Exhibit 99.3
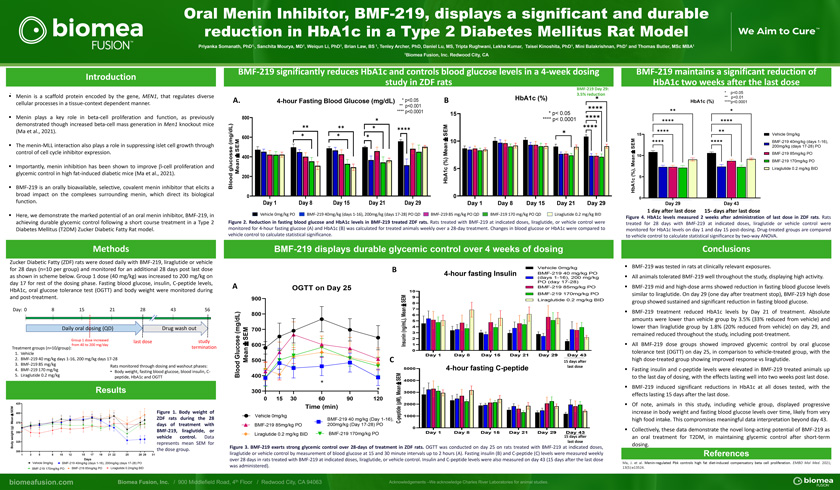
Oral Menin Inhibitor, BMF-219, displays a significant and durable reduction in HbA1c in a Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Rat ModelPriyanka Somanath, PhD1,, Sanchita Mourya, MD1, Weiqun Li, PhD1, Brian Law, BS 1, Tenley Archer, PhD, Daniel Lu, MS, Tripta Rughwani, Lekha Kumar, Taisei Kinoshita, PhD1, Mini Balakrishnan, PhD1 and Thomas Butler, MSc MBA1 1Biomea Fusion, Inc. Redwood City, CAIntroduction. diverse Menin is a scaffold protein encoded by the gene, MEN1, that regulates cellular processes in a tissue-context dependent manner. Menin plays a key role in beta-cell proliferation and function, as previously demonstrated though increased beta-cell mass generation in Men1 knockout mice(Ma et al., 2021). The menin-MLL interaction also plays a role in suppressing islet cell growth through control of cell cycle inhibitor expression. Importantly, menin inhibition has been shown to improve b-cell proliferation and glycemic control in high fat-induced diabetic mice (Ma et al., 2021). BMF-219 is an orally bioavailable, selective, covalent menin inhibitor that elicits a broad impact on the complexes surrounding menin, which direct its biological function. Here, we demonstrate the marked potential of an oral menin inhibitor, BMF-219, in achieving durable glycemic control following a short course treatment in a Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) Zucker Diabetic Fatty Rat model.MethodsZucker Diabetic Fatty (ZDF) rats were dosed daily with BMF-219, liraglutide or vehicle for 28 days (n=10 per group) and monitored for an additional 28 days post last dose as shown in scheme below. Group 1 dose (40 mg/kg) was increased to 200 mg/kg on day 17 for rest of the dosing phase. Fasting blood glucose, insulin, C-peptide levels,HbA1c, oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) and body weight were monitored during and post-treatment.Day: 0 8 15 21 28 43 56Daily oral dosing (QD) Drug wash outGroup 1 dose increased last dose study from 40 to 200 mg/dayTreatment groups (n=10/group): termination1. Vehicle2. BMF-219 40 mg/kg days 1-16, 200 mg/kg days 17-283. BMF-219 85 mg/kgRats monitored through dosing and washout phases: 4. BMF-219 170 mg/kg• Body weight, fasting blood glucose, blood insulin, C-5. Liraglutide 0.2 mg/kg peptide, HbA1c and OGTTResults425SE M 400 Figure 1. Body weight of±ea n ZDF rats during the 28M 375(g) days of treatment with BMF-219, liraglutide, orht 350 i gw e vehicle control. Data ody 325 represents mean SEM for B the dose group.3001 3 5 8 10 12 15 17 19 21 22 25 28 29 31DaysVehicle 0mg/kg BMF-219 40mg/kg (days 1-16), 200mg/kg (days 17-28) PO BMF-219 170mg/kg PO BMF-219 85mg/kg PO Liraglutide 0.2mg/kg BIDBMF-219 significantly reduces HbA1c and controls blood glucose levels in a 4-week dosing study in ZDF ratsBMF-219 Day 29: 3.5% reductionHbA1c (%) A. 4-hour Fasting Blood Glucose (mg/dL) * p<0.05 B** p<0.001 **** p<0.0001 15 * p< 0.05800 **** p< 0.0001 M SE 600mg/dL)± 10( SEM ean M± 400 an ( %) glucosse c 5 Me 1o d 200 b Alo H B0 0Day 1 Day 8 Day 15 Day 21 Day 29 Day 1 Day 8 Day 15 Day 21 Day 29Vehicle 0mg/kg PO BMF-219 40mg/kg (days 1-16), 200mg/kg (days 17-28) PO QD BMF-219 85 mg/kg PO QD BMF-219 170 mg/kg PO QD Liraglutide 0.2 mg/kg BIDFigure 2. Reduction in fasting blood glucose and HbA1c levels in BMF-219 treated ZDF rats. Rats treated with BMF-219 at indicated doses, liraglutide, or vehicle control were monitored for 4-hour fasting glucose (A) and HbA1c (B) was calculated for treated animals weekly over a 28-day treatment. Changes in blood glucose or HbA1c were compared to vehicle control to calculate statistical significance.BMF-219 displays durable glycemic control over 4 weeks of dosingB Vehicle 0mg/kg4-hour fasting Insulin BMF-219 40 mg/kg PO(days 1-16), 200 mg/kg PO (day 17-28) A OGTT on Day 25 BMF-219 85mg/kg PO10BMF-219 170mg/kg PO900 EM 9Liraglutide 0.2 mg/kg BIDS 8± an 7800 eM 6dL) L), 5g/g/m 4M 700 (n(m E n 3e S uni 2s o± 600 Ins 1 c n0lu aG Day 1 Day 8 Day 15 Day 21 Day 29 Day 43 d Me 500 C 15 days after o last doseo 5000 4-hour fasting C-peptidelB 400 E MS 4000*±a n300 * M e 30000 15 30 60 90 120 M),(p 2000Time (min) d eVehicle 0mg/kg pepti 1000 BMF-219 40 mg/kg (Day 1-16),—CBMF-219 85mg/kg PO 200mg/kg (Day 17-28) PO 0Liraglutide 0.2 mg/kg BID BMF-219 170mg/kg PO Day 1 Day 8 Day 15 Day 21 Day 29 Day 4315 days after last doseFigure 3. BMF-219 exerts strong glycemic control over 28-days of treatment in ZDF rats. OGTT was conducted on day 25 on rats treated with BMF-219 at indicated doses, liraglutide or vehicle control by measurement of blood glucose at 15 and 30 minute intervals up to 2 hours (A). Fasting insulin (B) and C-peptide (C) levels were measured weekly over 28 days in rats treated with BMF-219 at indicated doses, liraglutide, or vehicle control. Insulin and C-peptide levels were also measured on day 43 (15 days after the last dose was administered).BMF-219 maintains a significant reduction of HbA1c two weeks after the last dose* p<0.05 ** p<0.01 HbA1c (%) ****p<0.0001 15 Vehicle 0mg/kgEM BMF-219 40mg/kg (days 1-16), S 200mg/kg (days 17-28) PO± BMF-219 85mg/kg PO n 10ae BMF-219 170mg/kg POM), Liraglutide 0.2 mg/kg BID( % c 5 HbA 10Day 29 Day 431 day after last dose 15- days after last doseFigure 4. HbA1c levels measured 2 weeks after administration of last dose in ZDF rats. Rats treated for 28 days with BMF-219 at indicated doses, liraglutide or vehicle control were monitored for HbA1c levels on day 1 and day 15 post-dosing. Drug-treated groups are compared to vehicle control to calculate statistical significance by two-way ANOVA.Conclusions BMF-219 was tested in rats at clinically relevant exposures. All animals tolerated BMF-219 well throughout the study, displaying high activity. BMF-219 mid and high-dose arms showed reduction in fasting blood glucose levels similar to liraglutide. On day 29 (one day after treatment stop), BMF-219 high dose group showed sustained and significant reduction in fasting blood glucose. BMF-219 treatment reduced HbA1c levels by Day 21 of treatment. Absolute amounts were lower than vehicle group by 3.5% (33% reduced from vehicle) and lower than liraglutide group by 1.8% (20% reduced from vehicle) on day 29, and remained reduced throughout the study, including post-treatment. All BMF-219 dose groups showed improved glycemic control by oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) on day 25, in comparison to vehicle-treated group, with the high dose-treated group showing improved response vs liraglutide. Fasting insulin and c-peptide levels were elevated in BMF-219 treated animals up to the last day of dosing, with the effects lasting well into two weeks post last dose. BMF-219 induced significant reductions in HbA1c at all doses tested, with the effects lasting 15 days after the last dose. Of note, animals in this study, including vehicle group, displayed progressive increase in body weight and fasting blood glucose levels over time, likely from very high food intake. This compromises meaningful data interpretation beyond day 43. Collectively, these data demonstrate the novel long-acting potential of BMF-219 as an oral treatment for T2DM, in maintaining glycemic control after short-term dosing.ReferencesMa, J. et al. Menin regulated Pbk controls high fat diet induced compensatory beta cell proliferation. EMBO Mol Med. 2021; 13(5):e13524.
