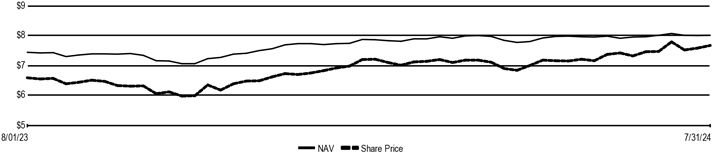
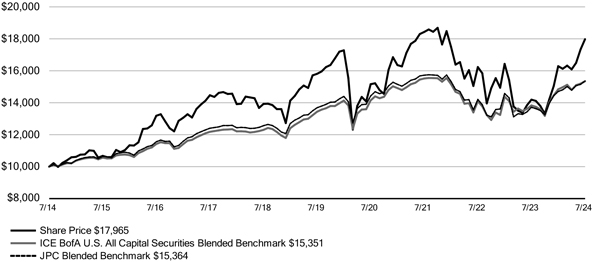
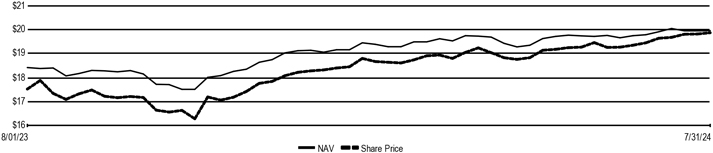
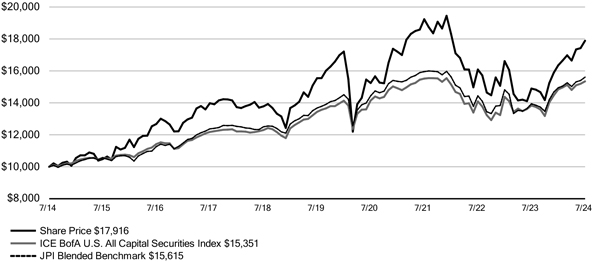
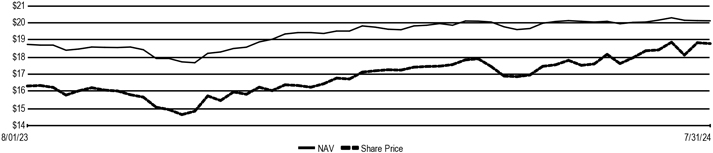
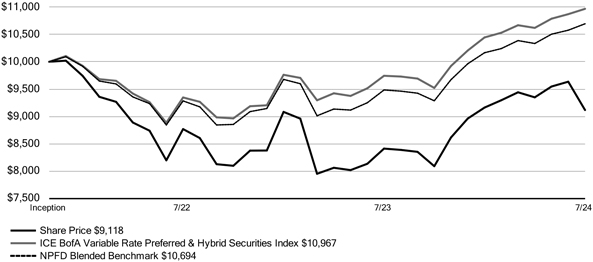
| | · | | The Fund’s name changed from Nuveen Preferred and Income Term Fund to Nuveen Preferred Securities & Income Opportunities Fund. |
| | · | | Nuveen Fund Advisors, LLC, the investment adviser to the Fund, will waive 50% of the Fund’s net management fees beginning August 19, 2024, and continuing over the first year following the elimination of the term. |
CURRENT INVESTMENT OBJECTIVE, INVESTMENT POLICIES AND PRINCIPAL RISKS OF THE FUNDS
NUVEEN FLOATING RATE INCOME FUND (JFR)
The Fund’s investment objective is to achieve a high level of current income.
The Fund invests at least 80% of its Assets (as defined below) in secured Senior Loans and unsecured Senior Loans, which unsecured Senior Loans will be, at the time of investment, investment grade quality.
With respect to the Fund’s Senior Loans included in the 80% policy, such instruments will at times have a dollar-weighted average time until the next interest rate adjustment of 90 days or less.
“Assets” mean the net assets of the Fund plus the amount of any borrowings for investment purposes. “Managed Assets” mean the total assets of the Fund, minus the sum of its accrued liabilities (other than Fund liabilities incurred for the express purpose of creating leverage). Total assets for this purpose shall include assets attributable to the Fund’s use of leverage (whether or not those assets are reflected in the Fund’s financial statements for purposes of generally accepted accounting principles), and derivatives will be valued at their market value.
Under normal circumstances:
| | · | | The Fund invests at least 65% of its Managed Assets in Senior Loans that are secured by specific collateral. |
| | · | | The Fund may invest its Managed Assets without limit in Senior Loans and other debt instruments that are, at the time of investment, rated below investment grade or unrated but judged to be of comparable quality. Investment grade quality securities are those securities that, at the time of investment, are (i) rated by at least one nationally recognized statistical rating organization NRSRO within the four highest grades (BBB- or Baa3 or better by S&P, Moody’s or Fitch, or (ii) unrated but judged to be of comparable quality. However, no more than 30% of the Fund’s Managed Assets may be invested in Senior Loans and other debt securities that are, at the time of investment, rated CCC+ or Caa or below by S&P, Moody’s or Fitch or that are unrated but judged to be of comparable quality. |
| | · | | The Fund may invest up to 20% of its Managed Assets in (i) other debt securities such as investment and non-investment grade debt securities, convertible securities and structured notes (other than structured notes that are designed to provide returns and risks that emulate those of Senior Loans, which may be treated as an investment in Senior Loans for purposes of the 80% requirement set forth above), (ii) mortgage-related and other asset-backed securities (including collateralized loan obligations and collateralized debt obligations), and (iii) debt securities and other instruments issued by government, government-related or supranational issuers (commonly referred to as sovereign debt securities). No more than 5% of the Fund’s Managed Assets may be invested in each of convertible securities, mortgage-related and other asset-backed securities, and sovereign debt securities. The debt securities in which the Fund may invest may have short-term, intermediate-term or long-term maturities. The Fund also may receive warrants and equity securities issued by a borrower or its affiliates in connection with the Fund’s other investments in such entities. |
| | · | | The Fund maintains an average duration of one year or less for its portfolio investments in Senior Loans and other debt instruments. |
| | · | | The Fund will not invest in inverse floating rate securities. |
| | · | | The Fund may invest up to 20% of its Managed Assets in securities of non-U.S. issuers (which includes borrowers) that are U.S. dollar or non- U.S. dollar denominated. The Fund’s Managed Assets to be invested in Senior Loans and other debt instruments of non-U.S. issuers may include debt securities of issuers located, or conducting their business in, emerging markets countries. |
| | · | | The Fund may not invest more than 20% of its Managed Assets in securities from an industry which (for purposes of this policy) generally refers to the classification of companies in the same or similar lines of business such as the automotive, textiles and apparel, hotels, media production and consumer retailing industries. The Fund may invest more than 20% of its Managed Assets in sectors which (for purposes of this policy) generally refers to broader classifications of industries, such as the consumer discretionary sector which includes the automotive, textiles and apparel, hotels, media production and consumer retailing industries, provided the Fund’s investment in a particular industry within the sector does not exceed the industry limitation. |
| | · | | The Fund may invest up to 5% of its Managed Assets in iBoxx Loan Total Return Swaps. An iBoxx Loan Total Return Swap is a specific type of total return swap on an index that is designed to provide exposure to the Senior Loan market. The iBoxx Loan Total Return Swap’s underlying index is the Markit iBoxx USD Liquid Leveraged Loans Total Return Index, which is one of a subset of indices designed to track the broader, rules-based Markit iBoxx USD Liquid Leveraged Loan Index. “iBoxx Loan Total Return Swaps” means total return swaps written on the Markit iBoxx USD Liquid Leveraged Loans Total Return Index. |
The foregoing policies apply only at the time of any new investment.
Approving Changes in Investment Policies
The Board of Trustees of the Fund may change the policies described above without a shareholder vote. However, with respect to the Fund’s policy of investing at least 80% of its Assets in secured Senior Loans and unsecured Senior Loans, which unsecured Senior Loans will be, at the time of investment, investment grade quality, such policy may not be changed without 60 days’ prior written notice.
The Fund generally invests in Senior Loans. Senior Loans typically hold the most senior position in the capital structure of a business entity, are typically secured with specific collateral and have a claim on the assets and/or stock of the issuer that is senior to that held by subordinated debt holders and stockholders of the issuer.
Senior Loans generally include: (i) Senior Loans made by banks or other financial institutions to U.S. and
non-U.S.
corporations, partnerships and other business entities (each a “Borrower” and, collectively, “Borrowers”), (ii) assignments of such interests in Senior Loans, or (iii) participation interests in Senior Loans. Generally, an assignment is the actual sale of the loan, in whole or in part. A participation, on the other hand, means that the original lender maintains ownership over the loan and the participant has only a contract right against the original lender, not a credit relationship with the Borrower. Senior Loans typically hold the most senior position in the capital structure of a Borrower, are typically secured with specific collateral and have a claim on the assets and/or stock of the Borrower that is senior to that held by subordinated debt holders and stockholders of the Borrower. The capital structure of a Borrower may include Senior Loans, senior and junior subordinated debt, preferred stock and common stock issued by the Borrower, typically in descending order of seniority with respect to claims on the Borrower’s assets. The proceeds of Senior Loans primarily are used by Borrowers to finance leveraged buyouts, recapitalizations, mergers, acquisitions, stock repurchases, refinancings, internal growth and for other corporate purposes. A Senior Loan is typically originated, negotiated and structured by a U.S. or
non-U.S.
commercial bank, insurance company, finance company or other financial institution (“Agent”) for a lending syndicate of financial institutions which typically includes the Agent (“Lenders”). The Agent typically administers and enforces the Senior Loan on behalf of the other Lenders in the syndicate. In addition, an institution, typically but not always the Agent, holds any collateral on behalf of the Lenders. The Fund normally will rely primarily on the Agent to collect principal of and interest on a Senior Loan. Also, the Fund usually will rely on the Agent to monitor compliance by the Borrower with the restrictive covenants in a loan agreement.
Senior loans in which the Fund invests generally pay interest at rates that are redetermined either daily, monthly, quarterly or semi-annually by reference to a base lending rate plus a premium or credit spread. The interest rates on senior loans are generally based on a percentage above the Secured Overnight Financing Rate (“SOFR”), a U.S. bank’s prime or base rate, the overnight federal funds rate or another rate. As adjustable rate loans, the frequency of how often a senior loan resets its interest rate will impact how closely such senior loans track current market interest rates. Senior loans typically have a stated term of between one and eight years.
The Fund may purchase participations in Senior Loans. By purchasing a participation interest in a loan, the Fund acquires some or all of the interest of a bank or other financial institution in a loan to a Borrower. Under a participation, the Fund generally will have rights that are more limited than the rights of lenders or of persons who acquire a Senior Loan by assignment. In a participation, the Fund typically has a contractual relationship with the lender selling the participation, but not with the Borrower. As a result, the Fund assumes the credit risk of the lender selling the participation in addition to the credit risk of the Borrower. In the event of insolvency of the lender selling the participation, the Fund may be treated as a general creditor of the lender and may not have a senior claim to the lenders’ interest in the Senior Loan. A lender selling a participation and other persons interpositioned between the lender and the Fund with respect to participations will likely conduct their principal business activities in the banking, finance and financial services industries.
The Fund may invest in corporate debt securities, including corporate bonds. Corporate debt securities are fully taxable debt obligations issued by corporations. These securities fund capital improvements, expansions, debt refinancing or acquisitions that require more capital than would ordinarily be available from a single lender. Investors in corporate debt securities lend money to the issuing corporation in exchange for interest payments and repayment of the principal at a set maturity date. Rates on corporate debt securities are set according to prevailing interest rates at the time of the issue, the credit rating of the issuer, the length of the maturity and other terms of the security, such as a call feature.
The Fund may utilize structured notes and similar instruments for investment purposes and also for hedging purposes. Structured notes are privately negotiated debt obligations where the principal and/or interest is determined by reference to the performance of a benchmark asset, market or interest rate (an “embedded index”), such as selected securities, an index of securities or specified interest rates, or the differential performance of two assets or markets.
The Fund may invest
in debtor-in-possession financings
(commonly called “DIP financings”). DIP financings are arranged when an entity seeks the protections of the bankruptcy court under chapter 11 of the U.S. Bankruptcy Code. These financings allow the entity to continue its business operations while reorganizing under chapter 11. Such financings are senior liens on unencumbered security (i.e., security not subject to other creditors claims).
The Fund may acquire equity securities and warrants issued by a Borrower or its affiliates as part of a package of investments in the Borrower or its affiliates issued in connection with a Senior Loan of the Borrower. The Fund also may convert a warrant so acquired into the underlying security. Investments in warrants and equity securities entail certain risks in addition to those associated with investments in Senior Loans. The value of these securities may be affected more rapidly, and to a greater extent, by company-specific developments and general market conditions. These risks may increase fluctuations in the Fund’s NAV. The Fund may possess
material non-public information
about a Borrower as a result of its ownership of a Senior Loan of such Borrower. Because of prohibitions on trading in securities of issuers while in possession of such information the Fund might be unable to enter into a transaction in a security of such a Borrower when it would otherwise be advantageous to do so.
The Fund may invest in convertible securities, which may include convertible debt, convertible preferred stock, synthetic convertible securities and may also include secured and unsecured debt, based upon the judgment of the Fund’s
sub-adviser.
Convertible securities may pay interest or dividends that are based on a fixed or floating rate. A convertible security is a preferred stock, warrant or other security that may be converted into or exchanged for a prescribed amount of common stock or other security of the same or a different issuer or into cash within a particular period of time at a specified price or formula.
The Fund may invest in mortgage-related securities, including mortgage-backed securities. Mortgage-related securities are debt instruments that provide periodic payments consisting of interest and/or principal that are derived from or related to payments of interest and/or principal on underlying mortgages. Additional payments on mortgage-related securities may be made out of unscheduled prepayments of principal resulting from the sale of the underlying property, or from refinancing or foreclosure, net of fees or costs that may be incurred. The mortgage-related securities in which the Fund invests will typically pay variable rates of interest, although the Fund may invest in
fixed-rate
obligations as well.
The Fund may invest in certain asset-backed securities (“ABS”). ABS are payment claims that are securitized in the form of negotiable paper that is issued by a financing company (generally called a Special Purpose Vehicle or “SPV”). These securitized payment claims are, as a rule, corporate financial assets brought into a pool according to specific diversification rules. The SPV is a company founded solely for the purpose of securitizing these claims and its only asset is the risk arising out of this diversified asset pool. On this basis, marketable securities are issued which, due to the diversification of the underlying risk, generally represent a lower level of risk than the original assets. The redemption of the securities issued by the SPV takes place at maturity out of the cash flow generated by the collected claims.
The Fund may invest in collateralized loan obligations (“CLOs”). A CLO is a structured credit security issued by an SPV that was created to reapportion the risk and return characteristics of a pool of assets. The assets, typically Senior Loans, are used as collateral supporting the various debt tranches issued by the SPV. The key feature of the CLO structure is the prioritization of the cash flows from a pool of debt securities among the several classes of CLO holders, thereby creating a series of obligations with varying rates and maturities appealing to a wide range of investors. CLOs generally are secured by an assignment to a trustee under an indenture pursuant to which the bonds are issued of collateral consisting of a pool of debt instruments, usually, non-investment grade bank loans. Payments with respect to the underlying debt securities generally are made to the trustee under the indenture. CLOs are designed to be retired as the underlying debt instruments are repaid. In the event of sufficient early prepayments on such debt instruments, the class or series of CLO first to mature generally will be retired prior to maturity. Therefore, although in most cases the issuer of CLOs will not supply additional collateral in the event of such prepayments, there will be sufficient collateral to secure their priority with respect to other CLO tranches that remain outstanding. The credit quality of these securities depends primarily upon the quality of the underlying assets, their priority with respect to other CLO tranches and the level of credit support and/or enhancement provided.
The Fund also may invest in collateralized debt obligations (“CDOs”). A CDO is a structured credit security issued by an SPV that was created to reapportion the risk and return characteristics of a pool of assets. The assets,
typically non-investment grade
bonds, leveraged loans, and other asset-backed obligations, are used as collateral supporting the various debt and equity tranches issued by the SPV. CDOs operate similarly to CLOs.
The Fund may invest in commercial paper. Commercial paper represents short-term unsecured promissory notes issued in bearer form by corporations such as banks or bank holding companies and finance companies. The rate of return on commercial paper may be linked or indexed to the level of exchange rates between the U.S. dollar and a foreign currency or currencies.
The Fund may invest in U.S. Government securities. U.S. Government securities include (1) U.S. Treasury obligations, which differ in their interest rates, maturities and times of issuance: U.S. Treasury bills (maturities of one year or less), U.S. Treasury notes (maturities of one year to ten years) and U.S. Treasury bonds (generally maturities of greater than ten years) and (2) obligations issued or guaranteed by U.S. Government agencies and instrumentalities that are supported by any of the following: (i) the full faith and credit of the U.S. Treasury, (ii) the right of the issuer to borrow an amount limited to a specific line of credit from the U.S. Treasury, (iii) discretionary authority of the U.S. Government to purchase certain obligations of the U.S. Government agency or instrumentality or (iv) the credit of the agency or instrumentality.
The Fund may invest in securities
of non-U.S. issuers
that are U.S. dollar
or non-U.S. dollar
denominated. The Fund may invest in any region of the world and invest in companies operating in developed countries such as Canada, Japan, Australia, New Zealand and most Western European countries. An “emerging market” country is any country determined to have an emerging markets economy, considering, among other things, factors such as whether the country has
economy according to the World Bank or its related organizations, the country’s credit rating, its political and economic stability and the development of its financial and capital markets. These countries generally include countries located in Latin America, the Caribbean, Asia, Africa, the Middle East and Eastern and Central Europe. Securities
of non-U.S. issuers
include American Depository Receipts (“ADRs”), Global Depositary Receipts (“GDRs”) or other securities representing underlying shares
of non-U.S. issuers.
Positions in those securities are not necessarily denominated in the same currency as the common stocks into which they may be converted. ADRs are receipts typically issued by an American bank or trust company evidencing ownership of the underlying securities. GDRs are U.S. dollar- denominated receipts evidencing ownership
of non-U.S. securities.
Generally, ADRs, in registered form, are designed for the U.S. securities markets and GDRs, in bearer form, are designed for use
in non-U.S. securities
markets. The Fund may invest in sponsored or unsponsored ADRs. In the case of an unsponsored ADR, the Fund is likely to bear its proportionate share of the expenses of the depository and it may have greater difficulty in receiving shareholder communications than it would have with a sponsored ADR.
The Fund may invest in Eurodollar instruments and Yankee bonds. Yankee bonds are U.S. dollar denominated bonds typically issued in the U.S. by non-U.S. governments and their agencies and non-U.S. banks and corporations. These investments involve risks that are different from investments in securities issued by U.S. issuers, including potential unfavorable political and economic
developments, non-U.S. withholding
or other taxes, seizure
of non-U.S. deposits,
currency controls, interest limitations or other governmental restrictions which might affect payment of principal or interest.
The Fund may invest in sovereign debt securities issued by issuers located, or conducting their business, in emerging markets countries, and a wide variety of bonds and other debt instruments of varying maturities issued by domestic and
non-U.S.
corporations, including high yield debt securities.
The Fund may invest in zero coupon bonds. A zero coupon bond is a bond that typically does not pay interest for the entire life of the obligation or for an initial period after the issuance of the obligation.
The Fund may invest in
securities (“PIKs”). PIKs pay dividends or interest in the form of additional securities of the issuer, rather than in cash. Each of these instruments is typically issued and traded at a deep discount from its face amount. The amount of the discount varies depending on such factors as the time remaining until maturity of the securities, prevailing interest rates, the liquidity of the security and the perceived credit quality of the issuer.
The Fund may buy and sell securities on a when-issued or delayed delivery basis, making payment or taking delivery at a later date, normally within 15 to 45 days of the trade date.
The Fund may invest in illiquid securities (i.e., securities that are not readily marketable), including, but not limited to, restricted securities (securities the disposition of which is restricted under the federal securities laws), securities that may be resold only pursuant to Rule 144A under the 1933 Act, and repurchase agreements with maturities in excess of seven days.
The Fund may enter into certain derivative instruments in pursuit of its investment objective, including to seek to enhance return, to hedge certain risks of its investments in Senior Loans or as a substitute for a position in the underlying asset. Such instruments include total return swaps; interest rate swaps; credit default swaps; interest rate caps; interest rate floors; interest rate collars; swaptions; credit-linked notes; securities indices; other indices or other financial instruments; stock and bond index futures; futures contracts on securities; options on securities; options on futures contracts; options on stock and bond indexes; interest rate futures; exchange-traded
and over-the-counter options
on securities or indices; index linked securities; currency exchange transactions; financial futures; options on financial futures; index futures; index options; index options on futures contracts; interest rate options; interest rate option on futures contracts; short sales; structured notes; options on U.S. Treasury security or U.S. Government Agency securities; U.S. Treasury security or U.S. Government Agency security futures contracts; and options on U.S. Treasury security or U.S. Government Agency security futures contracts.
The Fund may also invest in securities of other open-
or closed-end investment
companies (including ETFs) that invest primarily in the types in which the Fund may invest directly, to the extent permitted by the Investment Company Act of 1940, as amended (the “1940 Act”) and the rules and regulations issued thereunder.
The Fund uses leverage to pursue its investment objective. The Fund may use leverage to the extent permitted by the 1940 Act. The Fund may source leverage through a number of methods including through borrowings, issuing Preferred Shares, the issuance of debt securities, and entering into reverse repurchase agreements (effectively a borrowing). In addition, the Fund may use derivatives that may have the economic effect of leverage, such as certain credit default swaps, total return swaps and bond futures. The amount and sources of leverage will vary depending on market conditions.
Temporary Defensive Periods
During temporary defensive periods (e.g., times when, in the Fund’s investment adviser’s and/or the Fund’s
sub-adviser’s opinion,
temporary imbalances of supply and demand or other temporary dislocations in the Senior Loan market adversely affect the price at which Senior Loans are available), the Fund may invest up to 100% of its assets in high quality, short-term securities, and in short-, intermediate-, or long-term U.S. Treasury securities. There can be no assurance that such techniques will be successful. Accordingly, during such periods, the Fund may not achieve its investment objective.
NUVEEN CREDIT STRATEGIES INCOME FUND (JQC)
The Fund’s primary investment objective is to achieve a high level of current income. The Fund’s secondary investment objective is total return.
The Fund will invest at least 80% of its Assets (as defined below), at time of purchase, in instruments that are senior to its common equity in the issuer’s capital structure, including but not limited to loans, debt securities and preferred securities.
“Assets” mean the net assets of the Fund plus the amount of any borrowings for investment purposes. “Managed Assets” mean the total assets of the Fund, minus the sum of its accrued liabilities (other than Fund liabilities incurred for the express purpose of creating leverage). Total assets for this purpose shall include assets attributable to the Fund’s use of leverage (whether or not those assets are reflected in the Fund’s financial statements for purposes of generally accepted accounting principles), and derivatives will be valued at their market value.
Under normal circumstances:
| | · | | The Fund may invest without limitation in instruments that are rated below investment grade or are unrated but judged to be of comparable quality. Investment grade quality instruments are those that are (i) rated by at least one NRSRO within the four highest grades (BBB- or Baa3 or better by S&P, Moody’s or Fitch), or (ii) unrated but judged to be of comparable quality. However, the Fund may not invest more than 30% of its Managed Assets in instruments that are rated CCC/Caa or lower at the time of investment (or are unrated but judged by the Fund’s sub-adviser to be of comparable quality). |
| | · | | The Fund may invest up to 20% of its Managed Assets in instruments of non-U.S. issuers that are U.S. dollar or non-U.S. dollar denominated, including instruments of issuers located, or conducting their business in, emerging markets countries. |
| | · | | The Fund may invest up to 25% of its Managed Assets in collateralized loan obligation (“CLO”) debt securities. |
The foregoing policies apply only at the time of any new investment.
Approving Changes in Investment Policies
The Board of Trustees of the Fund may change the policies described above without a shareholder vote. However, with respect to the Fund’s policy of investing at least 80% of its Assets, at time of purchase, in instruments that are senior to its common equity in the issuer’s capital structure, such policy may not be changed without 60 days’ prior written notice.
The Fund may invest in collateralized loan obligations (“CLOs”). A CLO is a structured credit security issued by an SPV that was created to reapportion the risk and return characteristics of a pool of assets. The assets, typically Senior Loans, are used as collateral supporting the various debt tranches issued by the SPV. The key feature of the CLO structure is the prioritization of the cash flows from a pool of debt securities among the several classes of CLO holders, thereby creating a series of obligations with varying rates and maturities appealing to a wide range of investors. CLOs generally are secured by an assignment to a trustee under an indenture pursuant to which the bonds are issued of collateral consisting of a pool of debt instruments, usually, non-investment grade bank loans. Payments with respect to the underlying debt securities generally are made to the trustee under the indenture. CLOs are designed to be retired as the underlying debt instruments are repaid. In the event of sufficient early prepayments on such debt instruments, the class or series of CLO first to mature generally will be retired prior to maturity. Therefore, although in most cases the issuer of CLOs will not supply additional collateral in the event of such prepayments, there will be sufficient collateral to secure their priority with respect to other CLO tranches that remain outstanding. The credit quality of these securities depends primarily upon the quality of the underlying assets, their priority with respect to other CLO tranches and the level of credit support and/or enhancement provided.
The Fund also may invest in collateralized debt obligations (“CDOs”). A CDO is a structured credit security issued by an SPV that was created to reapportion the risk and return characteristics of a pool of assets. The assets,
typically non-investment grade
bonds, leveraged loans, and other asset-backed obligations, are used as collateral supporting the various debt and equity tranches issued by the SPV. CDOs operate similarly to CLOs.
The Fund may invest in corporate debt instruments. Corporate debt instruments generally are used by corporations to borrow money from investors. The Issuer pays the investor a fixed or variable rate of interest and normally must repay the amount borrowed on or before maturity. Certain debt instruments in which the Fund may invest may be “perpetual” in that they have no maturity date and some may be convertible into equity securities of the Issuer or its affiliates. The Fund may invest in debt instruments of any quality and such debt instruments may be secured or unsecured. In addition, certain debt instruments in which the Fund may invest may be subordinated to the payment of an Issuer’s senior debt.
The Fund may in senior loans. Senior loans typically hold the most senior position in the capital structure of a business entity, are typically secured with specific collateral and have a claim on the assets and/or stock of the issuer that is senior to that held by subordinated debt holders and stockholders of the issuer.
Senior loans generally include: (i) senior loans made by banks or other financial institutions to U.S. and
non-U.S.
corporations, partnerships and other business entities (each a “Borrower” and, collectively, “Borrowers”), (ii) assignments of such interests in senior loans, or (iii) participation interests in senior loans. Generally, an assignment is the actual sale of the loan, in whole or in part. A participation, on the other hand, means that the original
lender maintains ownership over the loan and the participant has only a contract right against the original lender, not a credit relationship with the Borrower. Senior loans typically hold the most senior position in the capital structure of a Borrower, are typically secured with specific collateral and have a claim on the assets and/or stock of the Borrower that is senior to that held by subordinated debt holders and stockholders of the Borrower. The capital structure of a Borrower may include senior loans, senior and junior subordinated debt, preferred stock and common stock issued by the Borrower, typically in descending order of seniority with respect to claims on the Borrower’s assets. The proceeds of senior loans primarily are used by Borrowers to finance leveraged buyouts, recapitalizations, mergers, acquisitions, stock repurchases, refinancings, internal growth and for other corporate purposes. A senior loan is typically originated, negotiated and structured by a U.S. or
non-U.S.
commercial bank, insurance company, finance company or other financial institution (“Agent”) for a lending syndicate of financial institutions which typically includes the Agent (“Lenders”). The Agent typically administers and enforces the senior loan on behalf of the other Lenders in the syndicate. In addition, an institution, typically but not always the Agent, holds any collateral on behalf of the Lenders. The Fund normally will rely primarily on the Agent to collect principal of and interest on a senior loan. Also, the Fund usually will rely on the Agent to monitor compliance by the Borrower with the restrictive covenants in a loan agreement.
Senior loans in which the Fund invests generally pay interest at rates that are redetermined either daily, monthly, quarterly or semi-annually by reference to a base lending rate plus a premium or credit spread. The interest rates on senior loans are generally based on a percentage above the Secured Overnight Financing Rate (“SOFR”), a U.S. bank’s prime or base rate, the overnight federal funds rate or another rate. As adjustable rate loans, the frequency of how often a senior loan resets its interest rate will impact how closely such senior loans track current market interest rates. Senior loans typically have a stated term of between one and eight years.
The Fund may invest in adjustable rate subordinated loans. The subordinated loans in which the Fund may invest are typically privately-negotiated investments that rank subordinate in priority of payment to senior debt, such as Senior Loans, and are often unsecured. However, such subordinated loans rank senior to common and preferred equity in a Borrower’s capital structure. Subordinated loans may have elements of both debt and equity instruments, offering fixed or adjustable rates of return in the form of interest payments associated with senior debt, while providing lenders an opportunity to participate in the capital appreciation of a Borrower, if any, through an equity interest. This equity interest may take the form of warrants or direct equity investments which will be in conjunction with the subordinated loans. Due to their higher risk profile and often less restrictive covenants as compared to Senior Loans, subordinated loans generally earn a higher return than secured Senior Loans. The warrants associated with subordinated loans are typically detachable, which allows lenders the opportunity to receive repayment of their principal on an agreed amortization schedule while retaining their equity interest in the Borrower. Subordinated loans also may include a “put” feature, which permits the holder to sell its equity interest back to the Borrower at a price determined through an agreed formula.
The Fund may invest in subordinated loans that are primarily unsecured and that provide for relatively high, adjustable rates of interest, providing the Fund with significant current interest income. The subordinated loans in which the Fund may invest may have interest-only payments in the early years, with amortization of principal deferred to the later years of the subordinated loans. In some cases, the Fund may acquire subordinated loans that, by their terms, convert into equity or additional debt instruments or defer payments of interest for the first few years after issuance. Also, in some cases the subordinated loans in which the Fund may invest will be collateralized by a subordinated lien on some or all of the assets of the Borrower. Typically, subordinated loans in which the Fund may invest will have maturities of four to eight years.
The Fund may invest in common stocks and other equity securities. Common stocks generally represent an ownership interest in an issuer, without preference over any other class of securities, including such issuer’s fixed income securities and senior equity securities. Dividend payments generally are not guaranteed and so may be discontinued by the issuer at its discretion or because of the issuer’s inability to satisfy its liabilities. Further, an issuer’s history of paying dividends does not guarantee that it will continue to pay dividends in the future. In addition to dividends, under certain circumstances the Fund may benefit from capital appreciation of an issuer’s common stock.
The Fund may invest in convertible securities, which may include convertible debt, convertible preferred stock, synthetic convertible securities and may also include secured and unsecured debt, based upon the judgment of the Fund’s
sub-adviser.
Convertible securities may pay interest or dividends that are based on a fixed or floating rate. A convertible security is a preferred stock, warrant or other security that may be converted into or exchanged for a prescribed amount of common stock or other security of the same or a different issuer or into cash within a particular period of time at a specified price or formula.
The Fund may utilize structured notes and similar instruments for investment purposes and also for hedging purposes. Structured notes are privately negotiated debt obligations where the principal and/or interest is determined by reference to the performance of a benchmark asset, market or interest rate (an “embedded index”), such as selected securities, an index of securities or specified interest rates, or the differential performance of two assets or markets.
For cash management purposes, the Fund may enter into repurchase agreements (a purchase of, and a simultaneous commitment to resell, a financial instrument at an agreed upon price on an agreed upon date) only with member banks of the Federal Reserve System and member firms of the New York Stock Exchange. When participating in repurchase agreements, the Fund buys securities from a vendor, e.g., a bank or brokerage firm, with the agreement that the vendor will repurchase the securities at a higher price at a later date. Such transactions afford an opportunity for the Fund to earn a return on available cash at minimal market risk, although the Fund may be subject to various delays and risks of loss if the vendor is unable to meet its obligation to repurchase.
The Fund may invest
in debtor-in-possession financings
(commonly called “DIP financings”). DIP financings are arranged when an entity seeks the protections of the bankruptcy court under chapter 11 of the U.S. Bankruptcy Code. These financings allow the entity to continue its business operations while reorganizing under chapter 11. Such financings are senior liens on unencumbered security (i.e., security not subject to other creditors claims).
The Fund may acquire equity securities and warrants issued by a Borrower or its affiliates as part of a package of investments in the Borrower or its affiliates issued in connection with a Senior Loan of the Borrower. The Fund also may convert a warrant so acquired into the underlying security. Investments in warrants and equity securities entail certain risks in addition to those associated with investments in Senior Loans. The value of these securities may be affected more rapidly, and to a greater extent, by company-specific developments and general market conditions. These risks may increase fluctuations in the Fund’s NAV. The Fund may possess
material non-public information
about a Borrower as a result of its ownership of a Senior Loan of such Borrower. Because of prohibitions on trading in securities of issuers while in possession of such information the Fund might be unable to enter into a transaction in a security of such a Borrower when it would otherwise be advantageous to do so.
The Fund may invest in mortgage-related securities, including mortgage-backed securities. Mortgage-related securities are debt instruments that provide periodic payments consisting of interest and/or principal that are derived from or related to payments of interest and/or principal on underlying mortgages. Additional payments on mortgage-related securities may be made out of unscheduled prepayments of principal resulting from the sale of the underlying property, or from refinancing or foreclosure, net of fees or costs that may be incurred. The mortgage-related securities in which the Fund invests will typically pay variable rates of interest, although the Fund may invest in
fixed-rate
obligations as well. The Fund may invest in certain ABS. ABS are payment claims that are securitized in the form of negotiable paper that is issued by a financing company (generally called a SPV). These securitized payment claims are, as a rule, corporate financial assets brought into a pool according to specific diversification rules. The SPV is a company founded solely for the purpose of securitizing these claims and its only asset is the risk arising out of this diversified asset pool. On this basis, marketable securities are issued which, due to the diversification of the underlying risk, generally represent a lower level of risk than the original assets. The redemption of the securities issued by the SPV takes place at maturity out of the cash flow generated by the collected claims.
The Fund may invest in commercial paper. Commercial paper represents short-term unsecured promissory notes issued in bearer form by corporations such as banks or bank holding companies and finance companies. The rate of return on commercial paper may be linked or indexed to the level of exchange rates between the U.S. dollar and a foreign currency or currencies.
The Fund may invest in U.S. Government securities. U.S. Government securities include (1) U.S. Treasury obligations, which differ in their interest rates, maturities and times of issuance: U.S. Treasury bills (maturities of one year or less), U.S. Treasury notes (maturities of one year to ten years) and U.S. Treasury bonds (generally maturities of greater than ten years) and (2) obligations issued or guaranteed by U.S. Government agencies and instrumentalities that are supported by any of the following: (i) the full faith and credit of the U.S. Treasury, (ii) the right of the issuer to borrow an amount limited to a specific line of credit from the U.S. Treasury, (iii) discretionary authority of the U.S. Government to purchase certain obligations of the U.S. Government agency or instrumentality or (iv) the credit of the agency or instrumentality.
The Fund may invest in securities
of non-U.S. Issuers
that are U.S. dollar
or non-U.S. dollar
denominated, including debt securities of issuers located, or conducting their business, in emerging markets countries. The Fund’s Managed Assets to be invested in Adjustable Rate Loans and other debt instruments
of non-U.S. Issuers
may include debt securities of Issuers located, or conducting their business in, emerging markets countries. The Fund may invest in any region of the world and invest in companies operating in developed countries such as Canada, Japan, Australia, New Zealand and most Western European countries. An “emerging market” country is any country determined to have an emerging markets economy, considering, among other things, factors such as whether the country has
a low-to-middle-income economy
according to the World Bank or its related organizations, the country’s credit rating, its political and economic stability and the development of its financial and capital markets. These countries generally include countries located in Latin America, the Caribbean, Asia, Africa, the Middle East and Eastern and Central Europe.
The Fund may invest in preferred securities. Preferred securities, which generally pay fixed or adjustable rate dividends or interest to investors, have preference over common stock in the payment of dividends or interest and the liquidation of a company’s assets, which means that a company typically must pay dividends or interest on its preferred securities before paying any dividends on its common stock. On the other hand, preferred securities are junior to all forms of the company’s debt, including both senior and subordinated debt. Because of their subordinated position in the capital structure of an issuer, the ability to defer dividend or interest payments for extended periods of time without triggering a default from legal action and certain other features, preferred securities are often treated as equity-like instruments by both issuers and investors, as their quality and value are heavily dependent on the profitability and cash flows of the issuer rather than on any legal claims to specific assets.
The Fund may invest in contingent capital securities (sometimes referred to as “CoCos”). CoCos are hybrid securities, issued primarily
by non-U.S. financial
institutions, which have loss absorption mechanisms benefitting the issuer built into their terms. CoCos generally provide for mandatory conversion into the common stock of the issuer or a write-down of the principal amount or value of the CoCos upon the occurrence of certain triggers linked to regulatory capital thresholds. In addition, they may provide for mandatory conversion or a principal write-down upon the occurrence of certain events such as regulatory actions calling into question the issuing banking institution’s continued viability as a going-concern. Equity conversion or principal write-down features are tailored to the issuer and its regulatory requirements and, unlike traditional convertible securities, conversions are not voluntary.
The Fund may invest in zero coupon bonds. A zero coupon bond is a bond that typically does not pay interest for the entire life of the obligation or for an initial period after the issuance of the obligation.
The Fund may invest in
securities (“PIKs”). PIKs pay dividends or interest in the form of additional securities of the issuer, rather than in cash. Each of these instruments is typically issued and traded at a deep discount from its face amount. The amount of the discount varies depending on such factors as the time remaining until maturity of the securities, prevailing interest rates, the liquidity of the security and the perceived credit quality of the issuer.
The Fund may buy and sell securities on a when-issued or delayed delivery basis, making payment or taking delivery at a later date, normally within 15 to 45 days of the trade date.
The Fund may invest in illiquid securities (i.e., securities that are not readily marketable), including, but not limited to, restricted securities (securities the disposition of which is restricted under the federal securities laws), securities that may be resold only pursuant to Rule 144A under the 1933 Act, and repurchase agreements with maturities in excess of seven days.
The Fund may enter into certain derivative transactions, primarily but not limited to credit default and interest rate swaps, as a hedging technique to protect against potential adverse changes in the market value of portfolio instruments. The Fund also may use derivatives to attempt to protect the NAV of the Fund, to facilitate the sale of certain portfolio instruments, to manage the Fund’s effective interest rate exposure, and as a temporary substitute for purchasing or selling particular instruments. From time to time, the Fund also may enter into derivative transactions to create investment exposure to the extent such transactions may facilitate implementation of its strategy more efficiently than through outright purchases or sales of portfolio instruments.
The Fund may also invest in securities of other open-
or closed-end investment
companies (including ETFs) that invest primarily in the types in which the Fund may invest directly, to the extent permitted by the 1940 Act and the rules and regulations issued thereunder.
The Fund uses leverage to pursue its investment objective. The Fund may use leverage to the extent permitted by the 1940 Act. The Fund may source leverage through a number of methods including through borrowings, issuing Preferred Shares and the issuance of debt securities. In addition, the Fund may use derivatives that may have the economic effect of leverage, such as certain credit default swaps, total return swaps and bond futures. The amount and sources of leverage will vary depending on market conditions.
Temporary Defensive Periods
During temporary defensive periods (e.g., times when, in the Fund’s investment adviser’s and/or the Fund’s
sub-adviser’s opinion,
temporary imbalances of supply and demand or other temporary dislocations in the Senior Loan market adversely affect the price at which Senior Loans are available), the Fund may invest up to 100% of its assets in high quality, short-term securities, and in short-, intermediate-, or long-term U.S. Treasury securities. There can be no assurance that such techniques will be successful. Accordingly, during such periods, the Fund may not achieve its investment objective.
NUVEEN PREFERRED & INCOME OPPORTUNITIES FUND (JPC)
The Fund’s primary investment objective is high current income. The Fund’s secondary investment objective is total return.
The Fund will invest at least 80% of its Assets (as defined below) in preferred securities and other income producing securities, including hybrid securities such as contingent capital securities and up to 20% in other securities, primarily income-oriented securities such as corporate and taxable municipal debt and common equity.
“Assets” mean the net assets of the Fund plus the amount of any borrowings for investment purposes. “Managed Assets” mean the total assets of the Fund, minus the sum of its accrued liabilities (other than Fund liabilities incurred for the express purpose of creating leverage). Total assets for this purpose shall include assets attributable to the Fund’s use of leverage (whether or not those assets are reflected in the Fund’s financial statements for purposes of generally accepted accounting principles), and derivatives will be valued at their market value.
Under normal circumstances:
| | · | | The Fund will invest at least 50% of its Managed Assets in securities rated investment grade (BBB/Baa and above) at the time of investment. Investment grade quality securities are those securities that, at the time of investment, are (i) rated by at least one nationally recognized statistical rating organization (“NRSRO”) within the four highest grades (Baa or BBB or better by Moody’s Investors Service, Inc. (“Moody’s”), Standard & Poor’s Corporation (“S&P”), or Fitch Ratings (“Fitch”), or are unrated but judged to be of comparable quality. |
| | · | | The Fund will invest more than 25% of its Managed Assets in the securities of companies principally engaged in financial services. |
| | · | | The Fund is not limited in the amount of its investments in non-U.S. issuers. The Fund may invest up to 10% of its Managed Assets in non- U.S. dollar-denominated securities. The Fund may invest up to 5% of its Managed Assets in preferred securities issued by companies located in emerging market countries. |
The foregoing policies apply only at the time of any new investment.
Approving Changes in Investment Policies
The Board of Trustees of the Fund may change the policies described above without a shareholder vote. However, with respect to the Fund’s policy of investing at least 80% of its Assets in preferred securities and other income producing securities, such policy may not be changed without 60 days’ prior written notice.
The Fund invests in preferred securities. The Fund may invest in all types of preferred securities, including both traditional preferred securities and non-traditional preferred securities. Traditional preferred securities are generally equity securities of the issuer that have priority over the issuer’s common shares as to the payment of dividends (i.e., the issuer cannot pay dividends on its common shares until the dividends on the preferred shares are current) and as to the payout of proceeds of bankruptcy or other liquidation, but are subordinate to an issuer’s senior debt and junior debt as to both types of payments. Additionally, in a bankruptcy or other liquidation, traditional preferred shares are generally subordinate to an issuer’s trade creditors and other general obligations.
Traditional preferred securities pay a dividend, typically contingent both upon declaration by the issuer’s board and at times approval by regulators, and on the existence of current earnings (or retained earnings) in sufficient amount to source the payment. Dividend payments can be either cumulative or non-cumulative and can be passed or deferred without limitation at the option of the issuer. Traditional preferred securities typically have no ordinary right to vote for the board of directors, except in some cases voting rights may arise if the issuer fails to pay the preferred share dividends. Traditional preferred securities may be perpetual, or have a term and typically have a fixed liquidation (or “par”) value.
While some preferred securities are issued with a final maturity date, others are perpetual in nature. In certain instances, a final maturity date may be extended and/or the final payment of principal may be deferred at the issuer’s option for a specified time without triggering an event of default for the issuer. No redemption can typically take place unless all cumulative payment obligations to preferred security investors have been met, although issuers may be able to engage in open-market repurchases without regard to any cumulative dividends or interest payable. A portion of the portfolio may include investments in non-cumulative preferred securities, whereby the issuer does not have an obligation to make up any arrearages to holders of such securities. Should an issuer default on its obligations under such a security, the amount of income earned by the Fund may be adversely affected. Non-traditional preferred securities include hybrid preferred securities, contingent convertible capital securities and other types of preferred securities that do not have the traditional features described above. Hybrid-preferred securities often behave similarly as investments in traditional preferred securities and are regarded by market investors as being part of the preferred securities market. Hybrid-preferred securities possess varying combinations of features of both debt and preferred shares and as such they may constitute senior debt, junior debt or preferred shares in an issuer’s capital structure. As such, hybrid-preferred securities may not be subordinate to a company’s debt securities (as are traditional preferred shares). Given the various debt and equity characteristics of hybrid-preferred securities, whether a hybrid-preferred security is classified as debt or equity for purposes of reporting the Fund’s portfolio holdings may be based on the portfolio managers’ determination as to whether its debt or preferred features are preponderant, or based on the assessment of an independent data provider. Such determinations may be subjective.
Hybrid-preferred securities include trust preferred securities. Trust preferred securities are typically issued by corporations, generally in the form of interest-bearing notes with preferred securities characteristics, or by an affiliated business trust of a corporation, generally in the form of beneficial interests in subordinated debentures or similarly structured securities. The trust preferred securities market consists of both fixed and adjustable coupon rate securities that are either perpetual in nature or have stated maturity dates. Trust preferred securities may defer payment of income without triggering an event of default. These securities may have many characteristics of equity due to their subordinated position in an issuer’s capital structure. Trust preferred securities may be issued by trusts or other special purpose entities.
Preferred securities may also include certain forms of debt that have many characteristics of preferred shares, and that are regarded by the investment marketplace to be part of the broader preferred securities market. Among these “preferred securities” are certain exchange-listed debt issues that historically have several attributes, including trading and investment performance characteristics, in common with exchange-listed traditional preferred stock and hybrid-preferred securities. Generally, these types of “preferred securities” are senior debt or junior debt in the capital structure of an issuer.
Preferred securities generally pay fixed or adjustable rate dividends or interest to investors and have preference over common stock in the payment of dividends or interest and generally the liquidation of a company’s assets, which means that a company typically must pay dividends or interest on its preferred securities before paying any dividends on its common stock. As a general matter, dividend or interest payments on preferred securities may be cumulative or non-cumulative. The dividend or interest rates on preferred securities may be fixed or floating, or convert from fixed to floating at a specified future time; the Fund may invest without limit in such floating-rate and
fixed-to-floating
rate preferred securities. Floating-rate and fixed-to-floating rate preferred securities may be traditional preferred or hybrid-preferred securities. Floating-rate preferred securities pay a rate of income that resets periodically based on short- and/or longer-term interest rate benchmarks. If the associated interest rate benchmark rises, the income received from the security may increase and therefore the return offered by the floating-rate security may rise as well, making such securities less price sensitive to rising interest rates (or yields). Similarly, a
fixed-to-floating
rate security may be less price sensitive to rising interest rates (or yields), because the period over which the rate of payment is fixed is shorter than the maturity term of the bond, after which period a floating rate of payment applies. On the other hand, preferred securities are junior to most other forms of the company’s debt, including both senior and subordinated debt. Because of their subordinated position in the capital structure of an issuer, the ability to defer dividend or interest payments for extended periods of time without triggering an event of default for the issuer, and certain other features, preferred securities may have, at times, risks similar to equity instruments. The Fund’s portfolio of preferred securities may consist of fixed rate preferred and adjustable rate preferred securities.
The preferred securities market continues to evolve. New securities may be developed that may be regarded by market investors as being part of the preferred securities market. Where such securities will fall in the capital structure of the issuer will depend on the structure and characteristics of the new security. For purposes of the Fund’s policy of investing at least 80% of its Assets in preferred securities and other income producing securities, the Fund considers all of the foregoing types of securities that are commonly viewed in the marketplace as preferred securities to be preferred securities, regardless of their classification in the capital structure of the issuer.
Preferred securities are typically issued by corporations, generally in the form of interest or dividend bearing instruments, or by an affiliated business trust of a corporation, generally in the form of beneficial interests in subordinated debentures or similarly structured securities. Preferred securities may either trade over-the-counter, or trade on an exchange. The preferred securities market is generally divided into the $25 par “retail” and the $1,000 par “institutional” segments. The $25 par segment is typified by securities that are listed on the New York Stock Exchange (“NYSE”), which trade and are quoted with accrued dividend or interest income, and which are often callable. The institutional segment is typified by $1,000 par value securities that are not exchange-listed. The Fund may invest in preferred securities of either segment.
The Fund may invest in contingent capital securities. Contingent capital securities (sometimes referred to as “CoCos”) are securities issued primarily by
non-U.S. financial
institutions. Specific CoCo structures vary by country of domicile and by each issue. All CoCos have mechanisms that absorb losses or reduces the value of the CoCo due to deterioration of the issuer’s financial condition and status as a going concern. Loss absorption mechanisms, which may include conversion into common equity and principal write-down, are intended for the benefit of the issuer and when triggered will likely negatively impact the value of the CoCo to the detriment of the CoCo investor. Loss absorption mechanisms can be triggered by capital levels or market value metrics of the issuers dropping below a certain predetermined level or at the discretion of the issuer regulator/ supervisory entity. Unlike traditional convertible securities, the conversion is not voluntary and the equity conversion or principal write-down features are tailored to the issuer and its regulatory requirements. Due to increased regulatory requirements for higher capital levels for financial institutions, the issuance of CoCo instruments has increased in the last several years and is expected to continue.
The Fund may invest in common stock. Common stock generally represents an equity ownership interest in an issuer. Although common stocks have historically generated higher average total returns than fixed-income securities over the long term, common stocks also have experienced significantly more volatility in those returns and may underperform relative to fixed-income securities during certain periods. An adverse event, such as an unfavorable earnings report, may depress the value of a particular common stock held by the Fund. Also, prices of common stocks are sensitive to general movements in the stock market and a drop in the stock market may depress the price of common stocks to which the Fund has exposure. Common stock prices fluctuate for several reasons including changes in investors’ perceptions of the financial condition of an issuer or the general condition of the relevant stock market, or the occurrence of political or economic events which affect the issuer. In addition, common stock prices may be particularly sensitive to rising interest rates, which increases borrowing costs and the costs of capital.
Additional types of equity securities (other than preferred securities) in which the Fund may invest include convertible securities, real estate investment trusts (“REITs”), warrants, rights, depositary receipts (which reference ownership of underlying non-U.S. securities) and other types of securities with equity characteristics. The Fund’s equity investments also may include securities of other investment companies (including open-end funds, closed-end funds and exchange-traded funds (“ETFs”)).
The Fund will invest in securities of companies primarily engaged in the financial services industry. A financial services company is one that is primarily involved in banking, mortgage finance, consumer finance, specialized finance, investment banking and brokerage, asset management and custody, corporate lending, insurance, financial instruments or real estate, including business development companies (“BDCs”) and REITs.
The Fund may invest in debt securities. The debt securities in which the Fund may invest include corporate debt securities and U.S. government and agency debt securities. Generally, debt securities typically, but not always, possess the following characteristics: a specified maturity or term, at which time the issuer is contractually obligated to pay the associated principal amount of debt to the debtholders; interest payments that are a contractual and enforceable obligation as of the stated payment date, and not contingent either
on payment-by-payment declaration by
the issuer’s board or on the demonstrated existence of company earnings as a source for the payment; and do not entitle the holder to exercise governance of or control over the issuer.
In the capital structure of an issuer, debt securities can be senior debt or junior debt. A senior debt security has priority over any other type of security in a company’s capital structure as to the payment of any promised income (typically denoted as interest) from the issuer, and as to payout of the proceeds of the bankruptcy or other liquidation of the company. At times, the issuer will have pledged specific assets or revenues to secure the rights of the holder of the debt security to payments of interest and principal such that the proceeds of the specific assets or revenues must be used to satisfy these debt obligations prior to being applied to any of the issuer’s other obligations in a bankruptcy or other liquidation. In the event that the assets securing the debt security are not sufficient to fully satisfy such obligations in a bankruptcy or other liquidation, the remainder of such obligations will generally have the same priority as an issuer’s trade creditors and other general obligations, but still have priority of payment relative to the issuer’s preferred shares and common shares. Sometimes referred to as subordinated or mezzanine debt, junior debt stands behind the senior debt as to its rights to receive promised income payments (again, typically denoted as interest) from the issuer, and payouts of the proceeds of bankruptcy or other liquidation, but will have priority of payment relative to the issuer’s preferred shares and common shares.
The Fund may invest in convertible securities. Convertible securities are hybrid securities that combine the investment characteristics of bonds and common stocks. Convertible securities typically consist of debt securities or preferred securities that may be converted within a specified period of time (typically for the entire life of the security) into a certain amount of common stock or other equity security of the same or a different issuer at a predetermined price. They also include debt securities with warrants or common stock attached and derivatives combining features of debt securities and equity securities. Convertible securities entitle the holder to receive interest paid or accrued on debt securities, or dividends paid or accrued on preferred securities, until the securities mature or are redeemed, converted or exchanged.
Before conversion, convertible securities have characteristics similar to nonconvertible income securities in that they ordinarily provide a stable stream of income with generally higher yields than those of common stocks of the same or similar issuers, but lower yields than comparable nonconvertible securities. The value of a convertible security is influenced by changes in interest rates, with investment value generally declining as interest rates increase and increasing as interest rates decline. The credit standing of the issuer and other factors also may have an effect on the convertible security’s investment value. Convertible securities are subordinate in rank to any senior debt obligations of the same issuer and, therefore, an issuer’s convertible securities entail more risk than its debt obligations.
The Fund may invest in REITs. REITs are typically publicly traded corporations or trusts that invest in residential or commercial real estate. REITs generally can be divided into the following three types: (i) equity REITs which invest the majority of their assets directly in real property and derive their income primarily from rents and capital gains or real estate appreciation; (ii) mortgage REITs which invest the majority of their assets in real estate mortgage loans and derive their income primarily from interest payments; and (iii) hybrid REITs which combine the characteristics of equity REITs and mortgage REITs. The Fund can invest in common stock, preferred securities, debt securities and convertible securities issued by REITs.
The Fund may invest in securities of foreign issuers through the direct investment in securities of such companies and through depositary receipts. For purposes of identifying foreign issuers, the Fund will use Bloomberg classifications, which employ the following factors listed in order of importance: (i) the country in which the company’s management is located, (ii) the country in which the company’s securities are primarily listed, (iii) the country from which the company primarily receives revenue and (iv) the company’s reporting currency. The Fund may purchase depositary receipts such as American Depositary Receipts (“ADRs”), European Depositary Receipts (“EDRs”) and Global Depositary Receipts (“GDRs”). ADRs, EDRs and GDRs are certificates evidencing ownership of shares of foreign issuers and are alternatives to purchasing directly the underlying foreign securities in their national markets and currencies.
The Fund may invest in securities of emerging markets issuers. Emerging markets issuers are those (i) whose securities are traded principally on a stock
exchange or over-the-counter in an
emerging market country, (ii) organized under the laws of an emerging market country or (iii) whose principal place of business or principal office(s) is in an emerging market country. Emerging market countries include any country other than Canada, the United States and the countries comprising the MSCI EAFE® Index (currently, Australia, Austria, Belgium, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Hong Kong, Ireland, Israel, Italy, Japan, Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Portugal, Singapore, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland and the United Kingdom).
The Fund may invest in U.S. government securities, including U.S. Treasury obligations and securities issued or guaranteed by various agencies of the U.S. government, or by various instrumentalities which have been established or sponsored by the U.S. government. U.S. Treasury obligations are backed by the “full faith and credit” of the U.S. government. Securities issued or guaranteed by federal agencies and U.S. government sponsored instrumentalities may or may not be backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. government.
The Fund may invest in zero coupon bonds. A zero coupon bond is a bond that typically does not pay interest for the entire life of the obligation or for an initial period after the issuance of the obligation.
The Fund may buy and sell securities on a when-issued or delayed delivery basis, making payment or taking delivery at a later date, normally within 15 to 45 days of the trade date.
The Fund may invest in illiquid securities (i.e., securities that are not readily marketable), including, but not limited to, restricted securities (securities the disposition of which is restricted under the federal securities laws), securities that may be resold only pursuant to Rule 144A under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “1933 Act”), and repurchase agreements with maturities in excess of seven days.
The Fund may use derivative instruments to seek to hedge some of the risk of the Fund’s investments or its leverage, to enhance return, to serve as a substitute for a position in an underlying asset, to reduce transaction costs, to manage the Fund’s effective interest rate exposure, to maintain full market exposure, to manage cash flows or to preserve capital. Such instruments may include financial futures contracts, swap contracts (including interest rate and credit default swaps), options on equity securities, options on financial futures or other derivative instruments.
The Fund may also invest in securities of other open-
or closed-end investment
companies (including ETFs) that invest primarily in the types in which the Fund may invest directly, to the extent permitted by the Investment Company Act of 1940, as amended (the “1940 Act”) and the rules and regulations issued thereunder.
The Fund uses leverage to pursue its investment objectives. The Fund may use leverage to the extent permitted by the 1940 Act, including the following forms of leverage: (a) borrowings, including loans from certain financial institutions, and/or the issuance of debt securities; (b) the issuance of preferred shares of beneficial interest (“Preferred Shares”); and (c) engaging in reverse repurchase agreements and economically similar transactions. The Fund also may borrow money for repurchase of its shares or as a temporary measure for extraordinary or emergency purposes, including the payment of dividends and the settlement of securities transactions which otherwise might require untimely dispositions of Fund securities.