UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM N-CSR
CERTIFIED SHAREHOLDER REPORT OF REGISTERED
MANAGEMENT INVESTMENT COMPANIES
Investment Company Act File Number: 811-22410
| T. Rowe Price Real Assets Fund, Inc. |
|
| (Exact name of registrant as specified in charter) |
| |
| 100 East Pratt Street, Baltimore, MD 21202 |
|
| (Address of principal executive offices) |
| |
| David Oestreicher |
| 100 East Pratt Street, Baltimore, MD 21202 |
|
| (Name and address of agent for service) |
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code: (410) 345-2000
Date of fiscal year end: December 31
Date of reporting period: June 30, 2013
Item 1. Report to Shareholders
| Real Assets Fund | June 30, 2013 |
The views and opinions in this report were current as of June 30, 2013. They are not guarantees of performance or investment results and should not be taken as investment advice. Investment decisions reflect a variety of factors, and the managers reserve the right to change their views about individual stocks, sectors, and the markets at any time. As a result, the views expressed should not be relied upon as a forecast of the fund’s future investment intent. The report is certified under the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, which requires mutual funds and other public companies to affirm that, to the best of their knowledge, the information in their financial reports is fairly and accurately stated in all material respects.
REPORTS ON THE WEB
Sign up for our E-mail Program, and you can begin to receive updated fund reports and prospectuses online rather than through the mail. Log in to your account at troweprice.com for more information.
Manager’s Letter
Fellow Shareholders
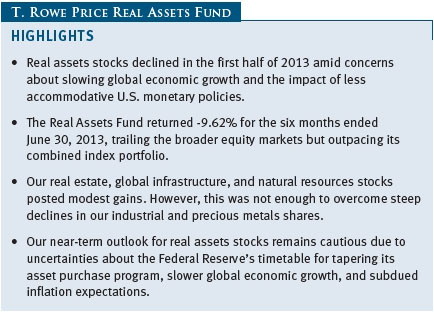
Real assets stocks declined for the first six months of 2013 amid a challenging economic and policy environment. Muted global economic growth, including a recession in Europe and a larger-than-expected slowdown in China, weighed heavily on energy and commodities demand. Investor sentiment deteriorated markedly late in the period after the Federal Reserve suggested that it may begin tapering its asset purchase program later in 2013, punishing interest rate-sensitive securities, including some real estate stocks. The Real Assets Fund was not immune to the broader ills affecting the asset class and lost ground during the period.
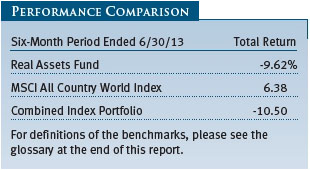
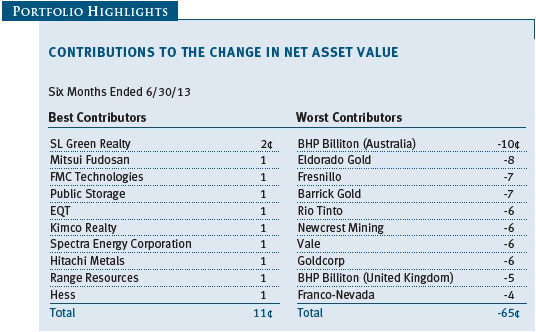
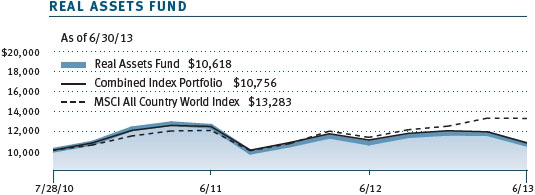
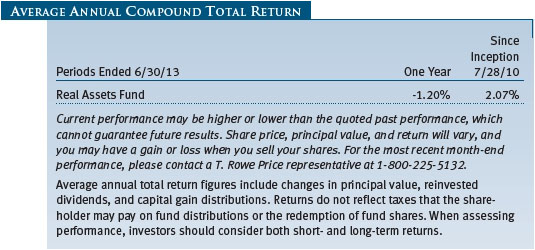
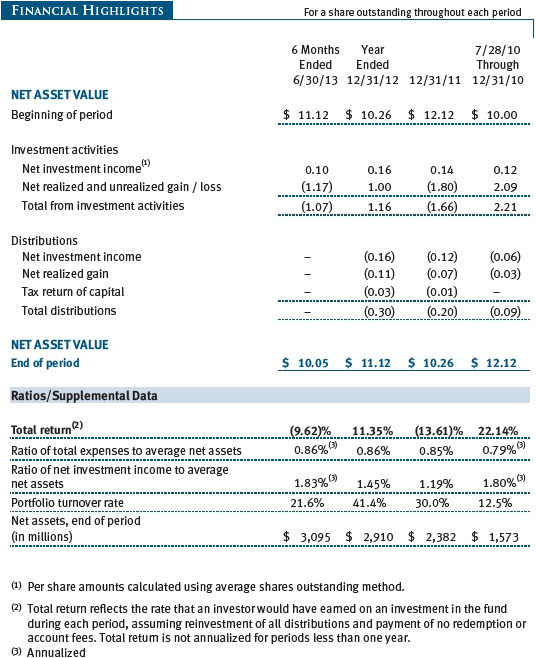
As shown in the Performance Comparison table, the Real Assets Fund returned -9.62% for the six months ended June 30, 2013. The fund modestly outpaced its blended benchmark for the period but trailed the MSCI All Country World Index—a broad measure of global equities—by a wide margin. Our real estate, global infrastructure, and natural resources stocks posted modest gains. However, this was not enough to overcome steep declines in our industrial and precious metals shares. Security selection in the underlying portfolios helped results versus our combined index portfolio.

MARKET ENVIRONMENT
The past six months have been challenging for most sectors in the real assets universe. On the plus side, the U.S. economy continued its modest recovery, with incremental improvements in housing, employment, and manufacturing. Corporate earnings growth was solid despite concerns about federal spending cuts and tax increases early in the year. The Federal Reserve kept short-term interest rates very low and continued its quantitative easing program through the monthly purchase of $85 billion of Treasury bonds and agency-backed and mortgage-backed securities.
There were signs of trouble elsewhere, however. Sluggish global economic growth weighed on demand for a broad range of commodities and energy, while supplies generally showed signs of improvement. Economic growth in China, which has been a particularly voracious consumer of natural resources, fell short of expectations, and many European countries were in recession. Markets tumbled in June after the Fed suggested that it may begin winding down its asset purchase program later in the year if the U.S. economy continues to show signs of progress, particularly on the employment front.
Overall, commodities shares managed a modest six-month gain but plunged late in the period as investors feared the global economic and market impact of less supportive U.S. monetary policy and a stronger U.S. dollar. Securities deemed more sensitive to interest rate movements were punished severely due to concerns that an era of loose monetary policy was coming to an end. Global infrastructure and U.S. real estate investment trusts (REITs) were up modestly for the period due largely to strong first-quarter gains but underperformed the broad global equities market. Global REITs were generally flat, with the notable exception of Japan, where real estate stocks surged as the government adopted extremely accommodative policies to kick-start the country’s moribund economy. Industrial metals shares fell sharply on concerns about slower global economic growth, particularly in China, while precious metals stocks tumbled on fears of rising interest rates and a stronger U.S. dollar.
PORTFOLIO REVIEW
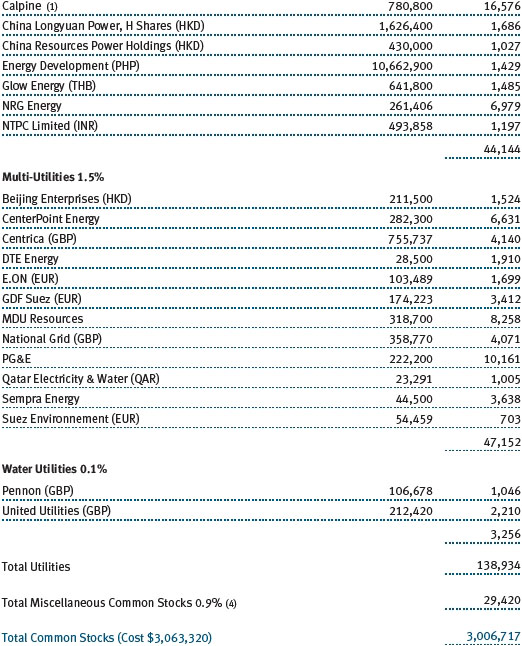
Our real estate stocks were modestly positive for the six-month period but lagged the broader global equities market. The overall gain was largely due to strength in the first quarter as interest rate-sensitive securities fell sharply in the second quarter after Fed Chairman Ben Bernanke suggested that the Fed may start tapering asset purchases later this year. He did not talk about raising short-term rates for some time to come, but many investors appear to have overreacted, driving yields on long-duration bonds sharply higher. REITs were caught up in the sell-off, and properties with long leases seen as having bond-like characteristics were especially hard hit.
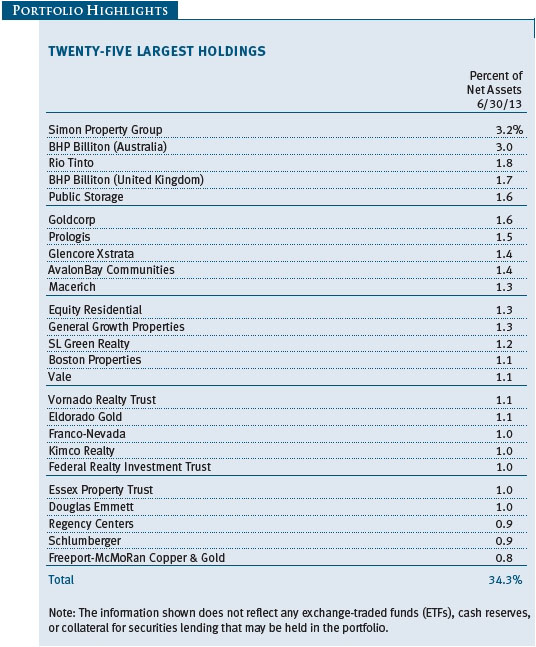
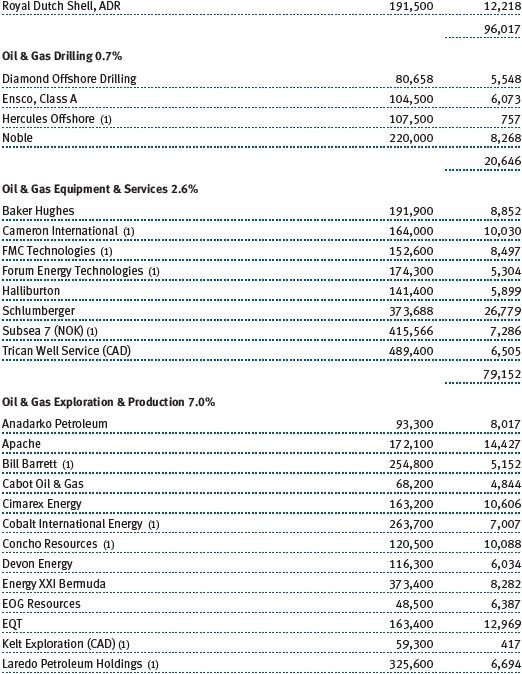
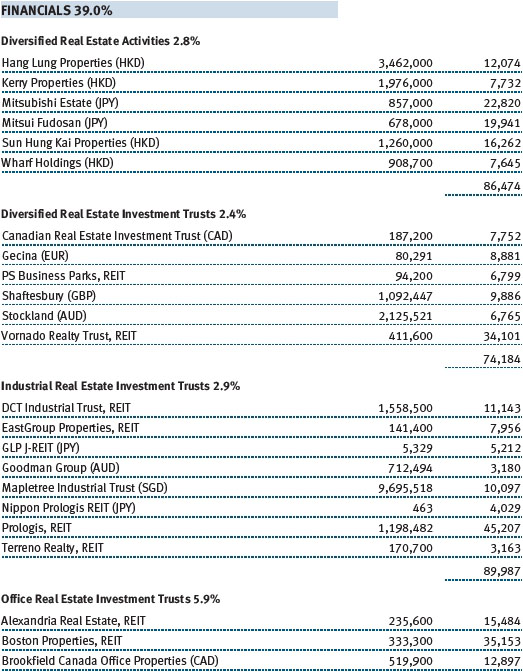
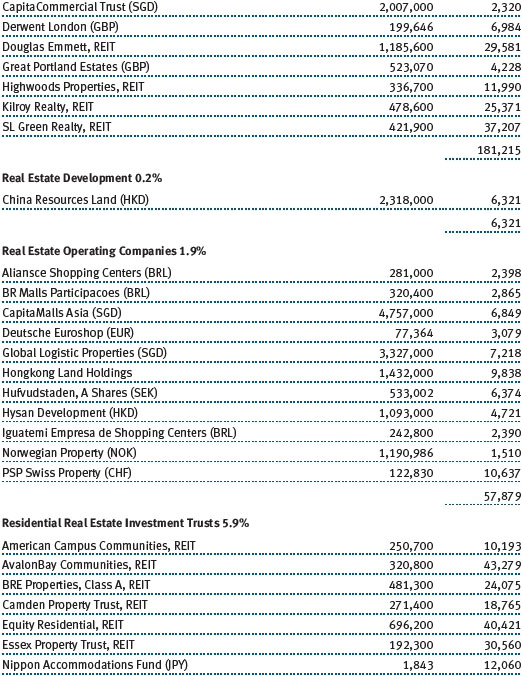
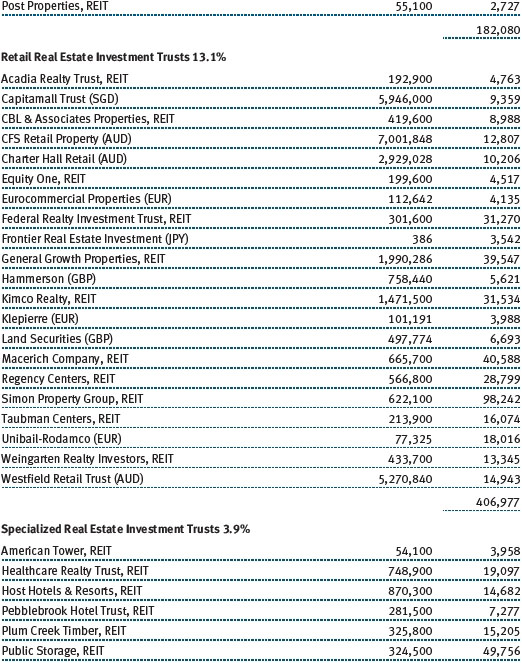
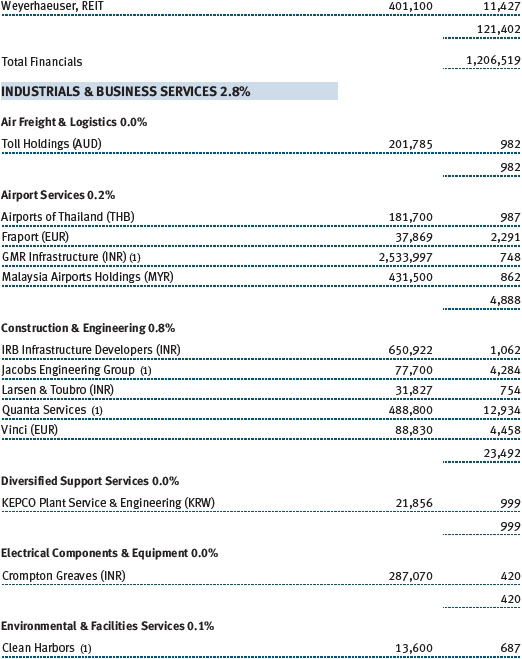
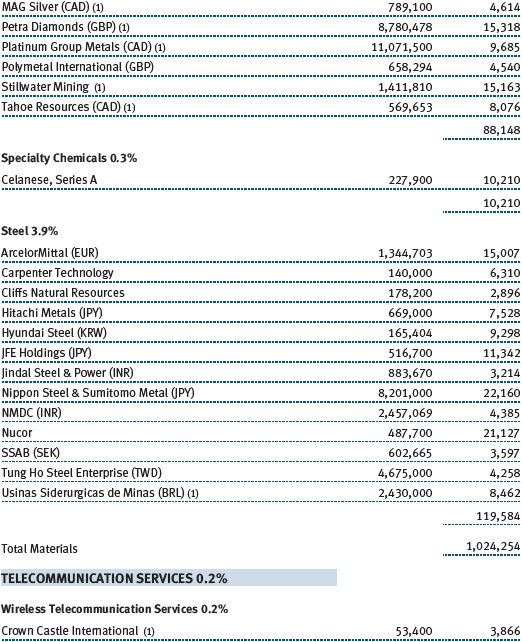
Investors showed a preference for higher-yielding, less-liquid real estate names, which often entail inferior asset quality and/or poor corporate track records. We avoided the chase for yield and were largely content with our holdings, which are biased toward quality. Modest job creation helped bolster select office markets, which benefited our West Coast holding of Kilroy Realty. On the East Coast, SL Green Realty continued to execute well with substantial leasing progress in its Manhattan portfolio. Neighborhood shopping center stocks were strong, reflected in good results from Kimco Realty. As small businesses have begun to recover, so too have the leasing dynamics of the smaller inline shops that populate the strip center portfolios. On a global basis, the Japanese market was the best-performing real estate market. While we have material exposure to Japan in our global real estate portfolio, we were still too underweight to fully benefit from that market’s surge. That said, Mitsubishi Estate and Mitsui Fudosan provided generously positive returns during the period. (Please refer to the portfolio of investments for a complete list of holdings and the amount each represents in the portfolio.)
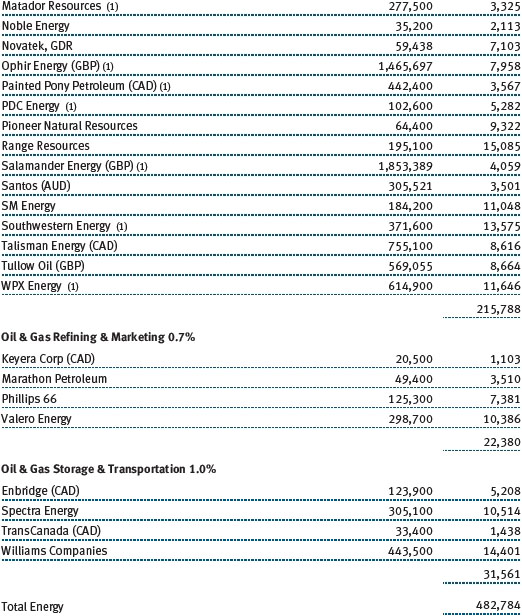
Our natural resources stocks generated modest gains in a tough environment, with security selection contributing to our outperformance versus the combined index portfolio. North American oil and gas producers were our strongest contributors for the period. Well-positioned natural gas producers like EQT and Range Resources benefited results due to growing production and stronger year-over-year natural gas prices. Our preference for Permian Basin oil producers, including Pioneer Natural Resources, over producers in higher-cost basins yielded positive results. PDC Energy, a lower-profile oil producer with an improving portfolio of assets, also performed well. Hess climbed as the company announced plans to monetize assets and refresh the membership of its Board of Directors.
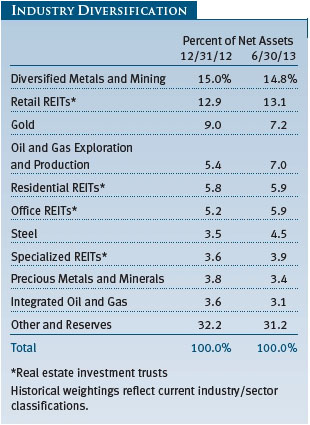
The industrial and precious metals industries were, by far, our worst performers for the period and the fund’s largest detractors. The lead time for developing an industrial metals mine is typically measured in years, and those developed to address growing Chinese demand are just starting to come on line. Unfortunately, China’s economy, which has accounted for the lion’s share of global metals demand growth in recent years, weakened more than expected as leaders shifted their focus from investment and infrastructure spending to domestic consumption. At the same time, gold prices fell to levels not seen for more than two years as indications of declining risk aversion, a pending reduction in U.S. quantitative easing, and muted inflation sparked a sharp sell-off. Stock selection helped to minimize the damage to our portfolio, but our positions were not immune to the broader downturn. BHP Billiton (Australia) and Rio Tinto (UK) were among our weakest industrial metals stocks, while Canada’s Eldorado Gold and Mexico’s Fresnillo were laggards among our precious metals stocks.
OUTLOOK
Our global growth expectations for the next several quarters remain modest. In the U.S., the Federal Reserve is maintaining interest rates at current low levels, although it is likely to begin winding down its quantitative easing program later this year. The domestic housing market continues to recover as household finances improve and builders respond to pent-up demand. Moderate employment growth and an uptick in personal income further support gradual economic improvement. Healthy balance sheets and good cash flow offer corporations some flexibility in the deployment of capital, which could contribute to increased hiring or capital spending, as well as activities such as stock buybacks or acquisitions. Earnings and revenue growth in the low- to mid-single digits are consistent with modest economic growth, and equity valuations are attractive relative to historical levels.
Outside the U.S., central bank policies in many advanced economies are still highly accommodative. Europe’s macroeconomic environment remains challenging, and resolving the region’s persistent debt crisis will be a slow process. Fiscal austerity continues to be a headwind for many countries, and the eurozone may benefit from a shift in policy to ease back on austerity in response to high unemployment and sluggish growth. Japan is taking steps to revive its stalled economy through aggressive, growth-oriented monetary policies and other economic stimulus. Early results are positive, but we await signs that policymakers are politically willing and able to address important structural reforms to labor markets, tax and regulatory regimes, and social spending. Although economic growth in emerging markets appears to be slowing, it remains superior to many developed markets, particularly over the long term. We believe that China’s growth rate will decline gradually as the economy, in keeping with government policy objectives, shifts to a more sustainable focus on domestic consumption. However, we expect the transition will take several years and produce periods of uneven economic and stock market performance.
The prospects for muted global economic growth are likely to weigh on energy and materials prices. Demand for commodities is expected to remain subdued as China shifts its growth model away from industrial production and exports toward domestic consumption. An improving economy supports favorable fundamentals on REITs in the U.S. and (hopefully) Japan, although valuations appear rich. The current environment of tame inflation constitutes a headwind for our fund. However, inflation remains a long-term concern as governments and central banks start to taper their accommodative policies and unwind massive balance sheets, making a strategy like ours a good inflation hedge for many investors. Until then, our goal is to perform well with average to below-average risk.
We expect markets to remain volatile as investors contemplate the broader impact and pace of the Federal Reserve’s shift to less accommodative monetary policies. The identification of attractive long-term investment opportunities will depend on strong fundamental research, disciplined security selection, and careful attention to risk. These attributes form the core of our investment approach, and we believe they will continue to add value for shareholders over the long term.
Respectfully submitted,

Wyatt A. Lee
Portfolio manager and chairman of the fund’s Investment Advisory Committee
July 29, 2013
The committee chairman has day-to-day responsibility for managing the fund and works with committee members in developing and executing its investment program.
RISKS OF STOCK INVESTING
The fund’s share price can fall because of weakness in the stock markets, a particular industry, or specific holdings. Stock markets can decline for many reasons, including adverse political or economic developments, changes in investor psychology, or heavy institutional selling. The prospects for an industry or company may deteriorate because of a variety of factors, including disappointing earnings or changes in the competitive environment. In addition, the investment manager’s assessment of companies held in a fund may prove incorrect, resulting in losses or poor performance even in rising markets. Funds that invest only in specific industries will experience greater volatility than funds investing in a broad range of industries. The rate of earnings growth of natural resources companies may be irregular since these companies are strongly affected by natural forces, global economic cycles, and international politics. For example, stock prices of energy companies can fall sharply when oil prices decrease.
GLOSSARY
Combined index portfolio: An unmanaged stock portfolio consisting of 25% global natural resources (65% MSCI All Country World Index Energy and 35% MSCI All Country World Index Materials), 20% U.S. real estate (Wilshire U.S. Real Estate Securities Index), 20% global real estate (FTSE EPRA/NAREIT Developed Index), 25% global metals and mining (MSCI All Country World Index Metals & Mining), 5% precious metals (80% MSCI All Country World Index IMI Gold and 20% MSCI All Country World Index IMI Precious Metals & Minerals), and 5% infrastructure (UBS World Infrastructure & Utilities Index).
- FTSE EPRA/NAREIT Developed Index: An index that tracks the performance of developed market real estate securities.
- MSCI All Country World Index Energy: An index that tracks the performance of companies engaged in the exploration and production of energy commodities.
- MSCI All Country World Index IMI Gold: An index that tracks the performance of companies engaged in the exploration and production of gold.
- MSCI All Country World Index IMI Precious Metals & Minerals: An index that tracks the performance of companies engaged in the exploration and production of precious metals and minerals.
- MSCI All Country World Index Materials: An index that tracks the performance of companies engaged in the exploration and production of basic materials.
- MSCI All Country World Index Metals & Mining: An index that tracks the performance of metals and mining companies.
- UBS World Infrastructure & Utilities Index: An index that tracks the performance of globally listed infrastructure and utilities stocks.
- Wilshire U.S. Real Estate Securities Index: An index that tracks the performance of publicly traded U.S. real estate securities.
MSCI All Country World Index: A capitalization-weighted index of stocks from developed and emerging markets worldwide.
Real estate investment trusts (REITs): Publicly traded companies that own, develop, and operate apartment complexes, hotels, office buildings, and other commercial properties.
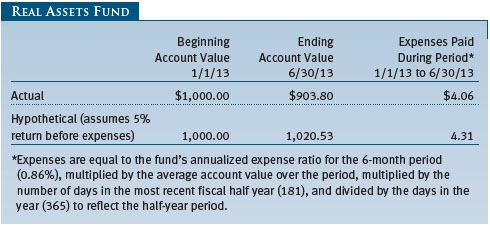
Performance and Expenses
This chart shows the value of a hypothetical $10,000 investment in the fund over the past 10 fiscal year periods or since inception (for funds lacking 10-year records). The result is compared with benchmarks, which may include a broad-based market index and a peer group average or index. Market indexes do not include expenses, which are deducted from fund returns as well as mutual fund averages and indexes.

As a mutual fund shareholder, you may incur two types of costs: (1) transaction costs, such as redemption fees or sales loads, and (2) ongoing costs, including management fees, distribution and service (12b-1) fees, and other fund expenses. The following example is intended to help you understand your ongoing costs (in dollars) of investing in the fund and to compare these costs with the ongoing costs of investing in other mutual funds. The example is based on an investment of $1,000 invested at the beginning of the most recent six-month period and held for the entire period.
Actual Expenses
The first line of the following table (Actual) provides information about actual account values and expenses based on the fund’s actual returns. You may use the information on this line, together with your account balance, to estimate the expenses that you paid over the period. Simply divide your account value by $1,000 (for example, an $8,600 account value divided by $1,000 = 8.6), then multiply the result by the number on the first line under the heading “Expenses Paid During Period” to estimate the expenses you paid on your account during this period.
Hypothetical Example for Comparison Purposes
The information on the second line of the table (Hypothetical) is based on hypothetical account values and expenses derived from the fund’s actual expense ratio and an assumed 5% per year rate of return before expenses (not the fund’s actual return). You may compare the ongoing costs of investing in the fund with other funds by contrasting this 5% hypothetical example and the 5% hypothetical examples that appear in the shareholder reports of the other funds. The hypothetical account values and expenses may not be used to estimate the actual ending account balance or expenses you paid for the period.
Note: T. Rowe Price charges an annual account service fee of $20, generally for accounts with less than $10,000. The fee is waived for any investor whose T. Rowe Price mutual fund accounts total $50,000 or more; accounts electing to receive electronic delivery of account statements, transaction confirmations, prospectuses, and shareholder reports; or accounts of an investor who is a T. Rowe Price Preferred Services, Personal Services, or Enhanced Personal Services client (enrollment in these programs generally requires T. Rowe Price assets of at least $100,000). This fee is not included in the accompanying table. If you are subject to the fee, keep it in mind when you are estimating the ongoing expenses of investing in the fund and when comparing the expenses of this fund with other funds.
You should also be aware that the expenses shown in the table highlight only your ongoing costs and do not reflect any transaction costs, such as redemption fees or sales loads. Therefore, the second line of the table is useful in comparing ongoing costs only and will not help you determine the relative total costs of owning different funds. To the extent a fund charges transaction costs, however, the total cost of owning that fund is higher.
Unaudited
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
Unaudited

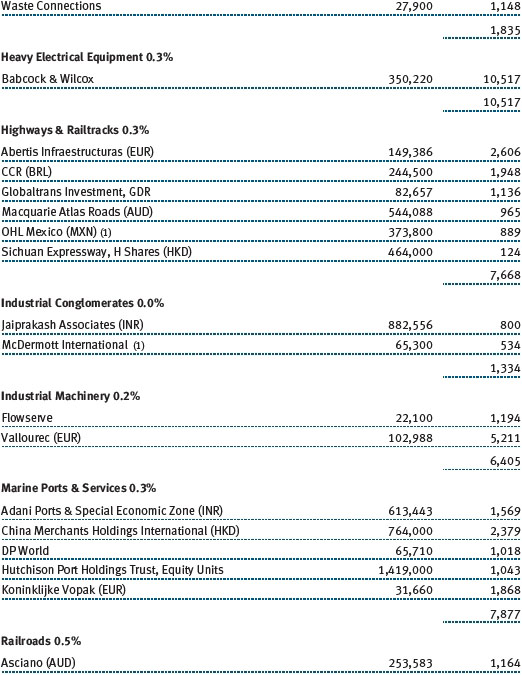
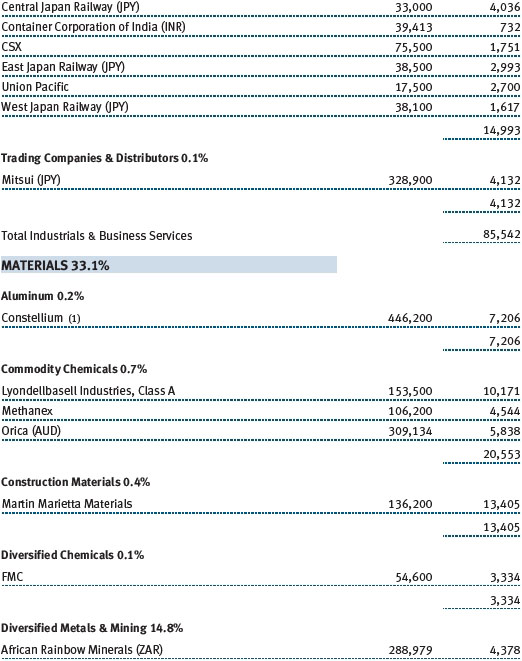
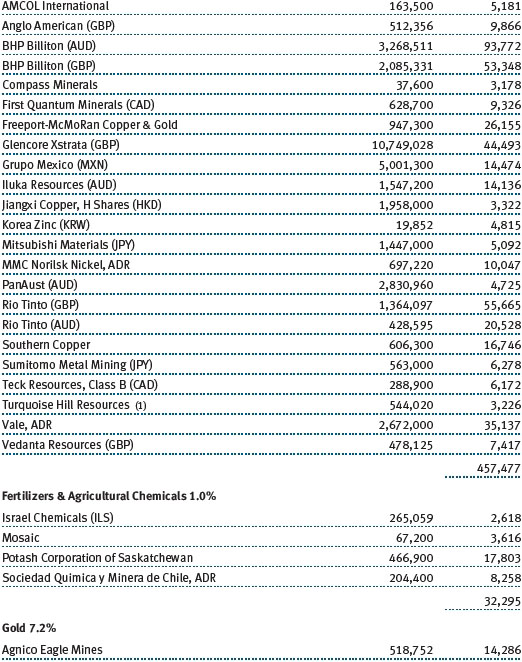
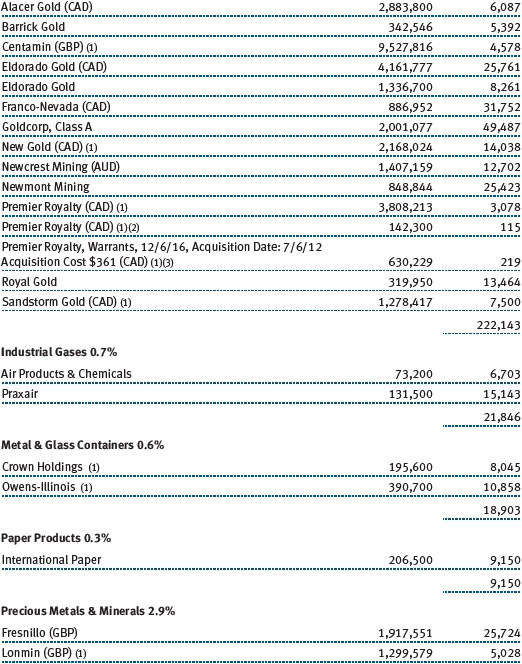


The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
Unaudited
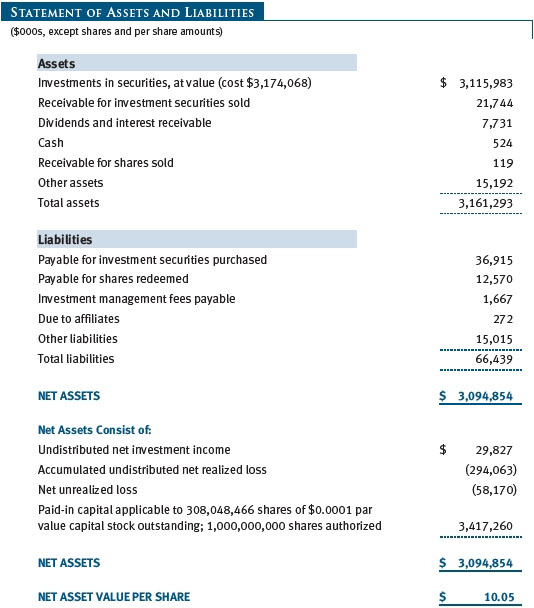
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
Unaudited
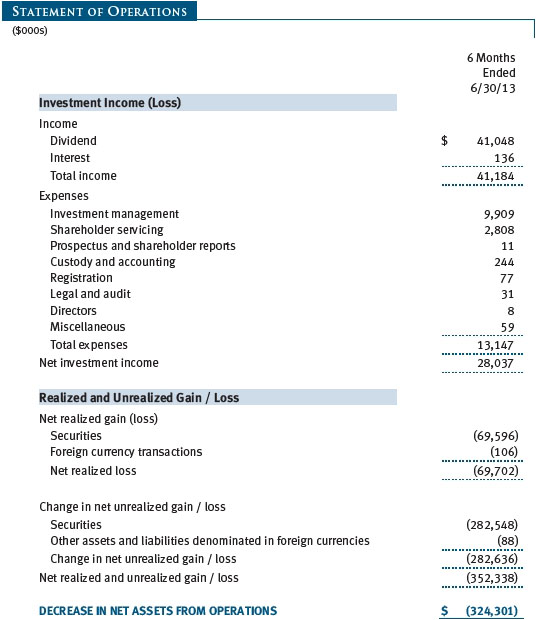
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
Unaudited

The accompanying notes are an integral part of these financial statements.
Unaudited
| Notes to Financial Statements |
T. Rowe Price Real Assets Fund (the fund), is registered under the Investment Company Act of 1940 (the 1940 Act) as a diversified, open-end management investment company. The fund commenced operations on July 28, 2010. The fund seeks to provide long-term growth of capital.
NOTE 1 - SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Basis of Preparation The accompanying financial statements were prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (GAAP), which require the use of estimates made by management. Management believes that estimates and valuations are appropriate; however, actual results may differ from those estimates, and the valuations reflected in the accompanying financial statements may differ from the value ultimately realized upon sale or maturity.
Investment Transactions, Investment Income, and Distributions Income and expenses are recorded on the accrual basis. Premiums and discounts on debt securities are amortized for financial reporting purposes. Dividends received from mutual fund investments are reflected as dividend income; capital gain distributions are reflected as realized gain/loss. Dividend income and capital gain distributions are recorded on the ex-dividend date. Income tax-related interest and penalties, if incurred, would be recorded as income tax expense. Investment transactions are accounted for on the trade date. Realized gains and losses are reported on the identified cost basis. Distributions to shareholders are recorded on the ex-dividend date. Income distributions are declared and paid annually. Capital gain distributions, if any, are generally declared and paid by the fund annually.
Currency Translation Assets, including investments, and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies are translated into U.S. dollar values each day at the prevailing exchange rate, using the mean of the bid and asked prices of such currencies against U.S. dollars as quoted by a major bank. Purchases and sales of securities, income, and expenses are translated into U.S. dollars at the prevailing exchange rate on the date of the transaction. The effect of changes in foreign currency exchange rates on realized and unrealized security gains and losses is reflected as a component of security gains and losses.
Rebates and Credits Subject to best execution, the fund may direct certain security trades to brokers who have agreed to rebate a portion of the related brokerage commission to the fund in cash. Commission rebates are reflected as realized gain on securities in the accompanying financial statements and totaled $16,000 for the six months ended June 30, 2013. Additionally, the fund earns credits on temporarily uninvested cash balances held at the custodian, which reduce the fund’s custody charges. Custody expense in the accompanying financial statements is presented before reduction for credits.
Redemption Fees A 2% fee is assessed on redemptions of fund shares held for 90 days or less to deter short-term trading and to protect the interests of long-term shareholders. Redemption fees are withheld from proceeds that shareholders receive from the sale or exchange of fund shares. The fees are paid to the fund and are recorded as an increase to paid-in capital. The fees may cause the redemption price per share to differ from the net asset value per share.
In-Kind Redemptions In accordance with guidelines described in the fund’s prospectus, the fund may distribute portfolio securities rather than cash as payment for a redemption of fund shares (in-kind redemption). For financial reporting purposes, the fund recognizes a gain on in-kind redemptions to the extent the value of the distributed securities on the date of redemption exceeds the cost of those securities. Gains and losses realized on in-kind redemptions are not recognized for tax purposes and are reclassified from undistributed realized gain (loss) to paid-in capital. During the six months ended June 30, 2013, the fund realized $18,143,000 of net gain on $73,125,000 of in-kind redemptions.
New Accounting Guidance In December 2011, the Financial Accounting Standards Board issued amended guidance requiring an entity to disclose information about offsetting and related arrangements to enable users of its financial statements to understand the effect of those arrangements on its financial position. The guidance is effective for fiscal years and interim periods beginning on or after January 1, 2013. Adoption had no effect on the fund’s net assets or results of operations.
NOTE 2 - VALUATION
The fund’s financial instruments are valued and its net asset value (NAV) per share is computed at the close of the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE), normally 4 p.m. ET, each day the NYSE is open for business.
Fair Value The fund’s financial instruments are reported at fair value, which GAAP defines as the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. The T. Rowe Price Valuation Committee (the Valuation Committee) has been established by the fund’s Board of Directors (the Board) to ensure that financial instruments are appropriately priced at fair value in accordance with GAAP and the 1940 Act. Subject to oversight by the Board, the Valuation Committee develops and oversees pricing-related policies and procedures and approves all fair value determinations. Specifically, the Valuation Committee establishes procedures to value securities; determines pricing techniques, sources, and persons eligible to effect fair value pricing actions; oversees the selection, services, and performance of pricing vendors; oversees valuation-related business continuity practices; and provides guidance on internal controls and valuation-related matters. The Valuation Committee reports to the fund’s Board; is chaired by the fund’s treasurer; and has representation from legal, portfolio management and trading, operations, and risk management.
Various valuation techniques and inputs are used to determine the fair value of financial instruments. GAAP establishes the following fair value hierarchy that categorizes the inputs used to measure fair value:
Level 1 – quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical financial instruments that the fund can access at the reporting date
Level 2 – inputs other than Level 1 quoted prices that are observable, either directly or indirectly (including, but not limited to, quoted prices for similar financial instruments in active markets, quoted prices for identical or similar financial instruments in inactive markets, interest rates and yield curves, implied volatilities, and credit spreads)
Level 3 – unobservable inputs
Observable inputs are developed using market data, such as publicly available information about actual events or transactions, and reflect the assumptions that market participants would use to price the financial instrument. Unobservable inputs are those for which market data are not available and are developed using the best information available about the assumptions that market participants would use to price the financial instrument. GAAP requires valuation techniques to maximize the use of relevant observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. When multiple inputs are used to derive fair value, the financial instrument is assigned to the level within the fair value hierarchy based on the lowest-level input that is significant to the fair value of the financial instrument. Input levels are not necessarily an indication of the risk or liquidity associated with financial instruments at that level but rather the degree of judgment used in determining those values.
Valuation Techniques Equity securities listed or regularly traded on a securities exchange or in the over-the-counter (OTC) market are valued at the last quoted sale price or, for certain markets, the official closing price at the time the valuations are made. OTC Bulletin Board securities are valued at the mean of the closing bid and asked prices. A security that is listed or traded on more than one exchange is valued at the quotation on the exchange determined to be the primary market for such security. Listed securities not traded on a particular day are valued at the mean of the closing bid and asked prices for domestic securities and the last quoted sale or closing price for international securities.
For valuation purposes, the last quoted prices of non-U.S. equity securities may be adjusted to reflect the fair value of such securities at the close of the NYSE. If the fund determines that developments between the close of a foreign market and the close of the NYSE will, in its judgment, materially affect the value of some or all of its portfolio securities, the fund will adjust the previous quoted prices to reflect what it believes to be the fair value of the securities as of the close of the NYSE. In deciding whether it is necessary to adjust quoted prices to reflect fair value, the fund reviews a variety of factors, including developments in foreign markets, the performance of U.S. securities markets, and the performance of instruments trading in U.S. markets that represent foreign securities and baskets of foreign securities. The fund may also fair value securities in other situations, such as when a particular foreign market is closed but the fund is open. The fund uses outside pricing services to provide it with quoted prices and information to evaluate and/or adjust those prices. The fund cannot predict how often it will use quoted prices and how often it will determine it necessary to adjust those prices to reflect fair value. As a means of evaluating its security valuation process, the fund routinely compares quoted prices, the next day’s opening prices in the same markets, and adjusted prices.
Actively traded domestic equity securities generally are categorized in Level 1 of the fair value hierarchy. Non-U.S. equity securities generally are categorized in Level 2 of the fair value hierarchy despite the availability of quoted prices because, as described above, the fund evaluates and determines whether those quoted prices reflect fair value at the close of the NYSE or require adjustment. OTC Bulletin Board securities, certain preferred securities, and equity securities traded in inactive markets generally are categorized in Level 2 of the fair value hierarchy.
Debt securities generally are traded in the OTC market. Securities with remaining maturities of one year or more at the time of acquisition are valued at prices furnished by dealers who make markets in such securities or by an independent pricing service, which considers the yield or price of bonds of comparable quality, coupon, maturity, and type, as well as prices quoted by dealers who make markets in such securities. Generally, debt securities are categorized in Level 2 of the fair value hierarchy; however, to the extent the valuations include significant unobservable inputs, the securities would be categorized in Level 3.
Investments in mutual funds are valued at the mutual fund’s closing net asset value per share on the day of valuation and are categorized in Level 1 of the fair value hierarchy. Assets and liabilities other than financial instruments, including short-term receivables and payables, are carried at cost, or estimated realizable value, if less, which approximates fair value.
Thinly traded financial instruments and those for which the above valuation procedures are inappropriate or are deemed not to reflect fair value are stated at fair value as determined in good faith by the Valuation Committee. The objective of any fair value pricing determination is to arrive at a price that could reasonably be expected from a current sale. Financial instruments fair valued by the Valuation Committee are primarily private placements, restricted securities, warrants, rights, and other securities that are not publicly traded.
Subject to oversight by the Board, the Valuation Committee regularly makes good faith judgments to establish and adjust the fair valuations of certain securities as events occur and circumstances warrant. For instance, in determining the fair value of an equity investment with limited market activity, such as a private placement or a thinly traded public company stock, the Valuation Committee considers a variety of factors, which may include, but are not limited to, the issuer’s business prospects, its financial standing and performance, recent investment transactions in the issuer, new rounds of financing, negotiated transactions of significant size between other investors in the company, relevant market valuations of peer companies, strategic events affecting the company, market liquidity for the issuer, and general economic conditions and events. In consultation with the investment and pricing teams, the Valuation Committee will determine an appropriate valuation technique based on available information, which may include both observable and unobservable inputs. The Valuation Committee typically will afford greatest weight to actual prices in arm’s length transactions, to the extent they represent orderly transactions between market participants; transaction information can be reliably obtained; and prices are deemed representative of fair value. However, the Valuation Committee may also consider other valuation methods such as market-based valuation multiples; a discount or premium from market value of a similar, freely traded security of the same issuer; or some combination. Fair value determinations are reviewed on a regular basis and updated as information becomes available, including actual purchase and sale transactions of the issue. Because any fair value determination involves a significant amount of judgment, there is a degree of subjectivity inherent in such pricing decisions and fair value prices determined by the Valuation Committee could differ from those of other market participants. Depending on the relative significance of unobservable inputs, including the valuation technique(s) used, fair valued securities may be categorized in Level 2 or 3 of the fair value hierarchy.
Valuation Inputs The following table summarizes the fund’s financial instruments, based on the inputs used to determine their fair values on June 30, 2013:
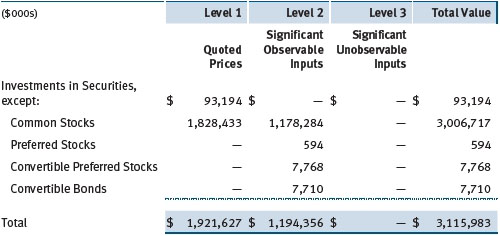
There were no material transfers between Levels 1 and 2 during the period.
NOTE 3 - OTHER INVESTMENT TRANSACTIONS
Consistent with its investment objective, the fund engages in the following practices to manage exposure to certain risks and/or to enhance performance. The investment objective, policies, program, and risk factors of the fund are described more fully in the fund’s prospectus and Statement of Additional Information.
Restricted Securities The fund may invest in securities that are subject to legal or contractual restrictions on resale. Prompt sale of such securities at an acceptable price may be difficult and may involve substantial delays and additional costs.
Other Purchases and sales of portfolio securities other than short-term securities aggregated $1,202,239,000 and $642,787,000, respectively, for the six months ended June 30, 2013.
NOTE 4 - FEDERAL INCOME TAXES
No provision for federal income taxes is required since the fund intends to continue to qualify as a regulated investment company under Subchapter M of the Internal Revenue Code and distribute to shareholders all of its taxable income and gains. Distributions determined in accordance with federal income tax regulations may differ in amount or character from net investment income and realized gains for financial reporting purposes. Financial reporting records are adjusted for permanent book/tax differences to reflect tax character but are not adjusted for temporary differences. The amount and character of tax-basis distributions and composition of net assets are finalized at fiscal year-end; accordingly, tax-basis balances have not been determined as of the date of this report.
The fund intends to retain realized gains to the extent of available capital loss carryforwards. Net realized capital losses may be carried forward indefinitely to offset future realized capital gains. As of December 31, 2012, the fund had $142,898,000 of available capital loss carryforwards.
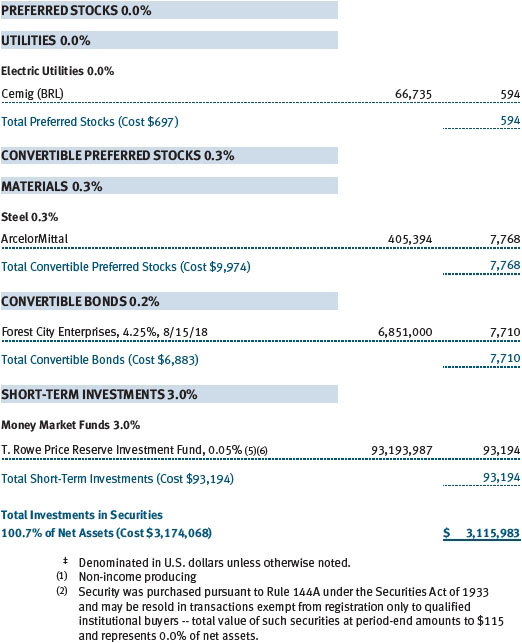
At June 30, 2013, the cost of investments for federal income tax purposes was $3,227,754,000. Net unrealized loss aggregated $111,856,000 at period-end, of which $326,941,000 related to appreciated investments and $438,797,000 related to depreciated investments.
NOTE 5 - RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
The fund is managed by T. Rowe Price Associates, Inc. (Price Associates), a wholly owned subsidiary of T. Rowe Price Group, Inc. (Price Group). The investment management agreement between the fund and Price Associates provides for an annual investment management fee, which is computed daily and paid monthly. The fee consists of an individual fund fee, equal to 0.35% of the fund’s average daily net assets, and a group fee. The group fee rate is calculated based on the combined net assets of certain mutual funds sponsored by Price Associates (the group) applied to a graduated fee schedule, with rates ranging from 0.48% for the first $1 billion of assets to 0.275% for assets in excess of $400 billion. The fund’s group fee is determined by applying the group fee rate to the fund’s average daily net assets. At June 30, 2013, the effective annual group fee rate was 0.30%.
The fund was also subject to a contractual expense limitation through April 30, 2013. During the limitation period, Price Associates was required to waive its management fee and reimburse the fund for any expenses, excluding interest, taxes, brokerage commissions, and extraordinary expenses, that would otherwise cause the fund���s ratio of annualized total expenses to average net assets (expense ratio) to exceed its expense limitation of 1.10%. For a period of three years after the date of any reimbursement or waiver, the fund is required to repay Price Associates for expenses previously reimbursed and management fees waived to the extent its net assets have grown or expenses have declined sufficiently to allow repayment without causing the fund’s expense ratio to exceed its expense limitation. At June 30, 2013, there were no amounts subject to repayment by the fund. For the six months ended June 30, 2013, the fund operated below its expense limitation.
In addition, the fund has entered into service agreements with Price Associates and two wholly owned subsidiaries of Price Associates (collectively, Price). Price Associates computes the daily share price and provides certain other administrative services to the fund. T. Rowe Price Services, Inc., provides shareholder and administrative services in its capacity as the fund’s transfer and dividend disbursing agent. T. Rowe Price Retirement Plan Services, Inc., provides subaccounting and recordkeeping services for certain retirement accounts invested in the fund. For the six months ended June 30, 2013, expenses incurred pursuant to these service agreements were $90,000 for Price Associates; $18,000 for T. Rowe Price Services, Inc.; and less than $1,000 for T. Rowe Price Retirement Plan Services, Inc. The total amount payable at period-end pursuant to these service agreements is reflected as Due to Affiliates in the accompanying financial statements.
Additionally, the fund is one of several mutual funds in which certain college savings plans managed by Price Associates may invest. As approved by the fund’s Board of Directors, shareholder servicing costs associated with each college savings plan are borne by the fund in proportion to the average daily value of its shares owned by the college savings plan. For the six months ended June 30, 2013, the fund was charged $129,000 for shareholder servicing costs related to the college savings plans, of which $90,000 was for services provided by Price. The amount payable at period-end pursuant to this agreement is reflected as Due to Affiliates in the accompanying financial statements. At June 30, 2013, approximately 5% of the outstanding shares of the fund were held by college savings plans.
The fund is also one of several mutual funds sponsored by Price Associates (underlying Price funds) in which the T. Rowe Price Spectrum Funds (Spectrum Funds) and T. Rowe Price Retirement Funds (Retirement Funds) may invest. Neither the Spectrum Funds nor the Retirement Funds invest in the underlying Price funds for the purpose of exercising management or control. Pursuant to separate special servicing agreements, expenses associated with the operation of the Spectrum and Retirement Funds are borne by each underlying Price fund to the extent of estimated savings to it and in proportion to the average daily value of its shares owned by the Spectrum and Retirement Funds, respectively. Expenses allocated under these agreements are reflected as shareholder servicing expenses in the accompanying financial statements. For the six months ended June 30, 2013, the fund was allocated $77,000 of Spectrum Funds’ expenses and $2,576,000 of Retirement Funds’ expenses. Of these amounts, $1,410,000 related to services provided by Price. The amount payable at period-end pursuant to this agreement is reflected as Due to Affiliates in the accompanying financial statements. At June 30, 2013, approximately 4% of the outstanding shares of the fund were held by the Spectrum Funds and 84% were held by the Retirement Funds.
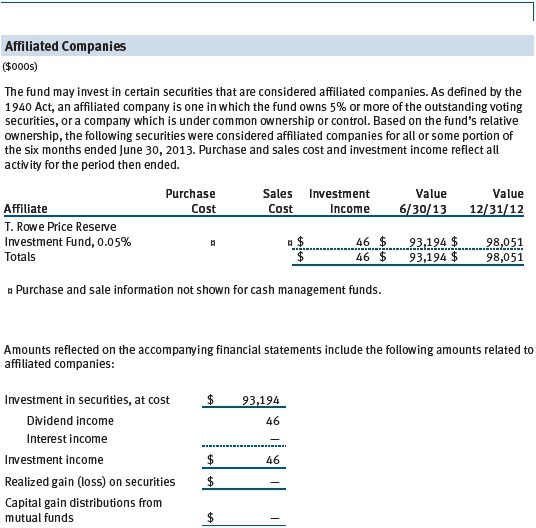
The fund may invest in the T. Rowe Price Reserve Investment Fund and the T. Rowe Price Government Reserve Investment Fund (collectively, the T. Rowe Price Reserve Investment Funds), open-end management investment companies managed by Price Associates and considered affiliates of the fund. The T. Rowe Price Reserve Investment Funds are offered as cash management options to mutual funds, trusts, and other accounts managed by Price Associates and/or its affiliates and are not available for direct purchase by members of the public. The T. Rowe Price Reserve Investment Funds pay no investment management fees.
Mutual funds and other accounts managed by T. Rowe Price and its affiliates (collectively, T. Rowe Price funds) may invest in the fund; however, no T. Rowe Price fund may invest for the purpose of exercising management or control over the fund. At June 30, 2013, approximately 6% of the fund’s outstanding shares were held by T. Rowe Price funds.
| Information on Proxy Voting Policies, Procedures, and Records |
A description of the policies and procedures used by T. Rowe Price funds and portfolios to determine how to vote proxies relating to portfolio securities is available in each fund’s Statement of Additional Information. You may request this document by calling 1-800-225-5132 or by accessing the SEC’s website, sec.gov.
The description of our proxy voting policies and procedures is also available on our website, troweprice.com. To access it, click on the words “Social Responsibility” at the top of our corporate homepage. Next, click on the words “Conducting Business Responsibly” on the left side of the page that appears. Finally, click on the words “Proxy Voting Policies” on the left side of the page that appears.
Each fund’s most recent annual proxy voting record is available on our website and through the SEC’s website. To access it through our website, follow the above directions to reach the “Conducting Business Responsibly” page. Click on the words “Proxy Voting Records” on the left side of that page, and then click on the “View Proxy Voting Records” link at the bottom of the page that appears.
| How to Obtain Quarterly Portfolio Holdings |
The fund files a complete schedule of portfolio holdings with the Securities and Exchange Commission for the first and third quarters of each fiscal year on Form N-Q. The fund’s Form N-Q is available electronically on the SEC’s website (sec.gov); hard copies may be reviewed and copied at the SEC’s Public Reference Room, 100 F St. N.E., Washington, DC 20549. For more information on the Public Reference Room, call 1-800-SEC-0330.
Approval of Investment Management Agreement and
Subadvisory Agreement |
On March 5, 2013, the fund’s Board of Directors (Board), including a majority of the fund’s independent directors, approved the continuation of the investment management agreement (Advisory Contract) between the fund and its investment advisor, T. Rowe Price Associates, Inc. (Advisor), as well as the continuation of the investment subadvisory agreement (Subadvisory Contract) that the Adviser had entered into with T. Rowe Price Singapore Private Ltd. (Subadvisor) beginning in February 2013 on behalf of the fund. In connection with its deliberations, the Board requested, and the Advisor provided, such information as the Board (with advice from independent legal counsel) deemed reasonably necessary. The Board considered a variety of factors in connection with its review of the Advisory Contract and Subadvisory Contract, also taking into account information provided by the Advisor during the course of the year, as discussed below:
Services Provided by the Advisor and Subadvisor
The Board considered the nature, quality, and extent of the services provided to the fund by the Advisor and Subadvisor. These services included, but were not limited to, directing the fund’s investments in accordance with its investment program and the overall management of the fund’s portfolio, as well as a variety of related activities such as financial, investment operations, and administrative services; compliance; maintaining the fund’s records and registrations; and shareholder communications. The Board also reviewed the background and experience of the Advisor’s and Subadvisor’s senior management teams and investment personnel involved in the management of the fund, as well as the Advisor’s compliance record. The Board concluded that it was satisfied with the nature, quality, and extent of the services provided by the Advisor and Subadvisor.
Investment Performance of the Fund
The Board reviewed the fund’s three-month, one-year, and year-by-year returns, as well as the fund’s average annualized total return since inception, and compared these returns with a wide variety of previously agreed upon comparable performance measures and market data, including those supplied by Lipper and Morningstar, which are independent providers of mutual fund data.
On the basis of this evaluation and the Board’s ongoing review of investment results, and factoring in the market conditions during certain of the performance periods along with the fund’s relatively limited operating history, the Board concluded that the fund’s performance was satisfactory.
Costs, Benefits, Profits, and Economies of Scale
The Board reviewed detailed information regarding the revenues received by the Advisor under the Advisory Contract and other benefits that the Advisor (and its affiliates, including the Subadvisor) may have realized from its relationship with the fund, including any research received under “soft dollar” agreements and commission-sharing arrangements with broker-dealers. The Board considered that the Advisor and Subadvisor may receive some benefit from soft-dollar arrangements pursuant to which research is received from broker-dealers that execute the applicable fund’s portfolio transactions. The Board received information on the estimated costs incurred and profits realized by the Advisor from managing T. Rowe Price mutual funds. The Board also reviewed estimates of the profits realized from managing the fund in particular, and the Board concluded that the Advisor’s profits were reasonable in light of the services provided to the fund.
The Board also considered whether the fund benefits under the fee levels set forth in the Advisory Contract from any economies of scale realized by the Advisor. Under the Advisory Contract, the fund pays a fee to the Advisor for investment management services composed of two components—a group fee rate based on the combined average net assets of most of the T. Rowe Price mutual funds (including the fund) that declines at certain asset levels and an individual fund fee rate based on the fund’s average daily net assets—and the fund pays its own expenses of operations. Under the Subadvisory Contract, the Advisor may pay the Subadvisor up to 60% of the advisory fee that the Advisor receives from the fund. The Board concluded that the advisory fee structure for the fund continued to provide for a reasonable sharing of benefits from any economies of scale with the fund’s investors.
Fees
The Board was provided with information regarding industry trends in management fees and expenses, and the Board reviewed the fund’s management fee rate, operating expenses, and total expense ratio in comparison with fees and expenses of other comparable funds based on information and data supplied by Lipper. The information provided to the Board indicated that the fund’s management fee rate was above the median for comparable funds. The information also indicated that the total expense ratio was above the median for certain groups of comparable funds and below the median for other groups of comparable funds.
The Board also reviewed the fee schedules for institutional accounts and private accounts with similar mandates that are advised or subadvised by the Advisor and its affiliates. Management provided the Board with information about the Advisor’s responsibilities and services provided to institutional account clients, including information about how the requirements and economics of the institutional business are fundamentally different from those of the mutual fund business. The Board considered information showing that the mutual fund business is generally more complex from a business and compliance perspective than the institutional business and that the Advisor generally performs significant additional services and assumes greater risk in managing the fund and other T. Rowe Price mutual funds than it does for institutional account clients.
On the basis of the information provided and the factors considered, the Board concluded that the fees paid by the fund under the Advisory Contract are reasonable.
Approval of the Advisory Contract and Subadvisory Contract
As noted, the Board approved the continuation of the Advisory Contract and Subadvisory Contract. No single factor was considered in isolation or to be determinative to the decision. Rather, the Board concluded, in light of a weighting and balancing of all factors considered, that it was in the best interests of the fund and its shareholders for the Board to approve the continuation of the Advisory Contract and Subadvisory Contract (including the fees to be charged for services thereunder). The independent directors were advised throughout the process by independent legal counsel.
Item 2. Code of Ethics.
A code of ethics, as defined in Item 2 of Form N-CSR, applicable to its principal executive officer, principal financial officer, principal accounting officer or controller, or persons performing similar functions is filed as an exhibit to the registrant’s annual Form N-CSR. No substantive amendments were approved or waivers were granted to this code of ethics during the registrant’s most recent fiscal half-year.
Item 3. Audit Committee Financial Expert.
Disclosure required in registrant’s annual Form N-CSR.
Item 4. Principal Accountant Fees and Services.
Disclosure required in registrant’s annual Form N-CSR.
Item 5. Audit Committee of Listed Registrants.
Not applicable.
Item 6. Investments.
(a) Not applicable. The complete schedule of investments is included in Item 1 of this Form N-CSR.
(b) Not applicable.
Item 7. Disclosure of Proxy Voting Policies and Procedures for Closed-End Management Investment Companies.
Not applicable.
Item 8. Portfolio Managers of Closed-End Management Investment Companies.
Not applicable.
Item 9. Purchases of Equity Securities by Closed-End Management Investment Company and Affiliated Purchasers.
Not applicable.
Item 10. Submission of Matters to a Vote of Security Holders.
Not applicable.
Item 11. Controls and Procedures.
(a) The registrant’s principal executive officer and principal financial officer have evaluated the registrant’s disclosure controls and procedures within 90 days of this filing and have concluded that the registrant’s disclosure controls and procedures were effective, as of that date, in ensuring that information required to be disclosed by the registrant in this Form N-CSR was recorded, processed, summarized, and reported timely.
(b) The registrant’s principal executive officer and principal financial officer are aware of no change in the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the registrant’s second fiscal quarter covered by this report that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, the registrant’s internal control over financial reporting.
Item 12. Exhibits.
(a)(1) The registrant’s code of ethics pursuant to Item 2 of Form N-CSR is filed with the registrant’s annual Form N-CSR.
(2) Separate certifications by the registrant's principal executive officer and principal financial officer, pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 and required by Rule 30a-2(a) under the Investment Company Act of 1940, are attached.
(3) Written solicitation to repurchase securities issued by closed-end companies: not applicable.
(b) A certification by the registrant's principal executive officer and principal financial officer, pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 and required by Rule 30a-2(b) under the Investment Company Act of 1940, is attached.
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 and the Investment Company Act of 1940, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
T. Rowe Price Real Assets Fund, Inc.
| | By | /s/ Edward C. Bernard |
| | Edward C. Bernard |
| | Principal Executive Officer |
| |
| Date August 16, 2013 | | |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 and the Investment Company Act of 1940, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| | By | /s/ Edward C. Bernard |
| | Edward C. Bernard |
| | Principal Executive Officer |
| |
| Date August 16, 2013 | | |
| |
| |
| By | /s/ Gregory K. Hinkle |
| | Gregory K. Hinkle |
| | Principal Financial Officer |
| |
| Date August 16, 2013 | | |