UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM N-CSR
CERTIFIED SHAREHOLDER REPORT OF REGISTERED
MANAGEMENT INVESTMENT COMPANIES
Investment Company Act File Number: 811-09995
| T. Rowe Price Global Technology Fund, Inc. |
| (Exact name of registrant as specified in charter) |
| 100 East Pratt Street, Baltimore, MD 21202 |
| (Address of principal executive offices) |
| David Oestreicher |
| 100 East Pratt Street, Baltimore, MD 21202 |
| (Name and address of agent for service) |
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code: (410) 345-2000
Date of fiscal year end: December 31
Date of reporting period: December 31, 2011
Item 1. Report to Shareholders
 |
| Global Technology Fund | December 31, 2011 |

The views and opinions in this report were current as of December 31, 2011. They are not guarantees of performance or investment results and should not be taken as investment advice. Investment decisions reflect a variety of factors, and the managers reserve the right to change their views about individual stocks, sectors, and the markets at any time. As a result, the views expressed should not be relied upon as a forecast of the fund’s future investment intent. The report is certified under the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, which requires mutual funds and other public companies to affirm that, to the best of their knowledge, the information in their financial reports is fairly and accurately stated in all material respects.
REPORTS ON THE WEB
Sign up for our E-mail Program, and you can begin to receive updated fund reports and prospectuses online rather than through the mail. Log in to your account at troweprice.com for more information.
Manager’s Letter
Fellow Shareholders
Global technology stocks slumped in the second half of 2011. Sovereign debt fears in Europe, concerns about political paralysis in the U.S., and mixed economic news about the sustainability of the global economic recovery caused markets to falter. Investors appeared to focus on whether European governments could stabilize sovereign bond yields and how the Chinese government would navigate a soft landing in its housing and construction markets. Semiconductor and telecommunications equipment companies began to fall short of earnings projections and showed signs of a midcycle slowdown. We remained focused on identifying share-gaining products and companies and navigating cyclical shifts to maximize performance.
PERFORMANCE COMPARISON

Our fund fell 1.64% in 2011 but outperformed the MSCI All Country World Index Information Technology, which tracks global technology stocks in various international markets, and the Lipper Global Science & Technology Funds Index. The fund fell more sharply during the last six months and lagged the MSCI benchmark but outperformed its Lipper index for the period. Telecommunications equipment, software, and hardware stocks were the best contributors to performance.
The fund’s long-term relative performance continued to be exceptional—it was Lipper’s top-ranked fund in its category for the 1-, 3-, and 5-year periods through December 31, 2011. Based on cumulative total return, Lipper ranked the Global Technology Fund 1 of 43, 1 of 31, 1 of 22, and 2 of 17 global science and technology funds for the 1-, 3-, 5-, and 10-year periods ended December 31, 2011, respectively. (Past performance cannot guarantee future results.)
MARKET ENVIRONMENT
Global markets gained ground in the first half of the year, supported by healthy corporate earnings, strong balance sheets, and increasing consumer demand. But economic conditions deteriorated in the summer of 2011 as fears of European sovereign bond defaults, a downturn in China’s economic growth, and intractable U.S. politics hurt business and investor confidence. We began to see encouraging signs in U.S. employment, housing, and consumption in the fourth quarter. But slowing growth elsewhere served to highlight concerns that the global recovery would continue to muddle along, thereby dampening investor enthusiasm.
Technology stocks began the year strong, benefiting from the tailwind of solid earnings in the second half of 2010. However, in the spring, global macroeconomic concerns began to pressure business conditions, and fundamentals softened. The second half of 2011 was characterized by low confidence and rising levels of volatility. By the end of 2011, the valuations of global technology stocks appeared increasingly attractive across the board.
It is clear to us that investors have shifted capital away from equities and other “risk assets.” The market seems to be bracing itself to absorb further setbacks stemming from the European debt crisis and the slow U.S. recovery. Still, global technology companies are flush with record amounts of cash and appear fortified by having survived many years of uncertainty.
PORTFOLIO REVIEW
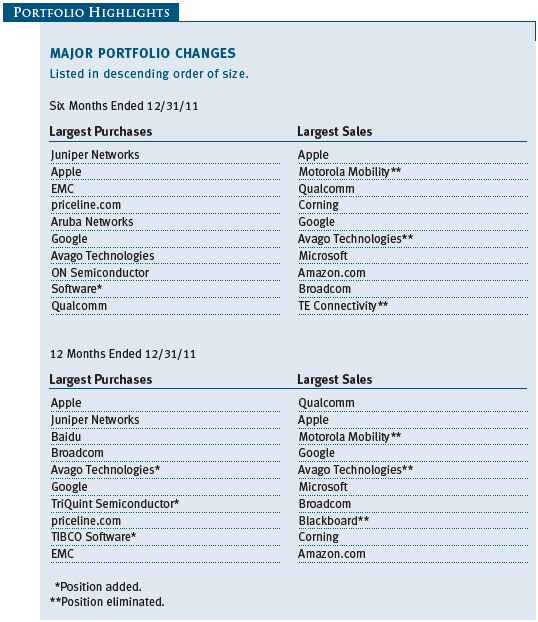
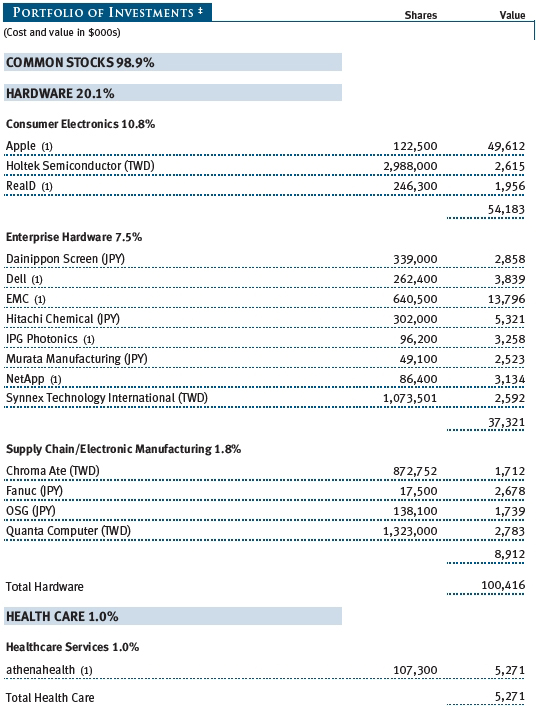
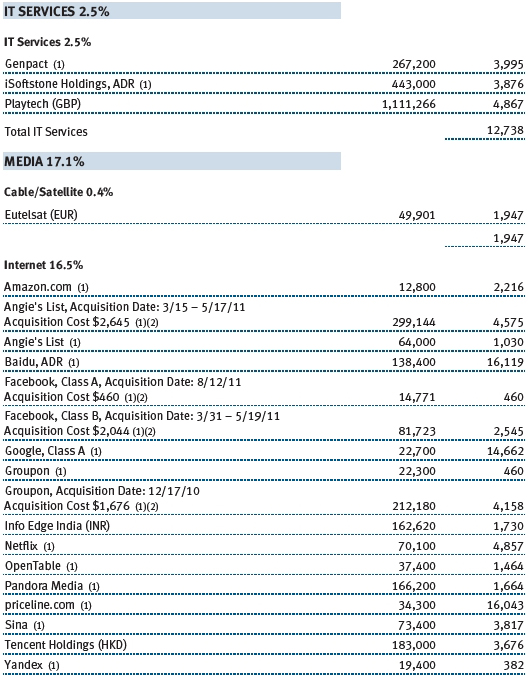
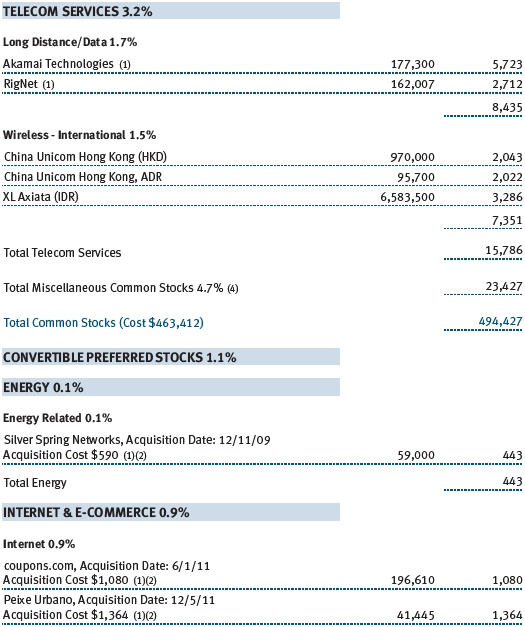
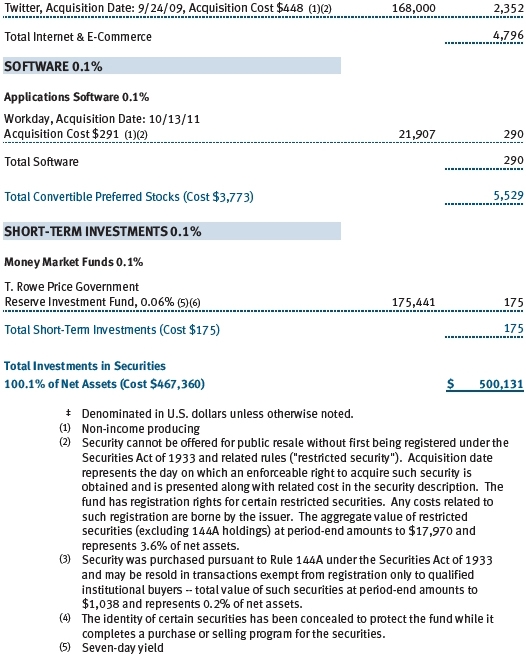
Communications equipment and software firms were key contributors to your fund’s performance. Apple, our largest holding, continues to redefine the way consumers—and, increasingly, businesses—use computers. We believe that investors have underestimated the revenue potential of Apple’s iPad and that, in the year ahead, we will begin to see the mass adoption of the Apple platform of products by business and government and in the private and public education arenas. Apple holds less than a 10% share of the global computer market, and we believe that it will show strong growth even as the total PC market shrinks. (Please refer to the fund’s portfolio of investments for a complete list of holdings and the amount each represents in the portfolio.)
Communications equipment did well in the first half of 2011 before lagging in the second half. Alcatel-Lucent, Motorola Mobility, and Qualcomm were strong contributors to performance. The fund benefited from the acquisition of Motorola by Google in August 2011. We also avoided large exposure to some weak stocks, including Nokia and Cisco Systems. We added to Cisco in the second half of 2011, however, after significant underperformance.
We increased our exposure to software stocks early in the year. Performance benefited from the acquisition of UK software company Autonomy by Hewlett-Packard. The fund also benefited from a position in Nuance Communications, which was instrumental in the development of Apple’s “Siri” language voice platform for the iPhone 4S.
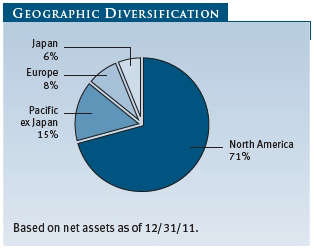
The fund reduced its exposure to international names at the end of 2011. We took advantage of opportunities in the U.S. and harvested gains in strong performers like Autonomy and Samsung Electronics. Samsung was a solid stock in the second half, due to the increase in mobile sales on the back of smartphone adoption and share gains in the Android platform. We expect our international exposure to increase in early 2012 as opportunities arise. Our strong global technology research team is one of the key differentiators of our long-term performance.

TriQuint Semiconductor, Juniper Networks, and Corning detracted from our performance in 2011. TriQuint was an important supplier for Apple’s iPhone but failed to expand its business with other customers, which hurt results. Corning struggled amid the decline in global LCD TV inventories and pricing pressures of its glass for LCD TVs. Juniper suffered from poor product execution, which hurt results in the second half of 2011. We significantly increased our weight in Juniper, as we see stability and recovery by the second half of 2012. We think Juniper’s technology and product position are being underestimated by the market.
STRATEGY REVIEW AND OUTLOOK
Investors are now more aware of risk and the potential for crisis than at any time in the past several decades, in our opinion. The market anticipates something going wrong. This caution is embedded in the prices of global technology stocks and reflected by the extremely high correlation of stock prices. Famed investor John Templeton said that “the time of maximum pessimism is the best time to buy, and the time of maximum optimism is the best time to sell.” We believe that we are closer to the former than the latter and that myriad risks have been priced into global equity markets.
We see a world with challenges but believe that global economies are more likely to muddle through this period of structural changes than face disaster. In this environment, we think that stock picking matters. We are looking for products and companies gaining market share and participating in extreme positive outcomes. The market is doing a poor job of differentiating the winners and losers at the moment, and this is where our global research platform should shine.
Tactically, we see solid near-term opportunities in semiconductors, components, and communications equipment. The market punished these groups in the second half, but we believe a classic cyclical recovery is at hand. We added to these areas in late 2011 and plan to continue in early 2012.
The key trends in which we are seeing opportunity include mobile computing; cloud software and services, which deliver applications via the Internet; and data analytics. We also think that the penetration of technology in emerging markets should continue to grow. These inventions and trends would be powerful even in isolation, but we believe that the intersection of these developments increases their potential.
In mobile computing we own Apple, Qualcomm, SanDisk, and Samsung. Competition between Intel and ARM Holdings has the potential to drive a capital cycle in semiconductor equipment as these companies race to gain market share. We also see the explosion of applications being built by Google, Facebook, Twitter, and others that will ride the mobile platform. Companies like Aruba Networks are increasing the value of mobility by enabling ubiquitous WiFi connectivity.
In cloud computing and software, we own Ariba, Akamai Technologies, Cornerstone OnDemand, and Salesforce.com to take advantage of steady share gains from traditional software companies. The adoption of mobility accelerates the shift to these cloud solutions.
Data analytics is what helps us make sense of all the data these new mobile and software tools are creating. We own Informatica, TIBCO Software, and Software in this space. Our position in EMC also reflects a world where more and more data are being created and need to be stored and transformed into information.
We believe valuations for global technology companies are attractive and that a significant amount of investor concern about global economic conditions is already reflected in stock prices. The trends in technology are unmistakable—rapid innovation, disruptive change, and new markets throughout the developed and emerging worlds. We are optimistic that our global research platform can turn over more stones and find attractive opportunities.
Once again, we thank you for your continued confidence and support.
Respectfully submitted,

David J. Eiswert
President of the fund and chairman of its Investment Advisory Committee
January 18, 2012
The committee chairman has day-to-day responsibility for managing the portfolio and works with committee members in developing and executing the fund’s investment program.
RISKS OF INVESTING IN THE FUND
Funds that invest only in specific industries will experience greater volatility than funds investing in a broad range of industries. Technology stocks, historically, have experienced unusually wide price swings, both up and down. The potential for wide variation in performance reflects the special risks common to companies in the rapidly changing field of technology. For example, products or services that at first appear promising may not prove commercially successful and may become obsolete quickly. Earnings disappointments and intense competition for market share can result in sharp price declines.
GLOSSARY
Lipper Global Science & Technology Funds Index: An index of science and technology mutual fund performance returns of funds that invest in technology companies around the world for specified periods as tracked by Lipper Inc.
MSCI All Country World Index Information Technology: An index that tracks information technology stocks in developed and emerging markets.

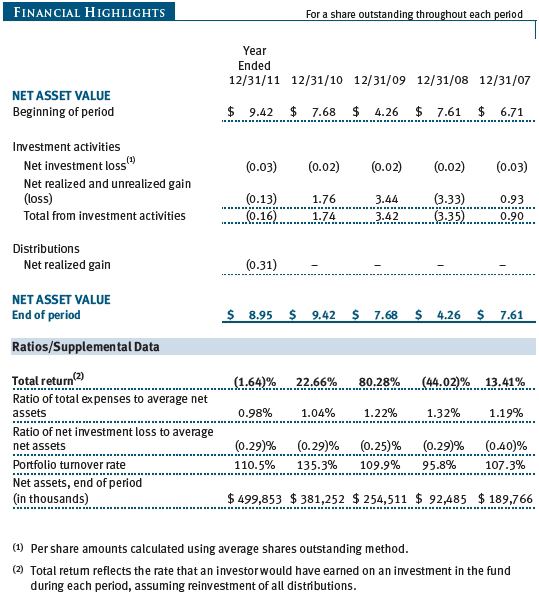
Performance and Expenses
| Growth of $10,000 |
This chart shows the value of a hypothetical $10,000 investment in the fund over the past 10 fiscal year periods or since inception (for funds lacking 10-year records). The result is compared with benchmarks, which may include a broad-based market index and a peer group average or index. Market indexes do not include expenses, which are deducted from fund returns as well as mutual fund averages and indexes.



| Fund Expense Example |
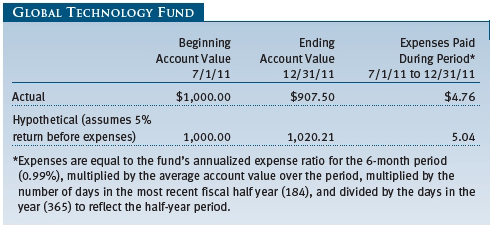
As a mutual fund shareholder, you may incur two types of costs: (1) transaction costs, such as redemption fees or sales loads, and (2) ongoing costs, including management fees, distribution and service (12b-1) fees, and other fund expenses. The following example is intended to help you understand your ongoing costs (in dollars) of investing in the fund and to compare these costs with the ongoing costs of investing in other mutual funds. The example is based on an investment of $1,000 invested at the beginning of the most recent six-month period and held for the entire period.
Actual Expenses
The first line of the following table (“Actual”) provides information about actual account values and expenses based on the fund’s actual returns. You may use the information on this line, together with your account balance, to estimate the expenses that you paid over the period. Simply divide your account value by $1,000 (for example, an $8,600 account value divided by $1,000 = 8.6), then multiply the result by the number on the first line under the heading “Expenses Paid During Period” to estimate the expenses you paid on your account during this period.
Hypothetical Example for Comparison Purposes
The information on the second line of the table (“Hypothetical”) is based on hypothetical account values and expenses derived from the fund’s actual expense ratio and an assumed 5% per year rate of return before expenses (not the fund’s actual return). You may compare the ongoing costs of investing in the fund with other funds by contrasting this 5% hypothetical example and the 5% hypothetical examples that appear in the shareholder reports of the other funds. The hypothetical account values and expenses may not be used to estimate the actual ending account balance or expenses you paid for the period.
Note: T. Rowe Price charges an annual account service fee of $20, generally for accounts with less than $10,000 ($1,000 for UGMA/UTMA). The fee is waived for any investor whose T. Rowe Price mutual fund accounts total $50,000 or more; accounts employing automatic investing; accounts electing to receive electronic delivery of account statements, transaction confirmations, prospectuses, and shareholder reports; accounts of an investor who is a T. Rowe Price Preferred Services, Personal Services, or Enhanced Personal Services client (enrollment in these programs generally requires T. Rowe Price assets of at least $100,000); and IRAs and other retirement plan accounts that utilize a prototype plan sponsored by T. Rowe Price (although a separate custodial or administrative fee may apply to such accounts). This fee is not included in the accompanying table. If you are subject to the fee, keep it in mind when you are estimating the ongoing expenses of investing in the fund and when comparing the expenses of this fund with other funds.
You should also be aware that the expenses shown in the table highlight only your ongoing costs and do not reflect any transaction costs, such as redemption fees or sales loads. Therefore, the second line of the table is useful in comparing ongoing costs only and will not help you determine the relative total costs of owning different funds. To the extent a fund charges transaction costs, however, the total cost of owning that fund is higher.
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.



The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.

The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.

The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
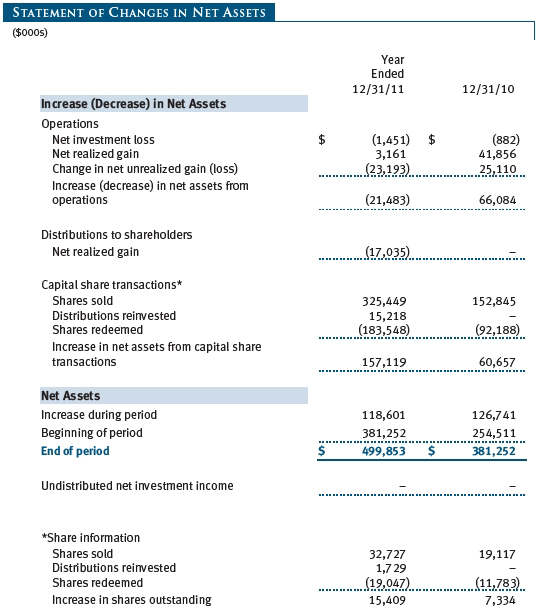
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
| Notes to Financial Statements |
T. Rowe Price Global Technology Fund, Inc. (the fund), is registered under the Investment Company Act of 1940 (the 1940 Act) as a diversified, open-end management investment company. The fund commenced operations on September 29, 2000. The fund seeks to provide long-term capital growth.
NOTE 1 - SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Basis of Preparation The accompanying financial statements were prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (GAAP), which require the use of estimates made by management. Management believes that estimates and valuations are appropriate; however, actual results may differ from those estimates, and the valuations reflected in the accompanying financial statements may differ from the value ultimately realized upon sale or maturity.
Investment Transactions, Investment Income, and Distributions Income and expenses are recorded on the accrual basis. Dividends received from mutual fund investments are reflected as dividend income; capital gain distributions are reflected as realized gain/loss. Dividend income and capital gain distributions are recorded on the ex-dividend date. Income tax-related interest and penalties, if incurred, would be recorded as income tax expense. Investment transactions are accounted for on the trade date. Realized gains and losses are reported on the identified cost basis. Distributions to shareholders are recorded on the ex-dividend date. Income distributions are declared and paid annually. Capital gain distributions, if any, are generally declared and paid by the fund annually.
Currency Translation Assets, including investments, and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies are translated into U.S. dollar values each day at the prevailing exchange rate, using the mean of the bid and asked prices of such currencies against U.S. dollars as quoted by a major bank. Purchases and sales of securities, income, and expenses are translated into U.S. dollars at the prevailing exchange rate on the date of the transaction. The effect of changes in foreign currency exchange rates on realized and unrealized security gains and losses is reflected as a component of security gains and losses.
Rebates and Credits Subject to best execution, the fund may direct certain security trades to brokers who have agreed to rebate a portion of the related brokerage commission to the fund in cash. Commission rebates are reflected as realized gain on securities in the accompanying financial statements and totaled $40,000 for the year ended December 31, 2011. Additionally, the fund earns credits on temporarily uninvested cash balances held at the custodian, which reduce the fund’s custody charges. Custody expense in the accompanying financial statements is presented before reduction for credits.
New Accounting Pronouncement In December 2011, the Financial Accounting Standards Board issued amended guidance to enhance disclosure for offsetting assets and liabilities. The guidance is effective for fiscal years and interim periods beginning on or after January 1, 2013; adoption will have no effect on the fund’s net assets or results of operations.
NOTE 2 - VALUATION
The fund’s financial instruments are reported at fair value as defined by GAAP. The fund determines the values of its assets and liabilities and computes its net asset value per share at the close of the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE), normally 4 p.m. ET, each day that the NYSE is open for business. Values in the accompanying Portfolio of Investments are as of December 30, 2011, the last business day in the fund’s fiscal year ended December 31, 2011. Some foreign markets were open between December 30 and the close of the fund’s reporting period on December 31, but any differences in values and foreign exchange rates subsequent to December 30 through December 31 were immaterial to the fund’s financial statements.
Valuation Methods Equity securities listed or regularly traded on a securities exchange or in the over-the-counter (OTC) market are valued at the last quoted sale price or, for certain markets, the official closing price at the time the valuations are made, except for OTC Bulletin Board securities, which are valued at the mean of the latest bid and asked prices. A security that is listed or traded on more than one exchange is valued at the quotation on the exchange determined to be the primary market for such security. Listed securities not traded on a particular day are valued at the mean of the latest bid and asked prices for domestic securities and the last quoted sale price for international securities.
Investments in mutual funds are valued at the mutual fund’s closing net asset value per share on the day of valuation. Forward currency exchange contracts are valued using the prevailing forward exchange rate.
Other investments, including restricted securities and private placements, and those financial instruments for which the above valuation procedures are inappropriate or are deemed not to reflect fair value, are stated at fair value as determined in good faith by the T. Rowe Price Valuation Committee, established by the fund’s Board of Directors (the Board). Subject to oversight by the Board, the Valuation Committee develops pricing-related policies and procedures and approves all fair-value determinations. The Valuation Committee regularly makes good faith judgments, using a wide variety of sources and information, to establish and adjust valuations of certain securities as events occur and circumstances warrant. For instance, in determining the fair value of private-equity instruments, the Valuation Committee considers a variety of factors, including the company’s business prospects, its financial performance, strategic events impacting the company, relevant valuations of similar companies, new rounds of financing, and any negotiated transactions of significant size between other investors in the company. Because any fair-value determination involves a significant amount of judgment, there is a degree of subjectivity inherent in such pricing decisions.
For valuation purposes, the last quoted prices of non-U.S. equity securities may be adjusted under the circumstances described below. If the fund determines that developments between the close of a foreign market and the close of the NYSE will, in its judgment, materially affect the value of some or all of its portfolio securities, the fund will adjust the previous closing prices to reflect what it believes to be the fair value of the securities as of the close of the NYSE. In deciding whether it is necessary to adjust closing prices to reflect fair value, the fund reviews a variety of factors, including developments in foreign markets, the performance of U.S. securities markets, and the performance of instruments trading in U.S. markets that represent foreign securities and baskets of foreign securities. A fund may also fair value securities in other situations, such as when a particular foreign market is closed but the fund is open. The fund uses outside pricing services to provide it with closing prices and information to evaluate and/or adjust those prices. The fund cannot predict how often it will use closing prices and how often it will determine it necessary to adjust those prices to reflect fair value. As a means of evaluating its security valuation process, the fund routinely compares closing prices, the next day’s opening prices in the same markets, and adjusted prices. Additionally, trading in the underlying securities of the fund may take place in various foreign markets on certain days when the fund is not open for business and does not calculate a net asset value. As a result, net asset values may be significantly affected on days when shareholders cannot make transactions.
Valuation Inputs Various inputs are used to determine the value of the fund’s financial instruments. These inputs are summarized in the three broad levels listed below:
Level 1 – quoted prices in active markets for identical financial instruments
Level 2 – observable inputs other than Level 1 quoted prices (including, but not limited to, quoted prices for similar financial instruments, interest rates, prepayment speeds, and credit risk)
Level 3 – unobservable inputs
Observable inputs are those based on market data obtained from sources independent of the fund, and unobservable inputs reflect the fund’s own assumptions based on the best information available. The input levels are not necessarily an indication of the risk or liquidity associated with financial instruments at that level. For example, non-U.S. equity securities actively traded in foreign markets generally are reflected in Level 2 despite the availability of closing prices because the fund evaluates and determines whether those closing prices reflect fair value at the close of the NYSE or require adjustment, as described above. The following table summarizes the fund’s financial instruments, based on the inputs used to determine their values on December 31, 2011:
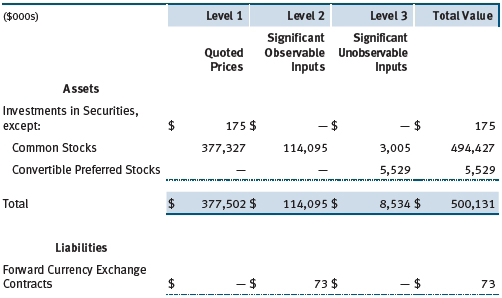
Following is a reconciliation of the fund’s Level 3 holdings for the year ended December 31, 2011. Transfers into and out of Level 3 are reflected at the value of the financial instrument at the beginning of the period. Gain (loss) reflects both realized and change in unrealized gain (loss) on Level 3 holdings during the period, if any, and is included on the accompanying Statement of Operations. The change in unrealized gain (loss) on Level 3 instruments held at December 31, 2011, totaled $2,182,000 for the year ended December 31, 2011.

NOTE 3 - DERIVATIVE INSTRUMENTS
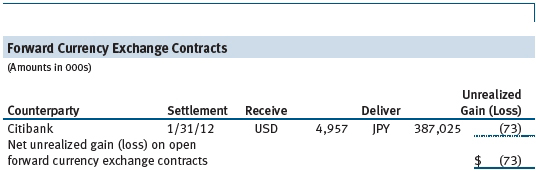
During the year ended December 31, 2011, the fund invested in derivative instruments. As defined by GAAP, a derivative is a financial instrument whose value is derived from an underlying security price, foreign exchange rate, interest rate, index of prices or rates, or other variable; it requires little or no initial investment and permits or requires net settlement. The fund invests in derivatives only if the expected risks and rewards are consistent with its investment objectives, policies, and overall risk profile, as described in its prospectus and Statement of Additional Information. The fund may use derivatives for a variety of purposes, such as seeking to hedge against declines in principal value, increase yield, invest in an asset with greater efficiency and at a lower cost than is possible through direct investment, or to adjust credit exposure. The risks associated with the use of derivatives are different from, and potentially much greater than, the risks associated with investing directly in the instruments on which the derivatives are based. Investments in derivatives can magnify returns positively or negatively; however, the fund at all times maintains sufficient cash reserves, liquid assets, or other SEC-permitted asset types to cover the settlement obligations under its open derivative contracts.
The fund values its derivatives at fair value, as described below and in Note 2, and recognizes changes in fair value currently in its results of operations. Accordingly, the fund does not follow hedge accounting, even for derivatives employed as economic hedges. The fund does not offset the fair value of derivative instruments against the right to reclaim or obligation to return collateral. As of December 31, 2011, the fund held foreign exchange derivatives with a fair value of $(73,000), included in Unrealized loss on forward currency exchange contracts, on the accompanying Statement of Assets and Liabilities.
Additionally, during the year ended December 31, 2011, the fund recognized $(331,000) of realized loss on Foreign Currency Transactions and a $32,000 change in unrealized gain on Foreign Currency Transactions related to its investments in foreign exchange derivatives; such amounts are included on the accompanying Statement of Operations.
Forward Currency Exchange Contracts The fund is subject to foreign currency exchange rate risk in the normal course of pursuing its investment objectives. It uses forward currency exchange contracts (forwards) primarily to protect its non-U.S. dollar-denominated securities from adverse currency movements relative to the U.S. dollar. A forward involves an obligation to purchase or sell a fixed amount of a specific currency on a future date at a price set at the time of the contract. Although certain forwards may be settled by exchanging only the net gain or loss on the contract, most forwards are settled with the exchange of the underlying currencies in accordance with the specified terms. Forwards are valued at the unrealized gain or loss on the contract, which reflects the net amount the fund either is entitled to receive or obligated to deliver, as measured by the difference between the forward exchange rates at the date of entry into the contract and the forward rates at the reporting date. Appreciated forwards are reflected as assets, and depreciated forwards are reflected as liabilities on the accompanying Statement of Assets and Liabilities. Risks related to the use of forwards include the possible failure of counterparties to meet the terms of the agreements; that anticipated currency movements will not occur, thereby reducing the fund’s total return; and the potential for losses in excess of the fund’s initial investment. During the year ended December 31, 2011, the fund’s exposure to forwards, based on underlying notional amounts, was generally between 0% and 2% of net assets.
NOTE 4 - OTHER INVESTMENT TRANSACTIONS
Consistent with its investment objective, the fund engages in the following practices to manage exposure to certain risks and/or to enhance performance. The investment objective, policies, program, and risk factors of the fund are described more fully in the fund’s prospectus and Statement of Additional Information.
Emerging Markets At December 31, 2011, approximately 15% of the fund’s net assets were invested, either directly or through investments in T. Rowe Price institutional funds, in securities of companies located in emerging markets, securities issued by governments of emerging market countries, and/or securities denominated in or linked to the currencies of emerging market countries. Emerging market securities are often subject to greater price volatility, less liquidity, and higher rates of inflation than U.S. securities. In addition, emerging markets may be subject to greater political, economic, and social uncertainty, and differing regulatory environments that may potentially impact the fund’s ability to buy or sell certain securities or repatriate proceeds to U.S. dollars.
Restricted Securities The fund may invest in securities that are subject to legal or contractual restrictions on resale. Prompt sale of such securities at an acceptable price may be difficult and may involve substantial delays and additional costs.
Securities Lending The fund lends its securities to approved brokers to earn additional income. It receives as collateral cash and U.S. government securities valued at 102% to 105% of the value of the securities on loan. Cash collateral is invested by the fund’s lending agent(s) in accordance with investment guidelines approved by management. Although risk is mitigated by the collateral, the fund could experience a delay in recovering its securities and a possible loss of income or value if the borrower fails to return the securities or if collateral investments decline in value. Securities lending revenue recognized by the fund consists of earnings on invested collateral and borrowing fees, net of any rebates to the borrower and compensation to the lending agent. In accordance with GAAP, investments made with cash collateral are reflected in the accompanying financial statements, but collateral received in the form of securities are not. At December 31, 2011, there were no securities on loan.
When-Issued Securities The fund may enter into when-issued purchases and/or sales commitments, pursuant to which it agrees to purchase or sell, respectively, the underlying security for a fixed unit price, with payment and delivery at a scheduled future date generally beyond the customary settlement period for such securities. When-issued refers to securities that have not yet been issued but will be issued in the future and may include new securities or securities obtained through a corporate action on a current holding. The fund normally purchases when-issued securities with the intention of taking possession but may enter into a separate agreement to sell the securities before the settlement date. Until settlement, the fund maintains cash reserves and liquid assets sufficient to settle its when-issued commitments. Amounts realized on when-issued transactions are included with realized gain/loss on securities in the accompanying financial statement.
Counterparty Risk and Collateral The fund has entered into collateral agreements with certain counterparties to mitigate counterparty risk associated with certain over-the-counter (OTC) financial instruments, including swaps, forward currency exchange contracts, TBA purchase commitments, and OTC options (collectively, covered OTC instruments). Subject to certain minimum exposure requirements (which typically range from $100,000 to $500,000), collateral requirements generally are determined and transfers made based on the net aggregate unrealized gain or loss on all covered OTC instruments covered by a particular collateral agreement with a specified counterparty. Collateral, both pledged by the fund to a counterparty and pledged by a counterparty to the fund, is held in a segregated account by a third-party agent and can be in the form of cash or debt securities issued by the U.S. government or related agencies. Securities posted as collateral by the fund to a counterparty are so noted in the accompanying Portfolio of Investments and remain in the fund’s net assets. As of December 31, 2011, no collateral was pledged by either the fund or counterparties.
At any point in time, the fund’s risk of loss from counterparty credit risk on covered OTC instruments is the aggregate unrealized gain on appreciated covered OTC instruments in excess of collateral, if any, pledged by the counterparty to the fund. In accordance with the terms of the relevant derivatives agreements, counterparties to OTC derivatives may be able to terminate derivative contracts prior to maturity after the occurrence of certain stated events, such as a decline in net assets above a certain percentage or a failure by the fund to perform its obligations under the contract. Upon termination, all transactions would typically be liquidated and a net amount would be owed by or payable to the fund.
Other Purchases and sales of portfolio securities other than short-term securities aggregated $690,459,000 and $539,379,000, respectively, for the year ended December 31, 2011.
NOTE 5 - FEDERAL INCOME TAXES
No provision for federal income taxes is required since the fund intends to continue to qualify as a regulated investment company under Subchapter M of the Internal Revenue Code and distribute to shareholders all of its taxable income and gains. Distributions determined in accordance with federal income tax regulations may differ in amount or character from net investment income and realized gains for financial reporting purposes. Financial reporting records are adjusted for permanent book/tax differences to reflect tax character but are not adjusted for temporary differences.
The fund files U.S. federal, state, and local tax returns as required. The fund’s tax returns are subject to examination by the relevant tax authorities until expiration of the applicable statute of limitations, which is generally three years after the filing of the tax return but which can be extended to six years in certain circumstances. Tax returns for open years have incorporated no uncertain tax positions that require a provision for income taxes.
Reclassifications to paid-in capital relate primarily to an overdistribution of taxable income not deemed a return of capital for tax purposes. Reclassifications between income and gain relate primarily to the offset of the current net operating loss against realized gains. For the year ended December 31, 2011, the following reclassifications were recorded to reflect tax character (there was no impact on results of operations or net assets):

Distributions during the year ended December 31, 2011 were characterized for tax purposes as $11,365,000 of ordinary income and $5,670,000, of long-term capital gain.
At December 31, 2011, the tax-basis cost of investments and components of net assets were as follows:

The difference between book-basis and tax-basis net unrealized appreciation (depreciation) is attributable to the deferral of losses from wash sales for tax purposes. Net realized capital losses may be carried forward indefinitely to offset future realized capital gains. All or a portion of the fund’s capital loss carryforwards may be from losses realized between November 1 and the fund’s fiscal year-end, which are deferred for tax purposes until the subsequent year but recognized for financial reporting purposes in the year realized. The fund intends to retain realized gains to the extent of available capital loss carryforwards. During the year ended December 31, 2011, the fund utilized $11,228,000 of capital loss carryforwards. The fund’s available capital loss carryforwards as of December 31, 2011, have no expiration. In accordance with federal tax laws applicable to investment companies, specified net losses realized between November 1 and December 31, are not recognized for tax purposes until the subsequent year (late-year ordinary loss deferrals); however, such losses are recognized for financial reporting purposes in the year realized.
NOTE 6 - FOREIGN TAXES
The fund is subject to foreign income taxes imposed by certain countries in which it invests. Acquisition of certain foreign currencies related to security transactions are also subject to tax. Additionally, capital gains realized by the fund upon disposition of securities issued in or by certain foreign countries are subject to capital gains tax imposed by those countries. All taxes are computed in accordance with the applicable foreign tax law, and, to the extent permitted, capital losses are used to offset capital gains. Taxes attributable to income are accrued by the fund as a reduction of income. Taxes incurred on the purchase of foreign currencies are recorded as realized loss on foreign currency transactions. Current and deferred tax expense attributable to net capital gains is reflected as a component of realized and/or change in unrealized gain/loss on securities in the accompanying financial statements. At December 31, 2011, the fund had no deferred tax liability attributable to foreign securities and $1,456,000 of foreign capital loss carryforwards, including $705,000 that expire in 2014, $701,000 that expire in 2015, $16,000 that expire in 2017, and $34,000 that expire in 2019.
NOTE 7 - RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
The fund is managed by T. Rowe Price Associates, Inc. (Price Associates), a wholly owned subsidiary of T. Rowe Price Group, Inc. (Price Group). The investment management agreement between the fund and Price Associates provides for an annual investment management fee, which is computed daily and paid monthly. The fee consists of an individual fund fee, equal to 0.45% of the fund’s average daily net assets, and a group fee. The group fee rate is calculated based on the combined net assets of certain mutual funds sponsored by Price Associates (the group) applied to a graduated fee schedule, with rates ranging from 0.48% for the first $1 billion of assets to 0.28% for assets in excess of $300 billion. The fund’s group fee is determined by applying the group fee rate to the fund’s average daily net assets. At December 31, 2011, the effective annual group fee rate was 0.30%.
In addition, the fund has entered into service agreements with Price Associates and two wholly owned subsidiaries of Price Associates (collectively, Price). Price Associates computes the daily share price and provides certain other administrative services to the fund. T. Rowe Price Services, Inc., provides shareholder and administrative services in its capacity as the fund’s transfer and dividend disbursing agent. T. Rowe Price Retirement Plan Services, Inc., provides subaccounting and recordkeeping services for certain retirement accounts invested in the fund. For the year ended December 31, 2011, expenses incurred pursuant to these service agreements were $126,000 for Price Associates; $427,000 for T. Rowe Price Services, Inc.; and $37,000 for T. Rowe Price Retirement Plan Services, Inc. The total amount payable at period-end pursuant to these service agreements is reflected as Due to Affiliates in the accompanying financial statements.
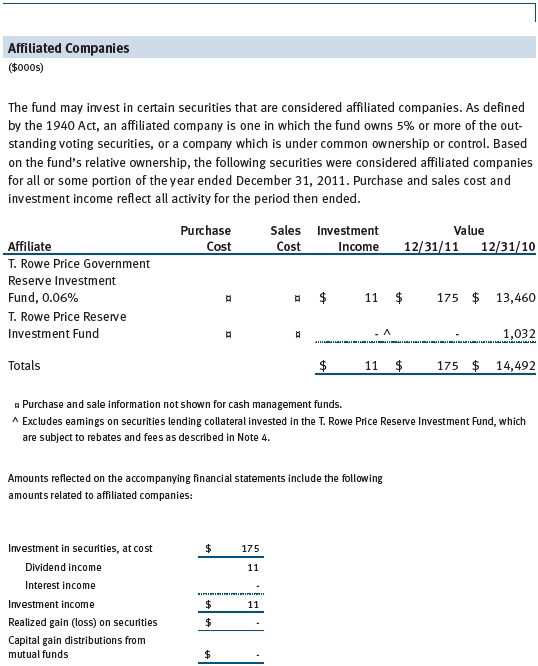
The fund may invest in the T. Rowe Price Reserve Investment Fund and the T. Rowe Price Government Reserve Investment Fund (collectively, the T. Rowe Price Reserve Investment Funds), open-end management investment companies managed by Price Associates and considered affiliates of the fund. The T. Rowe Price Reserve Investment Funds are offered as cash management options to mutual funds, trusts, and other accounts managed by Price Associates and/or its affiliates and are not available for direct purchase by members of the public. The T. Rowe Price Reserve Investment Funds pay no investment management fees.
As of December 31, 2011, T. Rowe Price Group, Inc., and/or its wholly owned subsidiaries owned 539,179 shares of the fund, representing 1% of the fund’s net assets.
| Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm |
To the Board of Directors and Shareholders of
T. Rowe Price Global Technology Fund, Inc.
In our opinion, the accompanying statement of assets and liabilities, including the portfolio of investments, and the related statements of operations and of changes in net assets and the financial highlights present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of T. Rowe Price Global Technology Fund, Inc. (the “Fund”) at December 31, 2011, and the results of its operations, the changes in its net assets and the financial highlights for each of the periods indicated therein, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. These financial statements and financial highlights (hereafter referred to as “financial statements”) are the responsibility of the Fund’s management; our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audits. We conducted our audits of these financial statements in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, and evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits, which included confirmation of securities at December 31, 2011 by correspondence with the custodian and brokers, and confirmation of the underlying funds by correspondence with the transfer agent, provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP
Baltimore, Maryland
February 17, 2012
| Tax Information (Unaudited) for the Tax Year Ended 12/31/11 |
We are providing this information as required by the Internal Revenue Code. The amounts shown may differ from those elsewhere in this report because of differences between tax and financial reporting requirements.
The fund’s distributions to shareholders included:
- $11,493,000 from short-term capital gains,
- $5,981,000 from long-term capital gains, subject to the 15% rate gains category.
For taxable non-corporate shareholders, $2,198,000 of the fund’s income represents qualified dividend income subject to the 15% rate category.
For corporate shareholders, $922,000 of the fund’s income qualifies for the dividends-received deduction.
| Information on Proxy Voting Policies, Procedures, and Records |
A description of the policies and procedures used by T. Rowe Price funds and portfolios to determine how to vote proxies relating to portfolio securities is available in each fund’s Statement of Additional Information, which you may request by calling 1-800-225-5132 or by accessing the SEC’s website, sec.gov. The description of our proxy voting policies and procedures is also available on our website, troweprice.com. To access it, click on the words “Our Company” at the top of our corporate homepage. Then, when the next page appears, click on the words “Proxy Voting Policies” on the left side of the page.
Each fund’s most recent annual proxy voting record is available on our website and through the SEC’s website. To access it through our website, follow the directions above, then click on the words “Proxy Voting Records” on the right side of the Proxy Voting Policies page.
| How to Obtain Quarterly Portfolio Holdings |
The fund files a complete schedule of portfolio holdings with the Securities and Exchange Commission for the first and third quarters of each fiscal year on Form N-Q. The fund’s Form N-Q is available electronically on the SEC’s website (sec.gov); hard copies may be reviewed and copied at the SEC’s Public Reference Room, 450 Fifth St. N.W., Washington, DC 20549. For more information on the Public Reference Room, call 1-800-SEC-0330.
| About the Fund’s Directors and Officers |
Your fund is overseen by a Board of Directors (Board) that meets regularly to review a wide variety of matters affecting the fund, including performance, investment programs, compliance matters, advisory fees and expenses, service providers, and other business affairs. The Board elects the fund’s officers, who are listed in the final table. At least 75% of the Board’s members are independent of T. Rowe Price Associates, Inc. (T. Rowe Price), and its affiliates; “inside” or “interested” directors are employees or officers of T. Rowe Price. The business address of each director and officer is 100 East Pratt Street, Baltimore, Maryland 21202. The Statement of Additional Information includes additional information about the fund directors and is available without charge by calling a T. Rowe Price representative at 1-800-638-5660.
| Independent Directors | ||
| Name | ||
| (Year of Birth) | Principal Occupation(s) and Directorships of Public Companies and | |
| Year Elected* | Other Investment Companies During the Past Five Years | |
| William R. Brody, M.D., Ph.D. | President and Trustee, Salk Institute for Biological Studies (2009 | |
| (1944) | to present); Director, Novartis, Inc. (2009 to present); Director, IBM | |
| 2009 | (2007 to present); President and Trustee, Johns Hopkins University | |
| (1996 to 2009); Chairman of Executive Committee and Trustee, | ||
| Johns Hopkins Health System (1996 to 2009) | ||
| Jeremiah E. Casey | Retired | |
| (1940) | ||
| 2005 | ||
| Anthony W. Deering | Chairman, Exeter Capital, LLC, a private investment firm (2004 | |
| (1945) | to present); Director, Under Armour (2008 to present); Director, | |
| 2001 | Vornado Real Estate Investment Trust (2004 to present); Director, | |
| Mercantile Bankshares (2002 to 2007); Director and Member of the | ||
| Advisory Board, Deutsche Bank North America (2004 to present) | ||
| Donald W. Dick, Jr. | Principal, EuroCapital Partners, LLC, an acquisition and management | |
| (1943) | advisory firm (1995 to present) | |
| 2000 | ||
| Karen N. Horn | Senior Managing Director, Brock Capital Group, an advisory and | |
| (1943) | investment banking firm (2004 to present); Director, Eli Lilly and | |
| 2003 | Company (1987 to present); Director, Simon Property Group (2004 | |
| to present); Director, Norfolk Southern (2008 to present); Director, | ||
| Fannie Mae (2006 to 2008) | ||
| Theo C. Rodgers | President, A&R Development Corporation (1977 to present) | |
| (1941) | ||
| 2005 | ||
| John G. Schreiber | Owner/President, Centaur Capital Partners, Inc., a real estate | |
| (1946) | investment company (1991 to present); Cofounder and Partner, | |
| 2001 | Blackstone Real Estate Advisors, L.P. (1992 to present); Director, | |
| General Growth Properties, Inc. (2010 to present) | ||
| Mark R. Tercek | President and Chief Executive Officer, The Nature Conservancy (2008 | |
| (1957) | to present); Managing Director, The Goldman Sachs Group, Inc. | |
| 2009 | (1984 to 2008) | |
| *Each independent director oversees 130 T. Rowe Price portfolios and serves until retirement, resignation, or election of a successor. | ||
| Inside Directors | ||
| Name | ||
| (Year of Birth) | ||
| Year Elected* | ||
| [Number of T. Rowe Price | Principal Occupation(s) and Directorships of Public Companies and | |
| Portfolios Overseen] | Other Investment Companies During the Past Five Years | |
| Edward C. Bernard | Director and Vice President, T. Rowe Price; Vice Chairman of the | |
| (1956) | Board, Director, and Vice President, T. Rowe Price Group, Inc.; | |
| 2006 | Chairman of the Board, Director, and President, T. Rowe Price | |
| [130] | Investment Services, Inc.; Chairman of the Board and Director, | |
| T. Rowe Price Retirement Plan Services, Inc., T. Rowe Price Savings | ||
| Bank, and T. Rowe Price Services, Inc.; Chairman of the Board, Chief | ||
| Executive Officer, and Director, T. Rowe Price International; Chief | ||
| Executive Officer, Chairman of the Board, Director, and President, | ||
| T. Rowe Price Trust Company; Chairman of the Board, all funds | ||
| Brian C. Rogers, CFA, CIC | Chief Investment Officer, Director, and Vice President, T. Rowe Price; | |
| (1955) | Chairman of the Board, Chief Investment Officer, Director, and Vice | |
| 2006 | President, T. Rowe Price Group, Inc.; Vice President, T. Rowe Price | |
| [74] | Trust Company | |
| *Each inside director serves until retirement, resignation, or election of a successor. | ||
| Officers | ||
| Name (Year of Birth) | ||
| Position Held With Global Technology Fund | Principal Occupation(s) | |
| Kennard W. Allen (1977) | Vice President, T. Rowe Price and T. Rowe Price | |
| Vice President | Group, Inc. | |
| Christopher W. Carlson (1967) | Vice President, T. Rowe Price and T. Rowe Price | |
| Vice President | Group, Inc. | |
| David J. Eiswert, CFA (1972) | Vice President, T. Rowe Price, T. Rowe Price | |
| President | Group, Inc., and T. Rowe Price International | |
| Henry M. Ellenbogen (1973) | Vice President, T. Rowe Price, T. Rowe Price | |
| Vice President | Group, Inc., and T. Rowe Price Trust Company | |
| Roger L. Fiery III, CPA (1959) | Vice President, Price Hong Kong, Price | |
| Vice President | Singapore, T. Rowe Price, T. Rowe Price Group, | |
| Inc., T. Rowe Price International, and T. Rowe | ||
| Price Trust Company | ||
| Robert N. Gensler (1957) | Vice President, T. Rowe Price, T. Rowe Price | |
| Vice President | Group, Inc., and T. Rowe Price International | |
| John R. Gilner (1961) | Chief Compliance Officer and Vice President, | |
| Chief Compliance Officer | T. Rowe Price; Vice President, T. Rowe Price | |
| Group, Inc., and T. Rowe Price Investment | ||
| Services, Inc. | ||
| Gregory S. Golczewski (1966) | Vice President, T. Rowe Price and T. Rowe Price | |
| Vice President | Trust Company | |
| Paul D. Greene II (1978) | Vice President, T. Rowe Price and T. Rowe Price | |
| Vice President | Group, Inc. | |
| Gregory K. Hinkle, CPA (1958) | Vice President, T. Rowe Price, T. Rowe Price | |
| Treasurer | Group, Inc., and T. Rowe Price Trust Company; | |
| formerly Partner, PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP | ||
| (to 2007) | ||
| Rhett K. Hunter (1977) | Vice President, T. Rowe Price and T. Rowe Price | |
| Vice President | Group, Inc.; formerly student, MIT Sloan School | |
| of Management (to 2007) | ||
| Patricia B. Lippert (1953) | Assistant Vice President, T. Rowe Price and | |
| Secretary | T. Rowe Price Investment Services, Inc. | |
| Daniel Martino, CFA (1974) | Vice President, T. Rowe Price and T. Rowe Price | |
| Vice President | Group, Inc. | |
| David Oestreicher (1967) | Director and Vice President, T. Rowe Price | |
| Vice President | Investment Services, Inc., T. Rowe Price | |
| Retirement Plan Services, Inc., T. Rowe Price | ||
| Services, Inc., and T. Rowe Price Trust | ||
| Company; Vice President, Price Hong Kong, | ||
| Price Singapore, T. Rowe Price, T. Rowe Price | ||
| Group, Inc., and T. Rowe Price International | ||
| Hiroaki Owaki, CFA (1962) | Vice President, T. Rowe Price Group, Inc., and | |
| Vice President | T. Rowe Price International | |
| Deborah D. Seidel (1962) | Vice President, T. Rowe Price, T. Rowe Price | |
| Vice President | Group, Inc., and T. Rowe Price Investment | |
| Services, Inc.; Assistant Treasurer and Vice | ||
| President, T. Rowe Price Services, Inc. | ||
| Joshua K. Spencer, CFA (1973) | Vice President, T. Rowe Price and T. Rowe Price | |
| Vice President | Group, Inc. | |
| Julie L. Waples (1970) | Vice President, T. Rowe Price | |
| Vice President | ||
| Thomas H. Watson (1977) | Vice President, T. Rowe Price and T. Rowe Price | |
| Vice President | Group, Inc. | |
| Alison Mei Ling Yip (1966) | Vice President, Price Hong Kong and T. Rowe | |
| Vice President | Price Group, Inc. | |
| Nalin Yogasundram (1975) | Vice President, T. Rowe Price and T. Rowe Price | |
| Vice President | Group, Inc. | |
| Unless otherwise noted, officers have been employees of T. Rowe Price or T. Rowe Price International for at least 5 years. | ||
Item 2. Code of Ethics.
The registrant has adopted a code of ethics, as defined in Item 2 of Form N-CSR, applicable to its principal executive officer, principal financial officer, principal accounting officer or controller, or persons performing similar functions. A copy of this code of ethics is filed as an exhibit to this Form N-CSR. No substantive amendments were approved or waivers were granted to this code of ethics during the period covered by this report.
Item 3. Audit Committee Financial Expert.
The registrant’s Board of Directors/Trustees has determined that Mr. Anthony W. Deering qualifies as an audit committee financial expert, as defined in Item 3 of Form N-CSR. Mr. Deering is considered independent for purposes of Item 3 of Form N-CSR.
Item 4. Principal Accountant Fees and Services.
(a) – (d) Aggregate fees billed to the registrant for the last two fiscal years for professional services rendered by the registrant’s principal accountant were as follows:
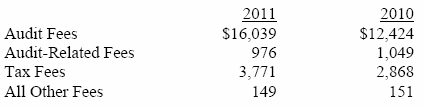
Audit fees include amounts related to the audit of the registrant’s annual financial statements and services normally provided by the accountant in connection with statutory and regulatory filings. Audit-related fees include amounts reasonably related to the performance of the audit of the registrant’s financial statements and specifically include the issuance of a report on internal controls and, if applicable, agreed-upon procedures related to fund acquisitions. Tax fees include amounts related to services for tax compliance, tax planning, and tax advice. The nature of these services specifically includes the review of distribution calculations and the preparation of Federal, state, and excise tax returns. All other fees include the registrant’s pro-rata share of amounts for agreed-upon procedures in conjunction with service contract approvals by the registrant’s Board of Directors/Trustees.
(e)(1) The registrant’s audit committee has adopted a policy whereby audit and non-audit services performed by the registrant’s principal accountant for the registrant, its investment adviser, and any entity controlling, controlled by, or under common control with the investment adviser that provides ongoing services to the registrant require pre-approval in advance at regularly scheduled audit committee meetings. If such a service is required between regularly scheduled audit committee meetings, pre-approval may be authorized by one audit committee member with ratification at the next scheduled audit committee meeting. Waiver of pre-approval for audit or non-audit services requiring fees of a de minimis amount is not permitted.
(2) No services included in (b) – (d) above were approved pursuant to paragraph (c)(7)(i)(C) of Rule 2-01 of Regulation S-X.
(f) Less than 50 percent of the hours expended on the principal accountant’s engagement to audit the registrant’s financial statements for the most recent fiscal year were attributed to work performed by persons other than the principal accountant’s full-time, permanent employees.
(g) The aggregate fees billed for the most recent fiscal year and the preceding fiscal year by the registrant’s principal accountant for non-audit services rendered to the registrant, its investment adviser, and any entity controlling, controlled by, or under common control with the investment adviser that provides ongoing services to the registrant were $1,764,000 and $1,417,000, respectively.
(h) All non-audit services rendered in (g) above were pre-approved by the registrant’s audit committee. Accordingly, these services were considered by the registrant’s audit committee in maintaining the principal accountant’s independence.
Item 5. Audit Committee of Listed Registrants.
Not applicable.
Item 6. Investments.
(a) Not applicable. The complete schedule of investments is included in Item 1 of this Form N-CSR.
(b) Not applicable.
Item 7. Disclosure of Proxy Voting Policies and Procedures for Closed-End Management Investment Companies.
Not applicable.
Item 8. Portfolio Managers of Closed-End Management Investment Companies.
Not applicable.
Item 9. Purchases of Equity Securities by Closed-End Management Investment Company and Affiliated Purchasers.
Not applicable.
Item 10. Submission of Matters to a Vote of Security Holders.
Not applicable.
Item 11. Controls and Procedures.
(a) The registrant’s principal executive officer and principal financial officer have evaluated the registrant’s disclosure controls and procedures within 90 days of this filing and have concluded that the registrant’s disclosure controls and procedures were effective, as of that date, in ensuring that information required to be disclosed by the registrant in this Form N-CSR was recorded, processed, summarized, and reported timely.
(b) The registrant’s principal executive officer and principal financial officer are aware of no change in the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the registrant’s second fiscal quarter covered by this report that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting.
Item 12. Exhibits.
(a)(1) The registrant’s code of ethics pursuant to Item 2 of Form N-CSR is attached.
(2) Separate certifications by the registrant's principal executive officer and principal financial officer, pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 and required by Rule 30a-2(a) under the Investment Company Act of 1940, are attached.
(3) Written solicitation to repurchase securities issued by closed-end companies: not applicable.
(b) A certification by the registrant's principal executive officer and principal financial officer, pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 and required by Rule 30a-2(b) under the Investment Company Act of 1940, is attached.
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 and the Investment Company Act of 1940, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
T. Rowe Price Global Technology Fund, Inc.
| By | /s/ Edward C. Bernard | |
| Edward C. Bernard | ||
| Principal Executive Officer | ||
| Date February 17, 2012 | ||
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 and the Investment Company Act of 1940, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| By | /s/ Edward C. Bernard | |
| Edward C. Bernard | ||
| Principal Executive Officer | ||
| Date February 17, 2012 | ||
| By | /s/ Gregory K. Hinkle | |
| Gregory K. Hinkle | ||
| Principal Financial Officer | ||
| Date February 17, 2012 | ||