- BMEA Dashboard
- Financials
- Filings
-
Holdings
-
Transcripts
- ETFs
- Insider
- Institutional
- Shorts
-
8-K Filing
Biomea Fusion (BMEA) 8-KOther Events
Filed: 29 Aug 22, 8:00am
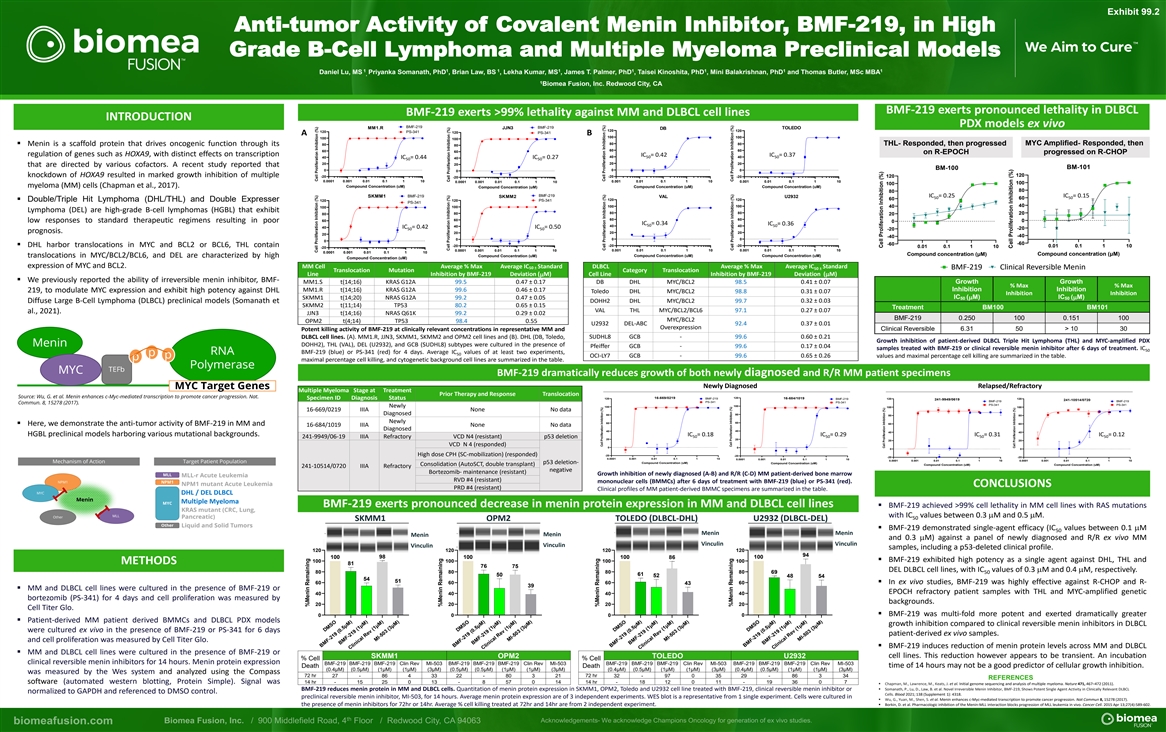
Exhibit 99.2 Anti-tumor Activity of Covalent Menin Inhibitor, BMF-219, in High Grade B-Cell Lymphoma and Multiple Myeloma Preclinical Models 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 Daniel Lu, MS Priyanka Somanath, PhD , Brian Law, BS , Lekha Kumar, MS , James T. Palmer, PhD , Taisei Kinoshita, PhD , Mini Balakrishnan, PhD and Thomas Butler, MSc MBA , 1 Biomea Fusion, Inc. Redwood City, CA BMF-219 exerts pronounced lethality in DLBCL BMF-219 exerts >99% lethality against MM and DLBCL cell lines INTRODUCTION PDX models ex vivo BMF-219 BMF-219 MM1.R JJN3 TOLEDO DB 120 120 120 PS-341 120 PS-341 A B 100 100 100 100 80 80 MYC Amplified- Responded, then ▪ Menin is a scaffold protein that drives oncogenic function through its 80 THL- Responded, then progressed 80 60 60 60 60 on R-EPOCH progressed on R-CHOP regulation of genes such as HOXA9, with distinct effects on transcription IC = 0.42 IC = 0.37 40 50 40 50 40 IC = 0.44 IC = 0.27 40 50 50 CTG-3794 CTG-3794 20 20 20 20 that are directed by various cofactors. A recent study reported that BM-101 125 125 BM-100 0 0 0 0 120 knockdown of HOXA9 resulted in marked growth inhibition of multiple -20 -20 -20 120 100 100 -20 0.0001 0.001 0.01 0.1 1 10 0.001 0.01 0.1 1 10 0.001 0.01 0.1 1 10 0.0001 0.001 0.01 0.1 1 10 100 100 75 75 myeloma (MM) cells (Chapman et al., 2017). Compound Concentration (uM) Compound Concentration (uM) Compound Concentration (uM) Compound Concentration (uM) 80 80 50 50 BMF-219 BMF-219 SKMM1 IC = 0.25 IC = 0.15 SKMM2 VAL U2932 50 50 60 60 120 120 ▪ Double/Triple Hit Lymphoma (DHL/THL) and Double Expresser 120 120 PS-341 PS-341 25 25 40 100 100 100 40 100 Lymphoma (DEL) are high-grade B-cell lymphomas (HGBL) that exhibit 0 0 80 80 80 20 80 20 60 60 -25 -25 60 60 0 low responses to standard therapeutic regimens resulting in poor 0 IC = 0.34 IC = 0.36 50 40 40 50 40 40 IC = 0.42 IC = 0.50 -50 -50 -20 50 50 -20 prognosis. 20 20 20 20 0.01 0.1 1 10 0.01100 0.1 1 10 100 -40 -75 -75 -40 0 0 0 0 [drug], μM [drug], μM -60 -60 -20 -20 -20 ▪ DHL harbor translocations in MYC and BCL2 or BCL6, THL contain 0.01 0.1 1 10 0.01 0.1 1 10 -20 0.001 0.01 0.1 1 10 0.001 0.01 0.1 1 10 0.0001 0.001 0.01 0.1 1 10 0.0001 0.001 0.01 0.1 1 10 Compound concentration (μM) Compound concentration (μM) Compound Concentration (uM) Compound Concentration (uM) Compound Concentration (uM) translocations in MYC/BCL2/BCL6, and DEL are characterized by high Compound Concentration (uM) expression of MYC and BCL2. MM Cell Average % Max Average IC Standard DLBCL Average % Max Average IC Standard 50 ± BMF-219 Clinical RBMF B ev M eF rs --i2 b 219 1 le 9 1 CC Cl lin liiin nic cia cla al R l R eR v ee e vr e v srer is bilb e sible l e 1 2 Menin Clinical Reversible 2 50 ± Translocation Mutation Category Translocation Line Inhibition by BMF-219 Deviation ( M) Cell Line Inhibition by BMF-219 Deviation (mM) m ▪ We previously reported the ability of irreversible menin inhibitor, BMF- MM1.S t(14;16) KRAS G12A 99.5 0.47 ± 0.17 DB DHL MYC/BCL2 98.5 0.41 ± 0.07 Growth Growth % Max % Max Inhibition Inhibition MM1.R t(14;16) KRAS G12A 99.6 0.46 ± 0.17 219, to modulate MYC expression and exhibit high potency against DHL Toledo DHL MYC/BCL2 98.8 0.31 ± 0.07 Inhibition Inhibition IC ( M) IC ( M) SKMM1 t(14;20) NRAS G12A 99.2 0.47 ± 0.05mm 50 50 0.32 ± 0.03 Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL) preclinical models (Somanath et DOHH2 DHL MYC/BCL2 99.7 SKMM2 t(11;14) TP53 80.2 0.65 ± 0.15 Treatment BM100 BM101 VAL THL MYC/BCL2/BCL6 97.1 0.27 ± 0.07 al., 2021). JJN3 t(14;16) NRAS Q61K 99.2 0.29 ± 0.02 BMF-219 0.250 100 0.151 100 MYC/BCL2 OPM2 t(4;14) TP53 98.4 0.55 U2932 DEL-ABC 92.4 0.37 ± 0.01 Overexpression Clinical Reversible 6.31 50 > 10 30 Potent killing activity of BMF-219 at clinically relevant concentrations in representative MM and DLBCL cell lines. (A). MM1.R, JJN3, SKMM1, SKMM2 and OPM2 cell lines and (B). DHL (DB, Toledo, SUDHL8 GCB - 99.6 0.60 ± 0.21 Growth inhibition of patient-derived DLBCL Triple Hit Lymphoma (THL) and MYC-amplified PDX DOHH2), THL (VAL), DEL (U2932), and GCB (SUDHL8) subtypes were cultured in the presence of Pfeiffer GCB - 99.6 0.17 ± 0.04 samples treated with BMF-219 or clinical reversible menin inhibitor after 6 days of treatment. IC 50 BMF-219 (blue) or PS-341 (red) for 4 days. Average IC values of at least two experiments, 50 OCI-LY7 GCB - 99.6 0.65 ± 0.26 values and maximal percentage cell killing are summarized in the table. maximal percentage cell killing, and cytogenetic background cell lines are summarized in the table. BMF-219 dramatically reduces growth of both newly diagnosed and R/R MM patient specimens Newly Diagnosed Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma Stage at Treatment Prior Therapy and Response Translocation 120 16-669/0219 Specimen ID Diagnosis Status 120 BMF-219 16-684/1019 120 120 BMF-219 241-9949/0619 241-10514/0720 BMF-219 BMF-219 PS-341 PS-341 PS-341 PS-341 100 Newly 100 100 100 16-669/0219 IIIA None No data Diagnosed 80 80 80 80 Newly 60 60 60 60 ▪ Here, we demonstrate the anti-tumor activity of BMF-219 in MM and 16-684/1019 IIIA None No data Diagnosed 40 40 40 40 HGBL preclinical models harboring various mutational backgrounds. IC = 0.18 IC = 0.29 IC = 0.31 IC = 0.12 50 50 50 50 241-9949/06-19 IIIA Refractory VCD N4 (resistant) p53 deletion 20 20 20 20 VCD N 4 (responded) 0 0 0 0 High dose CPH (SC-mobilization) (responded) -20 -20 -20 -20 0.0001 0.001 0.01 0.1 1 10 0.0001 0.001 0.01 0.1 1 10 0.0001 0.001 0.01 0.1 1 10 0.0001 0.001 0.01 0.1 1 10 Compound Concentration (uM) p53 deletion- Compound Concentration (uM) Consolidation (AutoSCT, double transplant) Compound Concentration (uM) Compound Concentration (uM) 241-10514/0720 IIIA Refractory negative Bortezomib- maintenance (resistant) Growth inhibition of newly diagnosed (A-B) and R/R (C-D) MM patient-derived bone marrow RVD #4 (resistant) mononuclear cells (BMMCs) after 6 days of treatment with BMF-219 (blue) or PS-341 (red). CONCLUSIONS PRD #4 (resistant) Clinical profiles of MM patient-derived BMMC specimens are summarized in the table. DHL / DEL DLBCL Multiple Myeloma BMF-219 exerts pronounced decrease in menin protein expression in MM and DLBCL cell lines ▪ BMF-219 achieved >99% cell lethality in MM cell lines with RAS mutations with IC values between 0.3mM and 0.5mM. 50 SKMM1 OPM2 TOLEDO (DLBCL-DHL) U2932 (DLBCL-DEL) ▪ BMF-219 demonstrated single-agent efficacy (IC values between 0.1mM 50 Menin Menin Menin Menin and 0.3mM) against a panel of newly diagnosed and R/R ex vivo MM Vinculin Vinculin Vinculin Vinculin samples, including a p53-deleted clinical profile. 120 120 120 120 94 98 100 100 100 100 86 ▪ BMF-219 exhibited high potency as a single agent against DHL, THL and 100 100 100 100 METHODS 81 76 75 DEL DLBCL cell lines, with IC values of 0.3mM and 0.4mM, respectively. 80 80 80 80 69 50 61 50 52 48 54 54 51 ▪ In ex vivo studies, BMF-219 was highly effective against R-CHOP and R- 60 60 60 60 43 39 ▪ MM and DLBCL cell lines were cultured in the presence of BMF-219 or EPOCH refractory patient samples with THL and MYC-amplified genetic 40 40 40 40 bortezomib (PS-341) for 4 days and cell proliferation was measured by backgrounds. 20 20 20 20 Cell Titer Glo. ▪ BMF-219 was multi-fold more potent and exerted dramatically greater 0 0 0 0 ▪ Patient-derived MM patient derived BMMCs and DLBCL PDX models growth inhibition compared to clinical reversible menin inhibitors in DLBCL were cultured ex vivo in the presence of BMF-219 or PS-341 for 6 days patient-derived ex vivo samples. and cell proliferation was measured by Cell Titer Glo. ▪ BMF-219 induces reduction of menin protein levels across MM and DLBCL ▪ MM and DLBCL cell lines were cultured in the presence of BMF-219 or cell lines. This reduction however appears to be transient. An incubation SKMM1 OPM2 TOLEDO U2932 % Cell % Cell clinical reversible menin inhibitors for 14 hours. Menin protein expression BMF-219 BMF-219 BMF-219 Clin Rev MI-503 BMF-219 BMF-219 BMF-219 Clin Rev MI-503 BMF-219 BMF-219 BMF-219 Clin Rev MI-503 BMF-219 BMF-219 BMF-219 Clin Rev MI-503 time of 14 hours may not be a good predictor of cellular growth inhibition. Death Death (0.4μM) (0.5μM) (1μM) (1μM) (3μM) (0.5μM) (0.5μM) (1μM) (1μM) (3μM) (0.4μM) (0.5μM) (1μM) (1μM) (3μM) (0.4μM) (0.5μM) (1μM) (1μM) (3μM) was measured by the Wes system and analyzed using the Compass 72 hr 72 hr 27 - 86 4 33 22 - 80 3 21 32 - 97 0 35 29 - 86 3 34 REFERENCES software (automated western blotting, Protein Simple). Signal was 14 hr - 15 25 0 13 - 8 57 0 14 14 hr - 18 12 0 11 - 19 36 0 7 ▪ Chapman, M., Lawrence, M., Keats, J. et al. Initial genome sequencing and analysis of multiple myeloma. Nature 471, 467–472 (2011). ▪ Somanath, P., Lu, D., Law, B. et al. Novel Irreversible Menin Inhibitor, BMF-219, Shows Potent Single Agent Activity in Clinically Relevant DLBCL BMF-219 reduces menin protein in MM and DLBCL cells. Quantitation of menin protein expression in SKMM1, OPM2, Toledo and U2932 cell line treated with BMF-219, clinical reversible menin inhibitor or normalized to GAPDH and referenced to DMSO control. Cells. Blood 2021; 138 (Supplement 1): 4318. preclinical reversible menin inhibitor, MI-503, for 14 hours. Average menin protein expression are of 3 independent experiments. WES blot is a representative from 1 single experiment. Cells were cultured in ▪ Wu, G., Yuan, M., Shen, S. et al. Menin enhances c-Myc-mediated transcription to promote cancer progression. Nat Commun 8, 15278 (2017). the presence of menin inhibitors for 72hr or 14hr. Average % cell killing treated at 72hr and 14hr are from 2 independent experiment.▪ Borkin, D. et al. Pharmacologic inhibition of the Menin-MLL interaction blocks progression of MLL leukemia in vivo. Cancer Cell. 2015 Apr 13;27(4):589-602. DMSO BMF-219 (0.5μM) BMF-219 (1μM) Clinical Rev (1μM) MI-503 (3μM) DMSO BMF-219 (0.5μM) BMF-219 (1μM) Clinical Rev (1μM) MI-503 (3μM) DMSO BMF-219 (0.5μM) BMF-219 (1μM) Clinical Rev (1μM) MI-503 (3μM) DMSO BMF-219 (0.5μM) BMF-219 (1μM) Clinical Rev (1μM) MI-503 (3μM) %Menin Remaining Cell Proliferation Inhibition (%) Cell Proliferation Inhibition (%) %Menin Remaining Cell Proliferation Inhibition (%) Cell Proliferation Inhibition (%) %Menin Remaining Cell Proliferation Inhibition (%) Cell Proliferation Inhibition (%) Cell Proliferation Inhibition (%) Cell Proliferation Inhibition (%) %Menin Remaining Cell Proliferation Inhibition (%) Cell Proliferation Inhibition (%) Cell Proliferation Inhibition (%) Cell Proliferation Inhibition (%) % Growth Inhibition % Growth Inhibition Cell Proliferation Inhibition (%) Cell Proliferation Inhibition (%)