Exhibit 99.2
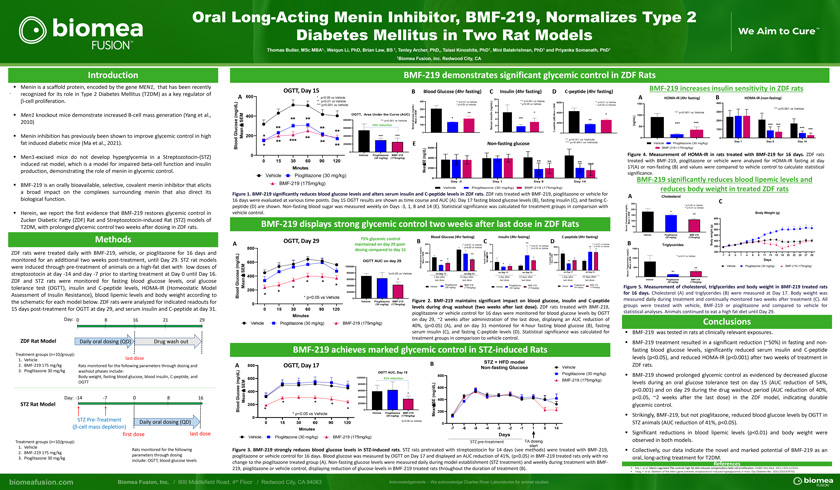
Menin is a scaffold protein, encoded by the gene MEN1, that has been recently . recognized for its role in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) as a key regulator of b-cell proliferation. Men1 knockout mice demonstrate increased B-cell mass generation (Yang et al., 2010) Menin inhibition has previously been shown to improve glycemic control in high fat induced diabetic mice (Ma et al., 2021). Men1-excised mice do not develop hyperglycemia in a Streptozotocin-(STZ) induced rat model, which is a model for impaired beta-cell function and insulin production, demonstrating the role of menin in glycemic control. BMF-219 is an orally bioavailable, selective, covalent menin inhibitor that elicits a broad impact on the complexes surrounding menin that also direct its biological function. Herein, we report the first evidence that BMF-219 restores glycemic control in Zucker Diabetic Fatty (ZDF) Rat and Streptozotocin-induced Rat (STZ) models of T2DM, with prolonged glycemic control two weeks after dosing in ZDF rats.MethodsZDF rats were treated daily with BMF-219, vehicle, or pioglitazone for 16 days monitored for an additional two weeks post-treatment, until Day 29. STZ rat models were induced through pre-treatment of animals on a high-fat diet with low doses streptozotocin at day -14 and day -7 prior to starting treatment at Day 0 until Day ZDF and STZ rats were monitored for fasting blood glucose levels, oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), insulin and C-peptide levels, HOMA-IR (Homeostatic Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance), blood lipemic levels and body weight according the schematic for each model below. ZDF rats were analyzed for indicated readouts 15 days post-treatment for OGTT at day 29, and serum insulin and C-peptide at dayDay: 0 8 16 21 29ZDF Rat Model Daily oral dosing (QD) Drug wash outTreatment groups (n=10/group): last dose1. Vehicle2. BMF-219 175 mg/kg Rats monitored for the following parameters through dosing and 3. Pioglitazone 30 mg/kg washout phases include: Body weight, fasting blood glucose, blood insulin, C-peptide, and OGTTDay: -14 -7 0 8 16STZ Rat ModelSTZ Pre-TreatmentDaily oral dosing (QD) (β-cell mass depletion) first dose last doseTreatment groups (n=10/group):1. VehicleRats monitored for the following 2. BMF-219 175 mg/kg parameters through dosing 3. Pioglitazone 30 mg/kg include: OGTT, blood glucose levelsBMF-219 demonstrates significant glycemic control in ZDF RatsOGTT, Day 15 B Blood Glucose (4hr fasting) C Insulin (4hr fasting) D C-peptide (4hr fasting)A 600 * p<0.05 vs Vehicle 10** p<0.01 vs Vehicle 400 ** p<0.01 vs Vehicle *** p<0.001 vs VehicleL) 6000 ** p<0.01 vs Vehicle*** p<0.001 vs Vehicle * p<0.05 vs Vehicle * p<0.05 vs Vehicle * p<0.05 vs VehicledL) g/m 8 SEM ± g/ 300 ( n g/dL) (m 6 an SEM ** lin * 4000OGTT, Area Under the Curve (AUC) Mem M 400 ± , *( E cose 200 * su 4 *** M)80000 u in (p*** p<0.001 vs Vehicle S ** ** gl ** ** ** Mean de 2000ï,± 54% reduction ood 100 2 i ptcose 60000 B l erum peu n ** **S -l 0 C** 0 0G Mea 200 * 40000 *** ***** ** p<0.01 vs Vehicle** *** ** *** p<0.001 vs Vehicle* ** 20000 E Non-fasting glucose Blood 60000 Vehicle Pioglitazone BMF-219 (mg/dL) (30 mg/kg) (175mg/kg) 4000 15 30 60 90 120 SE ** ** **ï,± ***Minutes Mean 200Vehicle Pioglitazone (30 mg/kg)0BMF-219 (175mg/kg) Day -3 Day 1 Day 8 Day 14Vehicle Pioglitazone (30 mg/kg) BMF-219 (175mg/kg)Figure 1. BMF-219 significantly reduces blood glucose levels and alters serum insulin and C-peptide levels in ZDF rats. ZDF rats treated with BMF-219, pioglitazone or vehicle for 16 days were evaluated at various time points. Day 15 OGTT results are shown as time course and AUC (A). Day 17 fasting blood glucose levels (B), fasting insulin (C), and fasting C-peptide (D) are shown. Non-fasting blood sugar was measured weekly on Days -3, 1, 8 and 14 (E). Statistical significance was calculated for treatment groups in comparison with vehicle control.BMF-219 displays strong glycemic control two weeks after last dose in ZDF RatsBlood Glucose (4hr fasting) Insulin (4hr fasting) C-peptide (4hr fasting)OGTT, Day 29 75% glycemic control B C DA maintained on day 29 post- 600 ** p<0.01 vs Vehicle 15 ** ** p<0.01 vs Vehicle ** p<0.01 vs Vehicle800 * p<0.05 vs Vehicle * p<0.05 vs Vehicle 6000 ** * p<0.05 vs Vehicledosing compared to day 15 dL) / *g(m 400 mL) M 10 M) EM 4000S ** SE ( pL) ng/ ( SEM± ï,± e n id ± cose lu ean * ean *OGTT AUC on day 29 g 200 ** M 5 pept **600 M—Mean 2000 d Insuli o * C(mg/d 100000 Bl o EMS 0 0 0 80000 on Day 17 on Day 31 on Day 17 on Day 31*p<0.05 vs Vehicle on Day 17 on Day 31ï,± 4001 day after 15 days after 1 day after 15 days after 1 day after 15 days after lucose 60000 * last dose last dose last dose last dose last dose last dose* *G 40000 Pioglitazone BMF-219 Pioglitazone BMF-219 Pioglitazone BMF-219 * Vehicle Vehicle VehicleMean 200 * (30 mg/kg) (175mg/kg) (30 mg/kg) (175mg/kg) (30 mg/kg) (175mg/kg) lood * 20000B * * p<0.05 vs Vehicle 0Vehicle Pioglitazone BMF-219 Figure 2. BMF-219 maintains significant impact on blood glucose, insulin and C-peptide0 (30 mg/kg) (175mg/kg)levels during drug washout (two weeks after last dose). ZDF rats treated with BMF-219,0 15 30 60 90 120 pioglitazone or vehicle control for 16 days were monitored for blood glucose levels by OGTT Minutes on day 29, ~2 weeks after administration of the last dose, displaying an AUC reduction ofVehicle Pioglitazone (30 mg/kg) BMF-219 (175mg/kg)40%, (p<0.05) (A), and on day 31 monitored for 4-hour fasting blood glucose (B), fasting serum insulin (C), and fasting C-peptide levels (D). Statistical significance was calculated for treatment groups in comparison to vehicle control.BMF-219 achieves marked glycemic control in STZ-induced Rats 800 B STZ + HFD modelA OGTT, Day 17 Non-fasting Glucose Vehicle dL) OGTT AUC, Day 15 Pioglitazone (30 mg/kg)/ 800 g 600 100000 41% reductionm M BMF-219 (175mg/kg)( SE 80000se /dL) 600oï,± 400 60000u c n * mgGl 40000(400 d Mea SE200 * * 20000loo *ï,± nB * * 0 ea 200* p<0.05 vs Vehicle Vehicle Pioglitazone BMF-219(30 mg/kg) (175mg/kg) M00 15 30 60 90 120 *p<0.05 vs Vehicle0Minutes -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 1 8 14DaysVehicle Pioglitazone (30 mg/kg) BMF-219 (175mg/kg)STZ pre-treatment TA dosing startFigure 3. BMF-219 strongly reduces blood glucose levels in STZ-induced rats. STZ rats pretreated with streptozotocin for 14 days (see methods) were treated with BMF-219, pioglitazone or vehicle control for 16 days. Blood glucose was measured by OGTT on Day 17 and displayed an AUC reduction of 41%, (p<0.05) in BMF-219 treated rats only with no change to the pioglitazone treated group (A). Non-fasting glucose levels were measured daily during model establishment (STZ treatment) and weekly during treatment with BMF-219, pioglitazone or vehicle control, displaying reduction of glucose levels in BMF-219 treated rats throughout the duration of treatment (B).BMF-219 increases insulin sensitivity in ZDF ratsA HOMA-IR (4hr fasting) B HOMA-IR (non-fasting)150 400*** p<0.001 vs Vehicle*** p<0.001 vs Vehicle 300100200(ng/mL) *** ***50 *** ***100 *** ***0 0Day 1 Day 8 Day 14Vehicle Pioglitazone (30 mg/kg) BMF-219 (175mg/kg)Figure 4. Measurement of HOMA-IR in rats treated with BMF-219 for 16 days. ZDF rats treated with BMF-219, pioglitazone or vehicle were analyzed for HOMA-IR fasting at day 17(A) or non-fasting (B) and values were compared to vehicle control to calculate statistical significance.BMF-219 significantly reduces blood lipemic levels and reduces body weight in treated ZDF ratsA CholesterolC250* p<0.05 vs Vehicle ** p<0.01 vs Vehicle(mg/dL) 200 * Body Weight (g)SEM 150 ** ± 600Cholesterol Mean 100 55050 (g)Serum 500 0 Vehicle Pioglitazone BMF-219 weight 450 (30 mg/kg) (175mg/kg) dy 400B B oTriglycerides3501500300(mg/dL) -7 -5 -3 1 4 6 8 11 13 15 18 20 22 25 27 29 1000 ** p<0.01 vs VehicleSEM Days± Vehicle Pioglitazone (30 mg/kg) BMF-219 (175mg/kg)Triglycerides Mean 500 ** Serum ** 0 Vehicle Pioglitazone BMF-219 (30 mg/kg) (175mg/kg)Figure 5. Measurement of cholesterol, triglycerides and body weight in BMF-219 treated rats for 16 days. Cholesterol (A) and triglycerides (B) were measured at Day 17. Body weight was measured daily during treatment and continually monitored two weeks after treatment (C). All groups were treated with vehicle, BMF-219 or pioglitazone and compared to vehicle for statistical analyses. Animals continued to eat a high fat diet until Day 29.Conclusions BMF-219 was tested in rats at clinically relevant exposures. BMF-219 treatment resulted in a significant reduction (~50%) in fasting and non-fasting blood glucose levels, significantly reduced serum insulin and C-peptide levels (p<0.05), and reduced HOMA-IR (p<0.001) after two weeks of treatment in ZDF rats. BMF-219 showed prolonged glycemic control as evidenced by decreased glucose levels during an oral glucose tolerance test on day 15 (AUC reduction of 54%, p<0.001) and on day 29 during the drug washout period (AUC reduction of 40%, p<0.05, ~2 weeks after the last dose) in the ZDF model, indicating durable glycemic control. Strikingly, BMF-219, but not pioglitazone, reduced blood glucose levels by OGTT in STZ animals (AUC reduction of 41%, p<0.05). Significant reductions in blood lipemic levels (p<0.01) and body weight were observed in both models. Collectively, our data indicate the novel and marked potential of BMF-219 as an oral, long-acting treatment for T2DM.References Ma, J. et al. Menin-regulated Pbk controls high fat diet-induced compensatory beta cell proliferation. EMBO Mol Med. 2021;13(5):e13524. Yang, Y. et al. Deletion of the Men1 gene prevents streptozotocin-induced hyperglycemia in mice. Exp Diabetes Res. 2010;2010:876701.
