants or events of default except certain notes totaling $174.6 million are cross-defaulted with the Credit Facility. Additionally, a portion of the abovementioned fuel hedge contracts totaling $12.8 million at December 31, 2014, is cross-defaulted with the Credit Facility. Additional borrowings from the financial affiliates of our primary revenue equipment suppliers and other lenders are available to fund most new tractors expected to be delivered in 2015, while any other property and equipment purchases, including trailers, will be funded with a combination of available cash, notes, operating leases, capital leases, and/or from the Credit Facility.
As of December 31, 2014, the scheduled principal payments of debt, excluding capital leases for which future payments are discussed in Note 8 are as follows:
| | | | |
| 2015 | | $ | 27,824 | |
| 2016 | | | 34,331 | |
| 2017 | | | 38,544 | |
| 2018 | | | 53,478 | |
| 2019 | | | 25,659 | |
| Thereafter | | $ | 7,519 | |
8. LEASES
We have operating lease commitments for office and terminal properties, revenue equipment, and computer and office equipment and capital lease commitments for revenue equipment, exclusive of owner/operator rentals and month-to-month equipment rentals, summarized for the following fiscal years (in thousands):
| | | | | | | |
| 2015 | | $ | 13,589 | | | $ | 2,096 | |
| 2016 | | | 11,927 | | | | 4,336 | |
| 2017 | | | 8,487 | | | | 1,507 | |
| 2018 | | | 5,599 | | | | 1,507 | |
| 2019 | | | 3,737 | | | | 1,507 | |
| Thereafter | | | 18,142 | | | | 5,963 | |
| Total minimum lease payments | | $ | 61,481 | | | $ | 16,916 | |
| Less: amount representing interest | | | | | | | (1,938 | ) |
| Present value of minimum lease payments | | | | | | | 14,978 | |
| Less: current portion | | | | | | | (1,606 | ) |
| Capital lease obligations, long-term | | | | | | $ | 13,372 | |
A portion of our operating leases of tractors and trailers contain residual value guarantees under which we guarantee a certain minimum cash value payment to the leasing company at the expiration of the lease. We estimate that the undiscounted value of the residual guarantees is approximately $4.0 million and $9.9 million at December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively. The residual guarantees at December 31, 2014 expire between August 2018 and February 2019. We expect our residual guarantees to approximate the market value at the end of the lease term. Additionally, certain leases contain cross-default provisions with other financing agreements and additional charges if the unit's mileage exceeds certain thresholds defined in the lease agreement.
Rental expense is summarized as follows for each of the three years ended December 31:
| (in thousands) | | 2014 | | | 2013 | | | 2012 | |
| Revenue equipment rentals | | $ | 20,935 | | | $ | 22,991 | | | $ | 19,746 | |
| Building and lot rentals | | | 3,561 | | | | 4,044 | | | | 3,714 | |
| Other equipment rentals | | | 317 | | | | 362 | | | | 679 | |
| | | $ | 24,813 | | | $ | 27,397 | | | $ | 24,139 | |
9. INCOME TAXES
Income tax expense (benefit) for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013, and 2012 is comprised of:
| (in thousands) | | | | | | | | | |
| Federal, current | | $ | (94 | ) | | $ | (816 | ) | | $ | (707 | ) |
| Federal, deferred | | | 12,830 | | | | 7,560 | | | | 6,897 | |
| State, current | | | 187 | | | | 102 | | | | 307 | |
| State, deferred | | | 1,851 | | | | 657 | | | | (162 | ) |
| | | $ | 14,774 | | | $ | 7,503 | | | $ | 6,335 | |
Income tax expense for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013, and 2012 is summarized below:
| (in thousands) | | | | | | | | | |
| Computed "expected" income tax expense | | $ | 11,404 | | | $ | 4,462 | | | $ | 4,340 | |
| State income taxes, net of federal income tax effect | | | 1,075 | | | | 421 | | | | 409 | |
| Per diem allowances | | | 2,304 | | | | 2,422 | | | | 2,550 | |
| Tax contingency accruals | | | (104 | ) | | | (496 | ) | | | (444 | ) |
| Valuation allowance (release), net | | | 18 | | | | 684 | | | | (251 | ) |
| Tax credits | | | (112 | ) | | | (250 | ) | | | (407 | ) |
| Other, net | | | 189 | | | | 260 | | | | 138 | |
| Actual income tax expense | | $ | 14,774 | | | $ | 7,503 | | | $ | 6,335 | |
Income tax expense varies from the amount computed by applying the federal corporate income tax rate of 35% to income before income taxes primarily due to state income taxes, net of federal income tax effect, adjusted for permanent differences, the most significant of which is the effect of the per diem pay structure for drivers. Drivers who meet the requirements to receive per diem receive non-taxable per diem pay in lieu of a portion of their taxable wages. This per diem program increases our drivers' net pay per mile, after taxes, while decreasing gross pay, before taxes. As a result, salaries, wages, and employee benefits are slightly lower and our effective income tax rate is higher than the statutory rate. Generally, as pre-tax income increases, the impact of the driver per diem program on our effective tax rate decreases, because aggregate per diem pay becomes smaller in relation to pre-tax income, while in periods where earnings are at or near breakeven, the impact of the per diem program on our effective tax rate is significant. Due to the partially nondeductible effect of per diem pay, our tax rate will fluctuate in future periods based on fluctuations in earnings.
The temporary differences and the approximate tax effects that give rise to our net deferred tax liability at December 31, 2014 and 2013 are as follows:
| (in thousands) | | 2014 | | | 2013 | |
| Deferred tax assets: | | | | | | |
Insurance and claims | | $ | 16,153 | | | $ | 11,691 | |
Net operating loss carryovers | | | 18,160 | | | | 13,681 | |
Other | | | 7,750 | | | | 6,035 | |
Deferred fuel hedge | | | 8,144 | | | | - | |
Valuation allowance | | | (1,001 | ) | | | (983 | ) |
| Total deferred tax assets | | | 49,206 | | | | 30,424 | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Deferred tax liabilities: | | | | | | | | |
Property and equipment | | | (103,186 | ) | | | (76,280 | ) |
Other | | | (2,186 | ) | | | (4,793 | ) |
Prepaid expenses | | | (2,838 | ) | | | (3,194 | ) |
| Total net deferred tax liabilities | | | (108,210 | ) | | | (84,267 | ) |
| | | | | | | | | |
| Net deferred tax liability | | $ | (59,004 | ) | | $ | (53,843 | ) |
Deferred taxes are classified in the accompanying consolidated balance sheet based on the nature of the related asset or liability as current or long-term, such that current deferred tax assets and liabilities provide a net asset of $14.7 million, while long-term deferred tax assets and liabilities provide a net liability of $73.7 million. The net deferred tax liability of $59.0 million primarily relates to differences in cumulative book versus tax depreciation of property and equipment, partially off-set by net operating loss carryovers and insurance claims that have been reserved but not paid. The carrying value of our deferred tax assets assumes that we will be able to generate, based on certain estimates and assumptions, sufficient future taxable income in certain tax jurisdictions to utilize these deferred tax benefits. If these estimates and related assumptions change in the future, we may be required to establish a valuation allowance against the carrying value of the deferred tax assets, which would result in additional income tax expense. On a periodic basis, we assess the need for adjustment of the valuation allowance. Based on forecasted taxable income resulting from the reversal of deferred tax liabilities, primarily generated by accelerated depreciation for tax purposes in prior periods, and tax planning strategies available to us, no valuation allowance has been established at December 31, 2014 or 2013, except for $1.0 million, for each year, related to certain state net operating loss and capital loss carry-forwards. If these estimates and related assumptions change in the future, we may be required to modify our valuation allowance against the carrying value of the deferred tax assets.
The activity in the valuation allowance on deferred tax assets (in thousands) is as follows:
Years ended December 31: | | Beginning balance January 1, | | | Additional provisions to allowance | | | Write-offs and other deductions | | | Ending balance December 31, | |
| 2014 | | $ | 983 | | | $ | 401 | | | $ | (383 | ) | | $ | 1,001 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| 2013 | | $ | 299 | | | $ | 684 | | | $ | - | | | $ | 983 | |
As of December 31, 2014, we had a $1.6 million liability recorded for unrecognized tax benefits, which includes interest and penalties of $0.7 million. We recognize interest and penalties accrued related to unrecognized tax benefits in tax expense. As of December 31, 2013, we had a $1.8 million liability recorded for unrecognized tax benefits, which included interest and penalties of $0.8 million. Interest and penalties recognized for uncertain tax positions provided for a $0.1 million benefit in 2014, and a $0.3 million benefit in each of 2013 and 2012.
The following tables summarize the annual activity related to our gross unrecognized tax benefits (in thousands) for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013, and 2012:
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Balance as of January 1, | | $ | 1,060 | | | $ | 1,563 | | | $ | 1,979 | |
Increases related to prior year tax positions | | | 246 | | | | - | | | | - | |
Decreases related to prior year positions | | | - | | | | - | | | | - | |
Increases related to current year tax positions | | | 42 | | | | 24 | | | | 2 | |
Decreases related to settlements with taxing authorities | | | (126 | ) | | | - | | | | - | |
Decreases related to lapsing of statute of limitations | | | (227 | ) | | | (527 | ) | | | (418 | ) |
| Balance as of December 31, | | $ | 995 | | | $ | 1,060 | | | $ | 1,563 | |
If recognized, $1.1 million and $1.2 million of unrecognized tax benefits would impact our effective tax rate as of December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively. Any prospective adjustments to our reserves for income taxes will be recorded as an increase or decrease to our provision for income taxes and would impact our effective tax rate.
Our 2011 through 2014 tax years remain subject to examination by the IRS for U.S. federal tax purposes, our major taxing jurisdiction. In the normal course of business, we are also subject to audits by state and local tax authorities. While it is often difficult to predict the final outcome or the timing of resolution of any particular tax matter, we believe that our reserves reflect the more likely than not outcome of known tax contingencies. We adjust these reserves, as well as the related interest, in light of changing facts and circumstances. Settlement of any particular issue would usually require the use of cash. Favorable resolution would be recognized as a reduction to our annual tax rate in the year of resolution. We do not expect any significant increases or decreases for uncertain income tax positions during the next year.
Our federal net operating loss carryforwards are available to offset future federal taxable income, if any, through 2030, while our state net operating loss carryforwards and state tax credits expire over various periods through 2032 based on jurisdiction.
10. EQUITY METHOD INVESTMENT
In May 2011, we acquired a 49.0% interest in TEL for $1.5 million in cash. Additionally, TEL's majority owners were eligible to receive an earn-out of up to $4.5 million for TEL's results through December 31, 2012, of which $1.0 million was earned based on TEL's 2011 results and $2.4 million was earned based on TEL's 2012 results. The earn-out payments increased our investment balance and there are no additional earn-outs payable for future results.
TEL is a tractor and trailer equipment leasing company and used equipment reseller. We have not guaranteed any of TEL's debt and have no obligation to provide funding, services, or assets. Under the agreement, we have an option to acquire 100% of TEL until May 31, 2016, by purchasing the majority owners' interest based on a multiple of TEL's average earnings before interest and taxes, adjusted for certain items including cash and debt balances as of the acquisition date. Subsequent to May 31, 2016, TEL's majority owners have the option to acquire our interest based on the same terms detailed above. For the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, we sold tractors and trailers to TEL for $14.0 million and $16.0 million, respectively, and received $2.7 million and $2.4 million, respectively, for providing various maintenance services, certain back-office functions, and for miscellaneous equipment. We reversed previously deferred gains totaling less than $0.1 million and deferred gains of $0.1 million for the years ending December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively, representing 49% of the gains on units sold to TEL less any gains previously deferred and recognized when the equipment was sold to a third party. Deferred gains totaling $0.8 million at December 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013, respectively, are being carried as a reduction in our investment in TEL. We had a receivable from TEL for 2014 and 2013 of $2.2 million and $1.9 million, respectively, related to cash disbursements made pursuant to our performance of certain back-office and maintenance functions on TEL's behalf.
We have accounted for our investment in TEL using the equity method of accounting and thus our financial results include our proportionate share of TEL's net income, or $3.7 million in 2014, $2.8 million in 2013, and $1.9 million in 2012. We received an equity distribution from TEL for $0.3 million in 2014, less than $0.1 million in 2013, and $0.3 million in 2012, which was distributed to each member based on its respective ownership percentage in order to satisfy estimated tax payments resulting from TEL's earnings. The distribution is the result of TEL being a limited liability company and thus its earnings are attributed to its members for tax purposes and are taxed for federal and certain state income on the members' respective tax returns. Our investment in TEL, totaling $12.2 million and $8.7 million at December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively, is included in other assets in the accompanying consolidated balance sheet. Our investment in TEL is comprised of the $4.9 million cash investment noted above and our equity in TEL's earnings since our investment, partially offset by dividends received since our investment for minimum tax withholdings as noted above and the abovementioned deferred gains on sales of equipment to TEL.
See TEL's summarized financial information subsequent to our investment below.
| (in thousands) | | As of the years ended December 31, | |
| | | | | | | |
| Current Assets | | $ | 14,525 | | | $ | 9,160 | |
| Non-current Assets | | | 64,731 | | | | 40,296 | |
| Current Liabilities | | | 16,733 | | | | 13,456 | |
| Non-current Liabilities | | | 45,687 | | | | 26,101 | |
| Total Equity | | $ | 16,836 | | | $ | 9,899 | |
| (in thousands) | | As of the years ended December 31, | |
| | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenue | | $ | 90,197 | | | $ | 58,484 | | | $ | 53,459 | |
| Operating Expenses | | | 79,771 | | | | 50,878 | | | | 48,382 | |
| Operating Income | | | 10,426 | | | | 7,606 | | | | 5,077 | |
| Net Income | | $ | 7,564 | | | $ | 5,643 | | | $ | 3,850 | |
11. DEFERRED PROFIT SHARING EMPLOYEE BENEFIT PLAN
We have a deferred profit sharing and savings plan under which all of our employees with at least six months of service are eligible to participate. Employees may contribute a percentage of their annual compensation up to the maximum amount allowed by the Internal Revenue Code. We may make discretionary contributions as determined by a committee of our Board of Directors. We made no contributions in 2014, 2013, and 2012 to the profit sharing and savings plan. The Board approved the suspension of employee matching "discretionary" contributions to be made beginning early in 2009 for an indefinite time period, noting that the match was reinstated effective January 2015.
12. RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
See Note 10 for discussions of the related party transactions associated with TEL.
13. DERIVATIVE INSTRUMENTS
We engage in activities that expose us to market risks, including the effects of changes in fuel prices. Financial exposures are evaluated as an integral part of our risk management program, which seeks, from time-to-time, to reduce the potentially adverse effects that the volatility of fuel markets may have on operating results. In an effort to seek to reduce the variability of the ultimate cash flows associated with fluctuations in diesel fuel prices, we periodically enter into various derivative instruments, including forward futures swap contracts (which we refer to as "fuel hedge contracts"). Historically diesel fuel has not been a traded commodity on the futures market so heating oil has been used as a substitute, as prices for both generally move in similar directions. Recently, however, we have been able to enter into hedging contracts with respect to both heating oil and ultra low sulfur diesel ("ULSD"). Under these contracts, we pay a fixed rate per gallon of heating oil or ULSD and receive the monthly average price of New York heating oil per the New York Mercantile Exchange ("NYMEX") and Gulf Coast ULSD, respectively. The retrospective and prospective regression analyses provided that changes in the prices of diesel fuel and heating oil and diesel fuel and ULSD were each deemed to be highly effective based on the relevant authoritative guidance except for a small portion of our hedge contracts, which we determined to be ineffective on a prospective basis. Consequently, we recognized approximately $1.4 million of additional fuel expense in 2014 to mark the related liability to market. We do not engage in speculative transactions, nor do we hold or issue financial instruments for trading purposes.
We recognize all derivative instruments at fair value on our consolidated balance sheets. Our derivative instruments are designated as cash flow hedges, thus the effective portion of the gain or loss on the derivatives is reported as a component of accumulated other comprehensive (loss) income and will be reclassified into earnings in the same period during which the hedged transaction affects earnings. The effective portion of the derivative represents the change in fair value of the hedge that offsets the change in fair value of the hedged item. To the extent the change in the fair value of the hedge does not perfectly offset the change in the fair value of the hedged item, the ineffective portion of the hedge is immediately recognized in our consolidated statements of operations. Ineffectiveness is calculated using the cumulative dollar offset method as an estimate of the difference in the expected cash flows of the respective fuel hedge contracts (heating oil or ULSD) compared to the changes in the all-in cash outflows required for the diesel fuel purchases.
At December 31, 2014, we had forward futures swap contracts on approximately 12.6 million, 12.1 million, and 3.0 million gallons of diesel to be purchased in 2015, 2016, and 2017, respectively, or approximately 23%, 22%, and 5% of our projected annual 2015, 2016, and 2017 fuel requirements, respectively.
The fair value of the contracts that were in effect at December 31, 2014 and 2013, of approximately $22.7 million and $1.4 million, respectively, are included in other liabilities and other assets, respectively, in the consolidated balance sheet, are included in accumulated other comprehensive (loss) income, net of tax. Changes in the fair values of these instruments can vary dramatically based on changes in the underlying commodity prices, as has been evident in the second half of 2014. For example, during 2014, market "spot" prices for ultra-low sulfur diesel peaked at a high of approximately $3.08 per gallon and hit a low price of approximately $1.58 per gallon. During 2013, market spot prices ranged from a high of $3.29 per gallon to a low of $2.72 per gallon. Market price changes can be driven by factors such as supply and demand, inventory levels, weather events, refinery capacity, political agendas, the value of the U.S. dollar, geopolitical events, and general economic conditions, among other items.
Additionally, $3.1 million, $0.6 million, and $5.0 million were reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive (loss) income to our results from operations for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013, and 2012, respectively, related to 2014 losses and 2013 and 2012 gains. Of the $3.1 million reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive loss for the year ended December 31, 2014, $1.5 million related to losses on contracts that expired or were sold and for which we completed the forecasted transaction by purchasing the hedged diesel fuel, $1.4 million and approximately $0.2 million were recorded as additional fuel expense related to contracts for which the hedging relationship was no longer deemed to be effective on a prospective basis and unfavorable ineffectiveness on the contracts that existed at December 31, 2014, respectively. The ineffectiveness was calculated using the cumulative dollar offset method as an estimate of the difference in the expected cash flows of the respective fuel hedge contracts compared to the changes in the all-in cash outflows required for the diesel fuel purchases. The calculation of ineffectiveness excludes approximately $0.1 million from the assessment of hedge ineffectiveness as a result of the related contracts being in an under-hedged position as of the date of the calculation.
Based on the amounts in accumulated other comprehensive loss as of December 31, 2014 and the expected timing of the purchases of the diesel hedged, we expect to reclassify approximately $8.0 million, net of tax, on derivative instruments from accumulated other comprehensive loss into our results from operations during the next year due to the actual diesel fuel purchases. The amounts actually realized will be dependent on the fair values as of the date of settlement.
We perform both a prospective and retrospective assessment of the effectiveness of our hedge contracts at inception and quarterly, including assessing the possibility of counterparty default. If we determine that a derivative is no longer expected to be highly effective, we discontinue hedge accounting prospectively and recognize subsequent changes in the fair value of the hedge in earnings. As a result of our effectiveness assessment at inception, quarterly, and at December 31, 2014 and 2013, we believe our hedge contracts have been and will continue to be highly effective in offsetting changes in cash flows attributable to the hedged risk, with the exception of the abovementioned contracts.
Outstanding financial derivative instruments expose us to credit loss in the event of nonperformance by the counterparties to the agreements. We do not expect any of the counterparties to fail to meet their obligations. Our credit exposure related to these financial instruments is represented by the fair value of contracts reported as assets. To manage credit risk, we review each counterparty's audited financial statements and credit ratings and obtain references.
If our fuel derivative instruments are in a net liability position with the counterparty and cash collateral is required, the cash collateral amounts provided are netted against the fair value of current outstanding derivative instruments. At December 31, 2014, and December 31, 2013, $5.0 million and $0.0 cash collateral deposits, respectively, were provided by us in connection with our outstanding fuel derivative instruments.
14. ACCUMULATED OTHER COMPREHENSIVE (LOSS) INCOME
Accumulated other comprehensive (loss) income ("AOCI") is comprised of net income and other adjustments, including changes in the fair value of certain derivative financial instruments qualifying as cash flow hedges.
The following tables summarize the change in the components of our AOCI balance for the periods presented (in thousands; presented net of tax):
| Details about AOCI Components | | Amount Reclassified from AOCI for the years ended December 31, | | Affected Line Item in the Statement of Operations | |
| | | 2014 | | | 2013 | | | 2012 | | |
| (Losses) gains on cash flow hedges | | | | | | | | | | |
| Commodity derivative contracts | | $ | (3,141 | ) | | $ | 643 | | | $ | 5,031 | | Fuel expense |
| | | | 1,206 | | | | (247 | ) | | | (1,932 | ) | Income tax expense |
| | | $ | (1,935 | ) | | $ | 396 | | | $ | 3,099 | | Net of tax |
15. COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENT LIABILITIES
From time-to-time, we are a party to ordinary, routine litigation arising in the ordinary course of business, most of which involves claims for personal injury and property damage incurred in connection with the transportation of freight. We maintain insurance to cover liabilities arising from the transportation of freight for amounts in excess of certain self-insured retentions. In management's opinion, our potential exposure under pending legal proceedings is adequately provided for in the accompanying consolidated financial statements.
On August 26, 2014, the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of Ohio issued a pre-trial decision in a lawsuit against SRT relating to a cargo claim incurred in 2008. The court awarded the plaintiff approximately $5.9 million plus prejudgment interest and costs and denied a cross-motion for summary judgment by SRT. Previously, the court had ruled in favor of SRT on all but one count before overturning its earlier decision and ruling in favor of the plaintiff. SRT filed a Notice of Appeal with the U.S. Sixth Circuit Court of Appeals on September 24, 2014 and that appeal is currently being briefed by the parties with oral arguments to be scheduled in the months ahead. As a result of this decision and pending final outcome of the appeal, we increased the reserve for this claim by approximately $7.5 million to approximately $8.1 million during the third quarter of 2014.
We had $34.3 million and $39.0 million of outstanding and undrawn letters of credit as of December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively. The letters of credit are maintained primarily to support our insurance programs.
Effective April 2013, we entered into an auto liability policy with a three-year term. The policy retains the $1.0 million per claim limit for the primary excess layer of our auto liability program, with no changes to the excess policies. Similar to the prior policy, the current policy contains a commutation option; however, this option is only available after the completion of the three-year policy term, unless both we and the insurance carrier agree to a commutation prior to the end of the policy term.
We had commitments outstanding at December 31, 2014, to acquire revenue equipment totaling approximately $116.8 million in 2014 versus commitments at December 31, 2013 of approximately $0.2 million. These commitments are cancelable, subject to certain adjustments in the underlying obligations and benefits. These purchase commitments are expected to be financed by operating leases, capital leases, long-term debt, proceeds from sales of existing equipment, and/or cash flows from operations.
See "Critical Accounting Policies And Estimates – Insurance and Other Claims" under Item 7 of Part II of this Annual Report on Form 10-K for additional information.
16. SEGMENT INFORMATION
As previously discussed, we have one reportable segment, our asset-based truckload services or Truckload. Our other operations consist of several operating segments, which neither individually nor in the aggregate meet the quantitative or qualitative reporting thresholds. As a result, these operations are grouped in "Other" in the tables below.
The accounting policies of the segments are the same as those described in the summary of significant accounting policies. Substantially all intersegment sales prices are market based. We evaluate performance based on operating income of the respective business units.
"Unallocated Corporate Overhead" includes expenses that are incidental to our activities and are not specifically allocated to one of the segments.
The following tables summarize our segment information:
Year Ended December 31, 2014 | | | | | | | | Unallocated Corporate Overhead | | | | |
| Revenue | | $ | 663,001 | | | $ | 59,796 | | | $ | - | | | $ | 722,797 | |
| Intersegment revenue | | | - | | | | (3,817 | ) | | | - | | | | (3,817 | ) |
| Operating income (loss) | | | 54,151 | | | | 3,894 | | | | (18,399 | ) | | | 39,646 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | | 45,669 | | | | 59 | | | | 656 | | | | 46,384 | |
| Total assets | | | 463,900 | | | | 27,338 | | | | 62,779 | | | | 554,017 | |
| Capital expenditures (proceeds), net (1) | | | 87,871 | | | | 14 | | | | 1,570 | | | | 89,455 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Year Ended December 31, 2013 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenue | | $ | 644,403 | | | $ | 51,702 | | | $ | - | | | $ | 690,327 | |
| Intersegment revenue | | | - | | | | (5,778 | ) | | | - | | | | (5,778 | ) |
| Operating income (loss) | | | 27,746 | | | | 1,271 | | | | (8,623 | ) | | | 20,394 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | | 42,848 | | | | 72 | | | | 775 | | | | 43,694 | |
| Total assets | | | 402,637 | | | | 20,883 | | | | 42,902 | | | | 466,422 | |
| Capital expenditures (proceeds), net (1) | | | 90,336 | | | | 10 | | | | 1,630 | | | | 91,976 | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Year Ended December 31, 2012 | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Revenue | | $ | 647,986 | | | $ | 33,250 | | | $ | - | | | $ | 681,236 | |
| Intersegment revenue | | | - | | | | (6,982 | ) | | | - | | | | (6,982 | ) |
| Operating income (loss) | | | 34,185 | | | | (741 | ) | | | (10,235 | ) | | | 23,209 | |
| Depreciation and amortization | | | 42,015 | | | | 26 | | | | 1,181 | | | | 43,222 | |
| Total assets | | | 363,223 | | | | 11,963 | | | | 25,046 | | | | 400,232 | |
| Capital expenditures, net | | | (16,677 | ) | | | - | | | | 939 | | | | (15,738 | ) |
| (1) | Includes equipment purchased under capital leases. |
17. QUARTERLY RESULTS OF OPERATIONS (UNAUDITED)
| | | (in thousands except per share amounts) | |
Quarters ended | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total revenue | | $ | 160,957 | | | $ | 173,654 | | | $ | 177,581 | | | $ | 206,788 | |
| Operating income | | | 354 | | | | 9,056 | | | | 5,586 | | | | 24,650 | |
| Net income (loss) | | | (1,374 | ) | | | 3,780 | | | | 1,857 | | | | 13,545 | |
| Basic (loss) income per share (1) | | | (0.09 | ) | | | 0.25 | | | | 0.12 | | | | 0.84 | |
| Diluted (loss) income per share (1) | | | (0.09 | ) | | | 0.25 | | | | 0.12 | | | | 0.82 | |
| | | (in thousands except per share amounts) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Quarters ended | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| Total revenue | | $ | 164,731 | | | $ | 172,488 | | | $ | 170,843 | | | $ | 176,487 | |
| Operating income | | | (715 | ) | | | 6,350 | | | | 5,882 | | | | 8,877 | |
| Net (loss) income | | | (1,959 | ) | | | 1,891 | | | | 1,973 | | | | 3,339 | |
| Basic and diluted (loss) income per share | | | (0.13 | ) | | | 0.13 | | | | 0.13 | | | | 0.22 | |
| (1) | Quarter totals do not aggregate to annual results due to the dilution related to the follow-on stock offering. |
| (2) | Includes $2.4 million gain on the sale of a terminal property. |
| (3) | Includes $7.5 million increase to claims reserves for a 2008 cargo claim. |
83